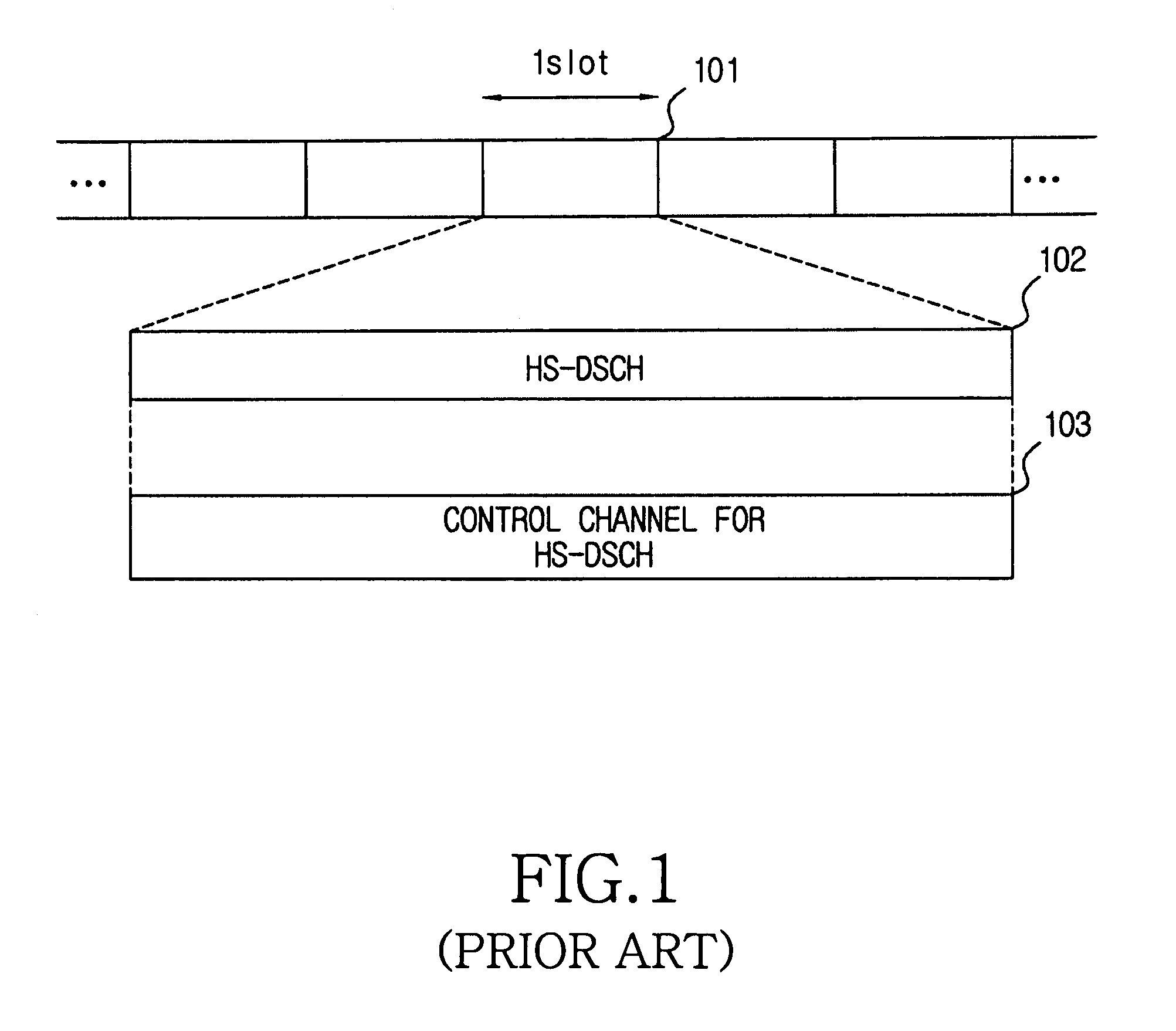
Patents
Literature
287 results about "W-CDMA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
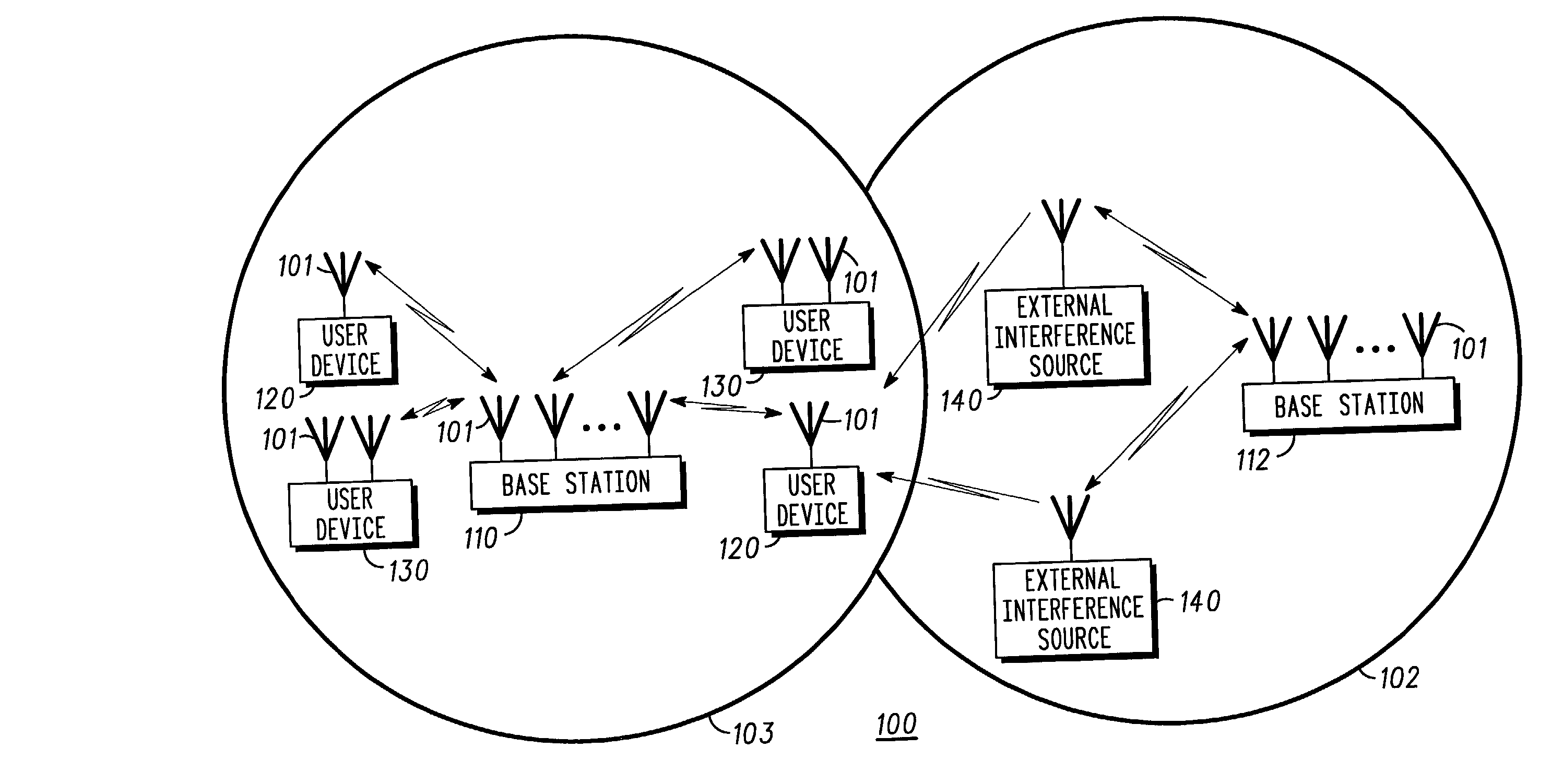
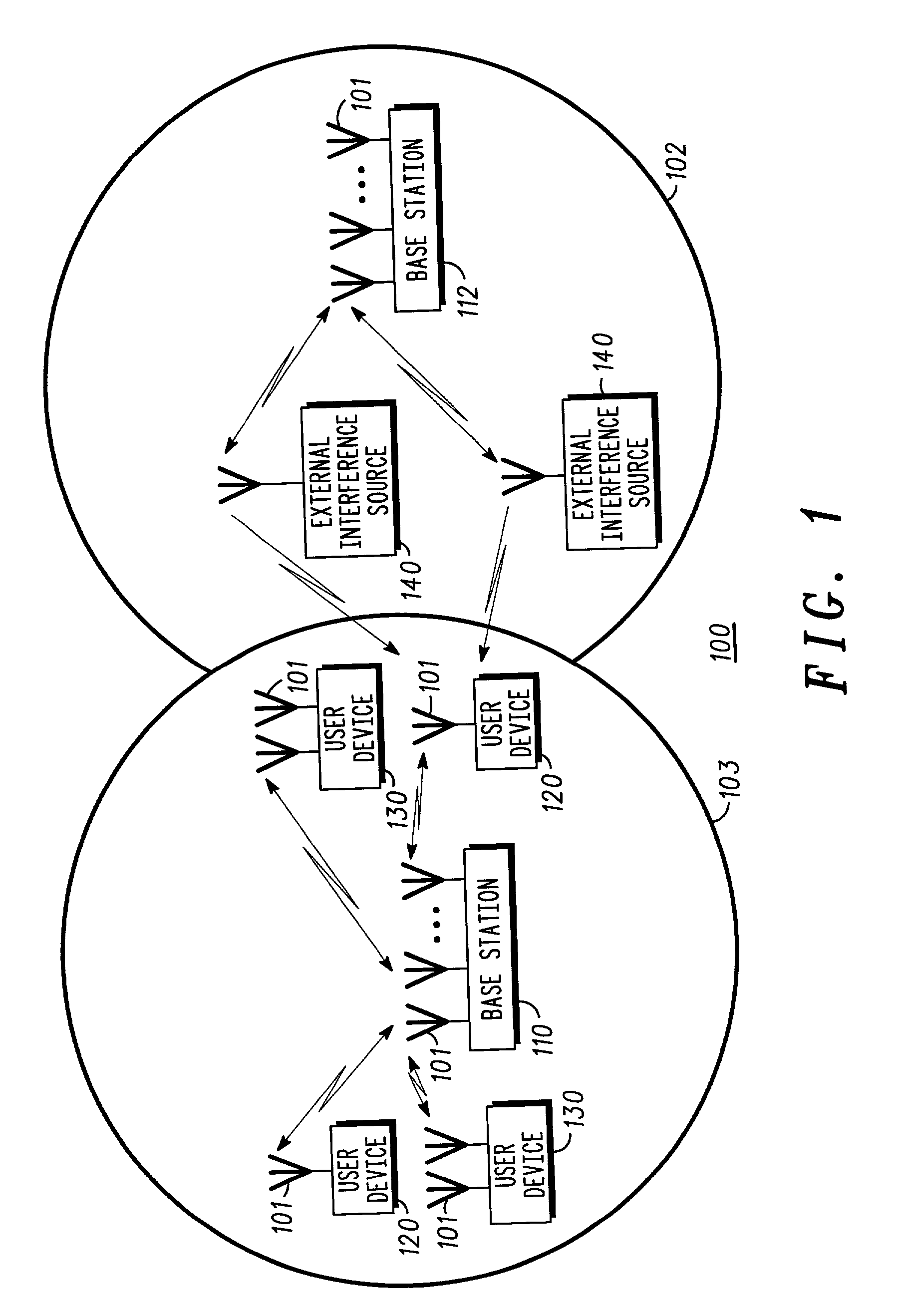
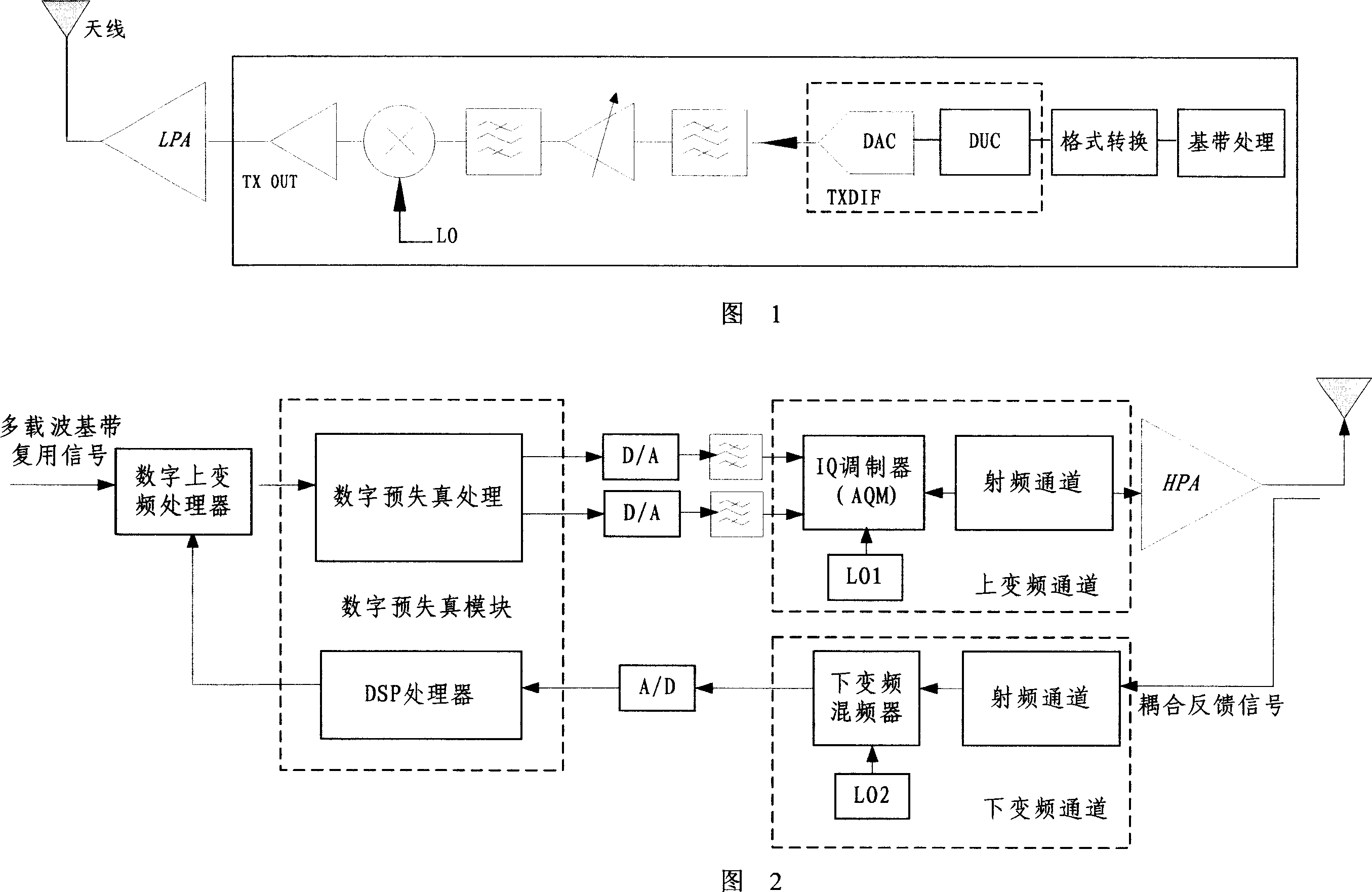
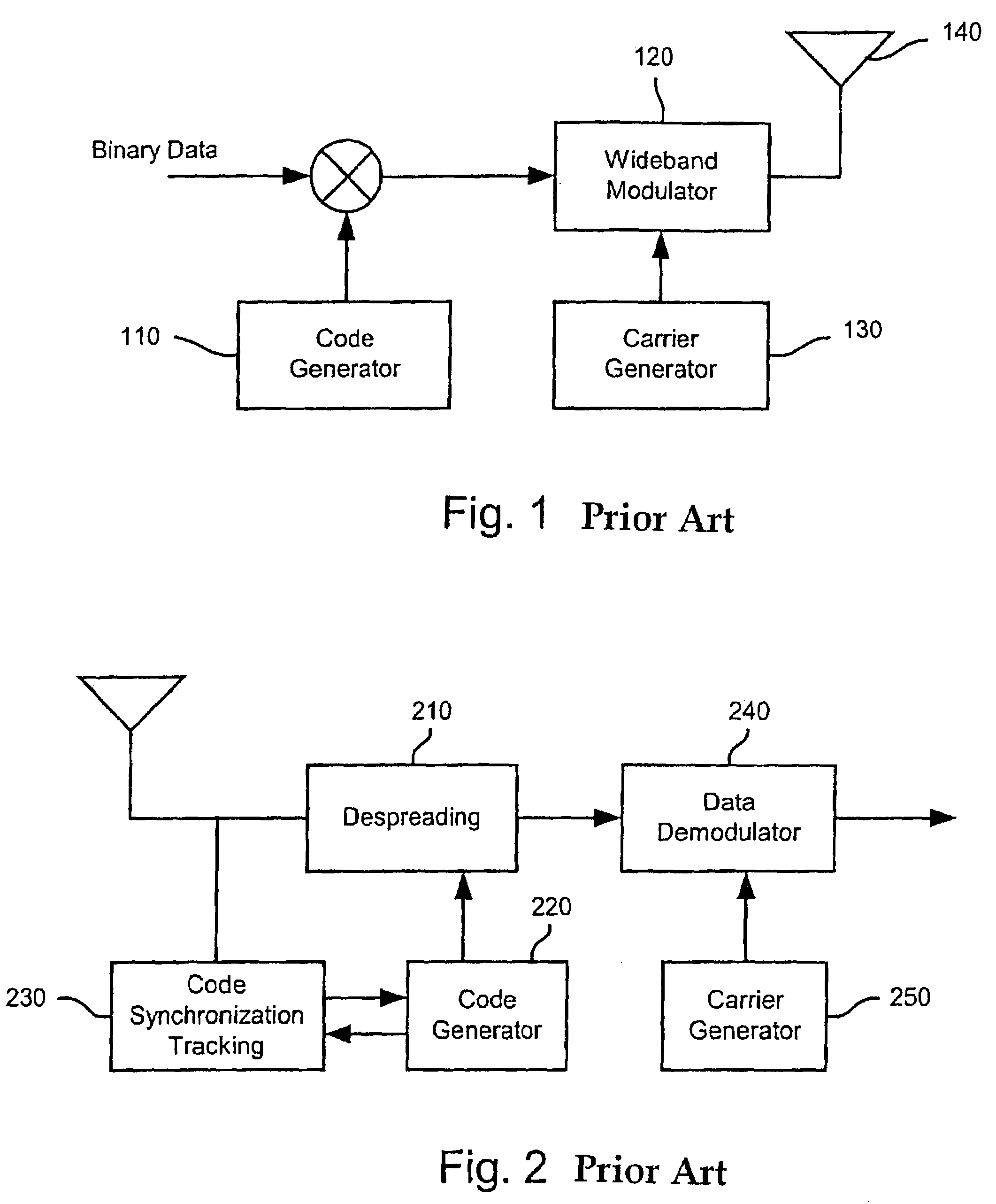
W-CDMA or WCDMA, along with UMTS-FDD, UTRA-FDD, or IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread is an air interface standard found in 3G mobile telecommunications networks. It supports conventional cellular voice, text and MMS services, but can also carry data at high speeds, allowing mobile operators to deliver higher bandwidth applications including streaming and broadband Internet access. W-CDMA is the basis of Japan's NTT DoCoMo's FOMA service and the most-commonly used member of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) family and sometimes used as a synonym for UMTS. It uses the DS-CDMA channel access method and the FDD duplexing method to achieve higher speeds and support more users compared to most previously used time division multiple access and time division duplex schemes. While not an evolutionary upgrade on the airside, it uses the same core network as the 2G GSM networks deployed worldwide, allowing dual mode mobile operation along with GSM/EDGE; a feature it shares with other members of the UMTS family.
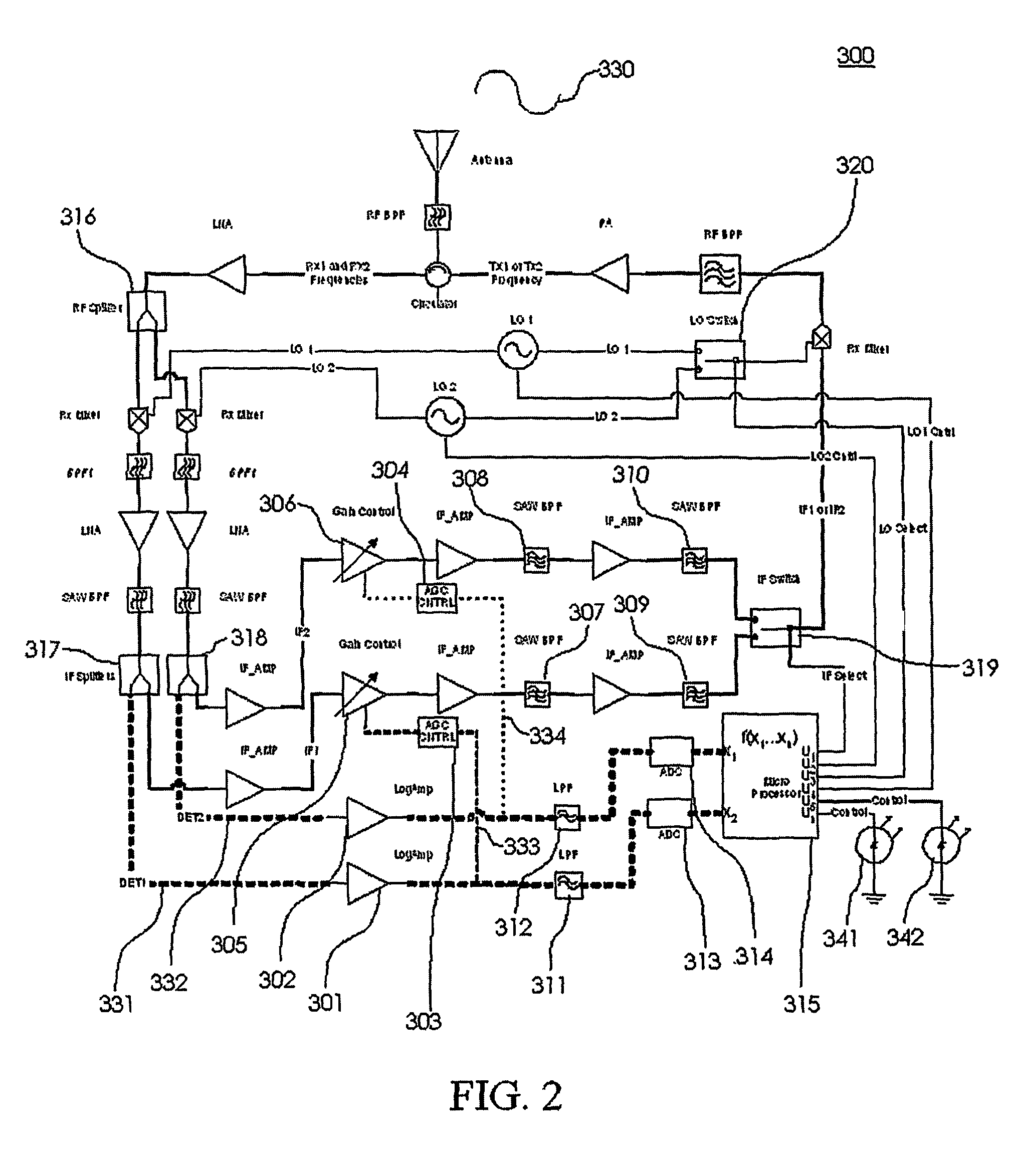
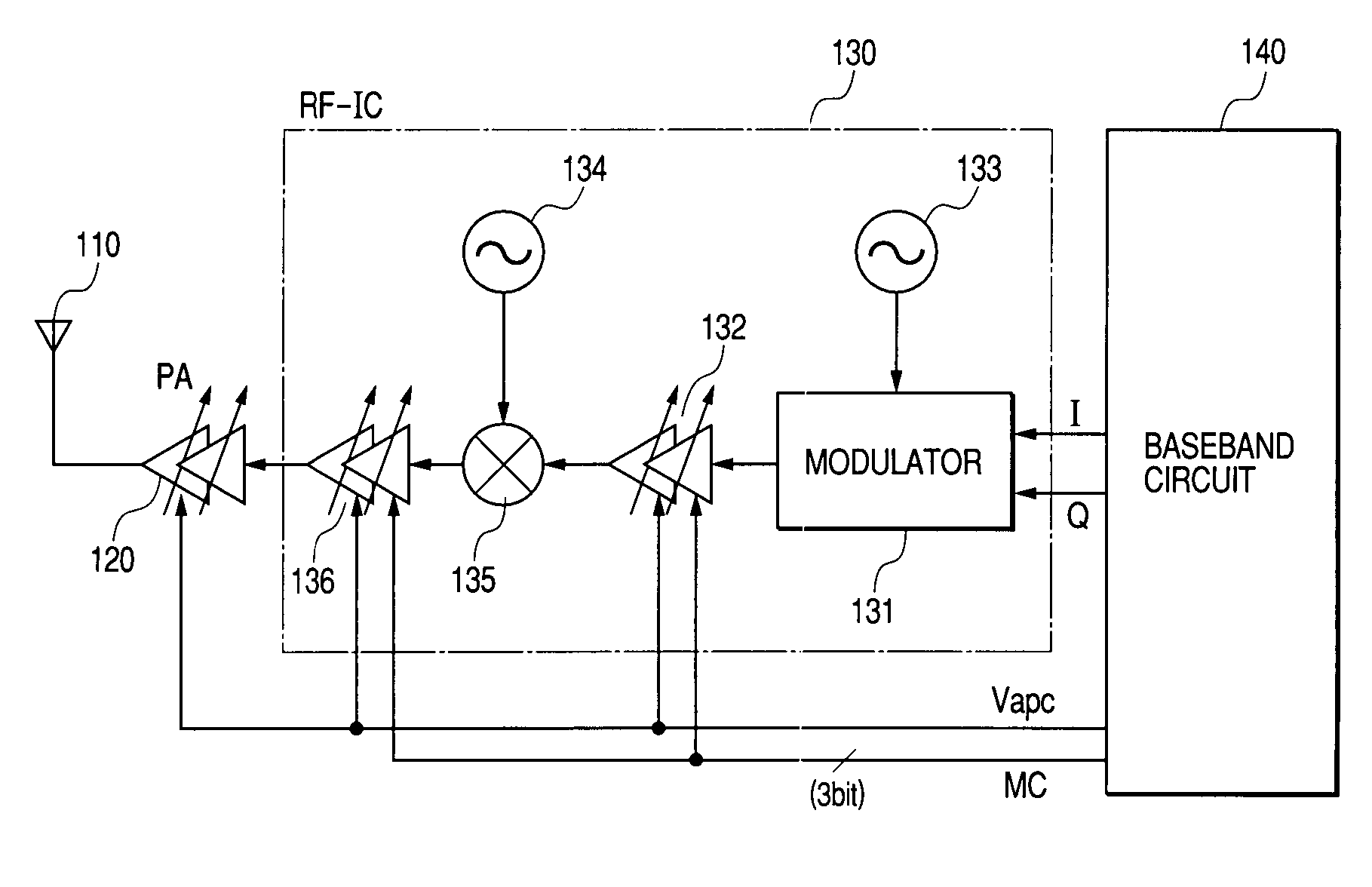
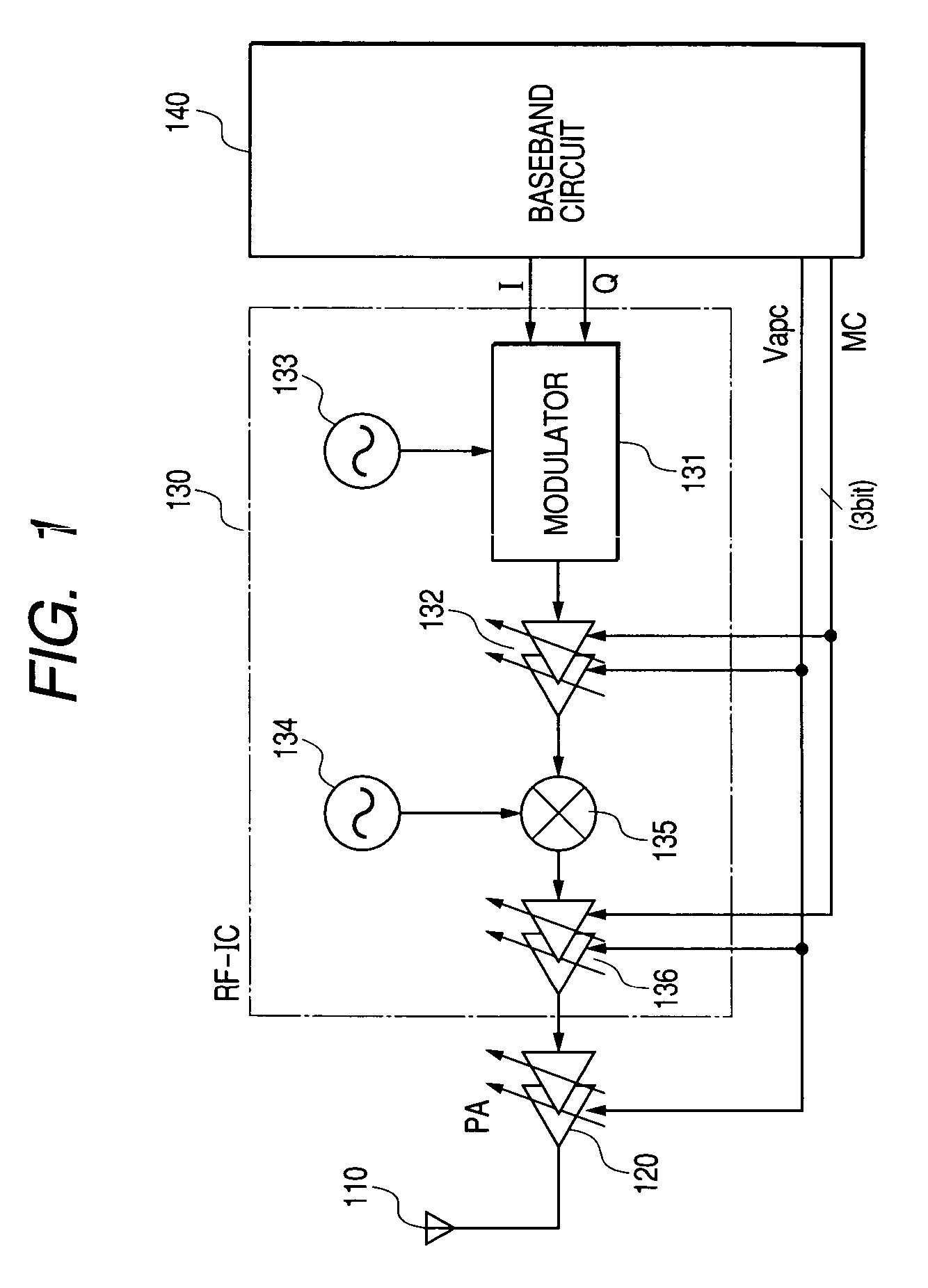
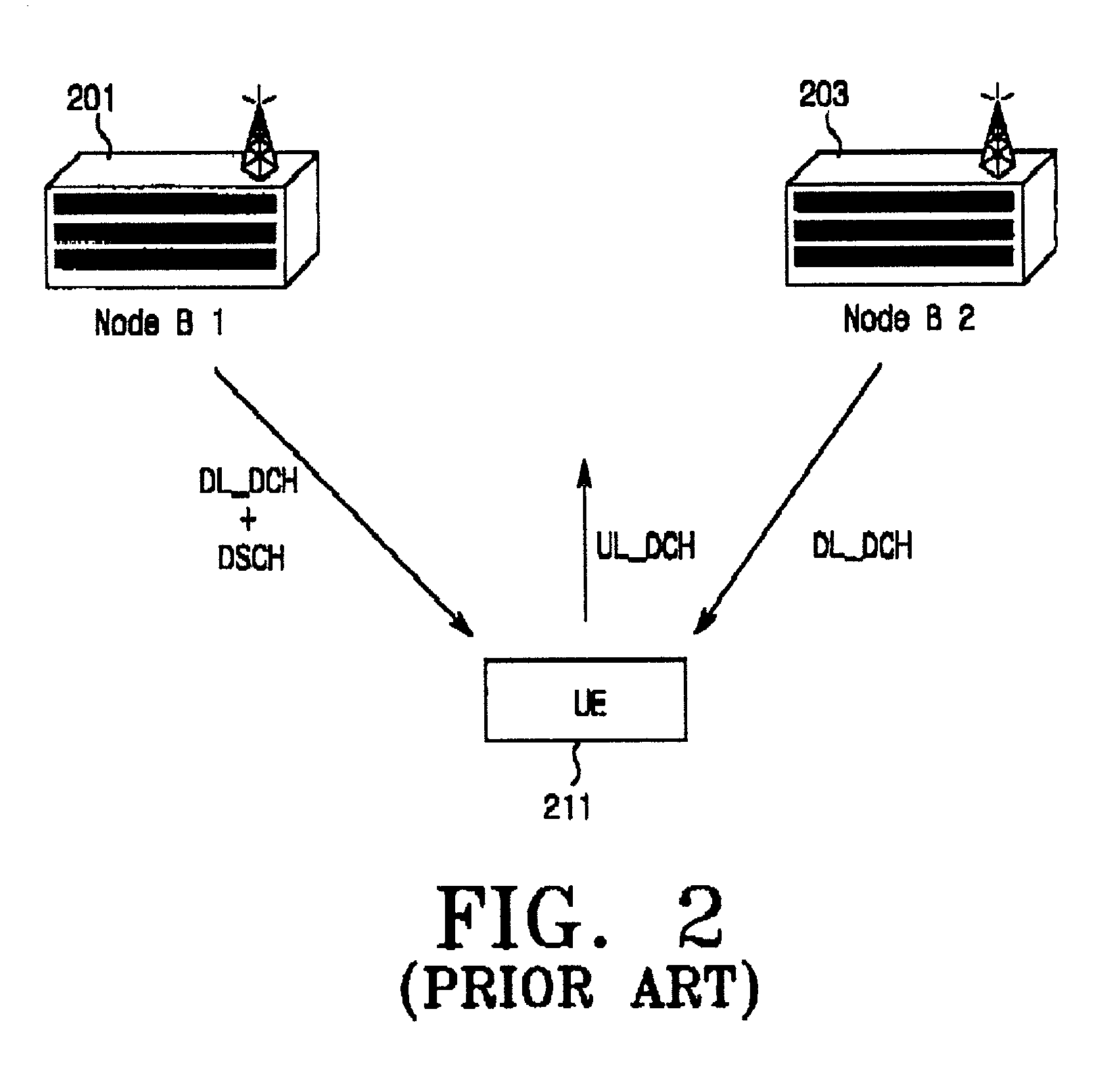
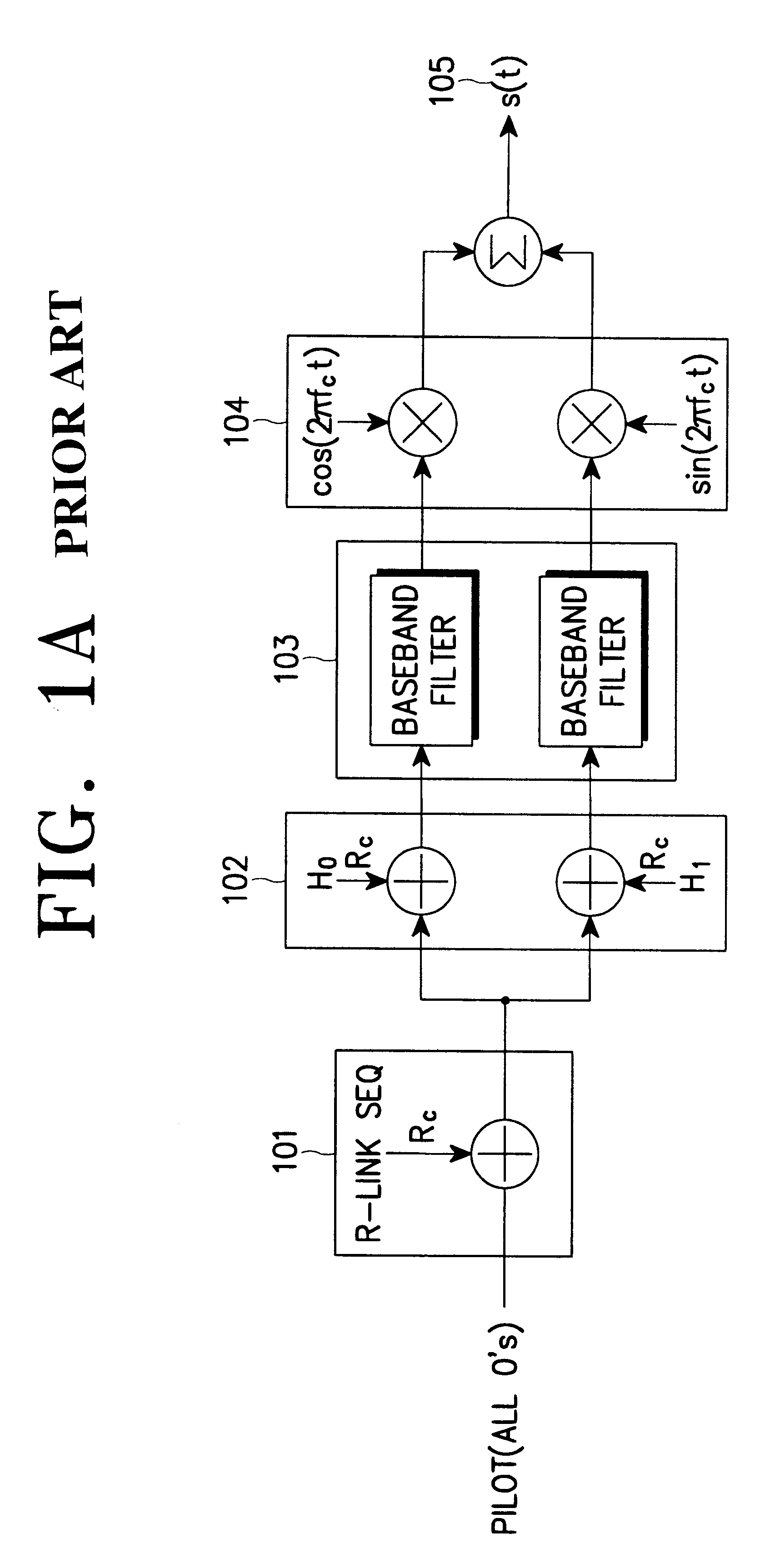
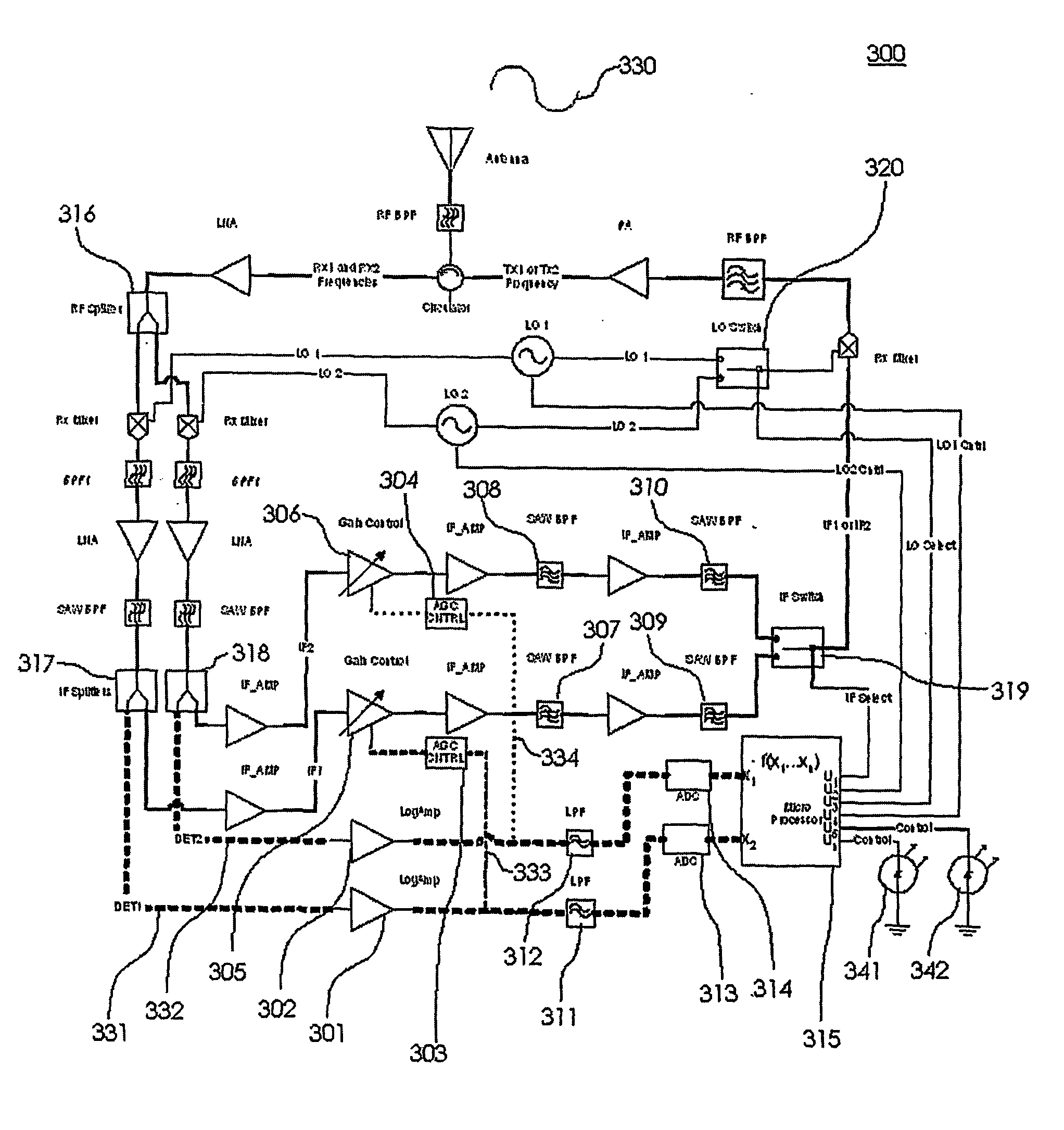
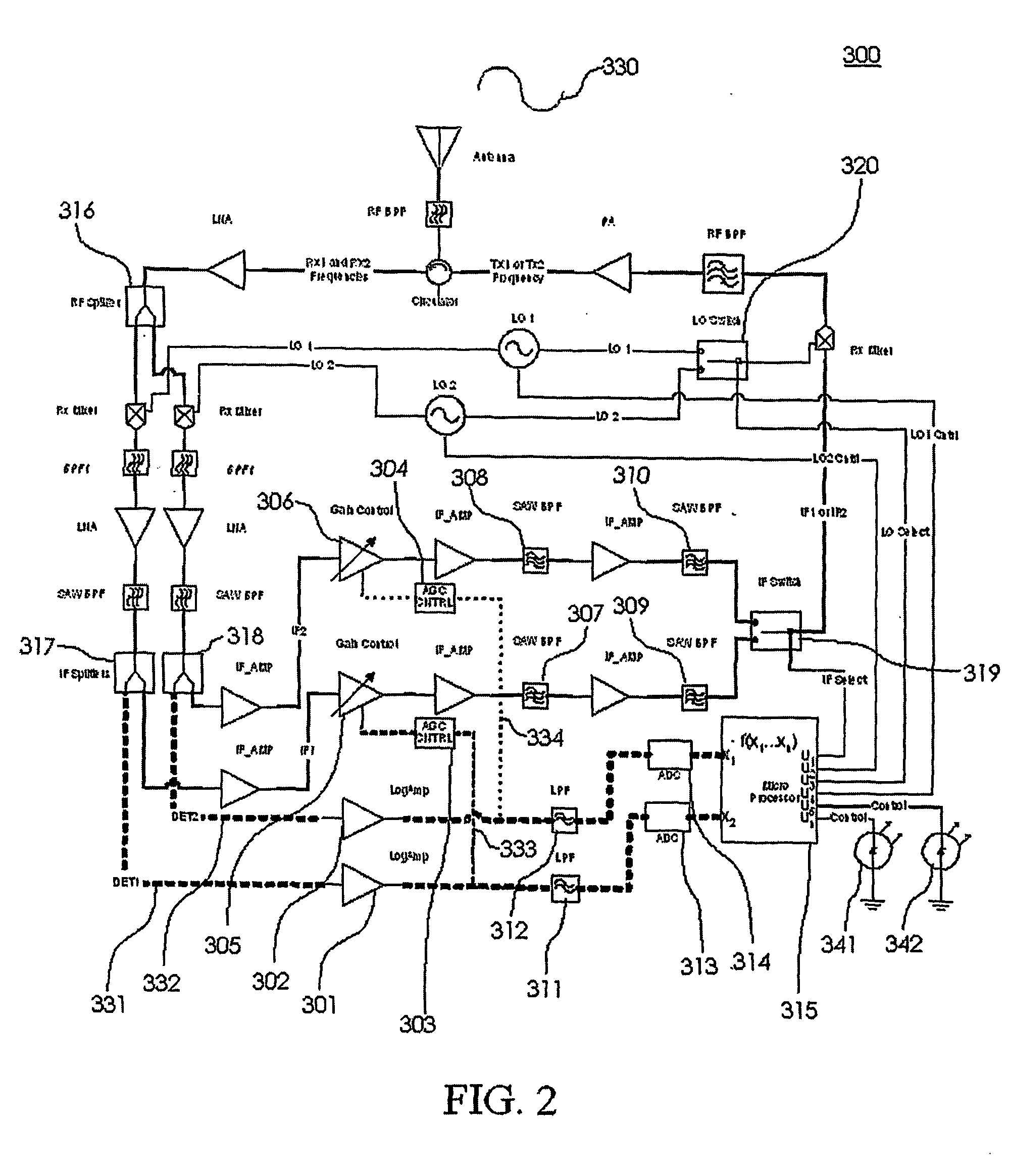
Method and apparatus for controlling transmit power of multiple channels in a CDMA communication system
ActiveUS20020009061A1Power managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmitted powerTime-sharing
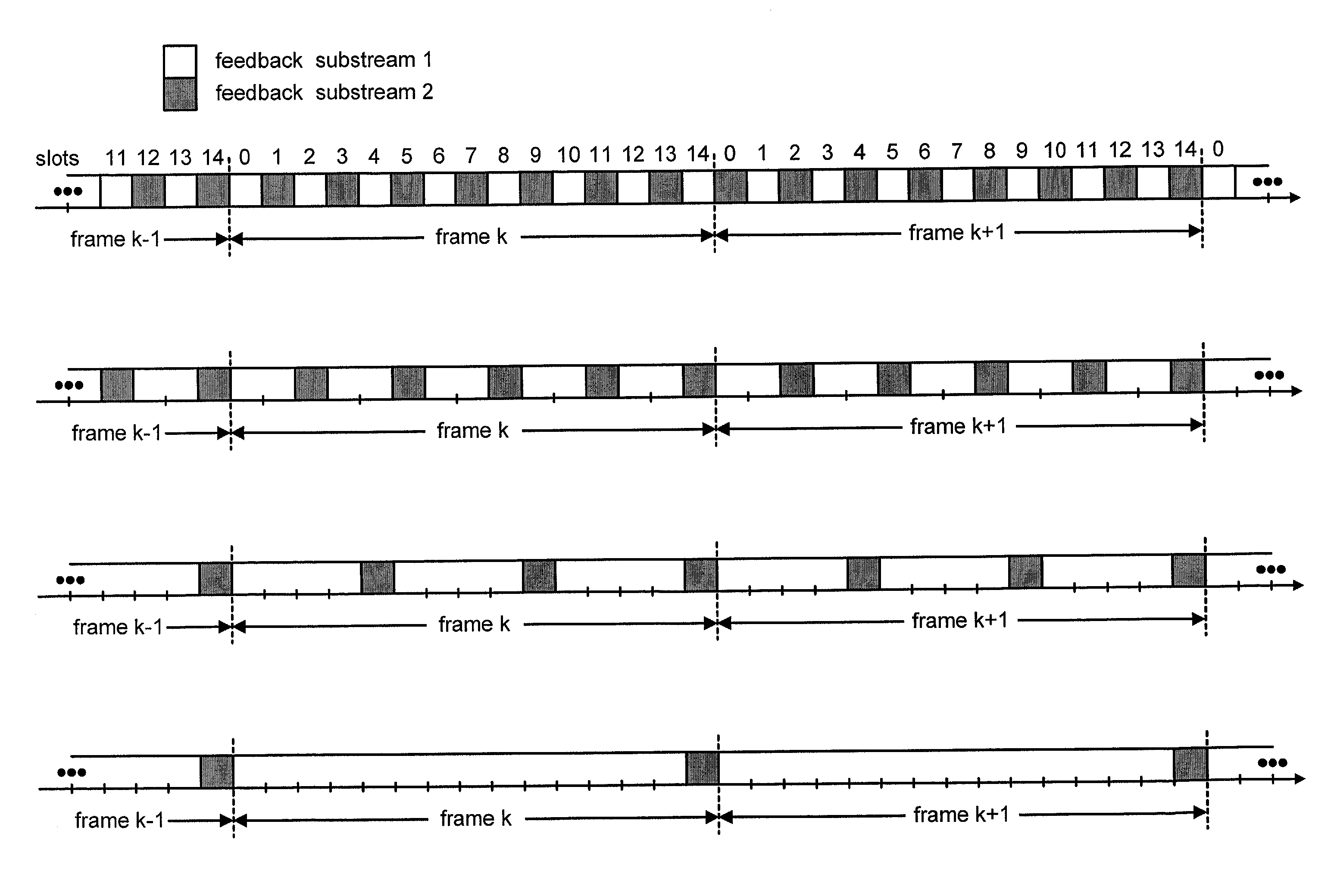
Techniques to support independent power control of multiple channels in CDMA systems (e.g., a W-CDMA system) that define a single power control feedback stream on the uplink, which is to be used for downlink power control. In one aspect, the single feedback stream is "time shared" among multiple channels requiring individual power control. Various time-sharing schemes may be used to implement multiple (substantially parallel) feedback substreams based on the single feedback stream, and different combination of feedback rates may also be achieved for the substreams. Each feedback substream may be assigned to, and used for power control of, a respective channel. In another aspect, multiple feedback substreams are implemented based on multiple fields in newly defined slot formats.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive power control in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6690652B1Maintain conductivityMaximizes controlEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsChannel powerControl signal
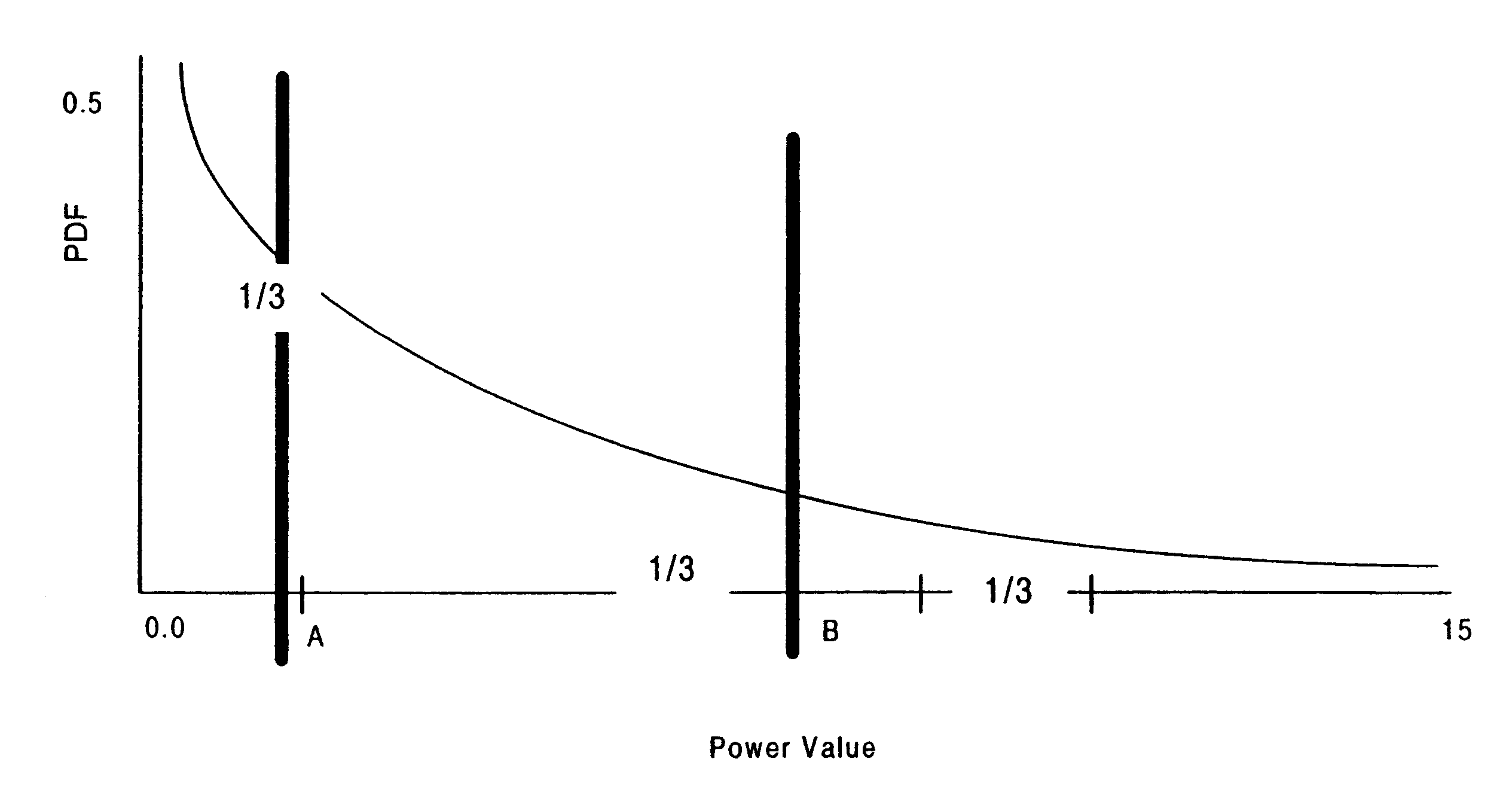
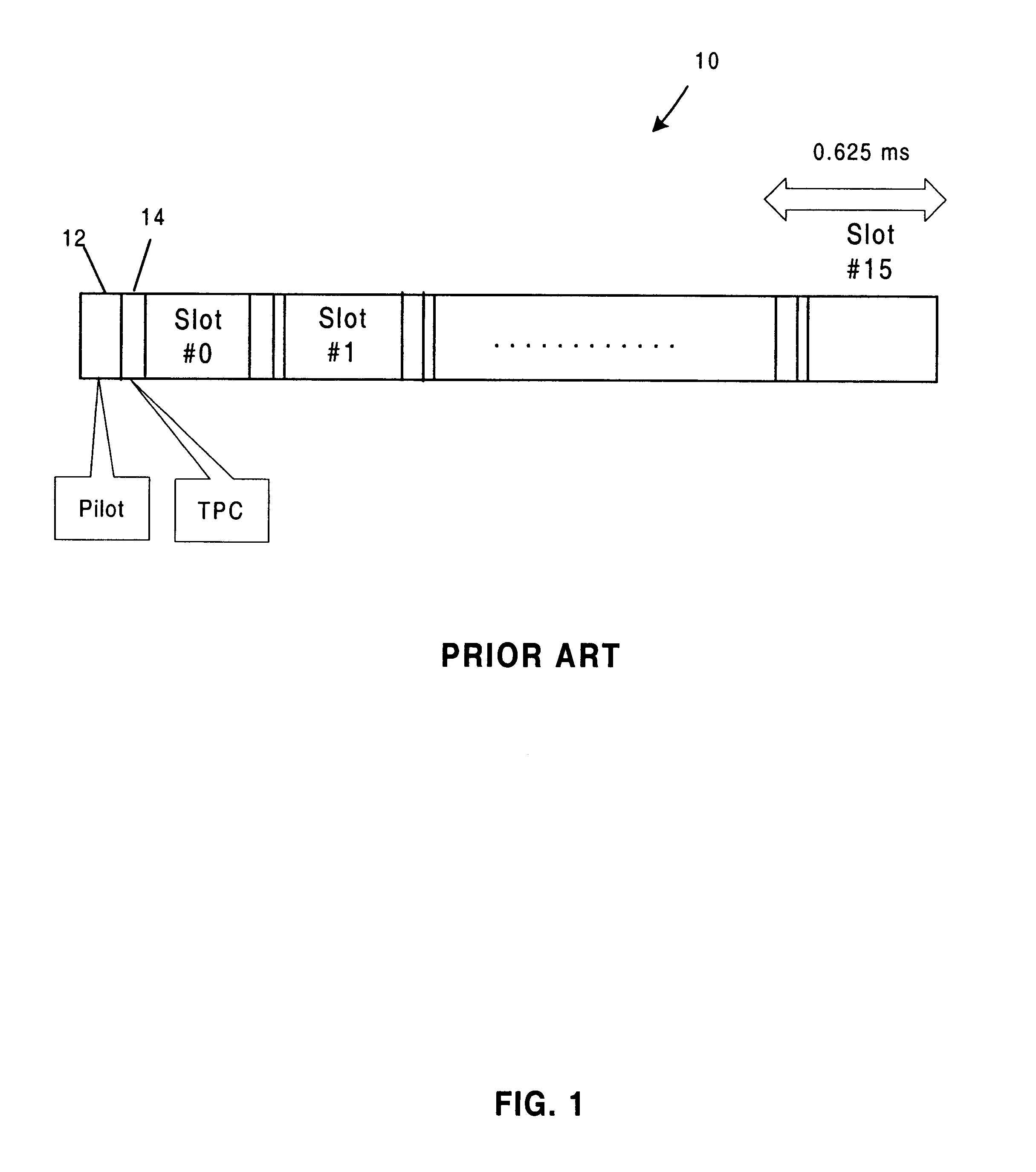
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) transmitter, or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between the BS and a Mobile Station (MS) to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver. Reconfiguration is performed according to the prediction of the channel attenuation and the threshold set at the BS or MS based on its channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. In one embodiment, Seamless Rate Change (SRC) / Transmitter Power Control (TPC) logic uses the predicted channel attenuation to signal both the transmitter and the receiver in a channel to reconfigure their transmit power level according to the power density function (pdf) of the channel power and threshold level. A transmission rate is reduced when the power level is below the threshold and increased when the channel power is above threshold. The pilot channel is used to signal the mobile station and the base station.
Owner:IBM CORP
Adaptive power control based on a rake receiver configuration in wideband CDMA cellular systems (WCDMA) and methods of operation
InactiveUS6621808B1Maximizes controlMaximize throughputPower managementTransmission control/equalisingChannel powerOperational system
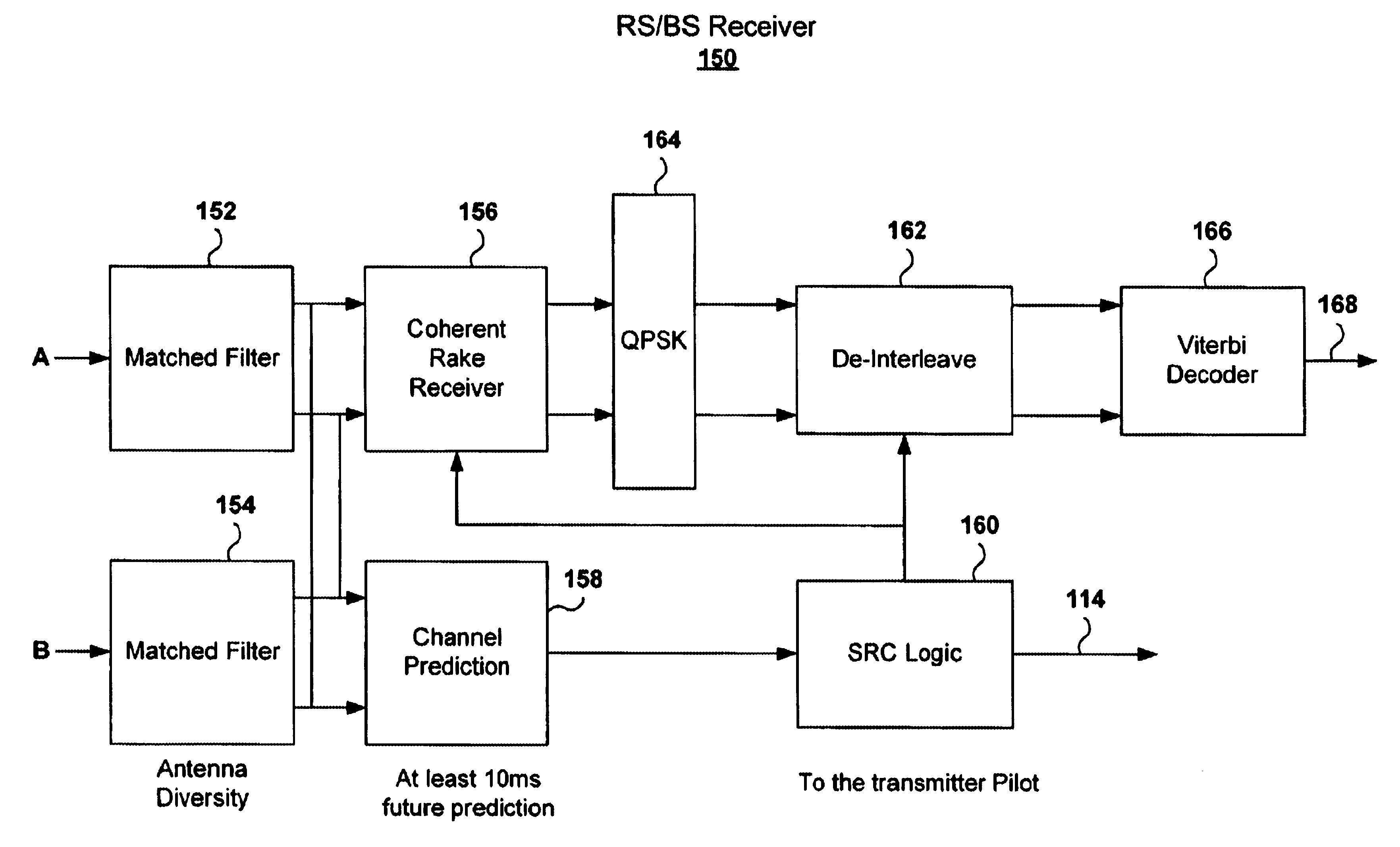
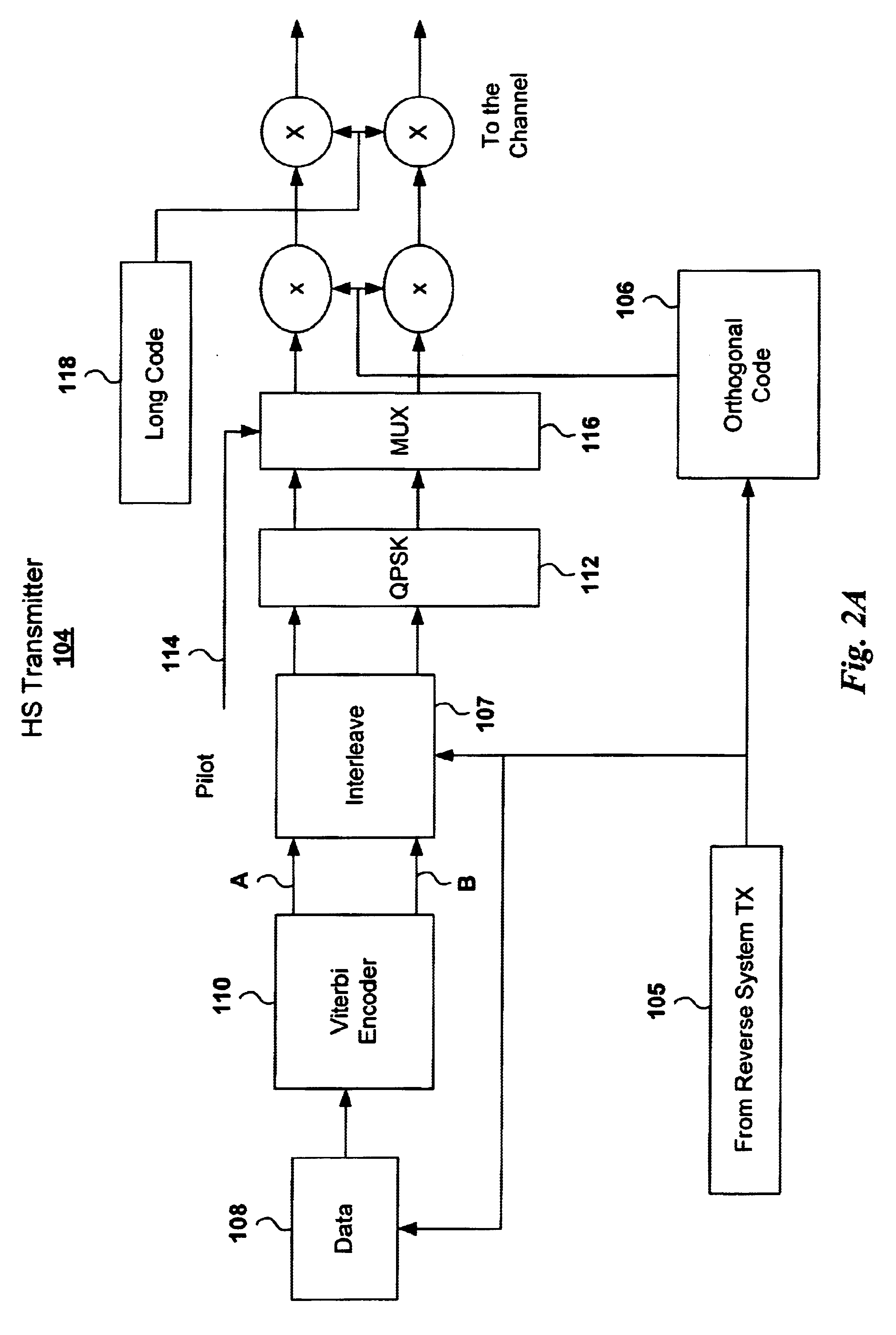
A WCDMA system includes a Base Station (BS) or forward transmitter and a pilot channel that transmits control signals between a Mobile Station (MS) and BS to reconfigure their transmitter / receiver according to the prediction of the channel power and channel power probability density function separated into three distinct equal probable regions. Data signals are encoded using a one-half Viterbi encoder and interleaved. The interleaved data bits are modulated using Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation. The QPSK data is multiplexed with the pilot channel and spread by an appropriate code in an OFDM transmitter modified by a long code. Output of the transmitter may be provided to two diverse antennas for reliable communications to the receiver. Data may be received at two diverse antennas. The outputs are provided to match filters coupled to a coherent rake receiver and a channel prediction system. The future attenuation of the channel coefficients and power are determined by the prediction system for several milliseconds. The power levels of each finger in the Rake receiver can be predicted and the strongest ones used in determining the optimum transmitter power or rate control for operating the system transmitters and receivers based on computing a long range power prediction of each finger of a rake receiver.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
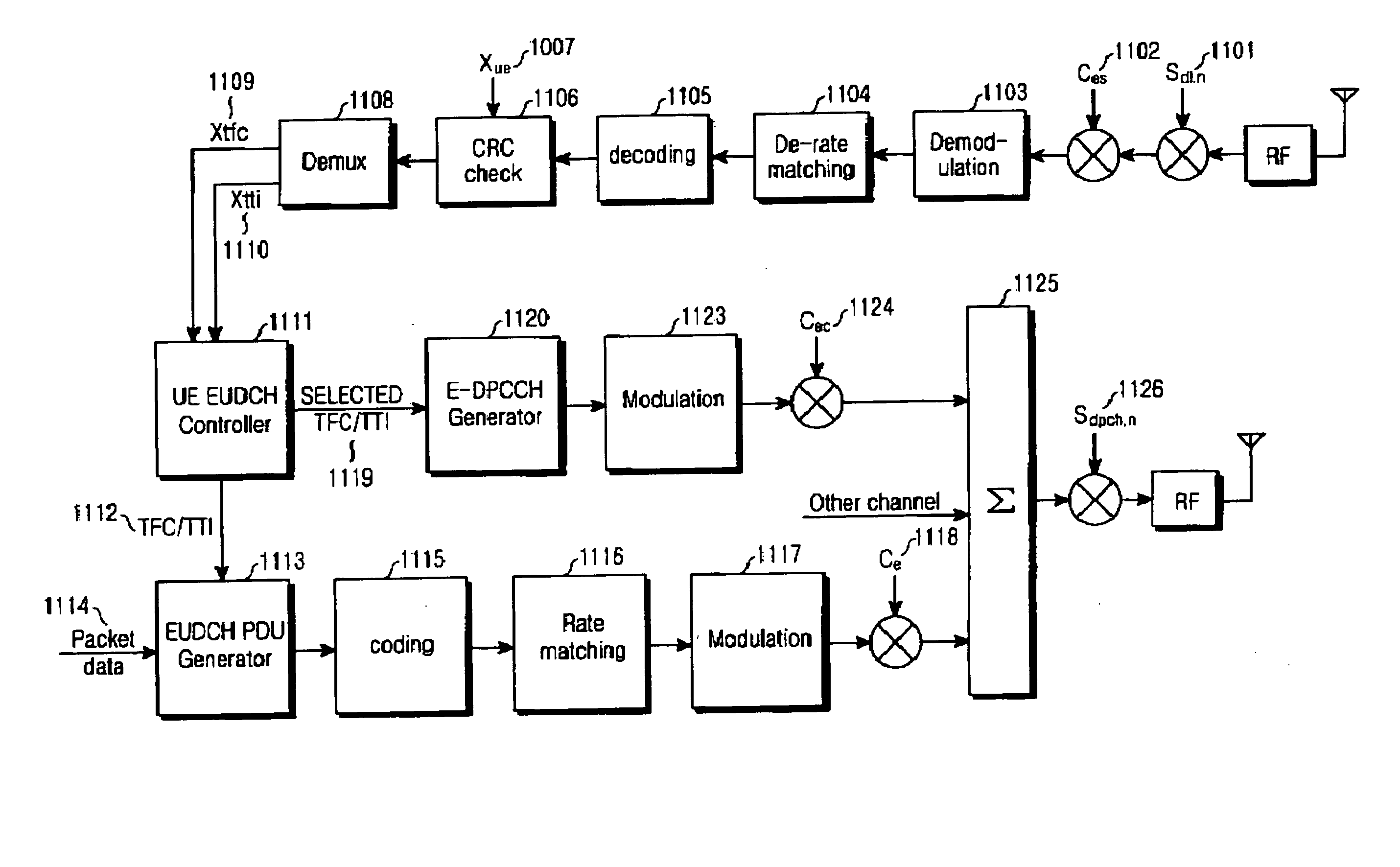
System and method for controlling a TTI in a W-CDMA communication system supporting enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel
InactiveUS20050073985A1Error preventionRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemMobile communication systems
A system and a method for enabling a node B to control a transmission time interval (TTI) in consideration of radio resources of a cell, a channel environment of a UE, and a buffer state of the UE, in an asynchronous wideband code division multiple access (W-CDMA) mobile communication system that supports a packet data service through an enhanced uplink dedicated transport channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
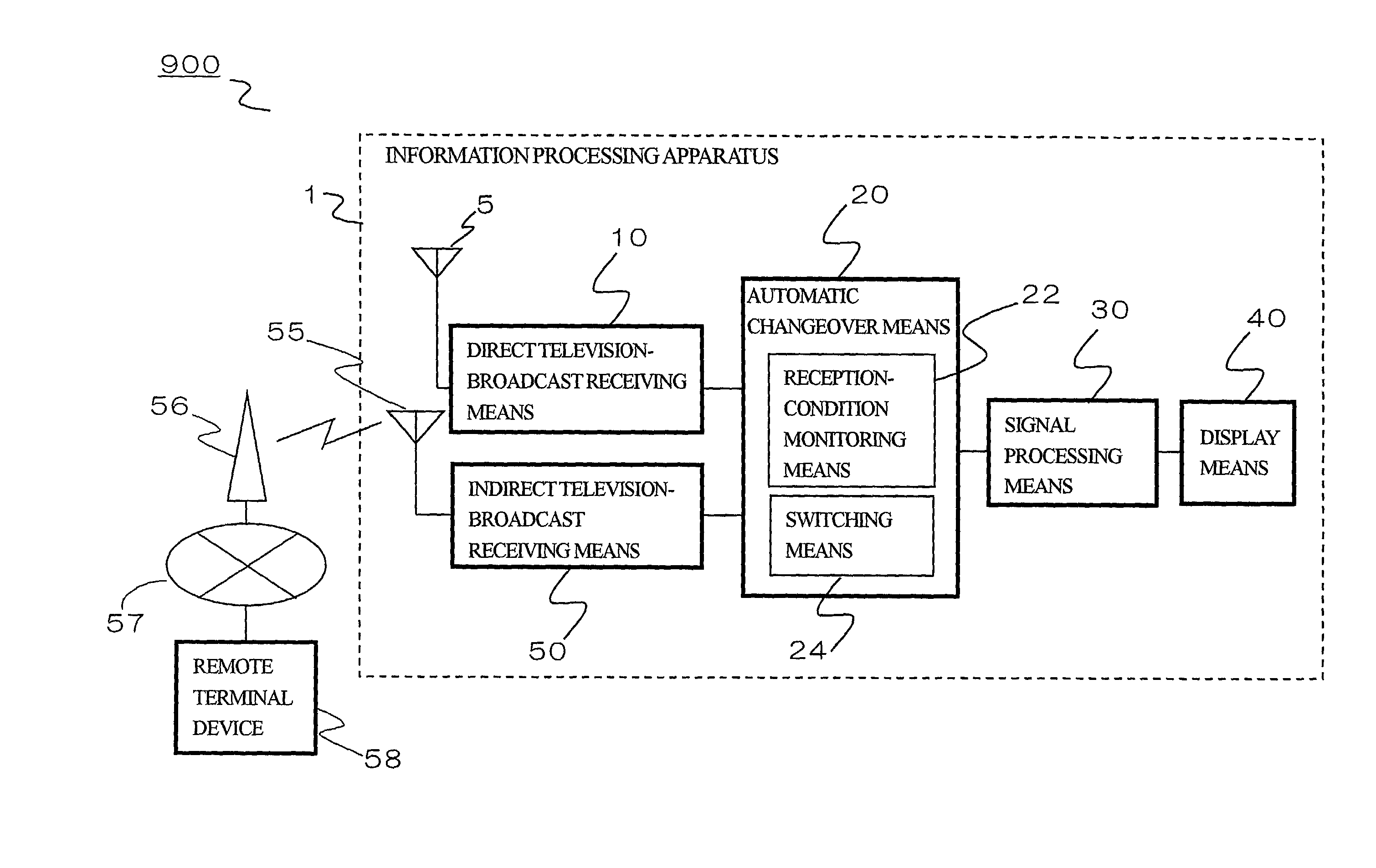
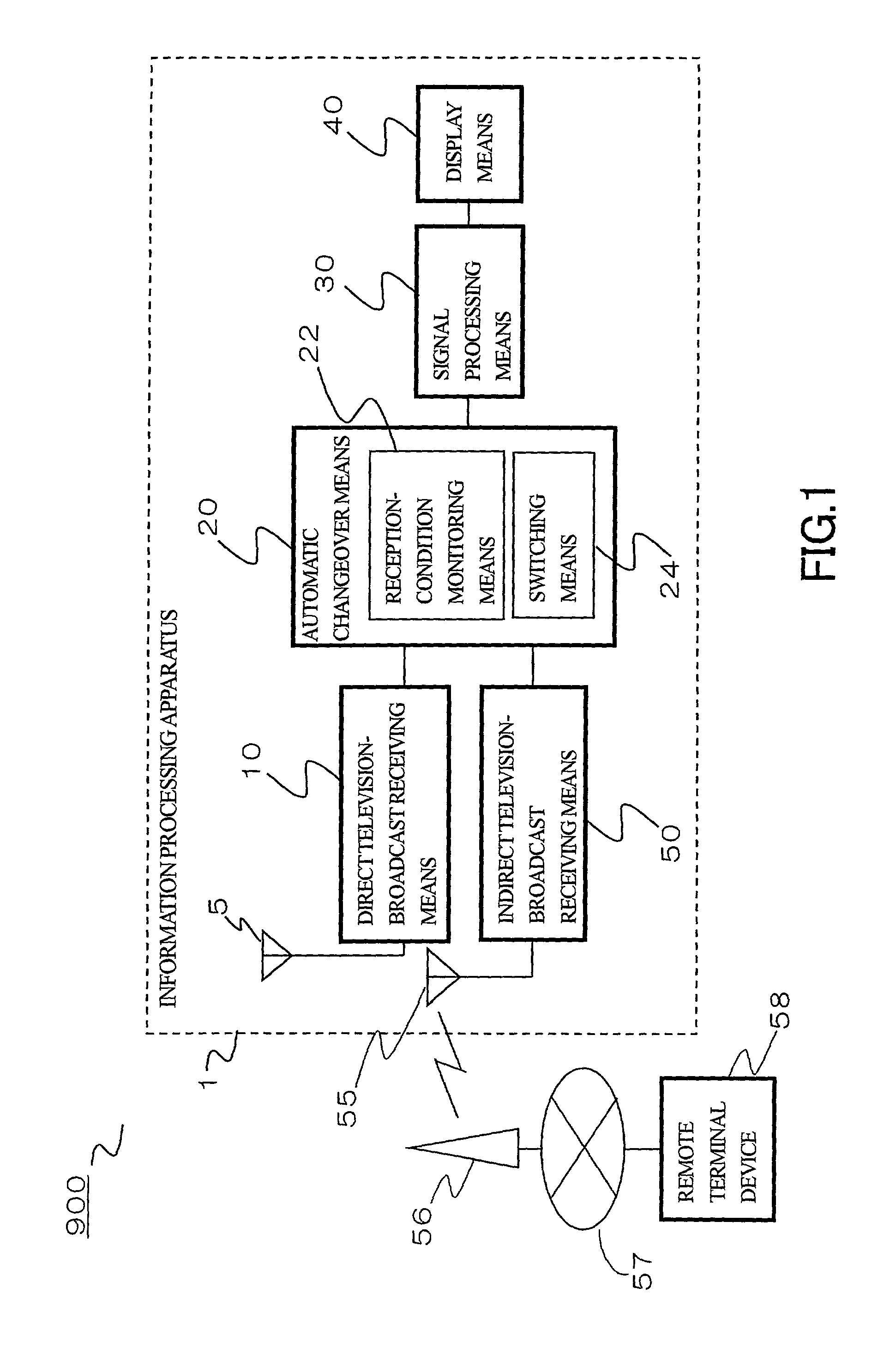
Information processing system and information processing apparatus
InactiveUS7106382B2Television system detailsSpatial transmit diversityInformation processingTime division multiple access
An information processing system and apparatus receiving a television broadcast includes: a direct receiving unit directly receiving television broadcast waves; an indirect receiving unit indirectly receiving the television broadcast waves; and a switching unit determining whether the television broadcast waves are to be received by the direct receiving unit or the indirect receiving unit by switching between the direct receiving unit and the indirect receiving unit based on their reception conditions. With this configuration, it is possible to obtain television-broadcast video signals from the selected receiving unit. The indirect receiving unit is preferably formed of a communication device provided with a wireless cellular telephone function using a wideband code division multiple access (W-CDMA) system in which signals having a large transmission capacity can be transmitted and received, or a communication device provided with a wireless LAN communication function.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
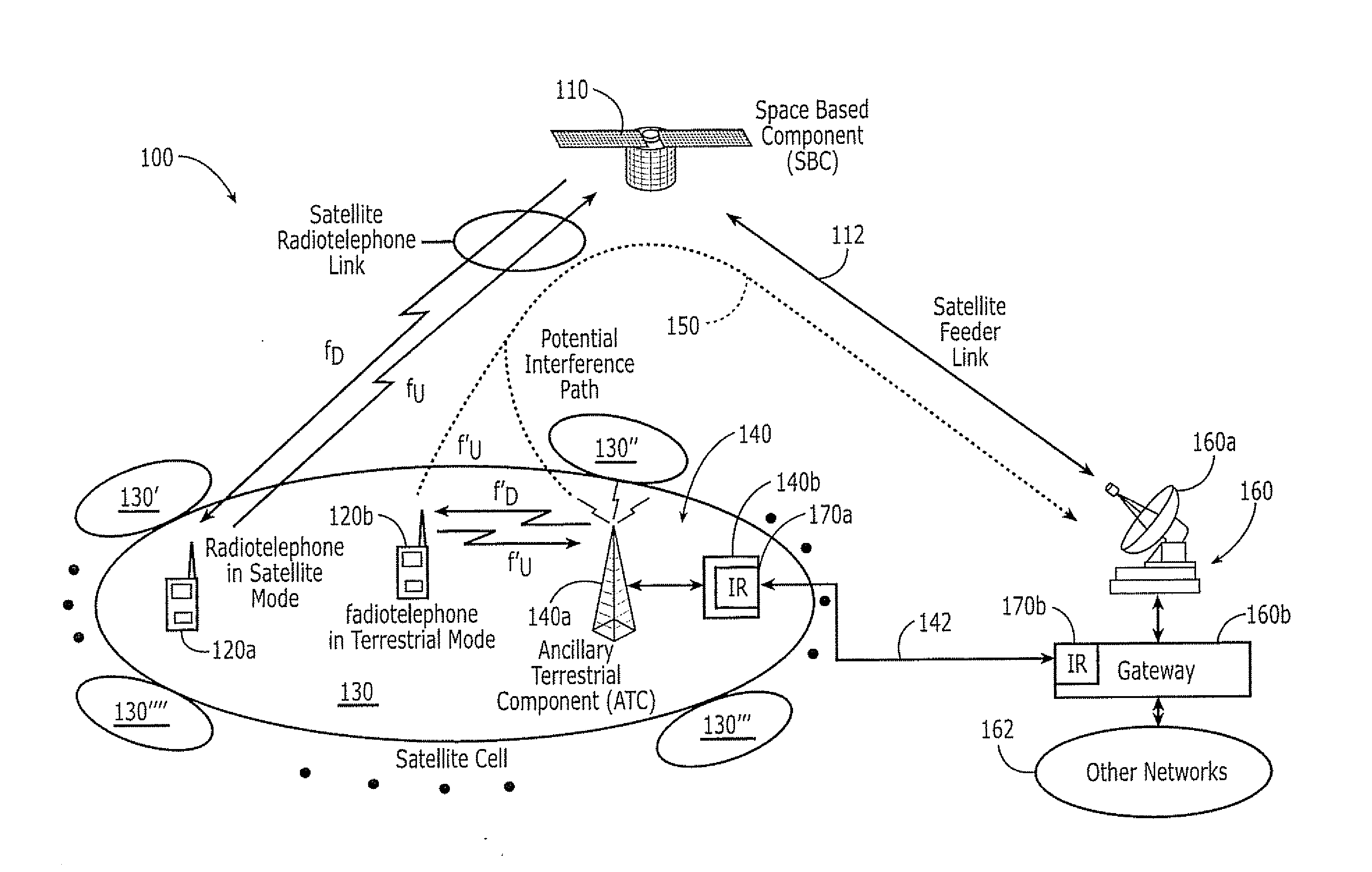
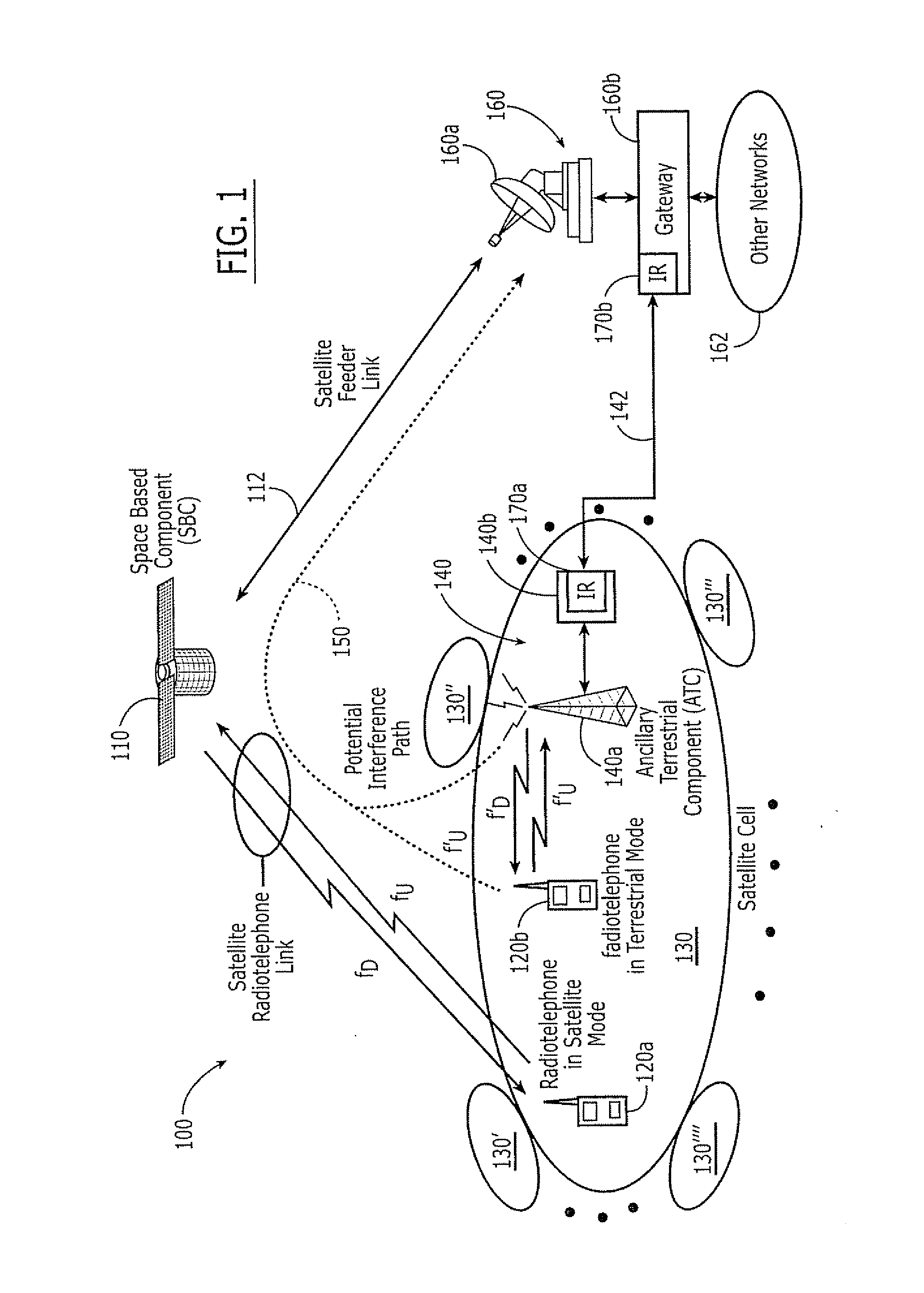
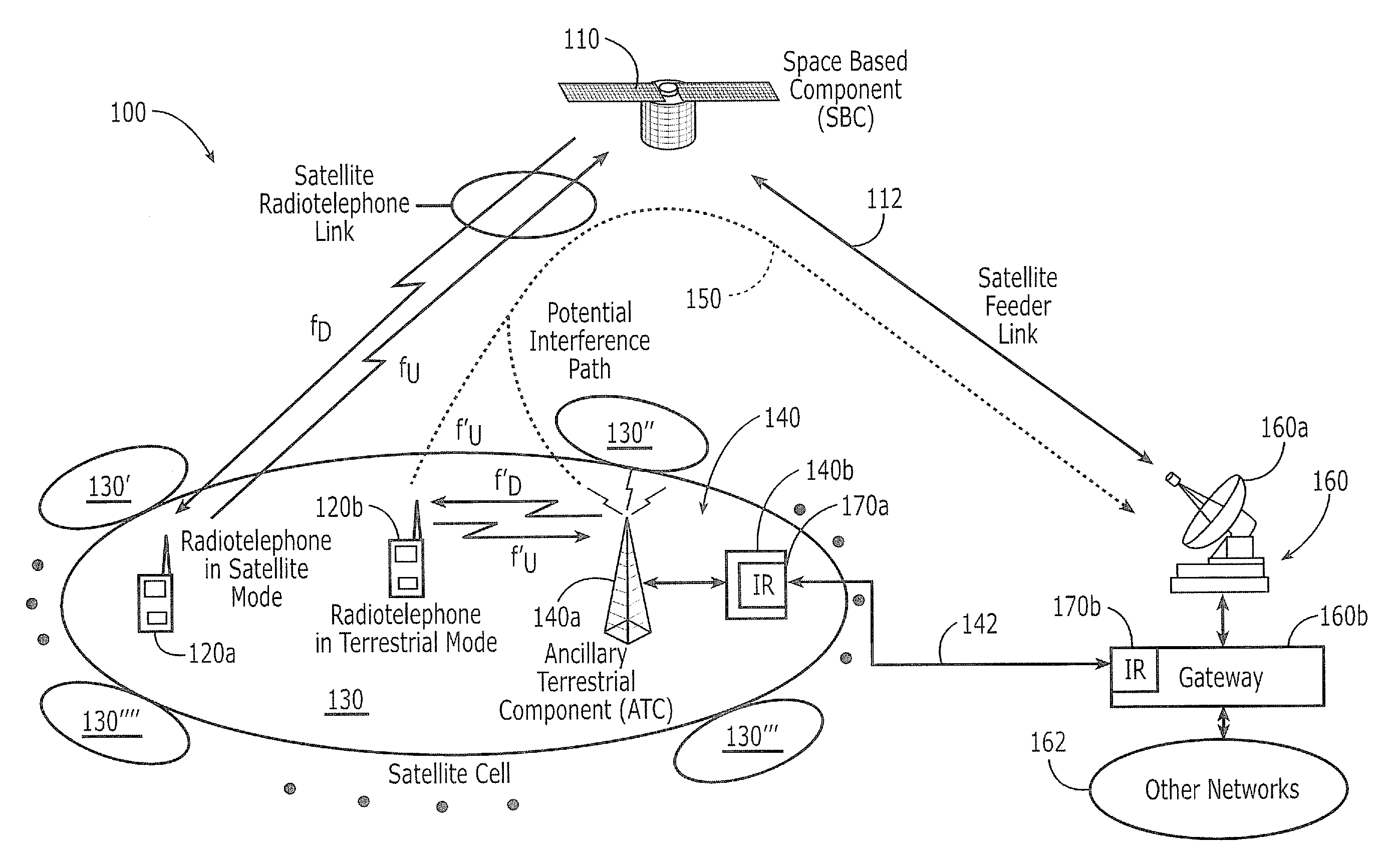
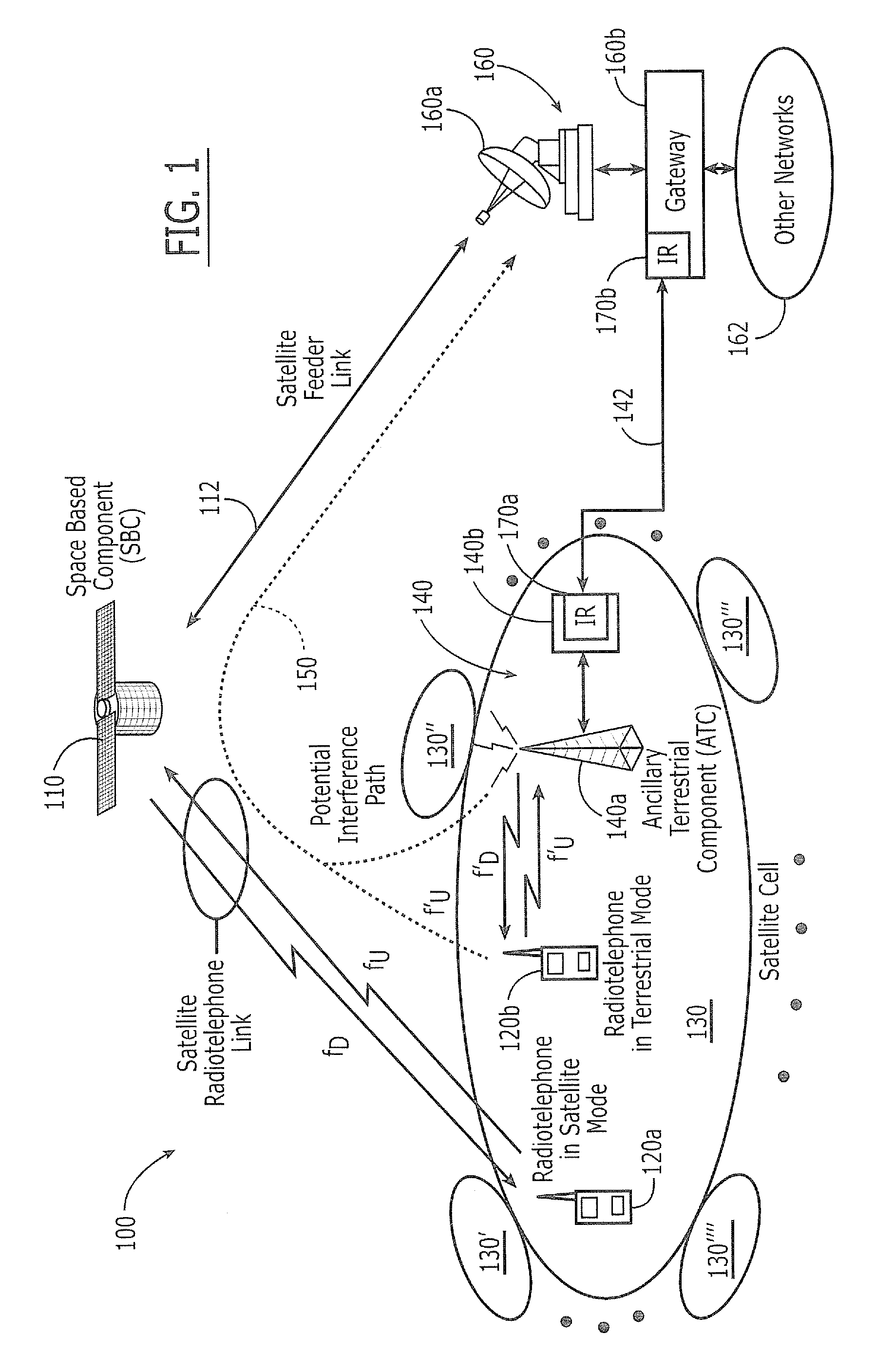
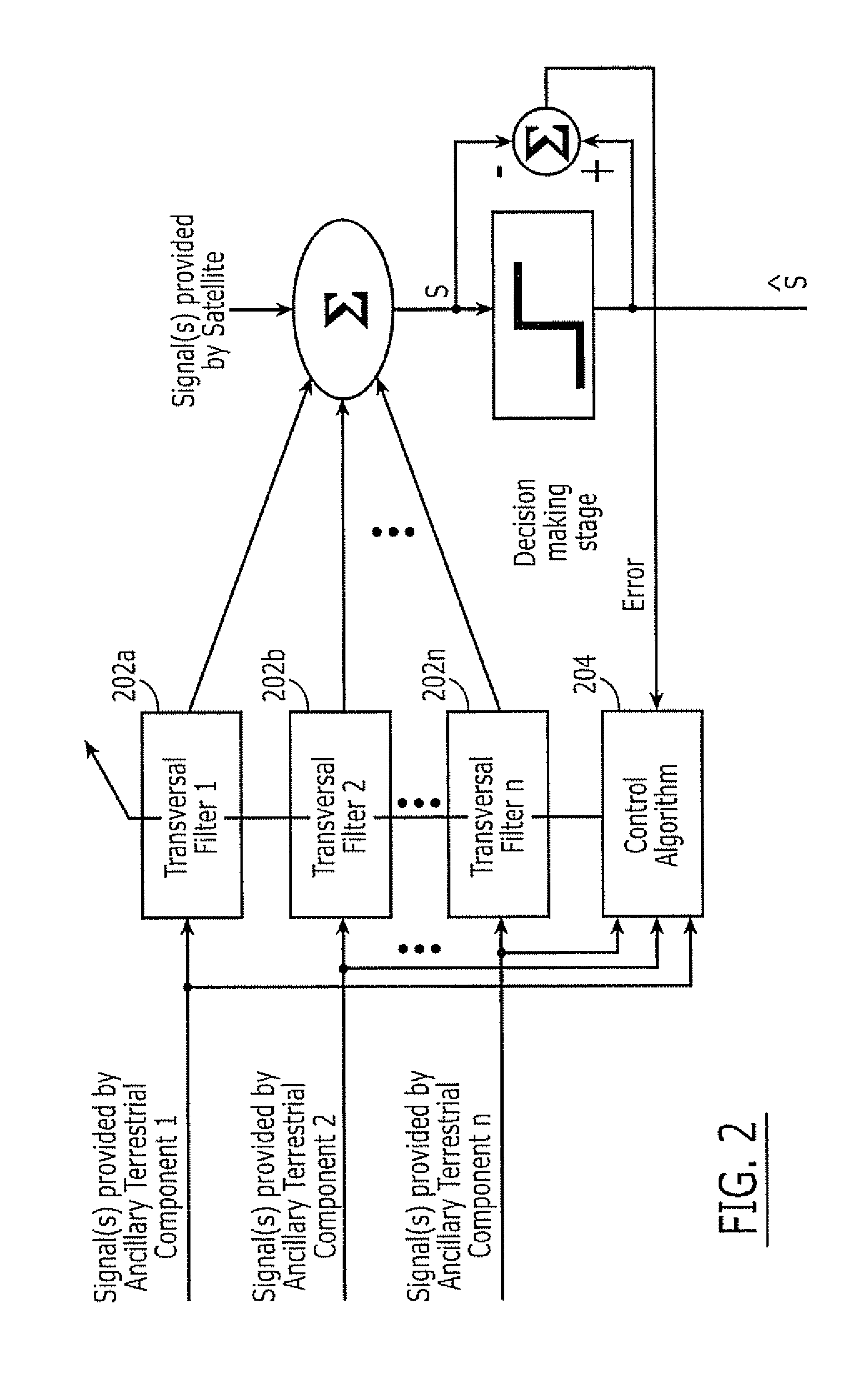
Additional aggregate radiated power control for multi-band/multi-mode satellite radiotelephone communications systems and methods
An Ancillary Terrestrial Network (ATN) includes at least one Ancillary Terrestrial Component (ATC) that is configured to provide wireless communications using frequencies of a satellite frequency band. The ATN provides communications based on a GSM, cdma2000 and / or W-CDMA air interface, under a constrained capacity measure. The capacity measure of the ATN may also be constrained when the ATN provides communications based on an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) and / or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) air interface. Analogous methods of controlling an ATN also may be provided.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
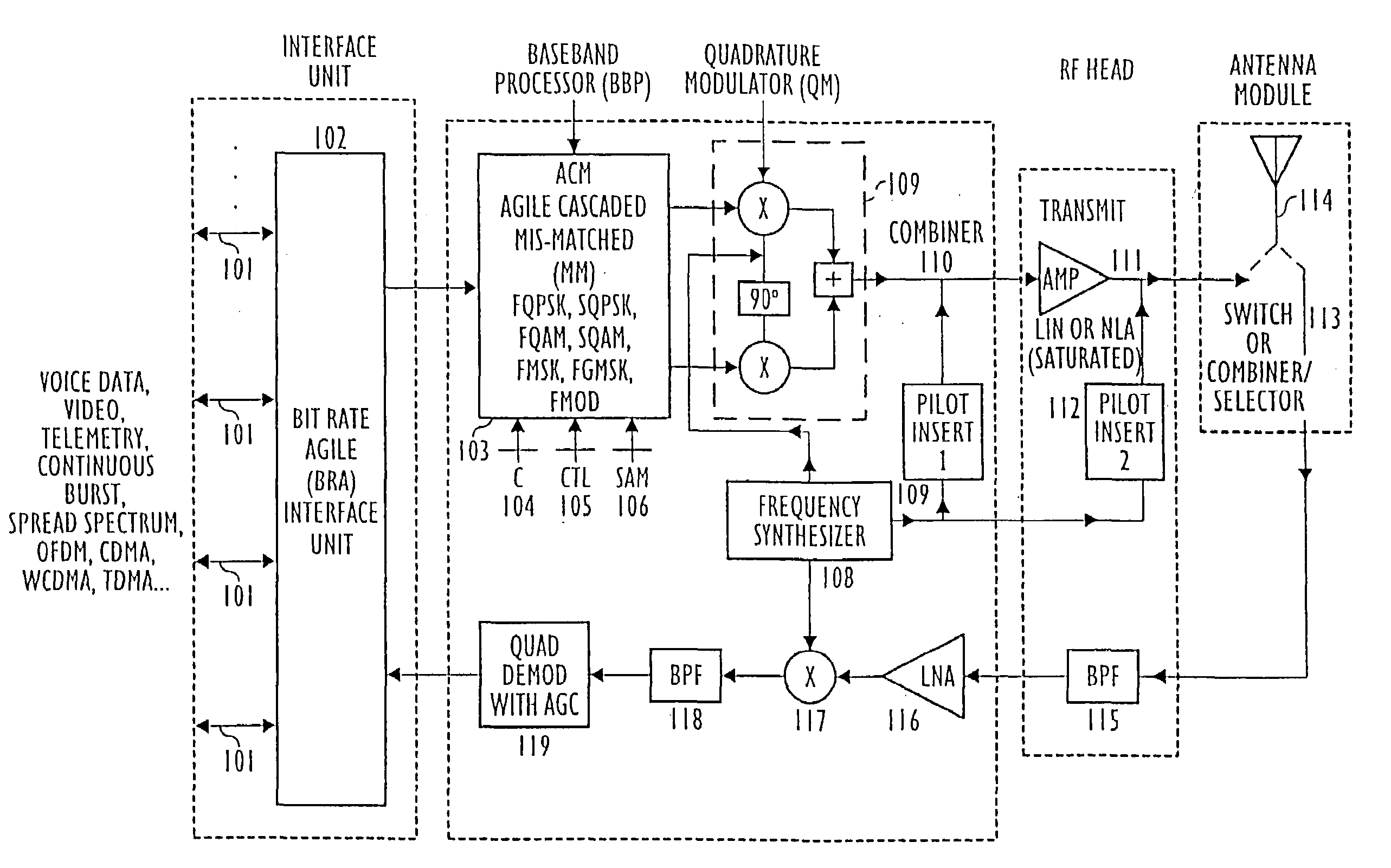
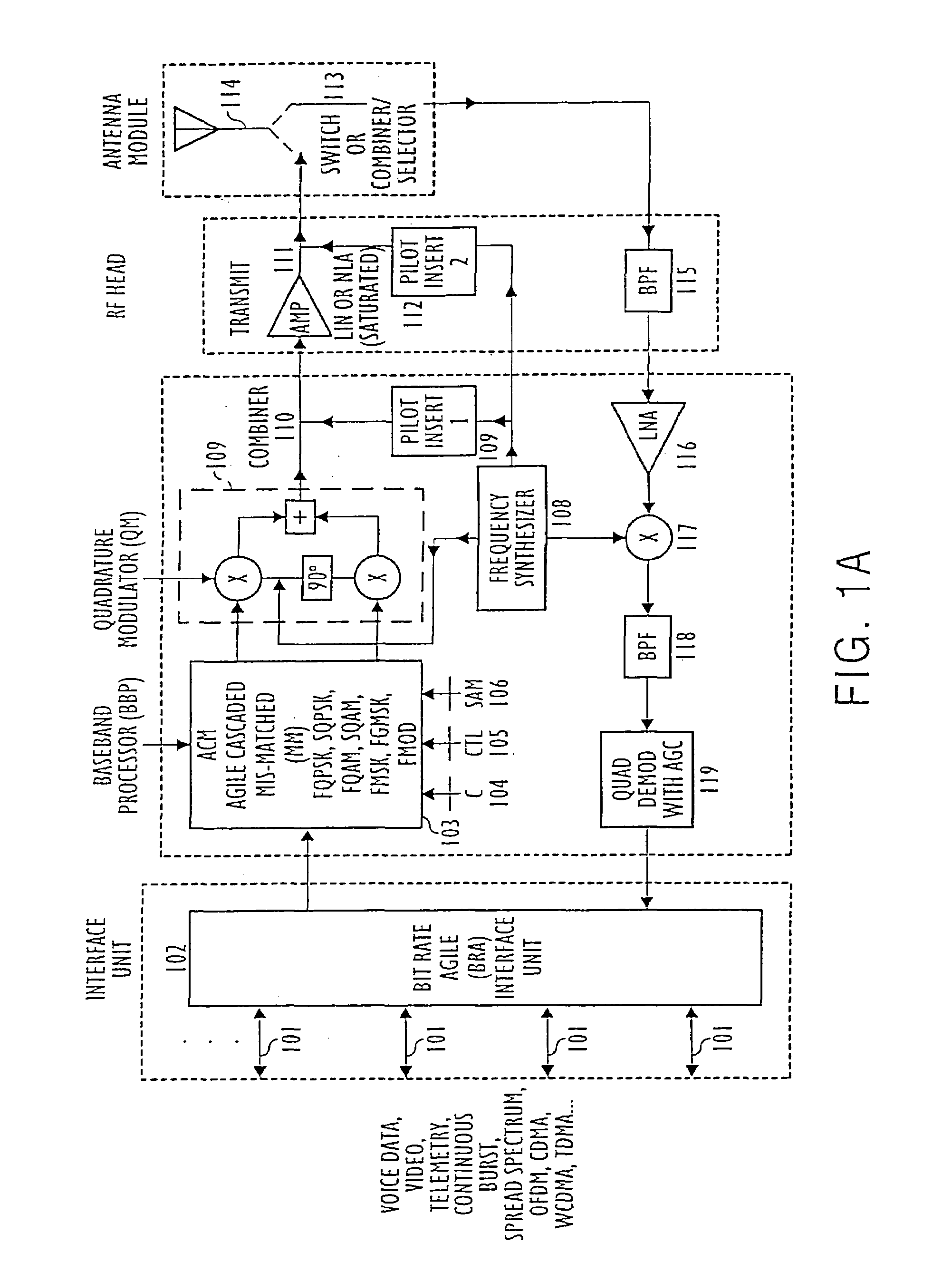
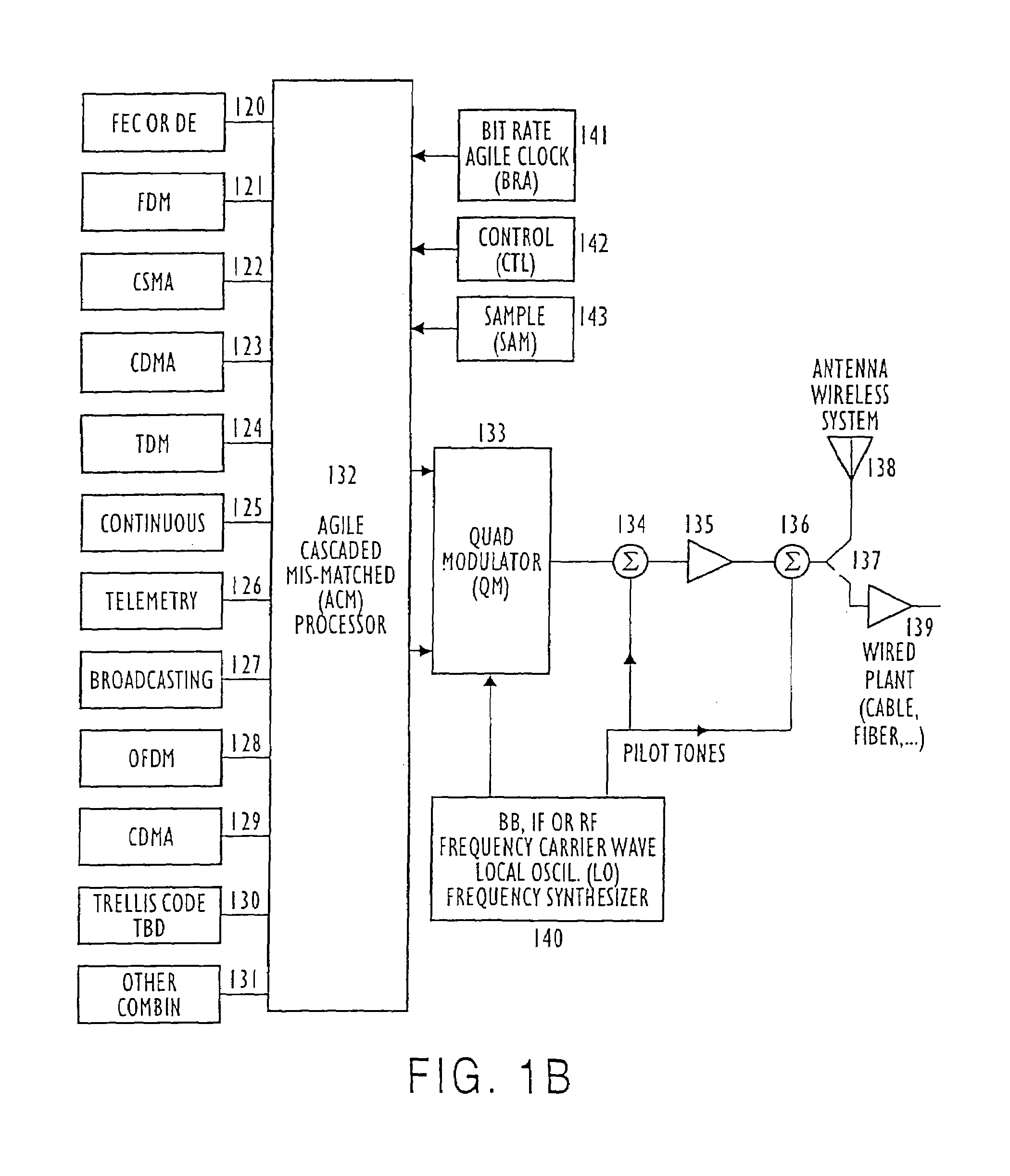
Modulation and demodulation format selectable system
InactiveUS7133456B2Improve efficiencyImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTError preventionQuadrature modulatorModem device
Modulation Demodulation (Modem) Format Selectable (MFS) and Code Selectable (CS) systems for new generations of wireless systems, including third generation “3G”, spread spectrum systems, CDMA,W-CDMA and GSM, OFDM systems having different bit rates, that is having bit rate selection or bit rate agile( BRA) operation. MFS and Code Selectable (CS) systems connected to one or more modulators, one or more transmit amplifiers and one or more antennas. The transmitted signals are received by single or multiple receivers and demodulators.Shaped Time Constrained Signal(TCS) wavelet processors and bit rate agile Long Response (LR) filters provide shaped Time Constrained Signal (TCS) waveforms / filtered signals in in-phase(I) and quadrature-phase(Q) baseband channels to one or more Quadrature Modulators(QM) connected to the baseband signal processing network. A control processor and signal selection device selects one or more of the baseband signals and provides these signals through one or more quadrature modulators(QM) having the same or different radio frequency(RF) signals for amplification by one or more amplifiers. A selection device for selecting a Linearly and / or a Non-Linearly Amplified (NLA) modulated signal is provided and the selected amplified signal is provided to one or more transmit antenna systems or to one or more transmission media.
Owner:WI LAN INC
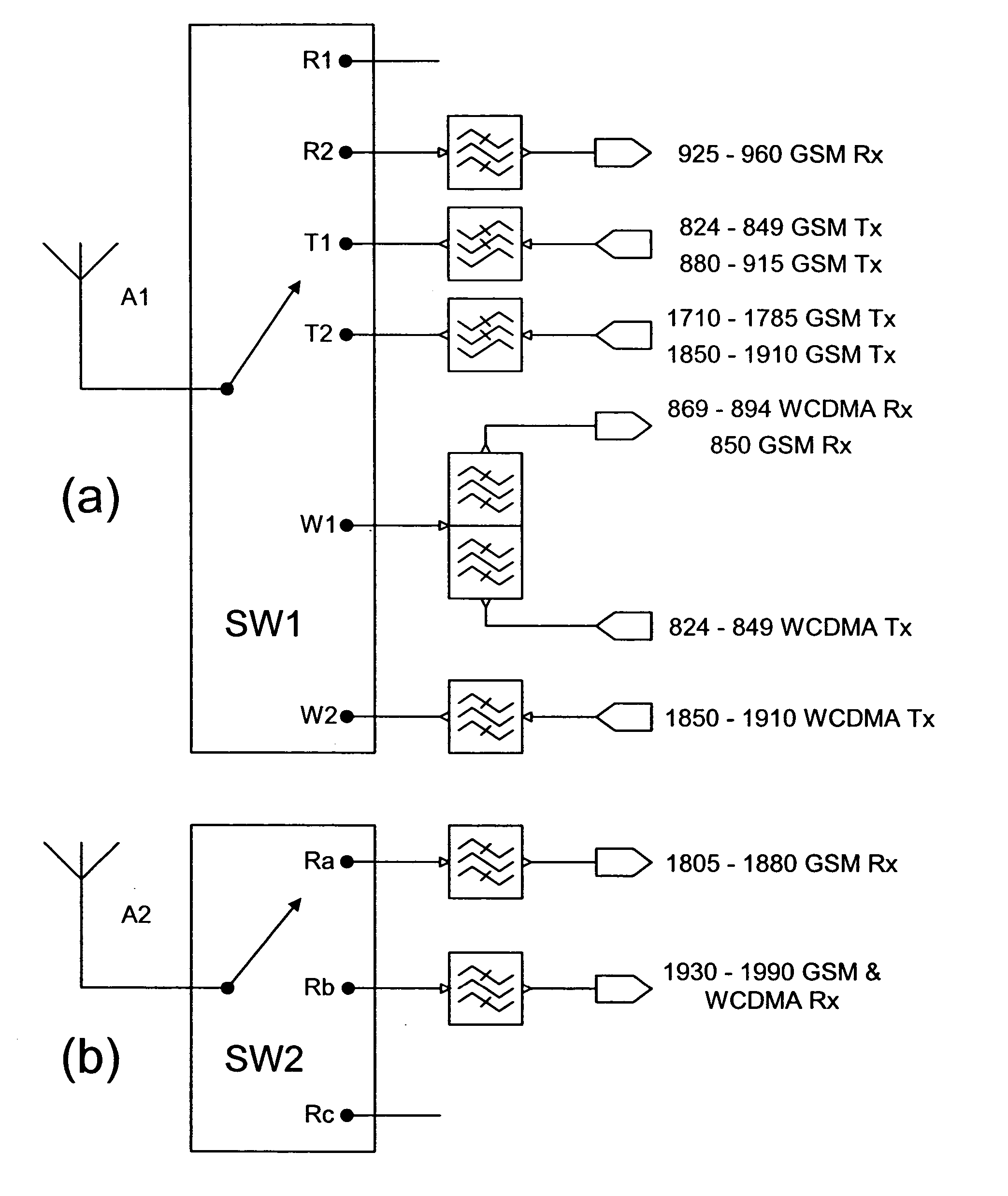
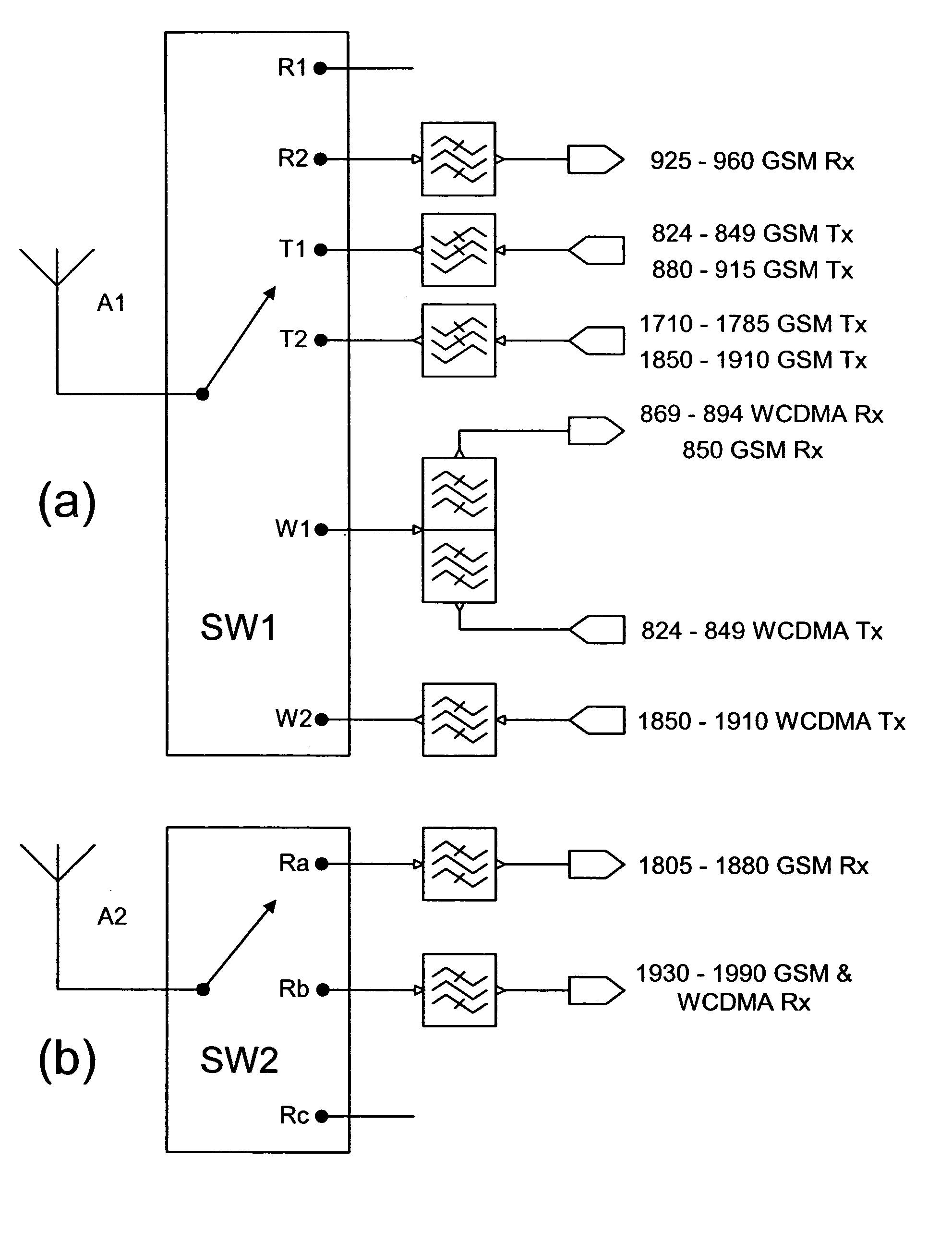
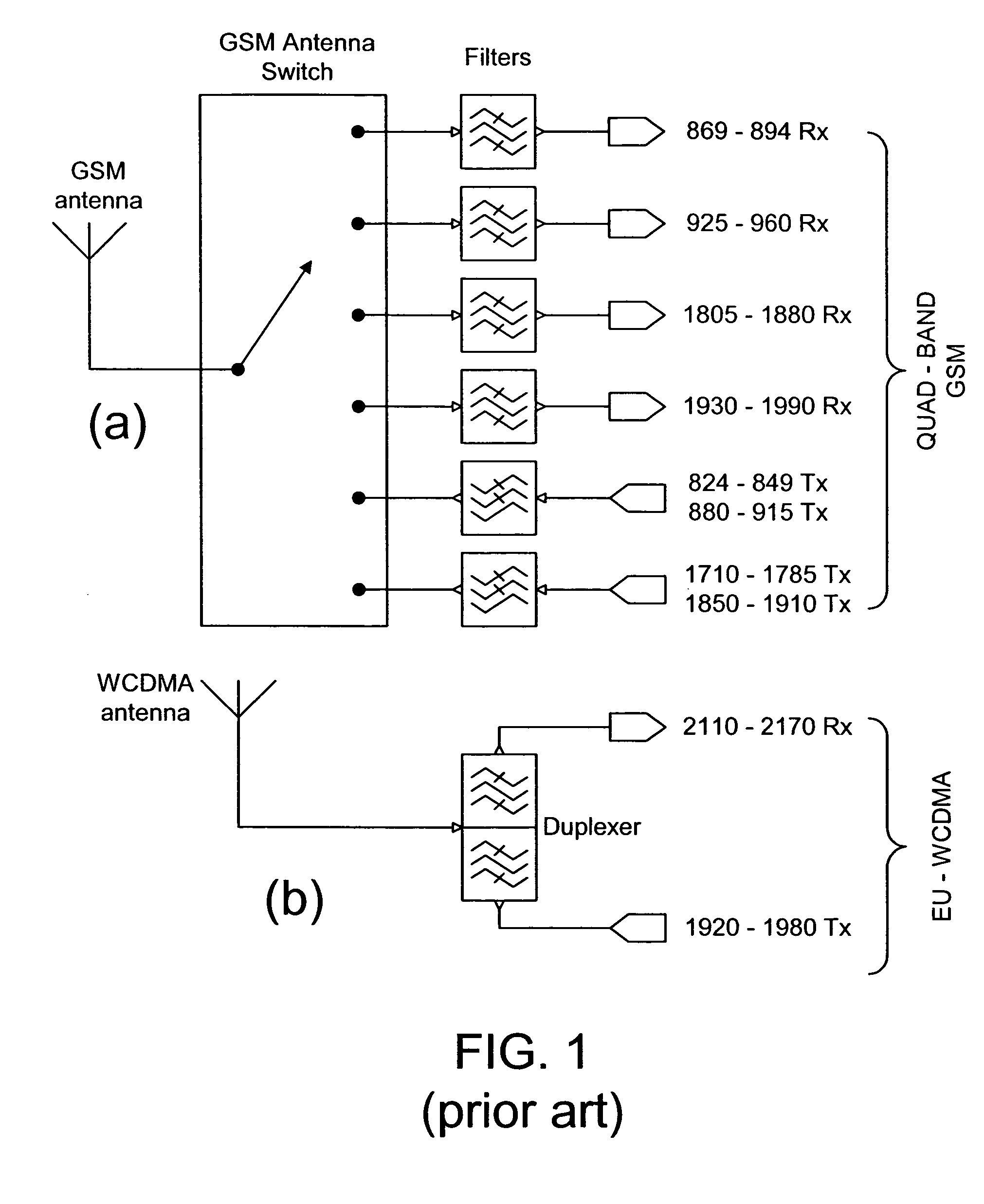
Versatile antenna switch architecture
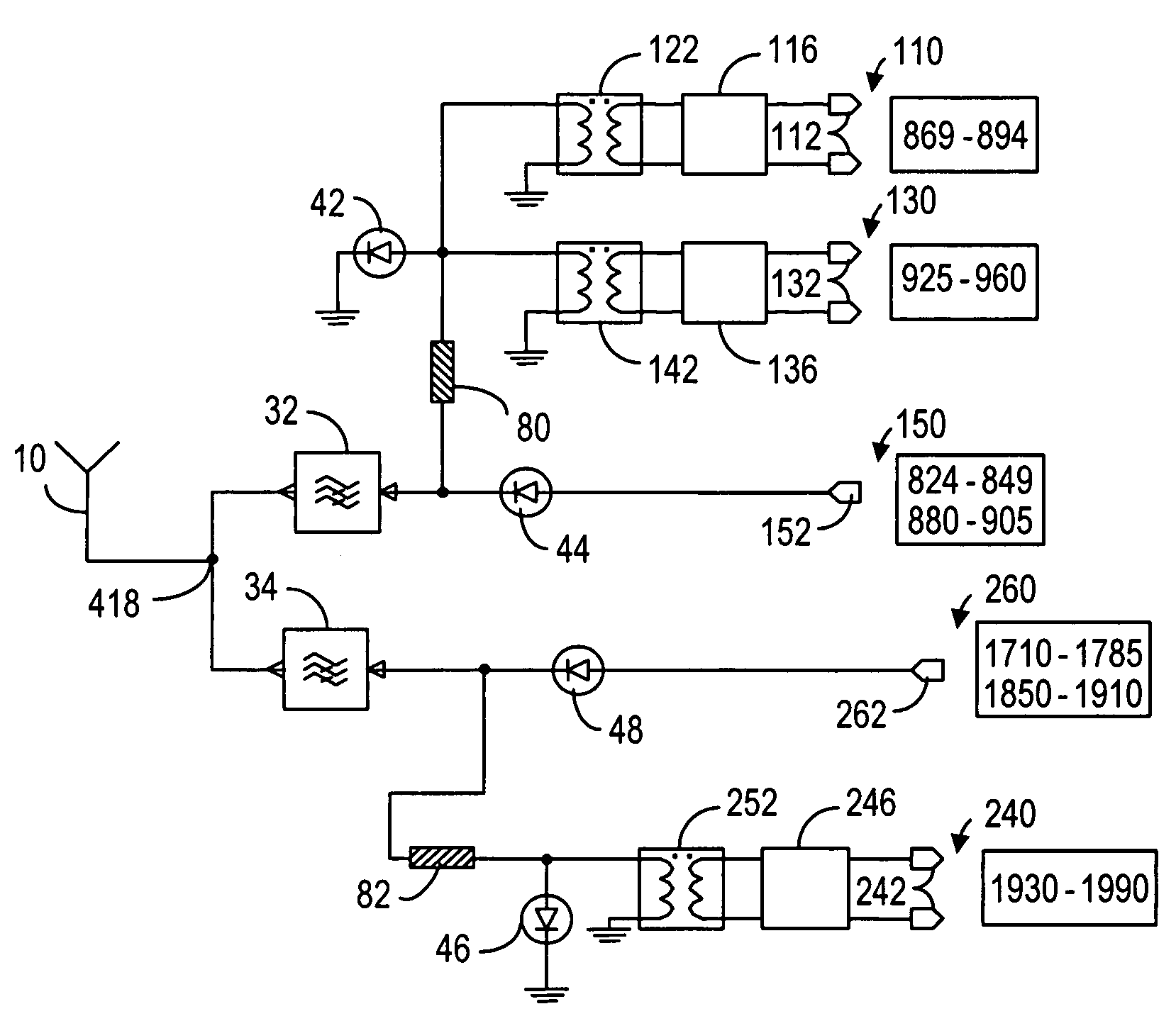
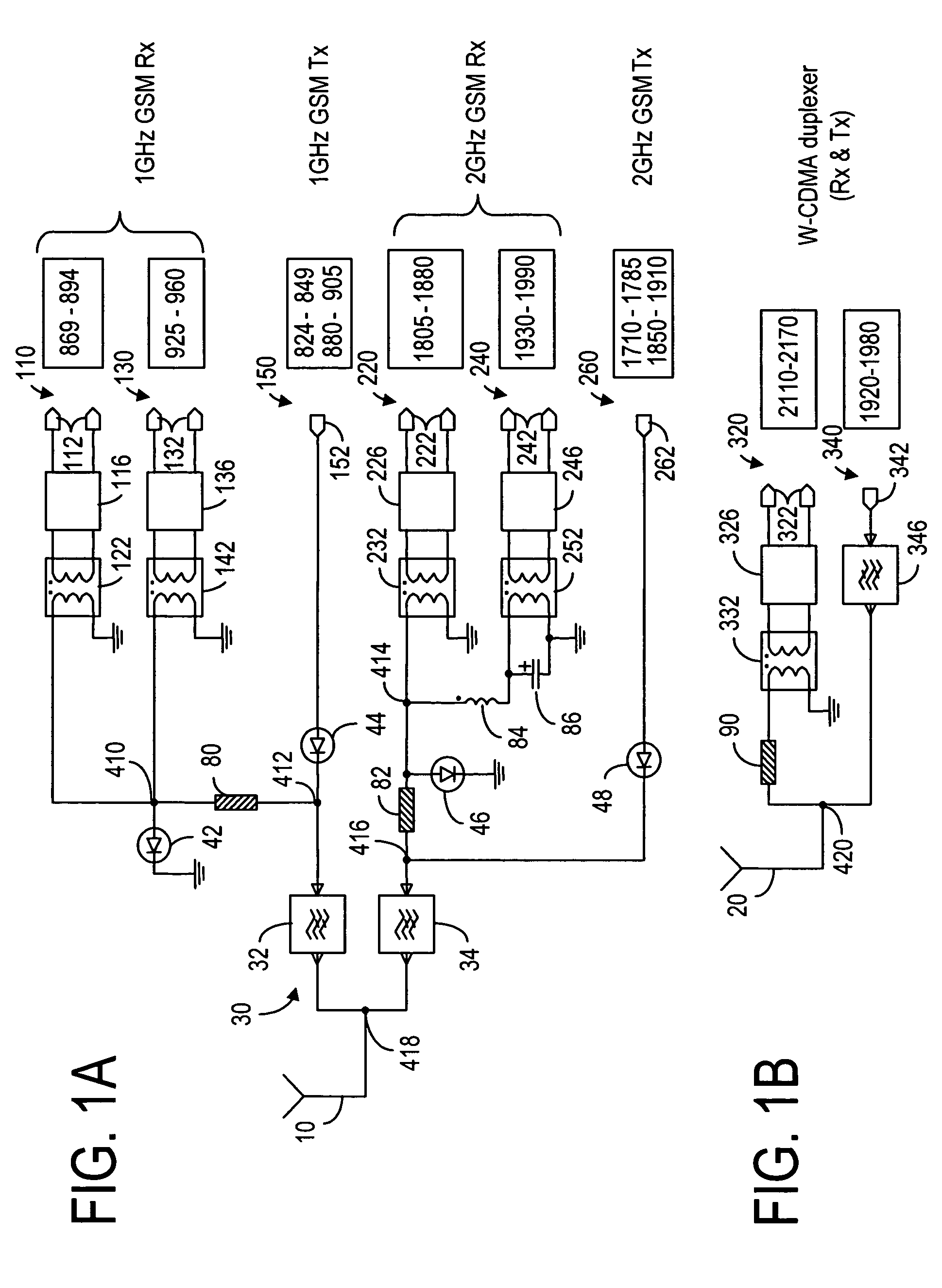
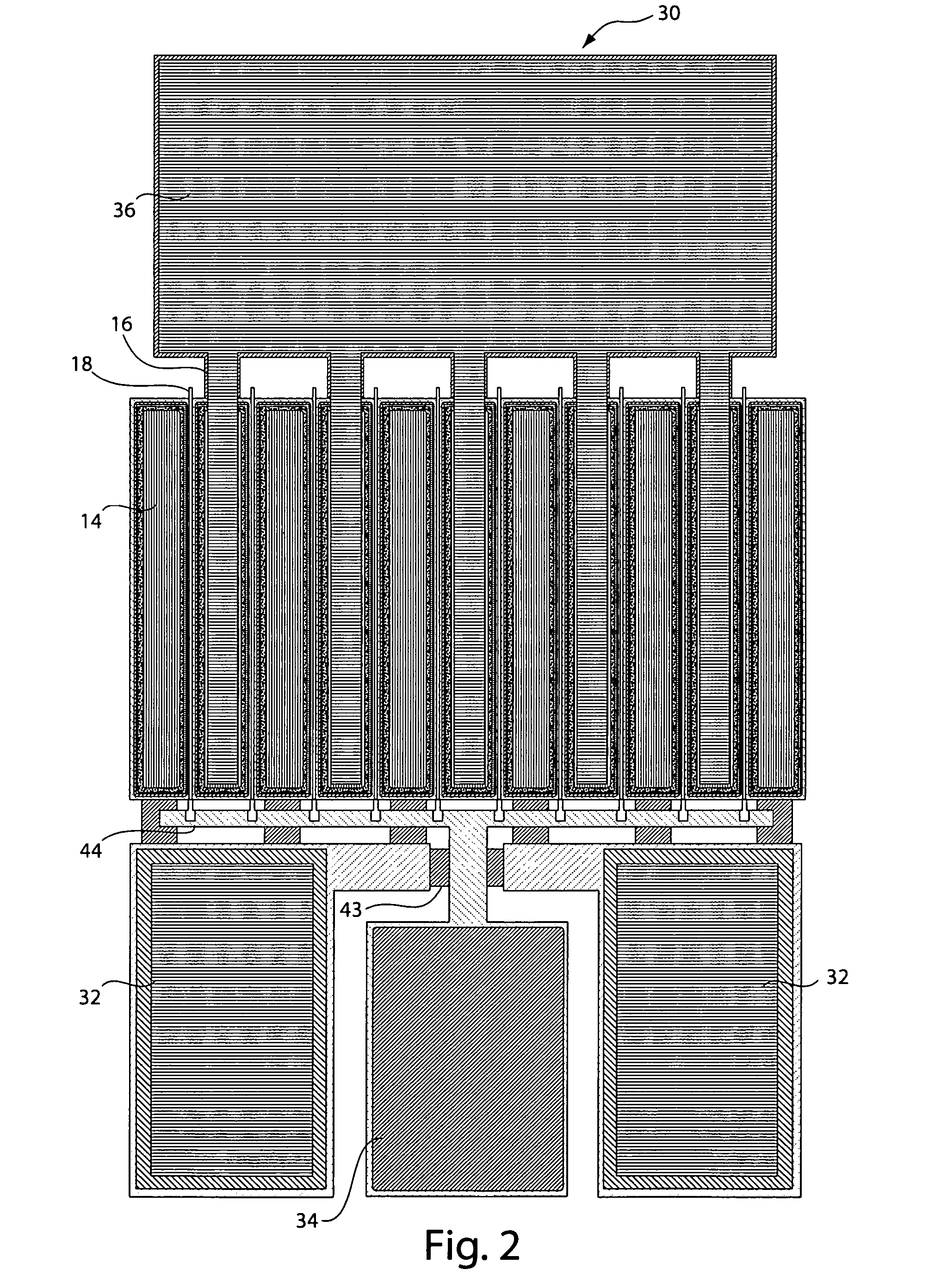
ActiveUS20050245202A1Discontinuous tuning for band selectionSubstation equipmentRF front endEngineering
A RF front-end having two antenna switches operatively connected to two separate antennas. The antenna switches can be used to route various transmit and receive paths to the antennas. In particular, one of the antenna switches has three switch position for use in selectively routing the 2 GHz receive paths, and another antenna switch has six switch positions for use in selectively routing the 2 GHz transmit paths and the 1 GHz signal paths. With the disclosed topology, the front-end can be used to support GSM and W-CDMA communications in many regional variants in the world. The supported variants include US1, US2, EU1, EU2 and EU / US modes. The same front-end can also be used in BT / WLAN connectivity. For MIMO purposes, one more antenna switch for the 2 GHz receive paths can be added to the same RF front-end.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
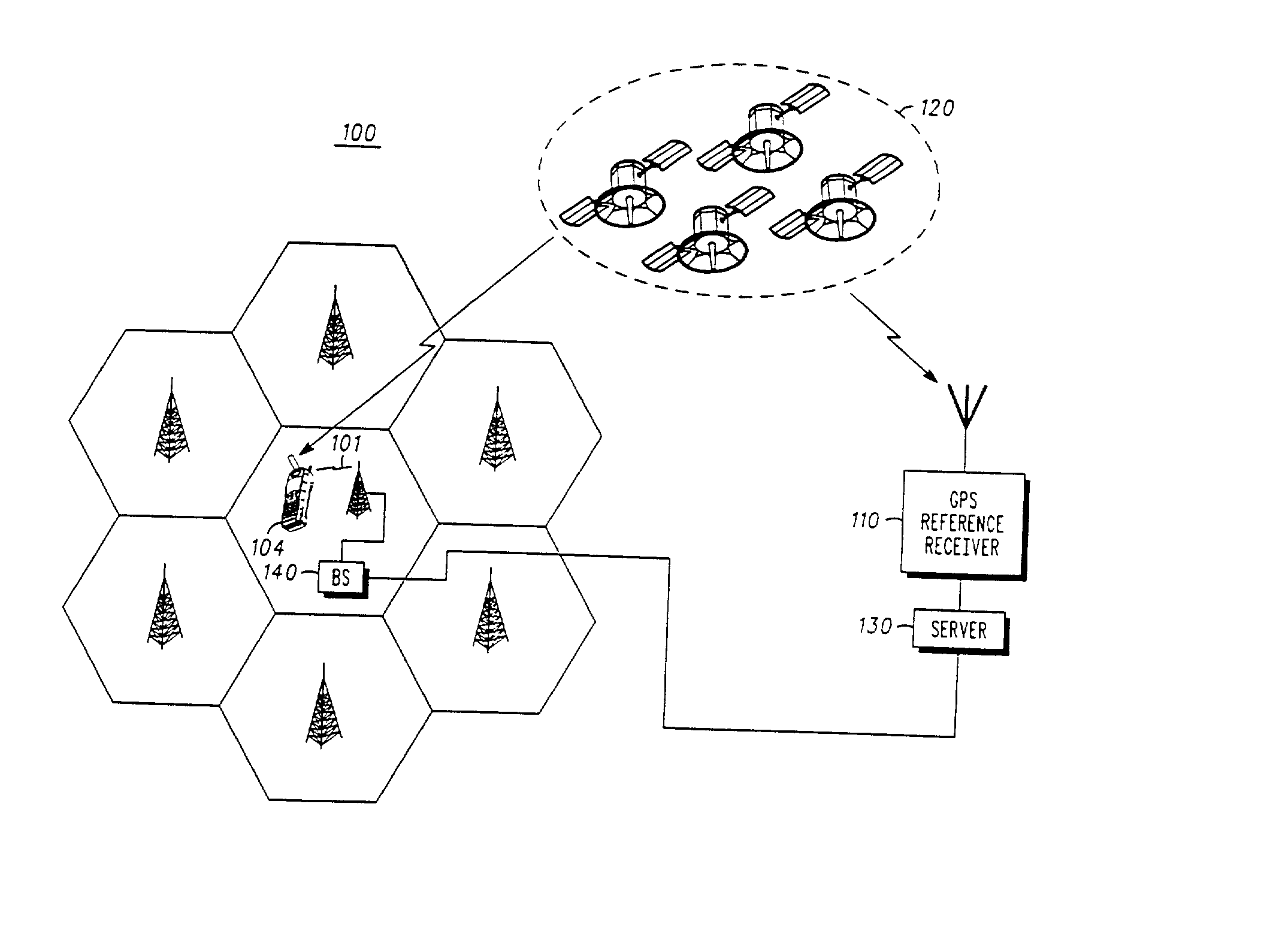
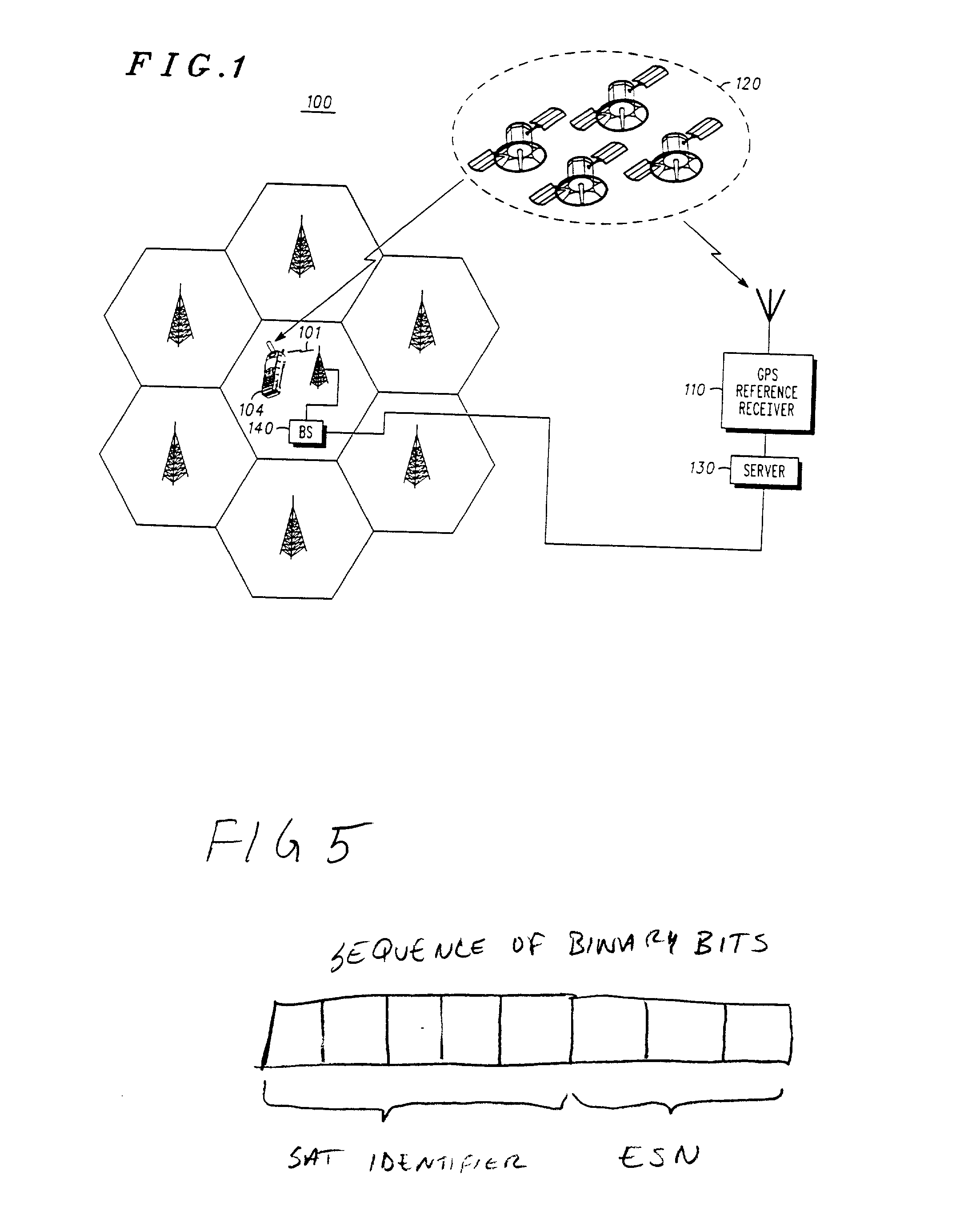
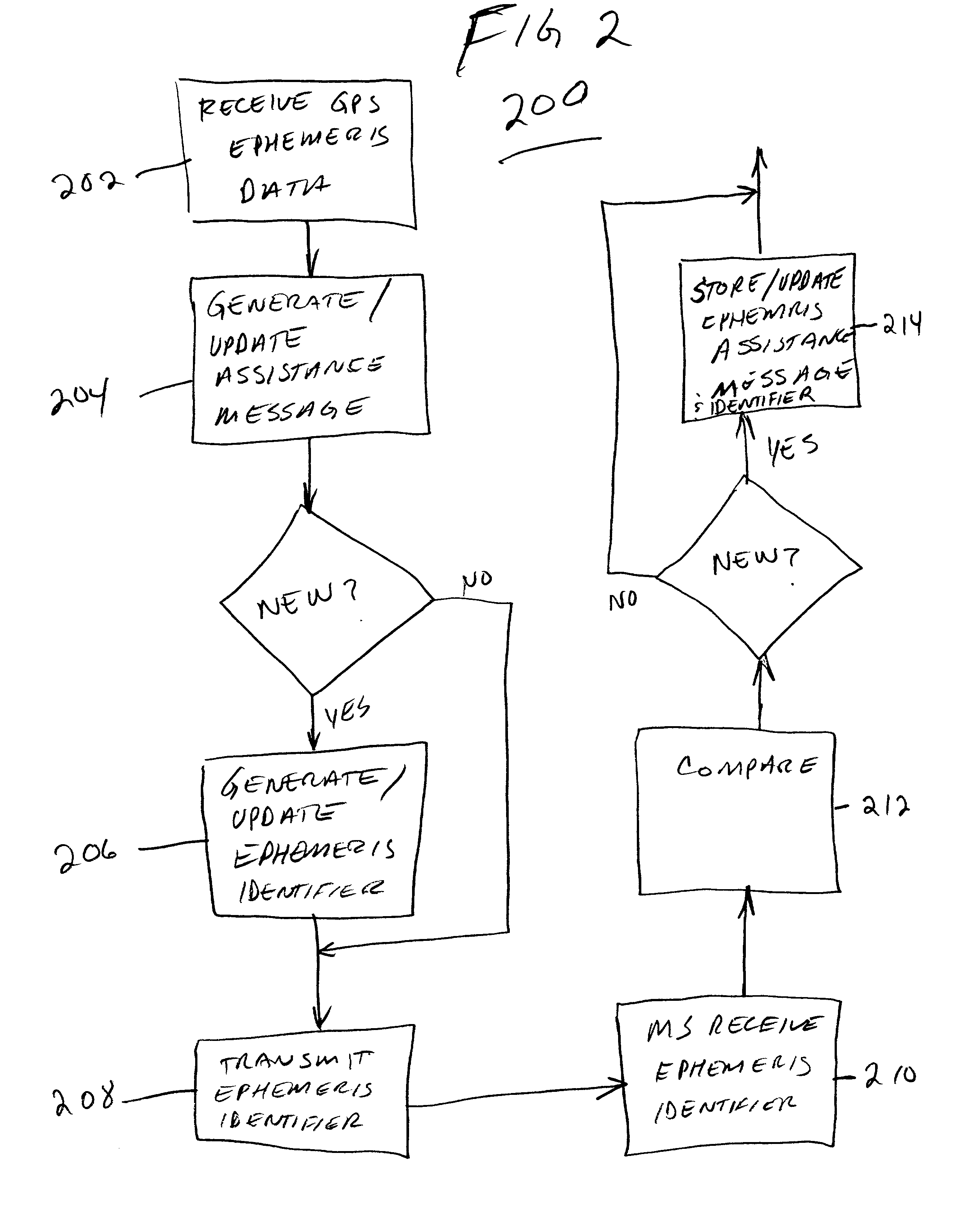
GPS assistance messages in cellular communications networks and methods therefor
InactiveUS20020168985A1Energy efficient ICTRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsEphemerisMobile station
GPS assistance message and data issue identifiers for transmission to GPS enabled mobile stations in cellular communications networks and methods therefor. The GPS data issue identifiers indicate whether GPS data, for example corresponding ephemeris and almanac data, stored at the mobile station requires updating. In the exemplary 3rd generation (W-CDMA / UMTS) architecture, the GPS assistance message is a System Information Block (SIB), and the GPS ephemeris data identifier and corresponding satellite identifier is encoded in a value tag included in a Master Information Block (MIB).
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Versatile antenna switch architecture
A RF front-end having two antenna switches operatively connected to two separate antennas. The antenna switches can be used to route various transmit and receive paths to the antennas. In particular, one of the antenna switches has three switch position for use in selectively routing the 2 GHz receive paths, and another antenna switch has six switch positions for use in selectively routing the 2 GHz transmit paths and the 1 GHz signal paths. With the disclosed topology, the front-end can be used to support GSM and W-CDMA communications in many regional variants in the world. The supported variants include US1, US2, EU1, EU2 and EU / US modes. The same front-end can also be used in BT / WLAN connectivity. For MIMO purposes, one more antenna switch for the 2 GHz receive paths can be added to the same RF front-end.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
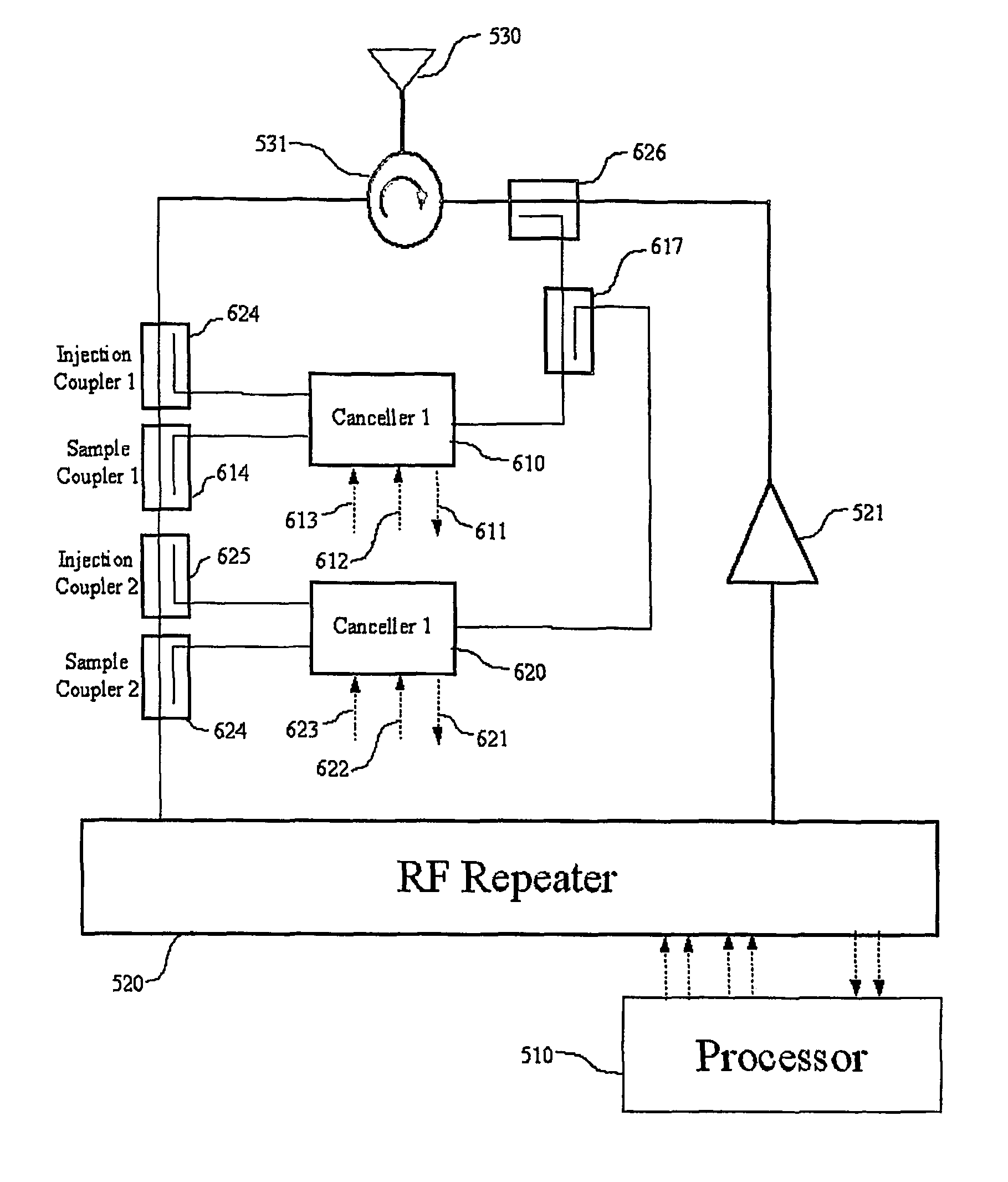
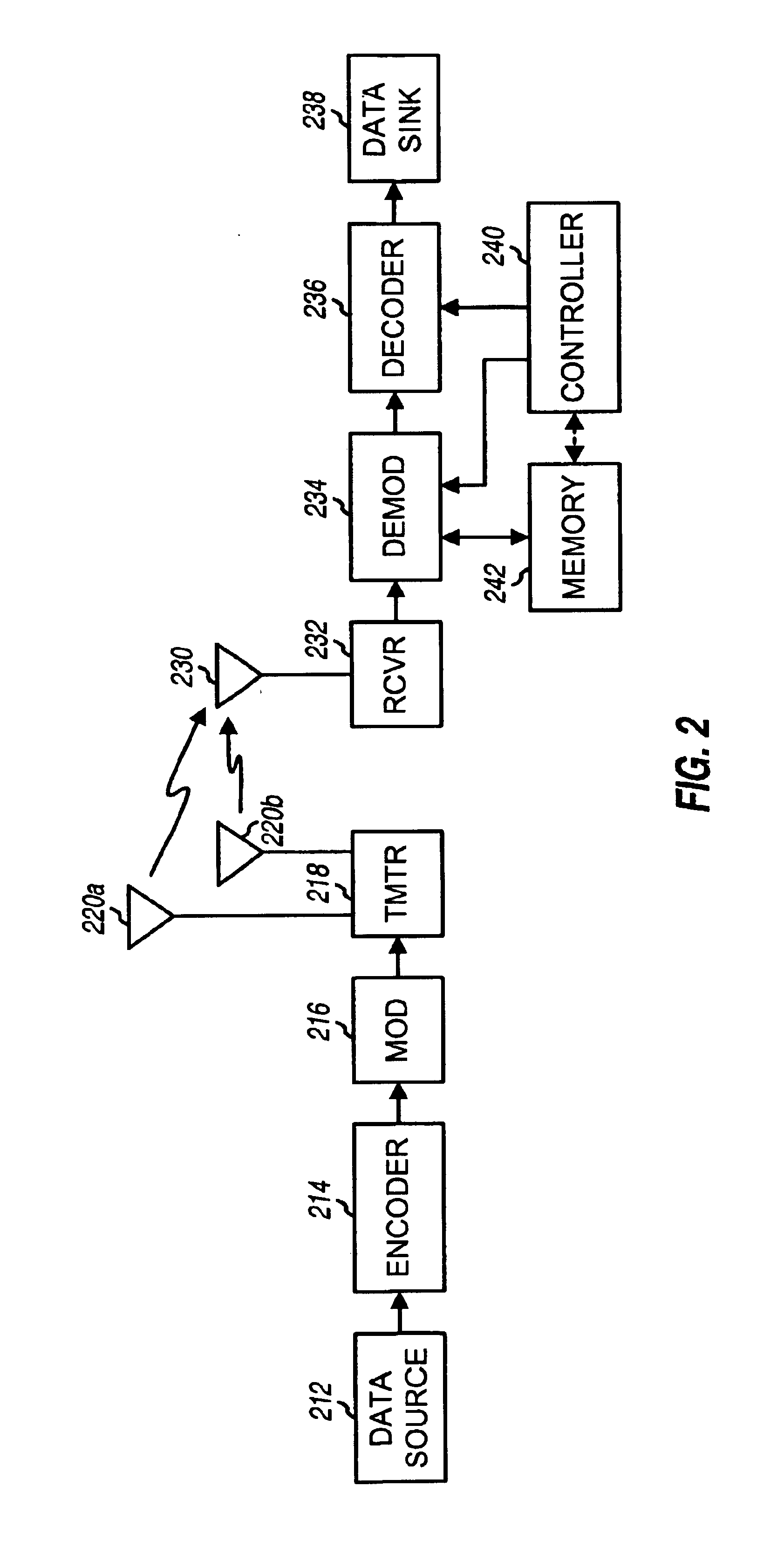
Transmission canceller for wireless local area network
InactiveUS8027642B2Improve performanceIncrease the areaPulse transformerFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverEngineering
A frequency translating repeater (200) for use in a wireless local area network includes a cancellation unit. Canceller (402) is controlled by control (401) to provide an injection signal for canceling leakage in a receive signal path. Reference coupler (403) provides a reference signal from the transmit signal, injection coupler (404) injects a correction signal, and sample coupler (405) provides a sample for feedback. A processor (510) receives the sample signal through a detector (415). Although the present invention is intended for a frequency translating repeater, it has broad applications in radio transceivers in general. One specific application is with frequency division duplex (FDD) handsets or base stations utilizing CDMA technologies such as W-CDMA and IS-2000 or 1XEV-DV / DO.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
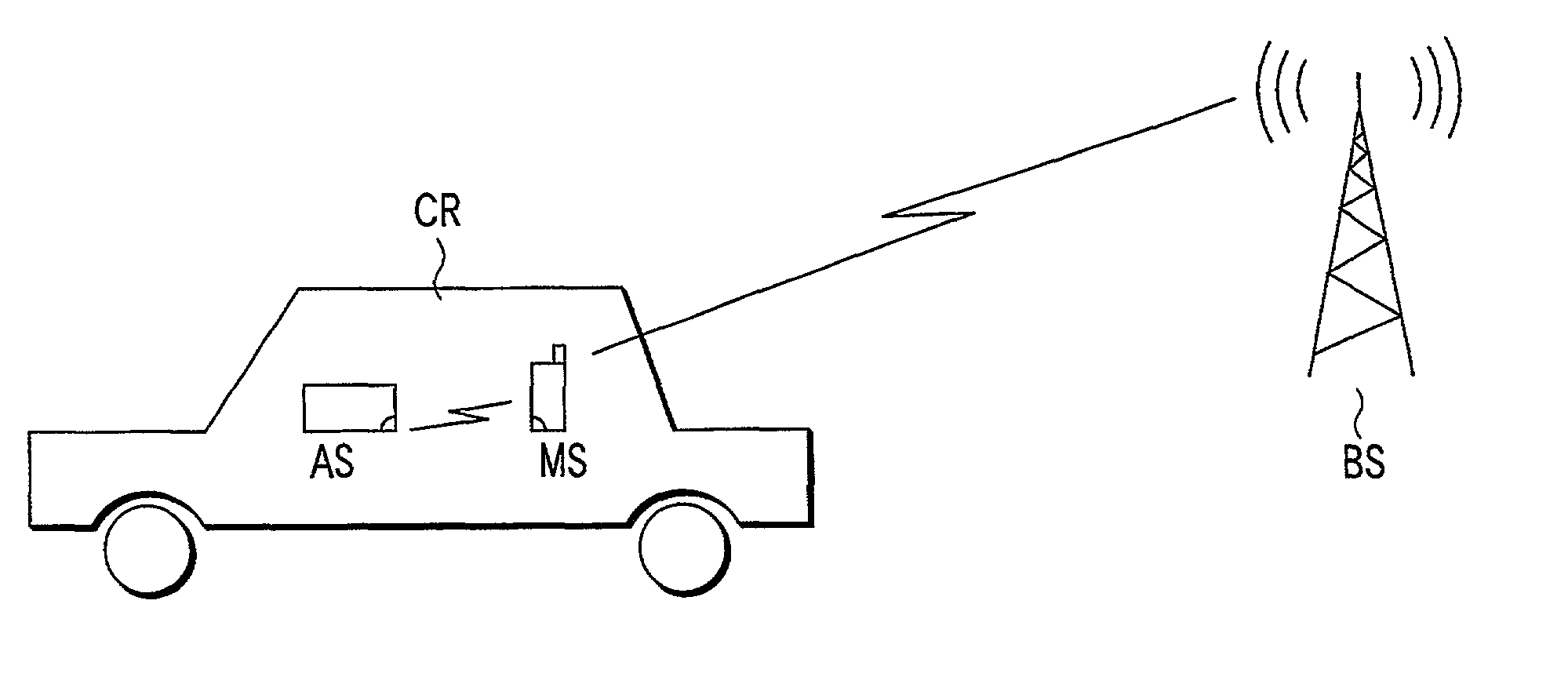
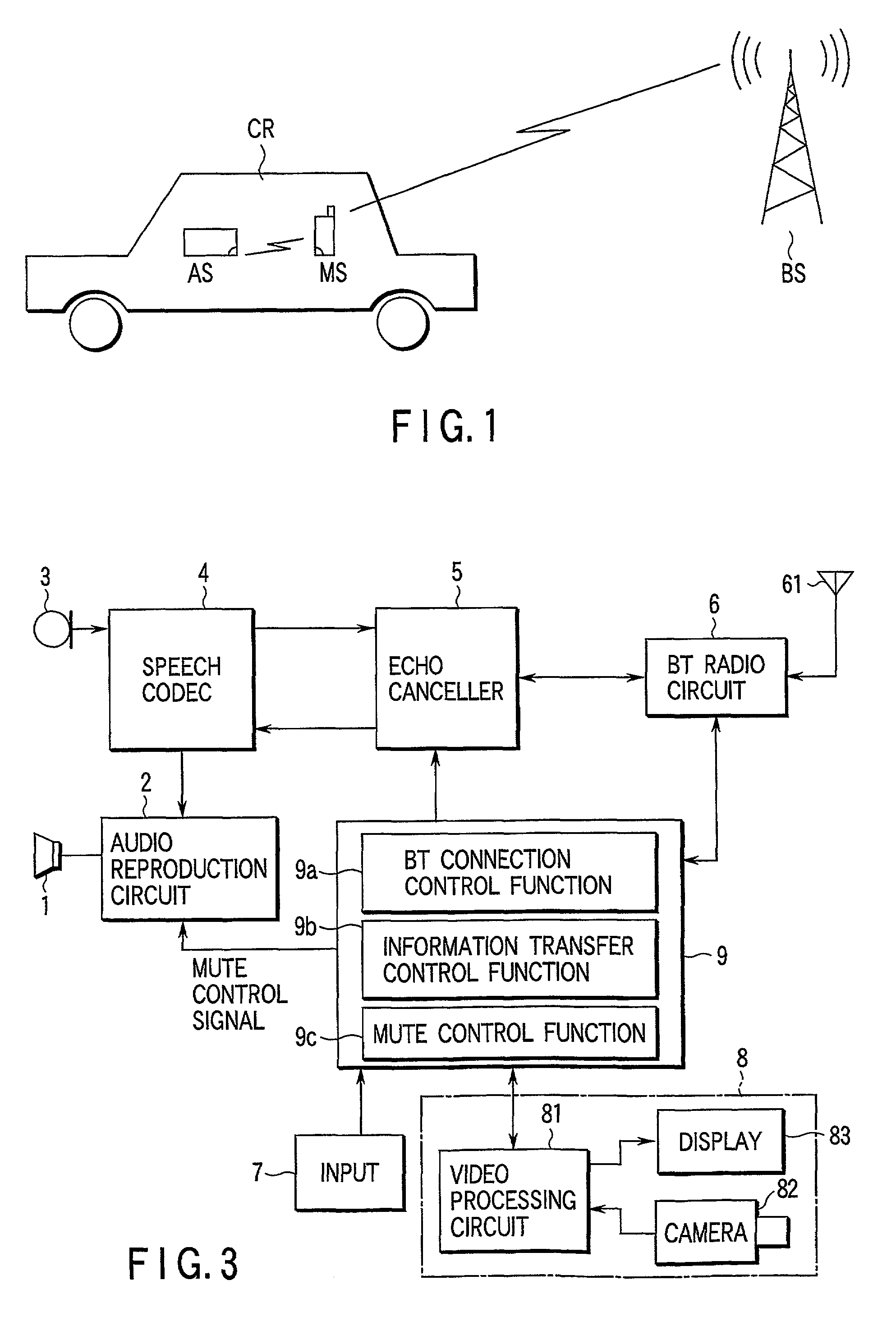
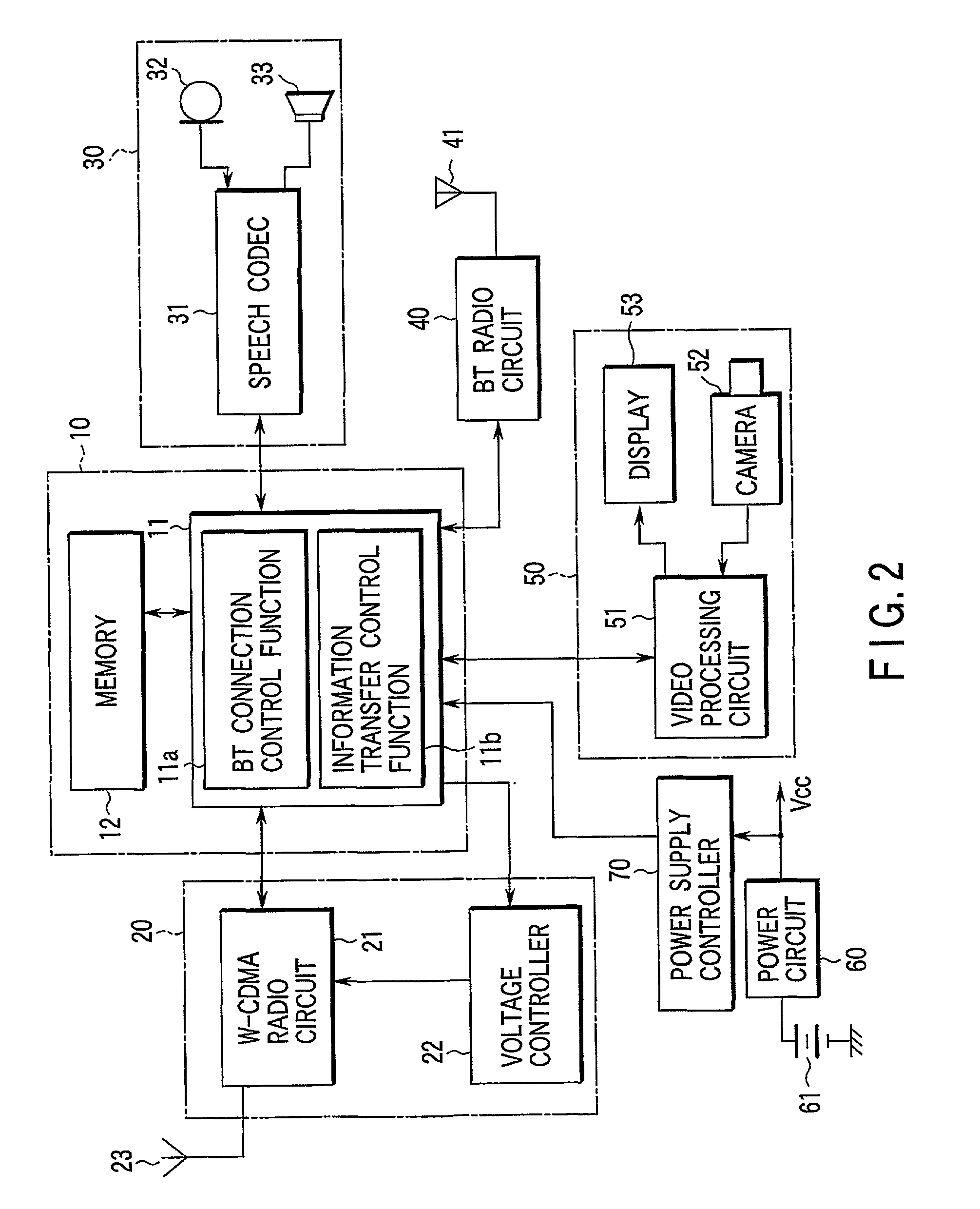
Mobile communication terminal and car mounted electronic device
InactiveUS20020142803A1Low costNetwork topologiesSubstation speech amplifiersComputer terminalHands free
BT wiring sections 40 and 6 are provided respectively at a mobile telephone set MS and a car audio device AS. When a user of the mobile telephone set MS gets on a car CR, a BT radio link is established between the mobile telephone set MS and the car audio device AS, and a hands-free communication mode is set to the mobile telephone set MS and car audio device AS. Then, the communication speech data received from / transmitted to a mobile communication network via a W-CDMA radio link is transferred between the mobile telephone set MS and the car audio device AS, thereby enabling hands-free communication.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
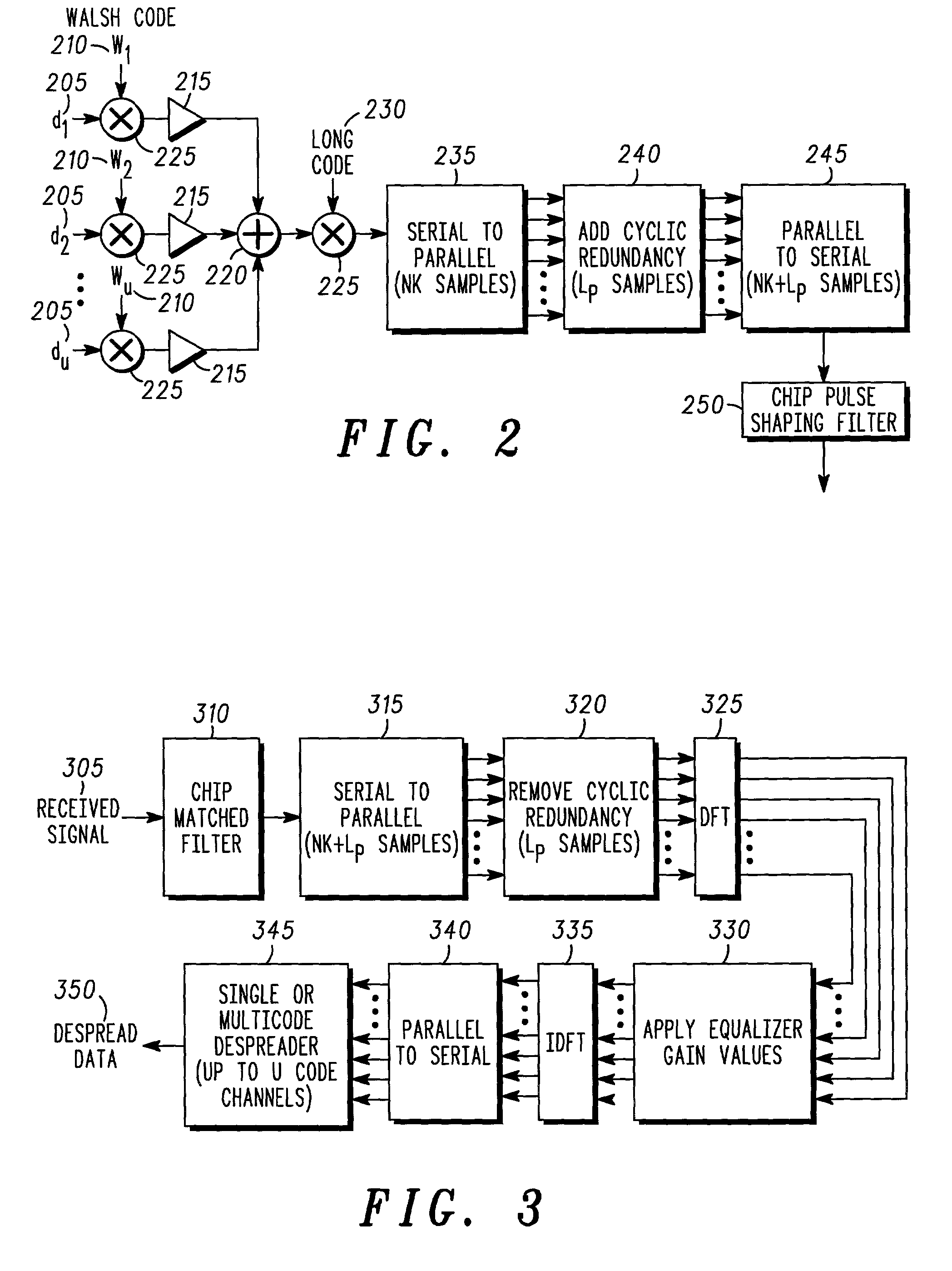
Method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA system
The invention provides a method and system for transmission and frequency domain equalization for wideband CDMA communications by providing at least one spread sequence portion, and inserting a cyclic redundancy to the spread sequence to form a transmitted baseband sequence. The invention further provides a method and system for converting a plurality of receive samples from at least one spread sequence portion into a plurality of frequency domain samples, determining a plurality of frequency domain equalization weights for the frequency domain samples, and determining a time domain signal estimate based on the frequency domain equalization weights and frequency domain samples.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
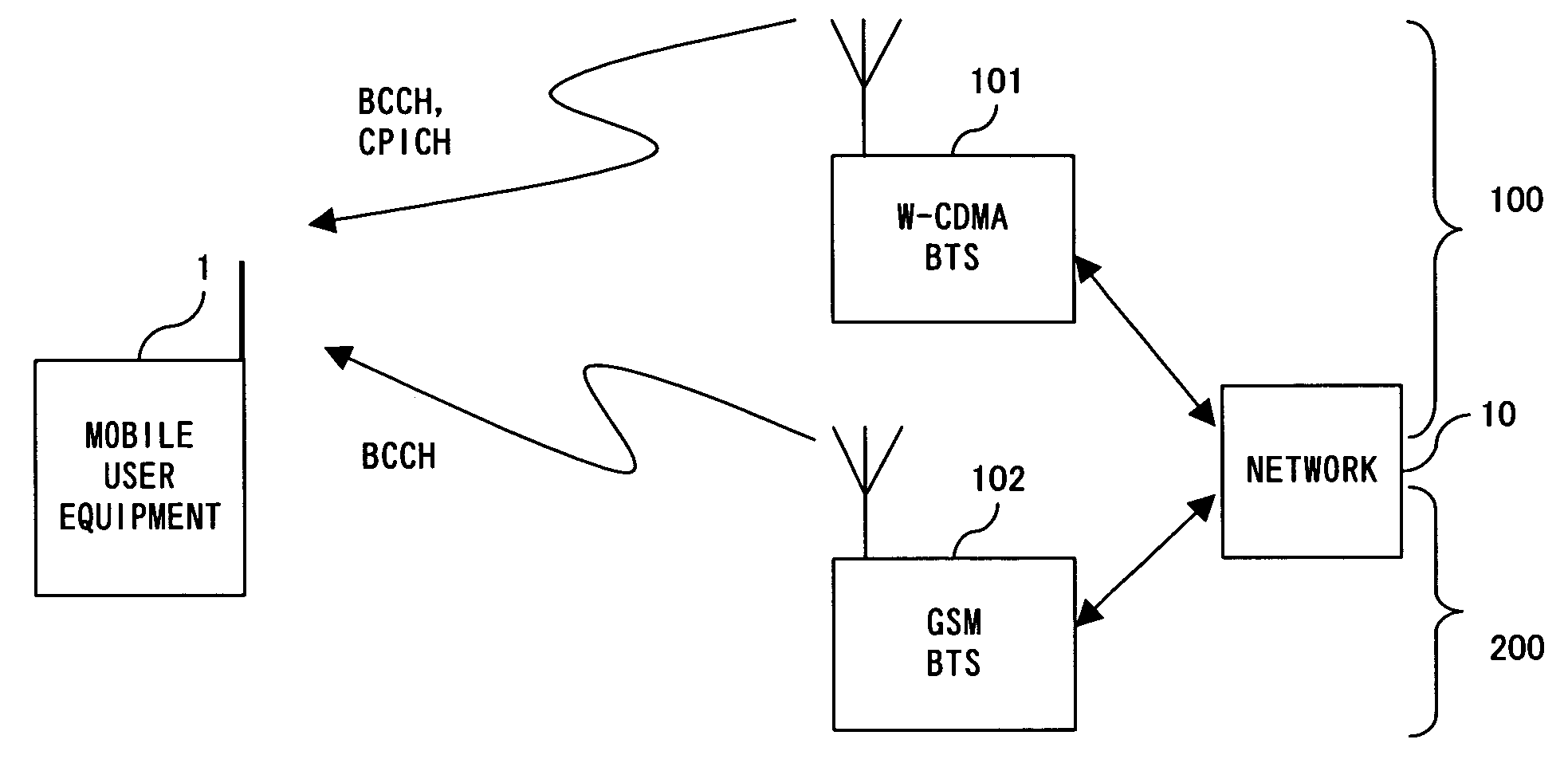
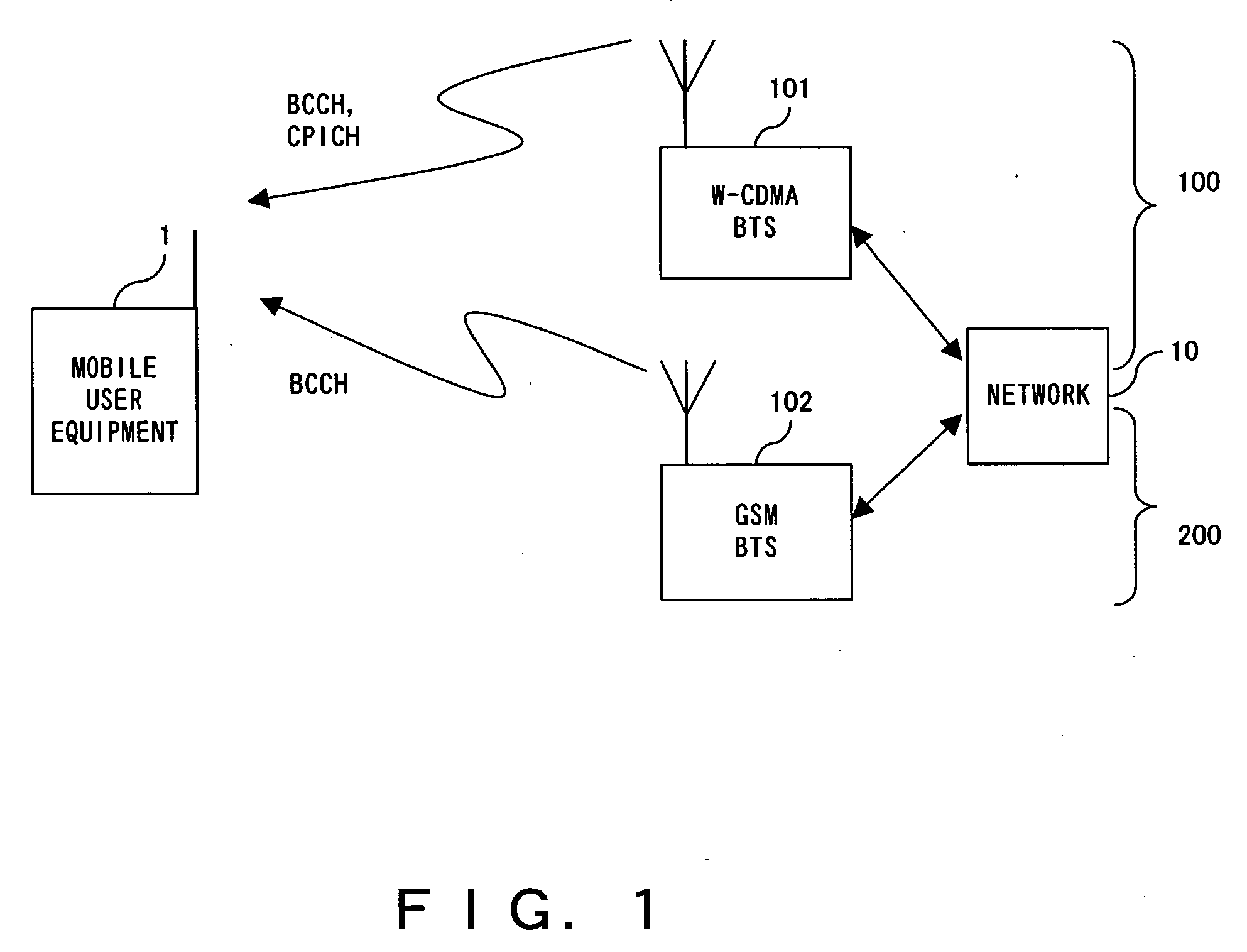
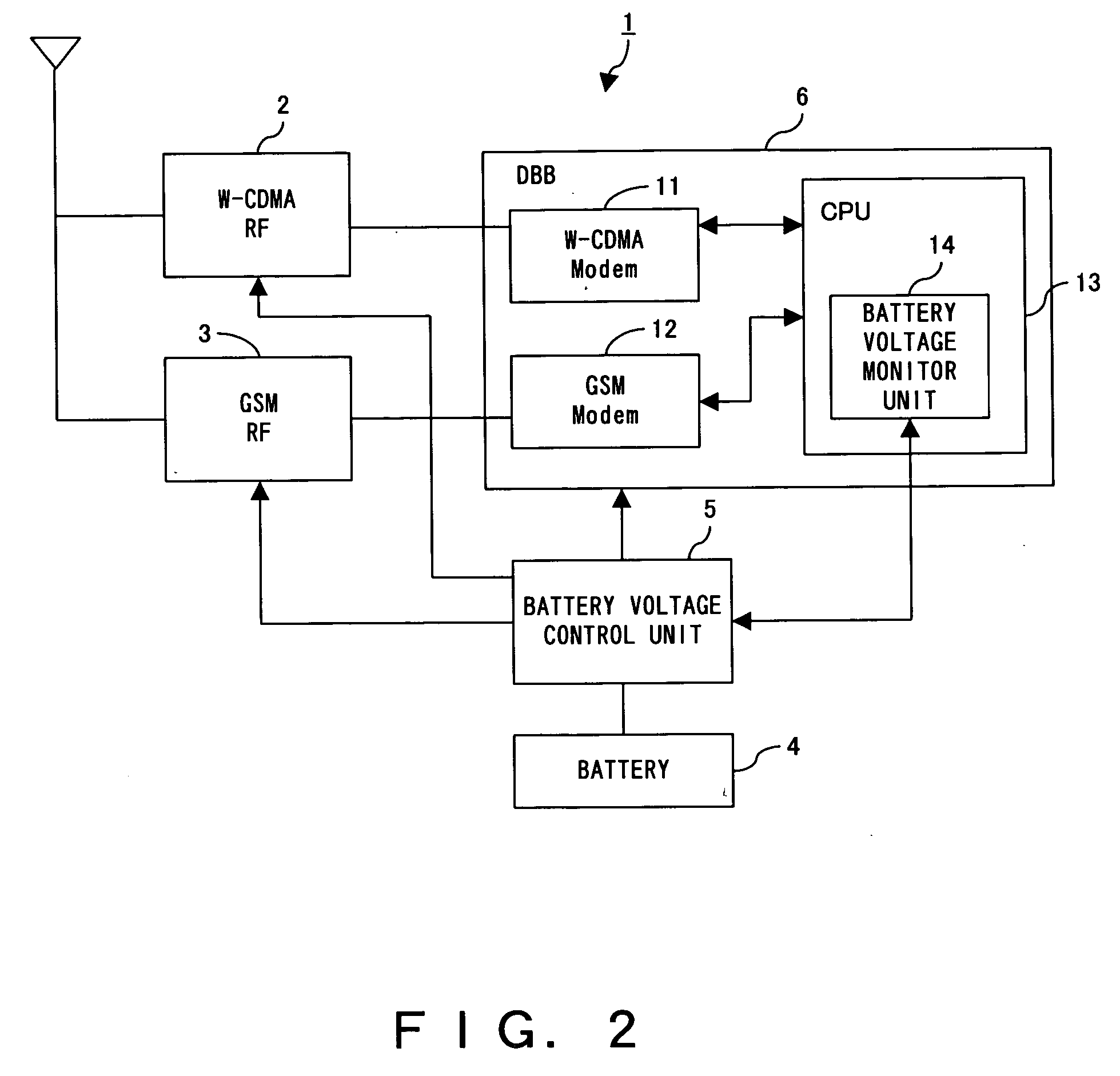
Dual mode communication system, dual mode communication method and dual mode communication user equipment
InactiveUS20060223465A1Add equipmentImprove operationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTCommunications systemDual mode
A dual mode communication system, with user equipment selectively connectable to a plurality of communication systems, for switching communication systems to which the user equipment should be connected, detects that the remaining battery level fell below a first threshold in the user equipment communicating over the W-CDMA system. In the system it is determined whether or not the user equipment can communicate using the GSM system, which can be operated with lower power consumption than the W-CDMA system. When it is determined that communication can be established with the GSM system, the system switches from a connection between the user equipment and the W-CDMA system to a connection between the user equipment and the GSM system without interrupting the communication over the W-CDMA.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
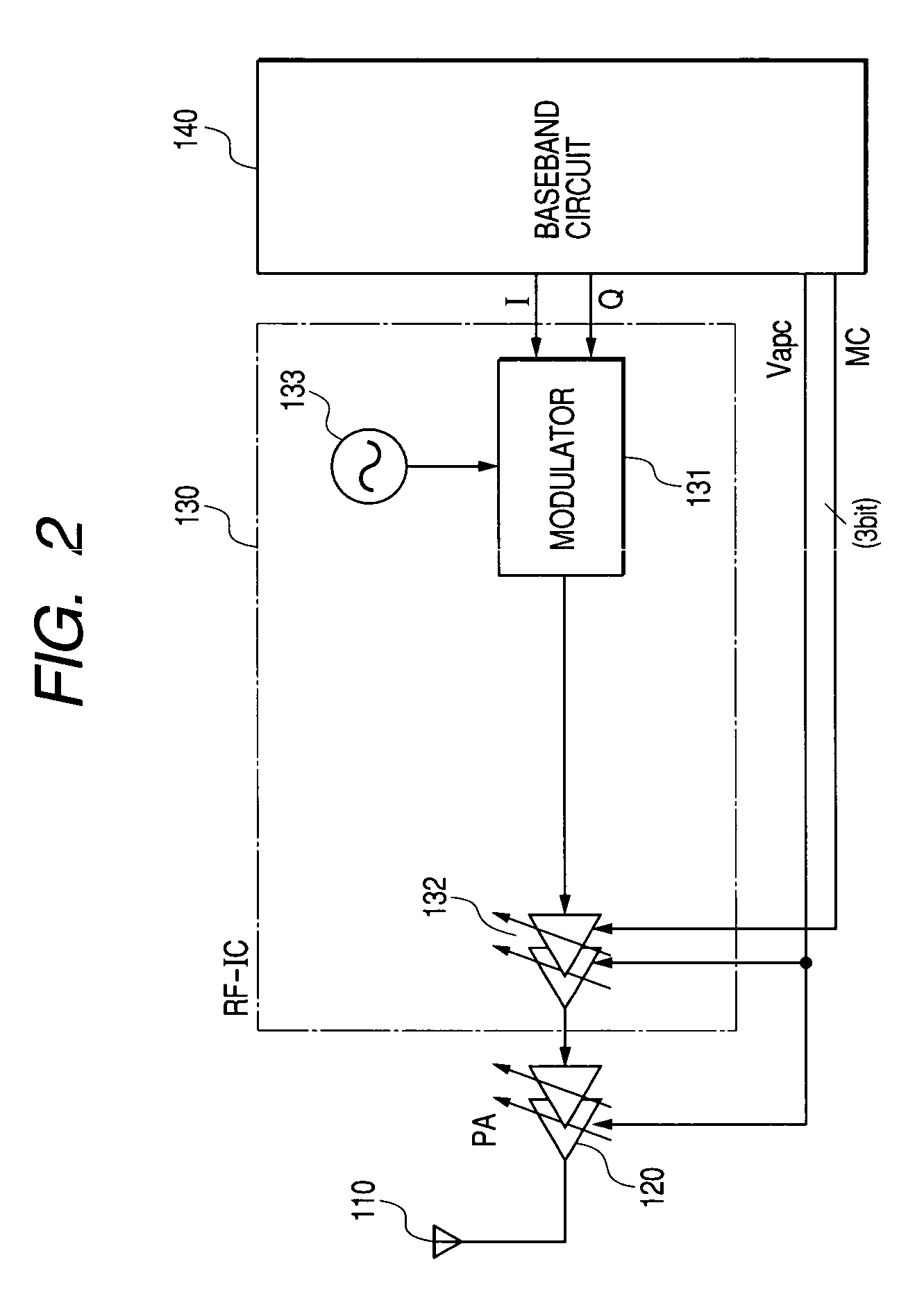
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
InactiveUS7116949B2Total current dropImprove dynamic rangeResonant long antennasGain controlCurrent consumptionEngineering
The dynamic range is changed by switching a current applied to an amplifying circuit to obtain the minimum ICP required to keep linearity with the number of multiplexes even when the number of multiplexes of data is changed by switching the operation current of the amplifying circuits of the transmission system and also supplying the information about number of multiplexes of data to be transmitted to the amplifying circuits of the transmission system from the baseband circuit. Thereby, the signal can be transmitted without distortion even when the number of multiplexes increases and the current of the amplifying circuit may be reduced when the number of multiplexes is small in order to reduce the current consumption in the communication semiconductor integrated circuit device which can form a wireless communication system of the code division multiplex system such as W-CDMA system.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for processing a physical channel with partial transport format information
InactiveUS6879576B1Radio transmission for post communicationMultiplex code allocationParallel computingCdma systems
Techniques for recovering data transmitted on a physical channel in which the channelization code is not known at the time of the data recovery. A modulated signal is received an processed to provide received samples. A hypothesized channelization code (e.g., an OVSF code in the W-CDMA system) is selected and used to process the received samples to generate partially processed symbols. The hypothesized channelization code is a “base” code that can be used to generate all possible channelization codes that may have been used for the physical channel. Intermediate results representative of the partially processed symbols are stored and, upon determination of the actual channelization code, further processed in accordance with the actual and hypothesized channelization codes to provide the final results.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
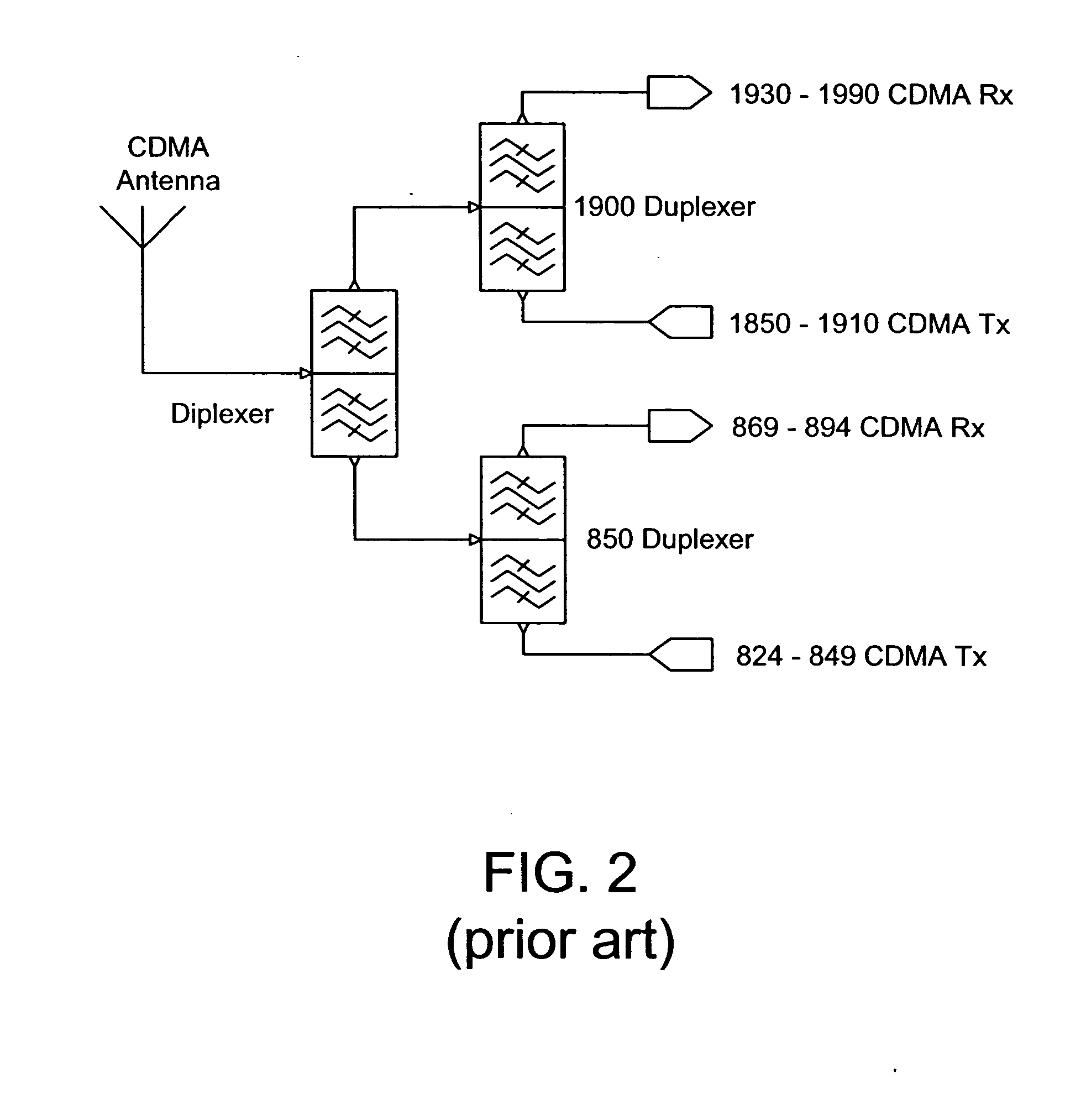
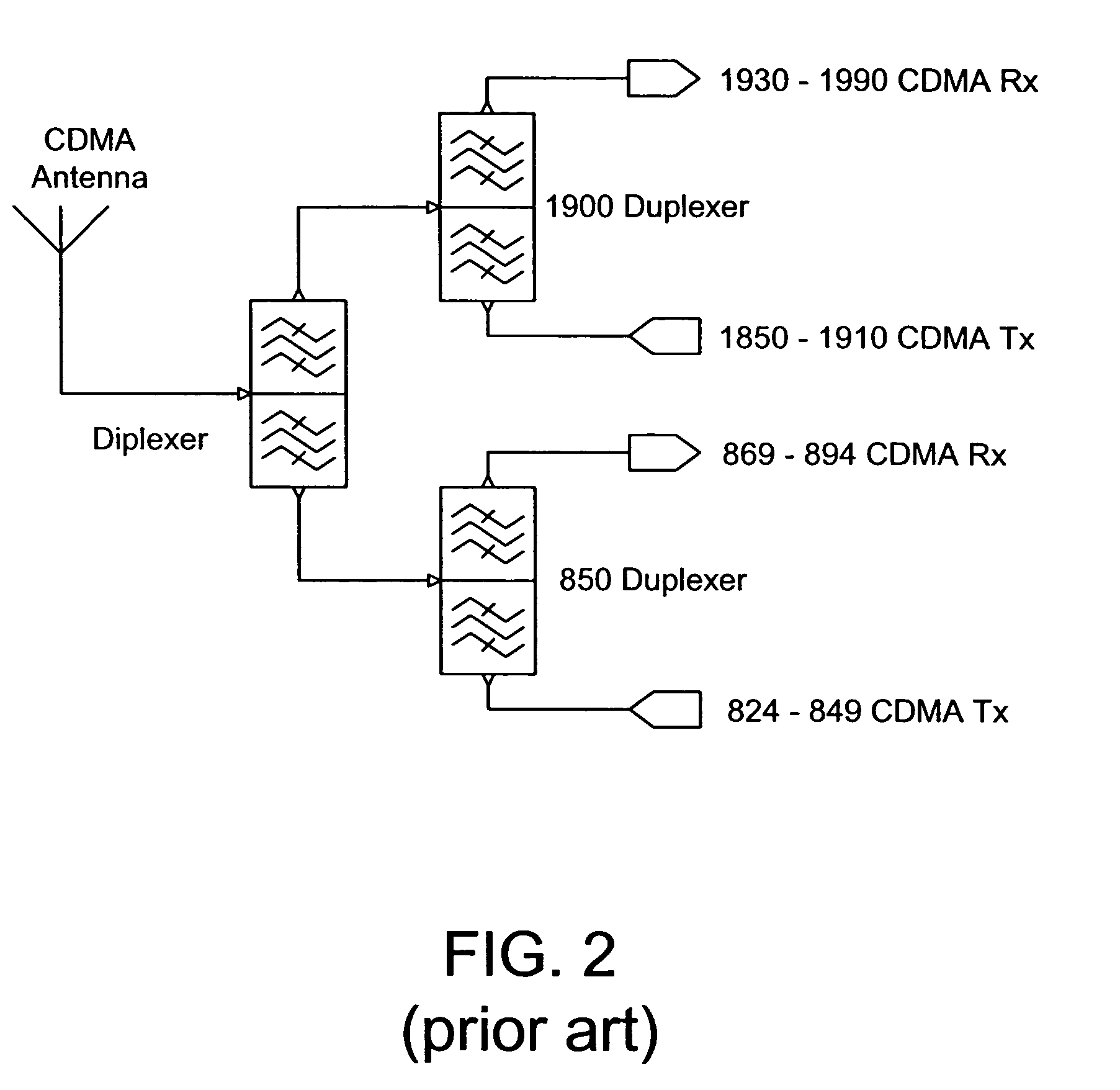
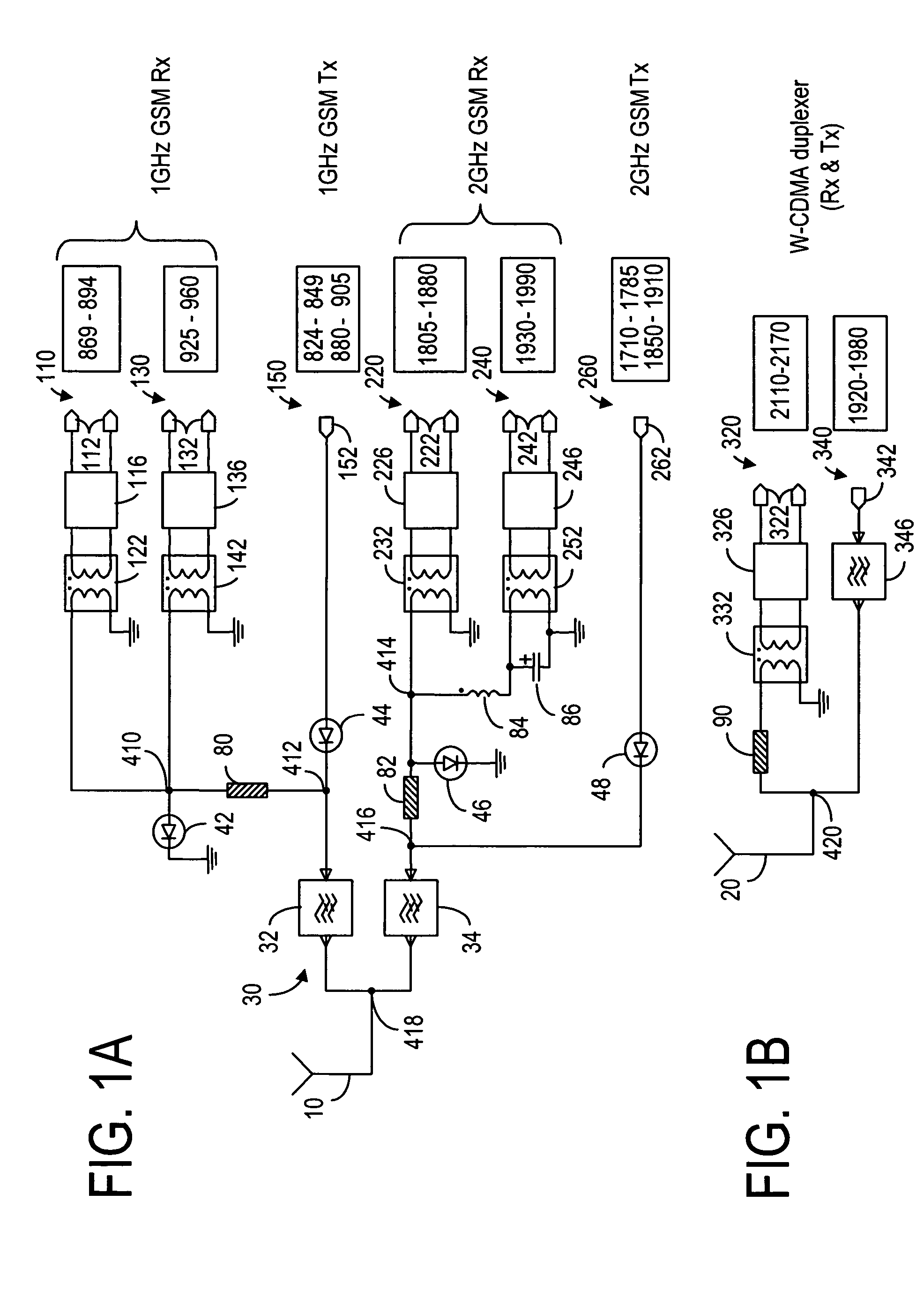
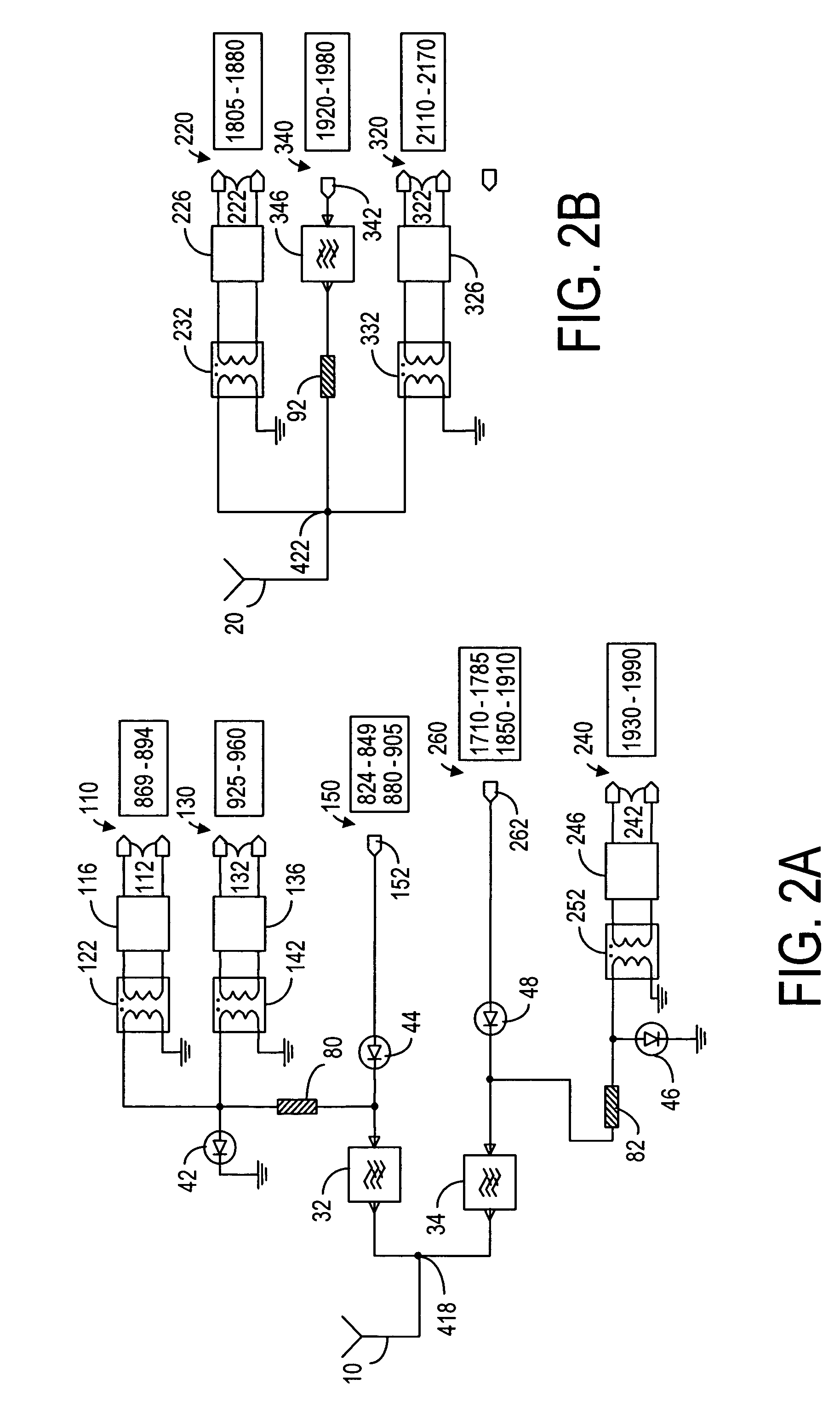
Front end module
ActiveUS20040224643A1Small sizeReduce weightSolid-state devicesSubstation equipmentElectrical conductorAcoustic wave
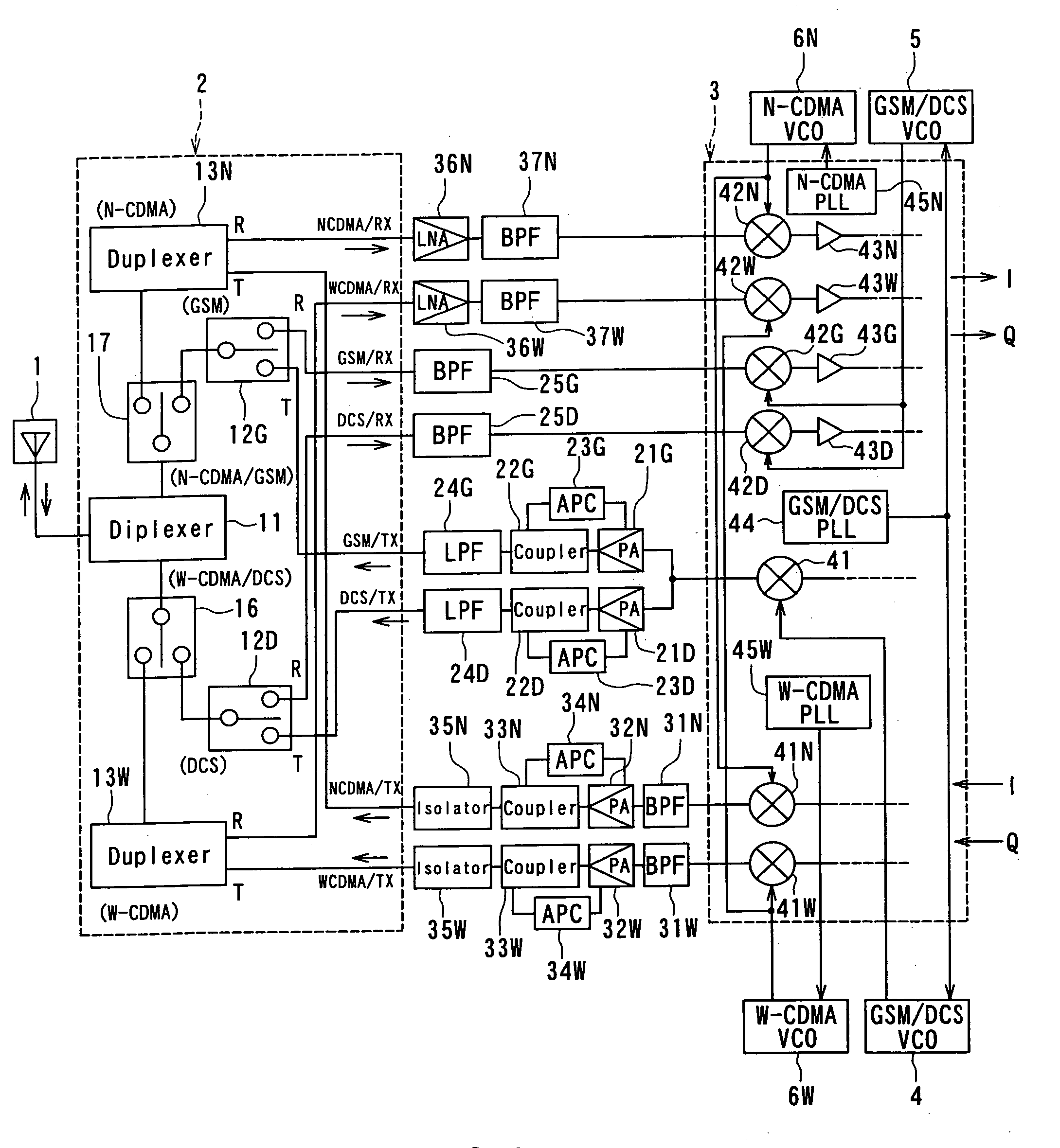
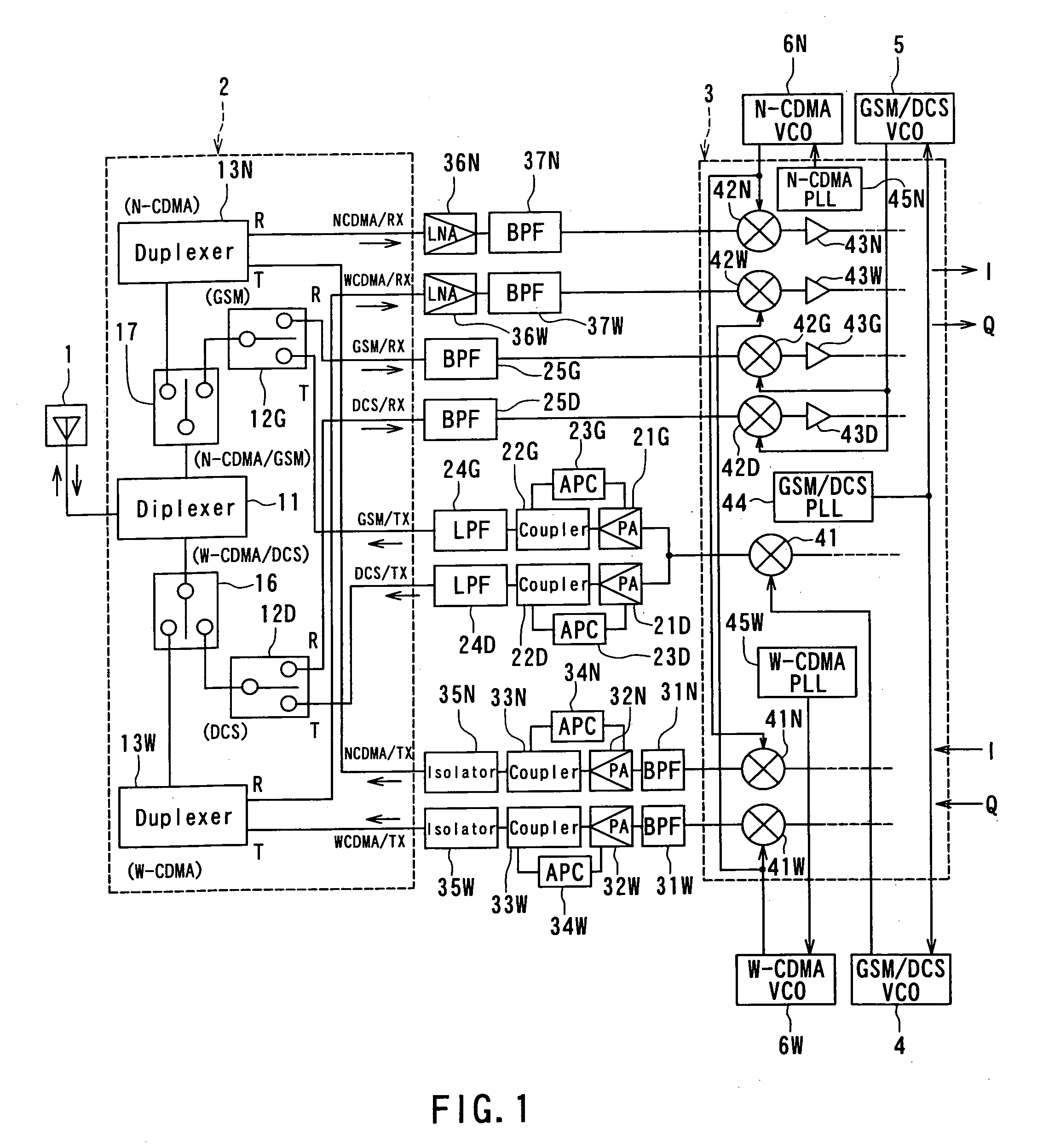
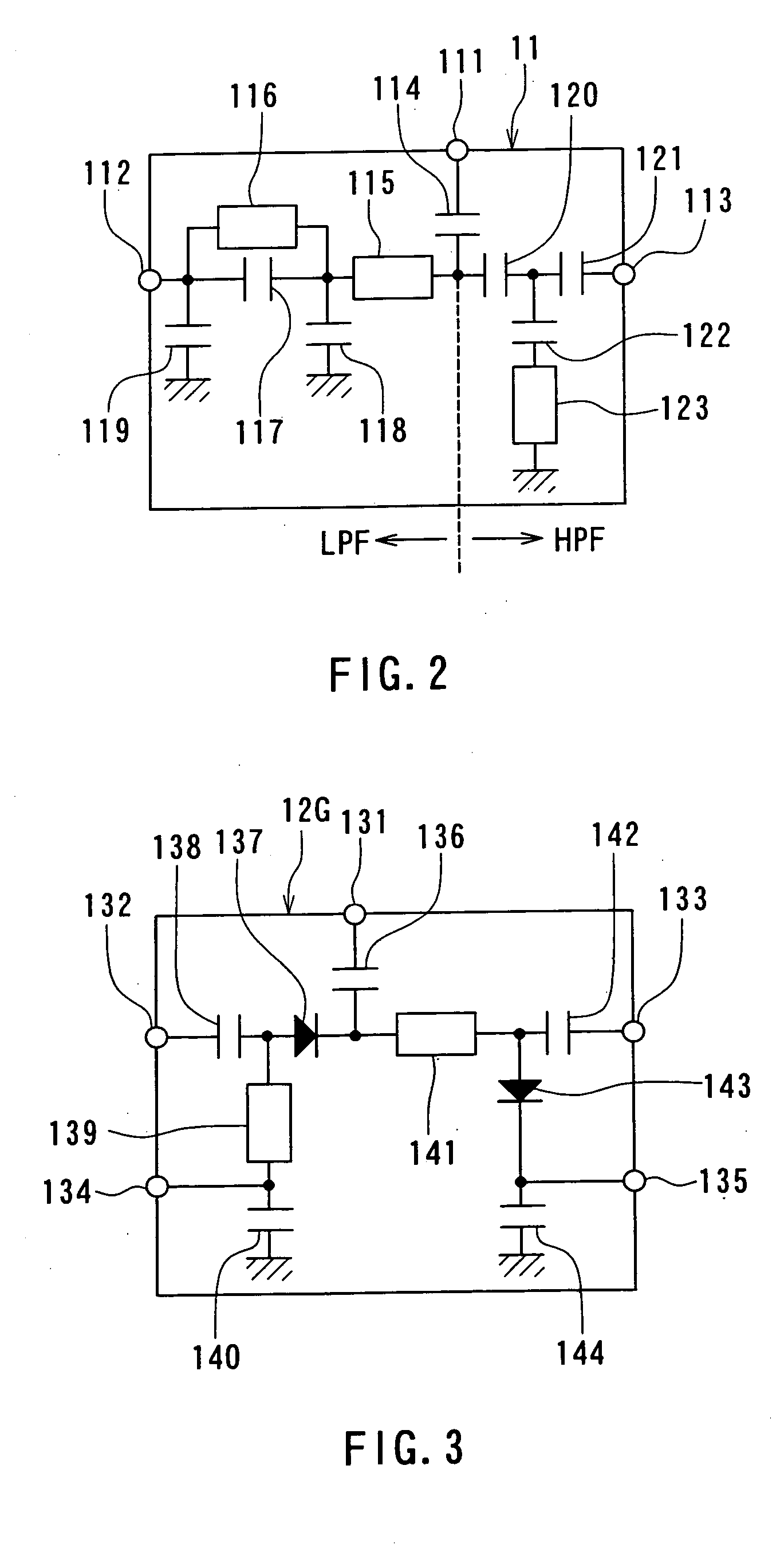
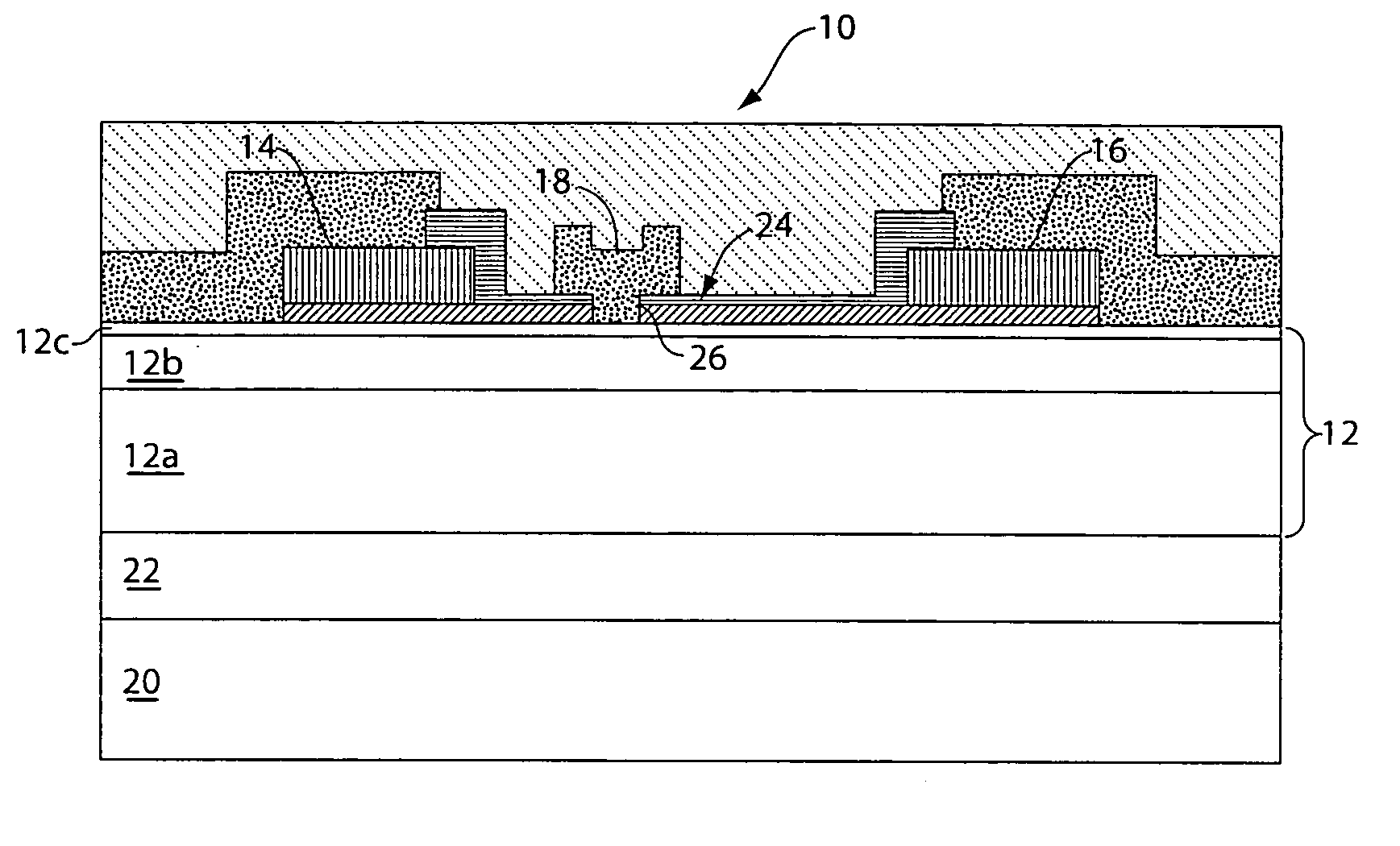
A front end module comprises a diplexer, a first duplexer, and a second duplexer. The first duplexer is connected to the diplexer through a first high frequency switch and separates transmission signals and reception signals of the N-CDMA from each other. The second duplexer is connected to the diplexer through a second high frequency switch and separates transmission signals and reception signals of the W-CDMA from each other. Each of the duplexers includes acoustic wave elements. A single multi-layer substrate for integration is used to integrate the components of the front end module. The diplexer is made up of a conductor layer located inside or on the surface of the multi-layer substrate.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
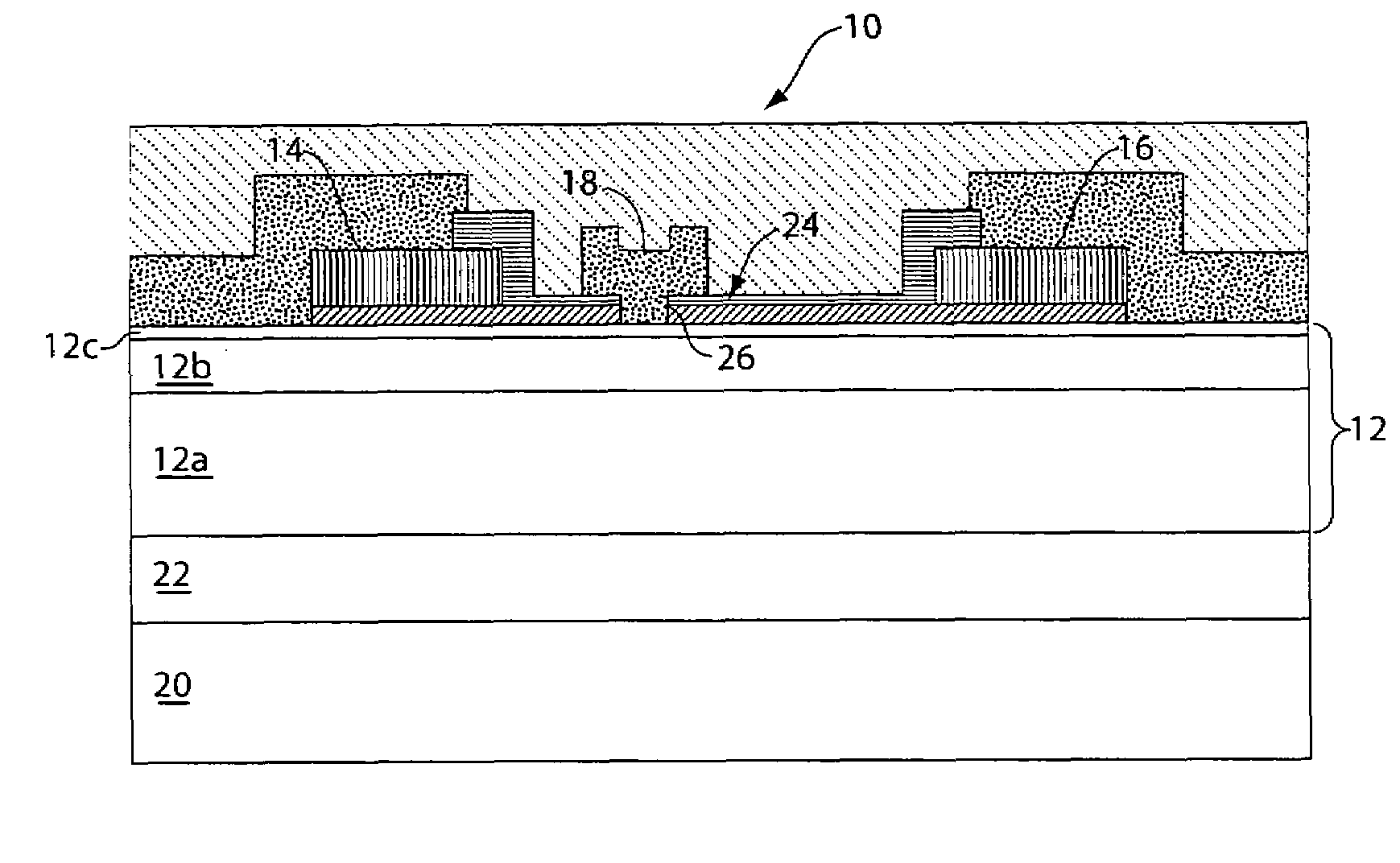
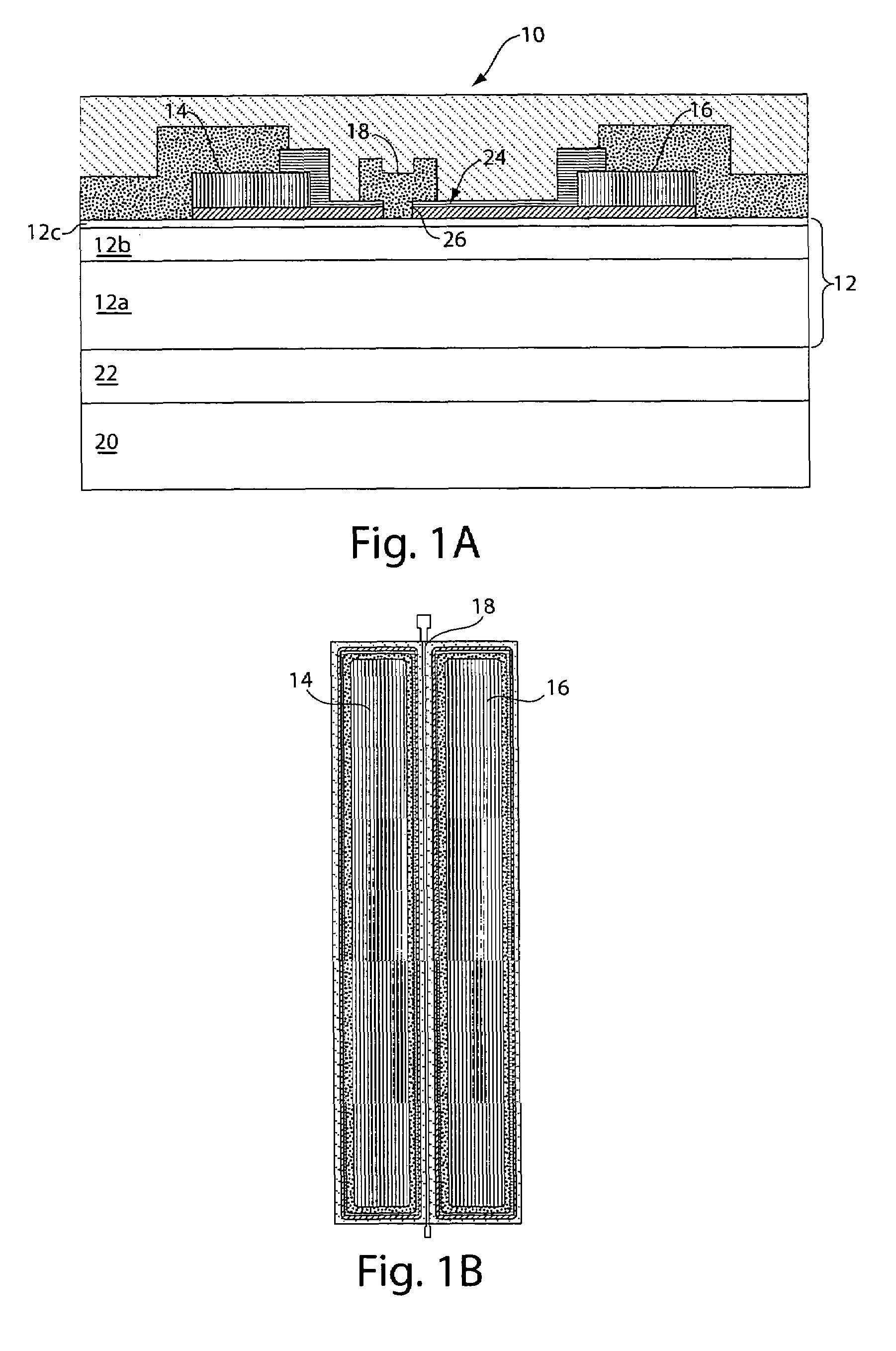
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods associated with the same
ActiveUS20050167775A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower applicationSignal quality
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods associated with the same are provided. The transistors may be used in power applications by amplifying an input signal to produce an output signal having increased power. The transistors may be designed to transmit the majority of the output signal within a specific transmission channel (defined in terms of frequency), while minimizing transmission in adjacent channels. This ability gives the transistors excellent linearity which results in high signal quality and limits errors in transmitted data. The transistors may be designed to achieve low ACPR values (a measure of excellent linearity), while still operating at high drain efficiencies and / or high output powers. Such properties enable the transistors to be used in RF power applications including third generation (3G) power applications based on W-CDMA modulation.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
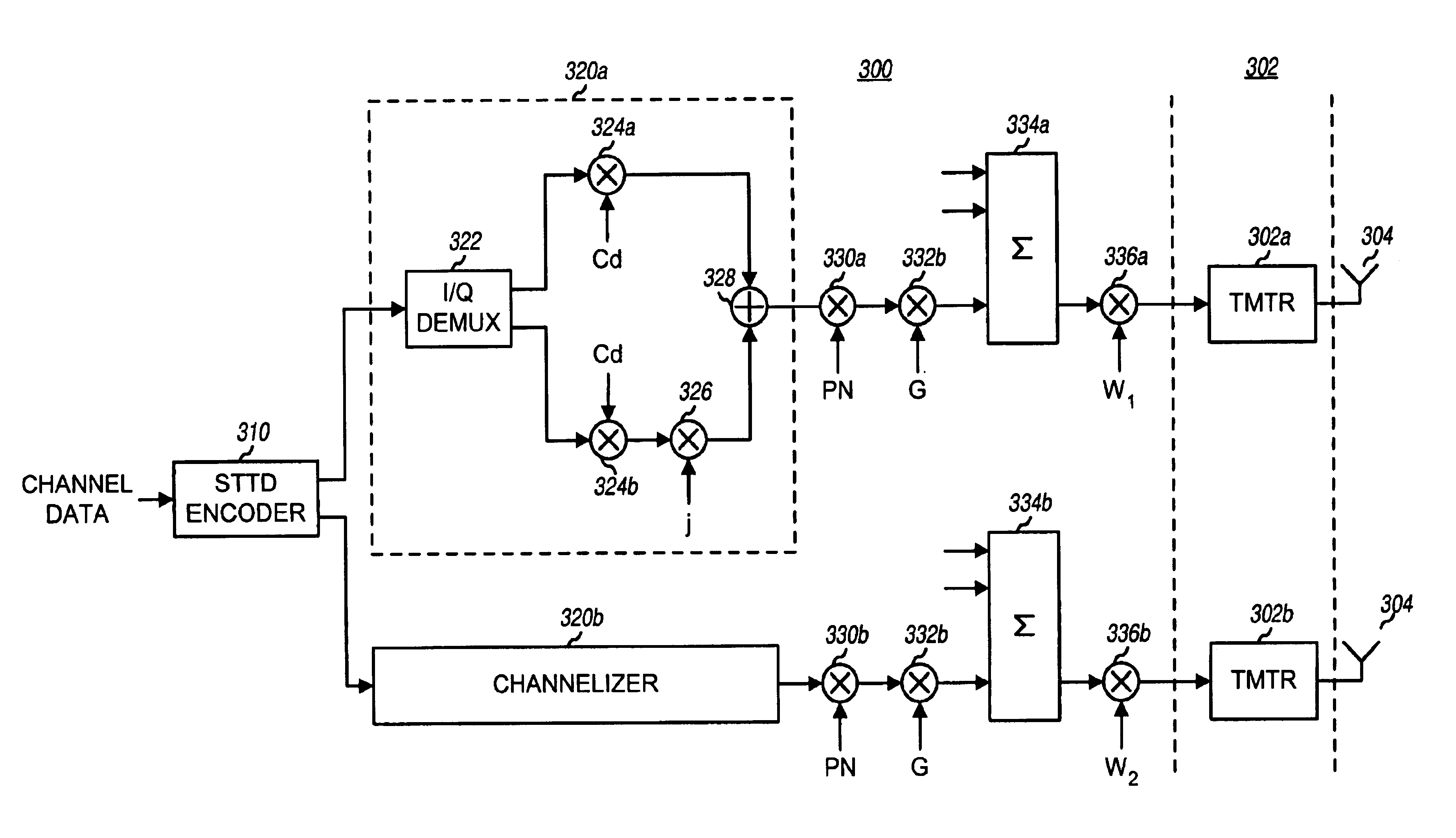
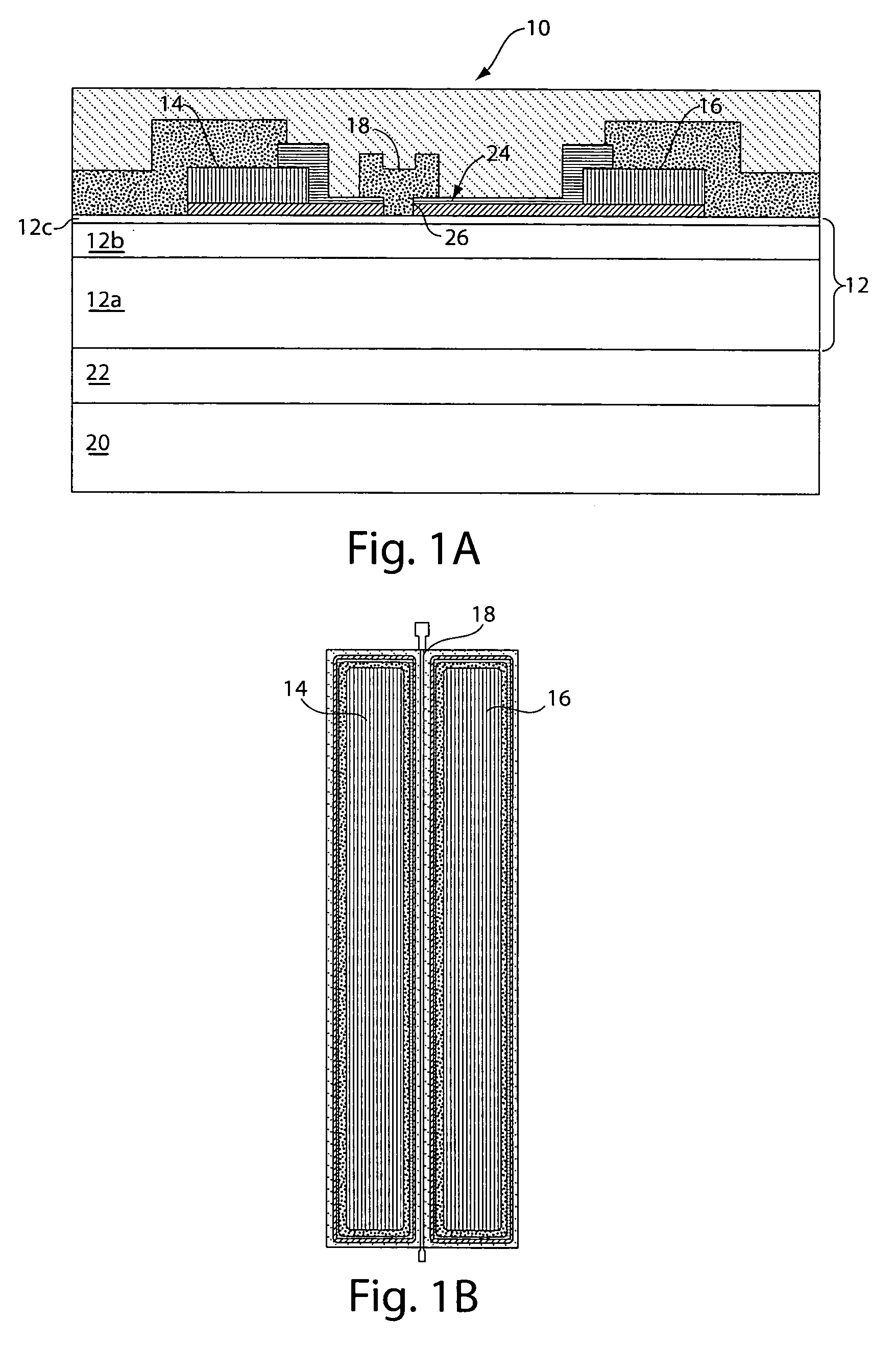
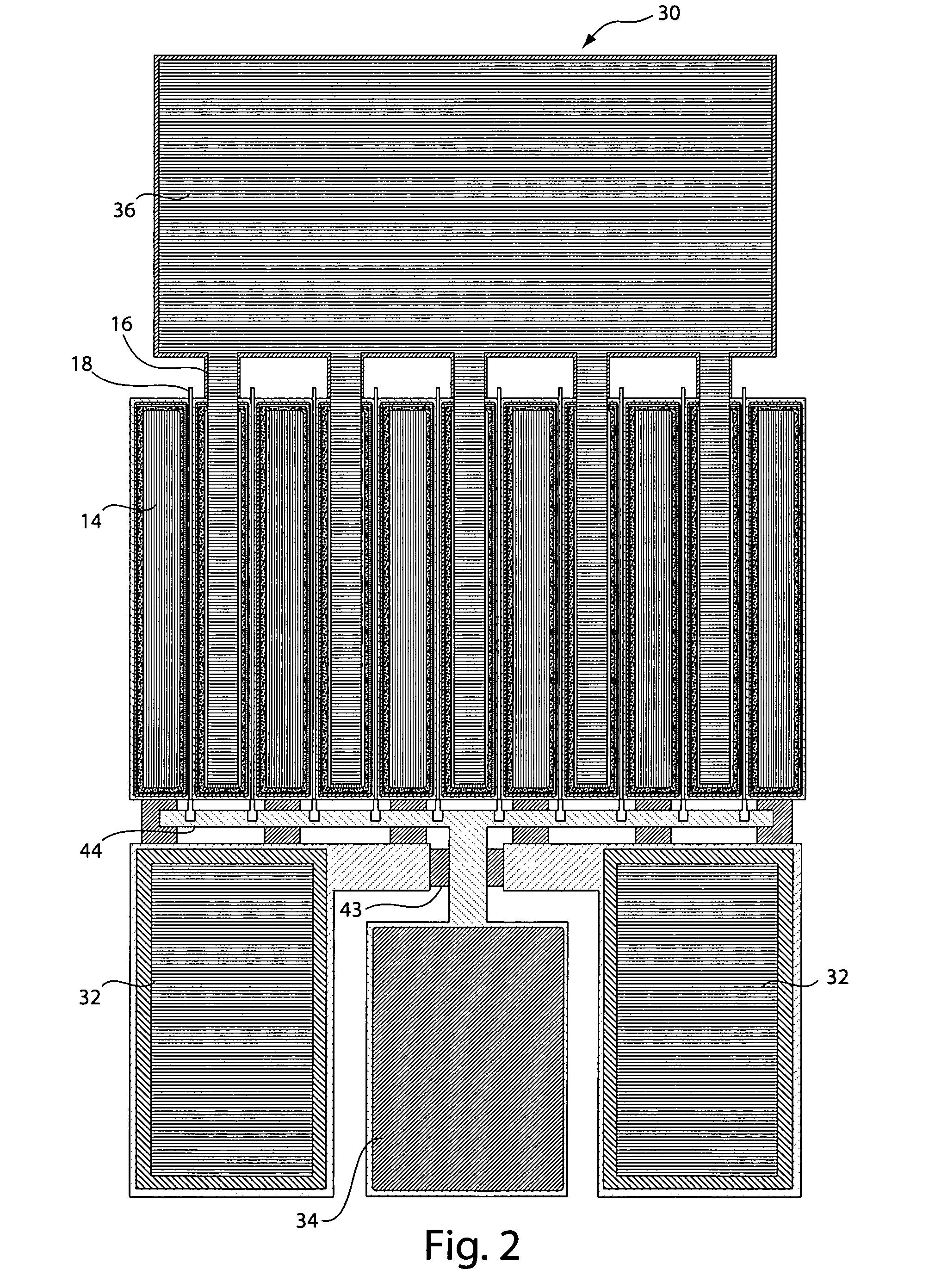
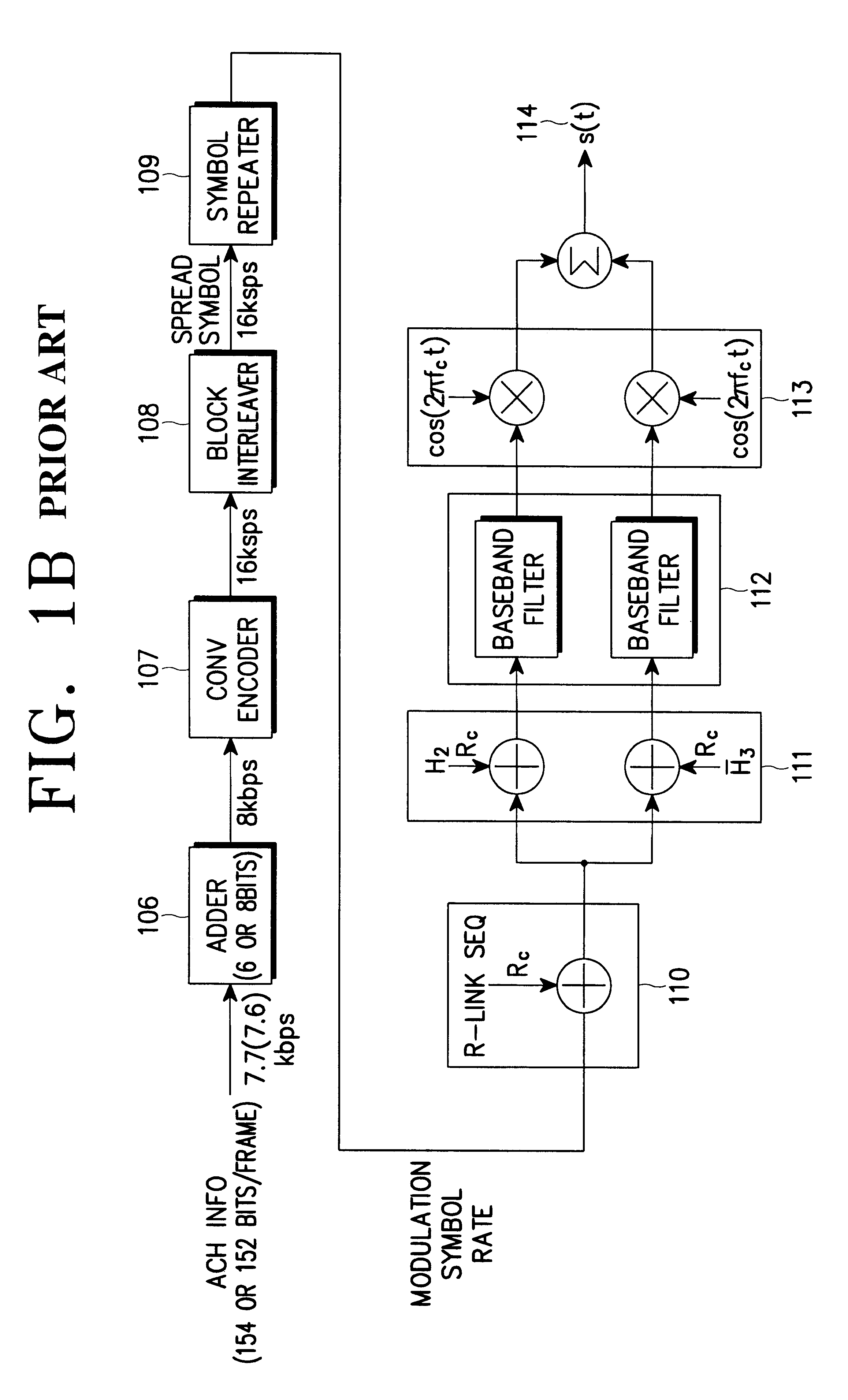
Apparatus and method for transmitting TFCI used for DSCH in a W-CDMA mobile communication system
InactiveUS7010317B2Reliable transmissionImprove transmission reliabilityPower managementTransmission control/equalisingChannel dataMobile communication systems
Disclosed is a method for determining transmission power of a second TFCI bit indicating transport format information of data on a downlink shared channel transmitted from a selected Node B to a UE in a mobile communication system including the UE existing in a handover zone and a plurality of Node Bs in an active set of the UE. The Node Bs transmit dedicated channel data including a first TFCI bit to the UE over dedicated channels. A first Node B transmits dedicated channel data over a dedicated channel and transmits downlink shared channel data over the downlink shared channel. The first Node B determines a transmission power level of the second TFCI bit to be higher than a ratio of transmission power of the dedicated channel data from a Node B transmitting only the dedicated channel data to transmission power of the first TFCI bit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Additional aggregate radiated power control for multi-band/multi-mode satellite radiotelephone communications systems and methods
An Ancillary Terrestrial Network (ATN) includes at least one Ancillary Terrestrial Component (ATC) that is configured to provide wireless communications using frequencies of a satellite frequency band. The ATN provides communications based on a GSM, cdma2000 and / or W-CDMA air interface, under a constrained capacity measure. The capacity measure of the ATN may also be constrained when the ATN provides communications based on an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM) and / or Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) air interface. Analogous methods of controlling an ATN also may be provided.
Owner:ATC TECH LLC
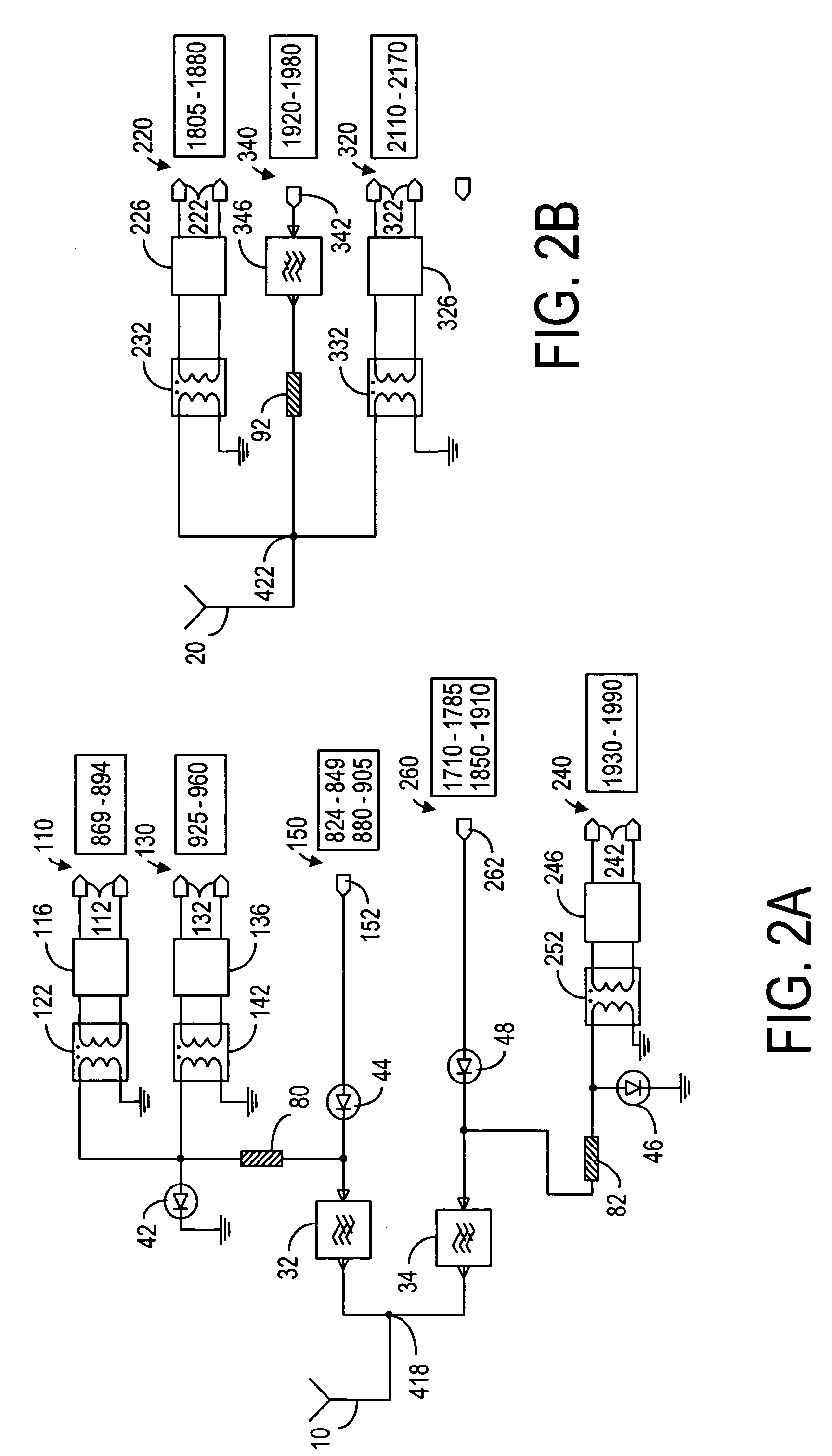
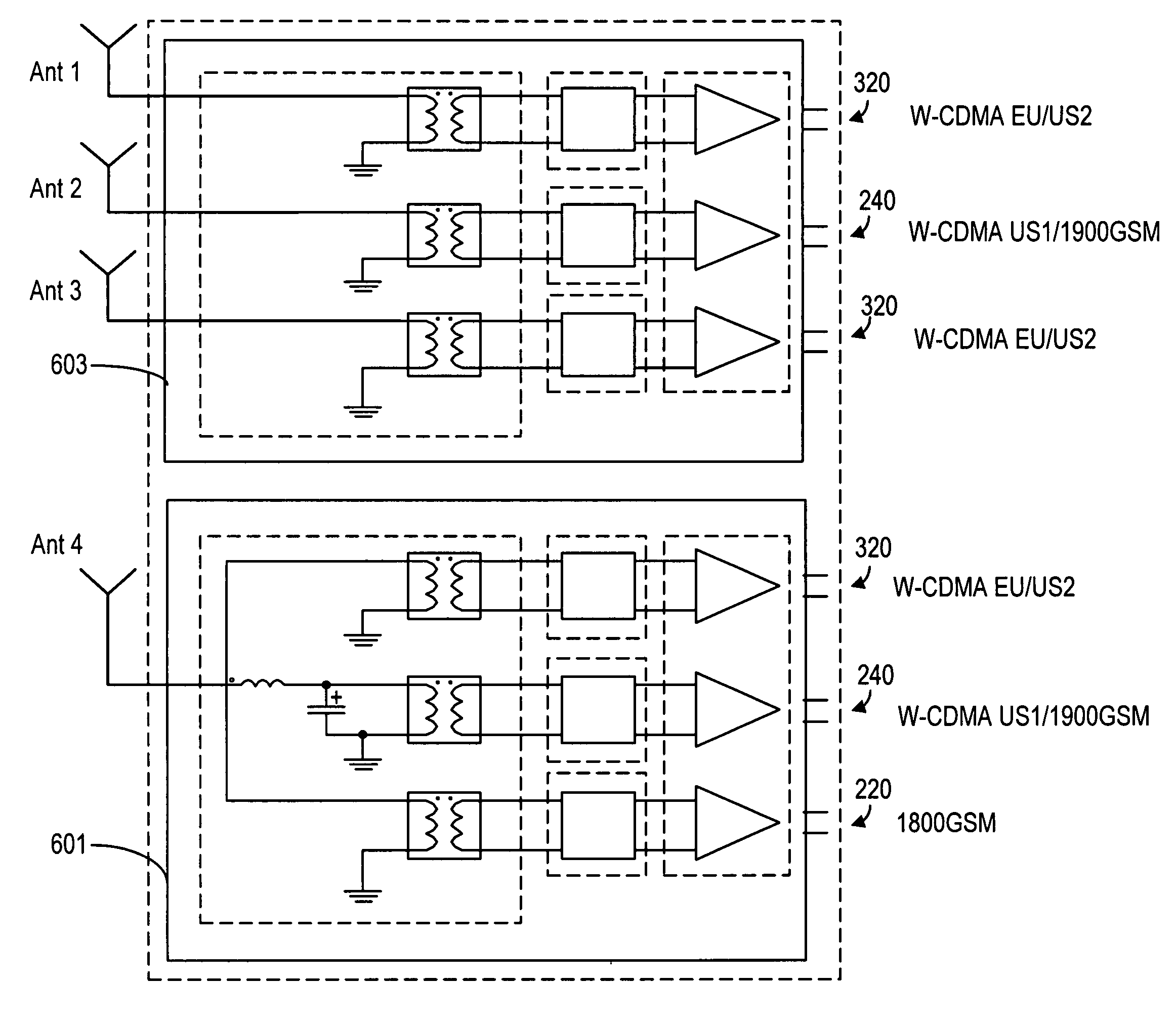
Front-end arrangements for multiband multimode communication engines
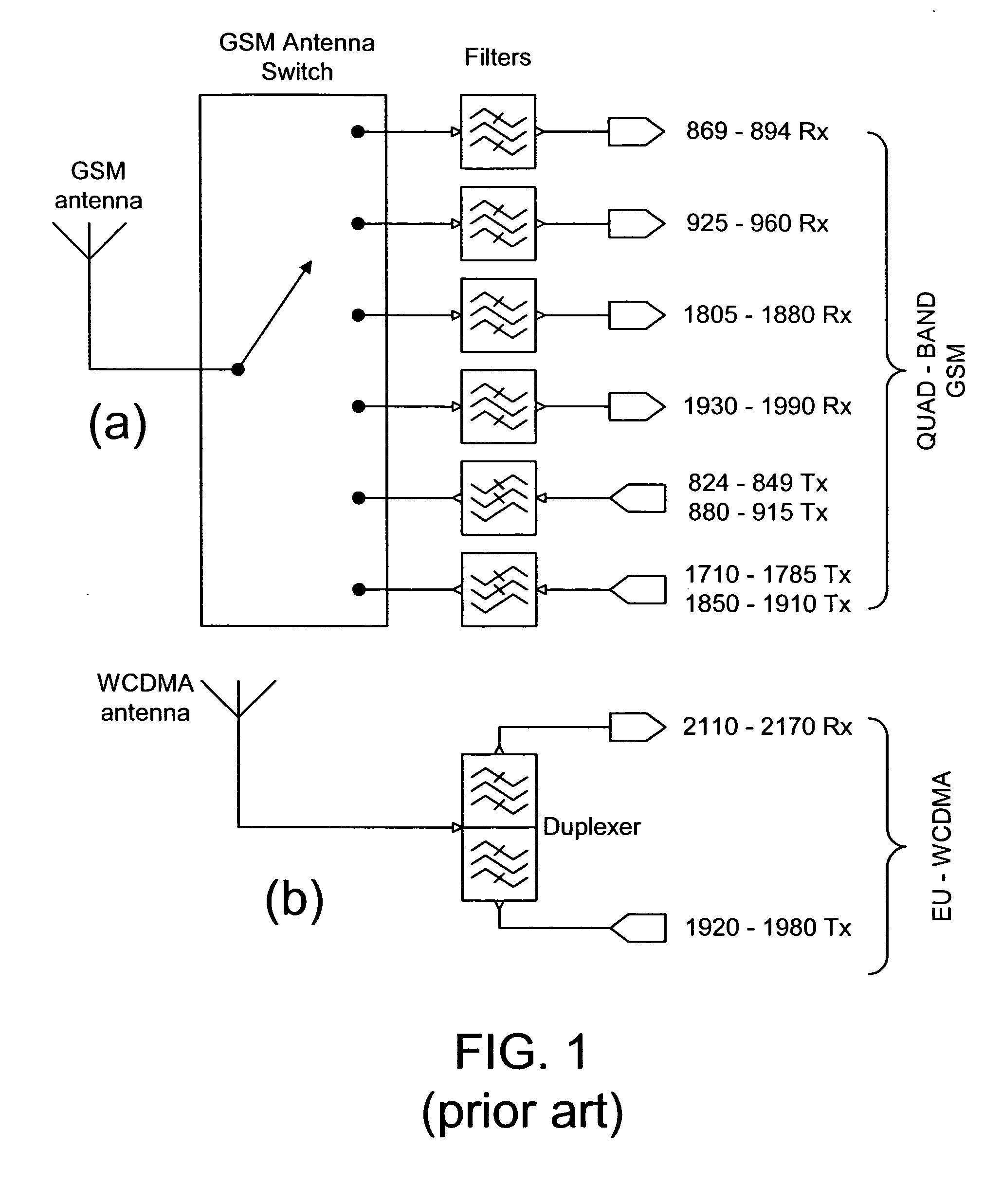
ActiveUS6990357B2Reduce complexityComponents be reduced evenSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionMulti bandGSM
A receive front-end module in a multi-band communication device. The communication device comprises a plurality of signal paths for receiving and transmitting communication signals in a plurality of frequency bands in GSM and W-CDMA modes. The signal paths in the receive front-end module are operatively connected to a common feed point, which is connected to one of the RF antennas of the communication device, and the signal paths are selected such that none of the frequency bands for receiving communication signals in the receive front-end module are overlapping. If the communication device also transmits the communication signal in at least one transmit frequency range partially overlapping with one of the frequency bands in the receive front-end module, switching means is provided to at least one of signal paths in the receive front-end module for providing cross-band isolation between the transmitted and received communication signals.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
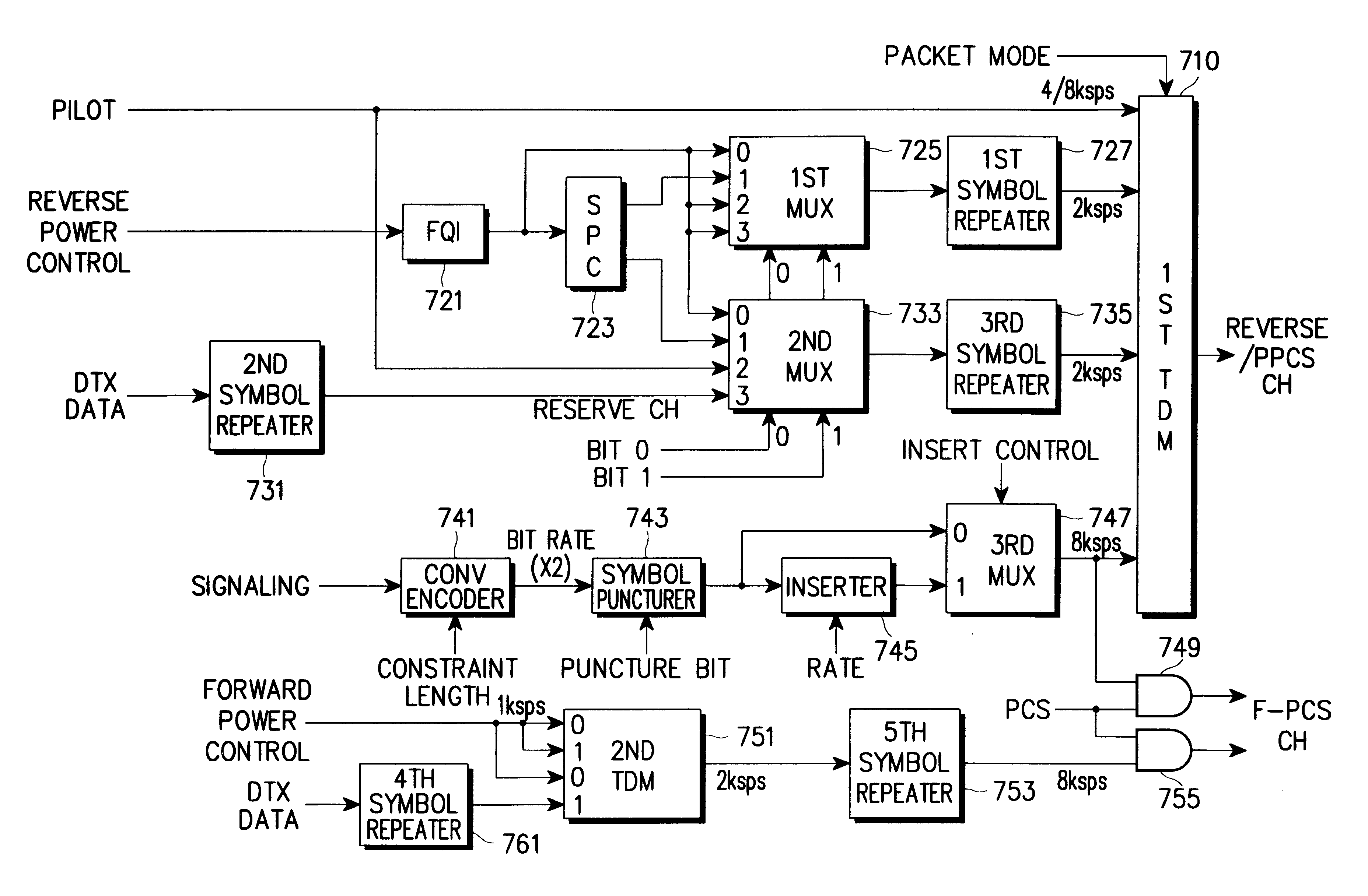
Variable channel device for wideband CDMA system
A traffic variable channel device for a W-CDMA system comprising a convolutional encoder for receiving traffic information bits; a symbol puncturer connected to the convolutional encoder; an inserter connected to the symbol puncturer; a multiplexer connected to the inserter and the symbol puncturer; a scramble code generator for receiving a scramble code seed; an AND gate connected to the scramble code generator, a scramble select signal and a forward / reverse select signal; and, a scramble code spreader connected to the multiplexer and the AND gate for generating a forward / reverse traffic channel signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods associated with the same
ActiveUS7135720B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower applicationSignal quality
Gallium nitride material transistors and methods associated with the same are provided. The transistors may be used in power applications by amplifying an input signal to produce an output signal having increased power. The transistors may be designed to transmit the majority of the output signal within a specific transmission channel (defined in terms of frequency), while minimizing transmission in adjacent channels. This ability gives the transistors excellent linearity which results in high signal quality and limits errors in transmitted data. The transistors may be designed to achieve low ACPR values (a measure of excellent linearity), while still operating at high drain efficiencies and / or high output powers. Such properties enable the transistors to be used in RF power applications including third generation (3G) power applications based on W-CDMA modulation.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Mimo and diversity front-end arrangements for multiband multimode communication engines
InactiveUS7155252B2Reduce complexityComponents be reduced evenCode division multiplexSubstation equipmentEngineeringCommunication device
A receive front-end module having one or more 2 GHz Rx paths and one or more W-CDMA Rx paths for use in a portable communication device, such as a mobile phone or a communicator device. The module comprises at least two feed points operatively connected to two electrically separate antennas for receiving communication signals. The module also comprises filters for filtering the communication signals in corresponding frequency band, and means for providing cross-band isolation. The cross-band isolation is achieved by using linear amplifiers in different signal paths, for example. Advantageously, the module comprising three signal paths so that one or more modules can be used together to achieve MIMO / diversity functionality.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Multiple path multiple carrier digital pre-distortion sender of wideband CDMA base station system
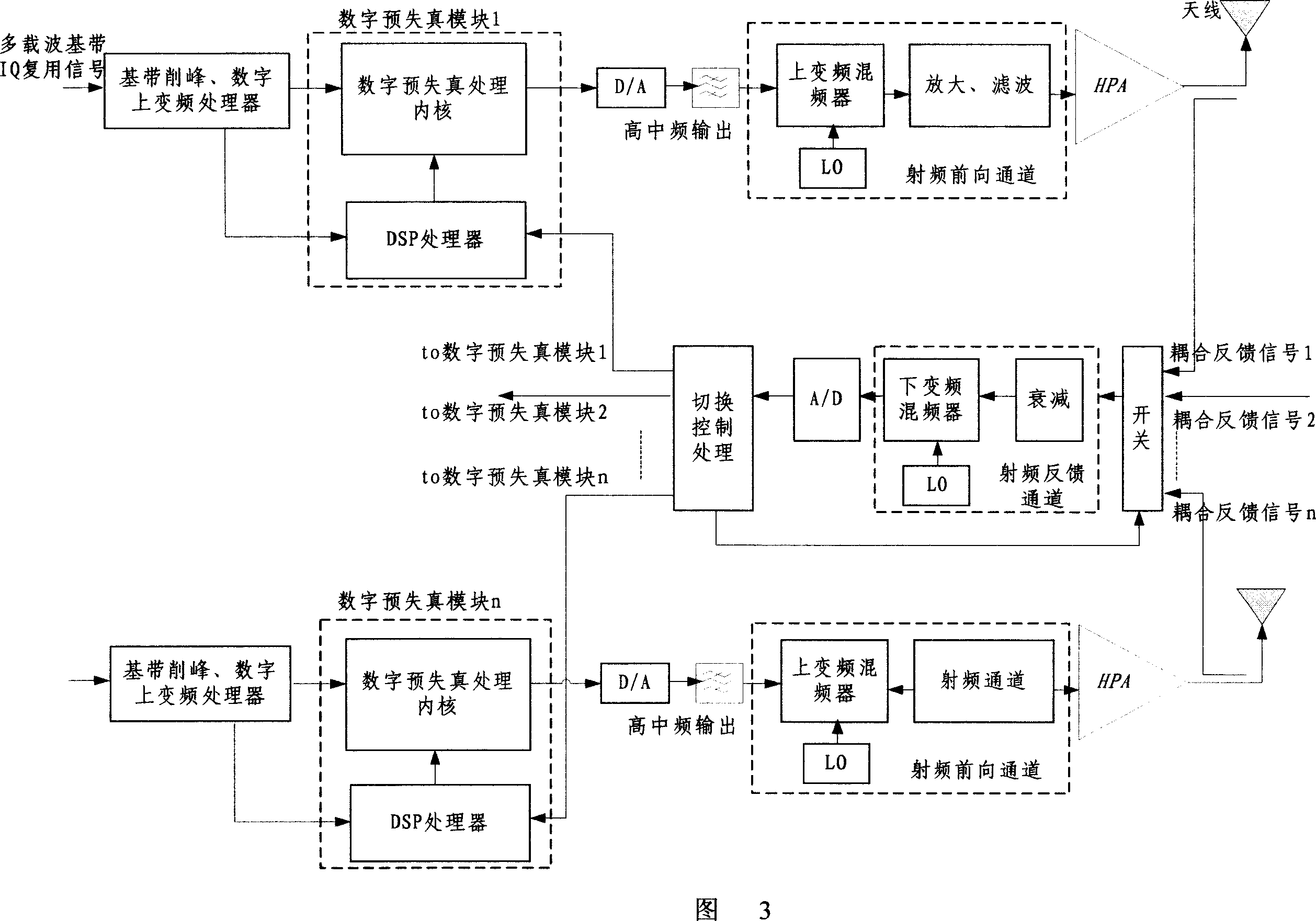
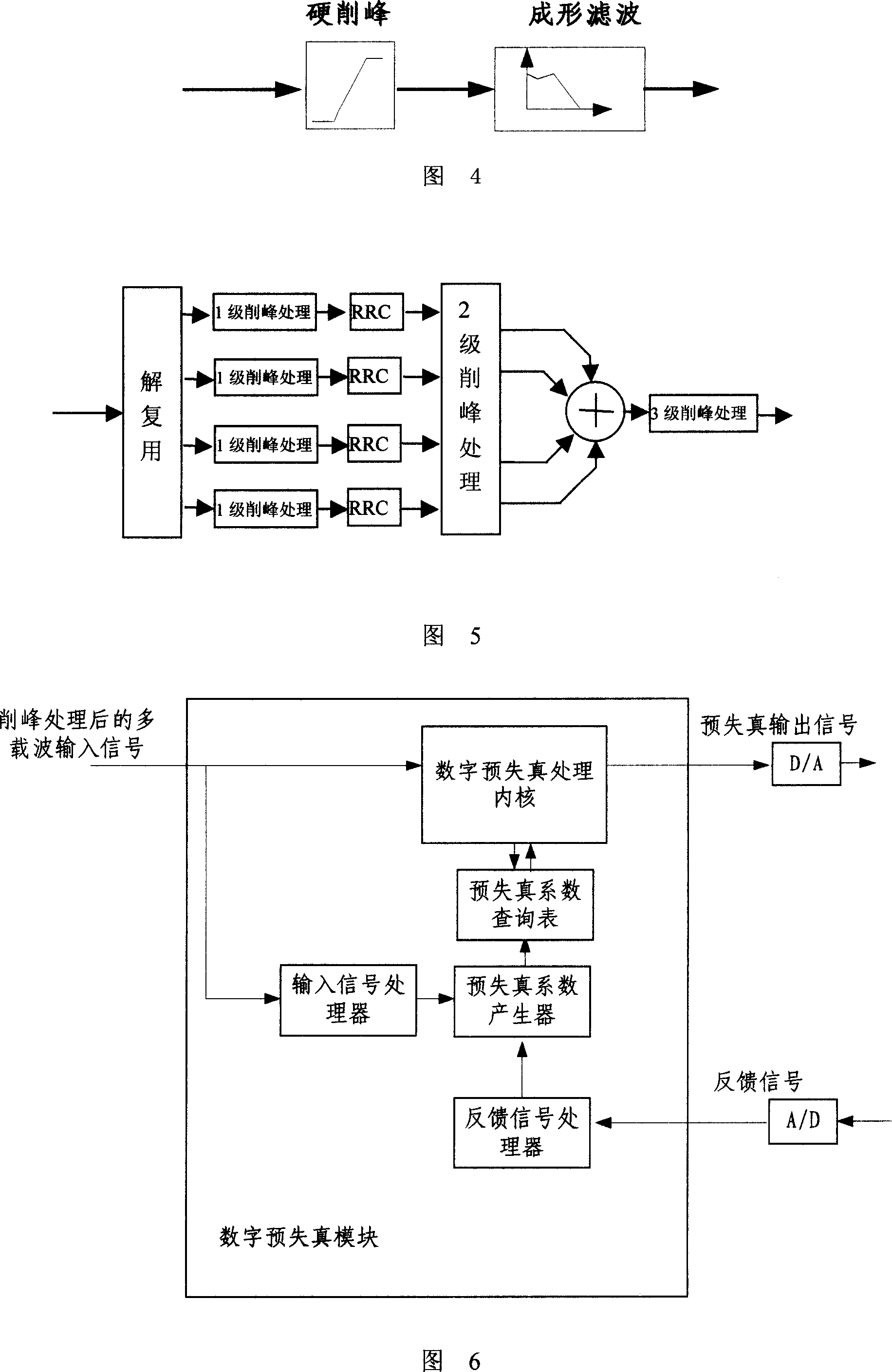
ActiveCN1988522AFlexible settingsGood peak clipping effectCode division multiplexMulti-frequency code systemsLinear power amplifierIntermediate frequency
A multi-channel and multi-carrier Digital Predistortion writing machine of wideband CDMA base station system includes the feedback signal processing channels and at least one multiplexing signal processing channels of multi-carrier base band, of which, each includes the digital base-band peak-clipping frequency processor, digital predistortion processing module, high-intermediate frequency output module and filter, radio frequency access and high power amplifier. The feedback signal processing channel includes the RF feedback channel and A / D converter. The invention uses the base band peak-clipping technology, digital predistortion technology and high-intermediate digital IF technology, to reduce the high cost by the use of the linear power amplifier, and can effectively enhance the launch performance and efficiency of the base station system. The invention does not use the feedback channel switching technology to achieve saving the cost of RF link.
Owner:ZTE CORP
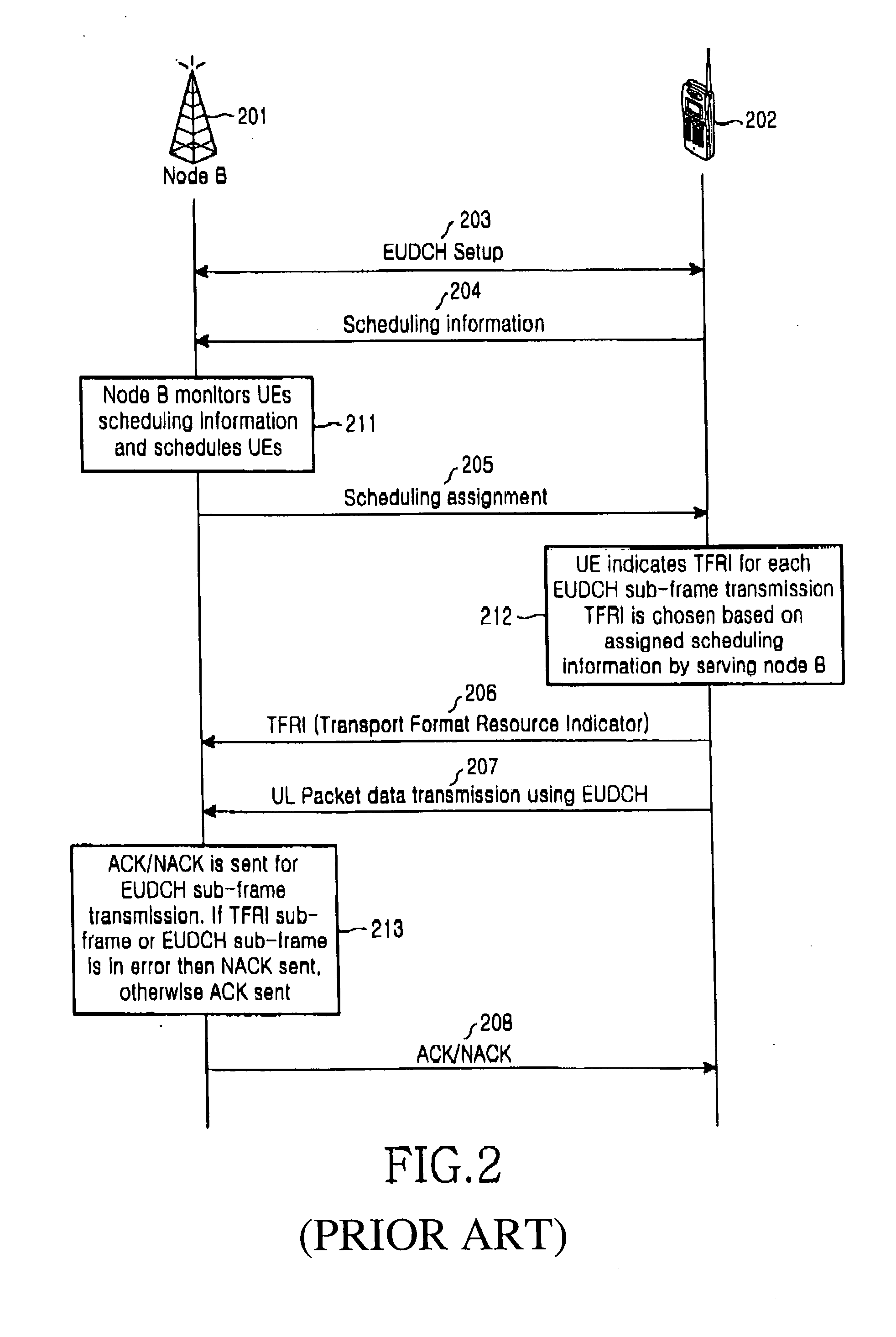
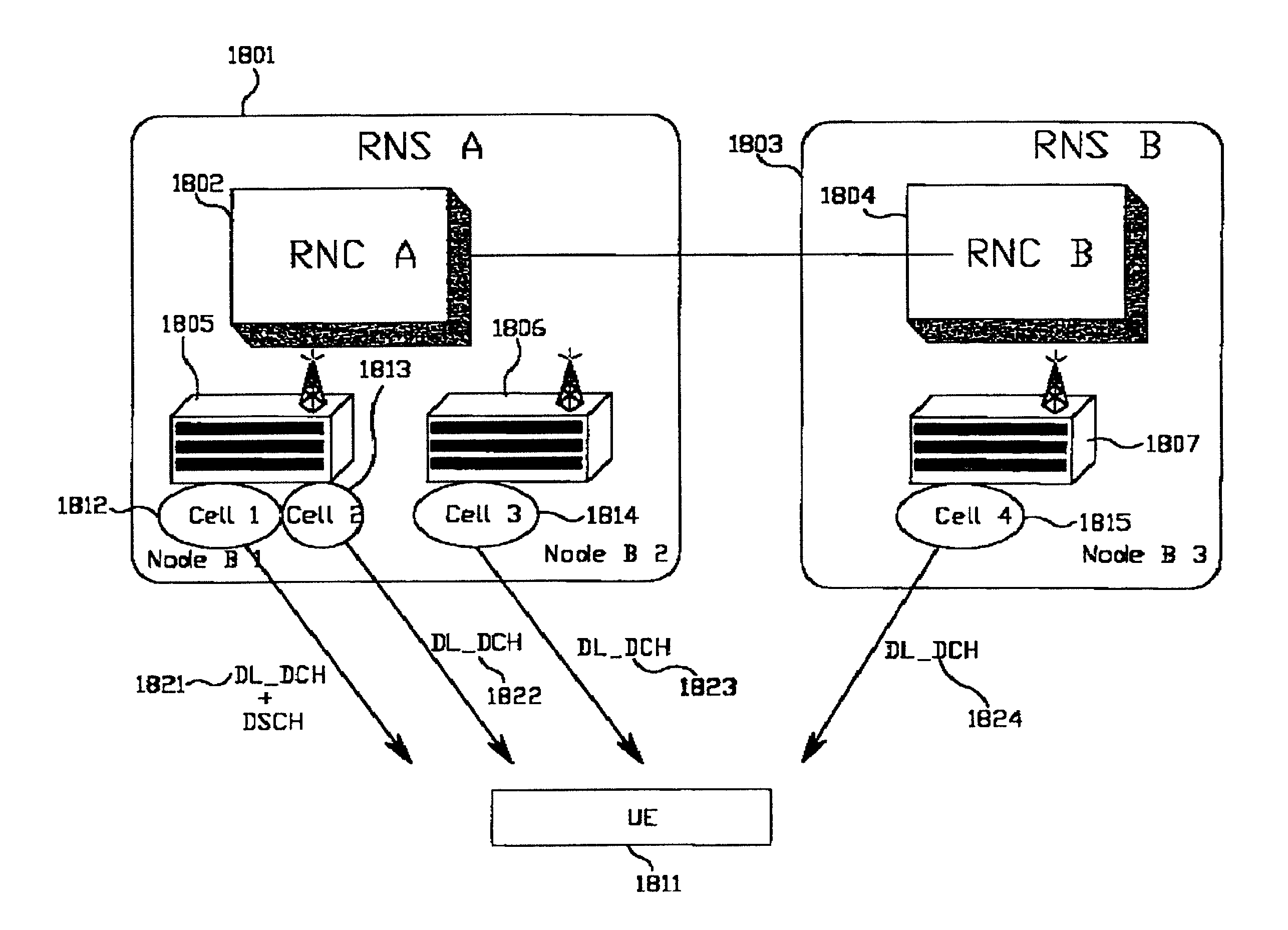
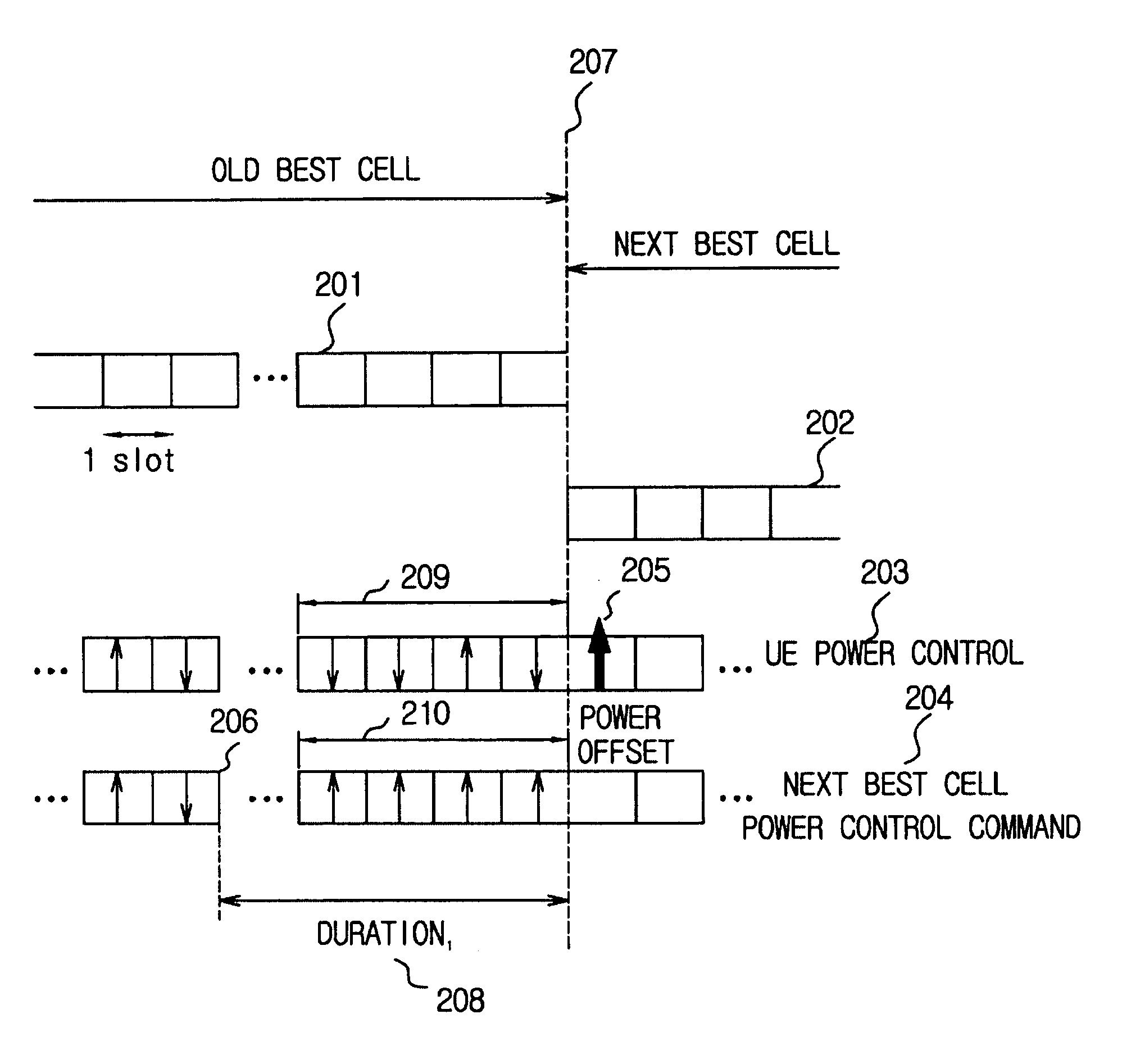
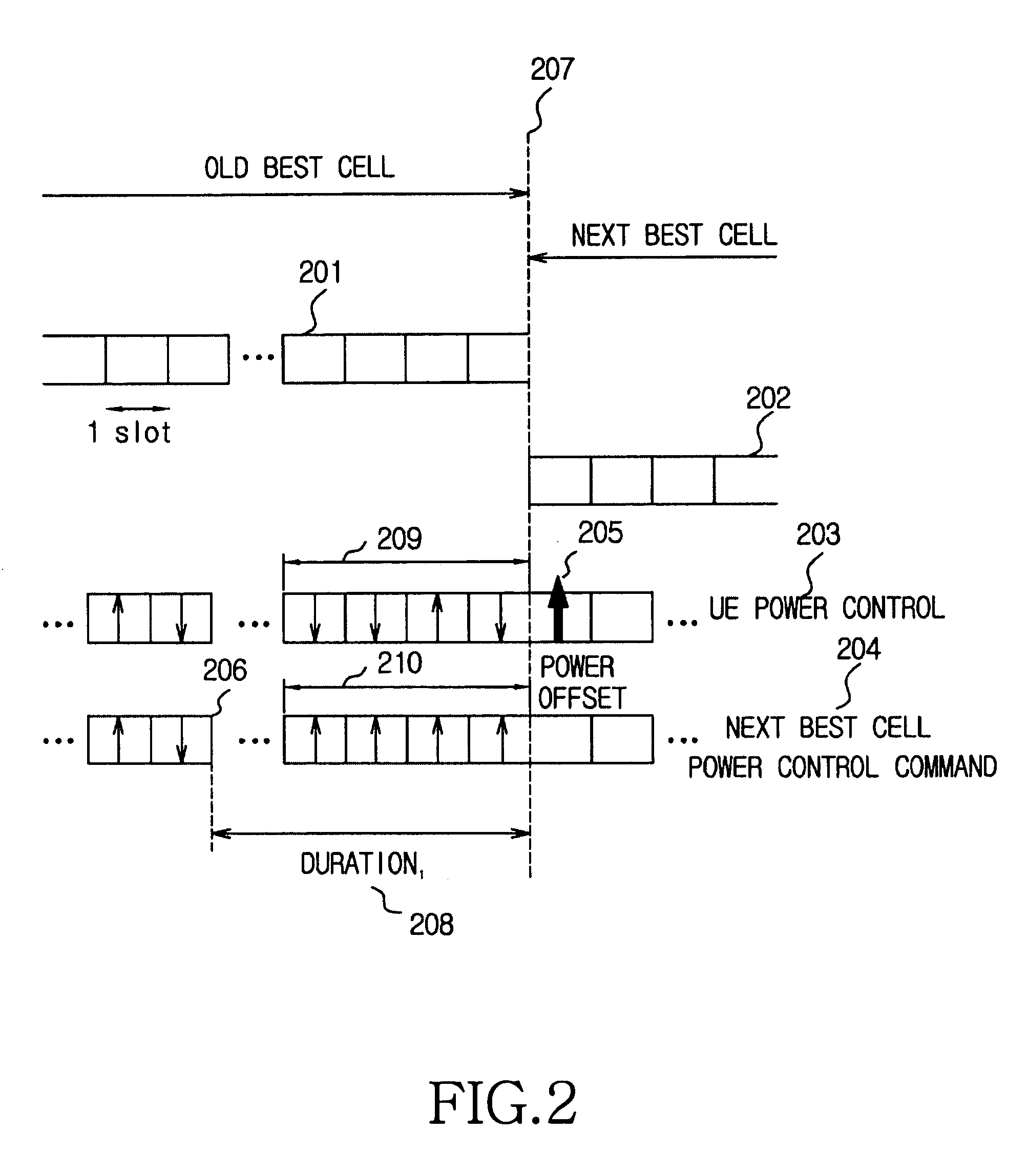
Power control apparatus and method for a W-CDMA communication system employing a high-speed downlink packet access scheme
Disclosed is a method for controlling uplink transmission power in a handover region by a UE in communication with a Node B using an FCS scheme. The UE stores TPC commands received for a specific duration from a plurality of cells in an active set, if the UE enters in the handover region during communication with a current best cell. If a next best cell is selected from the plurality of the cells, the UE determines a transmission power offset by comparing TPC commands from the current best cell with TPC commands from the next best cell for the specific duration at a time point where the best cell is changed from the current best cell to the next best cell. The UE transmits initial transmission power for the next best cell at a transmission power level determined considering the transmission power offset.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
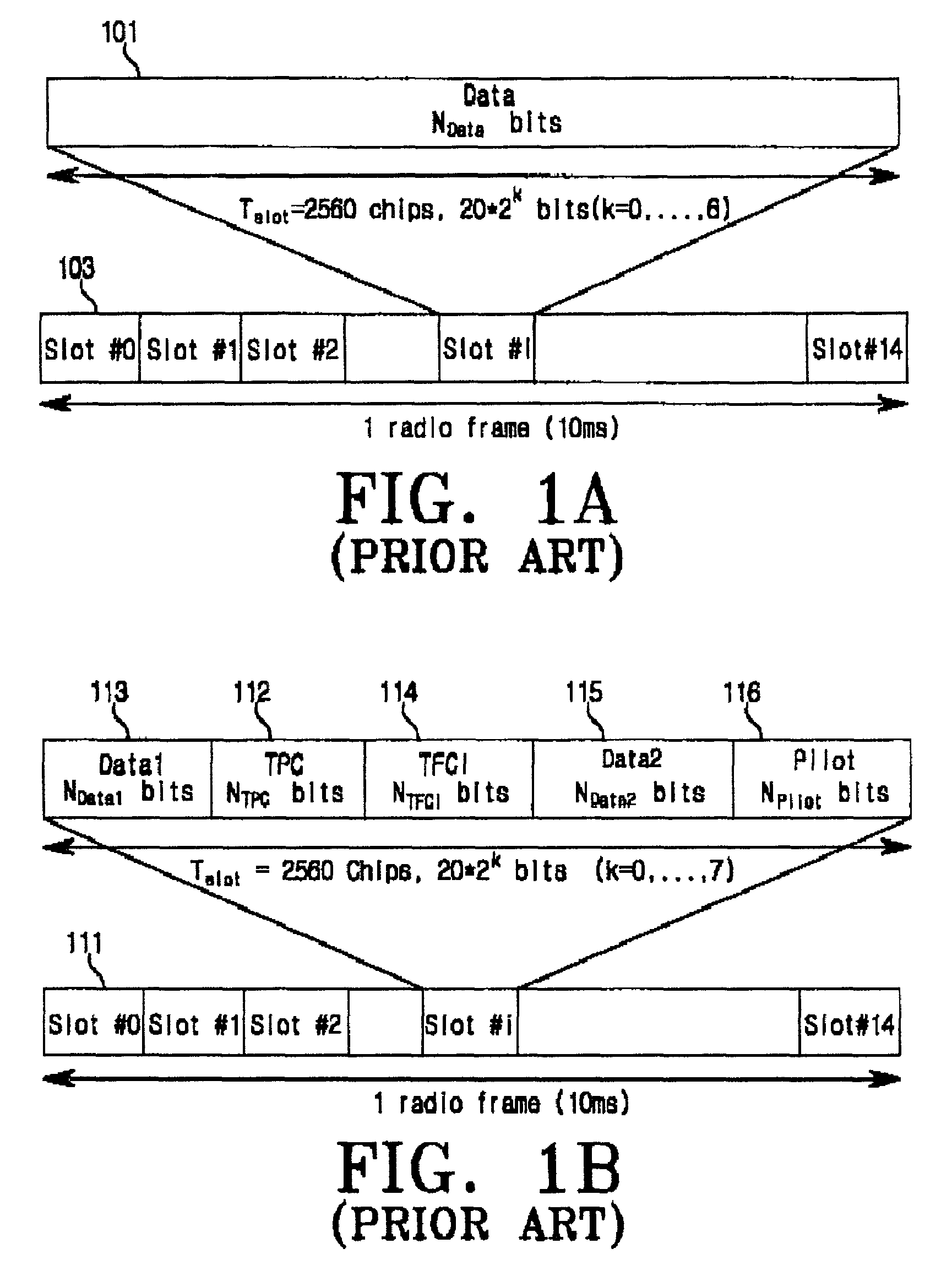
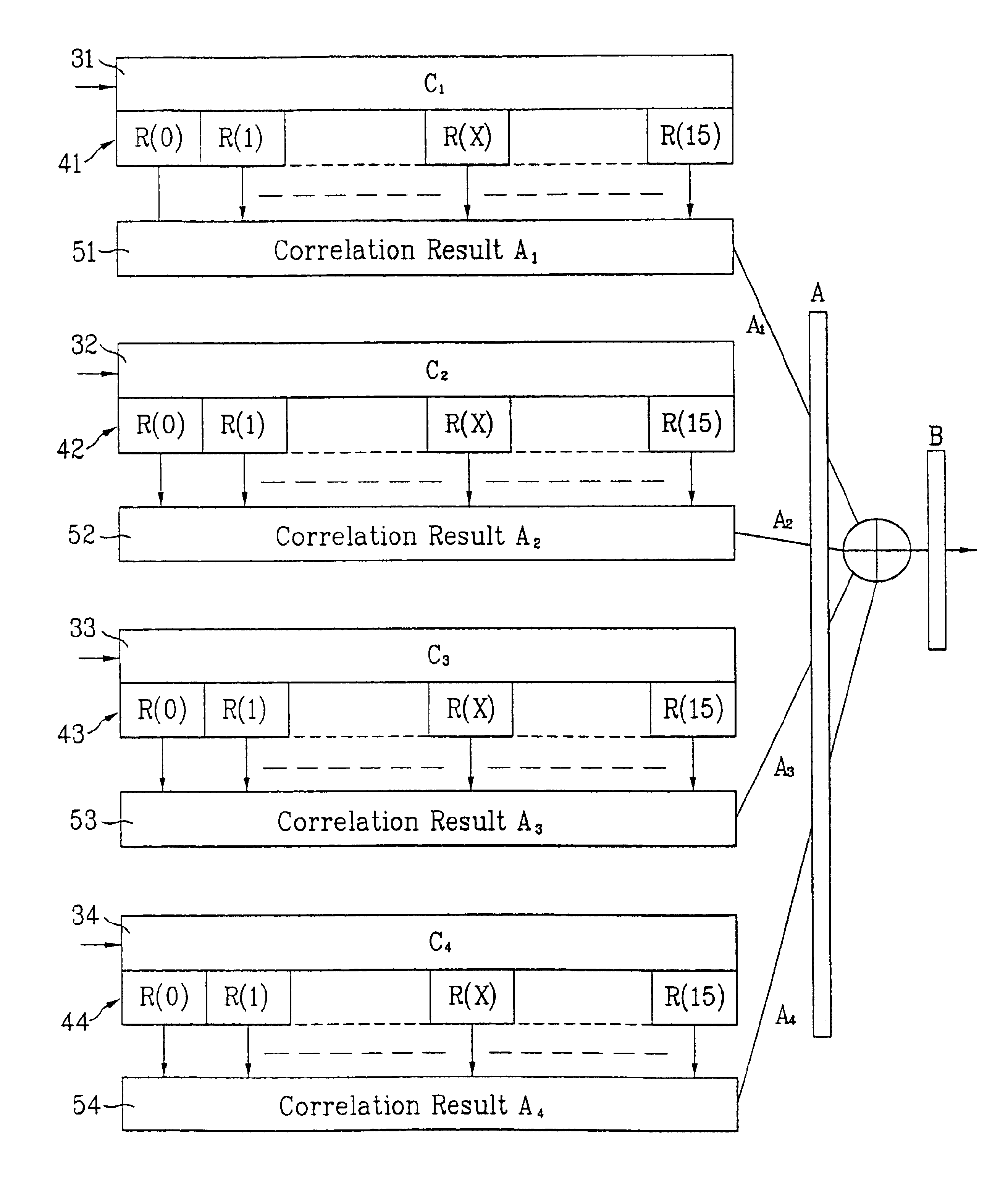
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS6891815B1Avoid poor resultsEliminate and prevent sidelobesBaseband system detailsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemSide lobe
There is provided a frame synchronization method using the correlation characteristic of a pilot having a minimum side lobe coefficient when the chip rate of the physical channel up-link or down-link is 3.8 Mcps in a W-CDMA mobile communication system. The frame synchronization method using an optimal pilot pattern, including the steps of receiving code sequences with the slot length of (2l+1) for a radio frame according to an arbitrary chip rate; arranging the received code sequences corresponding to the slot length for the radio frame and performing auto correlation according to a reception location of the code sequences, and simultaneously, arranging the code sequences corresponding to the slot length for the radio frame and performing cross correlation according to a reception location of the code sequences; and observing the correlation results, to detect frame synchronization.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
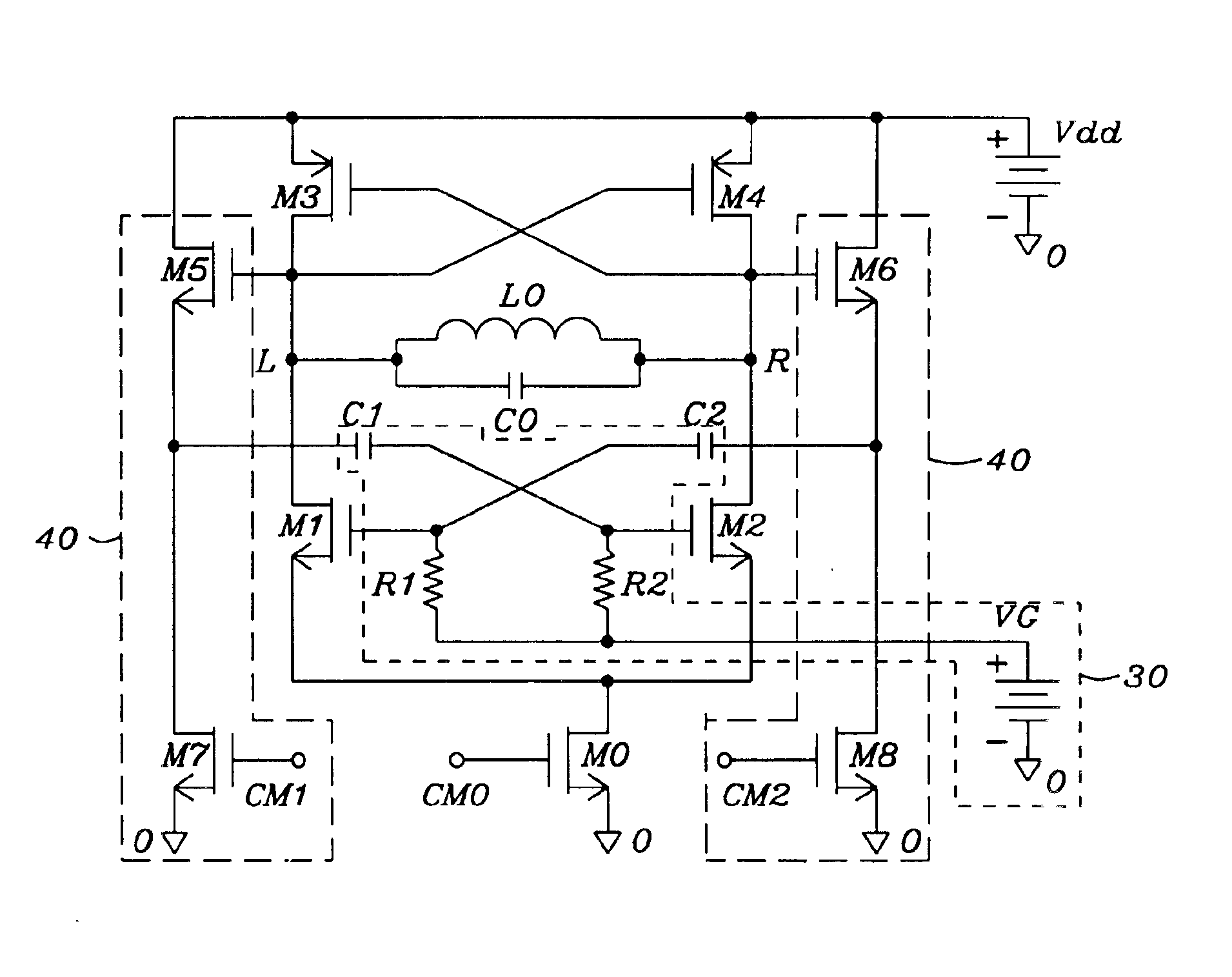
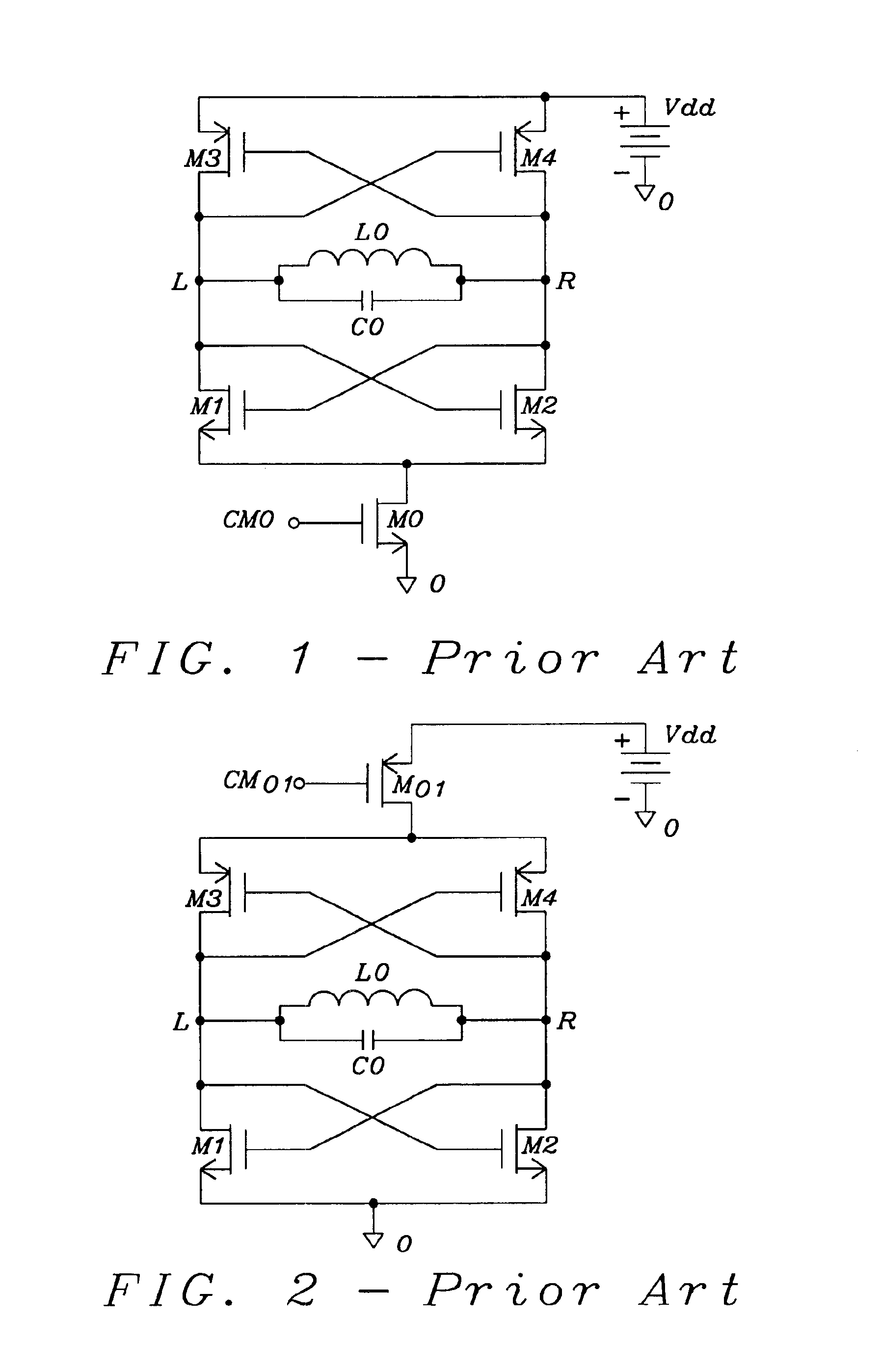
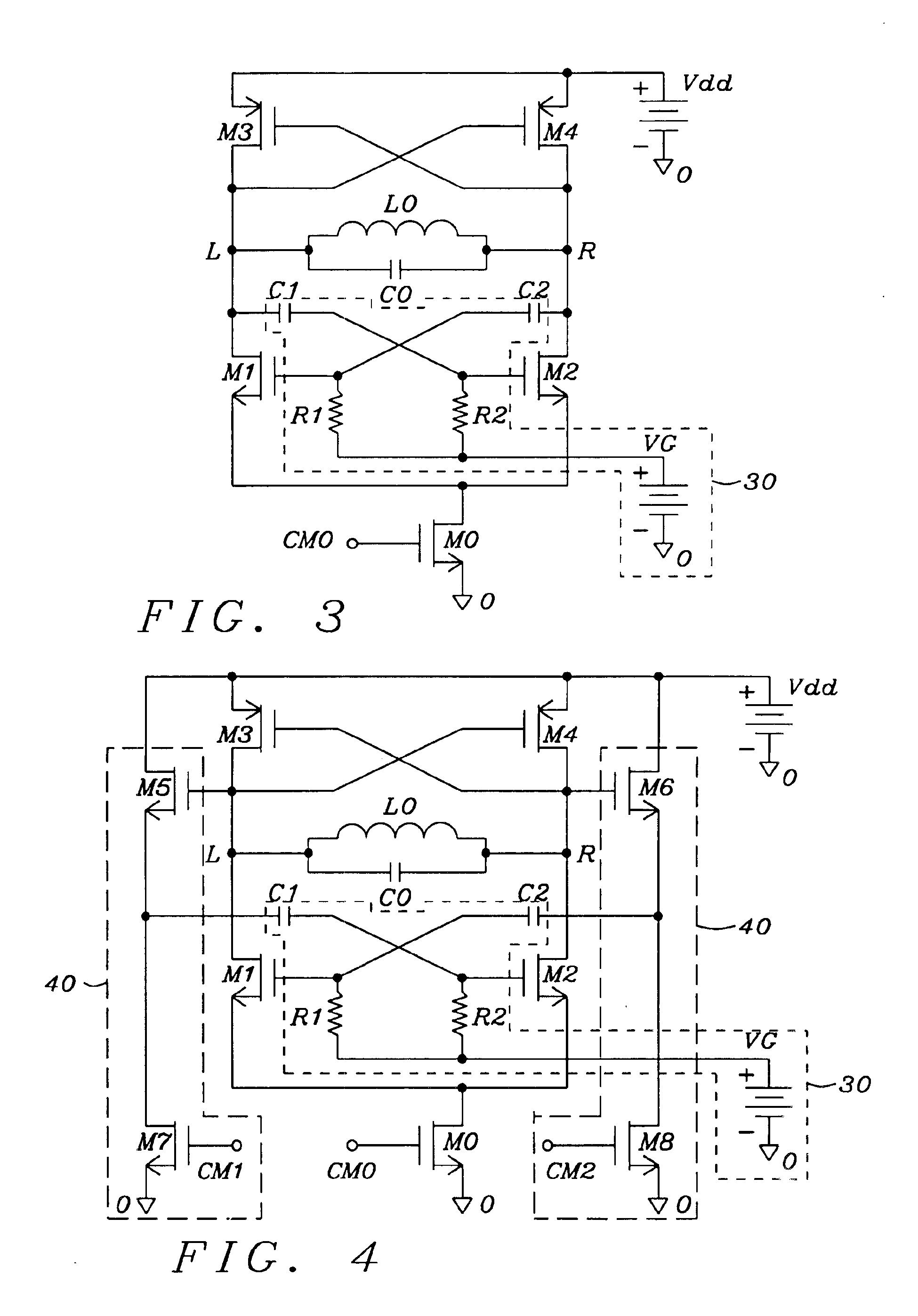
Enhanced architectures of voltage-controlled oscillators with single inductor (VCO-1L)
InactiveUS6867658B1Reduce phase noiseReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlPhase noiseEngineering
Five circuit topologies of Voltage-Controlled Oscillators with Single Inductor (VCO-1L) are proposed. They offer lower power consumption, higher output amplitude, broader tuning range, cleaner s-rum and higher frequency stability seen as lower phase-noise. Most of the achievements are based on the development of active pull-down control circuitries of the timing and active charge dissipation in the transistors. The applications of the present invention are of critical importance for wireless communication systems not allowing any limitations in the frequency range. Among them are base stations and mobile terminals mobile phones, GSM, PCS / DCS, W-CDMA etc., as well BlueTooth, Wireless LAN, Automotive and ISM band etc. The advanced performance of the circuits is based on important architectural specifics and proven by simulation on advanced CMOS process. The architectures are not limited to use on CMOS; they can be efficiently used in any semiconductor process where complimentary polarity transistors are available, for example BiCMOS, SiGe / BiCMOS, GaAs etc.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
Transmission canceller for wireless local area network
ActiveUS20060240769A1Improve performanceIncrease the areaPulse transformerFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransceiverRepeater
A frequency translating repeater (200) for use in a wireless local area network includes a cancellation unit. Canceller (402) is controlled by control (401) to provide an injection signal for canceling leakage in a receive signal path. Reference coupler (403) provides a reference signal from the transmit signal, injection coupler (404) injects a correction signal, and sample coupler (405) provides a sample for feedback. A processor (510) receives the sample signal through a detector (415). Although the present invention is intended for a frequency translating repeater, it has broad applications in radio transceivers in general. One specific application is with frequency division duplex (FDD) handsets or base stations utilizing CDMA technologies such as W-CDMA and IS-2000 or 1XEV-DV / DO.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
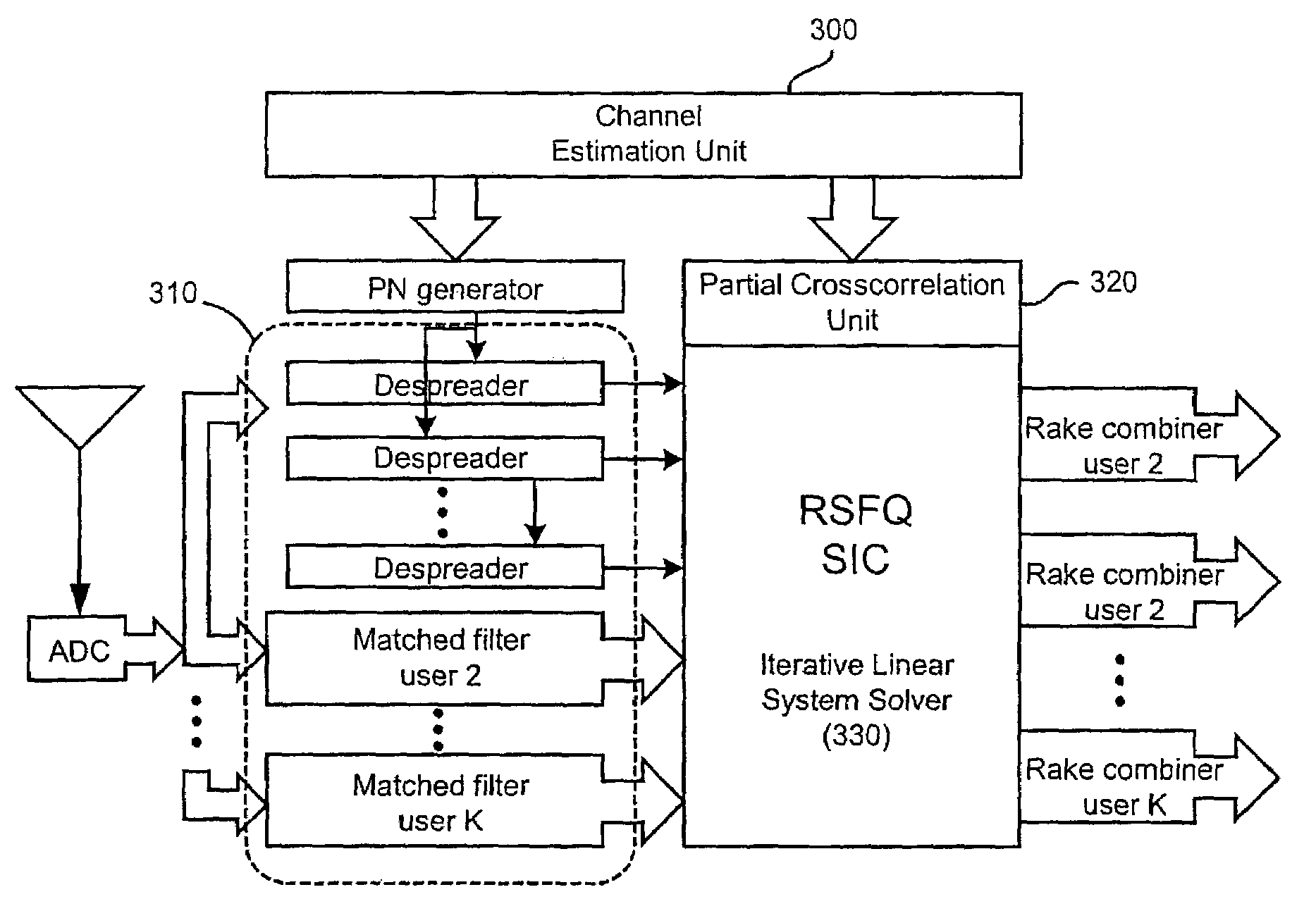
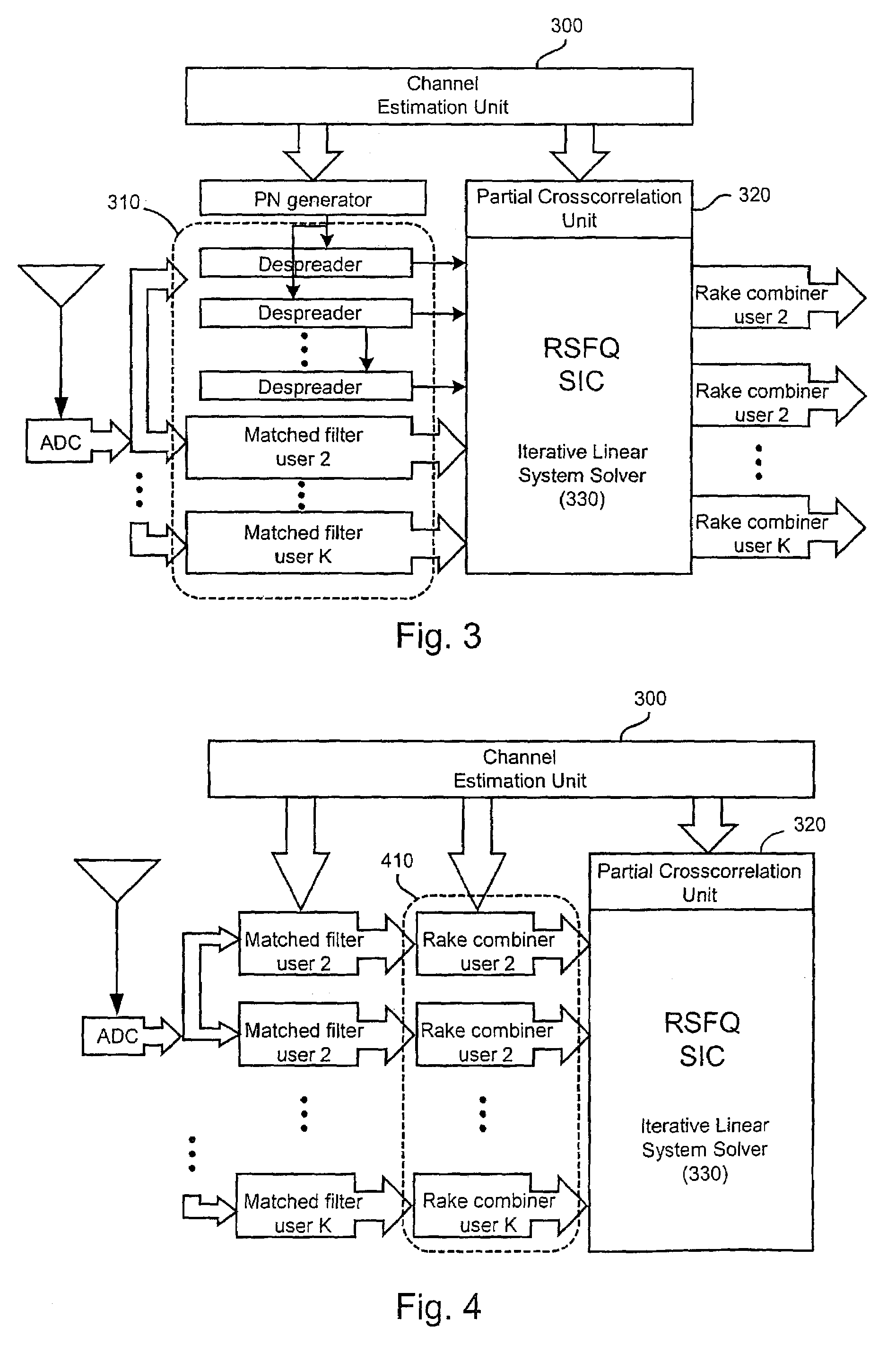
Method and apparatus for multi-user detection using RSFQ successive interference cancellation in CDMA wireless systems
InactiveUS7440490B2Reduce distractionsIncrease uplink capacityRadio transmissionInterference cancellerSystem capacity
A method and apparatus for using a multi-user detector for reducing multiple access interference (MAI) in a direct sequence CDMA wireless system such as W-CDMA. A superconducting rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) RF digital receiver operating in combination with an RSFQ successive interference canceller (SIC) is located in the base stations of the wireless system. In the present invention, the RSFQ SIC is a vector machine capable of processing the cross-correlation matrices using an iterative method to decorrelate the user binary code sequences from the input signal in which the interference components are removed. According, the reduction in interference results in a significant increase in system capacity while improving cellular coverage area.
Owner:KIDIYAROVA SHEVCHENKO ANNA +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com