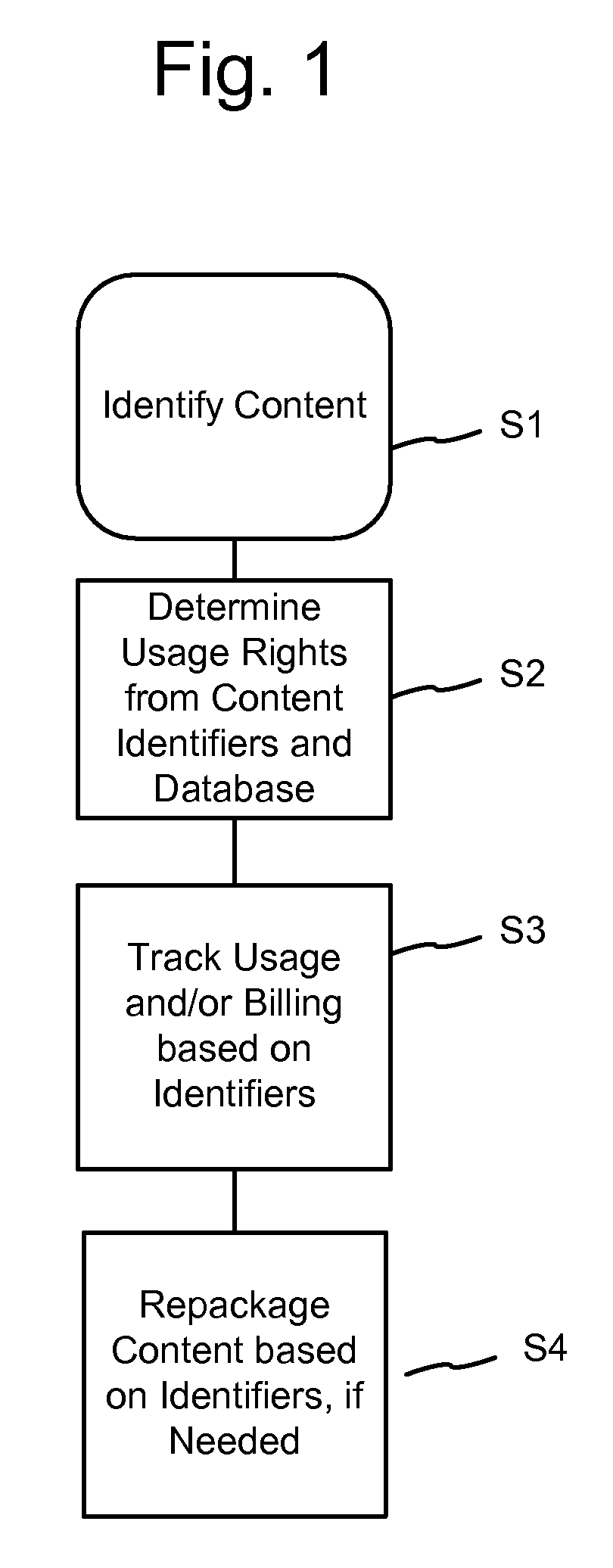
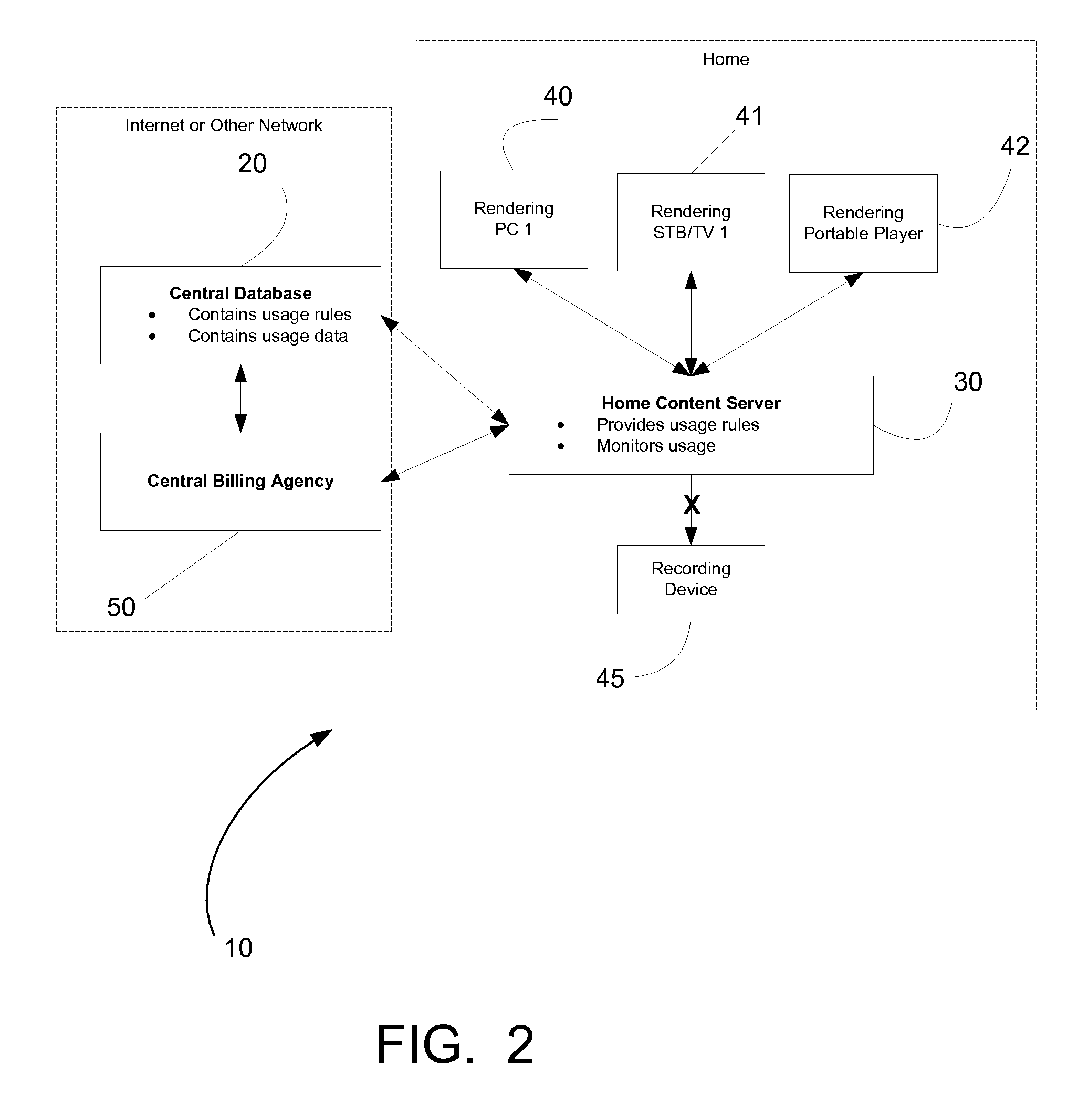
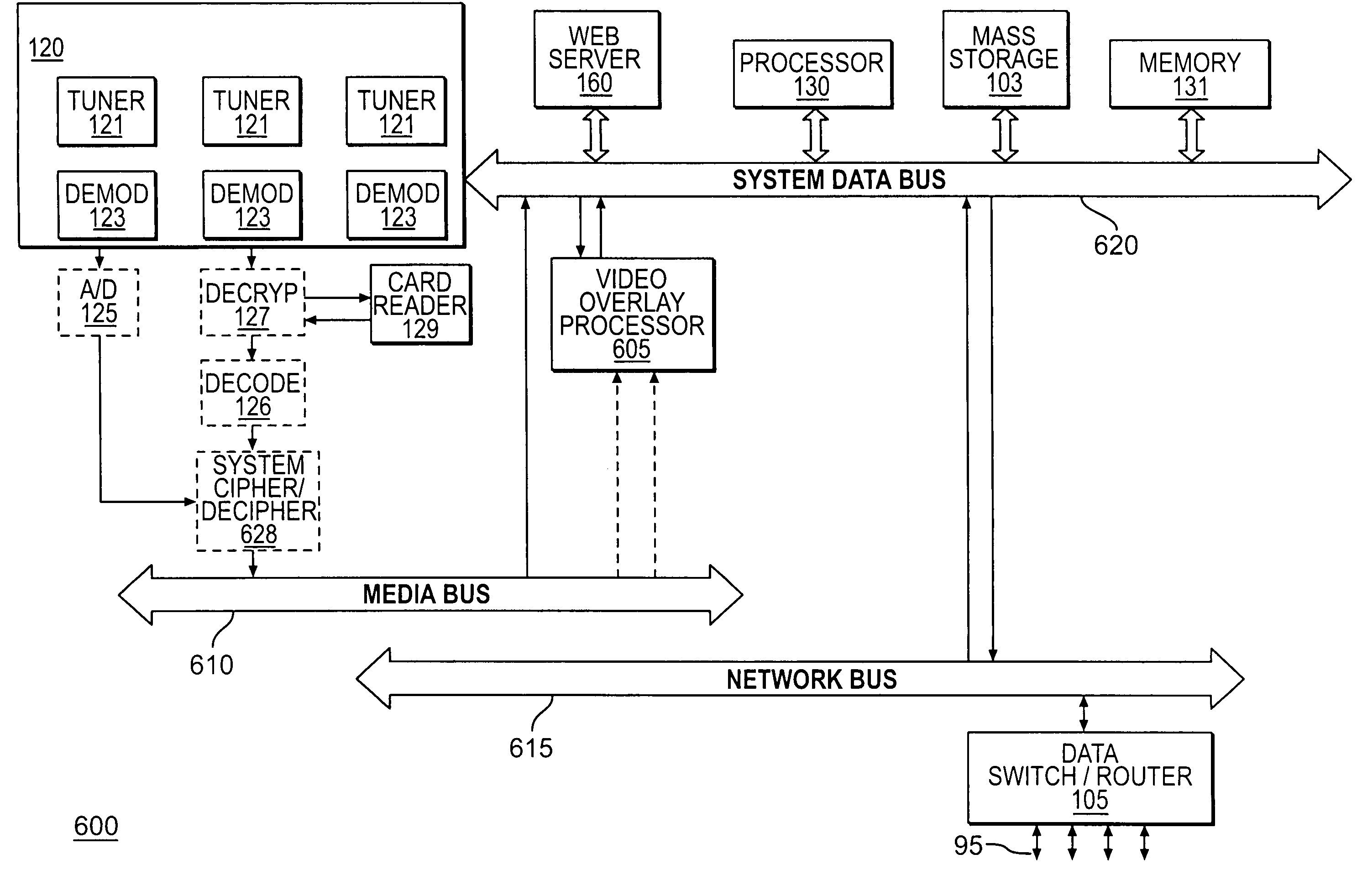
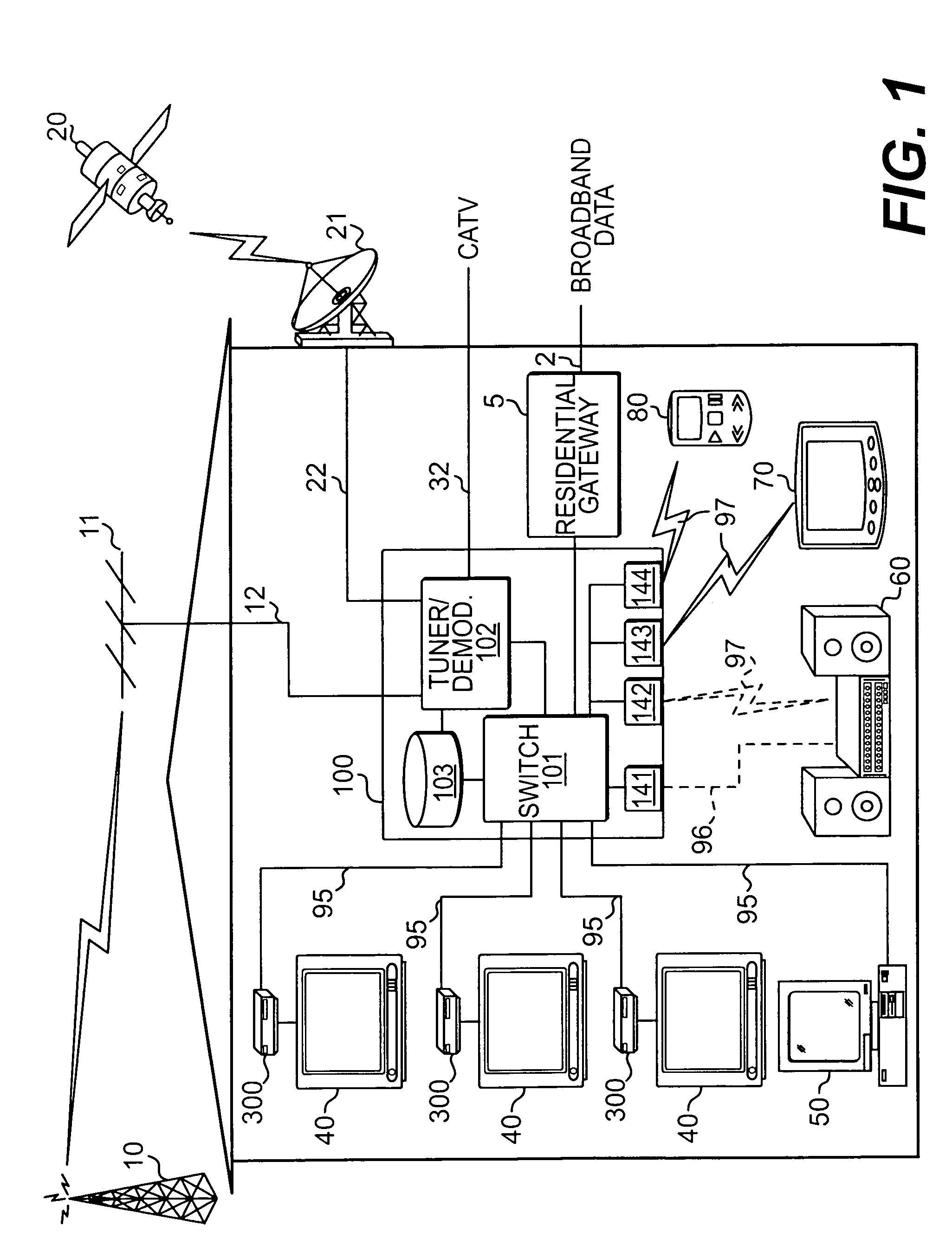
Patents
Literature
537 results about "Content Identifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
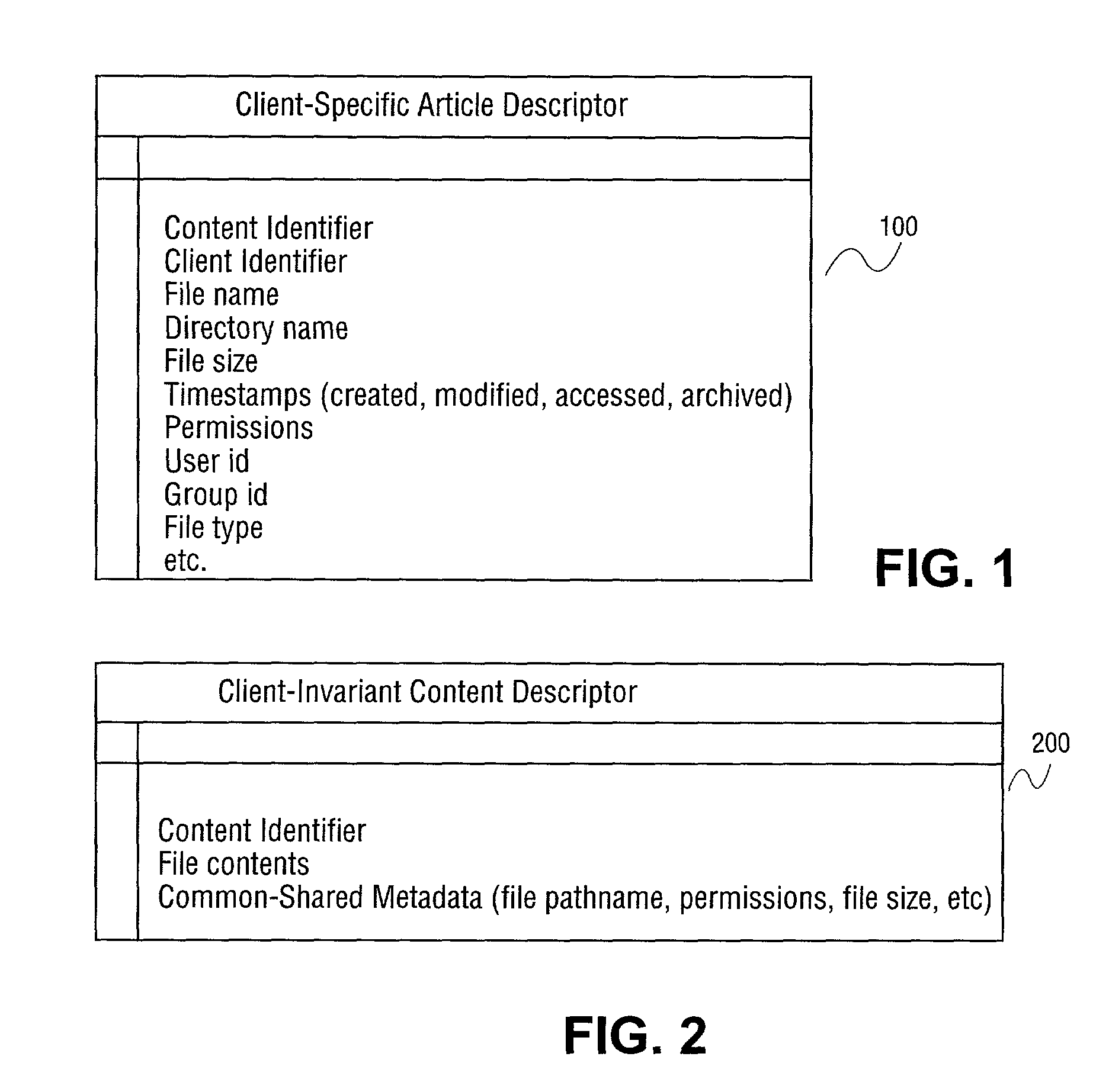
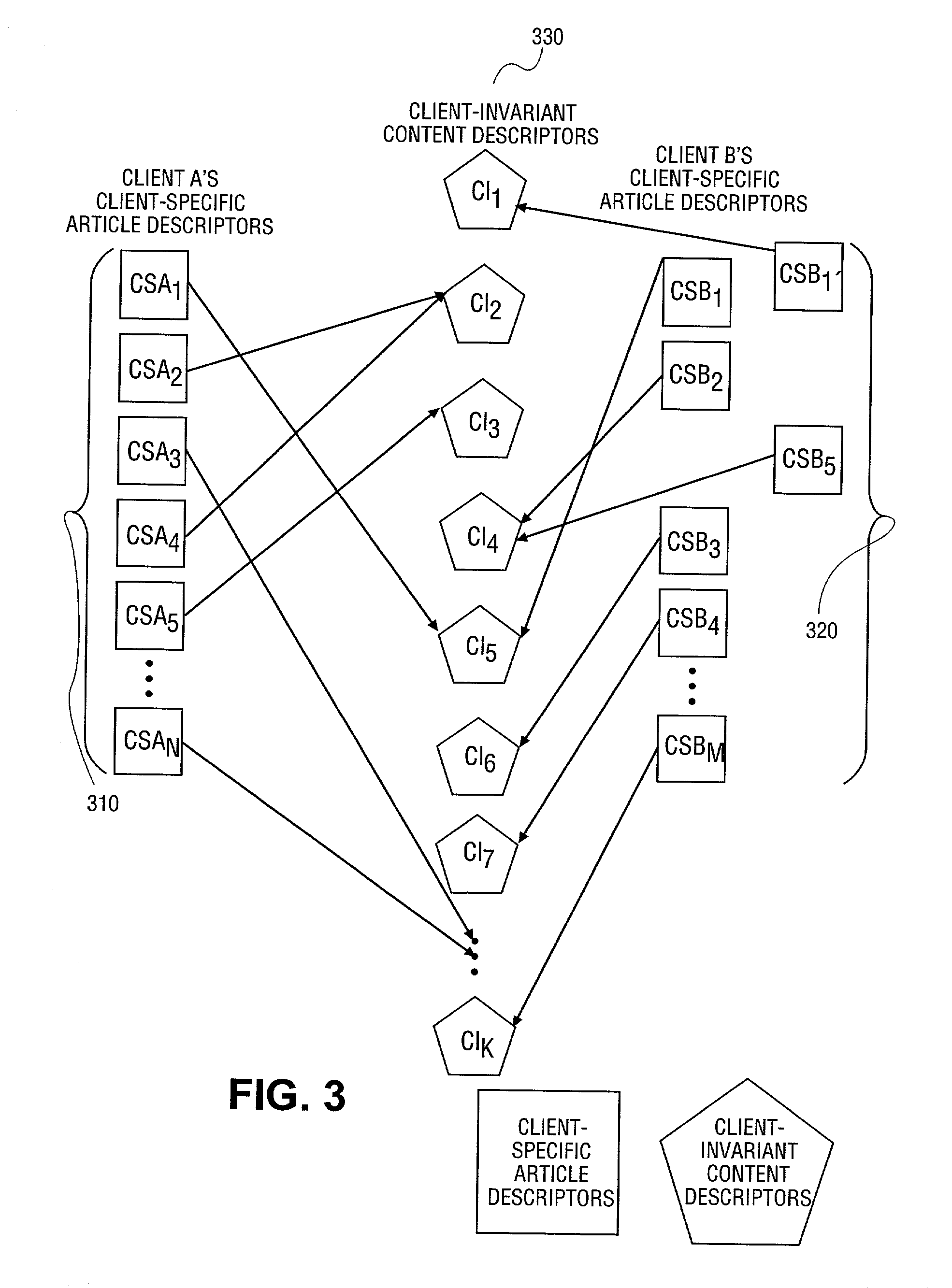
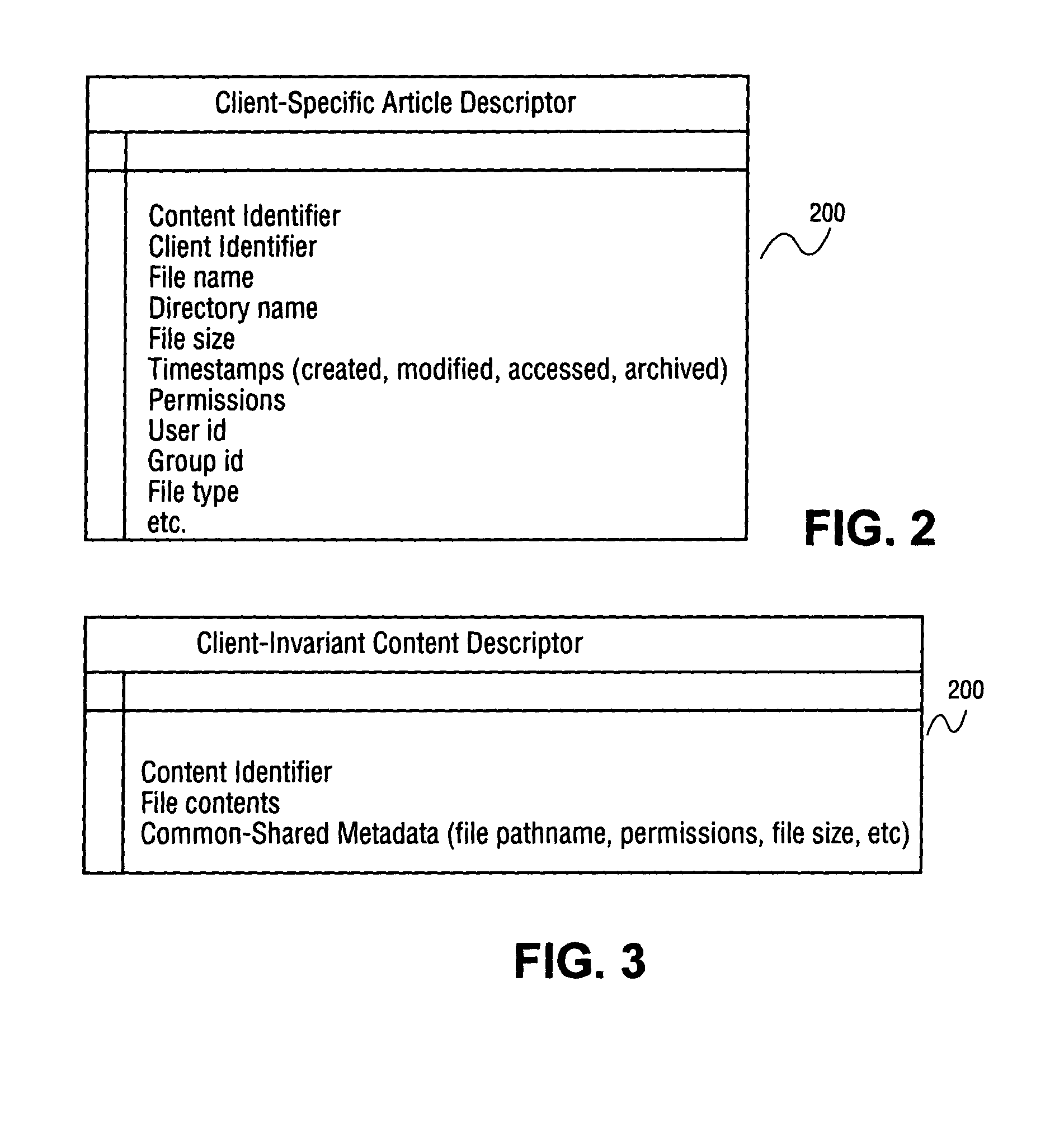
The unique identifier for a piece of Content such as a document, image, or other media in a specified context. [NCI]
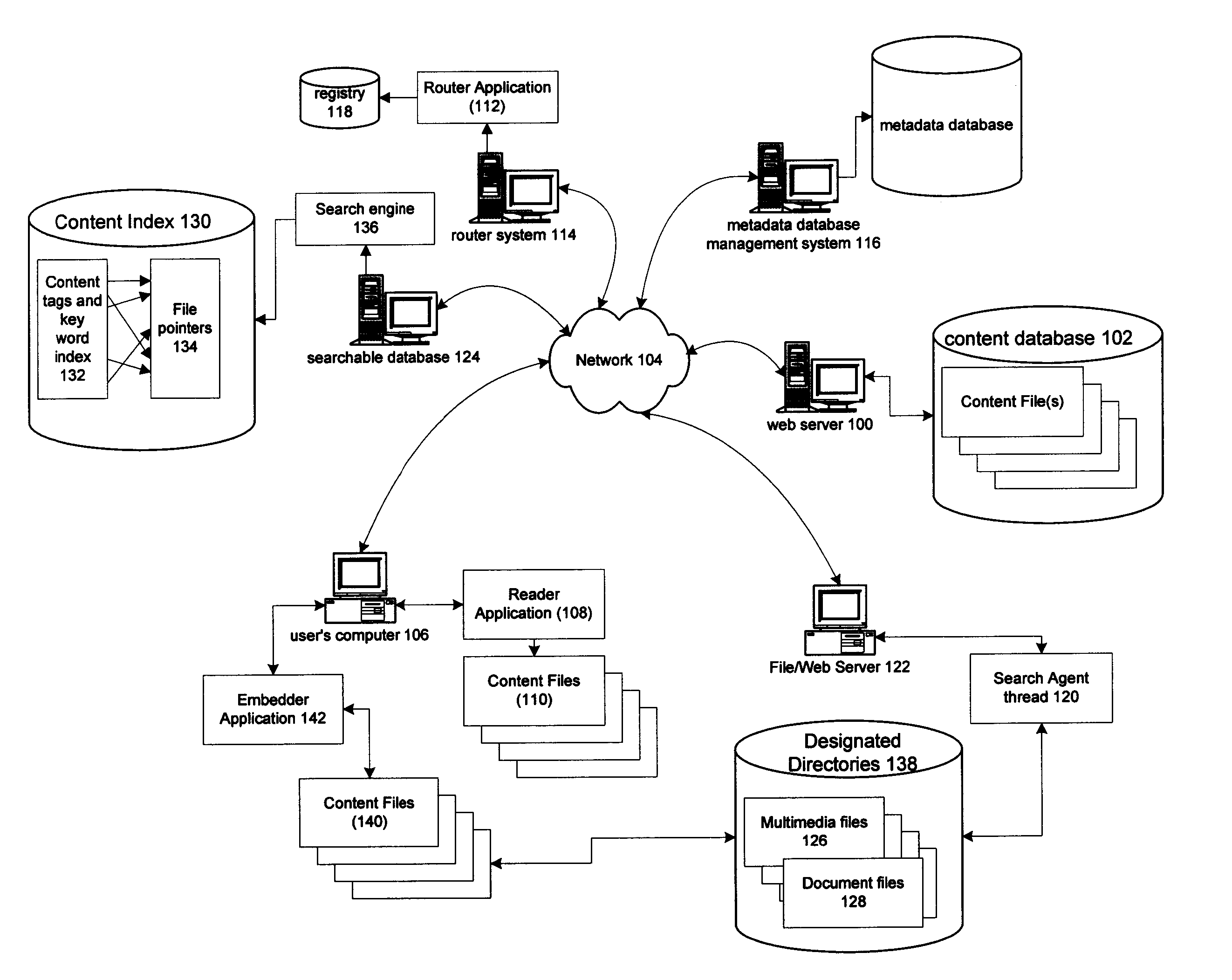
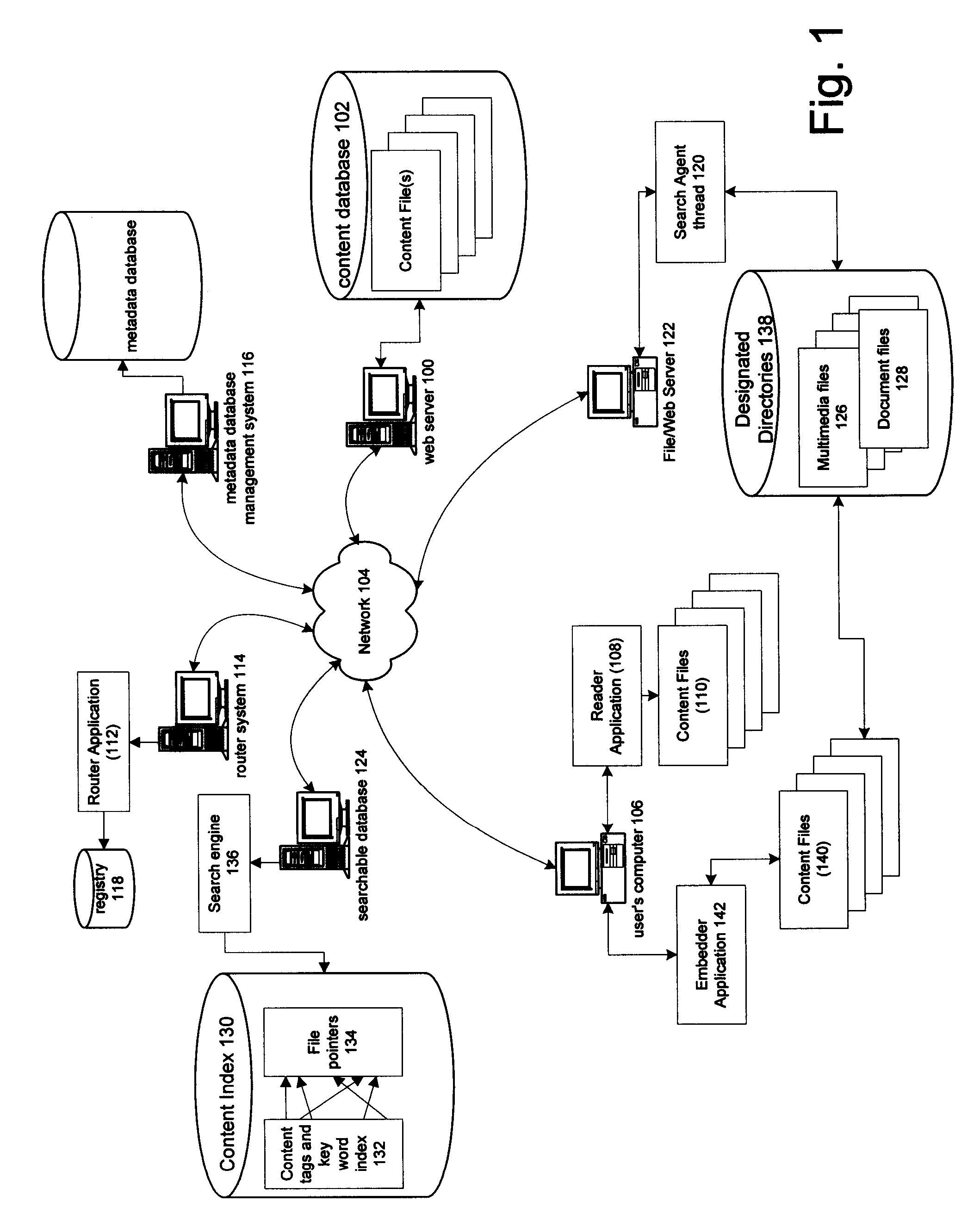
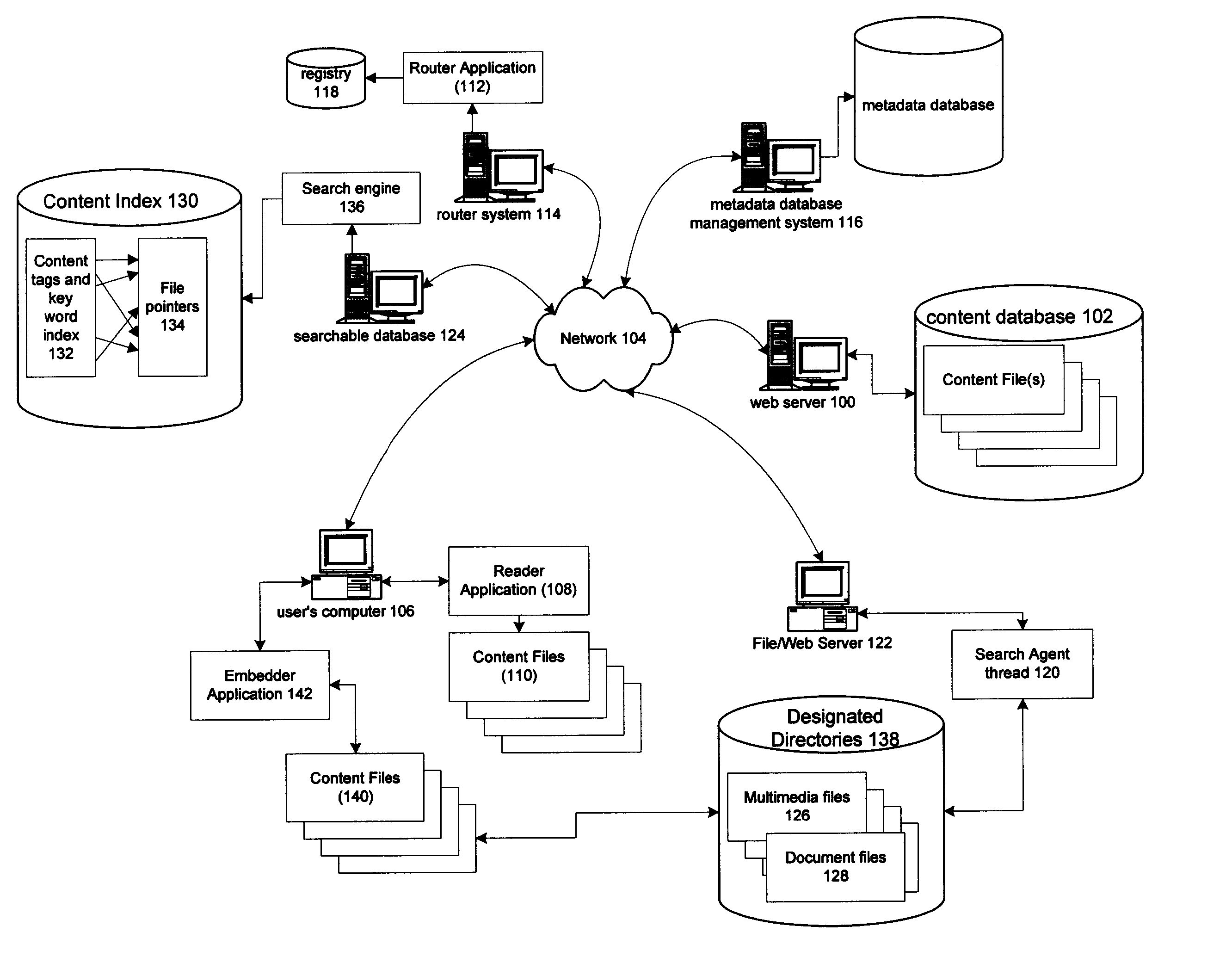
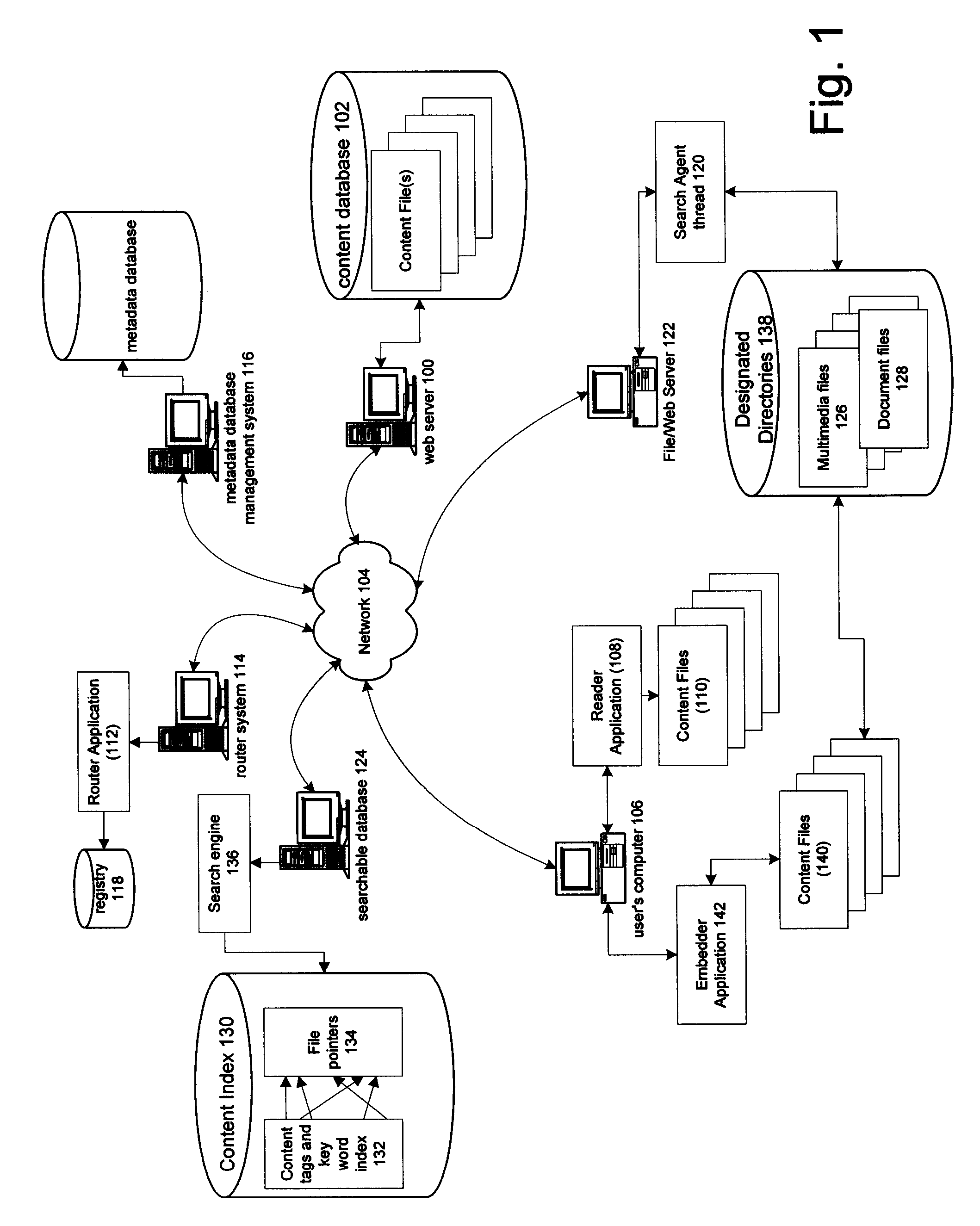
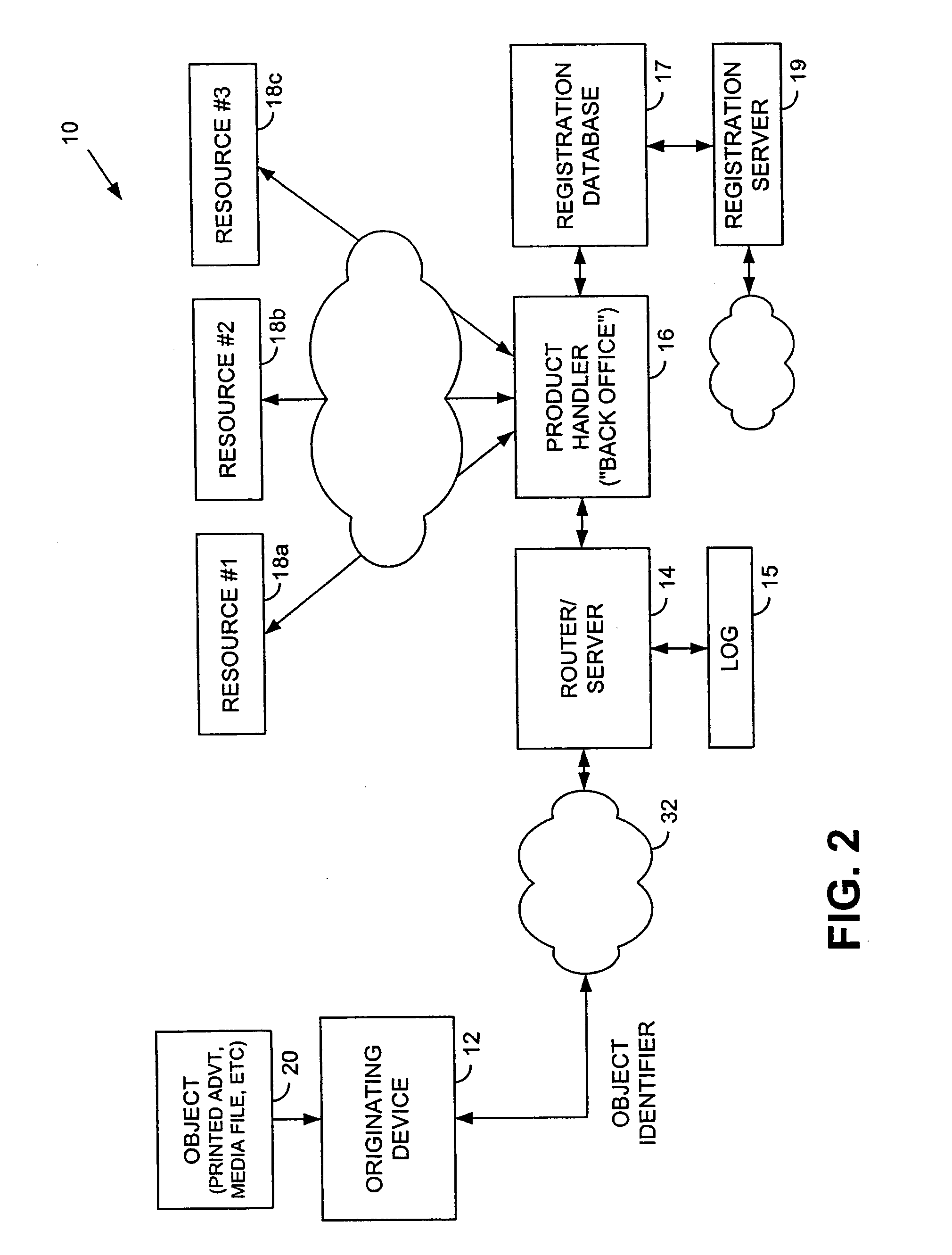
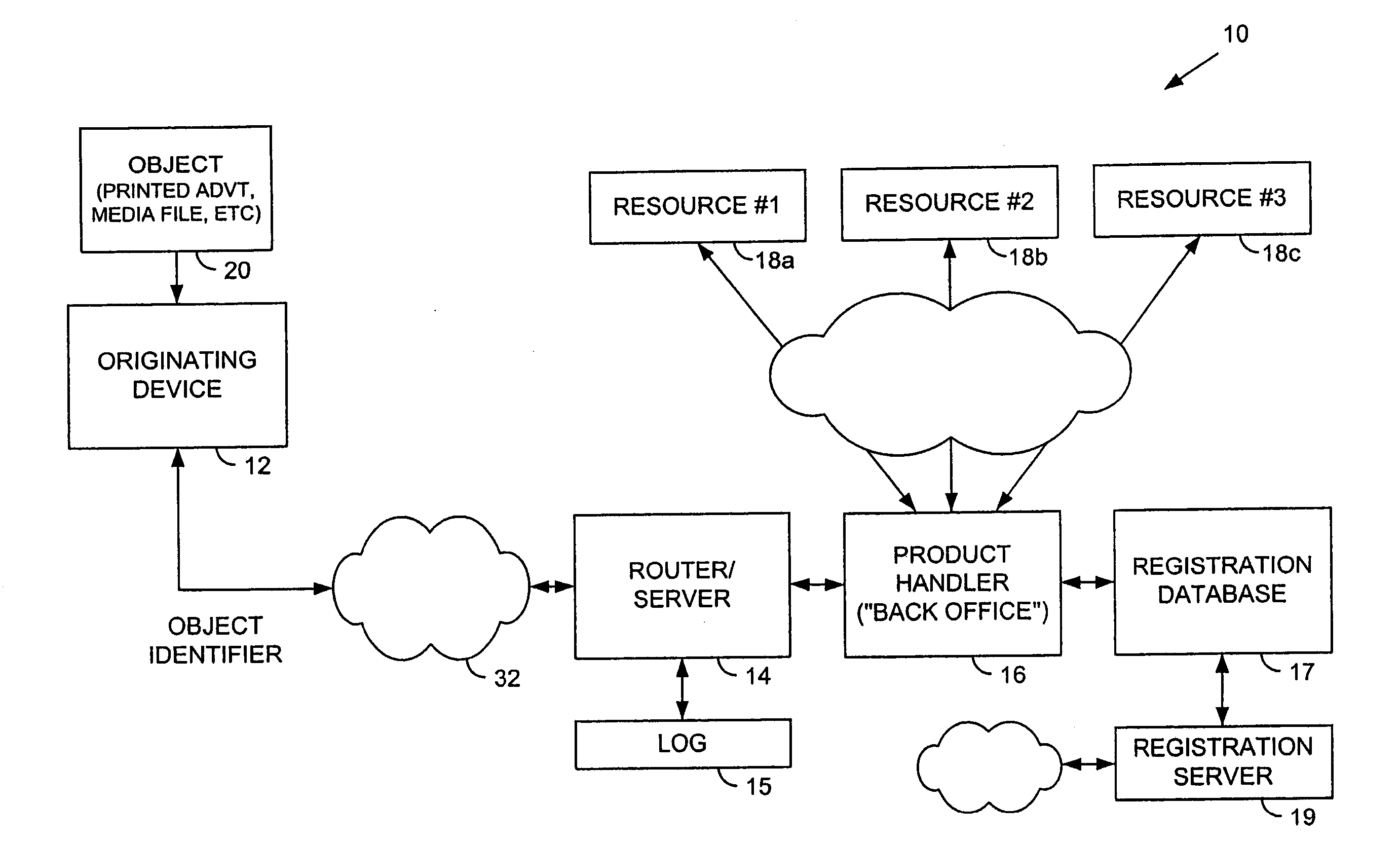
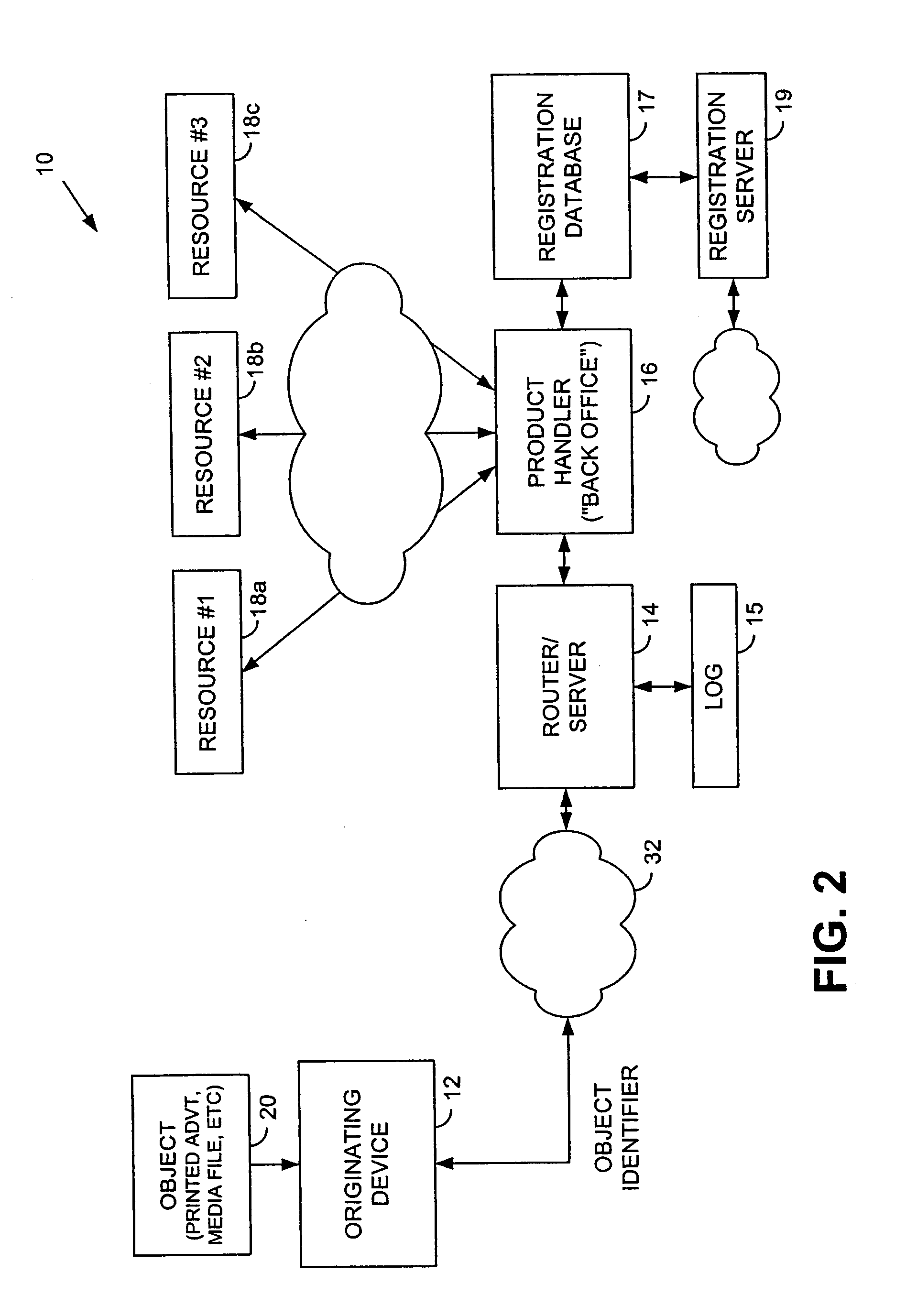
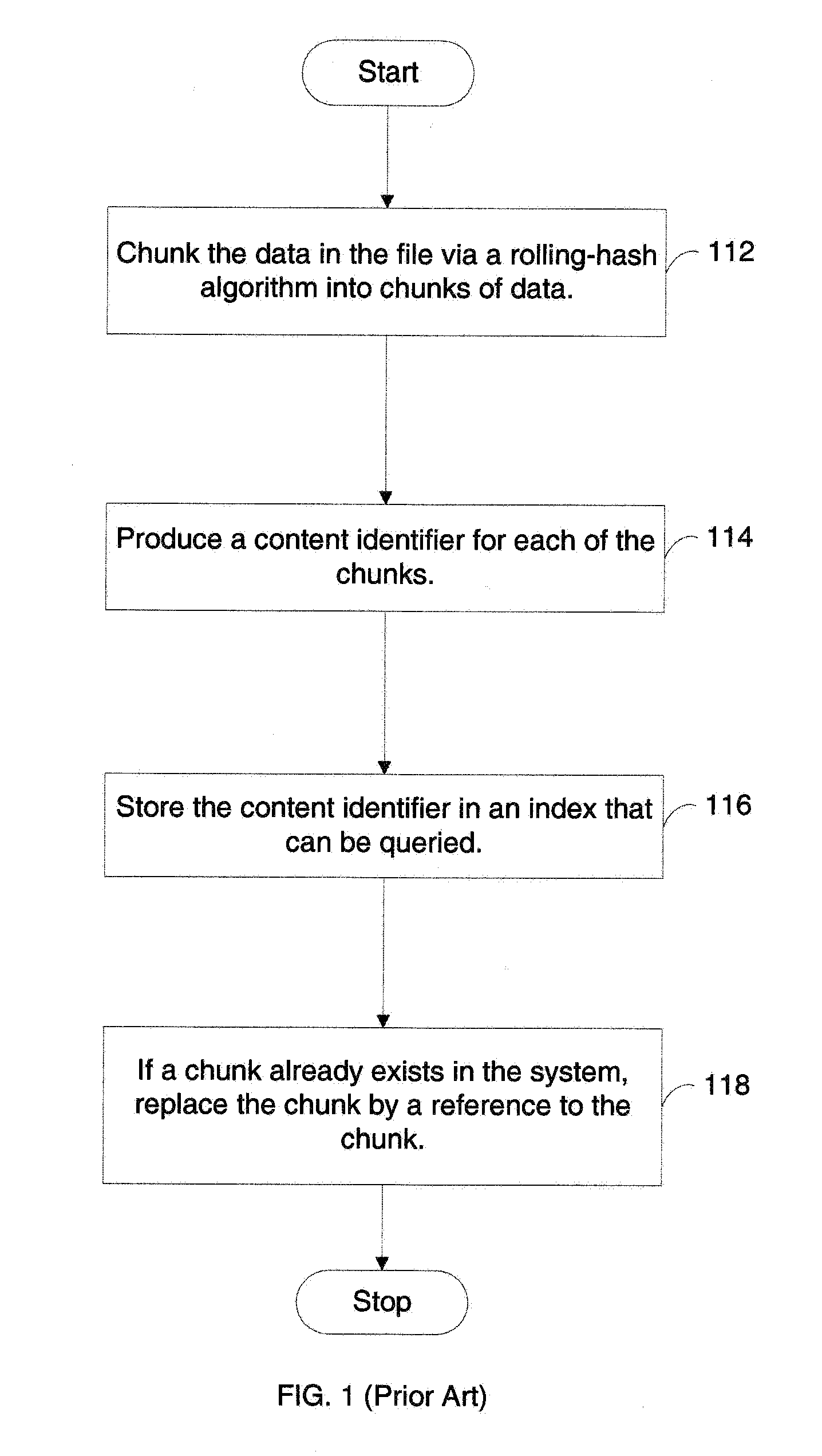
Information record infrastructure, system and method
InactiveUS20130159021A1Low costIncrease the number ofTelemedicineComputer security arrangementsContent IdentifierRecordset
A method of controlling access to records stored within databases, each record having associated access rules, a location identifier, and a content identifier maintained in a centralized index, comprising: receiving a request, communicated from a requestor to a security processor, the request containing a specified content identifier; querying the centralized index to find entries corresponding to the specified content identifier; for each entry, applying the access rules for the record to determine whether the record is accessible; for each accessible record, automatically communicating from the security processor to the database storing the accessible record sufficient information to determine whether it is releasable per a set of native access rules of the database; logically associating the releasable accessible records into a linked set of releasable records; and communicating the linked set of releasable records to the requestor.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method and apparatus for uniquely identifying a customer purchase in an electronic distribution system
InactiveUS6389403B1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierUser device
A system for tracking usage of digital content on user devices. Content sites for distributing digital content over a computer readable medium to users. The content sites associate unique content identifier with the content associated. Electronic stores coupled to a network sell licenses to play digital content data to users. The licenses contain a unique transaction identifier for uniquely identifying the transaction, and the licenses contain a unique item identifier for uniquely identifying at least one item in the transaction. Content players, which receive from the network the licensed content data, are used to play the licensed content data. The content players produce a purchase identifier based upon the mathematical combination of the content identifier, the transaction identifier and the item identifier.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Content Metadata Directory Services
ActiveUS20070156726A1Improve interoperabilityIncrease the number ofMultimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierSystems management
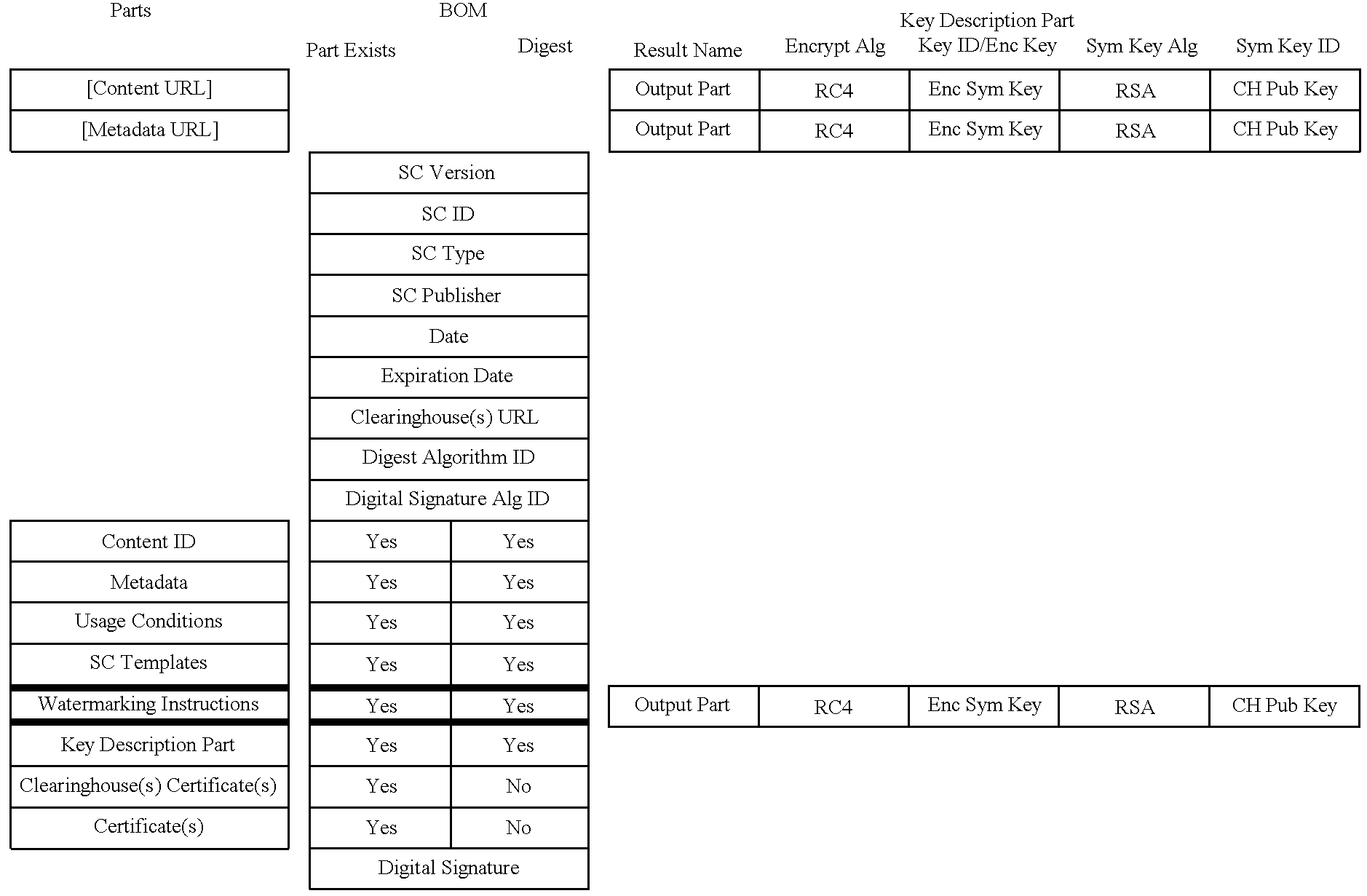
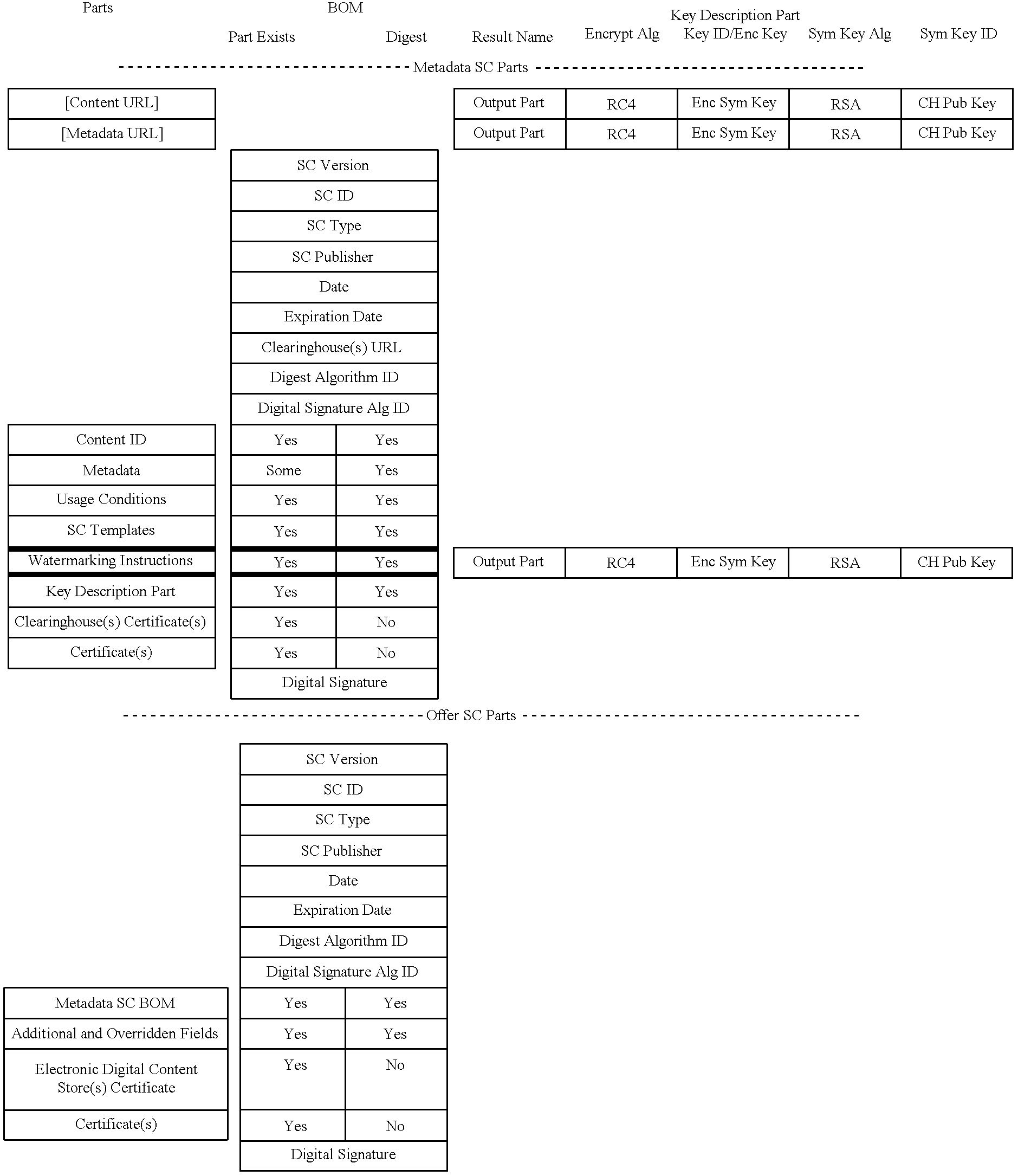
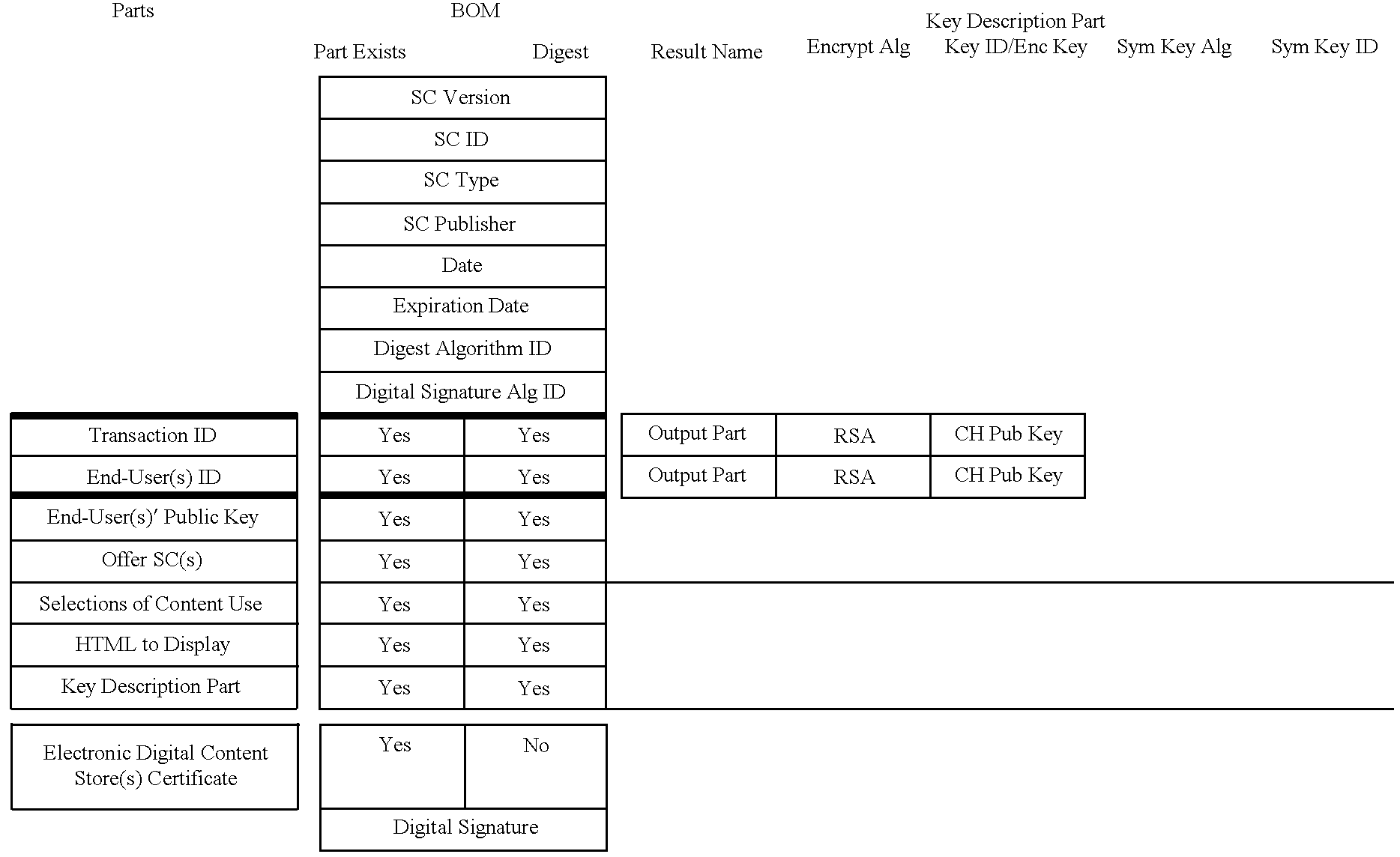
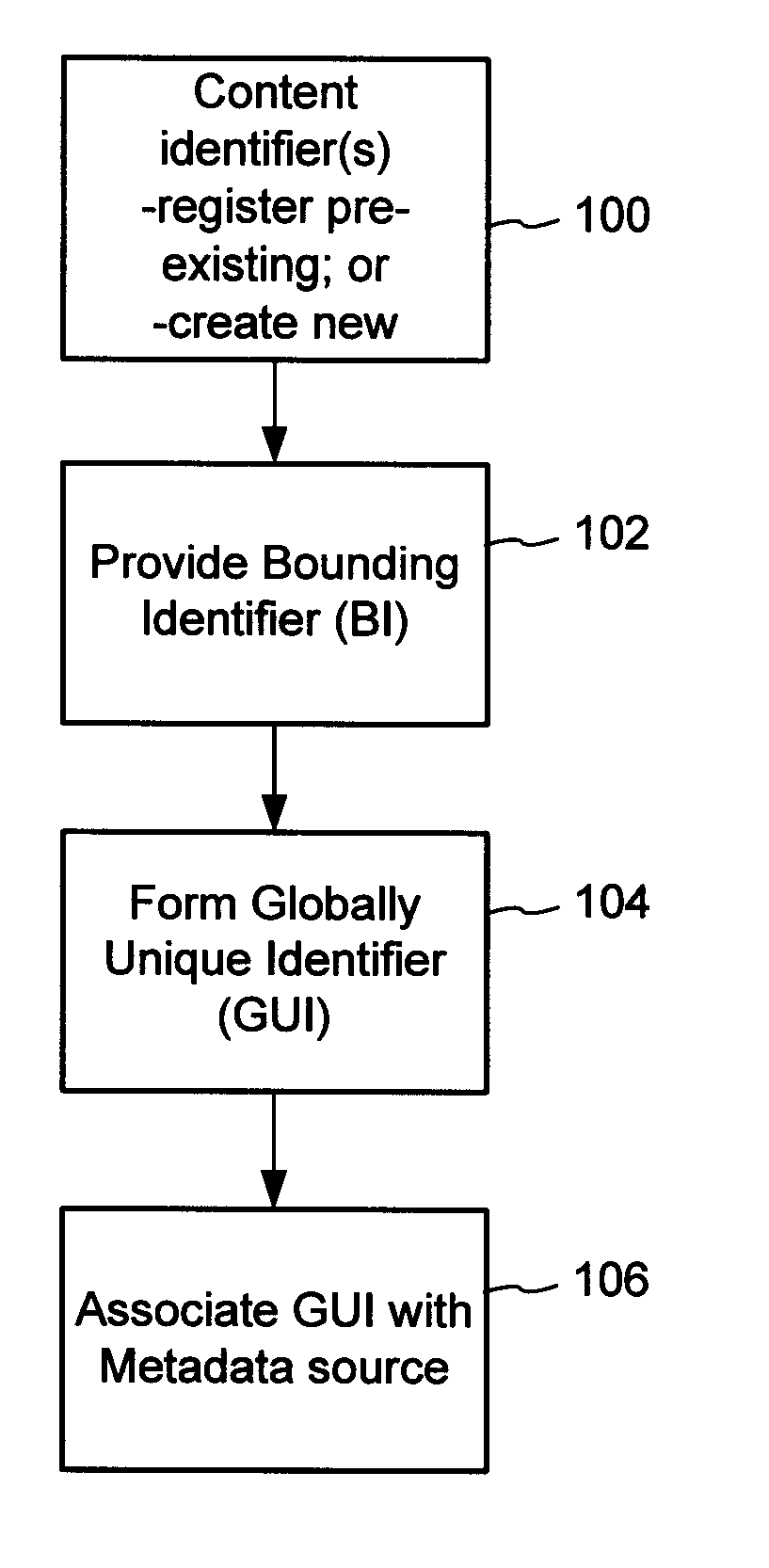
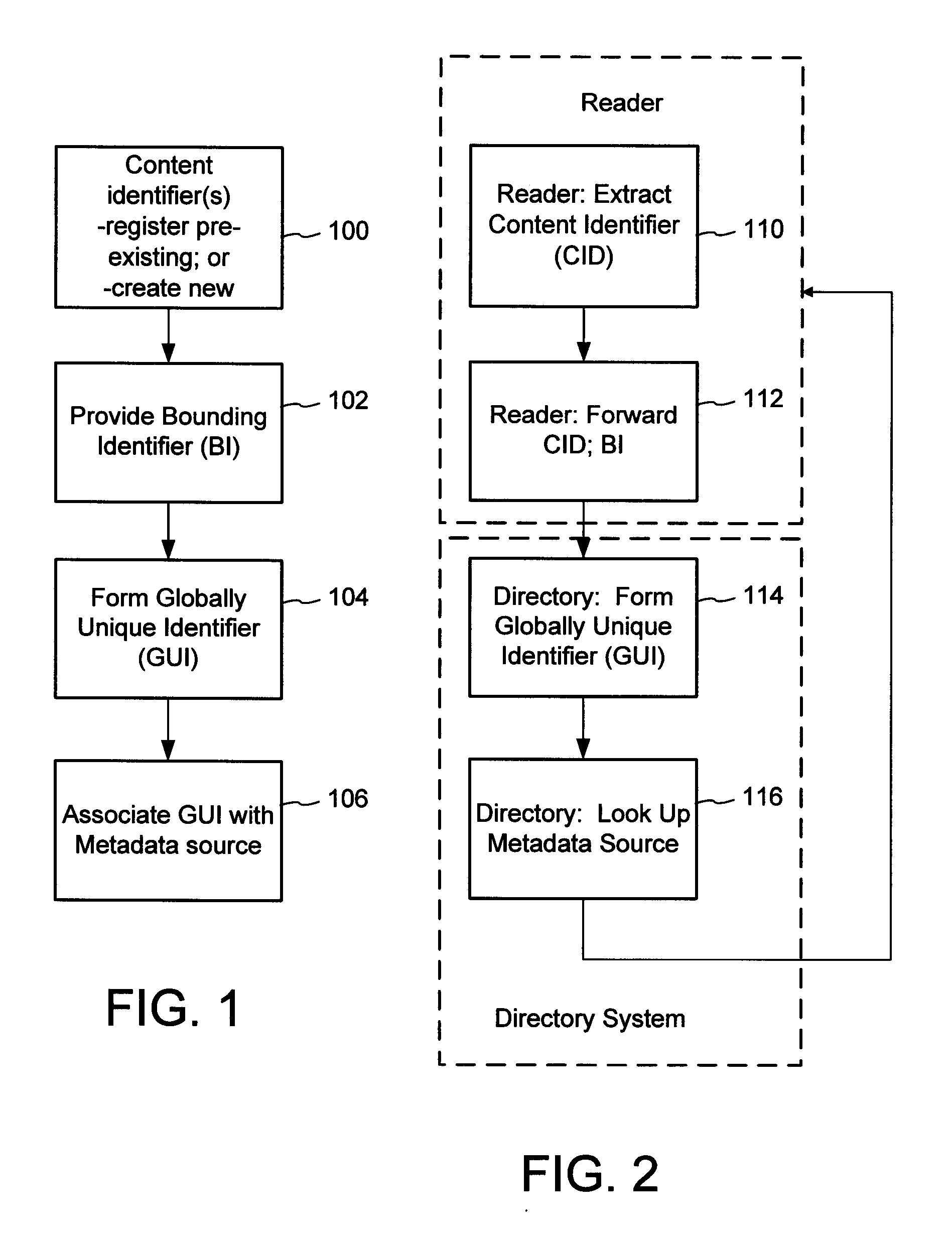
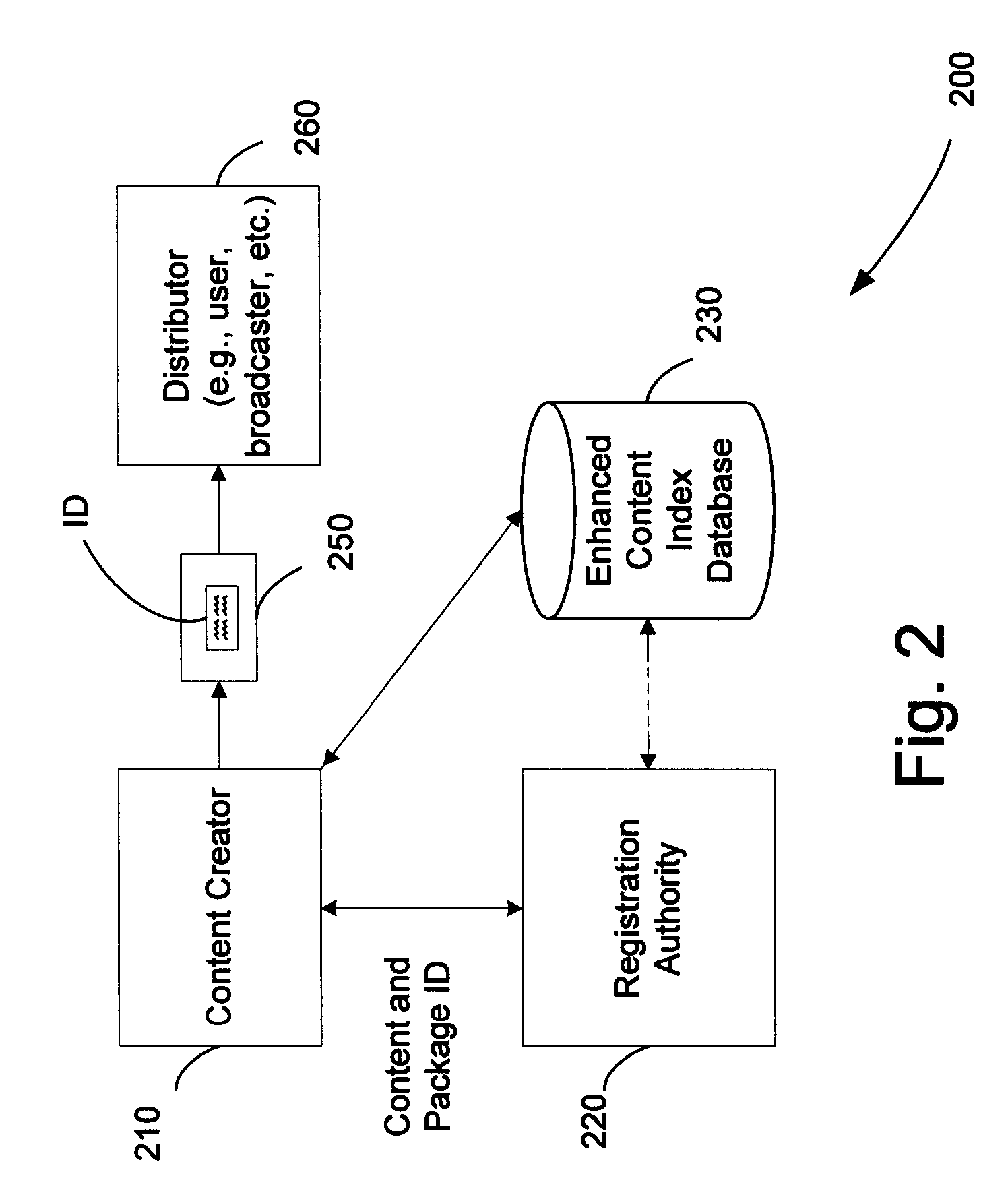
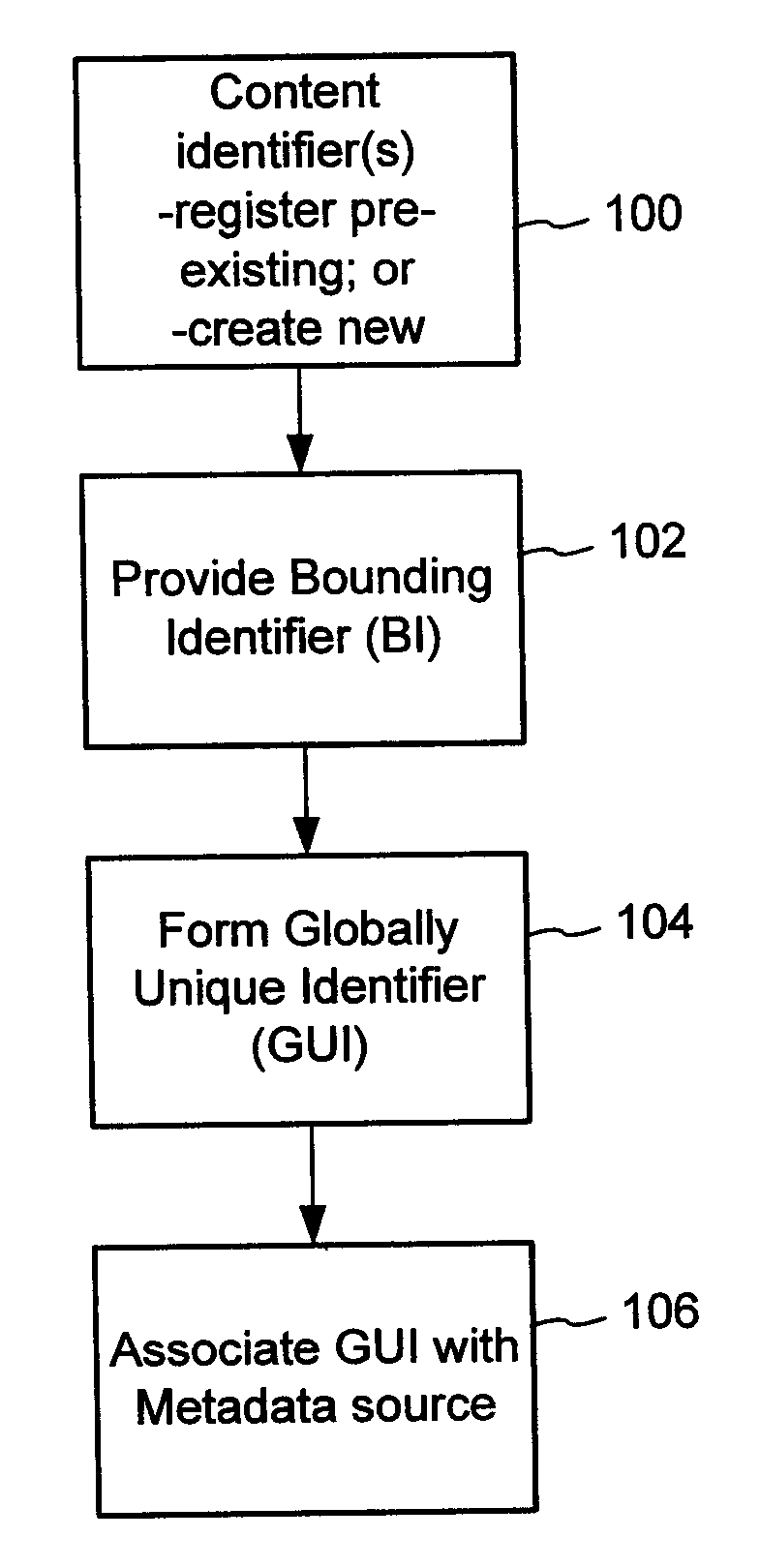
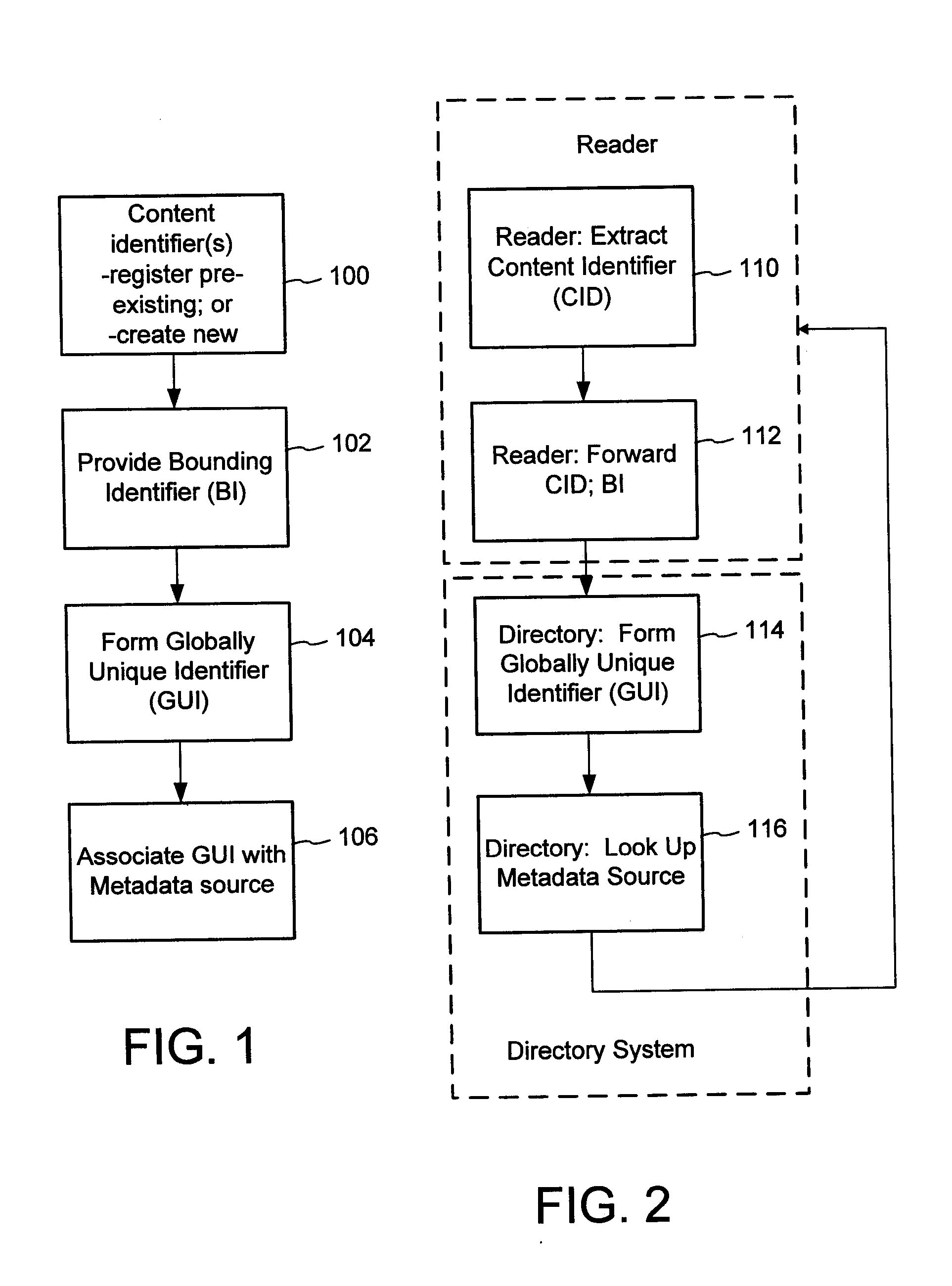
The content metadata directory system connects consumers of identified content to managed metadata databases and other digital resources. The system manages links between identifiers in content objects and metadata sources. It supports a variety of different type of content identifiers and allows for overlap among different content identification schemes. One method of associating a content object with metadata uses a combination of a content identifier and a bounding identifier to enable handling of disparate sets of content identifiers for content objects with potentially conflicting content identifiers. The method receives a content identifier for a content object from among a set of content identifiers and provides a unique bounding identifier for the set of content identifiers. This unique bounding identifier is used in combination with the content identifier to form a globally unique identifier for the content object. This globally unique identifier is associated with a metadata source, which enables routing of a user to the metadata source.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Rights management systems and methods using digital watermarking
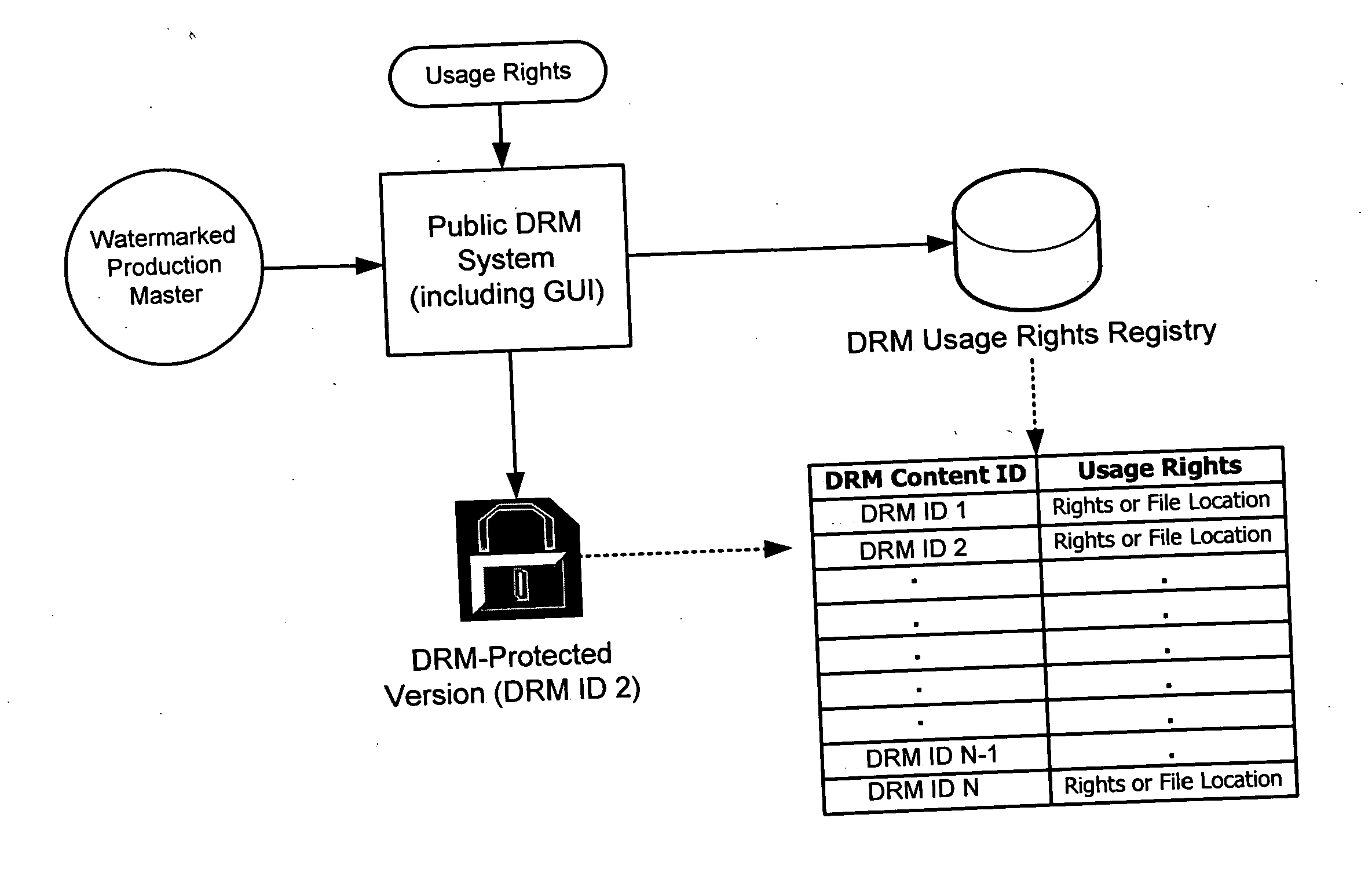
ActiveUS20060062426A1Difficult to controlDifficult to trackUser identity/authority verificationAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsContent IdentifierRights management
A digital watermark (DWM) content identifier is steganographically embedded in content. The DWM content identifier provides a link to a rights registry storing usage rights associated with the content. In some implementations the rights registry provides an association between the DWM content identifier and a digital rights management (DRM) content identifier. The DRM content identifier is used to find associated usage rights. The DWM content identifier can also be used to transfer content from a first DRM system to a second DRM system.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP (FORMERLY DMRC CORP)
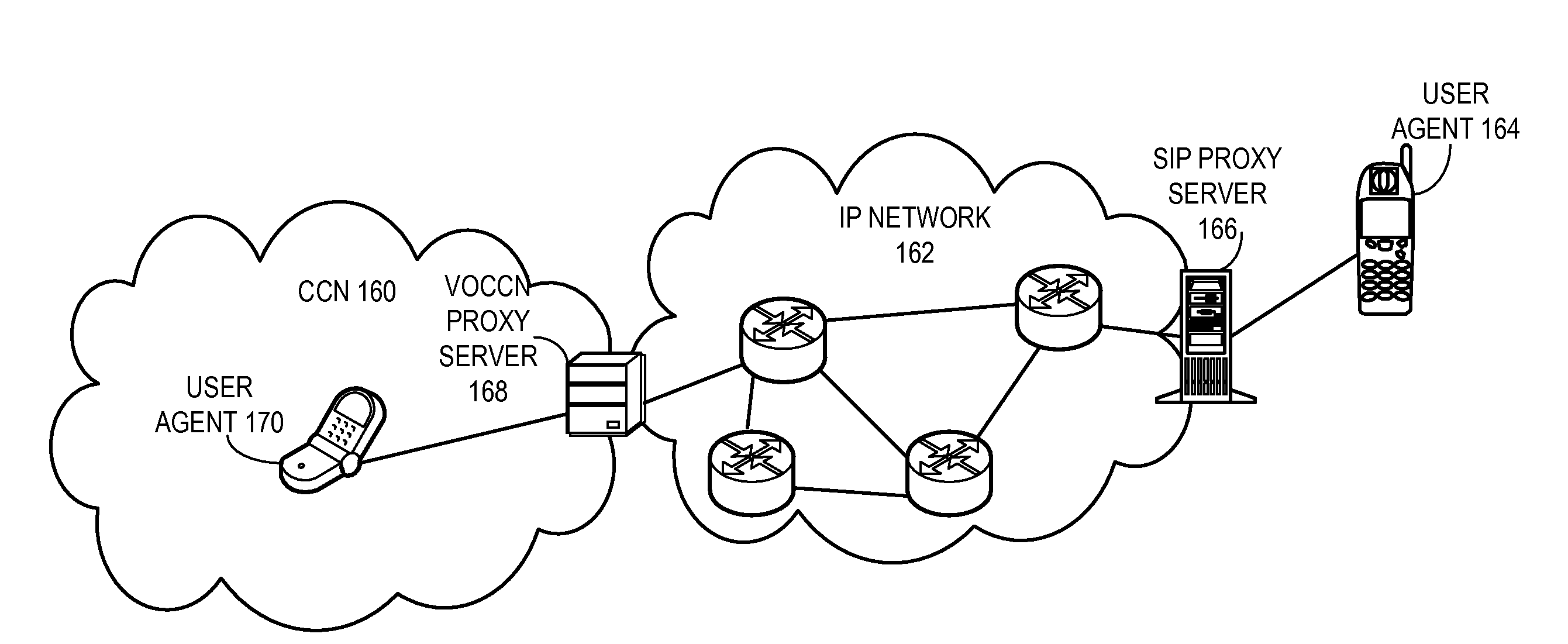
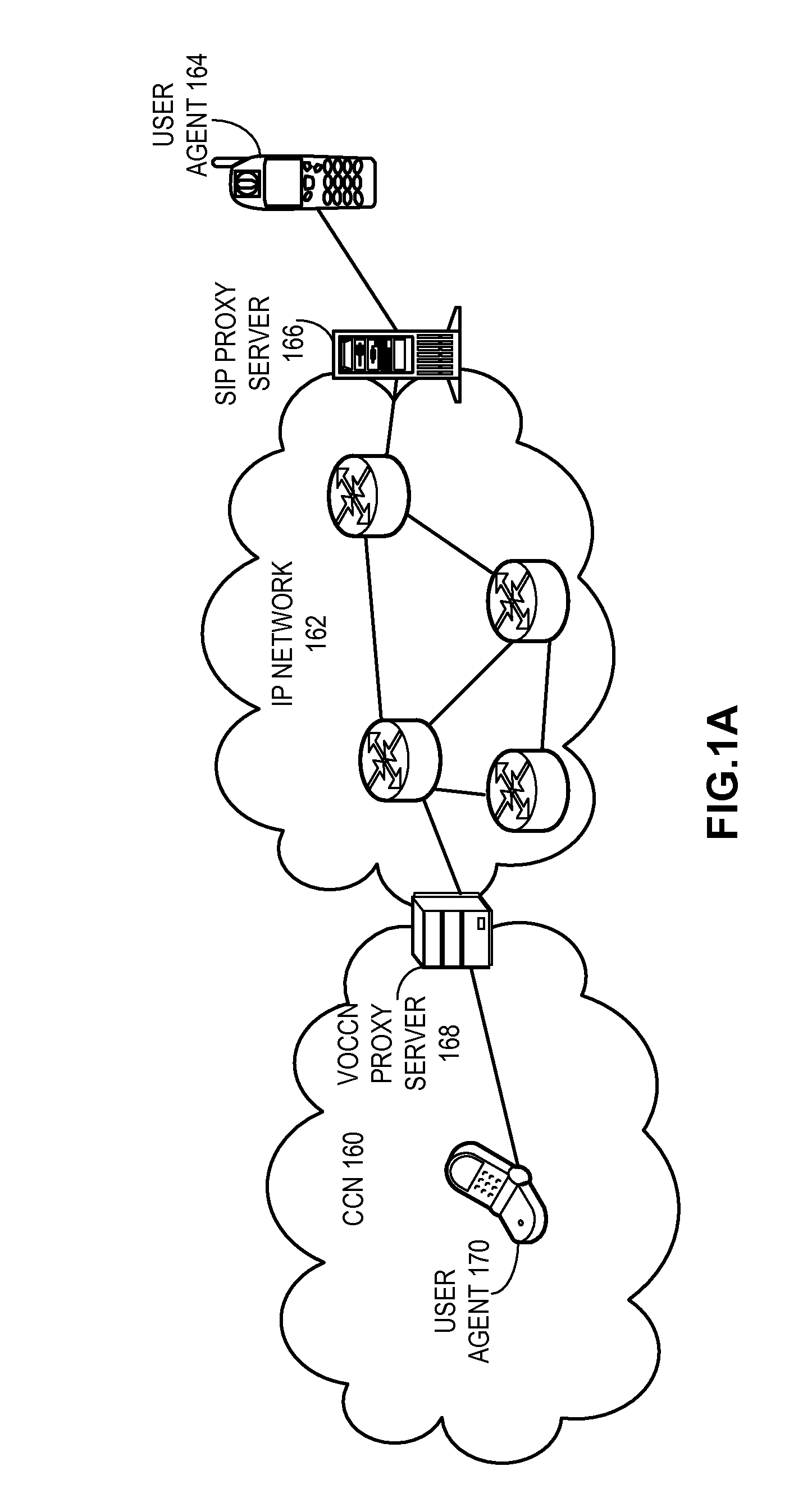
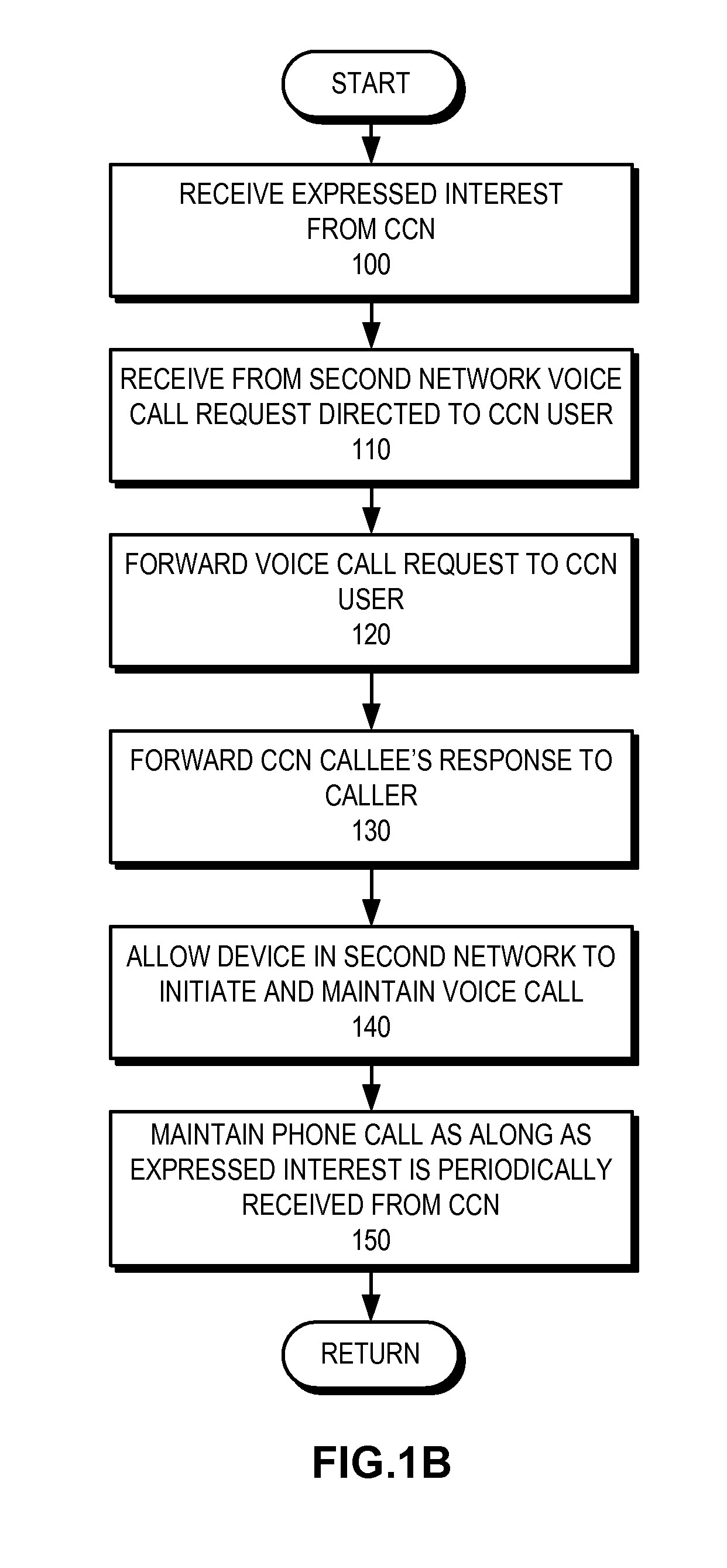
Voice over content centric networks
ActiveUS20090285209A1Special service for subscribersData switching by path configurationContent IdentifierComputer network
A system for facilitating voice calls over a content centric network (CCN) receives from a CCN user an expressed interest in receiving voice calls directed to the CCN user, wherein information in the CCN can be addressed, located, and disseminated by its content identifier and wherein data packets in the CCN are self-authenticating. Next, the system receives from a second network a packet for a voice call directed to the CCN user. The system then forwards to the CCN user the packet received from the second network with a CCN identifier corresponding to the interest expressed by the CCN user and forwards a packet from the CCN user for the voice call to the second network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Content indexing and searching using content identifiers and associated metadata
A method of indexing content for network searching comprises identifying media content signals stored at sites distributed over a distributed computer network; extracting content identifiers from the content signals; using the content identifiers to obtain metadata used to classify the media content signals; and creating a searchable index of the media content signals based on the metadata, wherein users access the searchable index on the distributed computer network to submit a search query for the searchable index to retrieve links to the media content signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Content Metadata Directory Services
ActiveUS20070192352A1Increase the number ofComplicate to identifyMultimedia data indexingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierWeb site
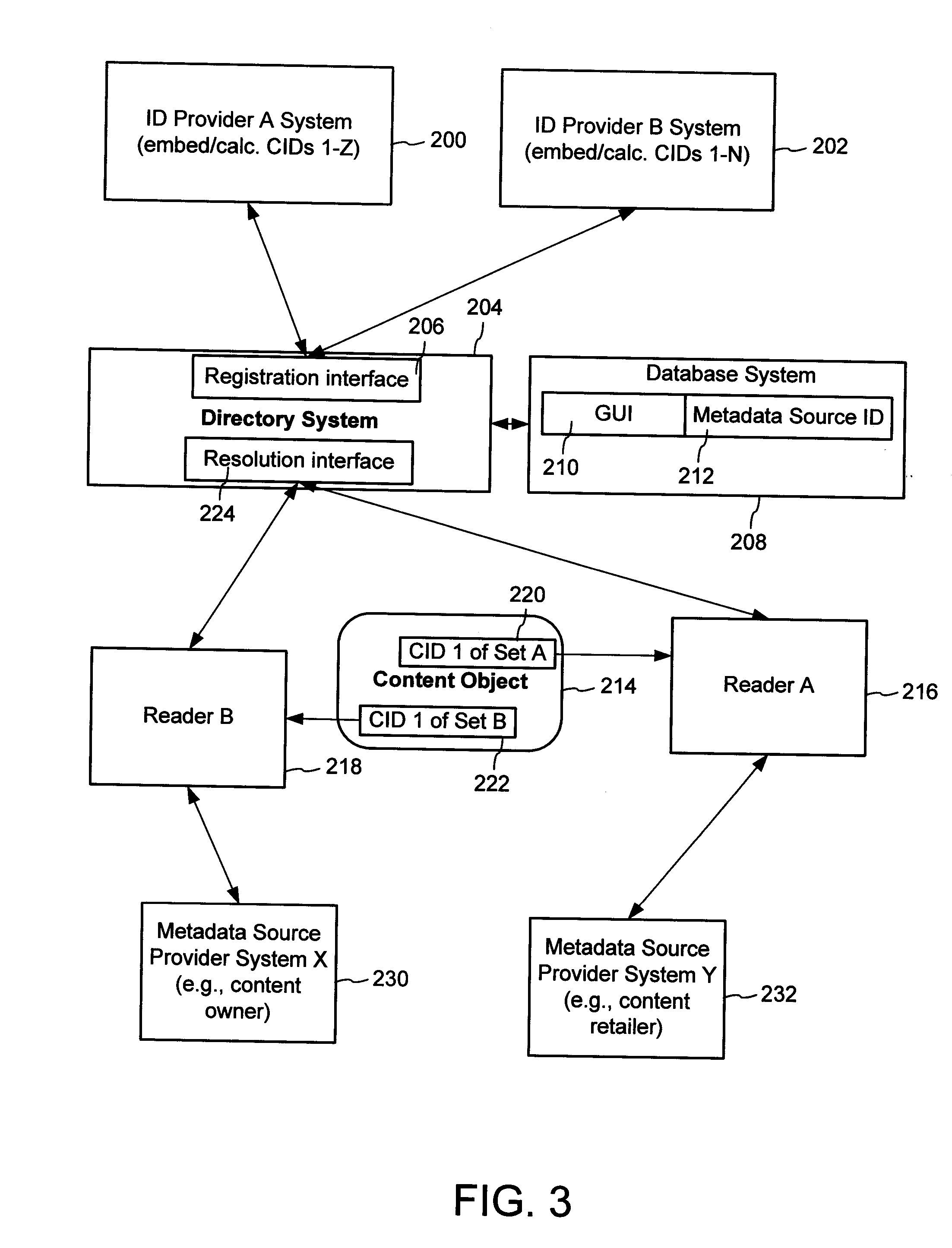
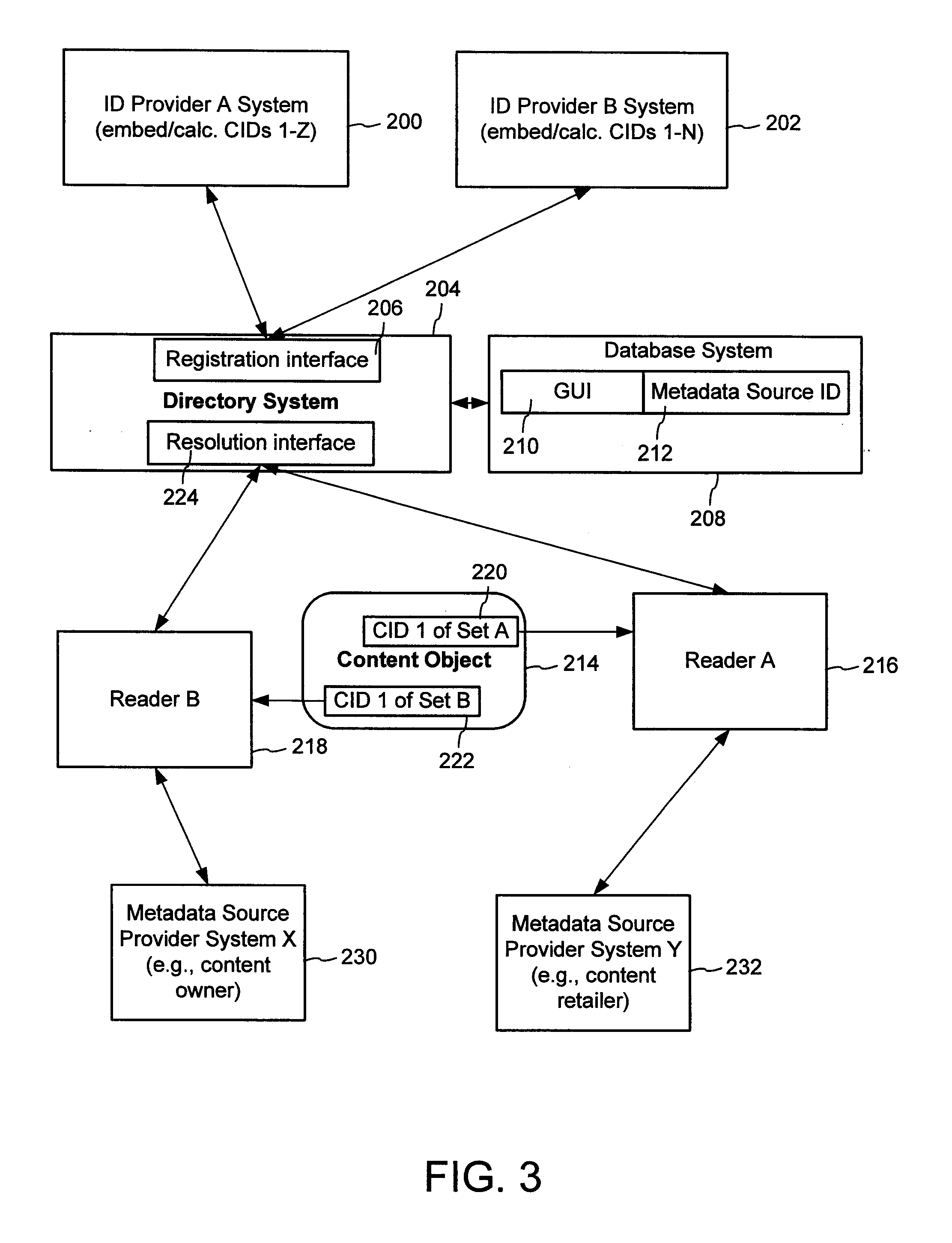
A method of associating a content object with metadata uses a combination of a content identifier and a bounding identifier to enable handling of disparate sets of content identifiers for content objects with potentially conflicting content identifiers. The method receives a content identifier for a content object from among a set of content identifiers. It provides a unique bounding identifier for the set of content identifiers. This unique bounding identifier is used in combination with the content identifier to form a globally unique identifier for the content object. This globally unique identifier is associated with a metadata source, which enables routing of a user to the metadata source. Another novel method addresses content objects with two or more content identifiers, potentially referencing different metadata sources. This method registers different globally unique identifiers for a content object. These globally unique identifiers each comprise a content identifier provided with the content object and a bounding identifier identifying a set of content identifiers of which the content identifier is a member. For each of the globally unique identifiers, information is maintained about a metadata source. The method receives a first content identifier for the content object, and uses a bounding identifier associated with the set of the first content identifier to determine the globally unique identifier for the first content identifier. The user is routed to the metadata source associated with globally unique identifier. This document describes a novel system that enables multiple identity providers (ID Providers) to register and use the system. The ID Provider registers with a metadata directory system, receives a unique bounding identifier, and uses this bounding ID (e.g., an ID provider ID) with subsequent interactions with the metadata directory system. Separately, metadata source providers register metadata sources with the metadata directory system. This enables many different participants to associate content objects with metadata sources using one or more identify providers. Examples of metadata source providers include content providers, like content owners or retailers that have the flexibility of working with different ID providers to associate content objects with metadata. Both content providers and ID providers can register and use the system. The metadata source is the system or device that provides the metadata, like a web site. The directory system uses an identifier for the metadata source, which enables it to maintain an association between a content object and its corresponding metadata source. For example, in some embodiments, a URL serves to identify the location of the source. The Content Metadata Directory Services (CMDS) is a global trusted directory service that connects consumers of identified content to content-provider authorized and managed metadata databases and other digital resources. It includes mostly links to metadata, forms globally unique IDs based upon overlapping content identifiers and unique bounding identifiers, enables multiple content identifiers within a content object, and enables multiple content identity technology providers, even when they are using different technology.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Content Centric M2M System
ActiveUS20150095514A1Reduce payloadReduce contentWeb data retrievalDigital computer detailsContent IdentifierContent centric
A method for routing data at a first node of a network including a second node. The method includes: providing the first node with a database storing an association between: an URL component identifying content at the first node, and a unique identifier associated to the second node, the unique identifier being specified by the second node; registering content locally stored in the second node by storing in the database an association between an URL component identifying the locally stored content and the unique identifier of the second node; and, upon reception from a requesting entity, by the first node, of a content request having a content identifier, the method includes: checking in the database whether the content identifier includes the URL component, and forwarding the content request to the second node if the content identifier includes the URL component associated with the unique identifier of the second node.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
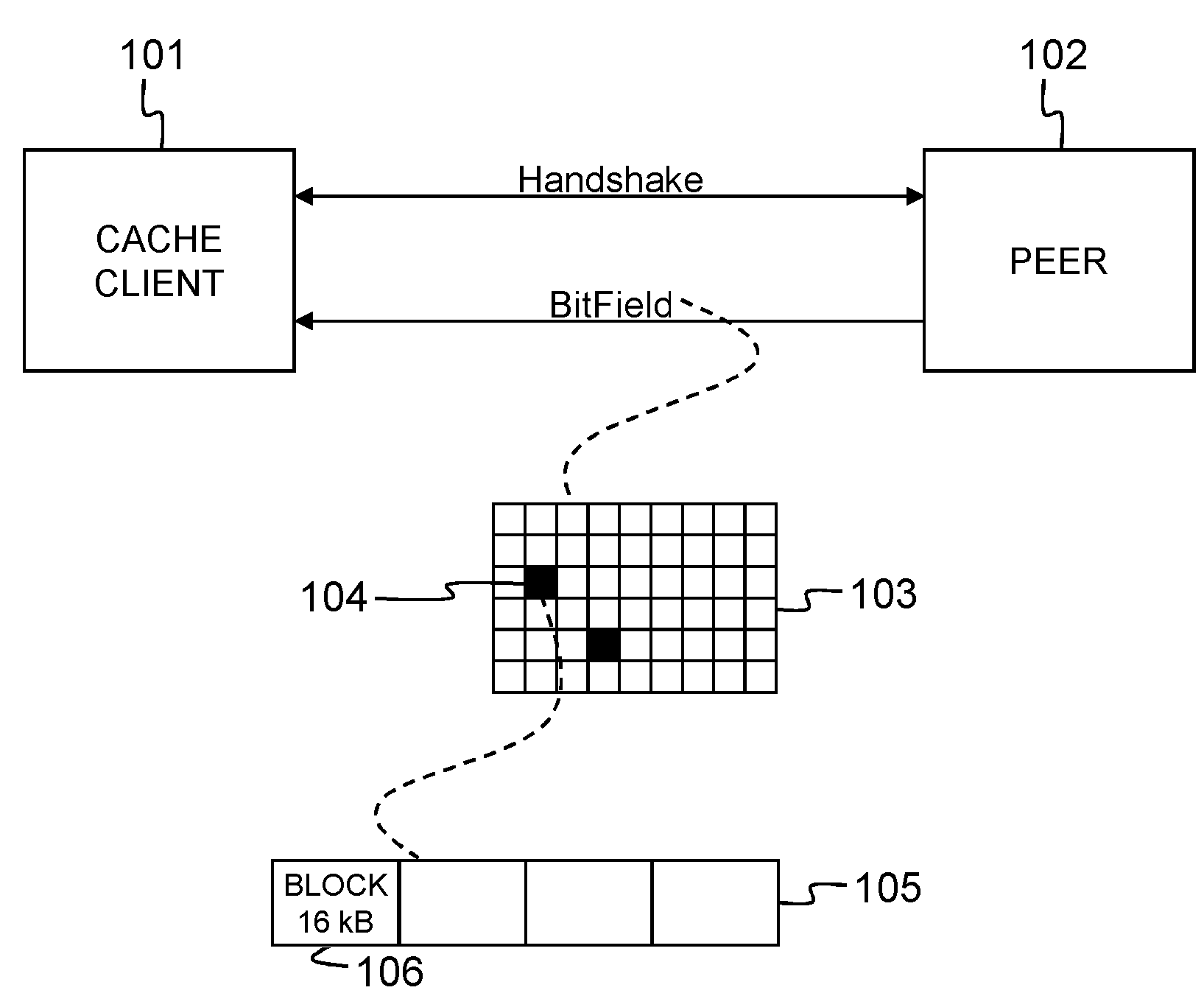
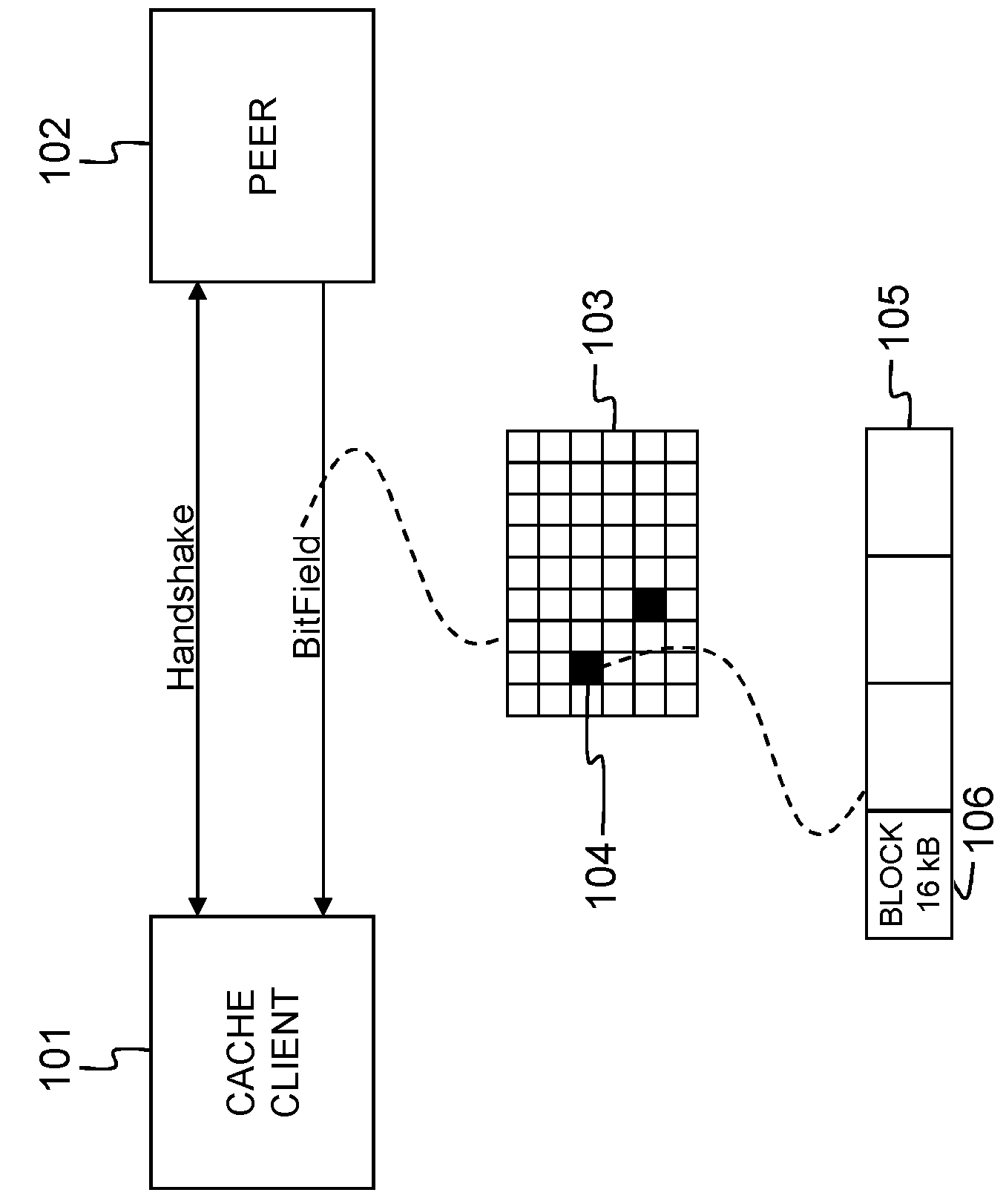
Method and apparatus for bandwidth-efficient and storage-efficient backups
InactiveUS7139808B2Unauthorized memory use protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsContent IdentifierWorld Wide Web
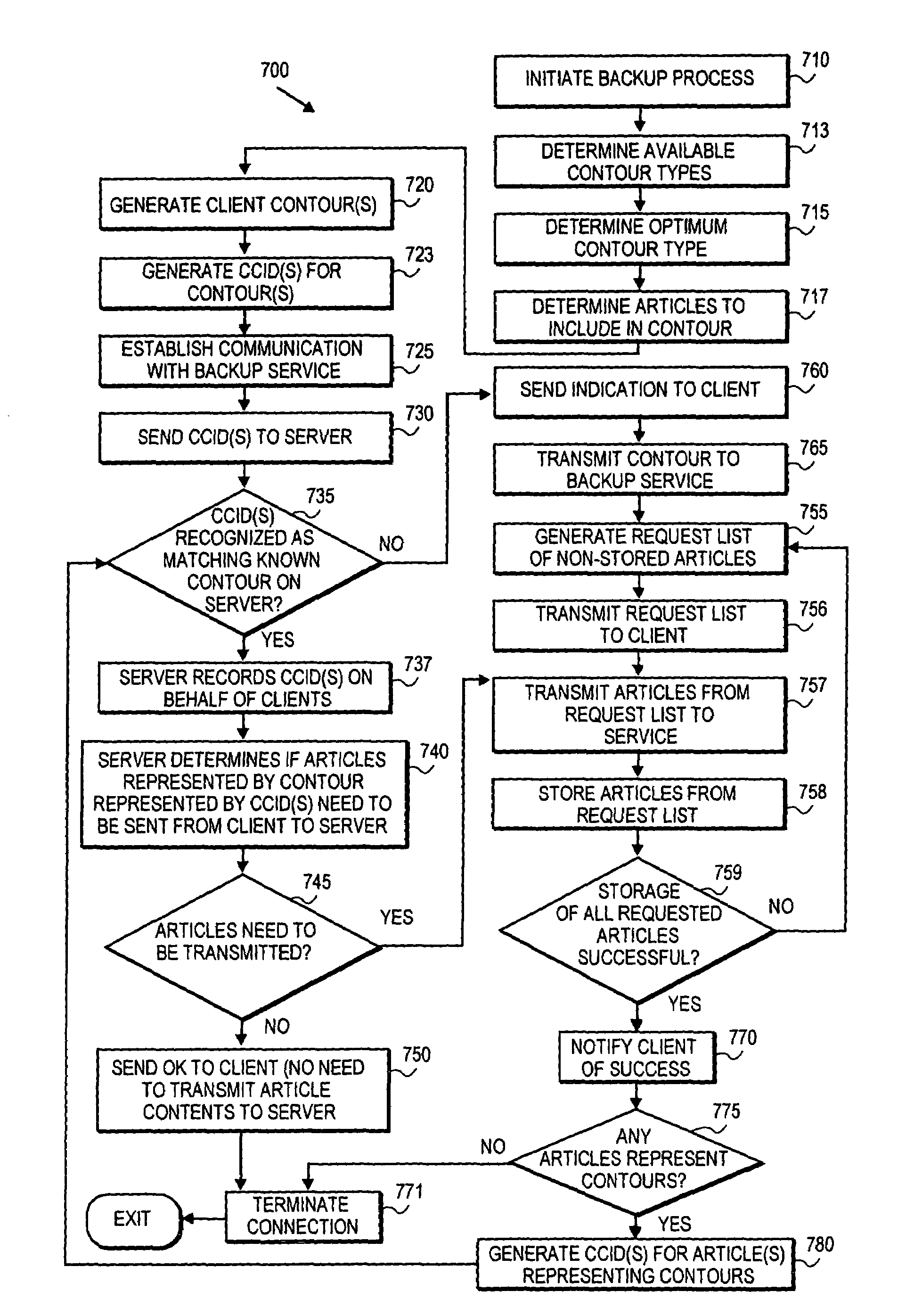
A method is presented that includes generating a content identifier for at least one article. The content identifier identifies the article. Also, determining if at least a portion of the at least one article is present on at least one device based on the content identifier. The at least one portion of the at least one article is stored if the at least one portion of the at least one article is determined to be not present on the at least one device. Also presented is a method including requesting at least one article by a content identifier representing the article. The at least one article is determined if it is present on at least one device based on the content identifier. At least one portion of the at least one article is returned if the at least one portion of the at least one article is determined to be present on the at least one device.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Content Indexing and Searching using Content Identifiers and associated Metadata
InactiveUS20070055689A1Difficult to controlDifficult to trackMultimedia data queryingDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierMetadata
A method of indexing content for network searching comprises identifying media content signals stored at sites distributed over a distributed computer network; extracting content identifiers from the content signals; using the content identifiers to obtain metadata used to classify the media content signals; and creating a searchable index of the media content signals based on the metadata, wherein users access the searchable index on the distributed computer network to submit a search query for the searchable index to retrieve links to the media content signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and method for managing distribution of content to a device
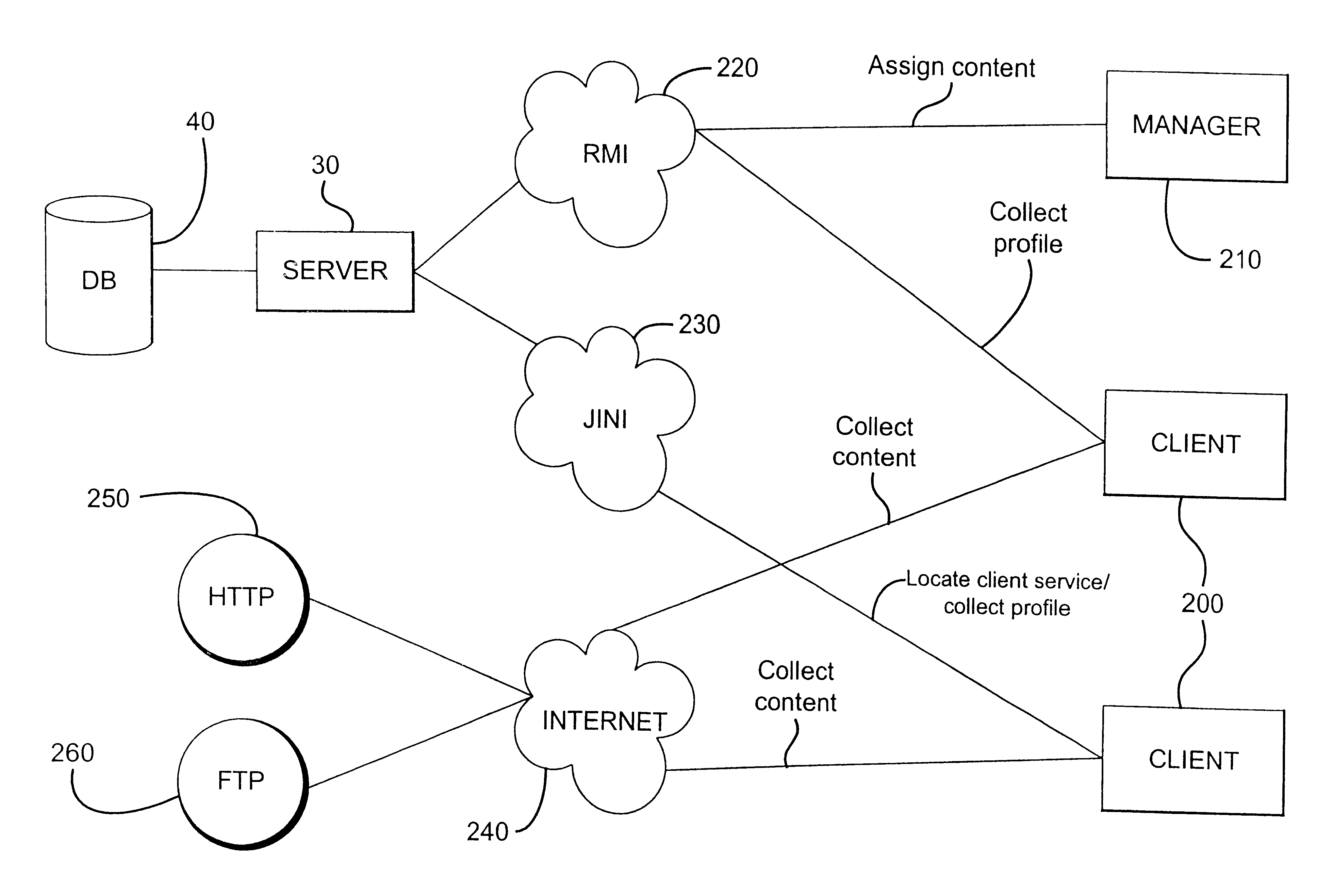
InactiveUS6886017B1Improve efficiencyEasy to useData processing applicationsProgram loading/initiatingContent IdentifierCitation database
The present invention provides a system and method for managing distribution of content to a device, the system comprising a database for storing a number of elements as a hierarchical structure, content identifiers being able to be associated with elements in the hierarchical structure, and one of the elements representing the device, and a server for referencing the hierarchical structure in the database to generate a profile for the device, the profile containing a number of content identifiers indicating content to be provided to the device. A device manager is associated with the device and arranged to receive the profile from the server and to use the content identifiers in the profile to cause the content indicated by the profile to be provided to the device, a record being kept identifying the content provided to the device in accordance with the profile. The device manager is arranged upon receipt of a subsequent profile from the server to compare the content identifiers in the subsequent profile with the record to determine new content not yet provided on the device and old content no longer to be provided on the device, the device manager being arranged to use the relevant content identifiers to cause the new content to be provided to the device, and to cause the old content to be removed. This approach facilitates the efficient management of distribution of content to devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods and Devices Employing Content Identifiers
InactiveUS20070276928A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionContent IdentifierMetadata
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
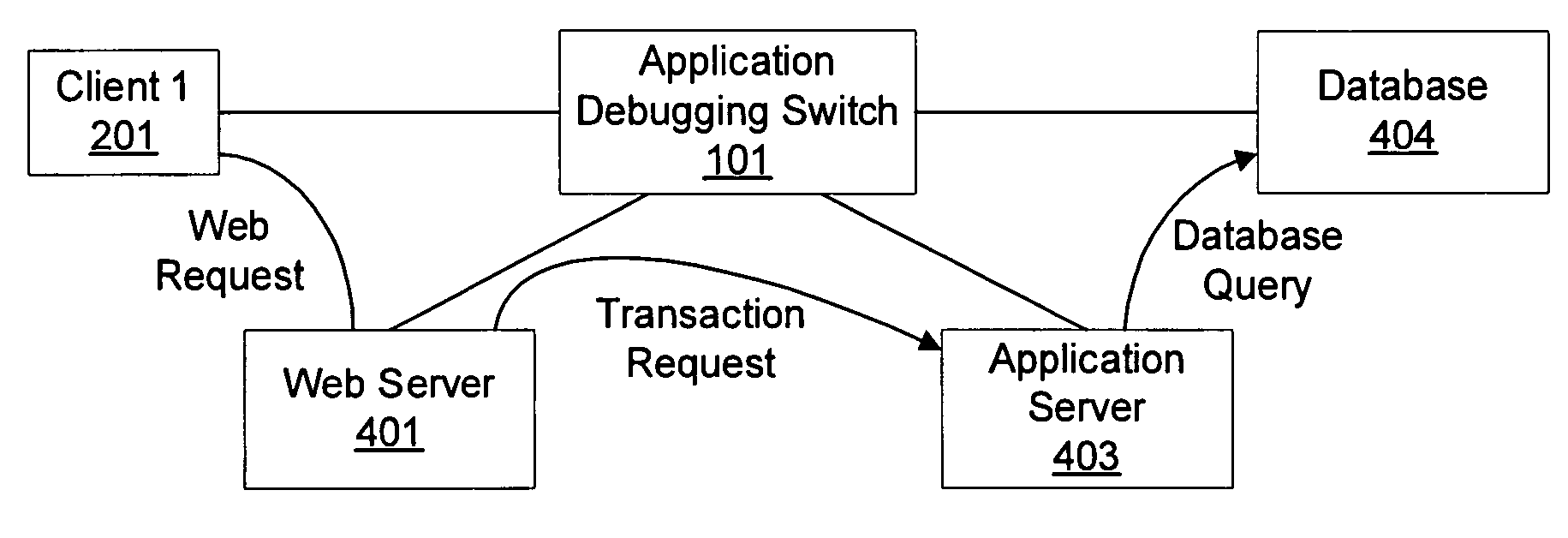
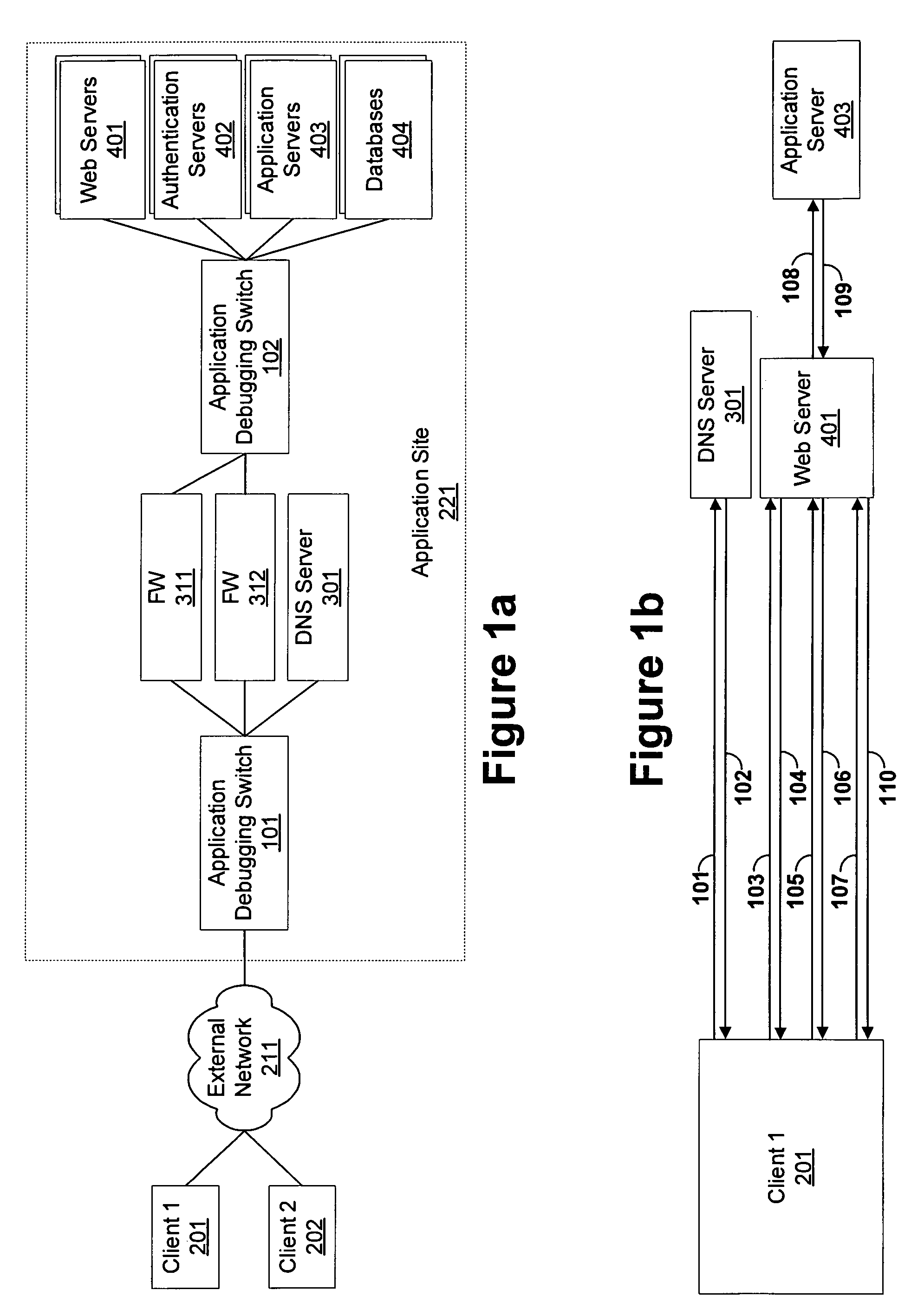
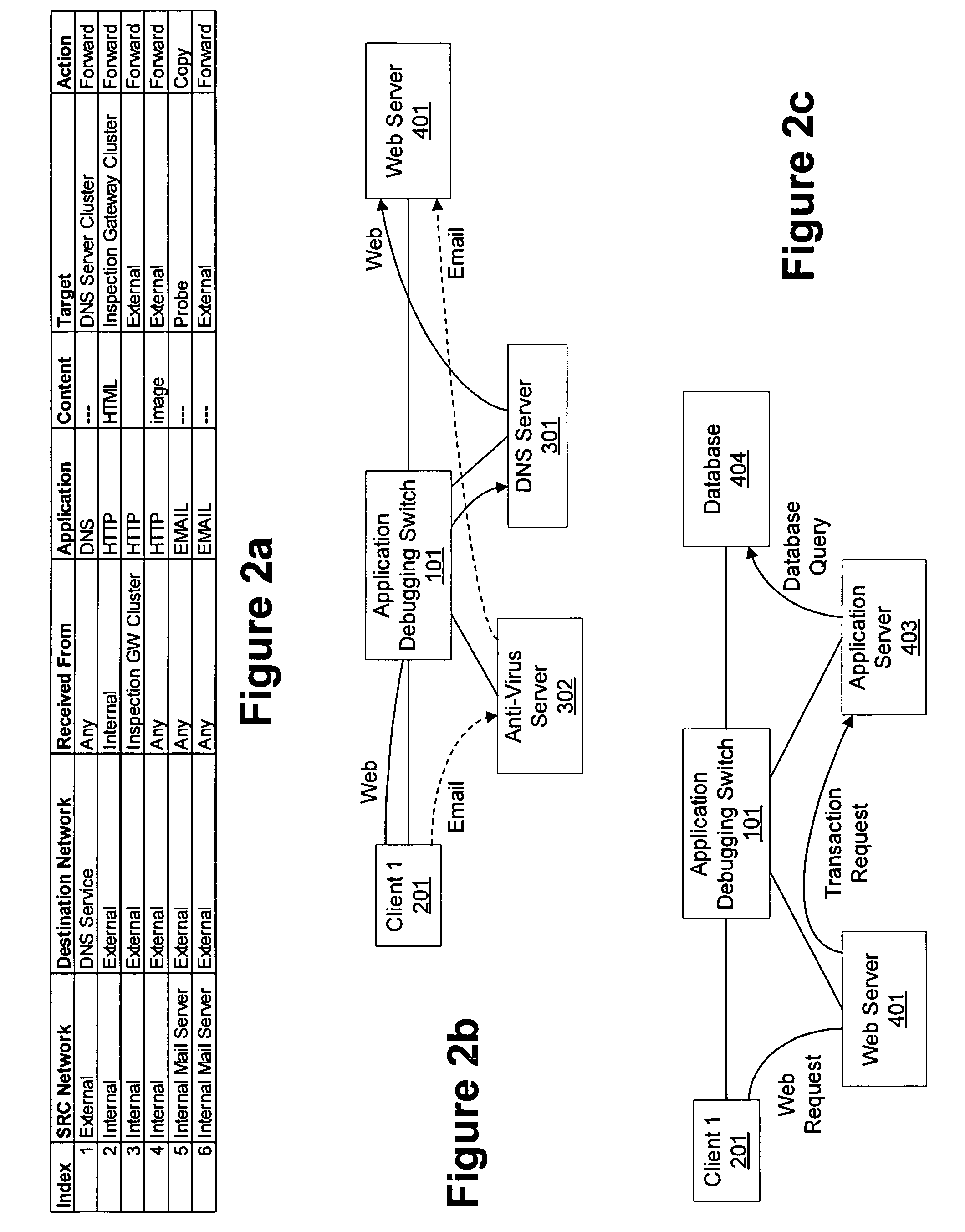
Debugging application performance over a network
InactiveUS20060029016A1Detection problemRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesContent IdentifierTimestamp
An application debugging switch also monitors application performance. The application debugging switch forwards the requests from a first host to a second host, and later forwards the response coming from that second host to that first host. As most of the applications work in a request—response architecture, the application debugging switch can measure the response time of the application. The switch attaches a timestamp to each request that it forwards. When the response to that request comes to the switch, the switch can determine the response time of that application. The application debugging switch collects multiple samples of response time over a certain period of time. These samples provide a good measurement for the average application response time. The response time is a combination of the network response time and the application response time. The application debugging switch holds multiple measurement classes. Each class defines different sources or destinations of traffic (IP addresses and networks) and different applications (TCP / UDP ports or content identifiers in the requests). Collecting the response time for each class separately allows zooming in to an application and user that experience bad service and detect the reason for their failure.
Owner:RADWARE
Methods and devices employing content identifiers
InactiveUS20070276841A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierMetadata
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and arrangement for facilitating the sharing of content items
InactiveUS20020165793A1Easy to useFacilitating content sharingMultiple digital computer combinationsSpecial data processing applicationsContent IdentifierUser device
An arrangement (100) and a method are disclosed for sharing a content item (101), such as a music title, with a second user. A first user (110) grabs a piece of music from the title and sends said piece of music to a friend (130). The user device (110) adds a content identifier and a user identifier identifying the sender to the transmitted piece of music. The recipient reproduces the piece of music (102). If he or she subsequently decides to buy the complete title, the sender will obtain an award from the content owner (130) for promoting the title. This electronic version of "mouth-to-mouth" marketing encourages people to spread music clips and may persuade friends to purchase content items.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods and Devices Employing Content Identifiers
InactiveUS20070192872A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierMetadata
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP (FORMERLY DMRC CORP) +1
Rights Management Systems and Methods Using Content Identifiers
InactiveUS20080140433A1Difficult to controlDifficult to trackRecord information storageAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsContent IdentifierRights management
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and method for multimedia on demand services
InactiveUS7698723B2Television system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMass storageContent Identifier
The exemplary embodiments describe systems and methods for multimedia-on-demand services. A multimedia-on-demand system includes a mass storage device that receives and stores multimedia content items. Memory couples to the mass storage device and stores a multimedia-on-demand data table and multimedia-on-demand instructions. The multimedia-on-demand data table includes a multimedia content identifier field corresponding to a multimedia content item stored on the mass storage device. The multimedia-on-demand data table may also include a multimedia content usage indicator field associated with the multimedia content item. The multimedia-on-demand instructions are executed by a processor and include instructions to automatically receive the multimedia content items. The multimedia-on-demand instructions also send a multimedia-on-demand usage message based at least in part on the multimedia content usage indicator.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Serving content-targeted ADS in e-mail, such as e-mail newsletters
ActiveUS20050076051A1AdvertisementsSpecial data processing applicationsContent IdentifierUnique identifier
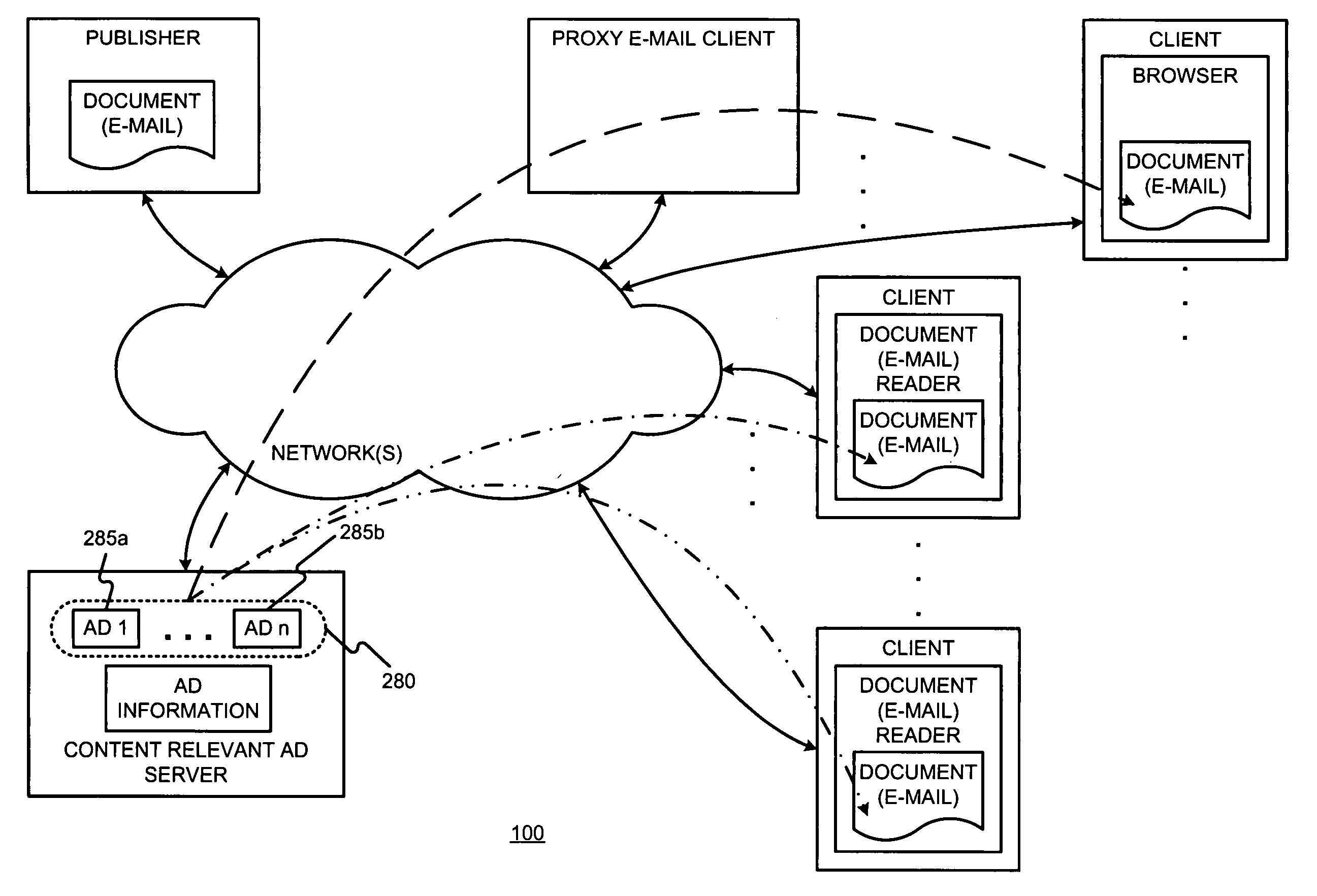
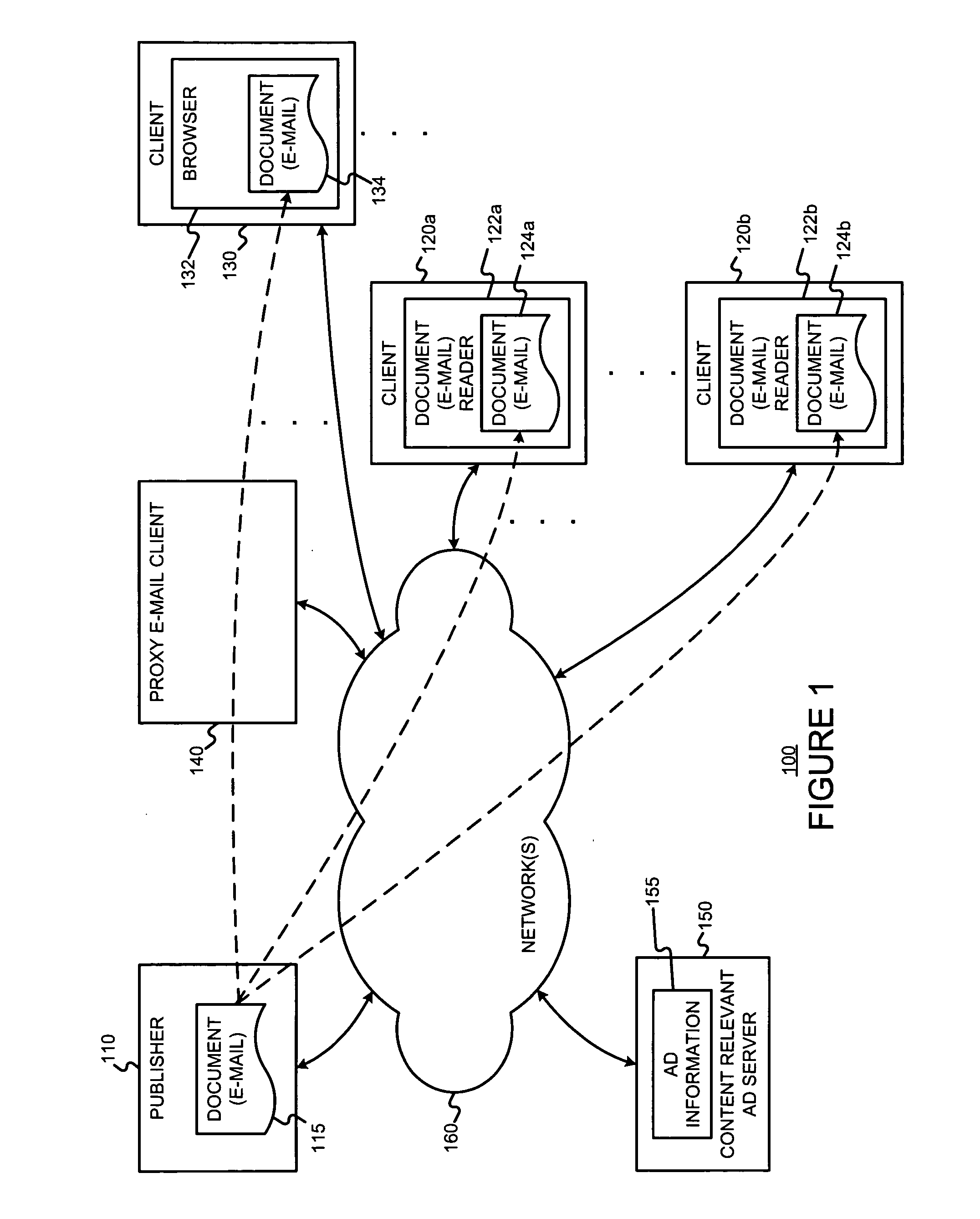
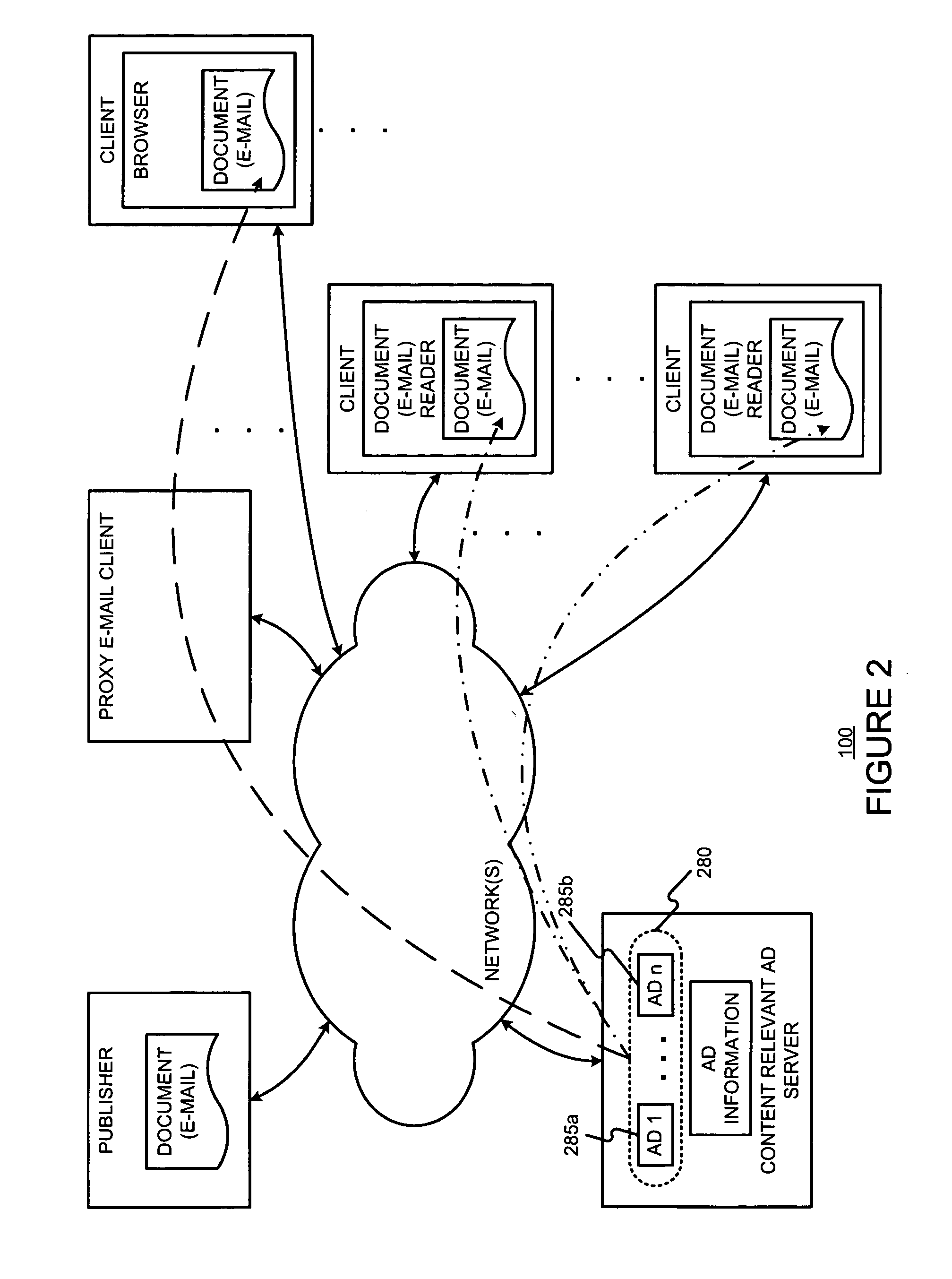
Content-targeted ads are served with e-mail messages, such as HTML e-mail messages by (i) having the document publisher include a unique content identifier in the content, (ii) having a client device pass the unique content identifier to a content-relevant ad server in a content-relevant ad request, and (iii) having the content-relevant ad server use the unique contend identifier to identify previously registered content for purposes of determining content-relevant ads. In the content-relevant ad server, multiple ads may compete for desired ad attributes (e.g., relative position on a page) or features. An arbitration process may be used to chose and / or order the ads. By having the client device pass the unique content identifier to the content-relevant ad server when it needs the ads, ads can be chosen and generated all at the time the user reads (or more generally “opens”) the e-mail document. This permits up-to-date ad information to be used when serving ads. User actions with respect to served ads may be tracked by (i) using an ad image to display ads in the document, and (ii) using an image map (included in the document originally served) to monitor user behavior with respect to an ad served in a document. All the information about the ad impression may be encoded in a unique identifier, which is returned, along with the ad image. The ad image and unique identifier may be provided to a client device. When a user selects an ad, this unique identifier may be returned to the ad server. A position of an image map clicked may also be returned to the ad server. The returned unique identifier and image position may be used to allow the ad server to determine which ad was selected. Thus, the unique identifier permits a selection to be matched with a previous ad serve.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Appliance and method for client-sided requesting and receiving of information
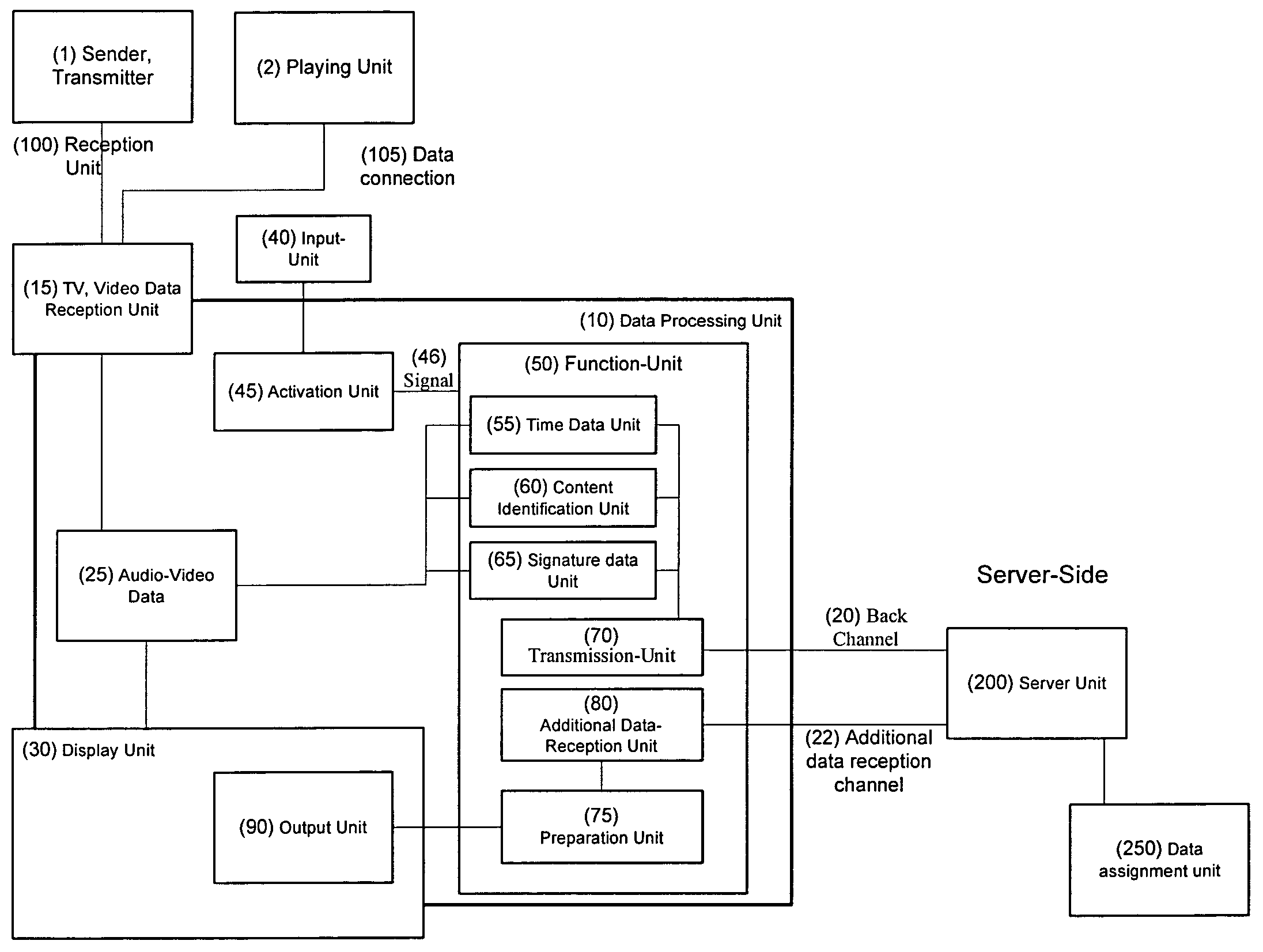
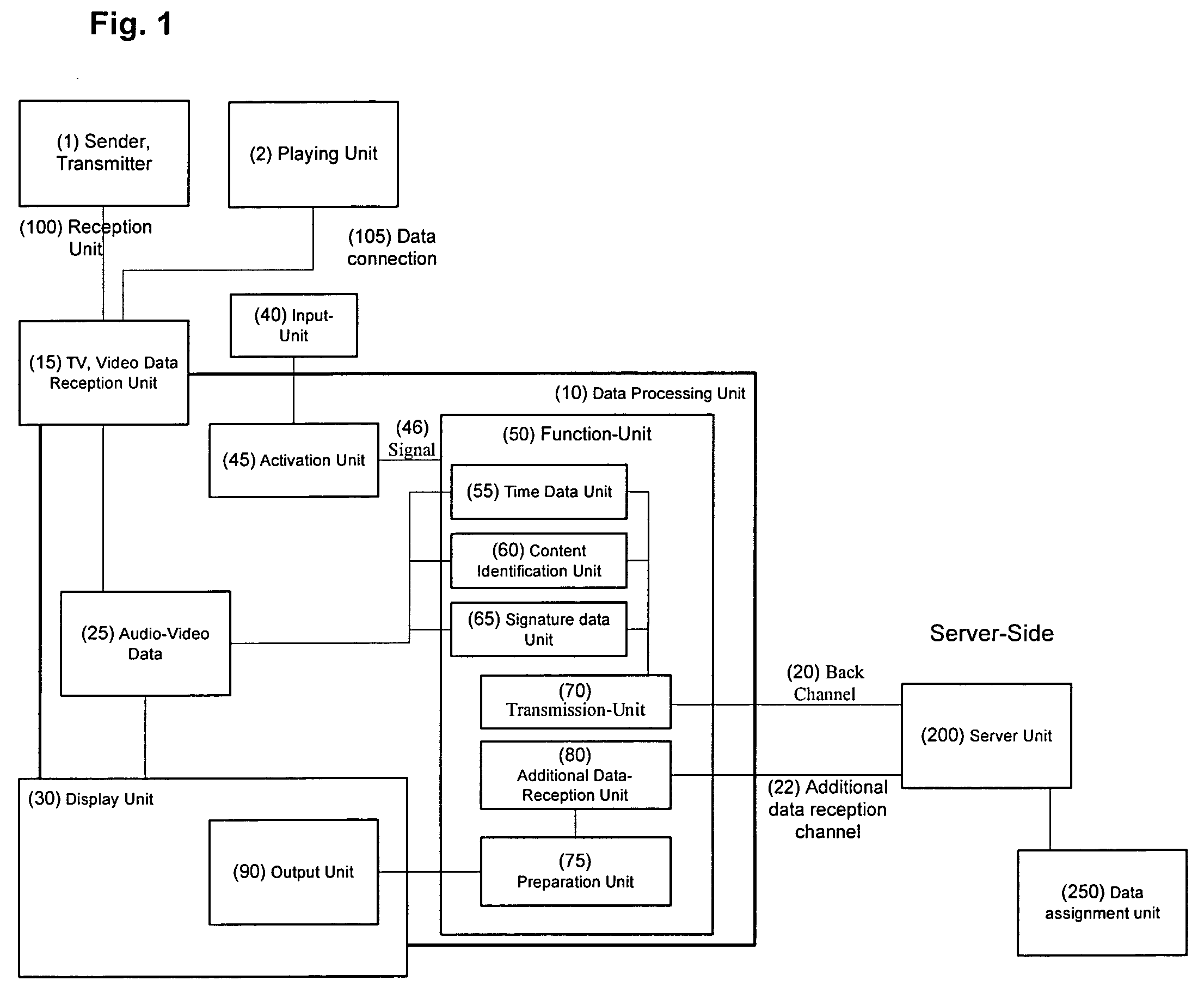
InactiveUS20070124796A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsContent IdentifierContext data
The Invention pertains to a device for the client-sided requesting, transmitting, receiving, delivering, outputting and displaying of server-sided stored data by means of context data and time index data and / or content identifier data, which are transferred to the server and to which server-sided additional data are stored and can be requested and can be displayed or outputted on the client-side.
Owner:WITTKOTTER ERLAND
Content location method and content delivery network node
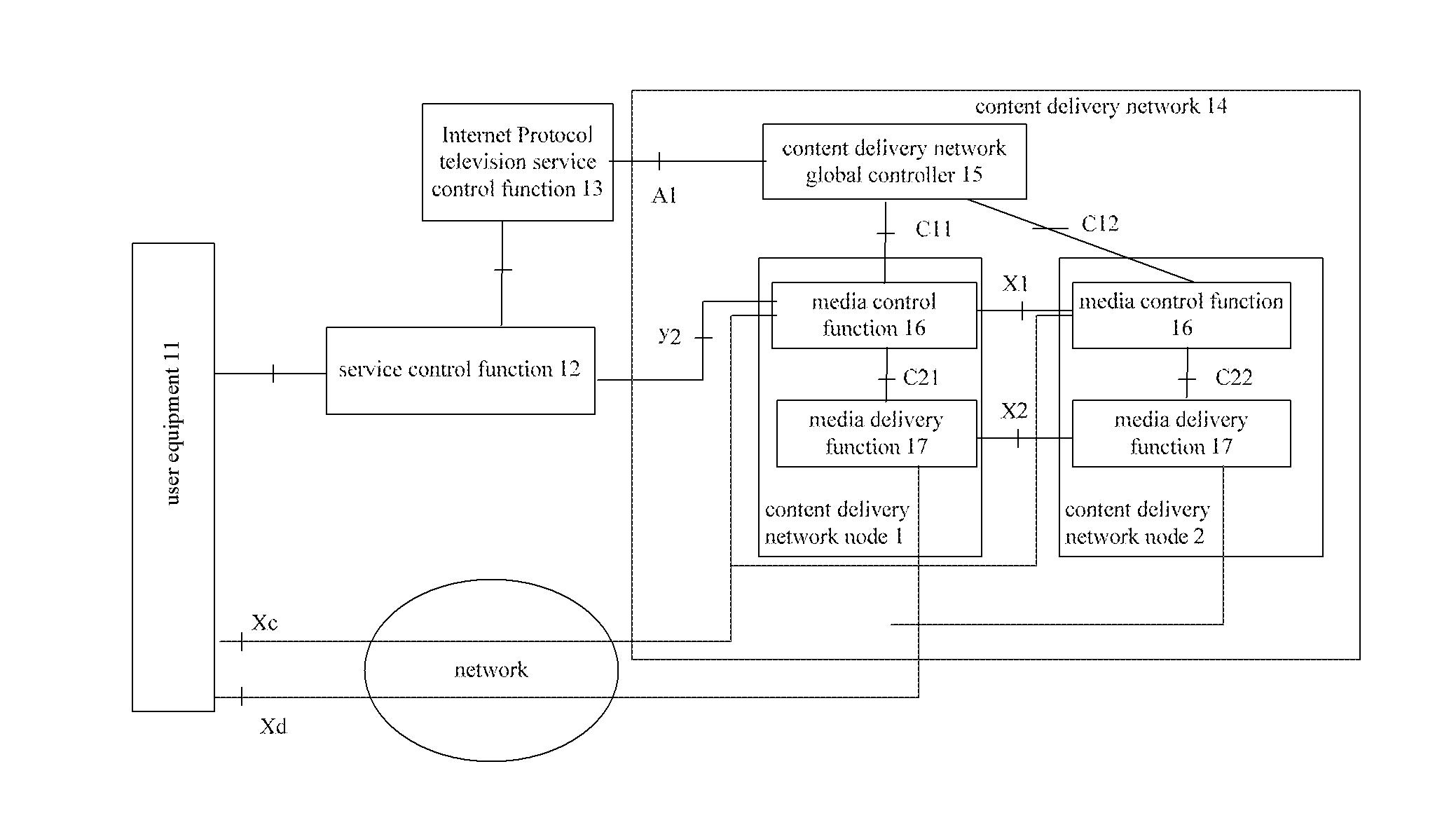
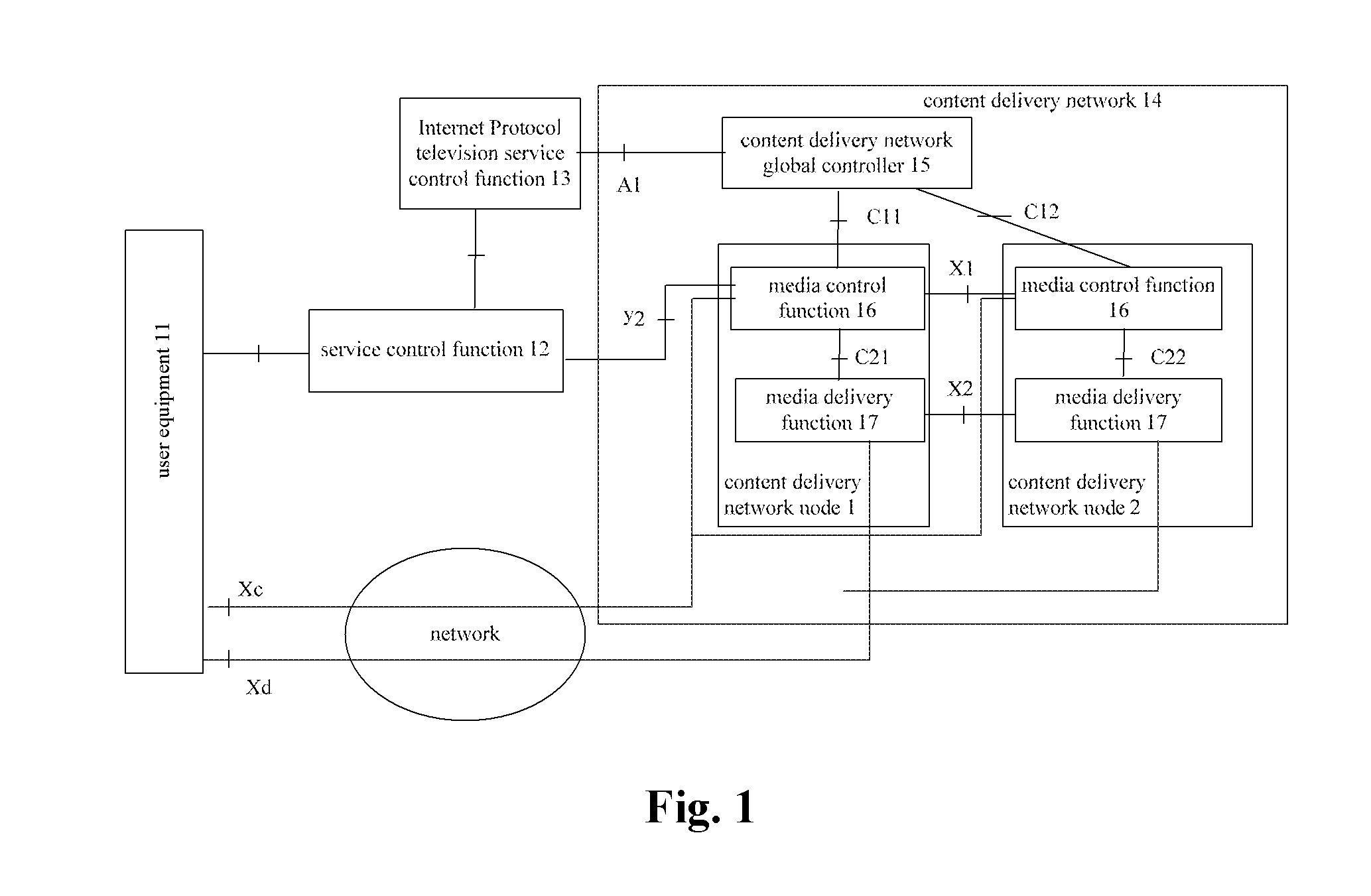
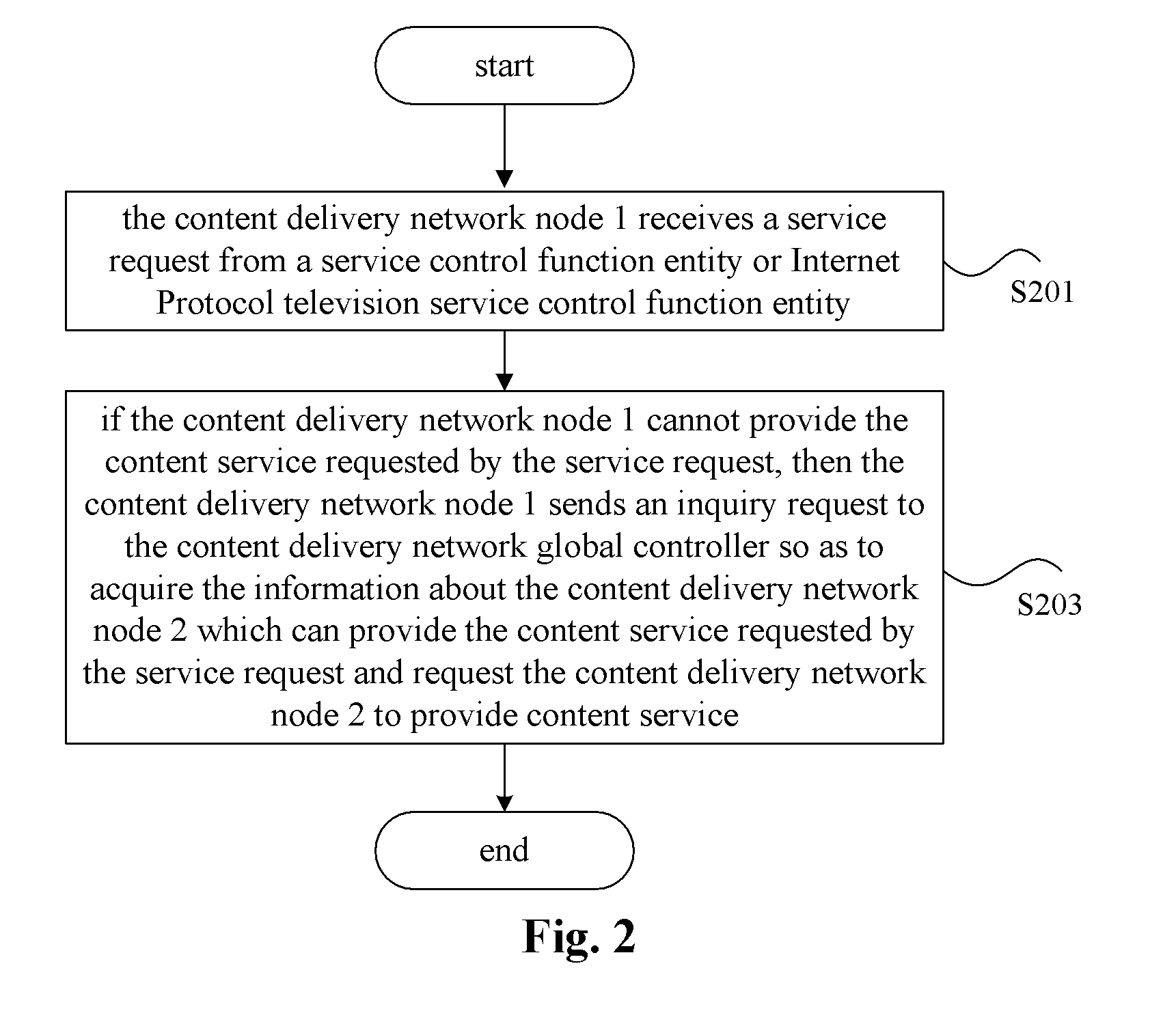
ActiveUS20120023530A1Long processing delayLow costTwo-way working systemsTransmissionContent IdentifierContent distribution
The present invention provides a content locating method and a content delivery network node. In this case, the content locating method provided by the present invention comprises: receiving by a first content delivery network CDN node a service request sent by a service control function entity or an IPTV service control function entity, wherein this service request carries a content identifier which is used to indicate requesting content corresponding to this content identifier; if the first CDN node cannot provide the content service requested by the service request, then the first CDN node sends an inquiry request to a CDN global controller so as to acquire the information about a second CDN node which can provide the content service requested by the service request and request the second CDN node to provide the content service. By way of the present invention, the pressure of the CDN global controller can be reduced and the processing delay of CDN can be shortened.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for differential, bandwidth-efficient and storage-efficient backups
InactiveUS7257257B2Error detection/correctionCharacter and pattern recognitionContent IdentifierBandwidth efficient
Owner:INTEL CORP
Rights Management System and Methods
ActiveUS20070294173A1Difficult to controlDifficult to trackDigital data processing detailsRecord information storageContent IdentifierRights management
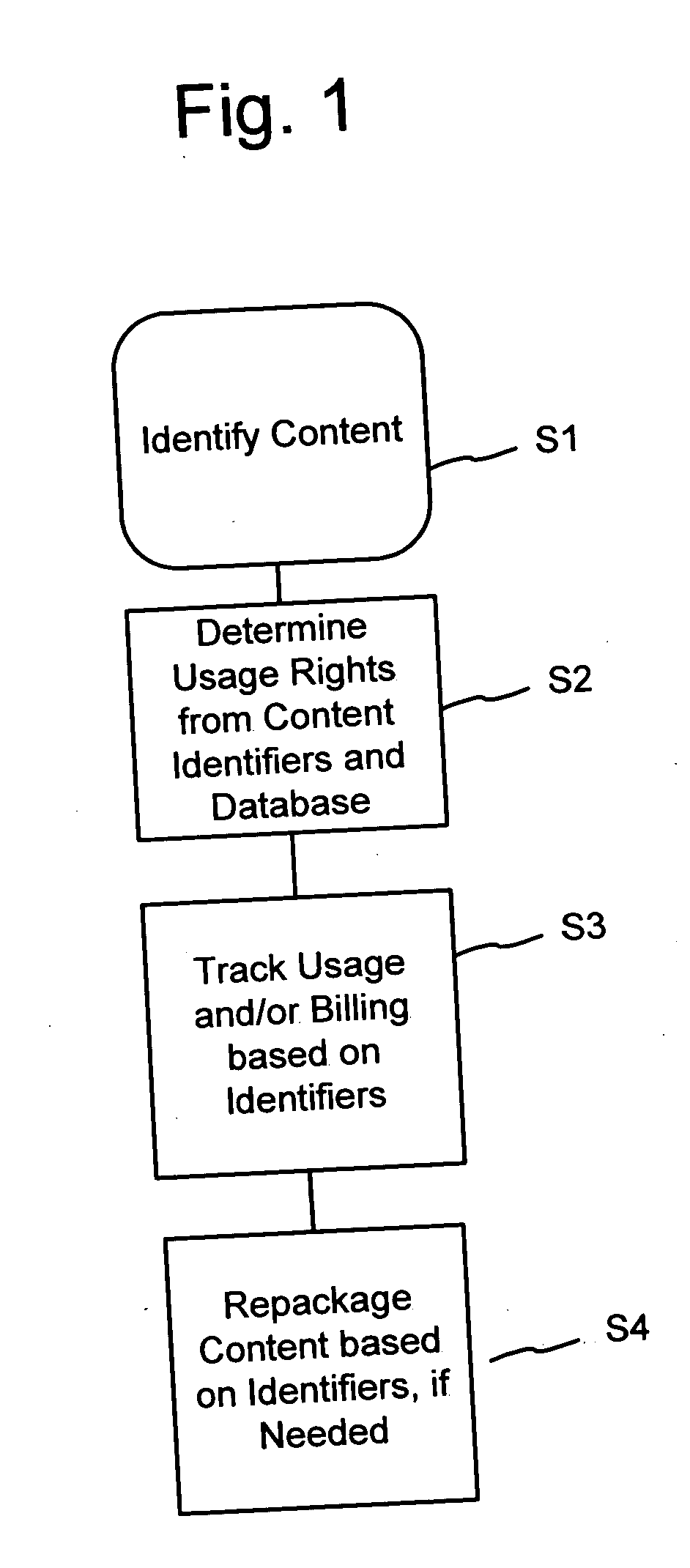
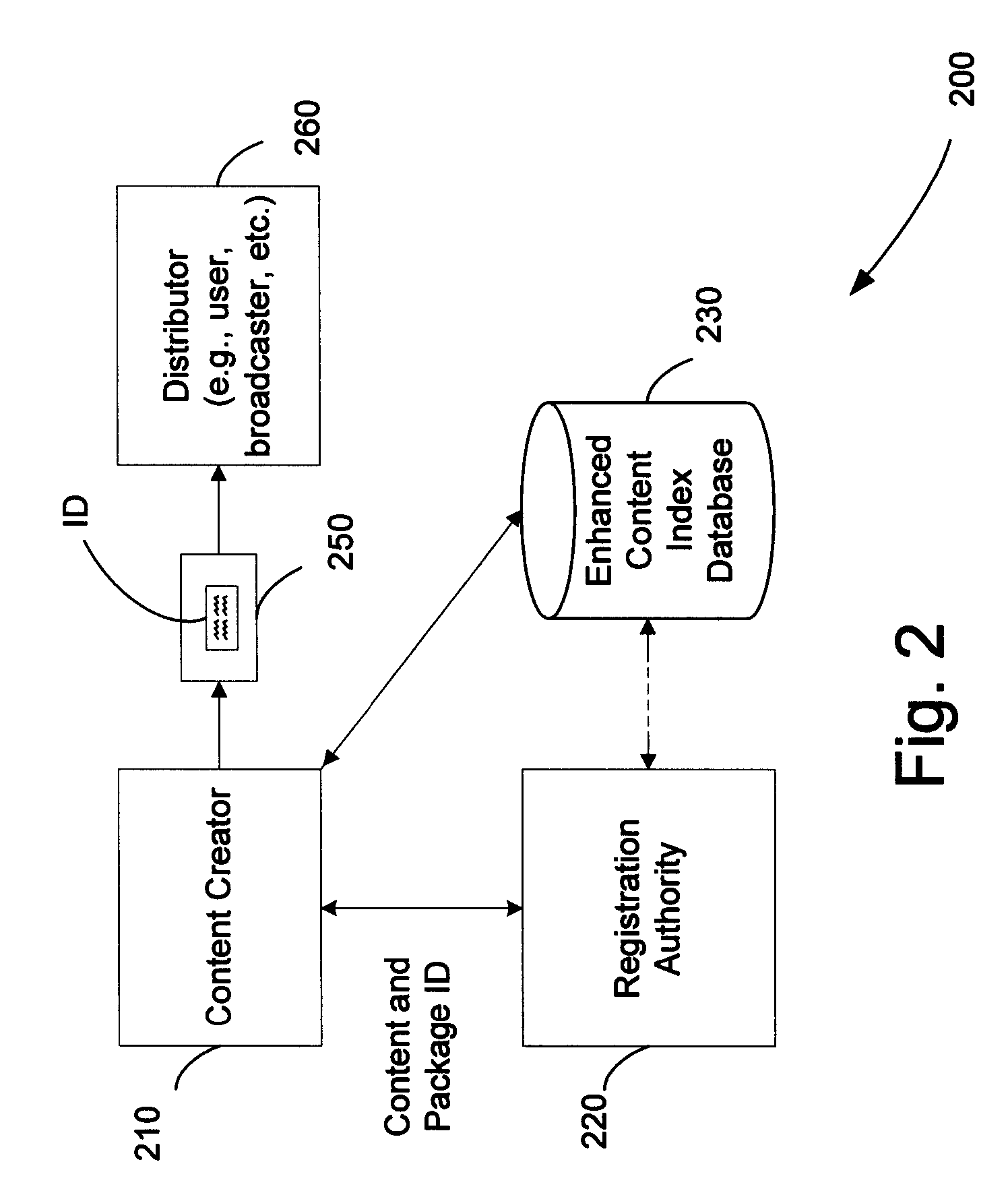
A method of performing digital asset management of content is provided. The content is identified with an identifier. The identifier can be identified with a digital watermark, header file, or both. The identifier is linked to usage rules to regulate usage and protect the content. The usage rules can be maintained on a remote or local database or server. Once extracted, an identifier is used to index the database to locate a corresponding usage rule, and can be used to override copy control information with proper purchase and subsequent protection. Content can be managed from such. In another embodiment, an identifier is used to track usage, such as amount of content viewed, time played, and copies made. In yet another embodiment, a content identifier is used to regulate content throughout a distribution chain, and a distributed set of databases with information relevant only to the owner of the database act as one database due to a central router.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Method and device for reconstructing torrent content metadata
A method for reconstructing torrent content metadata, i.e. a torrent identifier, a segment length and an amount of segments of a torrent content file, without access to the torrent content metafile, comprises the steps of: A. obtaining the torrent content identifier from torrent signaling from a client; B. obtaining a torrent content file size from said torrent signaling from said client; C. obtaining a tracker address from said torrent signaling from said client: D. obtaining a peer address from a tracker; E. contacting a peer via the peer address; F. downloading sequential minimum size blocks of a full size segment from the peer in order to determine the segment length; G. calculating the amount of segments from the torrent content file size and the segment length.
Owner:PIECE FUTURE PTE LTD
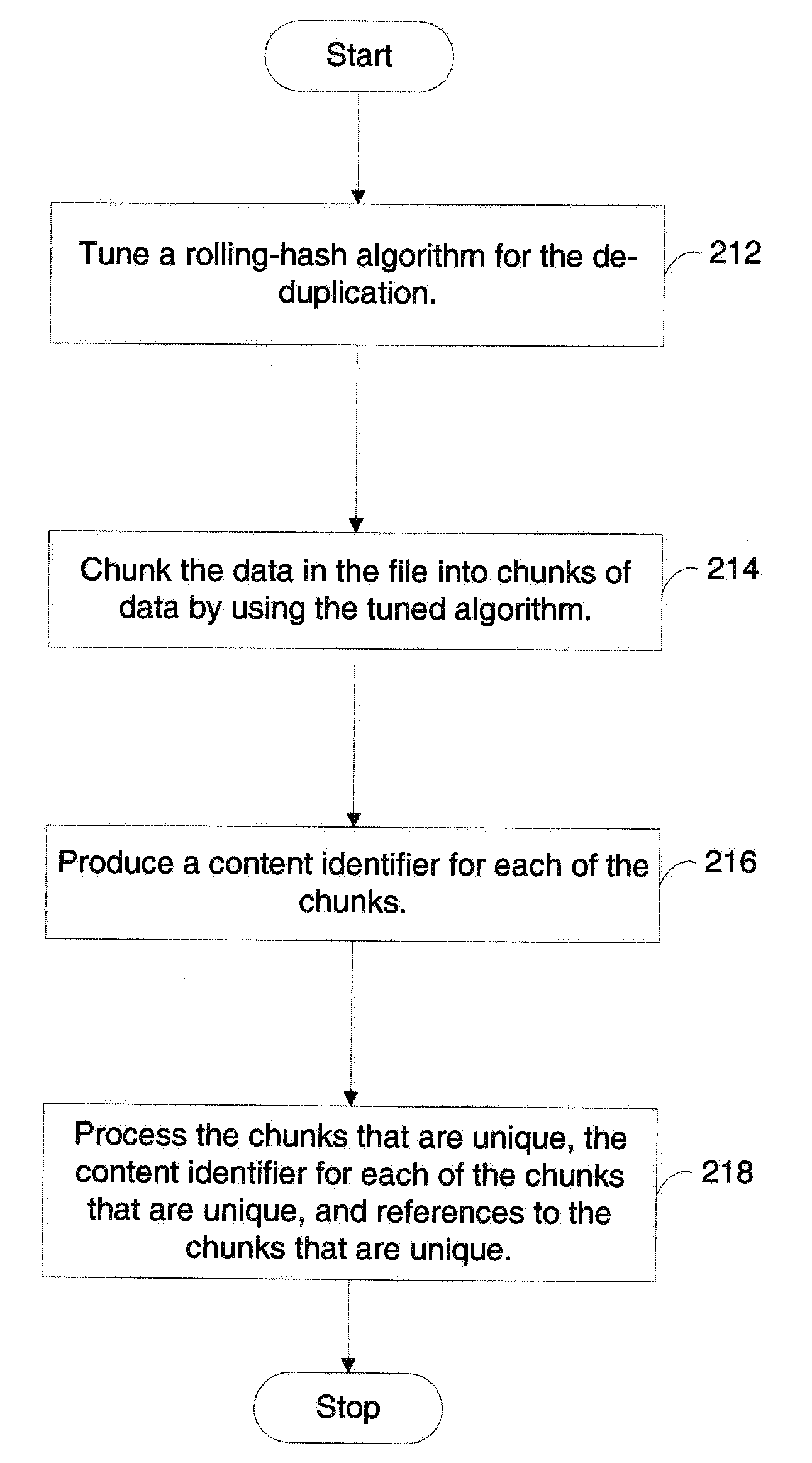
Performing de-duplication for at least one computer file in a computer system
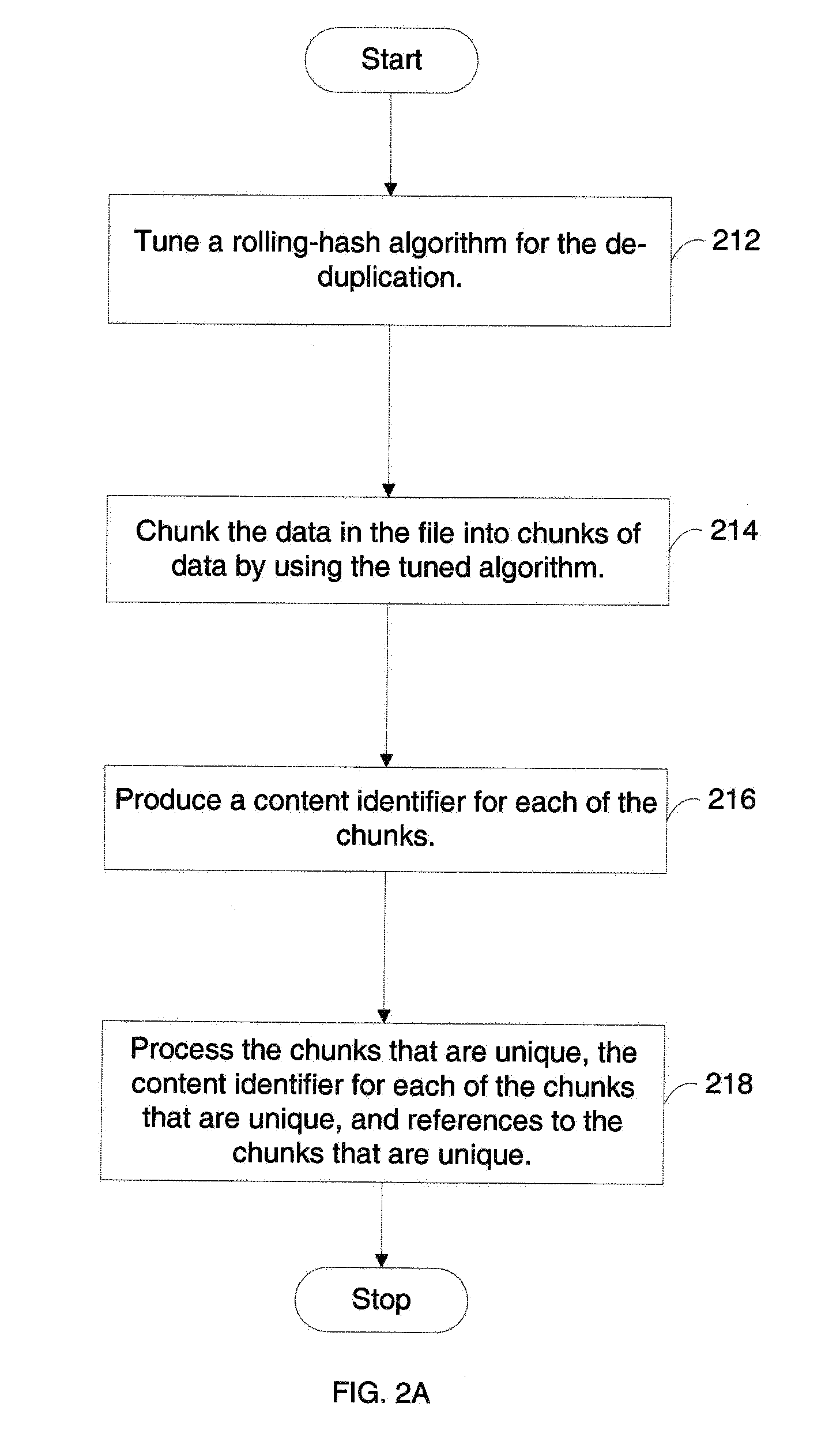
InactiveUS20090276454A1Decreasing chunk sizeIncreased chunk sizeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsContent IdentifierRolling hash
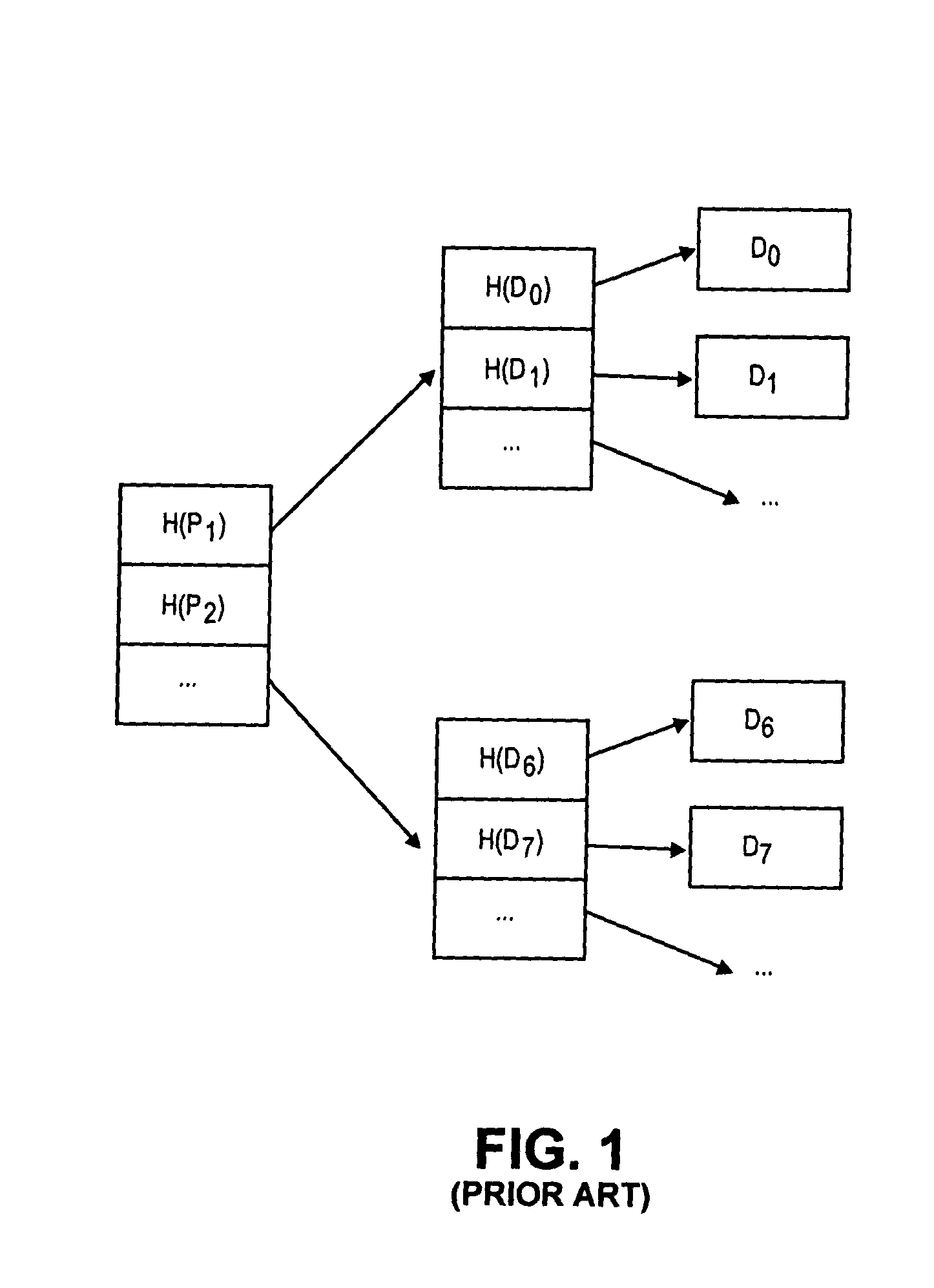
The present invention provides a method and system of performing de-duplication for at least one computer file in a computer system. In an exemplary embodiment, the method and system include (1) tuning a rolling-hash algorithm for the de-duplication, (2) chunking the data in the file into chunks of data by using the tuned algorithm, (3) producing a content identifier for each of the chunks, and (4) processing the chunks that are unique, the content identifier for each of the chunks that are unique, and references to the chunks that are unique. In an exemplary embodiment, the computer system includes a de-duplication-enabled data store. In an exemplary embodiment, the computer system includes (a) a transferor computer system that is configured to transfer the file to a de-duplication-enabled computer system and (b) the de-duplication-enabled computer system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Content Indexing and Searching Using Content Identifiers and Associated Metadata
A method of indexing content for network searching comprises obtaining media content signals stored on a computer network; deriving content identifiers from the content signals; using the content identifiers to obtain metadata used to classify the media content signals; and creating a searchable index of the media content signals based on the metadata, wherein users access the searchable index on the distributed computer network to submit a search query for the searchable index to retrieve links to the media content signals.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and method for automatically verifying storage of redundant contents into communication equipments, by data comparison
InactiveUS9130918B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationContent IdentifierRedundant code
A method is intended for verifying storage of contents into communication equipments connected to at least one communication network. This method consists, when a first communication equipment stores a content and wants to verify that this content is still stored into a second communication equipment: i) in transmitting a first request, comprising at least an identifier of this content and first data representative of this content and requiring verification of the storage of this content into the second communication equipment, to an auxiliary communication equipment acting as an interface between the communication network and the second communication equipment, ii) in transmitting a second request, comprising at least the content identifier, to the second communication equipment, to require transmission of second data representative of the content to the auxiliary communication equipment, and in triggering a timeout having a chosen duration, and iii) if the auxiliary communication equipment has received the second data before expiration of this timeout, in comparing these received second data, possibly after having processed them, to the received first data, and in transmitting a message representative of the result of this comparison to the first communication equipment.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
System and method of using a proxy server to manage lazy content distribution in a social network
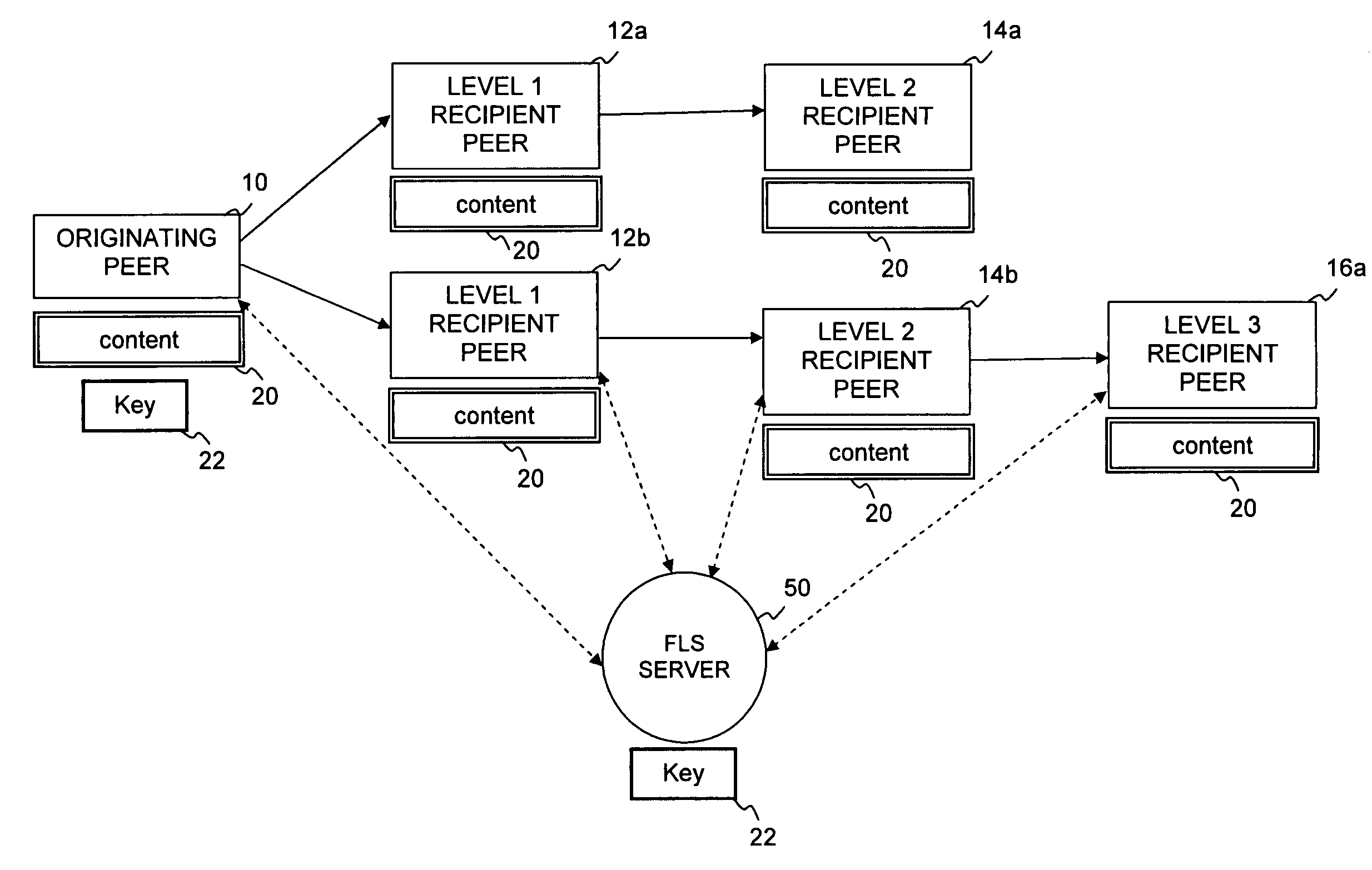
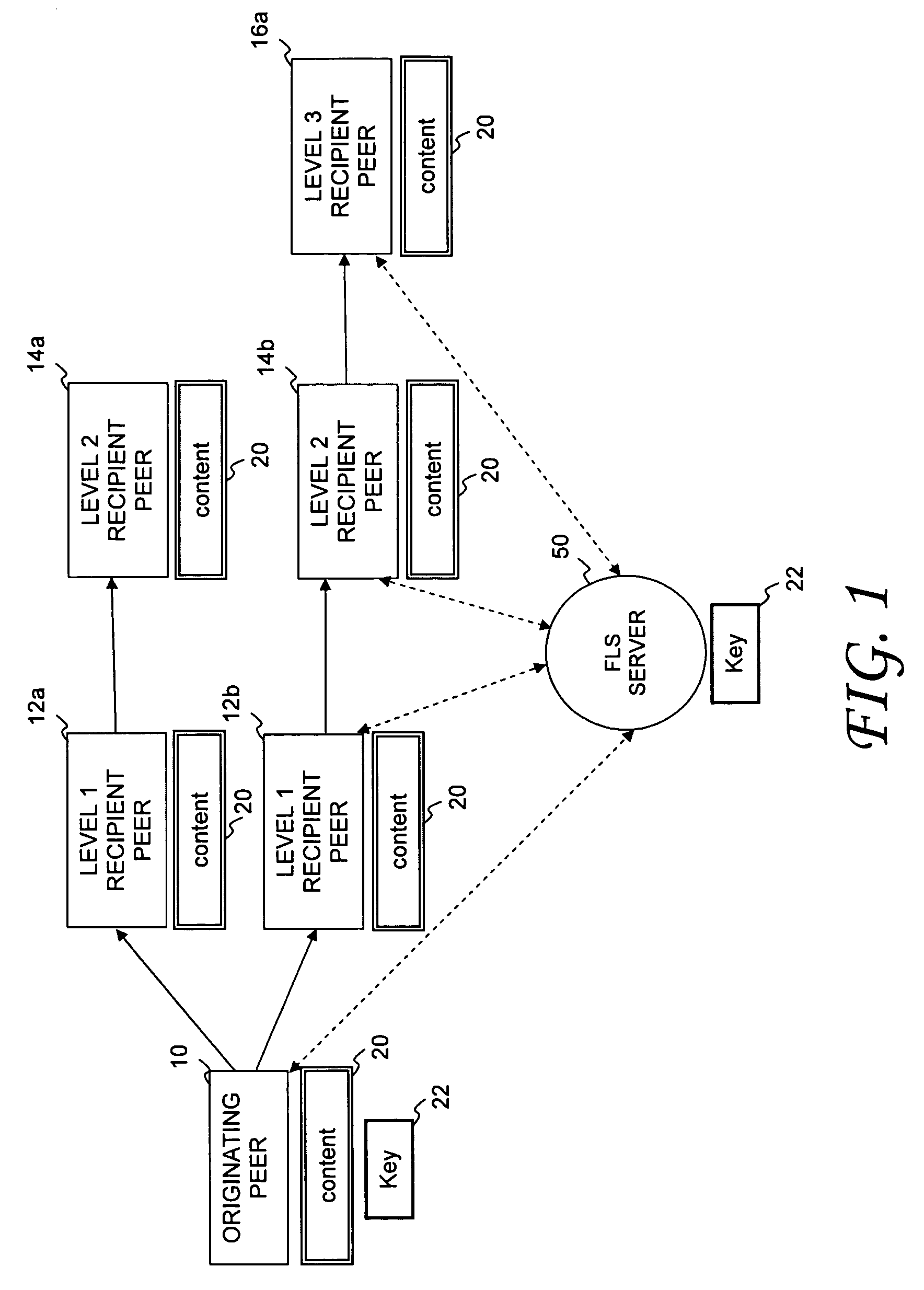
InactiveUS7925592B1Secret communicationProgram/content distribution protectionContent distributionContent Identifier
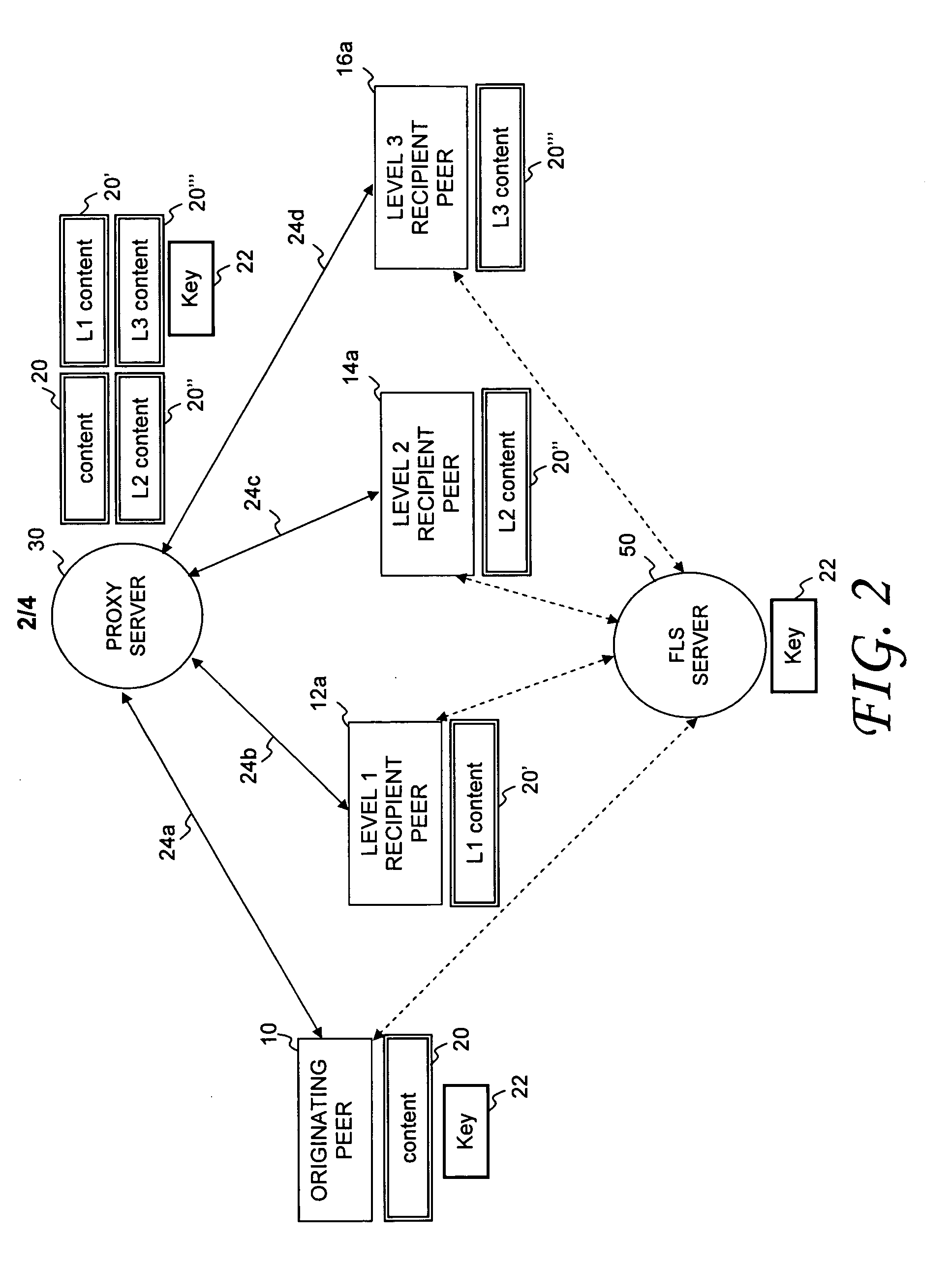
A proxy server and corresponding method are provided for managing the controlled distribution of digital content as it propagates through a social network. A proxy server receives digital content and associated distribution parameters from an originating peer. The distribution parameters define access rights for n allowable levels of possible network distribution. After other peers are invited to share the digital content or the invited peers request access to the digital content, the proxy server generates a rights-managed form of the requested digital content in accordance with the access rights established by the originating peer for the level associated with the requesting peer(s). The proxy server forwards a copy of a content key and other content identifiers to an associated license server and then sends the rights-managed form of digital content to the requesting peer(s).
Owner:QURIO HLDG
Method and system for data distribution
InactiveUS20030028660A1Special service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsContent IdentifierService provision
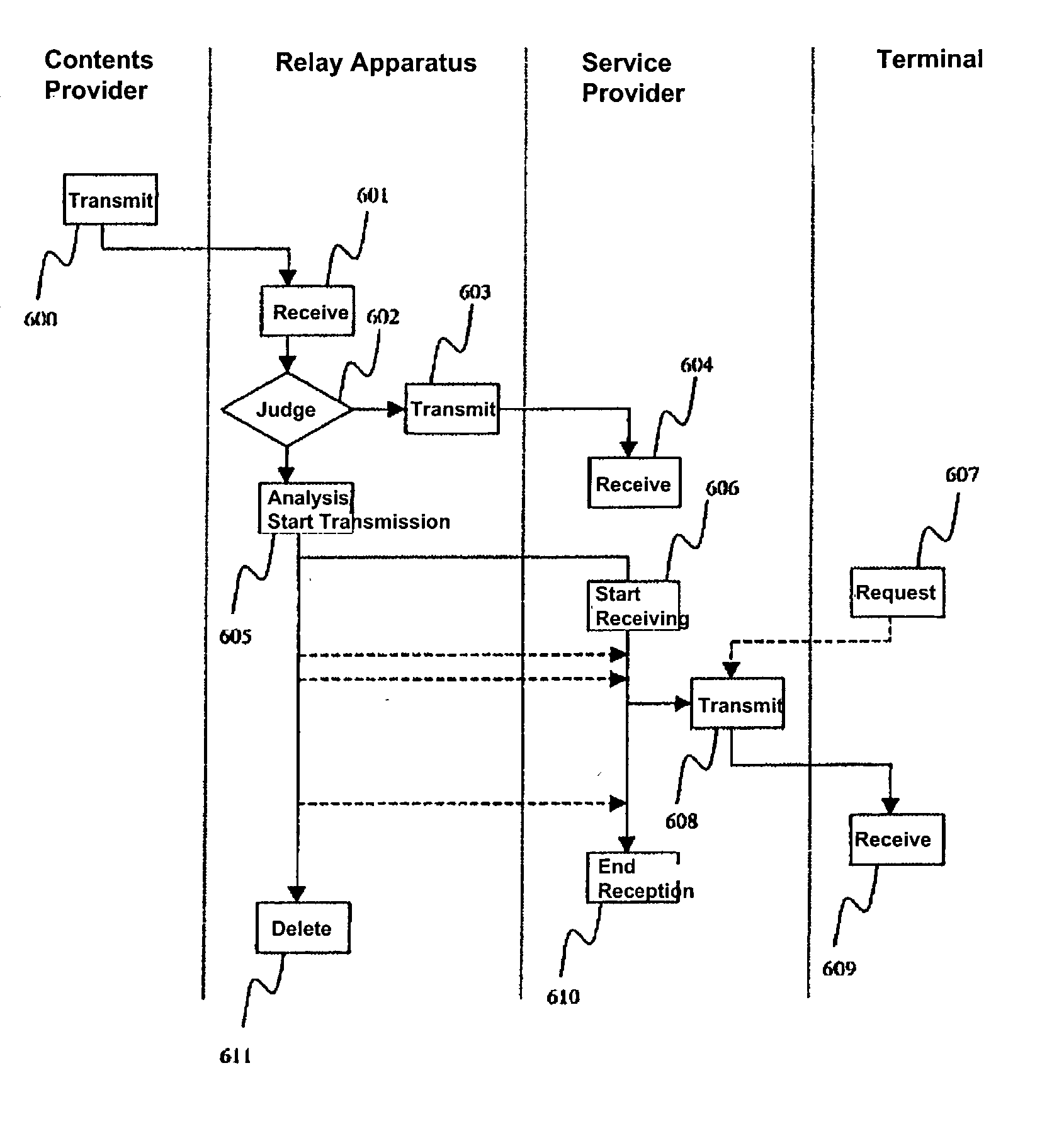
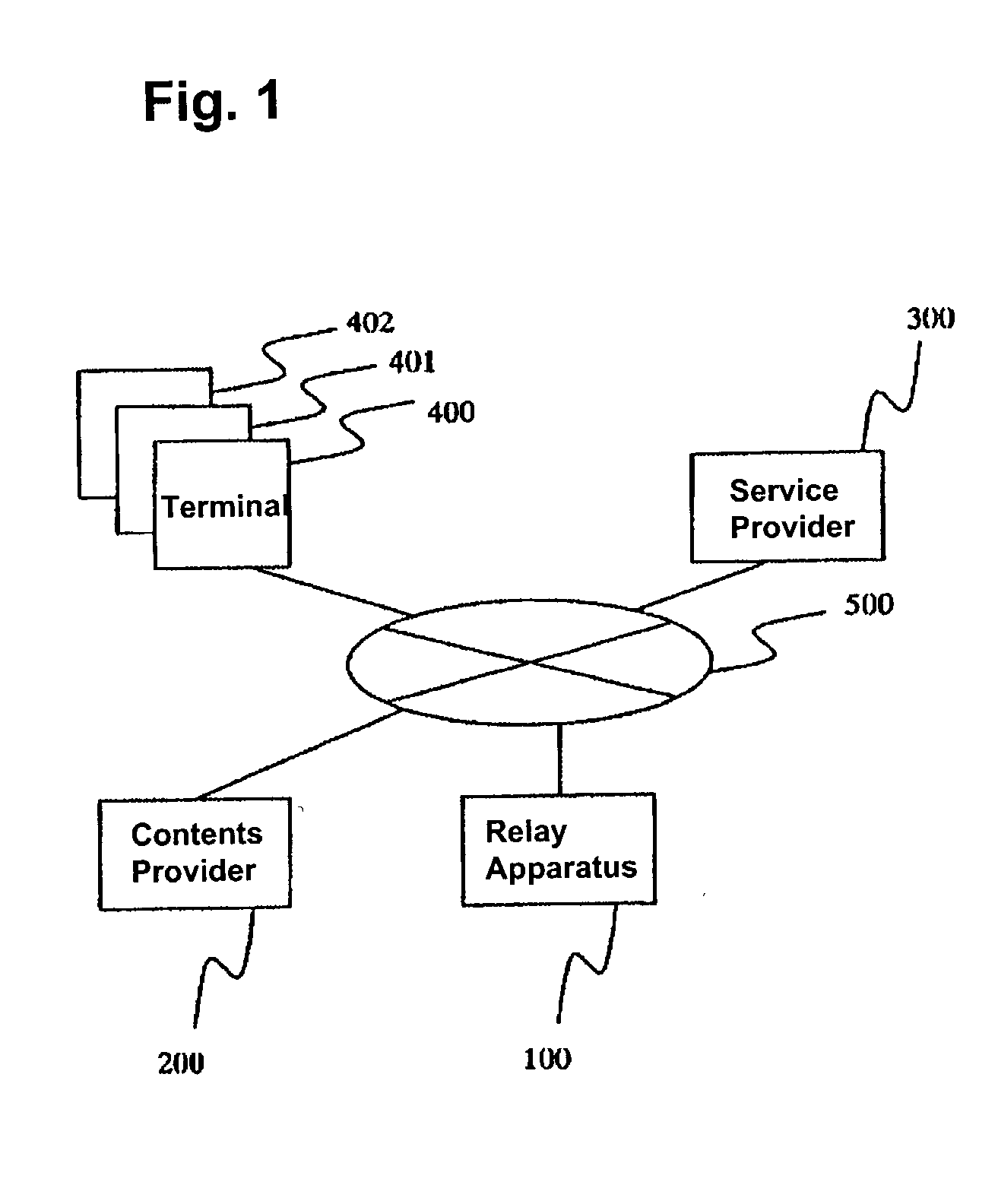
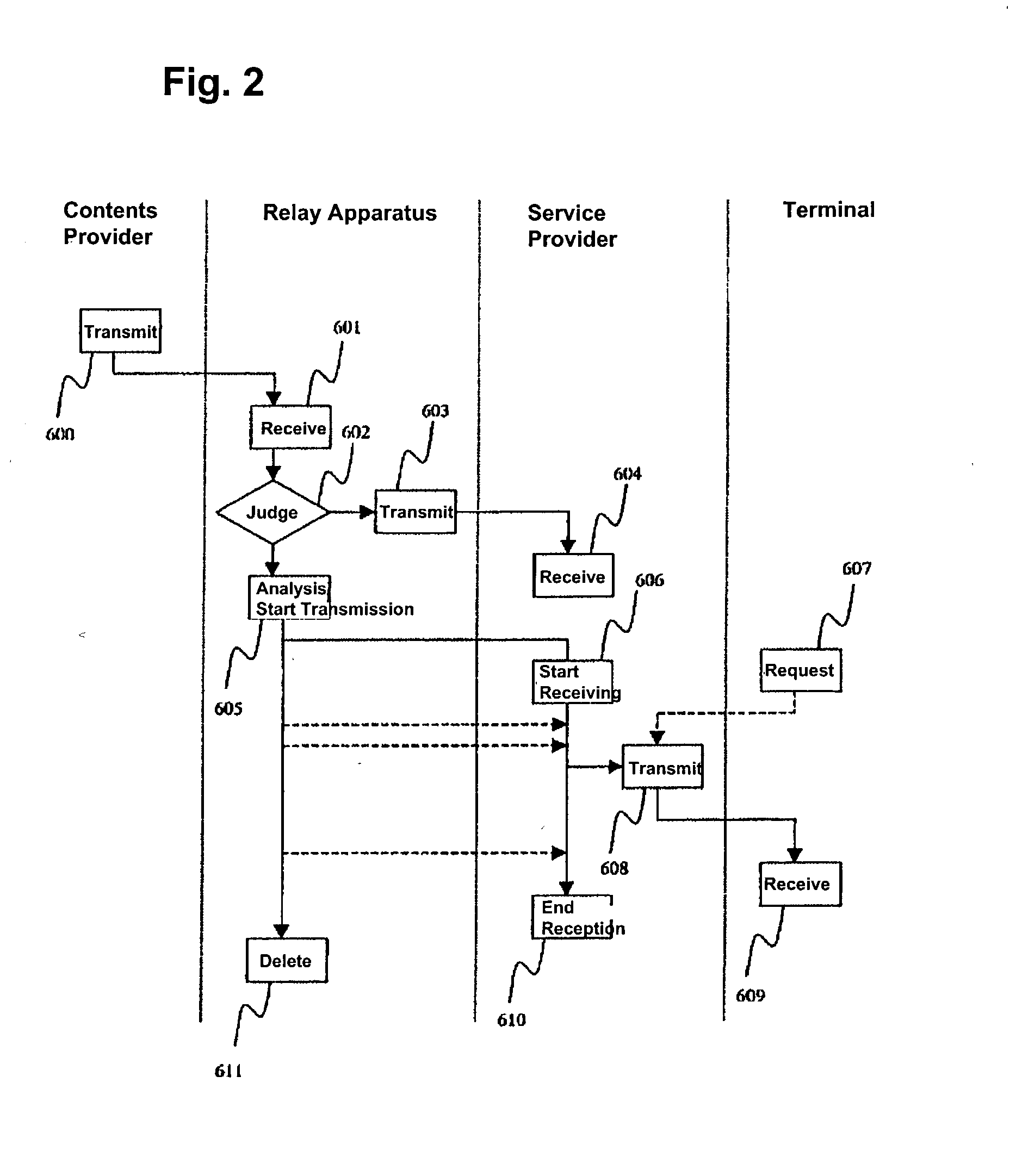
A relay apparatus on a network includes an analysis section that analyzes multimedia contents transmitted from a contents provider. The relay apparatus temporarily stores contents identifiers, component information of the contents, and element data pointed by pointers of the component information, and creates a transmission sequence for transmitting the element data. A transmission section transmits the contents identifier, the contents component information and the element data according to the transmission sequence to a service provider. When the relay apparatus receives a request from a terminal or from a service provider even before the service provider completes registration of the entire multimedia contents, the relay apparatus or the service provider can start rendering multimedia transmission services to the terminal.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
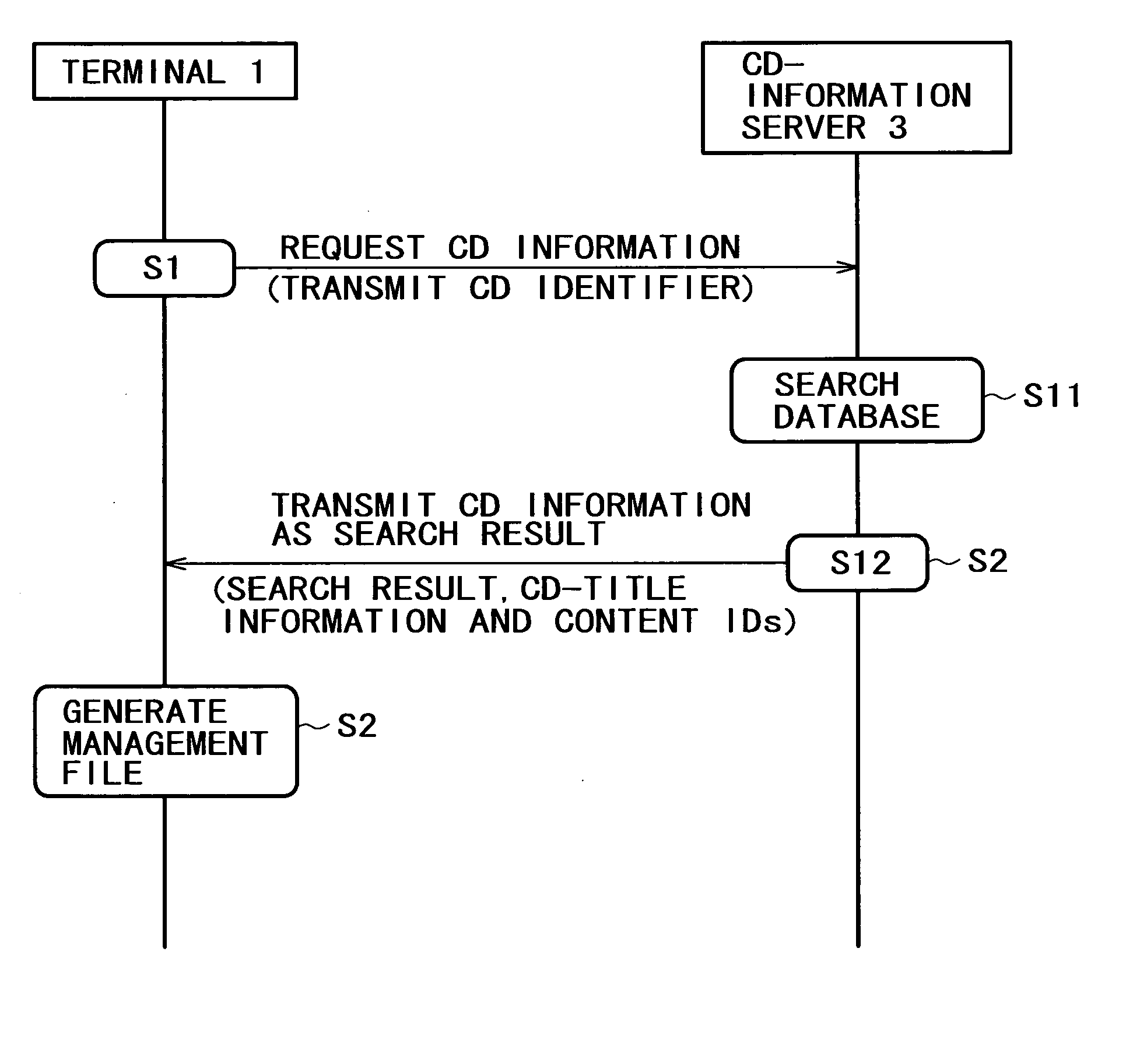
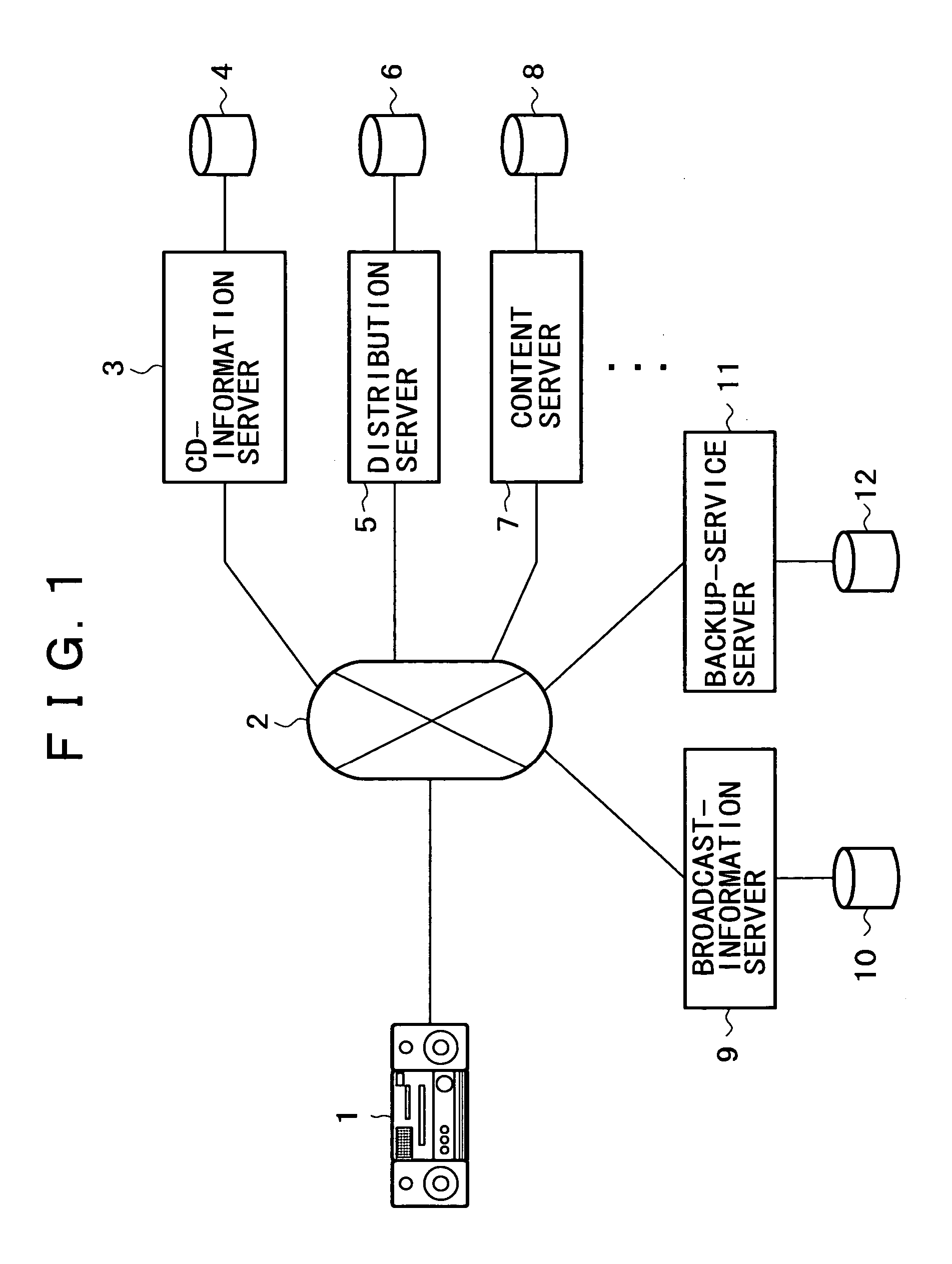
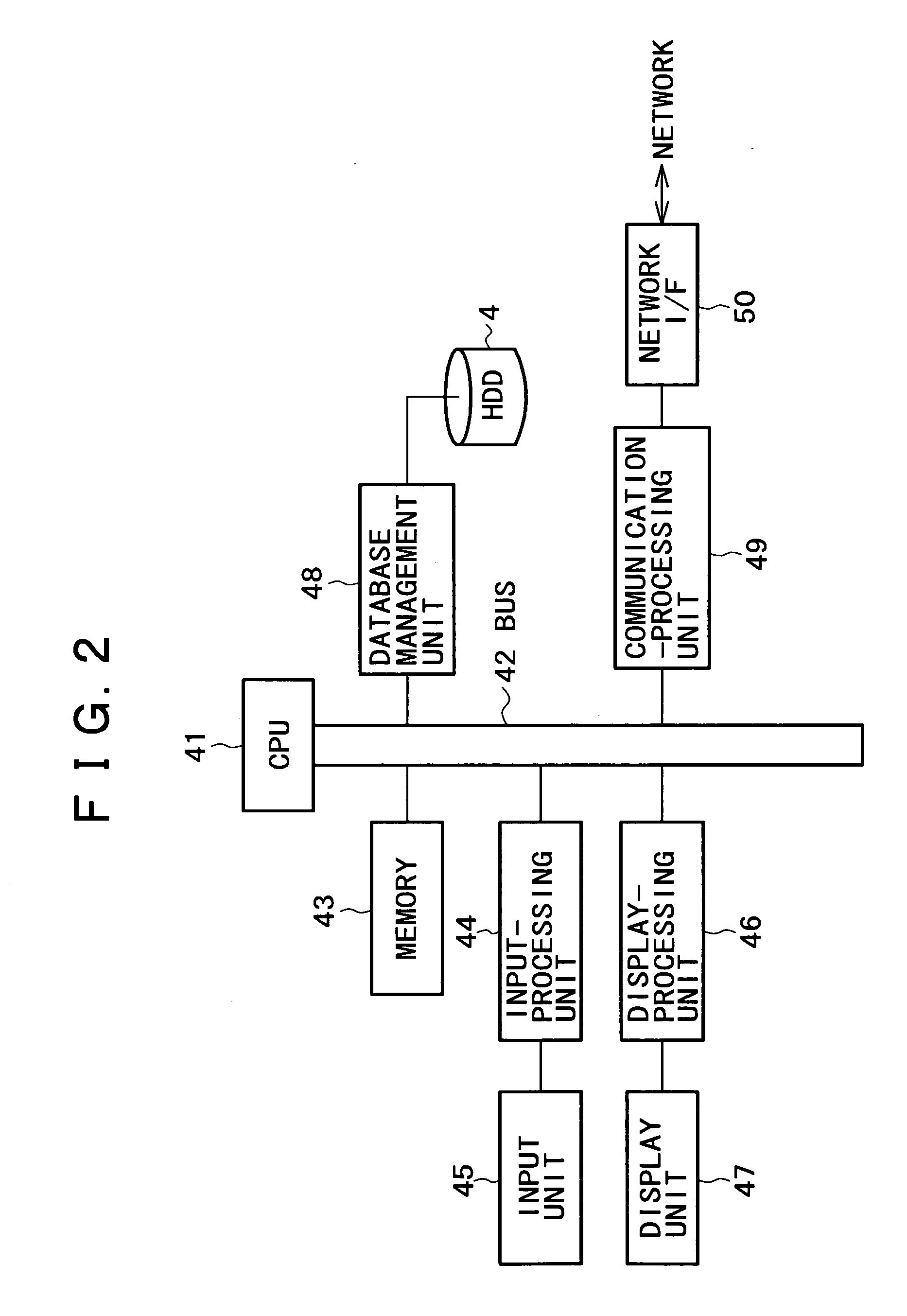
Information communicating terminal, information distributing apparatus, information distributing system, content managing method, broadcast receiving method, information distributing method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20050203992A1Function increaseMetadata audio data retrievalMetadata multimedia retrievalContent IdentifierHard disc drive
In a server serving as an information distribution apparatus and an information communication terminal, contents are managed by using content identifiers (content IDs) managed as IDs conforming to a rule of uniformity. Particularly, in the information communication terminal, a content ripped from a recording medium such as a CD, and stored in a storage element, such as a hard disk drive, is also managed by using a content identifier acquired from the information distribution apparatus. In this way, contents stored in the storage element can be managed by using content IDs each managed as an ID common to the information communication terminal and the information distribution apparatus. In communication between the information communication terminal and the information distribution apparatus, a content identifier conforming to a rule of uniformity is used for identifying a content to which the content identifier is assigned, so that the terminal is capable of downloading the content as well as acquiring additional information relevant to the content from the apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com