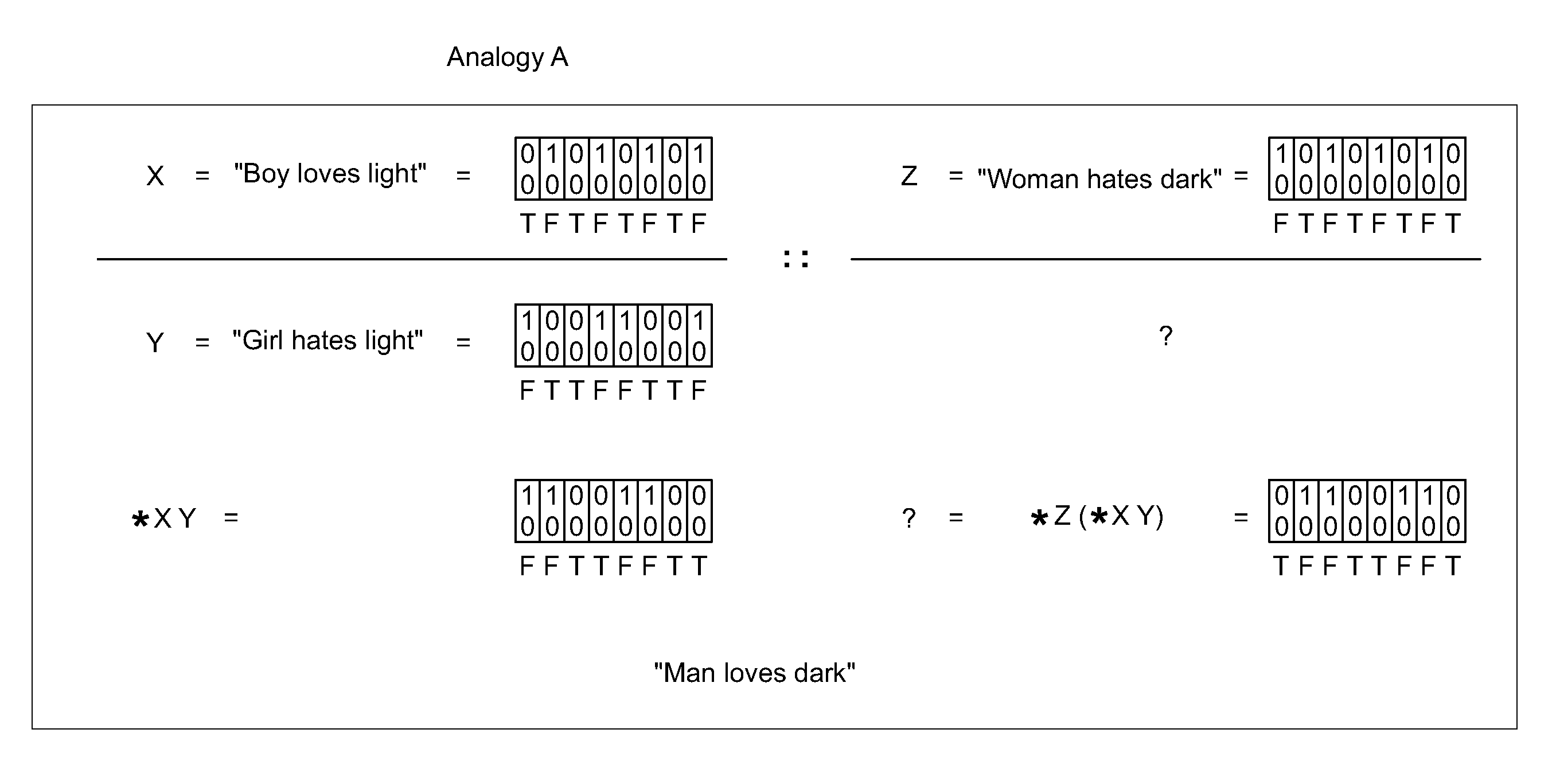Patents
Literature
31 results about "Transformation operator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
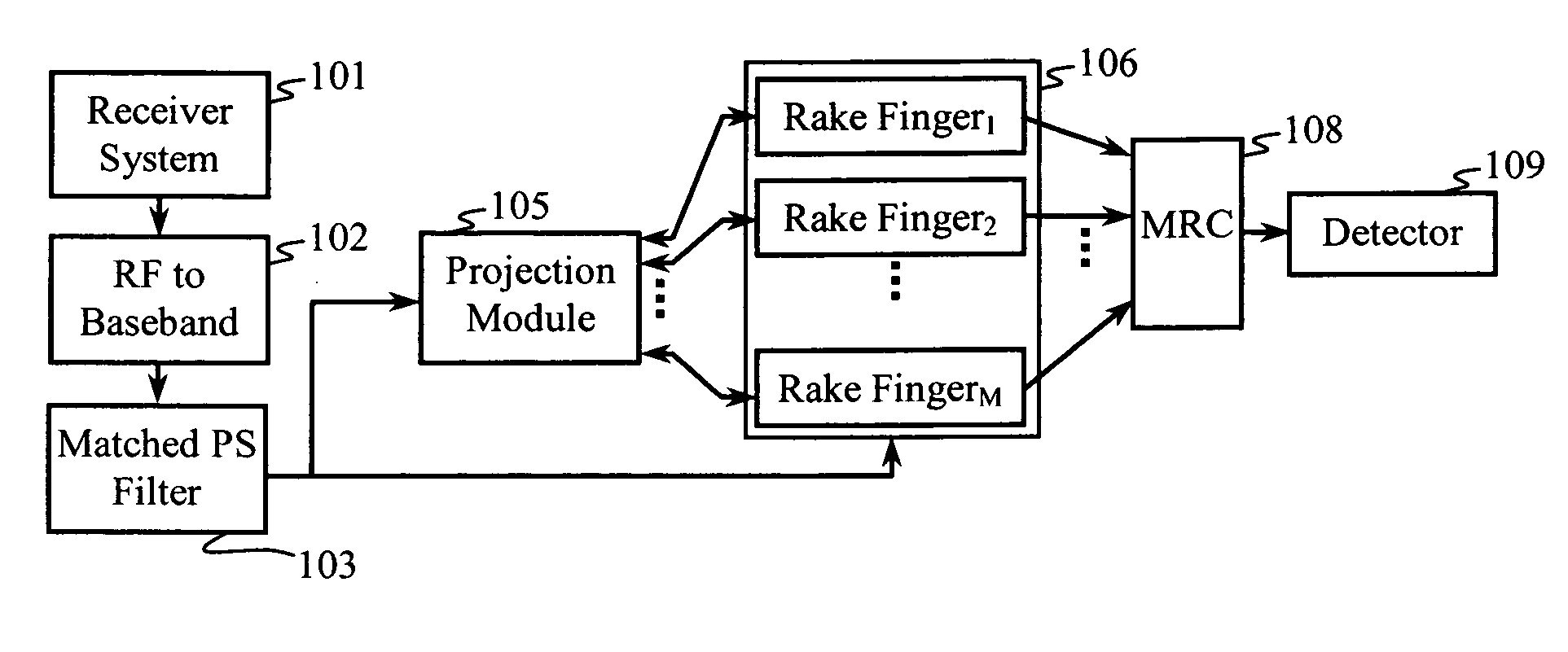
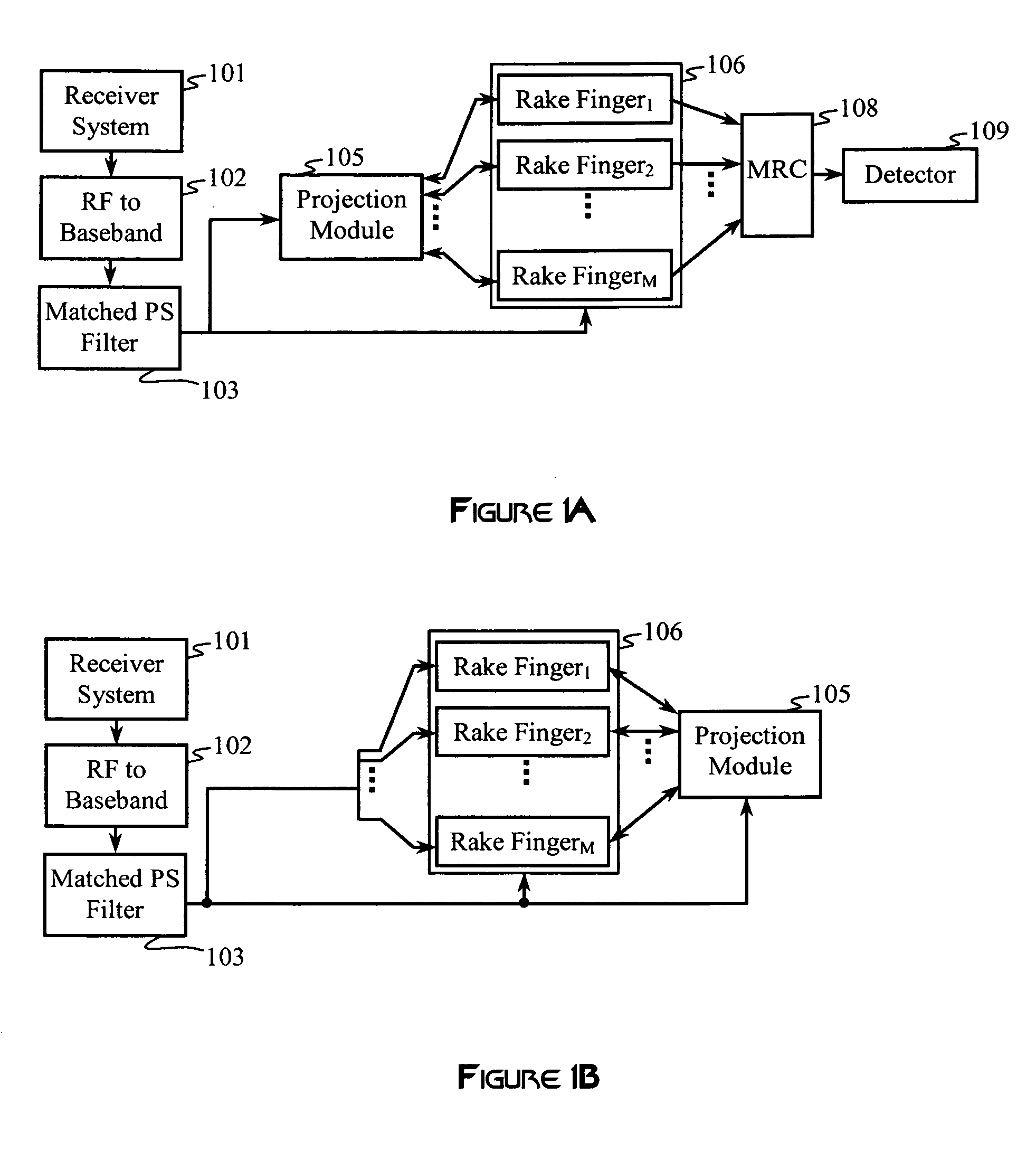
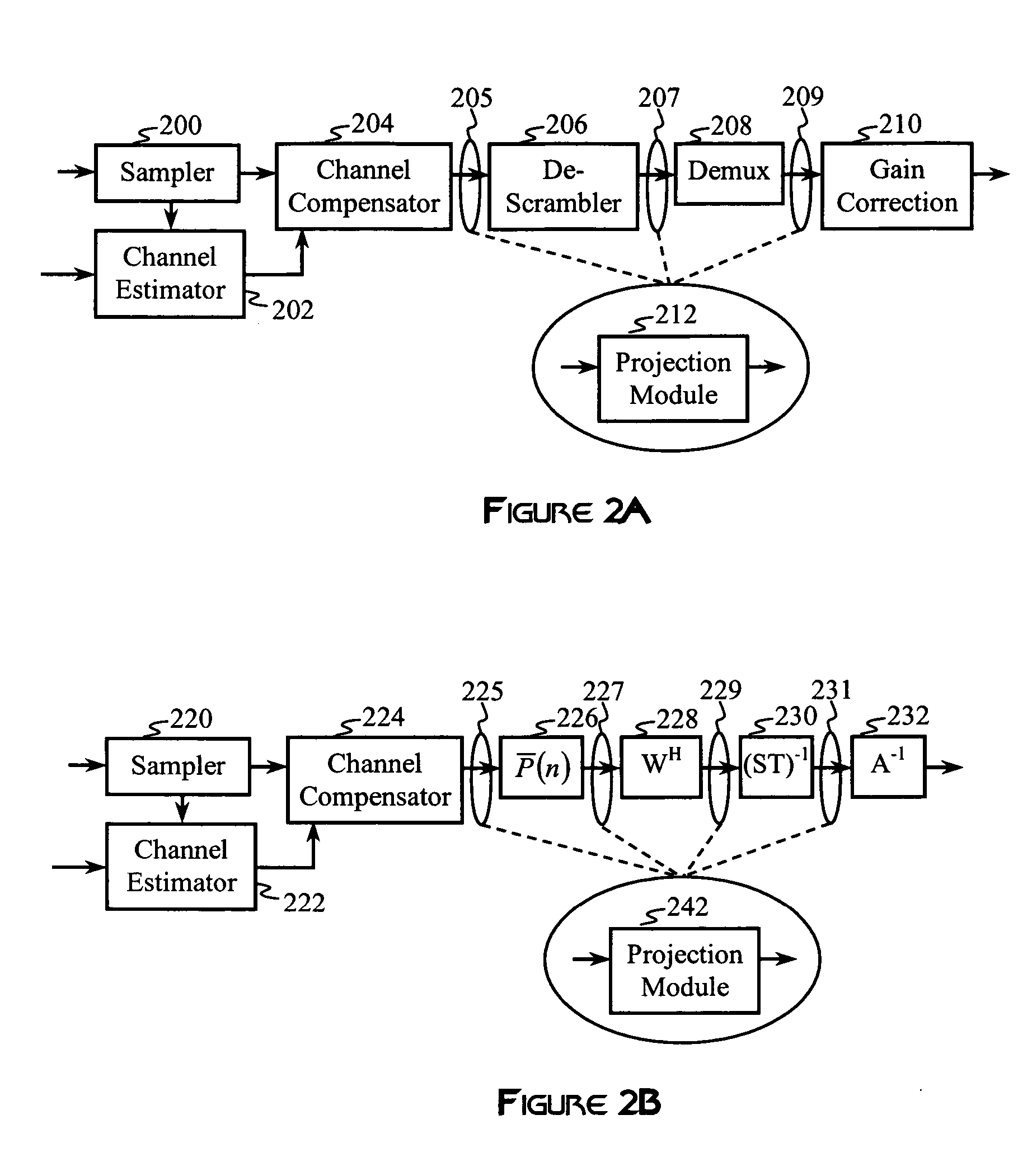
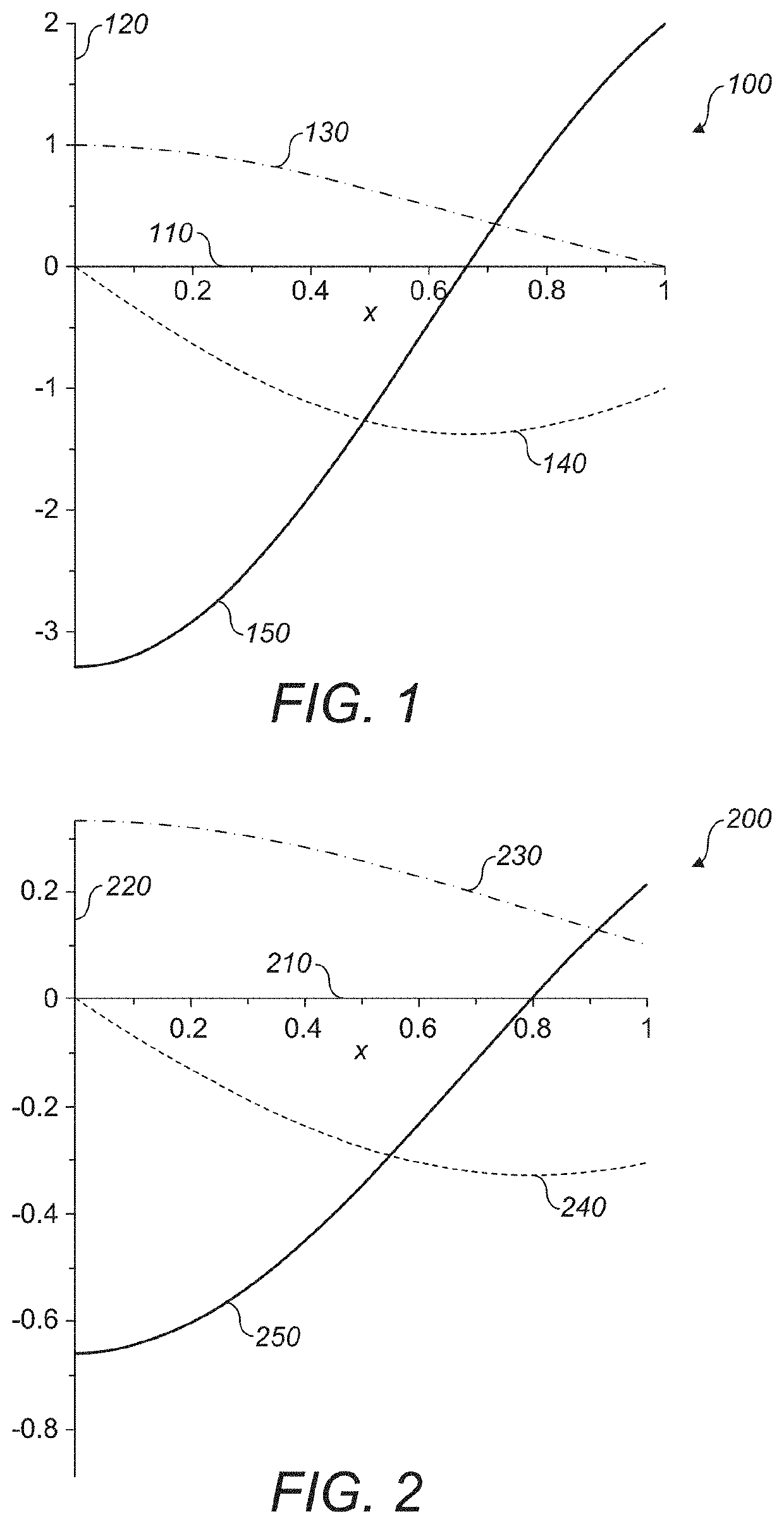
Construction of projection operators for interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050180364A1Reduce in quantityReduce complexitySecret communicationRadio transmissionTime domainTransceiver
Interference cancellation is performed in a CDMA receiver by projecting a received signal onto a subspace that is orthogonal to a signal selected for removal. An interference matrix or a combined interference vector is used to construct an interference-canceling projection operator. Confidence weights may be provided to components of the interference matrix or the interference vector based on estimation errors or relative strengths of interfering signals. Complexity reduction of the orthogonal projection operator may be achieved by providing for simplifying approximations that remove terms and operations. A linear transformation operator may be applied to the rows and / or columns of the interference matrix or the interference vector prior to construction of the orthogonal projection. Interference cancellation techniques may be configured for processing signals in a transmit-diversity system or a receive-diversity system using time and / or frequency-domain implementations and space and / or wave-number implementations of the transceiver.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
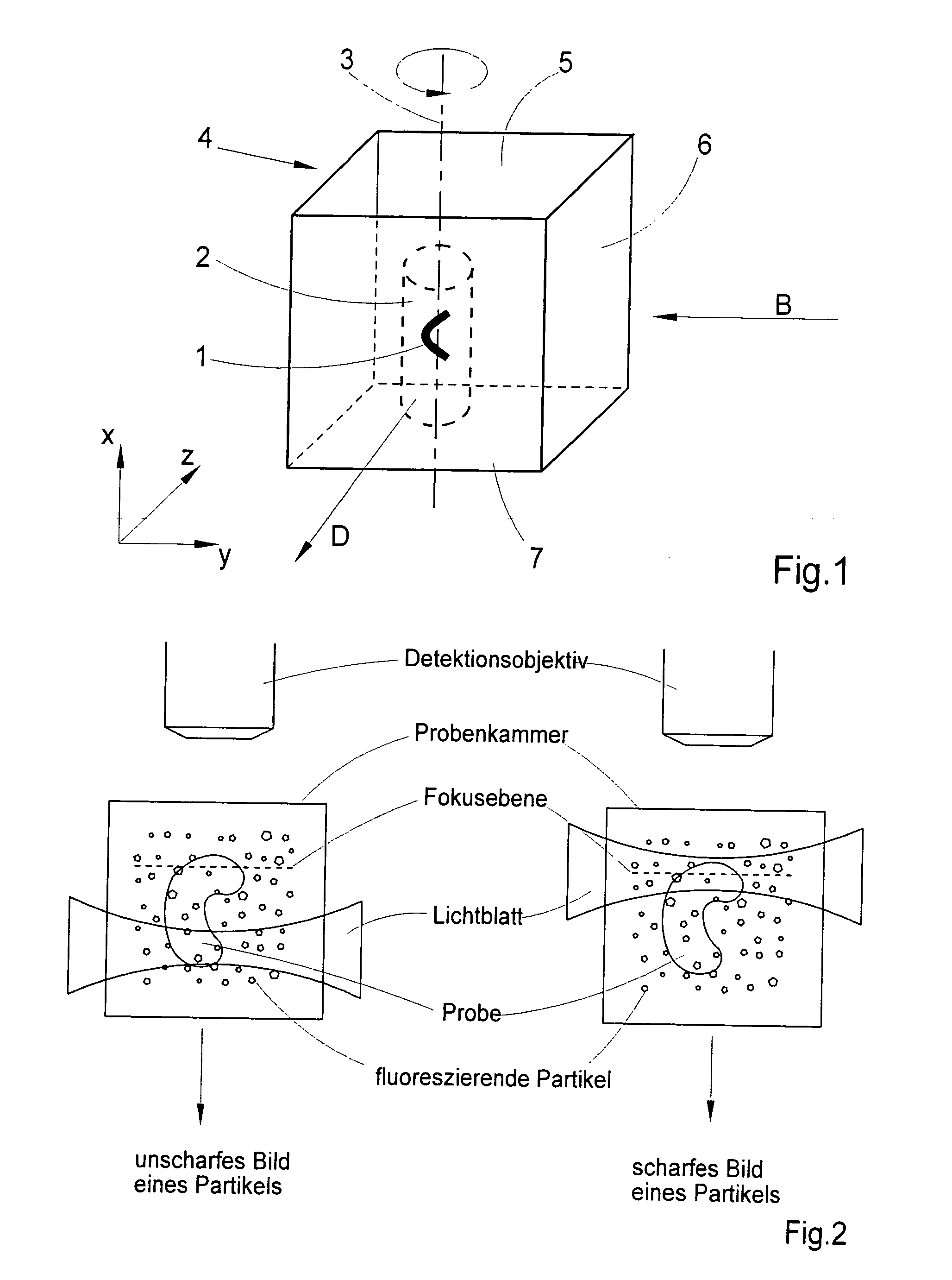
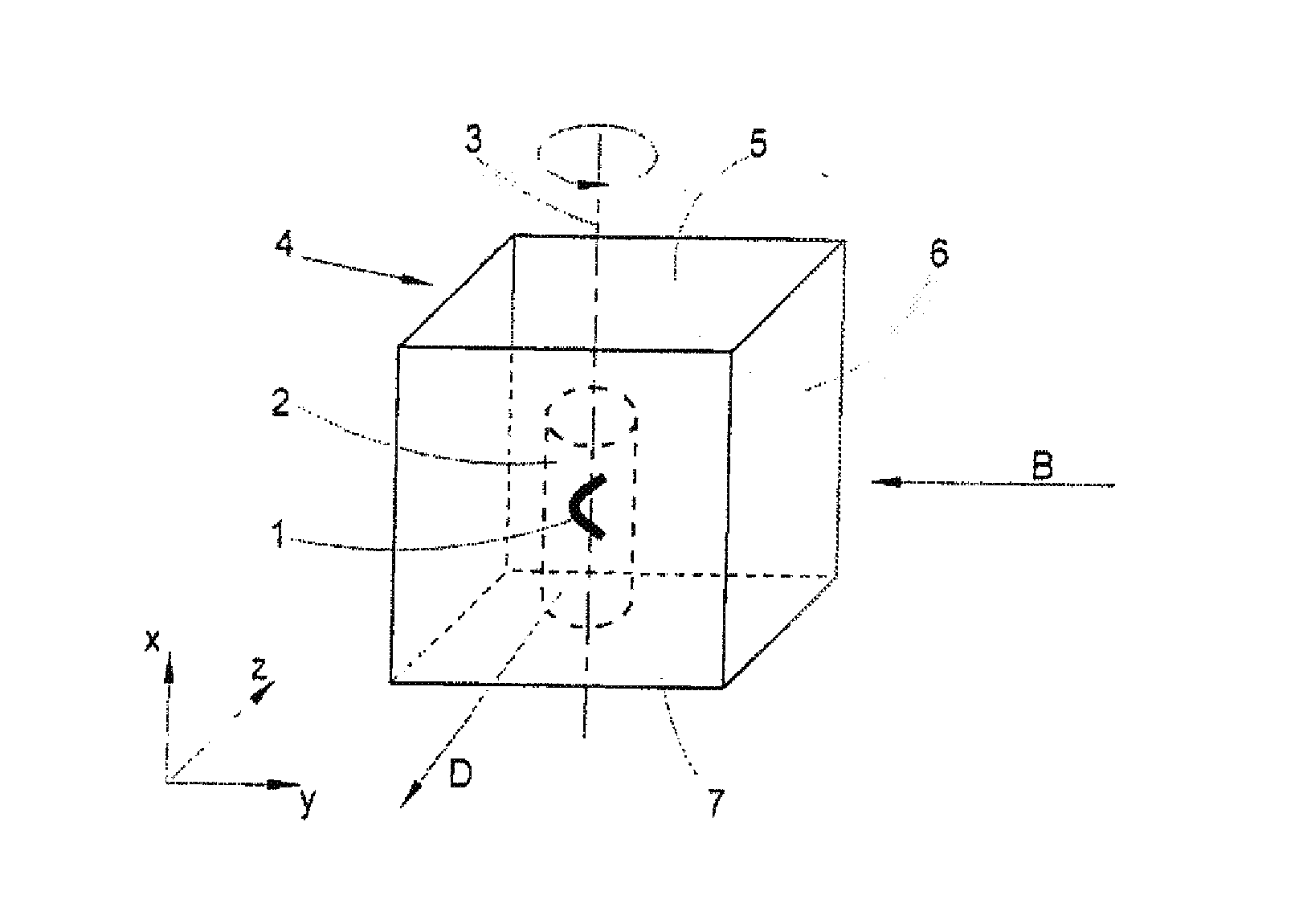
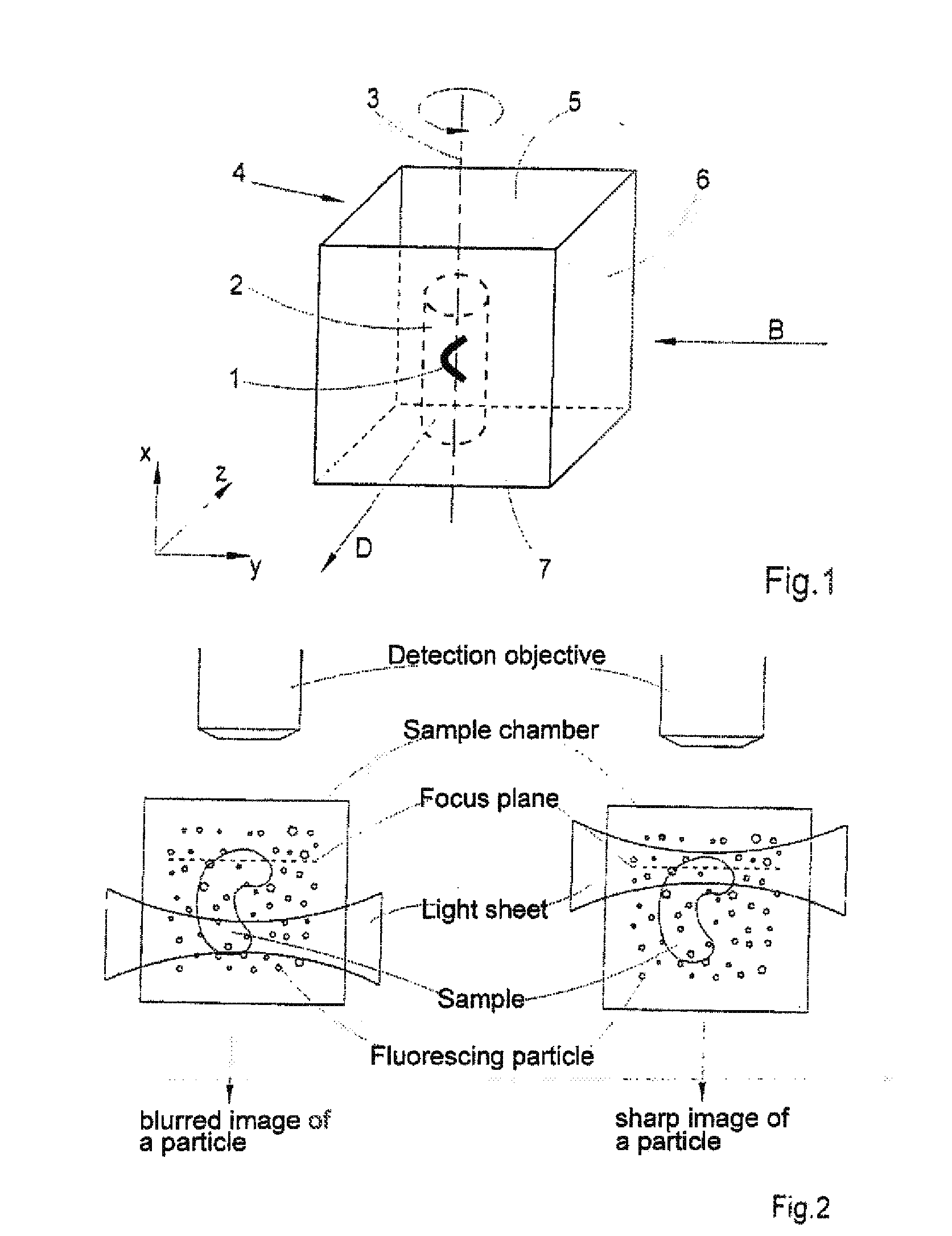
Method for the microscopic three-dimensional reproduction of a sample
InactiveUS20100201784A1Avoid shadow effectMore resolutionImage analysisMicroscopesSpatially resolvedFluorescence
A method for the three-dimensional imaging of a sample in which image information from different depth planes of the sample is stored in a spatially resolved manner, and the three-dimensional image of the sample is subsequently reconstructed from this stored image information is provided. A reference structure is applied to the illumination light, at least one fluorescing reference object is positioned next to or in the sample, images of the reference structure of the illumination light, of the reference object are recorded from at least one detection direction and evaluated. The light sheet is brought into an optimal position based on the results and image information of the reference object and of the sample from a plurality of detection directions is stored. Transformation operators are obtained on the basis of the stored image information and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional image of the is based on these transformation operators.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method for the microscopic three-dimensional reproduction of a sample
ActiveUS20130094755A1Improve image qualityLess subjectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatially resolvedFluorescence
A method for the three-dimensional imaging of a sample in which image information from different depth planes of the sample is stored in a spatially resolved manner, and the three-dimensional image of the sample is subsequently reconstructed from this stored image information is provided. A reference structure is applied to the illumination light, at least one fluorescing reference object is positioned next to or in the sample, images of the reference structure of the illumination light, of the reference object are recorded from at least one detection direction and evaluated. The light sheet is brought into an optimal position based on the results and image information of the reference object and of the sample from a plurality of detection directions is stored. Transformation operators are obtained on the basis of the stored image information and the reconstruction of the three-dimensional image of the is based on these transformation operators.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
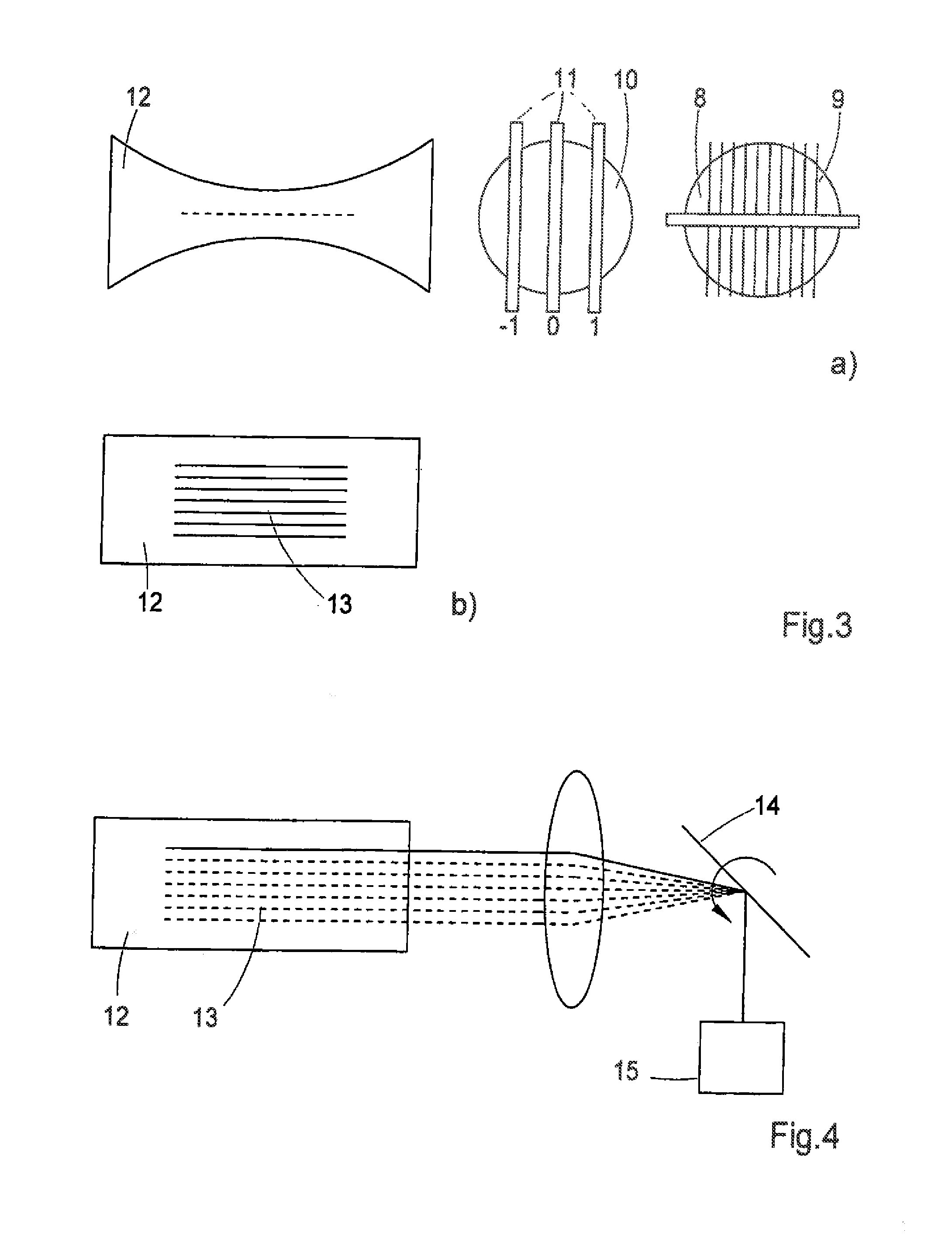
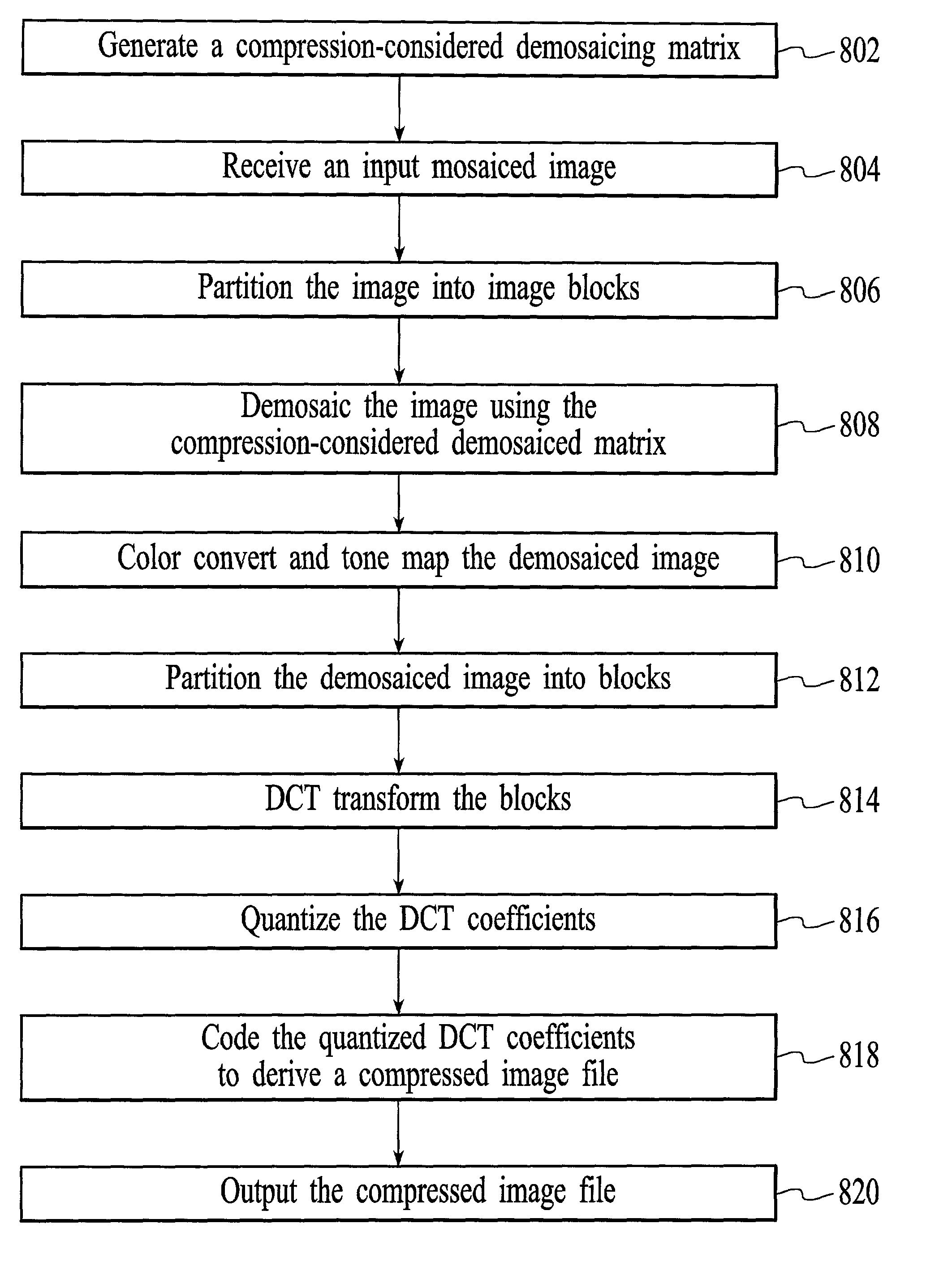
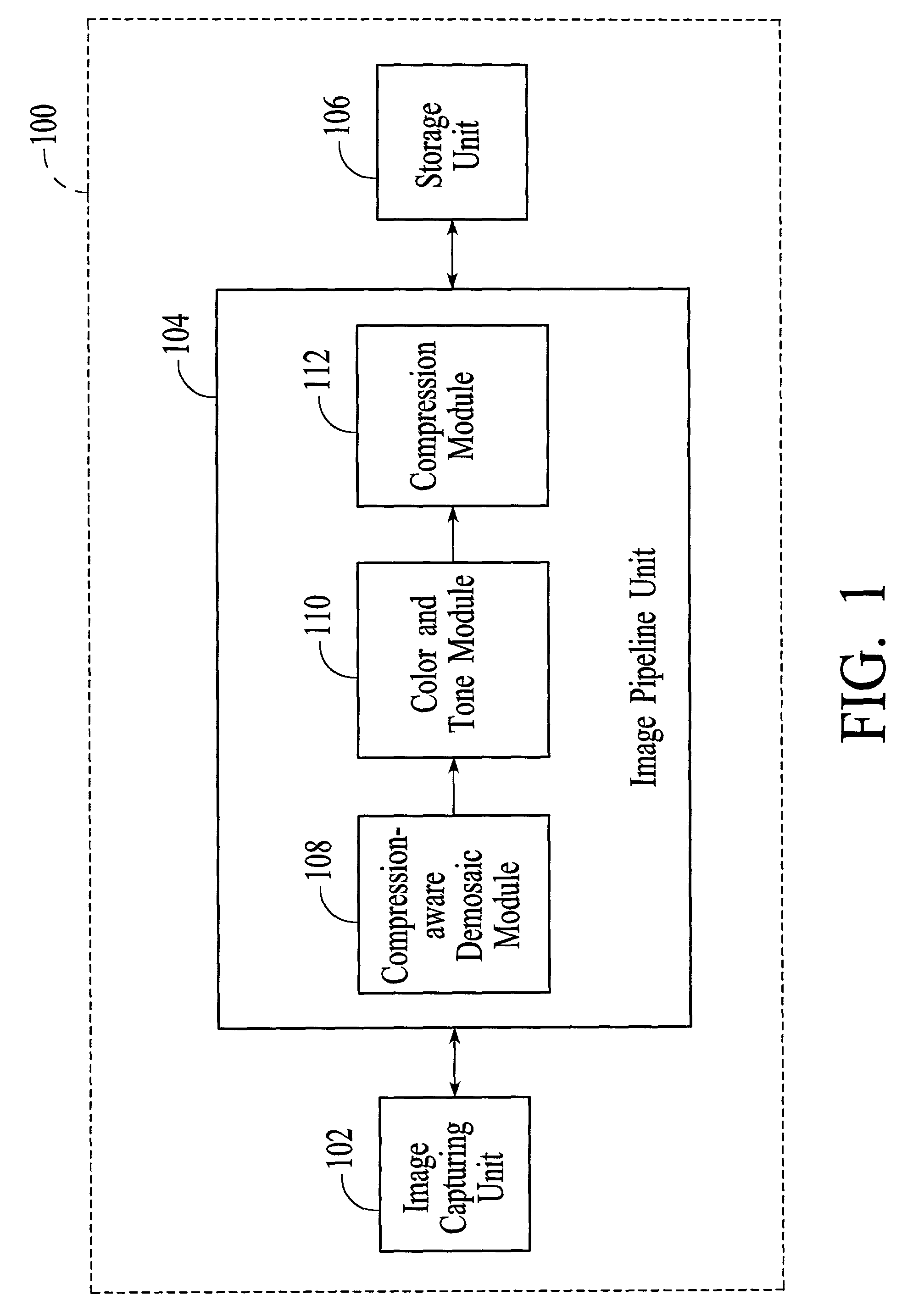
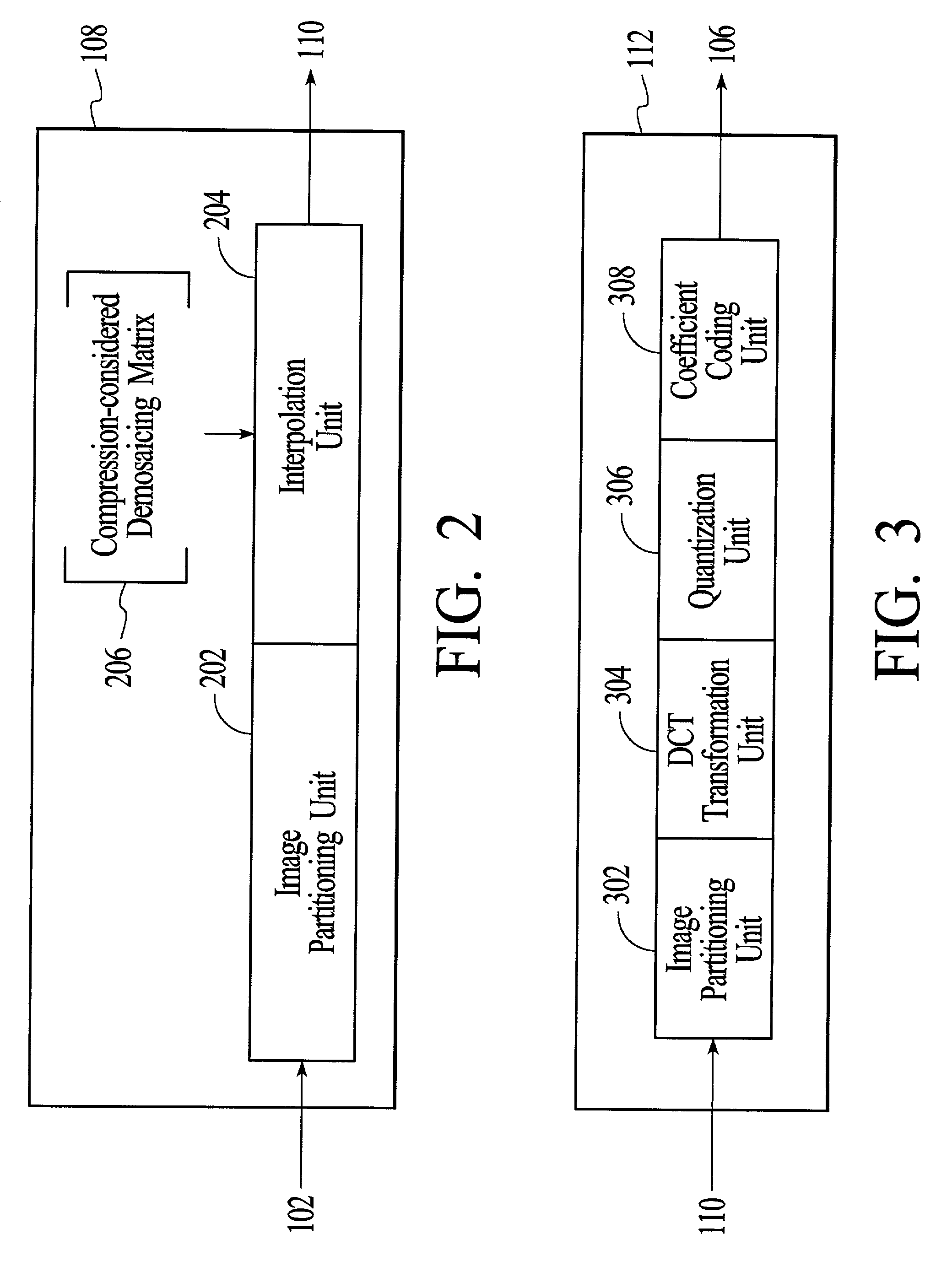
System and method for demosaicing raw data images with compression considerations
InactiveUS7155066B2Quality improvementImprove methodImage enhancementColor television with pulse code modulationColor imageOriginal data
A system and method for processing mosaiced images utilizes a compression-aware demosaicing process that takes into consideration a subsequent compression process. The compression-aware demosaicing process is performed using a compression-considered demosaicing operator that incorporates a color space conversion operator and a frequency-based transformation operator, which are typically associated with the compression process. Consequently, the overall efficiency of the system and method is significantly increased. Furthermore, the compression-aware demosaicing process produces artifacts that complement the artifacts produced by the subsequent compression process such that the artifacts are less visible in the final color images, which increases the quality of the final color images.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
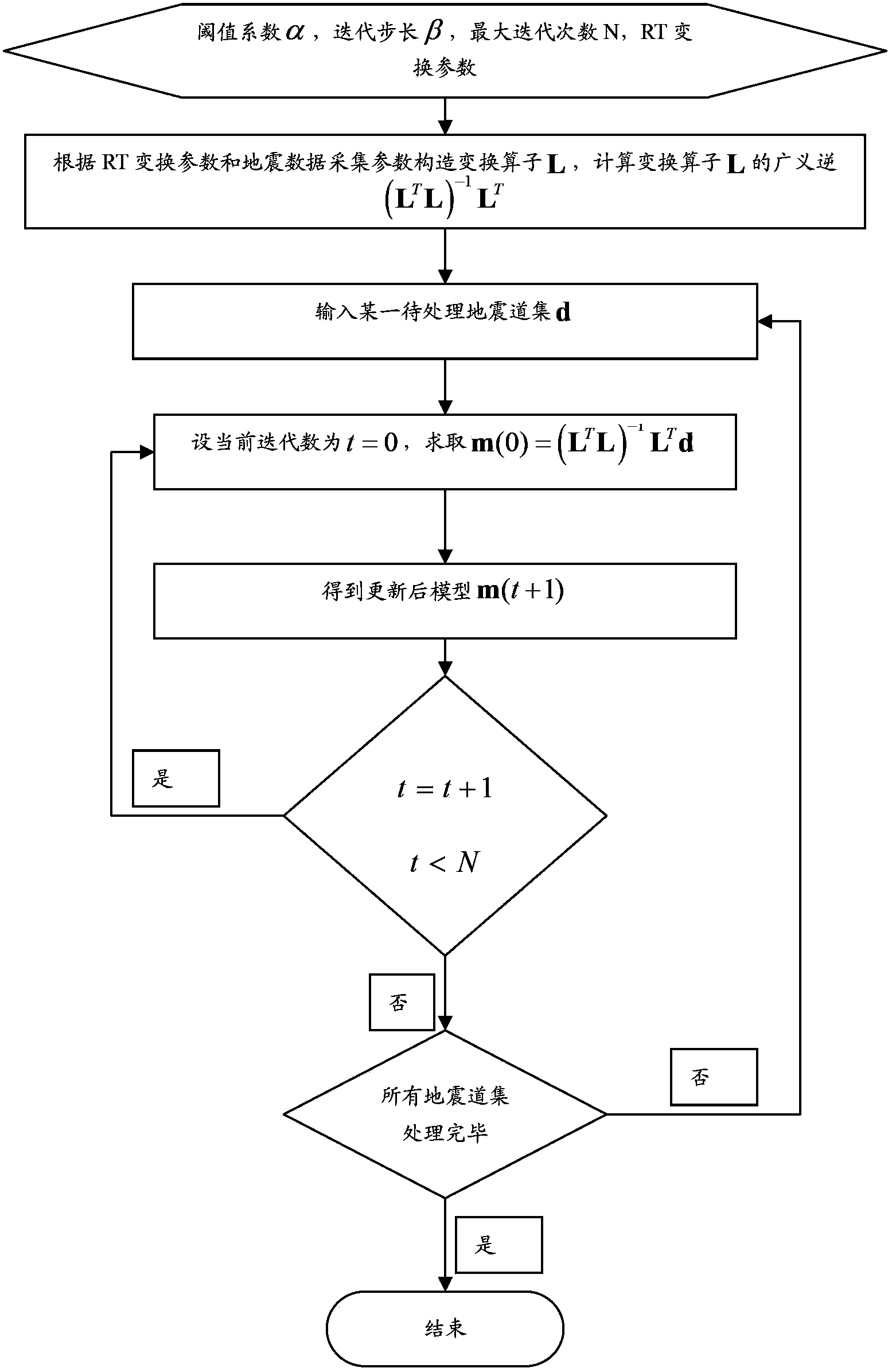
Quick sparse Radon transformation method based on iterative shrinkage
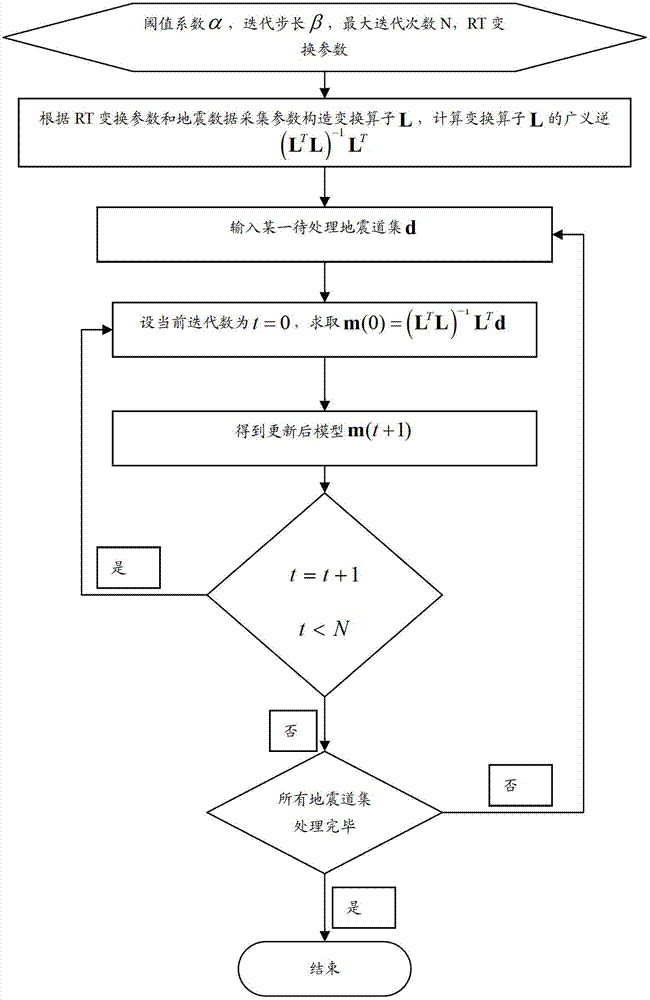
ActiveCN102879824ASmall amount of calculationAdaptive processingSeismic signal processingGeneralized inverseRadon
The invention discloses a quick sparse Radon transformation method based on iterative shrinkage. The quick sparse Radon transformation method comprises the following steps: firstly, setting an initial variable value; secondly, constructing a transformation operator L and calculating generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L; thirdly, treating a seismic channel set d to be treated by utilizing the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L; and lastly, judging if all channel sets in a seismic data cube are treated, if not, continuing to treat the seismic channel set d to be treated by utilizing the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L, and if so, ending. According to the quick sparse Radon transformation method, for one seismic data cube collected by adopting the same collection parameters, the generalized inverse of the transformation operator L only needs to be calculated once, then the transformation operator L and the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L are applied to all seismic channel sets, thereby greatly reducing calculated amount; and the iterative shrinkage algorithm only includes product operation of simple matrixes and vectors and threshold operation, greatly reduces the calculated amount relative to the conventional sparse Radon transformation, and better adapts to treatment of practical seismic data.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
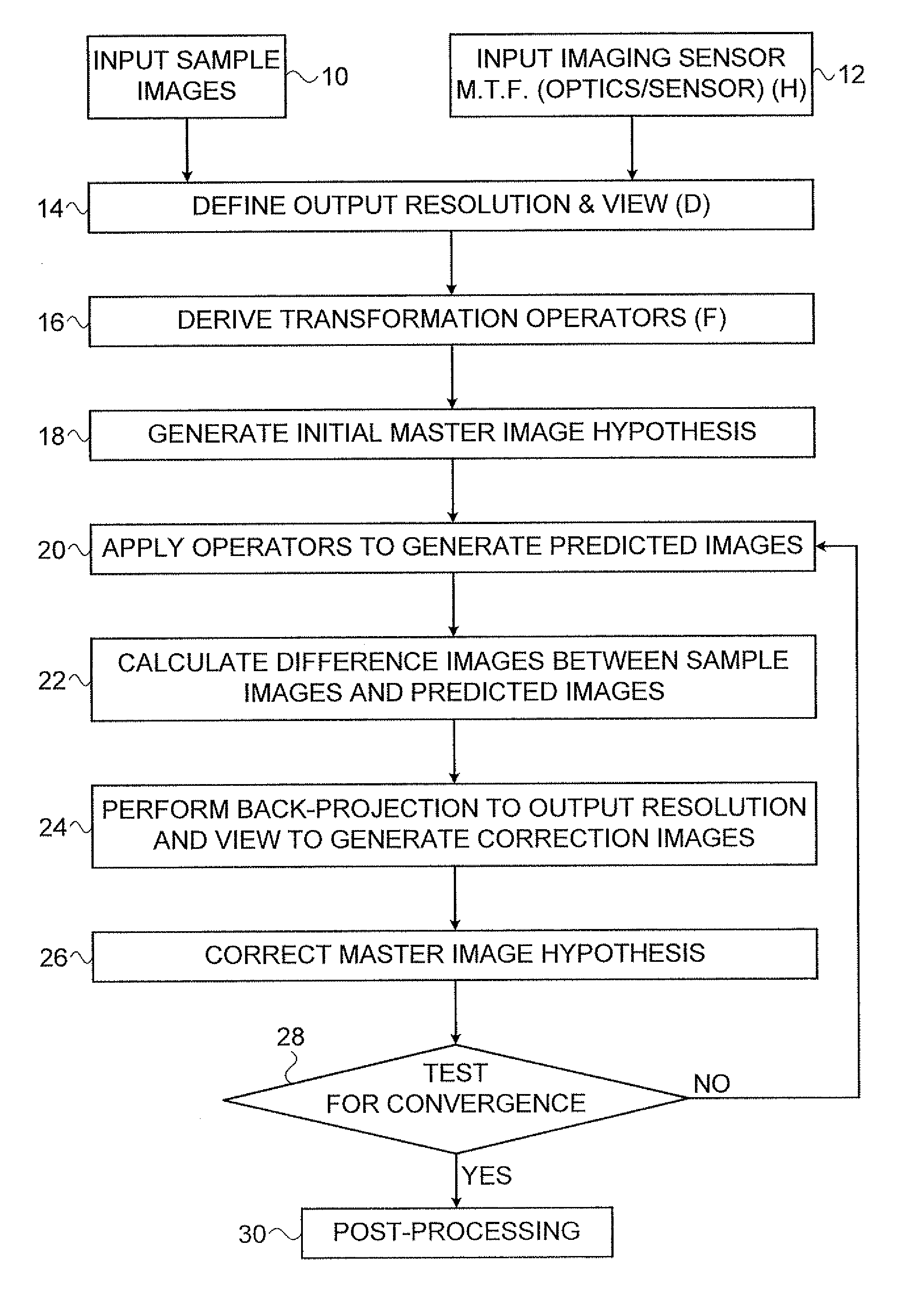
Super-resolution image processing
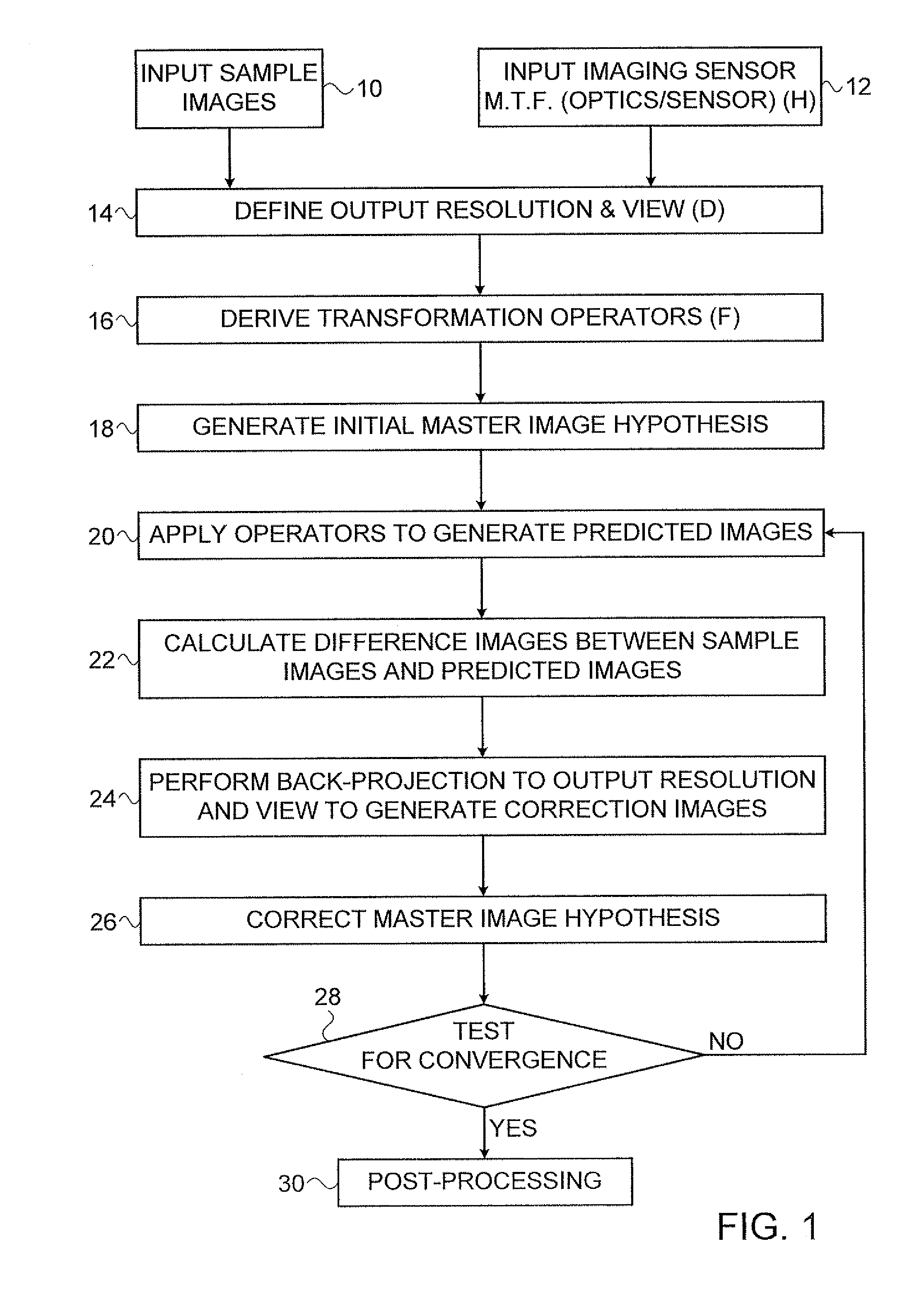
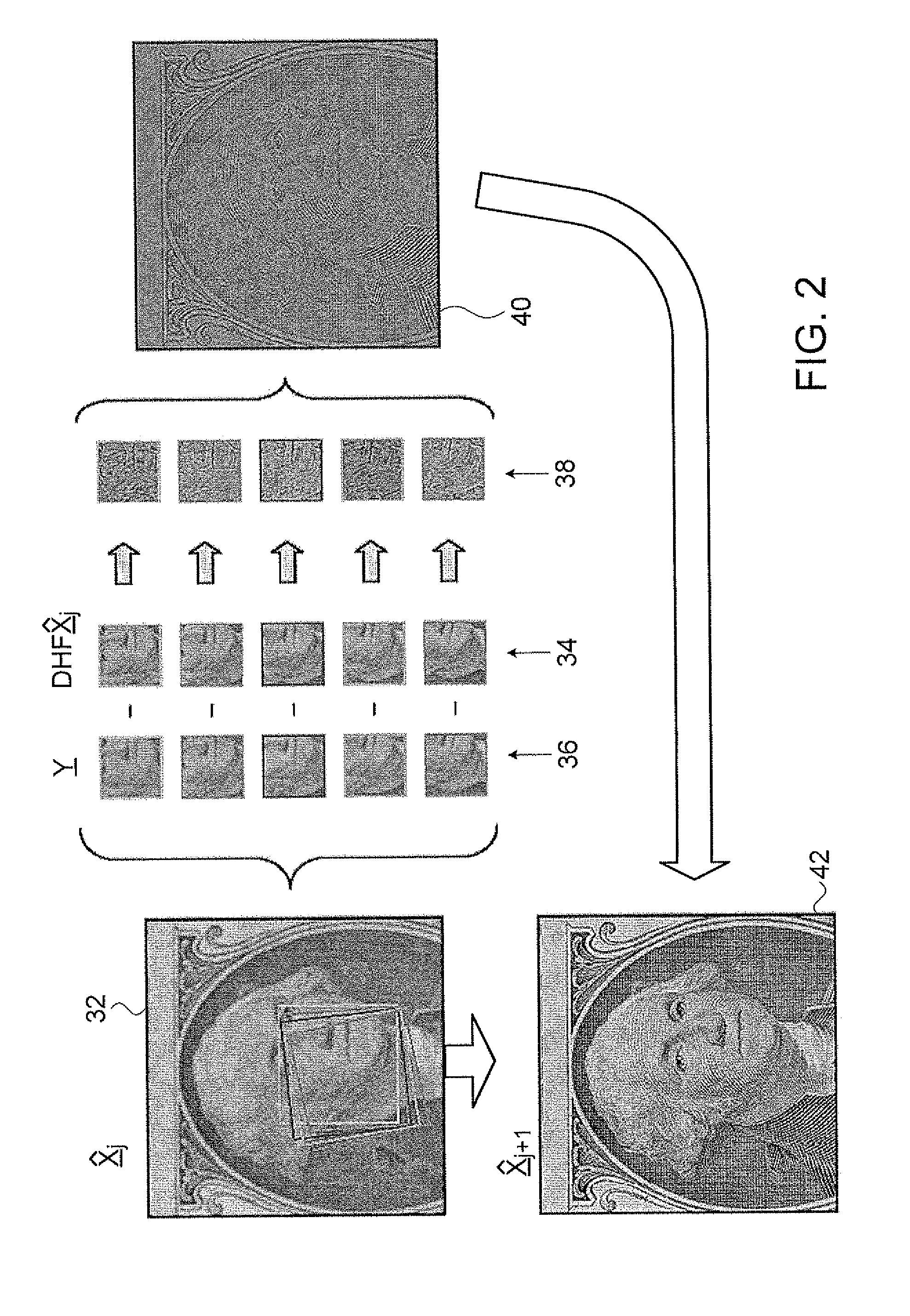
ActiveUS20080260279A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage resolution
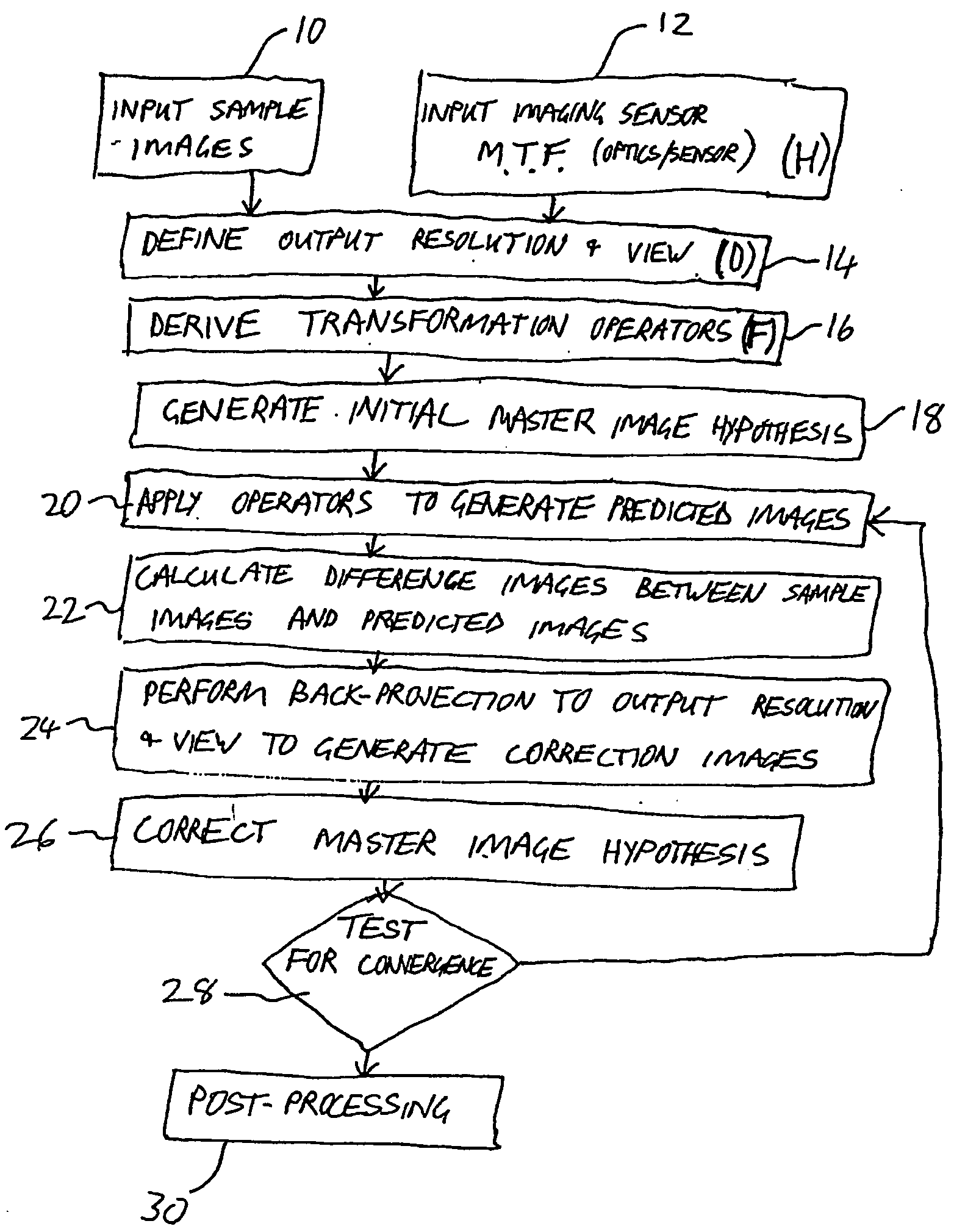
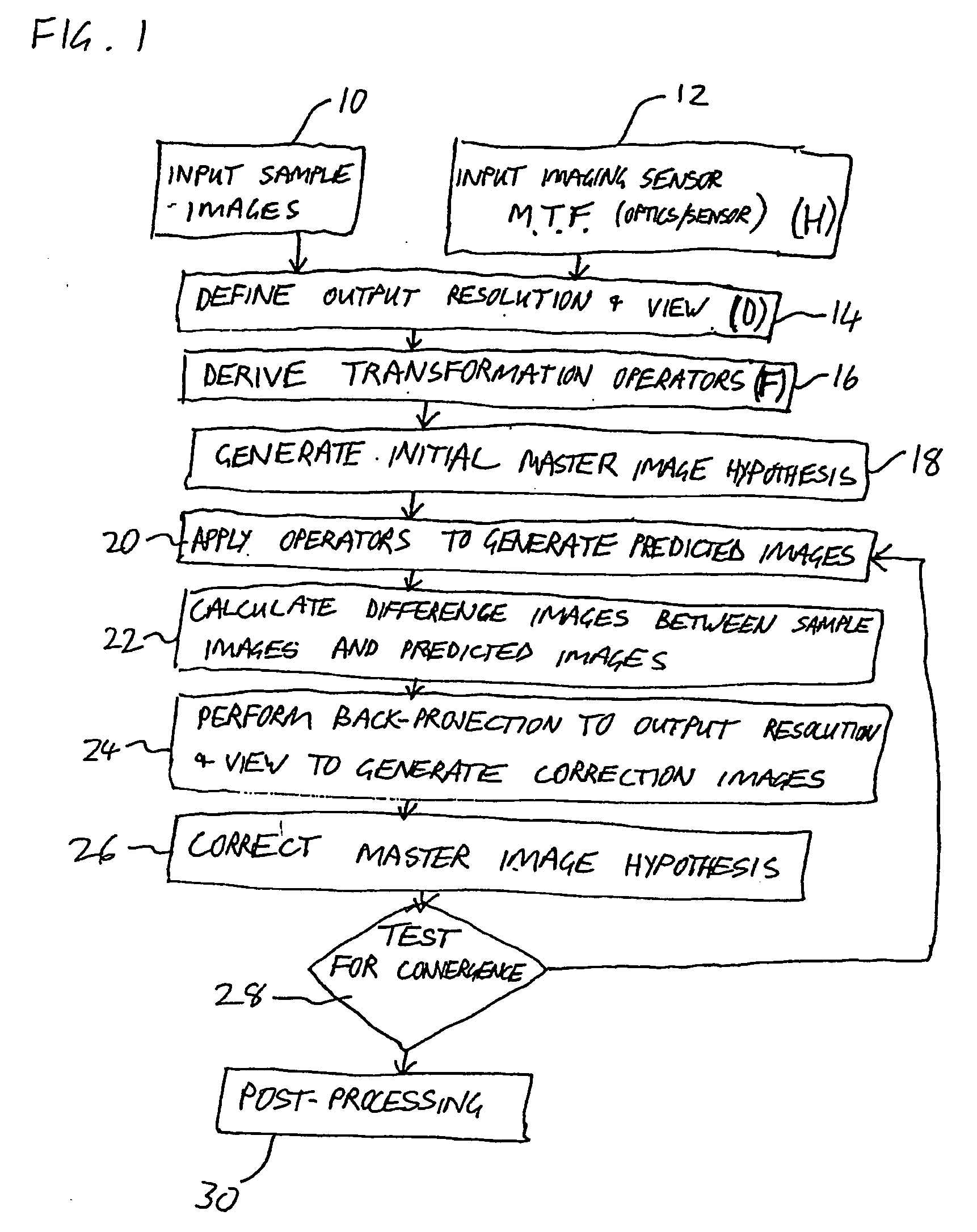
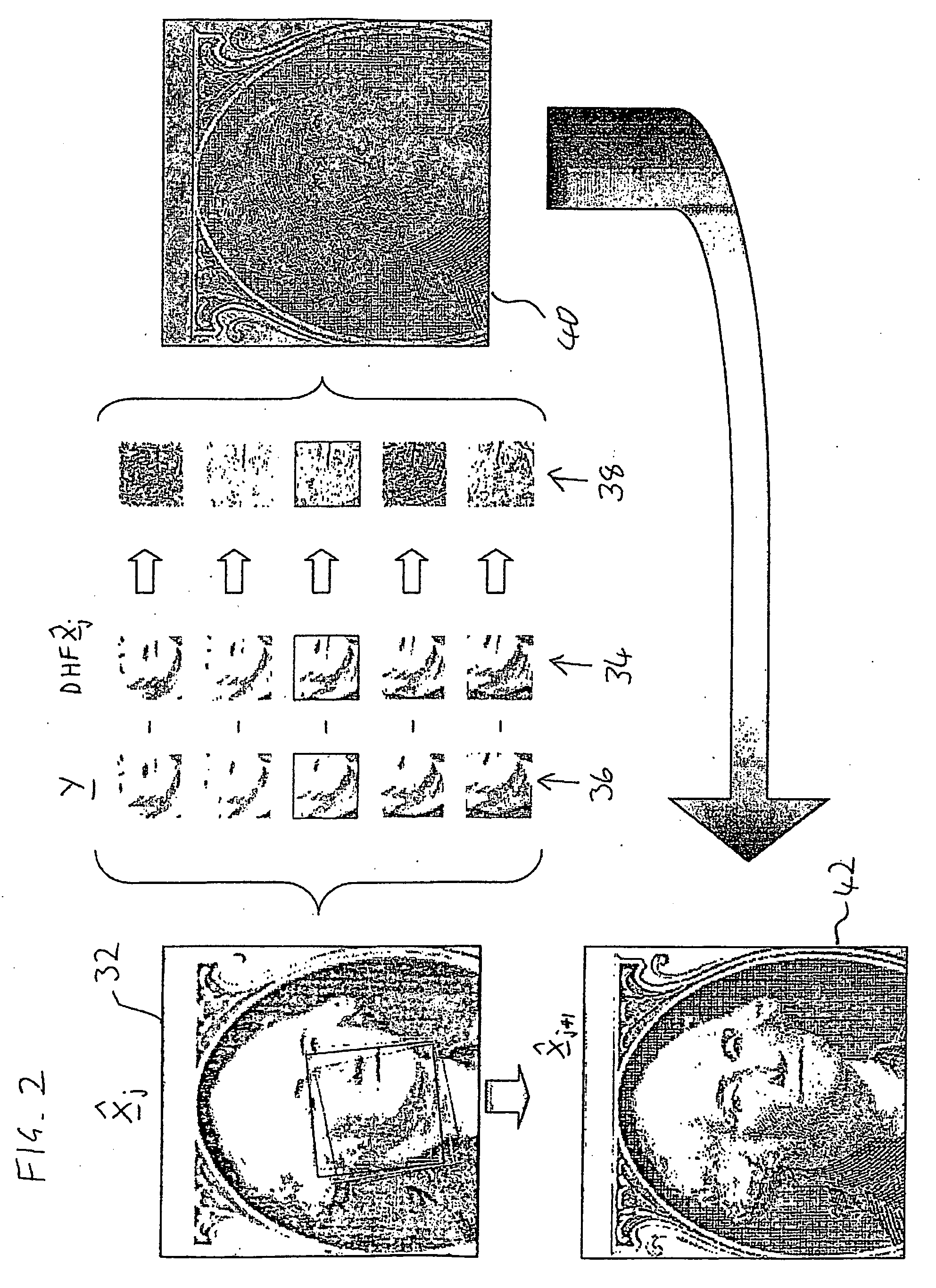
A method for iterative derivation of a master image from sampled images of non-identical, at least partially overlapping, regions of a scene. The method includes defining a transformation operator mapping positions within the master image to corresponding positions in the sampled image; a distortion operator simulating a modulation transfer function associated with an imaging sensor from which the sampled image was generated; and a sampling operator for reducing an image from the output resolution to the resolution of the sampled image. For each sampled image the transformation operator, distortion operator and sampling operator are applied to a current master image hypothesis to generate a predicted image A difference image is calculated which has pixel values corresponding to the difference in corresponding pixel values between the sampled image and the predicted image. A back-projection of each of the difference images is performed to generate a correction image for the current master image hypothesis. Finally, the correction images are employed to perform a correction to the current master image hypothesis to generate a new master image hypothesis. The correction to the current master image hypothesis includes combining the correction images by deriving a weighted average of values of corresponding pixels in the correction images. The weight of each pixel in each correction image is calculated as a function of a distance as measured in the sampled image between: a point in the sampled image to which the pixel in the correction image is mapped by the transformation operator, and at least one pixel centroid proximal to that point.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
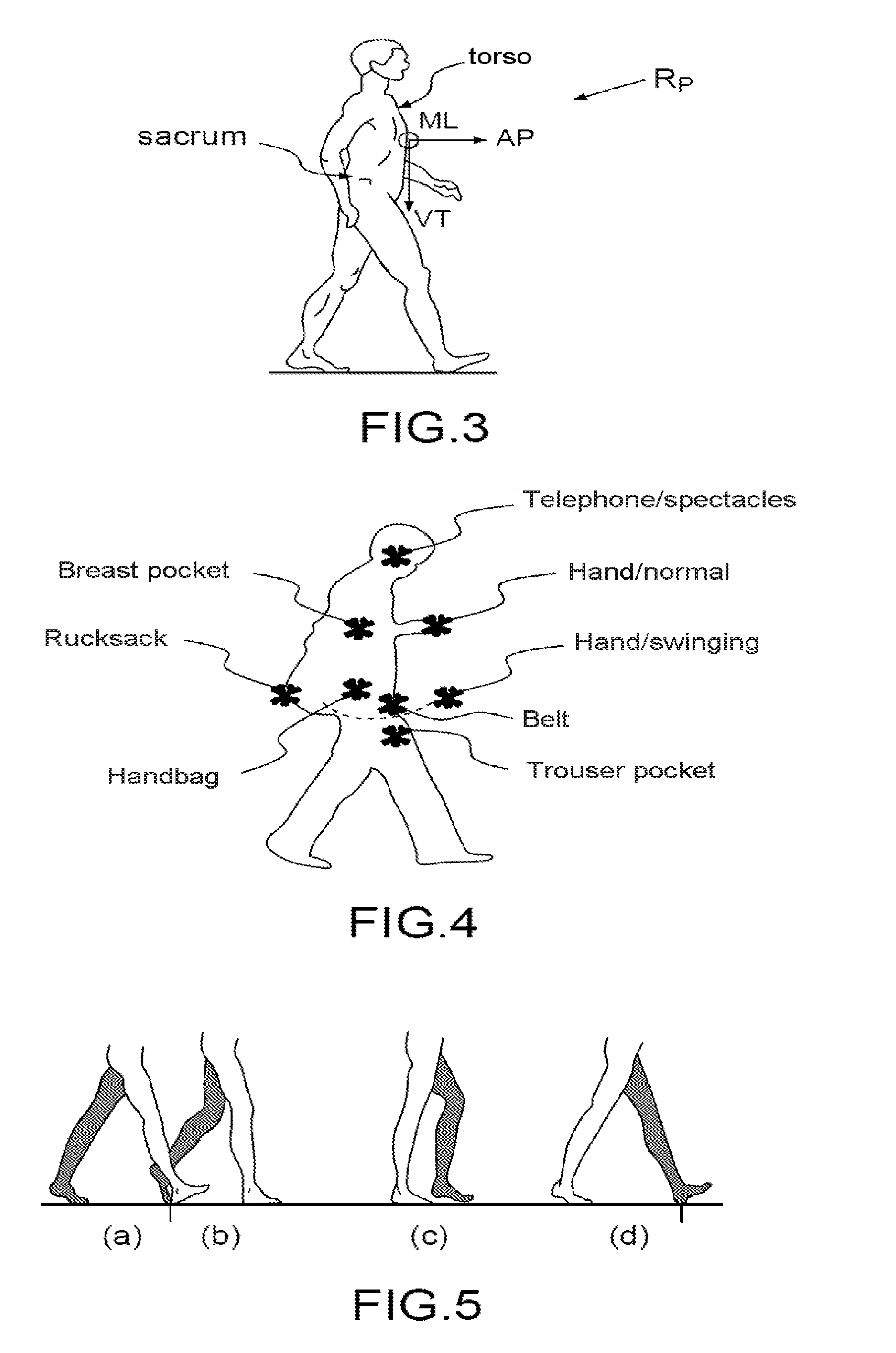
Method for determining the orientation of a sensor frame of reference tied to a mobile terminal furnished with a sensor assembly, carried or worn by a user and comprising at least one motion tied motion sensor
ActiveUS20160313126A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigational calculation instrumentsEngineeringPedestrian
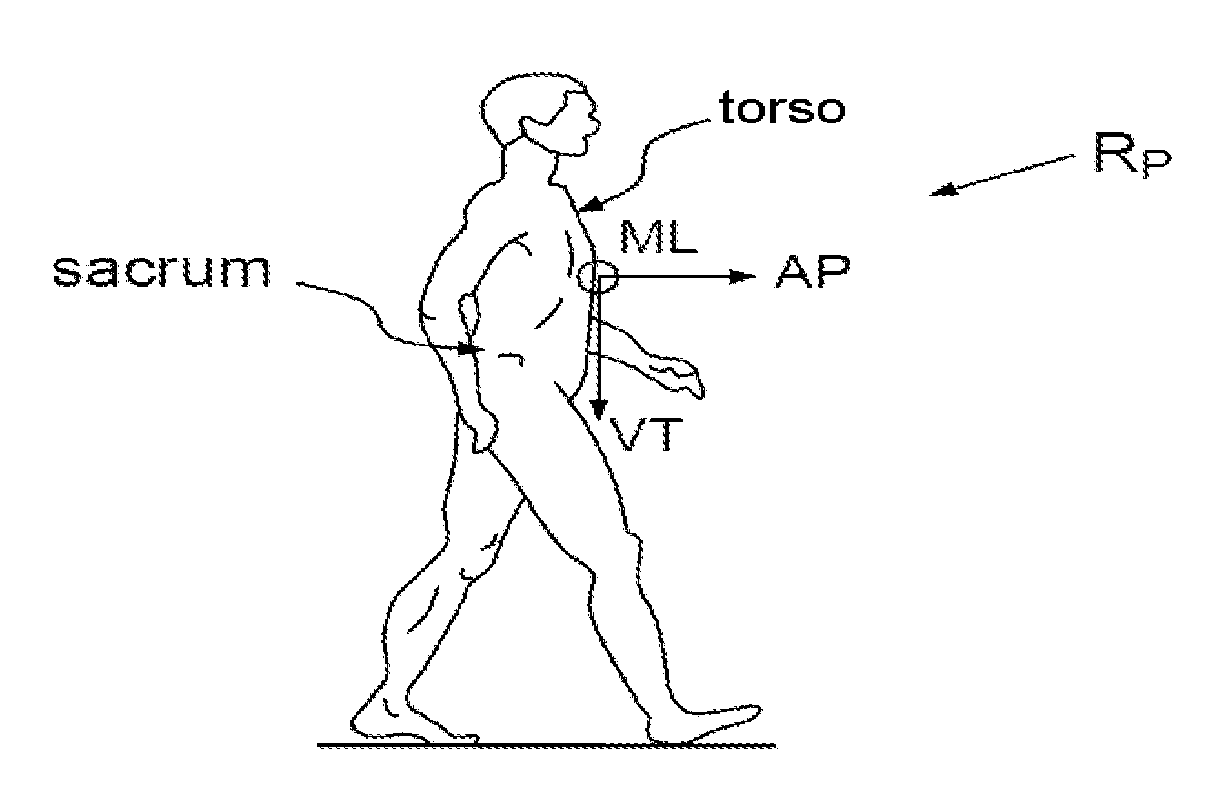
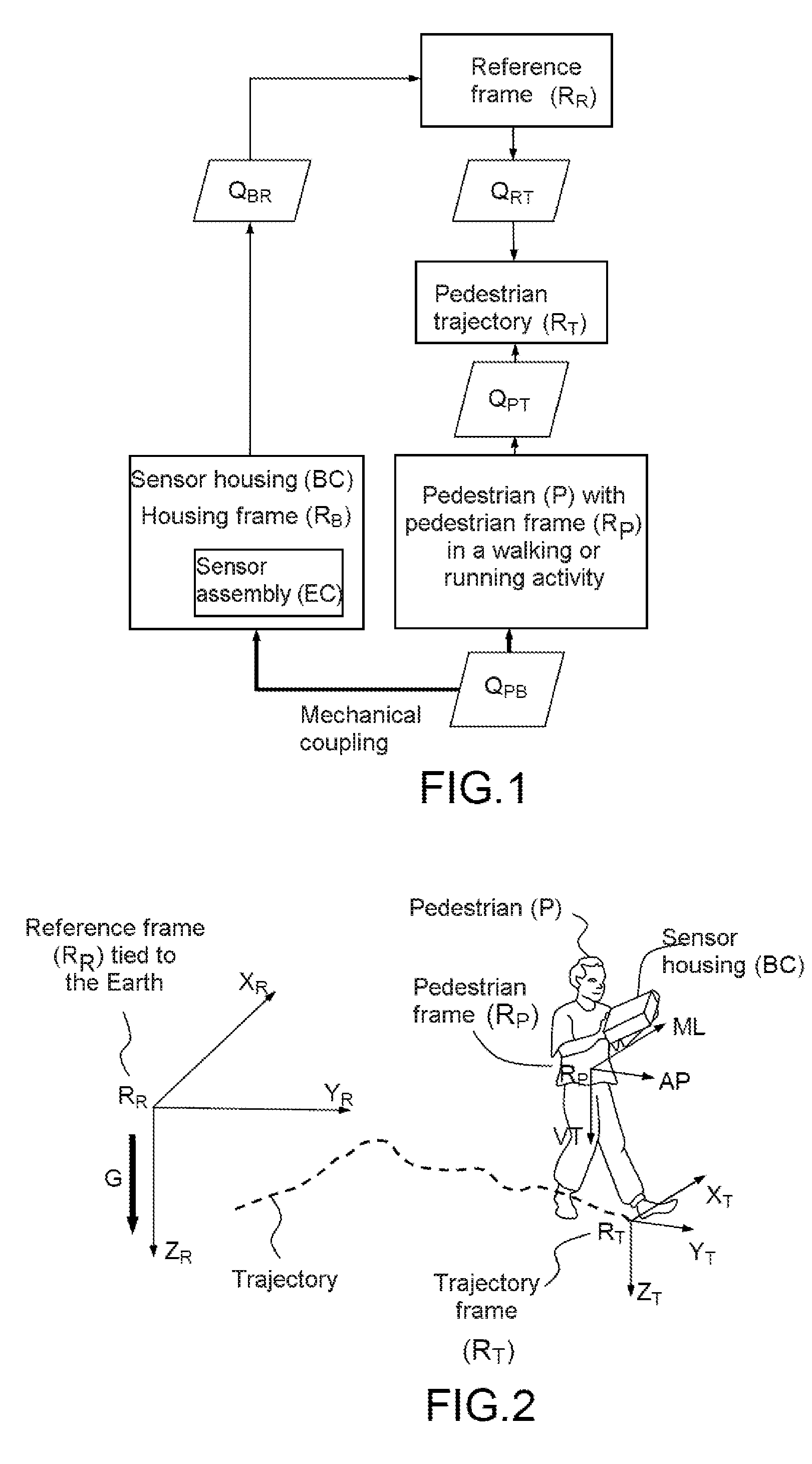
Method for determining the orientation of the trajectory followed by a pedestrian, associated with a trajectory frame, with respect to a reference frame, said pedestrian being furnished with a sensor housing comprising a sensor assembly comprising at least one motion sensor, comprising the steps consisting in:generating data representative of the motion of the sensor housing on the basis of said sensor assembly in the reference frame, andcomputing the value of a first rotation transformation operator representative of the orientation of the reference frame with respect to the trajectory frame, in such a way that the data representative of the motion which are thus obtained in the previous step, in the reference frame, and transformed by said first operator, exhibit at least one characteristic of a set of characteristics which are representative of signals of walking or running motion of a pedestrian and are expressed in the pedestrian frame.
Owner:MOVEA
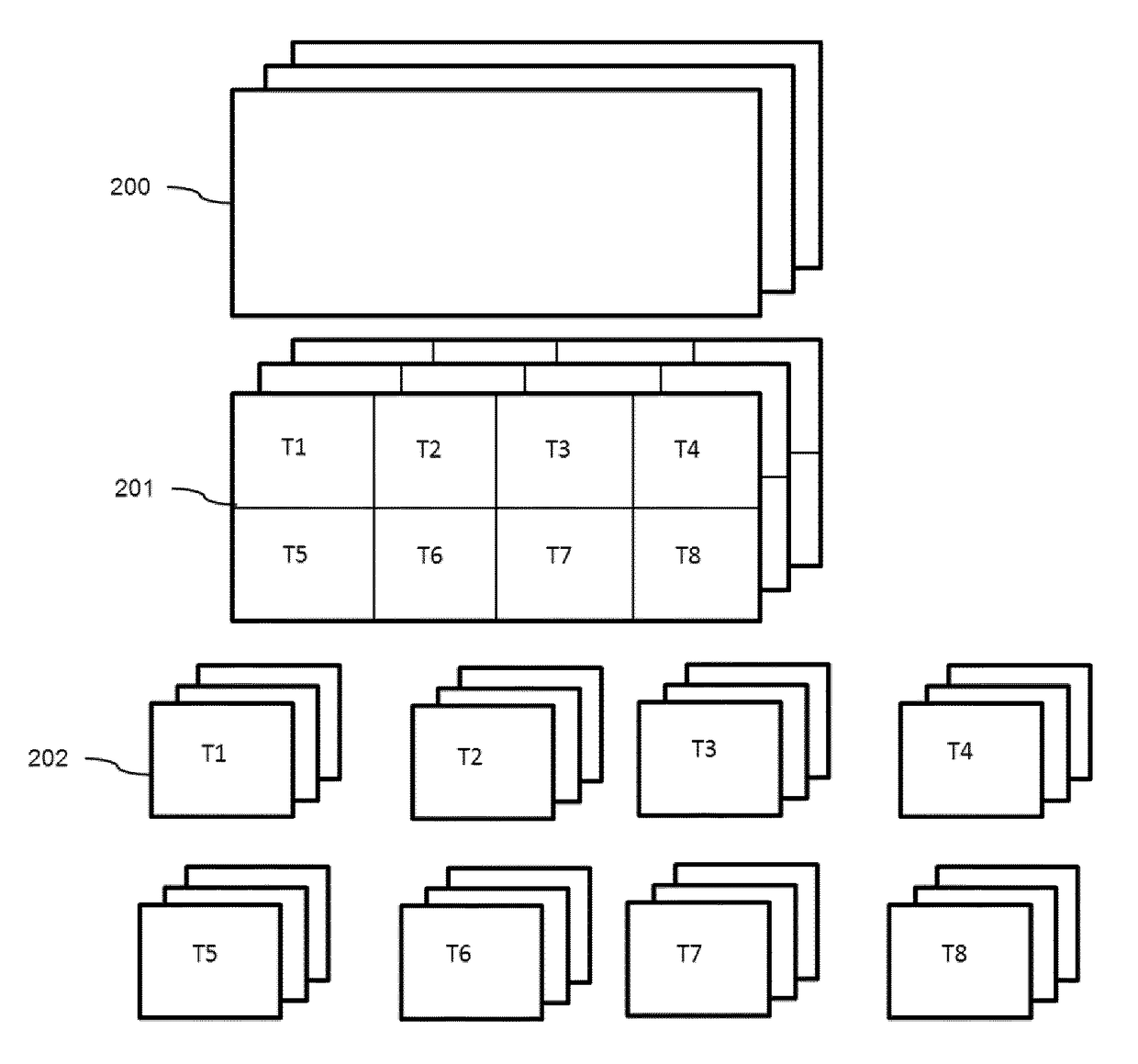
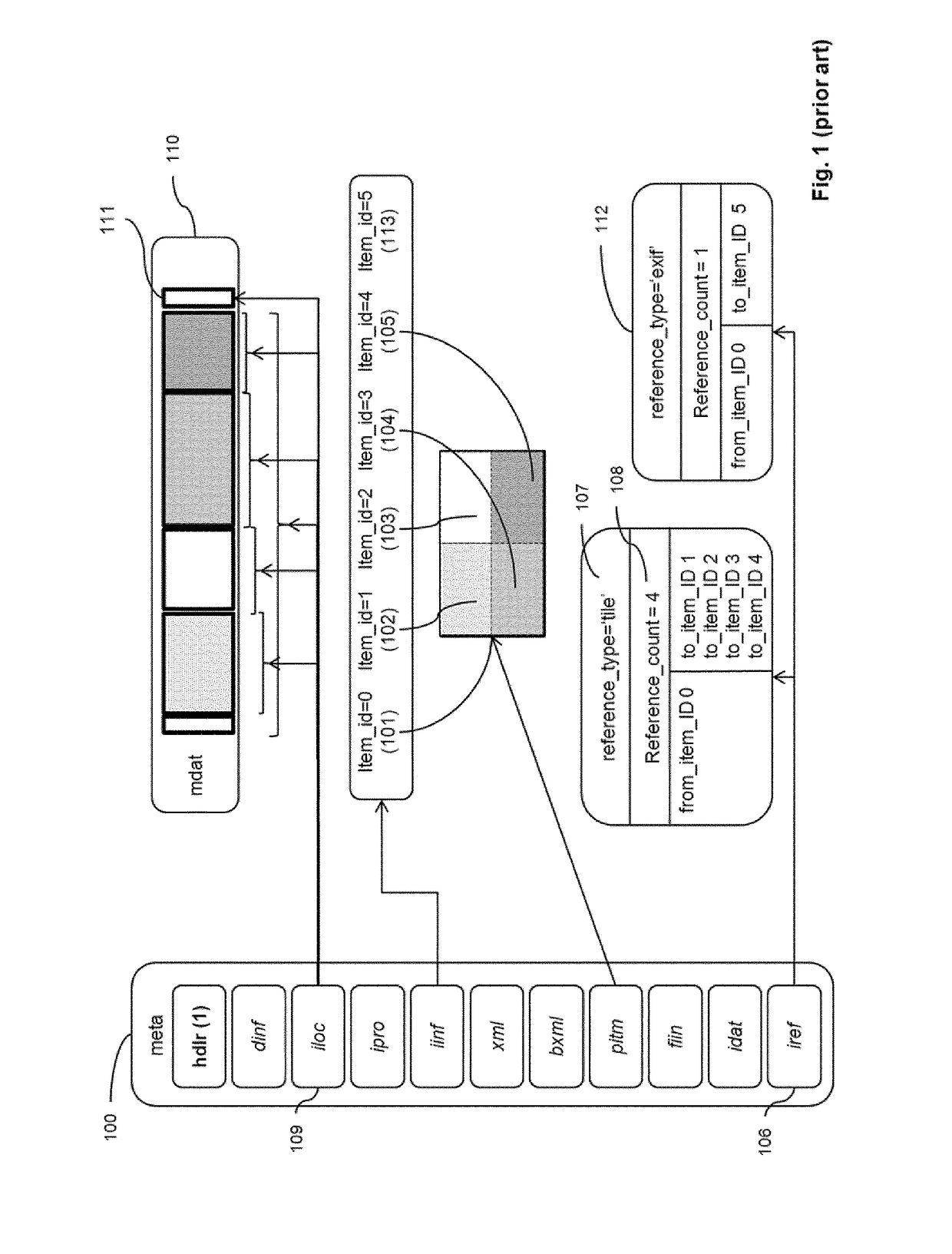
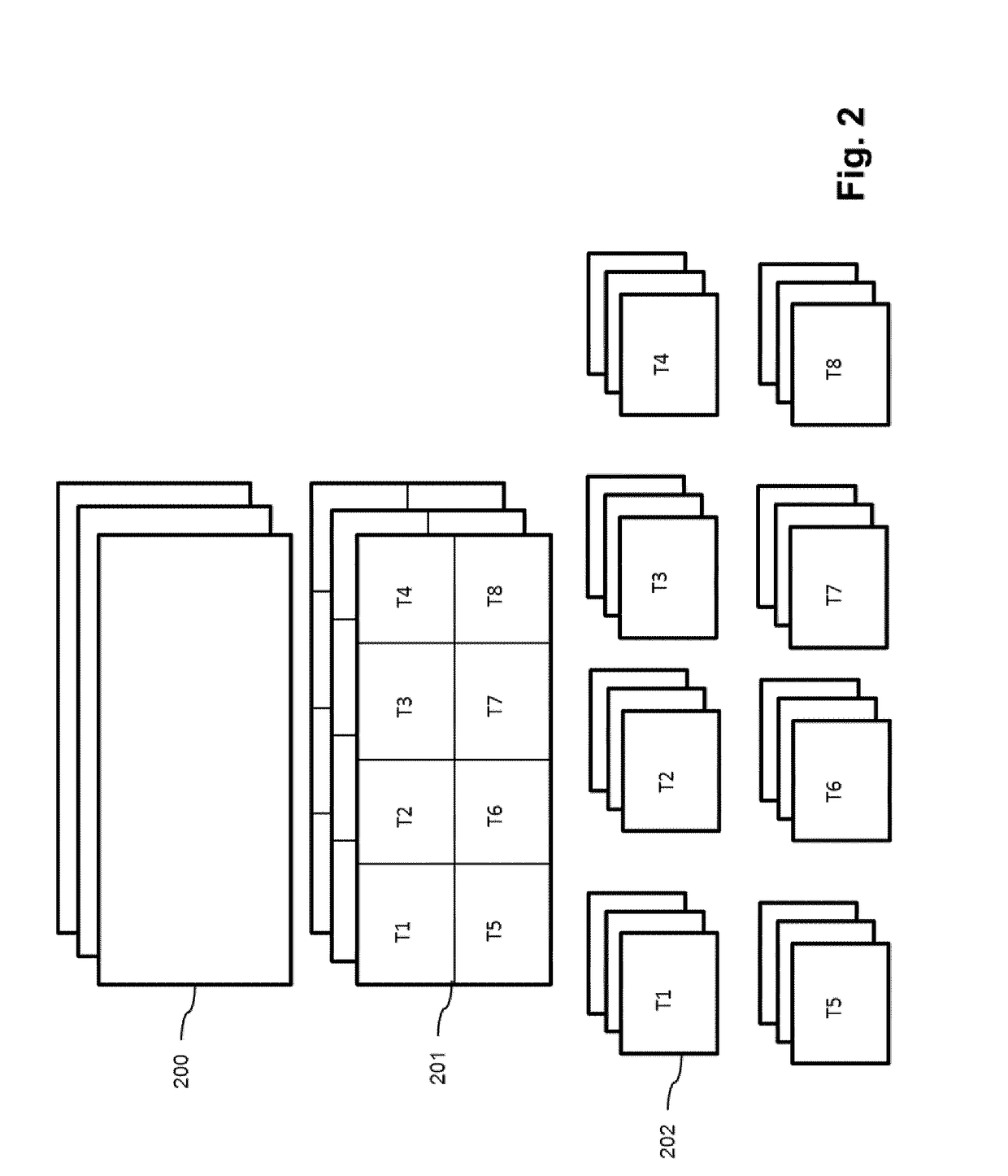
Image data encapsulation
ActiveUS20180007407A1Easy to identifyEasy selectionDigital video signal modificationTransmissionEncapsulated dataSingle image
A method of encapsulating an encoded bitstream representing one or more images, the encapsulated bitstream comprising a data part and a metadata part. The method including providing image item information identifying a portion of the data part representing a sub-image or an image of a single image; providing image description information comprising parameters including display parameters and / or transformation operators relating to one or more images and outputting said bitstream together with said provided information as an encapsulated data file, wherein the image description information is stored in the metadata part.
Owner:CANON KK
Accelerated Hardware Using Dual Quaternions
PendingUS20210303758A1Without compromising efficiencyComputationally efficientConcurrent instruction executionDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmMatrix space
Techniques for concatenating, interpolating and upsampling pose transforms represented as dual quaternions are described, including: (1) derivation of a complex-valued matrix form of dual quaternions and dual quaternion operations; (2) derivation of a transformation operator on position vectors which obviates an explicit conversion to a classical 4×4 spatial transformation matrix and keeps results in complex-valued matrix space; (3) design for a generic lookup table system for functions to supply logarithm and exponentiations of the dual quaternion in its native format with trigonometry lookup tables to avoid precision issues when denominators tend to zero; and (4) a mechanism for wrapping the complex-exponentiation together with a simple complex arithmetic unit for computing dual quaternion macro-operations in both native dual quaternion space and through simplifications of the equivalent complex-valued matrix to compute dual quaternion operations such as inverses, multiplications, logarithms and exponentials in order to chain the pose transformations encoded within.
Owner:ULTRALEAP LTD
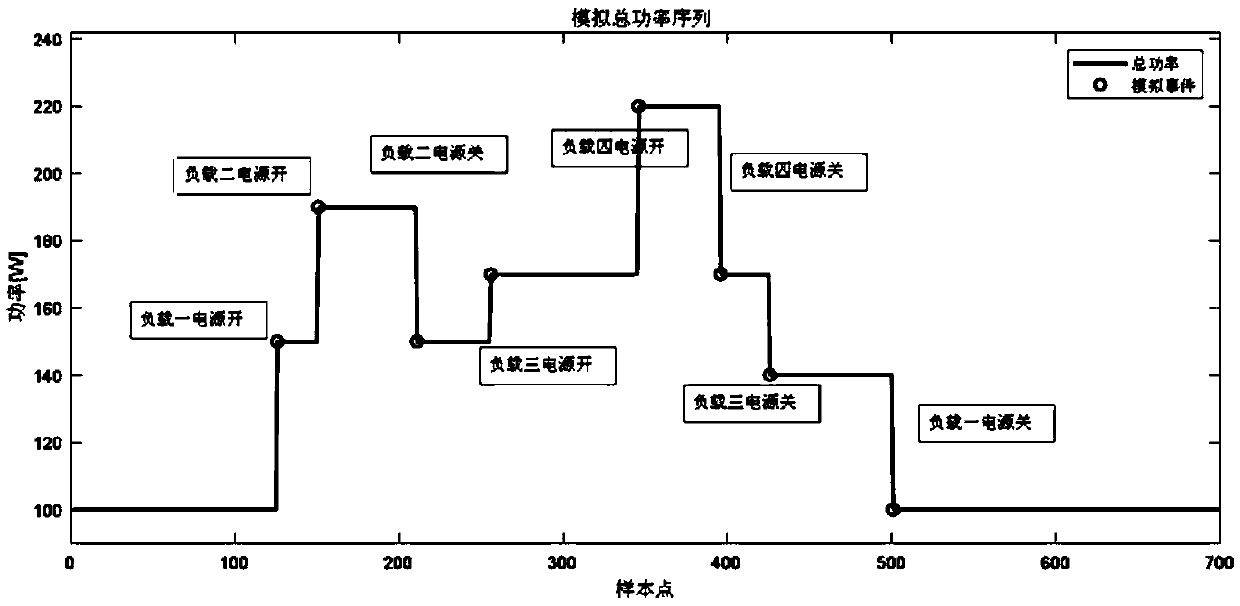
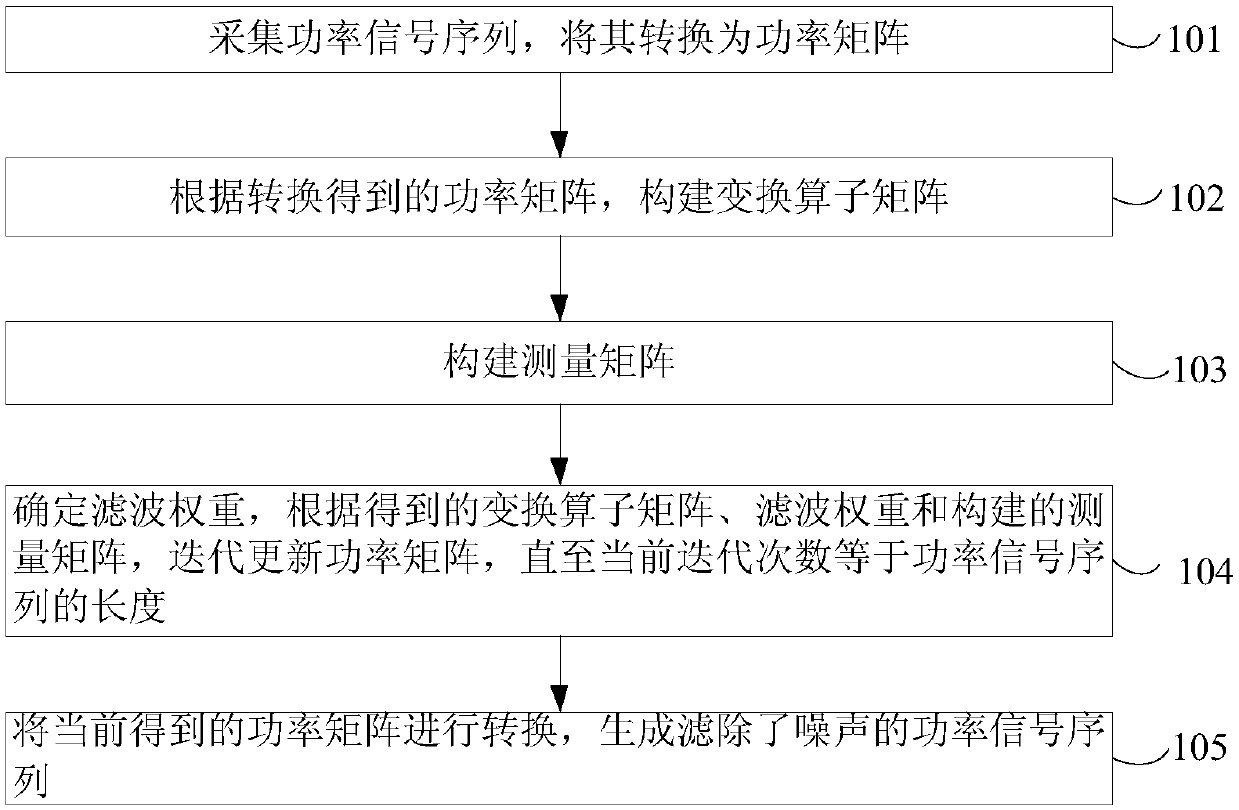
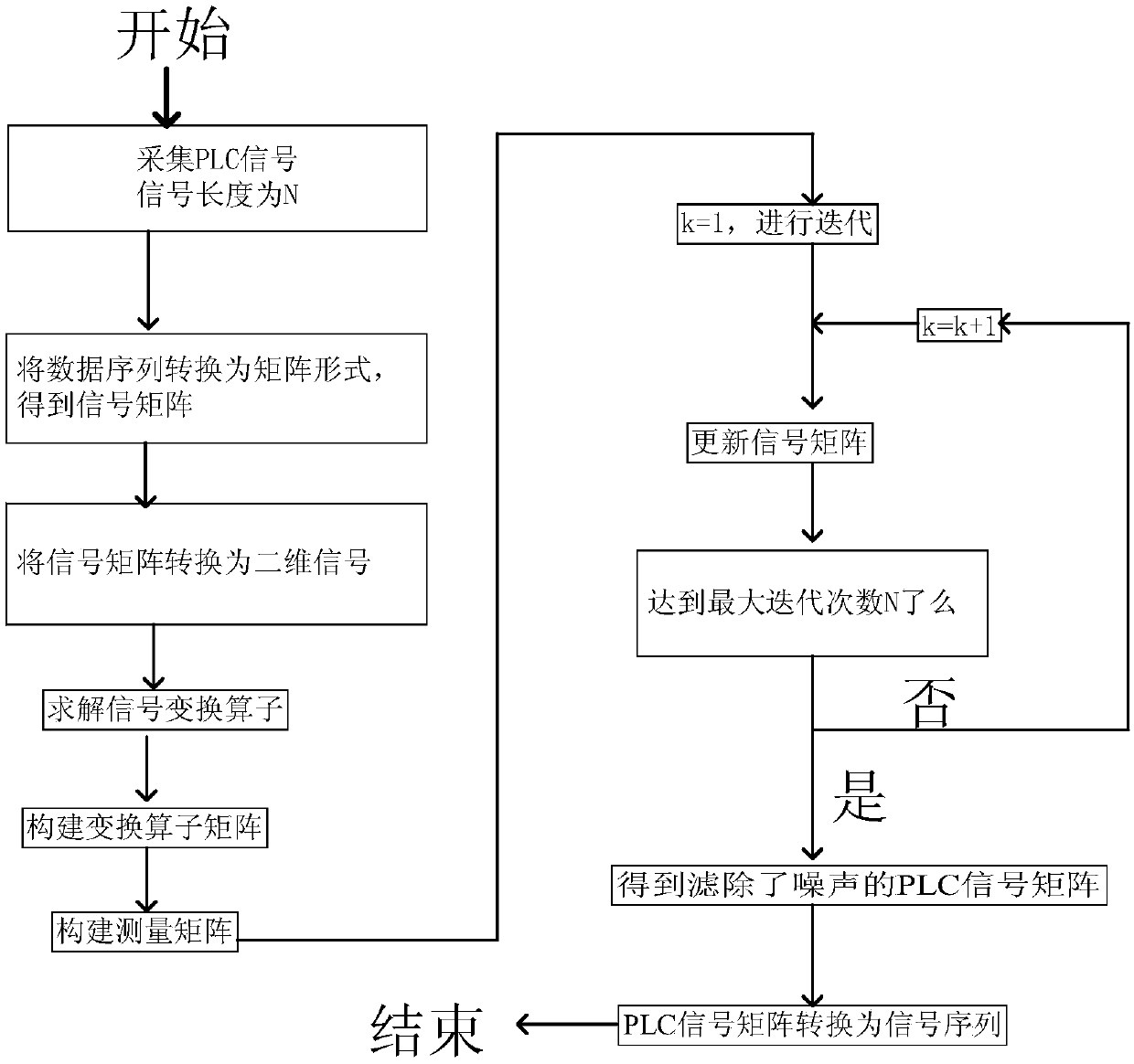
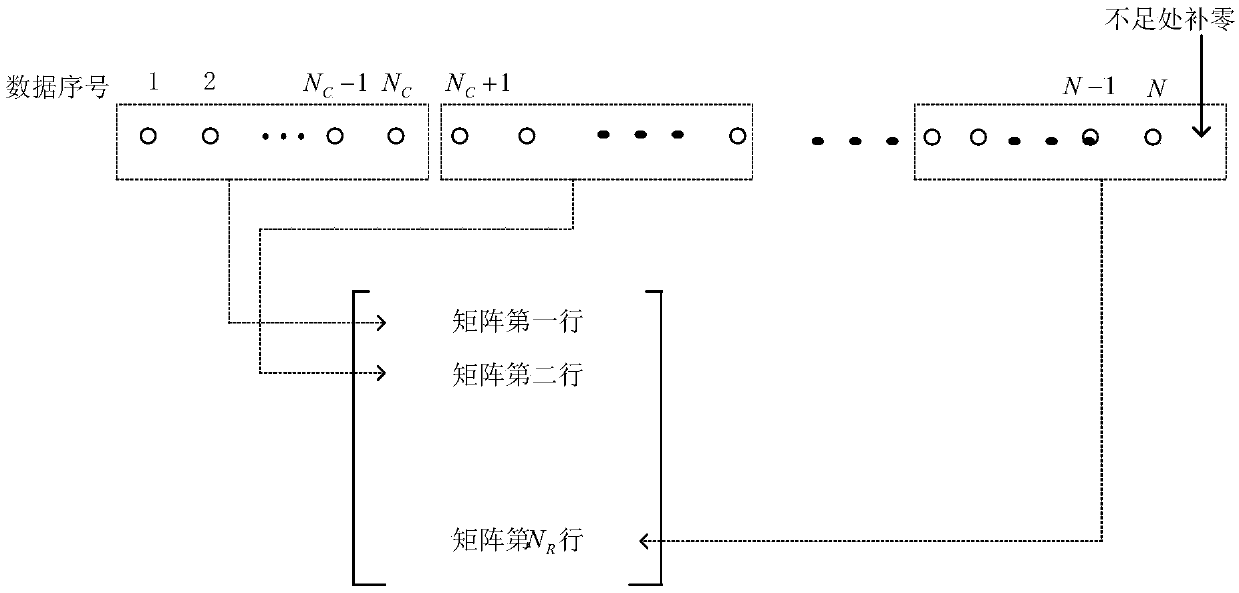
Adaptive filtering method of power signals in load decomposition
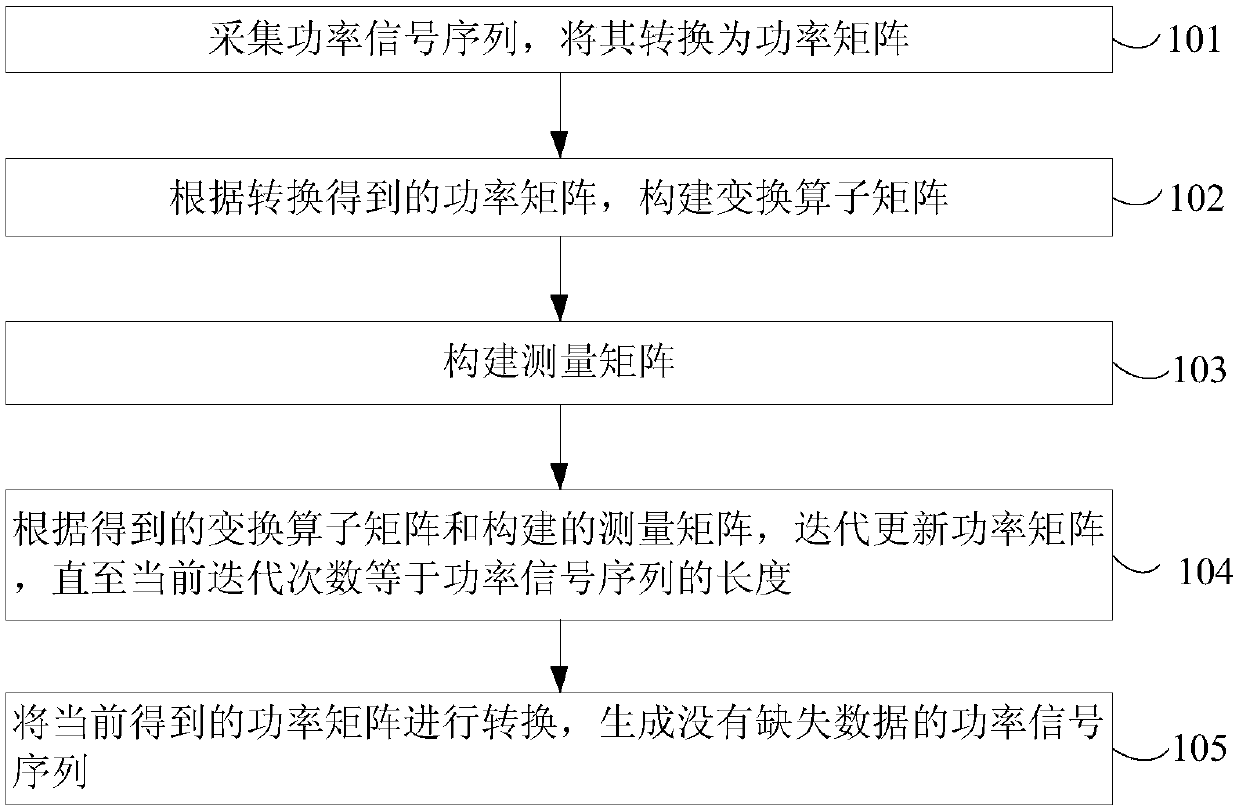
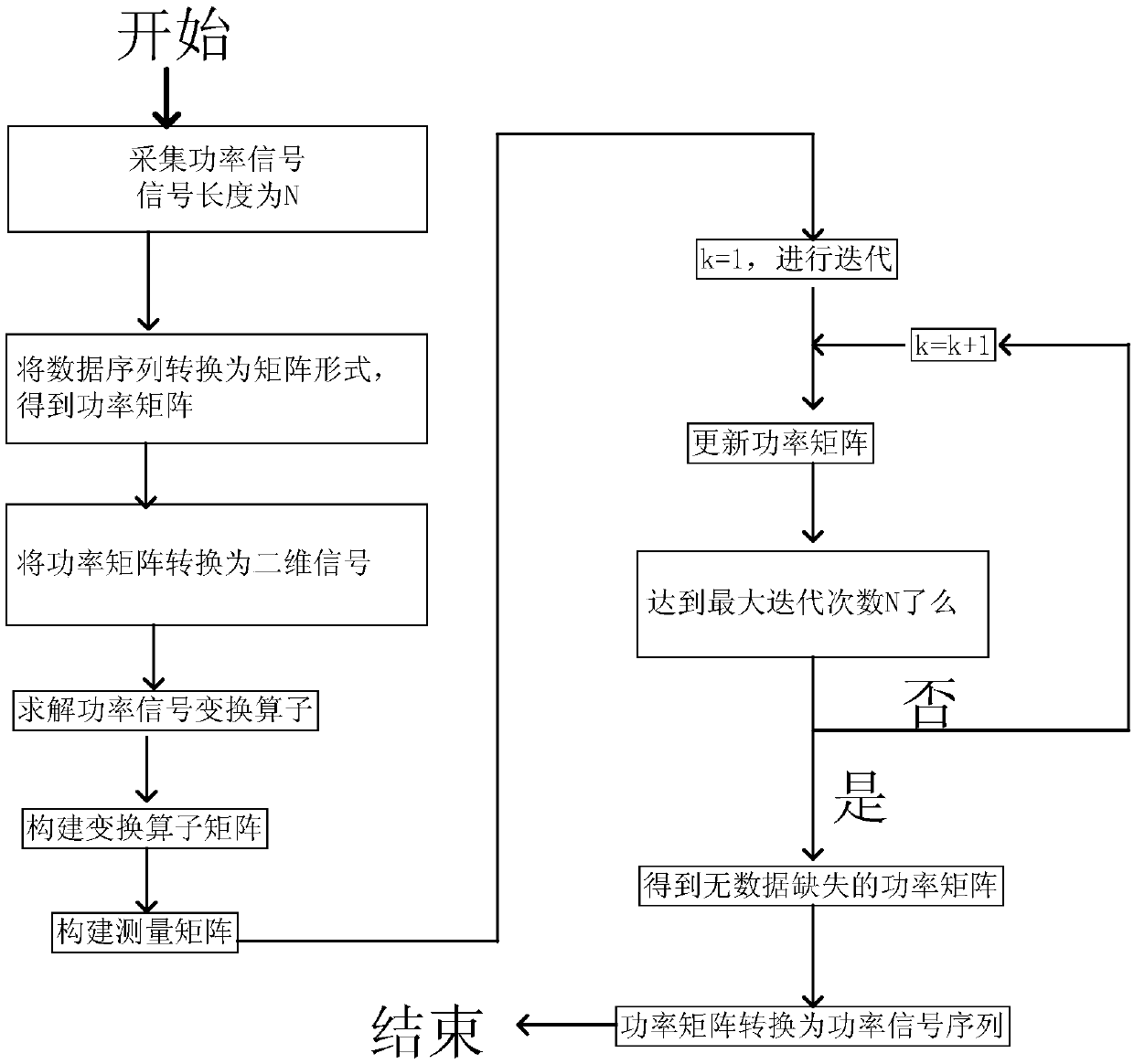
The invention provides an adaptive filtering method of power signals in load decomposition. The impulse noise in power signals can be effectively filtered. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a power signal sequence, converting the power signal sequence into a power matrix; constructing a transformation operator matrix according to the converted power matrix; constructing a measurement matrix; determining a filtering weight, and iteratively updating a power matrix according to the obtained transformation operator matrix, the filtering weight and the constructed measurement matrix, until the current number of iterations is equal to the length of the power signal sequence; and converting the currently obtained power matrix to generate a power signal sequence with filtered noise. The invention relates to the power field.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
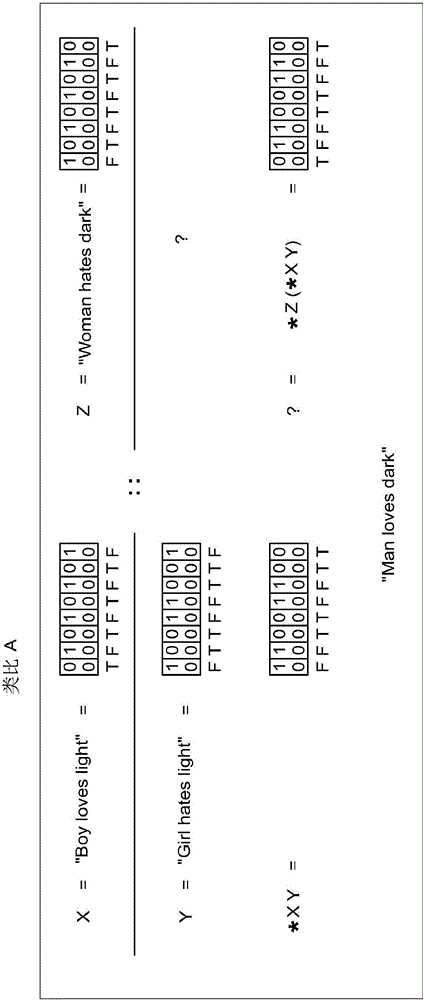
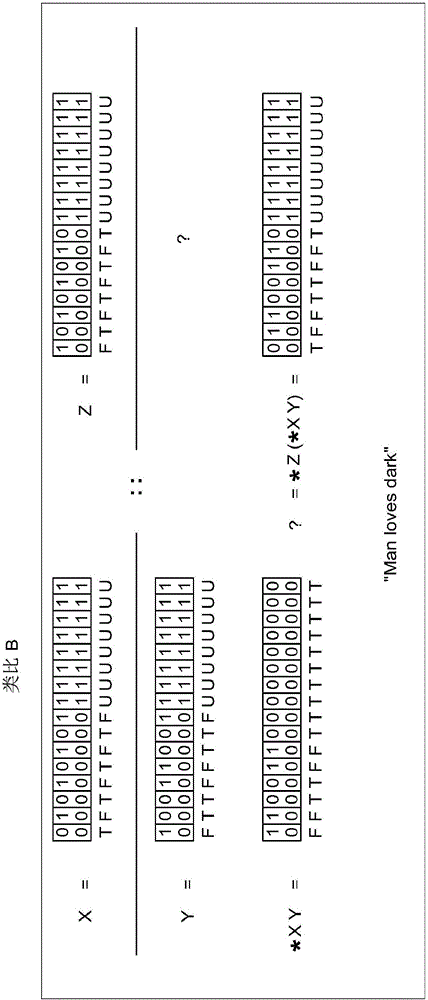
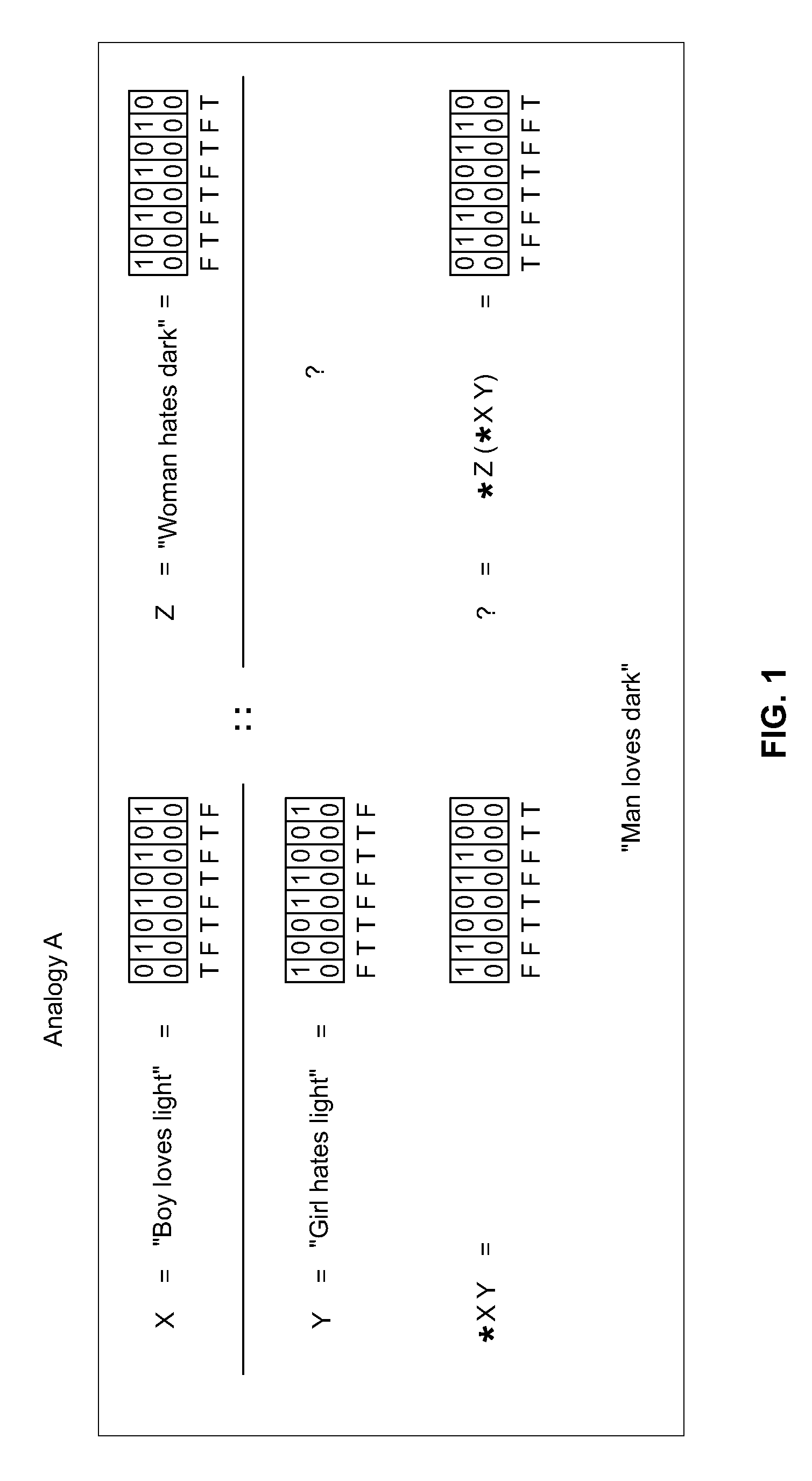
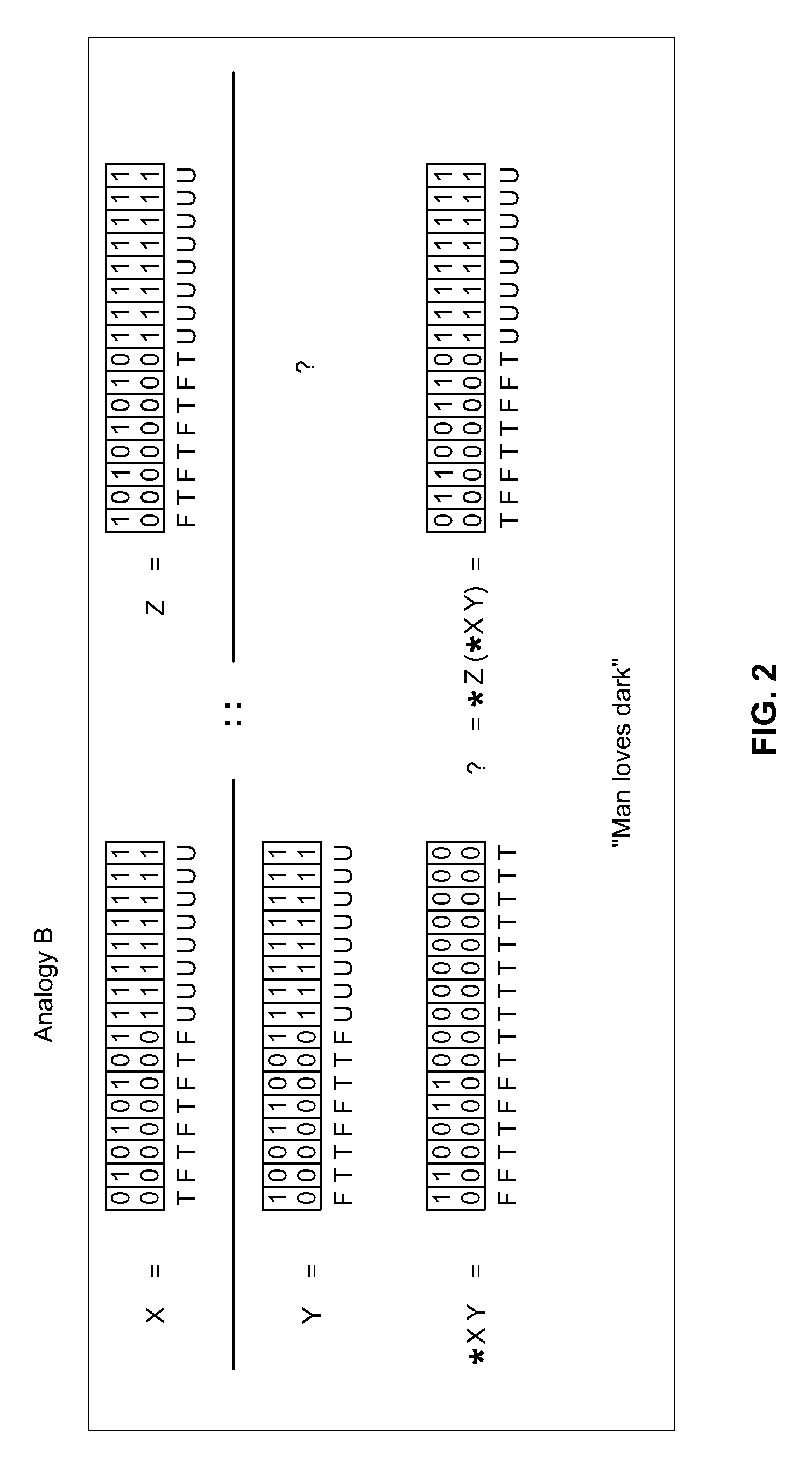
Methods and Systems of Four Valued Analogical Transformation Operators Used in Natural Language Processing and Other Applications
ActiveUS20150066476A1Overcome deficienciesNatural language analysisKnowledge representationKnowledge sourcesShort-term memory
A system for the dynamic encoding in a semantic network of both syntactic and semantic information into a common four valued logical notation. The encoding of new information being benign to prior syntactic constructions, tests for N conditionals in time O(C) and allows for the proper quantification of variables at each recursive step. The query / inference engine constructed from such an implementation is able to optimize short term memory for maximizing long term storage in the automaton. In a parallel context this can be viewed as optimizing communication and memory allocation between processes. The self-referencing system is capable of analogically extending knowledge from one knowledge source to another linearly. Disclosed embodiments include machine translation, text summarization, natural language speech recognition natural language.
Owner:MIDMORE ROGER
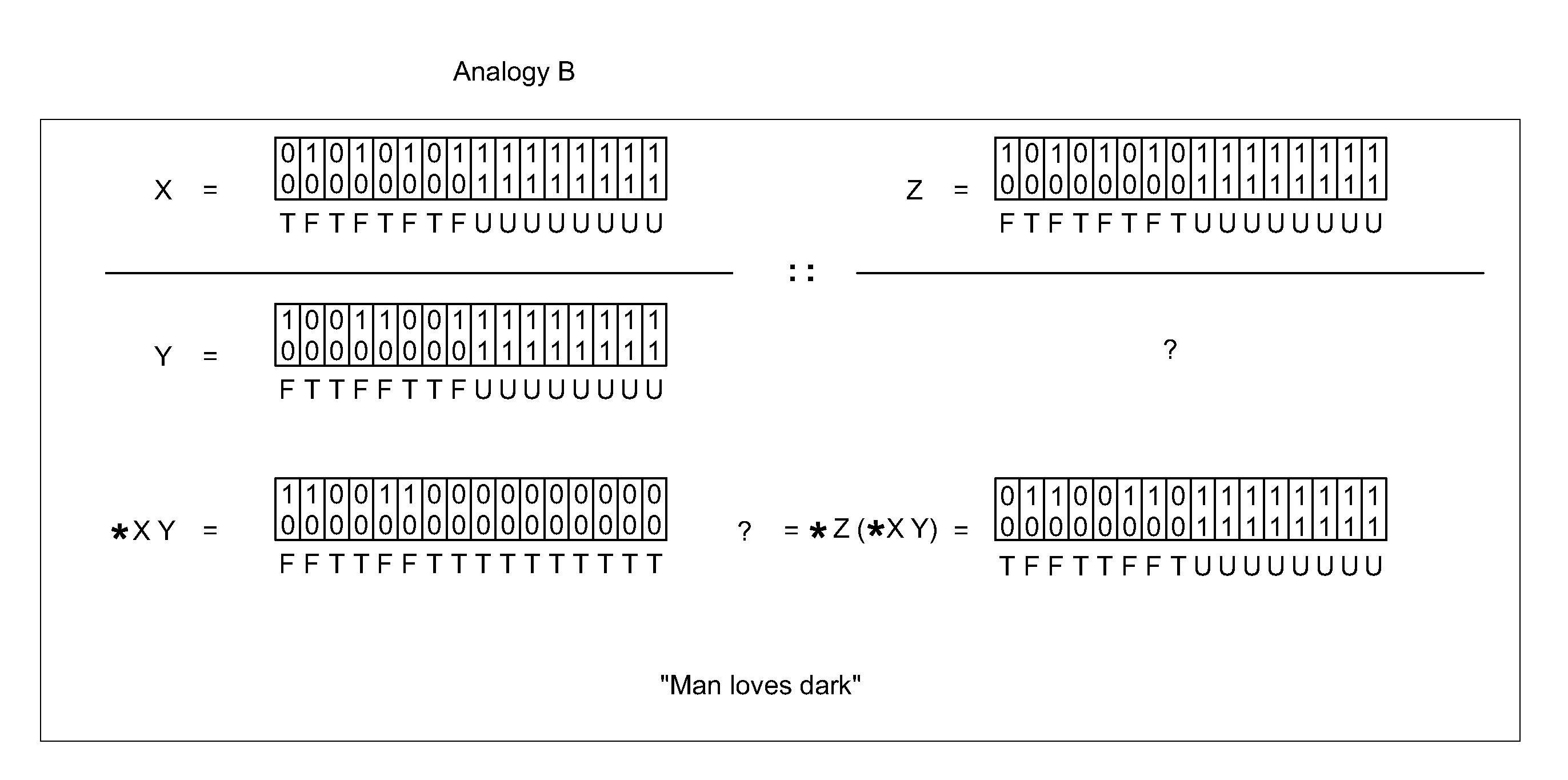
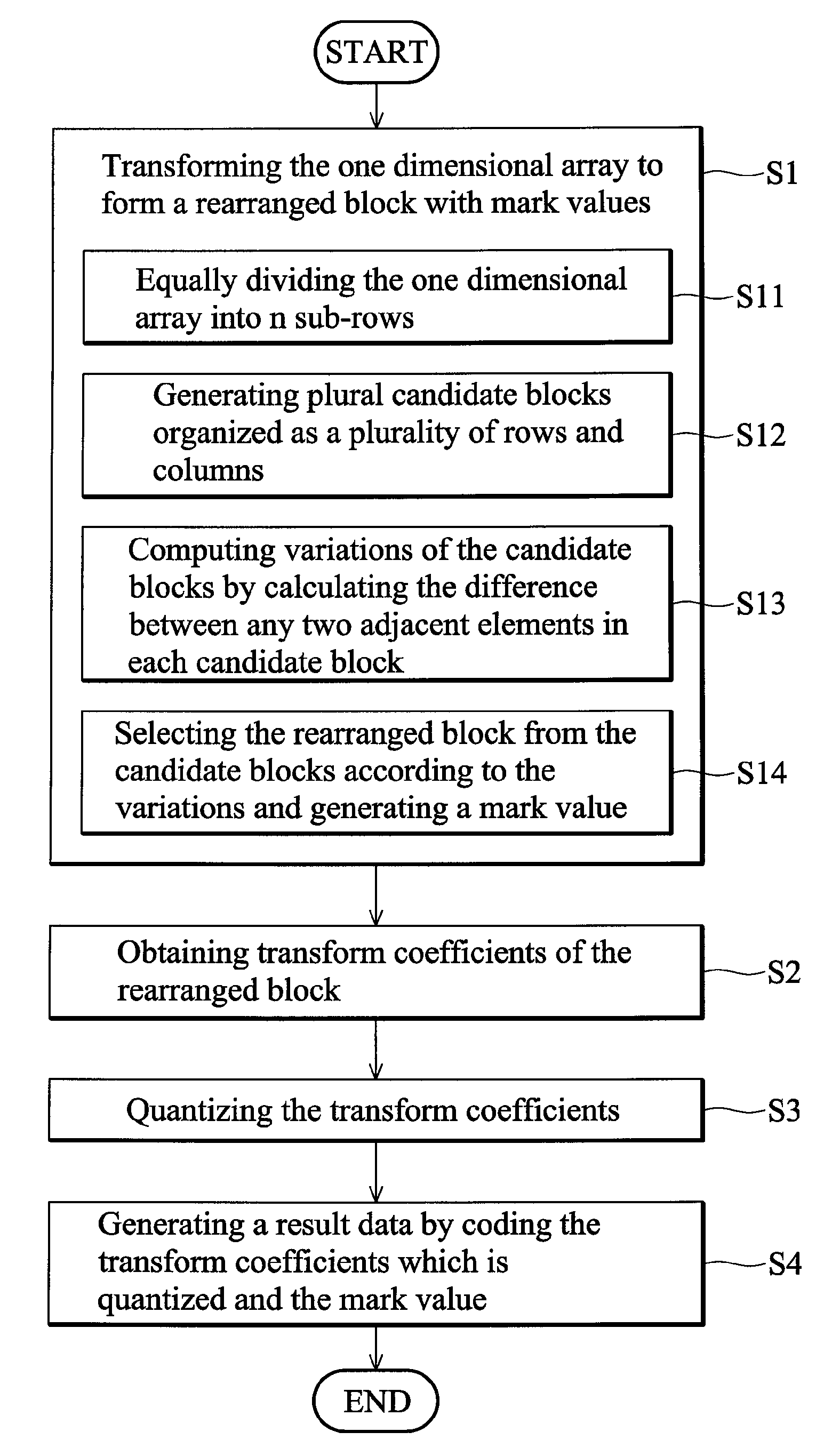
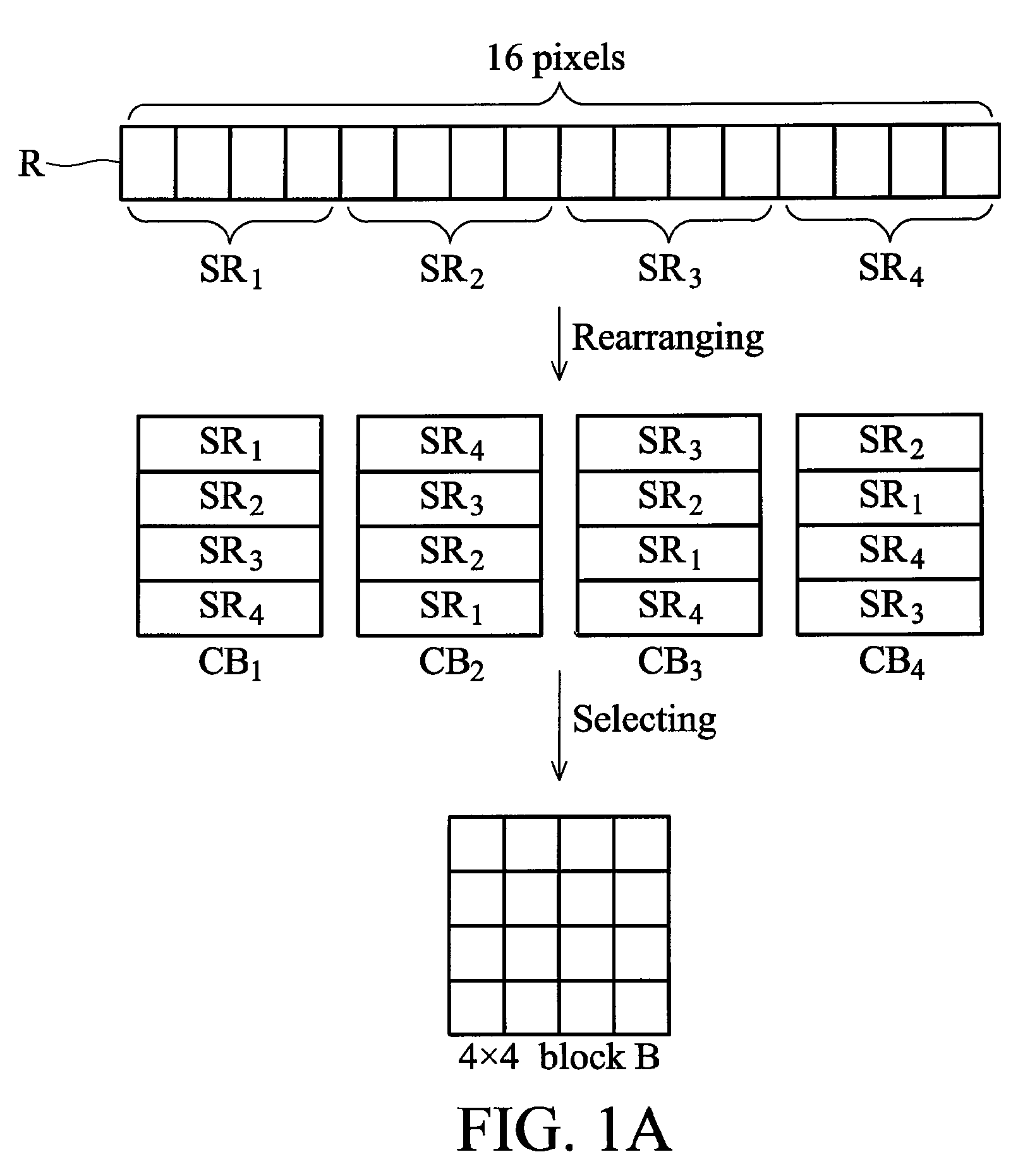
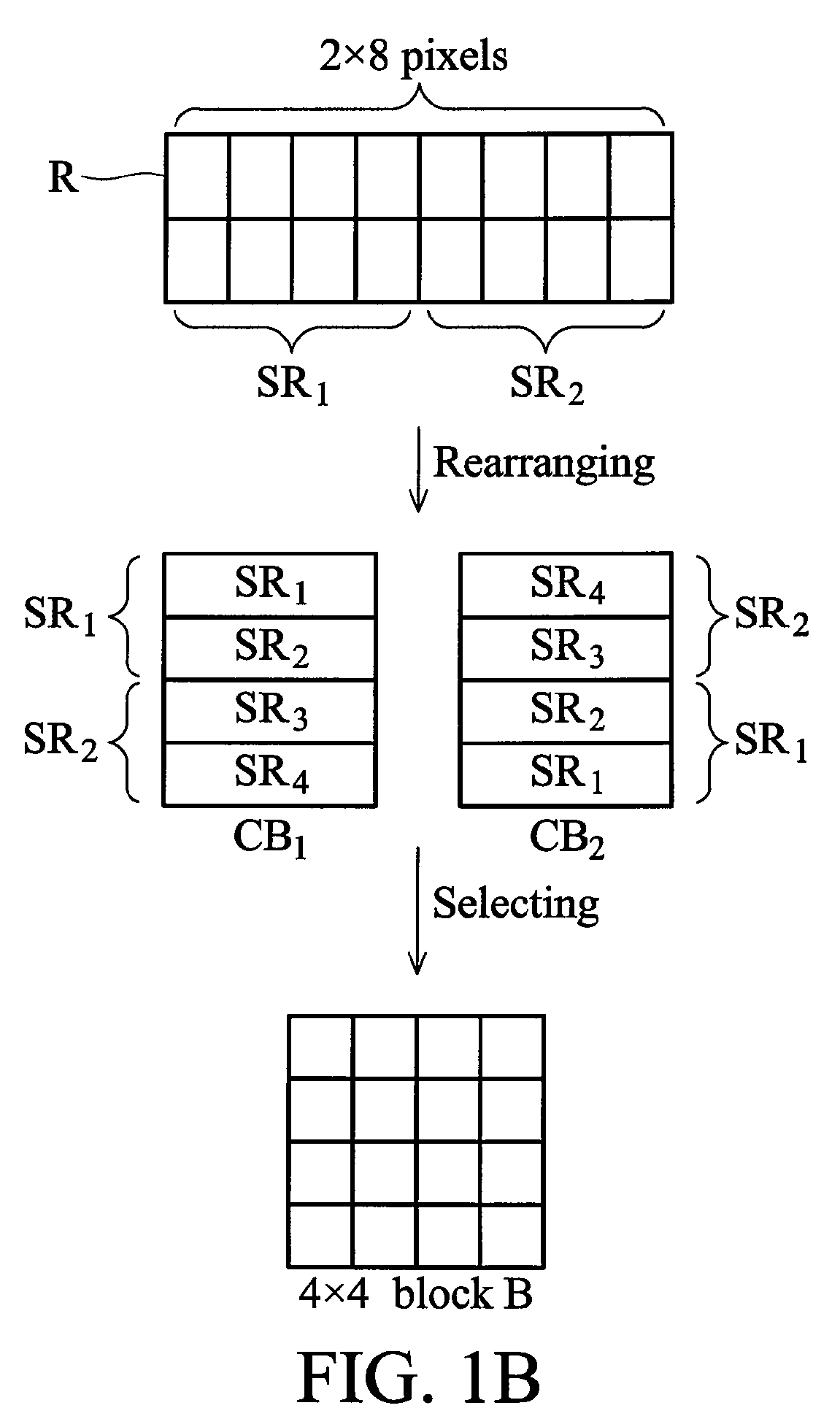
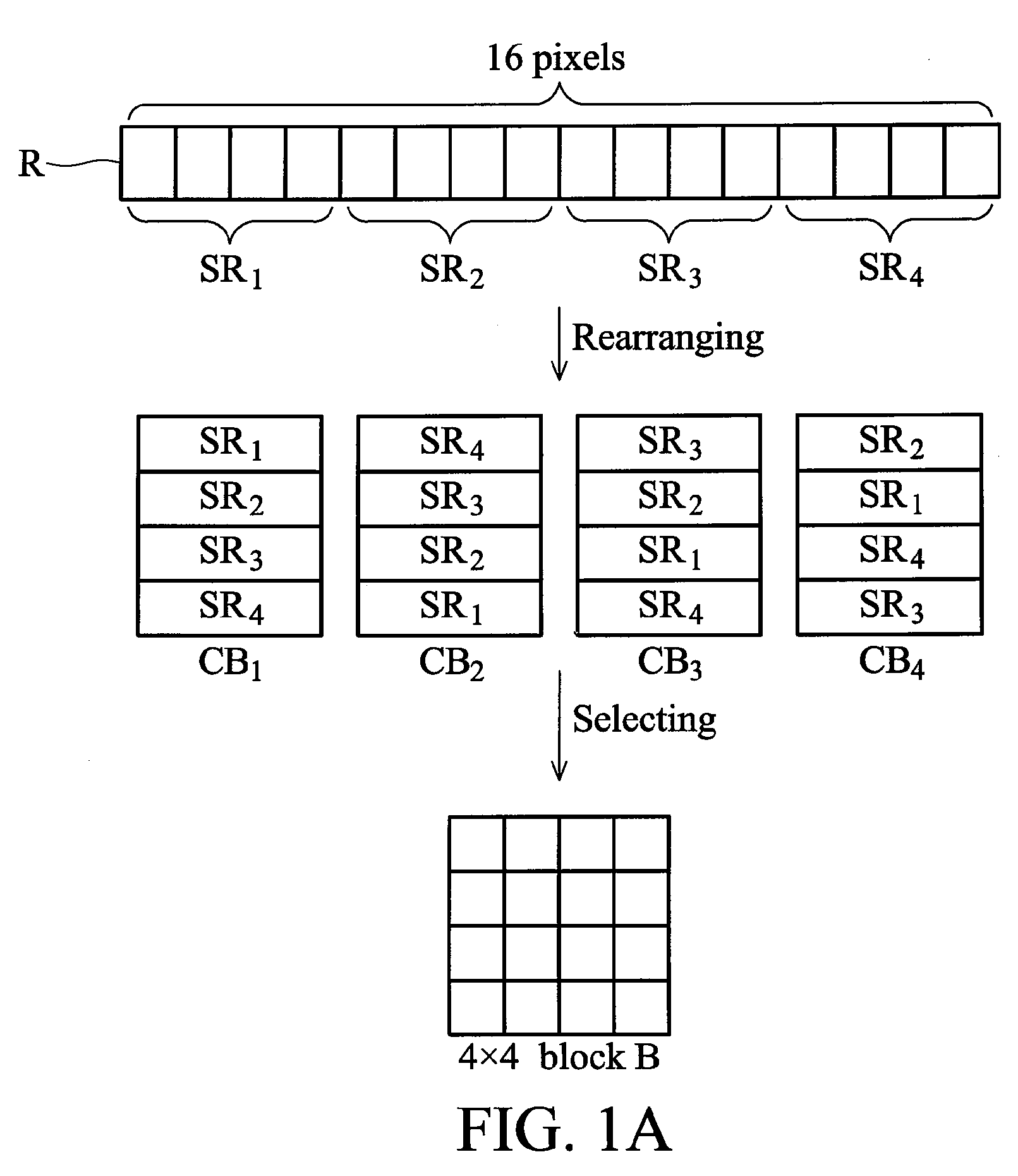
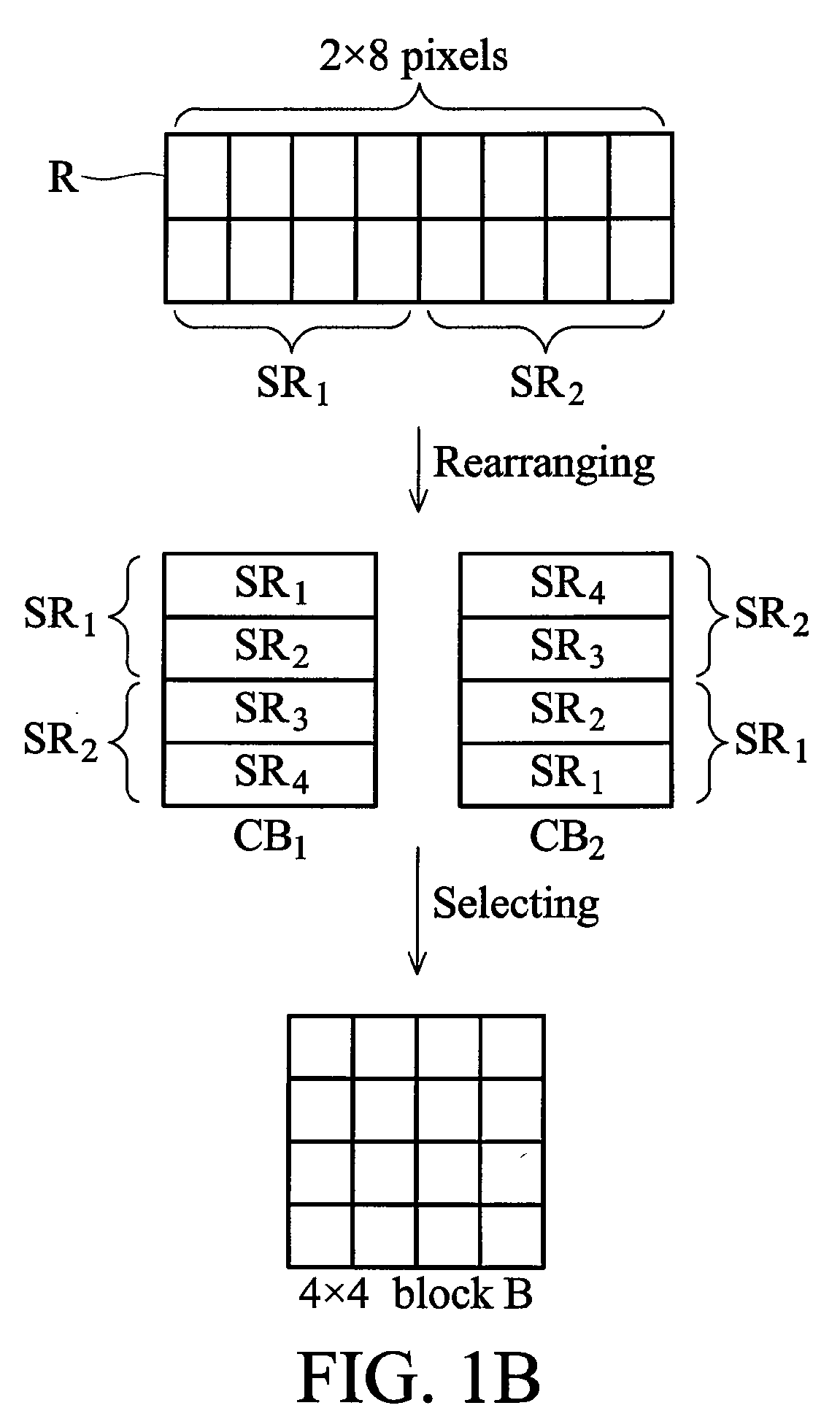
Apparatus of compressing image data and a method thereof
InactiveUS7876968B2Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionImaging data
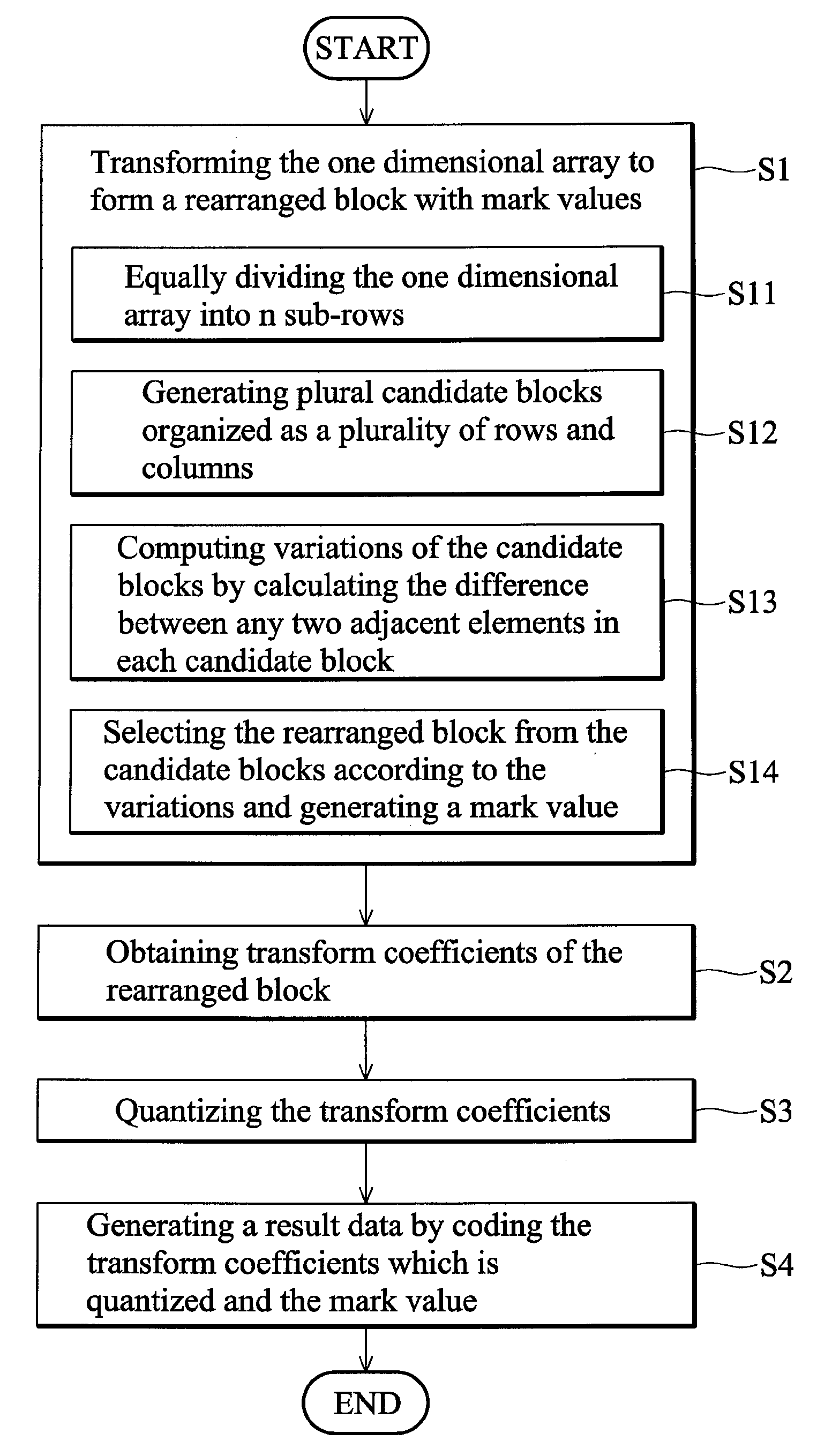
An apparatus for compressing an image data with an array of pixels comprising a data length is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a rearranging unit, a transformation operator, a quantizer and a coding operator. The rearranging unit is configured to transform the array to form a rearranged block with a mark value. The transformation operator is configured to obtain transform coefficients of the rearranged block according to a predetermined transformation. The quantizer is configured to quantize the transform coefficients. The coding operator is configured to generate a result data by coding the transform coefficients which is quantized and the mark value according to a predetermined coding method.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Website error-reporting screenshot classification method based on feature fusion
InactiveCN110414571AReduce workloadImprove operational efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setClassification methods
The invention discloses a website error-reporting screenshot classification method based on feature fusion. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out data enhancement on an imagedata set of error-reporting screenshots; zooming the image data to a uniform size, and randomly dividing the image data into a training set, a verification set and a test set; performing feature extraction on the image by using a part of network layer of the VGG16 convolutional neural network; extracting features of the image by using a scale-invariant feature transformation operator; fusing thetwo features through feature splicing to serve as final features of the image; and enabling the final features of the image to pass through a full connection layer, a Dropout layer and a Softmax layerto realize correct classification of error-reporting screenshots. According to the invention, machine learning is used to train the neural network for image classification, the workload of customer service staff is reduced, and the enterprise operation efficiency is improved; the data set is expanded by performing data enhancement on the data set image, so that the training is more sufficient; and the two image features are fused to obtain better classification accuracy.
Owner:浙江网新数字技术有限公司
Self-adaptive filtering method for power line communication signals
ActiveCN108880621AQuick filterSystems using filtering and bypassingPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringSelf adaptive
The invention provides a self-adaptive filtering method for power line communication signals, capable of effectively filtering out impulse noise in the power line communication signals. The method comprises the steps of collecting a power line communication signal sequence, converting the power line communication signal sequence into a signal matrix; constructing a transformation operator matrix according to the signal matrix obtained by conversion; constructing a measurement matrix; determining a filtering weight, updating the signal matrix in iterative mode according to the obtained transformation operator matrix, the filtering weight and the constructed measurement matrix until the current iteration frequency is equal to the length of the power line communication signal sequence; converting the currently obtained signal matrix, and generating a power line communication signal sequence in which noise is filtered out. The invention relates to the field of communication.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
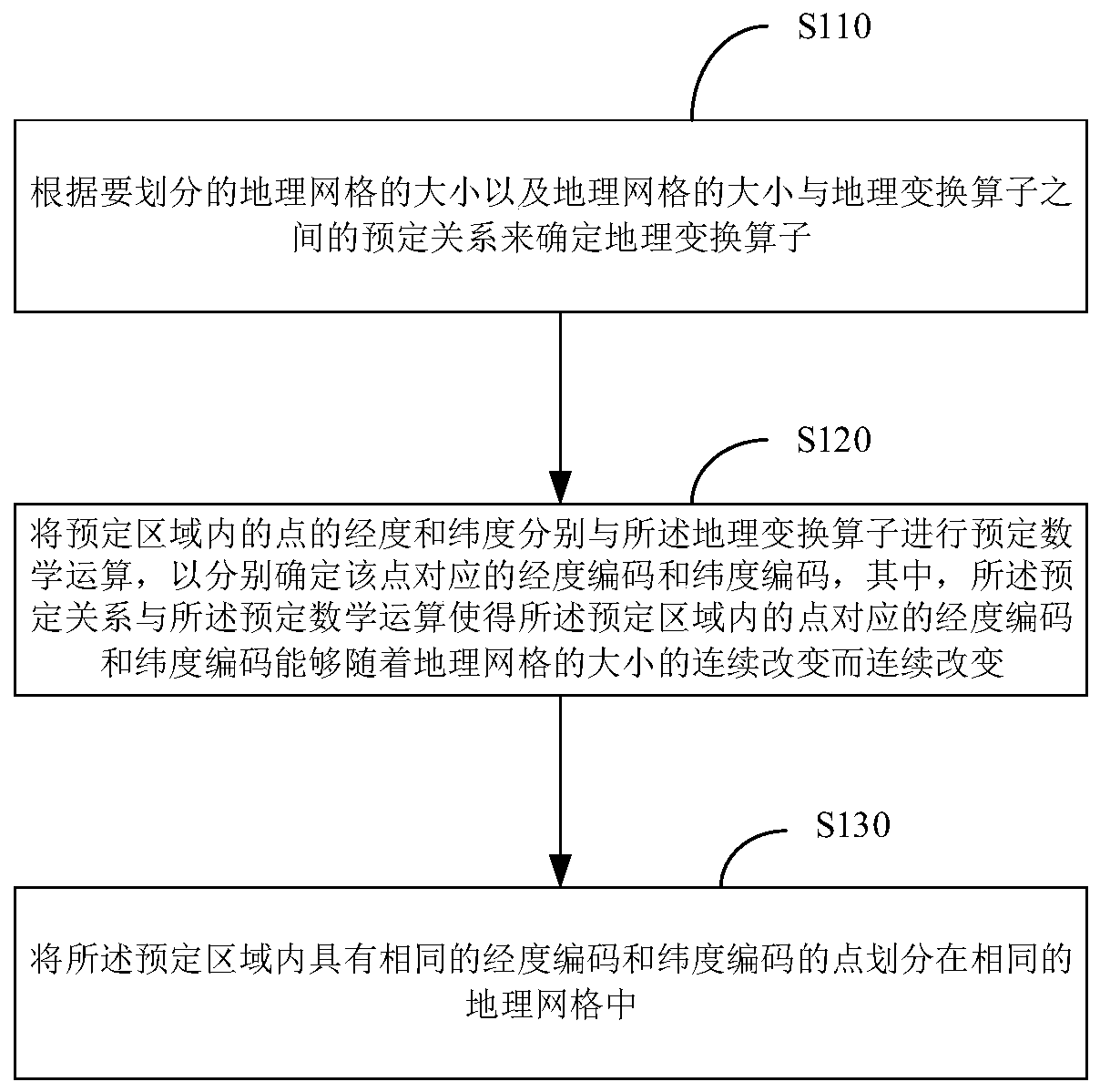
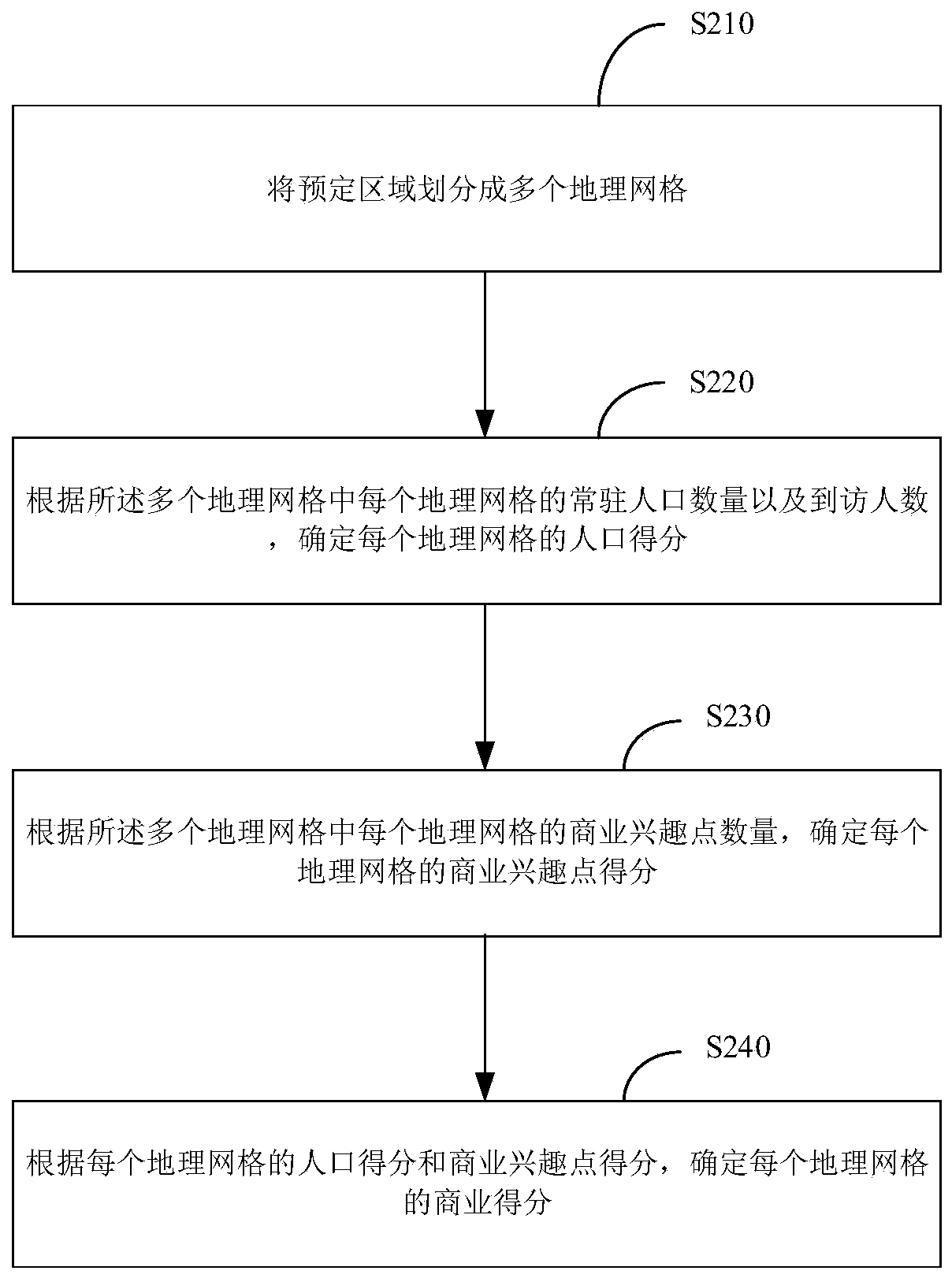
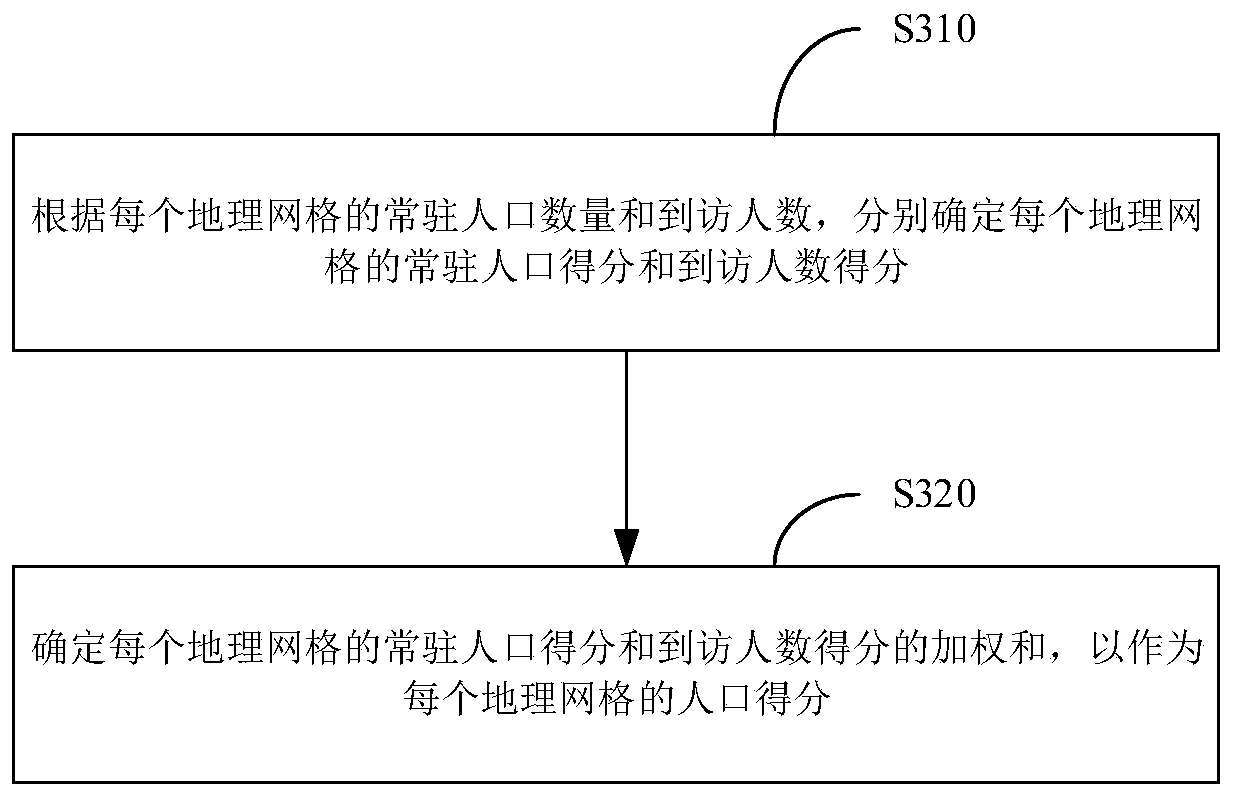
Geographic grid division method, business district determination method and equipment
PendingCN110348896AAccuracy continuously adjustableAccurate score calculationMarketingLongitudeComputer science
The invention provides a geographic grid division method, a business district determination method and equipment. The geographic grid division method comprises the following steps: determining a geographic transformation operator according to the size of the geographic grids to be divided and a predetermined relationship between the size of the geographic grids and the geographic transformation operator; respectively carrying out predetermined mathematical operation on the longitude and latitude of the point in the predetermined area and the geographical transformation operator, wherein the predetermined relationship and the predetermined mathematical operation enable the longitude codes and the latitude codes corresponding to the points in the predetermined region to be continuously changed along with the continuous change of the size of the geographic grid; and dividing the points with the same longitude codes and latitude codes in the predetermined area into the same geographic grid. According to the embodiment of the invention, the geographic grid division method can achieve the continuous adjustment of the geographical range precision of the business district.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
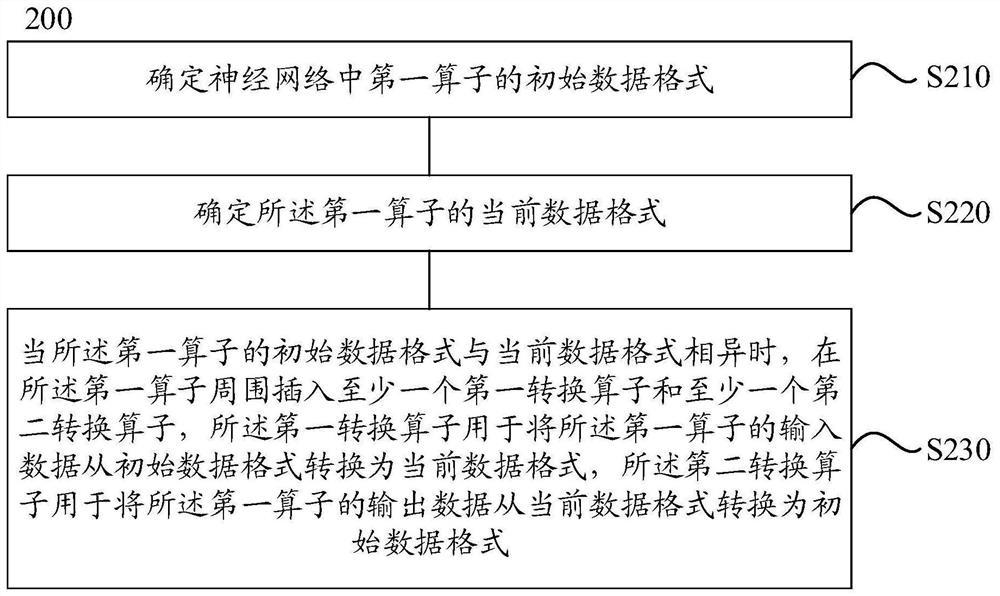
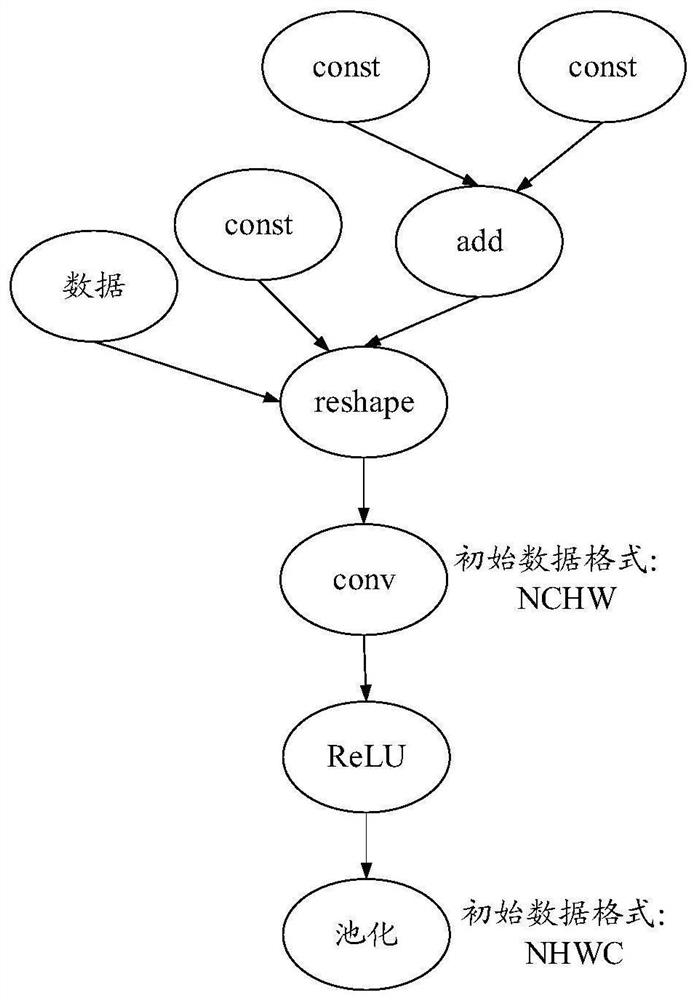
Method and device for inserting conversion operator
The invention provides a method for inserting a conversion operator. The method comprises the following steps: determining an initial data format of a first operator in a neural network; determining a current data format of the first operator; and when the initial data format of the first operator is different from the current data format, inserting at least one first conversion operator and at least one second conversion operator around the first operator, wherein the first conversion operator is used for converting the input data of the first operator into the current data format from the initial data format, and the second conversion operator is used for converting the output data of the first operator from the current data format to the initial data format. In the method, the initial data format is a data format beneficial to hardware performance, and the current data format is a data format beneficial to improving the processing efficiency of the first operator, therefore, the conversion operator is inserted according to the initial data format and the current data format of the first operator, and the requirements of the operator and the requirements of hardware can be met at the same time.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Super-resolution image processing
ActiveUS8213746B2Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingImage resolution
A method for iterative derivation of a master image from sampled images of non-identical, at least partially overlapping, regions of a scene. The method includes defining a transformation operator mapping positions within the master image to corresponding positions in the sampled image; a distortion operator simulating a modulation transfer function associated with an imaging sensor from which the sampled image was generated; and a sampling operator for reducing an image from the output resolution to the resolution of the sampled image. For each sampled image the transformation operator, distortion operator and sampling operator are applied to a current master image hypothesis to generate a predicted image A difference image is calculated which has pixel values corresponding to the difference in corresponding pixel values between the sampled image and the predicted image. A back-projection of each of the difference images is performed to generate a correction image for the current master image hypothesis. Finally, the correction images are employed to perform a correction to the current master image hypothesis to generate a new master image hypothesis. The correction to the current master image hypothesis includes combining the correction images by deriving a weighted average of values of corresponding pixels in the correction images. The weight of each pixel in each correction image is calculated as a function of a distance as measured in the sampled image between: a point in the sampled image to which the pixel in the correction image is mapped by the transformation operator, and at least one pixel centroid proximal to that point.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
Methods and systems of four valued analogical transformation operators used in natural language processing and other applications
ActiveCN105706091AIncrease search queryNatural language analysisKnowledge representationKnowledge sourcesShort-term memory
Owner:罗杰密德茂尔
Special handcart switch circuit electrical inspection device for 35KV switch cabinet
InactiveCN102222864ASimple structureSimple and fast operationSwitchgear shutters/guardsElectromagnetic lockClose contact
The embodiment of the invention provides a special handcart switch circuit electrical inspection device for a 35KV switch cabinet, comprising a rear handcart switch cabinet door, an electrical inspection door, a lock, an electromagnetic lock, a lock blade and an electrical displayer, wherein the electromagnetic lock and the electrical inspection door are arranged on the rear handcart switch cabinet door; the lock is arranged on the electrical inspection door; the lock blade is interlocked with the electromagnetic lock; the electromagnetic lock can be electrified only when a normally-closed contact of the handcart travel switch and a normally-closed contact of a relay controlled by the electrical displayer are closed simultaneously. The special handcart switch circuit electrical inspection device for the 35KV switch cabinet has a simple structure, can be operated simply and conveniently, has reliable performance, can reduce the operation of an electrical transformation operator, and ensures to achieve the requirement of safe and reliable power supply during the power supply running process.
Owner:NINGBO ELECTRIC POWER BUREA
Power signal adaptive reconstruction method in load decomposition
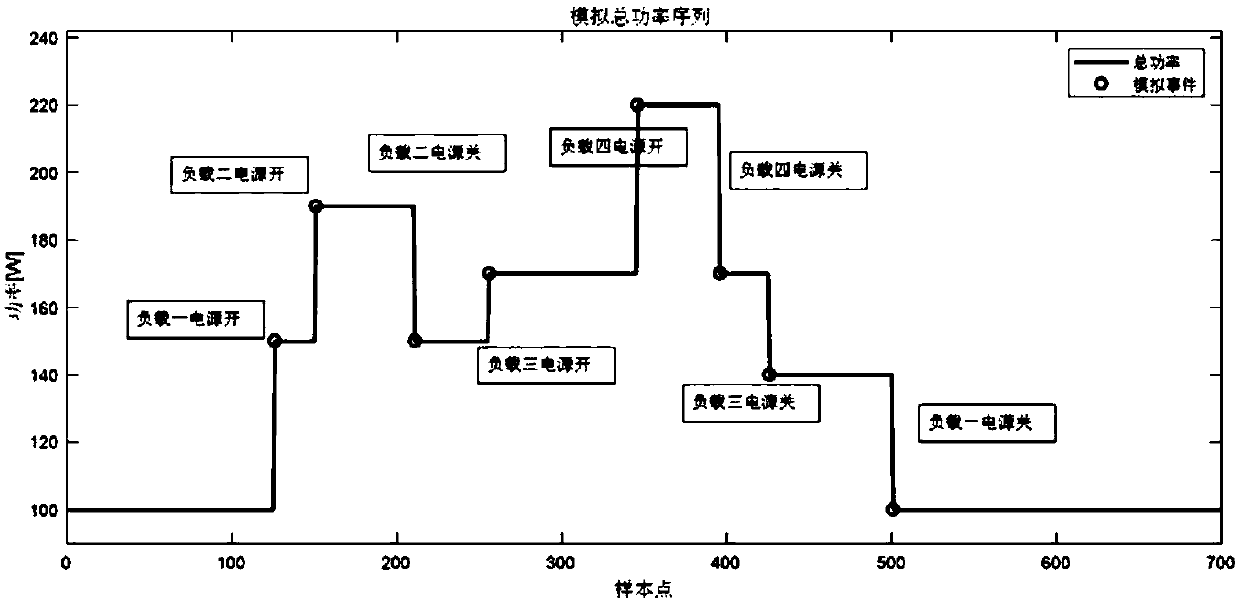
InactiveCN108918928ARapid refactoringAvoid missingTime integral measurementMissing dataElectric power system
The invention discloses a power signal adaptive reconstruction method in load decomposition, and the method can reconstruct a power signal sequence without missing data. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the power signal sequence, and converting the power signal sequence into a power matrix; according to the power matrix obtained through conversion, constructing a transformationoperator matrix; constructing a measurement matrix; according to the obtained transformation operator matrix and the constructed measurement matrix, iteratively updating the power matrix, until the current iteration times is equal to length of the power signal sequence; and converting the currently obtained power matrix, and generating the power signal sequence without missing data. The method provided by the invention relates to the field of electric power.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
Apparatus of compressing image data and a method thereof
InactiveUS20090097766A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionImaging data
An apparatus for compressing an image data with an array of pixels comprising a data length is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a rearranging unit, a transformation operator, a quantizer and a coding operator. The rearranging unit is configured to transform the array to form a rearranged block with a mark value. The transformation operator is configured to obtain transform coefficients of the rearranged block according to a predetermined transformation. The quantizer is configured to quantize the transform coefficients. The coding operator is configured to generate a result data by coding the transform coefficients which is quantized and the mark value according to a predetermined coding method.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
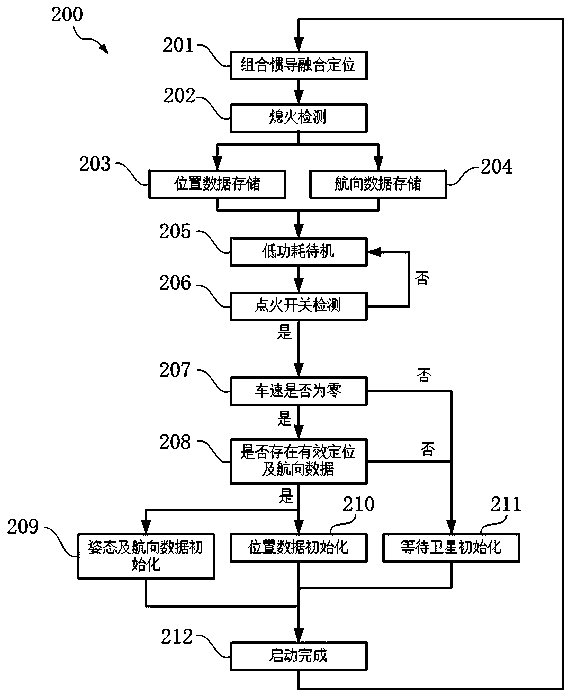
Starting method for vehicle-used integrated inertial navigation system under the condition of no observation value, vehicle-used integrated inertial navigation system and vehicle
ActiveCN109798890ANavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial navigation systemSpace vector
The invention discloses a starting method for a vehicle-used integrated inertial navigation system under the condition of no observation value, a vehicle-used integrated inertial navigation system anda vehicle. The method is characterized by including the following steps: S1. in the process of vehicle movement, calculating, by the integrated inertial navigation system, a transformation operator Tbetween a vehicle body coordinate system and an earth coordinate system in real time; S2. when the vehicle is judged to be in a parking state, recording the last transformation operator T in a nonvolatile manner; and S3. when the vehicle is restarted, when the vehicle is judged to be in a parking state, converting a space vector under the current vehicle body coordinate system into a space vectorunder the earth coordinate system through the transformation operator T to realize the startup of the integrated inertial navigation system.
Owner:上海戴世智能科技有限公司
Quick sparse Radon transformation method based on iterative shrinkage
ActiveCN102879824BOutput processing resultsAdaptive processingSeismic signal processingGeneralized inverseRadon
The invention discloses a quick sparse Radon transformation method based on iterative shrinkage. The quick sparse Radon transformation method comprises the following steps: firstly, setting an initial variable value; secondly, constructing a transformation operator L and calculating generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L; thirdly, treating a seismic channel set d to be treated by utilizing the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L; and lastly, judging if all channel sets in a seismic data cube are treated, if not, continuing to treat the seismic channel set d to be treated by utilizing the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L, and if so, ending. According to the quick sparse Radon transformation method, for one seismic data cube collected by adopting the same collection parameters, the generalized inverse of the transformation operator L only needs to be calculated once, then the transformation operator L and the generalized inverse (LTL)-1LT of the transformation operator L are applied to all seismic channel sets, thereby greatly reducing calculated amount; and the iterative shrinkage algorithm only includes product operation of simple matrixes and vectors and threshold operation, greatly reduces the calculated amount relative to the conventional sparse Radon transformation, and better adapts to treatment of practical seismic data.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
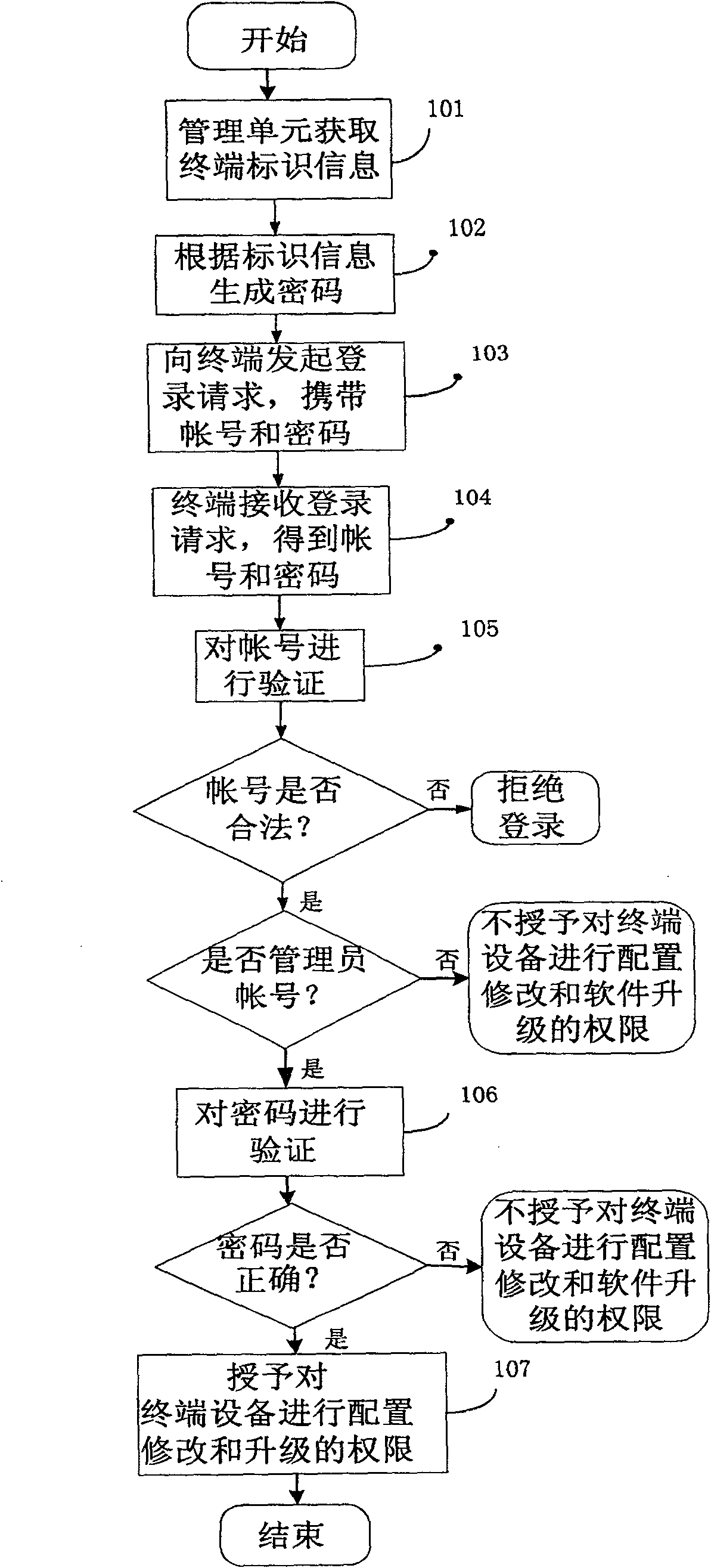
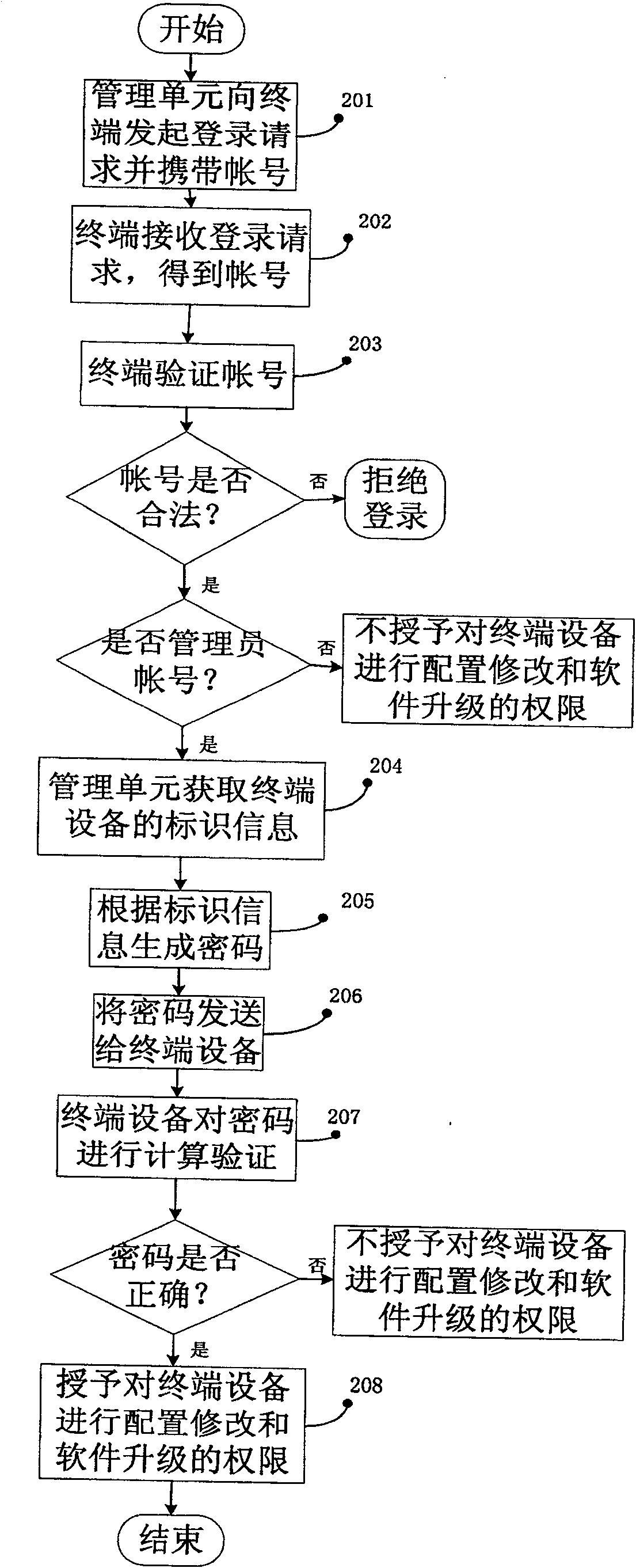
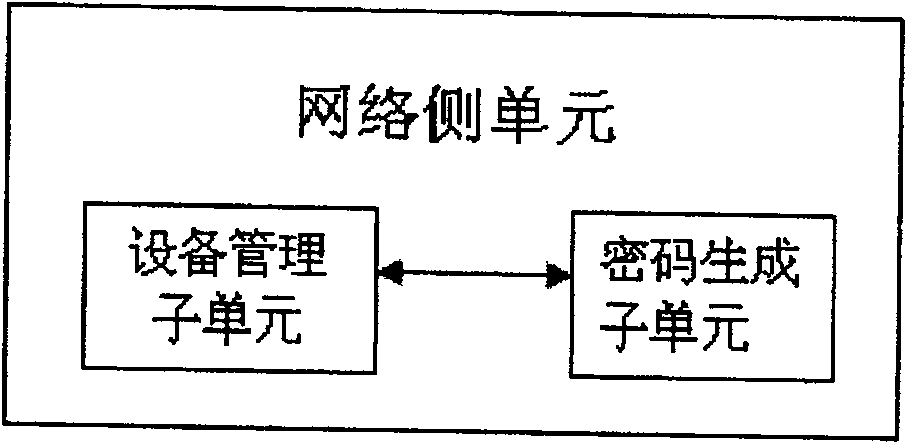
Method for revising terminal configuration, network side management unit, terminal and system
ActiveCN100571470CReduce churnSimplify the configuration processSecurity arrangementNetwork data managementManagement unitPassword
The invention discloses a method for restricting configuration modification and software upgrade of terminal equipment, which is applied to a network side management unit and terminal equipment, including: the management unit acquires terminal identification information; the management unit automatically generates a password according to the identification information , the password is calculated and generated according to the encryption algorithm and the identification information; the management unit initiates a login request to the terminal device, and sends the password to the terminal device; the terminal device receives the login request and the password; the terminal device calculates and verifies the correctness of the password, and if the verification is passed, the terminal device grants the login user the authority to modify the configuration and upgrade the software of the terminal device. The invention also discloses a system for realizing the method of the invention. The present invention can effectively restrict configuration modification and software upgrade of terminal equipment, and improve security; it can be used to prevent equipment from switching networks, reduce loss of operator assets, simplify operator terminal configuration and upgrade, and facilitate network expansion and transformation .
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Auto feature preparation for high performance online inferencing
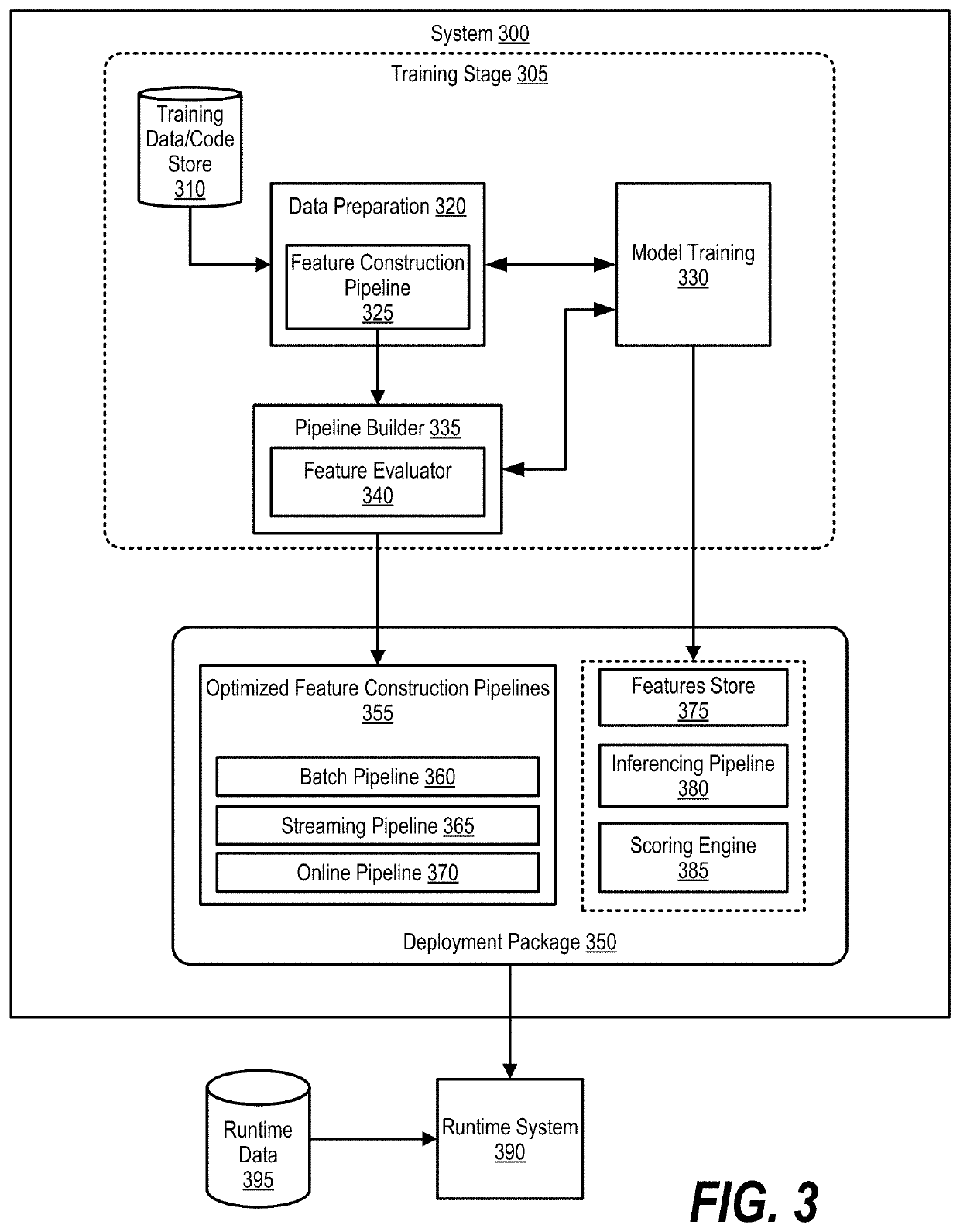
PendingUS20220318652A1Database updatingCharacter and pattern recognitionData transformationSoftware engineering
An approach is provided in which a method, system, and program product analyze, while training a machine learning model, a set of first data transformation operators in a first data preparation pipeline that generates a plurality of constructed features from a set of training data. The method, system, and program product create a plurality of second data preparation pipelines from the first data preparation pipeline, wherein the set of first data transformation operators are converted to a set of second data transformation operators and each assigned to one of the plurality of second data preparation pipelines. The method, system, and program product deploy the plurality of second data preparation pipelines to a runtime system.
Owner:IBM CORP
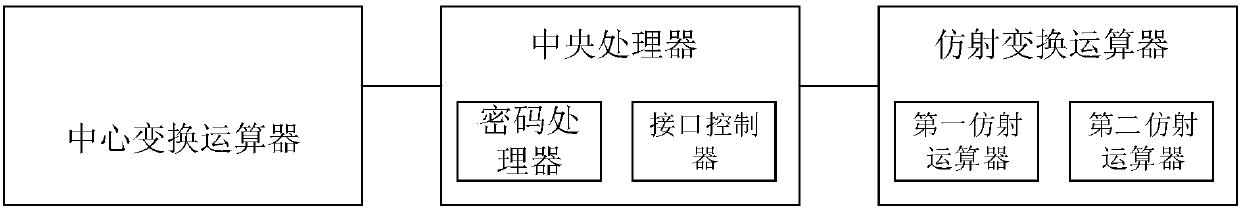
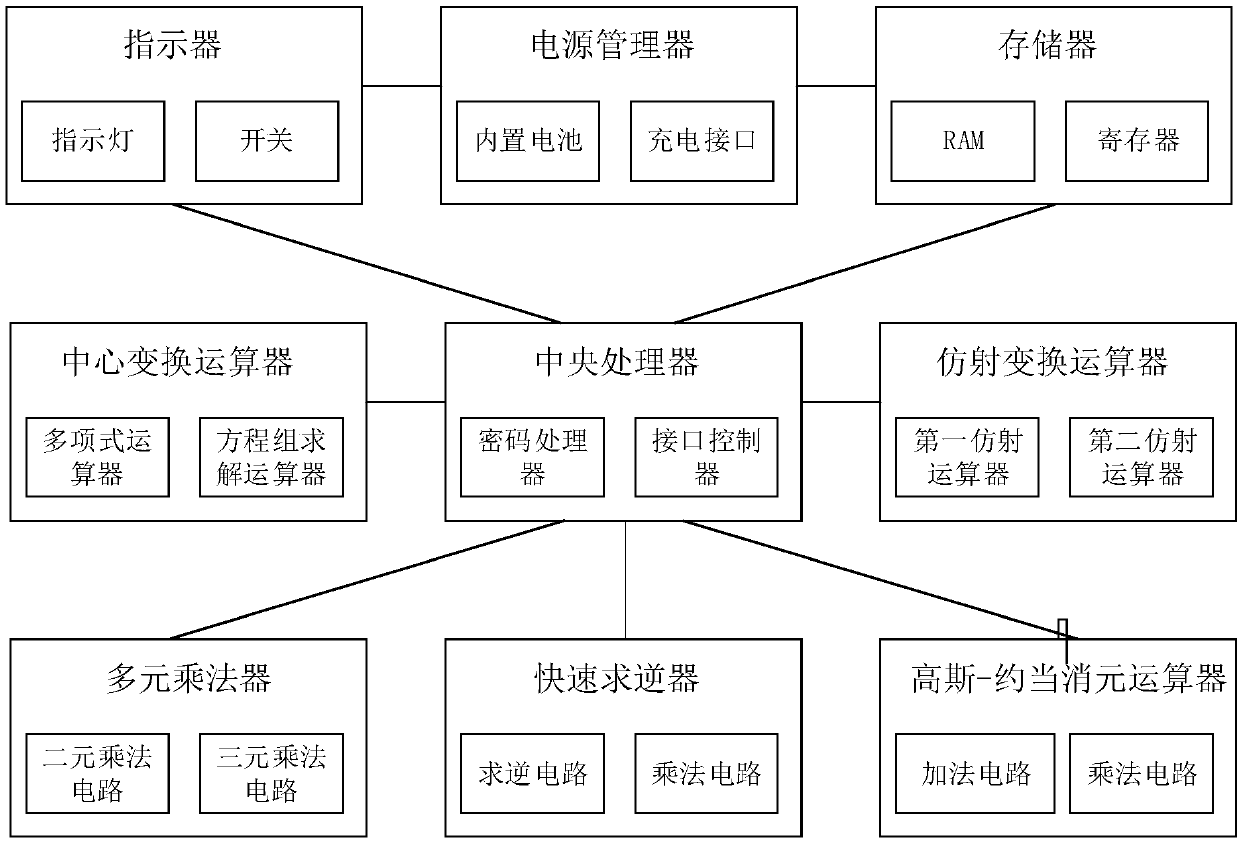
Rainbow signing device
InactiveCN108880816AResist attackFast signatureUser identity/authority verificationHigh level techniquesRainbowSecurity level
The invention discloses a rainbow signing device, comprising a central processing unit, a central transformation operator and an affine transformation operator. The central processing unit comprises acipher processor and an interface controller. The affine transformation operator comprises a first affine operator and a second affine operator. The interface controller is used for inputting to-be-signed information y and private keys L1, F and L2. The central processing unit is used for calling the first affine operator and carrying out L1 linear affine transformation on the to-be-signed information y based on the L1, thereby obtaining a first transformation result y-bar; calling the central transformation operator and carrying out central mapping inverse transformation on the first transformation result y-bar based on the F, thereby obtaining a second transformation result x-bar; and calling the second affine operator, and carrying out L2 linear affine transformation on the second transformation result x-bar based on the L2, thereby obtaining a rainbow signature x. Through adoption of the embodiment of the invention, the signing speed is fast, computing resources are few, and a security level is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
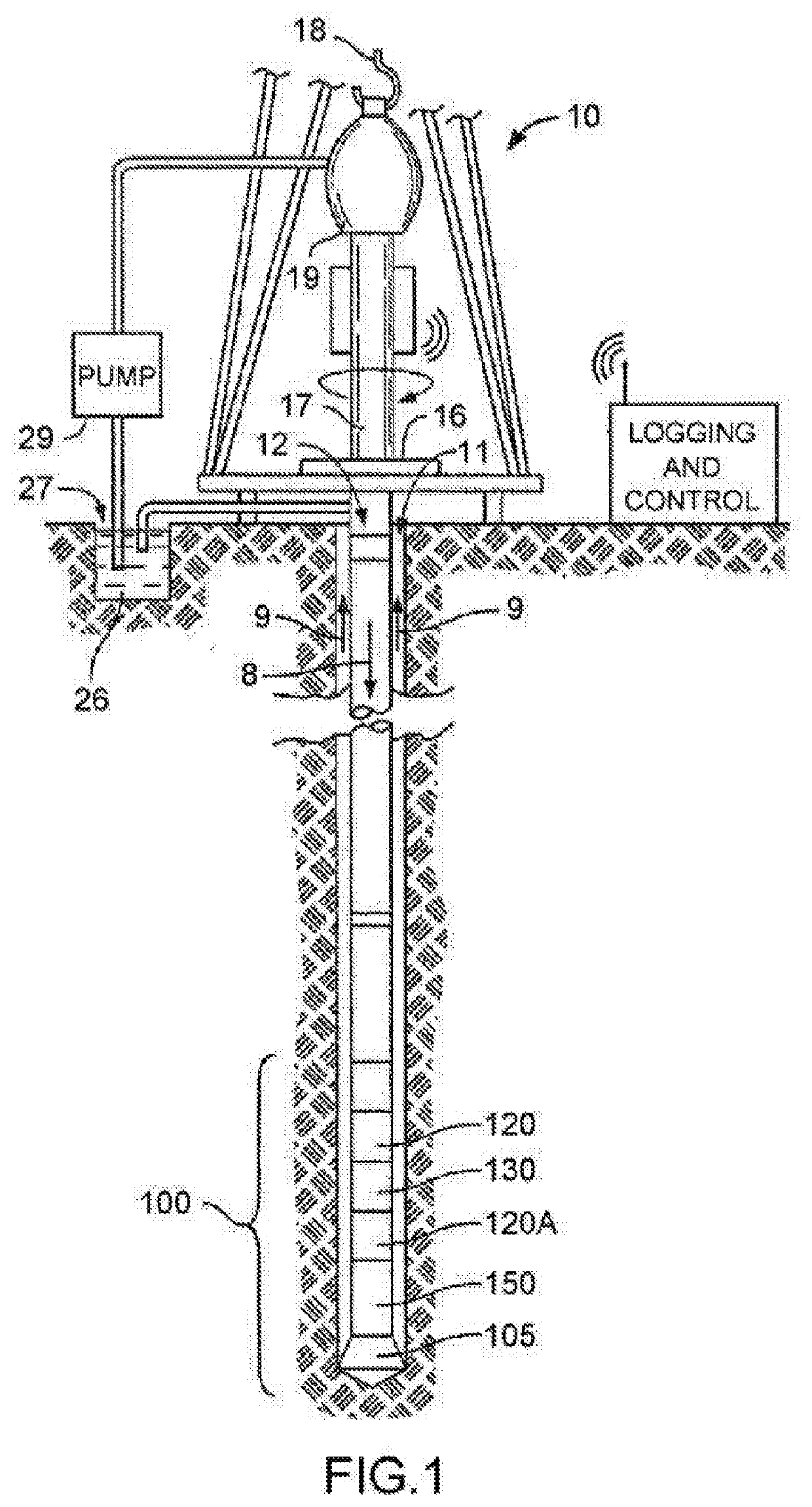
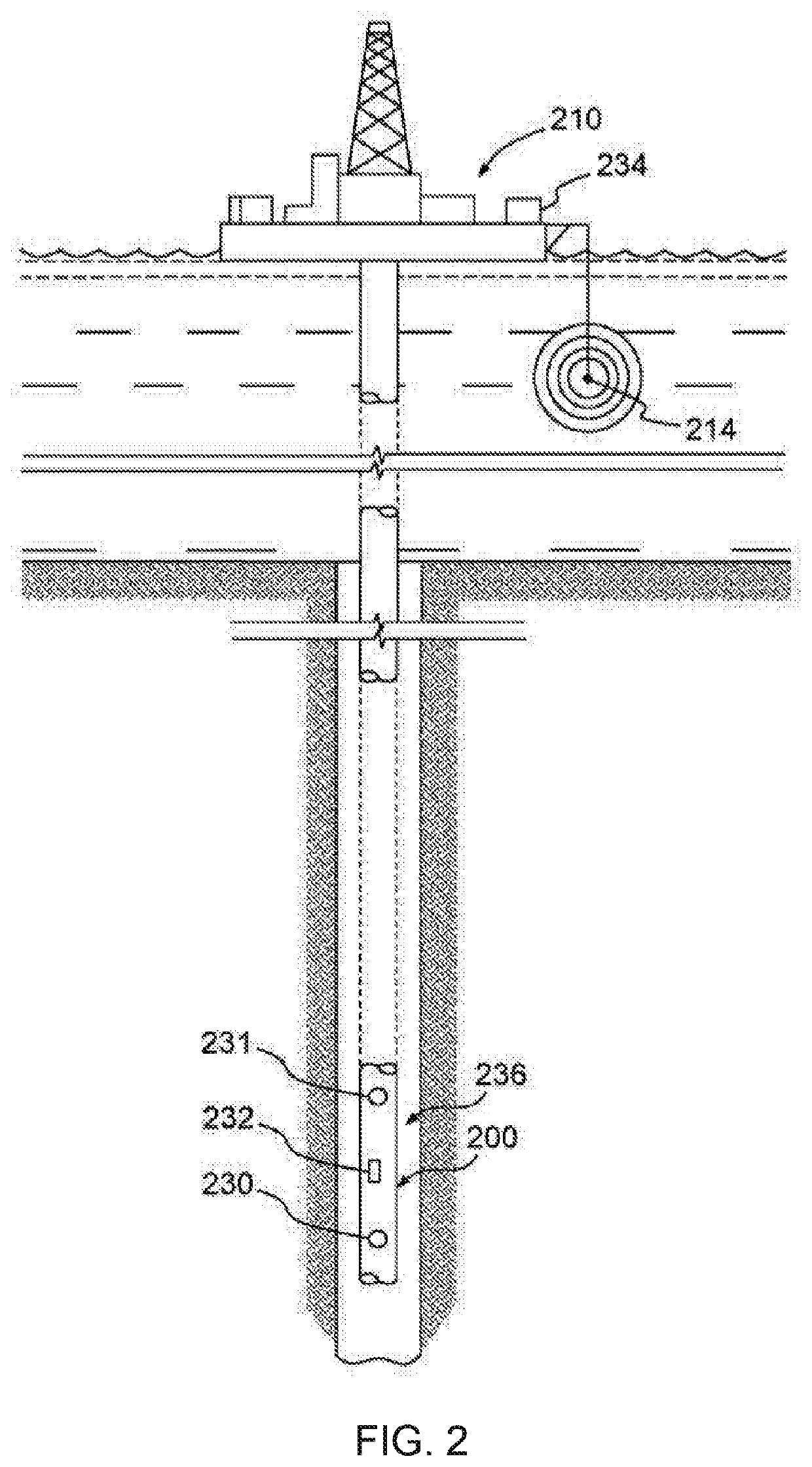
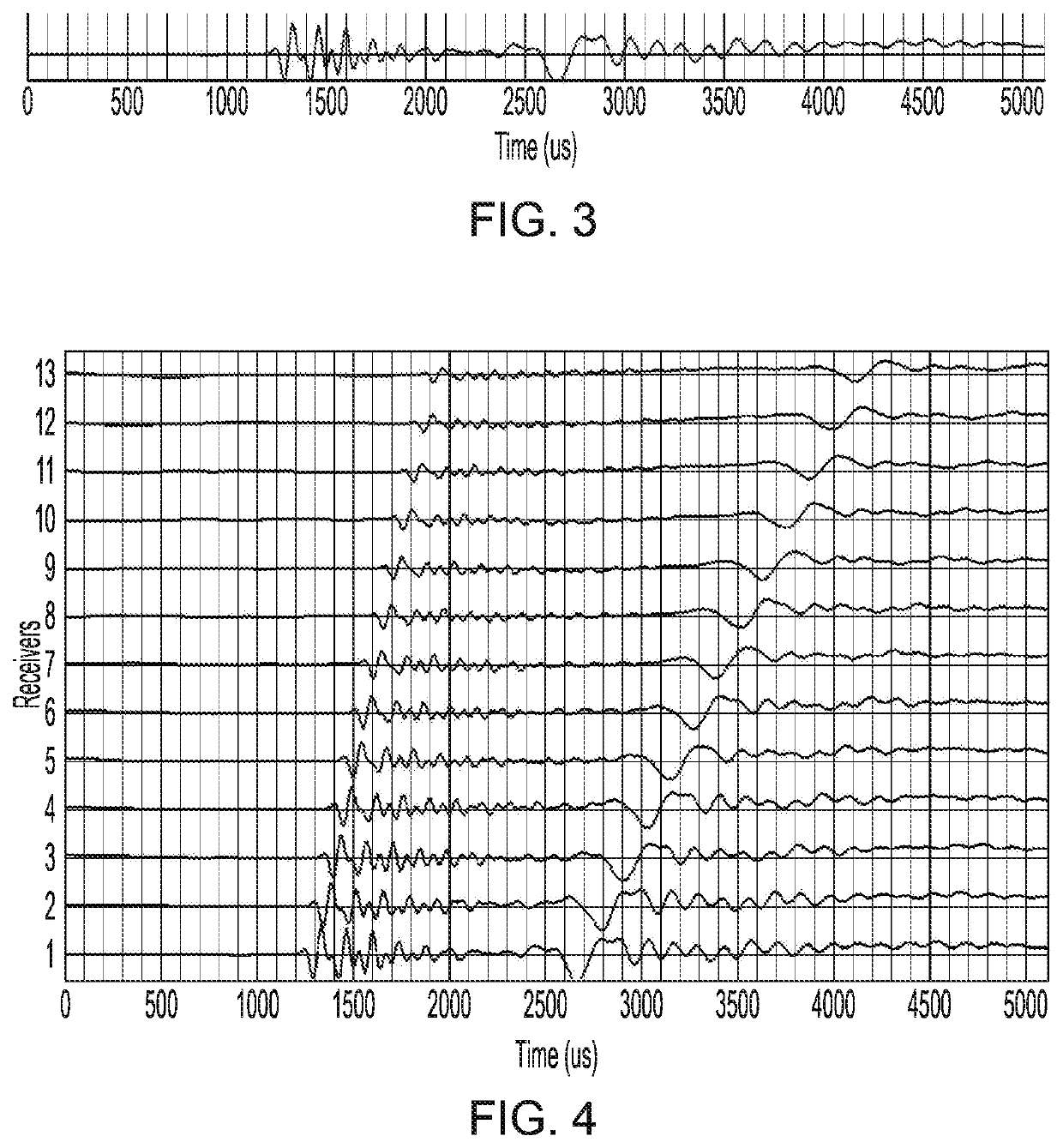
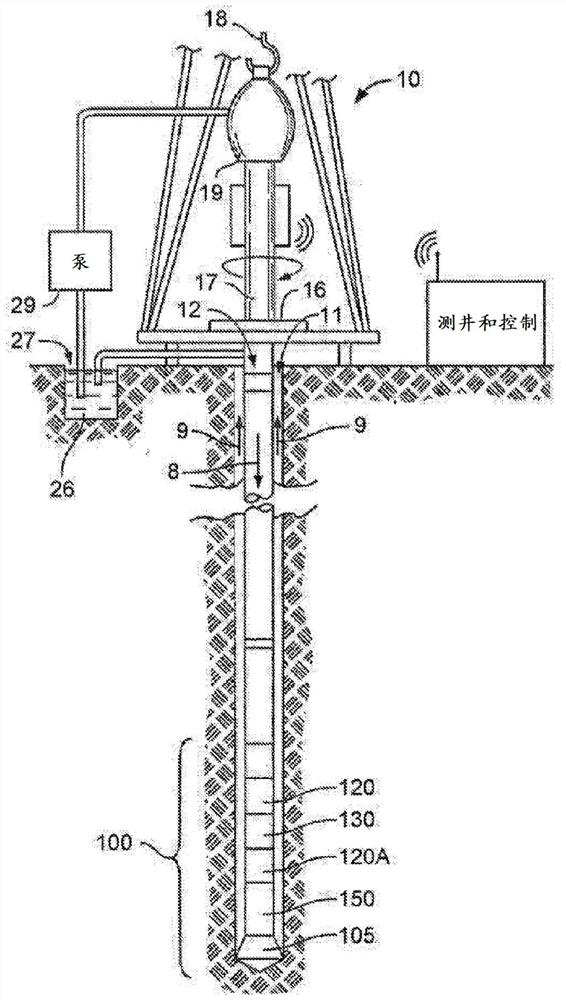
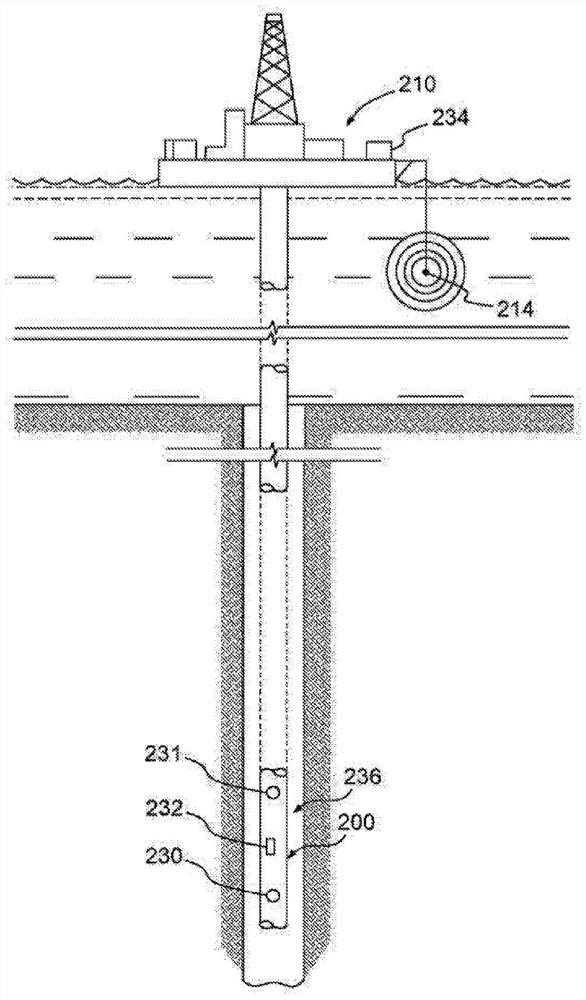
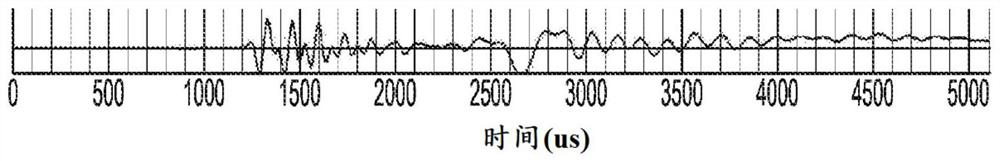
Method and device for determining sonic slowness
Sonic logging data including a sonic waveform associated with a plurality of shot gathers is accessed. A transformation operator is applied to the sonic logging data to provide a transformed sonic image, the transformation operator including at least one of a short time average long time average (STA / LTA) operator, a phase shift operator, and a deconvolution operator. A machine learning process is performed using the transformed sonic image to determine a sonic slowness associated with the sonic logging data. The sonic slowness is provided as an output.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods and systems of four valued analogical transformation operators used in natural language processing and other applications
A system for the dynamic encoding in a semantic network of both syntactic and semantic information into a common four valued logical notation. The encoding of new information being benign to prior syntactic constructions, tests for N conditionals in time O(C) and allows for the proper quantification of variables at each recursive step. The query / inference engine constructed from such an implementation is able to optimize short term memory for maximizing long term storage in the automaton. In a parallel context this can be viewed as optimizing communication and memory allocation between processes. The self-referencing system is capable of analogically extending knowledge from one knowledge source to another linearly. Disclosed embodiments include machine translation, text summarization, natural language speech recognition natural language.
Owner:MIDMORE ROGER
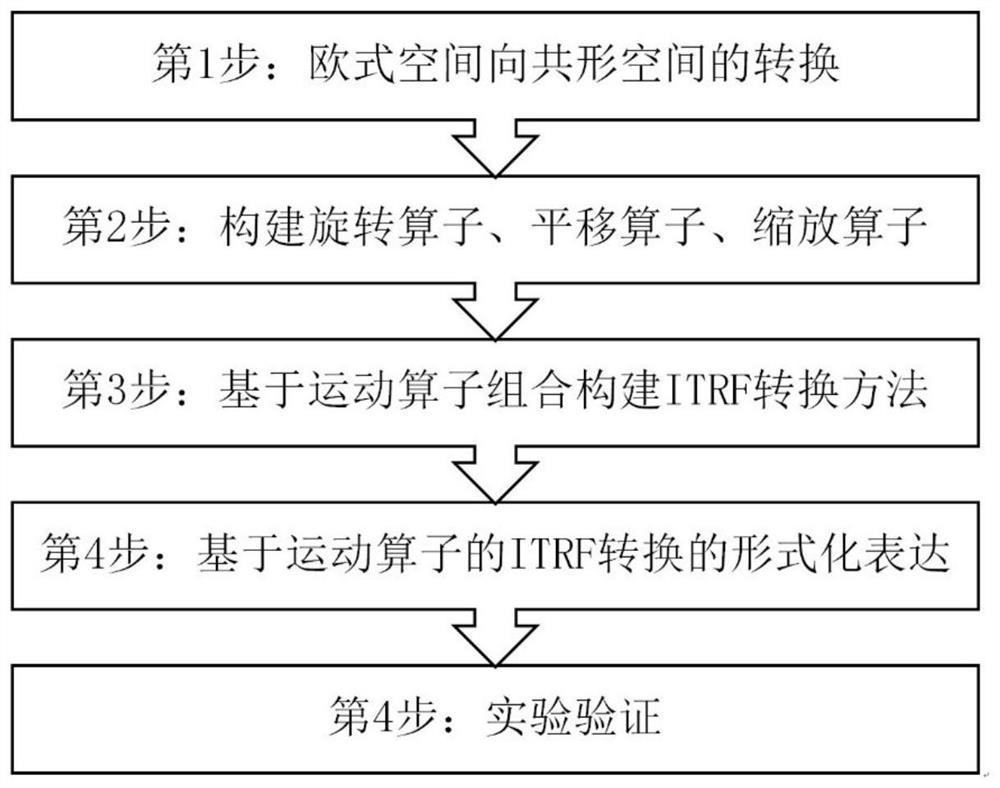
ITRF conversion method based on conformal geometric algebra
PendingCN113468483AComplex mathematical operations3D-image renderingTransformation operatorRotation operator
The invention discloses an ITRF conversion method based on conformal geometric algebra. The ITRF conversion method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining a to-be-converted station and coordinates of the to-be-converted station in an Euclidean space E3; 2, introducing a reference origin e0 and an infinite point e-infinity based on a covariant view angle, and converting the coordinates of the to-be-converted station point in an Euclidean space E3 into the coordinates of the to-be-converted station point in a conformal space; 3, in the conformal space, constructing a rotation operator, a translation operator and a scaling operator which have the same effect as rotation, translation and scaling in the Euclidean space E3; 4, according to the conversion type of the reference frame and the rotation operator, the translation operator and the scaling operator constructed in the step 3, converting the coordinates of the to-be-converted station point in the conformal space from any reference frame state at any moment to another reference frame state. According to the method, on the basis of unified operator expression, the conversion operator is directly calculated according to the conversion parameters, and then conversion is directly carried out, so complex matrix conversion is avoided, and a tedious conversion form and a complex calculation process are simplified.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for determining sonic slowness
Sonic logging data including a sonic waveform associated with a plurality of shot gathers is accessed. A transformation operator is applied to the sonic logging data to provide a transformed sonic image, the transformation operator including at least one of a short time average long time average (STA / LTA) operator, a phase shift operator, and a deconvolution operator. A machine learning process is performed using the transformed sonic image to determine a sonic slowness associated with the sonic logging data. The sonic slowness is provided as an output.
Owner:GEOQUEST SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com