Patents
Literature
31 results about "Hemoglobin G Szuhu" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
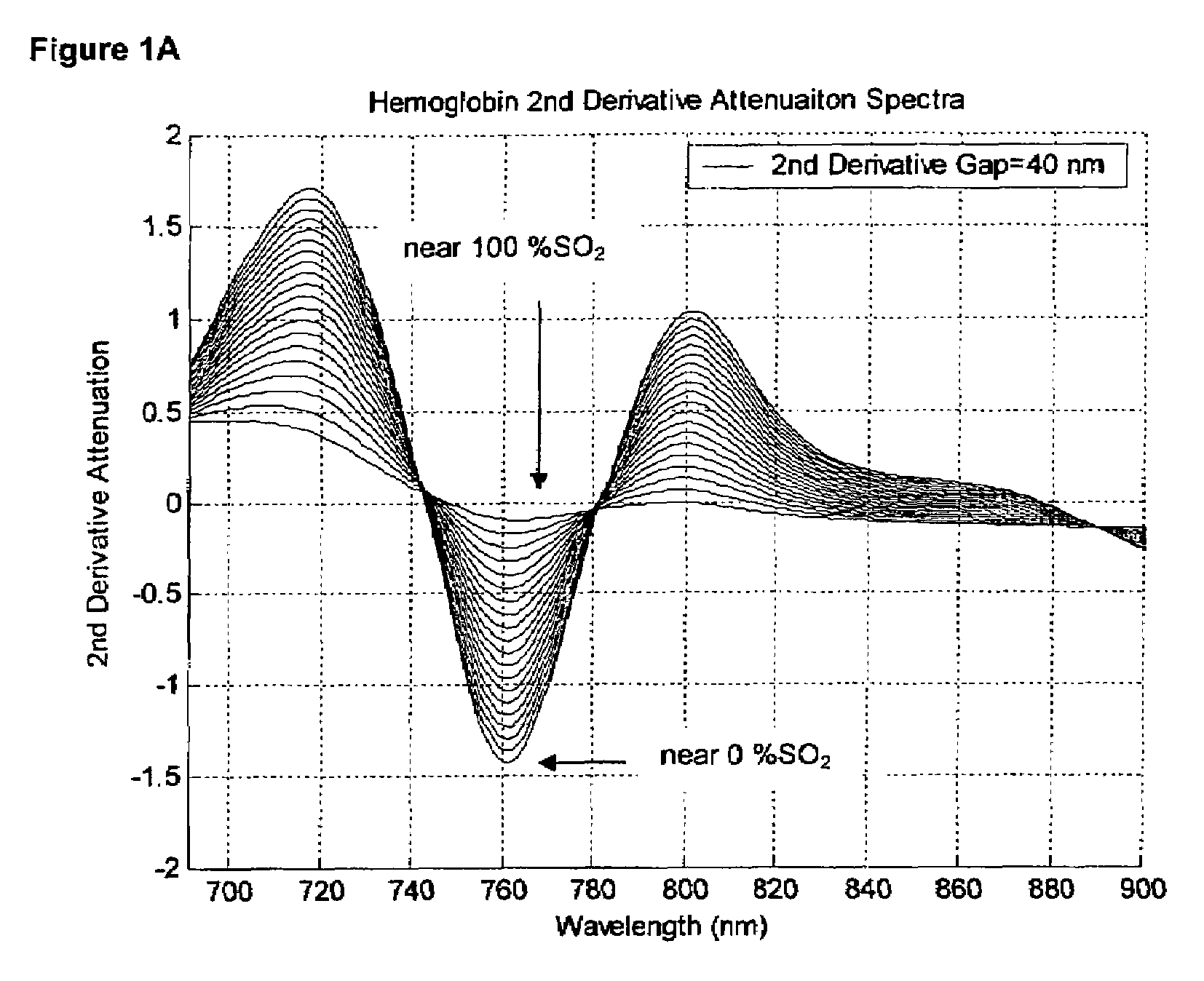
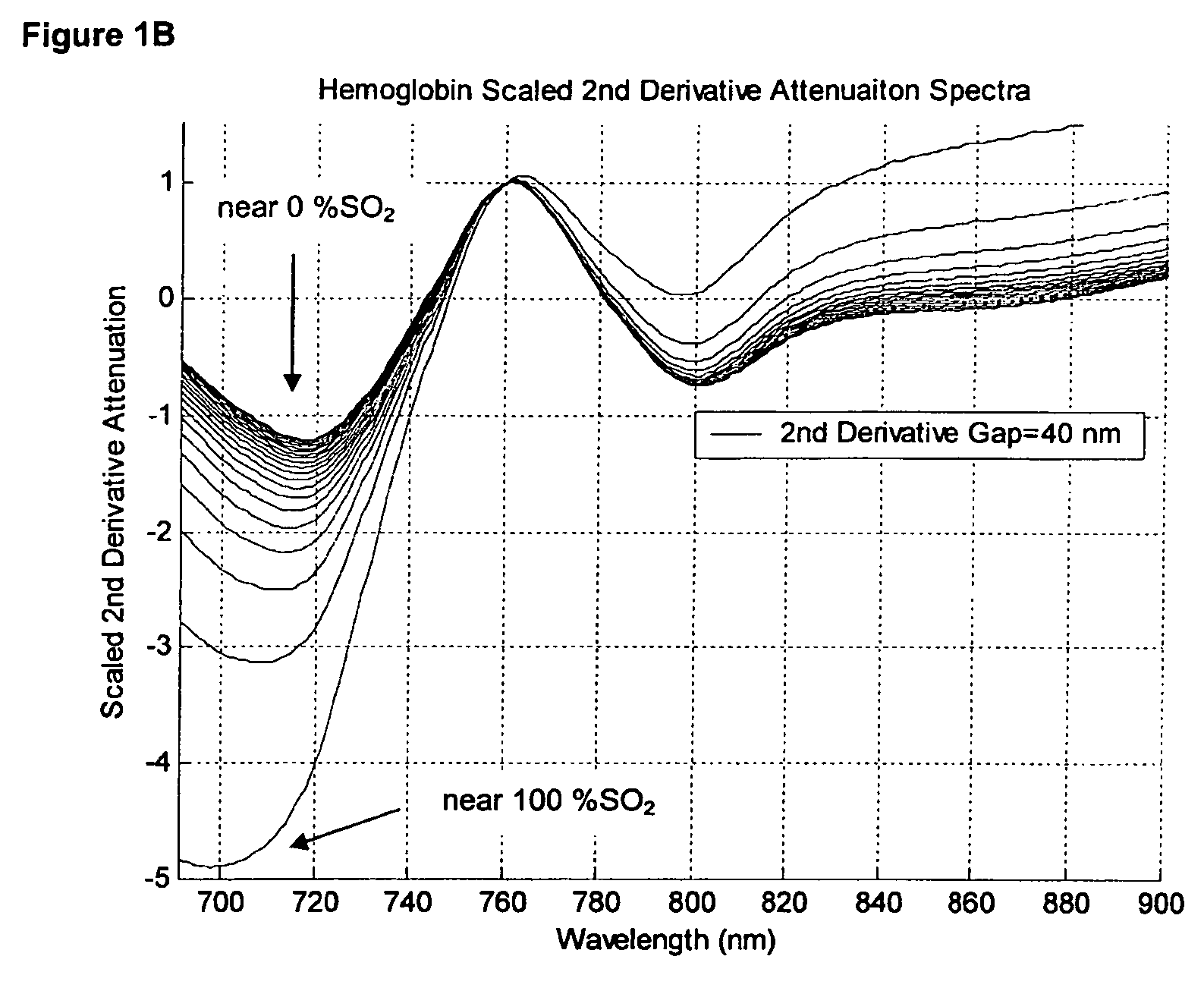
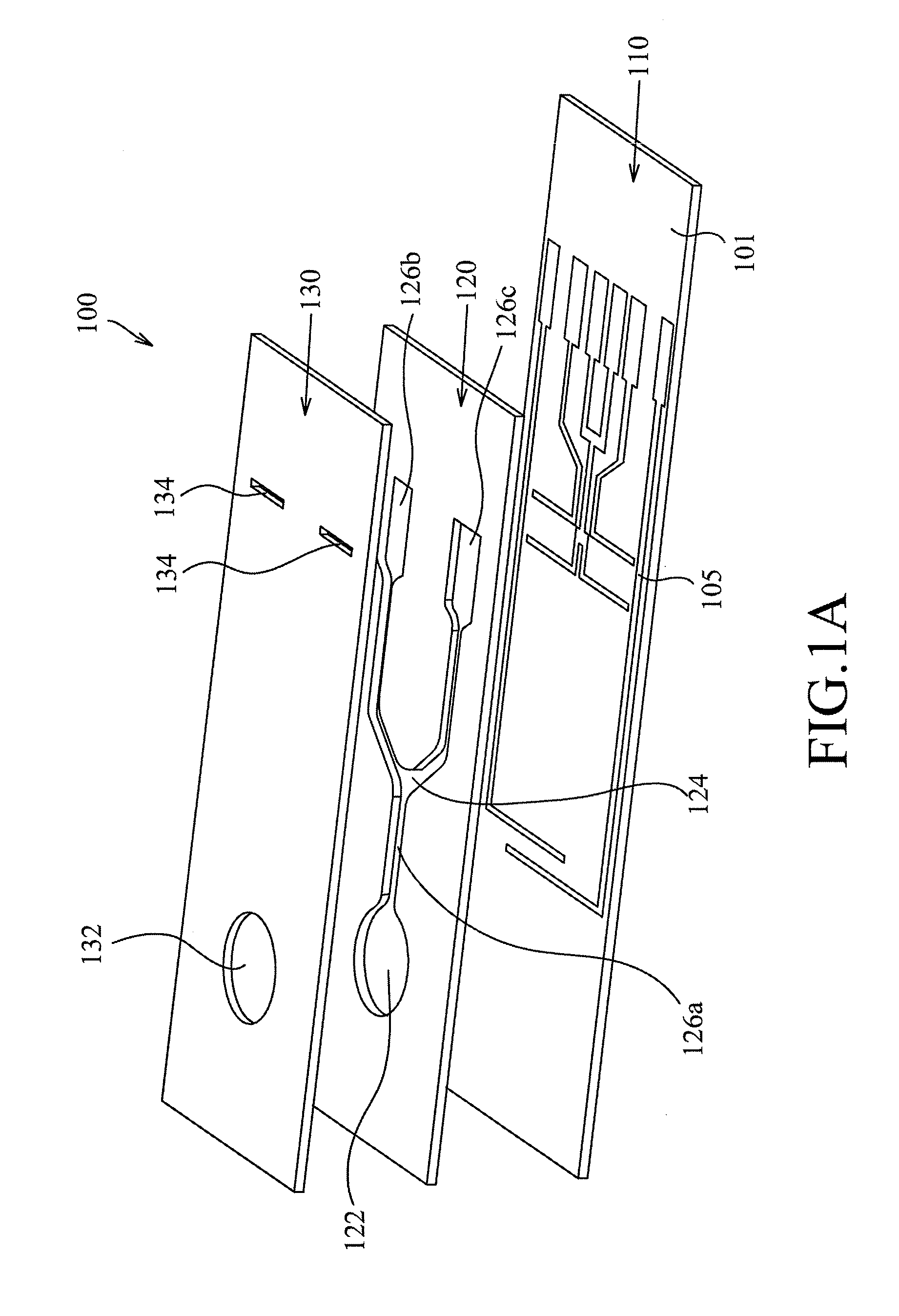
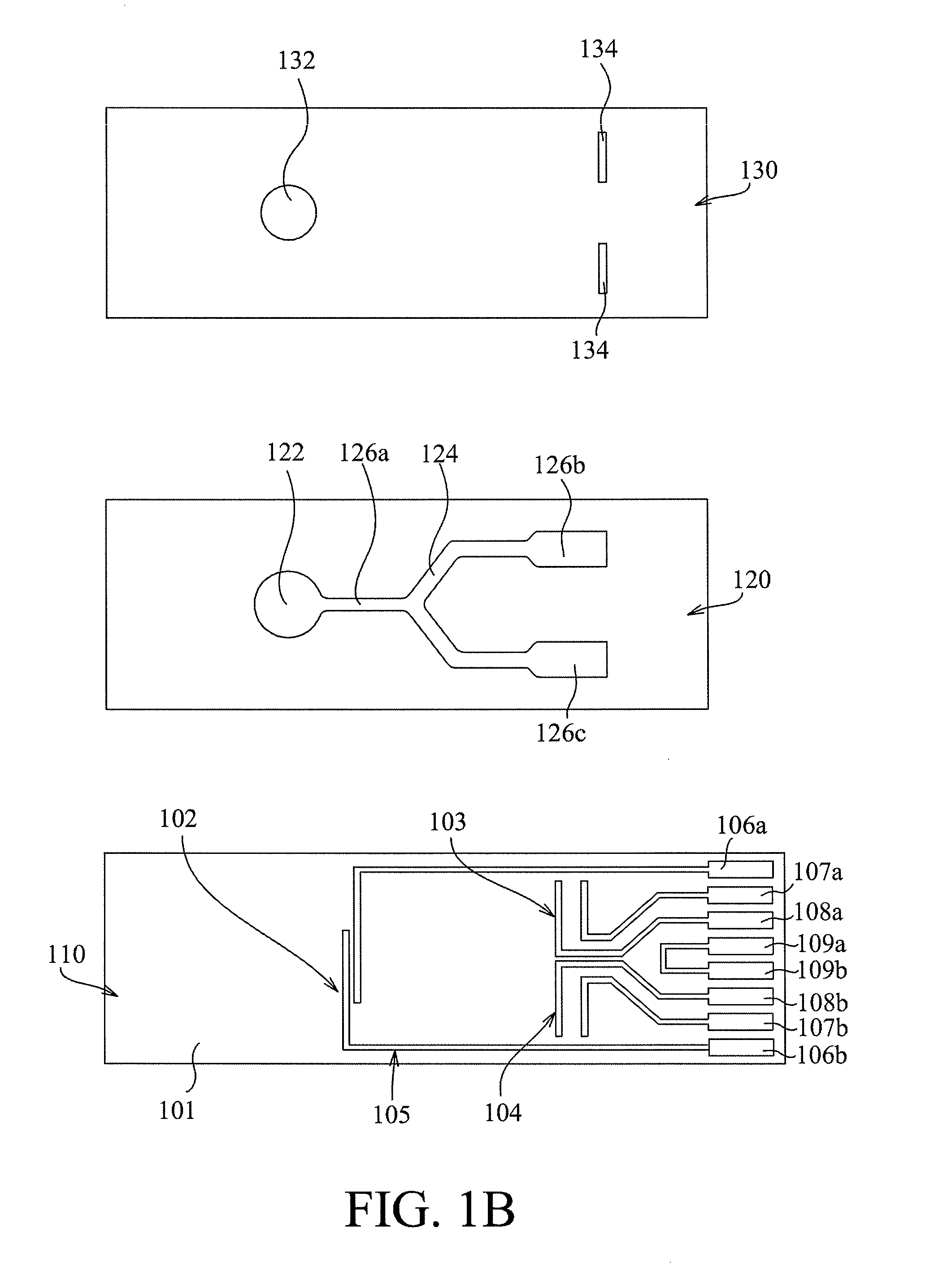
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
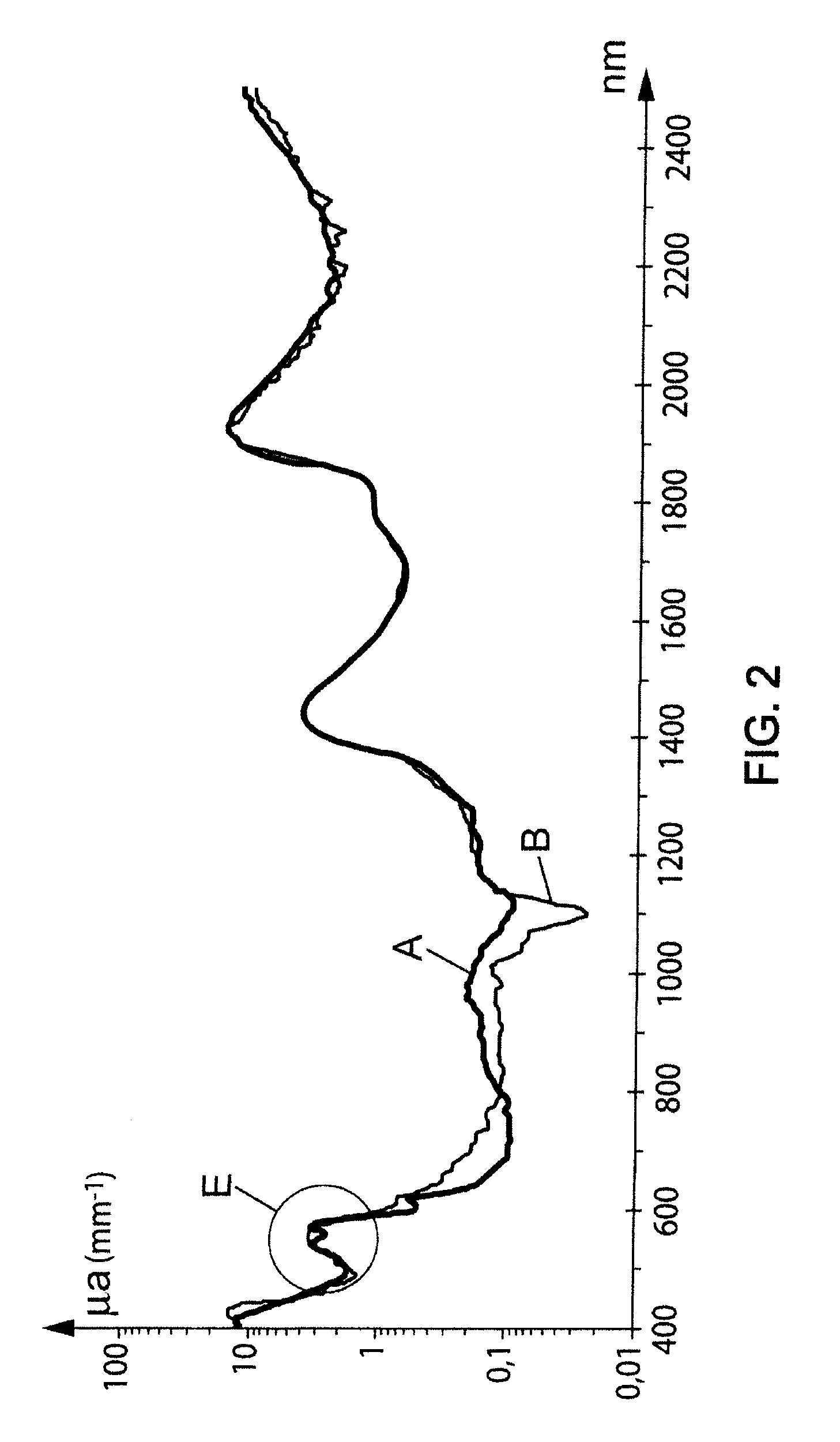
InactiveUS6181958B1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveHemoglobin G Szuhu
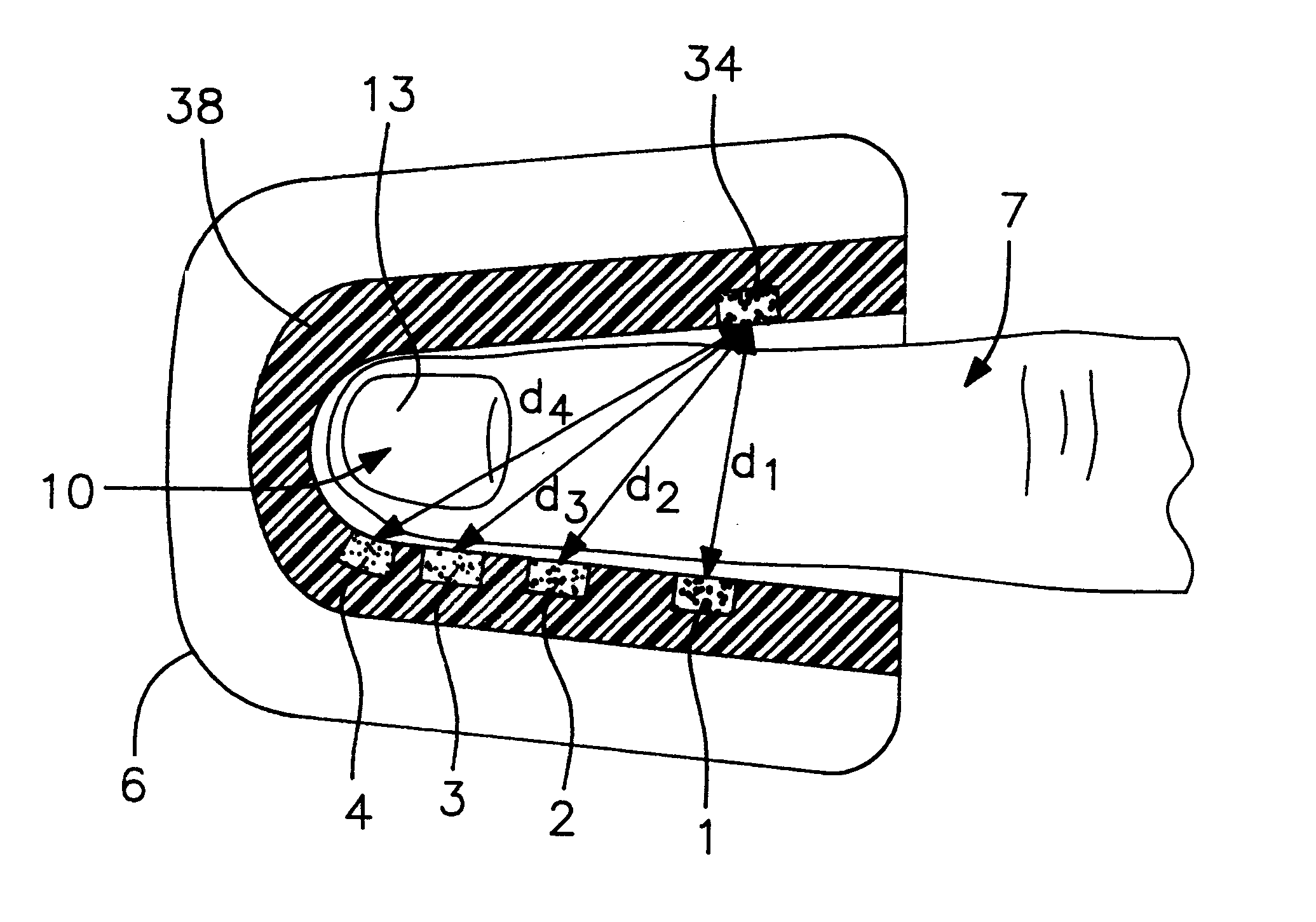
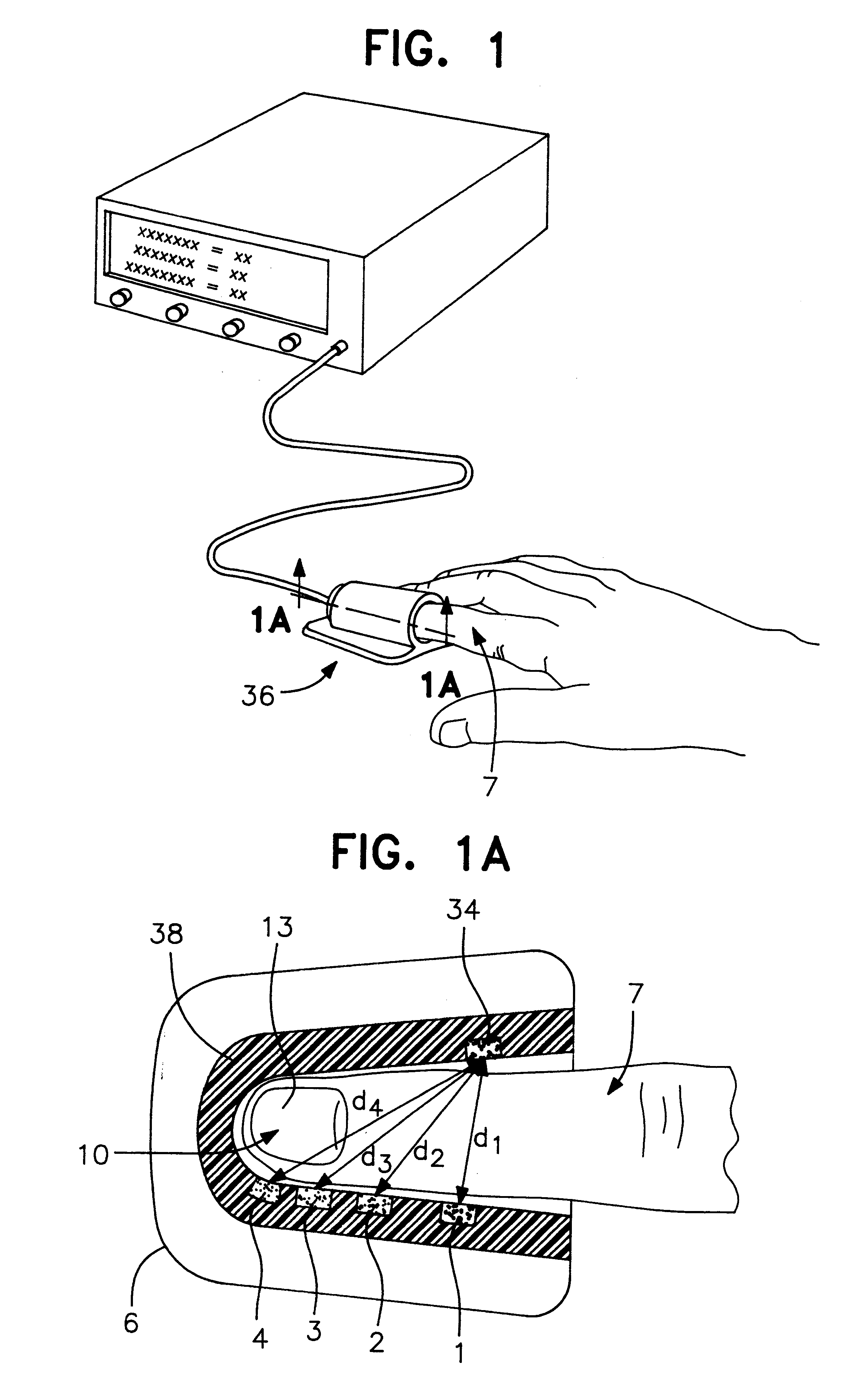
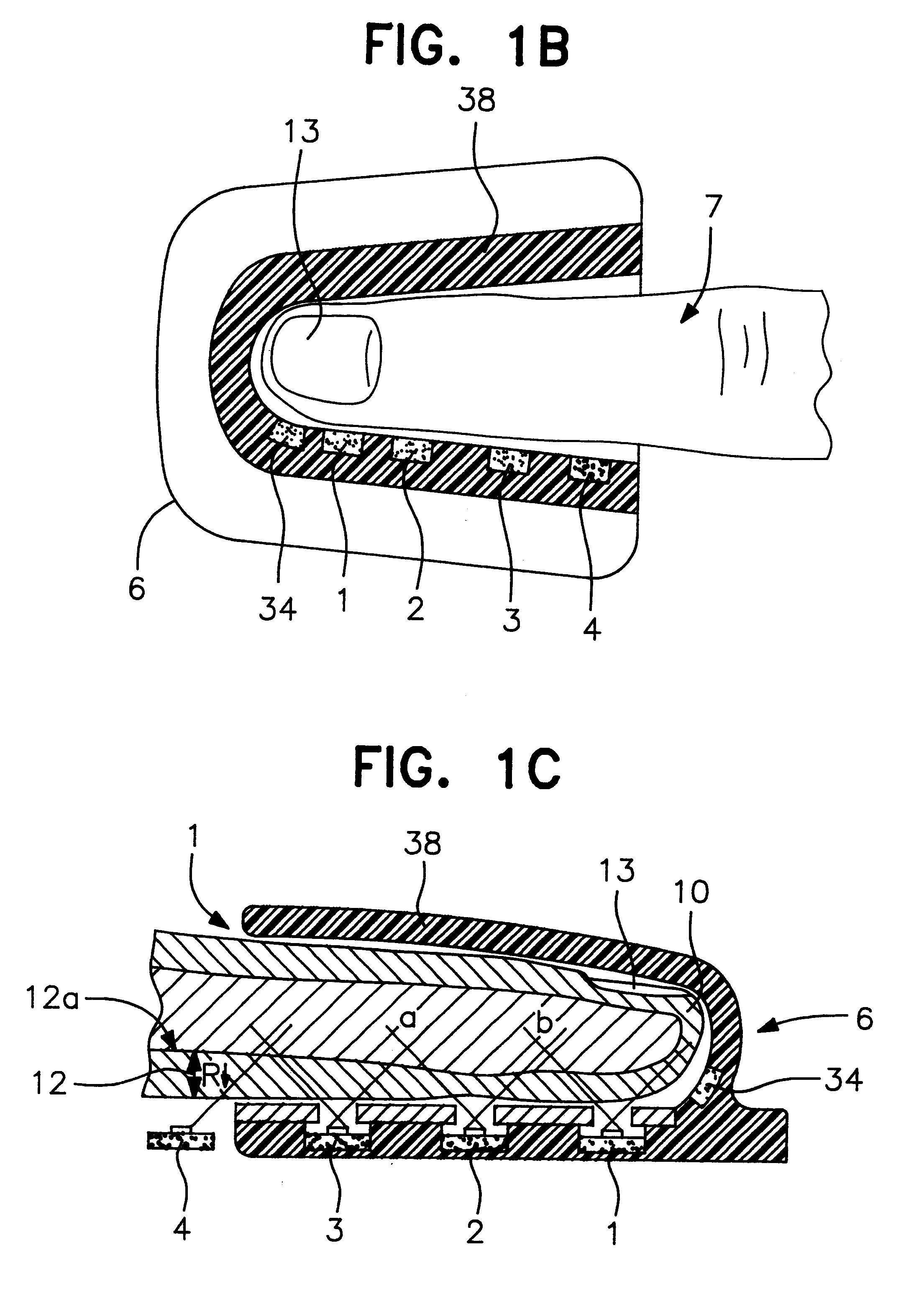
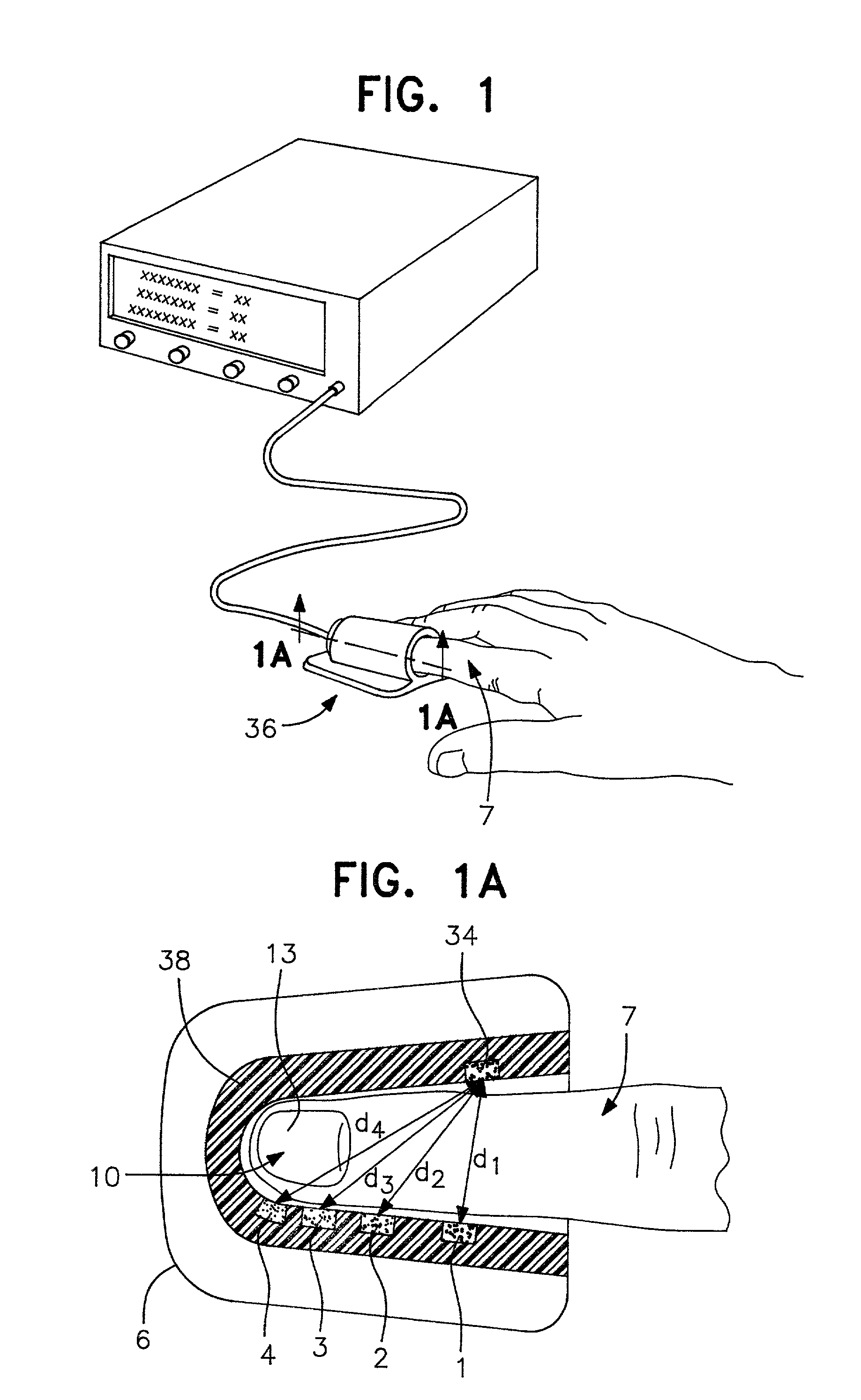
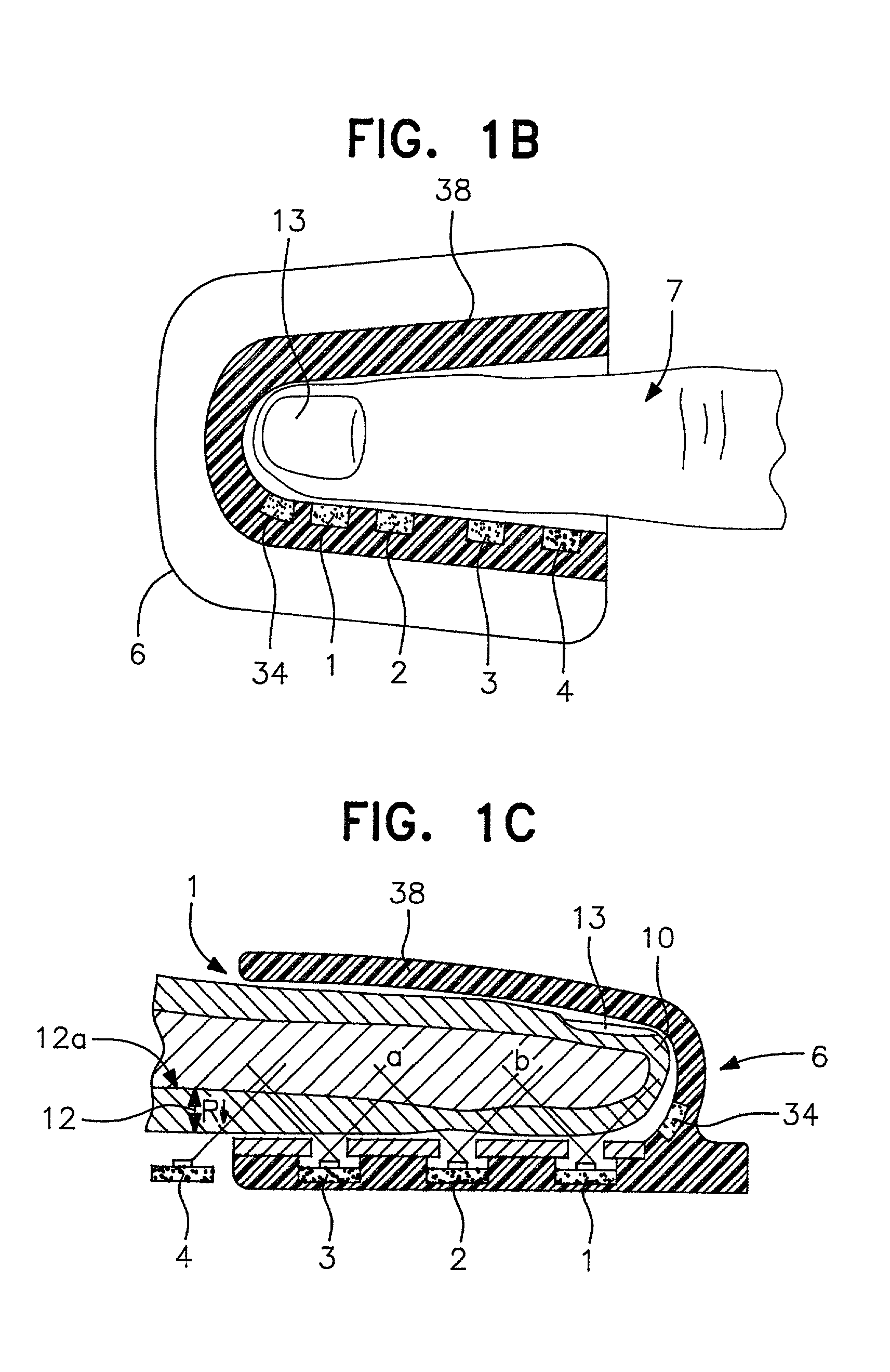
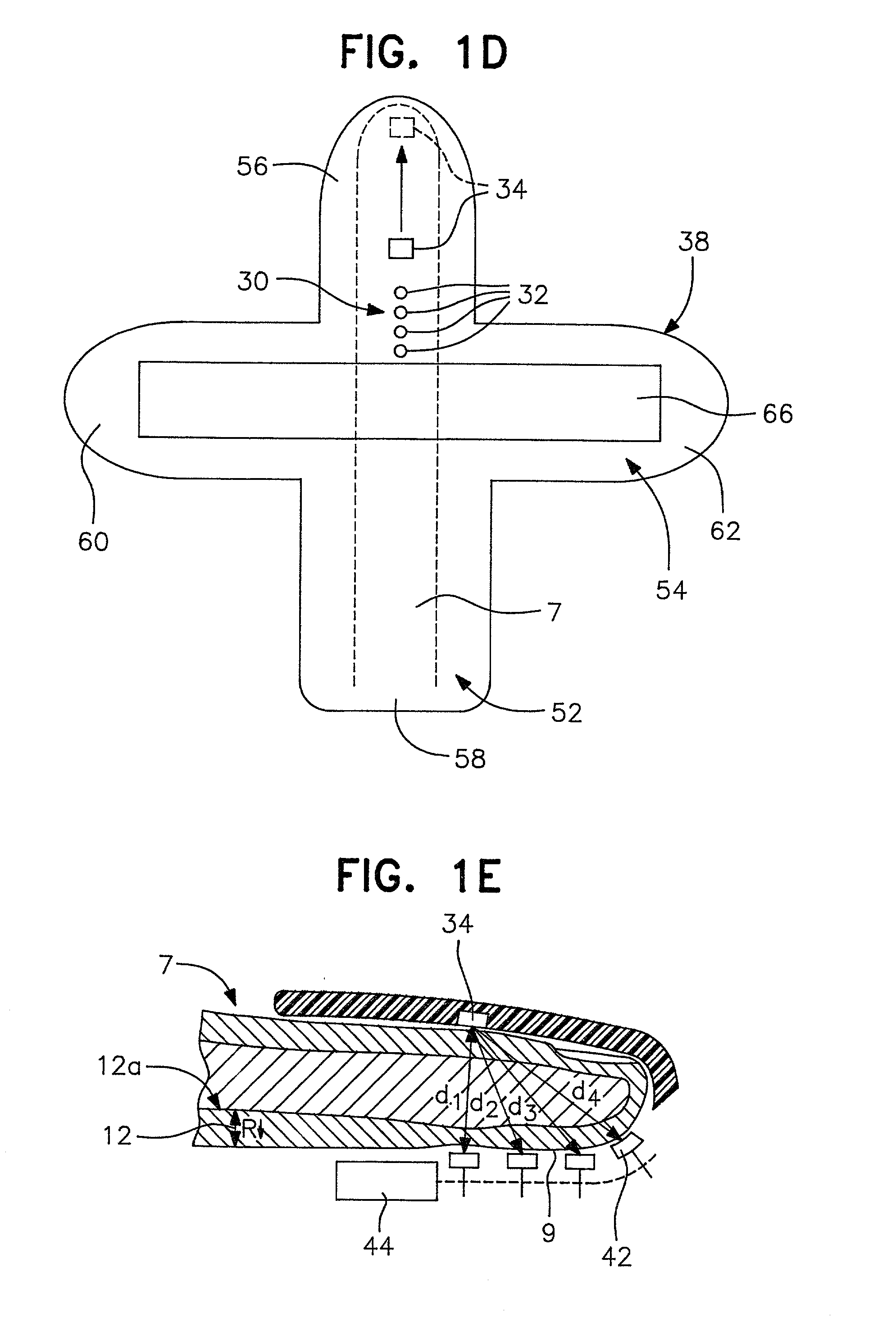
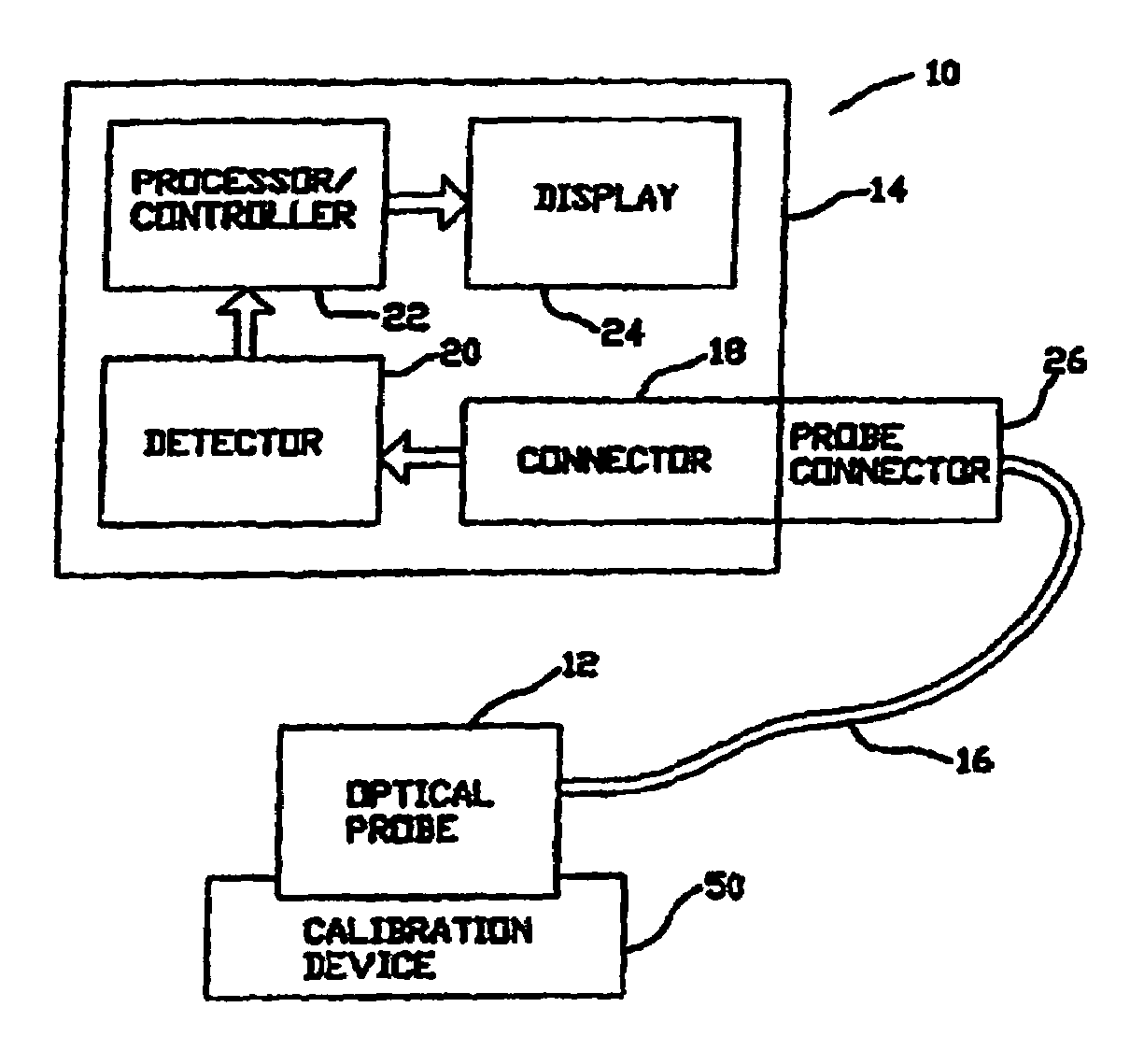
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Multiple-wavelength spectroscopic quantitation of light-absorbing species in scattering media
InactiveUS6015969ASimplified determinationRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric discharge tubesFiberMultiwavelength spectroscopy
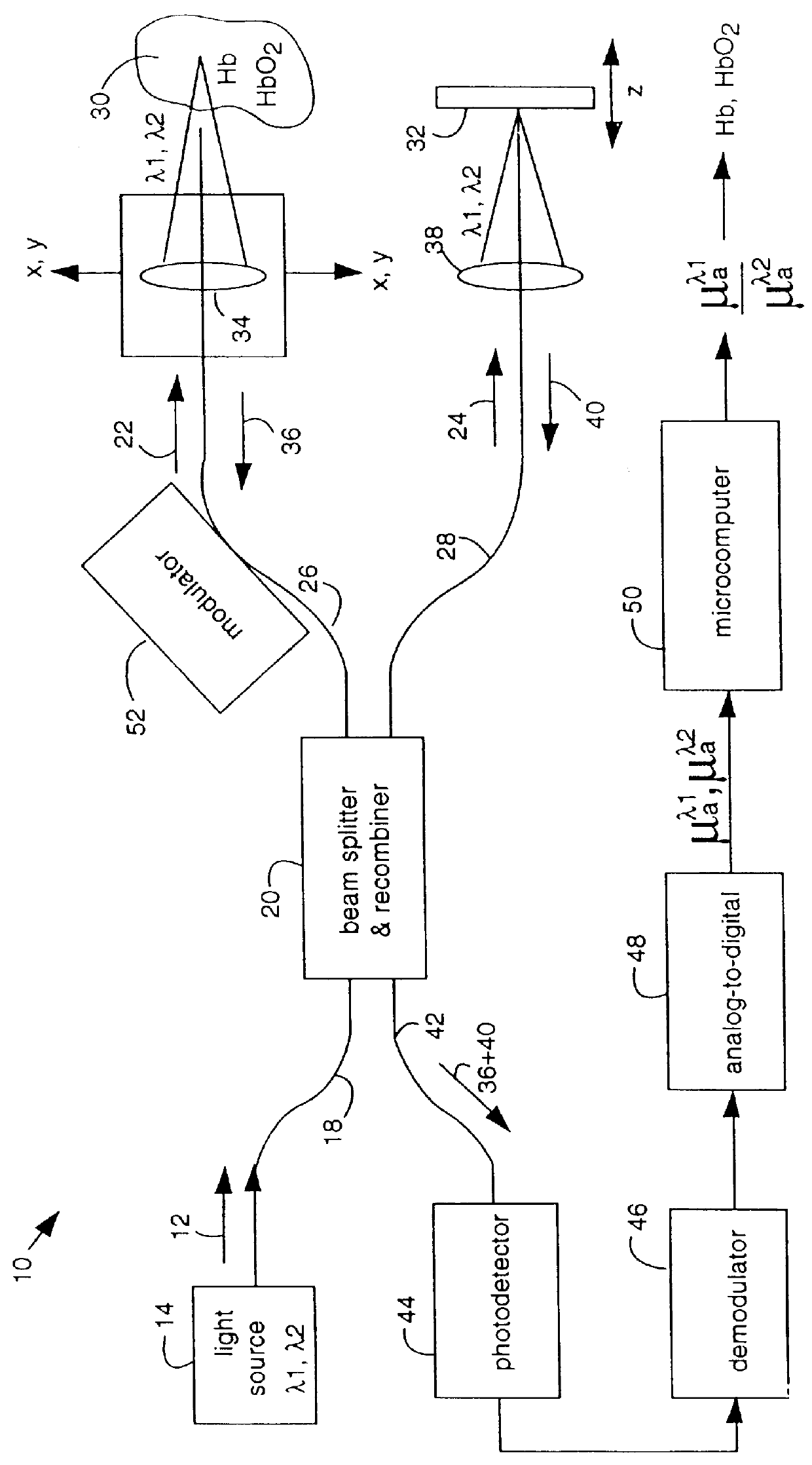
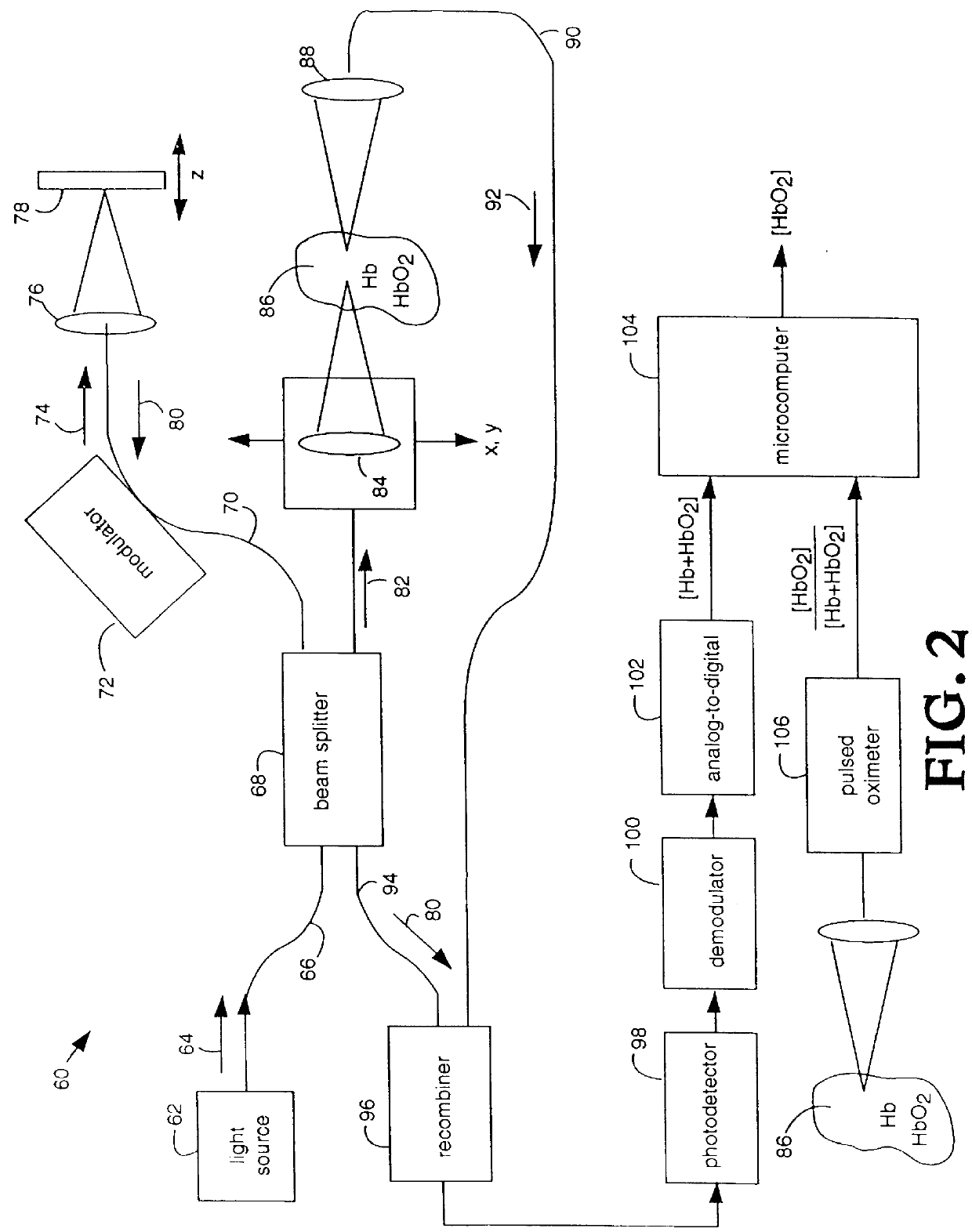
An oxygen concentration measurement system for blood hemoglobin comprises a multiple-wavelength low-coherence optical light source that is coupled by single mode fibers through a splitter and combiner and focused on both a target tissue sample and a reference mirror. Reflections from both the reference mirror and from the depths of the target tissue sample are carried back and mixed to produce interference fringes in the splitter and combiner. The reference mirror is set such that the distance traversed in the reference path is the same as the distance traversed into and back from the target tissue sample at some depth in the sample that will provide light attenuation information that is dependent on the oxygen in blood hemoglobin in the target tissue sample. Two wavelengths of light are used to obtain concentrations. The method can be used to measure total hemoglobin concentration [Hb.sub.deoxy +Hb.sub.oxy ] or total blood volume in tissue and in conjunction with oxygen saturation measurements from pulse oximetry can be used to absolutely quantify oxyhemoglobin [HbO.sub.2 ] in tissue. The apparatus and method provide a general means for absolute quantitation of an absorber dispersed in a highly scattering medium.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Method and apparatus for non-invasive blood constituent monitoring
InactiveUS20010039376A1Repeatable and reliableEasy to implementSensorsBlood characterising devicesNon invasiveTwo step
A system for determining a biologic constituent including hematocrit transcutaneously, noninvasively and continuously. A finger clip assembly includes including at least a pair of emitters and a photodiode in appropriate alignment to enable operation in either a transmissive mode or a reflectance mode. At least one predetermined wavelength of light is passed onto or through body tissues such as a finger, earlobe, or scalp, etc. and attenuation of light at that wavelength is detected. Likewise, the change in blood flow is determined by various techniques including optical, pressure, piezo and strain gage methods. Mathematical manipulation of the detected values compensates for the effects of body tissue and fluid and determines the hematocrit value. If an additional wavelength of light is used which attenuates light substantially differently by oxyhemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin, then the blood oxygen saturation value, independent of hematocrit may be determined. Further, if an additional wavelength of light is used which greatly attenuates light due to bilirubin (440 nm) or glucose (1060 nm), then the bilirubin or glucose value may also be determined. Also how to determine the hematocrit with a two step DC analysis technique is provided. Then a pulse wave is not required, so this method may be utilized in states of low blood pressure or low blood flow.
Owner:HEMA METRICS
Biological tissue blood flow, blood oxygen and blood volume multi-parameter detection method and device
ActiveCN105395184ASolve the disadvantage that it is difficult to achieve accurate time synchronizationAvoid the disadvantage of increasing costsSensorsBlood flow measurementMulti cameraTime-sharing
The invention discloses a biological tissue blood flow, blood oxygen and blood volume multi-parameter detection method and device. According to the method, two laser beams, differing in wavelength, simultaneously irradiate a biological tissue; and multiple frames of biological tissue colored images, which are illuminated by the laser beams, are continuously acquired by a photoelectric imaging system. The light intensity values of a red channel and a green channel on each pixel of the images are obtained for respectively constituting a red channel image and a green channel image. By virtue of a laser speckle blood flow imaging data analysis method and a dual-wavelength spectroscopic data analysis method, the red channel image and the green channel image are processed, so that two-dimensional spatial distribution and dynamic variation information thereof of a plurality of physiological parameters including blood flow, oxyhemoglobin concentration and reduced hemoglobin concentration of the corresponding biological tissue are obtained. The method and the device disclosed by the invention solve the shortcoming that a multi-wavelength time-sharing imaging based multi-parameter blood flow imaging system has difficulty in achieving the synchronization of accurate time and also avoid the shortcoming that a multi-camera shooting based multi-parameter blood flow imaging system is high in cost due to the use of a plurality of cameras.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optimized wavelength gap for improved StO2 measurement
InactiveUS7613489B2Degree of robustnessOptimize gapDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOxygenLength wave
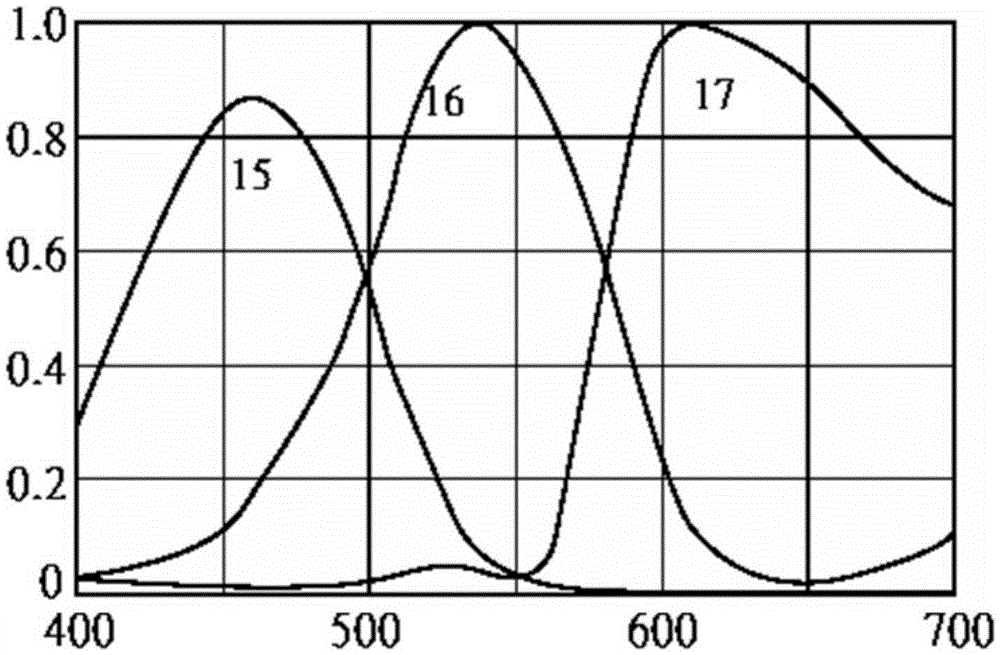
A method and system for producing improved more accurate measurements of oxyhemoglobin levels in tissue when measured using near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Light sources and processing methods are selected to such that the effects of a confounding chromophore in the tissue under study are minimized.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
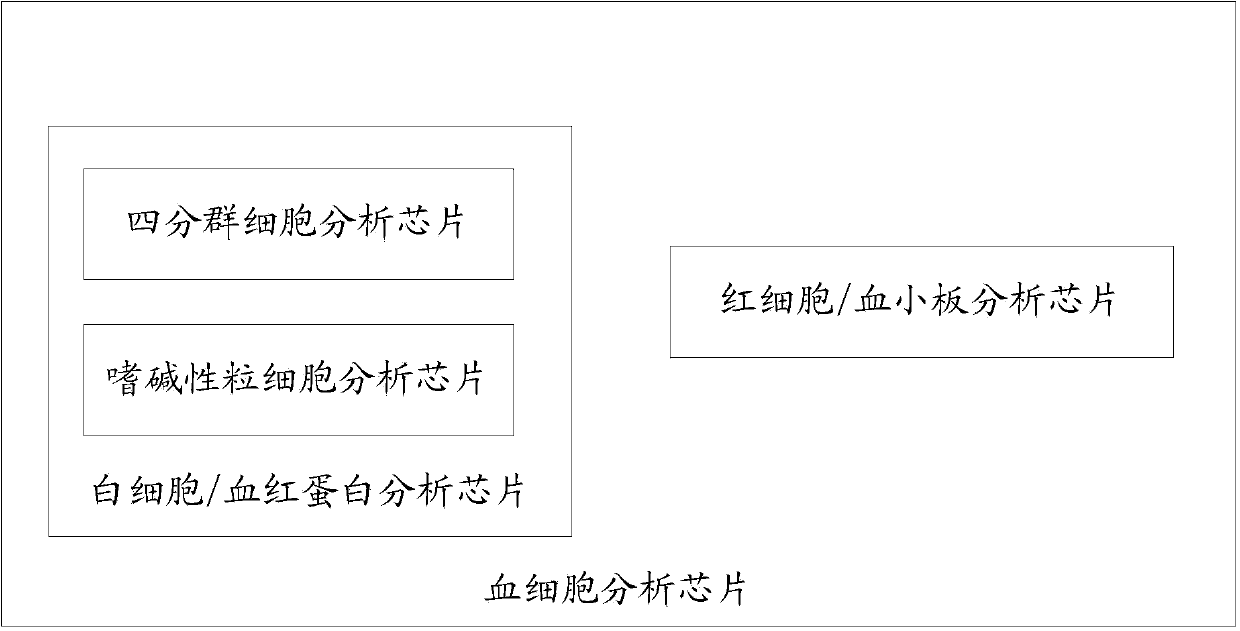
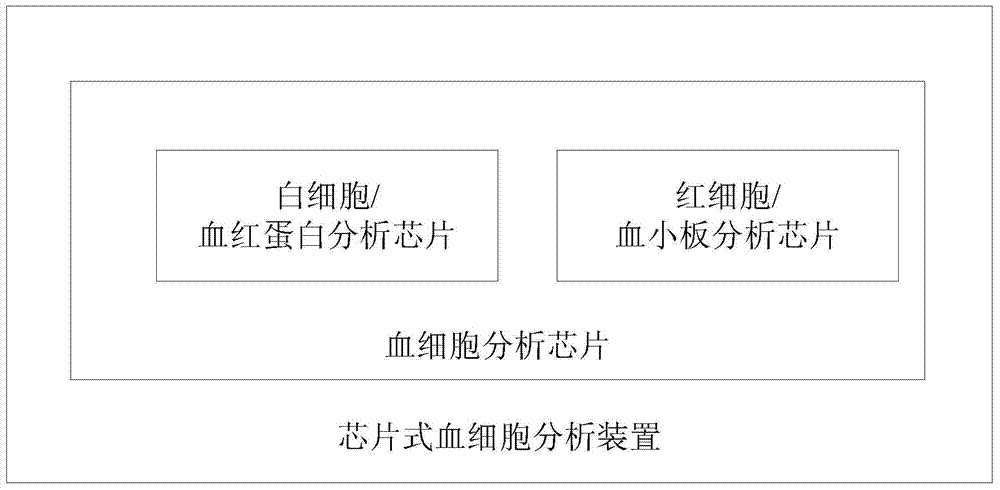
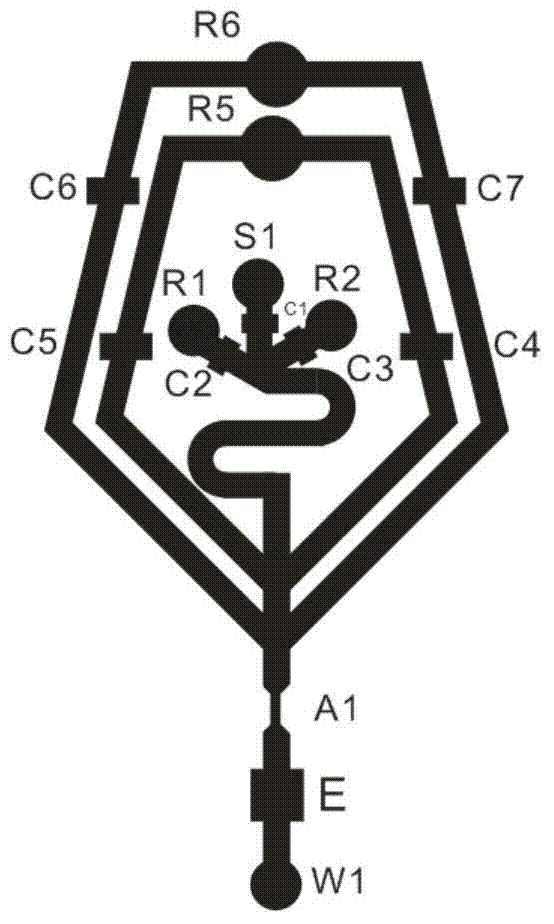
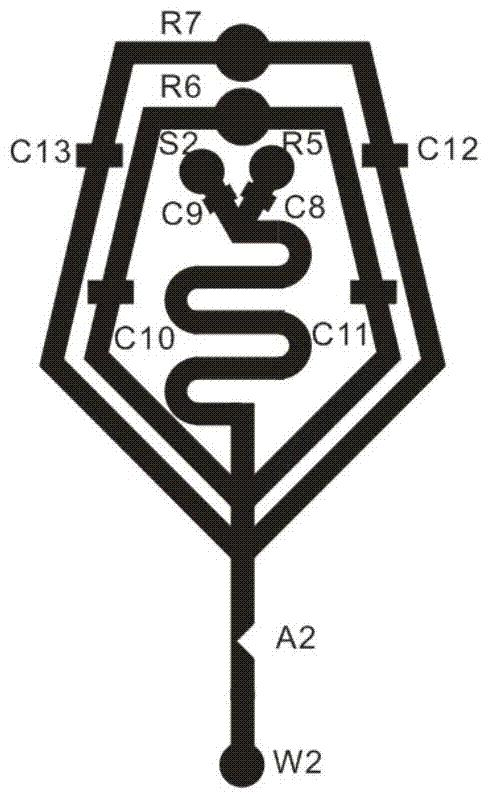
Hemocyte analysis chip, analyzer and analysis method
InactiveCN103472216ASimple structureReduce volumeColor/spectral properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisWhite blood cellDissolution
The invention belongs to the technical field of hemocyte analysis, and relates to a hemocyte analysis chip, a hemocyte analyzer and a hemocyte analysis method. The hemocyte analysis chip comprises a leucocyte / ferrohemoglobin analysis chip and an erythrocyte / thrombocyte analysis chip; the leucocyte / ferrohemoglobin analysis chip comprises a quartile group cell analysis chip and a basophils analysis chip; the quartile group cell analysis chip performs cell sorting by utilizing a chemical dyeing method, an electrical impedance technology and a light adsorption method, and detects haematoglobin by adopting a colourimetry; the basophils analysis chip performs leucocyte counting and basophile detection by utilizing a bio-dissolution technique, an electric impedance measurement method and a threshold landmark method; the erythrocyte / thrombocyte analysis chip is used for counting erythrocytes and thrombocytes by adopting an electric impedance technology and a landmark technology. The hemocyte analysis chip, the hemocyte analyzer and the hemocyte analysis method has the advantages of simple structure, small size, low cost, high convenience for operation, high easiness maintenance and transportation, and disposable chip and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGKE QIANGHUA TECH
Backwashing flow path system of glycated hemoglobin analyzer
Owner:JIANGSU AUDICOM MEDICAL TECH
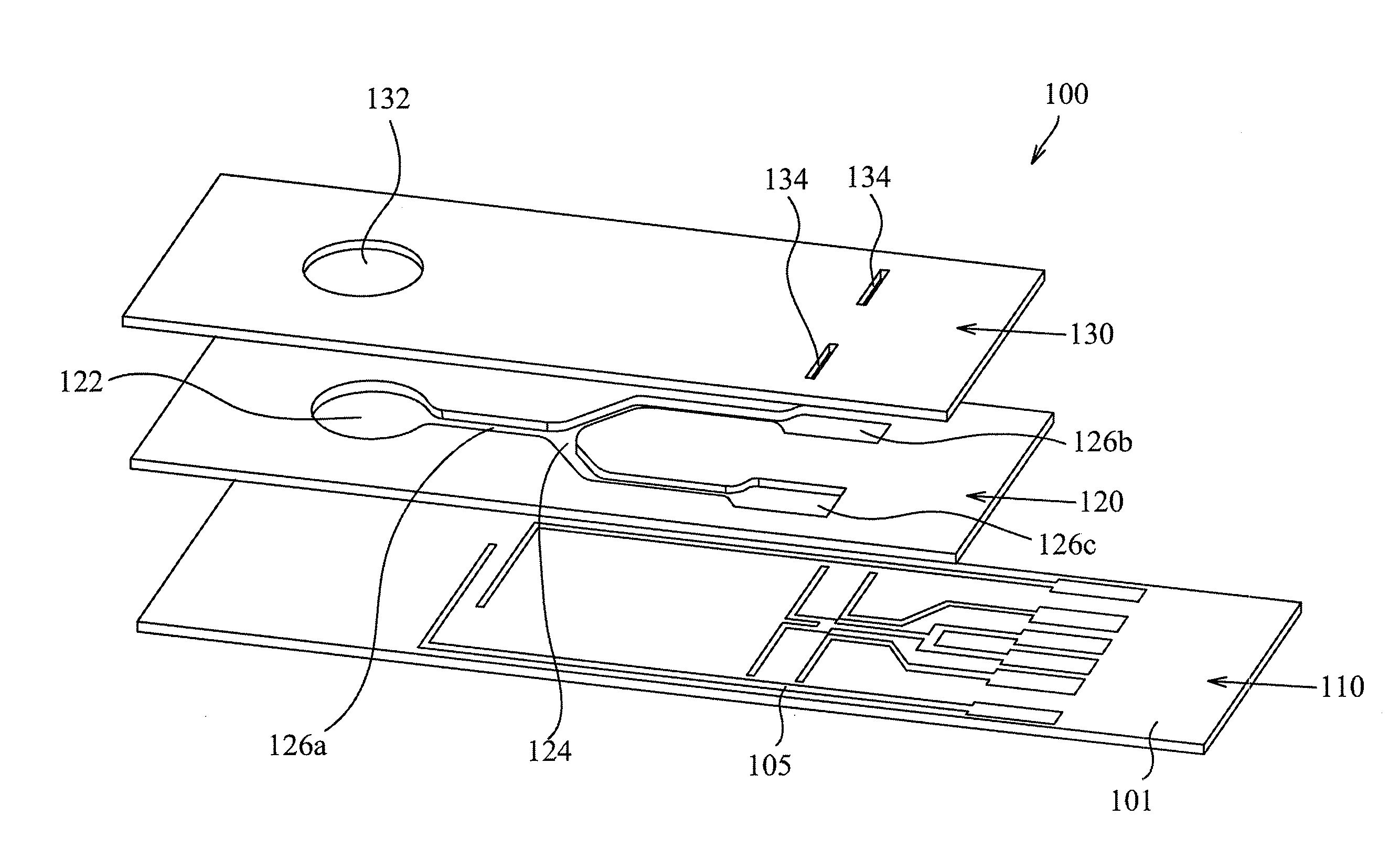
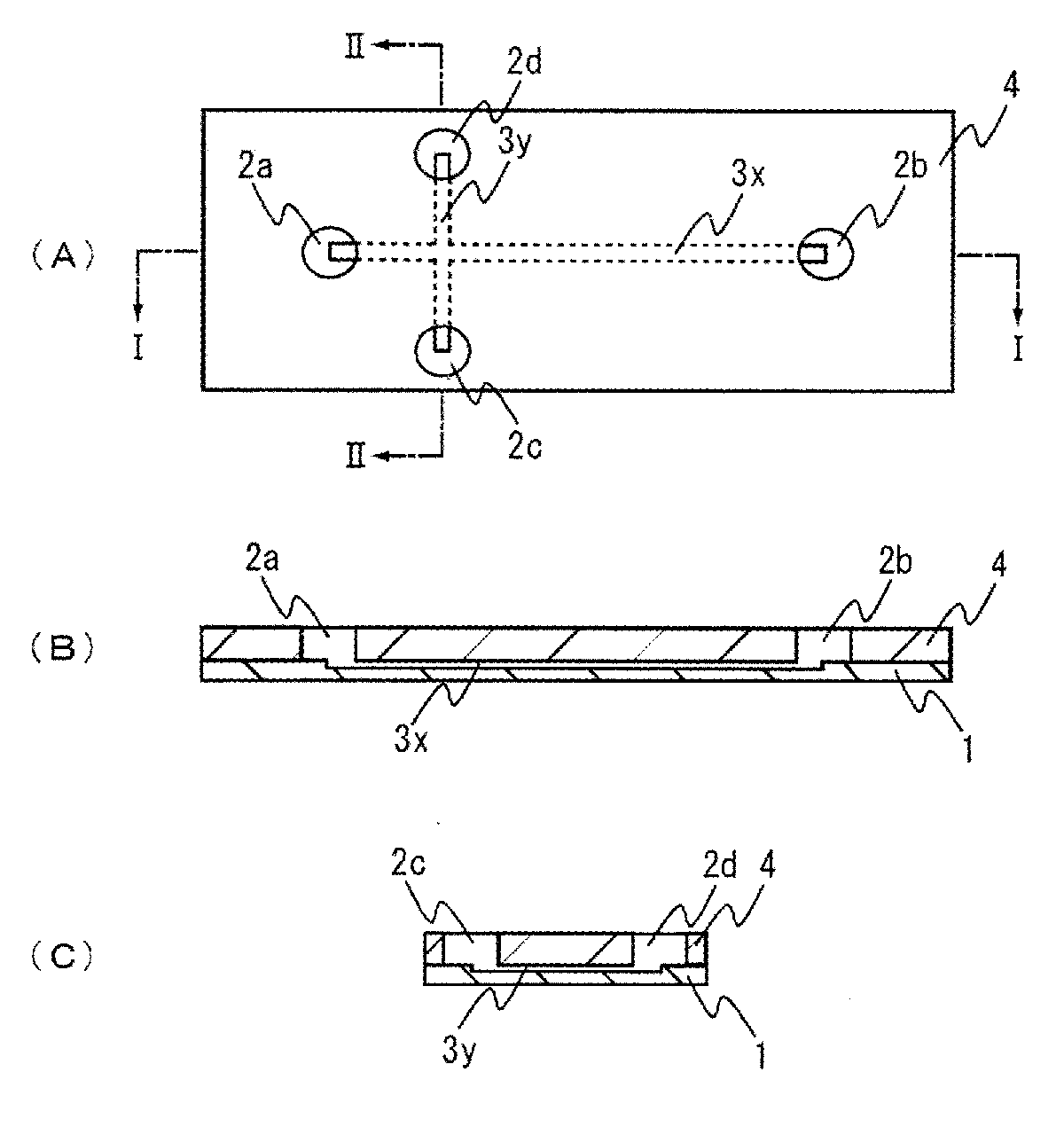
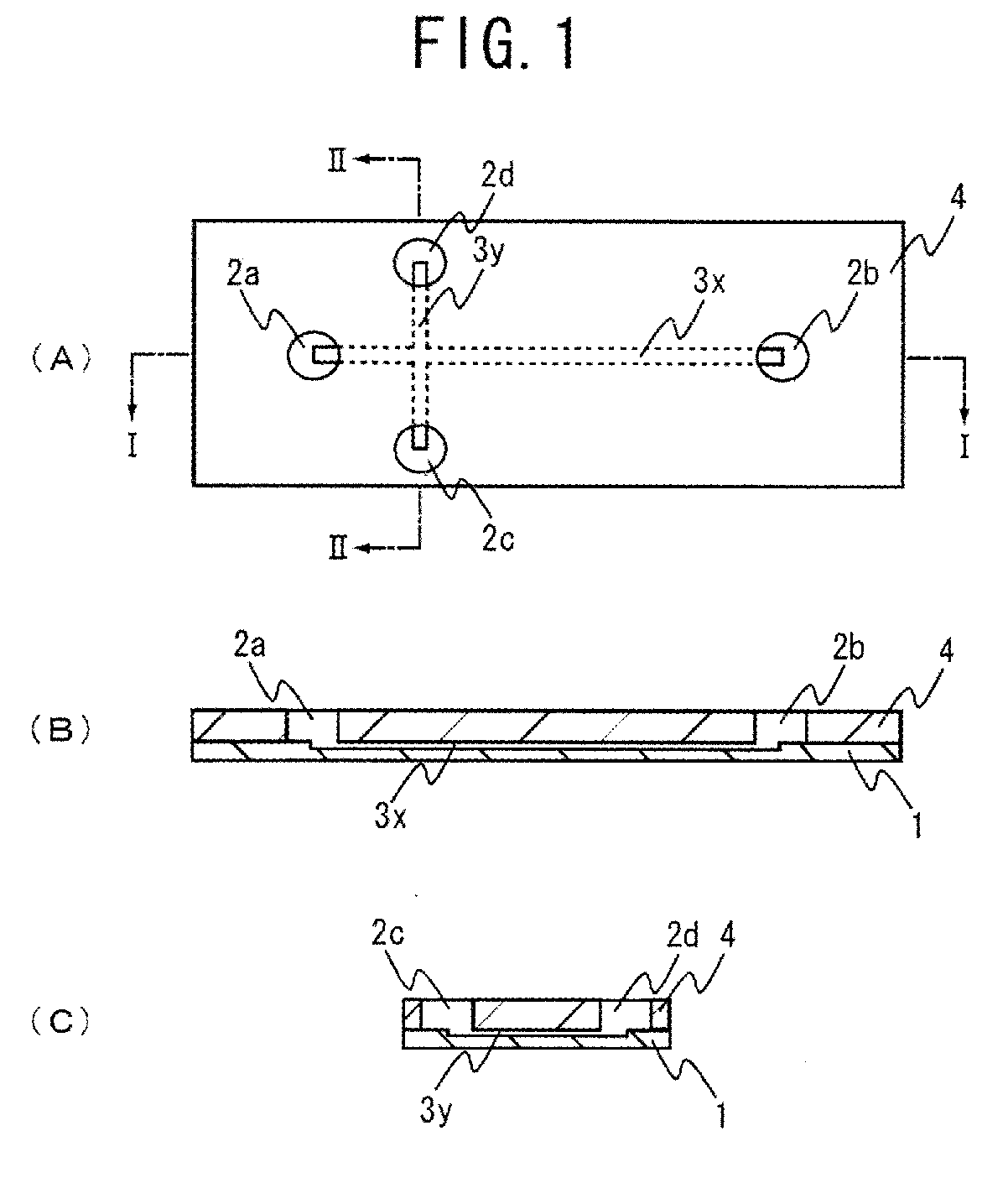
Electrophoresis Chip and Electrophoresis Apparatus
InactiveUS20120012462A1Short analysis timeAccurate analysisCellsSludge treatmentElectrophoresisCapillary channel
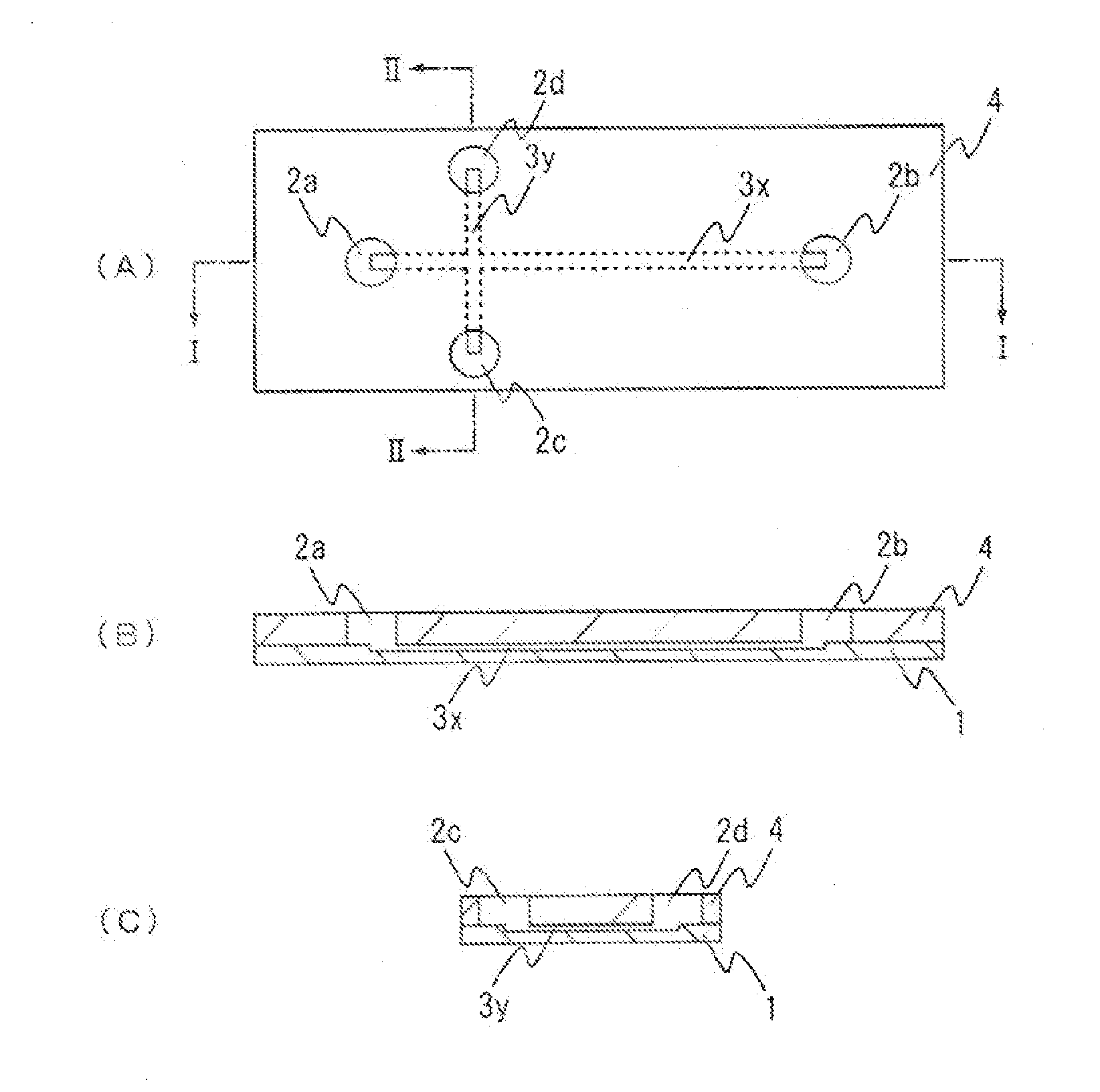
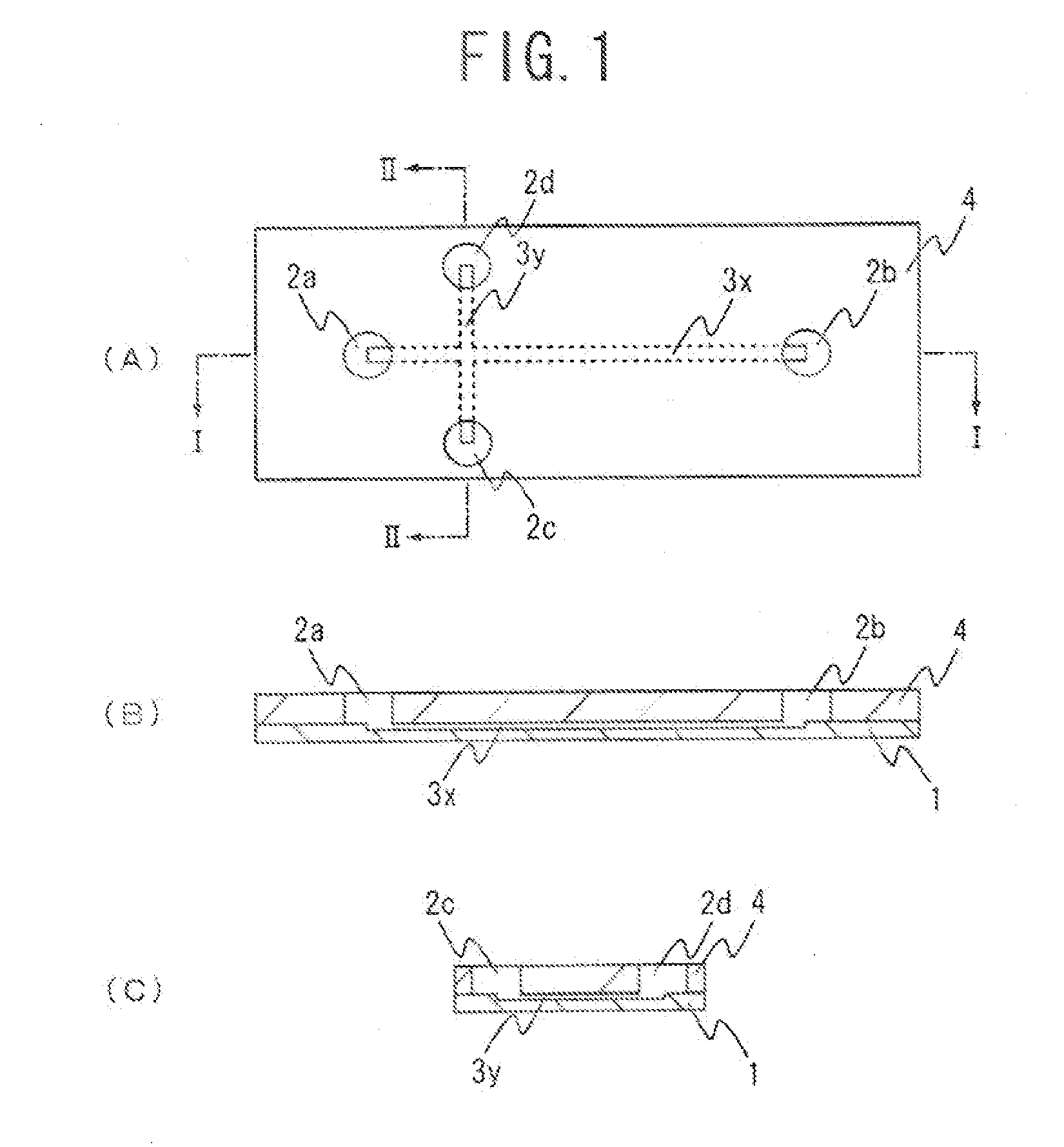
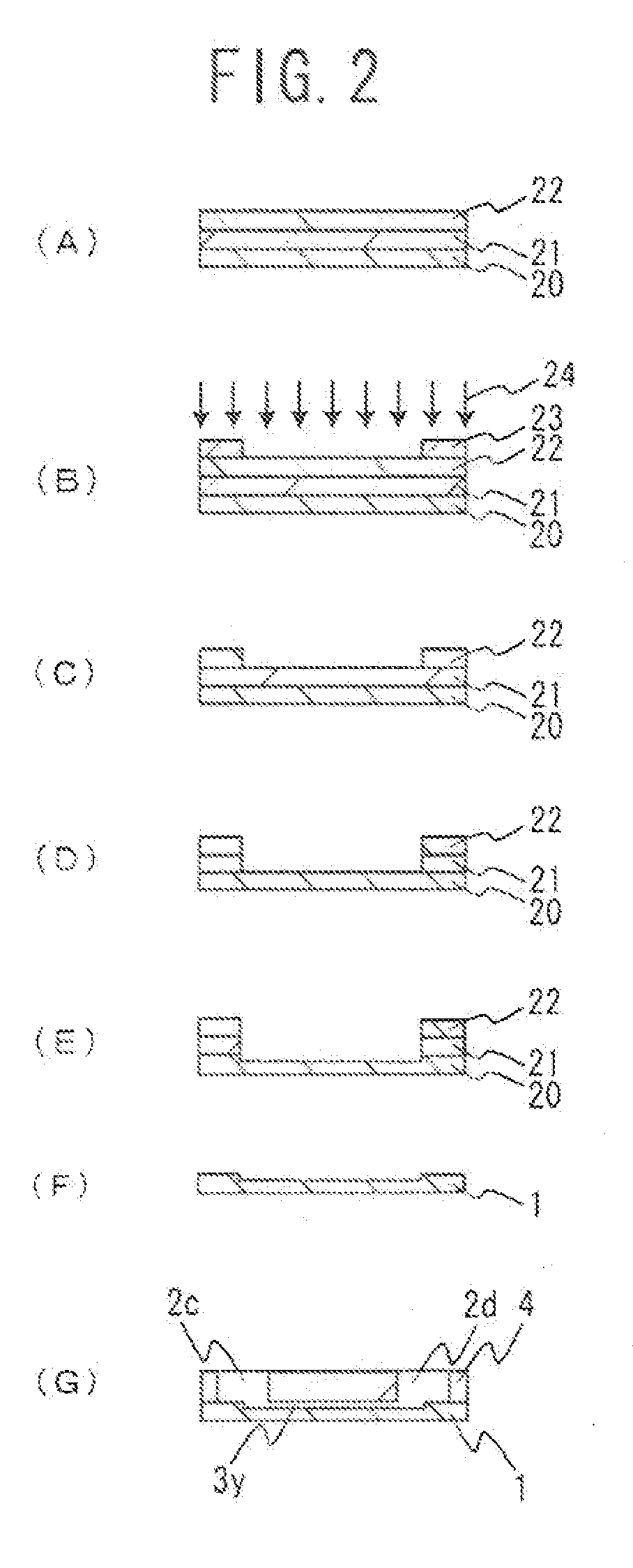
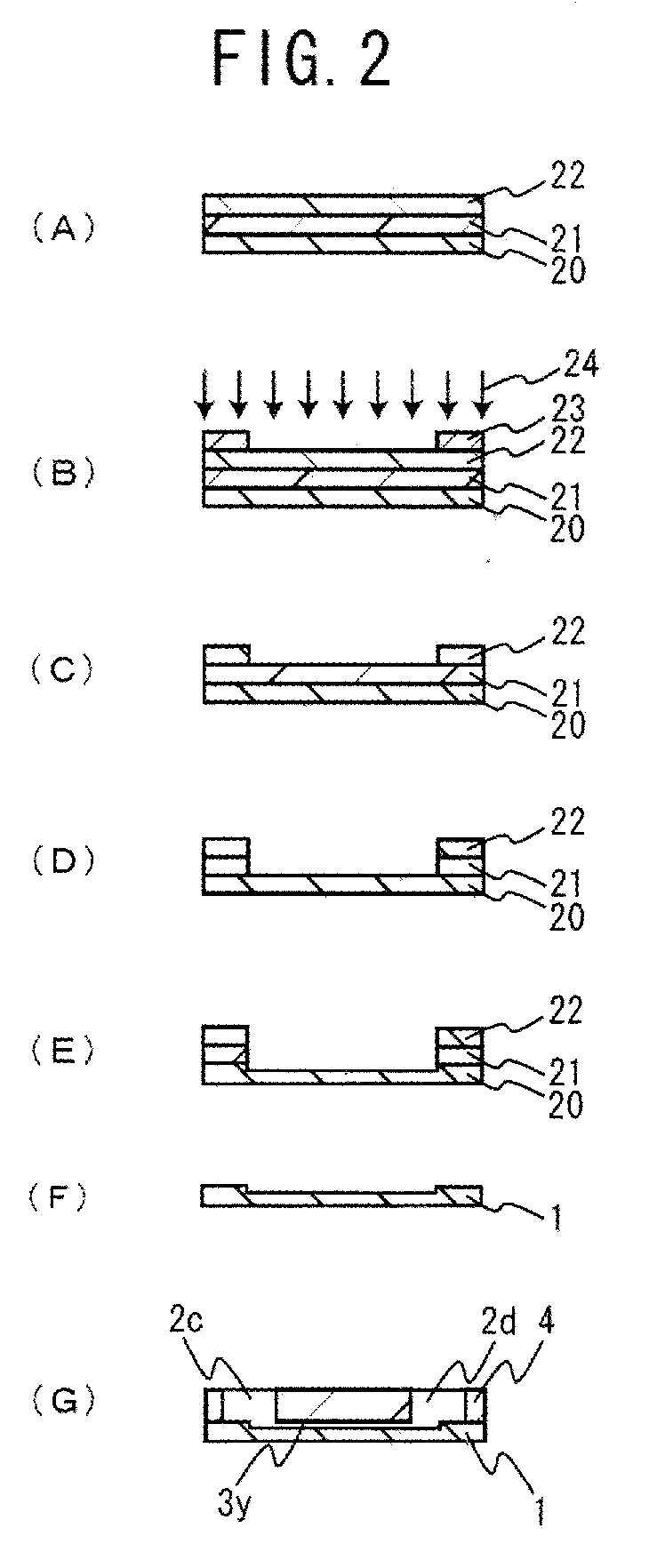
An electrophoresis chip that enables an apparatus to be small, analysis time to be short and glycosylated hemoglobin to be analyzed highly accurately is provided. The electrophoresis chip includes an upper substrate 4, a lower substrate 1, a first introduction reservoir 2a, a first recovery reservoir 2b and a capillary channel for sample analysis 3x; the first introduction reservoir 2a and the first recovery reservoir 2b are formed in the lower substrate 1; and the first introduction reservoir 2a and the first recovery reservoir 2b are in communication with each other via the capillary channel for sample analysis 3x.
Owner:SUGIYAMA KOJI +2
Collection liquid for protecting and stabilizing hemoglobin in manure and application of collection liquid
ActiveCN105716917ALong storage timePreparing sample for investigationPreservativePolyethylene glycol
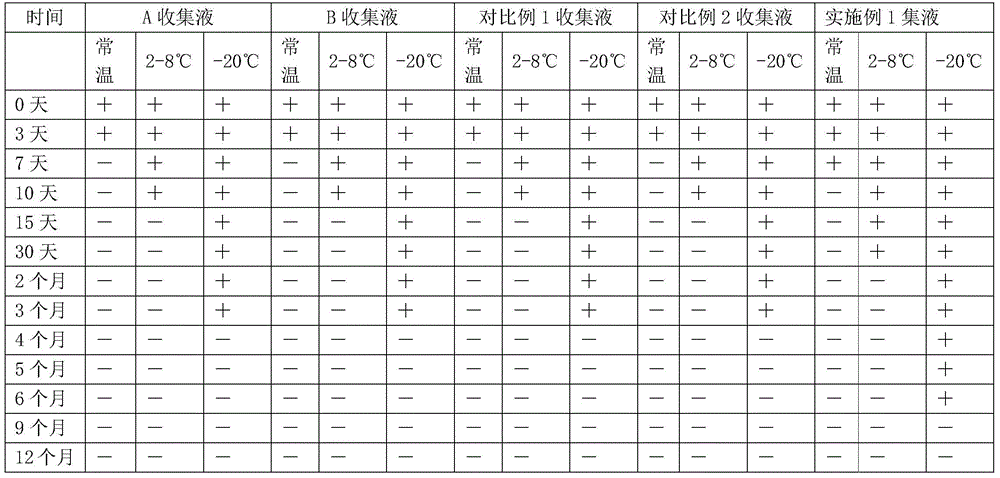
The invention discloses collection liquid for protecting and stabilizing hemoglobin in manure and application of the collection liquid. The collection liquid comprises 25-45 g / L of chelating agent, 0.2-1 g / L of preservative, 1-10 g / L of sealing agent, 6-12 g / L of buffering agent and 25-30 g / L of polyethylene glycol, wherein the chelating agent is a mixture of two of HIDS, EDTA and sodium tripolyphosphate. After fresh manure and the collection liquid are mixed well according to a proportion of 50 mg:2 ml, the collection liquid can be stored for 7 days at normal temperature, one month at 2-8 DEG C and six months at minus 20 DEG C. The collection liquid can further stabilize hemoglobin and prolong storage time of hemoglobin in manure in protection liquid.
Owner:HANGZHOU ALLTEST BIOTECH
Cigarette filter containing material selectively decreasing biological harm of carbon monoxide (CO) in smoke and preparation method of cigarette filter
ActiveCN102763898AHas the function of biological hazard reductionKeep aliveTobacco smoke filtersPolyethylene glycolMesoporous material
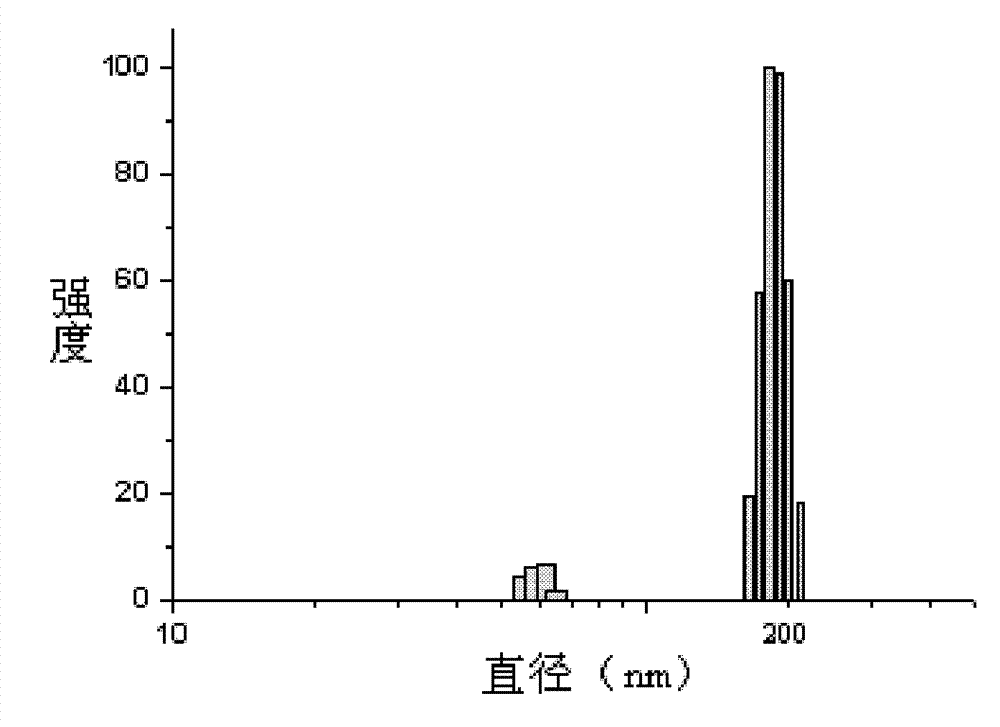
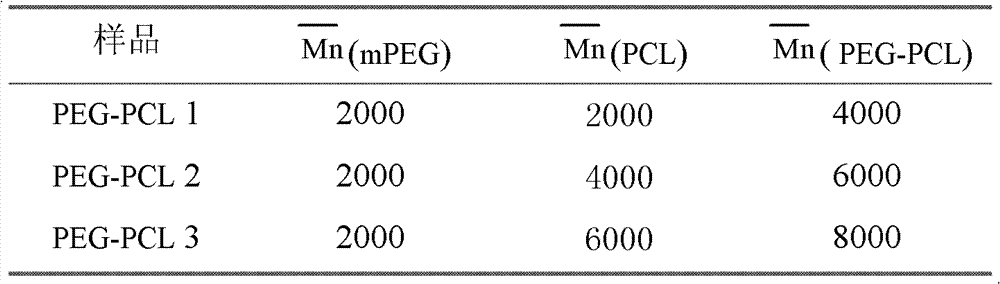
The invention discloses a cigarette filter containing a material selectively decreasing biological harm of carbon monoxide (CO) in smoke and a preparation method of the cigarette filter, belonging to the technical field of the cigarette filter. The cigarette filter provided by the invention is characterized in that a nanometer mesoporous material of self-assembling immobilized hemoglobin of amphiphilic diblock copolymer of polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone is added into a tow material, wherein the nanometer mesoporous material accounts for 10-25% of the total weight of the tow material. The preparation method of the cigarette filter provided by the invention comprises the following steps: [1] immobilizing hemoglobin in the amphiphilic diblock copolymer of polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone with the average molecular weight of 8000, 6000 or 4000; and [2] adding the HINH material (nanometer mesoporous material) into the tow material of the cigarette filter. The cigarette filter provided by the invention has a function of selectively decreasing the biological harm of CO in the smoke. An immobilization condition of the PEG-PCL (polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone) immobilized hemoglobin is mild, the activity of the hemoglobin is guaranteed, the storage period is long and the fragrance of flue-cured type cigarettes is not damaged.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +1
Method of validating a biometric capture, notably a body print
ActiveUS8508337B2Simple and quick to implementElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsFluenceBody area
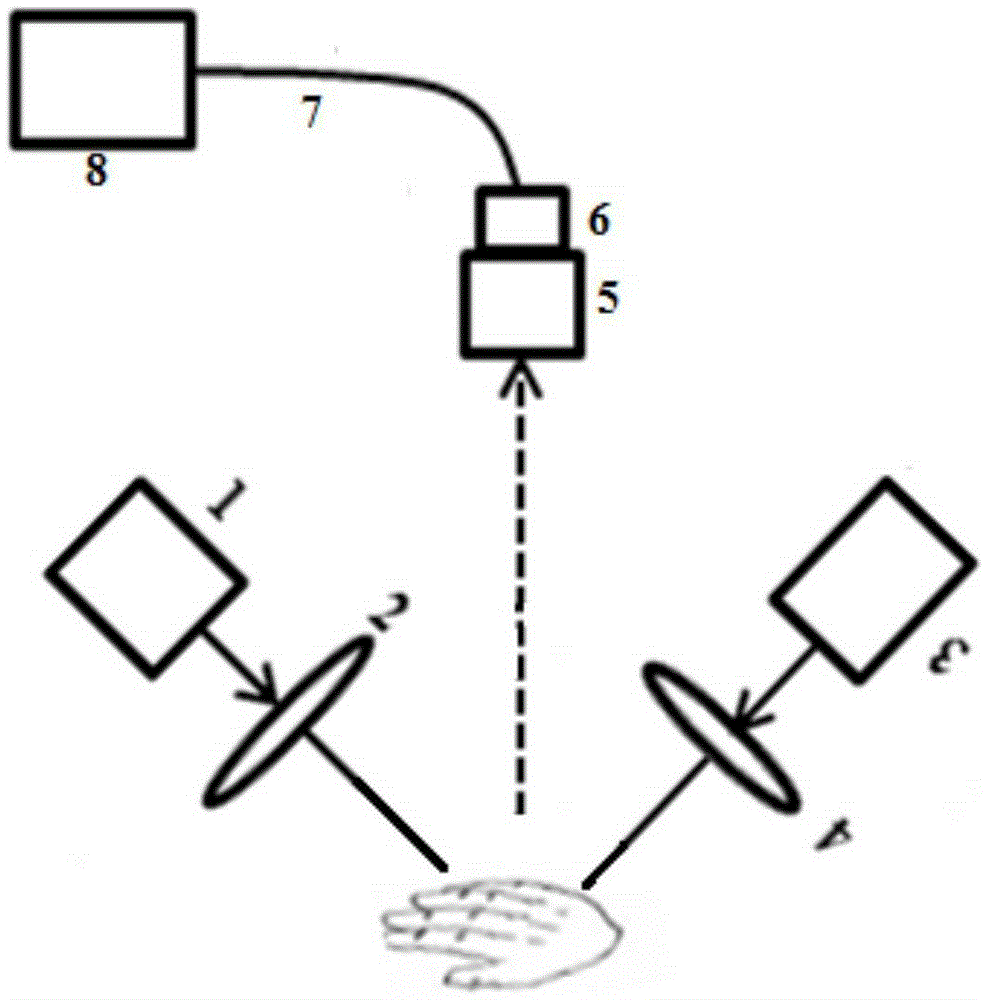
The invention relates to a method for validating a biometrical acquisition, mainly the acquisition of a body imprint of a body area such as fingerprints or a face imprint, wherein the method involves together with the biometric acquisition: lighting the body area using at least one radiation having at least two respective different wavelengths between approximately 500 nm and 1150 nm; taking at least two reflectometry measurements concerning said and at least two wavelengths for measuring the reflection index of the tissues for these wavelengths; calculating the ratio for two measured indices; and comparing the ratio with a range of reference values characterizing a haemoglobin-containing living tissue in terms of proportions of oxygenated and non-oxygenated forms characteristic of the living states for the wavelengths in question; if the ratio is included in said range, the body area is considered as living and the biometrical acquisition is validated; and conversely, if the body area is considered as not living, the biometrical acquisition cannot be validated.
Owner:IDEMIA IDENTITY & SECURITY FRANCE +1
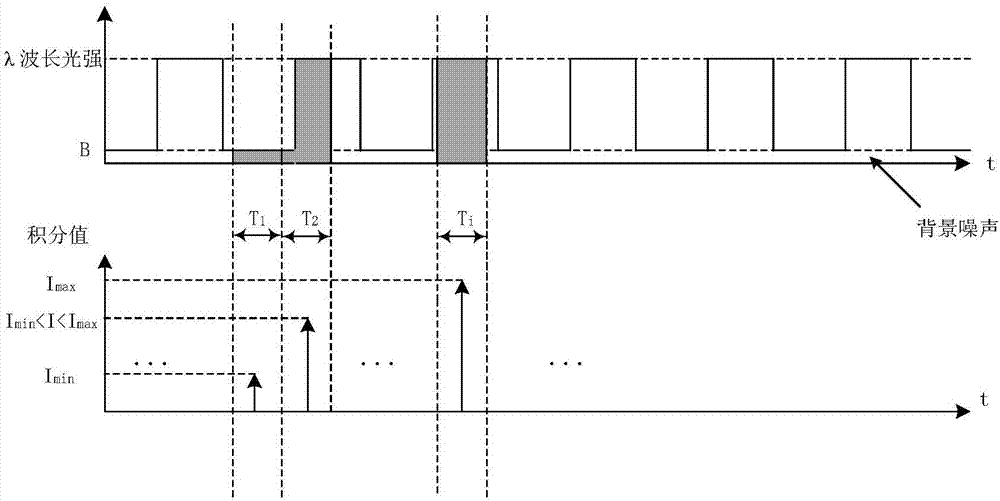
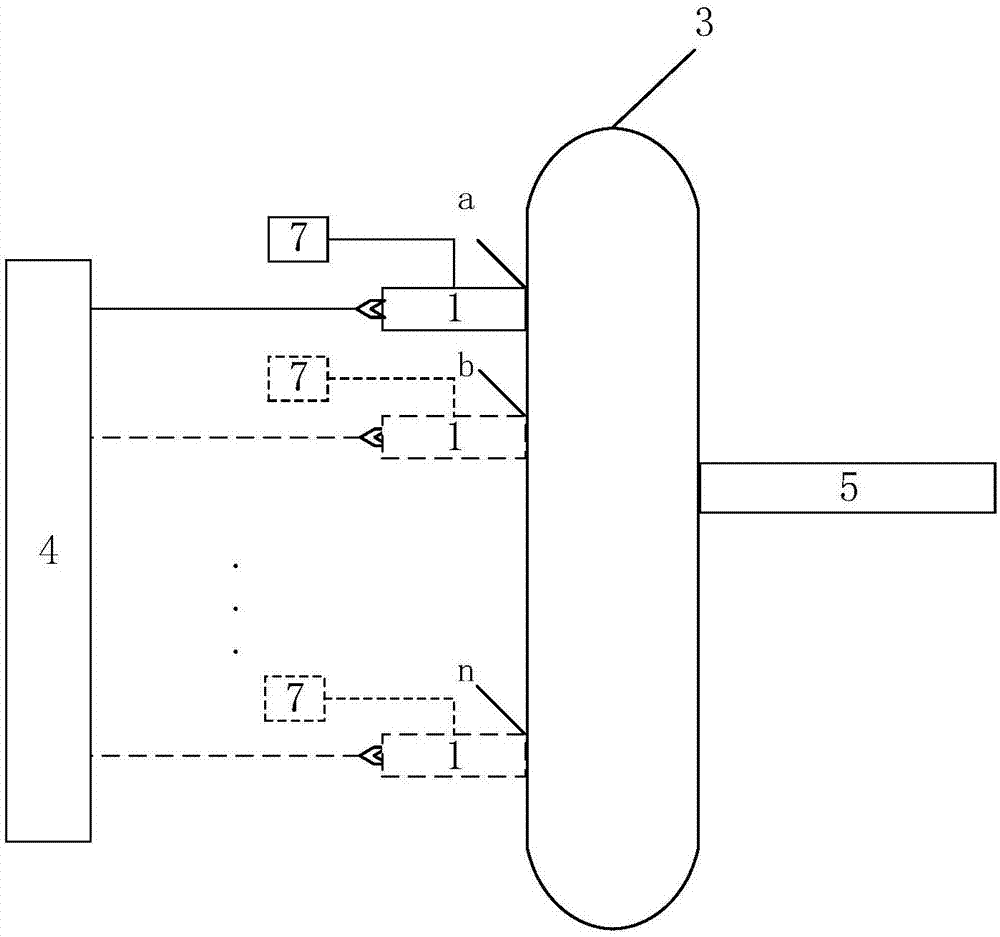
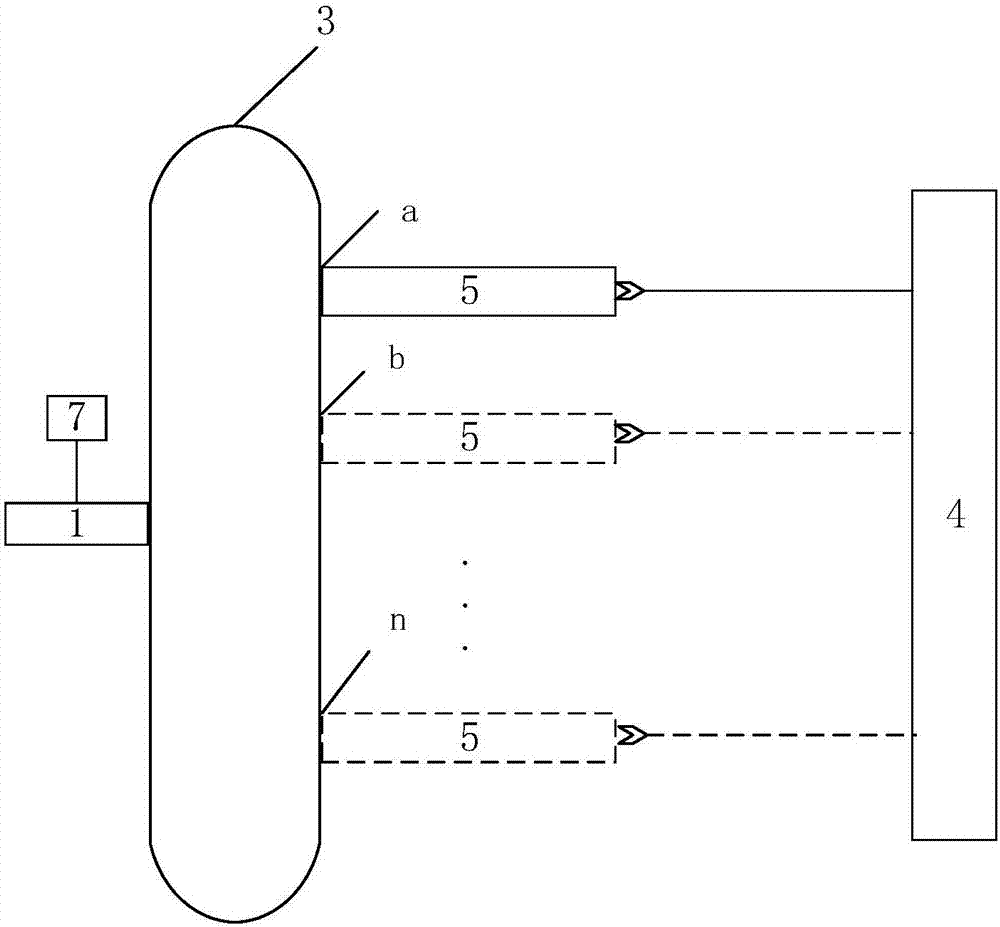
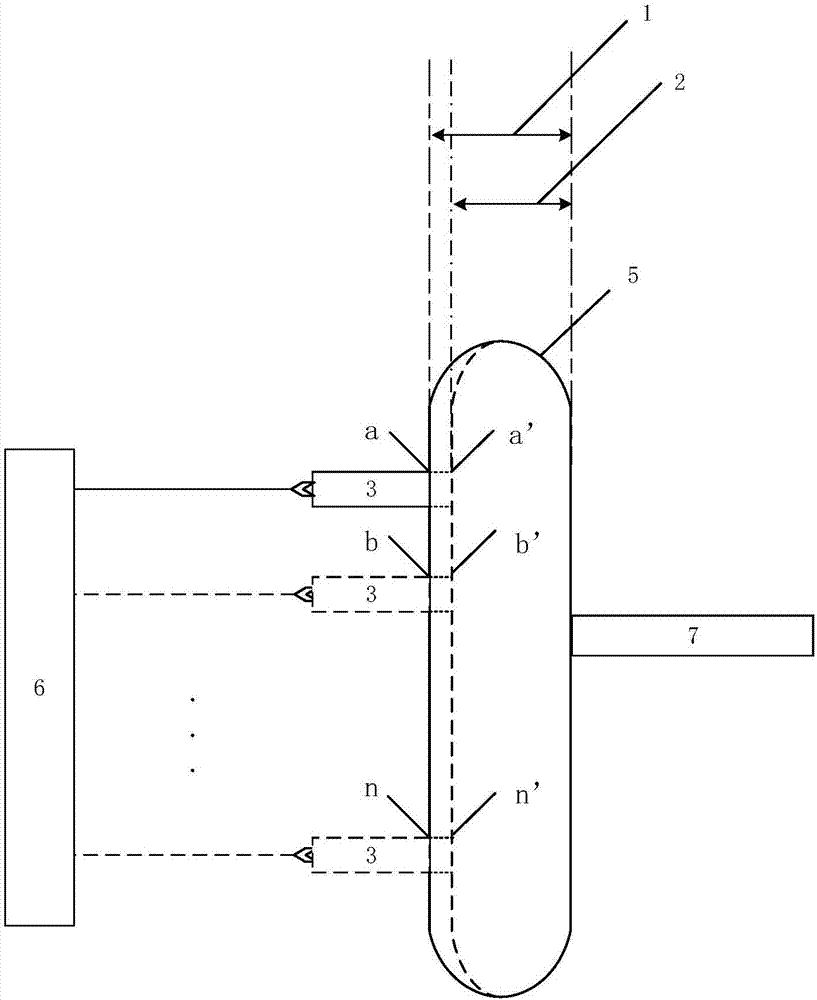
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag by multiple-position modulated light source
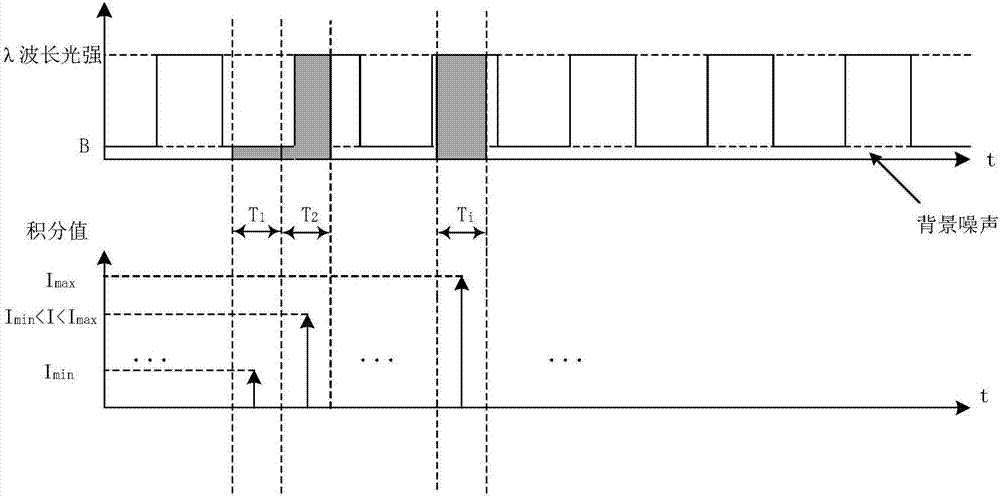
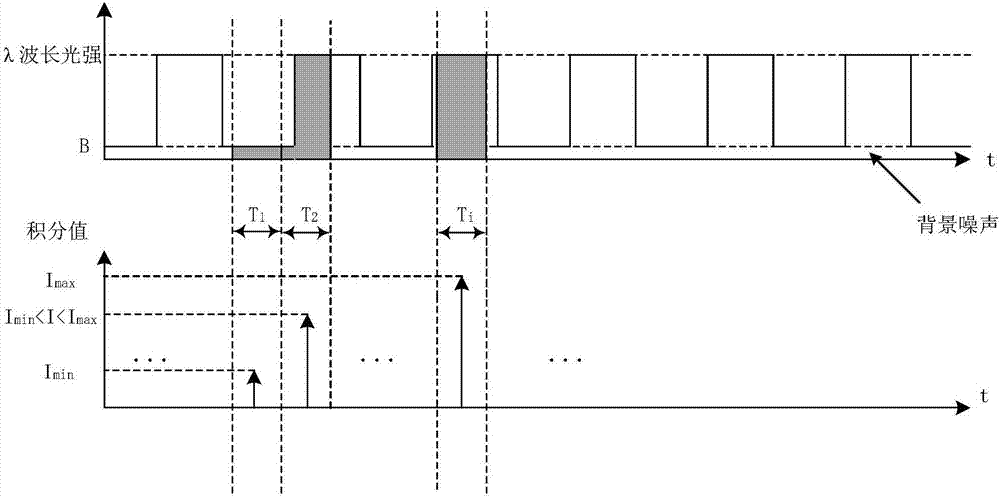
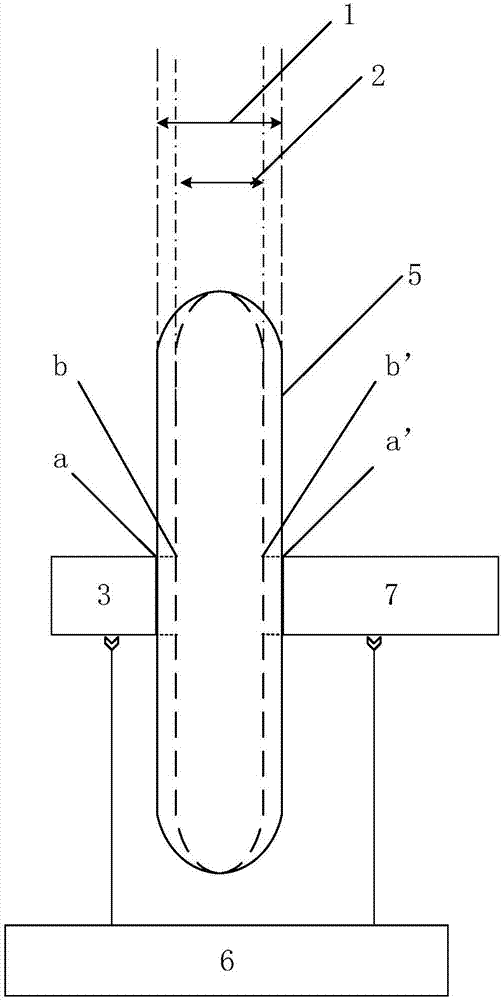
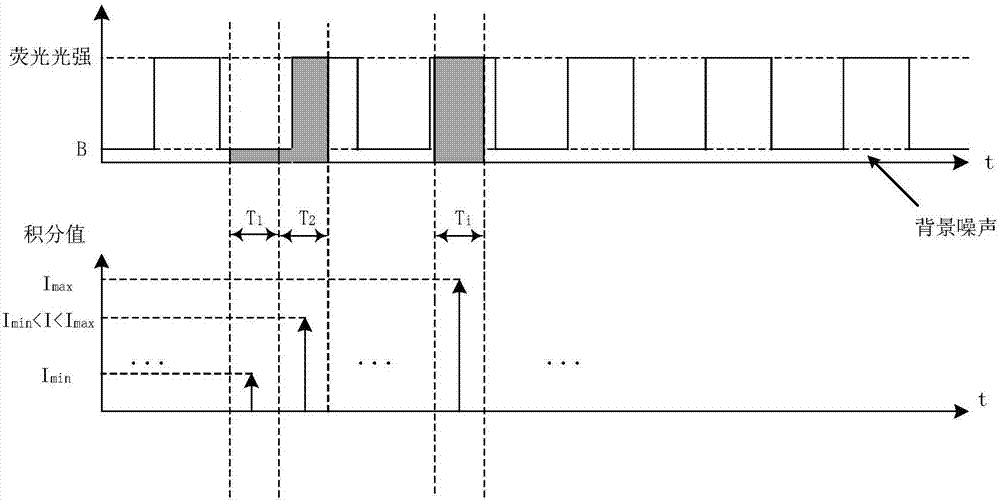
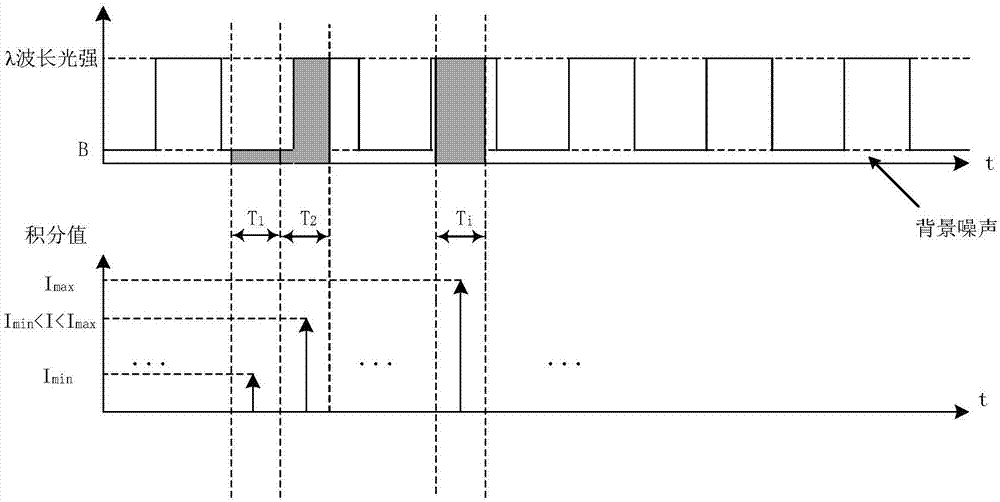
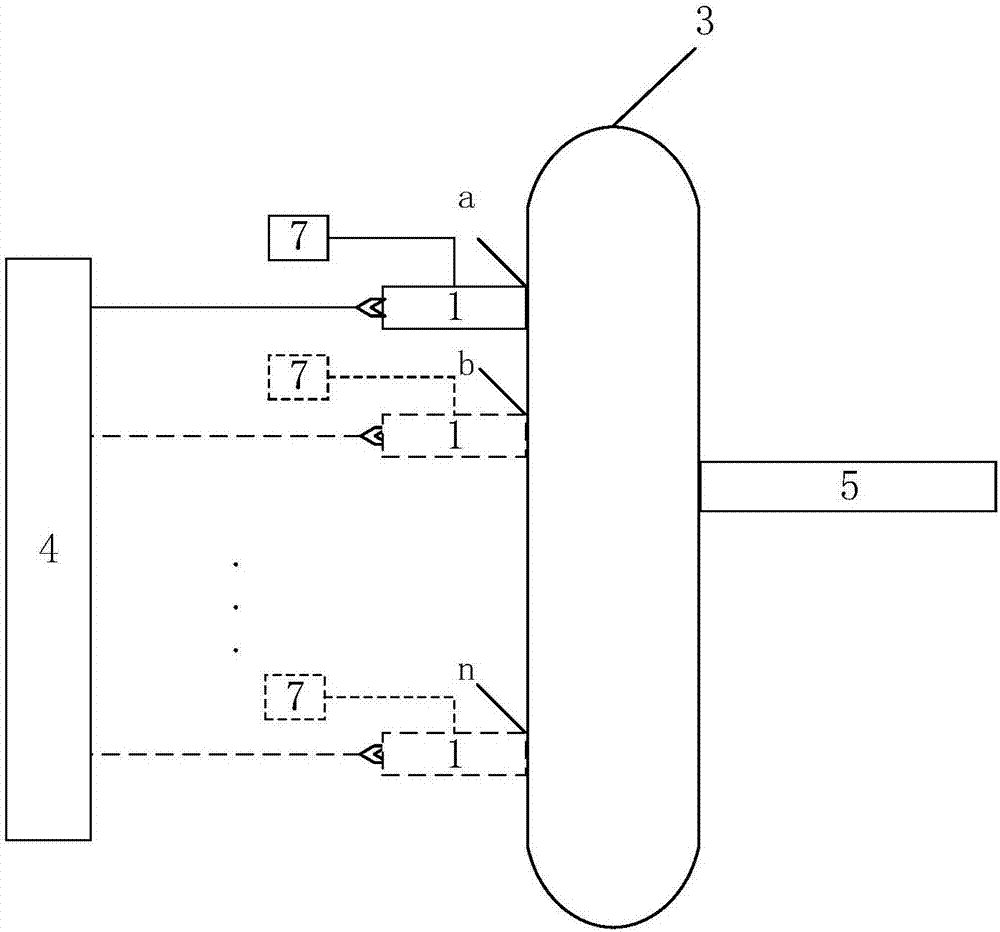
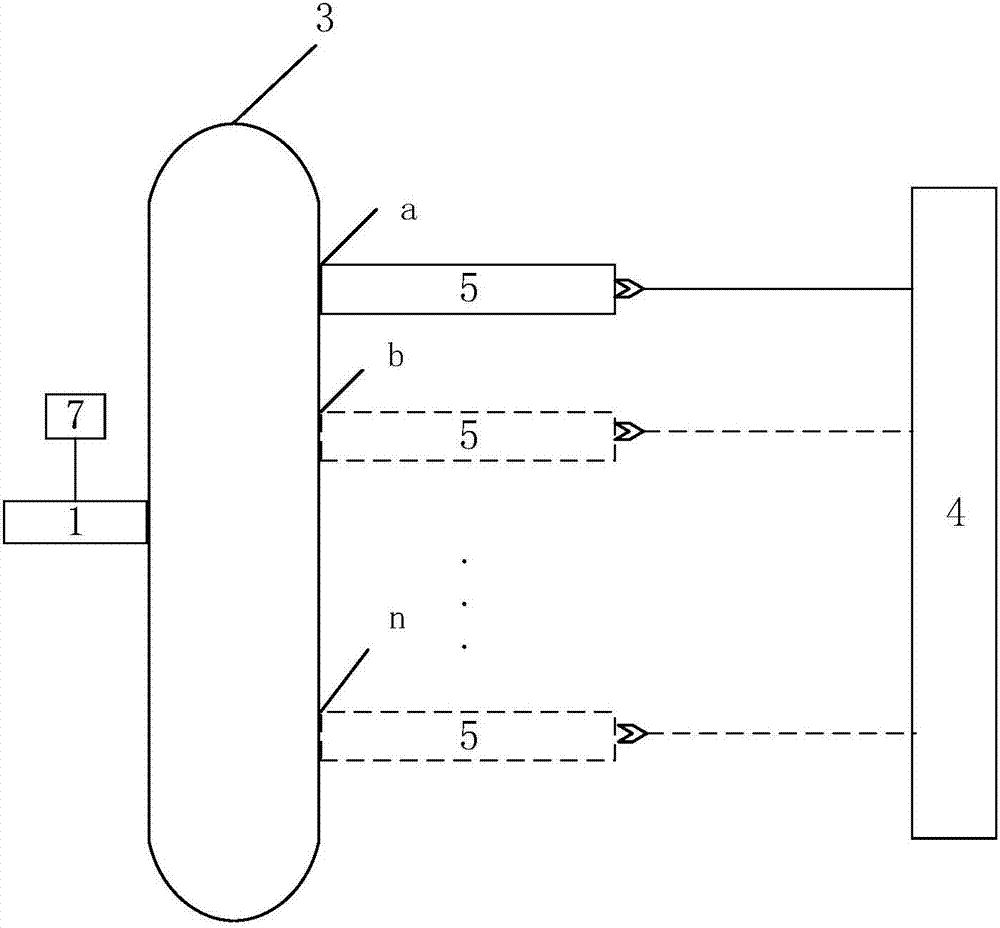
InactiveCN107356533ARemove background noiseLarge amount of informationColor/spectral properties measurementsFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag by a multiple-position modulated light source. The method comprises the following steps: modulating a light source by a modulation device, allowing the light exit port of the light source and the entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device to cling to the blood bag, controlling the light source to move to multiple positions by a displacement platform in order to transmit a blood sample, and acquiring the transmission spectrum by the spectrum receiving device; transforming the time sequence of every wavelength in the acquired transmission spectrum into a frequency domain, constructing a transmission spectrum in the frequency domain based on the fundamental wave component of every wavelength, carrying out normalization processing, comparing the obtained result with existing chemical analysis results, and establishing a mathematical model; and acquiring the transmission spectrum in the frequency domain of an unknown blood sample through using above steps, normalizing the obtained transmission spectrum, and substituting the normalization result into the mathematical model in order to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin. The method eliminates the influences brought by spectral background noises and scattering, increases the information content of all components in the blood, and improves the precision of the free hemoglobin content analysis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Feces sampling container, method for measuring components in feces sample, method for stabilizing components in feces sample, and method for storing feces sample
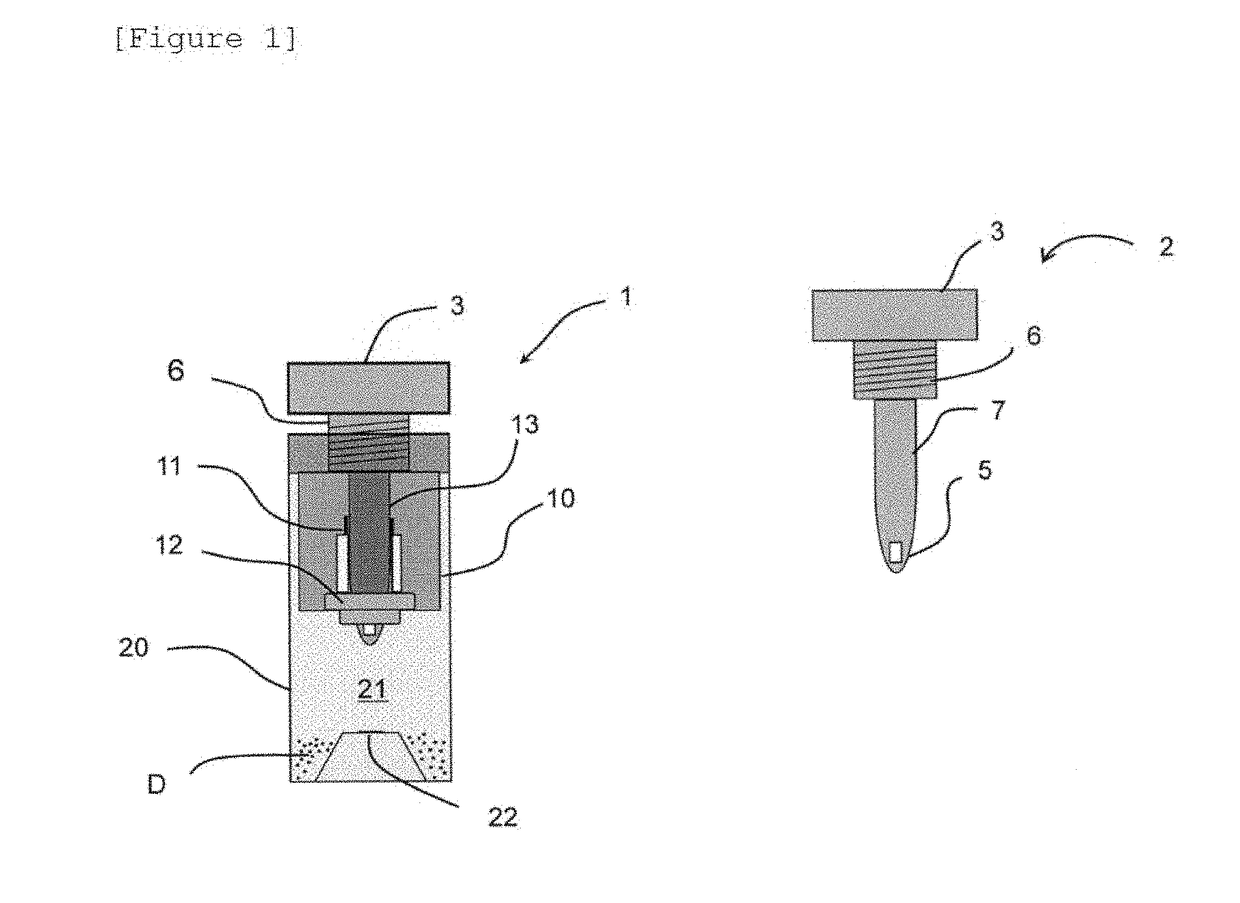
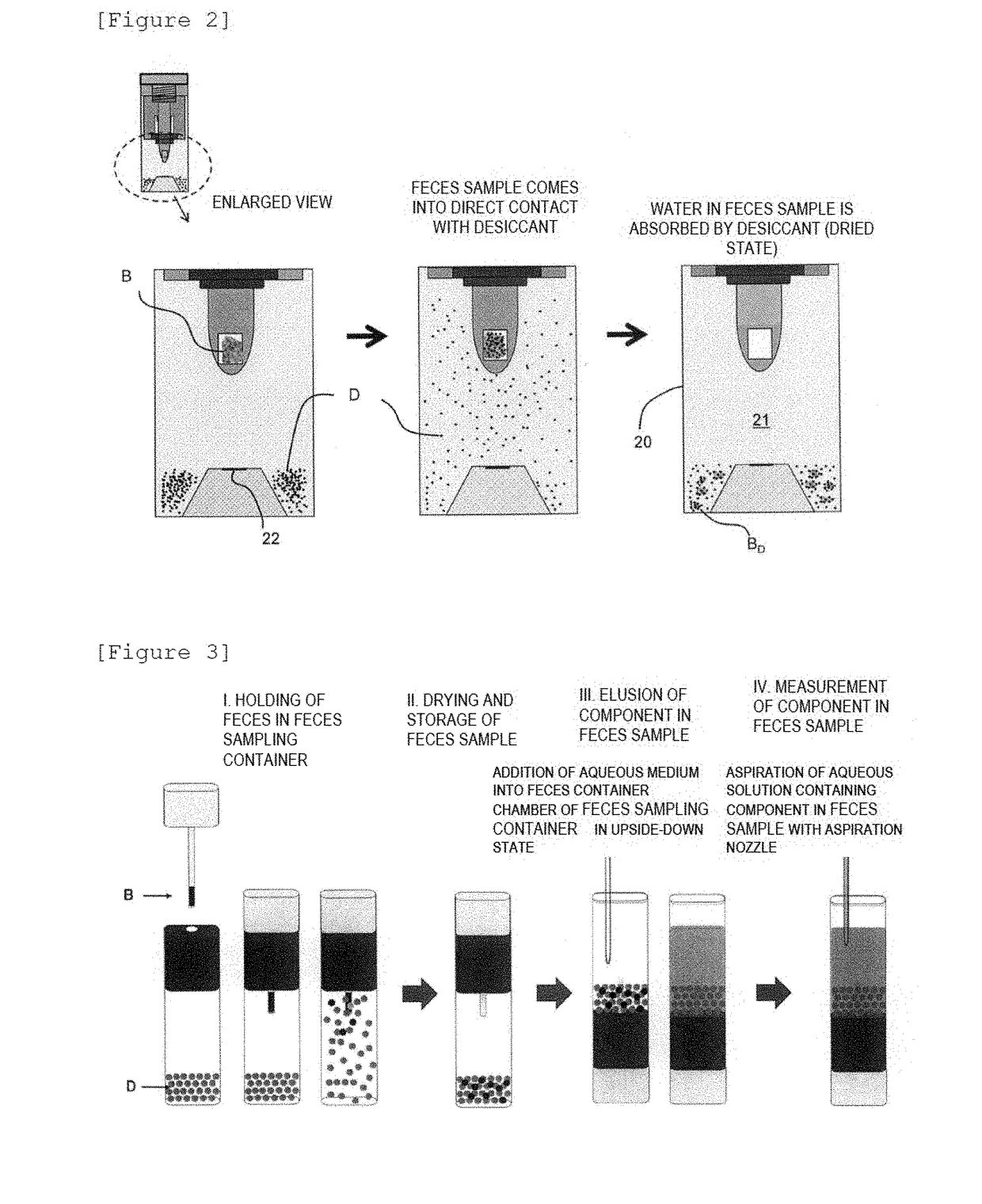
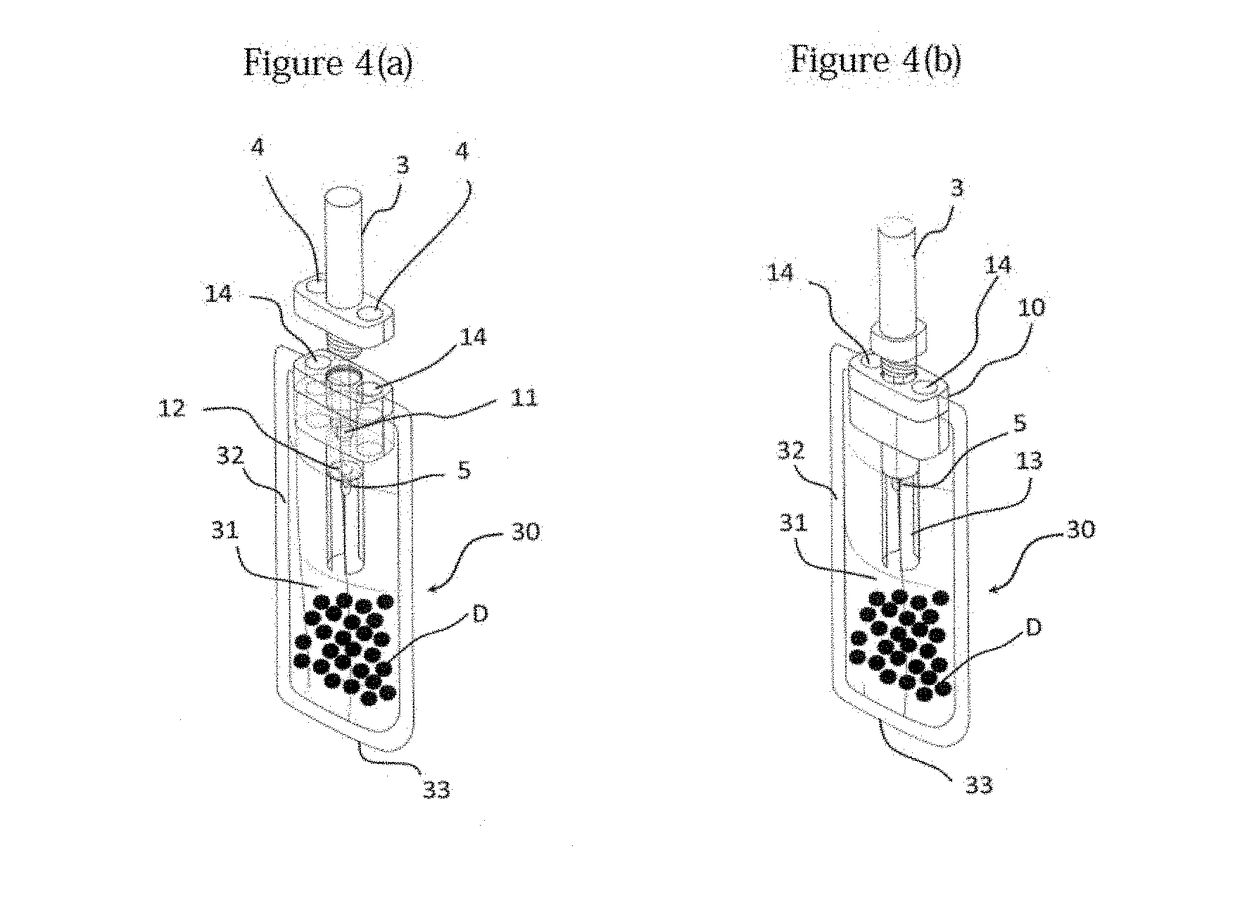
ActiveUS20190011462A1Good storage stabilityAccurate measurementWithdrawing sample devicesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDesiccantAnimal feces
A feces sampling container having an increased storage stability of a component in a feces sample such as hemoglobin to enable the measurement of a component in a feces sample with a small amount of feces collected. The container includes a container body, and a feces sampling stick having a gripping part on one side and a stick part on the other side, the stick part having a feces sampling part in the vicinity of the tip, wherein the container body comprises an opening part through which the feces sampling part of the feces sampling stick is inserted, and a feces container chamber in which a desiccant is enclosed, wherein the feces sample held by the feces sampling part is dried by a contact of the feces sampling part, which is inserted through the opening part and holding the feces sample, with the desiccant.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM DIAGNOSTICS SYST CO LTD
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmittance and fluorescence spectra
InactiveCN107421922ASuppression of non-linear effectsQuick measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMathematical modelOptical path length
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmittance and fluorescence spectra. The method includes transmitting a blood sample in a blood bag by a transmittance light source, and exciting the blood sample in the blood bag by the fluorescence excitation light source, wherein light sources include the transmittance light source and the fluorescence excitation light source; controlling the light sources to move by a displacement platform on the premise that the light outlets of the light sources are coaxial with a entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device, and collecting the transmittance spectra and the fluorescence spectra by the spectrum receiving device; solving the logarithm of the light intensity ratio of the double-optical-path transmittance spectra under each wavelength to acquire absorption spectra, combining and normalizing the absorption spectra and the two fluorescence spectra, combining with chemical testing data, and creating a mathematical model; collecting transmittance spectra and fluorescence spectra of an unknown blood sample under two optical paths, and after normalization, inputting the absorption spectra, acquired by solving the logarithm of the ratio of the two transmittance spectra, and the two fluorescence spectra into the mathematical model for calculation to acquire the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Detection of hemolysis using a chromatographic detection pad
In one aspect, the inventive concepts disclosed herein are directed to a chromatographic assay device for detecting the presence of free hemoglobin in a whole blood sample. The device comprising a chromatographic detection pad with a sample application site and a detection side. The chromatographic detection pad defines a path for capillary fluid flow. The chromatographic detection pad has a pore size. The sample application site on the chromatographic detection pad is for application of a portion of the whole blood sample. The detection site on the chromatographic detection pad is spaced apart from the application site and is downstream of the sample application site. The chromatographic detection pad is devoid of a compound located downstream of the application site that is reactive to the whole blood sample.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
A chip type blood cell analysis device and method
ActiveCN103471980BSimple structureReduce volumeIndividual particle analysisWhite blood cellLaser scattering
Owner:深圳中科芯海智能科技有限公司
Electrochemical blood test strips and diagnosis systems using the same
ActiveUS9000770B2Reduce chanceHigh measurement accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBlood testEngineering
Owner:APEX BIOTECH CORP
Electrophoresis Chip and Electrophoresis Apparatus
InactiveUS20100032297A1Short analysis timeAccurate analysisCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesElectrophoresisCapillary channel
An electrophoresis chip that enables an apparatus to be small, analysis time to be short and glycosylated hemoglobin to be analyzed highly accurately is provided. The electrophoresis chip includes an upper substrate 4, a lower substrate 1, a first introduction reservoir 2a, a first recovery reservoir 2b and a capillary channel for sample analysis 3x; the first introduction reservoir 2a and the first recovery reservoir 2b are formed in the lower substrate 1; and the first introduction reservoir 2a and the first recovery reservoir 2b are in communication with each other via the capillary channel for sample analysis 3x.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
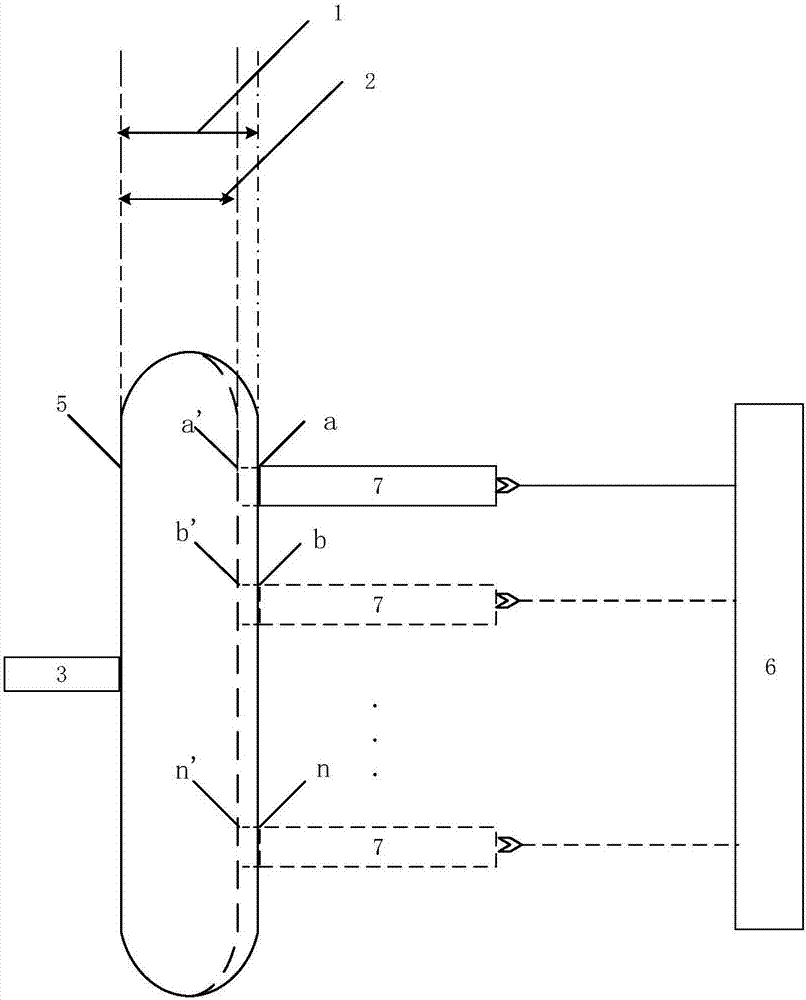
Method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmission and fluorescence spectrums at multiple positions
InactiveCN107421923AStrongly nonlinearSuppress nonlinearityColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path transmission and fluorescence spectrums at multiple positions. According to the method, a displacement platform controls a light source to move to a plurality of positions, blood is transmitted and excited, a double-optical-path transmission and fluorescence spectrum at each position is acquired by a spectrum receiving device, transmission spectrum ratios under two optical paths at each position are subjected to logarithm to obtain a blood absorption spectrum at the position, absorption spectrums at a plurality of positions and double-optical-path fluorescence spectrums at plurality of positions are normalized together, a mathematical model is built according to chemical examination data, double-optical-path transmission spectrums and fluorescence spectrums at a plurality of positions of unknown blood are acquired, transmission spectrum ratios under two light paths at each position are subjected to logarithm to obtain a blood absorption spectrum at the position, and absorption spectrums at a plurality of positions and double-optical-path fluorescence spectrums at plurality of positions are normalized and substituted into the mathematical model to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin by calculation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Determination of physical parameters associated with erythrocytes
ActiveUS9423342B2Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one orRequired laboratory skill of the user is reduced dramaticallyPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansRed blood cellElectromagnetic radiation
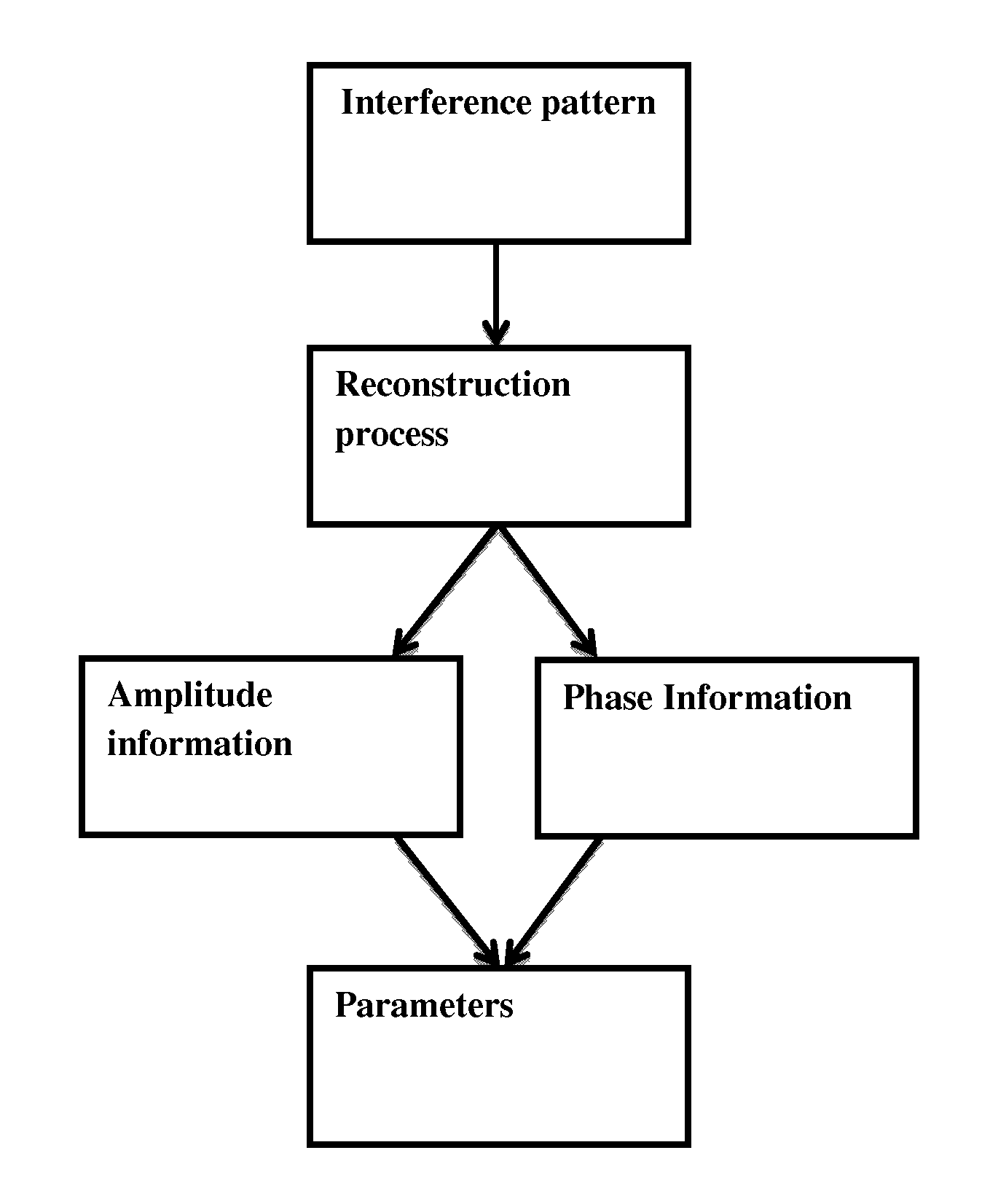
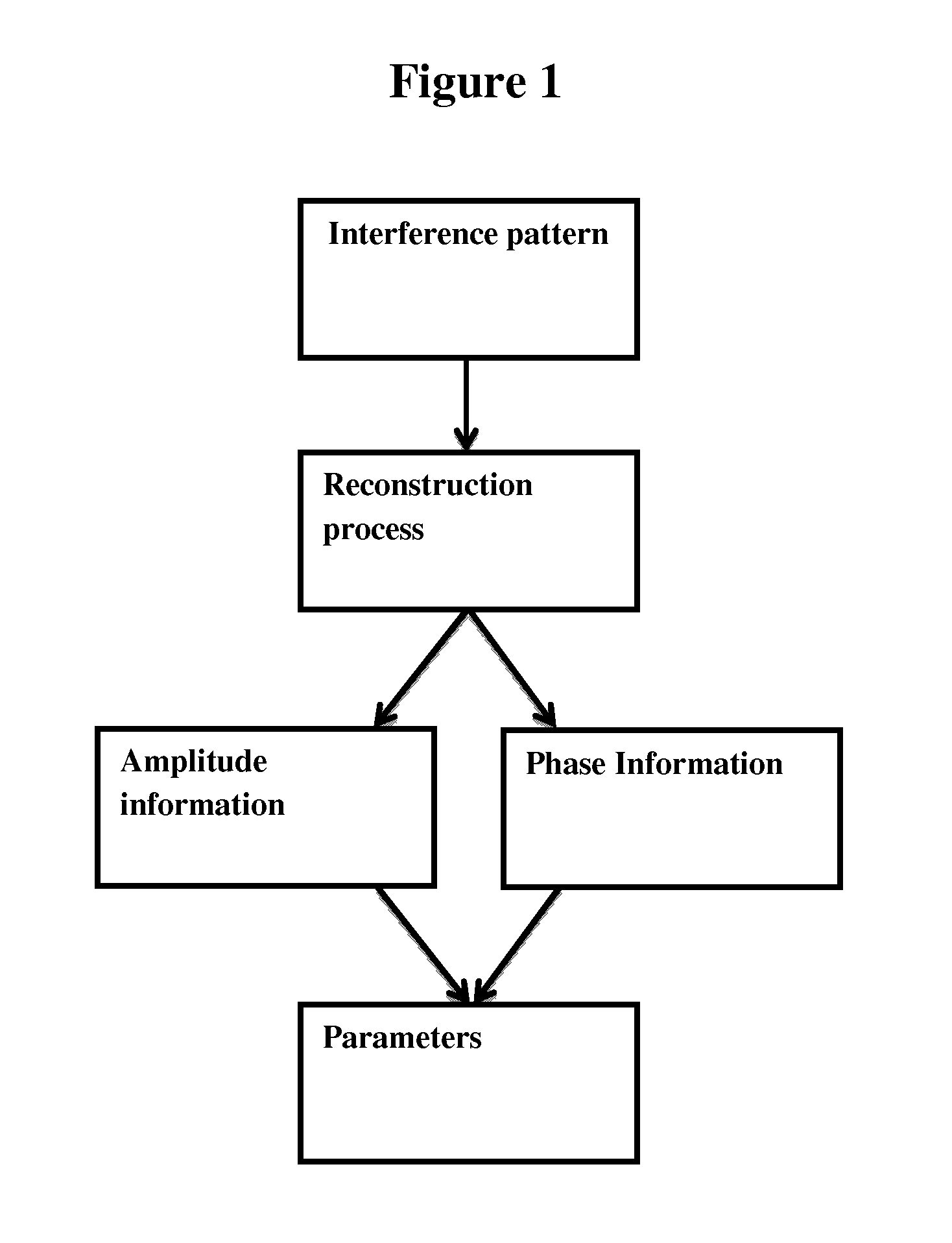
A method based on digital holography for determining parameters of at least one erythrocyte is provided, said method comprising the steps of: constructing an interference pattern comprising a wave front representative of said at least one erythrocyte arised from the interaction of said at least one erythrocyte and electromagnetic radiation, reconstructing amplitude-and phase information representative of said at least one erythrocyte wave front from said interference pattern and determining the mean corpuscular volume and / or mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration and / or oxygen saturation and / or mean corpuscular hemoglobin of at least one erythrocyte by combining phase information and amplitude information representative of said at least one erythrocyte.
Owner:PHASE HOLOGRAPHIC IMAGING PHI
Backwashing flow path system of glycated hemoglobin analyzer
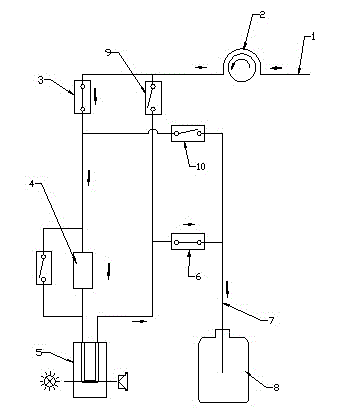
The invention belongs to medical equipment, relates to a flow path structure of a glycated hemoglobin analyzer, in particular to a backwashing flow path structure of a glycated hemoglobin analyzer. The backwashing flow path system of the glycated hemoglobin analyzer comprises a peristaltic pump positioned on a liquid feeding pipeline, wherein a liquid discharging hole of the peristaltic pump is introduced into a waste liquid bottle through a liquid discharging pipe after sequentially passing through a first electromagnetic valve, a cation exchange resin chromatographic column, a cuvette cell and a second electromagnetic valve; and a third electromagnetic valve is connected between the liquid discharging hole of the peristaltic pump and an outlet of the cuvette cell, and a branching pipeline is arranged in front of the inlet end of the cation exchange resin chromatographic column and is connected with the liquid discharging pipeline through a fourth electromagnetic pipeline. The invention has the advantages of being capable of avoiding aggregation and blockage of floccules in a detected sample at the chromatographic column and a filter screen of the glycated hemoglobin analyzer, prolonging the service life of the chromatographic column, improving reliability of a detection process, and being convenient for operation and maintenance and low in cost.
Owner:JIANGSU AUDICOM MEDICAL TECH
Measurement systems and methods for oxygenated hemoglobin saturation level
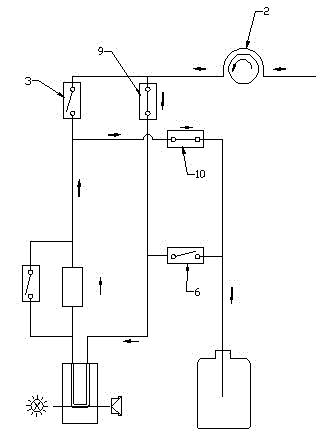
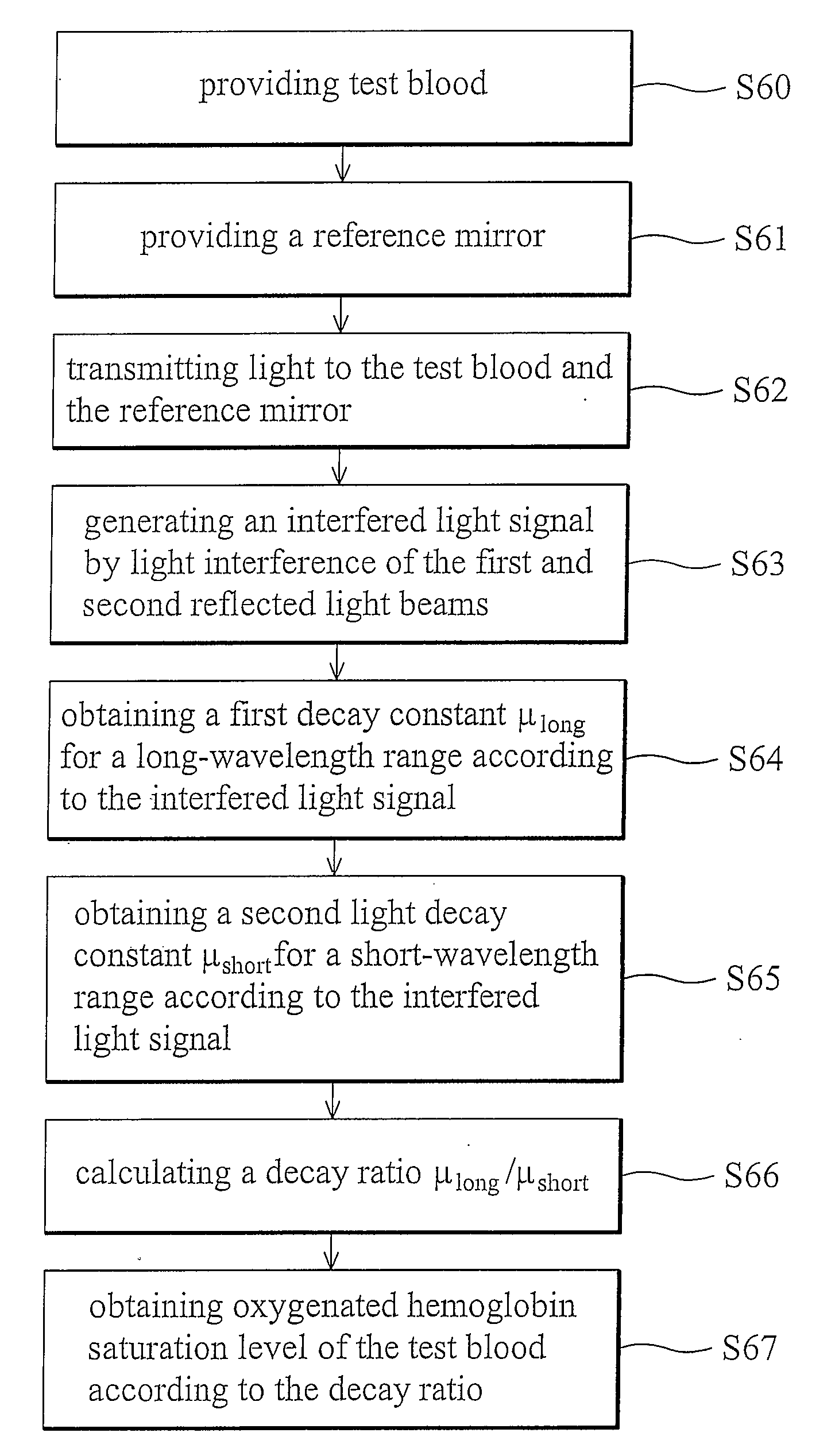
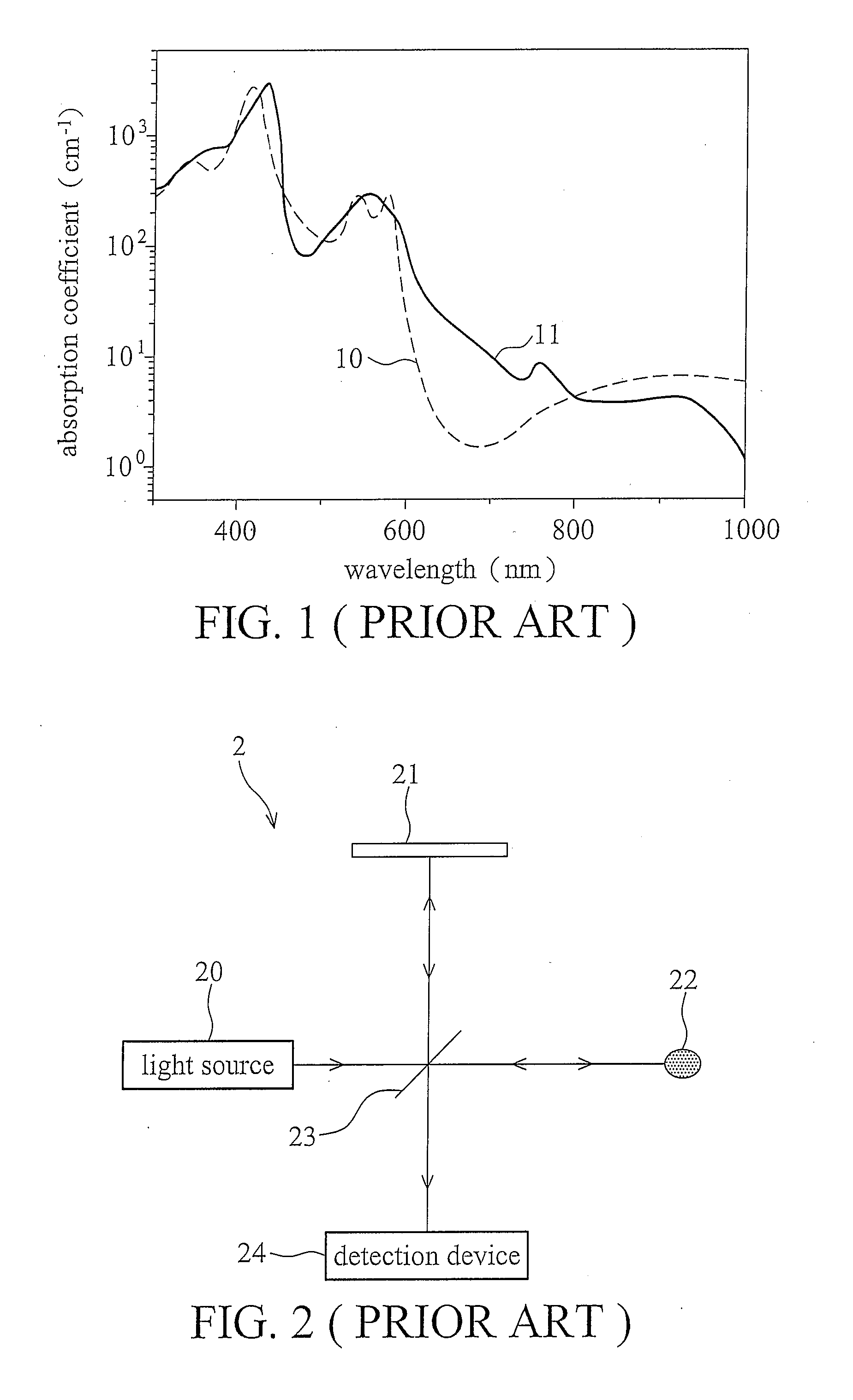
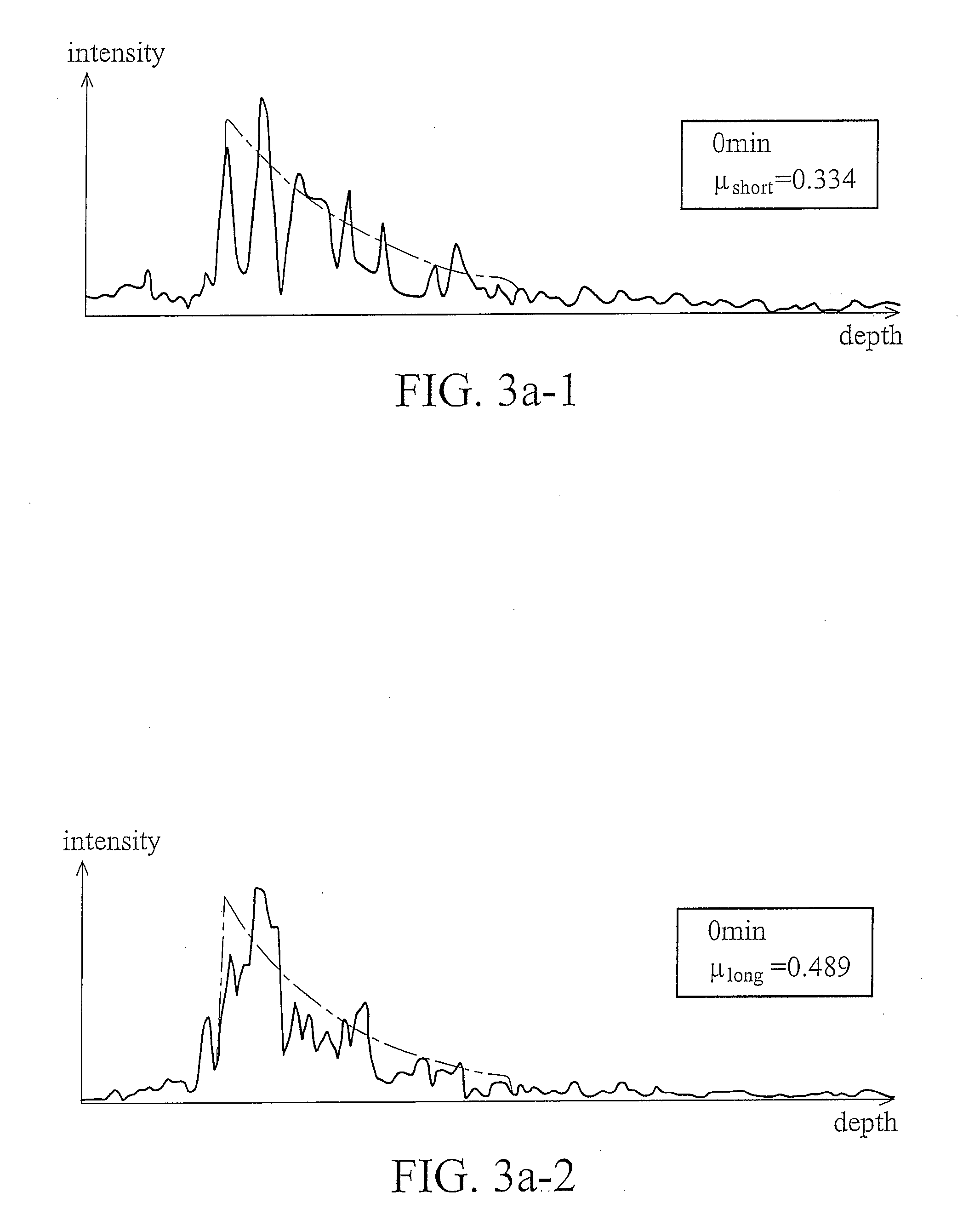
InactiveUS20090115997A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringOxygenated HemoglobinLight beam
Measurement system and methods for measuring oxygenated hemoglobin saturation level are provided. Light is transmitted to test blood and a reference mirror. The reference mirror provides a first reflected light beam, and backscattered light from different depths of the test blood generates a second reflected light beam. An interfered light signal is generated by light interference of the first and second reflected light beams. According to the interfered light signal, a first light decay constant for a first light wavelength range and a second light decay constant for a second light wavelength range are obtained according to the interfered light signal. A decay ratio of the first light decay constant to the second light decay constant is obtained. Oxygenated hemoglobin saturation level of the test blood is obtained according to the decay ratio.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
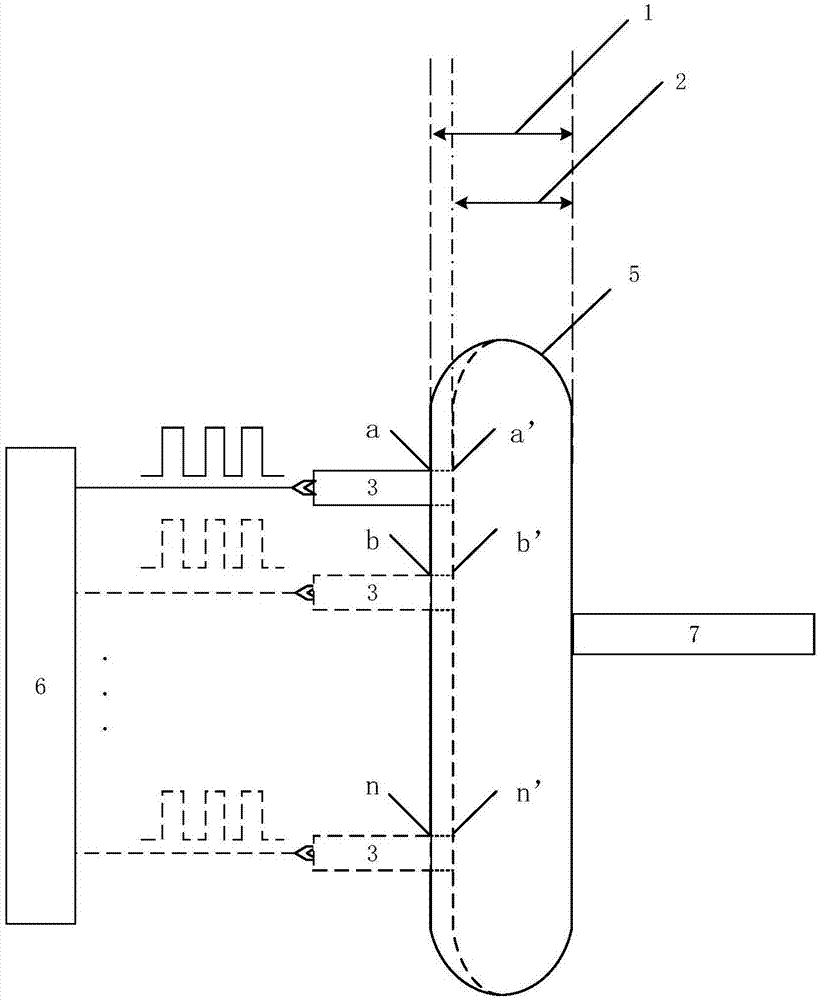
Method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path-length and multi-position modulation fluorescent excitation light source
InactiveCN107389634ASuppress nonlinearityEliminate background noise effectsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin by a double-optical-path-length and multi-position modulation fluorescent excitation light source. The method comprises the following steps that a light outlet opening of the fluorescent excitation light source and an incident slit of a spectrum receiving device are tightly attached to a blood bag; a modulation device modulates the fluorescent excitation light source; the fluorescent excitation light source excites the blood sample; the spectrum receiving device collects the fluorescence spectrum; a displacement platform controls the fluorescent excitation light source to move to different positions; the optical path length measurement is changed; the fluorescence spectrum collected in a plurality of positions under the conditions of the two optical path lengths is converted into the fluorescence spectrum in the frequency domains of the frequency domain structures; the fluorescence spectrum in a plurality of frequency domains is subjected to normalization processing; the chemical inspection data is combined; a mathematical model is built; the fluorescence spectrum of an unknown blood sample in the plurality of positions under the condition of the two optical path lengths is collected; after the fluorescence spectrum is converted into the fluorescence spectrum in the frequency domains of the frequency domain structures, normalization processing is performed; the data is substituted into the mathematical model to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
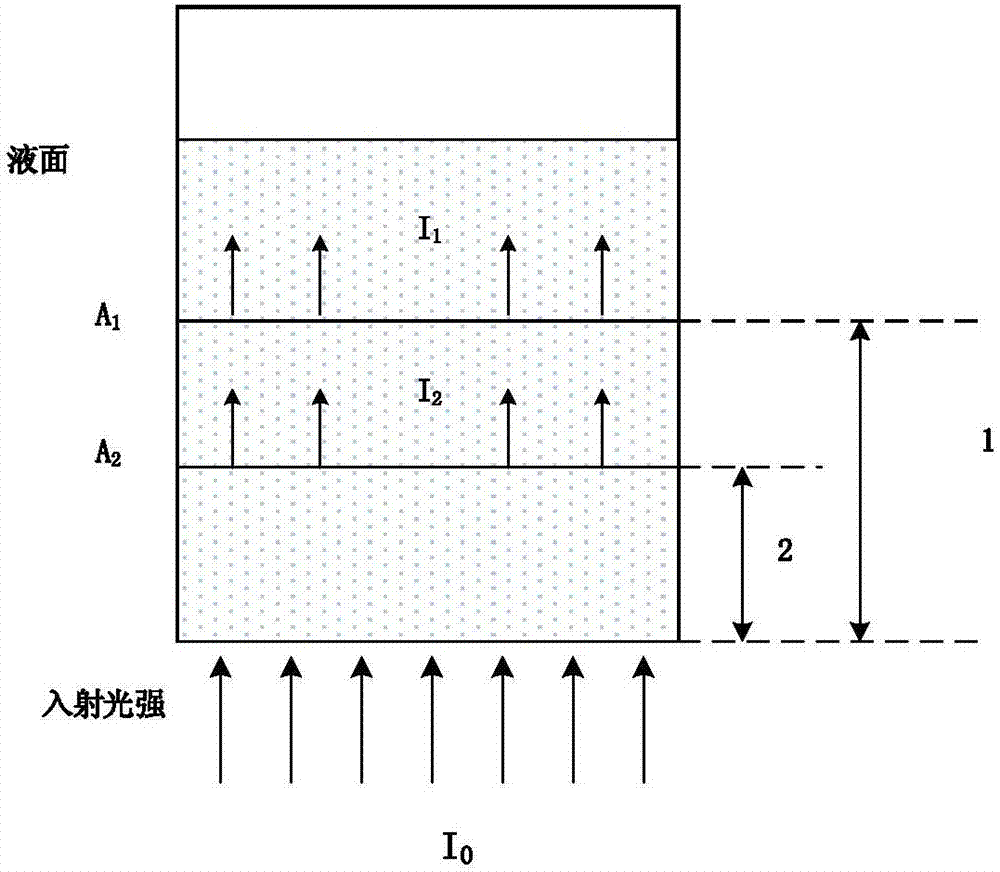
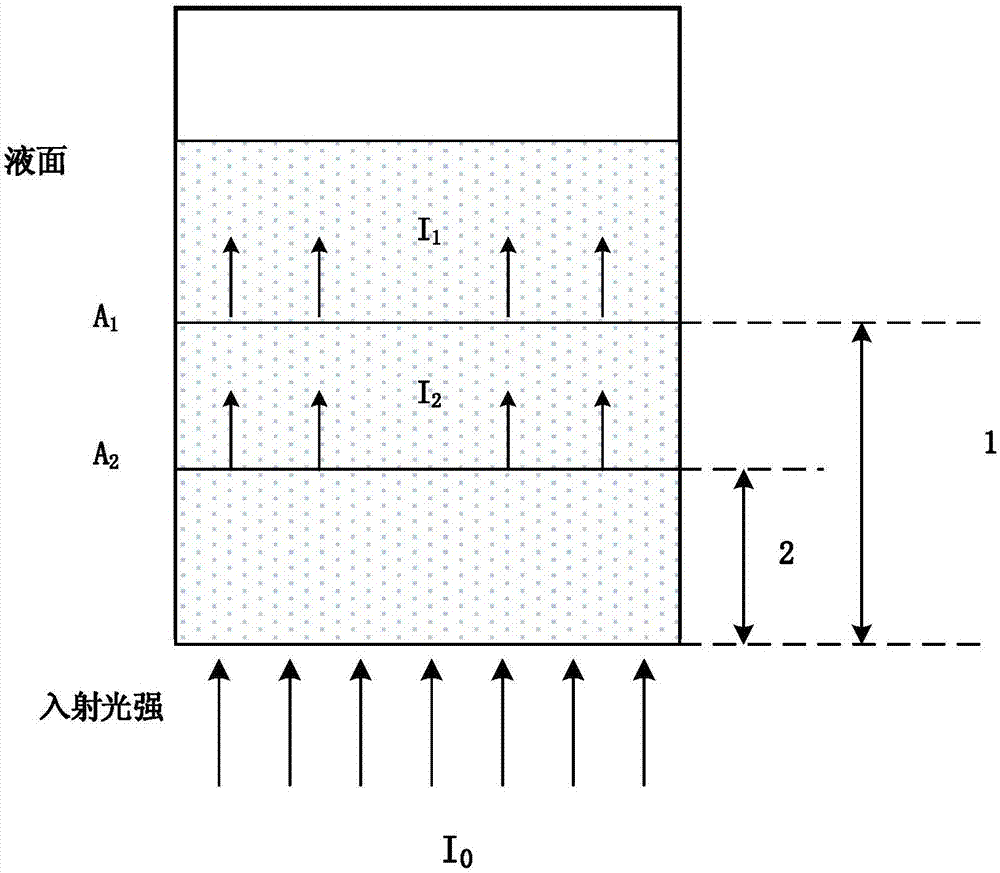
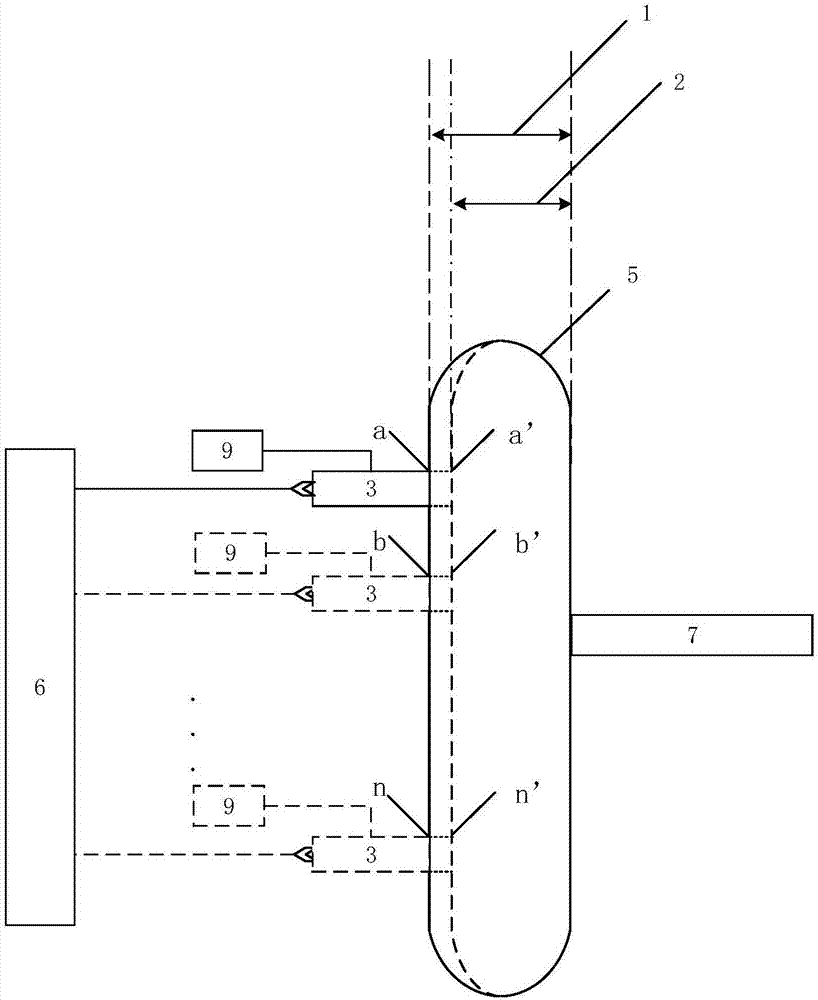
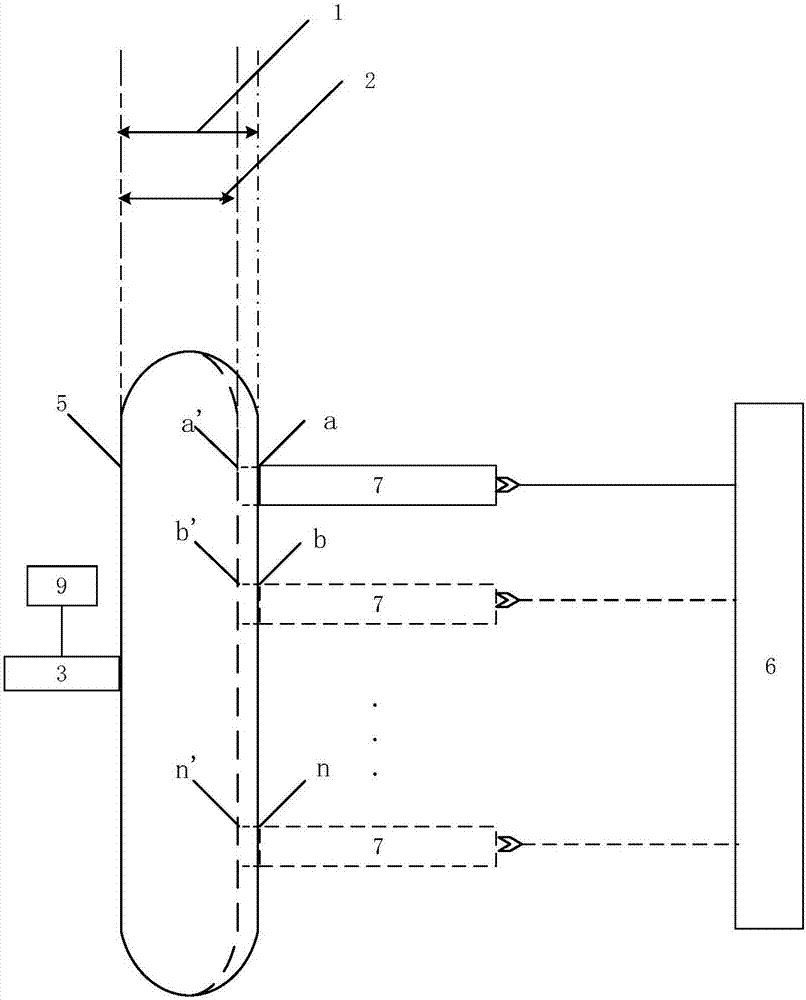
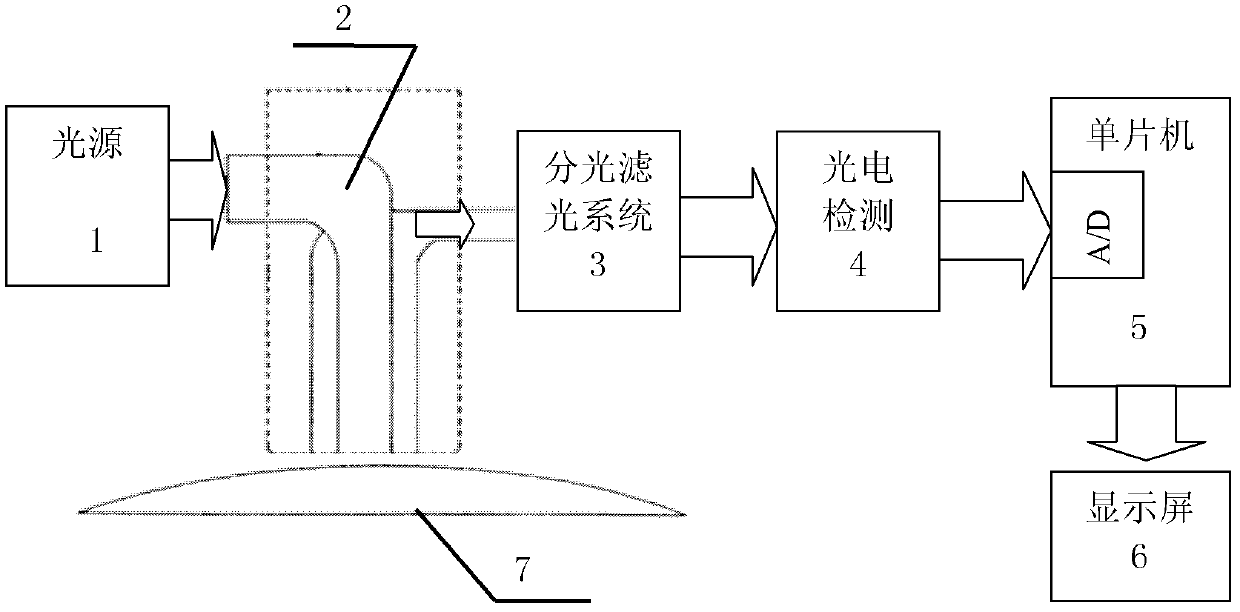
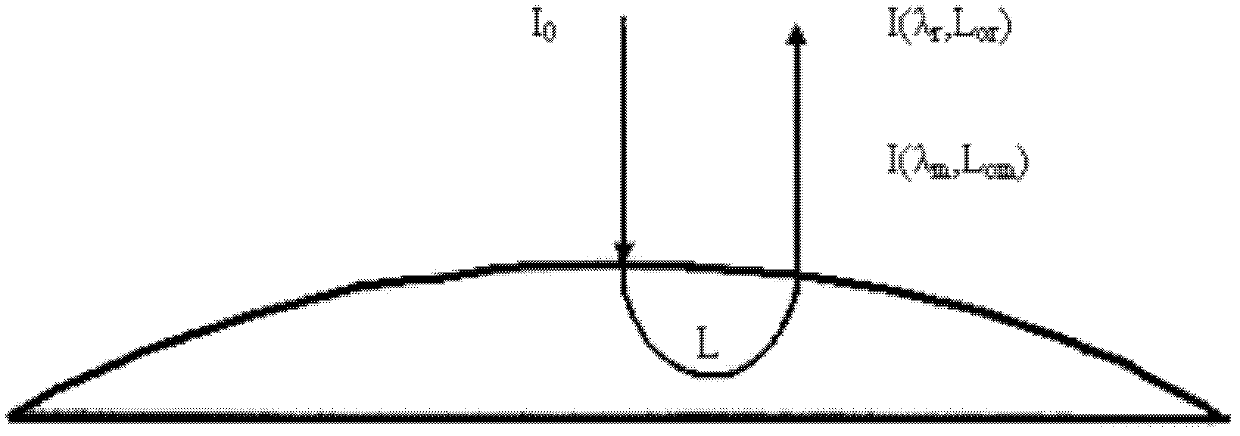
Optical detection device and method for concentration of components in turbid medium based on limited range wavelength method
InactiveCN102564983BImprove reliabilityHigh measurement accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsPrismNon invasive
The invention relates to an optical detection device and a method for concentration of components in a turbid medium based on a limited range wavelength method. The device is characterized in that a light source is connected with the turbid medium through a coupled optical fiber detecting head, the turbid medium is connected with a spectral filtering system through the coupled optical fiber detecting head, and the spectral filtering system is sequentially connected with a photoelectric detection unit, a single chip microcomputer and a display screen. The spectral filtering system is composed of a transflective prism and a light filter and is used for splitting into 2, 4, 8, ... and 2n beams of light. In the method, for the determination of limited number of wavelengths, the absorption information of bilirubin at a benchmark wavelength is adopted to remove skin background and stray light interference, and the wavelengths relevant to hemoglobin and melanin absorption with largest influence on the concentration detection of bilirubin are adopted to remove the influence of these influencing factors; and an optimal optical path length principle is adopted to calculate the optimal optical path length during the optical detection of bilirubin and is used for designing an optical detecting head. According to the device and the method, the concentration of a certain component in the turbid medium can be measured more accurately and conveniently, and the non-invasive, dynamic and continuous detection for the concentration of components in the turbid medium can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
Test card of haemolobin in use for volunteer blood donor
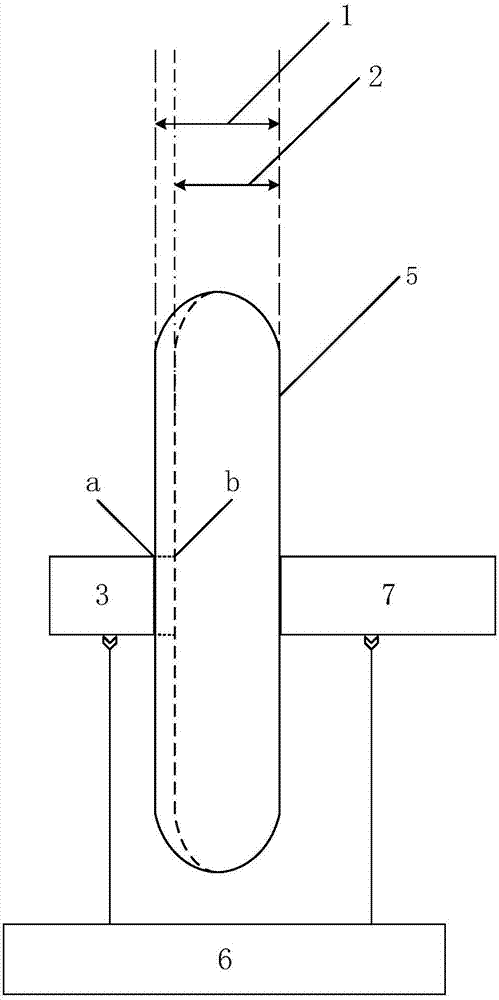
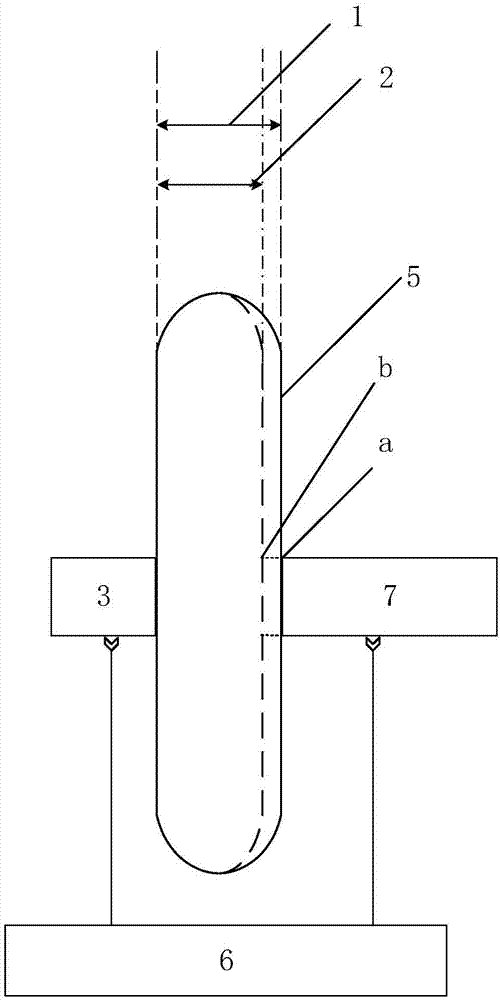
The test card includes test scrip and standard color grade card. Test scrips are put in transparent plastic bag in sequence. The bag and color grade card are pasted on left and right of folding respectively. There are two red areas a and b in different dark and light on the color grade card. The a area is for female, whose normal value of haemoglobin is 110g / L, and b area is for male, whose normal value of haemoglobin is 120g / L. an interpretation hole is located in center of a and b area respectively. Blood is dropped to a piece of test scrip. After about 30 seconds, spot of sampled blood is compared with color in color grade card through the hole. Based on result, determing whether a blood donor is qualified is made. Features of the test card are simple design, easy of carrying, fast and reliable testing.
Owner:周明非
Method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path modulating transmittance and fluorescence excitation light sources
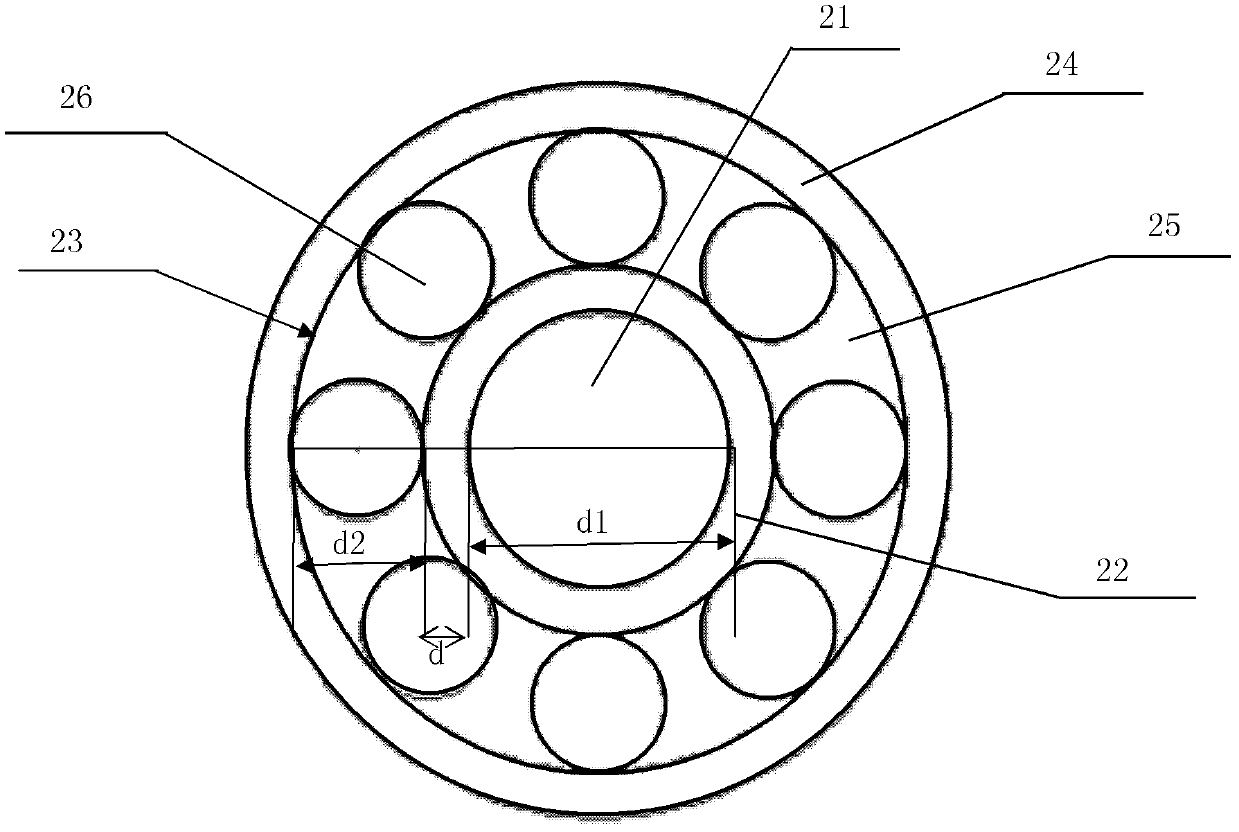
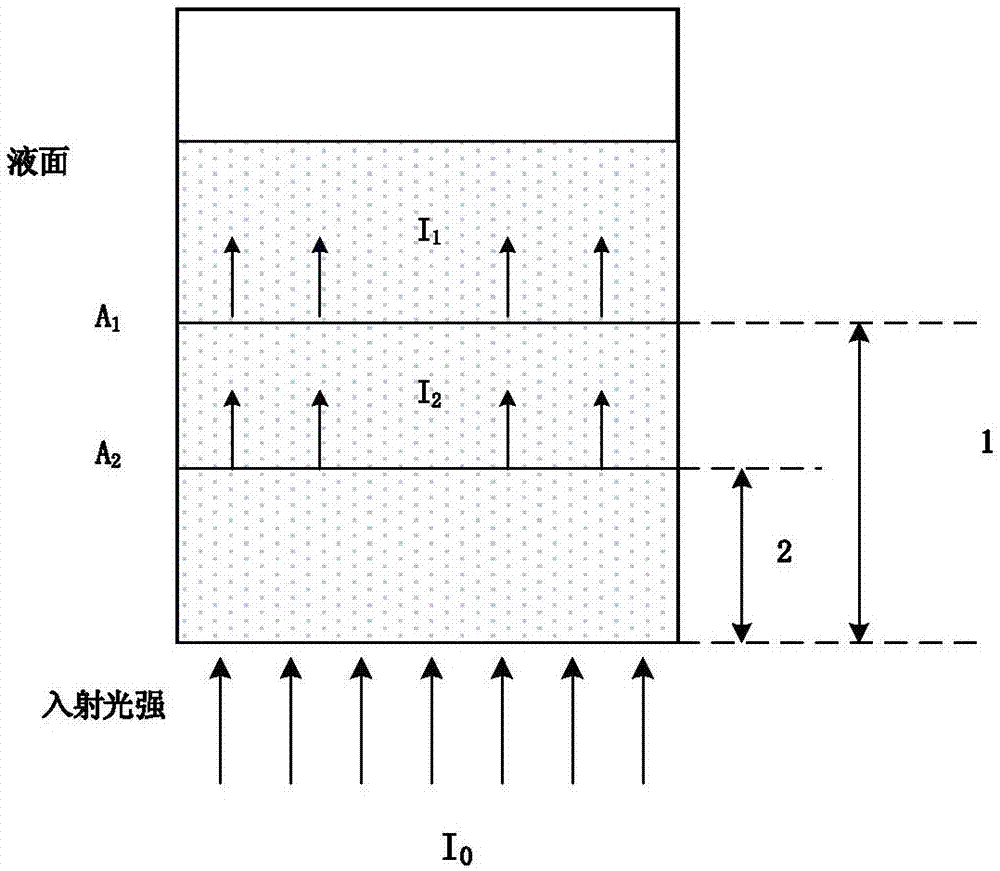
InactiveCN107421926ARemove background noiseSuppression of non-linear effectsColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMathematical modelHemoglobin G Szuhu
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path modulating transmittance and fluorescence excitation light sources. The method includes modulating the transmittance light source and the fluorescence excitation light source by a modulating device, and transmitting and exciting blood in a blood bag by the transmittance light source and the fluorescence excitation light source respectively; controlling the light sources to move by a displacement platform, and collecting transmittance spectra and fluorescence spectra by a spectrum receiving device; transforming time sequence of each wavelength of the transmittance spectra and the fluorescence spectra into a frequency domain, creating the intra-frequency-domain transmittance spectra and the intra-frequency-domain fluorescence spectra by fundamental wave component of each wavelength, solving the logarithms of light intensity ratios of the two created intra-frequency-domain transmittance spectra under each wavelength to acquire absorption spectra, normalizing the absorption spectra and the two intra-frequency-domain fluorescence spectra, comparing with existing chemical analysis results and creating a mathematical model; collecting absorption spectra and intra-frequency-domain fluorescence spectra of blood in an unknown blood bag according to the same method, and inputting the absorption spectra and the intra-frequency-domain fluorescence spectra into the mathematical model after normalization to acquire the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of occult blood critical value quality control material
InactiveCN103048478AEasy to degradeImprove adsorption capacityPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingMaterials preparationDistilled water
The invention provides a preparation method of an occult blood critical value quality control material, which comprises the following steps: (1) quality control material container sealing: filling a centrifugal tube with a specification of 0.5 ml by using 0.5-2.0 percent bovine serum albumin, putting into a refrigerator with a temperature of 4 DEG C, sealing for 24 hours, then abandoning liquid in the centrifugal tube and putting the centrifugal tube into a biological safety cabinet to naturally air for standby; (2) critical quality control material preparation: taking a blood routine test specimen of a normal healthy physical examinee, dissolving blood with distilled water according to hemoglobin test results, diluting into 1-2 mg / L, adding a protein stabilizer as well as sodium azide till the final concentration is 2.0-7.0 g / L and 0.2-2.0 g / L respectively and sub-packaging into 0.5 ml sealed centrifugal tube, wherein a solution in each tube is 50-500 ul; and (3) quality control material preservation: preserving the sub-packaged critical value quality control material at a temperature of 4-20 DEG C. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the preparation is simple, whether a corresponding reagent deteriorates during the processes of circulation, preservation and use or not can be monitored, and the period of validity is long.
Owner:许瑞娜
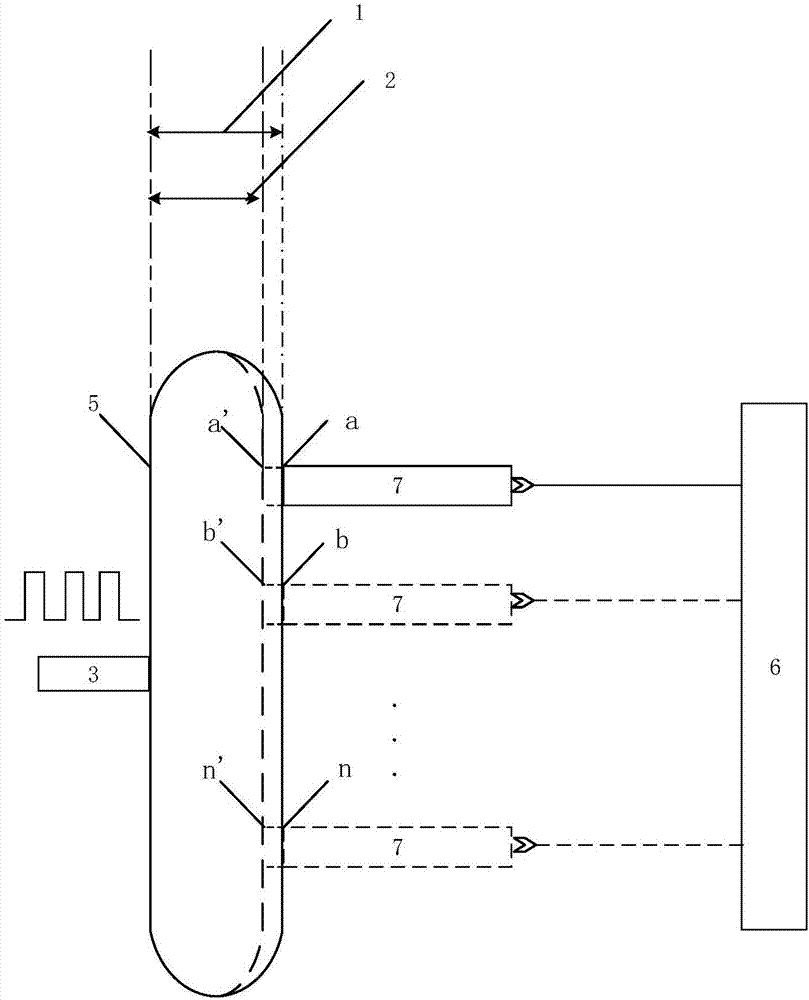
Method for measuring content of free hemoglobin in blood bag by double-light-path fluorescent light intensity
InactiveCN107202783ARealize non-destructive testingLarge amount of informationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinNon destructive
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of free hemoglobin in a blood bag by double-light-path fluorescent light intensity. The method comprises the following steps of making a light outlet of a fluorescent excitation light source and an entrance slit of a light intensity receiving device cling to the blood bag and be further coaxial, exciting a blood sample by the fluorescent excitation light source, and receiving fluorescent light intensity by the light intensity receiving device; controlling the fluorescent excitation light source to move by a displacement platform on the premise of guaranteeing the light outlet of the fluorescent excitation light source and the entrance silt of the light intensity receiving device to be coaxial, and receiving the fluorescent light intensity by the light intensity receiving device; subjecting two pieces of the collected fluorescent light intensity to normalization treatment, and establishing a mathematic model by combining with the data of a chemical examination; collecting the fluorescent light intensity of an unknown blood sample at two positions, subjecting to normalization, and substituting into the mathematic model, so as to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin. By using the method, the non-destructive examination of the free hemoglobin is realized; the method is high-efficiency and pollution-free, and is high in measurement pertinence; the analysis accuracy of the content of the free hemoglobin is obviously improved; further, the measurement by the fluorescent light intensity is simple and convenient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path multiposition intra-frequency-domain fluorescence light intensity
InactiveCN107421929AEliminate the effects of background noiseNon-linearFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceOptical path length
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin by double-optical-path multiposition intra-frequency-domain fluorescence light intensity. The method includes driving a fluorescence excitation light source by square wave signals, clinging a light outlet of a fluorescence excitation light source and an entrance slit of a light intensity receiving device to a blood bag, exciting a blood sample by the fluorescence excitation light source, and receiving fluorescence light intensity by the light intensity receiving device; controlling the fluorescence excitation light source to move to different positions and changing optical path measurement by a displacement platform, transforming the fluorescence light intensities collected at multiple positions under the two optical paths into a frequency domain, creating intra-frequency-domain fluorescence light intensities, combining with chemical testing data after normalization, and creating a mathematical model; collecting fluorescence light intensities of an unknown blood sample at multiple positions under the two optical paths, transforming the fluorescence light intensities into a frequency domain, creating intra-frequency-domain fluorescence light intensities, and inputting the fluorescence light intensities into the mathematical model after normalization to acquire the content of the free hemoglobin. The method has the advantages that influences of fluorescence background noise are eliminated, and light intensity nonlinearity caused by fluorescence self-absorption, blood scattering and the like is inhibited.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for measuring free hemoglobin in blood bag by multi-position modulation of fluorescence excitation light source
InactiveCN107421924ASolving NDT ProblemsSuppression of non-linear effectsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFree hemoglobinMathematical model
The invention discloses a method for measuring free hemoglobin in a blood bag by multi-position modulation of a fluorescence excitation light source. According to the method, the fluorescence excitation light source is modulated by a modulation device, a light outlet of the fluorescence excitation light source and an entrance slit of a spectrum receiving device cling to a packaging bag, the fluorescence excitation light source excites the free hemoglobin to generate fluorescence, a displacement platform controls the fluorescence excitation light source to move to a plurality of positions, fluorescence spectrums are acquired by the spectrum receiving device, the time sequence of each wavelength in the fluorescence spectrums acquired at a plurality of positions is transformed to a frequency domain, fluorescence spectrums in the frequency domains are constructed by the aid of fundamental components with various wavelengths, the fluorescence spectrums are normalized and then compared with existing chemical analysis results, a mathematical model is built, fluorescence spectrums in frequency domains at a plurality of positions of a blood sample in an unknown blood bag are acquired by the same method and substituted into the mathematical model after normalization to obtain the content of the free hemoglobin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com