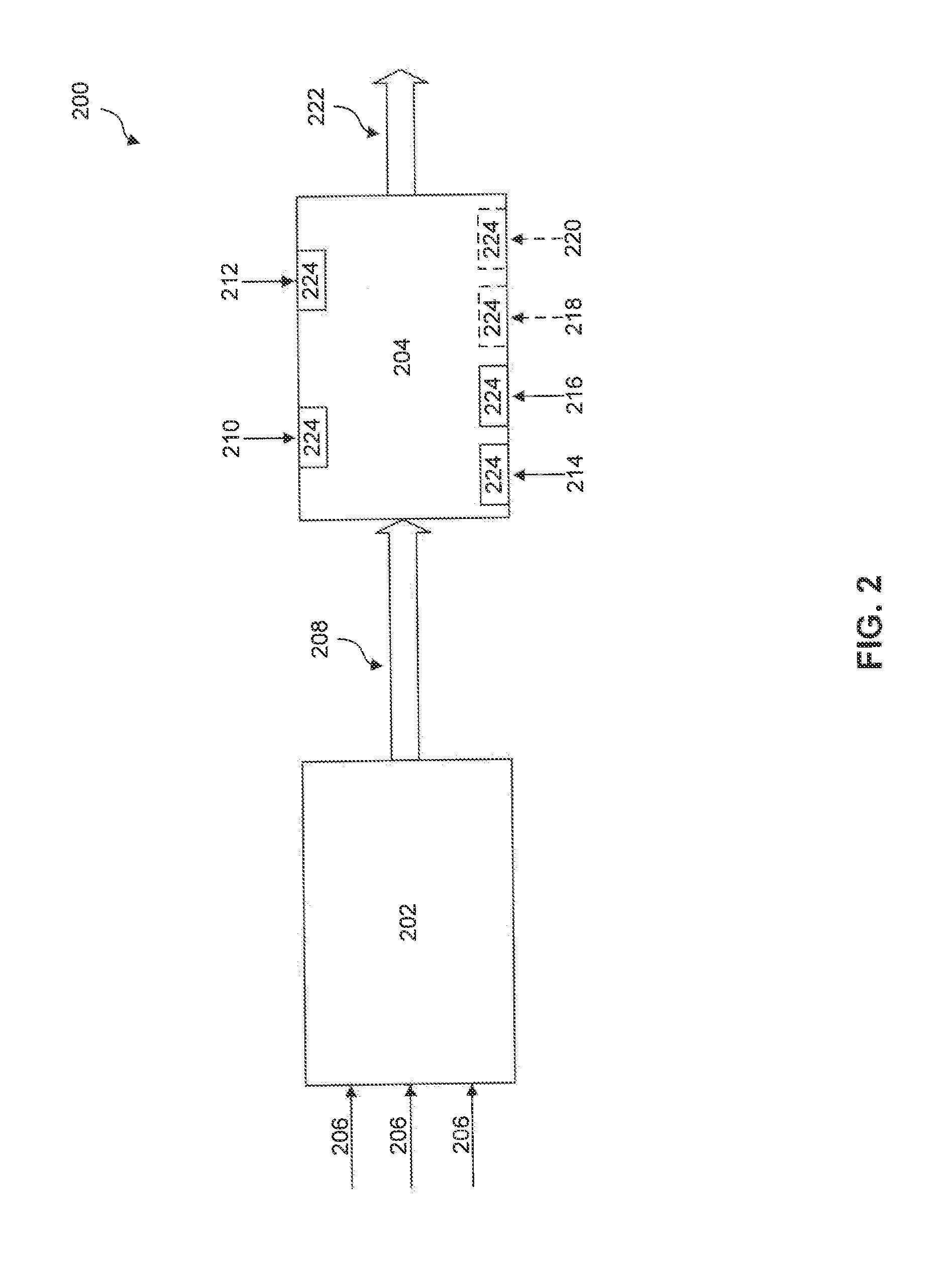
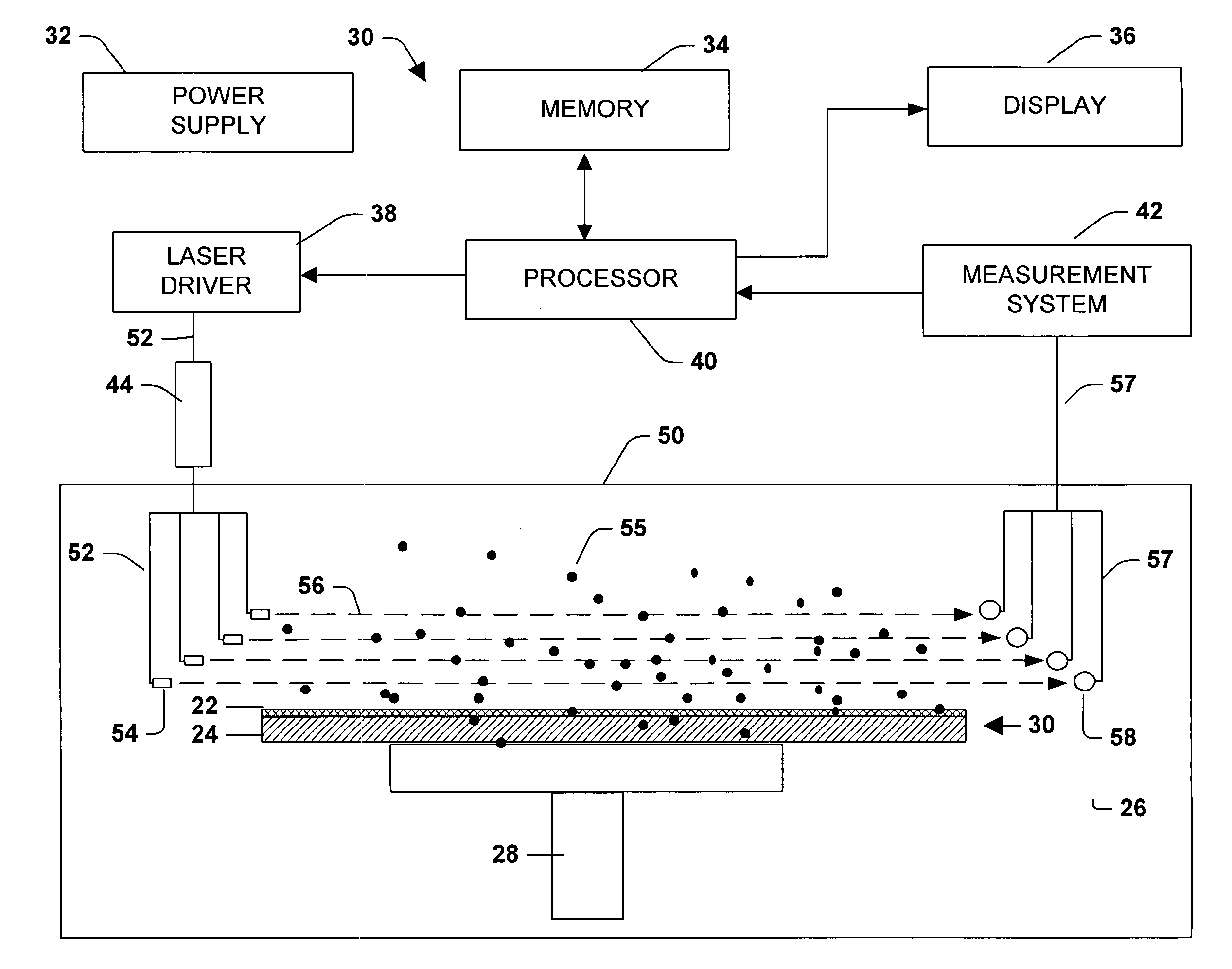
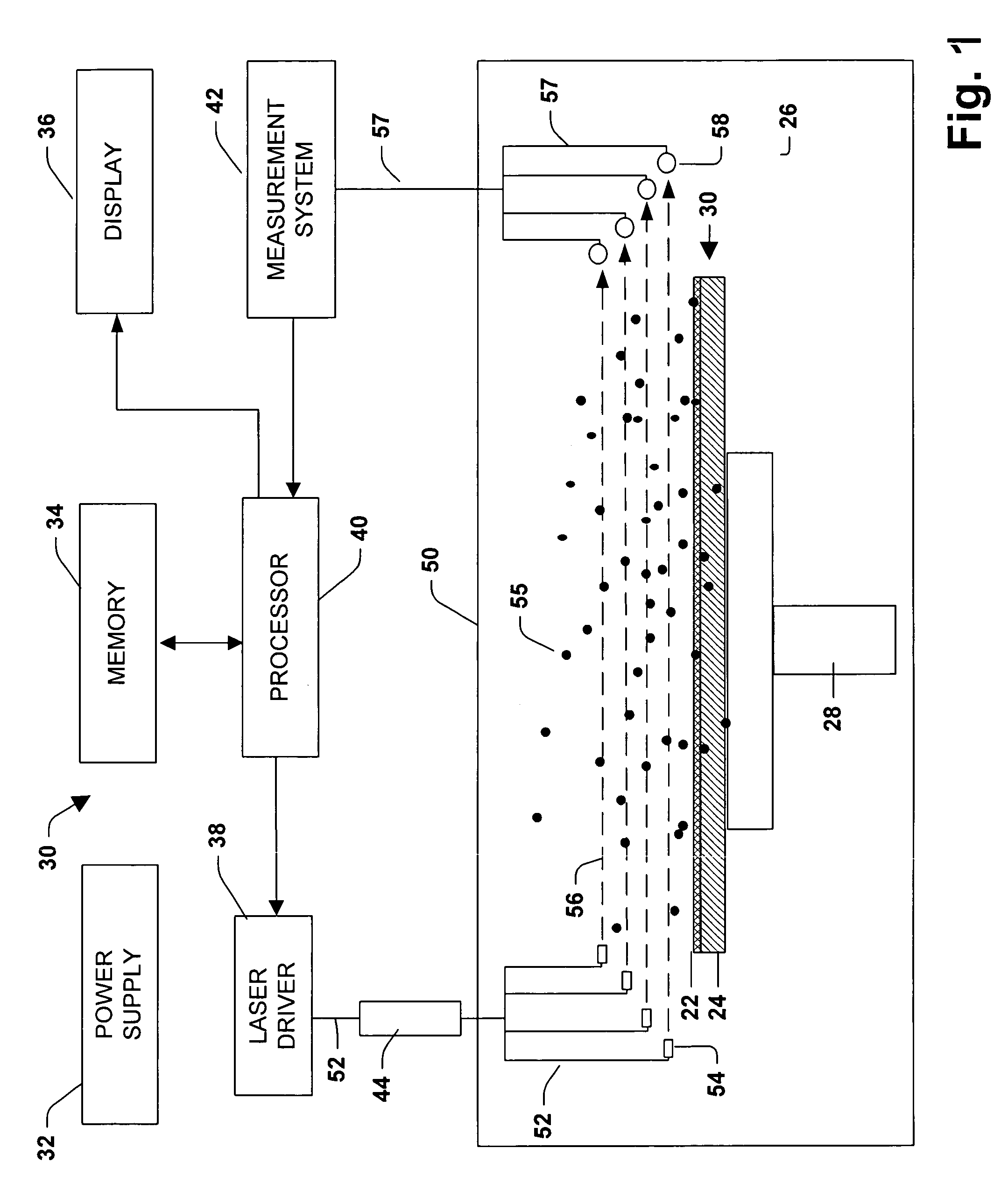
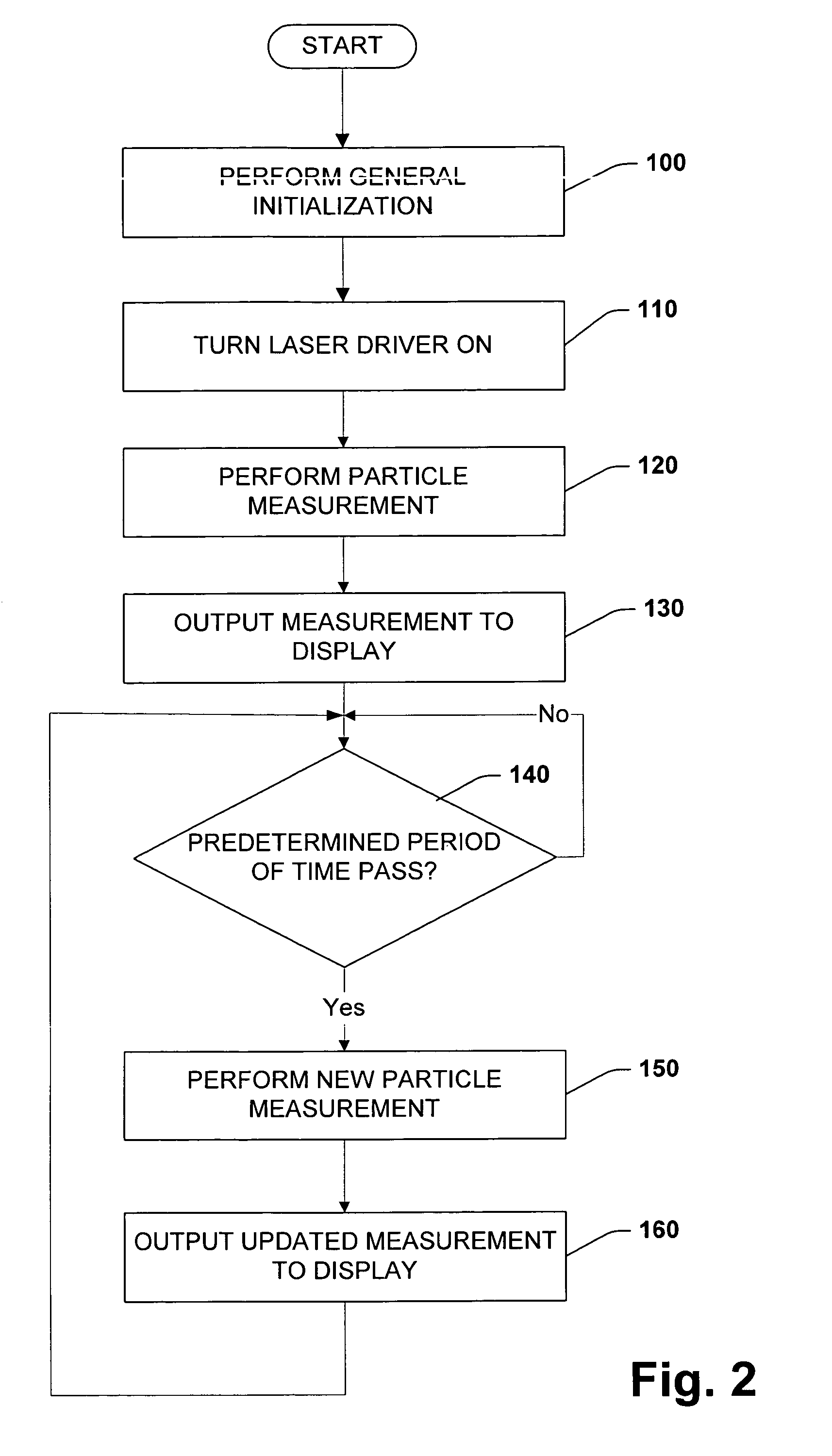
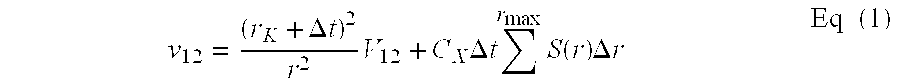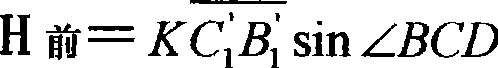Patents
Literature
307 results about "Laser scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Red Nitride Phosphor and Production Method Thereof
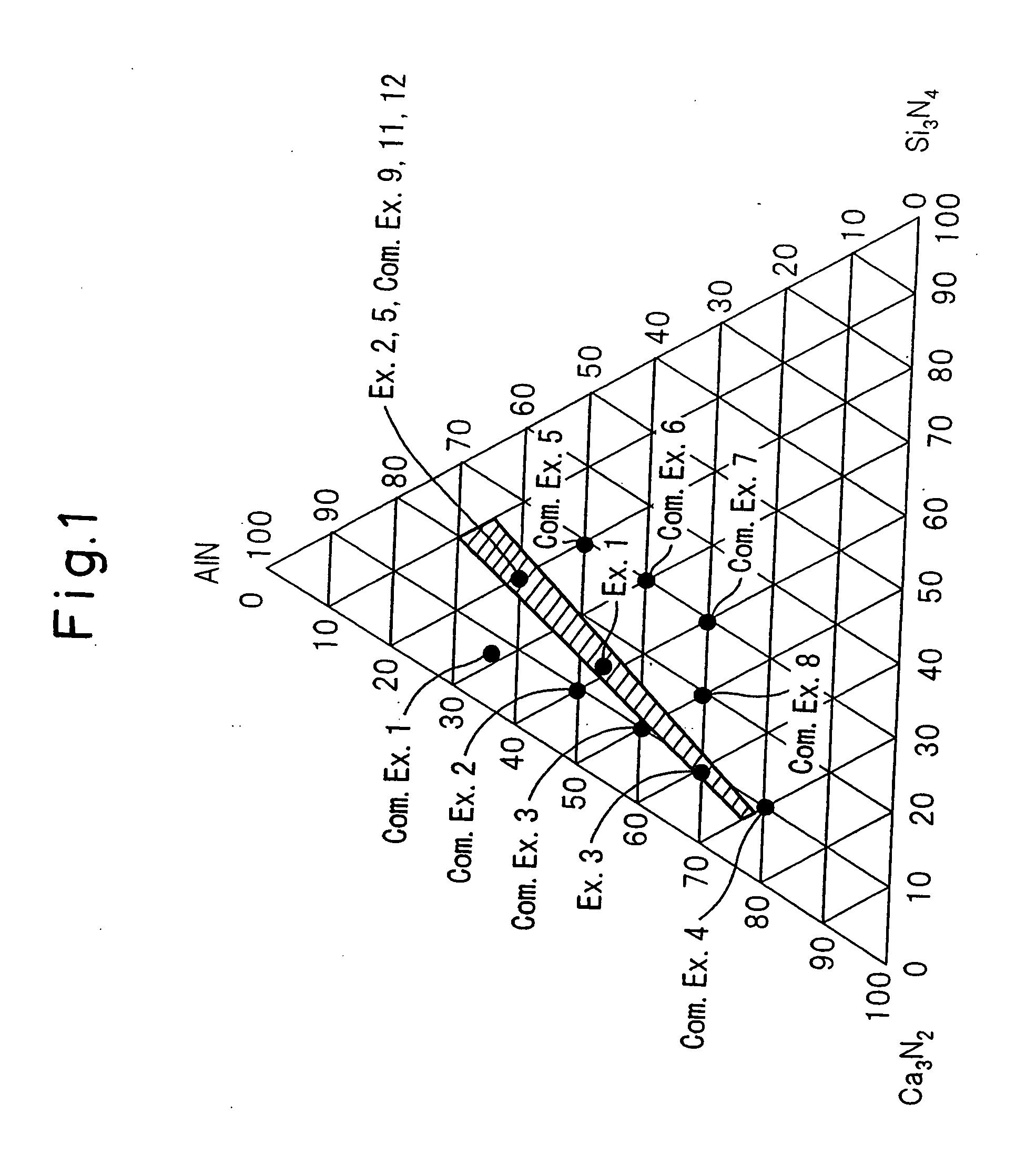
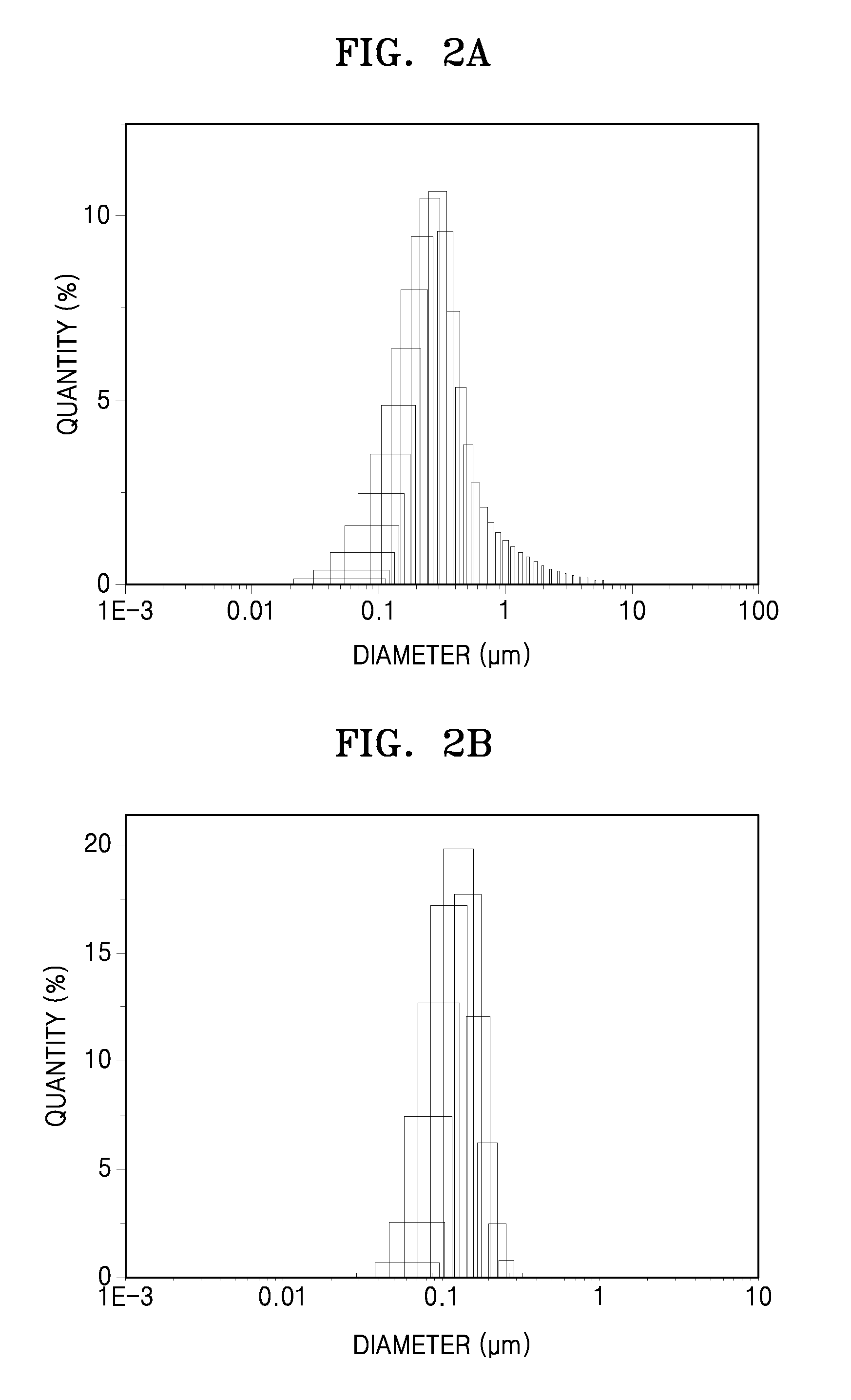
A red phosphor where the crystal phase constituting the phosphor is monoclinic Eu-activated CaAlSiN3. A red phosphor which is Eu-activated CaAlSiN3 powder having an average particle diameter of 10 μm or less as measured in the non-pulverized state by the laser scattering particle size distribution analysis. A light-emitting device comprising a blue light-emitting element, a yellow phosphor capable of converting the blue light emitted from the blue light-emitting element into yellow light, and the above-described red phosphor capable of converting the blue light emitted from the blue light-emitting element into red light. A method for producing Eu-activated CaAlSiN3, comprising firing a raw material powder comprising Ca3N2, AlN, Si3N4 and EuN at 1,400 to 2,000° C. in a nitrogen-containing atmosphere, the Ca3N2, AlN and Si3N4 giving a composition falling in the region surrounded by a straight line connecting the following four points A to D in the composition diagram of FIG. 1 and EuN being contained in an amount of 0.01 to 10 parts by weight as Eu per 100 parts by weight in total of Ca3N2, AlN and Si3N4.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring micro structures, anisotropy and birefringence in polymers using laser scattered light
InactiveUS6097488AGood process reproducibilityImprove efficiencyPolarisation-affecting propertiesLight polarisation measurementMicro structureFiber
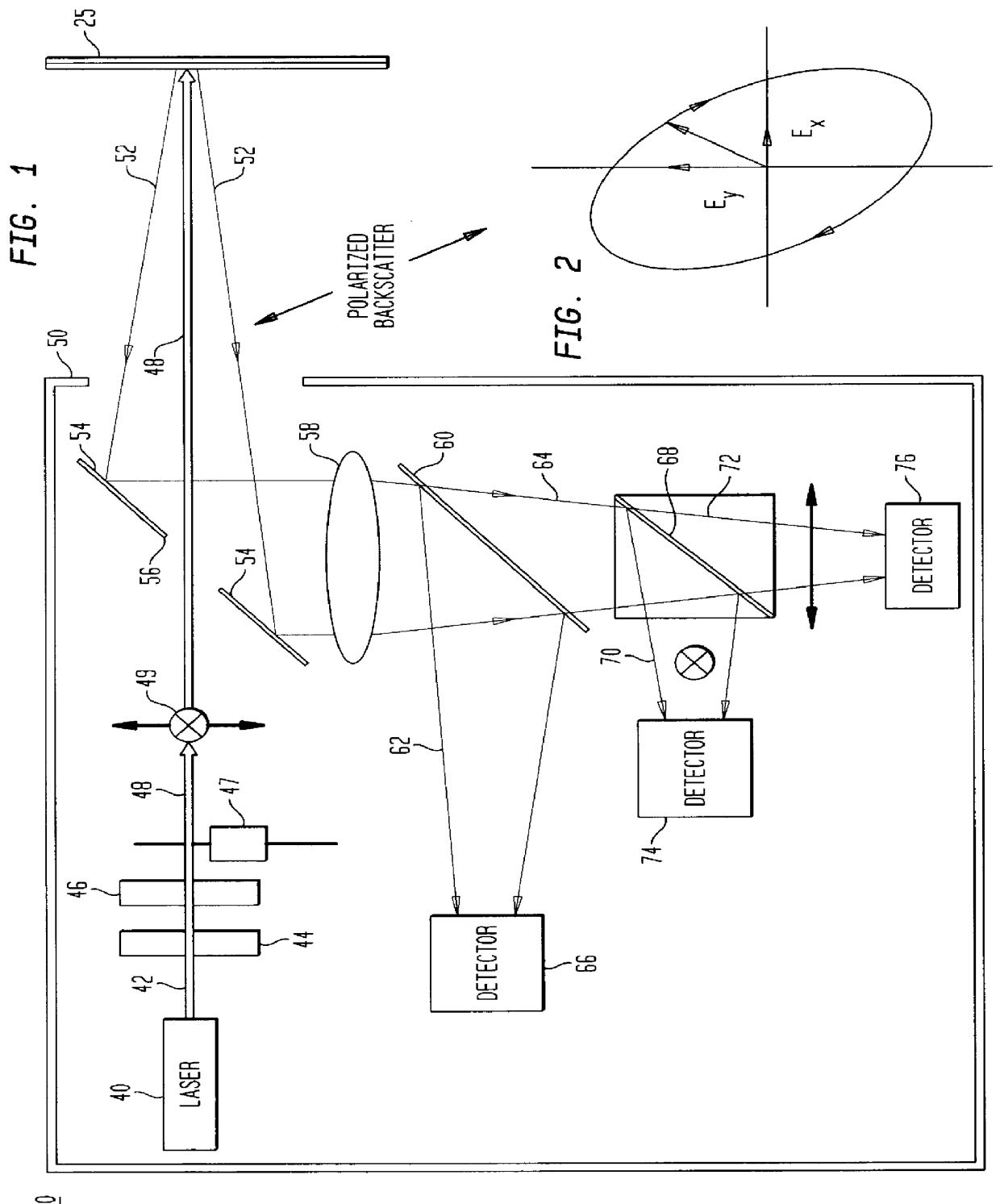
A method and apparatus for measuring microstructures, anistropy and birefringence in polymers using laser scattered light includes a laser which provides a beam that can be conditioned and is directed at a fiber or film which causes the beam to scatter. Backscatter light is received and processed with detectors and beam splitters to obtain data. The data is directed to a computer where it is processed to obtain information about the fiber or film, such as the birefringence and diameter. This information provides a basis for modifications to the production process to enhance the process.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
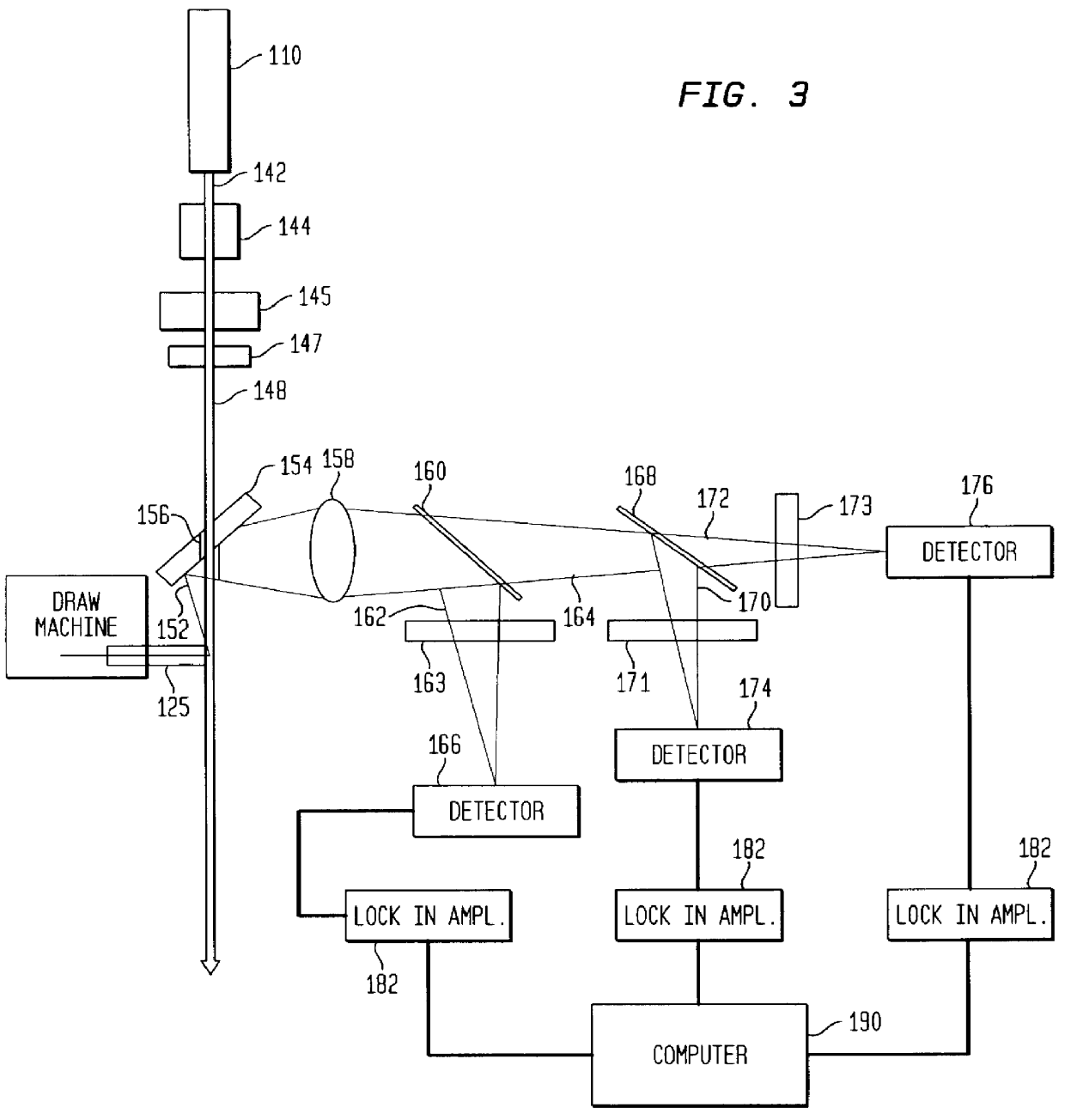
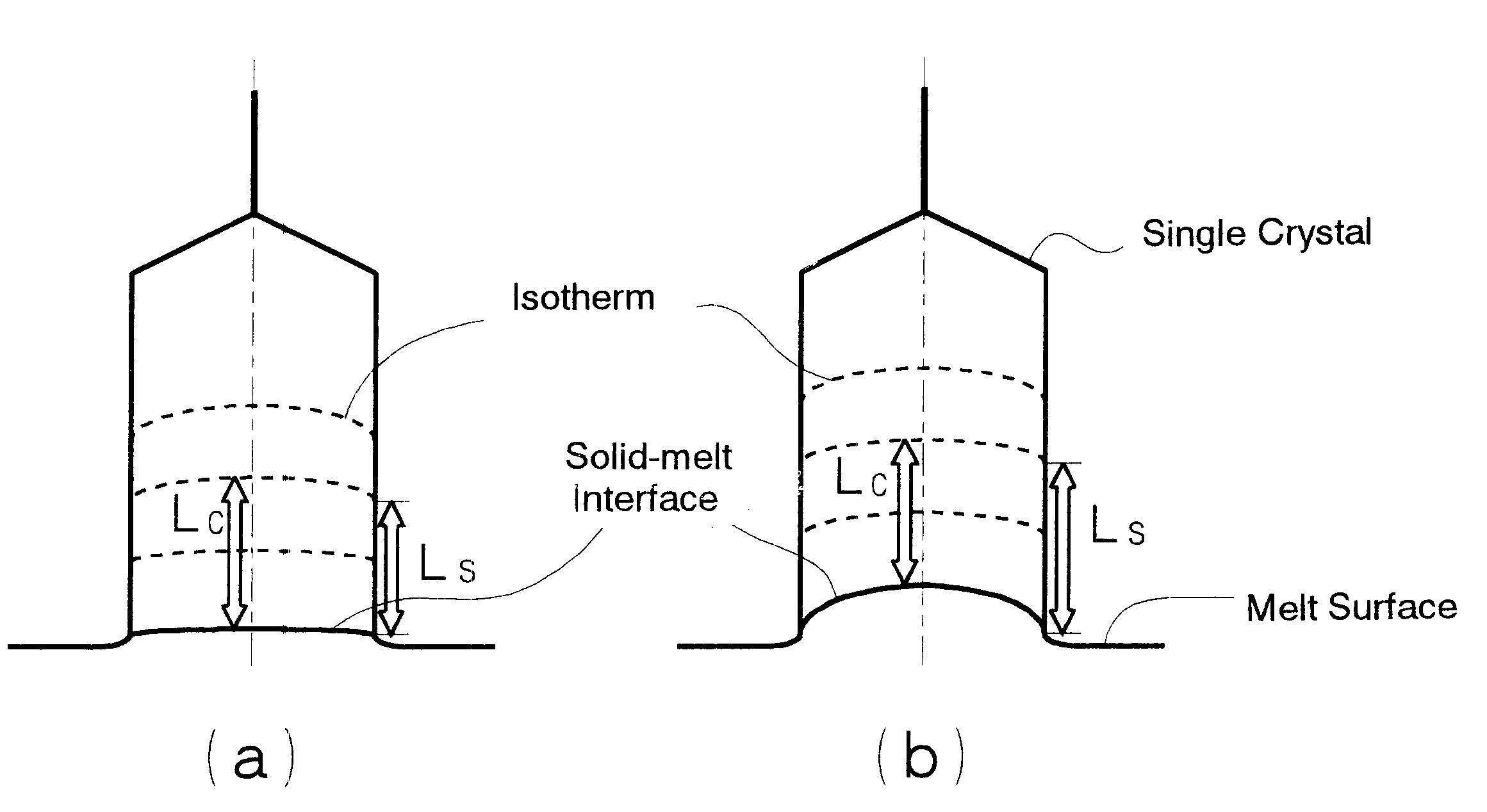
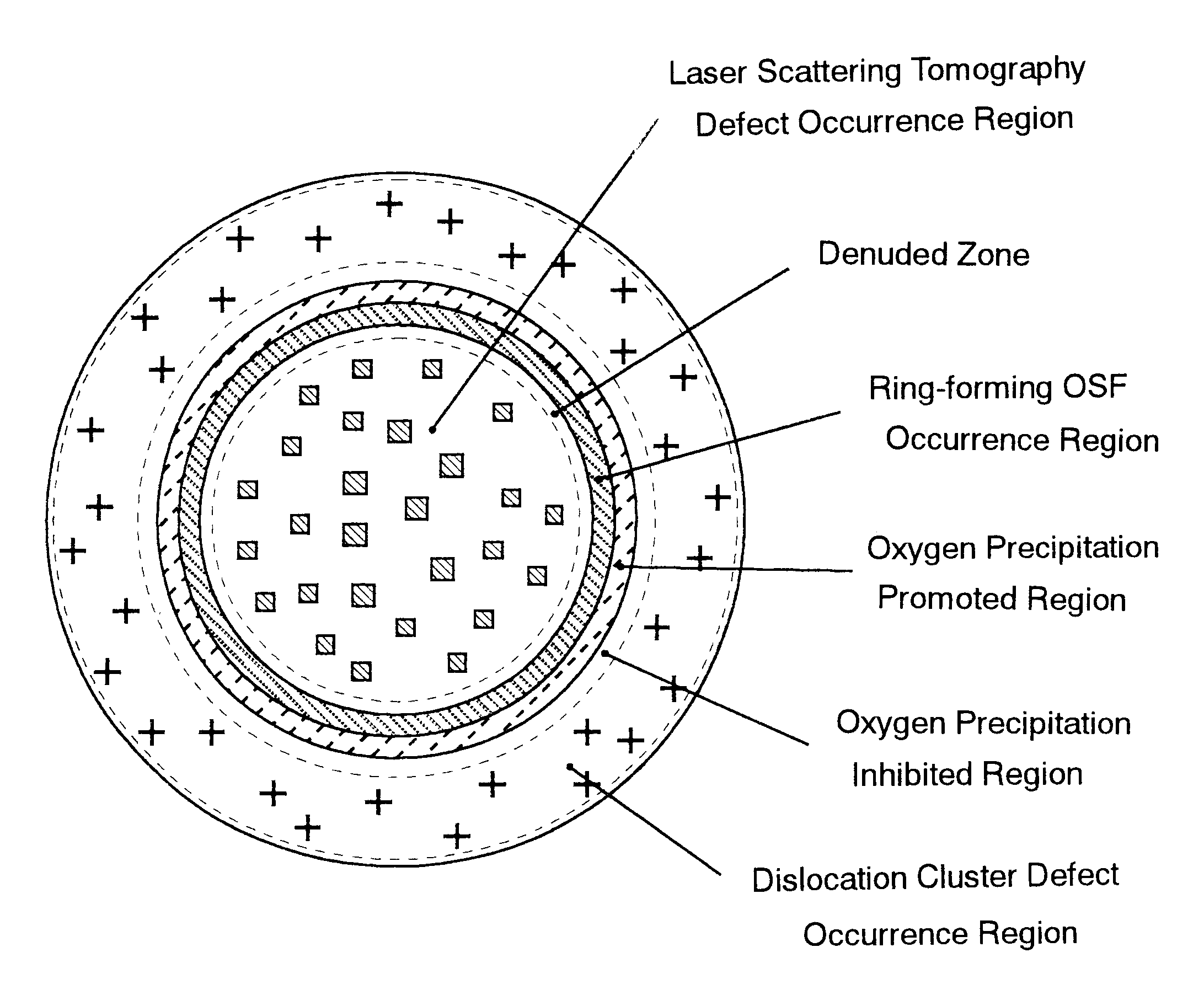
Method of producing high-quality silicon single crystals
InactiveUS6458204B1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser scatteringSingle crystal
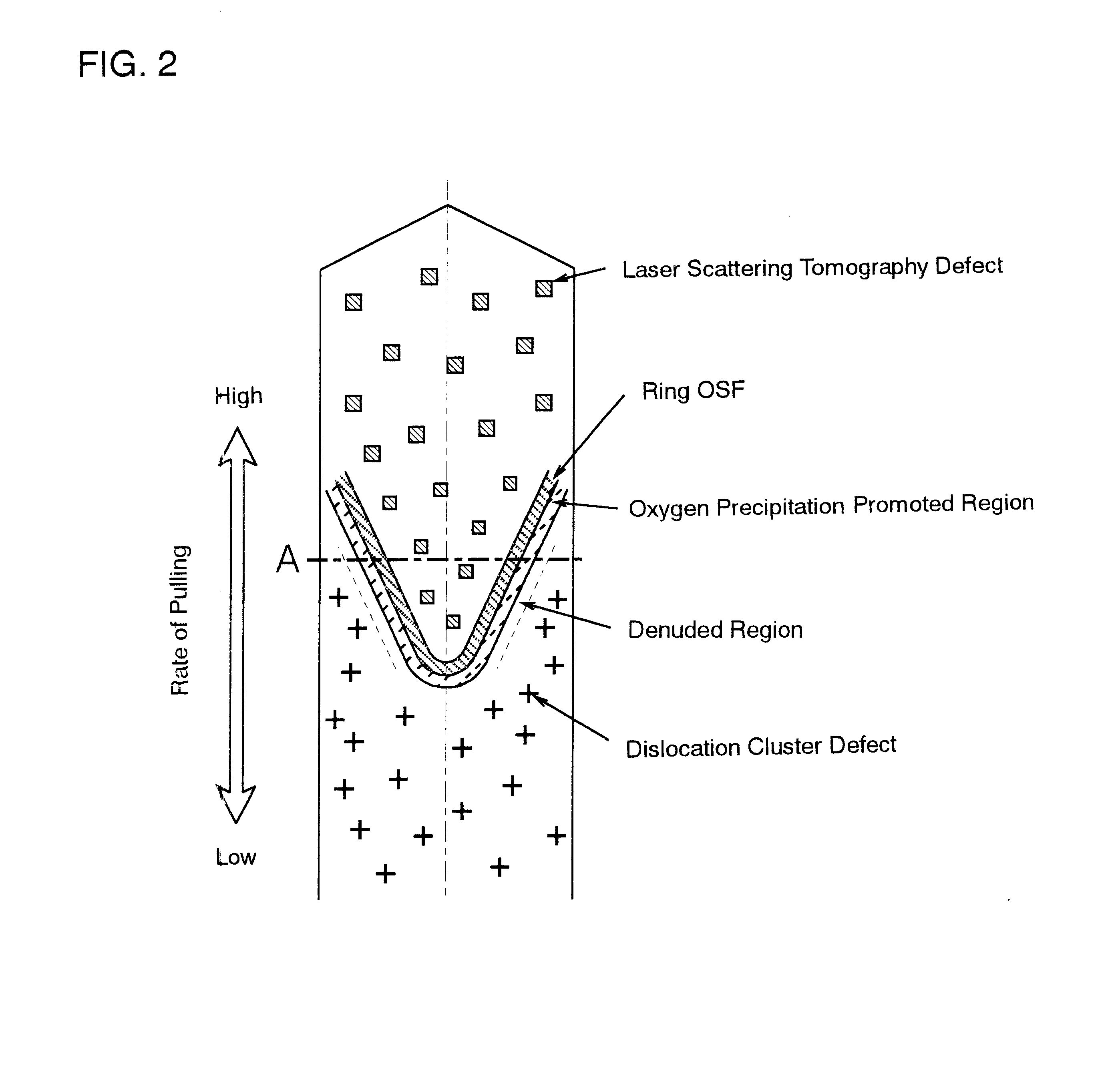
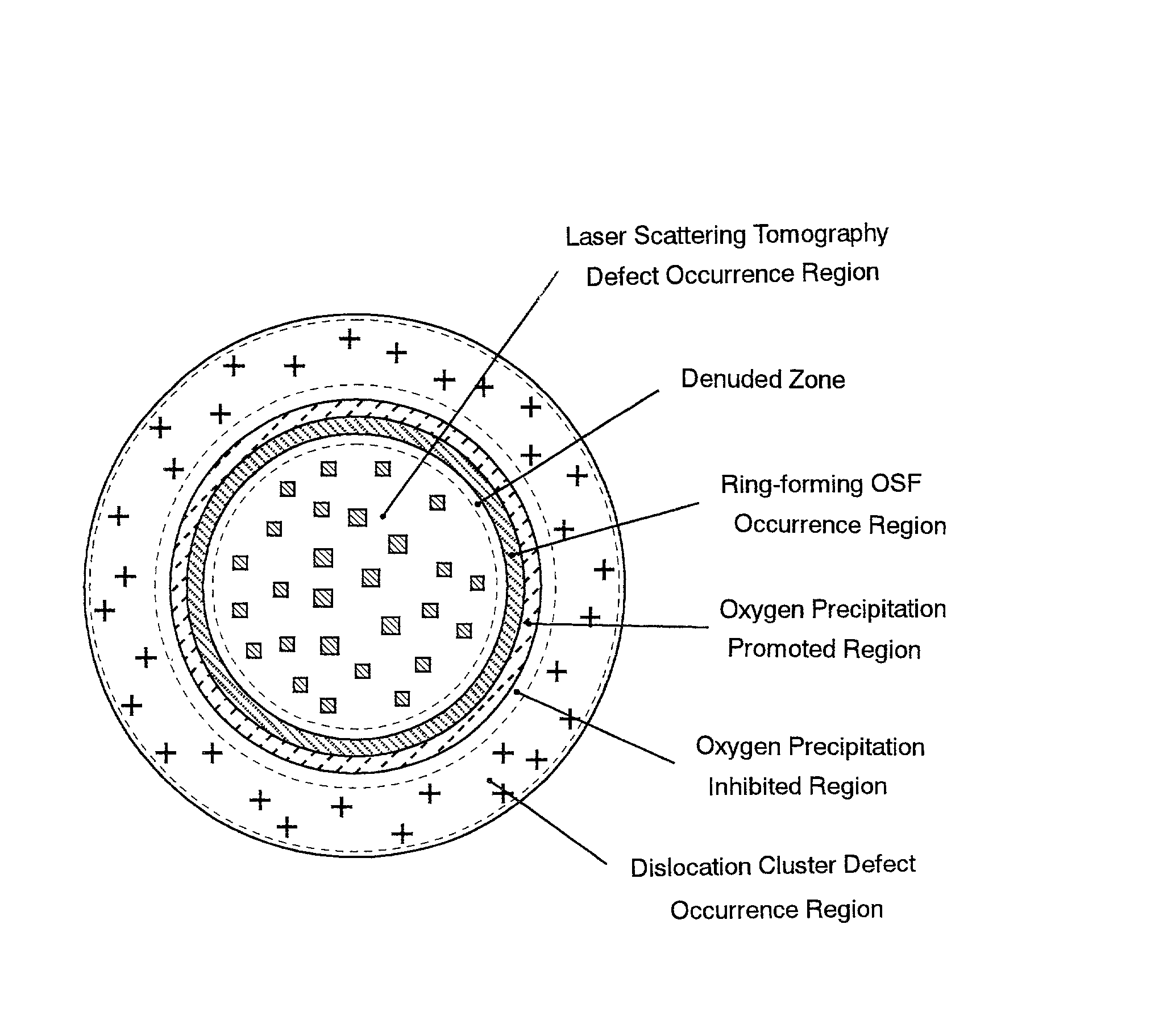
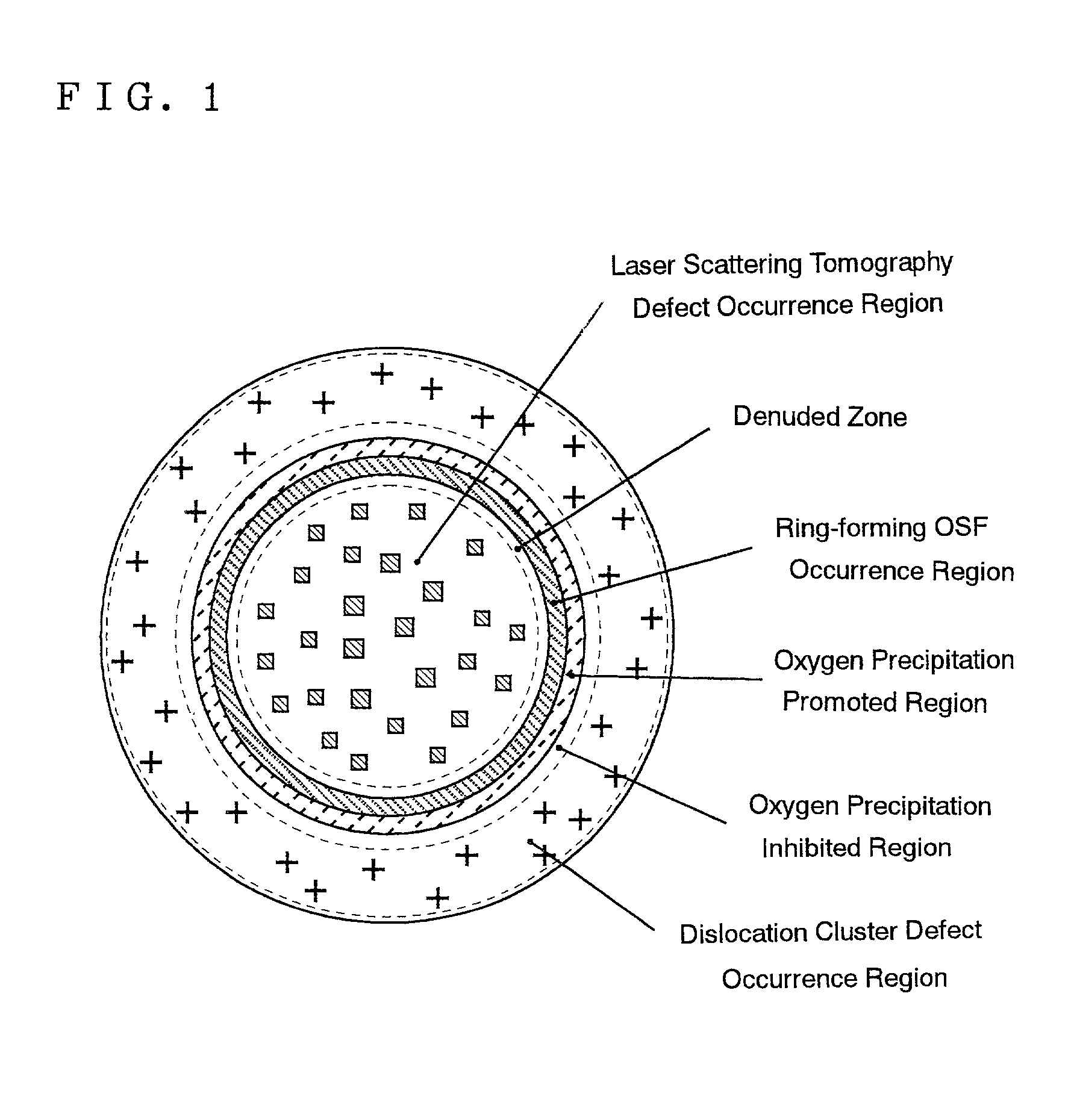
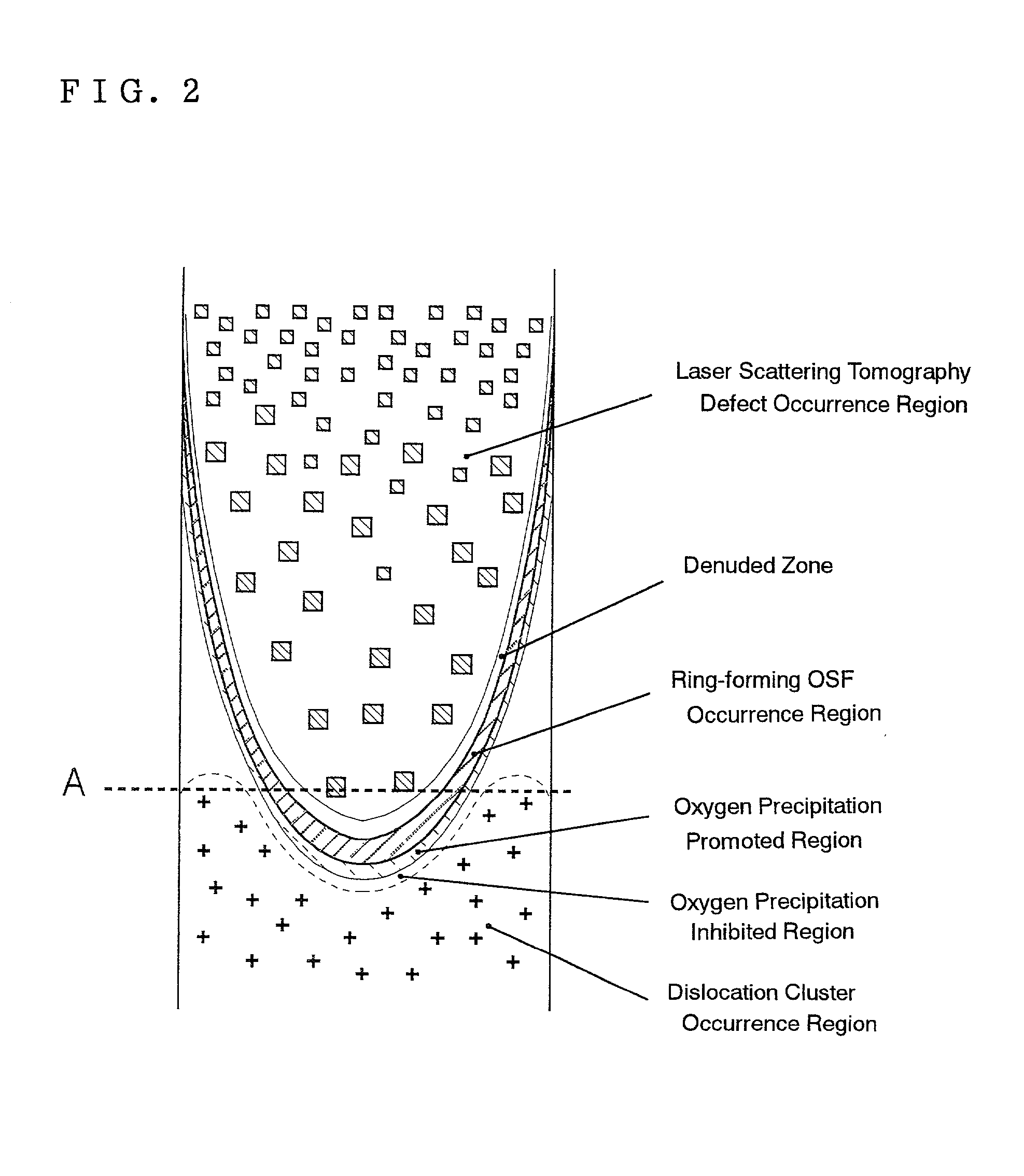
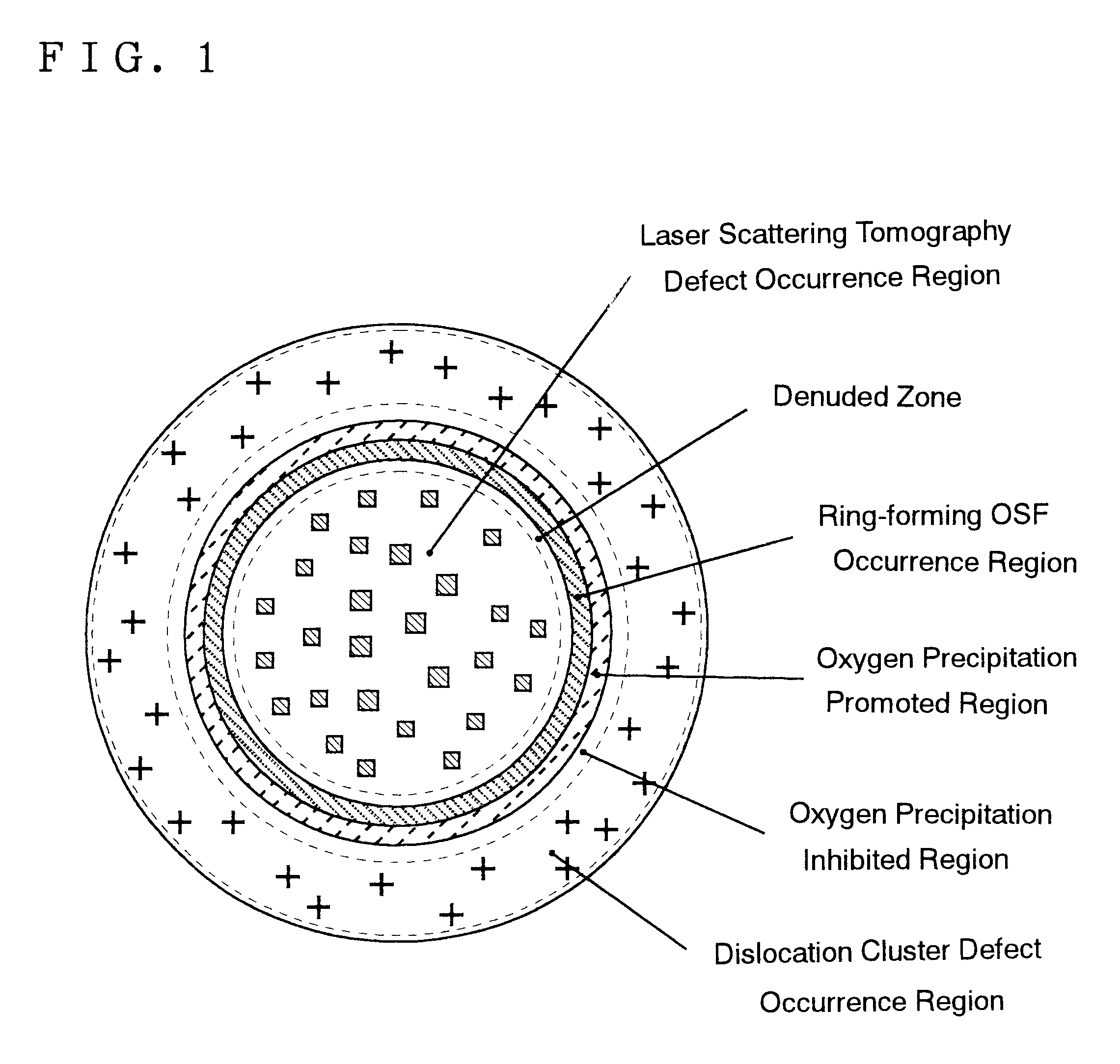
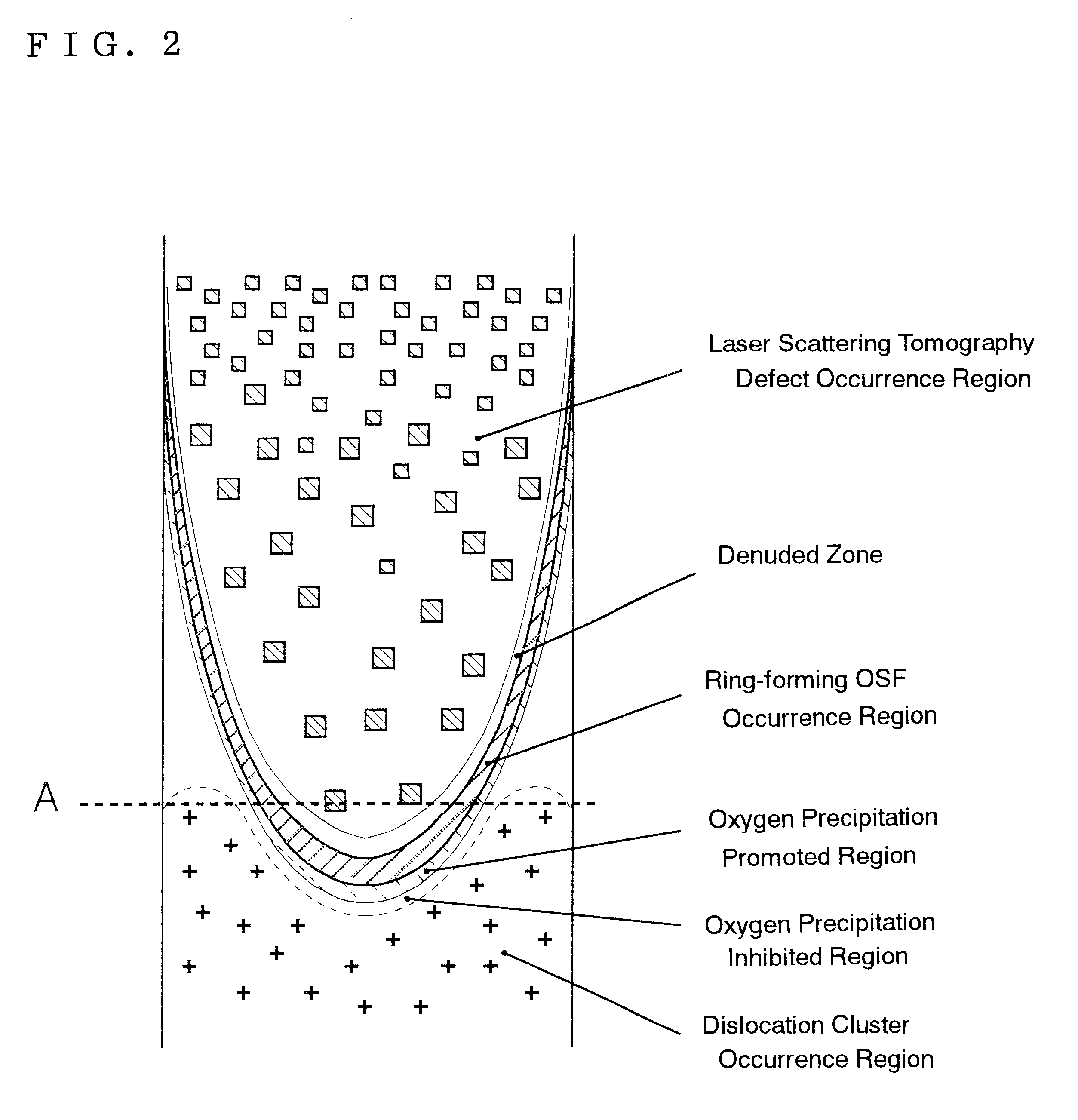
A method of producing high-quality and large-diameter single crystals by the Czochralski method is disclosed which can provide wafers with a minimized number of such grown-in defects as dislocation clusters and laser scattering tomography defects. Specifically, it is a method of producing silicon single crystals which comprises carrying out the crystal pulling while maintaining the solid-melt interface during pulling in the shape of an upward convex with the central portion of the interface being higher by at least 5 mm than the peripheral region thereof and while applying a magnetic field, and optionally in addition to the above, while maintaining the temperature gradient in the direction of axis of pulling in the peripheral region at a level lower than that in the central portion in the range of from the melting point to 1,200° C. In this case, it is desirable that the portion of the single crystal surface lying at least 50 mm above the melt surface be shielded from direct radiant heat from the heater and / or crucible wall, that a horizontal magnetic field of 0.08 to 0.3 T be applied in parallel with the melt surface or a cusped magnetic field showing an intensity of 0.02 to 0.07 T at a crucible wall site on the melt surface be applied and that the crucible be rotated at a speed of not more than 5 min-1 and the single crystal at a speed of not less than 13 min-1.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
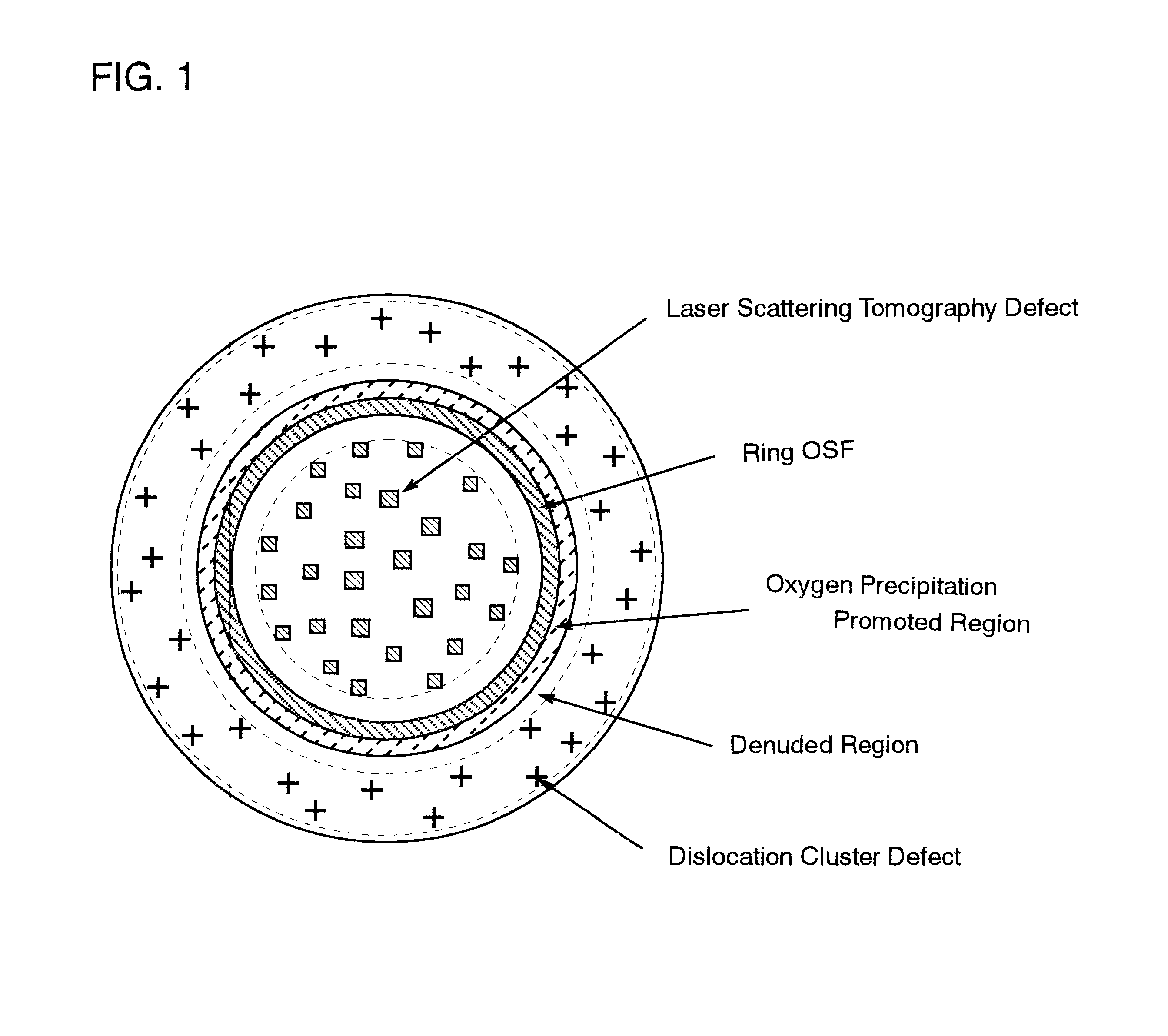
Silicon wafer and epitaxial silicon wafer utilizing same
InactiveUS20020081440A1Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor materialsLaser scattering
A silicon wafer characterized in that the laser scattering tomography defect occurrence region accounts for at least 80% of the wafer surface area and that the laser scattering tomography defects have a mean size of not more than 0.1 mum, with the density of those defects which exceed 0.1 mum in size being not more than 1x105 cm-3, and wafers derived from this wafer as the raw material by heat treatment for oxide precipitate formation, by heat treatment for denuded layer formation or by epitaxial layer formation on the surface are useful as semiconductor materials. In producing this wafer, a single crystal is pulled up under pulling conditions such that while the temperature of the central portion of the single crystal being pulled up from the melt is within the range from the melting point to 1,370° C., the temperature gradient Gc in the central portion in the single crystal pulling axis direction is not less than 2.8° C. / mm and the ratio Gc / Ge, where Ge is the temperature gradient in the peripheral portion in the pulling axis direction, is not less than 1. By doing so, silicon wafers very low in surface defect density and allowing the uniform and sufficient formation of BMDs can be obtained.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
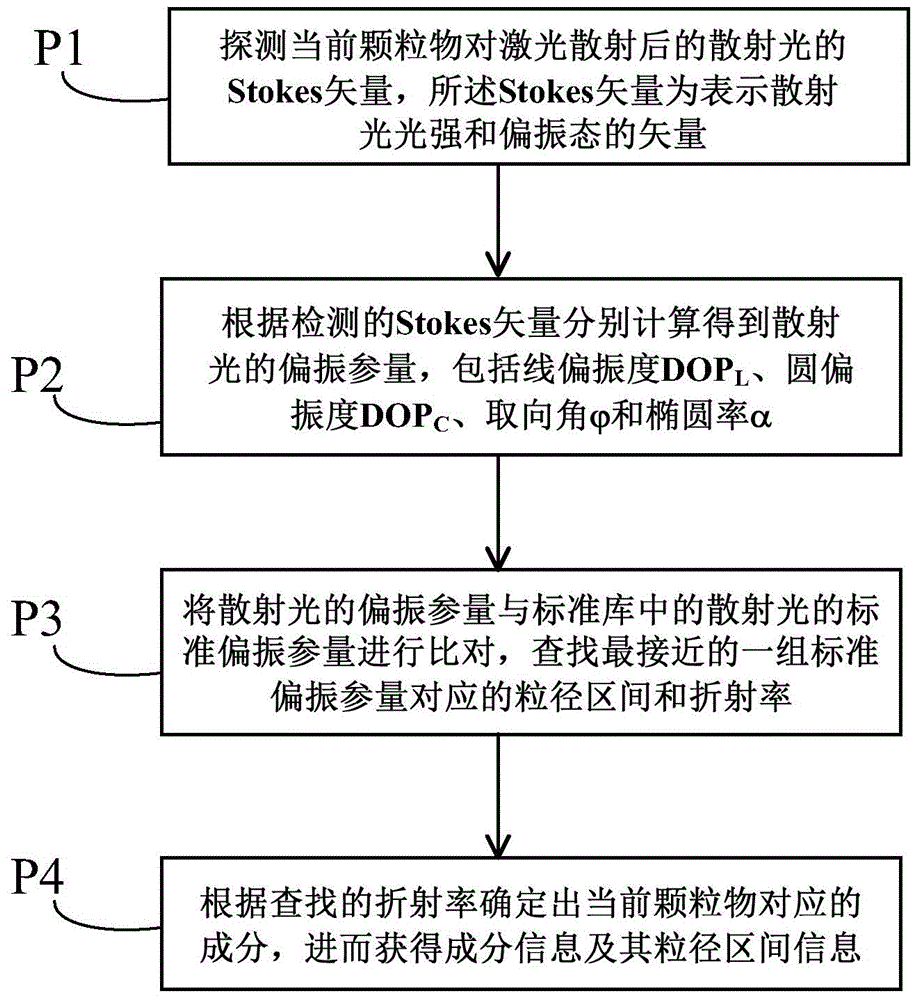
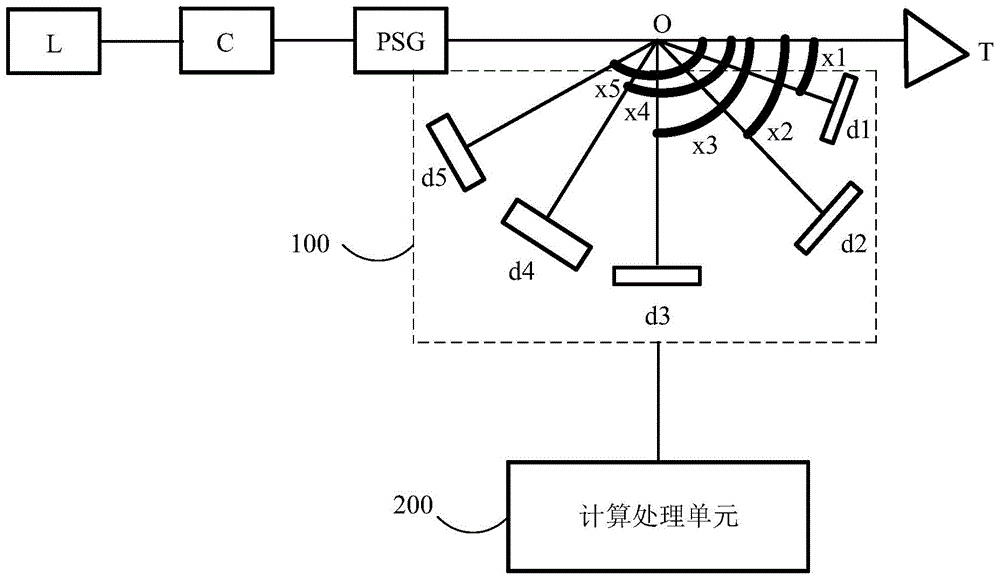
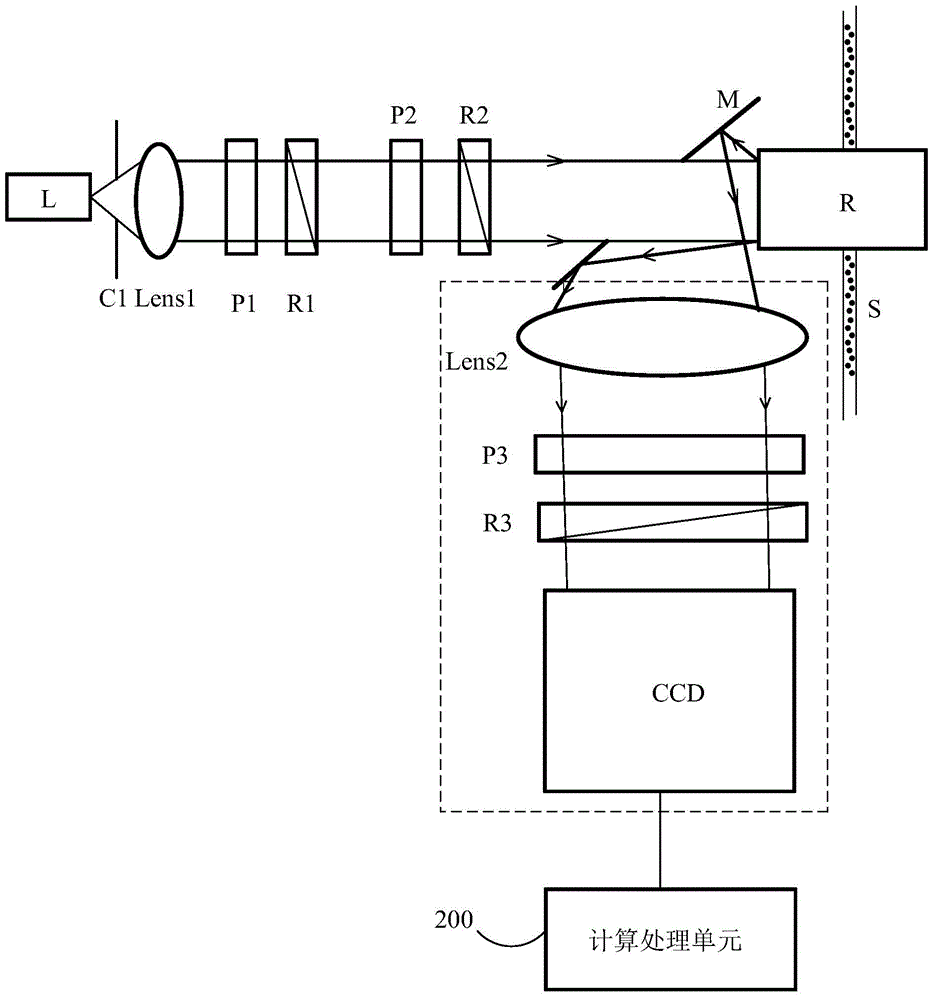
Method and device for measuring particles by polarized light scattering
The invention discloses a method and device for measuring particles by polarized light scattering. In a measurement process, an air sample to be detected flows through a testing region at a constant flow speed and laser is irradiated to the testing region after being subjected to focusing and polarization. The method comprises the following steps: (1) detecting Strokes vectors of scattered light of current particles after laser scattering, wherein the Strokes vectors represent the light intensity and a polarization state of the scattered light; (2) respectively calculating according to the Strokes vectors to obtain polarization parameters of the scattered light; (3) comparing the polarization parameters of the scattered light with standard polarization parameters of the scattered light in a standard library, and finding a particle diameter region and a refractive index which correspond to the proximate group of standard polarization parameters; and (4) determining the corresponding components of the current particles according to the refractive index so as to obtain component information and particle diameter range information thereof. The method and the device disclosed by the invention can be used for analyzing to obtain the component information of the particles; the particle diameter distribution of the small-diameter particles can be accurately distinguished accurately when being analyzed; meanwhile, the cost can be controlled well.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
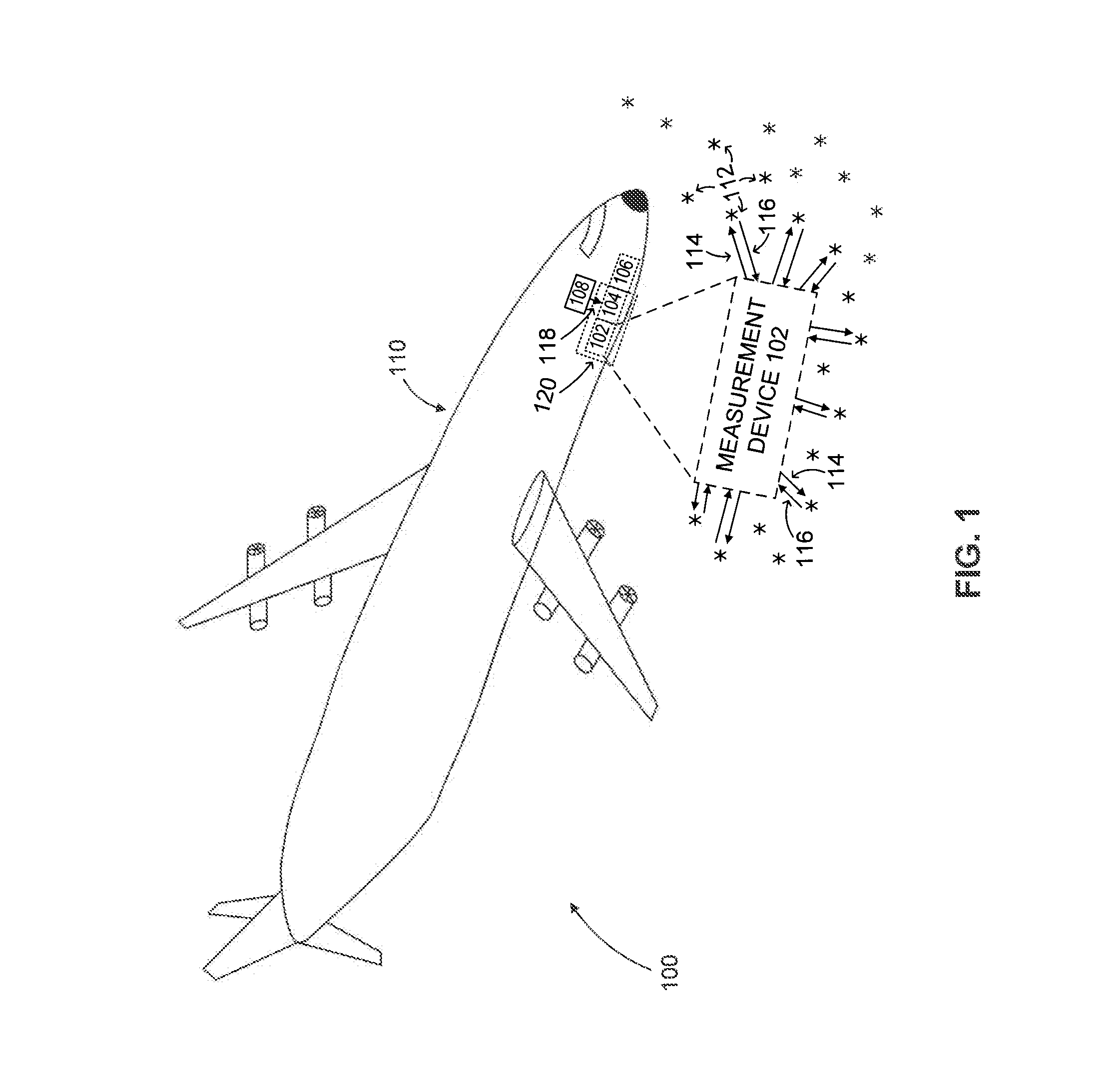
Optical air data sensor
ActiveUS20110219869A1Reduce shakingEfficient executionIndication/recording movementNavigation instrumentsLaser scatteringLaser light
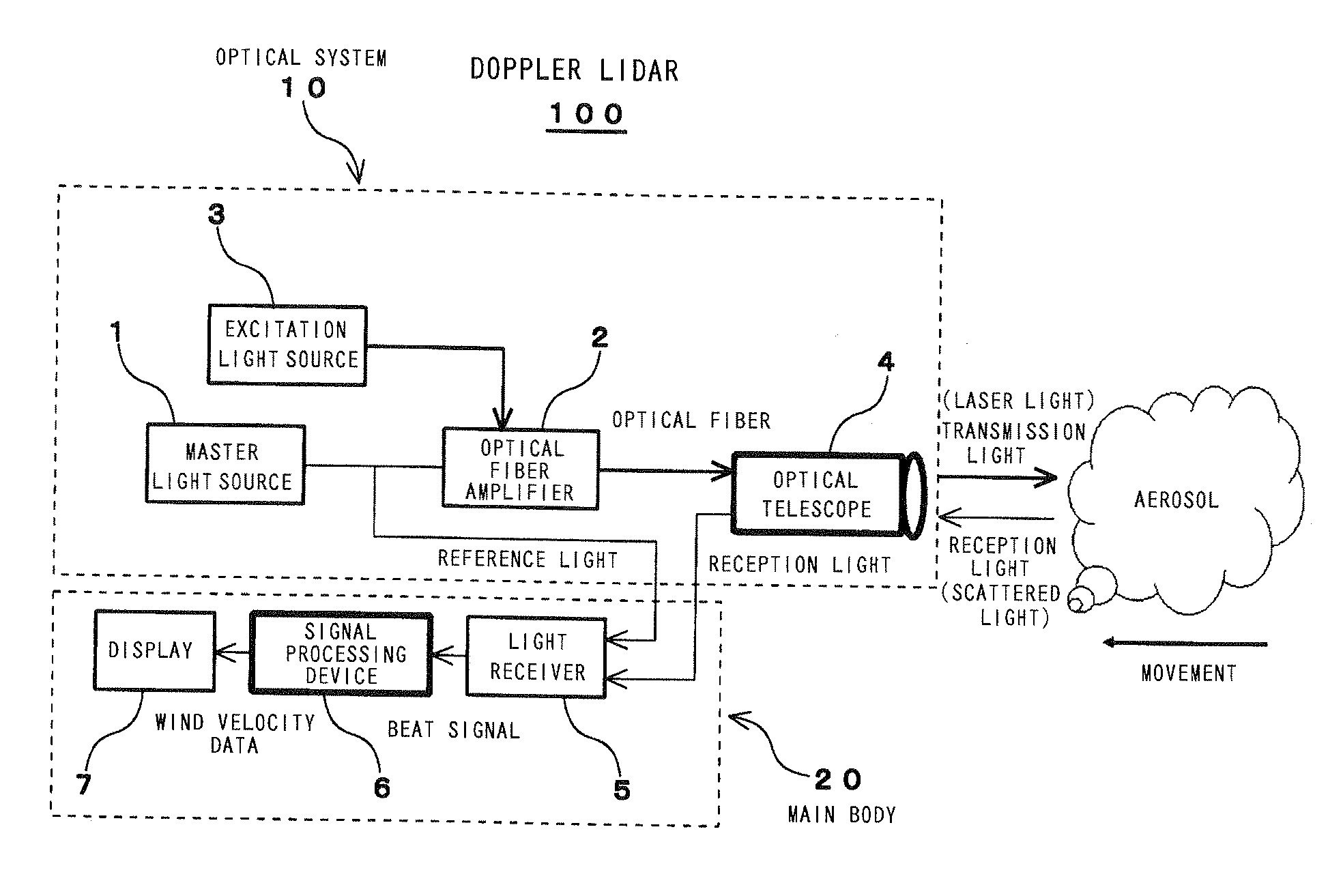
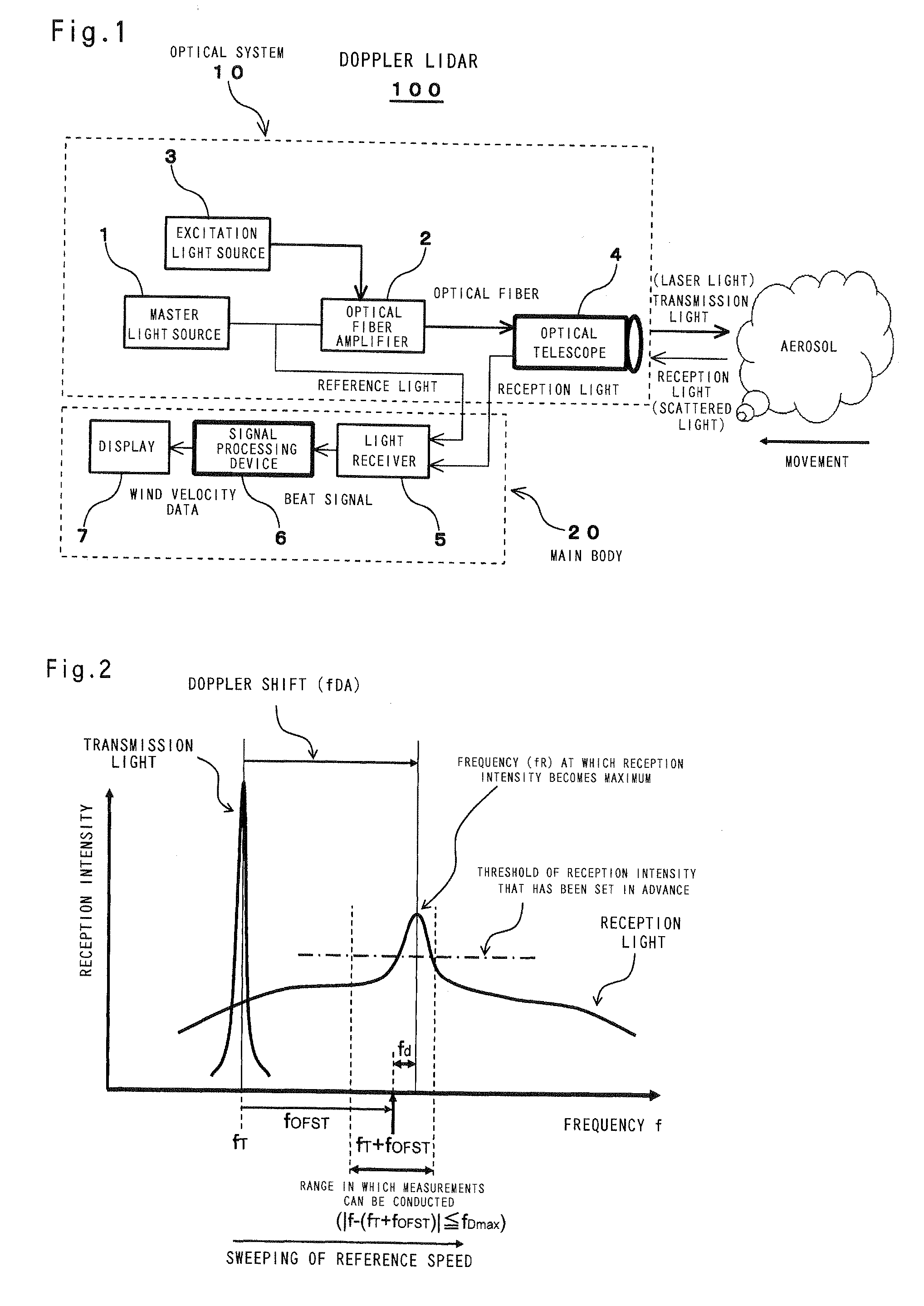
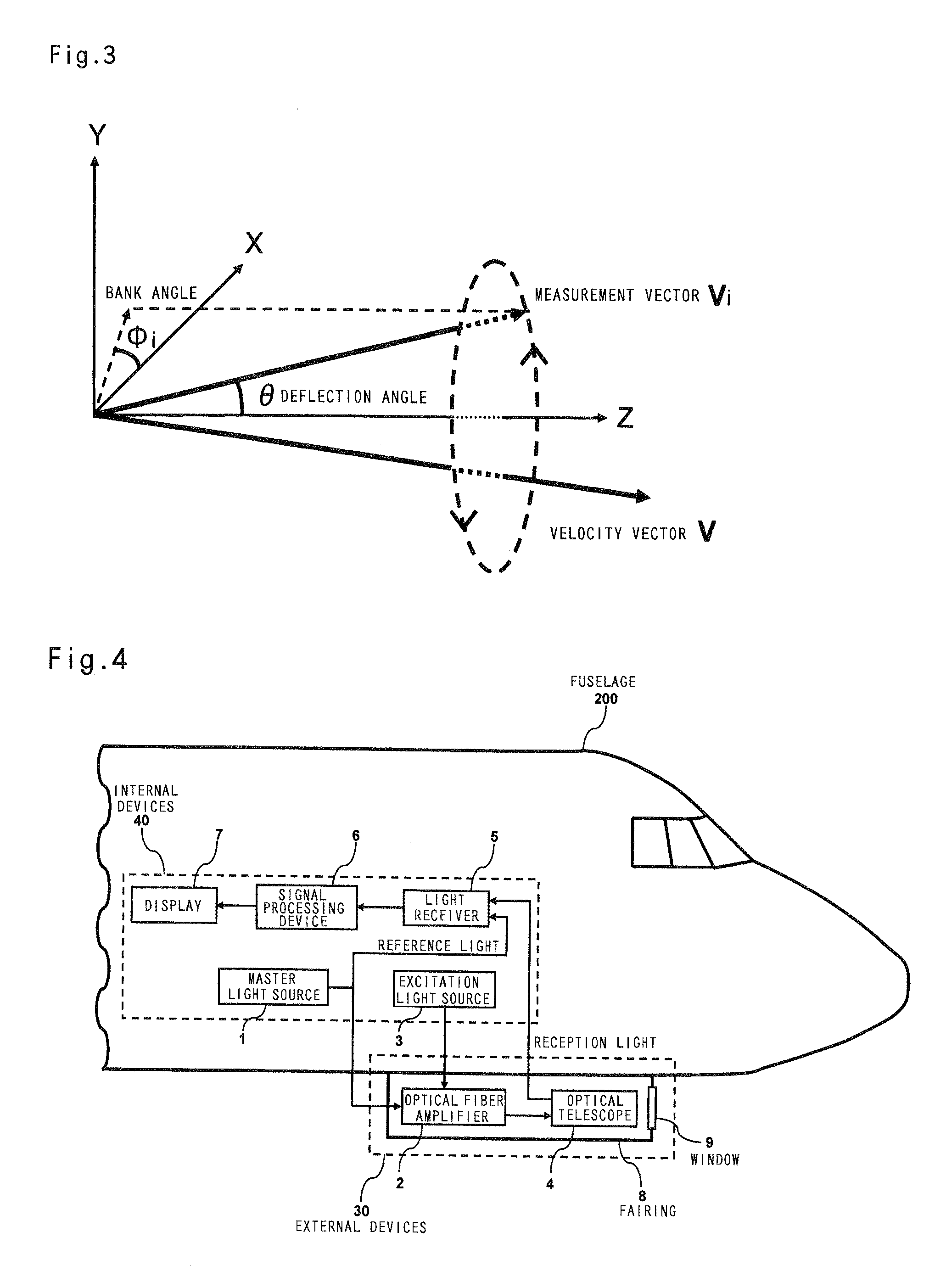
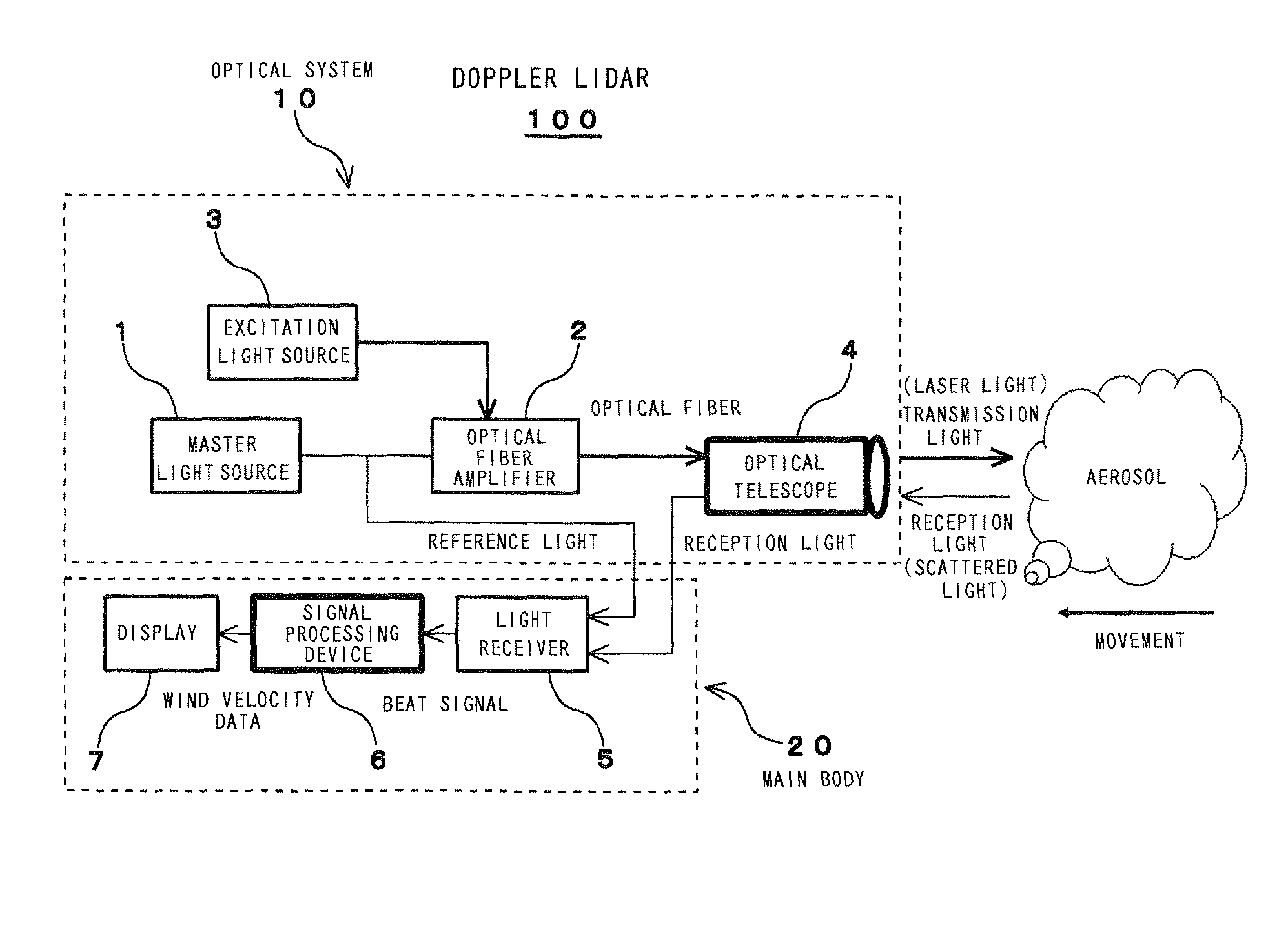
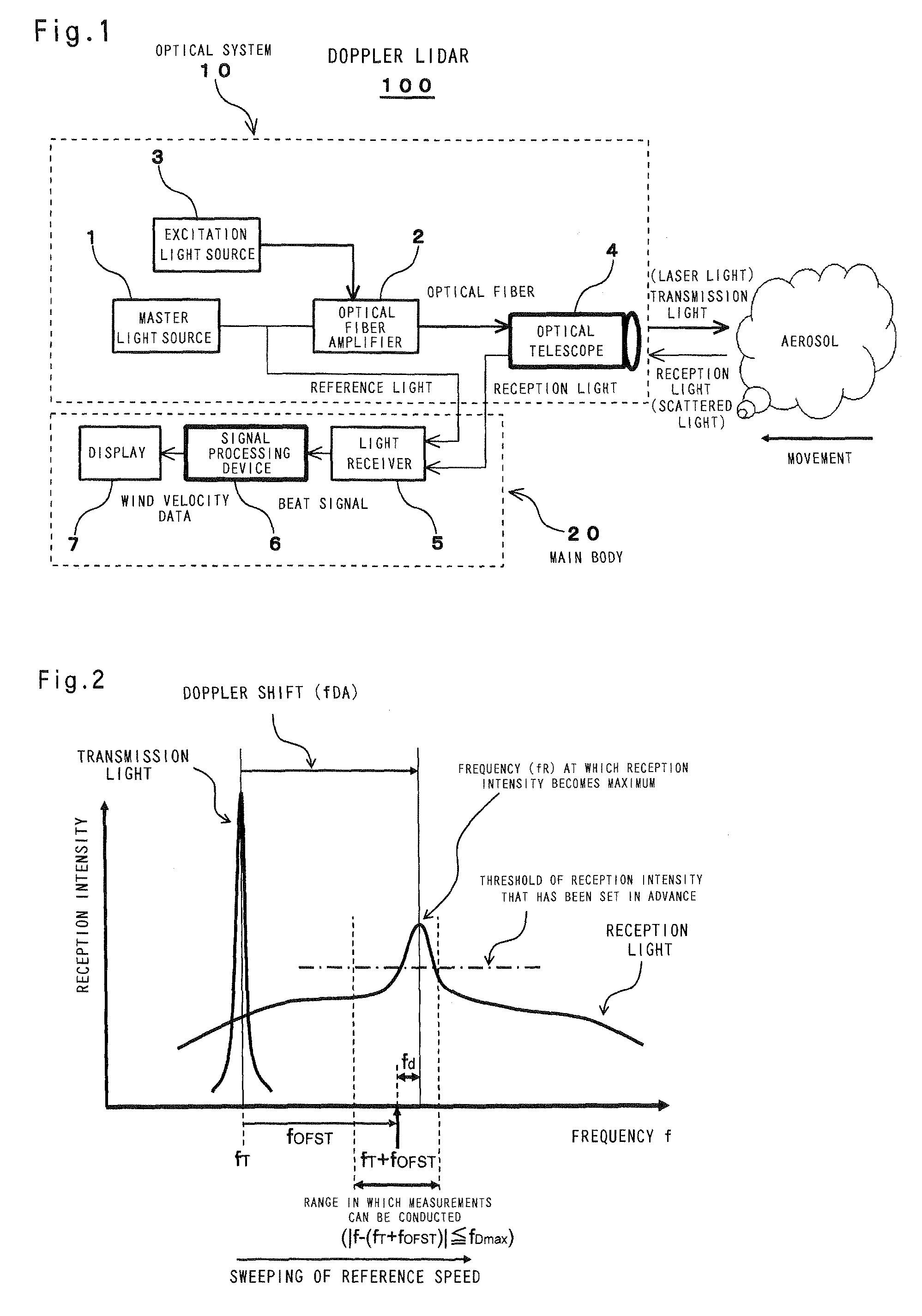
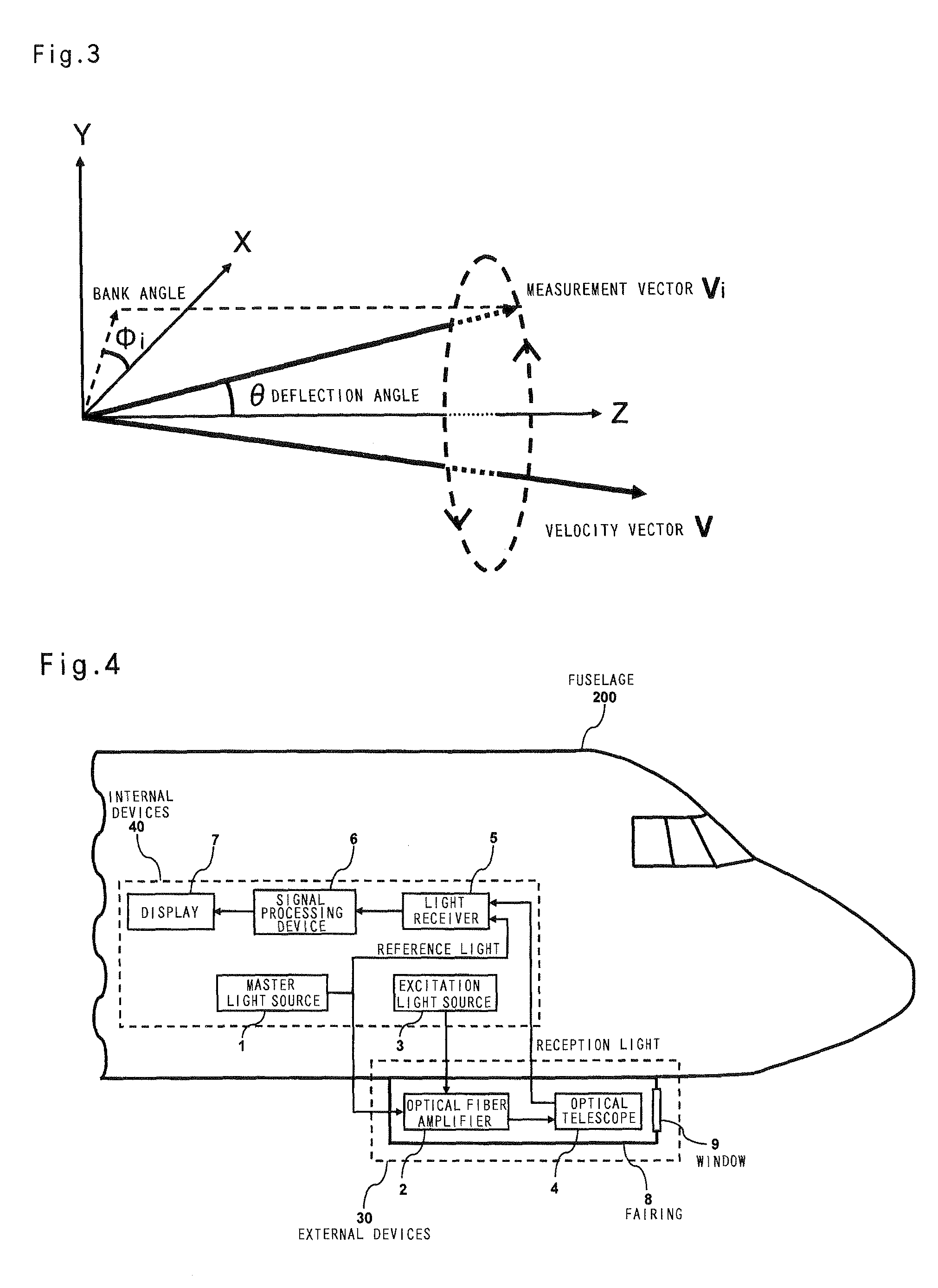
The object of the present invention is to provide an air data sensor that does not require an external input of a reference velocity as a Doppler LIDAR, has a function of autonomously determining the absolute airspeed, and has no position error. The optical air data sensor in accordance with the present invention is an optical air data sensor, mounted on an aircraft, for emitting a laser light as a transmission light into atmosphere, and then receiving a laser scattered light produced by scattering of the laser light by aerosol present in the atmosphere as a reception light, thereby to measure an airspeed and a wind velocity of airflow in a distant region on the basis of a Doppler shift amount between the transmission light and the reception light, wherein a true airspeed is autonomously measured, without setting a reference velocity, by successively sweeping a frequency offset corresponding to a reference velocity for providing an offset to a measurement frequency, and performing this sweeping within a frequency range in which the Doppler shift amount is measured.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
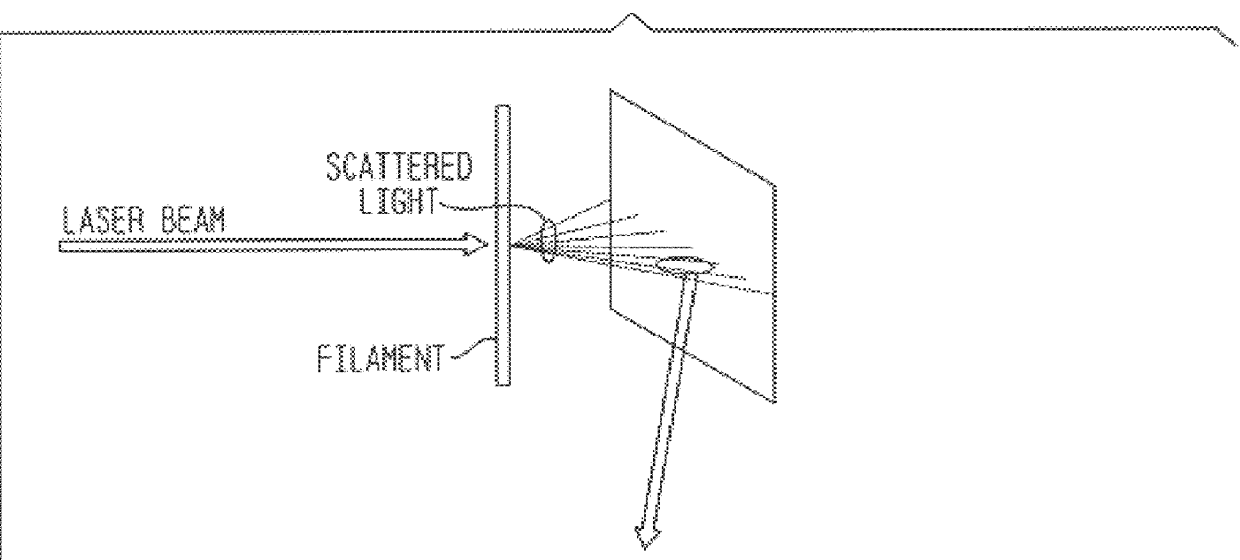
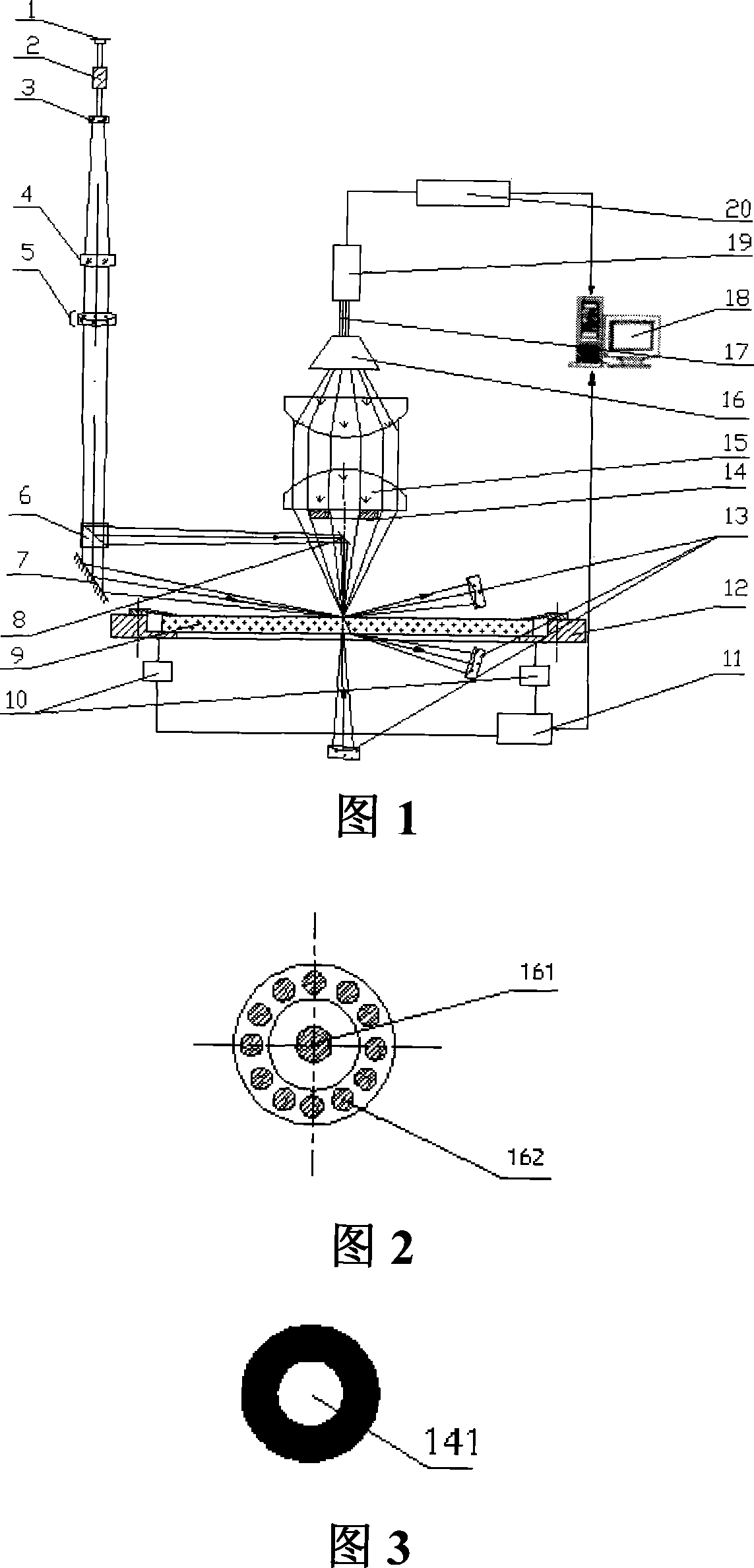
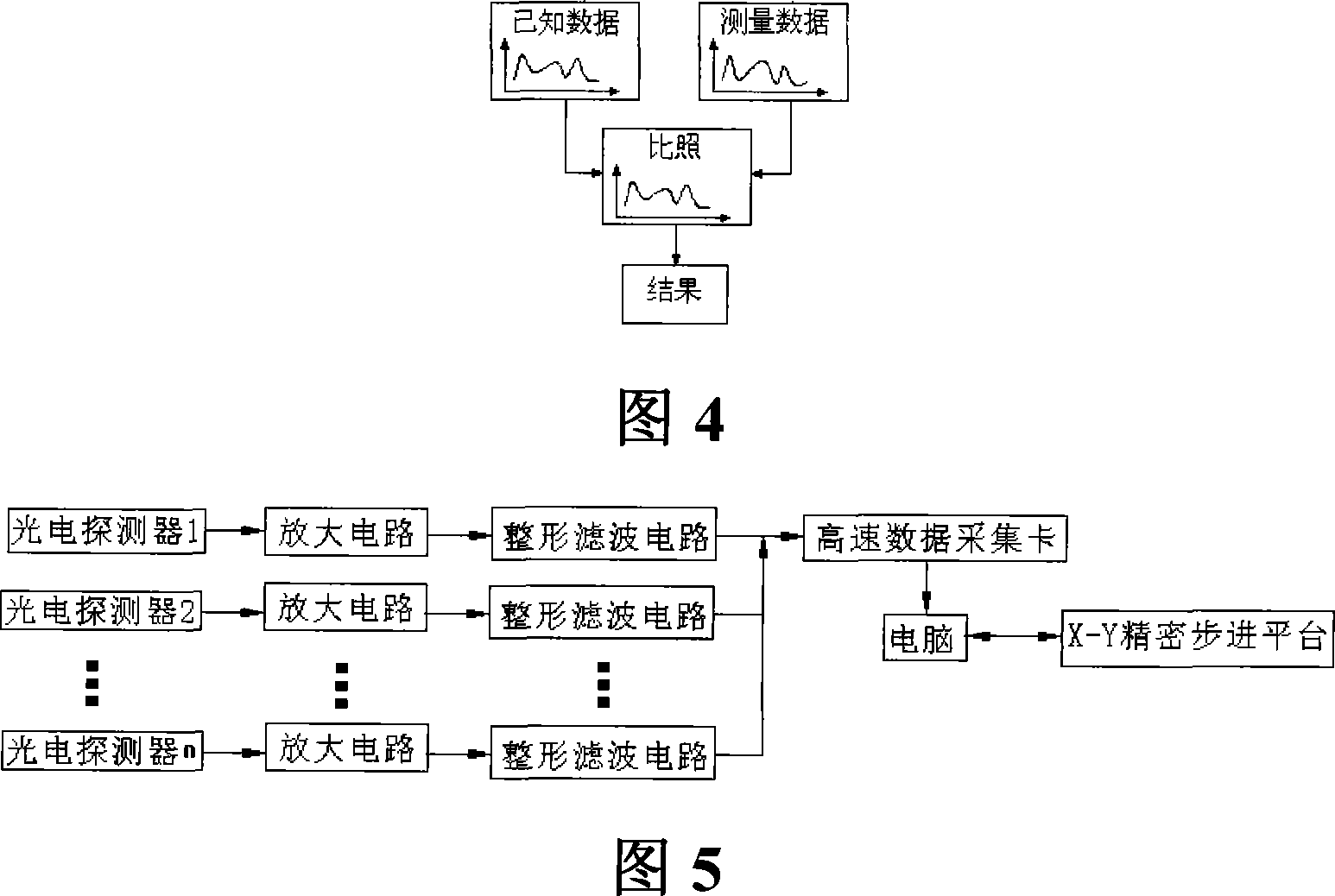
Laser scattering detecting system of optical flat surface blemishes
InactiveCN101135653AImprove signal-to-noise ratioHigh resolutionScattering properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsImage resolution
The system comprises: a X-Y precise stepping platform used for placing the optical component under test; using two laser beams to illuminate the surface of the optical component from both vertical and inclined directions; the generated scattered lights are collected by multi photoelectric detectors from different azimuth angles; converting the collected scattered lights into the electrical signals which are inputted into the computer; the computer controls the X-Y precise stepping platform to drive the optical component under test; making scan measurement, and comparing the scattered light signals with the scattered light signals used for showing the faults on the optical flat surface in order to realizing the location, classification and level of the faults on the optical flat surface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
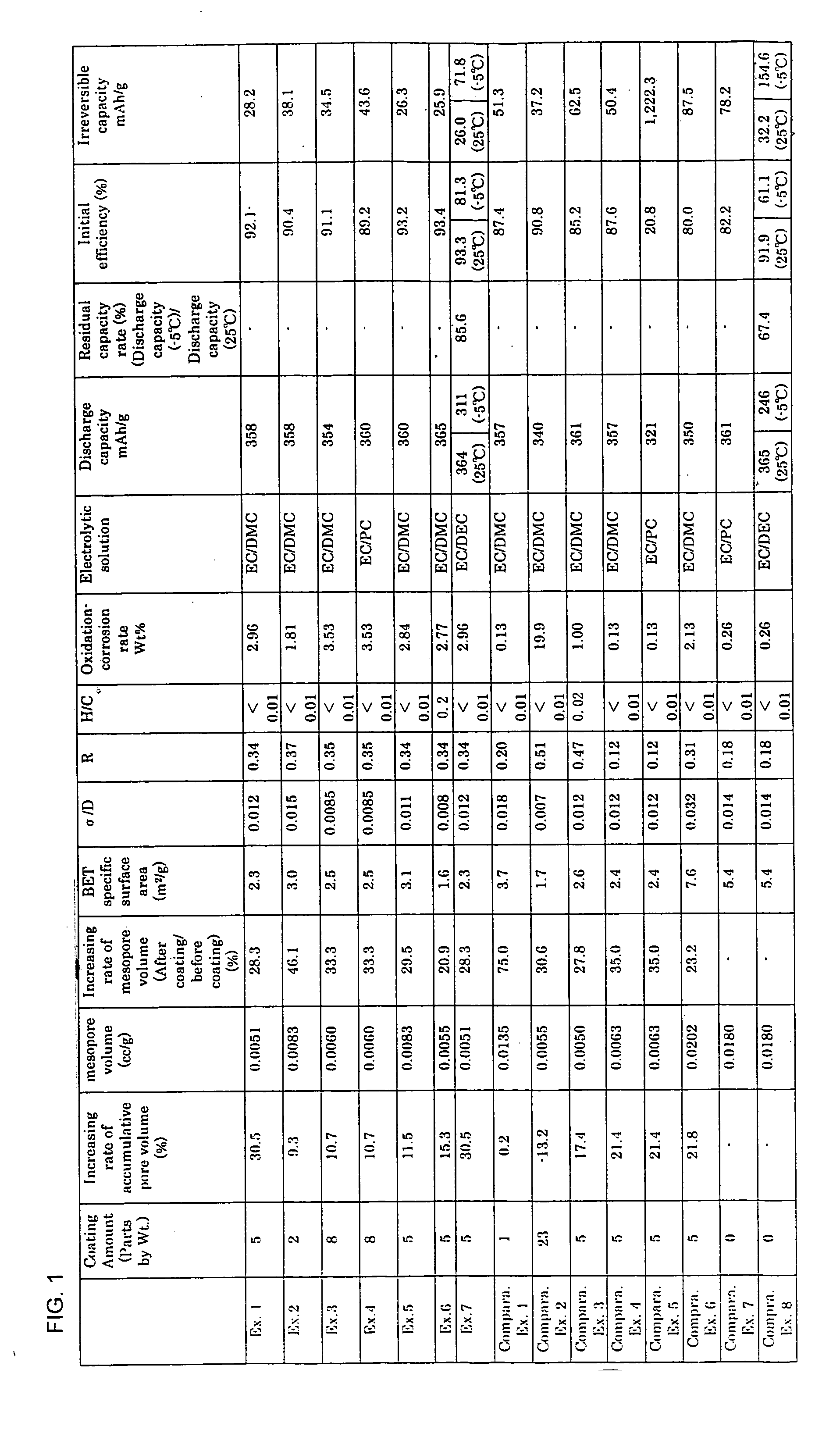
Negative electrode material for lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20050158550A1Good effectTrimming is irreversibleSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsLaser scatteringLithium
The invention provides an anode material for lithium ion secondary battery using a coated graphite powder as a raw material. The coated graphite powder is coated with carbonized material of thermoplastic resin of a carbonization yield of not more than 20 wt % in a proportion of not more than 10 parts by weight the carbonized material per 100 parts by weight graphite powder. The graphite powder as coated with thermoplastic resin increases 5% or more in accumulative pore volume of the graphite powder having a pore size of 0.012 μm to 40 μm as measured by a mercury porosimeter method, as compared with the graphite powder before coated with the thermoplastic resin. The coated graphite powder has a mesopore volume defined by IUPAC of 0.01 cc / g or less as calculated with the BJH method as viewed from desorption isotherm, which is also equal to 60% or less of the pore volume of the graphite powder before coated with the thermoplastic resin, an average particle size ranging from 10 μm to 50 μm, as measured by a laser-scattering-particle-size-distribution measuring device, and a ratio of standard deviation to the average particle size (σ / D) of 0.02 or less.
Owner:TOYO TANSO KK
Electrolyte membrane for energy storage device, energy storage device including the same, and method of preparing the electrolyte membrane for energy storage device
An electrolyte membrane for an energy storage device, an energy storage device including: a matrix including an ionically conductive polymer composition including a polymer and a lithium salt; and a metal-organic framework in the matrix, wherein the metal-organic frame work is in the form of a plurality of primary particles, each having diameter distribution represented by Inequation 1:0<σ2 / μ<1.0 Inequation 1wherein, in Inequiation 1, σ2 is a diameter variance for the plurality of primary particles obtained by dynamic laser scattering, and μ is an average particle diameter of the plurality of primary particles.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for preparing lithium cobalt oxide of lithium-ion secondary battery cathode materials
ActiveCN101694874AImprove featuresImprove discharge capacityCell electrodesSecondary cellsLaser scatteringOxygen
The invention provides a process for preparing lithium cobalt oxide of lithium-ion secondary battery cathode materials. The process includes that cobalt oxide or hydroxyl cobalt oxide powders and lithium carbonate powders are mixed according to a lithium / cobalt molar ratio of 1.0-1.1 and calcined in an atmosphere containing oxygen at the temperature of 850-1100 DEG C; obtained mixture is calcined for 5-55 hours in the atmosphere containing oxygen at the temperature of 850-1100 DEG C; calcined products are naturally cooled to reach room temperature and then grinded; laser scattered grain size distribution measuring device is used for classifying; lithium cobalt oxide semi-finished products are obtained by selecting an average grain diameter D50 of 8-20 micrometers; and a device with high-speed shear strength function is used for conducting coating composition treatment process on the surfaces of the lithium cobalt oxide semi-finished products. The process has the advantages of low raw material cost, high volume energy density, good safety, fine charge-discharge cycle performance, high pressurizing density and superior productivity.
Owner:NANTONG RESHINE NEW MATERIAL
Method for calibrating and measuring supersonic flow field density field
ActiveCN102706529ALarge measuring rangeIncreased spatio-temporal resolutionAerodynamic testingNanoparticleImage resolution
The invention provides a method for calibrating a supersonic flow field density field. According to the method, a supersonic flow field density-nanoparticle-based planar laser scattering (NPLS) image gray curve is calibrated by adopting a comprehensive oblique shock wave and expansion wave calibration method based on an NPLS technology. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, uniformly scattering trace particles in supersonic incoming flow, and shooting a particle image according to the instruction of a computer by a charge coupled device (CCD); 2, continuously adjusting obliqueness of an attack angle alpha in a supersonic wind tunnel, and acquiring a group of (rhoi, Ii) (i=1, 2, L, n-1) data by changing the oblique attack angle alpha; 3, placing expansion wave generators in the supersonic wind tunnel, and acquiring the other group of (rhoi, Ii) (i=n, n+1, L, N) data by placing the expansion wave generators with different deflection angles; and 4, performing polynomial fitting on the two groups of data to obtain the supersonic flow field density-NPLS image gray relation curve, namely rho=alapha0+alpha1I+alpha2I2+alpha3I3+K. The method aims to solve the technical problems of low spatial resolution and low signal-noise ratio and high error on measurement of a low-density area.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Particulate matter sensor and particulate matter monitoring method
InactiveCN104266948ASmall divergence angleHigh precisionParticle suspension analysisParticulatesLight energy
The invention provides a particulate matter sensor and a particulate matter monitoring method. The particulate matter sensor comprises an upper cover and a base which form a light shading space comprising an airflow channel and a light transmission channel, wherein the airflow channel is perpendicular to the light transmission channel, and a photoelectric detector is arranged under the crossed region of the airflow channel and the light transmission channel; a laser device is arranged at one end of the light transmission channel, and a light absorption device is arranged at the other end of the light transmission channel; a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) circuit is connected with the photoelectric detector; a laser beam output by the laser device is adopted as a monitoring light source in the particulate matter sensor, so that a light signal generated by laser scattering of particulate matters still can be monitored by the photoelectric detector even if the PM2.5 particulate matters or the particulate matters with relatively small diameters are monitored as laser is collimating light with small divergence angle and high light energy density in unit area, and the monitoring accuracy of the particulate matter sensor during monitoring of the PM2.5 particulate matters or the particulate matters with relatively small diameters in air is improved.
Owner:北京云彤科技有限公司
Method for measuring airspeed by optical air data sensor
ActiveUS8434358B2Reduce shakingEfficient executionIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementContinuous scanningLaser scattering
The object of the present invention is to provide an air data sensor that does not require an external input of a reference velocity as a Doppler LIDAR, has a function of autonomously determining the absolute airspeed, and has no position error. The optical air data sensor in accordance with the present invention is an optical air data sensor, mounted on an aircraft, for emitting a laser light as a transmission light into atmosphere, and then receiving a laser scattered light produced by scattering of the laser light by aerosol present in the atmosphere as a reception light, thereby to measure an airspeed and a wind velocity of airflow in a distant region on the basis of a Doppler shift amount between the transmission light and the reception light, wherein a true airspeed is autonomously measured, without setting a reference velocity, by successively sweeping a frequency offset corresponding to a reference velocity for providing an offset to a measurement frequency, and performing this sweeping within a frequency range in which the Doppler shift amount is measured.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Inkjet recording liquid and process for the production thereof
InactiveUS6235099B1High processing temperatureImprove waterproof performanceDuplicating/marking methodsInksWater basedInorganic salts
A water-dispersed inkjet recording liquid excellent in water resistance and transparency and also excellent in the property of ejection from a nozzle, containing, as a colorant, a water-based dispersion of an organic pigment (A) which is at least one member selected from the group consisting of a quinacridone pigment, a benzimidazolone pigment, an insoluble azo pigment, a fuzed azo pigment, a quinophthalone pigment, a naphthol pigment, a perylene pigment and an isoindolinone pigment and has an average particle diameter of 10 to 150 nm (measured by laser scattering), the water-based dispersion of the organic pigment (A) being obtained by mechanically kneading a mixture containing at least three components of the organic pigment (A), a water-soluble inorganic salt (B) in an amount by weight at least three times as large as the amount of the organic pigment (A) and a water-soluble solvent (C) to finely mill the organic pigment (A), and then removing the water-soluble inorganic salt (B) and the water-soluble solvent (C) by washing the kneaded mixture with water, and a process for the production thereof.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
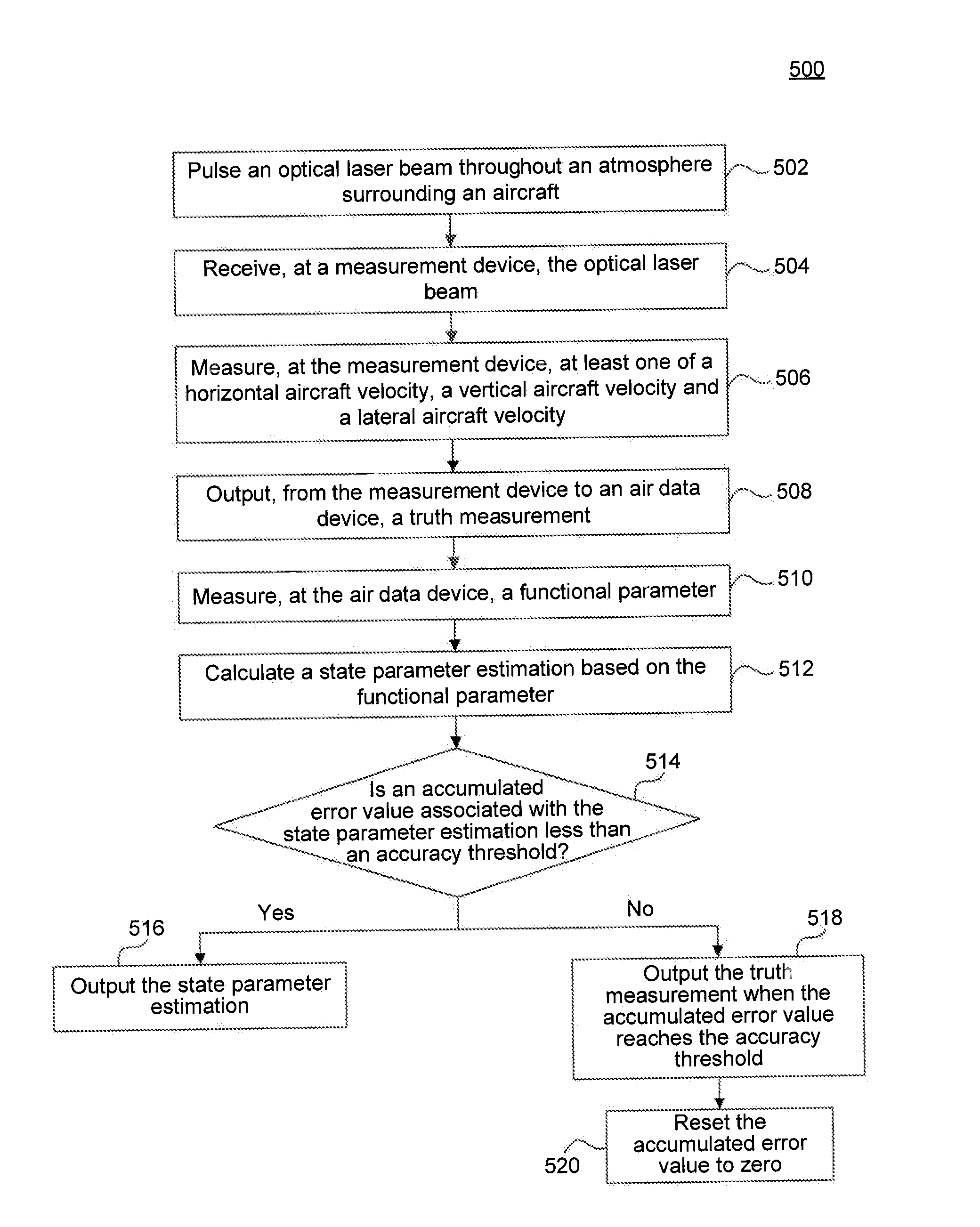
Measurement Assisted Aerodynamic State Estimator
An aerodynamic state estimation system includes a real-time actual measurement device, an air data computer, and a plurality of sensors. The measurement device receives laser scatter energy indicative of one or more atmospheric data parameters and outputs one or more truth measurements. The air data computer module receives the one or more truth measurements, calculates one or more state parameter estimations based on a plurality of functional parameters, and outputs at least one of the one or more truth measurements and the one or more state parameter estimations as one or more high accuracy state parameters, The plurality of sensors, located at the air data computer module, measure the plurality of functional parameters.
Owner:OPTICAL AIR DATA SYST
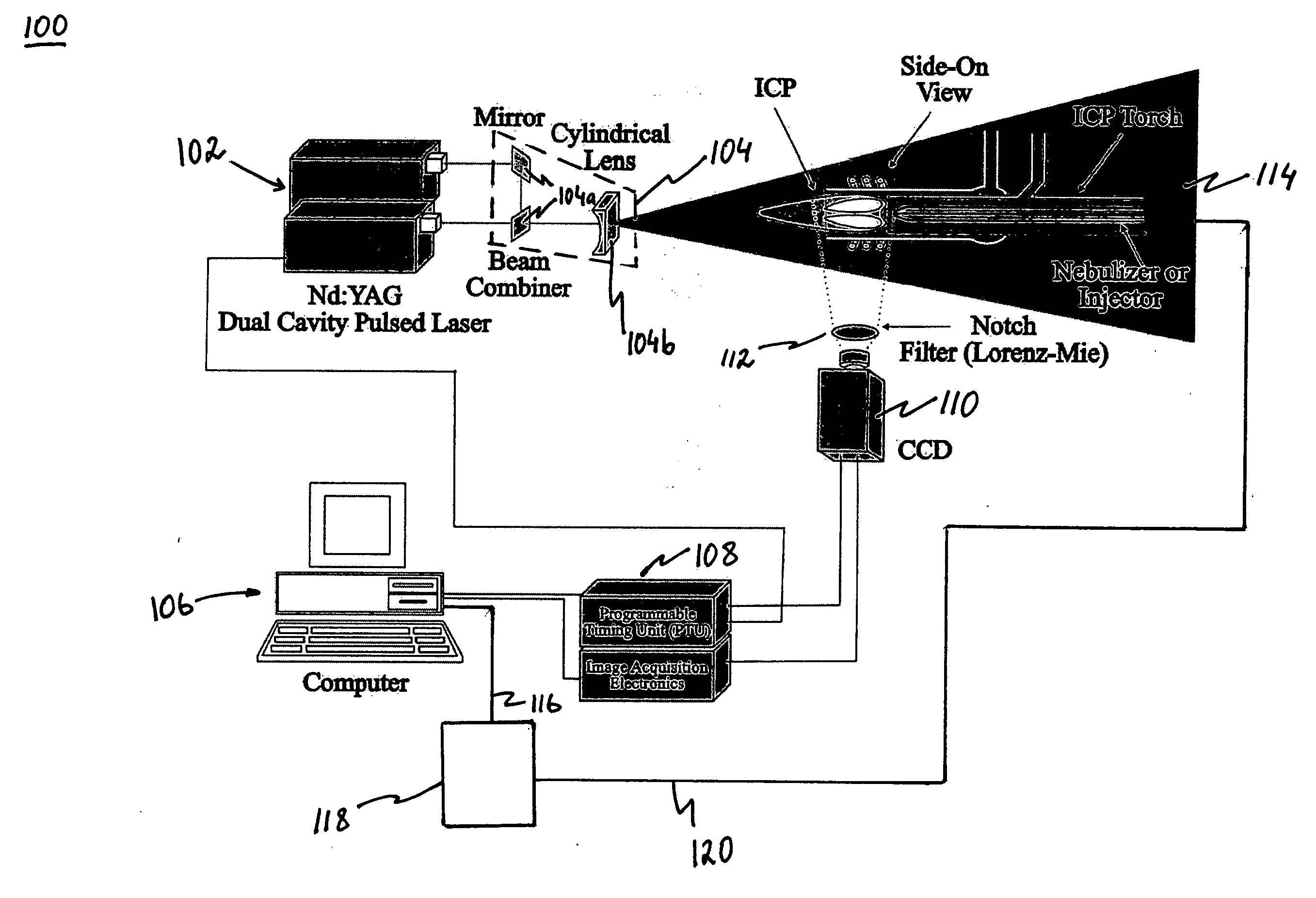
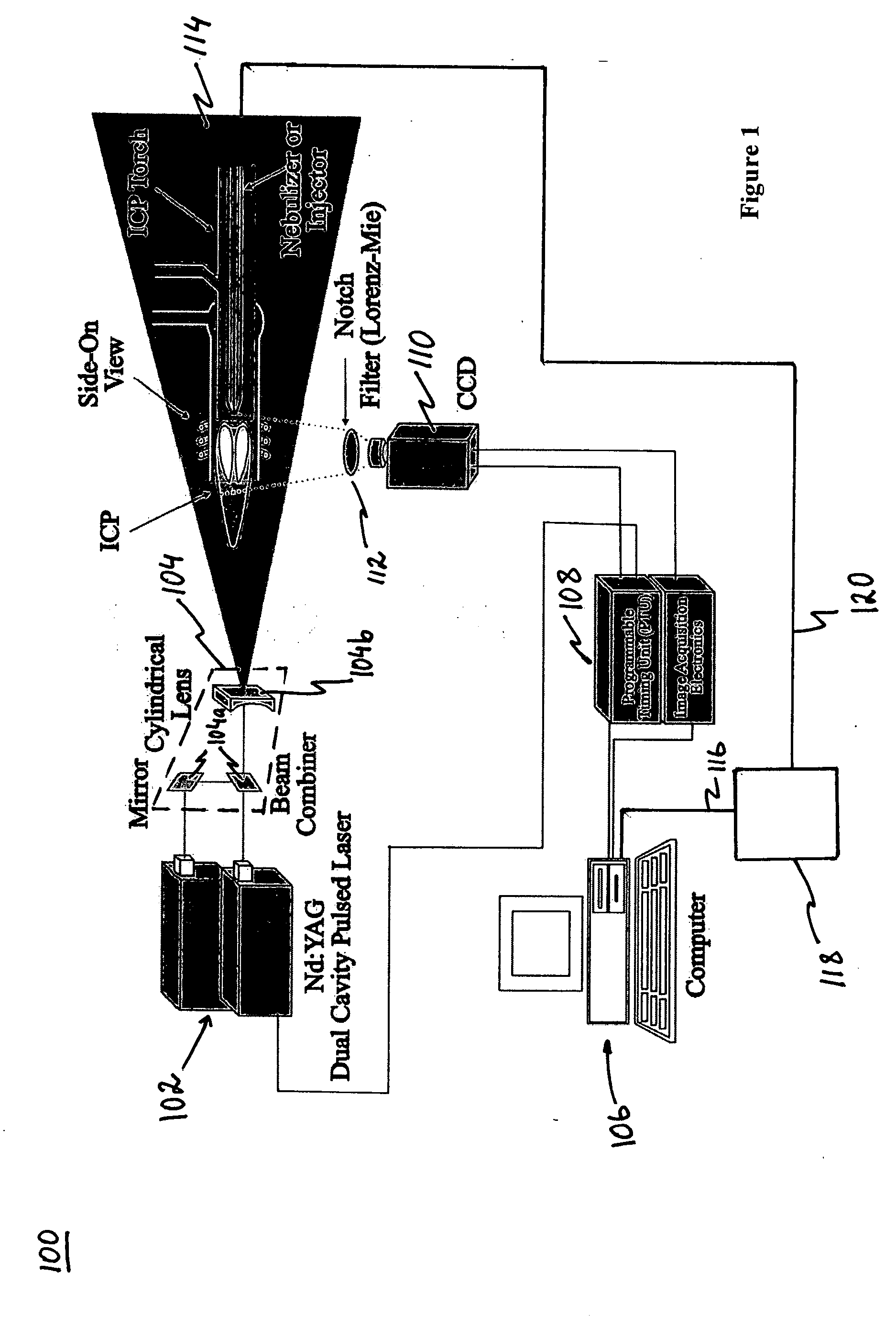
In-situ droplet monitoring for self-tuning spectrometers
ActiveUS20060087651A1Fast dropletStable analytical signalParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansLow noiseLaser scattering
A laser scattering based imaging technique is utilized in order to visualize the aerosol droplets in an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) torch from an aerosol source to the site of analytical measurements. The resulting snapshots provide key information about the spatial distribution of the aerosol introduced by direct and indirect injection devices: 1) a direct injection high efficiency nebulizer (DIHEN); 2) a large-bore DIHEN (LB-DIHEN); and 3) a PFA microflow nebulizer with a PFA Scott-type spray chamber. Moreover, particle image velocimetry (PUV) is used to study the in-situ behavior of the aerosol before interaction with, for example, plasma, while the individual surviving droplets are explored by particle tracking velocimetry (PTV). Further, the velocity distribution of the surviving droplets demonstrates the importance of the initial droplet velocities in complete desolvation of the aerosol for optimum analytical performance in ICP spectrometries. These new observations are important in the design of the next-generation direct injection devices for lower sample consumption, higher sensitivity, lower noise levels, suppressed matrix effects, and for developing smart spectrometers. For example, a controller can be provided to control the output of the aerosol source by controlling the configuration of the source or the gas flow rate via feedback information concerning the aerosol.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIV THE
Silicon wafer and epitaxial silicon wafer utilizing same
InactiveUS6569535B2Polycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor materialsLaser scattering
A silicon wafer characterized in that the laser scattering tomography defect occurrence region accounts for at least 80% of the wafer surface area and that the laser scattering tomography defects have a mean size of not more than 0.1 mum, with the density of those defects which exceed 0.1 mum in size being not more than 1x105 cm-3, and wafers derived from this wafer as the raw material by heat treatment for oxide precipitate formation, by heat treatment for denuded layer formation or by epitaxial layer formation on the surface are useful as semiconductor materials.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP
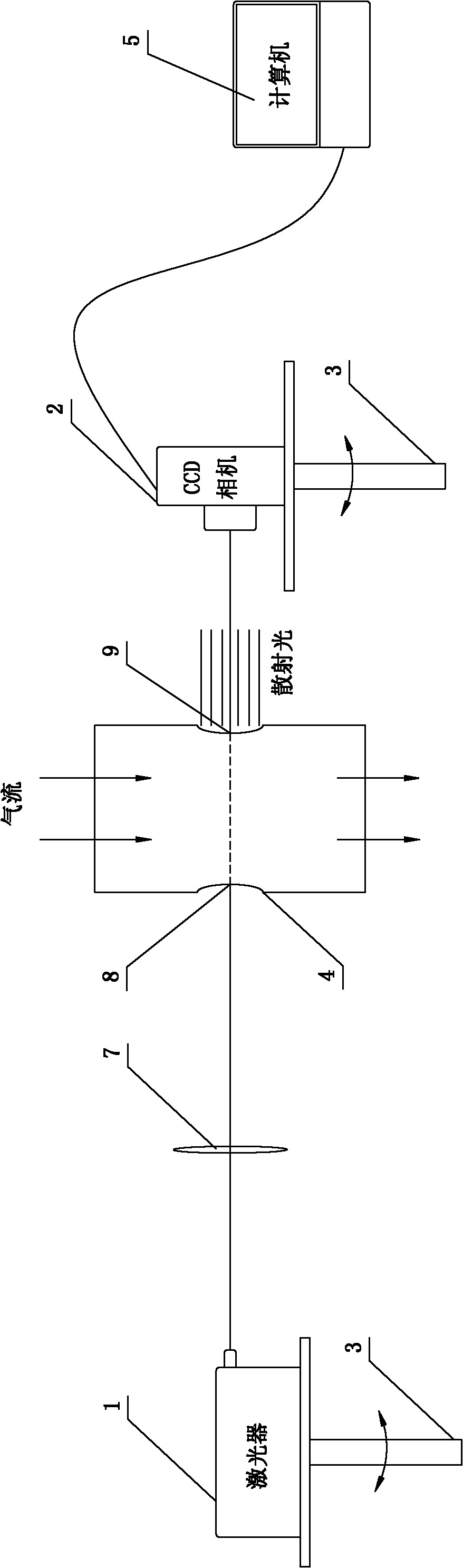
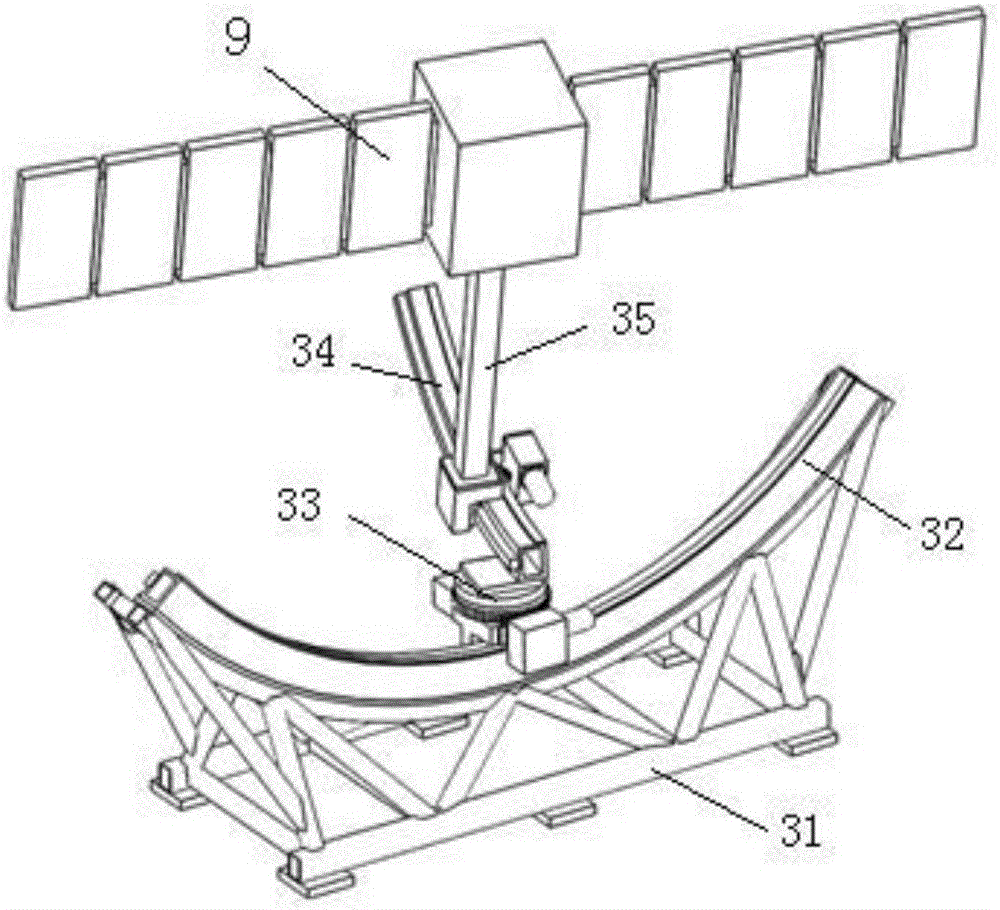
Display system and display method for NPLS (nano-tracer planar laser scattering) three-dimensional structure of supersonic flow field
ActiveCN102853990ARealize the flow displayAchieve stereo imagingHydrodynamic testingSynchronous controlControl signal
The invention provides a display system and a display method for the NPLS (nano-tracer planar laser scattering) three-dimensional structure of a supersonic flow field. The display system is used for displaying the supersonic flow field in a test cabin, and comprises a synchronous controller, a computer connected with the synchronous controller and used for controlling the synchronous controller to send out a control signal, and a nano-particle generator, wherein the nano-particle generator is used for scattering nano-particles in the test cabin; the display system further comprises a pulse laser connected to the synchronous controller, wherein the laser beam emitted by the pulse laser forms a curved-surface light source or a conic light source via a lens group, and illuminates the supersonic flow field carring the nano-particles in the test cabin; a plurality of CCD (charge coupled device) cameras connected to the synchronous controller are used for imaging the supersonic flow field simultaneously and thus obtaining a plurality of nano-particle images of the supersonic flow field under different viewing angles simultaneously, and transmitting the images to the computer; the computer is used for analysing the plurality of nano-particle images of the supersonic flow field under the different viewing angles, and measuring a curved-surface flow field structure or reconstructing the three-dimensional structure of the flow field.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Non-scanning photon counting non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging apparatus and method
ActiveCN106772428AIncrease frame rateOptical detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser scatteringOptoelectronics
The invention relates to laser imaging technologies, in particular to a non-scanning photon counting non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging apparatus and method and is intended to solve the problem that the prior art is unable to image a non-visual-field scene. A pulse laser emits laser and gives a time signal to a multi-channel time-dependent single-photon counter; the reformed laser enters a wall, the laser scattered by the wall is reflected by a target and enters again the wall; the laser returned by the wall is received by a receiving optical system, an image side of the receiving optical system is given as many visual fields as a single-photon detector array; the multi-channel time-dependent single-photon counter calculates photon flight time taken by a photo entering the single-photon detector array from the pulse laser back to the single-photon detector array, so as to obtain time-photon counting diaphragms; a computer reconstructs a three-dimensional image of a target according to multiple time-photon counting diaphragms to obtain a three-dimensional image. The non-scanning photon counting non-visual-field three-dimensional imaging apparatus and method are applicable to three-dimensional imaging of a non-visual-field target.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
System for monitoring PM2.5 by smart phone
ActiveCN103868835AReduce volumeImprove firmnessParticle suspension analysisNetworked systemLaser scattering
The invention discloses a system for monitoring PM2.5 by a smart phone. The networked system is rapid and light and is low in cost. In addition to the general smart phone, the system is also provided with a small and intelligent air sampling head. The intelligent air sampling head can perform inhaling sampling through a human mouth and also can perform sampling by a sampling air pump. The intelligent air sampling head and the smart phone can communicate with each other. The intelligent air sampling head measures the number and particle size of dust in air by a laser scattering method under the guide of the smart phone, the gas flow is measured by a capillary heat transfer temperature difference measurement method, and the measurement result is transmitted to the smart phone for processing and displaying. The smart phone wirelessly uploads the location of the smart phone and the measurement result of PM2.5, so that nationwide automatic PM2.5 networking coverage is realized, and the pollution source and diffusion direction are determined. According to the system, the intelligent air sampling head can be automatically maintained and corrected by a user under the guide of the smart phone.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV +1
Laser scattering-based optical-fiber prefabricated rod defect detection method
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical detection, and particularly relates to a laser scattering-based optical-fiber prefabricated rod defect detection method. A laser and a camera are fixed on a two-dimensional displacement platform, an optical-fiber prefabricated rod is immersed in matching liquid, and linear beams outputted by a laser vertically shine on the optical-fiber prefabricated rod; the two-dimensional displacement platform is adjusted through a computer, so that the linear beams can scan the entire optical-fiber prefabricated rod; a picture is obtained by the computer through the camera, and defects and the position of each defect of the optical-fiber prefabricated rod are judged according to the laser scattering spots. By adopting the method, the weaknesses of the manual observation such as low efficiency, low reliability and poor consistency can be eliminated, and the advantages such as high efficiency, high precision and full automation can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Air quality monitoring method based on multisensor fusion
InactiveCN105823856AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityAir quality improvementMaterial analysisParticulatesLaser scattering
The invention relates to an air quality monitoring method. Mainly aiming at the defects that a portable air quality monitor adopting a laser scattering method for measurement is poor in measurement consistency, large in noise, low in measurement accuracy and the like, multiple sensors are adopted for simultaneous measurement, data fusion is conducted on measurement results of the multiple sensors with a multi-layer neural network, and therefore atmospheric pollution particulate matter is monitored at high reliability and high accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INSIGHTS VALUE TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
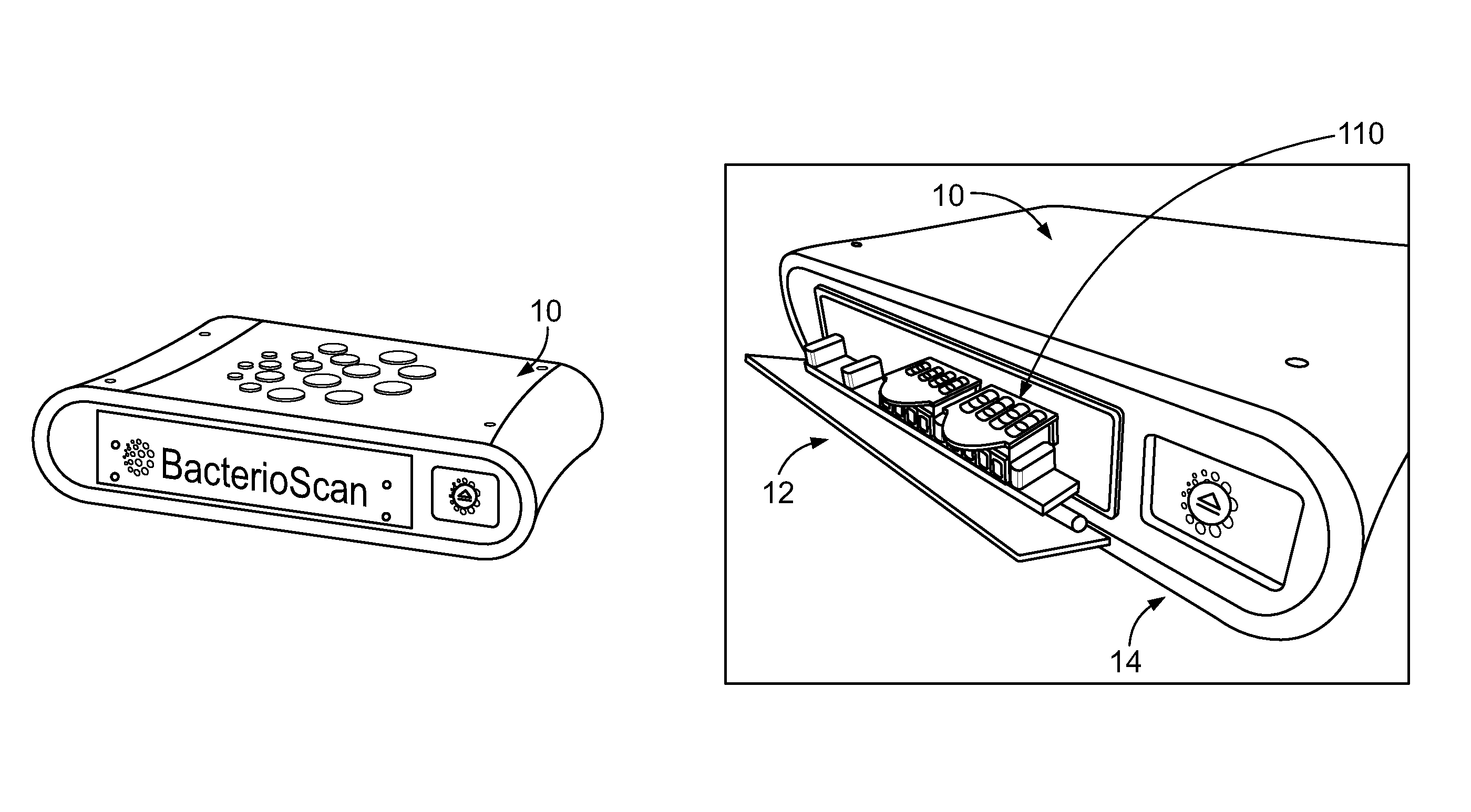
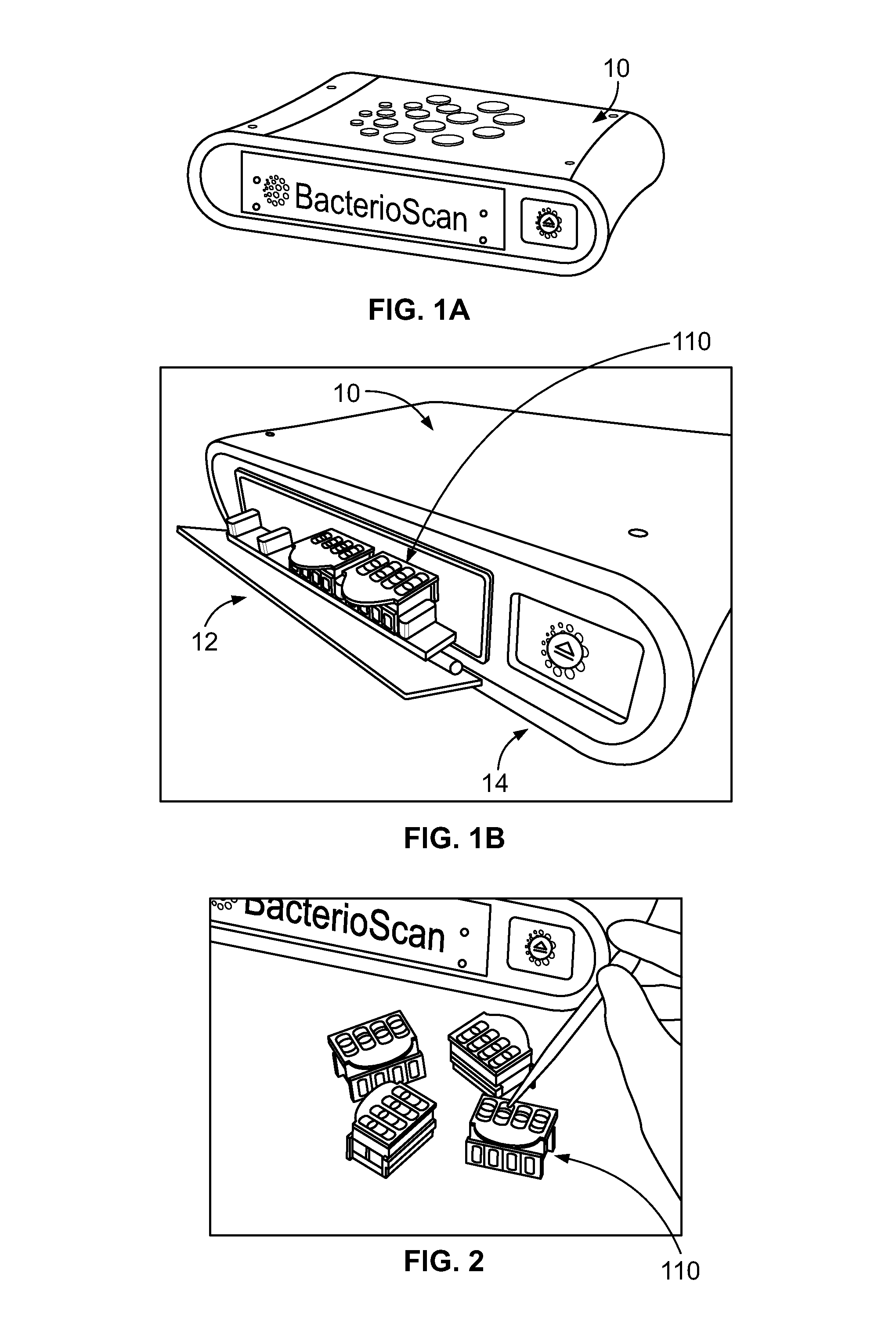
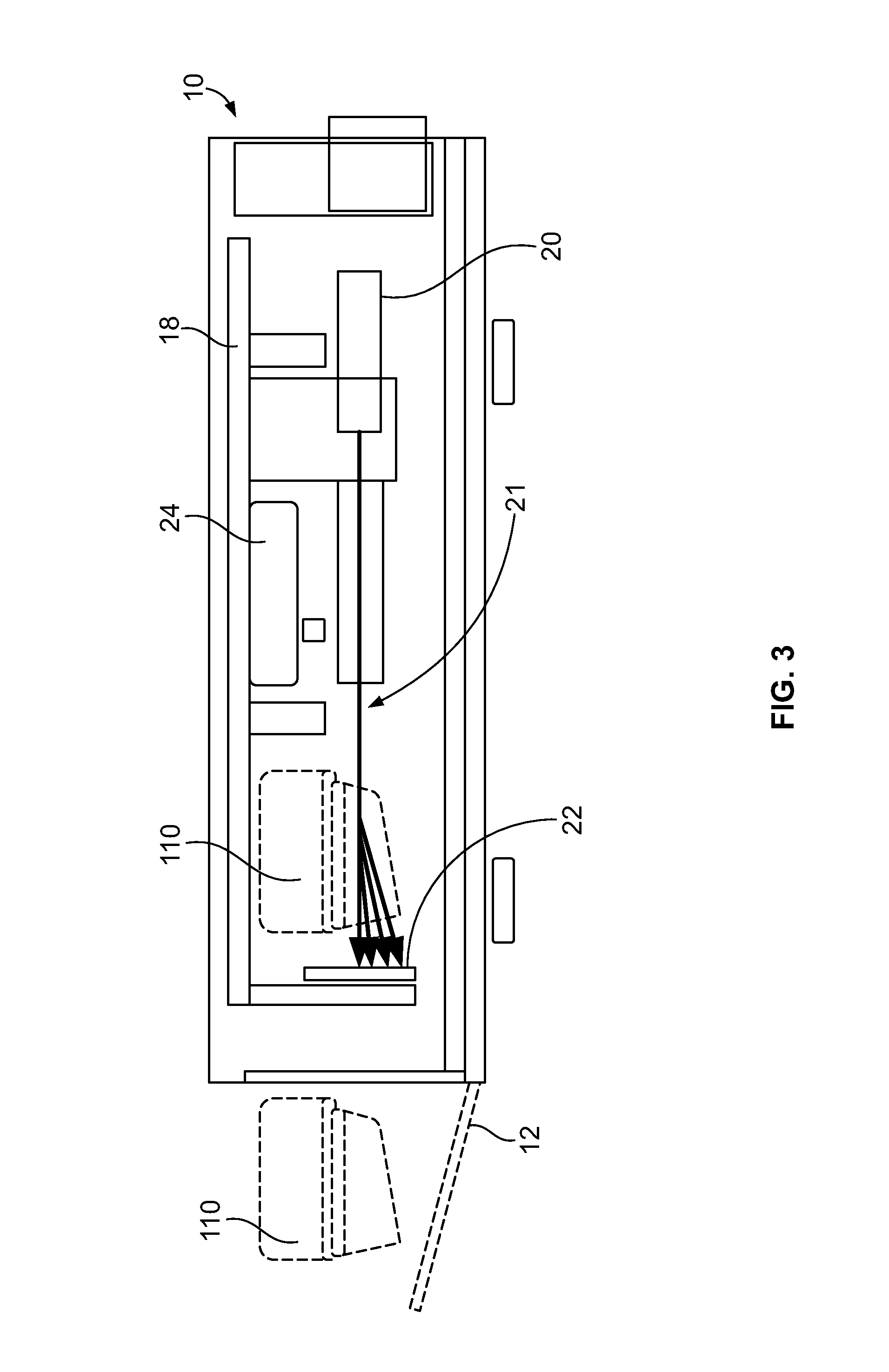
Multi-Sample Laser-Scatter Measurement Instrument With Incubation Feature And Systems For Using The Same
ActiveUS20160160260A1Improve concentrationReduce the burden onBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyCuvette
An optical measurement instrument is an integrated instrument that includes an optical cavity with a light source, a sample cuvette, and an optical sensor. The light source and sensor are on a bench that is on a translational or rotational mechanical platform such that optical beam can be moved to multiple sample containers. The instrument can be used for taking measurements of organism concentration in multiple samples as a production tool for microbiology. Preferably, the instrument holds multiple, individually-loaded, independent fluid samples and determines bacteria concentration via a forward-scattering signal. The instrument can incorporate onboard incubation to promote bacterial growth in the samples during the test. In another aspect, the instrument can be a part of a network for medical diagnostic testing data where data is stored in a manner that is inherently untainted by patient identifiable information.
Owner:IP SPECIALISTS LTD
Method and device for measuring steam humidity and diameter of water droplet of non-contact type turbine
InactiveCN101819146AMake sure to enterWill not affect workScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOptical axisLaser scattering
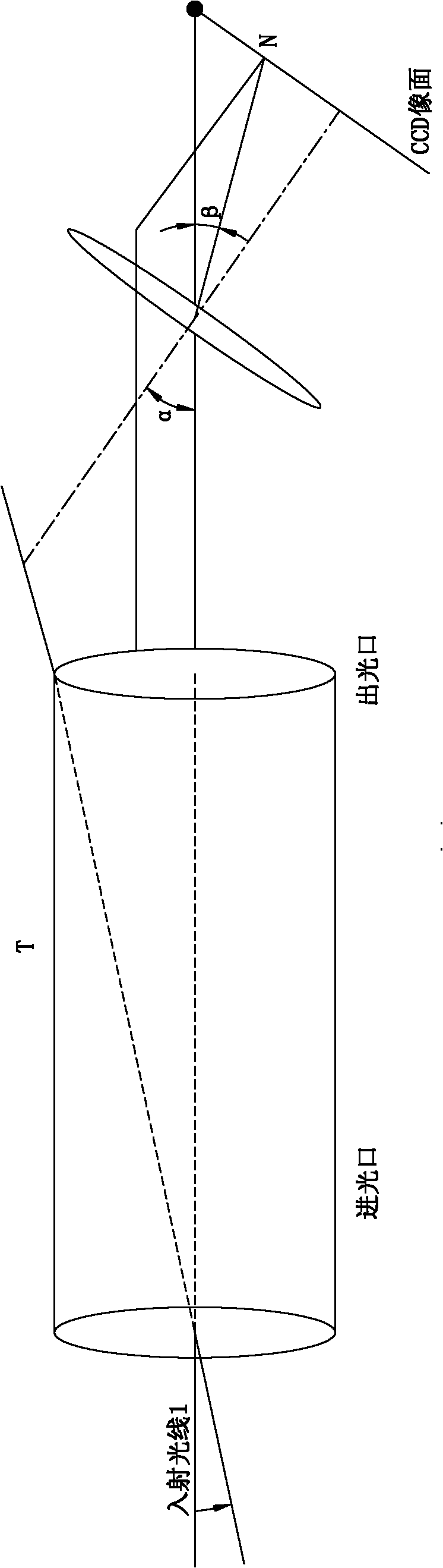
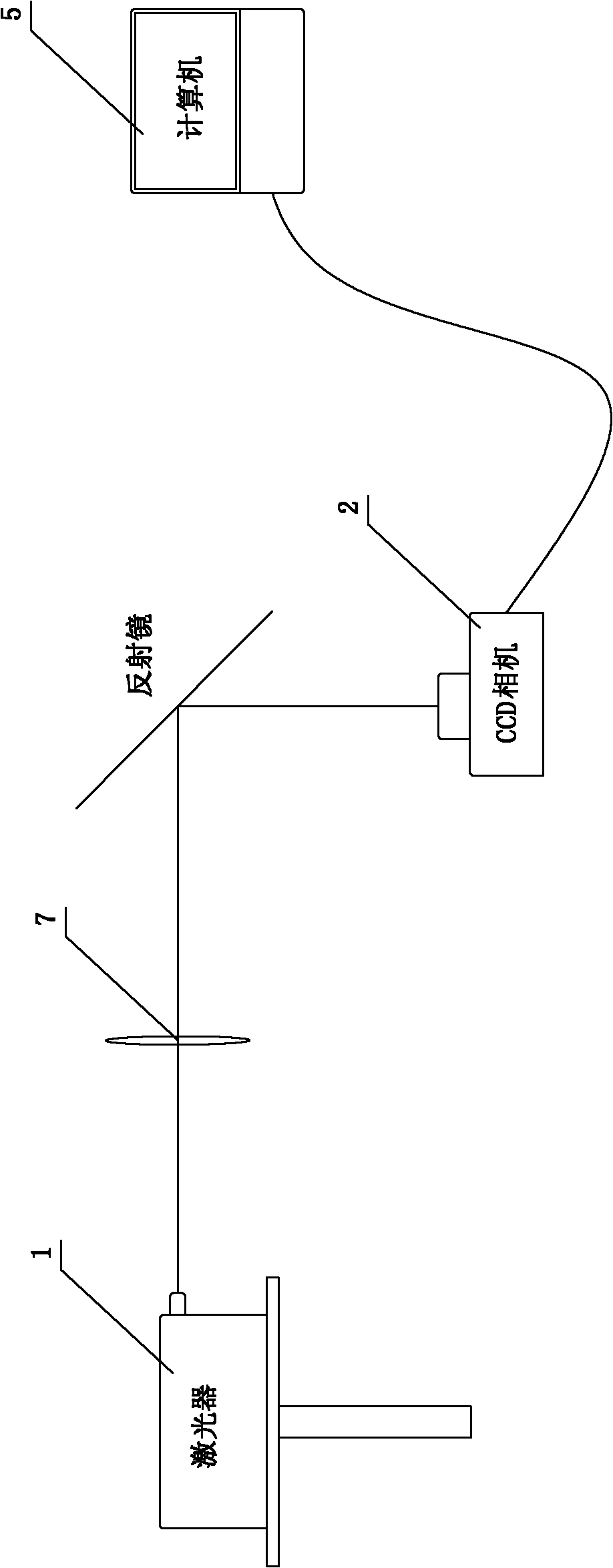
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring the steam humidity and diameter of a water droplet of a non-contact type turbine. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively arranging a laser device and a CCD camera at the two sides of an observation window of a lower pressure cylinder of the turbine, and fixing the laser device and the CCD camera on a two-dimensional rotary table so as to precisely adjust the included angle between the incidence light and the optical axis of the CCD; maintaining a certain angle between the incidence light and the optical axis of the CCD so as to separate a slight scattered light from the strong incidence light to ensure that the CCD camera can detect the weak scattered light signal; adjusting the included angle between the incidence light and the CCD and maintaining a certain angle; measuring the intensity of the scattered light of the laser to the steam within 0-10 degrees, and calculating the steam humidity and the diameter of water droplet in the lower pressure cylinder of the turbine according to the relevant knowledge of distribution of the light intensity, laser scattering theory and the like. The device comprises the laser device, the CCD camera, a computer and the two-dimensional rotary table. The invention has advantages of high degree of automation, high precision of measuring, wide application range, high efficiency of measurement, online measurement and the like.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
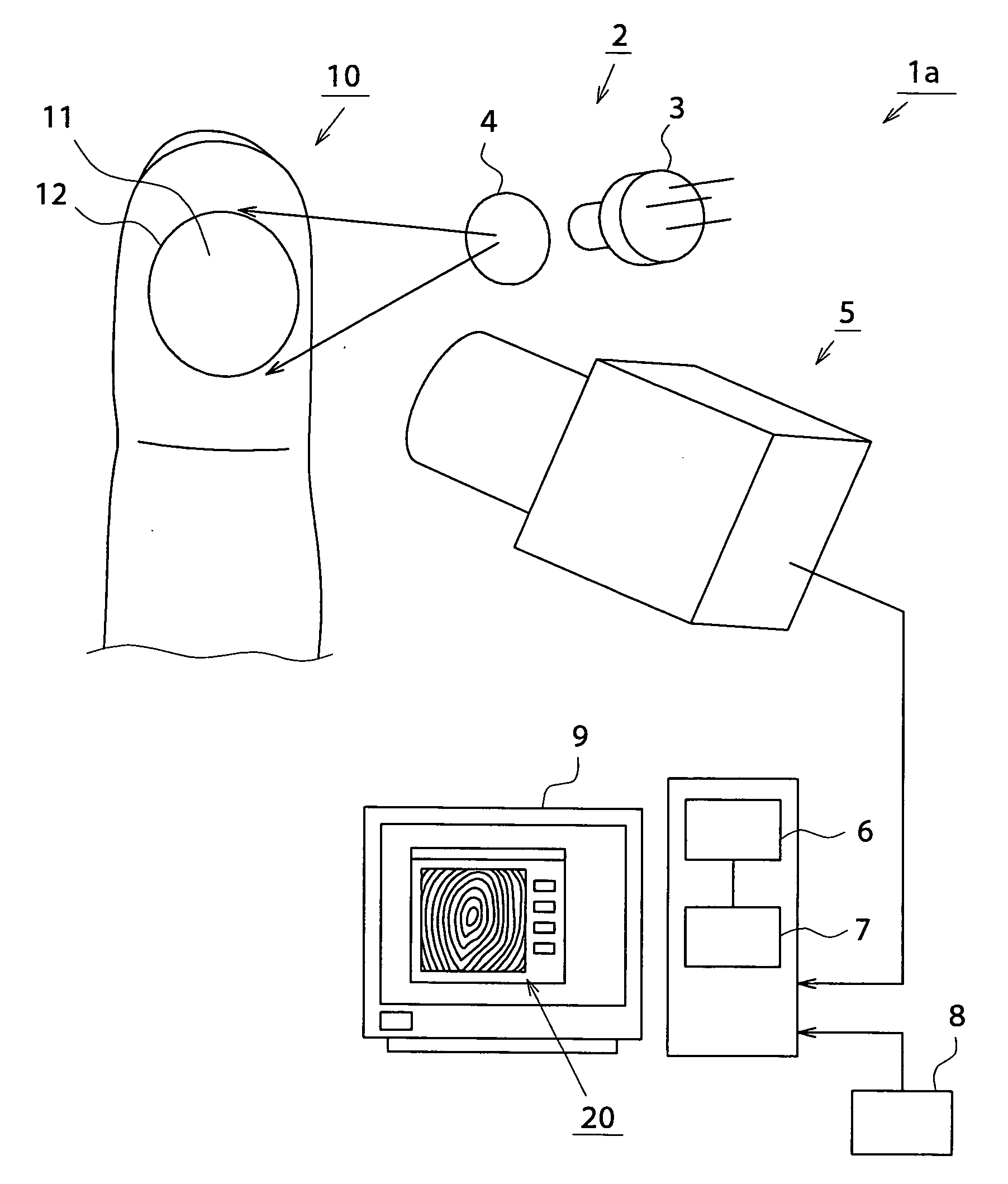
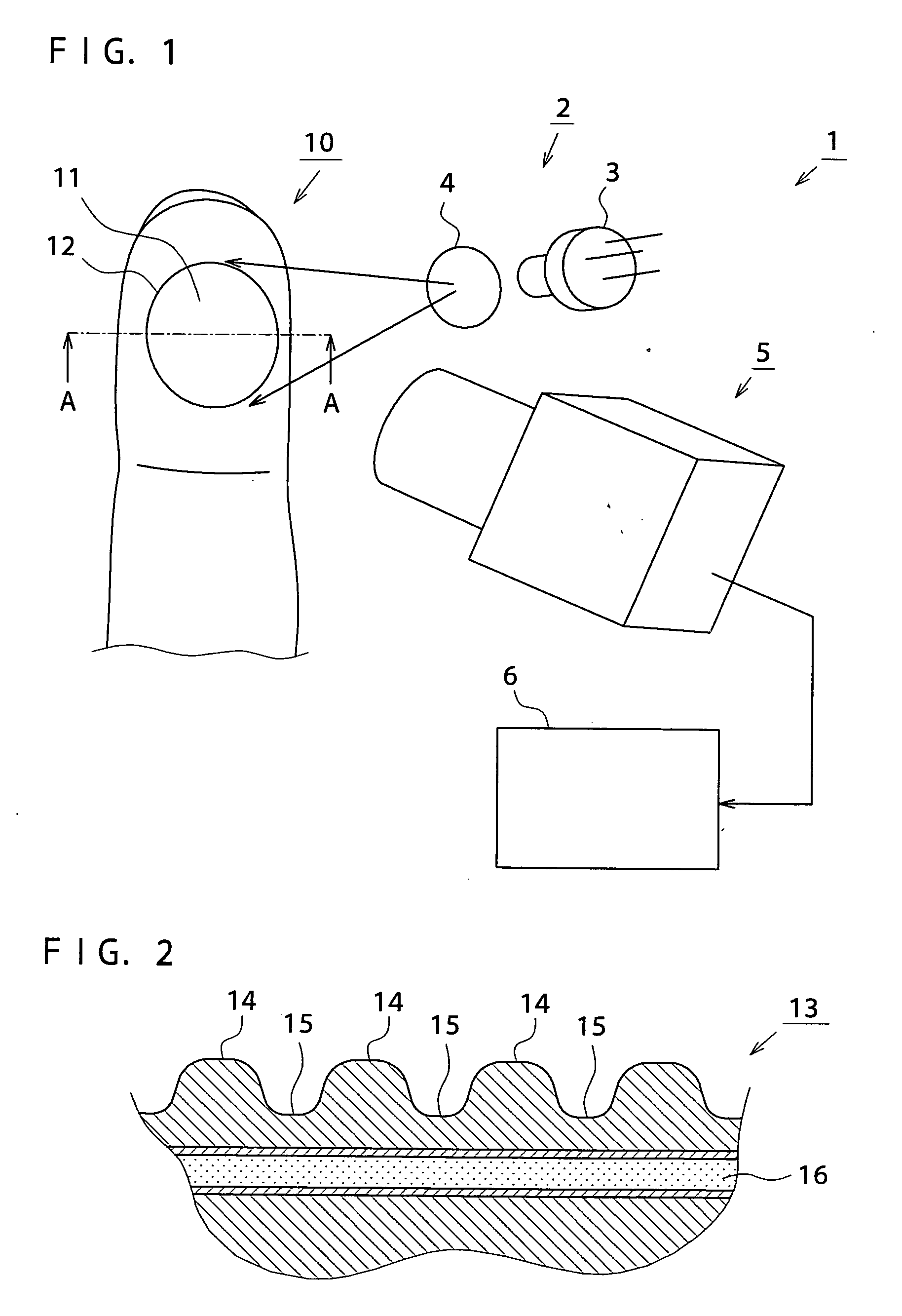
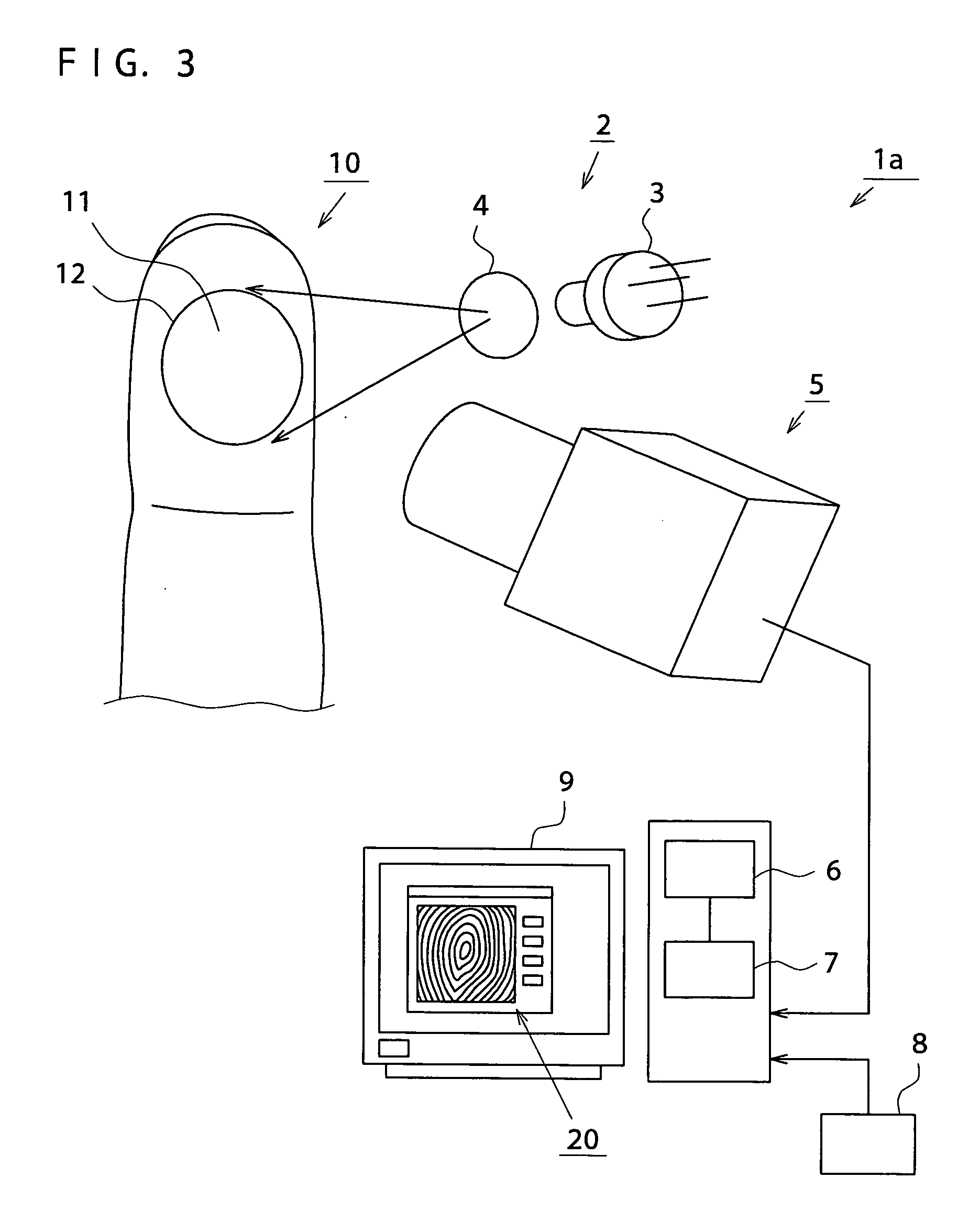
Method for acquiring personal identification data, personal identification method, apparatus for acquiring personal identification data, and personal identification apparatus
ActiveUS20070177772A1Good effectImprove reliabilityPerson identificationCatheterFeature extractionLaser scattering
Owner:NAT UNIV CORP KYUSHU INST OF TECH (JP) +1
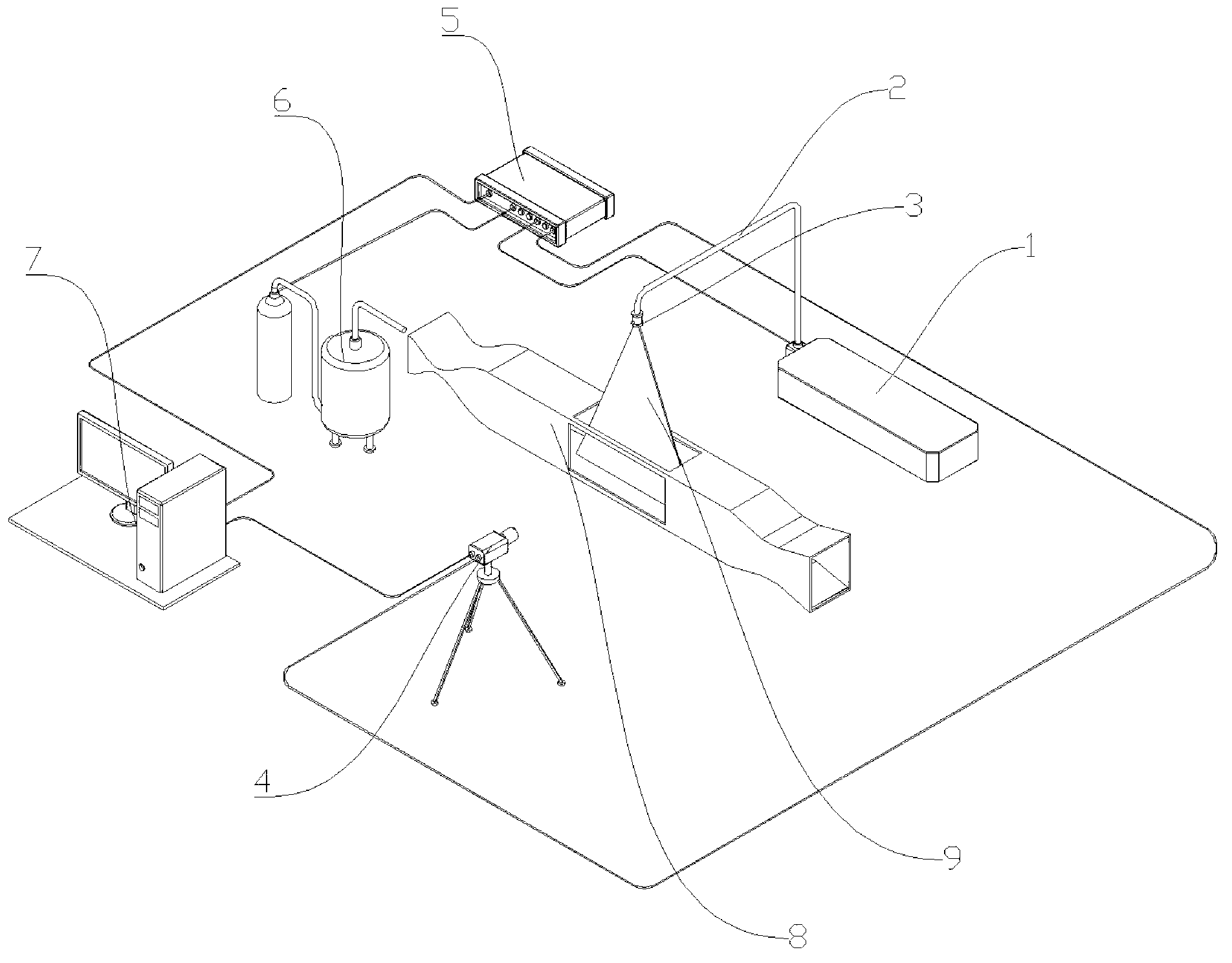
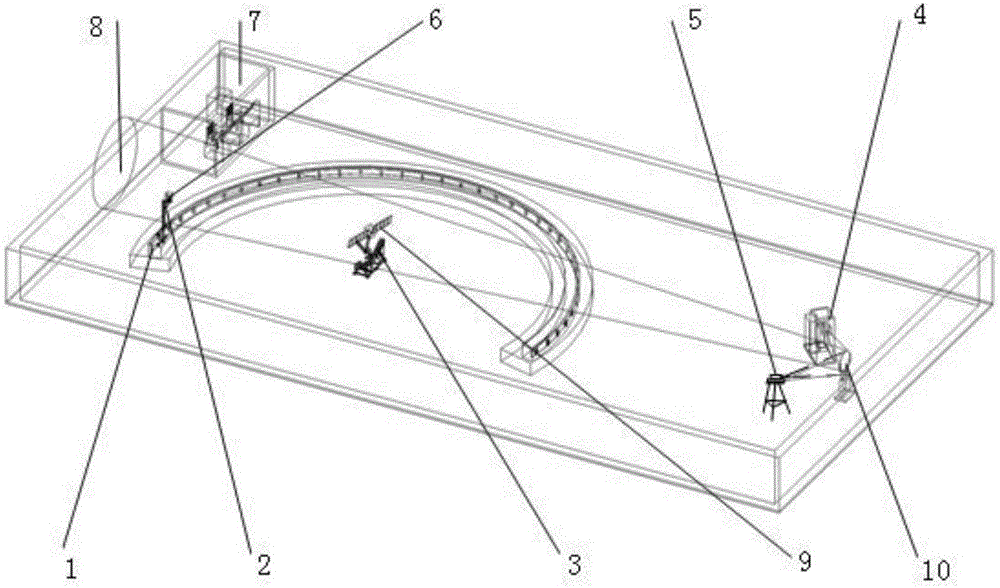
Integrated testing system for dynamic characteristics of visible light scattering and laser scattering of space target
InactiveCN106054160ASolving Visible Light Scattering PropertiesWave based measurement systemsLaser scatteringTest platform
The invention provides an integrated testing system for dynamic characteristics of visible light scattering and laser scattering of a space target. The system comprises a test track, a panoramic test platform, an attitude simulation subsystem, a solar simulator, a laser transmitting / receiving subsystem, a visible light detecting subsystem, a low reflection / scattering background and a central control subsystem. With the system, simulated measurement of visible light scattering characteristics of a measured target at different observation azimuth angles and angular altitudes in space with different sun illumination azimuth angles and angular altitudes in a laboratory can be realized; and the testing result can be used as a basis of the research of a visible-light detection sensor. Meanwhile, simulated measurement of laser scattering characteristics of a measured target in space at different laser radiation azimuth angles and angular altitudes in a laboratory can be realized and the testing result can be used as a basis of the research of a laser detection sensor.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE SYST ENG INST
In situ particle monitoring for defect reduction
InactiveUS7145653B1Excessive removalAutomatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationResistMonitoring system
A system and method is provided for monitoring and controlling the contaminant particle count contained in an aerosol during a photoresist coating and / or development process of a semiconductor. The monitoring system monitors the contaminate particle count present in the environment of the photoresist coating and / or development process, such as in a process chamber or a cup, enclosing the wafer during the process. The present invention employs in situ laser scattering or laser doppler anemometry techniques to detect the particle count level in the chamber or cup. A plurality of lasers and detectors can be positioned at different heights in or outside of a chamber or cup to facilitate detecting particles at different height levels. A laser could be used in conjunction with mirrors to provide a similar measurement. The particle count level can be used to compare with the defect level, so that it can be determined if a cleaner environment and / or process should be implemented.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Symmetrical multi-beam collimation laser pavement track detection system
InactiveCN101476277AReduce or eliminate errorsExtended service lifeUsing optical meansRoads maintainenceLaser scatteringLight beam
The invention relates to a symmetrical multiple collimated layers pavement rut detection system used for detecting the rut indexes on pavement, which consists of two downward shooting cameras disposed on both sides of the rear upper part of the system carrying vehicle, a plurality of rear lasers transversely installed on the rear outer lower part of the carrying vehicle body side by side through foldable door shaped rods and front layers installed on the inner lower part of the system carrying vehicle body side by side through transverse connection rods. In practical work, the front and rear lasers send out collimated layer beams to the inclined downwards direction respectively which projects on pavement to form laser scattered lines, and the information of depth, left and right and size of the rut on the pavement can be obtained through the shooting camera imaging, digital image processing and calculating. Compared with the current technologies, By using a plurality of collimated layers instead of high bright line laser, the invention can reduce the damage to human eyes caused by the laser, increases the safety in pavement rut detection by laser, while greatly increases the service life of the detection system.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus and working method thereof
InactiveCN105572683ARealize acquisitionRealize full-angle signal acquisitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationImage resolutionLaser scattering
The present invention belongs to the laser radar field and provides a laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus. The laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus includes a laser output device which is used for outputting collimated laser, a laser scattering device which is arranged on the laser path of the laser output device and is used for scattering the collimated laser to 360-degree ring-shaped laser, and image sensing devices which are arranged around the laser output device and can receive laser signals reflected by a measured object in an all-direction manner. With the laser radar acquisition and ranging apparatus adopted, 360-degree full-angle signal acquisition can be realized, and angle resolution and scanning frequency can be improved.
Owner:LEISHEN INTELLIGENT SYST CO LTD
Inorganic Fiber Paper
ActiveUS20070292673A1Good self-adhesiveHigh mechanical strengthInorganic fibres/flakesHybrid capacitor separatorsPorosityLaser scattering
This invention provides an inorganic fiber paper that consists essentially of inorganic materials and has a basis weight of less than 100 g / m2 and has been mainly produced by a wet sheet making method. The inorganic fiber paper comprises inorganic fibers and an inorganic binder as materials, wherein the inorganic fibers have been bound to each other with the inorganic binder. In the inorganic fiber paper, the content of impurities during wet sheet making is low, the water resistance and flexibility are good, and satisfactory strength and high porosity can be realized. The inorganic fiber paper is produced from a material comprising 60 to 97% by mass of inorganic fibers having an average fiber diameter of not more than 5 μm and 3 to 40% by mass of an inorganic binder composed mainly of a silica-based flaky inorganic material that has a hydroxyl group content per specific surface area of not less than 20 μmol / m2 as measured by a BET method, an average particle diameter of not more than 2 μm as measured by a laser scattering method and an aspect ratio of not less than 10.
Owner:ENTEK ASIA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com