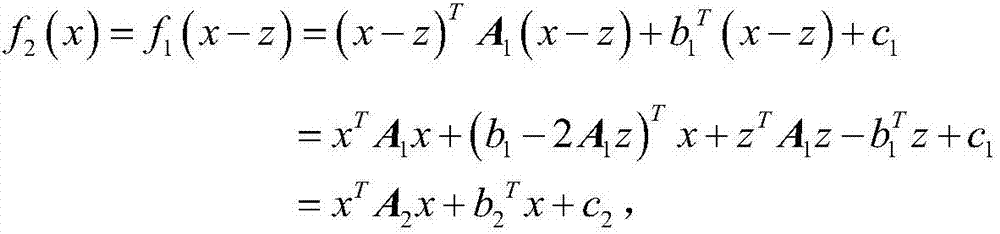Dense trajectory covariance descriptor-based behavior recognition method
A recognition method and descriptor technology, applied in the field of video processing, can solve the problems of low accuracy of behavior recognition results, failure to consider dynamic characteristics of behavior subjects, and inability to accurately describe behavior and motion, and achieve the effect of improving description ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] The implementation of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
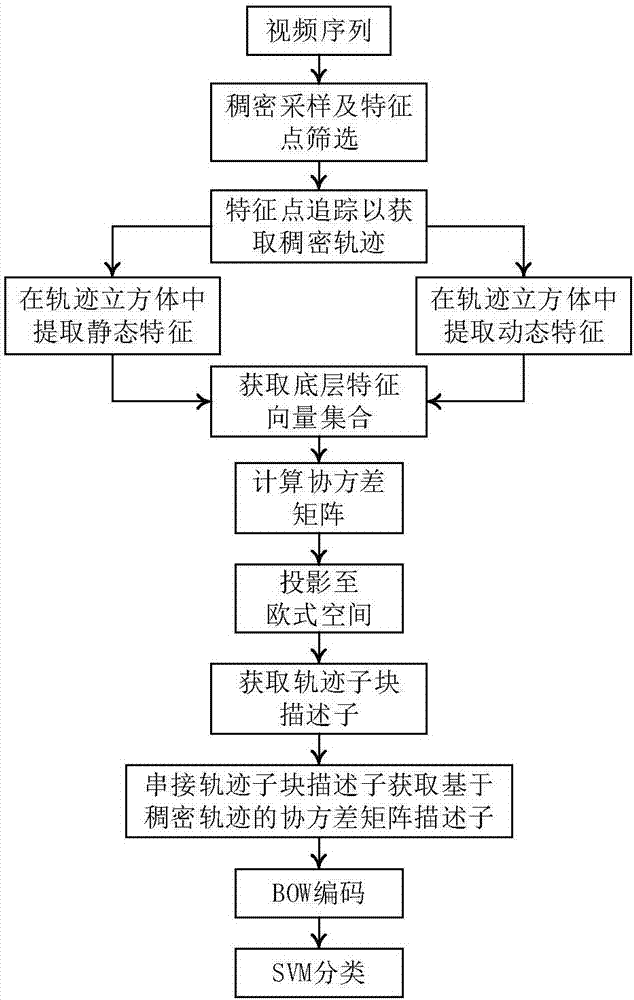
[0024] refer to figure 1 , the behavior recognition steps based on the dense trajectory covariance descriptor of the present invention are as follows:
[0025] Step 1, densely sample the video sequence, and calculate the dense optical flow f at the sampling point.
[0026] (1.1) Carry out grid sampling every w pixels of the video frame to obtain sampling points, and the value of parameter w is set to 5;
[0027] (1.2) Use Gunnar for the sampling points obtained in (1.1) Algorithm to calculate optical flow:
[0028] (1.2a) Express the neighborhood pixel values of each pixel in the image as a quadratic polynomial:
[0029] f(x)=x T Ax+b T x+c,
[0030] Among them, f(x) represents the pixel value corresponding to the neighborhood x, A is a symmetric matrix, b is a vector, and c represents the offset. These parameters can be estima...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com