Patents
Literature
115 results about "Blood pressure change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Most people do not realize their blood pressure is constantly changing minute by minute in response to mood, activity, body position, etc. In fact, simple changes can cause blood pressure to fluctuate between 5 and 40 mmHg.
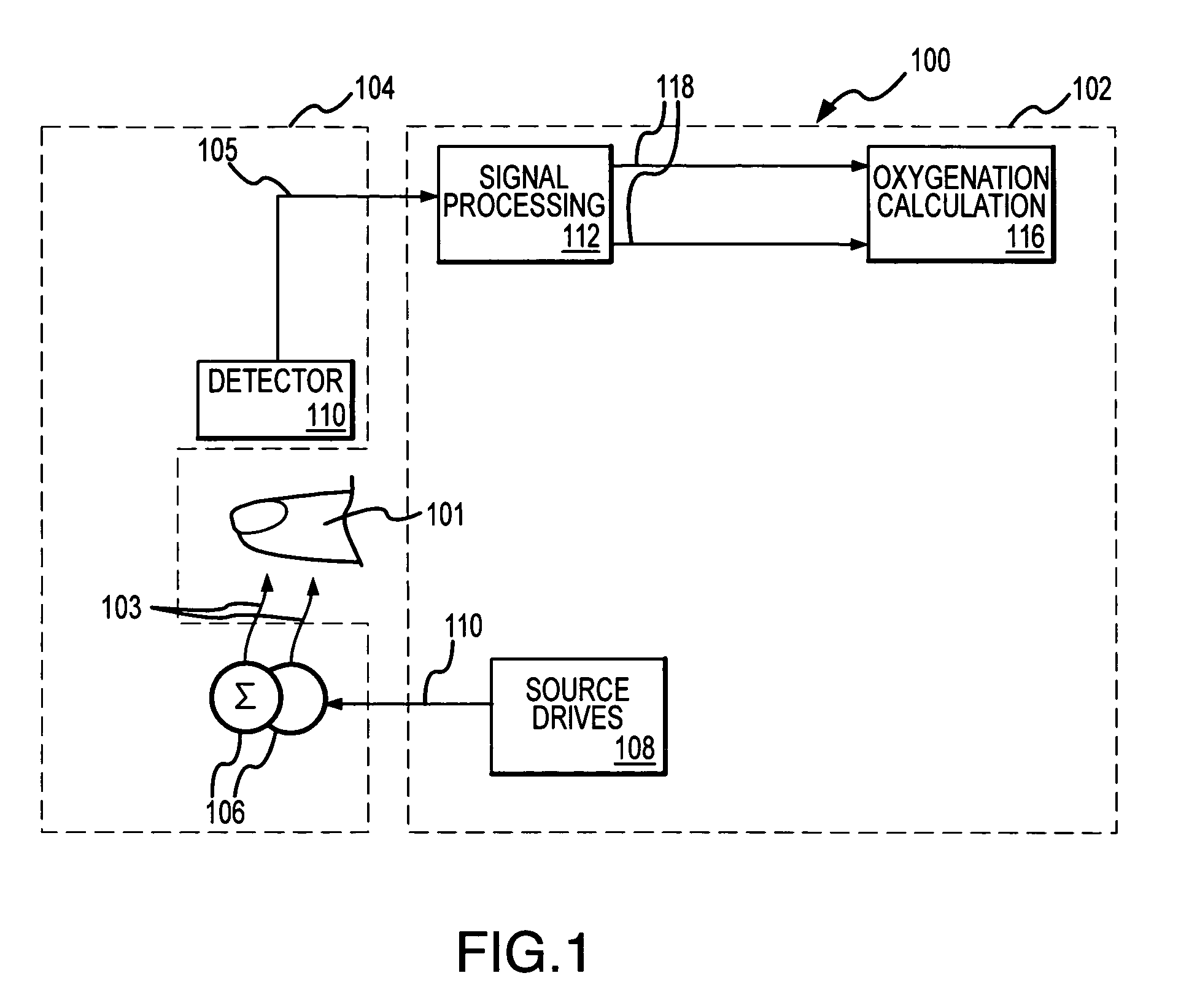
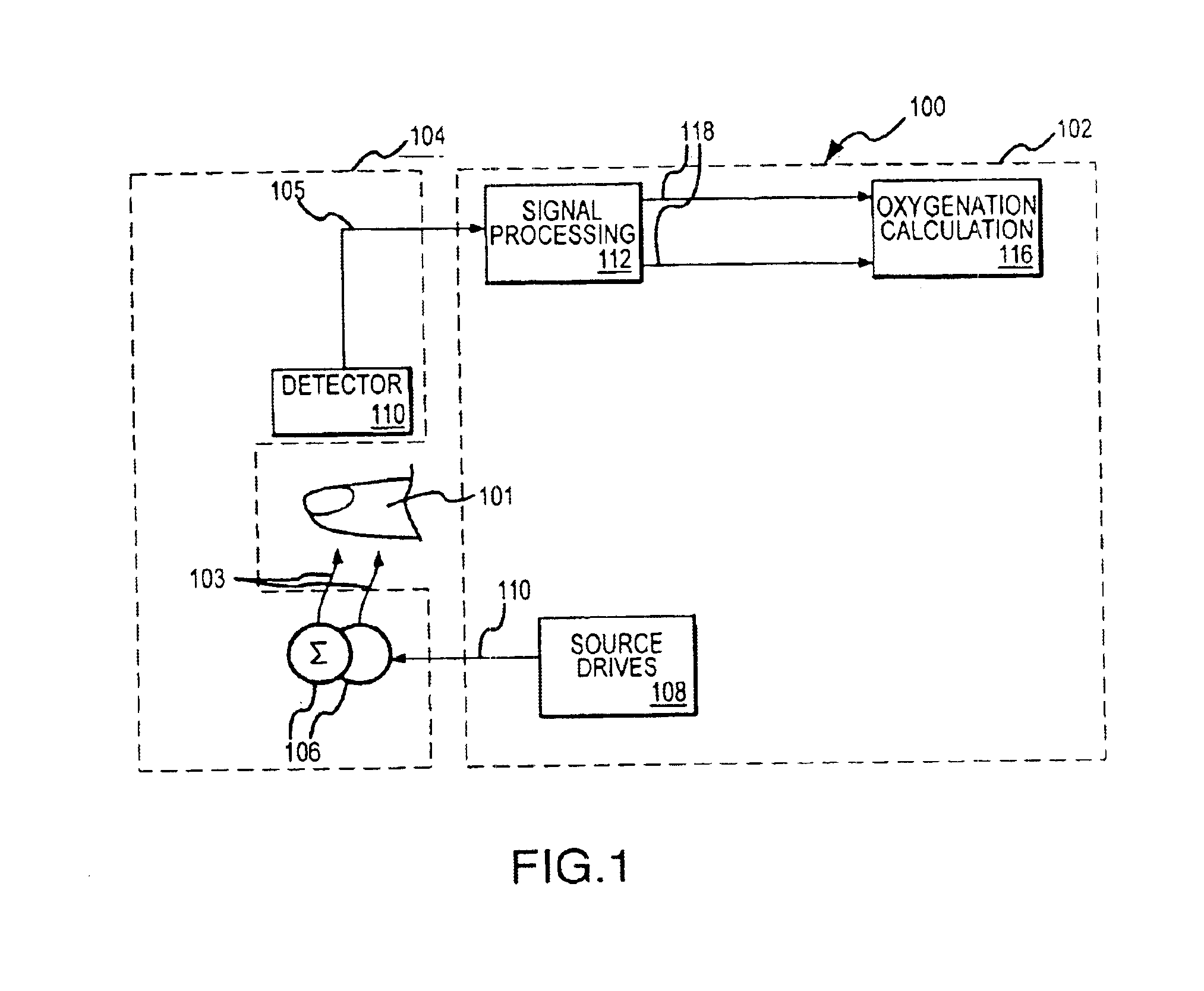
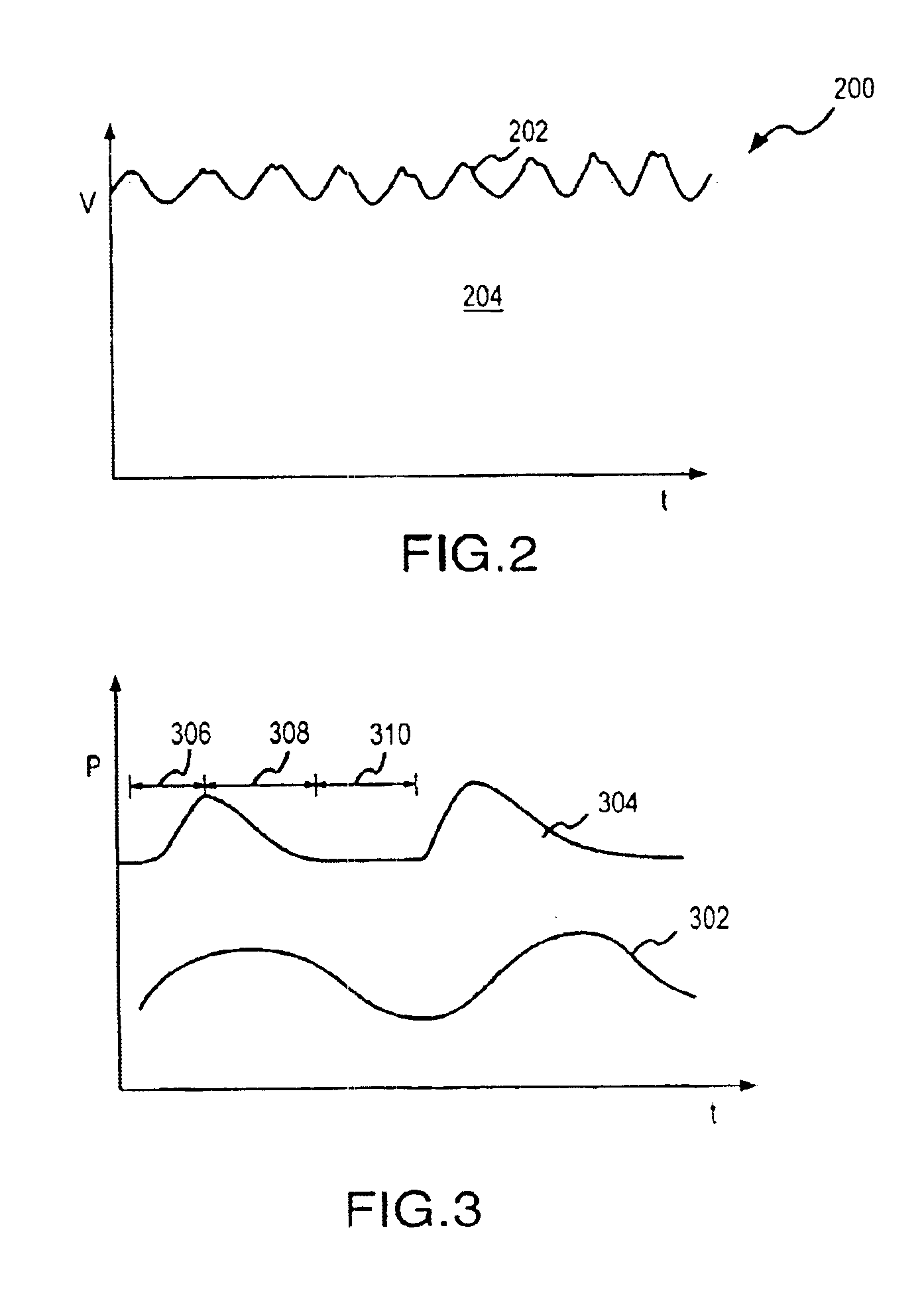
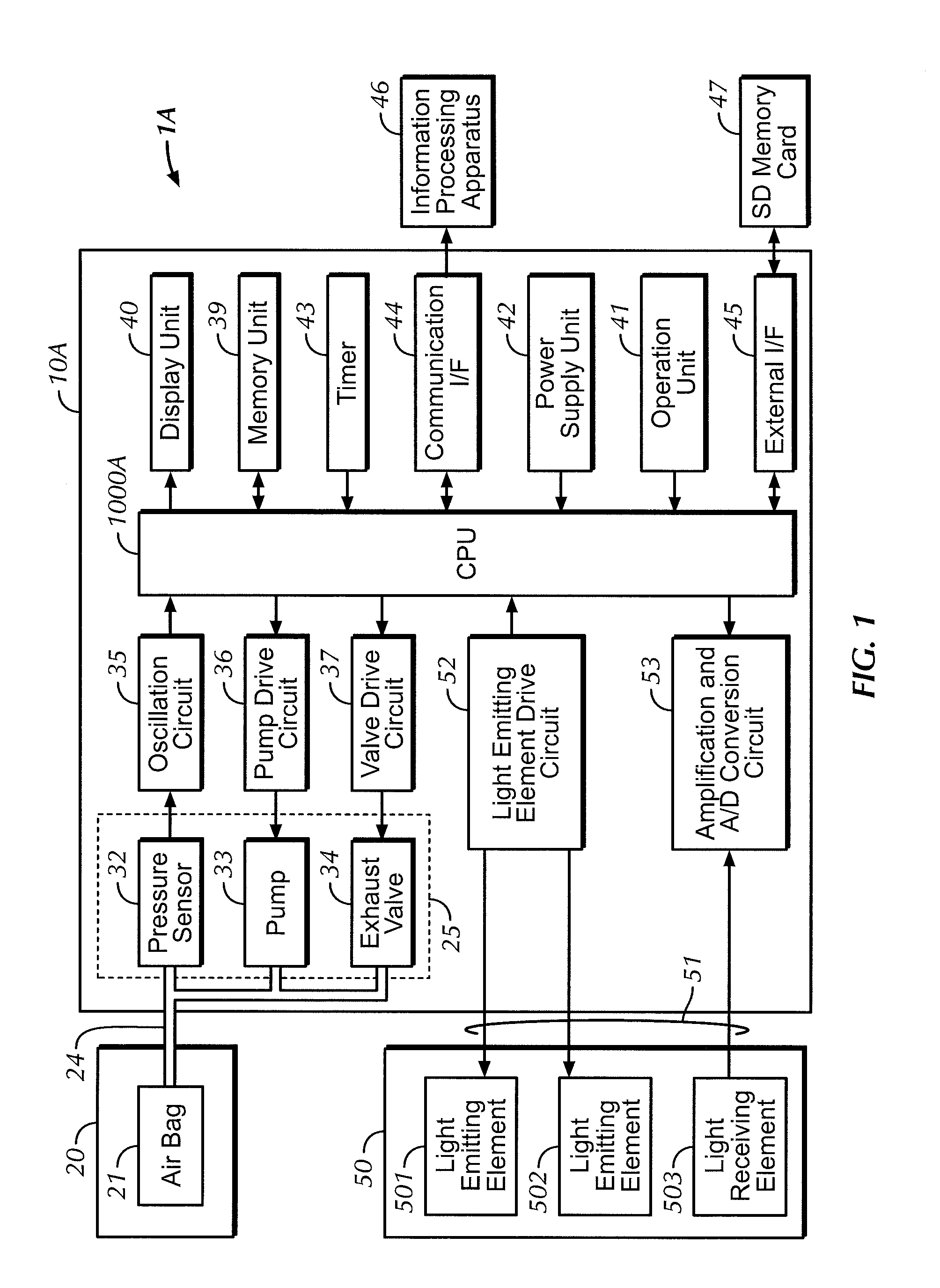
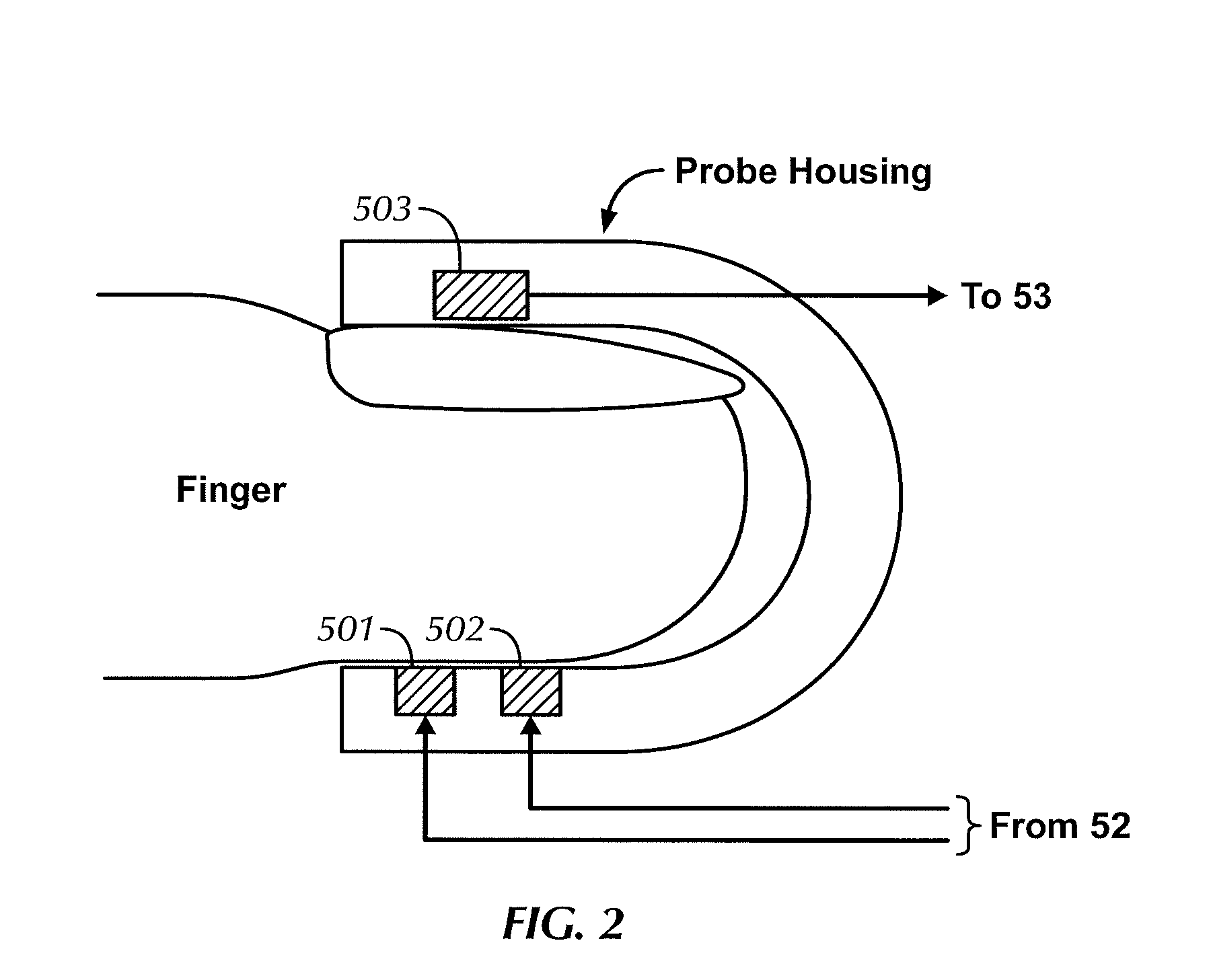
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic signal
InactiveUS7001337B2Fast and robust and computationally efficientRobust processingEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterNervous systemRR interval
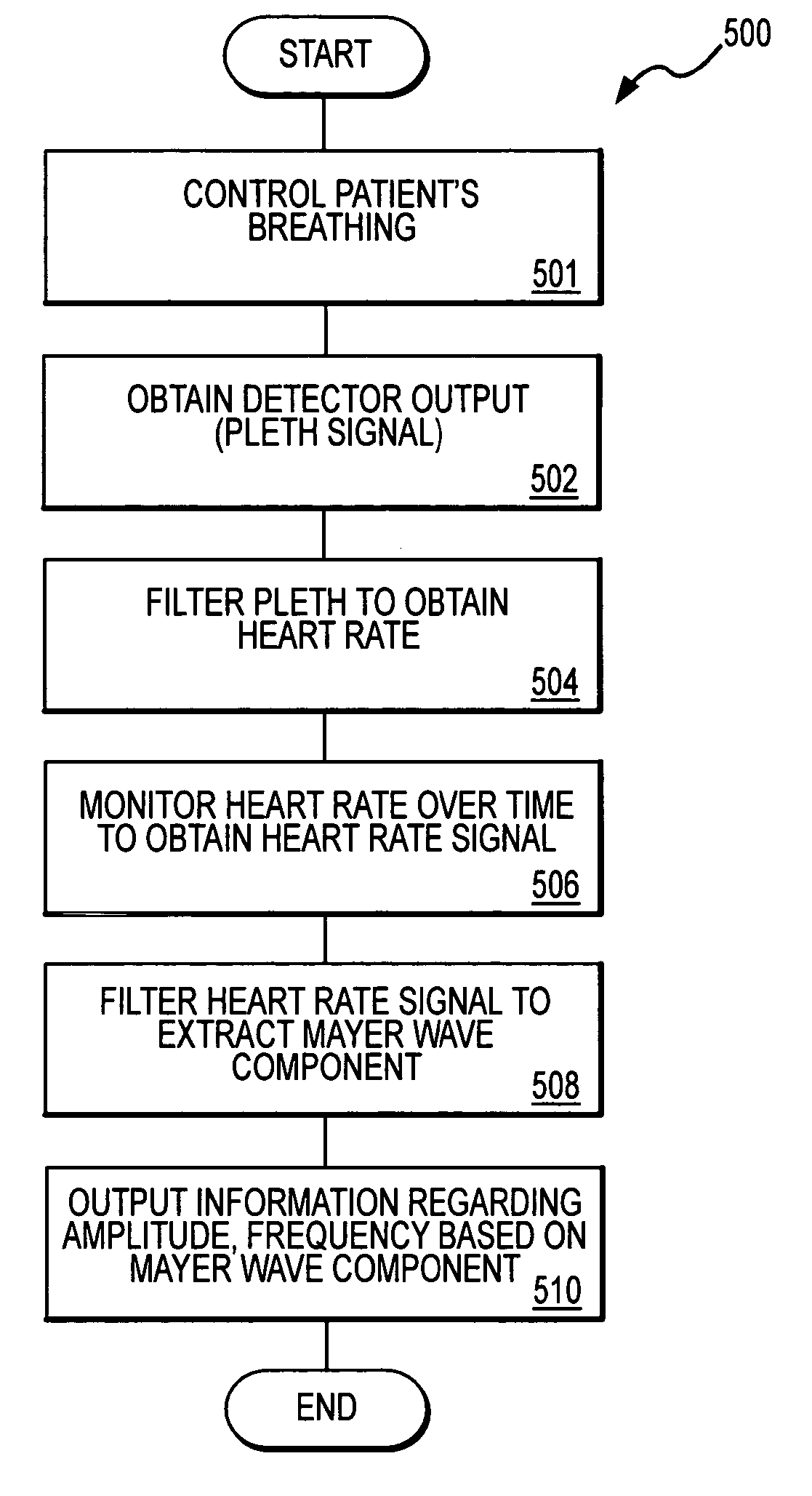
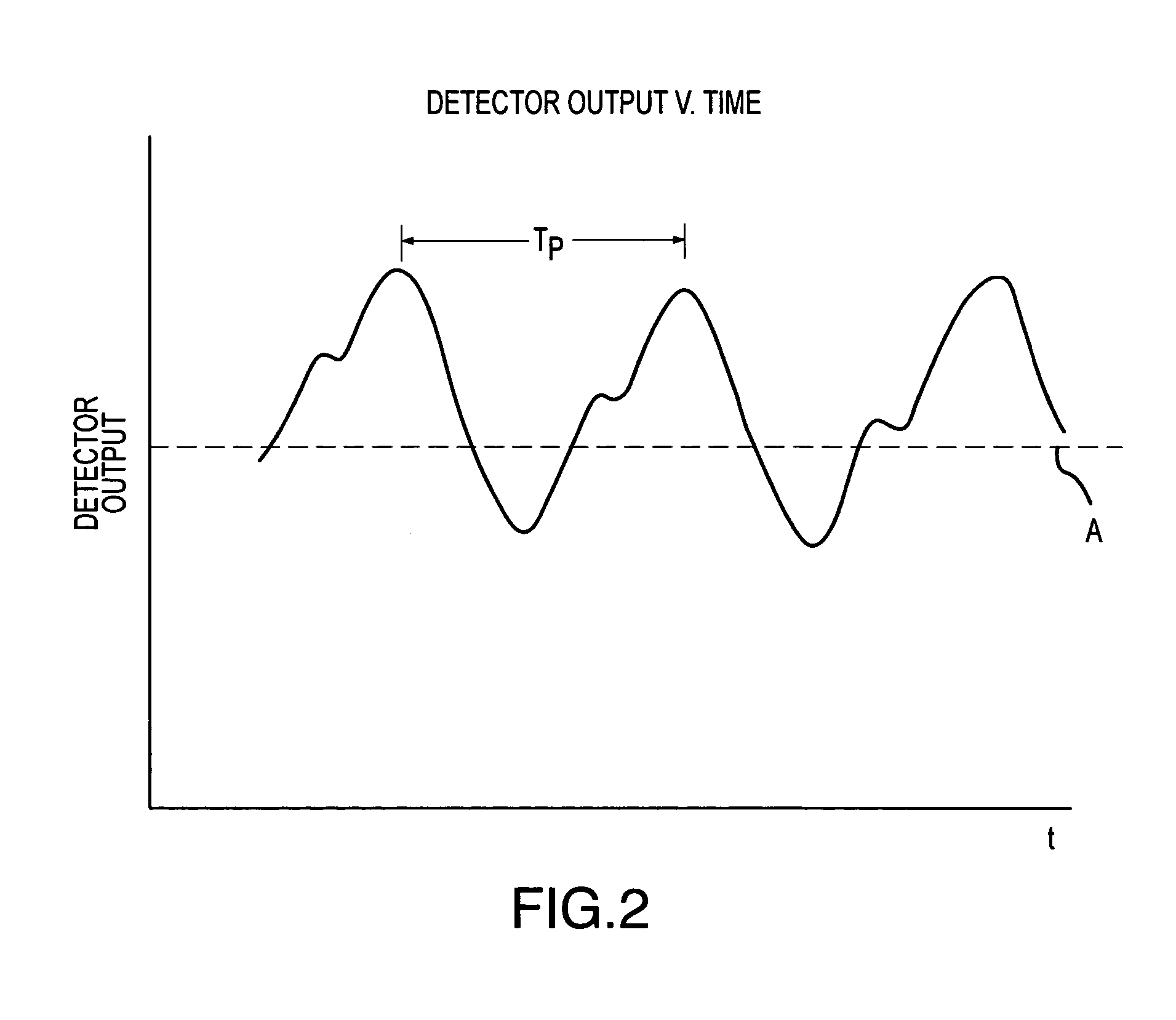
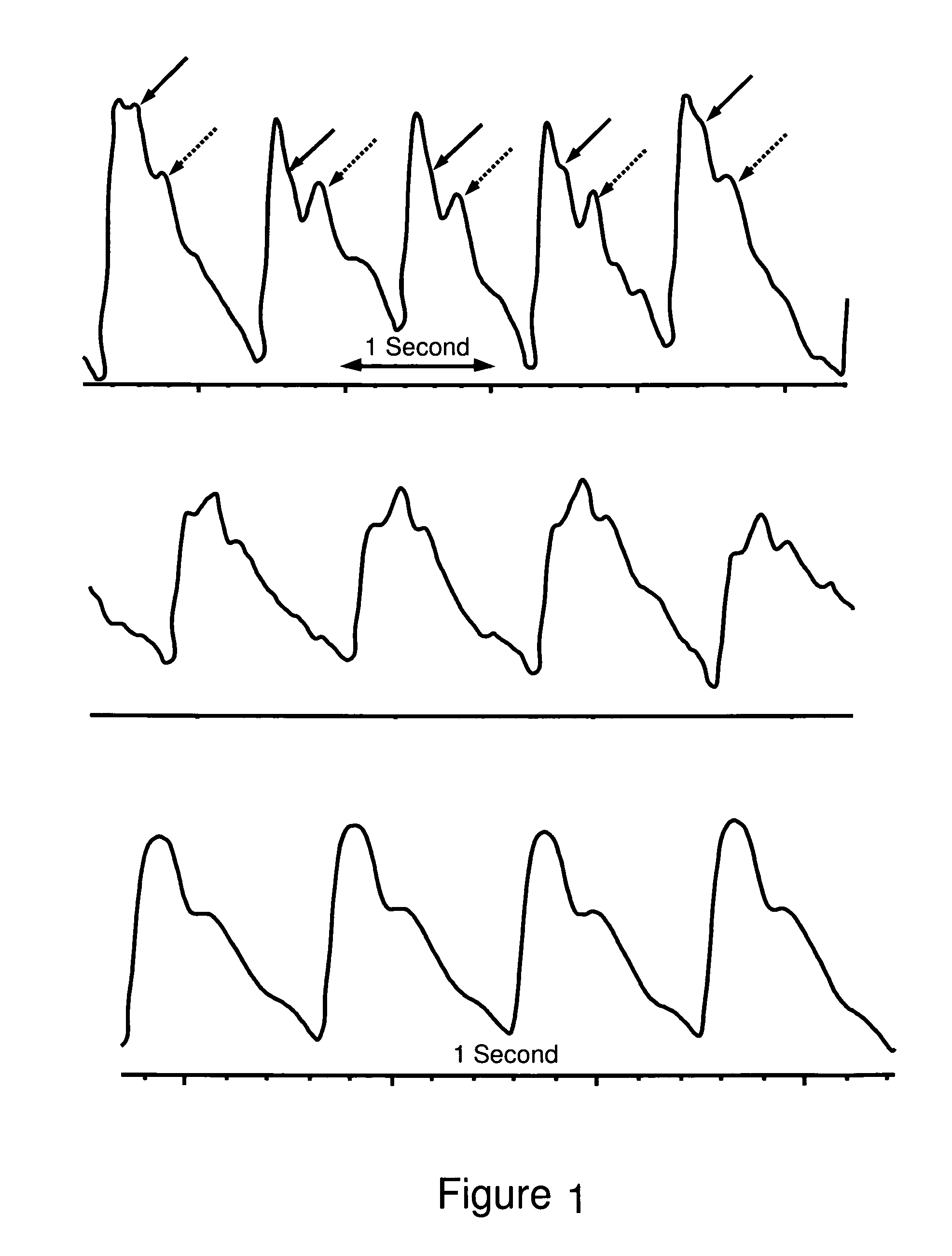
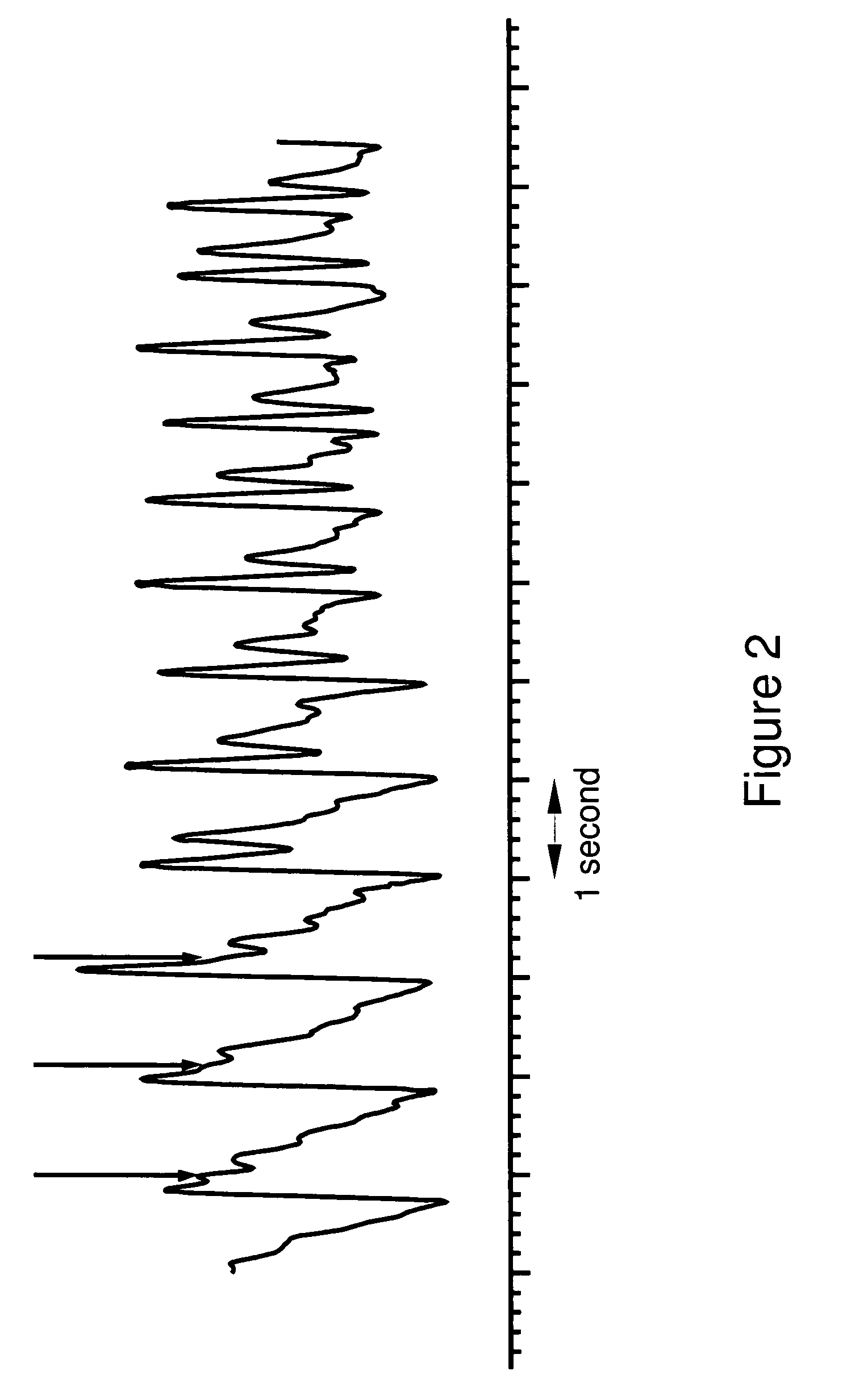
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration rate, heart rate, heart rate variability, blood volume variability and / or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (2502) a pleth, filtering (2504) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (2506) a signal component of interest, monitoring (2508) blood pressure changes, monitoring (2510) heart rate, and performing (2512) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this relationship, the component of interest may be identified (2514) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (2516), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (2520). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (2518) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
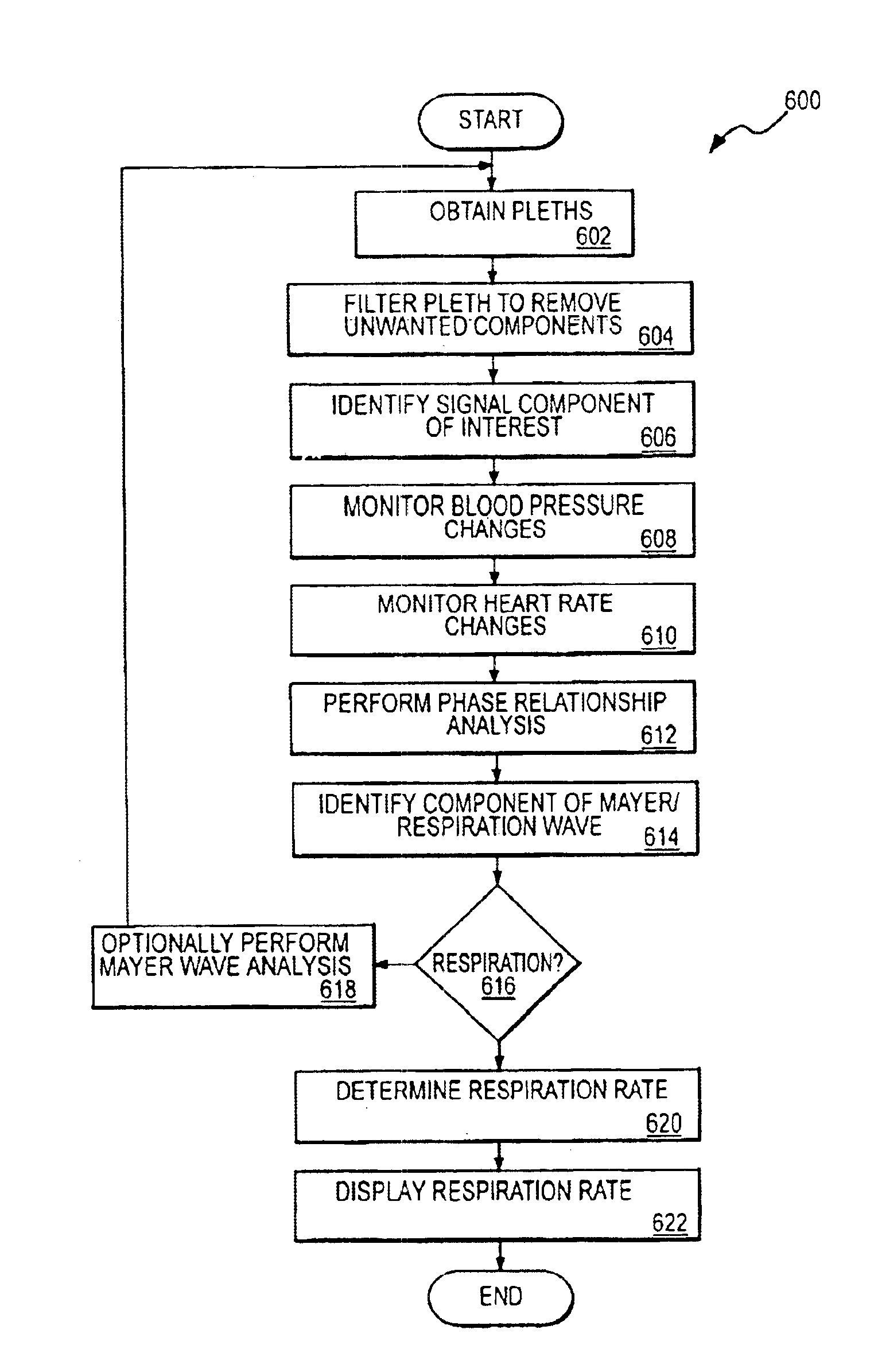
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic baseline signal
InactiveUS6896661B2Function increaseReduce the amount requiredCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationNervous systemMedicine
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (602) a pleth, filtering (604) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (606) a signal component of interest based on the filtered signal, monitoring (608) blood pressure changes, monitoring (610) heart rate, and performing (612) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a phase relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this phase relationship, the component of interest may be identified (614) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (616), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (620). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (618) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
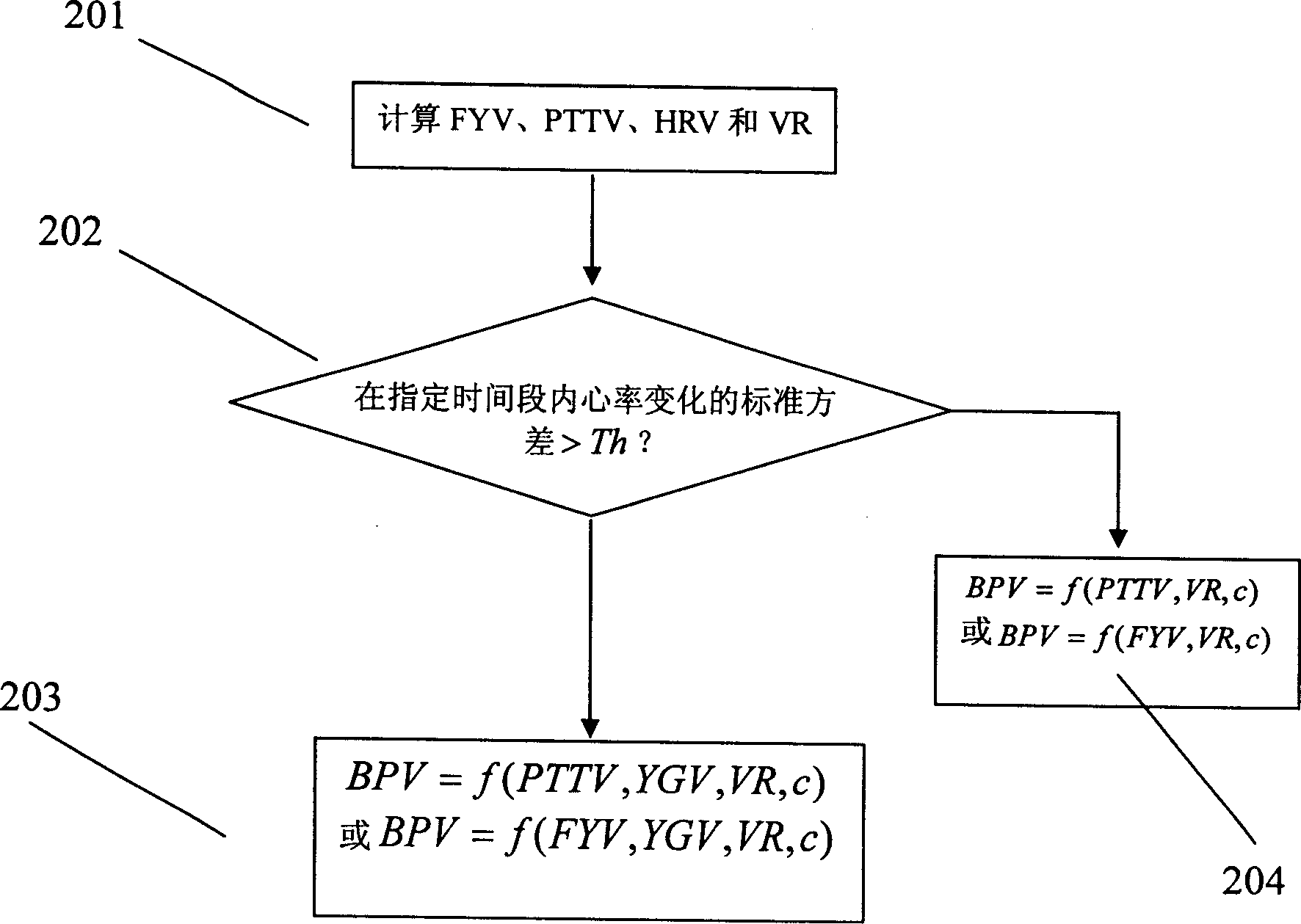
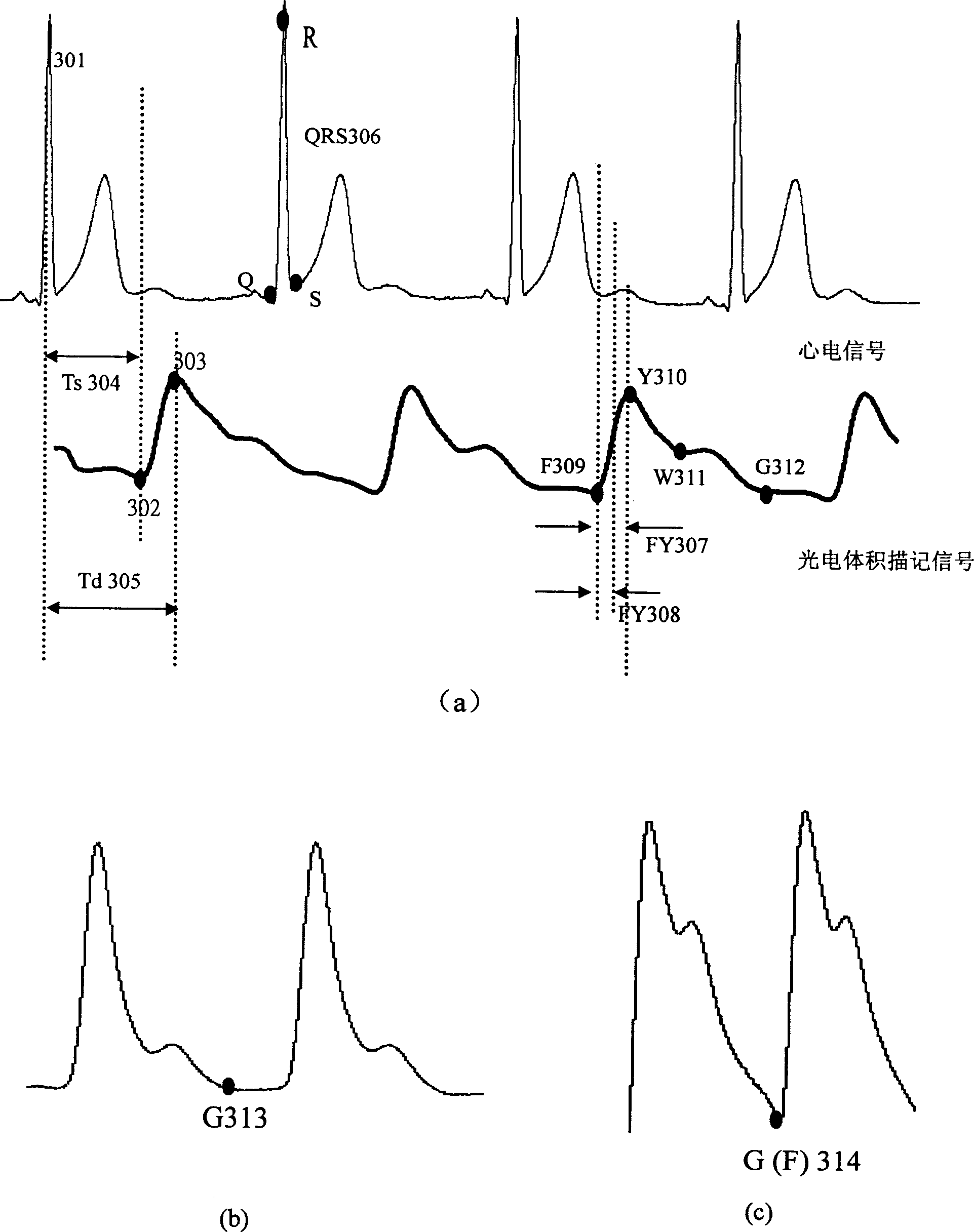
Calibration of pulse-transit-time to blood pressure model using multiple physiological sensors and various methods for blood pressure variation
Disclosed are devices and methods for estimating blood pressure, which implement a pulse-transit-time-based blood pressure model that can be calibrated. Some implementations provide reliable and user friendly means for calibrating the blood pressure model using blood pressure perturbation methods and multiple sensors.
Owner:FITBIT INC
Detection of drastic blood pressure changes
InactiveUS20130116587A1Rapid blood pressureReliable markerElectrocardiographyMedical devicesBlood treatmentsEvent type
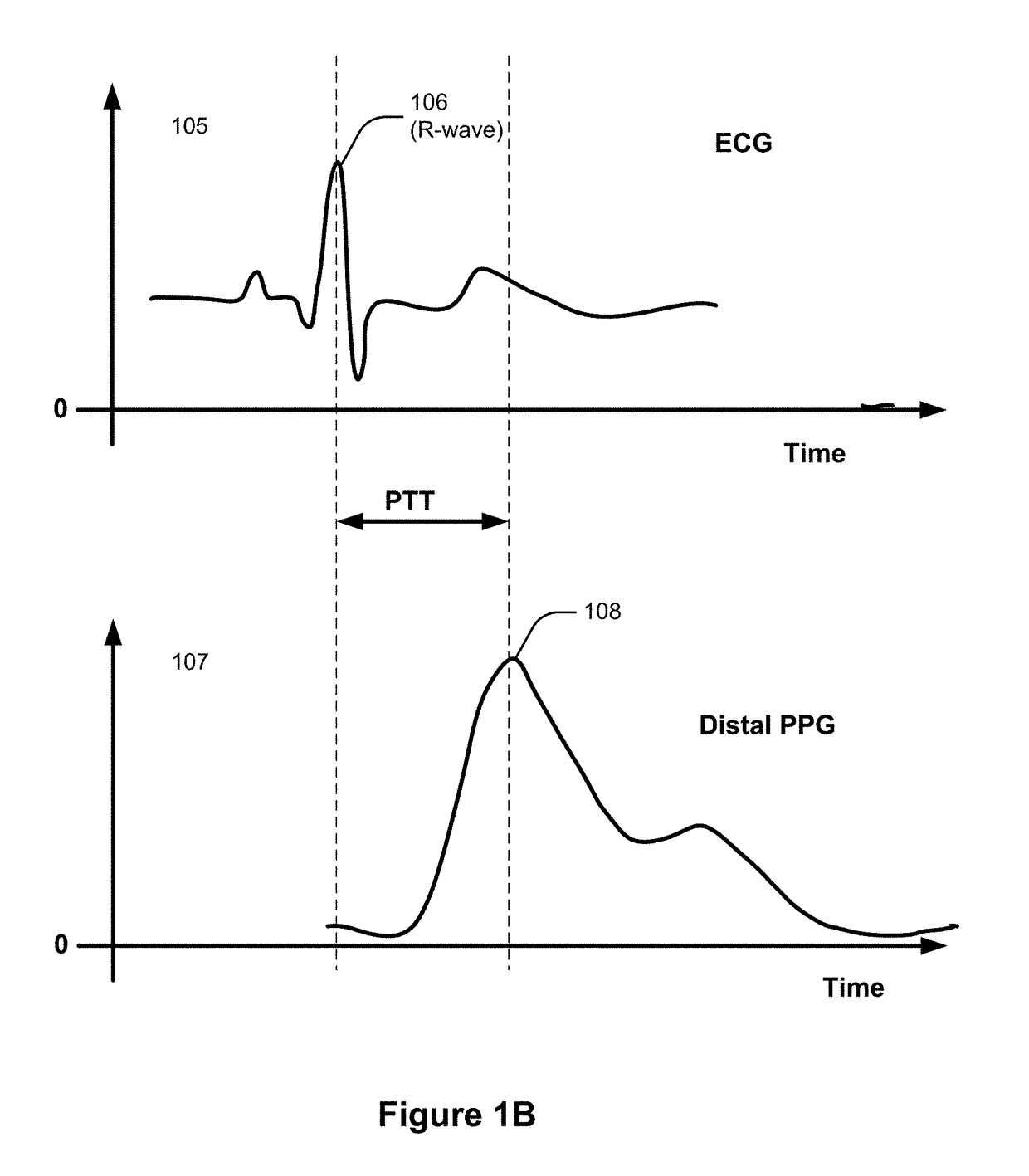
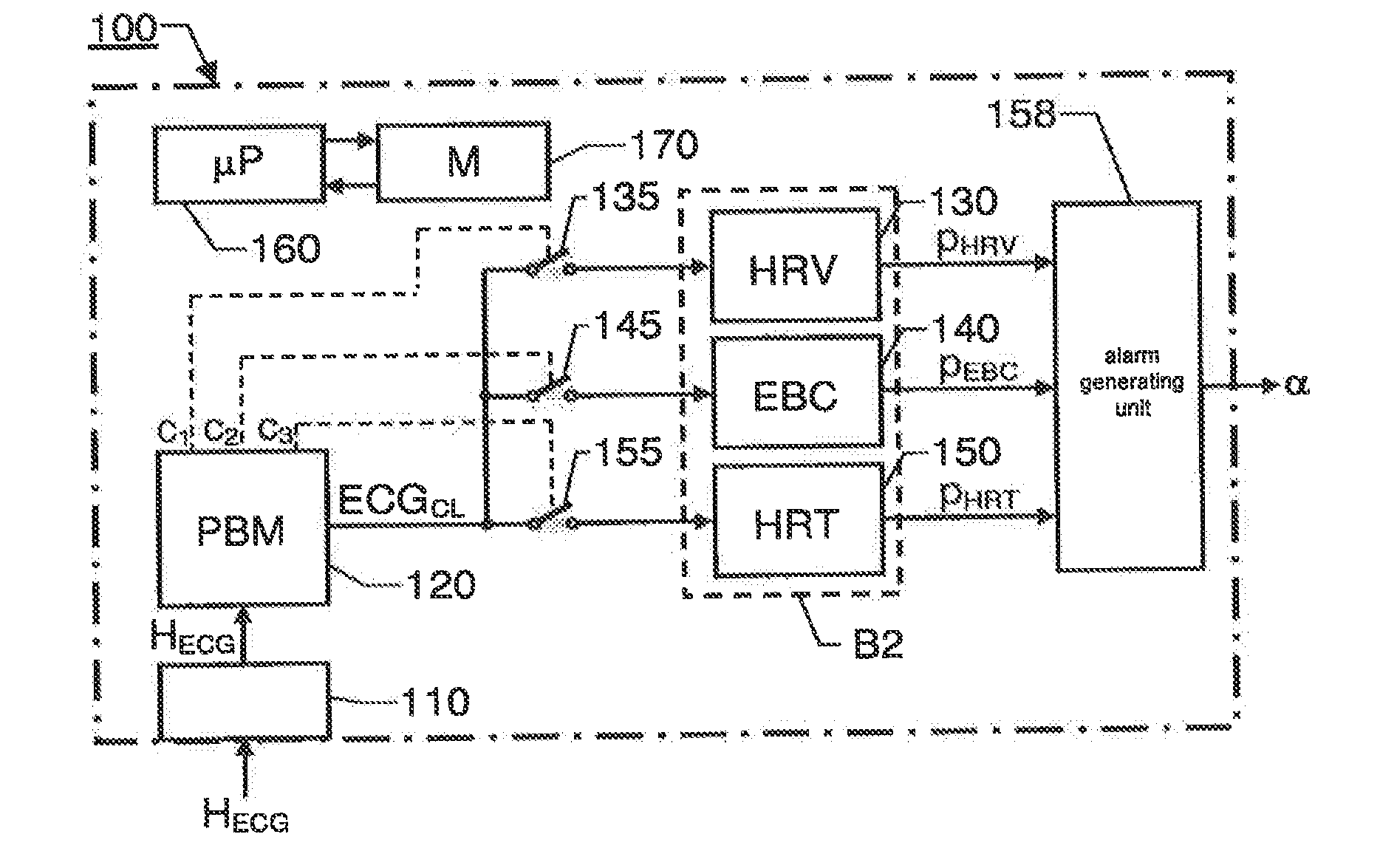
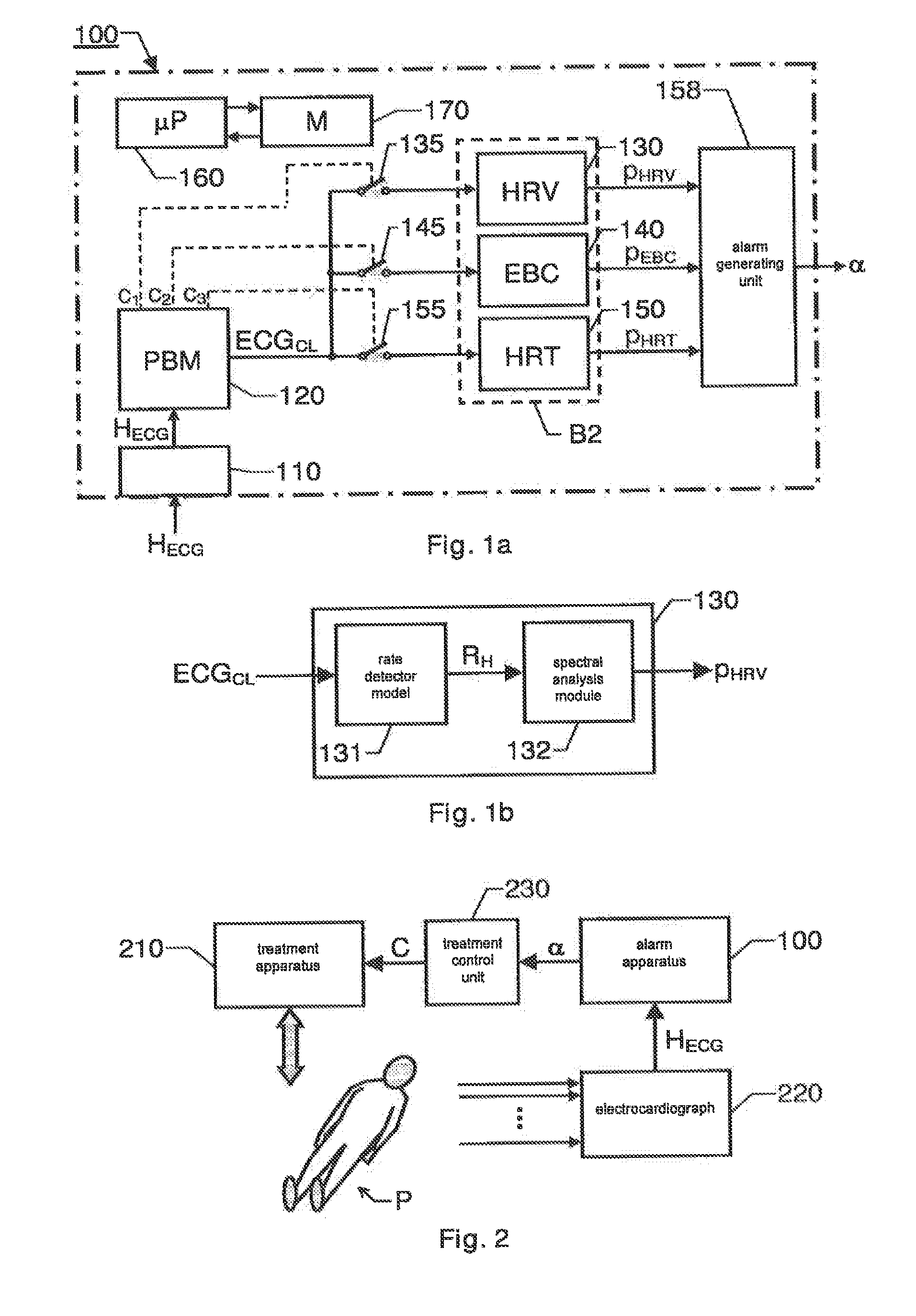
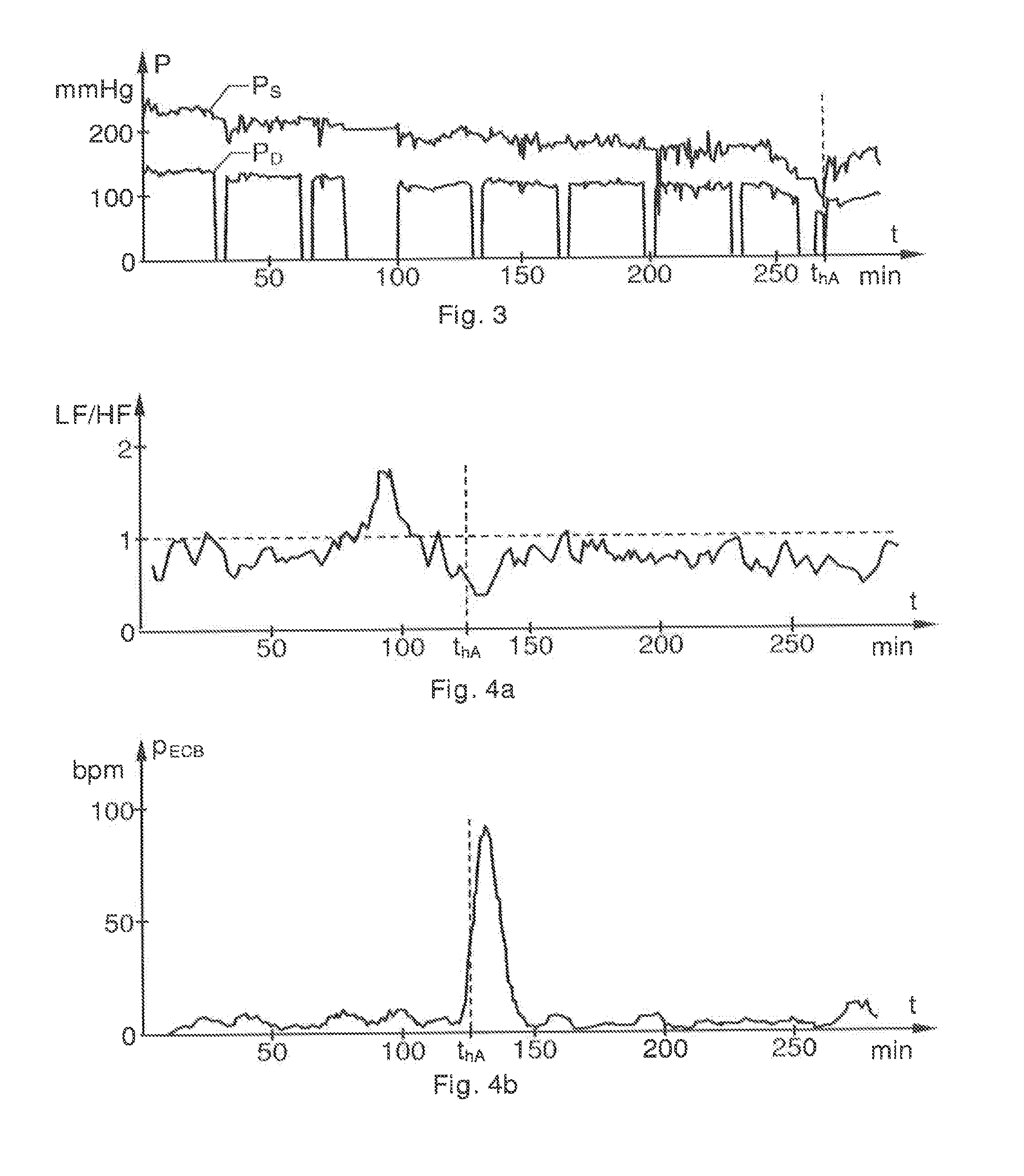
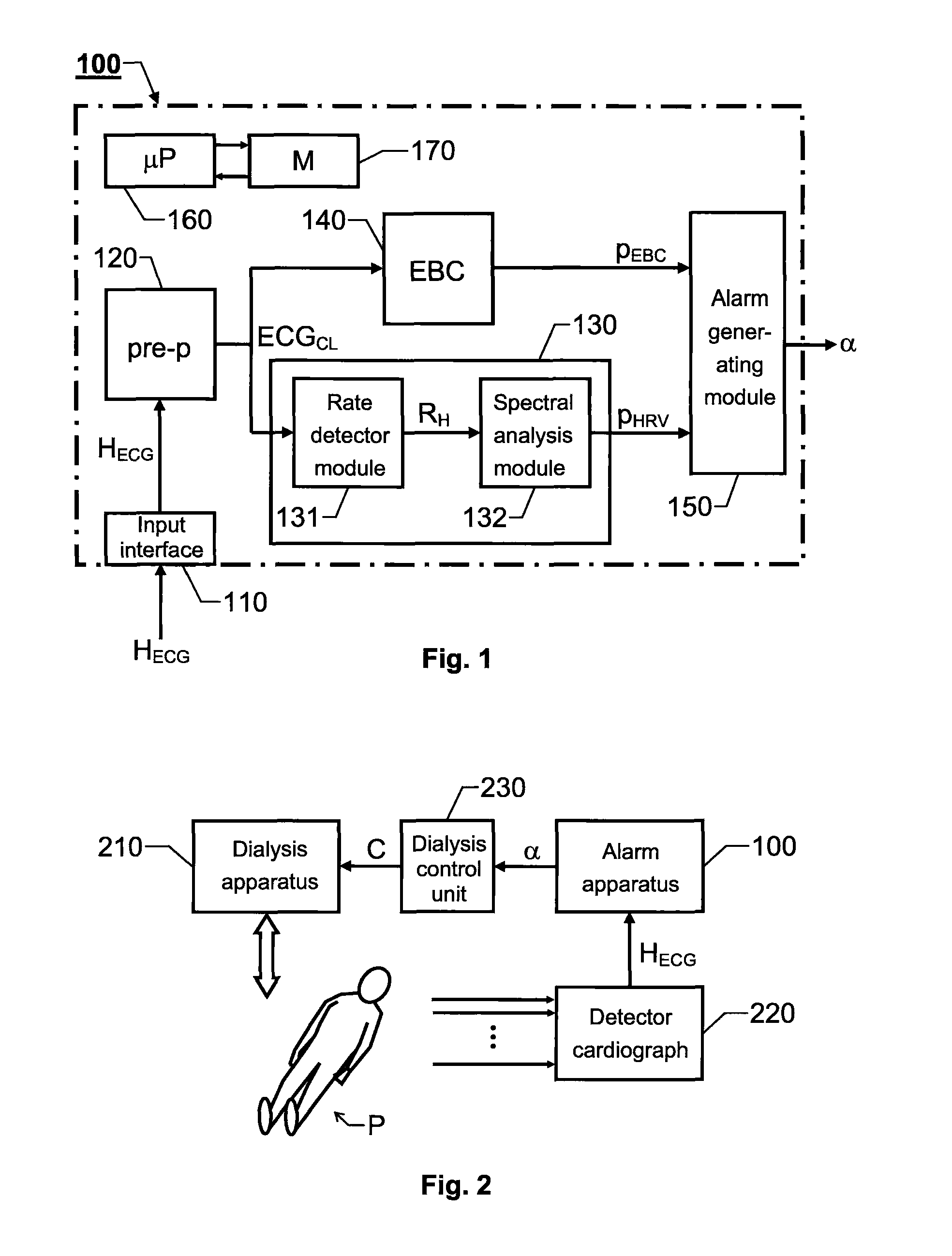
A cardiac-activity based prediction of a rapid drop in a patient's blood pressure during extracorporeal blood treatment is disclosed. A proposed alarm apparatus includes a primary beat morphology analysis unit bank of secondary analysis units and an alarm generating unit. The primary beat morphology analysis unit discriminates heart beats in a received basic electrocardiogram signal, classifies each beat into one out of at least two different beat categories, and associates each segment of the signal with relevant event-type data. The event-type data and the basic electrocardiogram signal together form an enhanced electrocardiogram signal, based upon which the primary beat morphology analysis unit determines whether one or more secondary signal analyses should be performed. Depending on the enhanced electrocardiogram signal's properties, the bank of secondary analysis units performs none, one or more of up to at least two different types of secondary analyses, and for each analysis performed produces a respective test signal. The alarm generating unit receives the test signals, and triggers an alarm signal indicative of an estimated rapid blood pressure decrease, if at least one alarm criterion is fulfilled.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
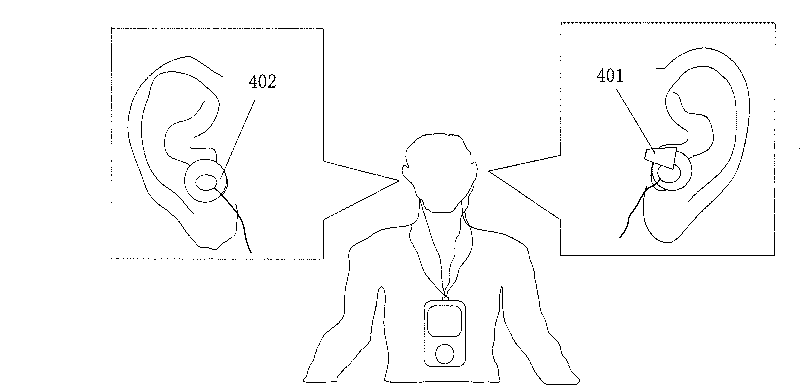
Earhook type low power consumption physiologic parameter monitoring device
ActiveCN101708121AEasy to useDoes not interfere with normal activitiesEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsElectricityHeart rate change
The invention relates to a physiologic parameter monitoring device comprising a sensor unit, a processing unit and a notification unit; the sensor unit is used for acquiring a biological signal from the surfaces of ears of a user; the processing unit is used for processing the biological signal and outputting physiologic parameters, such as heart rate, heart rate change rate, blood pressure, blood pressure change rate, degree of blood oxygen saturation and body temperature; and the notification unit issues the physiologic parameters in a visual or audio way. The physiologic parameter monitoring device continuously detects one or a plurality of items of physiologic signals and parameters for the user under the condition of not interfering with the daily activities of the user. A power supply of a piezoelectric device of the sensor unit supplies power for the sensor unit by utilizing the piezoelectricity and can be used as a switch of the device and reduce the reliance on to batteries.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
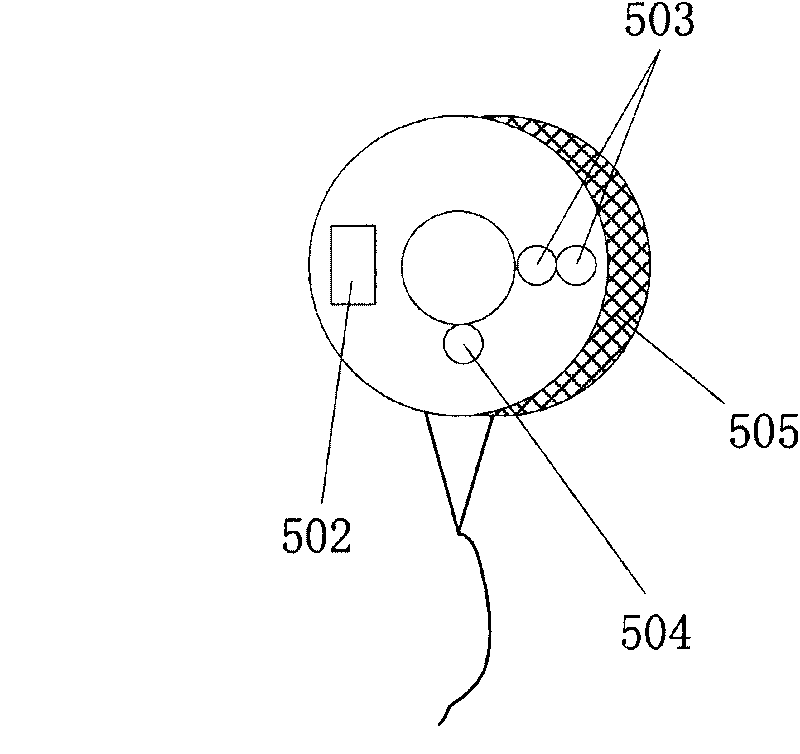
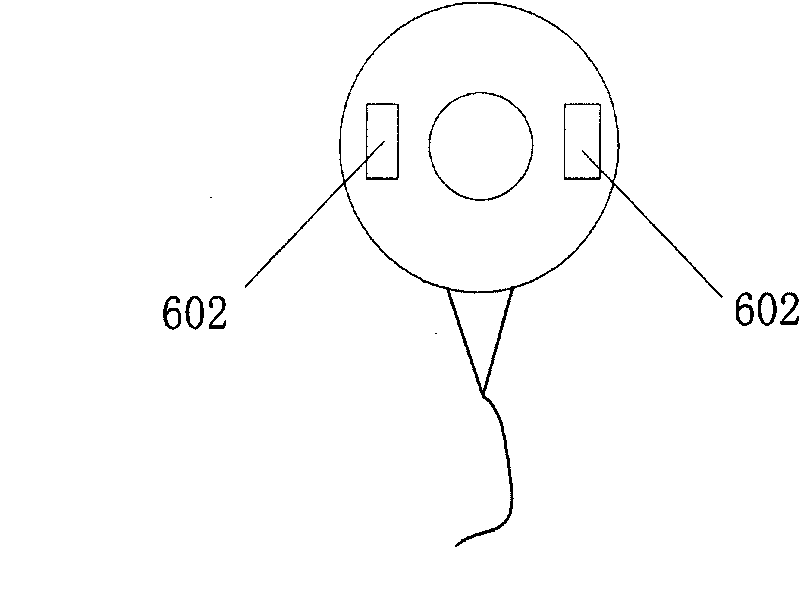
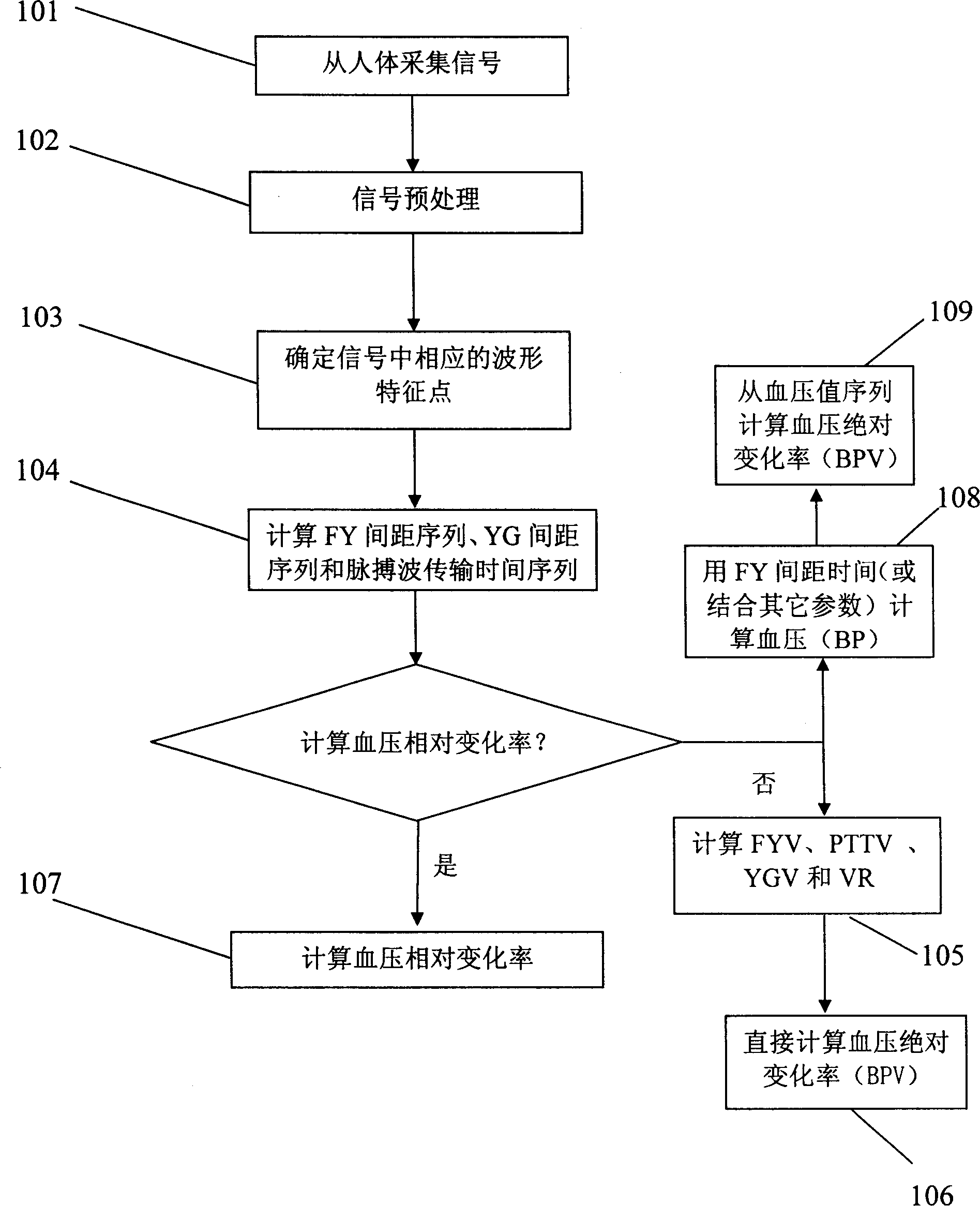
Method for measuring blood pressure change rate
The invention discloses a method for measuring blood pressure change rate which comprises the steps of, (1) collecting a series of signals related to human body pulses wave production and transmission characteristics, (2) obtaining characteristic parameter sequence of the collected signal, (3) determining blood pressure parameter according to the obtained signal characteristic parameter sequence.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Method for measuring arterial pressure, apparatus and individual correction tech. therefor
InactiveCN1868399AHigh implementabilityReduce mistakesEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyContinuous measurementPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
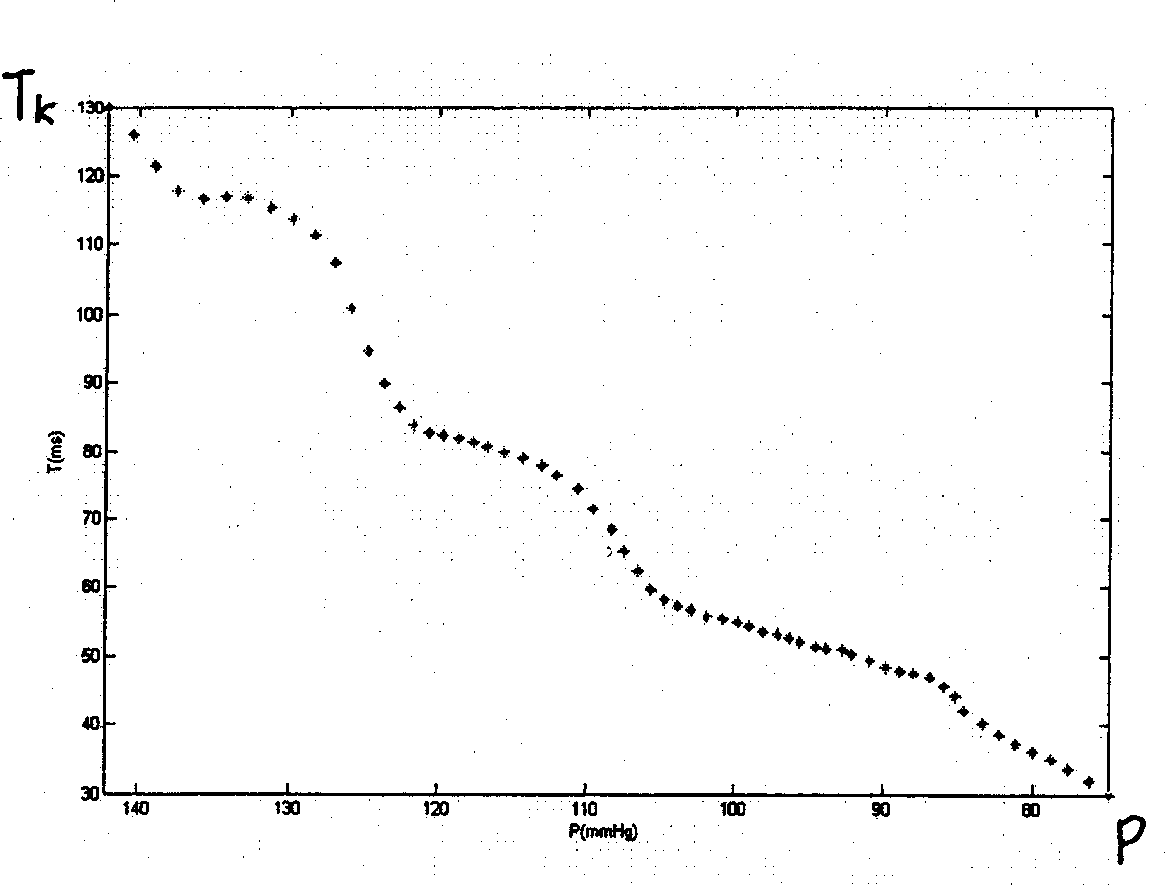
A method and device for measuring the blood pressure of artery and its personalized correction technique are disclosed. A series of the pressure values (P) for sleeve band and the time delay values (Tk) of the relative remote Ke's sounds are obtained. The function relation Tk(P) between said pressure change and sound delay is in turn obtained. Measuring a Tk relative to a P can calculate out the blood pressure change. A regression equation for continuous measurements of arteral blood pressure is used to obtain a personalized correction coefficient.
Owner:BEIJING XINXING YANGSHENG TECHN CORP +1
Monitoring physiological parameters based on variations in a photoplethysmographic signal
InactiveCN1646055AFunction increaseEvaluation of blood vesselsSurgical instrument detailsNervous systemRR interval
A method and apparatus are disclosed for using photoplethysmography to obtain physiological parameter information related to respiration rate, heart rate, heart rate variability, blood volume variability and / or the autonomic nervous system. In one implementation, the process involves obtaining (2502) a pleth, filtering (2504) the pleth to remove unwanted components, identifying (2506) a signal component of interest, monitoring (2508) blood pressure changes, monitoring (2510) heart rate, and performing (2512) an analysis of the blood pressure signal to the heart rate signal to identify a relationship associated with the component of interest. Based on this relationship, the component of interest may be identified (2514) as relating to the respiration or Mayer Wave. If it is related to the respiration wave (2516), a respiratory parameter such as breathing rate may be determined (2520). Otherwise, a Mayer Wave analysis (2518) may be performed to obtain parameter information related to the autonomic nervous system.
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
Detection of Drastic Blood Pressure Changes
InactiveUS20080319332A1Rapid blood pressureReliable markerElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisBlood treatmentsEvent type
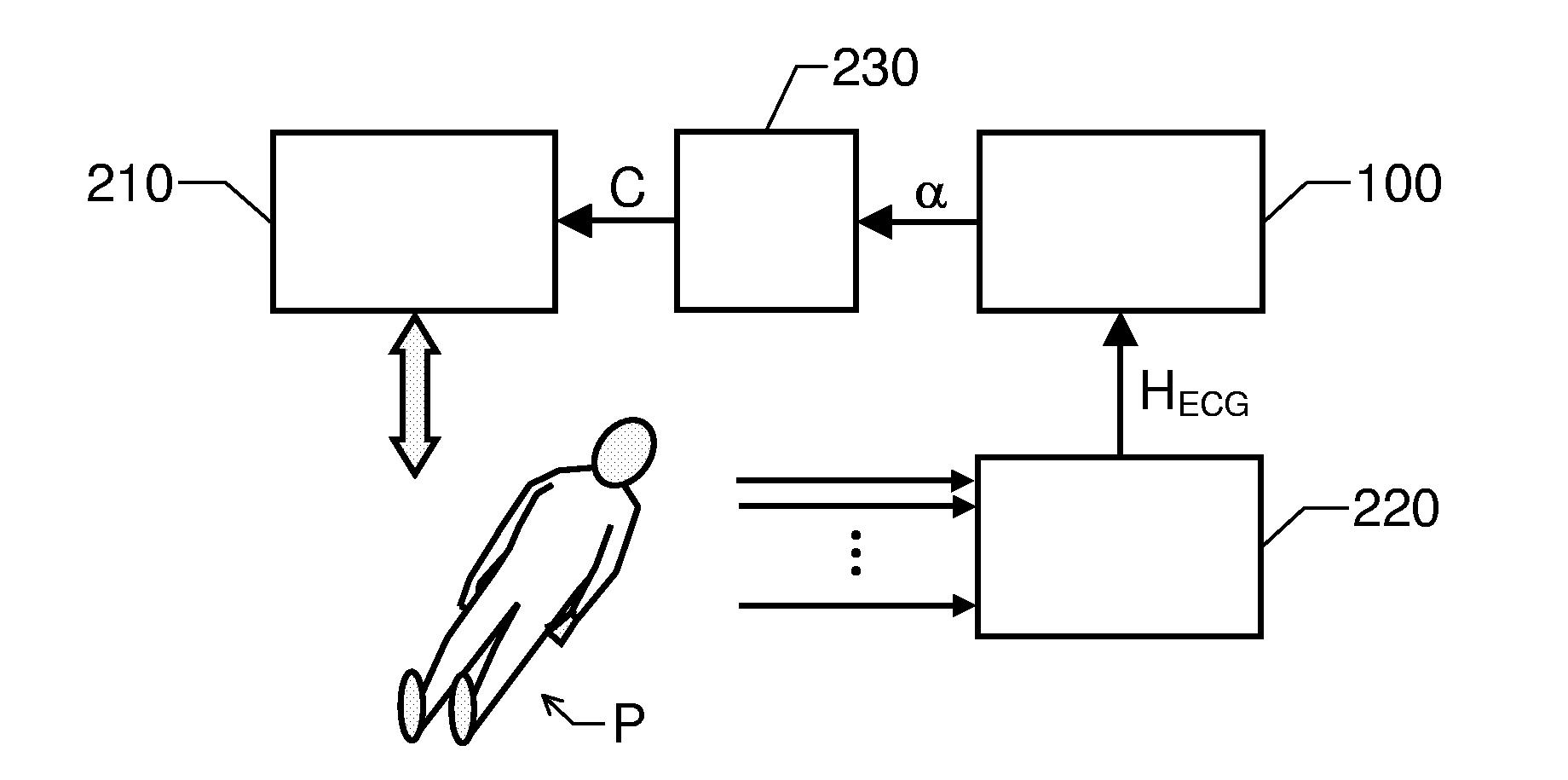
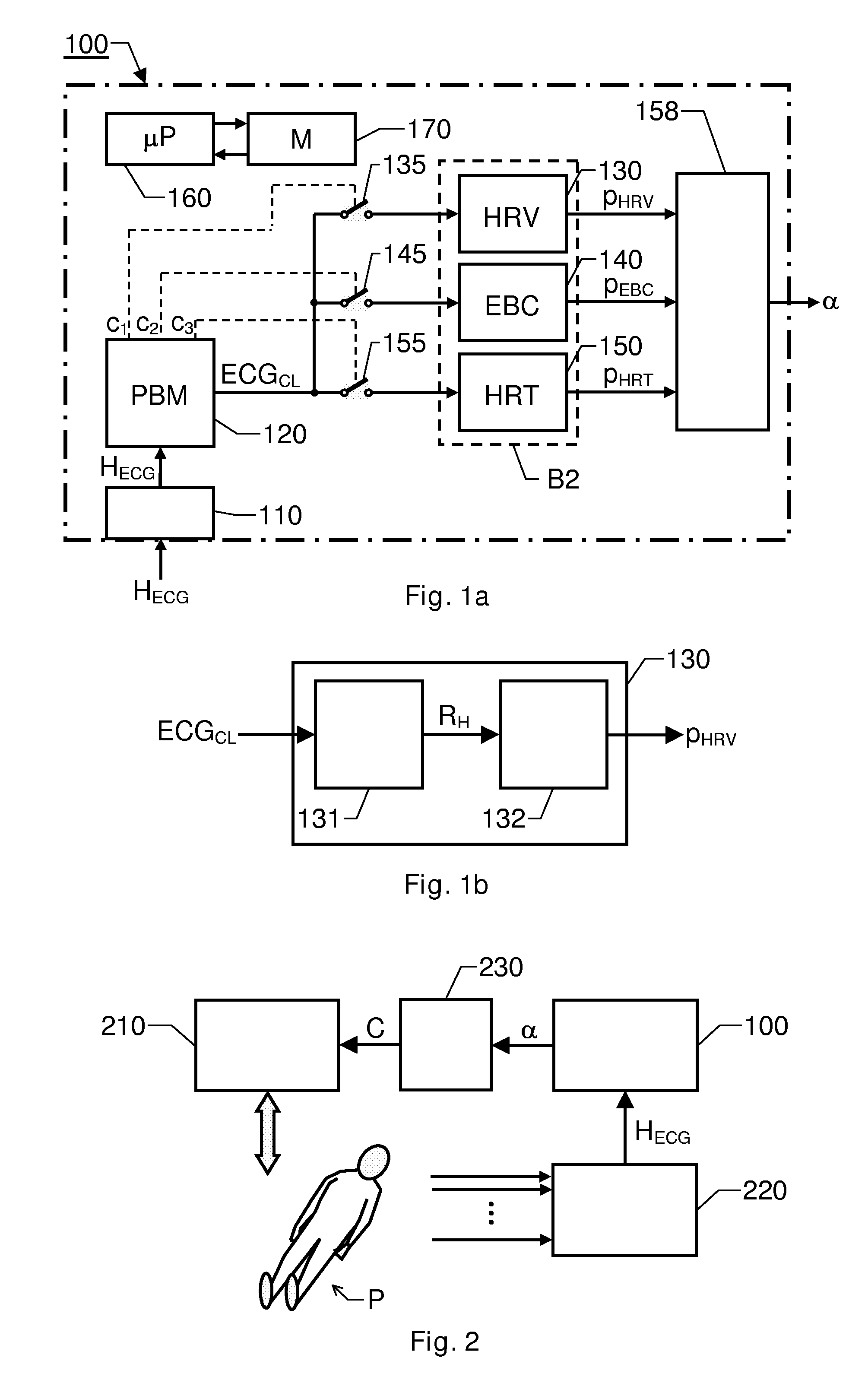
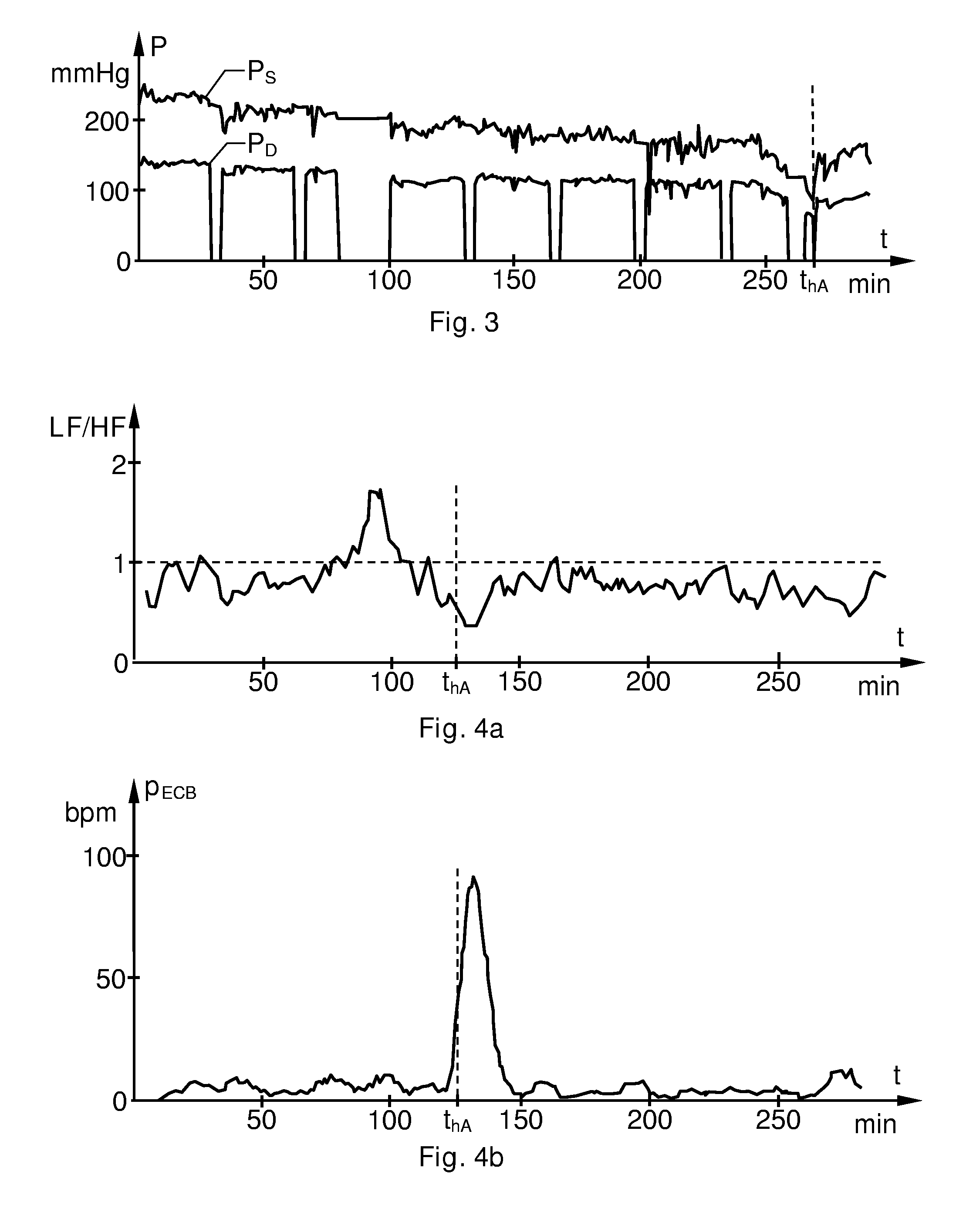
The invention relates to cardiac-activity based prediction of a rapid drop in a patient's blood pressure during extracorporeal blood treatment. A proposed alarm apparatus (100) includes a primary beat morphology analysis unit (120), a bank of secondary analysis units (B2) and an alarm generating unit (158). The primary beat morphology analysis unit (120) discriminates heart beats in a received basic electrocardiogram signal (HECG), classifies each beat into one out of at least two different beat categories, and associates each segment of the signal (HECG) with relevant event-type data. The event-type data and the basic electrocardiogram signal (HECG) together form an enhanced electrocardiogram signal (ECGCL), based upon which the primary beat morphology analysis unit (120) determines whether one or more secondary signal analyses should be performed. Depending on the enhanced electrocardiogram signal's (ECGCL) properties, the bank of secondary analysis units (B2) performs none, one or more of up to at least two different types of secondary analyses, and for each analysis performed produces a respective test signal (PHRV, PEBC, PHRT)—The alarm generating unit (158) receives the test signals (PHRV, PEBC, PHRT), and triggers an alarm signal (α) indicative of an estimated rapid blood pressure decrease, if at least one alarm criterion is fulfilled.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Arterial pulse decomposition analysis for vital signs determination
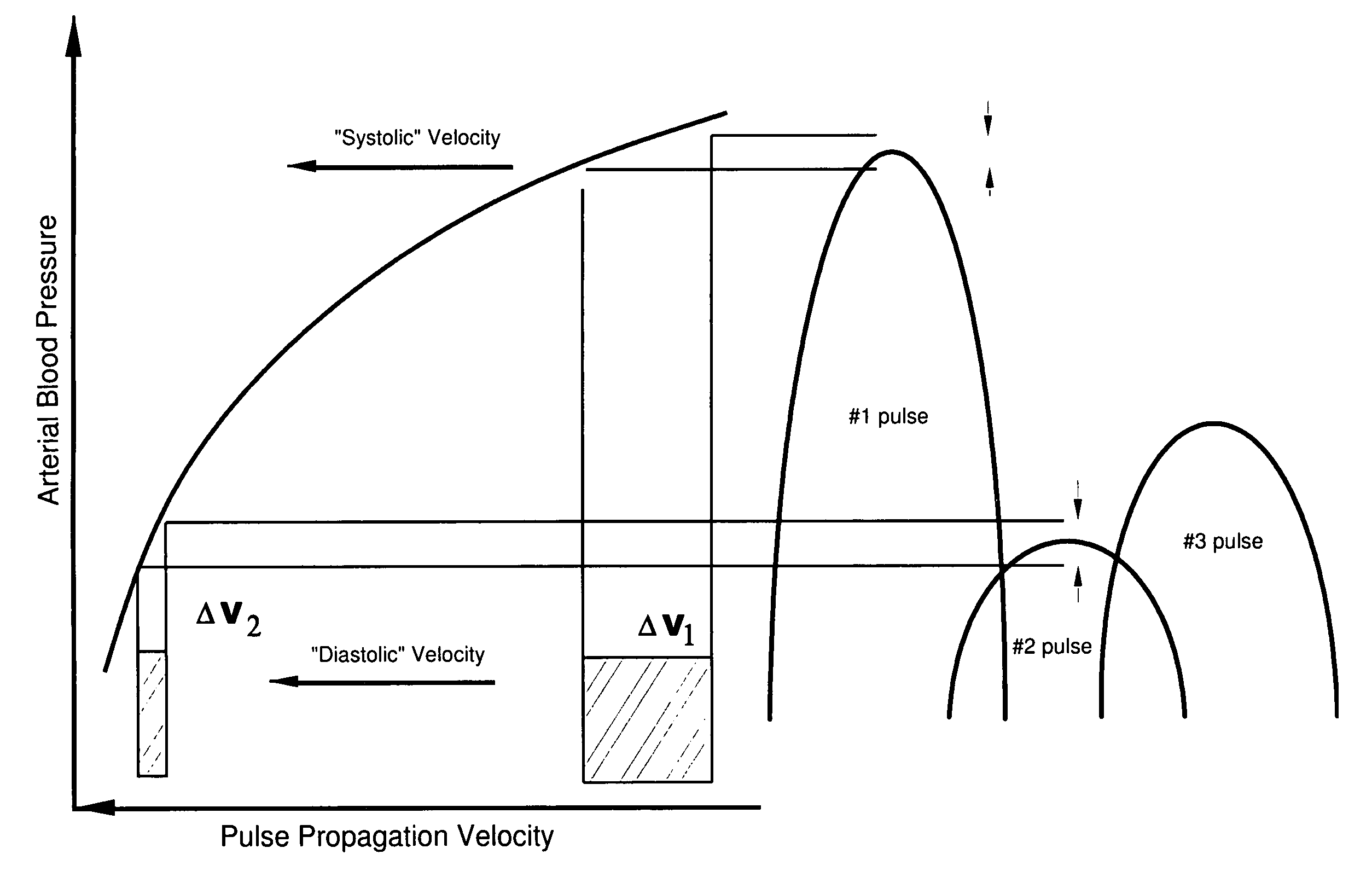
Determining physiological life signs, with a sensor that is in contact with the surface of a patient's skin at point proximate an artery, and measuring arterial blood vessel displacement and / or blood pressure changes. A data stream of measurements of is collected and a set of parameters from the collected data, a number of physiological life signs parameters, is extracted from the data. The physiological life signs that can be extracted include heart rate, breathing rate, systolic blood pressure, and diastolic blood pressure.
Owner:BARUCH MARTIN
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring system for improving measuring accuracy and monitoring method thereof
InactiveCN104814729AImprove accuracyEasy to judgeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEmergency medicineBlood pressure change
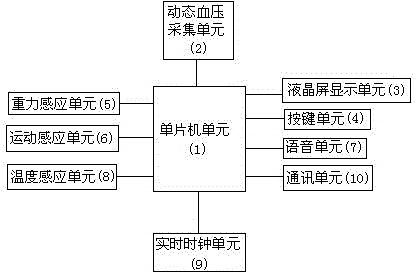
The invention relates to an ambulatory blood pressure monitoring system for improving measuring accuracy and a monitoring method thereof, wherein the ambulatory blood pressure monitoring system for improving measuring accuracy comprises a single chip microcomputer, an ambulatory blood pressure collecting unit, a liquid crystal display screen display unit, a keyboard unit, a gravity induction unit, a motion induction unit, a temperature induction unit, a speech unit, a real-time clock unit and a communication unit, and the positions of the gravity induction unit and a sleeve band for measuring blood pressure are arranged in parallel. The monitoring method is that the ambulatory blood pressure monitoring system for improving measuring accuracy rectifies ambulatory blood pressure measuring valve according to the change of body positions of measured people, obtains an accurate blood pressure measuring value, marks motion state and environment temperature, displays an ambulatory blood pressure valve, the motion state and the environment temperature, enables doctors to know the change of blood pressure of the measured people in the round to comprehensively judge, and is beneficial for treatment of diseases.
Owner:王天星
Dialyzing apparatus
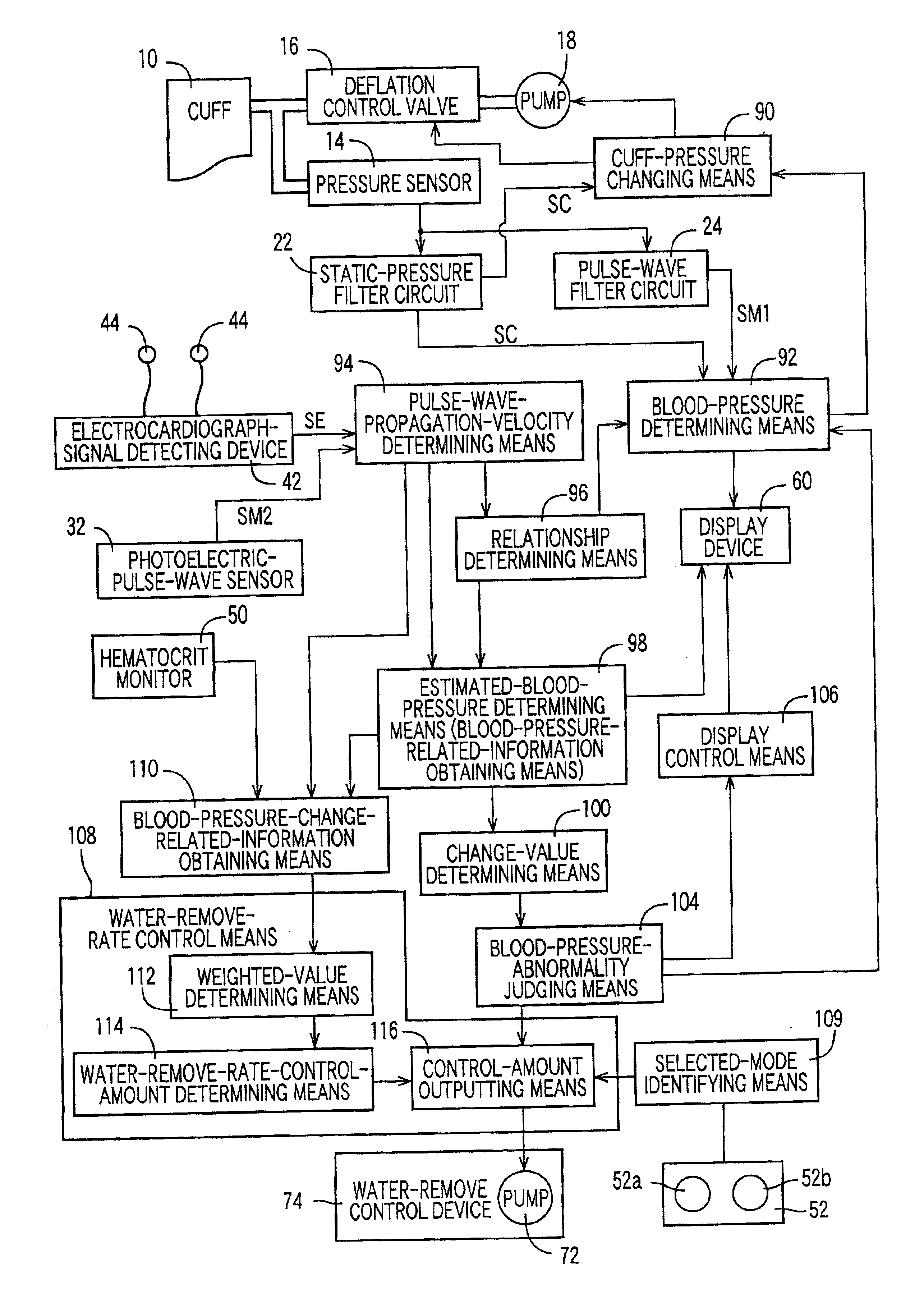
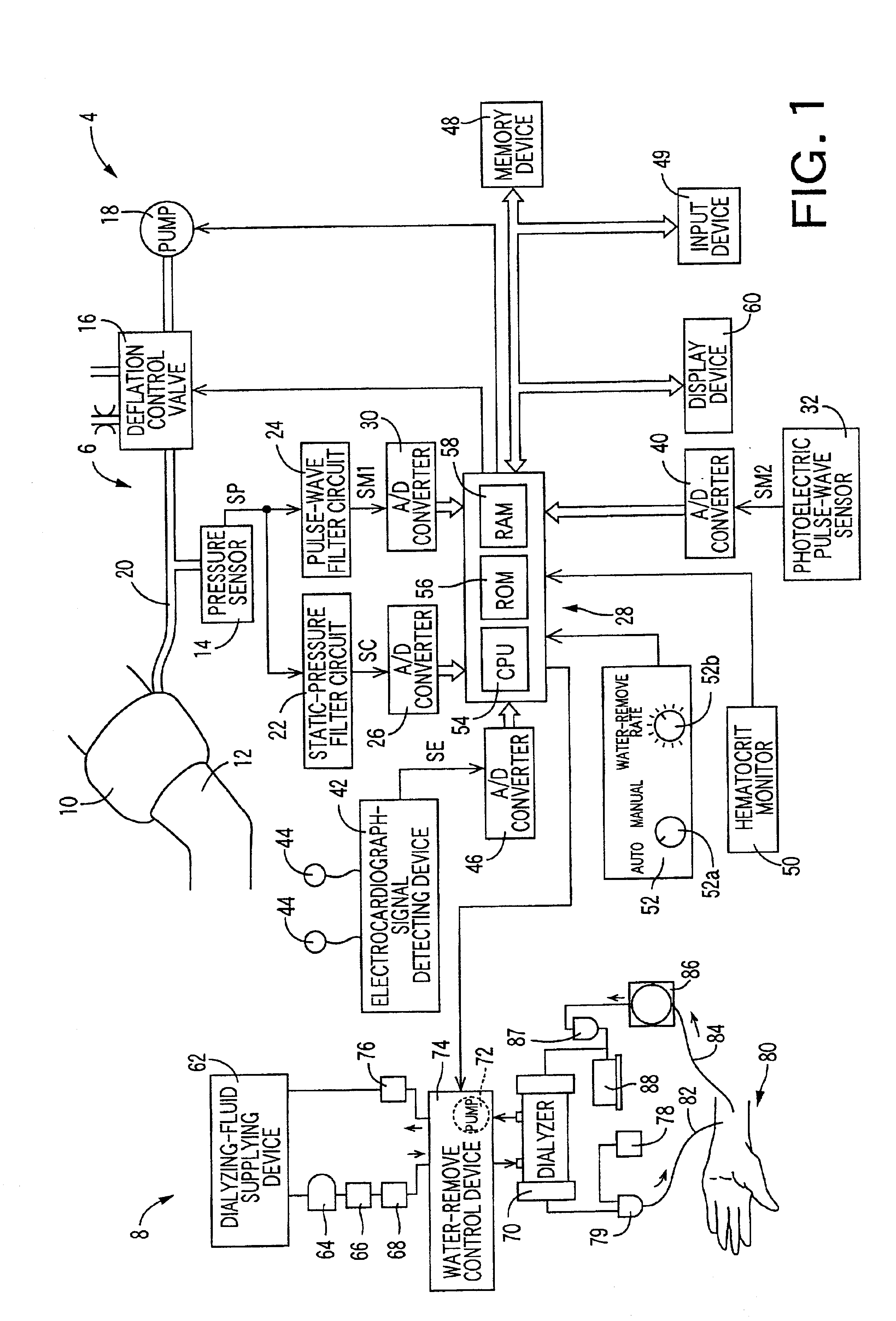
InactiveUS6878272B2Efficient removalReduce operating costsIon-exchanger regenerationDialysis systemsControl mannerIntensive care medicine
A dialyzing apparatus includes a dialyzer which removes water from blood of a patient at a water-remove rate during a dialysis operation, a blood-pressure-change-related-information obtaining device which obtains a plurality of sorts of blood-pressure-change-related information each of which is related to a change of a blood pressure of the patient during the dialysis operation, and a water-remove-rate control device which controls the water-remove rate of the dialyzer, based on the plurality of sorts of blood-pressure-change-related information, according to a predetermined control manner.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
Detection of drastic blood pressure changes
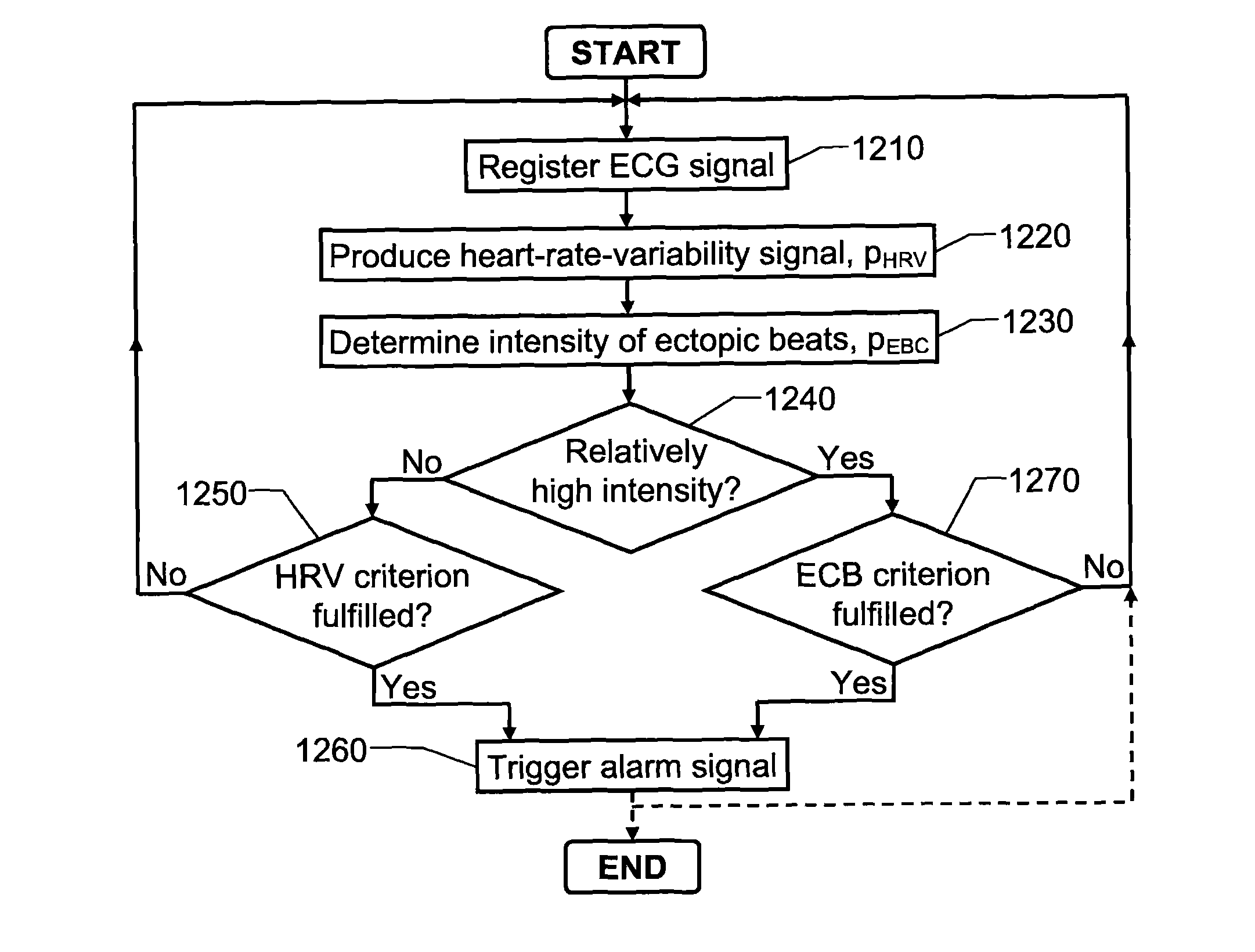
InactiveUS8060190B2Rapid blood pressureElectrocardiographyDialysis systemsHemodialysisHaemodialysis machine
The invention relates to cardiac-activity based prediction of a rapid drop in a patient's blood pressure during hemodialysis. A proposed alarm apparatus includes an input interface, primary and secondary analysis units and an alarm-generating unit. An electrocardiogram signal (HECG) of the patient is received via the input interface by the primary analysis unit, which in response thereto produces a heart-rate-variability signal (PHRV). The secondary analysis unit determines an intensity of ectopic beats (PEBC) based on the electrocardiogram signal (HECG). The alarm-generating unit investigates whether the intensity of ectopic beats (PEBC) is relatively low or relatively high. In case of a relatively low intensity, the unit triggers an alarm signal (α) indicative of an estimated rapid blood pressure decrease if the heart-rate-variability signal (PHRV) fulfills a first alarm criterion. In case of a relatively high intensity, however, the unit triggers the alarm signal (α) if the intensity of the ectopic beats (PEBC) fulfills a second alarm criterion.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
System for measuring blood pressure by using psychological state verification
ActiveCN105725998AEffective and precise measurementEffectively and precisely measureDiagnostics using lightEvaluation of blood vesselsBlood pressure kitRate change
The invention discloses a system for measuring blood pressure by using psychological state verification. According to one embodiment, the position of an artery on a human's skin is determined, and a tension pressure sensor is positioned on the position of the artery for measuring blood pressure so as to obtain pressure pulse data of an examination object. When in operation according to the embodiment, a measuring logic of a measuring verification system can uses the pressure pulse data to extract blood pressure data, heart rate data, blood pressure changing data, and heat rate changing data. The aforementioned data can be used to identify whether the blood pressure measuring appropriately and accurately reflect the conditions of the examination object.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for measuring change in blood pressure by respiration control
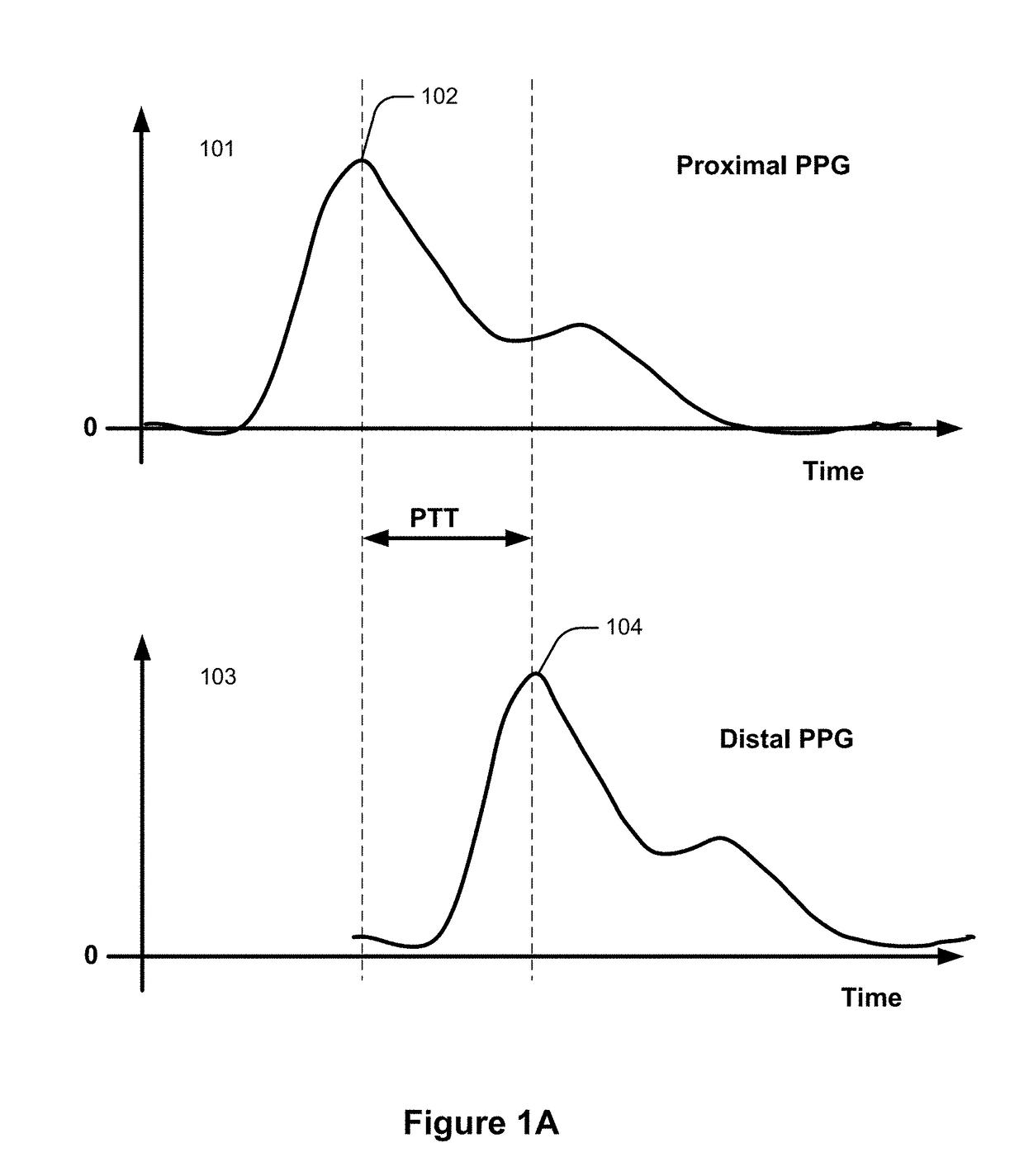
A method and an apparatus are provided for measuring a change in blood pressure caused by respiration control. A number of respirations per minute is measured based on a heart rate when a respiration exercise begins. Respiration of a subject is induced until the number of respirations per minute reaches a predetermined number of respirations per minute. A pulse transit time is calculated during the respiration exercise, a blood pressure value associated with the pulse transit time is calculated, and the blood pressure value is outputted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
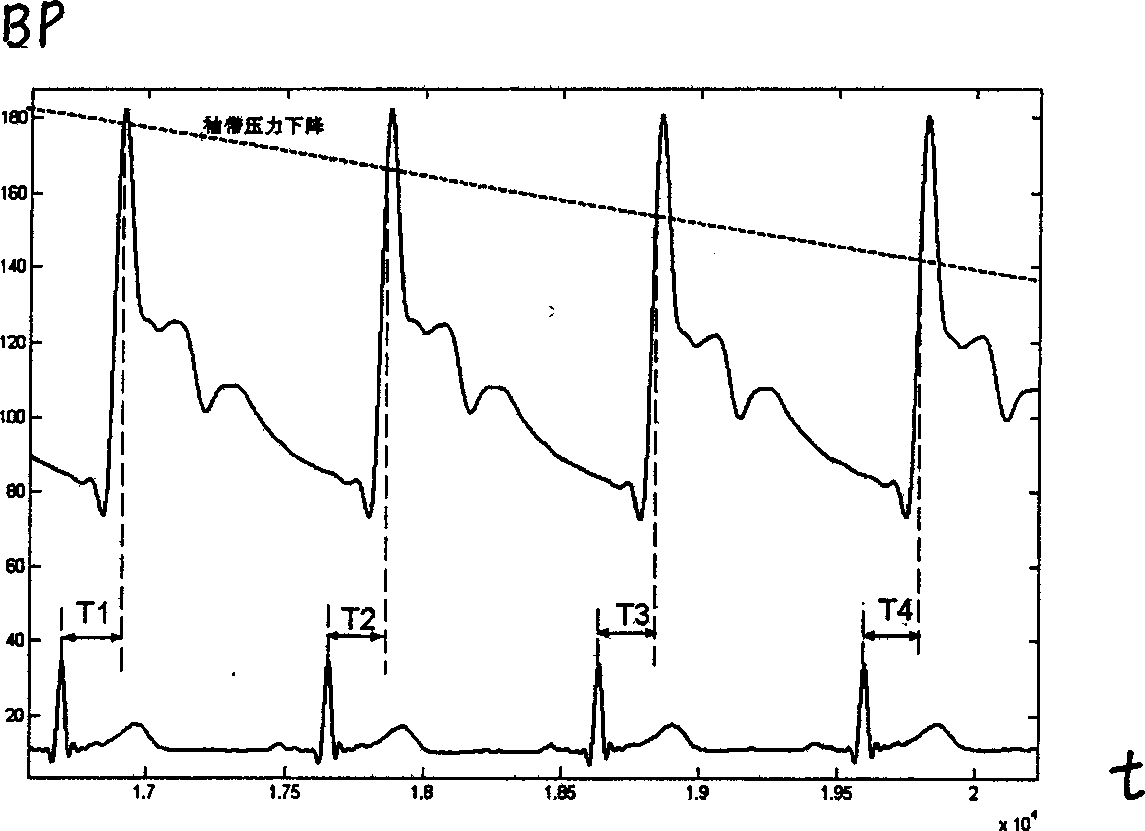
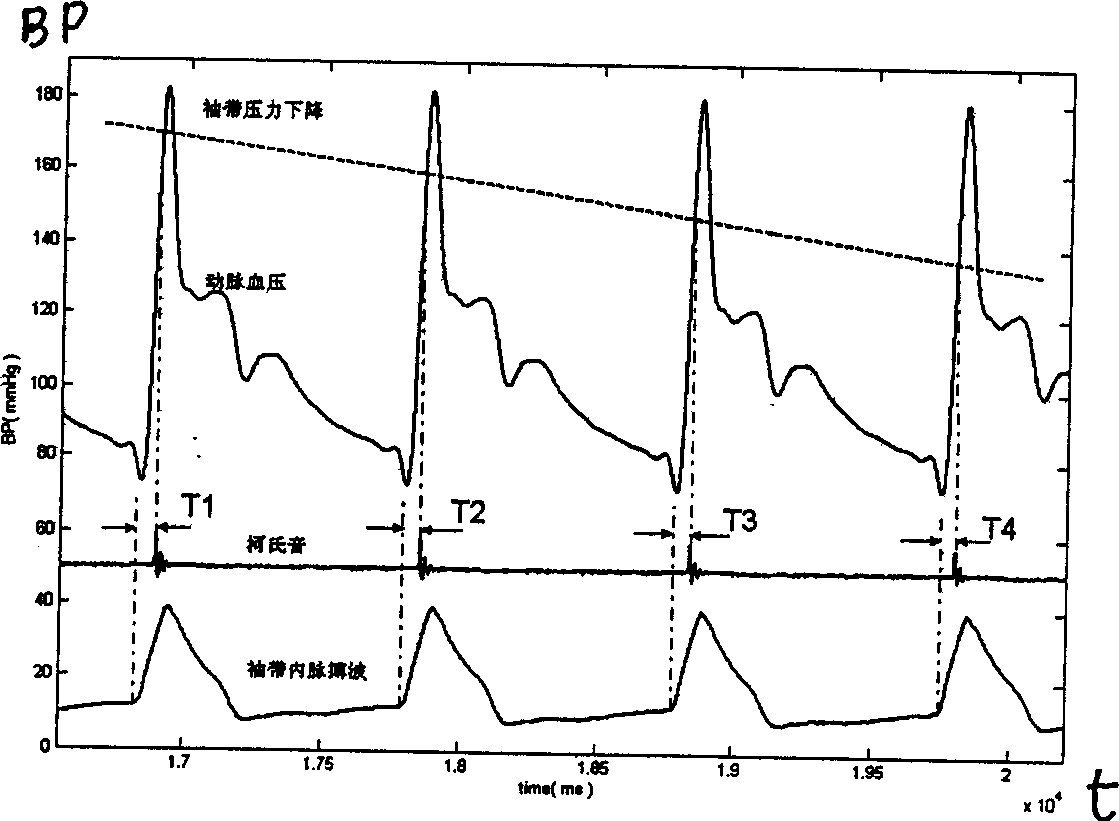
Method and apparatus for arterial blood pressure measurement and individualized rectifying technology using this method
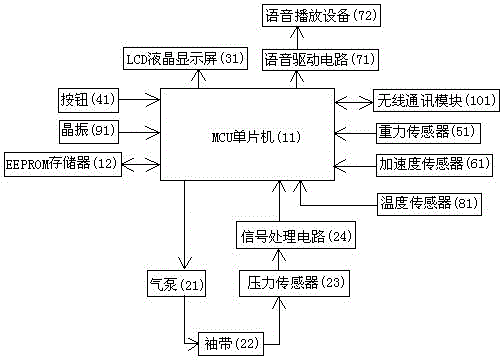
InactiveUS20080033310A1Increase rangeShort delay timeCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineDelayed time
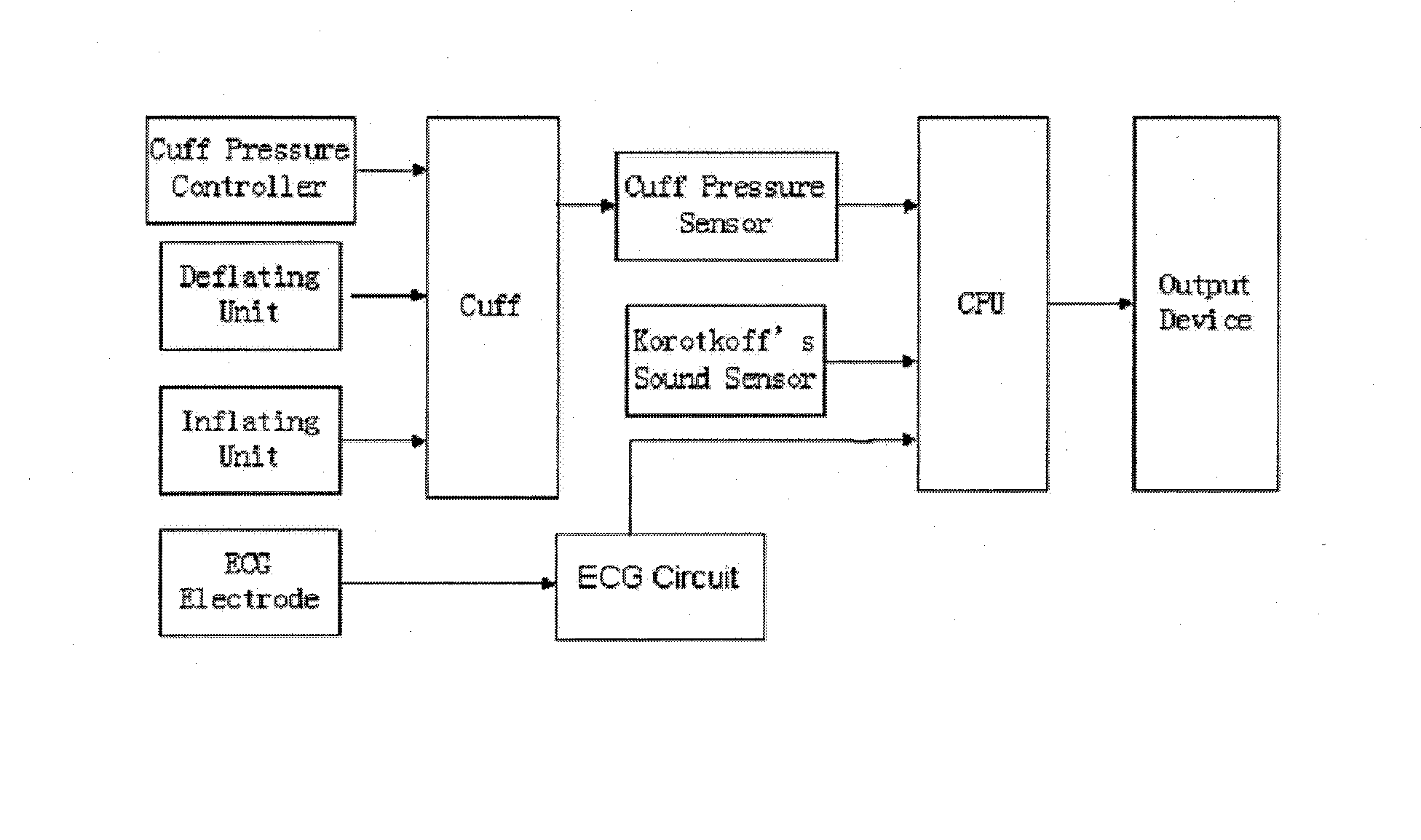
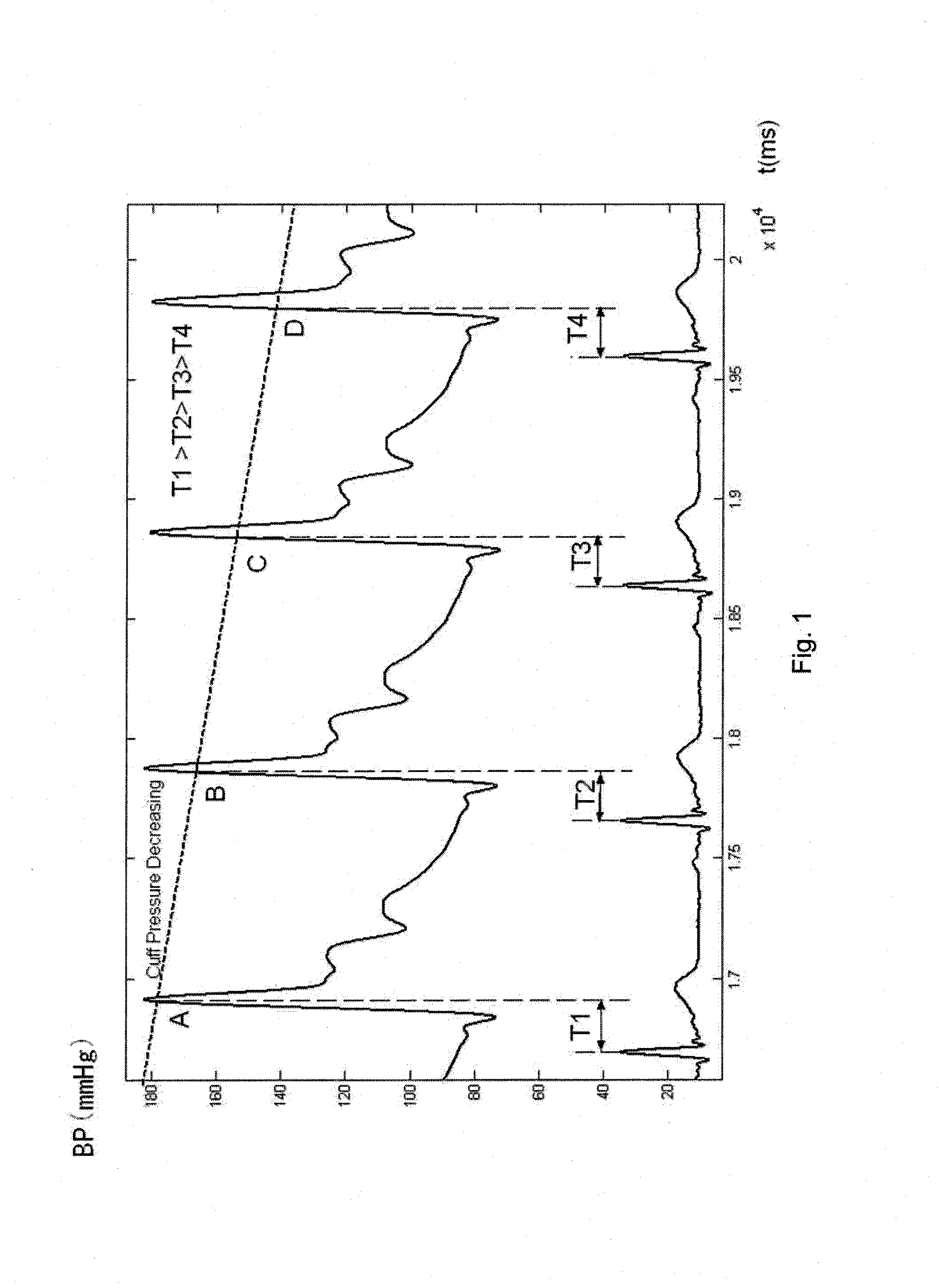
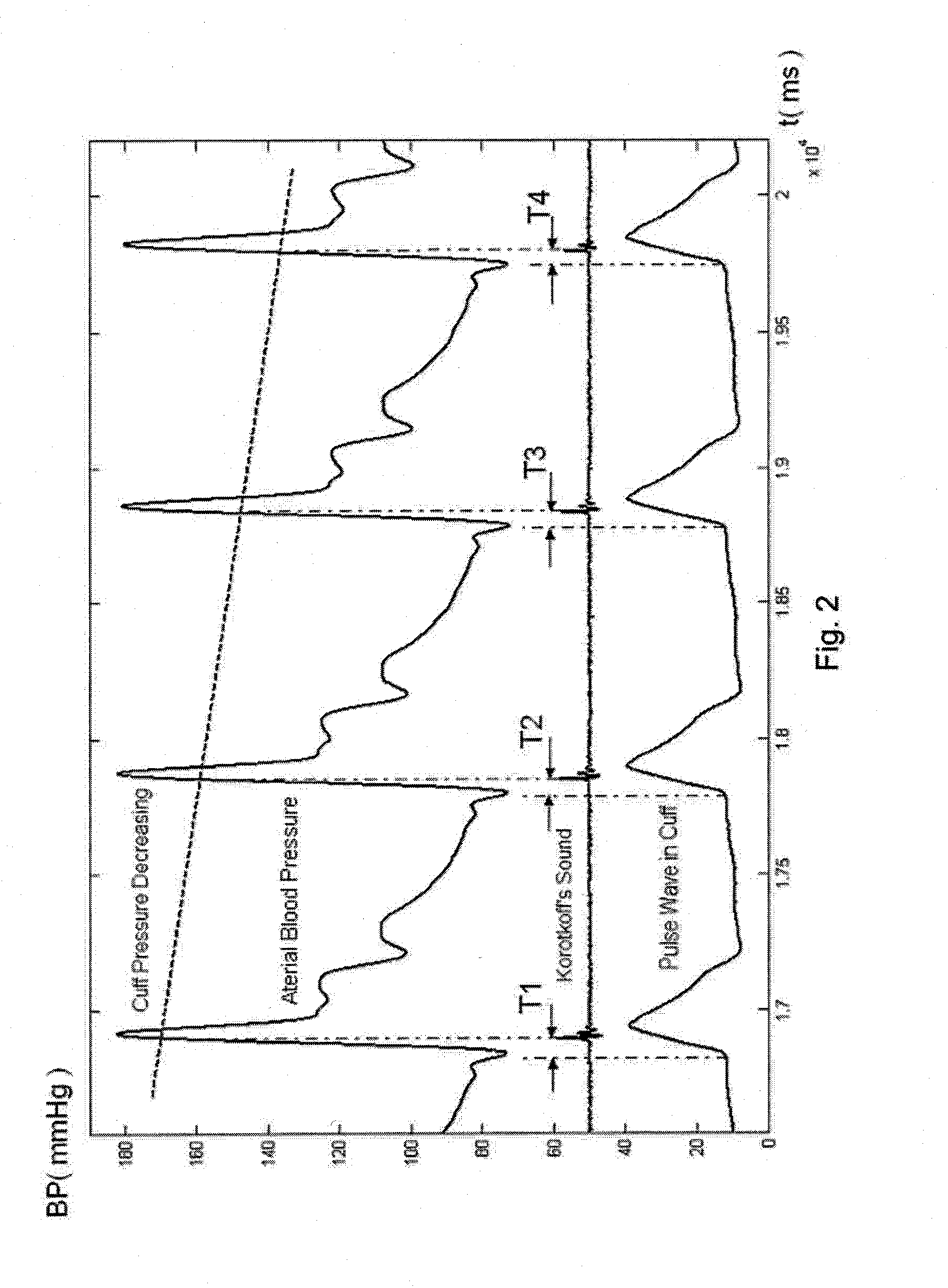
A method and an apparatus for indirect, quantitative estimation of beat-to-beat arterial blood pressure utilizing individualized rectifying technology. A function of TK=H(P) that describes the relationship between Korotkoff's sound delay time Tk and cuff pressure P is obtained by measuring different cuff pressures P and the corresponding Korotkoff's sound delay times Tk in a Korotkoff's sound sensor that is distal to the cuff. Keeping the cuff pressure at a constant value Pm, the blood pressure change can be calculated by using the Korotkoff's sound delay time Tkm according to the function of Tk=H(P). The invention can measure beat-to-beat arterial blood pressures indirectly. The technology can be applied to obtain individualized coefficients of a regress equation for continuous arterial blood pressure measurement by the instantaneous blood pressure fluctuation, and the technology makes the rectifying technique more safe, effective, and less erroneous and makes the operation of noninvasive continuous blood pressure measurement for long times more practical.
Owner:YU MENG SU +2
Dynamic optical tomographic imaging devices, methods and systems
The disclosed subject matter includes optical tomographic systems for acquiring and displaying dynamic data representing changes in a target tissue sample to external provocation. For example, the disclosed devices, methods and systems may be used for quantifying dynamic vascular changes caused by imposed blood pressure changes for diagnosing peripheral artery disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for estimating stress and strain of coronary artery blood vessel wall
InactiveCN103190932AFully reflect the elastic characteristicsReflect elastic characteristicsOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesUltrasound angiographyCoronary atherosclerosis
Disclosed is a method for estimating stress and strain of coronary artery blood vessel wall. According to the technical scheme, the method includes: firstly, acquiring a motion field of blood vessel wall tissues generated with blood pressure changes from an IVUS (intravascular ultrasound) gray scale image sequence; and secondly obtaining stress and strain values of points on blood vessel wall cross-section images of each frame. The stress and strain values of the blood vessel wall are directly obtained from the conventional IVUS gray scale image sequence, the algorithm is simple, and application conditions of the method are lowered. By the method compared with the methods based on radiofrequency signal analysis, strain values (including two master strains and a shear strain) of optional-direction points on the blood vessel cross section of each frame image can be calculated, elasticity of the blood vessel wall and plaque tissues can be reflected more comprehensively, and more reliable basis is provided for the analysis on pathogenesis of coronary arterial atherosclerosis, the estimation on vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaque, the prediction on development tendency of the atherosclerotic plaque and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
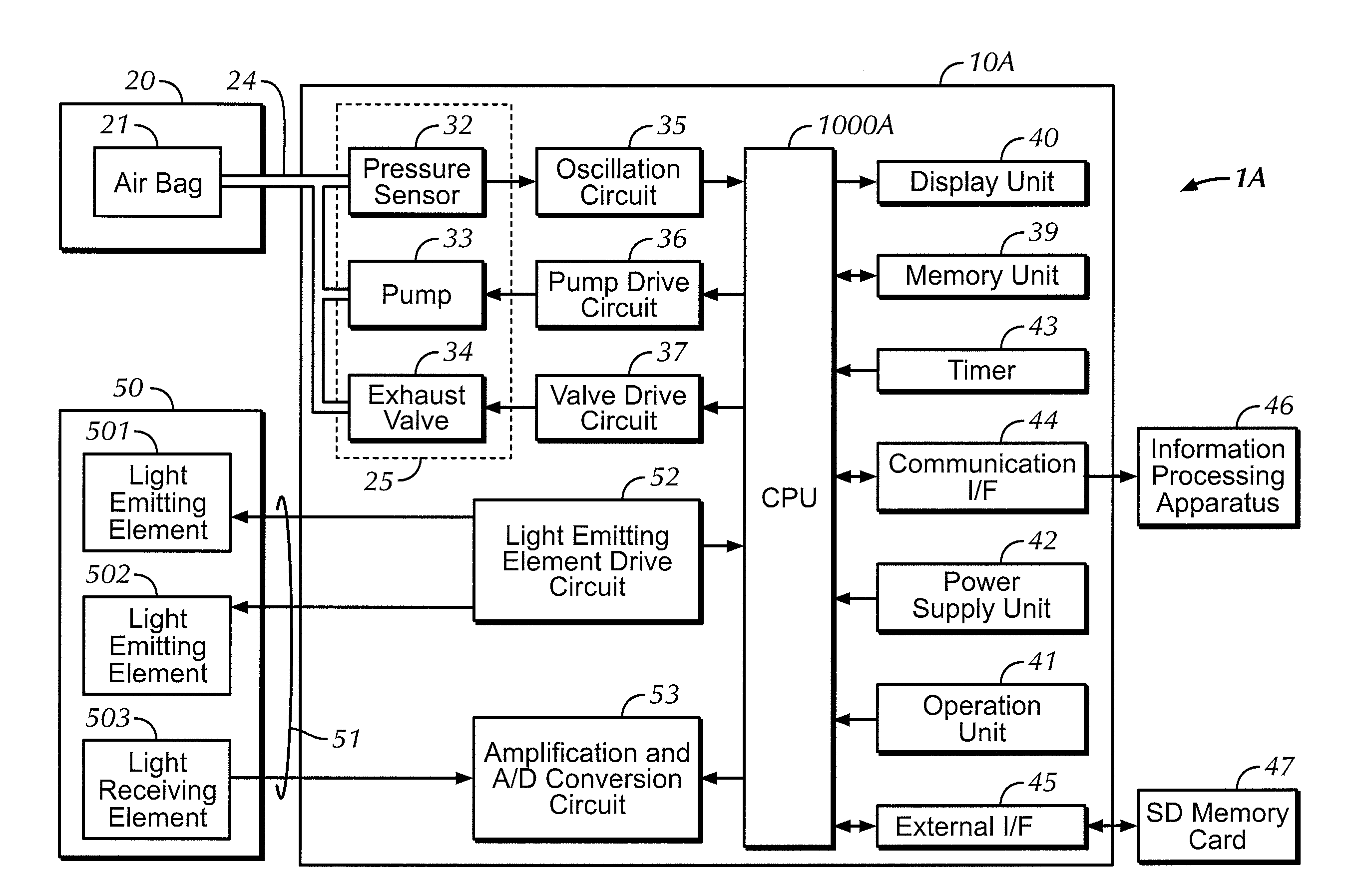
Blood pressure measurement apparatus
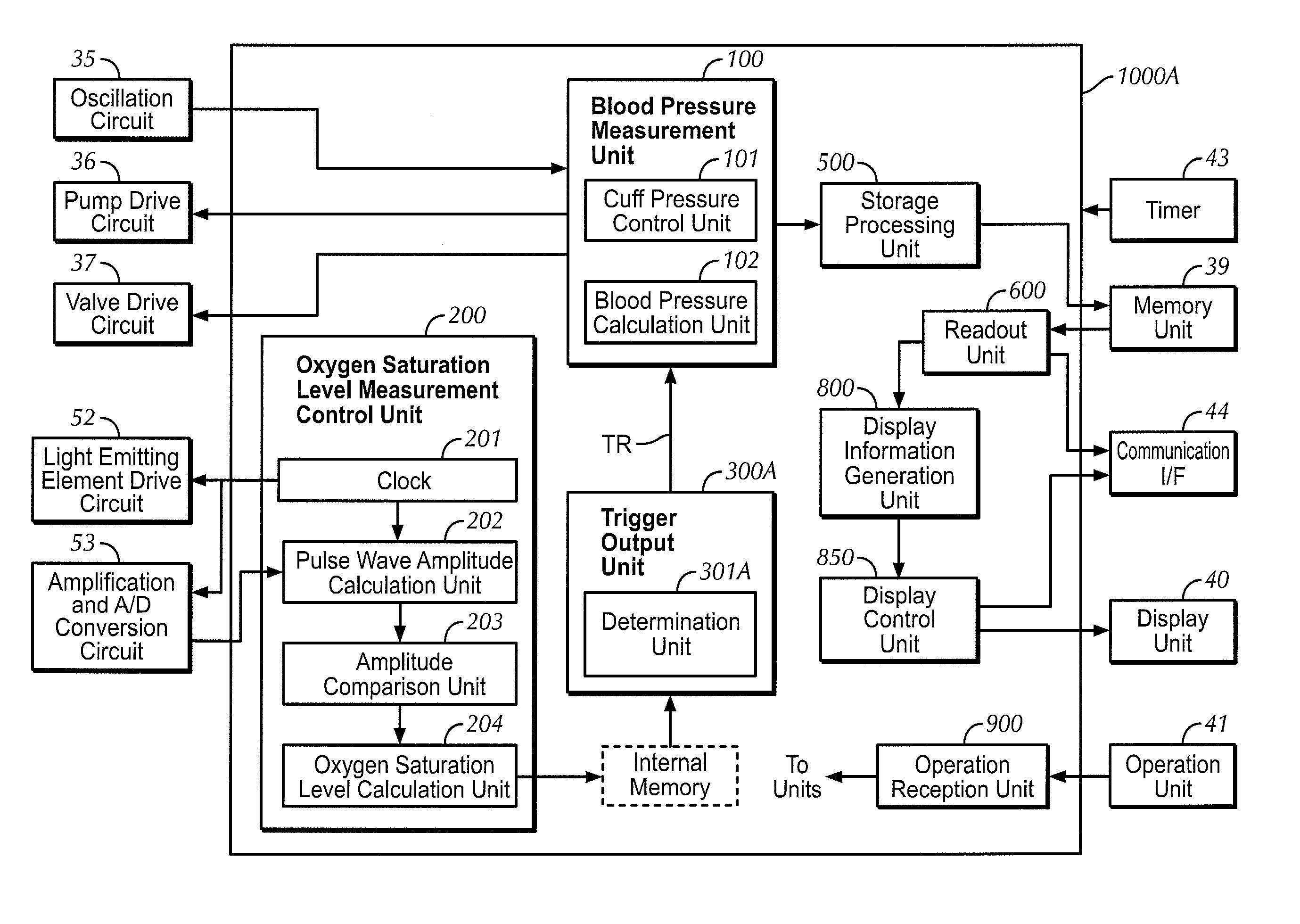
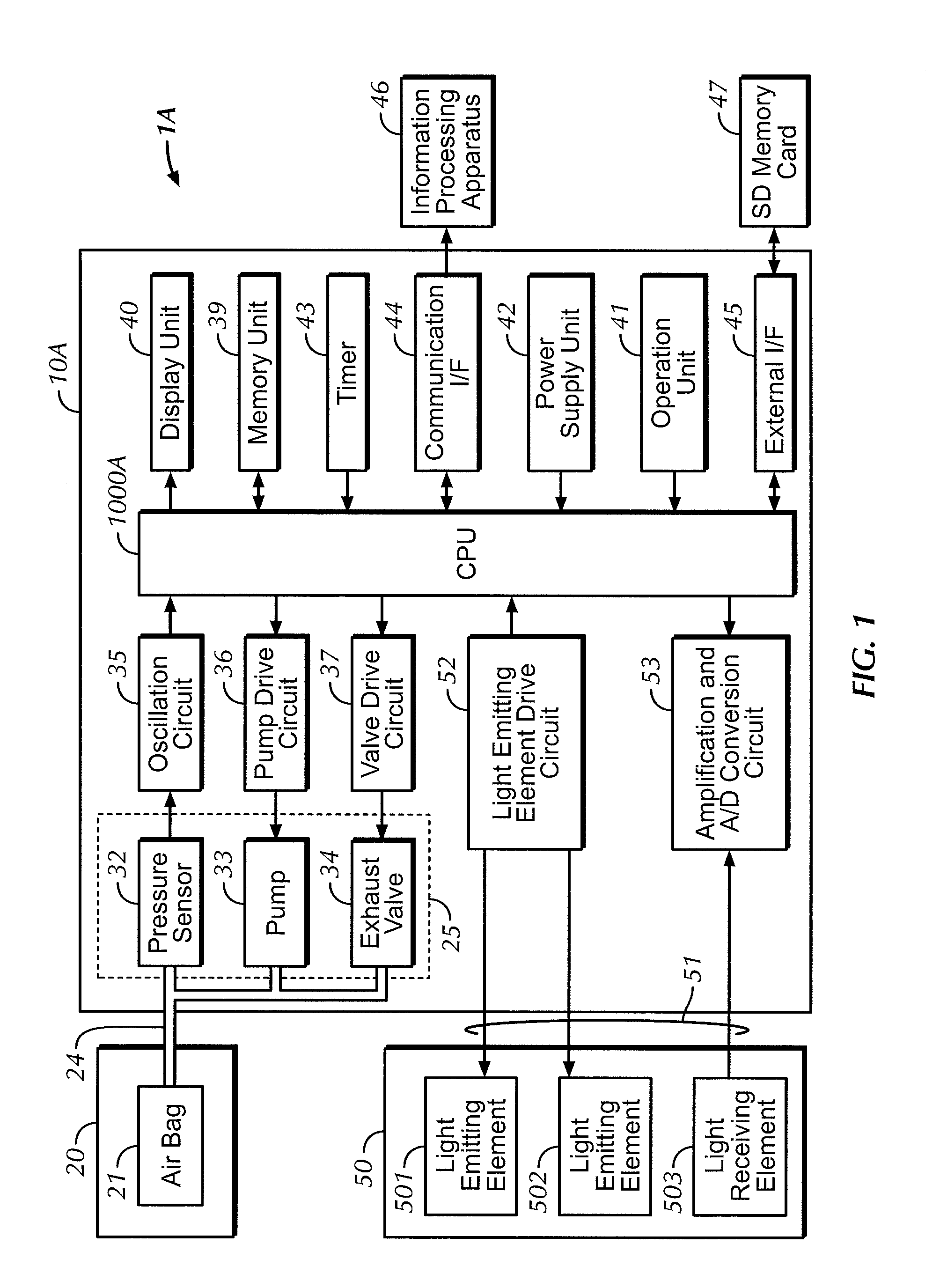
A blood pressure measurement apparatus for measuring blood pressure in a predetermined period includes a blood pressure measuring unit for measuring the blood pressure of a subject, an information acquiring unit for acquiring information that is related to variation in blood pressure and changes in a time-series in the predetermined period, a determining unit for determining whether or not the information acquired by the information acquiring unit satisfies a predetermined condition, and a trigger output unit for, in a case where the determining unit determines that the predetermined condition is satisfied, causing the blood pressure measuring unit to start and execute blood pressure measurement. The predetermined condition is expressed as a function of time that varies and is measured in the predetermined period.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD +1
Method and device for measuring and analyzing blood pressure
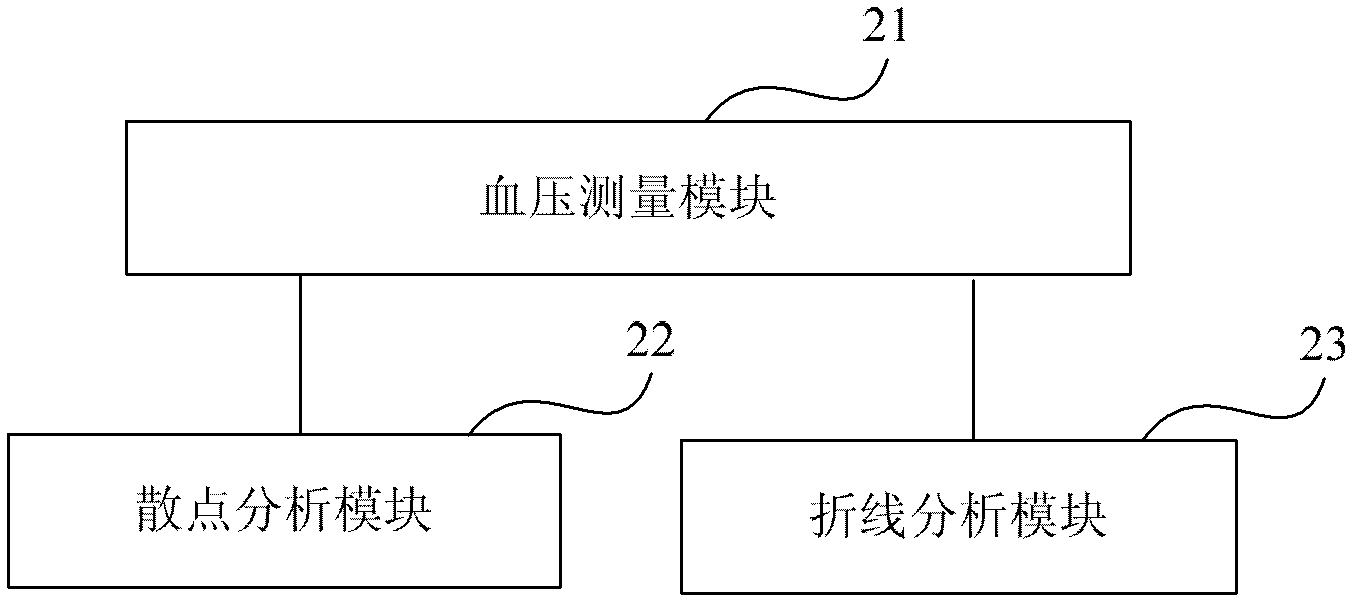
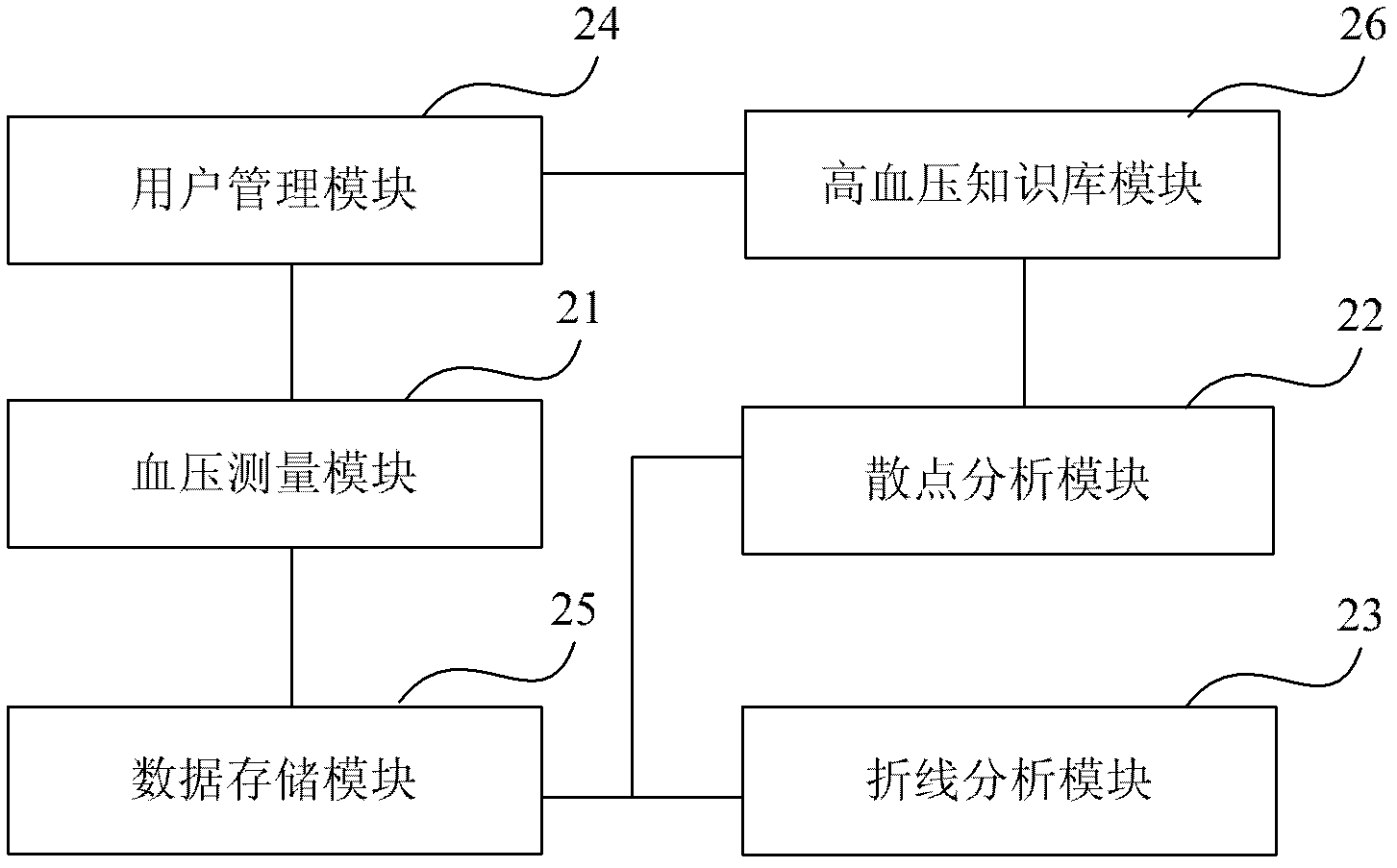
InactiveCN103181760AReasonable medicationAccurate judgmentEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyBlood pressure kitEmergency medicine
The embodiment provides a method and a device for measuring and analyzing blood pressure. The method comprises the following steps: measuring and obtaining the measuring results and the measuring time of a user's blood pressure for many times; carrying out splattering analysis according to the measuring results and the measuring time of the user's blood pressure for many times so as to judge the blood pressure level of the user; and performing broken line analysis according to the measuring results and the measuring time of the user's blood pressure for many times so as to observe the change tendency of the user's blood pressure in a period of time. On the basis of realizing user management, the measuring results are stored respectively for the users, and two blood pressure analysis modes comprising splattering analysis and broken line analysis are provided. According to the splattering analysis, hypertension knowledge matched with the user information can be automatically retrieved from a hypertension knowledge base. According to the broken line analysis, the change tendency of the user's blood pressure in a period of time can be seen clearly, knowledge of the blood pressure change tendency and medicine use can be automatically retrieved from the hypertension knowledge base, and the user is guided to use medicines reasonably and regulate blood pressure in daily life.
Owner:北京润池润生科技有限公司
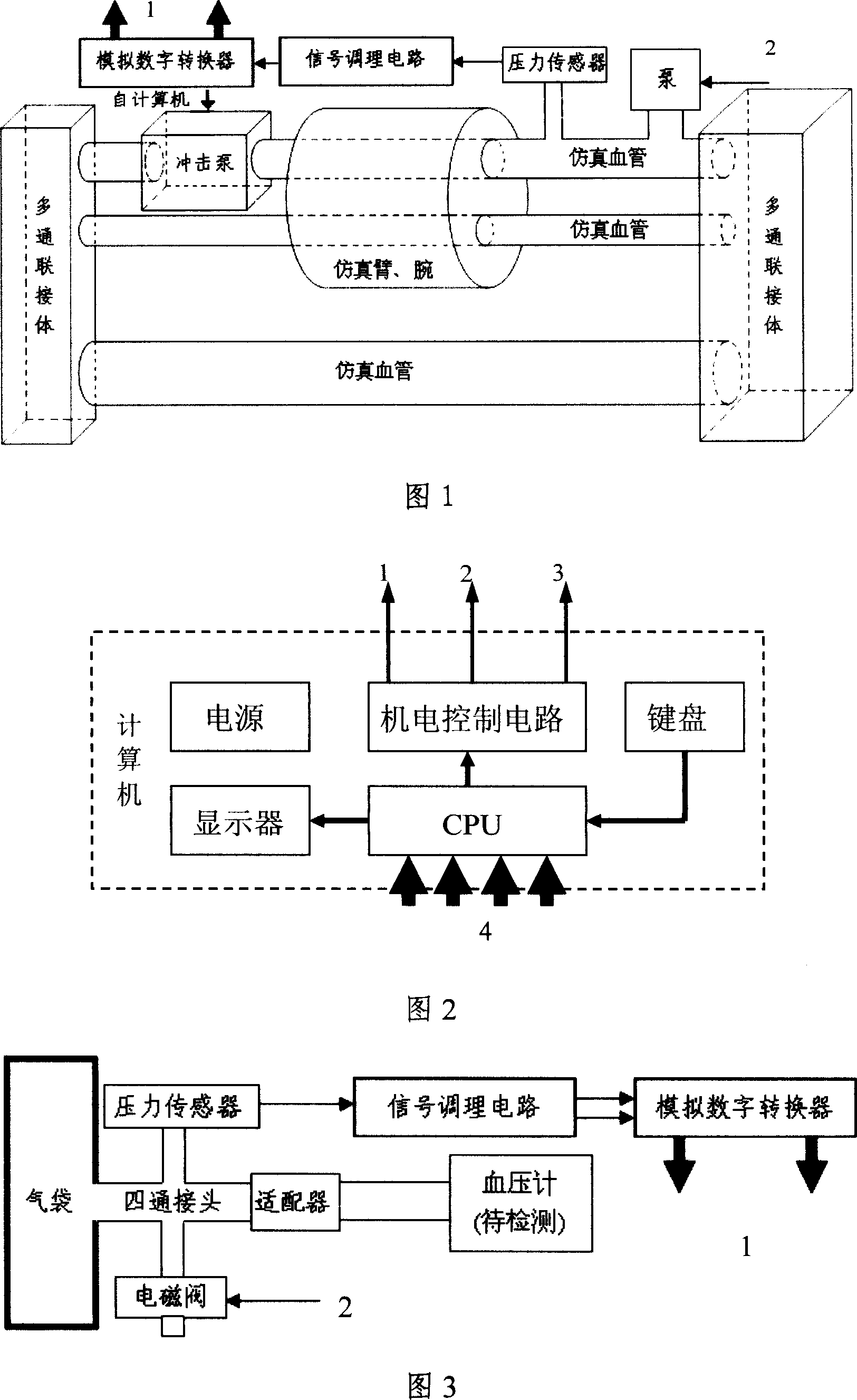
Non-invasive blood pressure measuring analyzer
The non-invasive sphygmomanometer analyzer includes one dynamic blood pressure simulator to simulate the blood pressure change of human body and to apply one dynamic blood pressure to the air bog of the sphygmomanometer adaptor and one standard pressure measuring device for the dynamic analysis of sphygmomanometer.
Owner:王卫东
Blood pressure measurement apparatus
A blood pressure measurement apparatus for measuring blood pressure in a predetermined period includes a blood pressure measuring unit for measuring the blood pressure of a subject, an information acquiring unit for acquiring information that is related to variation in blood pressure and changes in a time-series in the predetermined period, a determining unit for determining whether or not the information acquired by the information acquiring unit satisfies a predetermined condition, and a trigger output unit for, in a case where the determining unit determines that the predetermined condition is satisfied, causing the blood pressure measuring unit to start and execute blood pressure measurement. The predetermined condition is expressed as a function of time that varies and is measured in the predetermined period.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD +1
Device for monitoring blood pressure of witness in court
InactiveCN101843495AOvercome the disadvantage of inconvenient useEasy to useEvaluation of blood vesselsPsychotechnic devicesMeasurement deviceMonitor blood pressure
The invention belongs to a human body sign signal measurement device, in particular to a device for monitoring the blood pressure of a witness in court. The body of the device comprises a gauge case and a gauge band, wherein two ends of the gauge case are respectively provided with an inflator pump and a deflating valve; the lower side of the gauge case is provided with an air bag respectively communicated with the inflator pump and the deflating valve; the gauge case is internally provided with a pressure sensor in contact with the air bag; the pressure sensor, the inflator pump and the deflating valve are respectively connected with a processing chip, and the processing chip is connected with a remote switch; the processing chip is also connected with a radio signal emitter through an analog to digital converter; and the gauge is internally provided with a power unit. The device is used for measuring the blood pressure changes of the witness in court at any time and provides a scientific technological assistant measure for lawyers and judges to know and control the testifying condition of the witness.
Owner:NEWAUTO SILICON VALLEY VIDEO TECH
Method and system for evaluating automatic regulation function of cerebral blood flow through external counterpulsation technique
InactiveCN106264513AEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyCerebral blood volumeCBF - Cerebral blood flow
The invention provides a method for evaluating the automatic regulation function of cerebral blood flow of an individual. The method comprises the following steps that 1, external counterpulsation operation is applied to the individual; 2, continuous blood pressure monitoring and cerebral blood flow speed monitoring are conducted on the individual before the external counterpulsation operation, during the external counterpulsation operation and after the external counterpulsation operation; 3, blood pressure changes and cerebral blood flow speed changes, responding to the external counterpulsation operation, of the individual are recorded, and the automatic regulation function of the cerebral blood flow of the individual is evaluated on the basis of the changes. The invention further provides a system for implementing the method.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Lie detection method and device
InactiveCN103040485AAdd funImprove experienceHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsRespiratory frequencyComputer science
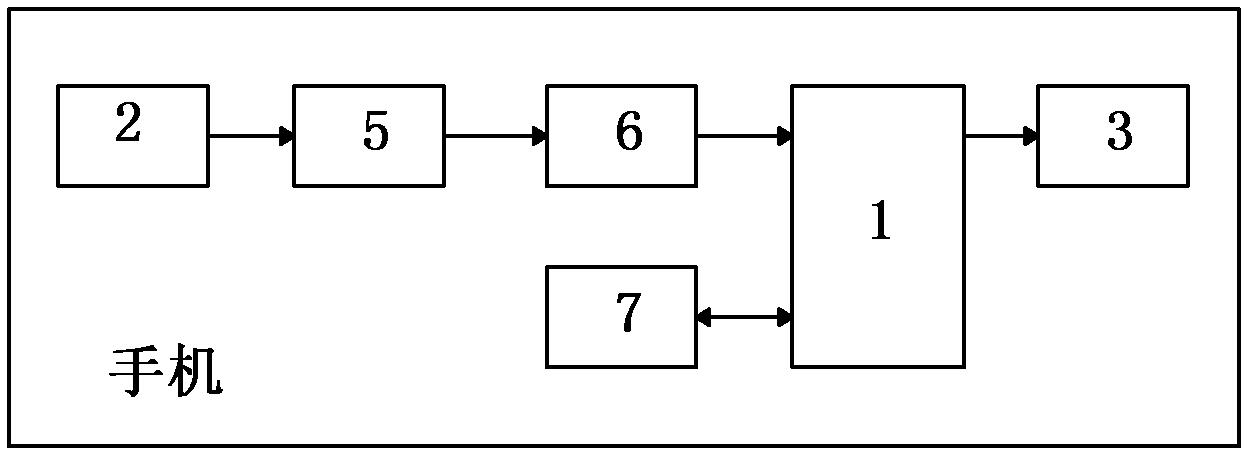
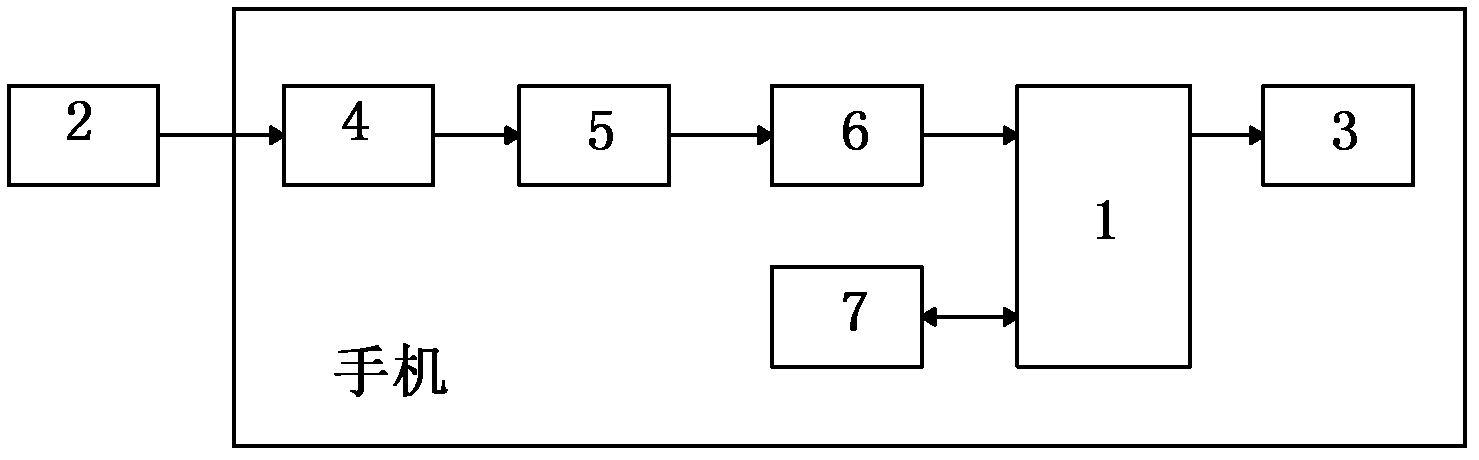
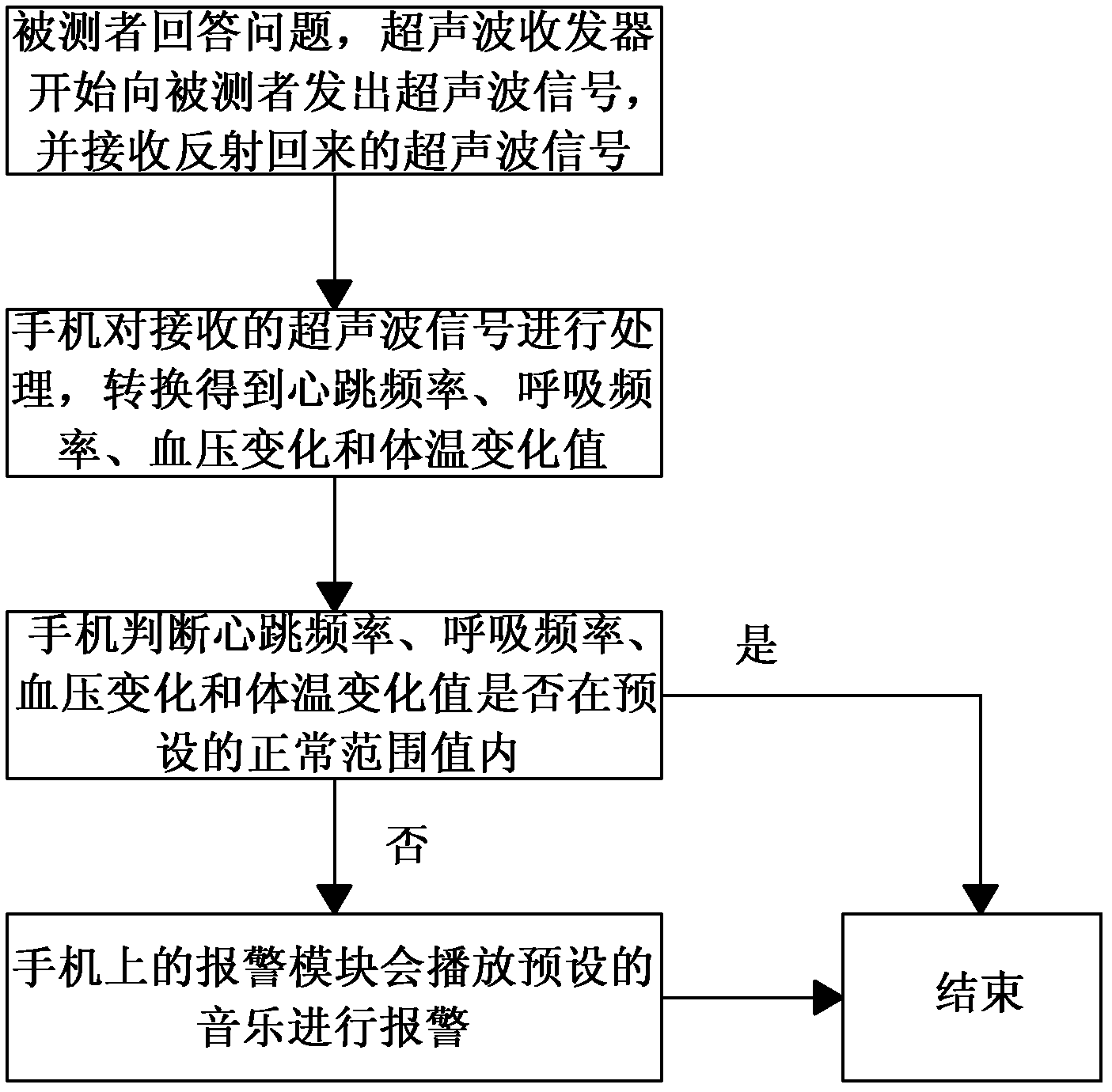
The invention discloses a lie detection method and device. The method comprises the following steps that S1 a mobile phone sends ultrasonic signals to a detected user and receives reflected ultrasonic signals; S2 the mobile phone processes the received ultrasonic signals and converts to obtain heartbeat frequency, respiratory frequency, blood pressure changes and temperature changes; and S3 the mobile phone judges whether the detected user tells a lie or not according to the heartbeat frequency, the respiratory frequency, the blood pressure changes and the temperature changes, and the mobile phone raises the alarm when the detected user tells a lie. The lie detection method and device can use the mobile phone to detect whether the user tells a lie or not, and the lie detection device is simple in structure, small in size, simple in operation and convenient to use.
Owner:沈锋艳
Blood pressure measuring apparatus and method for calibrating central blood pressure estimation parameter
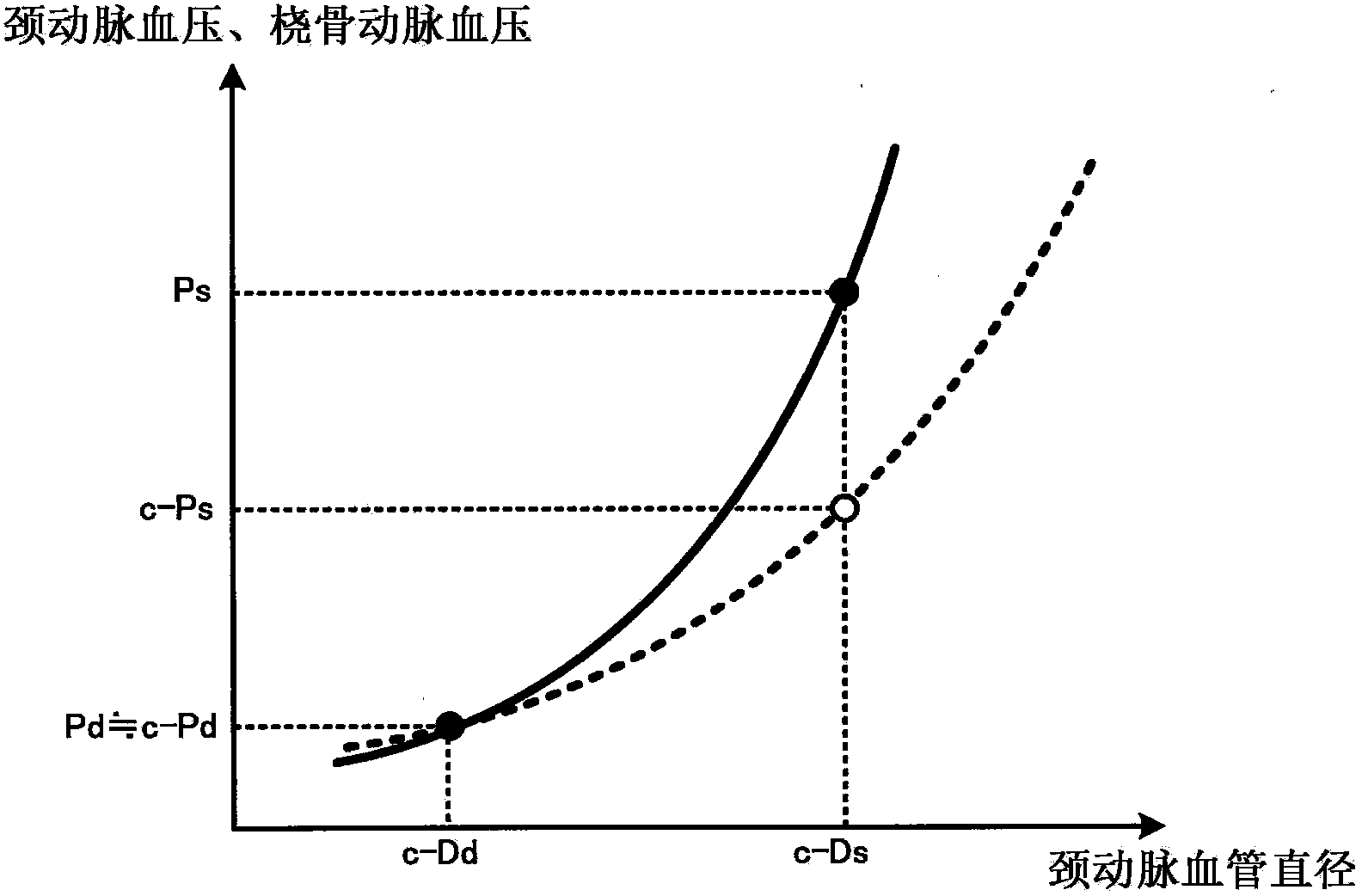
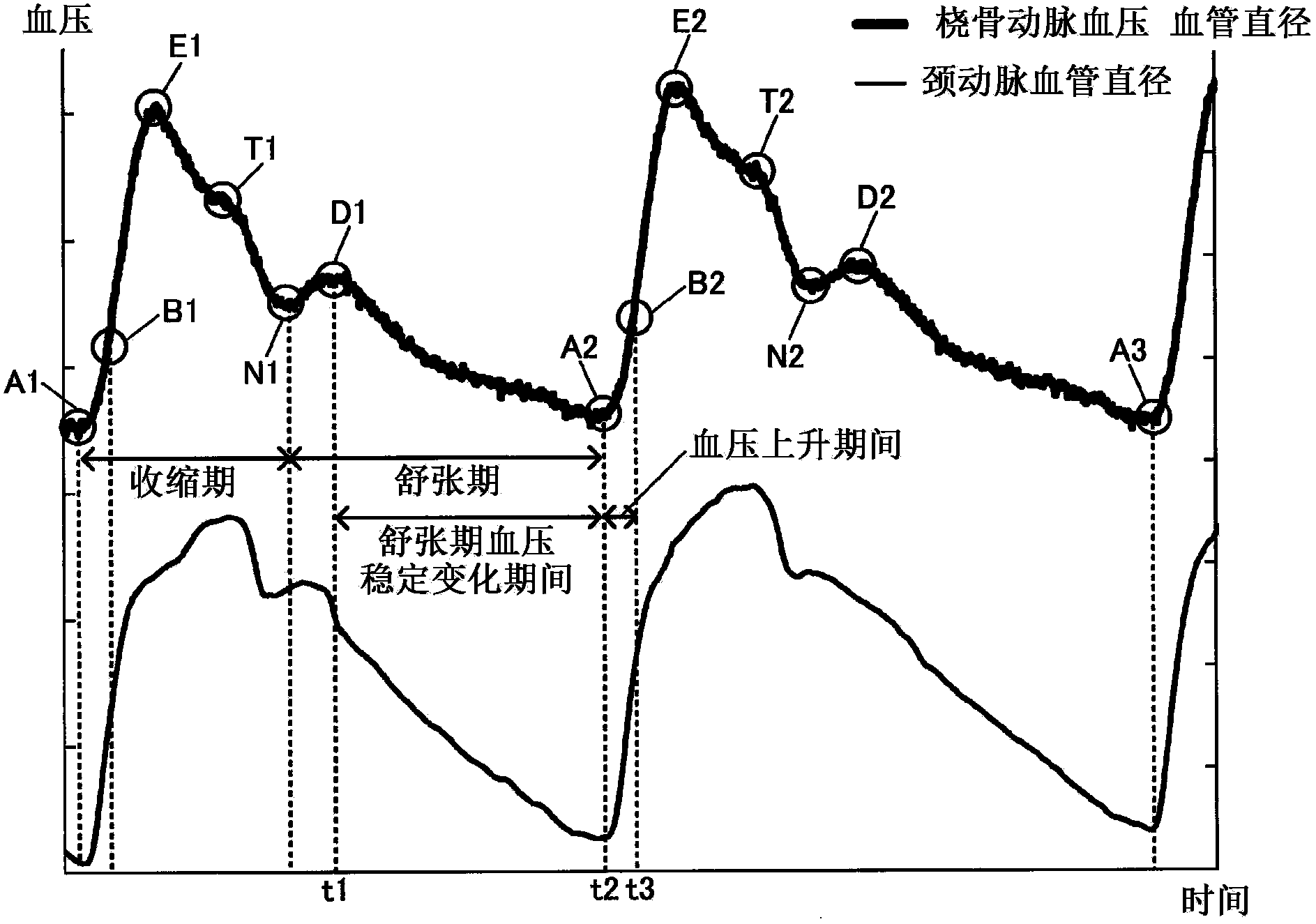
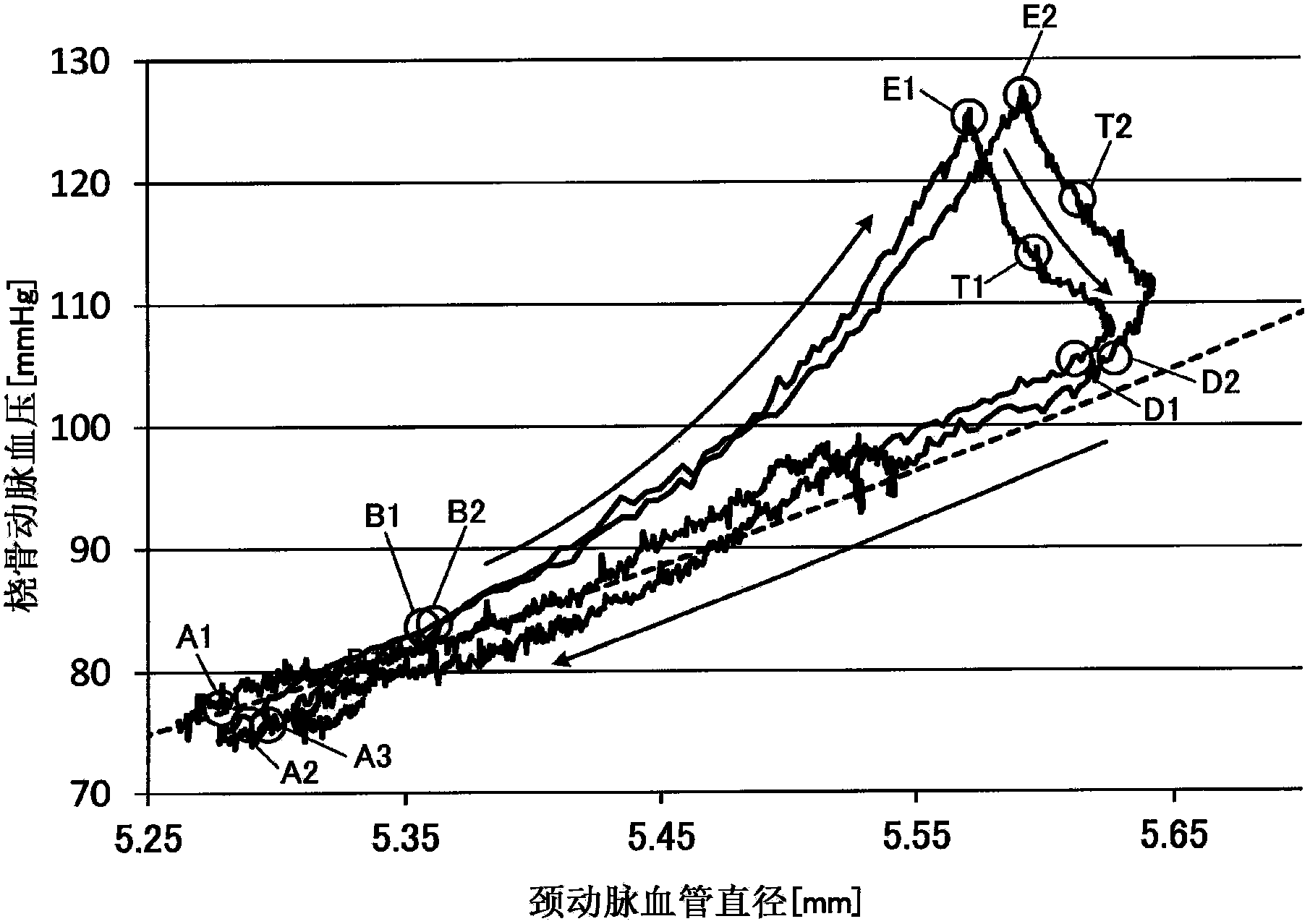
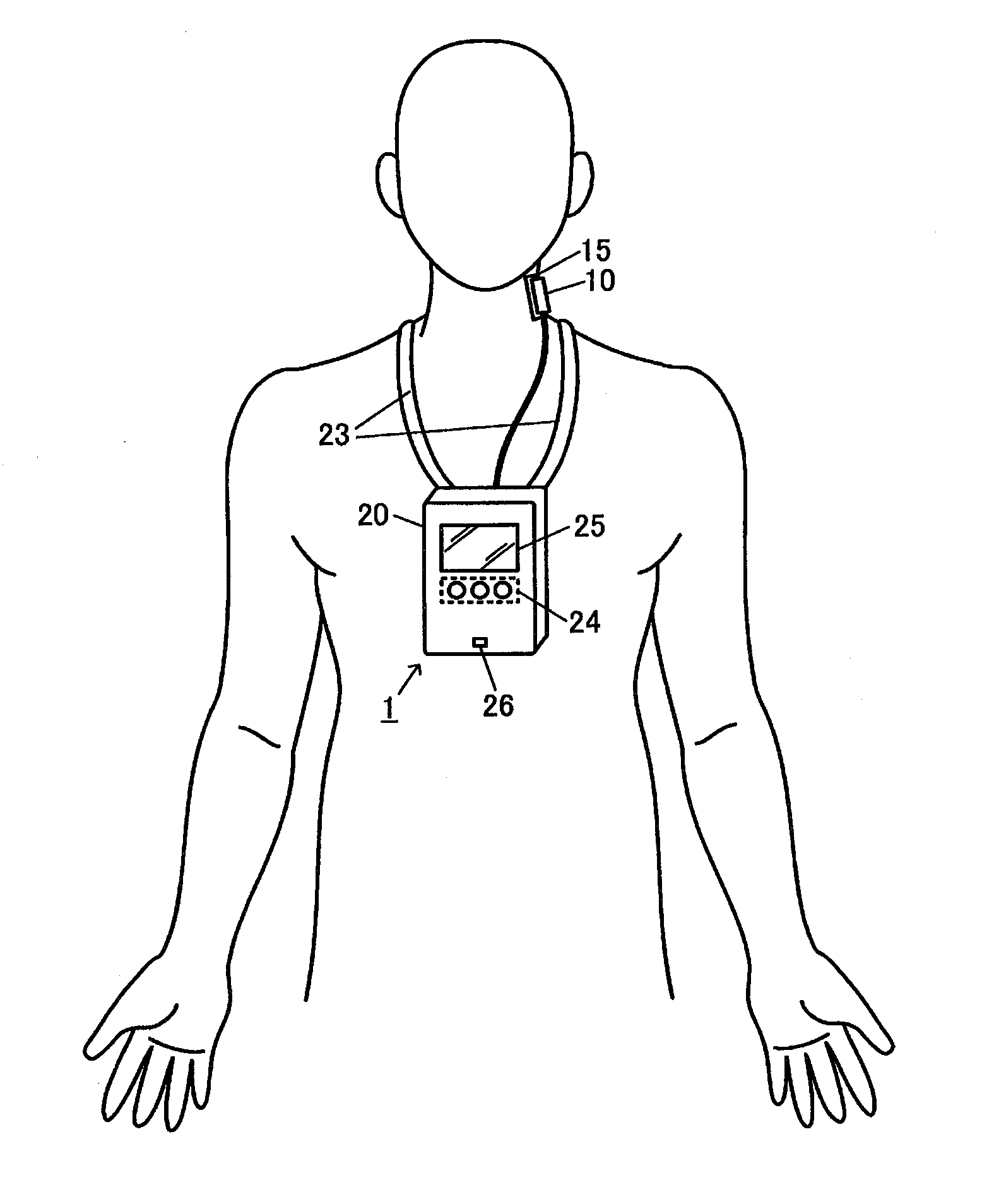
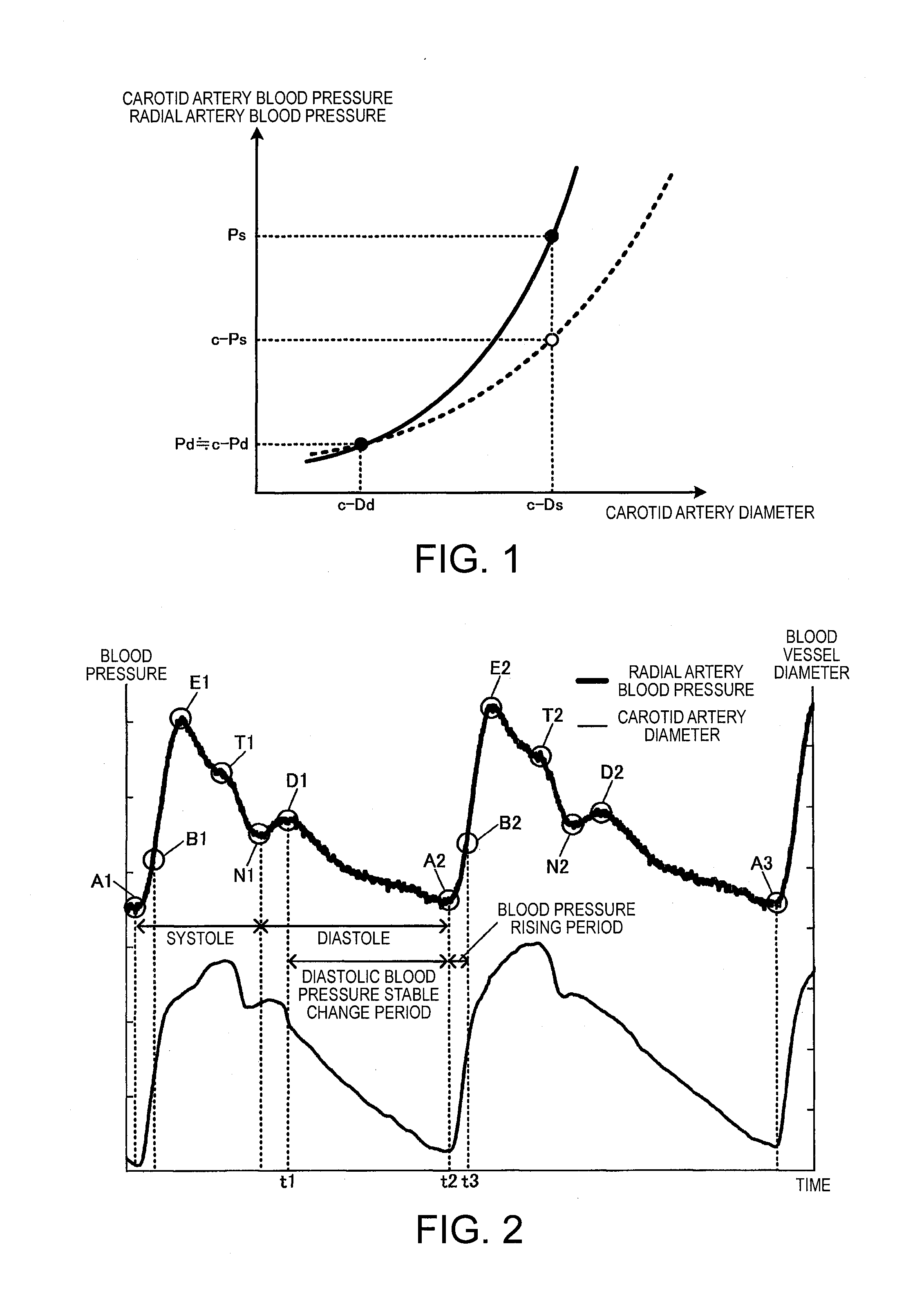
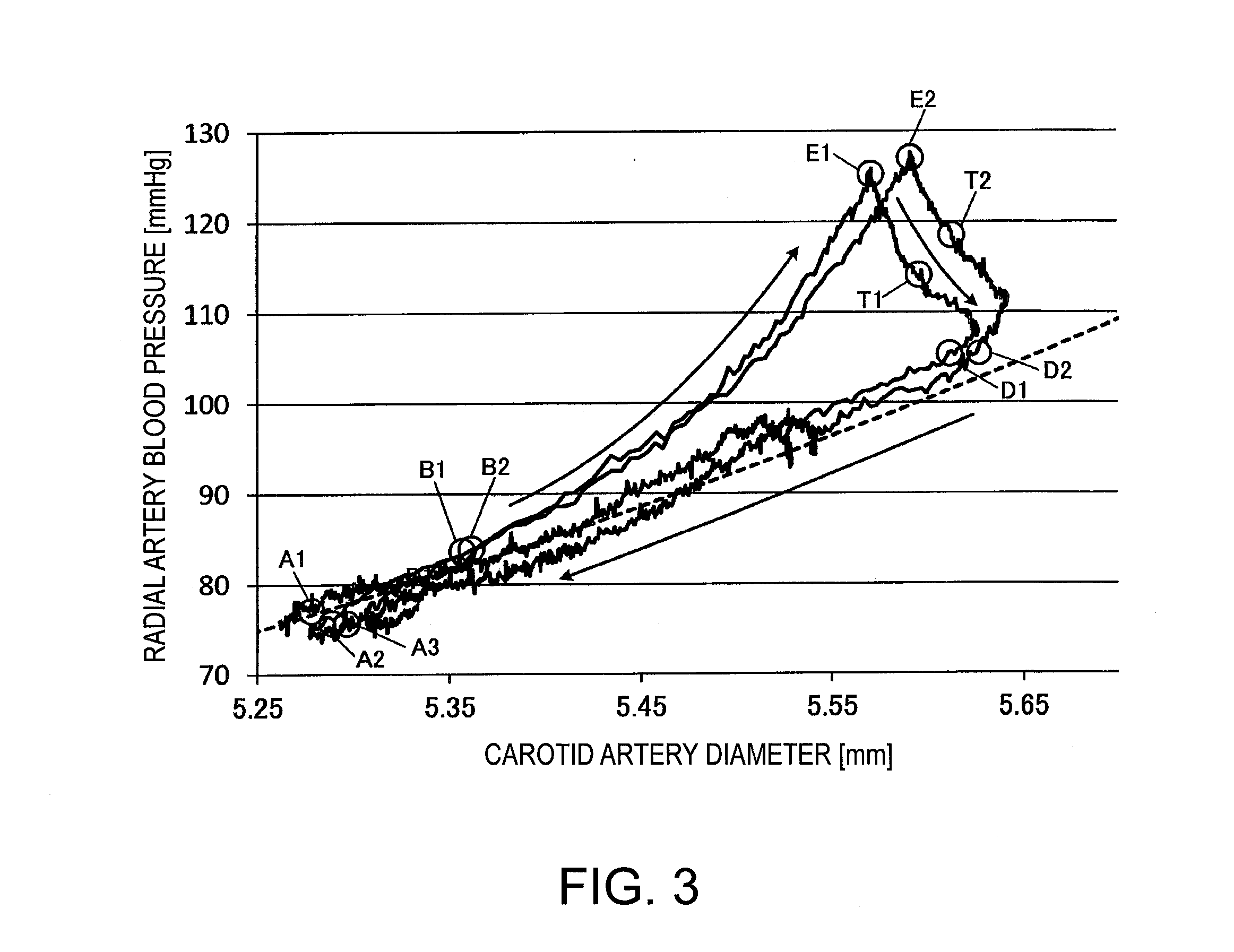
In an ultrasonic blood pressure meter 1, changes in blood pressure in a peripheral artery measured by a blood pressure meter 2 are input from an input unit 40. A blood vessel diameter measuring unit 120 measures changes in the blood vessel diameter of a central artery using ultrasound. A calibrating unit 130 calibrates a parameter related to a blood pressure estimation process for estimating central blood pressure from the blood vessel diameter of the central artery, using results of measurement by the blood pressure meter 2 and the blood vessel diameter measuring unit 120 during a given correspondence period, of a one-heartbeat period, in which the relationship between the blood vessel diameter of the central artery and the blood pressure in the peripheral artery corresponds to the relationship between the blood vessel diameter of the central artery and the central blood pressure.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Dynamic physical examination method and automatic corporeity evaluation system
InactiveCN103976719ALow costEffective jointDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical Exam MethodBreath holds
The invention provides a dynamic physical examination method and an automatic corporeity evaluation system. The dynamic physical examination method includes two modes: 1) measuring blood oxygen, blood pressure and heart rhythm by enabling a person to hold breath; 2) measuring the blood oxygen, the blood pressure and the heart rhythm by enabling the person to continuously squat. Normal value of a static examination is used as a reference base line of a dynamic physical examination performed by using the dynamic physical examination method, and therefore heart and lung functions and a circulatory system of the person under pressure are evaluated. A breath holding examination aims at examining high value of the blood pressure and heart rhythm changes under the circumstance of organ tissue ischemia, and a continuous squatting examination aims at examining high value of the heart rhythm and blood pressure changes under the circumstance of exercise. The automatic corporeity evaluation system analyzes corporeity and potential disease risk of the person by combining dynamic physical sign measurement value with static physical examination normal value and using front end embedded software and background big data cloud computing. Then, corresponding health advice and corresponding medical service recommendation are provided.
Owner:INSPUR GROUP CO LTD
Novel index for testing partial elasticity of artery
InactiveCN102805616AOrgan movement/changes detectionEvaluation of blood vesselsPulse pressureBasic research
The invention provides a novel index for testing the partial elasticity of the artery, belonging to the field of cardiovascular mechanics and having great significance to the related basic research and clinical work. At present, a variety of indexes are used for reflecting the elasticity of the whole blood vessel, but no index is available to reflect the partial elasticity of the blood vessel, and the basic research and the clinical work have an urgent need for a novel index for measuring the partial elasticity of the artery. The novel index provided by the invention fills the blank. The novel index is obtained by measuring the stress of the blood vessel wall on different parts and in different directions (circumferential direction and longitudinal direction) when the blood vessel wall is subjected to one blood-pressure change through deducing and calculating according to the Laplace's law and essentially reflects that the force (pulse pressure) needed by the partial blood vessel wall to generate a certain stress in a certain direction represents the elasticity of the partial blood vessel. The novel index can be also used for directly calculating the Young modulus of the partial blood vessel.
Owner:曹铁生 +2
Blood vessel physiological parameter measurement method and device, computer device and storage medium
ActiveCN110559015AImprove measurement efficiencyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationElement model
The invention relates to a blood vessel physiological parameter measurement method and device, a computer device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a first reference ultrasonic image sequence of a to-be-measured blood vessel when the to-be-measured blood vessel is not loaded and at least one group of ultrasonic image sequences of the to-be-measured blood vessel when the to-be-measured blood vessel is loaded with a preset load, and ranking to obtain a target first reference ultrasonic image sequence and at least one group of target ultrasonic image sequence in a cardiac cycle; obtaining a displacement field sequence group according to the target first reference ultrasonic image sequence and the at least one group of target ultrasonic image sequence; and inputting the preset load into a preset to-be-measured blood vessel finite element model, simulating and matching the displacement field sequence group, to obtain a cardiac cycle blood pressure change waveform and a relationship between the blood vessel elasticity modulus and the cardiac cycle blood pressure. According to the method, the blood pressure change waveform of the cardiac cycle and the blood vessel elasticity modulus can be obtained at the same time, and the blood vessel physiological parameter measurement efficiency is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Blood pressure measuring apparatus and method for calibrating central blood pressure estimation parameter
InactiveUS20140018687A1Accurate CalibrationAccurate estimateEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterSphygmomanometerCentral Artery
In an ultrasonic blood pressure meter 1, changes in blood pressure in a peripheral artery measured by a blood pressure meter 2 are input from an input unit 40. A blood vessel diameter measuring unit 120 measures changes in the blood vessel diameter of a central artery using ultrasound. A calibrating unit 130 calibrates a parameter related to a blood pressure estimation process for estimating central blood pressure from the blood vessel diameter of the central artery, using results of measurement by the blood pressure meter 2 and the blood vessel diameter measuring unit 120 during a given correspondence period, of a one-heartbeat period, in which the relationship between the blood vessel diameter of the central artery and the blood pressure in the peripheral artery corresponds to the relationship between the blood vessel diameter of the central artery and the central blood pressure.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com