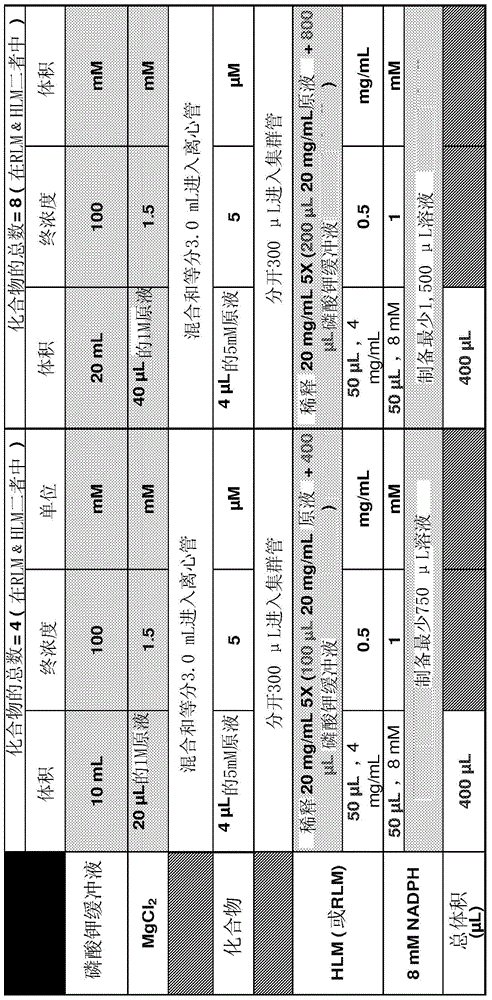
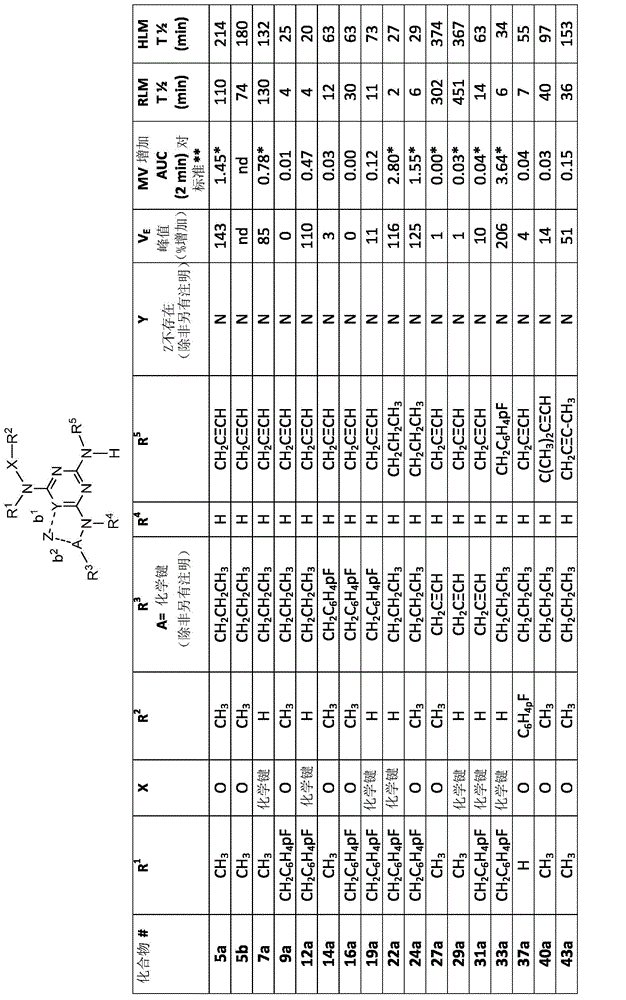
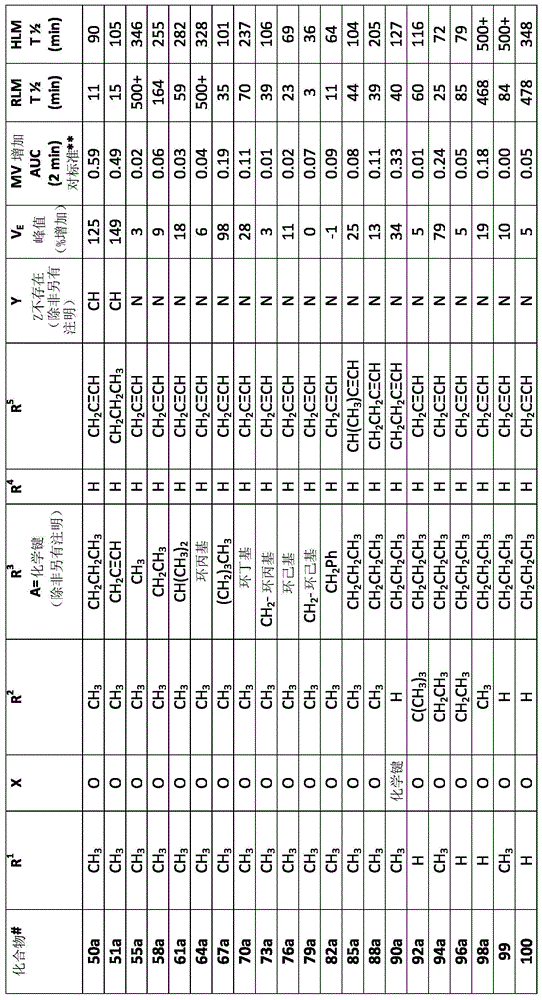
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Breathing control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
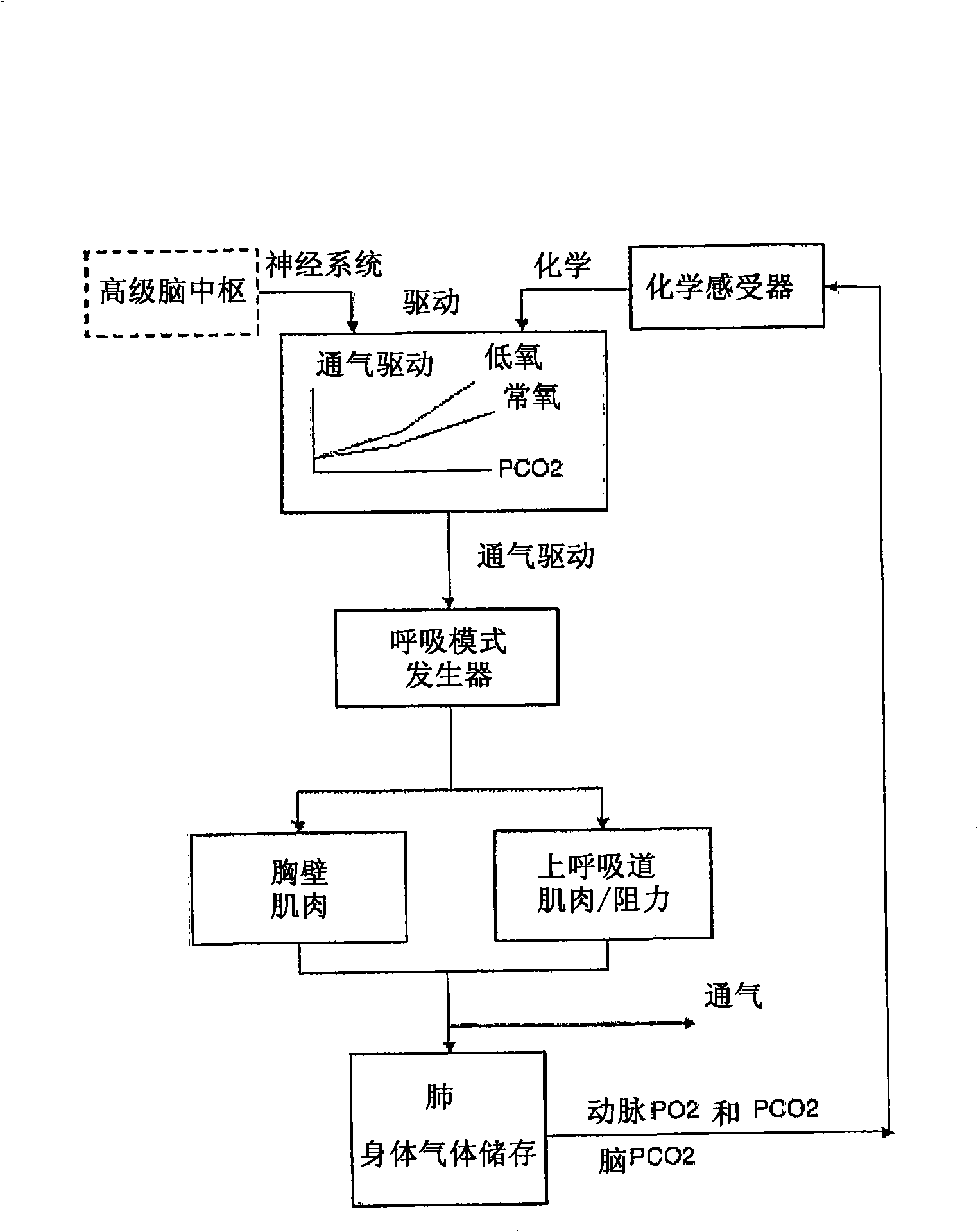
Breathing is usually automatic, controlled subconsciously by the respiratory center at the base of the brain. Breathing continues during sleep and usually even when a person is unconscious. People can also control their breathing when they wish, for example during speech, singing, or voluntary breath holding.
Respiration control apparatus
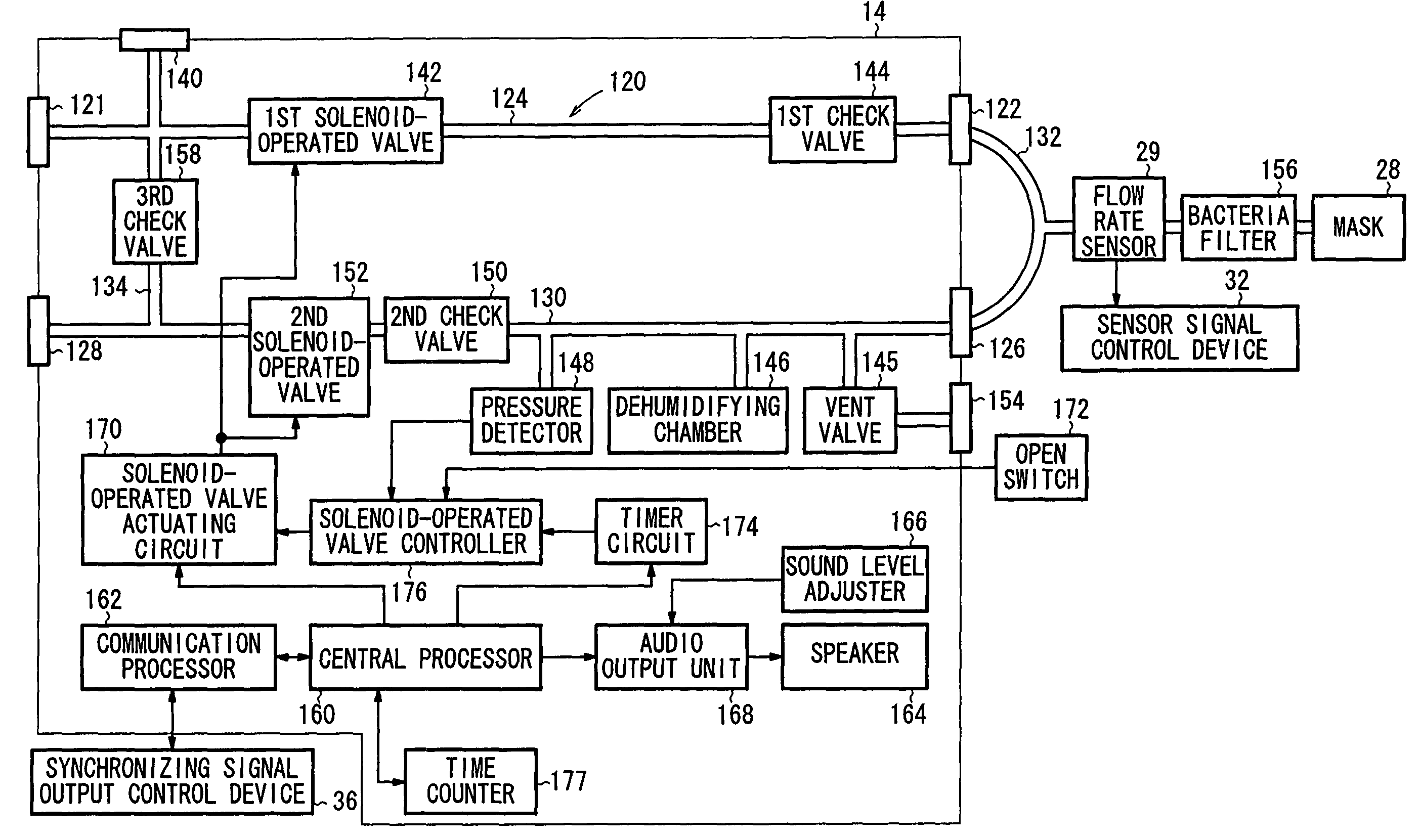
InactiveUS7448381B2Improve accuracyFirmly connectedRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl signalInhalation
A respiration control apparatus connected to a controlled body includes a respiration circuit having an inhalation circuit and an exhalation circuit. The inhalation circuit includes a first solenoid-operated valve and a first check valve. The exhalation circuit includes a vent valve, a dehumidifying chamber, a pressure detector, a second check valve, and a second solenoid-operated valve. A central processor closes the first solenoid-operated valve and the second solenoid-operated valve based on a respiration control signal supplied from a synchronizing signal output control device, disconnecting the respiratory system of the controlled body from the outside of the respiration control apparatus.
Owner:ANZAI SOGYO
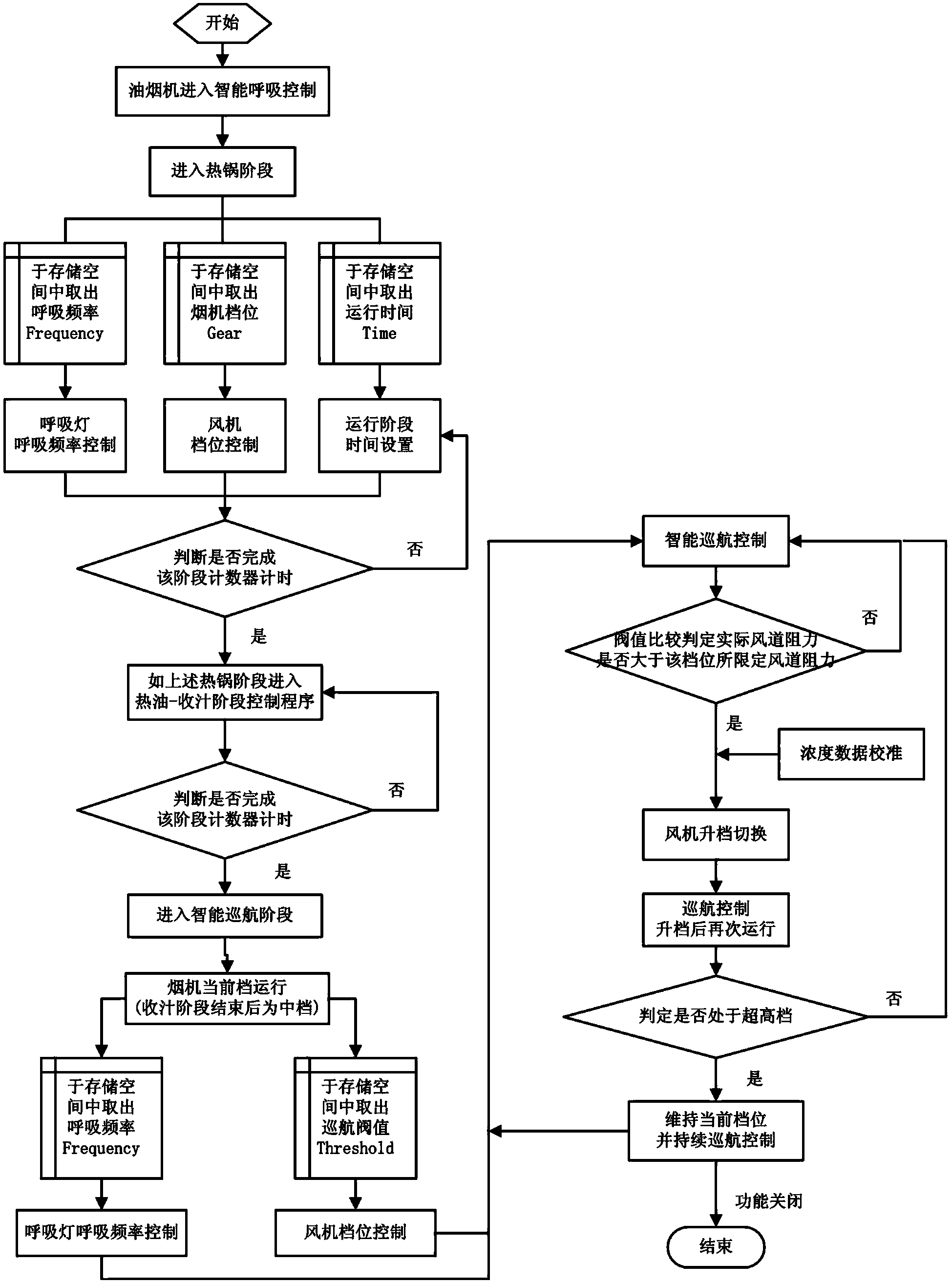
Oil fume suction control method of intelligent breathing range hood and range hood
ActiveCN104251506AImprove performanceEasy to useDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringBreathing control
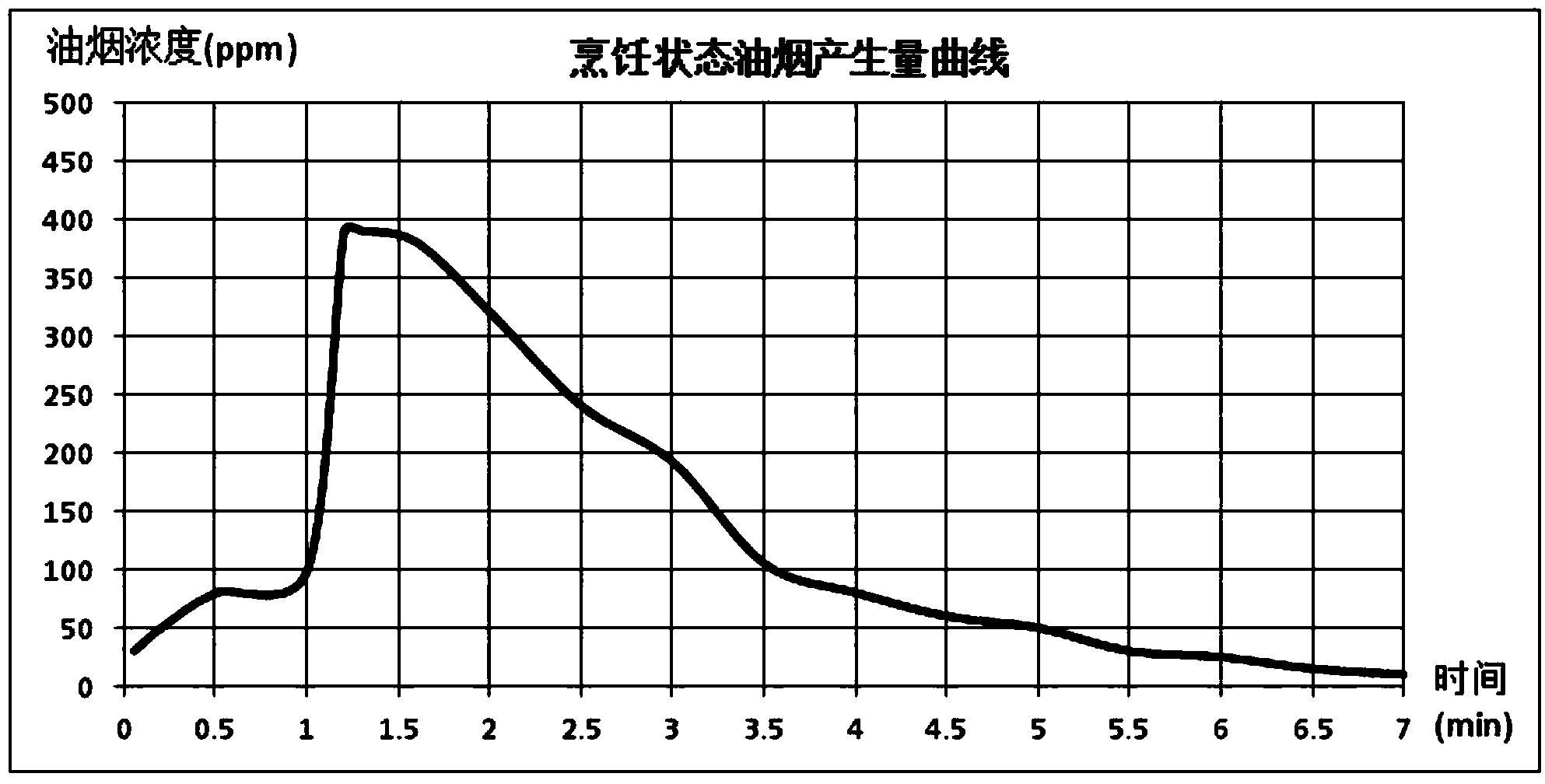
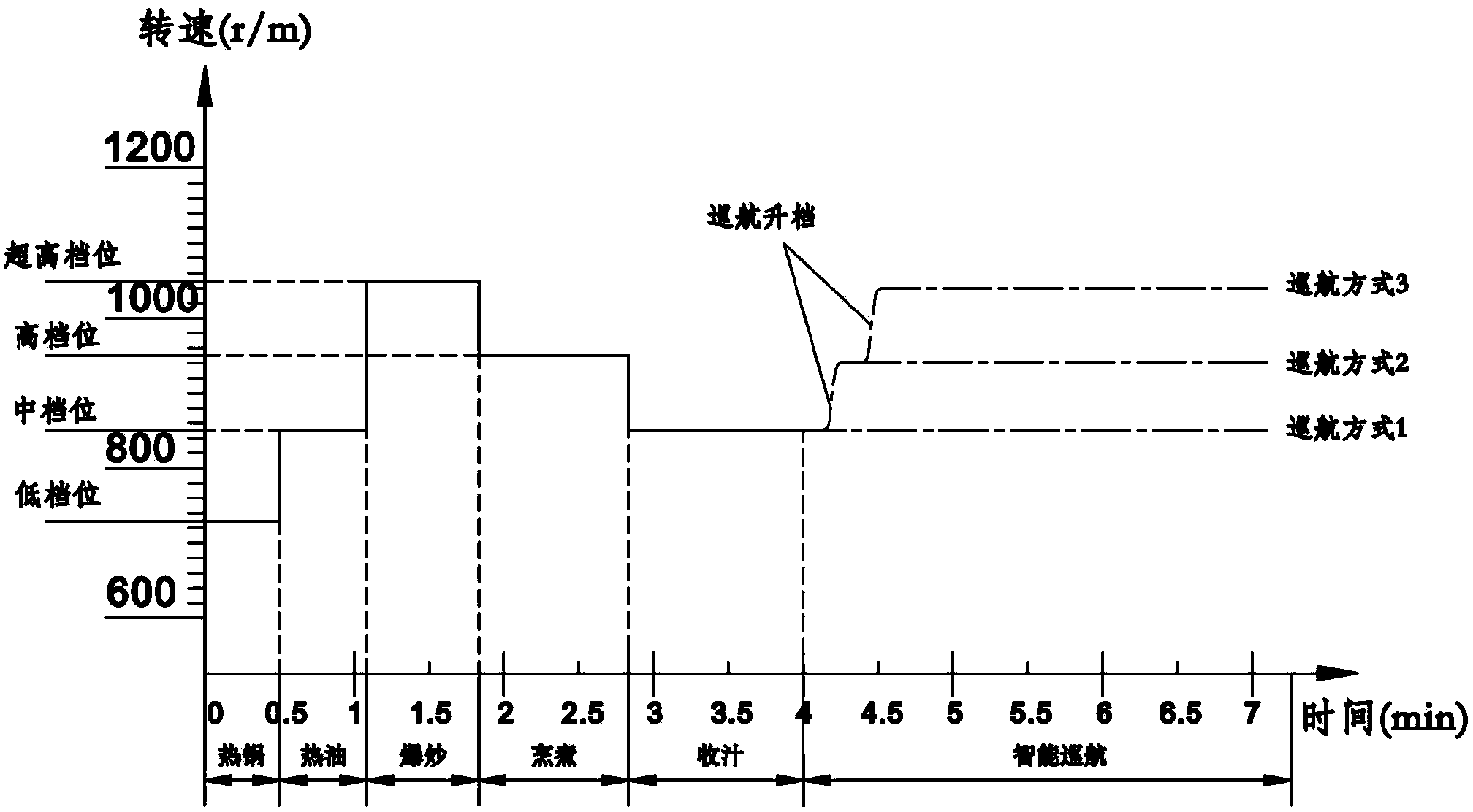
The invention discloses an oil fume suction control method of an intelligent breathing range hood. The range hood comprises a machine body, a fan and a main controller, wherein the main controller controls the fan to operate, the control method comprises a stir-frying stage and a post-processing stage, the range hood is provided with an ultra-high gear, the revolving speed of the fan under the ultra-high gear V is not less than 1000 and not more than 1250 rpm (Revolutions Per Minute), the fan is operated under the ultra-high gear during the stir-frying stage, the stir-frying stage is started after the oil fume suction control method is carried out for 0-80 seconds, and ended after the oil fume suction control method is carried out for 100-180 seconds, and the fan downshifts to operate after the stir-frying stage is ended. According to the invention, the range hood carries out an intelligent multistage breathing control method to realize maximum utilization of energy efficiency; meanwhile, the range hood disclosed by the invention lowers impacts of range hood noises on users at the greatest extent to optimize use feel of the range hood.
Owner:JOYOUNG CO LTD
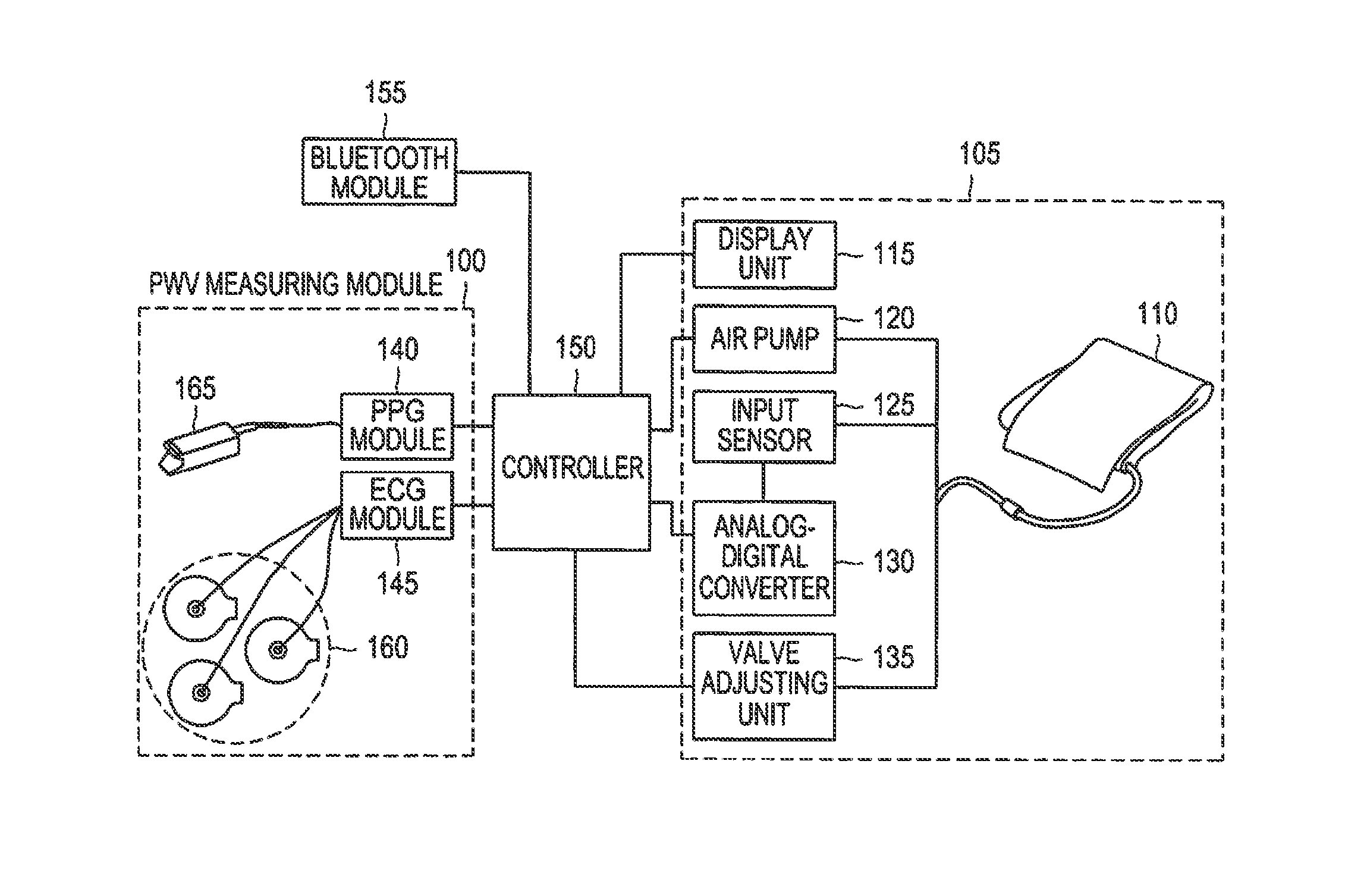
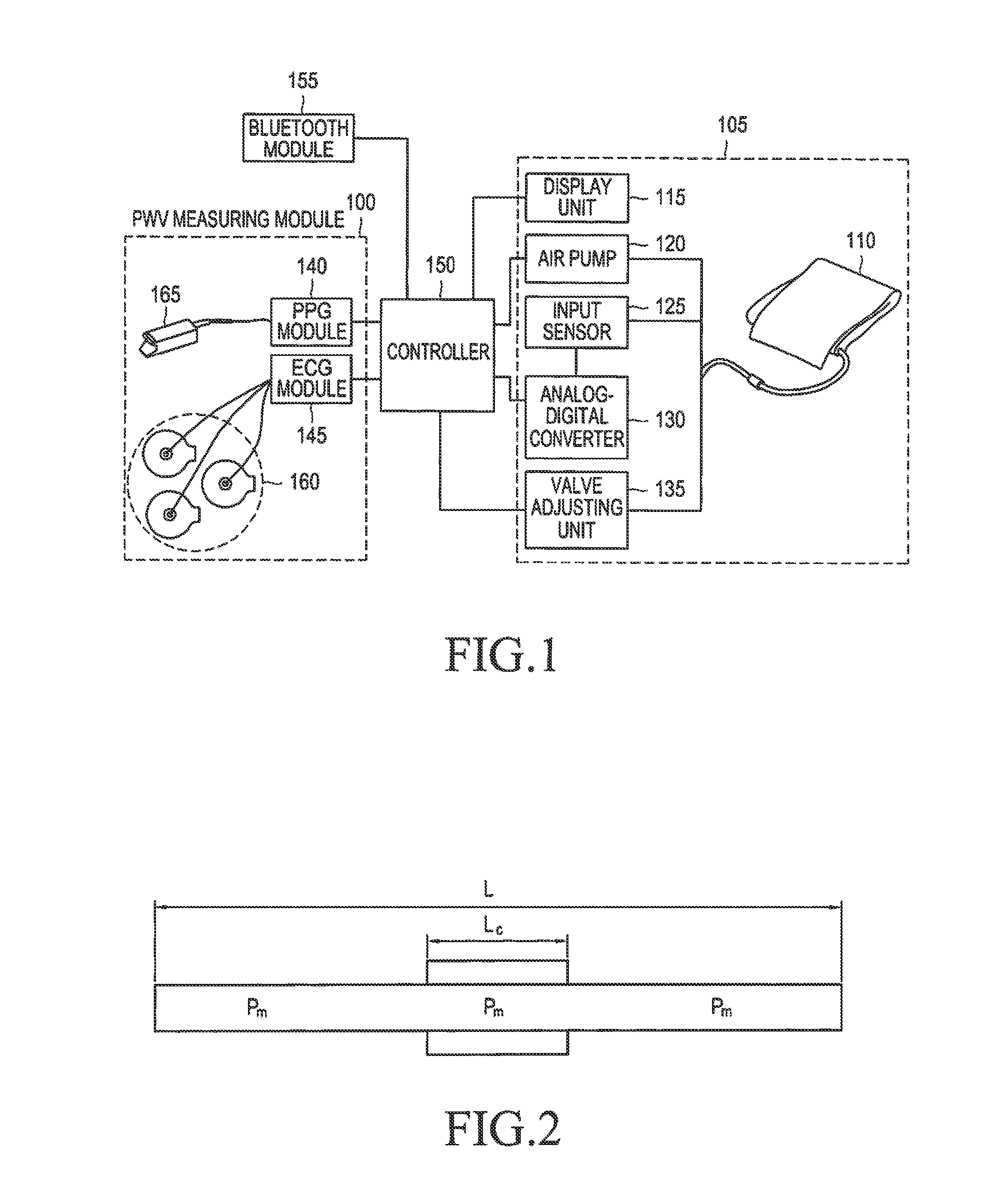
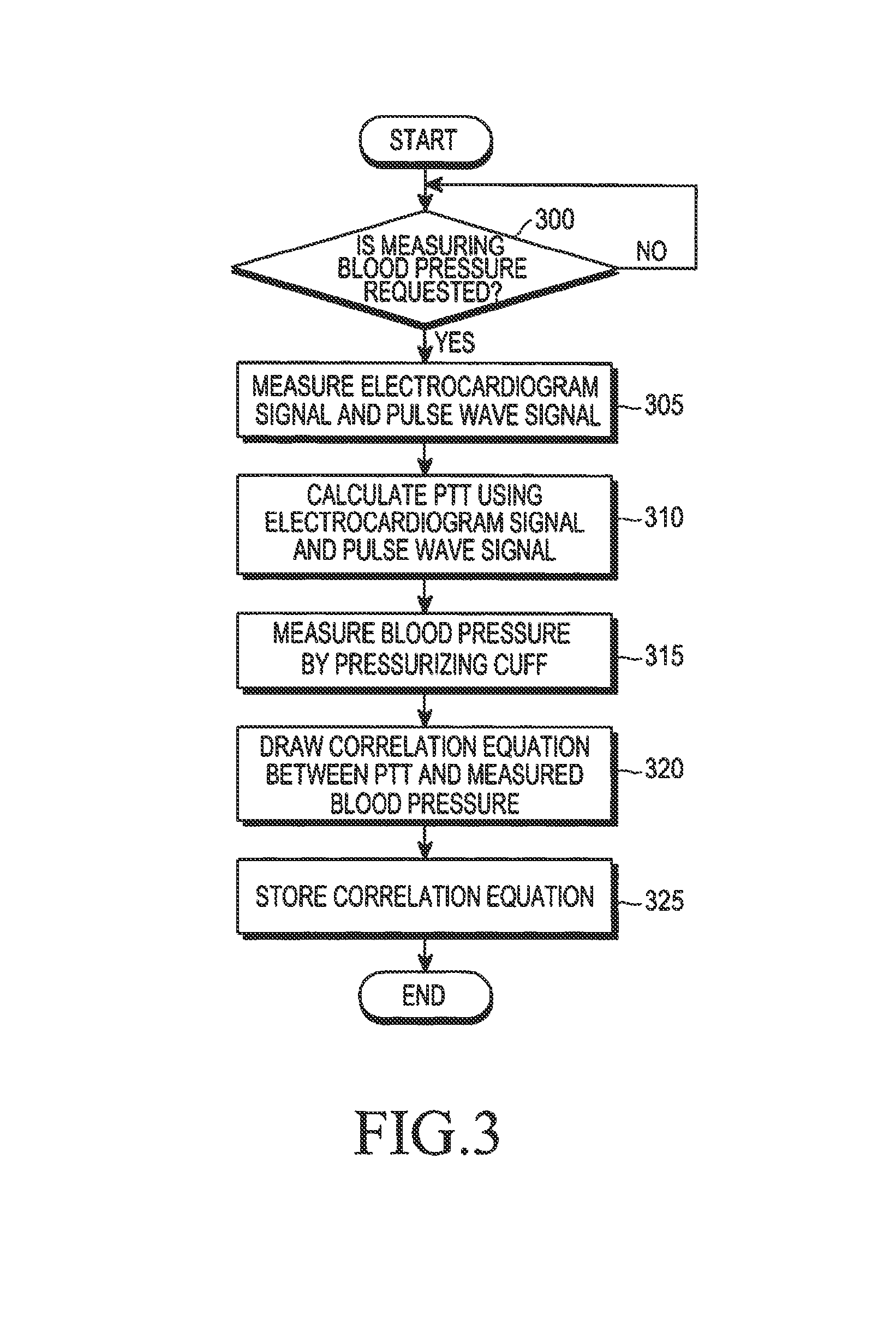
Method and apparatus for measuring change in blood pressure by respiration control
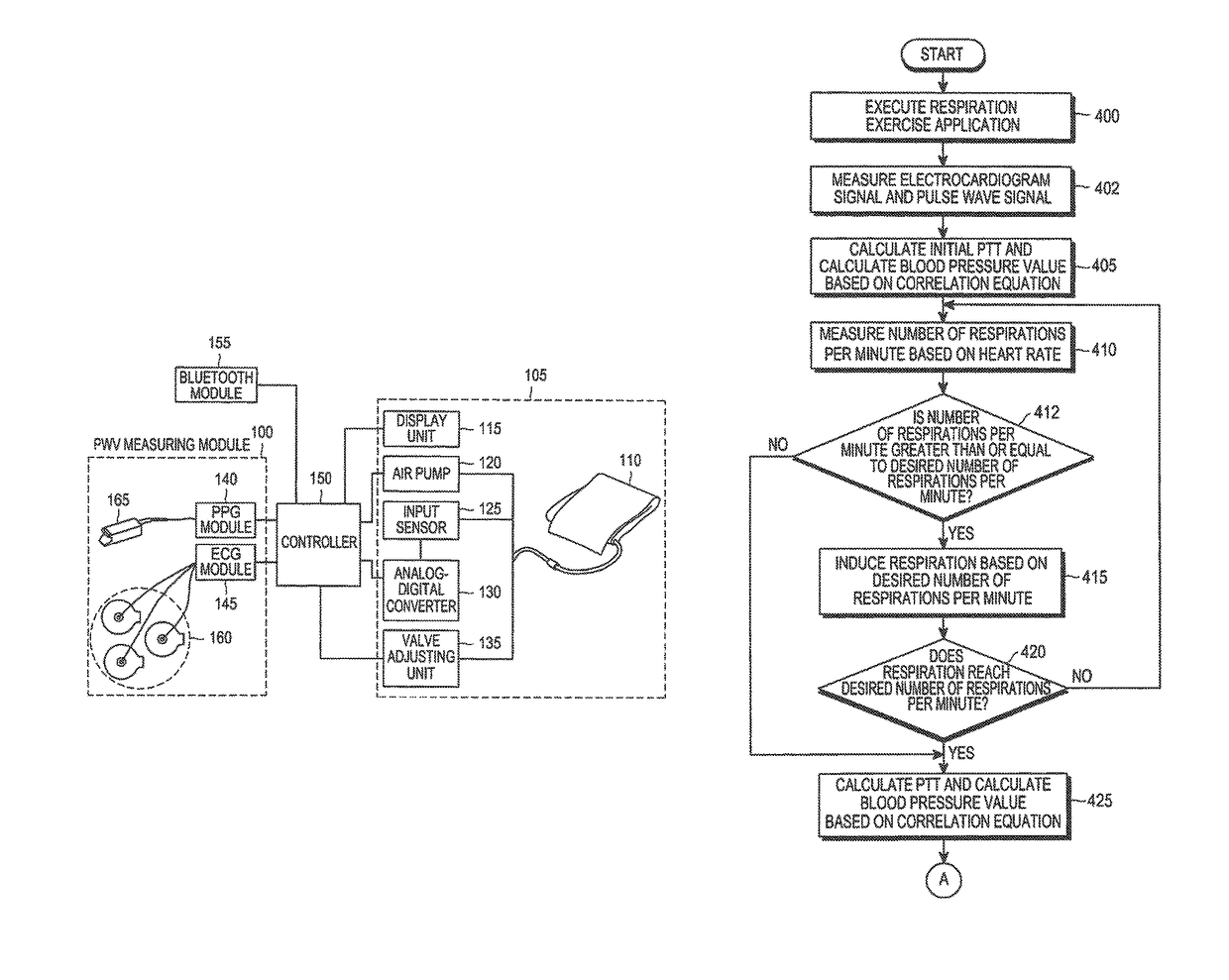
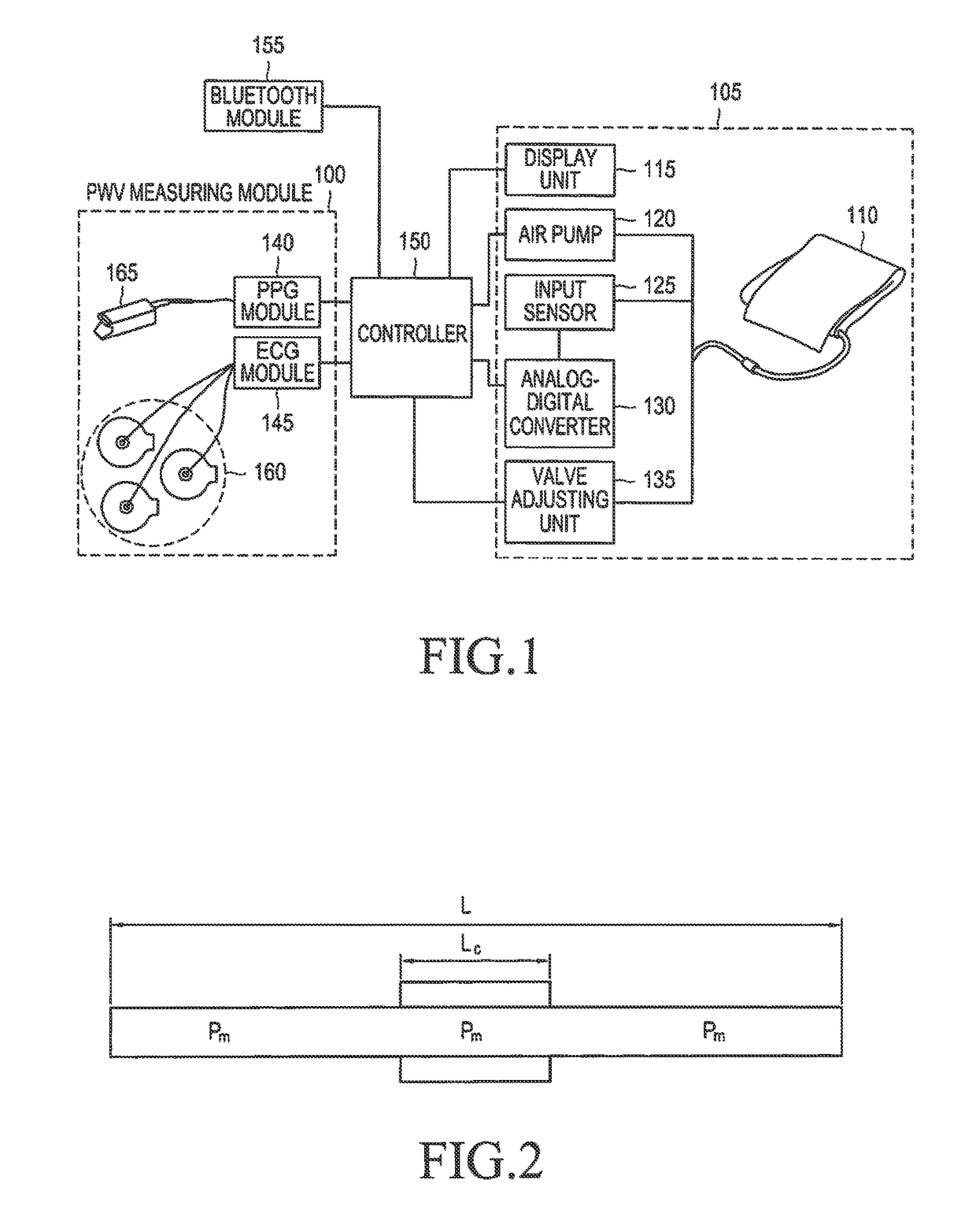
A method and an apparatus are provided for measuring a change in blood pressure caused by respiration control. A number of respirations per minute is measured based on a heart rate when a respiration exercise begins. Respiration of a subject is induced until the number of respirations per minute reaches a predetermined number of respirations per minute. A pulse transit time is calculated during the respiration exercise, a blood pressure value associated with the pulse transit time is calculated, and the blood pressure value is outputted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Anesthesia vital sign monitoring and controlling system
InactiveCN105769144ASecurity guardPrecise monitoringAutomatic syringesEvaluation of blood vesselsNasal cavityMedical ward
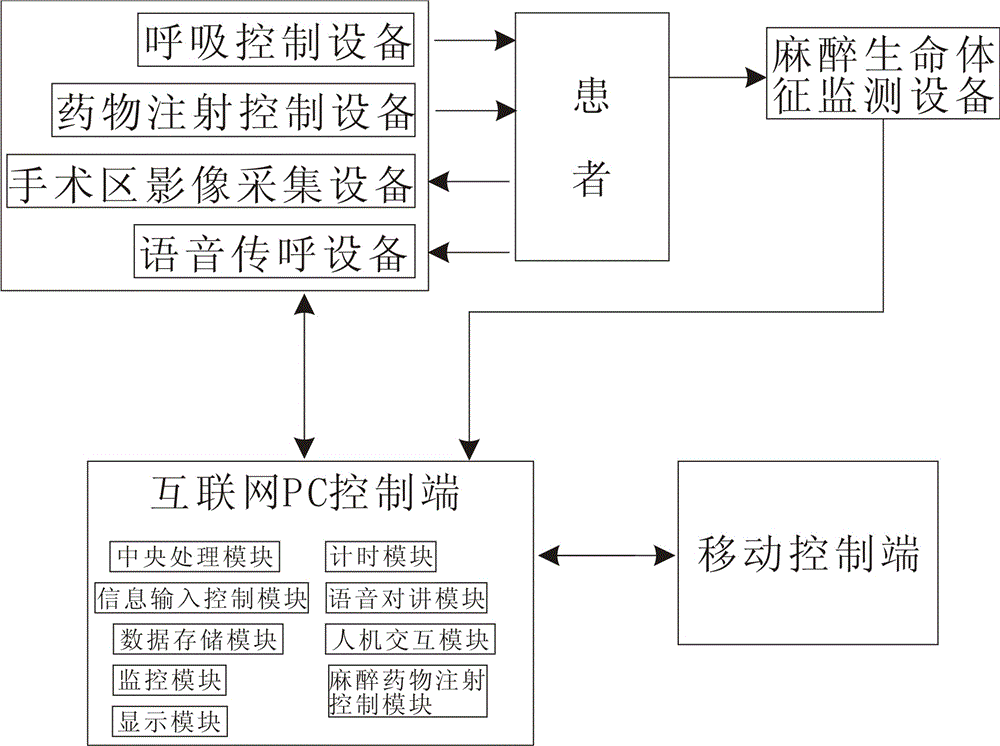
The invention provides an anesthesia vital sign monitoring and controlling system. The anesthesia vital sign monitoring and controlling system comprises an anesthesia vital sign collecting and testing device, a respiration control device, an anaesthetic injection control device, an operation-area image collecting device, a voice calling device, a mobile control end and an internet PC control end, wherein the anesthesia vital sign collecting and testing device directly acts on a patient, and collects the vital sign information of the patient through a sensor, and the output end of the anesthesia vital sign collecting and testing device is connected with the internet PC control end, and the internet PC control end is synchronous with the mobile control end; one end of the respiration control device is connected with the nasal cavity of the patient, and collects the respiration information of the patient through a pressure sensor, and the other end of the respiration control device is connected with the internet PC control end; one end of the anaesthetic injection control device is connected with the injection part of the patient, and the other end of the anaesthetic injection control device is connected with the internet PC control end; the operation-area image collecting device and the voice calling device are arranged in a ward of the patient, and collect the real-time state information and the voice information of the patient in the ward, and the output ends of the operation-area image collecting device and the voice calling device are connected with the internet PC control end.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
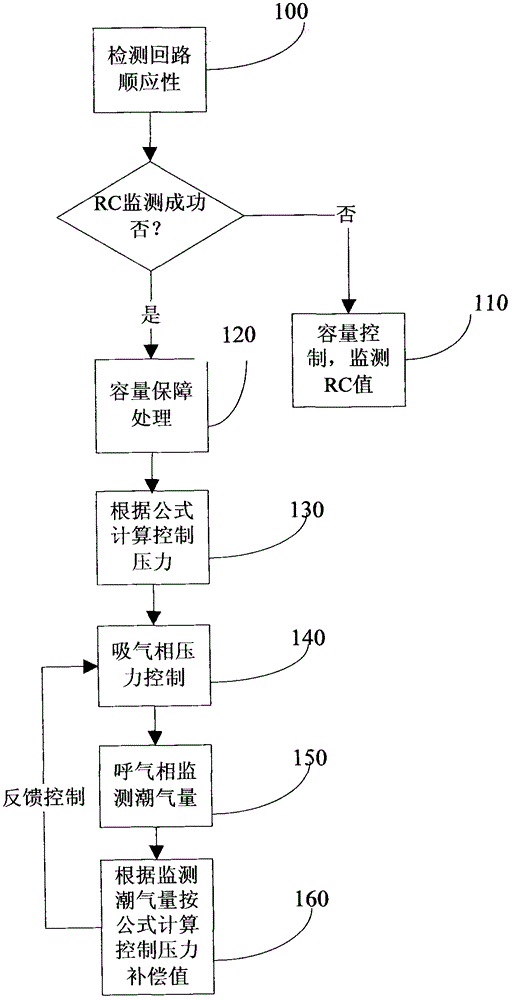
Ventilation method for ensuring volume and limiting pressure of anesthesia machine and breathing machine
InactiveCN102397609AImprove comfortHigh control precisionRespiratorsPressure differenceVentilation mode
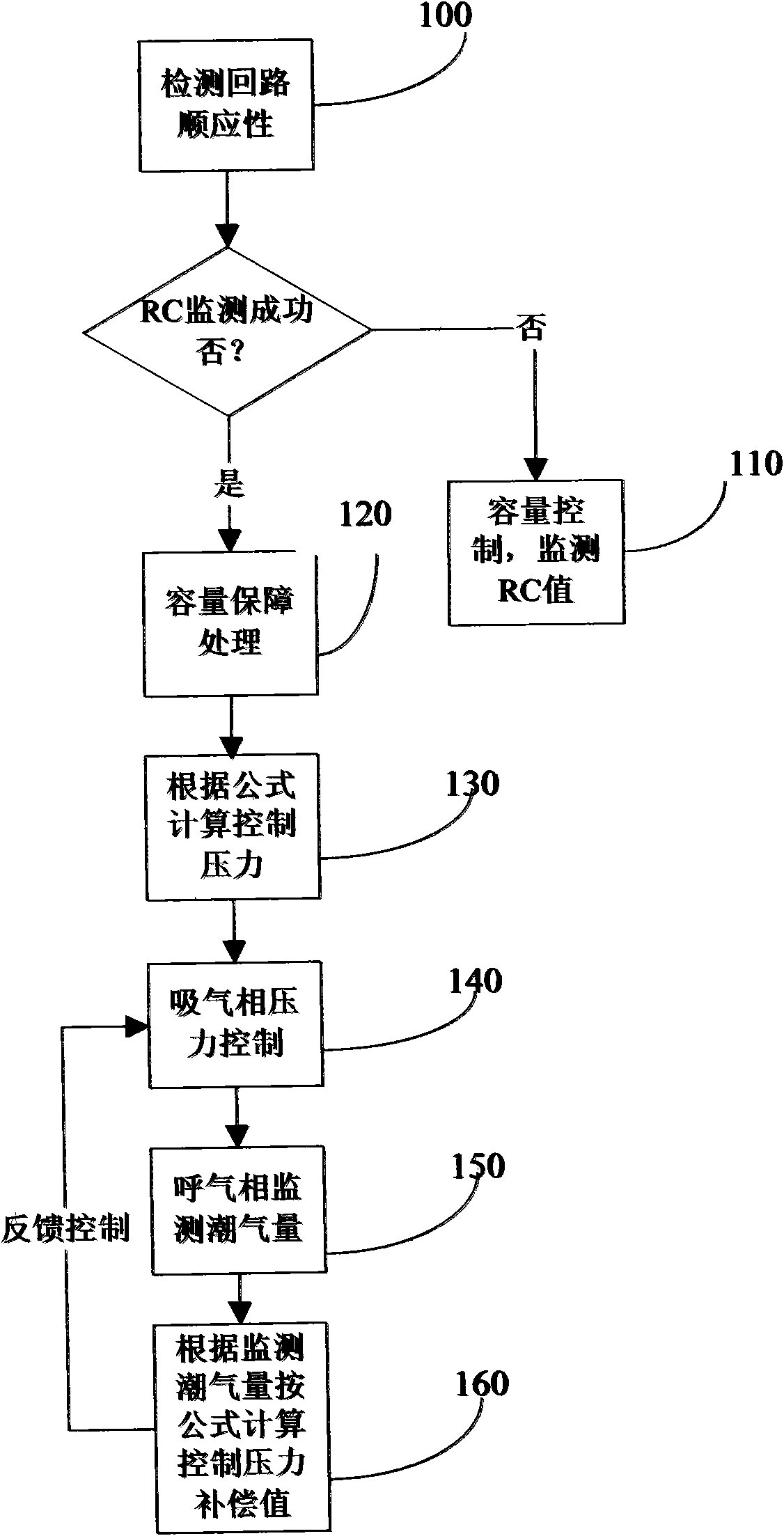
The invention discloses a ventilation method for ensuring volume and limiting pressure of an anesthesia machine and a breathing machine. The method comprises the following steps of: self-detecting the pipeline compliance of the anesthesia machine and the breathing machine in the startup process; in the process of starting breathing control, when the air resistance (R) value and the compliance (C) value of a patient are not monitored correctly, using a volume ventilation mode and monitoring the R value and the C value of the patient in the ventilation period; if the R value and the C value of the patient are correctly monitored, monitoring the suction volume of the patient in a suction period by a compliance compensated volume ensuring method, and performing volume ensuring processing after a set volume is achieved; and calculating a standard control pressure value P of a system, performing suction valve and expiration valve cooperative pressure control according to the value P, calculating the expiration tidal volume of the patient, a volume difference value and a pressure difference value Delta P at an expiration stage, and performing feedback compensation control on the calculated value P according to the Delta P so as to ensure the volume and the pressure.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CHANGFENG CO LTD
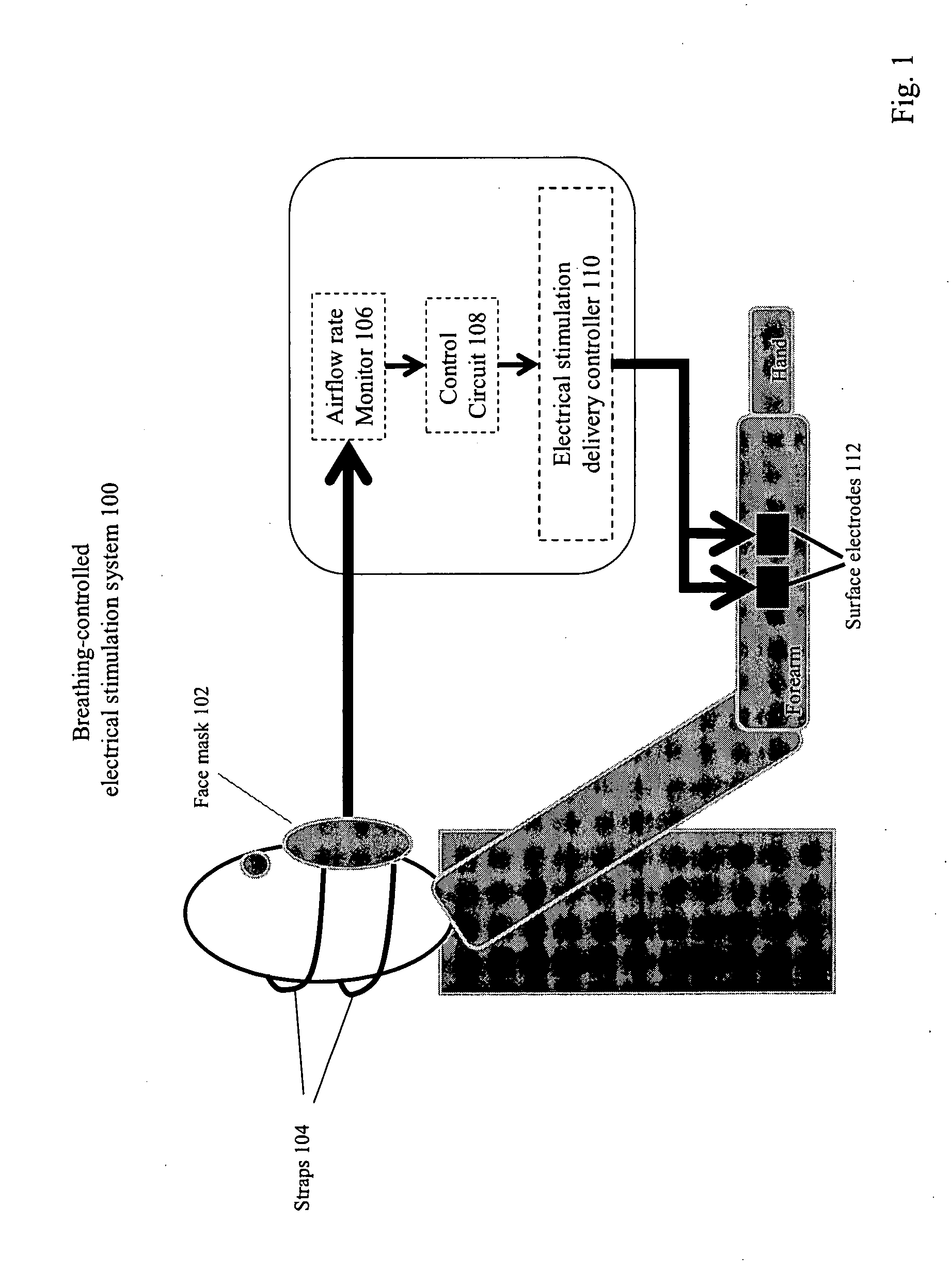
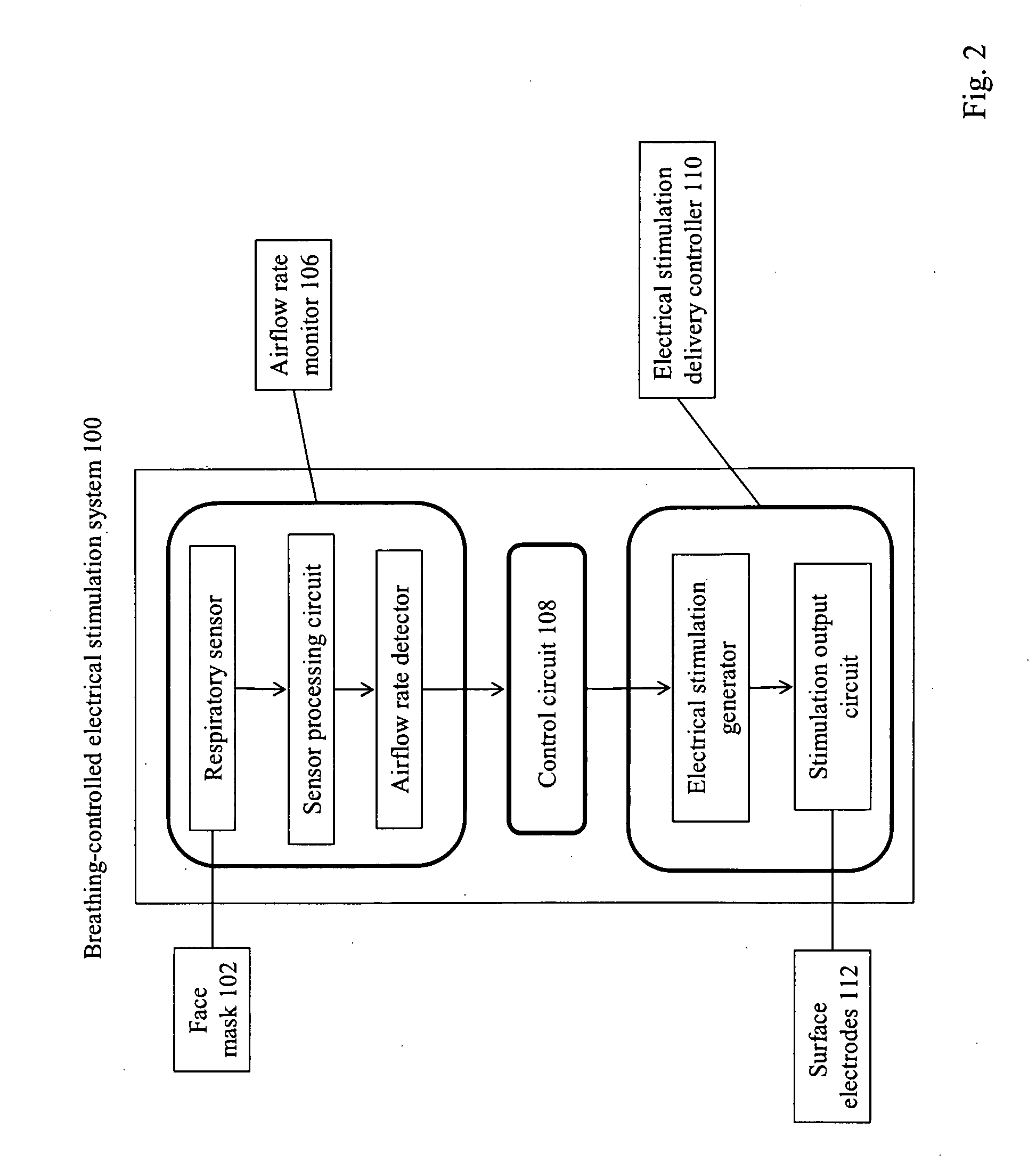
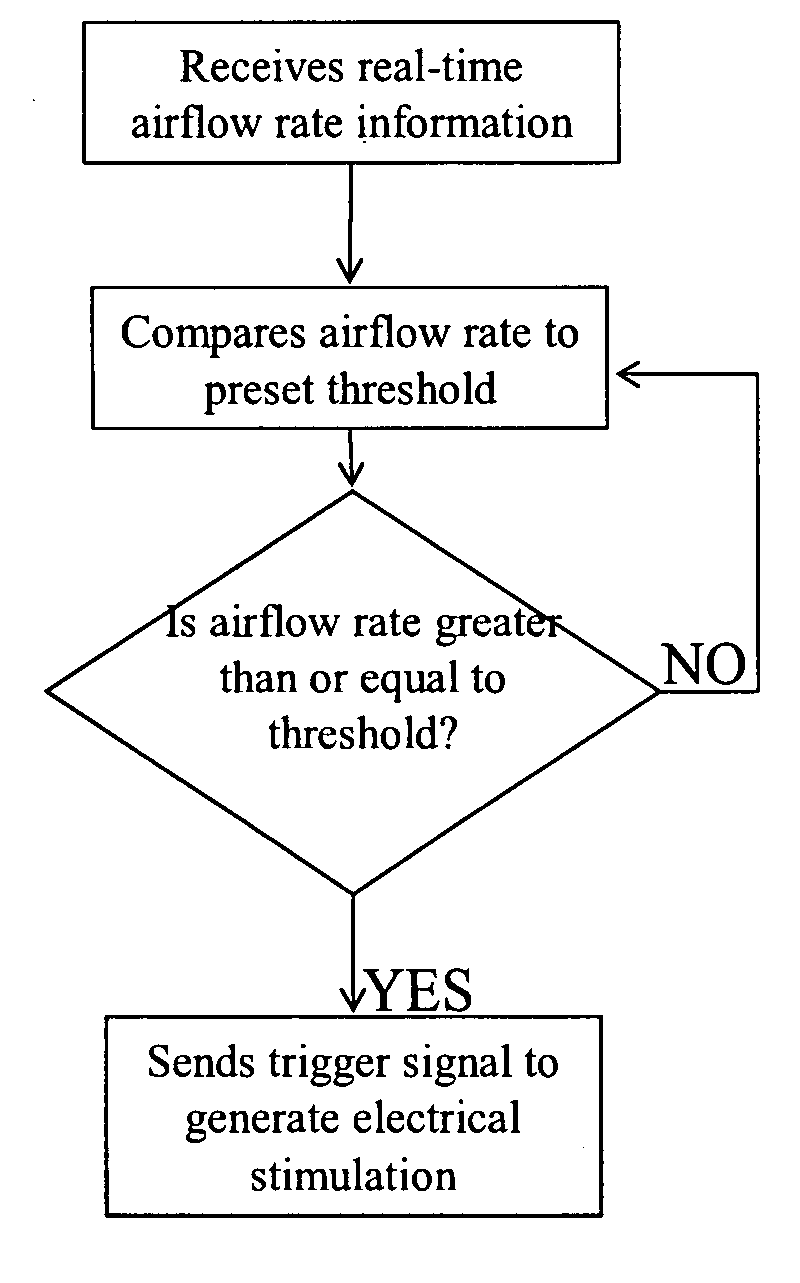
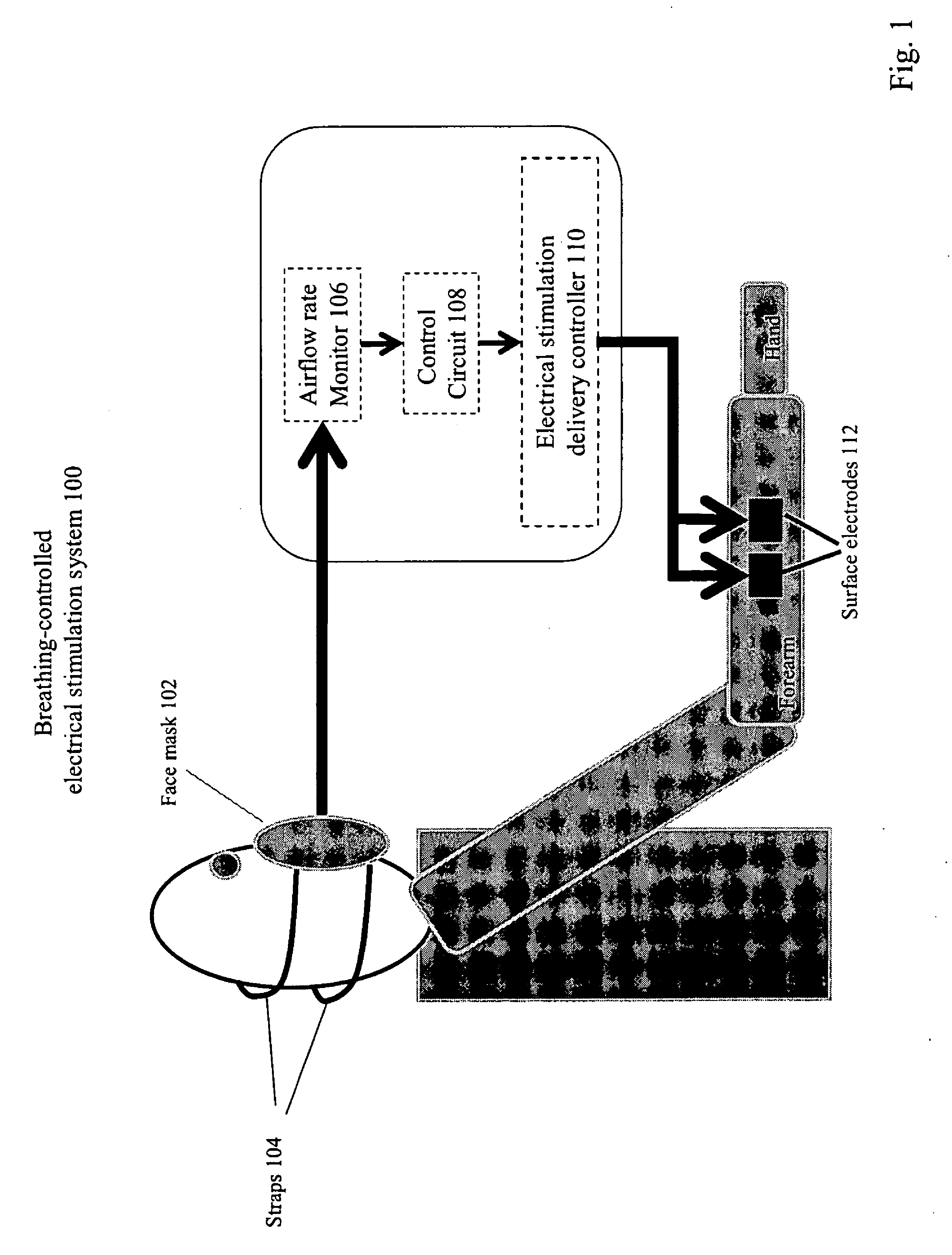
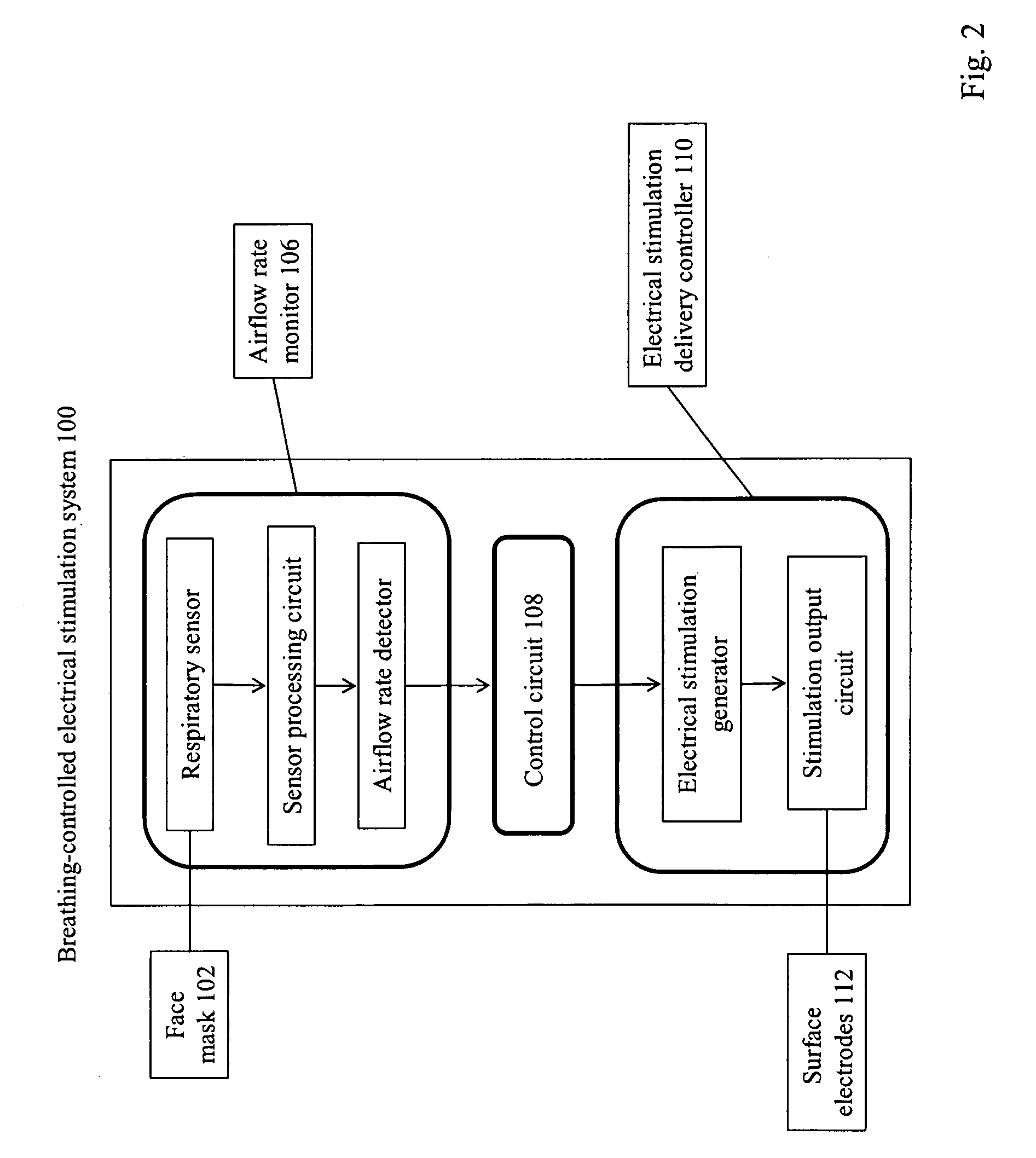
Method and Apparatus of Breathing-Controlled Electrical Stimulation for Skeletal Muscles
ActiveUS20090326606A1Improve efficiencyAvoid excessive problemElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAutonomous breathing
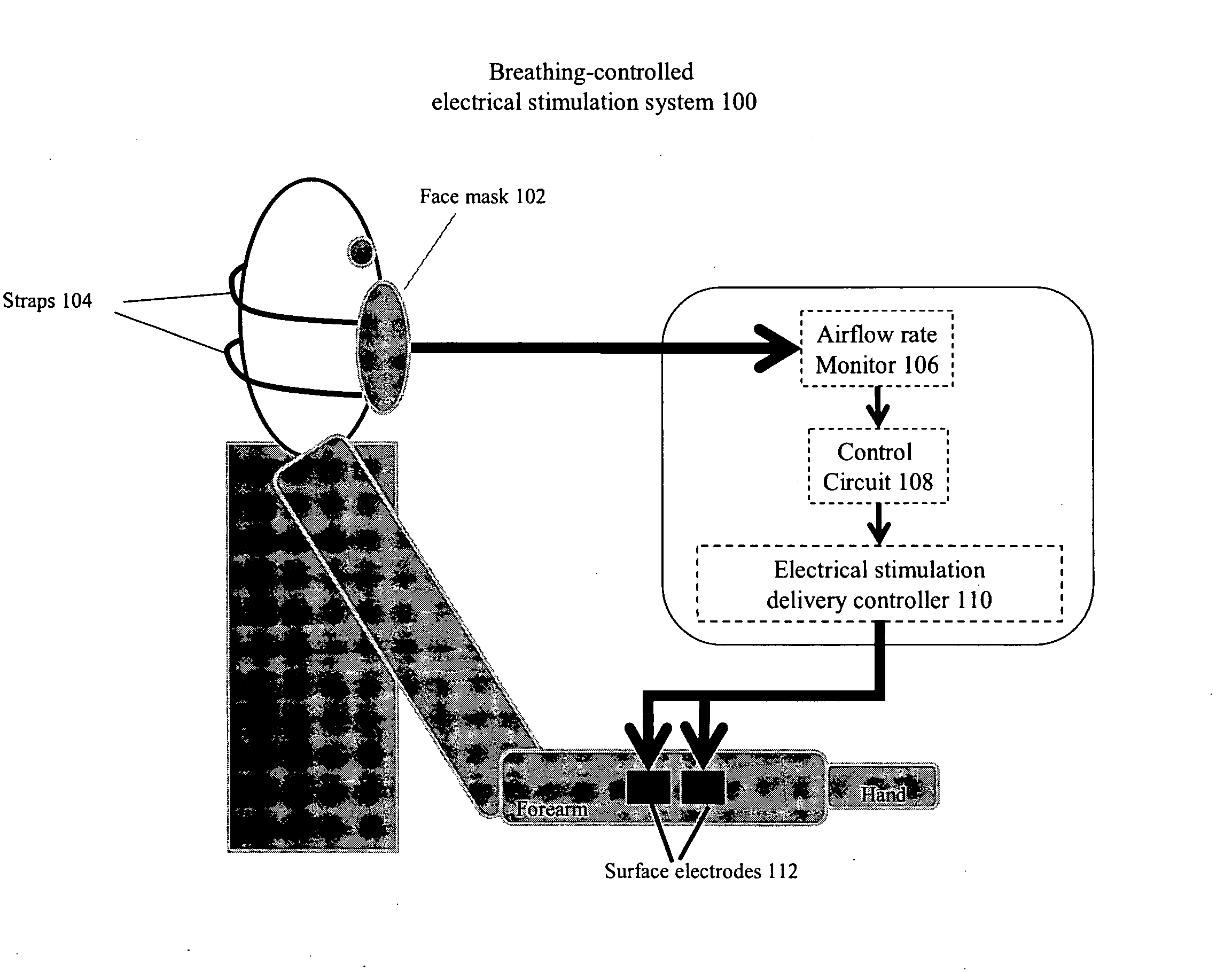
Methods and devices are provided such that electrical stimulation can be delivered to a patient's skeletal muscles in response to certain respiratory signals, such as when voluntary breathing is detected.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and apparatus of breathing-controlled electrical stimulation for skeletal muscles
ActiveUS8229566B2Improve efficiencyAvoid excessive problemElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationPhysical medicine and rehabilitationAutonomous breathing
Methods and devices are provided such that electrical stimulation can be delivered to a patient's skeletal muscles in response to certain respiratory signals, such as when voluntary breathing is detected.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Breathing apparatus
InactiveUS20160271429A1Simple working processImprove accuracyBreathing filtersBreathing masksElectrical conductorEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a breathing apparatus whose a breath monitoring apparatus does not comprise an inhale valve or an exhale valve and whose number of elements is less than that of the conventional breathing apparatus. A breathing apparatus comprises a face piece for covering the whole face or part of the face, an inhale valve, an exhale valve, a voice conductor, a motor fan for supplying external air into the face piece through the inhale valve, a filter for cleaning the external air sucked into the motor fan, a breath monitoring apparatus not comprising the inhale valve or the exhale valve, and a controller for controlling the operation of the motor fan synchronously with the breath based on the detection signal from the breath monitoring apparatus, wherein the inhale valve, the exhale valve, the voice conductor, the motor fan, the filter, the breath monitoring apparatus and the controller are attached to the face piece, and wherein the breath monitoring apparatus detects deflection of a vibration member of the voice conductor.
Owner:SHIGEMATSU WORKS CO LTD
Equine inhalation mask
InactiveUS20040231672A1Economically and easy to handleBreathing filtersBreathing masksInhalationFilter system
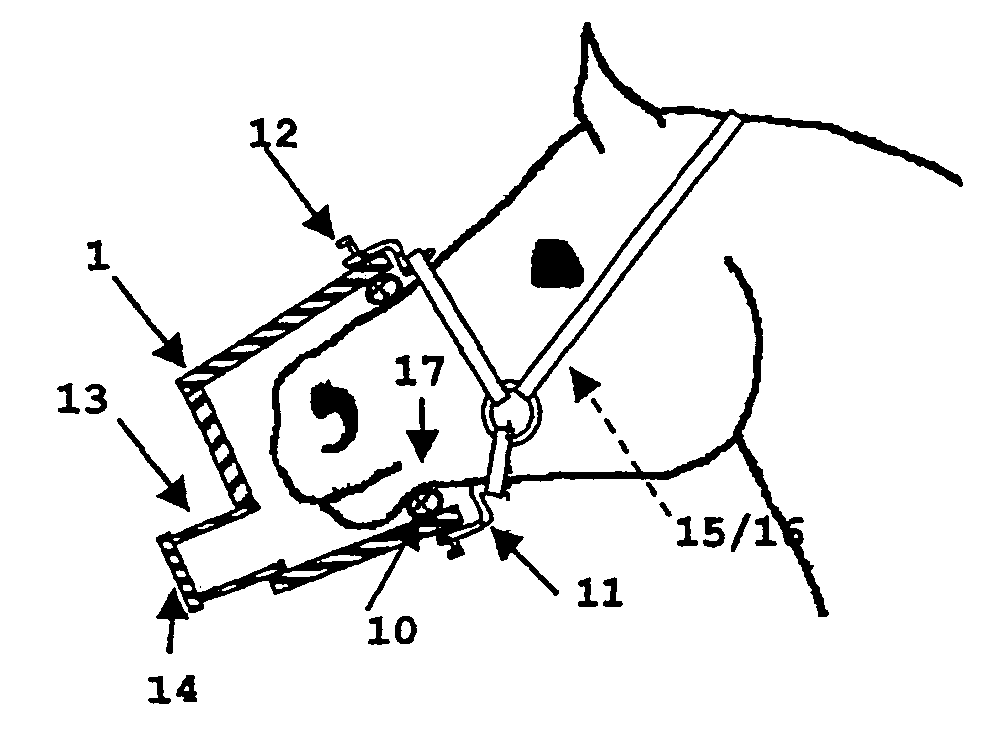
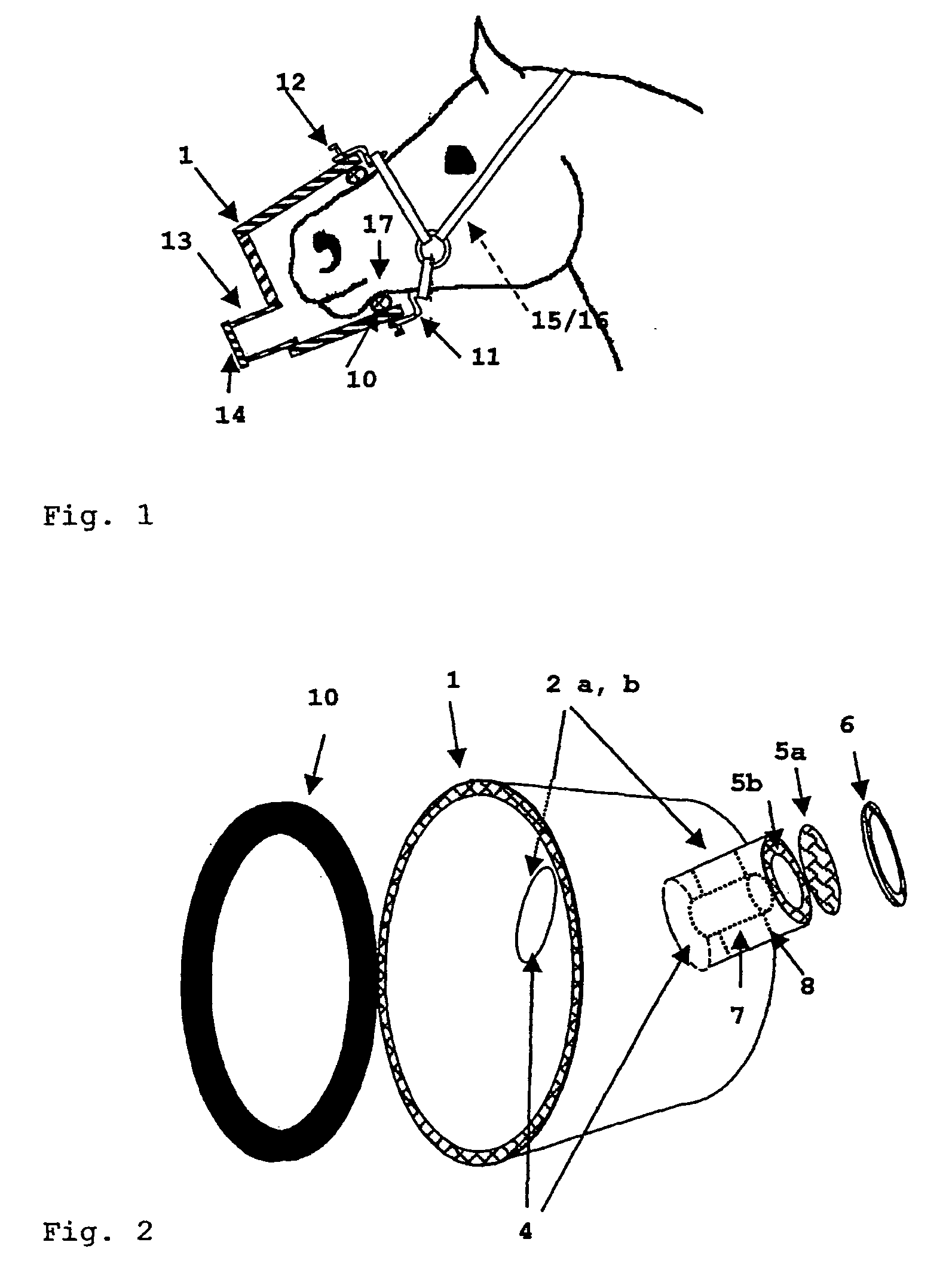
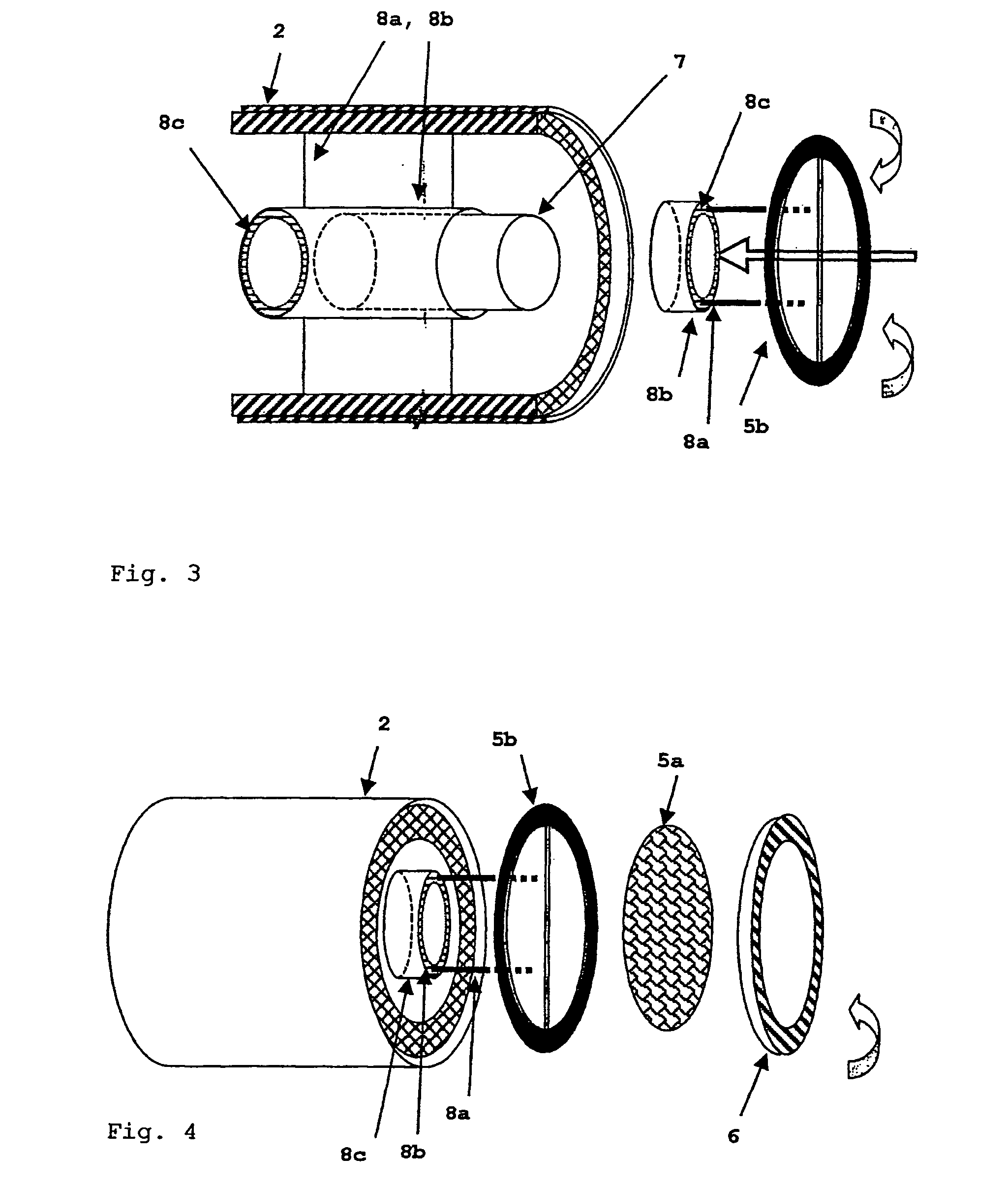
The invention relates to an equine inhalation mask, comprising at least one valveless combined inhalation and exhalation conduit, into which inhalant sources comprising respiration control elements and an energy supply that does not require supply lines are interchangeably integrated. A filter system is mounted on the outer end of the inhalation and exhalation conduit facing away from the head of the horse. Said system and the fact that the mask is effectively sealed when on the head of the horse prevent any escape of the aerosol into the environment, thus permitting a reliable inhalation therapy lasting several minutes under normal respiratory conditions.
Owner:TRANSMIT GES FUER TECHTRANSFER
Breathing apparatus controlled through breath
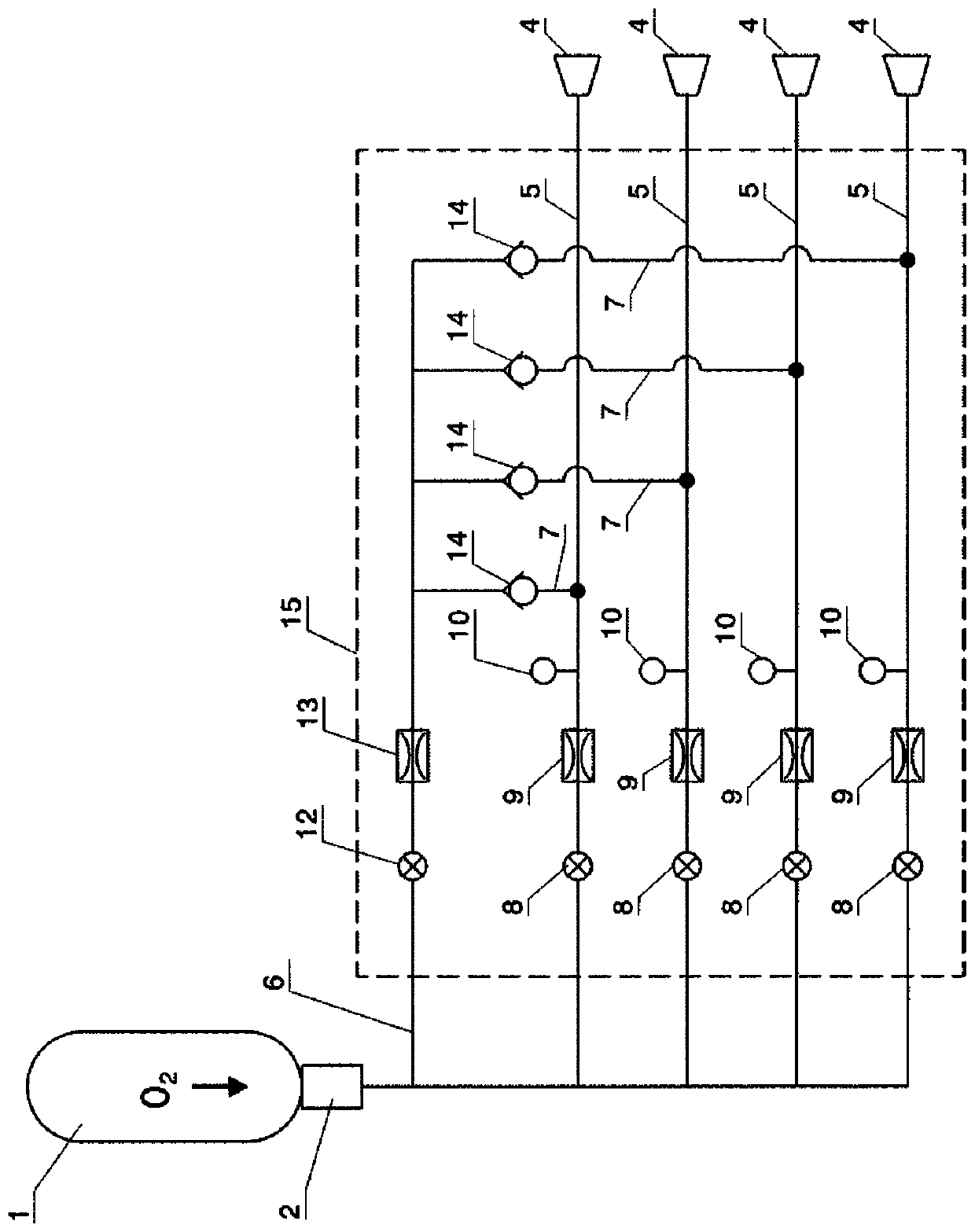
The invention discloses a breathing apparatus controlled through breath. The breathing apparatus comprises a face mask and a breathing control connector. A gas inlet connector of the face mask is connected with the breathing control connector through threads. A partition plate integrally formed together with the breathing control connector is arranged in the middle of an inner cavity of the breathing control connector. A plurality of vent holes are formed in the surface of the partition plate. Electromagnetic valves are arranged in the vent holes. A gas pressure sensor and a humidity sensor are arranged on the inner surface of the face mask. A gas flow sensor is arranged on the inner wall of the gas inlet connector of the face mask. According to the breathing apparatus, the oxygen requiring situations of patients are identified through the gas pressure sensor and the humidity sensor on the inner surface of the face mask, the opening and closing number of the electromagnetic valves in the vent holes in the partition plate is controlled through a breathing controller, and therefore the oxygen circulation amount of the breathing apparatus is controlled in this way, the oxygen requirement amounts of patients at each stage are ensured, and anoxia caused to patients when the breathing apparatus is not regulated in time is prevented.
Owner:田春燕
Breathing-controlled inhalation device for dry powders
InactiveUS20050118111A1Limit its operationImprove integrityRespiratorsPowder deliveryMedicineMeander
The invention relates to a breathing-controlled inhalation device for dry powders, having an air guide unit consisting of an essentially cylindrical body, said air guide unit comprising a flow passage provided alternately with constrictions and in each instance following enlargements, said constrictions and enlargements passing continuously one into another, and the flow passage for the air flowing through the air guide unit being of three-dimensional meander-like conformation.
Owner:GOLDEMANN RAUL +2
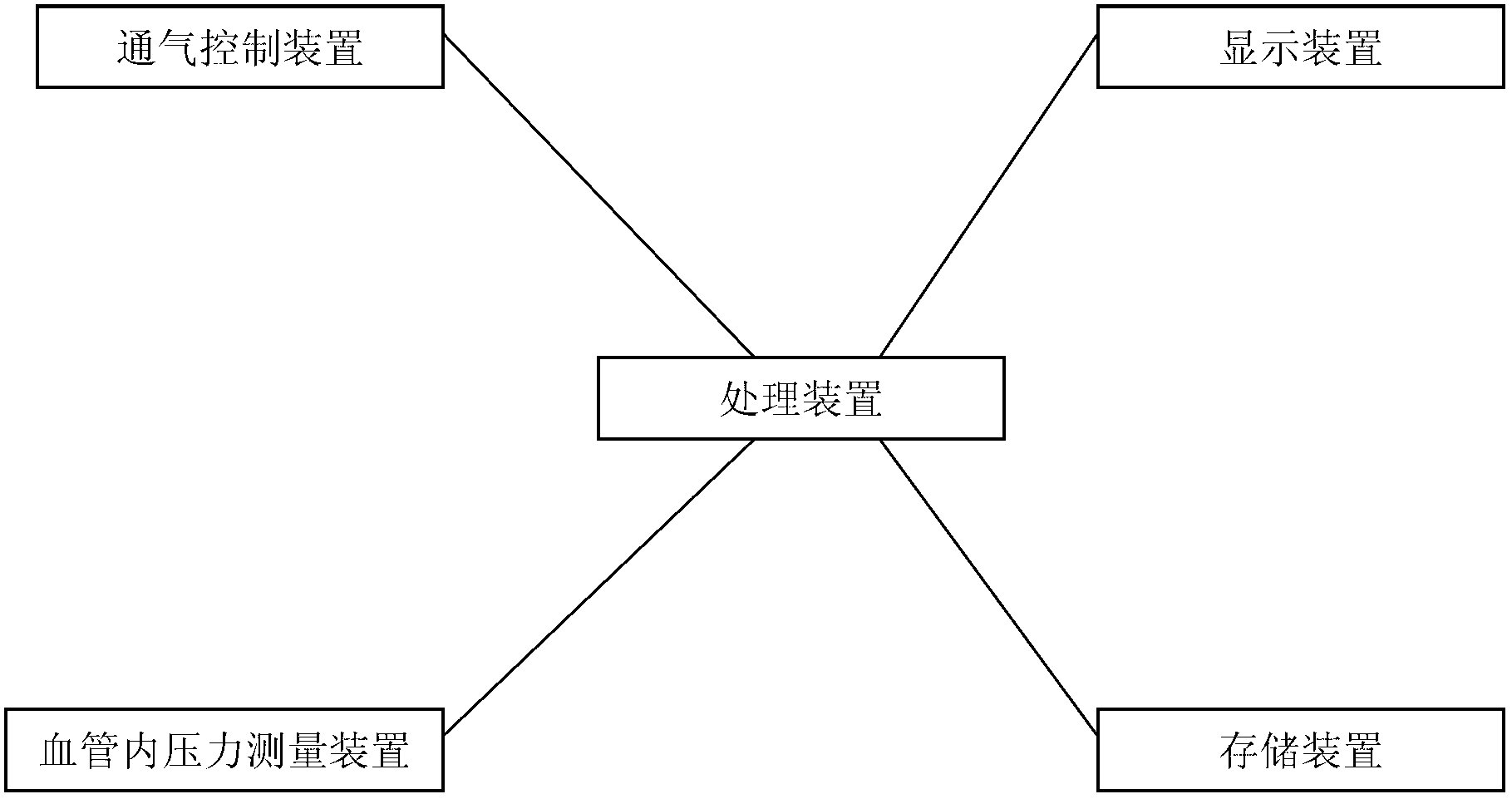
Breathing control system
PendingCN111420196AImprove accuracyImprove stability and securityRespiratorsMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationControl system
The invention discloses a breathing control system, and belongs to the field of breathing control. The system comprises a face mask, a first control device, a second control device, a buffer cavity, an air source device, an oxygen device and a humidifying device, wherein the face mask, the second control device, the buffer cavity and the first control device are sequentially connected; each of theair source device, the oxygen device and the humidifying device is provided with two interfaces; the two interfaces are respectively connected with the first control device and the second control device through air pipes; each corresponding air pipe is provided with an electromagnetic valve; and a plurality of monitoring and control modules are arranged in the first control device and the secondcontrol device and are used for realizing double control. Therefore, the whole respiratory control system has better safety stability and more timely response.
Owner:SOOCHOW UNIV AFFILIATED CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
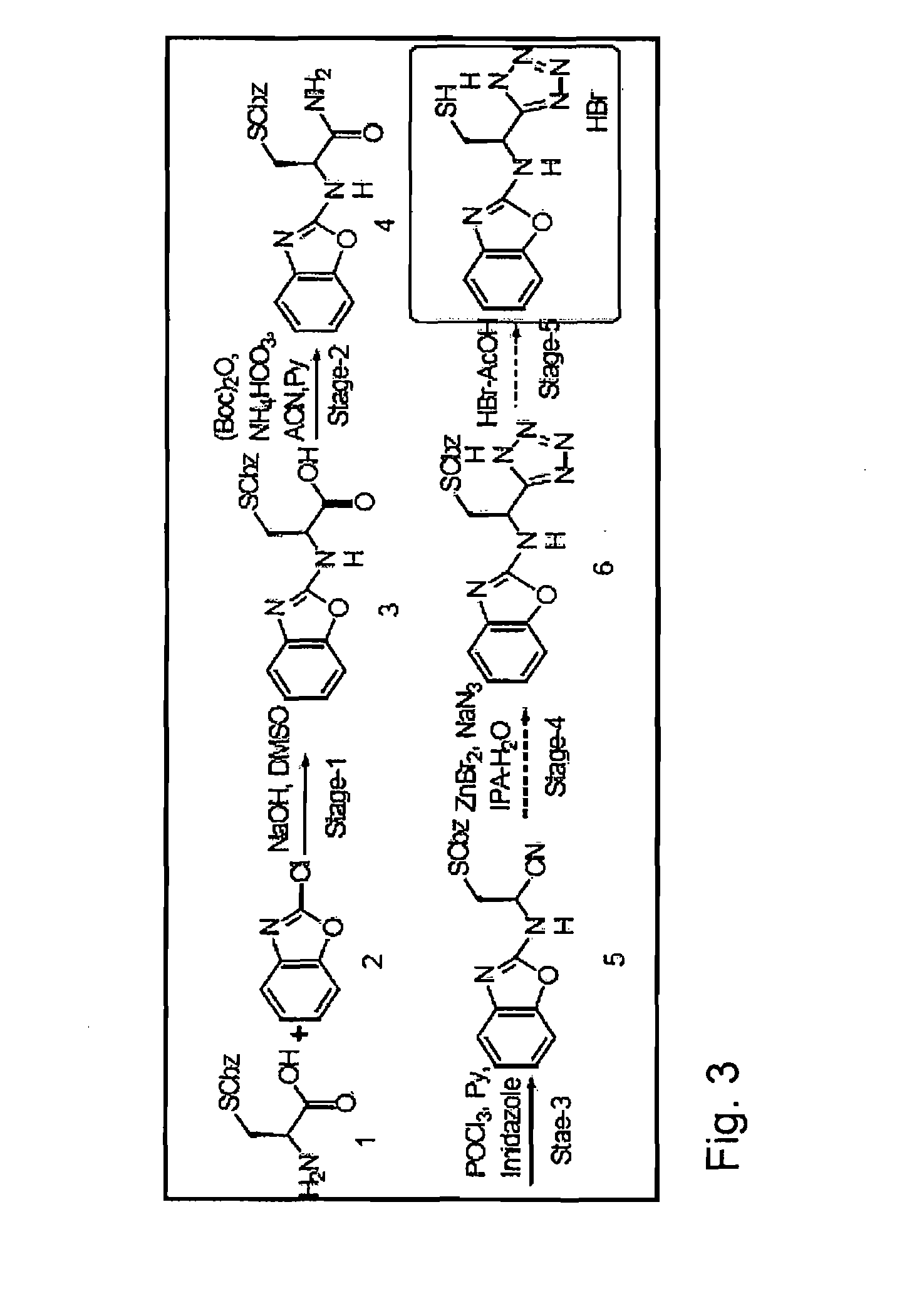
Breathing control modulating compounds, and methods of making and using same
ActiveUS10294228B2Minimizes deliveryMaximizes deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseMedicine
The present invention includes compounds that are useful in the prevention and / or treatment of breathing control diseases or disorders in a subject in need thereof. The present invention also includes a method of preventing and / or treating a respiratory disease or disorder in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound and / or composition of the invention. The present invention further includes a method of preventing destabilization or stabilizing breathing rhythm in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a compound and / or composition of the invention.
Owner:NEURAD LTD
Movable infectious disease isolating and transferring device
The invention relates to a movable infectious disease isolating and transferring device, and belongs to the technical field of medical instrument. The movable infectious disease isolating and transferring device comprises a main body, wherein a patient lying plate is arranged on the upper side of the main body; a breathing mask fixed platform is arranged on the front side of a pillow; a breathing mask connecting tube is arranged on the breathing mask fixed platform; the breathing mask connecting tube is connected to a breathing mask connecting head; a breathing mask is arranged on the breathing mask connecting head; an oxygen tube connecting nozzle is arranged on the front side of an oxygen bottle; the oxygen tube connecting nozzle is connected to a breathing box by virtue of an oxygen tube; a ventilation hose is arranged on the upper side of the breathing box; the upper side of a high-temperature sterilization box is connected to a breathing control box by virtue of a connecting tube; the high-temperature sterilization box is connected to a filter disinfection bottle by virtue of a high-temperature gas conduit; a built-in cannula is arranged inside the filter disinfection bottle; and an exhaust tube is arranged on the right side of the high-temperature gas conduit. The isolating and transferring device disclosed by the invention is complete in function and convenient; and the device, when used for transferring patients of infectious diseases, is time-saving and labor-saving, scientific and convenient, safe and efficient, so that the working difficulty of doctors is relieved.
Owner:翟德翠
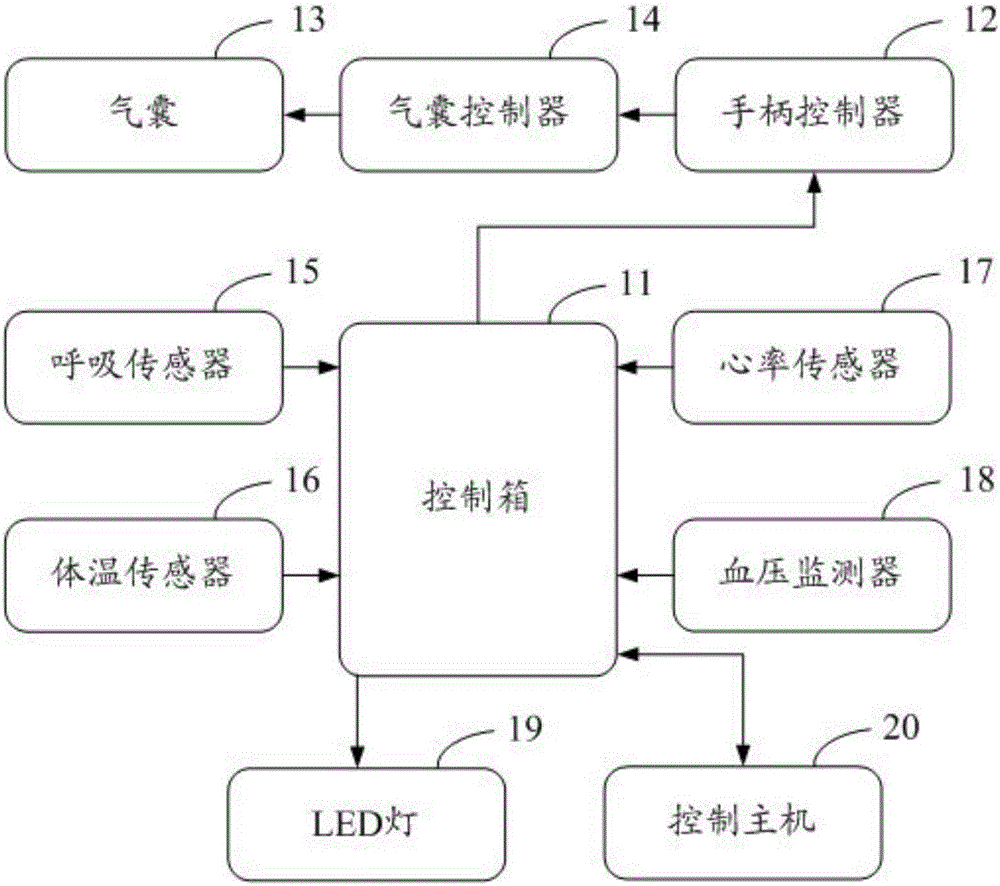
Active breathing control system
InactiveCN106237548ABreath-hold safetyClose safeEvaluation of blood vesselsRespiratory organ evaluationControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses an active breathing control system which comprises a control box, a handle controller, an airbag, an airbag controller, a respiration sensor, a body temperature sensor, a heart rate sensor, a blood pressure monitor, an LED lamp and a control host machine. The airbag controller is connected to the airbag. The control box is connected to the airbag controller and is used for controlling the airbag controller to allow the airbag to be inflated or deflated. The handle controller is arranged between the control box and the air controller and is used for manually controlling the inflation and deflation of the airbag. The respiration sensor, the body temperature sensor, the heart rate sensor, and the blood pressure monitor are connected to the control box. The LED lamp is connected to the control box and is started when the airbag is inflated. The control box is connected to the control host machine which is used for emitting a beam closing command to a linear accelerator according to the signals monitored by the body temperature sensor, the heart rate sensor, and the blood pressure monitor. According to the system, the closing of a ray beam can be timely controlled, and the effect of precise radiotherapy is improved.
Owner:广州市岱尼欣贸易有限公司
Method for controlling tidal volume of anaesthesia machine by adjusting volume and pressure
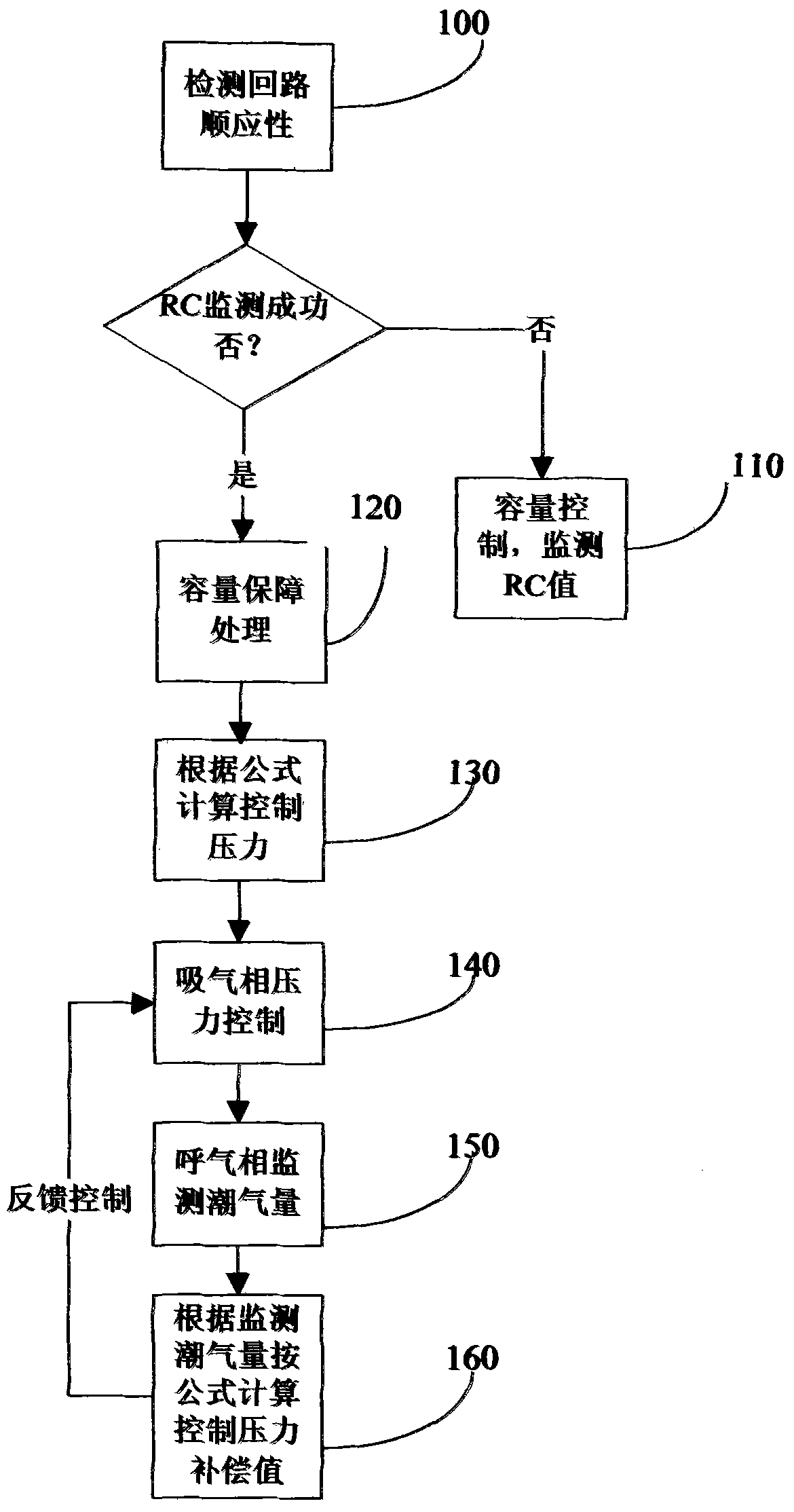
The invention discloses a method for controlling the tidal volume of an anaesthesia machine by adjusting the volume and pressure. The method comprises the steps that pipeline compliance self-checking is carried out on the anaesthesia machine and a breathing machine in the starting process; when breathing control is started and the R and C values of a patient are not correctly monitored, a volume ventilation mode is adopted, and the R and C values of the patient in the ventilation period are monitored; if the R and C values of the patient are correctly monitored, a compliance compensation volume ensuring method is utilized for monitoring the inhalation volume of the patient in the inhalation period, and volume ensuring treatment is carried out after the volume reaches a set value; a system standard control pressure value P is calculated, inhalation valve and exhalation valve collaborative pressure control is carried out according to the value P, the tidal volume, volume difference value and pressure difference value deltaP of the patient are calculated in the exhalation stage, feedback compensation control is carried out on the calculated value P according to deltaP, and the volume and the pressure are both ensured.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE CHANGFENG CO LTD
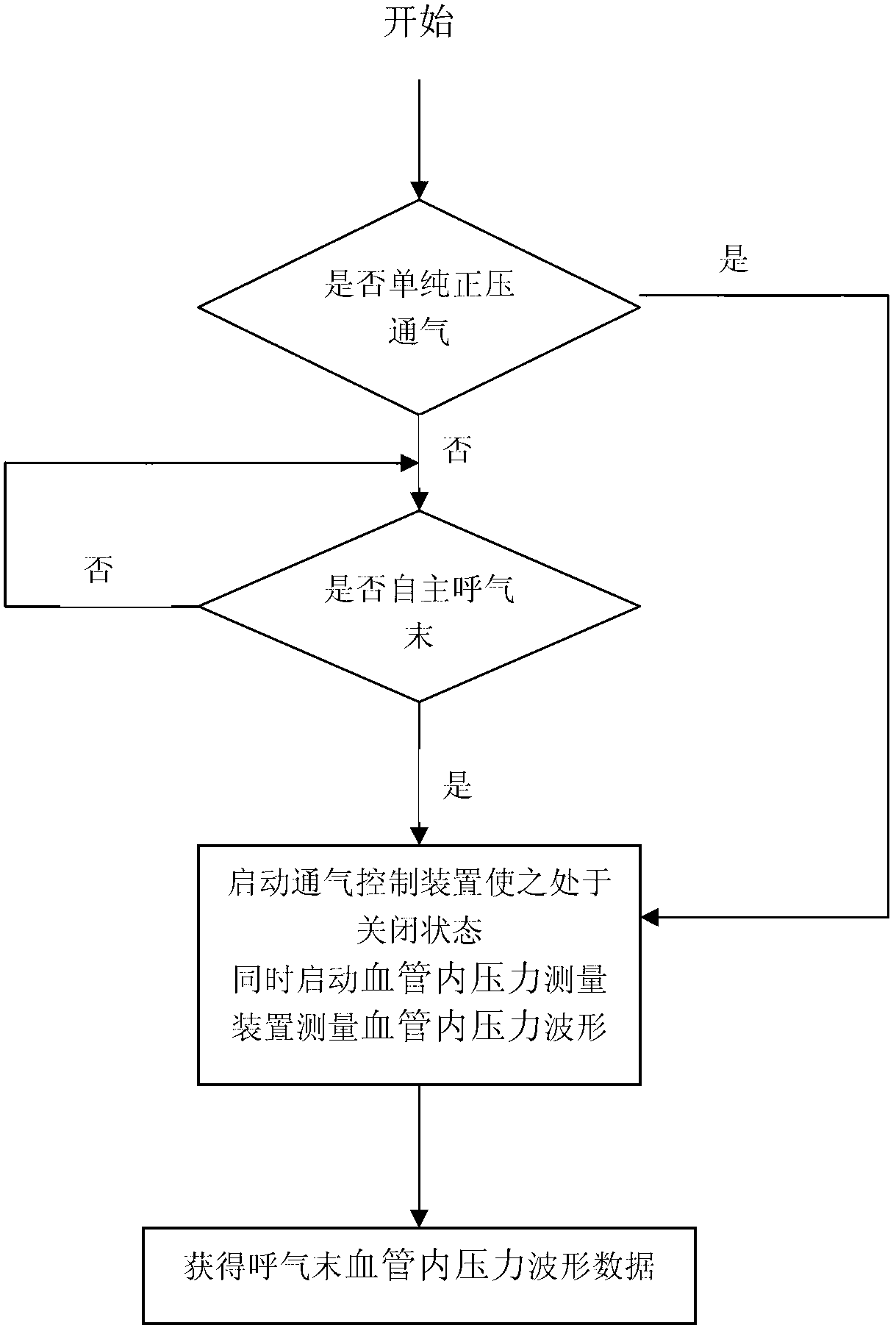
Method for acquiring end expiration intravascular pressure wave data through expiratory apnea method
InactiveCN102697489AFast and accurate analysisEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyAutonomous breathingBlood vessel
The invention provides a method for acquiring end expiration intravascular pressure wave data through an expiratory apnea method. The method specifically comprises the following steps: for a patient with pure positive airway pressure, a breathing control device is started directly to enable a breathing machine to be in an expiratory apnea state, air supply of positive airway pressure is stopped, at the time, positive airway pressure is of an expiration phase, when the control device is stopped, the breathing machine supplies air normally, accordingly, variation is caused to vascular pressure wave, and the flat part before the variation is intravascular pressure end expiration point, so that the intravascular pressure wave of the expiration phase can be obtained; and for patient combining positive airway pressure with autonomous respiration, the breathing control device is enabled to be in a close state through being started at the end of autonomous inspiration, positive airway pressure is stopped to supply air, at the time, autonomous respiration of the patient and positive airway pressure of the breathing machine are both of an expiration phase, when the control device is stopped or autonomous respiration occurs, accordingly, variation is caused to vascular pressure wave, and the flat part before the variation is intravascular pressure end expiration point, so that end expiration intravascular pressure wave data can be obtained. The method is rapid and accurate in analysis, and the obtained intravascular pressure is closer to objective end expiration intravascular pressure. The method is high in clinical compliance and is particularly applicable to emergency department, anesthesia department, cardiology, department of cardiac surgery, ICU (Intensive Care Unit) and other departments where patients are required to be saved quickly.
Owner:天津市第五中心医院
Control of Breathing During MRI-Based Procedures
ActiveUS20170135599A1Measure directlyReduce in quantityRespiratory masksMedical devicesEngineeringBreathing control
The valve of an active breathing control (ABC) device can be driven by the output of the navigator channel of the MRI scanner, rather than by inference from a measured breath flow rate. Where the MRI scanner is integrated with a radiotherapy device, the MRI data can be used to trigger the enforced breath-hold by the ABC, and the radiotherapy delivered while the ABC valve is shut. If the MRI data pertains to the actual position of the tumour, then the ABC device will (in effect) hold the tumour at a precise and reproducible point for treatment.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
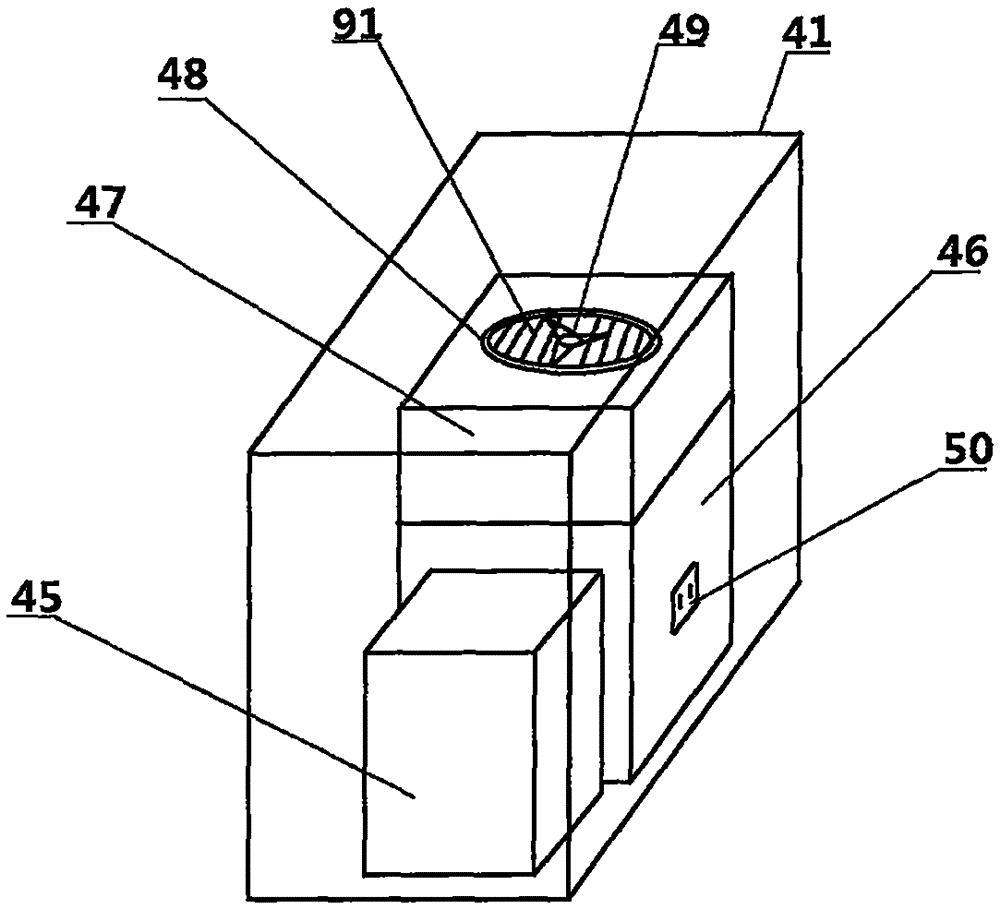
Low-energy-consumption type intelligent physiotherapy breathing equipment
InactiveCN105797248AAvoid displacementImprove stabilityRespiratorsMedical devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceRespirator
The invention relates to low-energy-consumption type intelligent physiotherapy breathing equipment. The equipment comprises a supporting frame, a central control console arranged on the supporting frame and a storage box arranged below the supporting frame, moving devices are arranged at the bottom of the storage box, the supporting frame is provided with a breathing mechanism, and the breathing mechanism comprises a breathing interface arranged on the supporting frame, a mouth mask support and a mouth mask. According to the low-energy-consumption type intelligent physiotherapy breathing equipment, brake pads are trodden through feet, then the brake pads can be stuck by universal wheels, thereby the universal wheels are prevented from displacement, and stability of the equipment is improved; after a non-steady-state oscillator in a breathing control circuit is powered on to work, the output end of an integrated circuit outputs oscillation impulse signals with the frequency being 25.40 Hz, a first audion and a second audion are made to be conductive intermittently, a relay and a motor work intermittently, work efficiency of the equipment is improved, and power consumption is lowered; meanwhile, the resistance value of an adjusting resistor is adjusted, working frequency of a breathing machine is changed, and power consumption of the equipment is further lowered.
Oxygen emergency supply device for passengers in aircraft, and aircraft with same
InactiveCN111434363ASimple structureReduce weightFire rescueRespiratory apparatusEmergency SupplyRespiratory mask
The invention relates to an oxygen emergency supply device for passengers in an aircraft. The oxygen emergency supply device for passengers in the aircraft comprises an oxygen source, the oxygen source is provided with a plurality of pulsed breathing masks which are connected to the oxygen source by pipelines, a single stop valve is arranged in each pipeline to the corresponding breathing mask, and each single stop valve is switched to a shut-off state in an inoperative state. Furthermore, the oxygen emergency supply device is provided with a pulse-type breathing control device for operating each single stop valve and auxiliary pipelines, the auxiliary pipelines connect the oxygen source with the breathing masks under the condition of bypassing the single stop valves, and each auxiliary pipeline is connected with the corresponding pipeline to the corresponding breathing mask or the corresponding breathing mask via the corresponding stop valve. The auxiliary pipelines are connected to the oxygen source via a central stop valve which is switched to an open state in an inoperative state.
Owner:B E 航空系统有限公司
Breathing control system used for accurate radiation therapy
InactiveCN106861057AReduce offsetImproved Healing AccuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyControl systemLung tumor
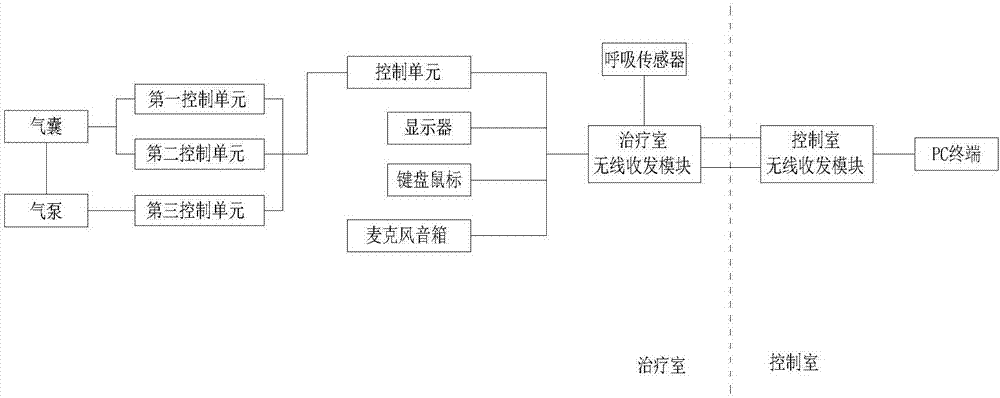
The invention discloses a breathing control system used for an accurate radiation therapy. The system comprises a gasbag, a gas pump, a control unit, a breathing sensor, a treatment-chamber wireless transmit-receive module, a control-chamber wireless transmit-receive module, a PC terminal and a communication tool. The control unit, the breathing sensor and the communication tool are connected to the treatment-chamber wireless transmit-receive module. The treatment-chamber wireless transmit-receive module is connected to the control-chamber wireless transmit-receive module. The control-chamber wireless transmit-receive module is connected to the PC terminal. The control unit comprises a first control unit, a second control unit and a third control unit. The first control unit is connected to the gas pump. The gas pump is connected to the gasbag. The second control unit and the third control unit are connected to the gasbag. The breathing control system used for the accurate radiation therapy can help a patient carry out breathing control so that a purpose of reducing lung tumor migration following human body breathing motion is achieved; treatment accuracy is increased; a clinic application condition is low; and the system is suitable for widespread popularity.
Owner:王玉廷
S-Nitrosothiol Compounds and Related Derivatives
InactiveUS20100105685A1Stabilizing breathing rhythm of a mammalConvenient and smoothBiocideOrganic chemistryS-NitrosylationMedicine
The present invention is directed to a method of treating a lack of normal breathing control including the treatment of apnea and hypoventilation associated with sleep, obesity, certain medicines and other medical conditions. In an aspect, the invention is directed to treating disordered control of breathing by administering an composition comprising a single compound which treats lack of normal breathing. In another aspect, the invention is directed to treating disordered control of breathing by administering an composition comprising a combination of two or more compounds, at least one of which treats lack of normal breathing. In an aspect, a compound is an S-nitrosylating agent.
Owner:GALLEON PHARMA INC
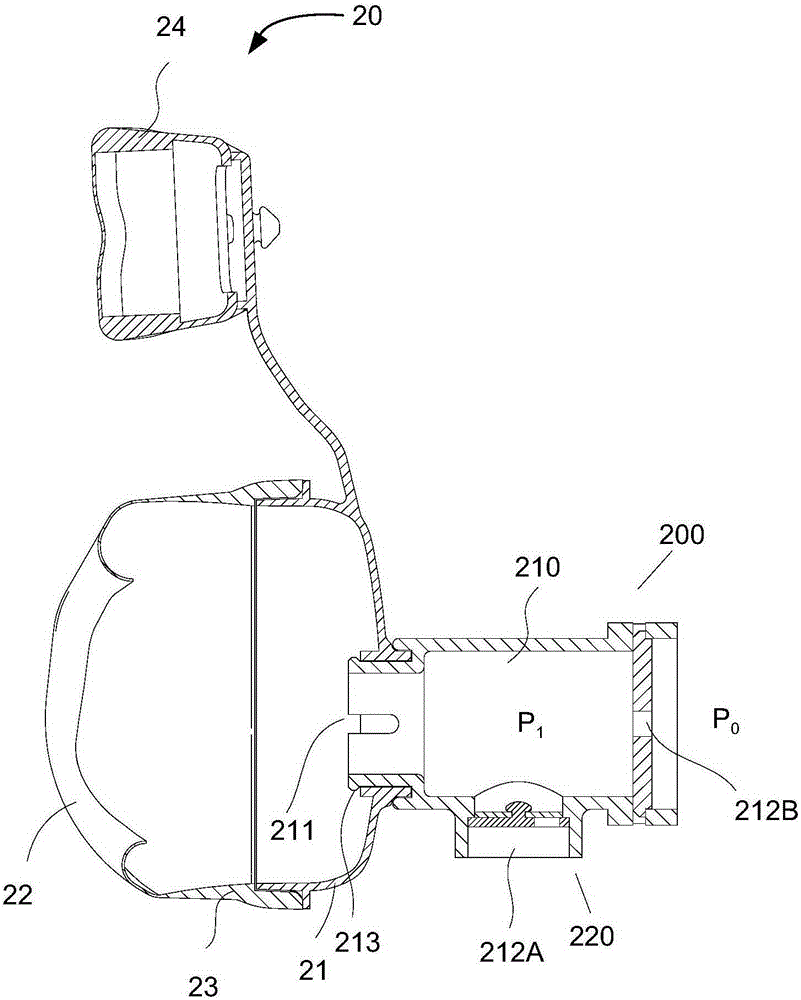
Breathing control device and breathing mask equipment with same
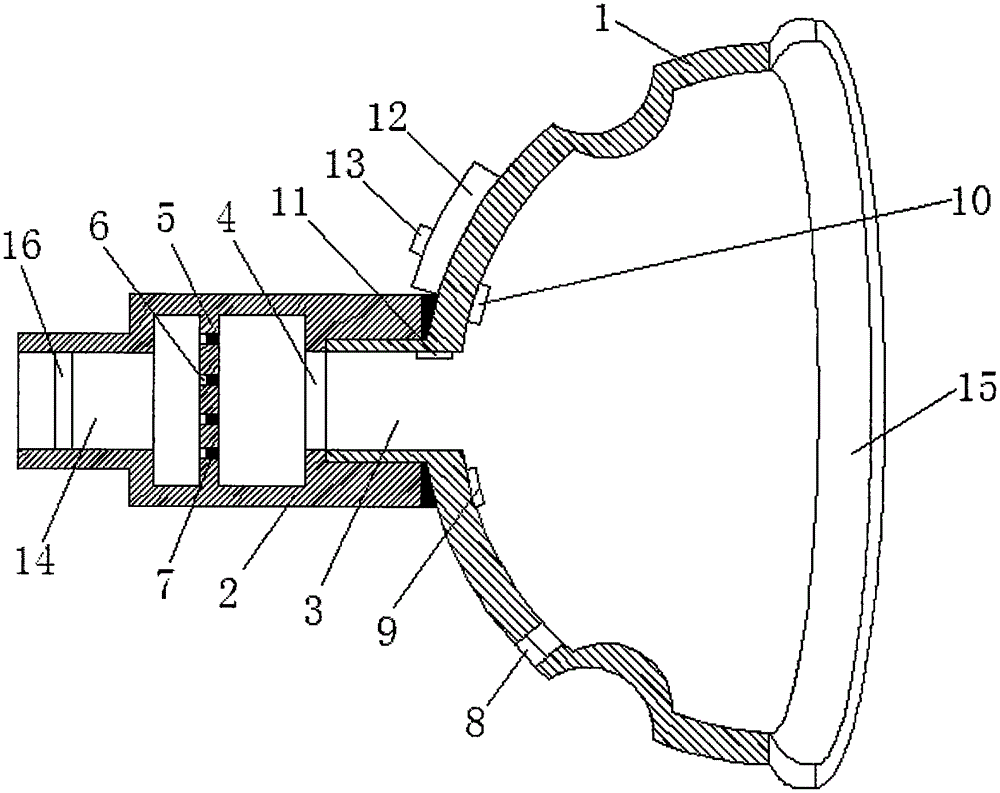
The invention provides a breathing control device and breathing mask equipment with the same. The breathing control device comprises a cavity, and one or more valve components, wherein one or more gas conveying openings as well as a mask vent communicated with a breathing mask are formed in the cavity; the valve components are arranged in one or more of the gas conveying openings, matched with the gas conveying openings to form a gas inlet and a gas outlet, and used for communicating the gas inlet with the mask vent when pressure in the cavity is lower than or equal to the atmosphere, and communicating the gas outlet with the mask vent when the pressure in the cavity is higher than the atmosphere; the cross section area of the gas inlet is larger than that of the gas outlet; the gas outlet is used for keeping the pressure in the cavity to be higher than the atmosphere when a patient expires. The breathing control device has the advantages that the positive pressure function of an expiring phase is realized, so as to avoid discomfort of the patient caused by continuous positive pressure; during use, the breathing control device and the breathing mask equipment are not required to be connected with a positive pressure gas supply device, pipeline and the like, so that the patient can move conveniently, and needs not to carry the positive pressure gas supply device while going out.
Owner:BMC MEDICAL
Breathing-controlled inhalation device for dry powders
InactiveUS7174890B2Limit its operationImprove integrityRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsMedicineMeander
The invention relates to a breathing-controlled inhalation device for dry powders, having an air guide unit consisting of an essentially cylindrical body, said air guide unit comprising a flow passage provided alternately with constrictions and in each instance following enlargements, said constrictions and enlargements passing continuously one into another, and the flow passage for the air flowing through the air guide unit being of three-dimensional meander-like conformation.
Owner:GOLDEMANN RAUL +2
Method and apparatus for measuring change in blood pressure by respiration control
InactiveUS9918645B2ElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsEmergency medicineBreathing control
A method and an apparatus are provided for measuring a change in blood pressure caused by respiration control. A number of respirations per minute is measured based on a heart rate when a respiration exercise begins. Respiration of a subject is induced until the number of respirations per minute reaches a predetermined number of respirations per minute. A pulse transit time is calculated during the respiration exercise, a blood pressure value associated with the pulse transit time is calculated, and the blood pressure value is outputted.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Control of breathing during MRI-based procedures
ActiveUS10433760B2Measure directlyReduce in quantityRespiratory masksMedical devicesEngineeringBreathing control
The valve of an active breathing control (ABC) device can be driven by the output of the navigator channel of the MRI scanner, rather than by inference from a measured breath flow rate. Where the MRI scanner is integrated with a radiotherapy device, the MRI data can be used to trigger the enforced breath-hold by the ABC, and the radiotherapy delivered while the ABC valve is shut. If the MRI data pertains to the actual position of the tumor, then the ABC device will (in effect) hold the tumor at a precise and reproducible point for treatment.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Novel orally bioavailable breathing control modulating compounds, and methods of using same
The present invention includes compositions that are useful in the prevention and / or treatment of breathing control diseases or disorders in a subject in need thereof. The present invention also includes a method of preventing and / or treating a respiratory disease or disorder in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a composition of the invention. The present invention further includes a method of preventing destabilization or stabilizing breathing rhythm in a subject in need thereof, comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a composition of the invention.
Owner:GALLEON PHARMA INC
Breathing machine with return air treatment function
ActiveCN113813483AGuaranteed fixed pressureAchieving assisted breathingRespiratorsEngineeringRespiratory disease
The invention relates to medical related equipment, in particular to a breathing machine with an air return treatment function, and solves the problems that an existing mechanically-controlled breathing machine can not adjust a fed oxygen supply amount according to the specific conditions of patients, in addition, parts of patients have respiratory diseases, when the breathing machine is adopted without treatment, an oxygen supply part in the breathing machine is polluted. An oxygen amount adjusting device, a breathing control device and a treatment pipeline are mounted and fixed on a shell; other devices are mounted through the shell; the oxygen amount adjusting device controls and adjusts an oxygen feeding amount according to the requirements of a patient; the breathing control device automatically controls breathing actions; and the treatment pipeline controls and processes air exhaled by the patient. By use of the breathing machine, the oxygen feeding amount can be adjusted, and the lung pressure of the patient is guaranteed to be fixed, and therefore, the functions of assisting in breathing and processing return air can be achieved.
Owner:深圳市大方牙科技有限公司
Combination s-nitrosothiol-based pharmaceutical products for restoring normal breathing rhythm
Owner:GALLEON PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com