Handling packet reordering at a network adapter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
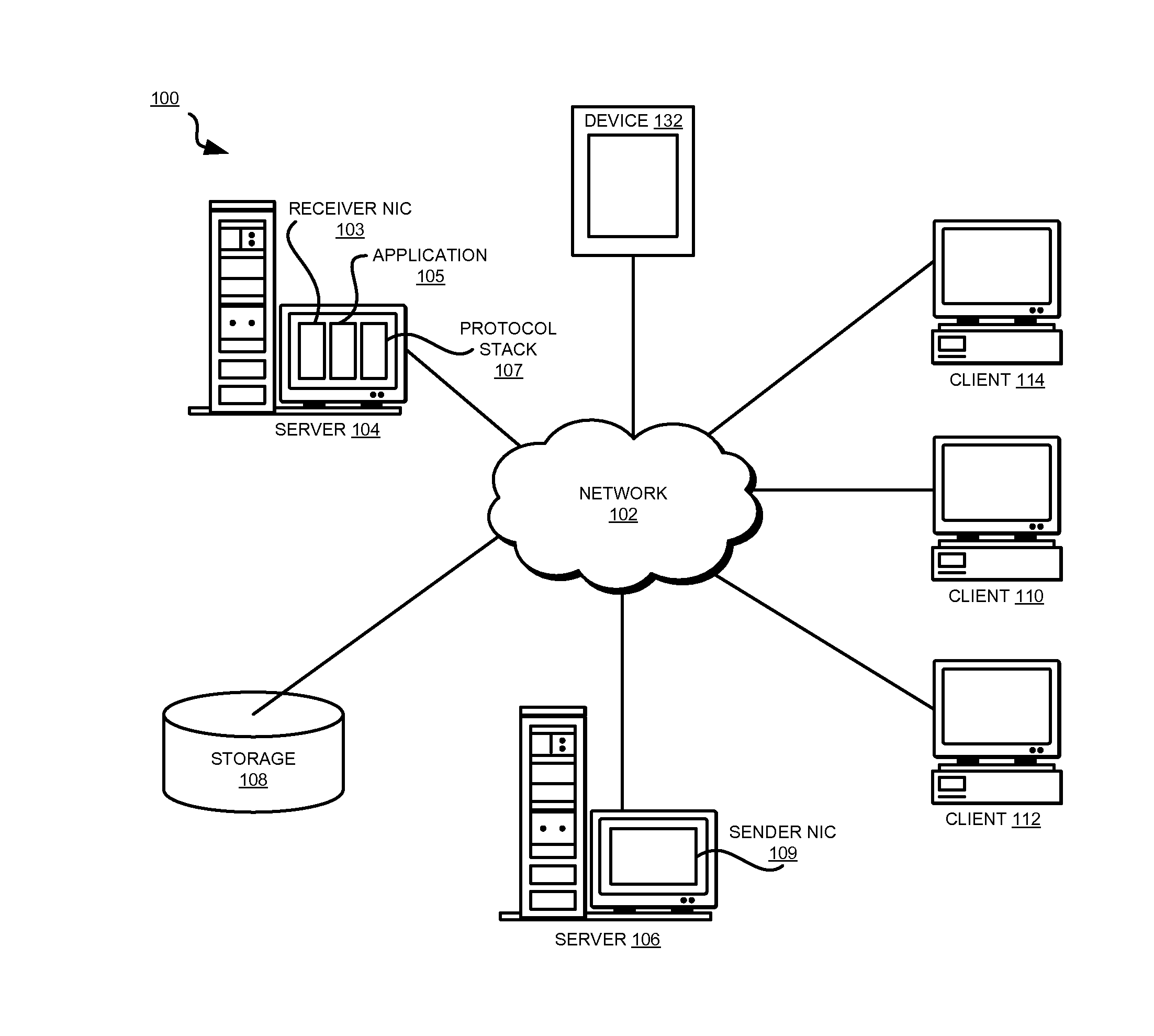
[0043]Changing the order or sequence of data packets from an original sequence in which the data packets are transmitted from a sender system to a changed sequence in which the data packets are received at a receiver system is called reordering of data packets, or packet reordering. Packet reordering also includes changing the sequence of the data packets by dropping, losing, or otherwise omitting a packet from the sequence.
[0044]For example, suppose that a sender system sends packets P0, P1, and P2 of a particular flow in that sequence. A receiver system receives reordered packets if the receiver system receives packets P1, P0, and P2, in that order. In this reordered sequence, P0 is an out of order or out of sequence packet. The receiver system also receives reordered packets if the receiver system receives packets P0 and P2 without timely receiving packet P1. In this reordered sequence, P2 is an out of sequence packet.
[0045]Now suppose that sender system A is sending packets P0, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com