Patents
Literature
68 results about "Time signature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are contained in each measure (bar), and which note value is equivalent to a beat.
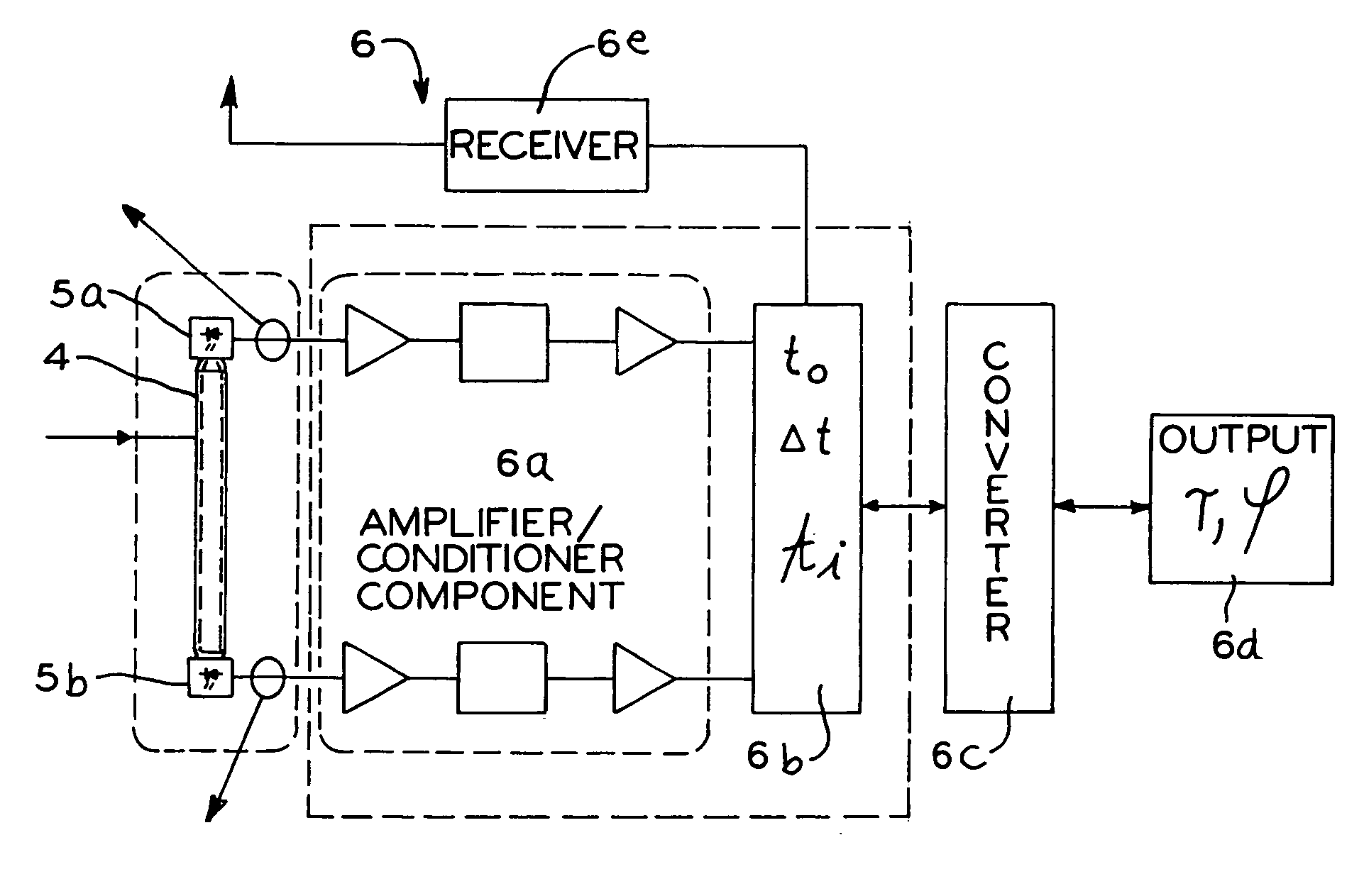
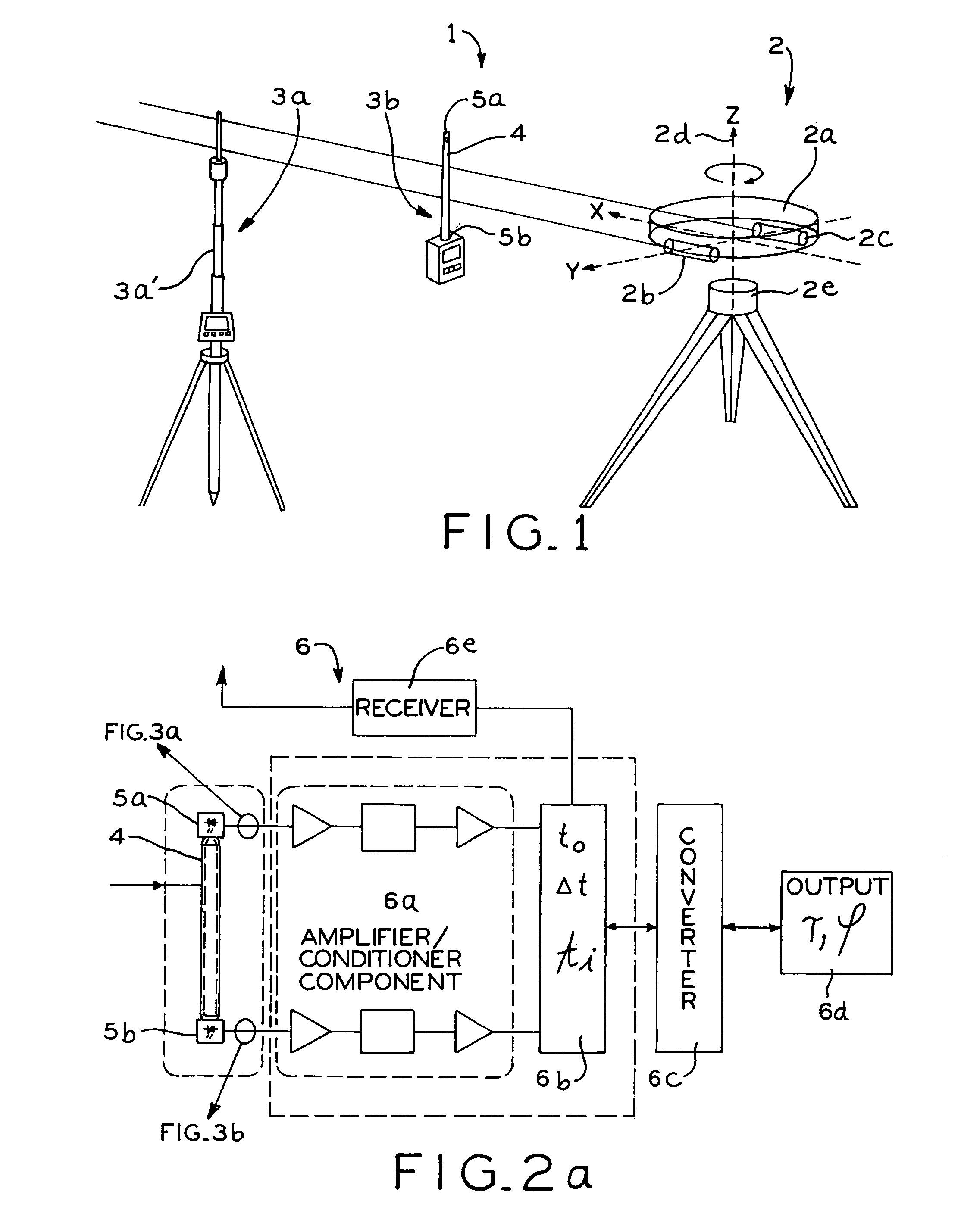
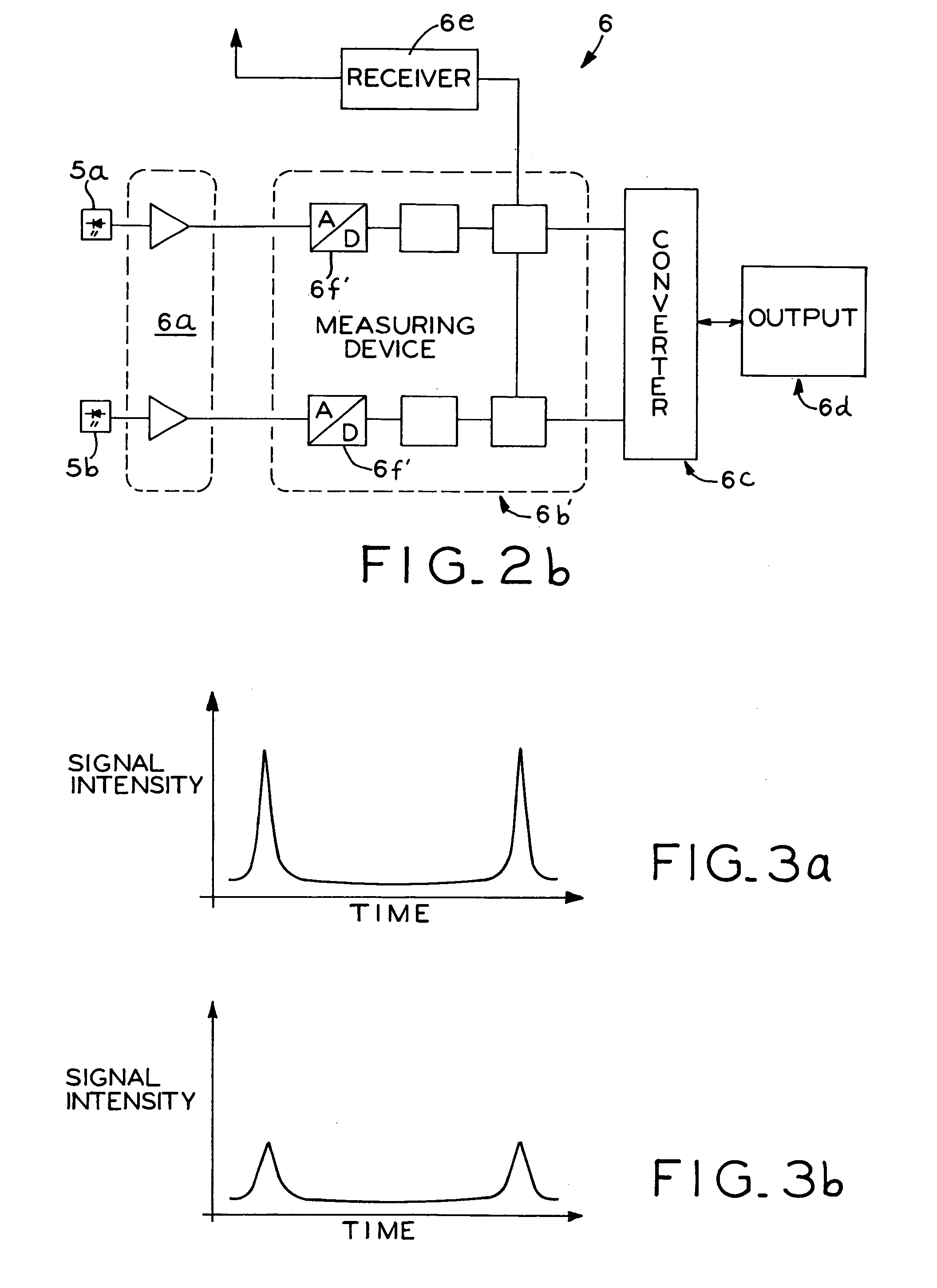
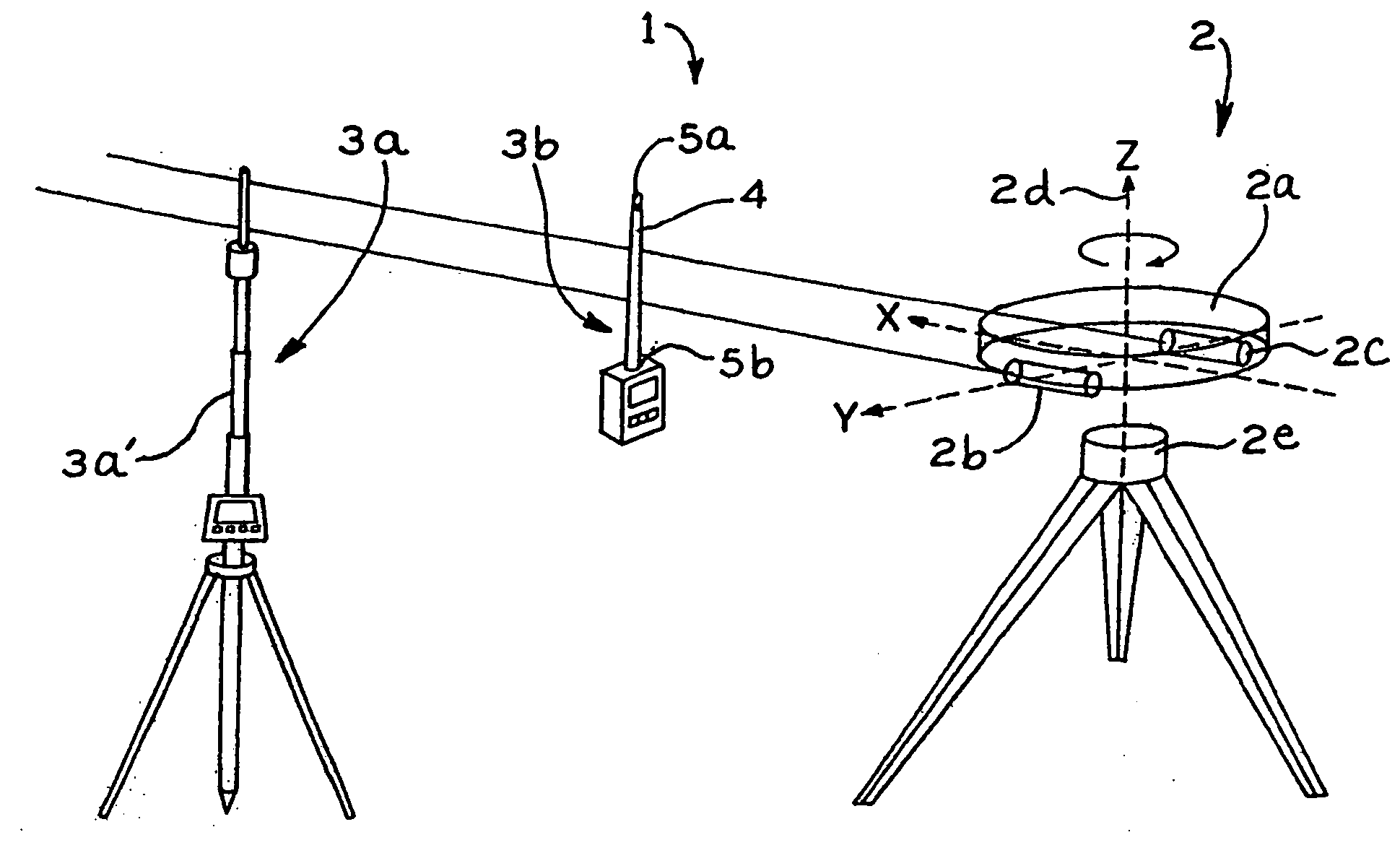
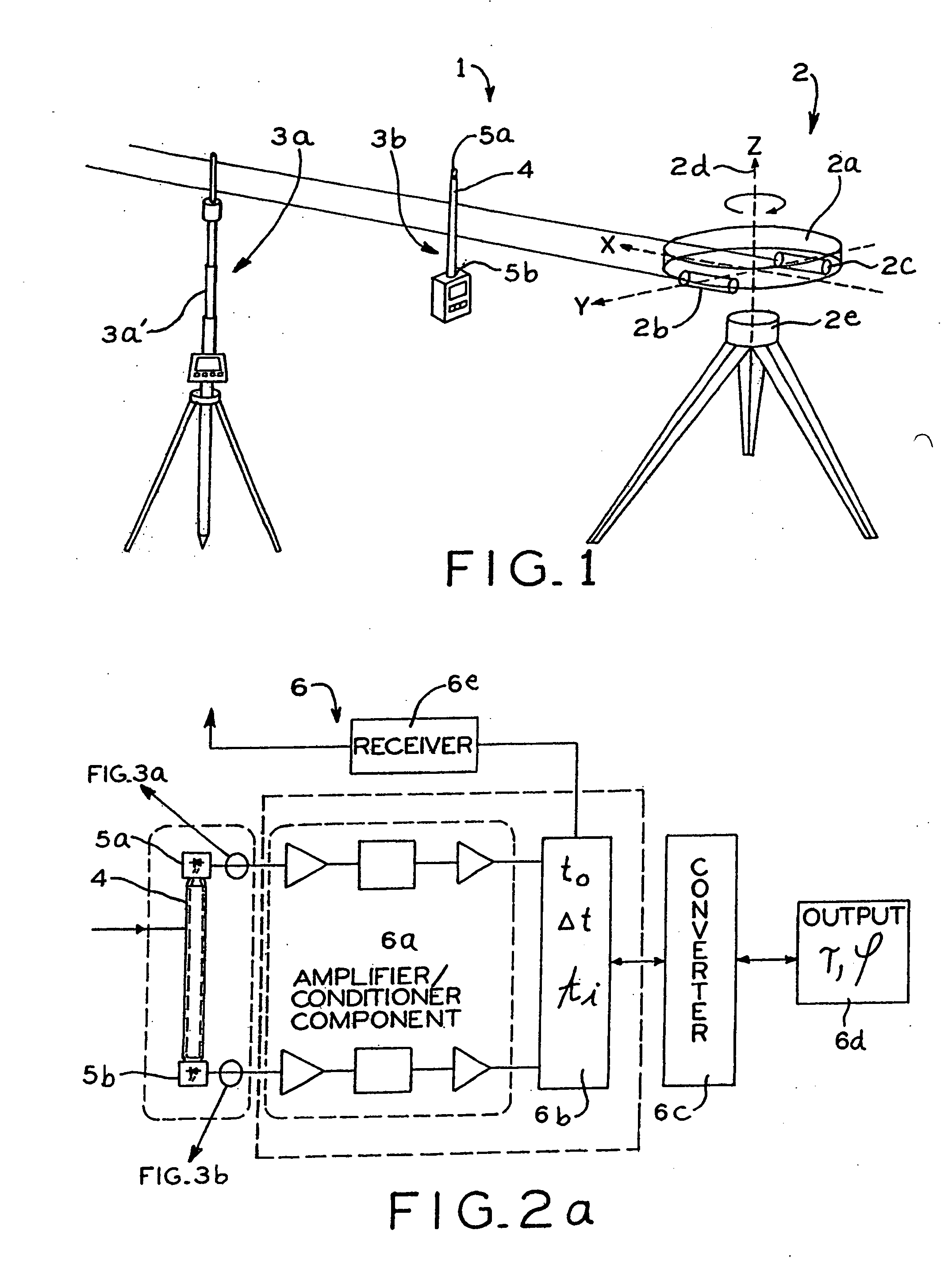
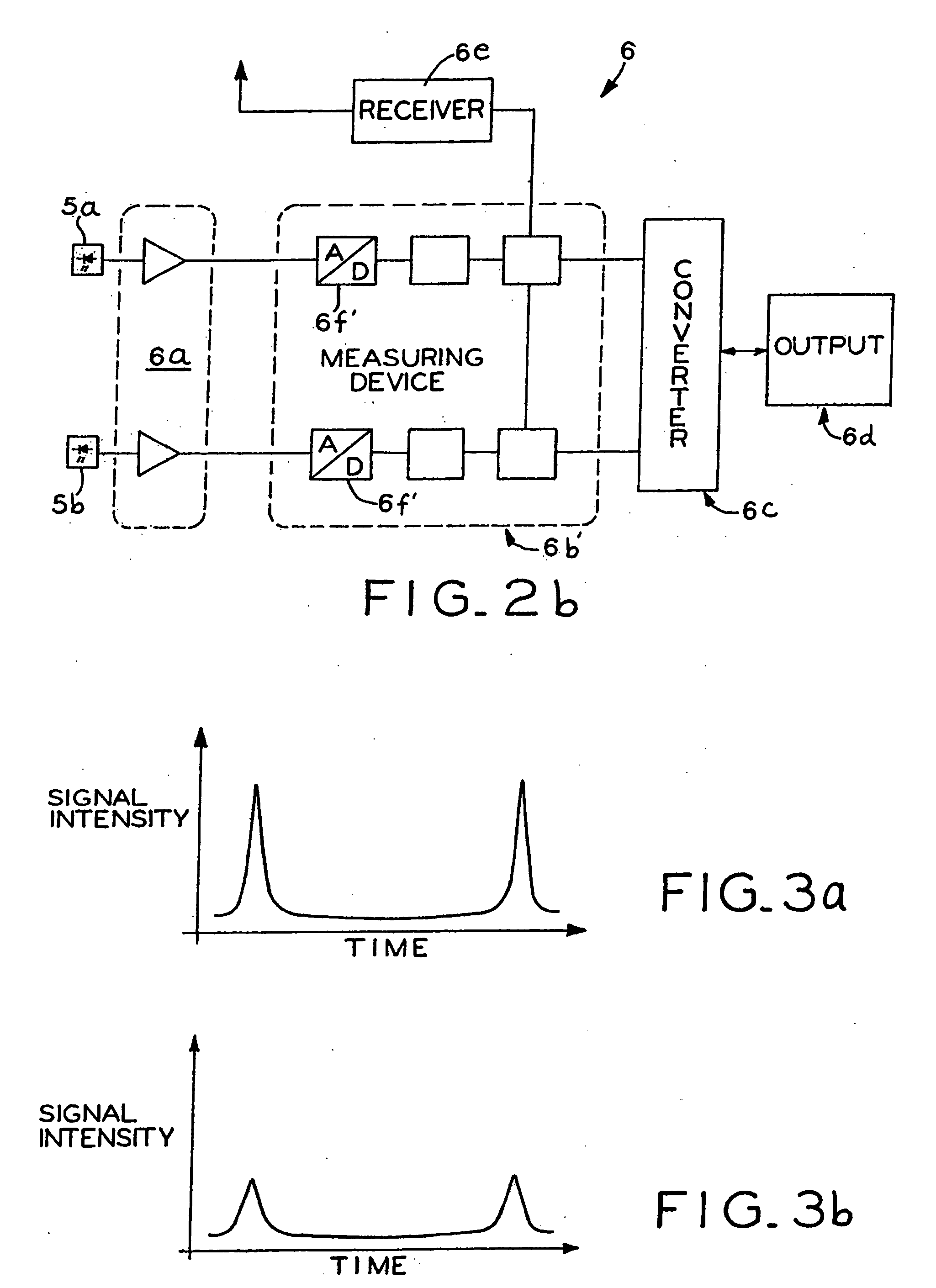
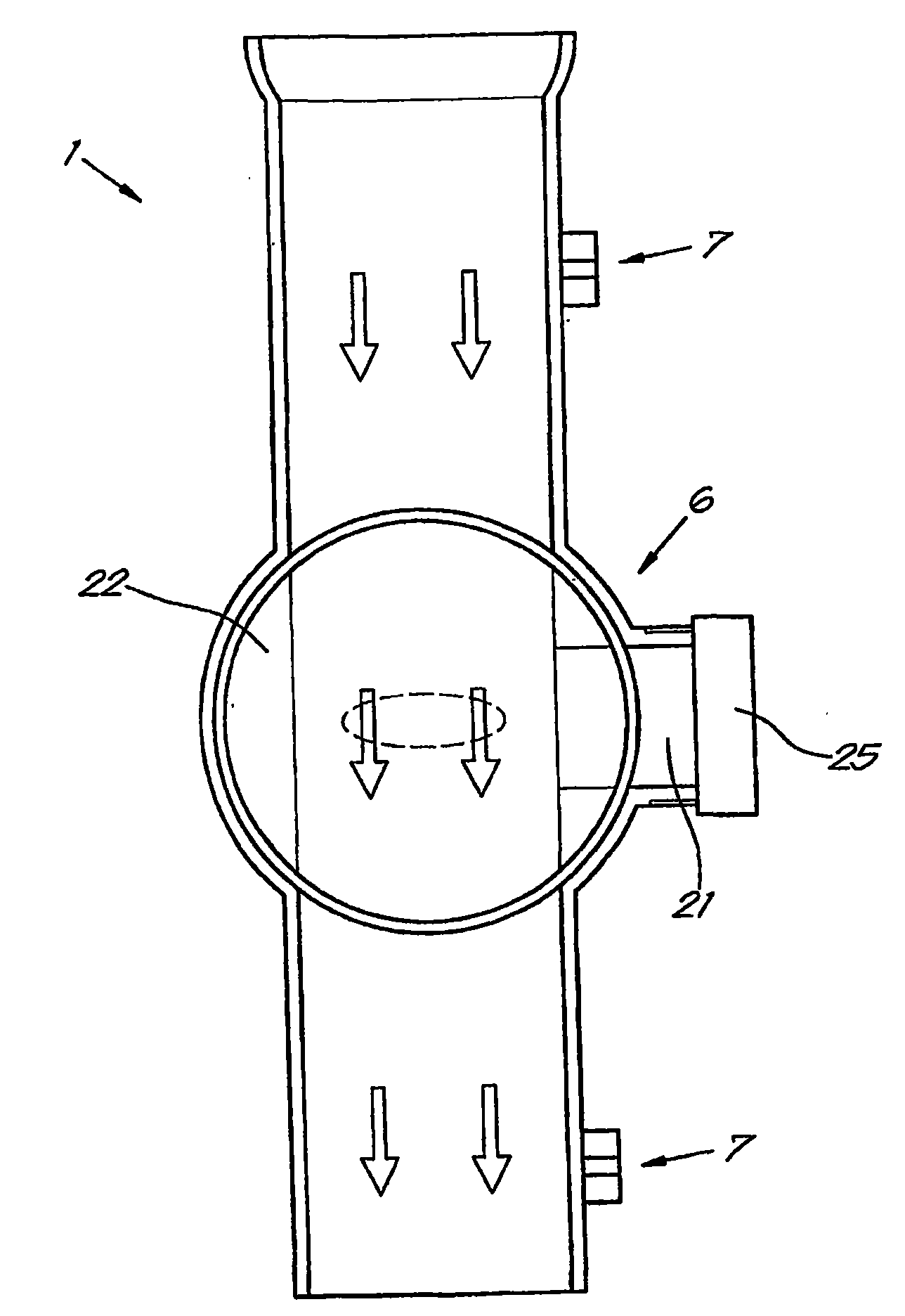
Measuring device and measuring method for determining distance and/or position
InactiveUS7110092B2Easy to controlIntuitive adjustmentAngle measurementOptical rangefindersMeasurement deviceSignal beam
A measuring device is provided with a signal generator and a signal receiver, which is located at a measurable distance from the signal generator. The signal generator is designed for the emission of at least two signal beams covering in given relationship to each other an area and the signal receiver is designed for the time-resolved reception of the signal beams in such a manner that the generator-receiver distance can be determined from the time signature of the signal beam reception.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
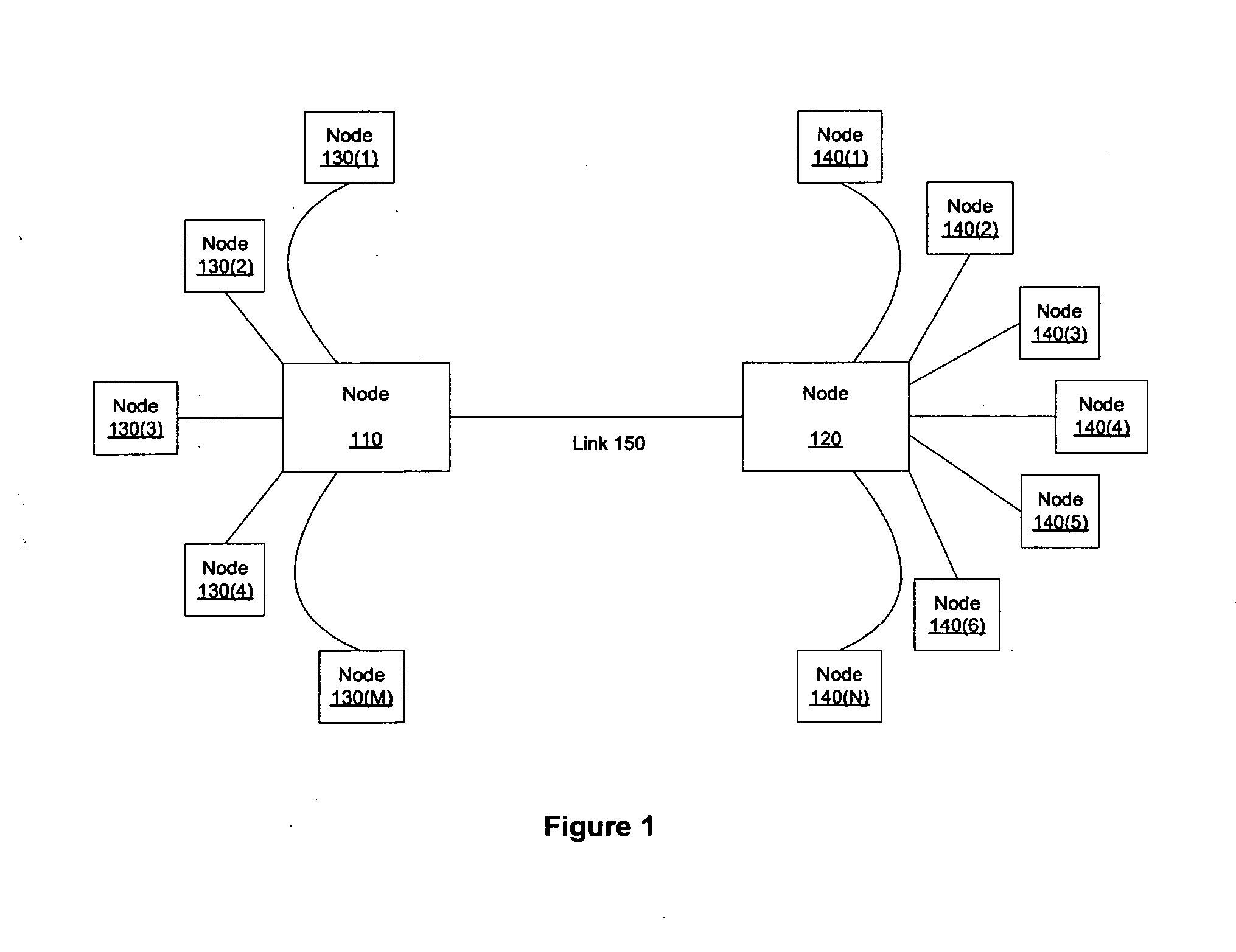
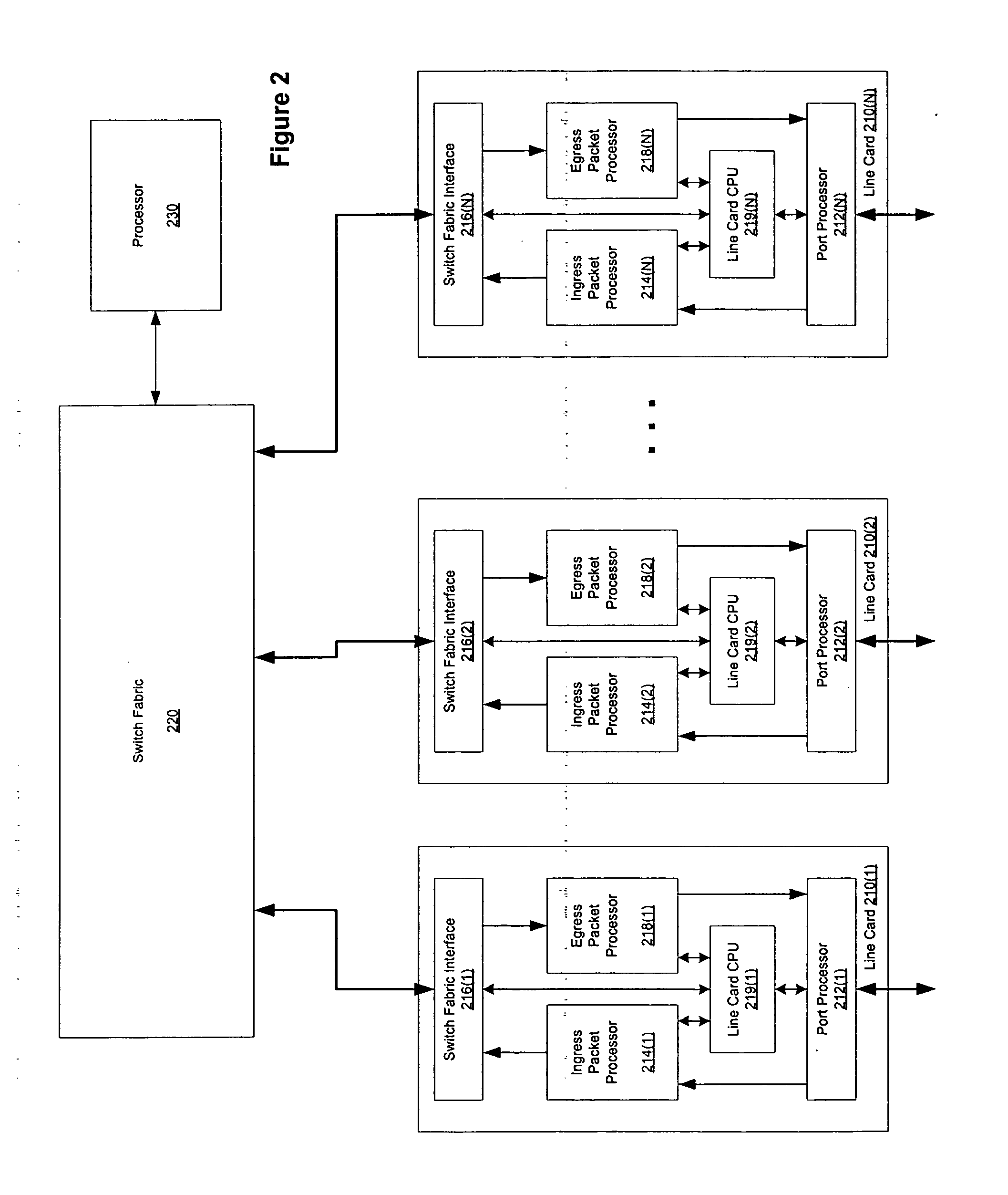
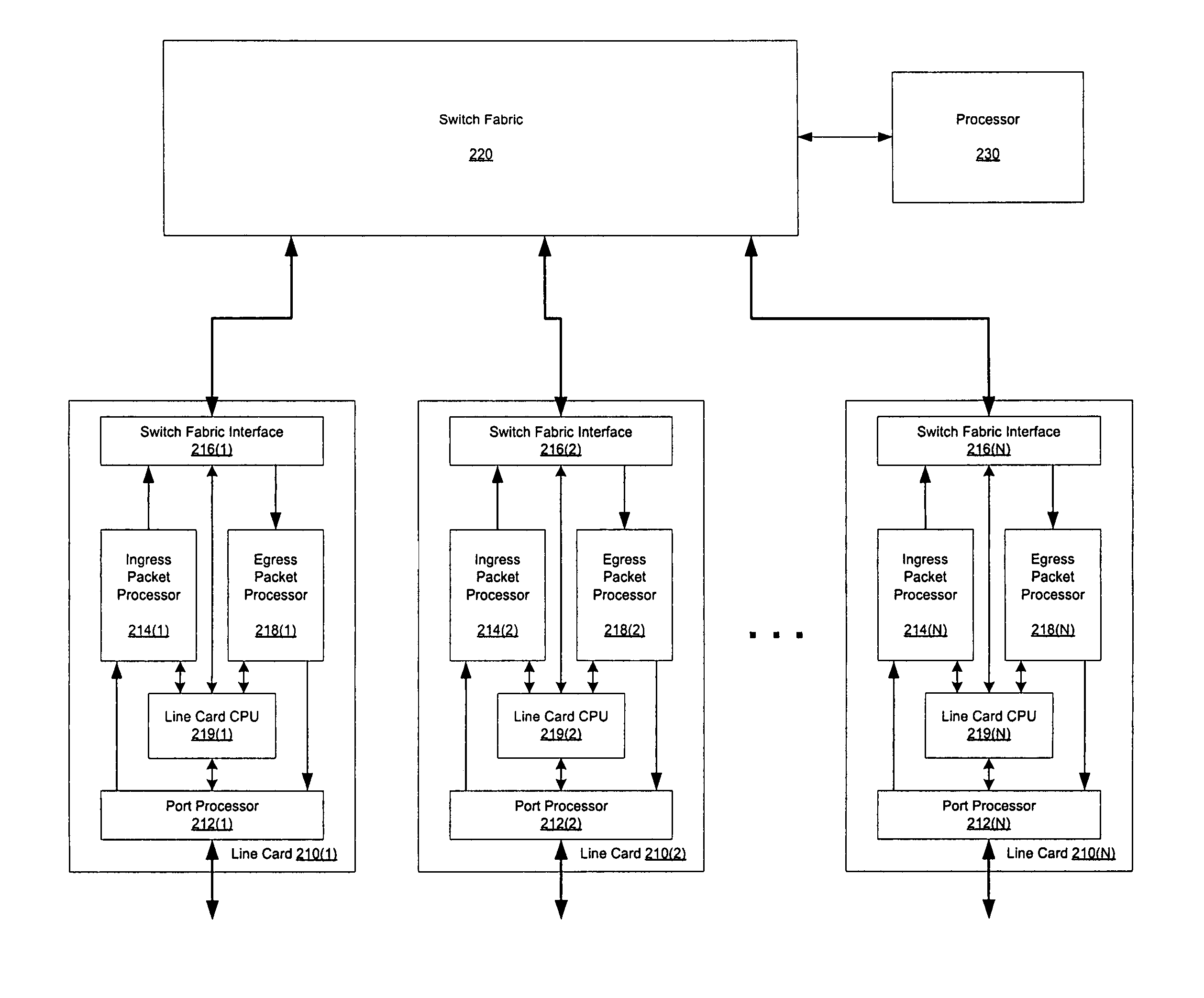
Constant time signature methods for scalable and bandwidth-efficient multicast
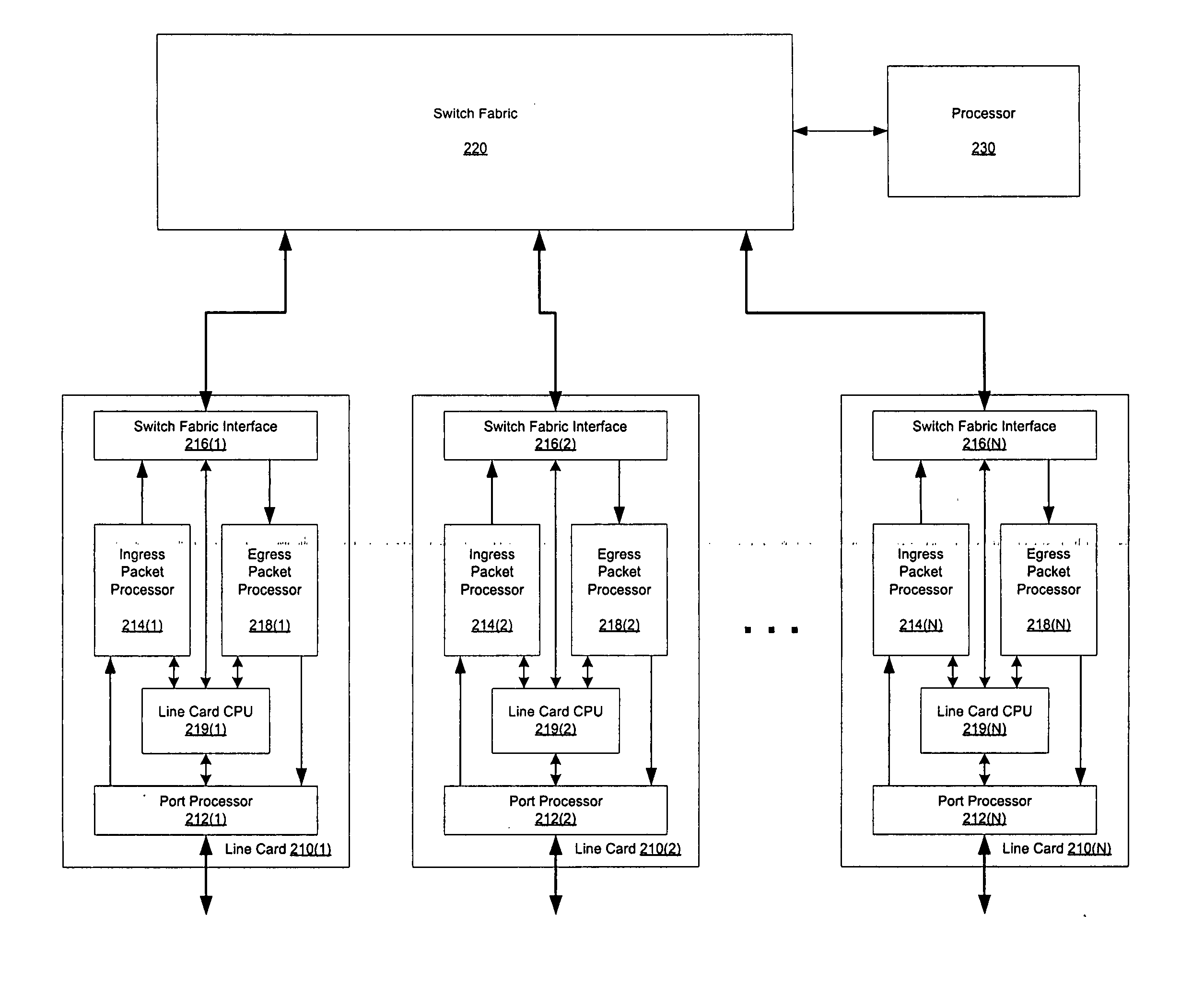
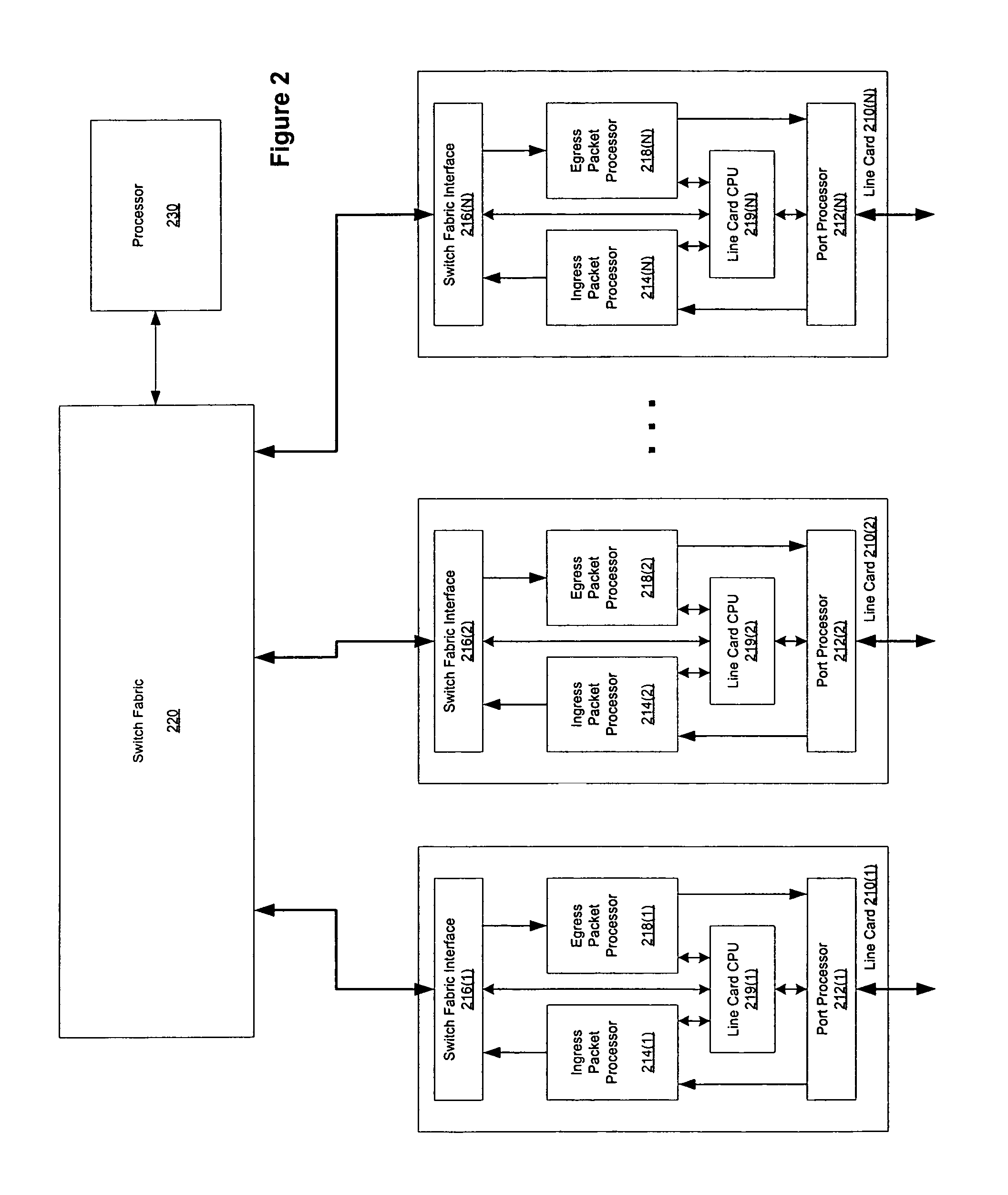
A method, computer program product, system and apparatus are presented for reducing wasted bandwidth due to supercasting multicast cells through a router switch fabric. In one embodiment of the present invention, signatures of a switch fabric destination address are generated and compared. A signature is an information-rich representation of the fabric destination address that is generated using the fabric destination address. Therefore, supercasting can be minimized by combining fabric destination addresses with like signatures. Aspects of the present invention include generating the signatures using random permutation maps of the set of switch fabric ports or determining intersections of a fabric destination address with a selection of subsets of the switch fabric ports. Signature-based solutions for supercast minimization can be performed in a time-efficient manner and be implemented online, while solutions that can generate a more optimal solution but may take a longer time to perform, such as row-clustering, can be implemented off-line. A further aspect of the invention, incorporates an off-line row-clustering supercast minimization method with an on-line signature-based supercast minimization method.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
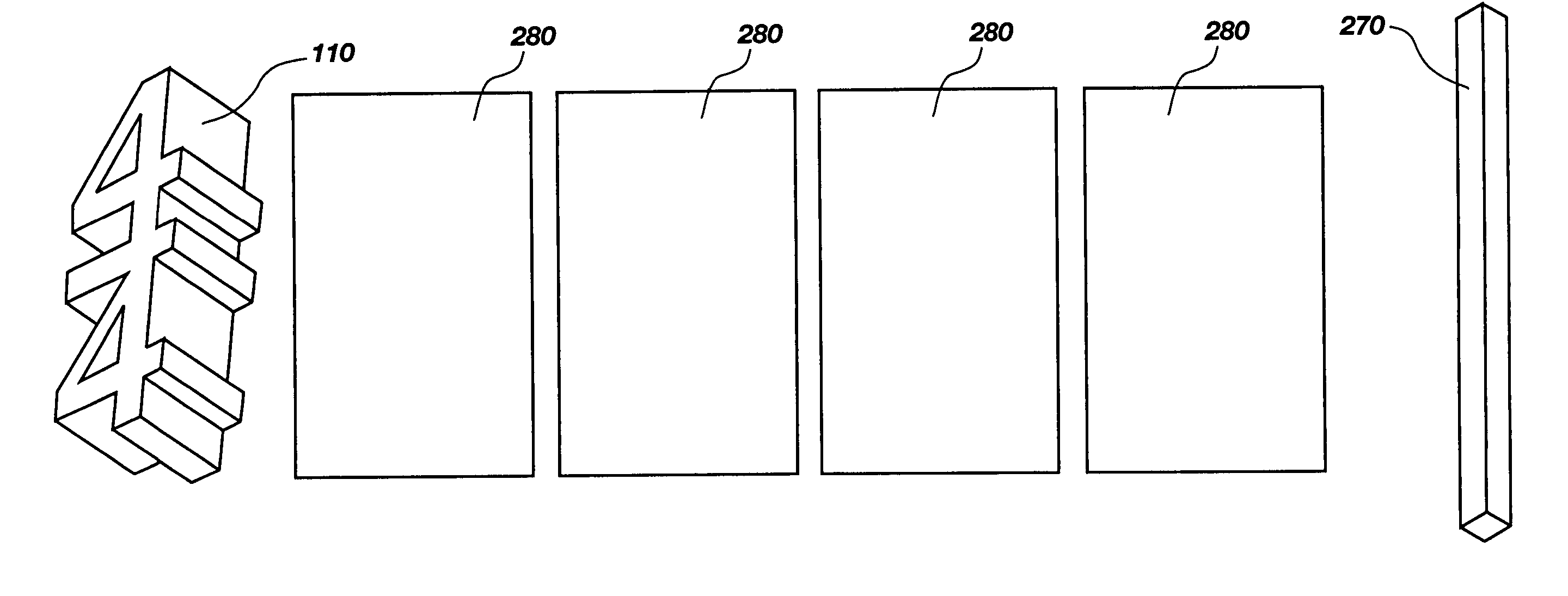
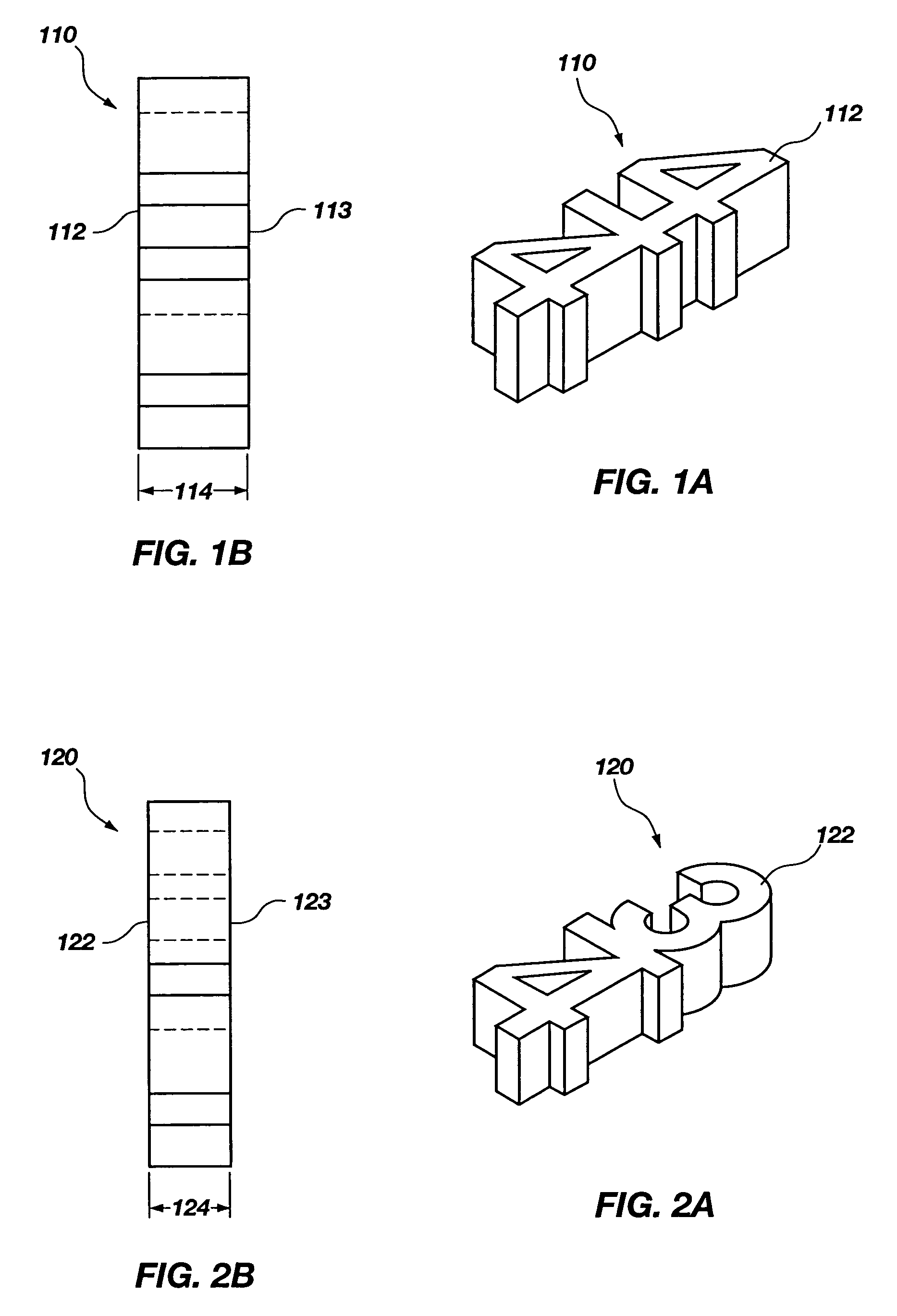
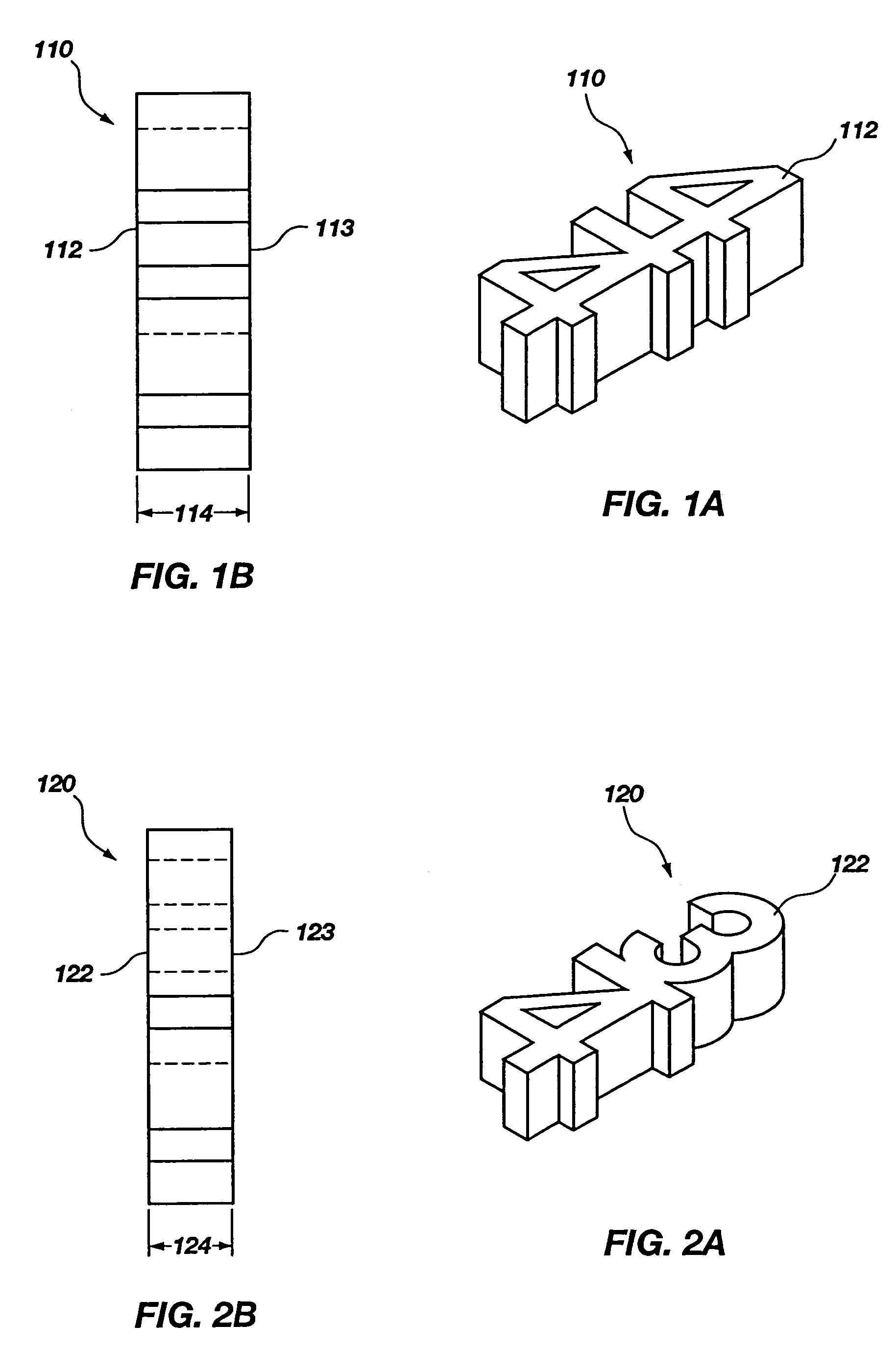
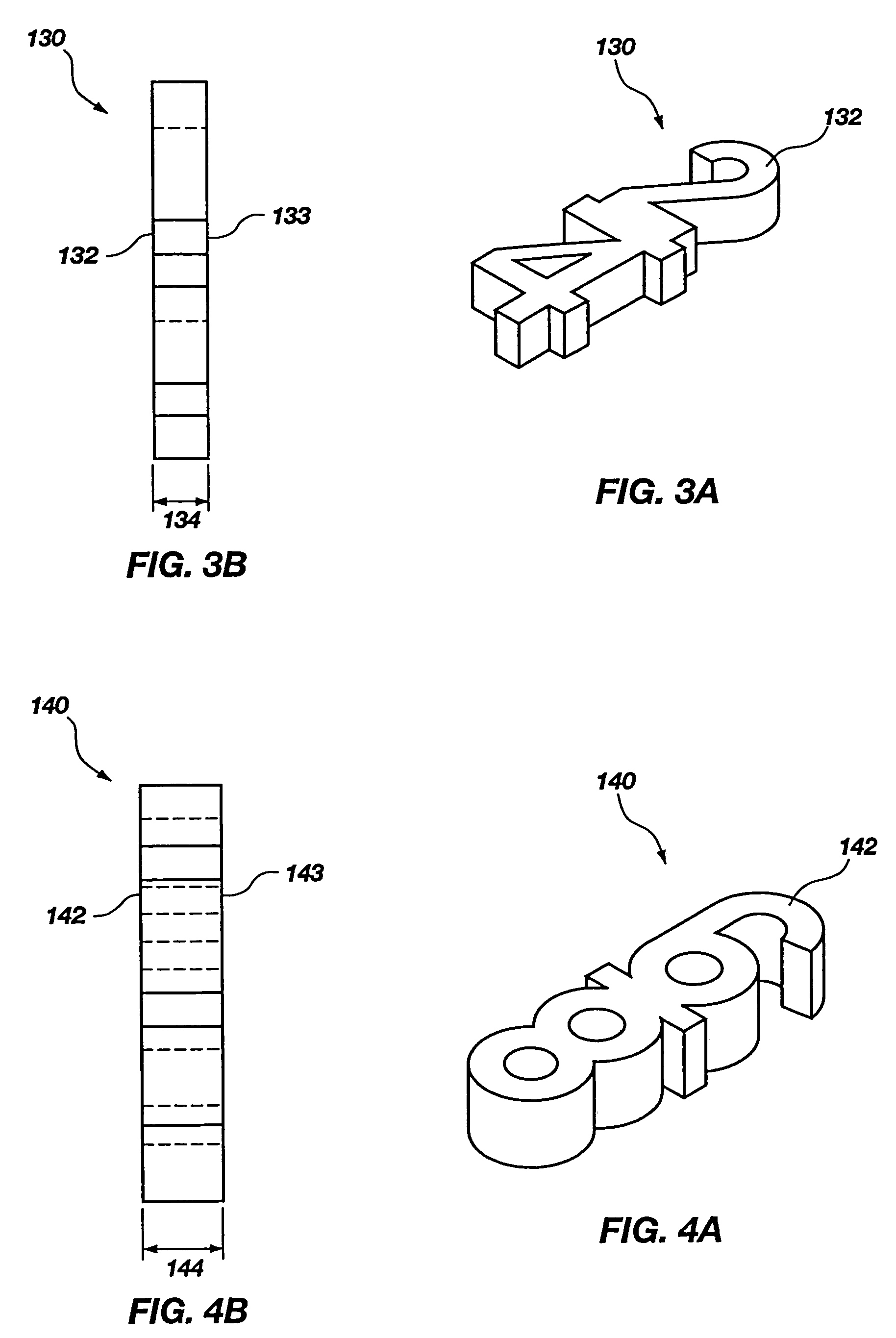
System and method for teaching music
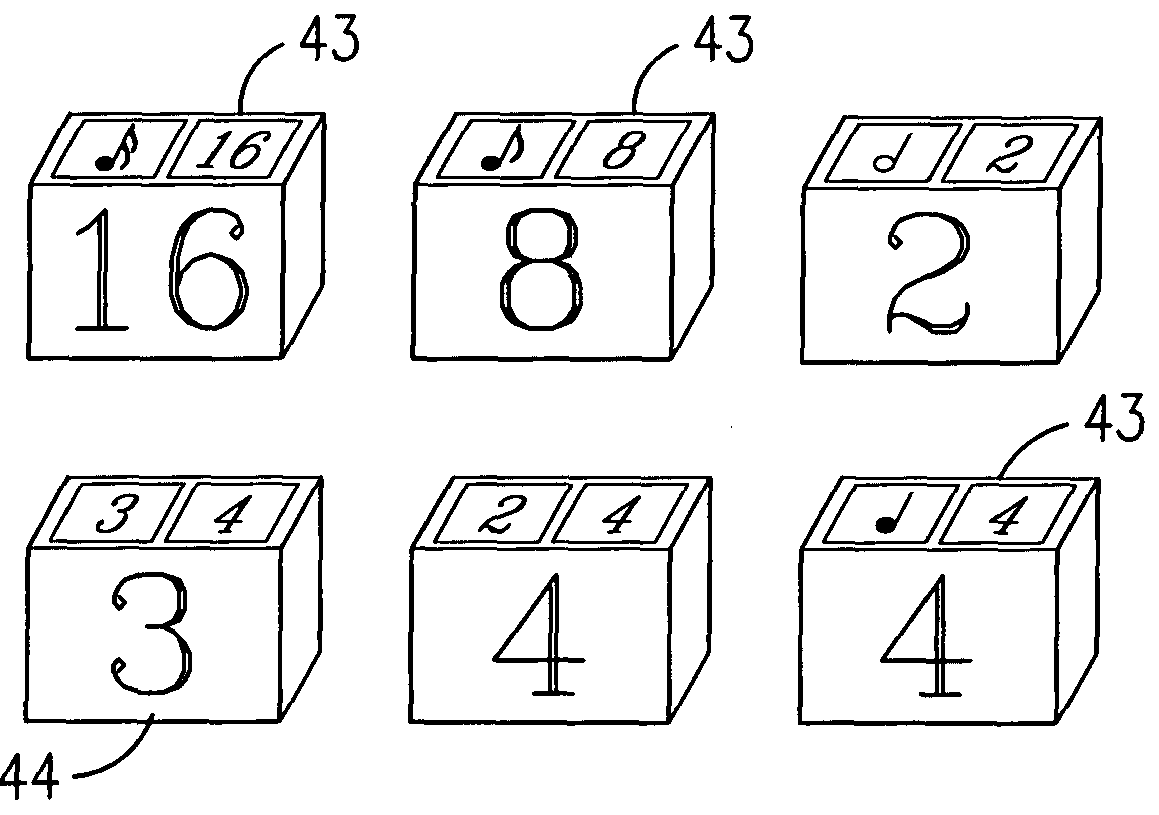
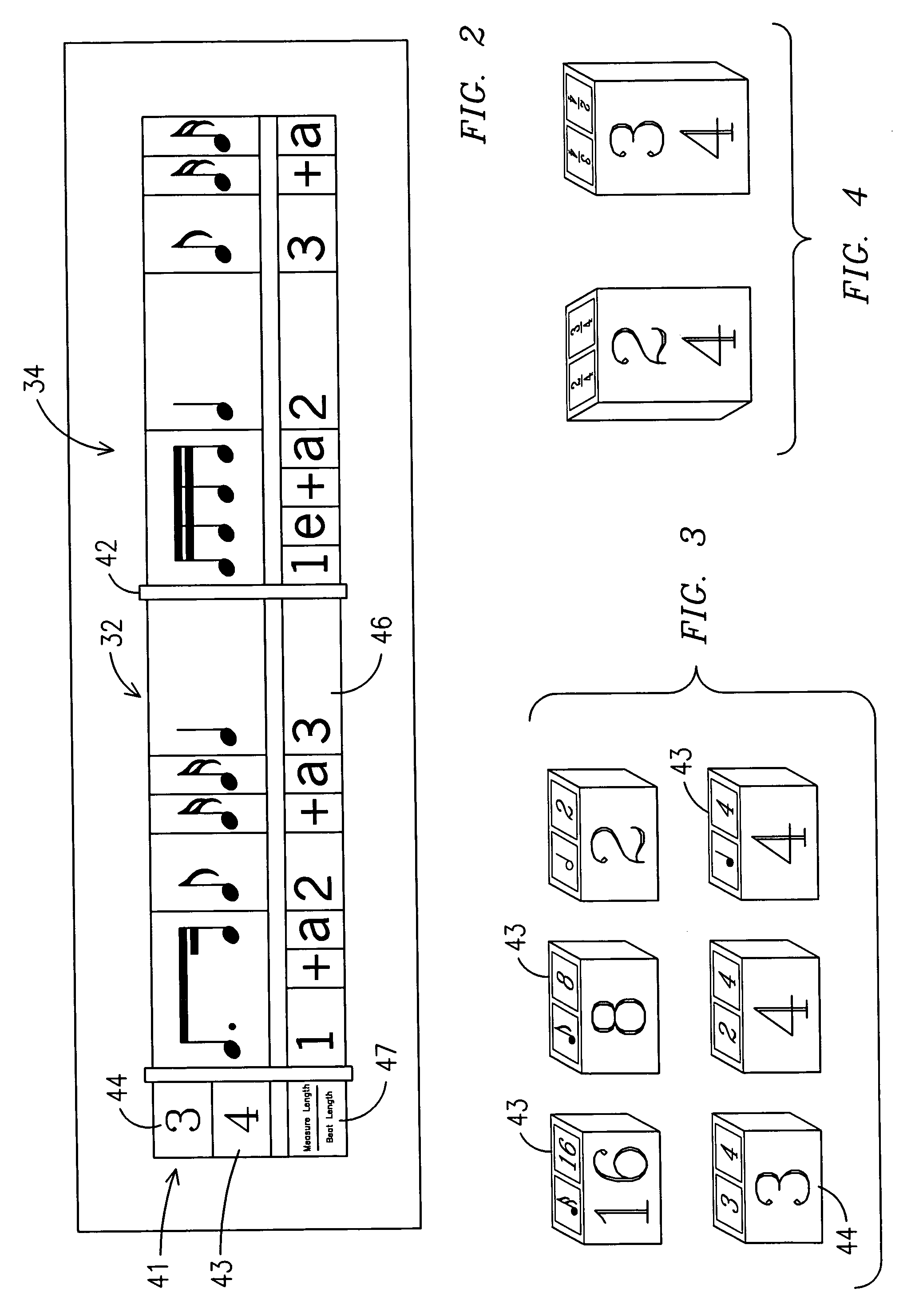
A system and method for teaching music both visually and tactilely. In one embodiment, the invention comprises blocks shaped to resemble musical symbols used to compose music, including time signatures, notes, rests, and dots. Each of the blocks are relative in thickness such that for a given time signature, the correct rhythm for a given measure can be determined by laying one or more of the notes, rests and dots one over the other to see if their combined thickness is equal to that of a preselected time signature. The thickness of the block shaped to resemble the time signature is such that it only allows the correct number of blocks shaped as notes, rests or dots to be of equal thickness to thereby determine the correct rhythm. In addition, the correct rhythm can be determined by simply reading the shaped blocks as one would read music. The use of the shaped blocks having relative thicknesses allows a student to learn rhythm by trial and error and does not necessarily require that the student understand complex music theory. In addition, the blocks can be used by the student when clapping the correct rhythms. Other musical notation can be represented by blocks as well such as bar lines and slurs.
Owner:STEPHANIE ROSS
Signature System and Signature Method
InactiveUS20080095360A1Improve securitySmall data sizePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationSmart cardOne-way function
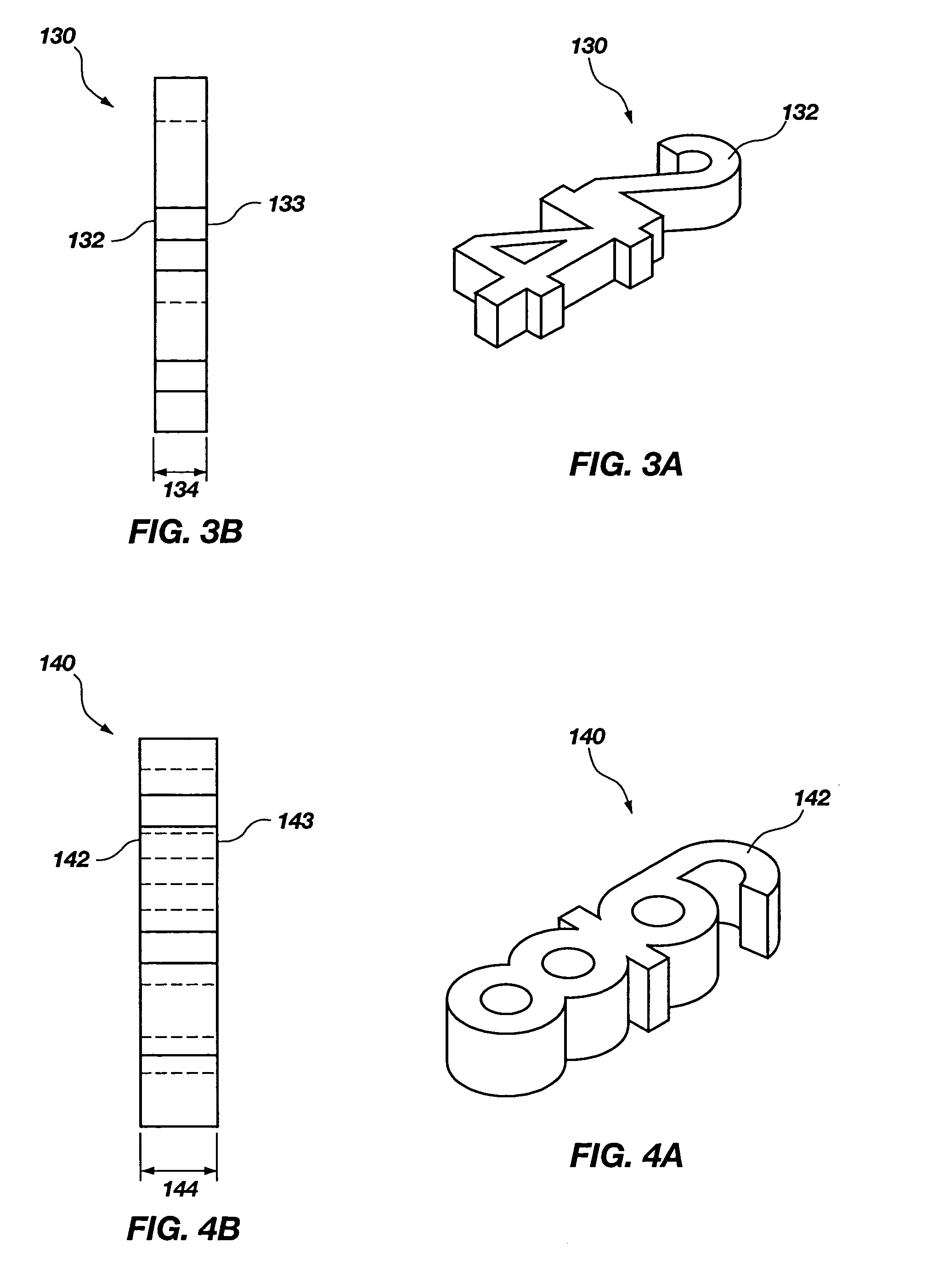
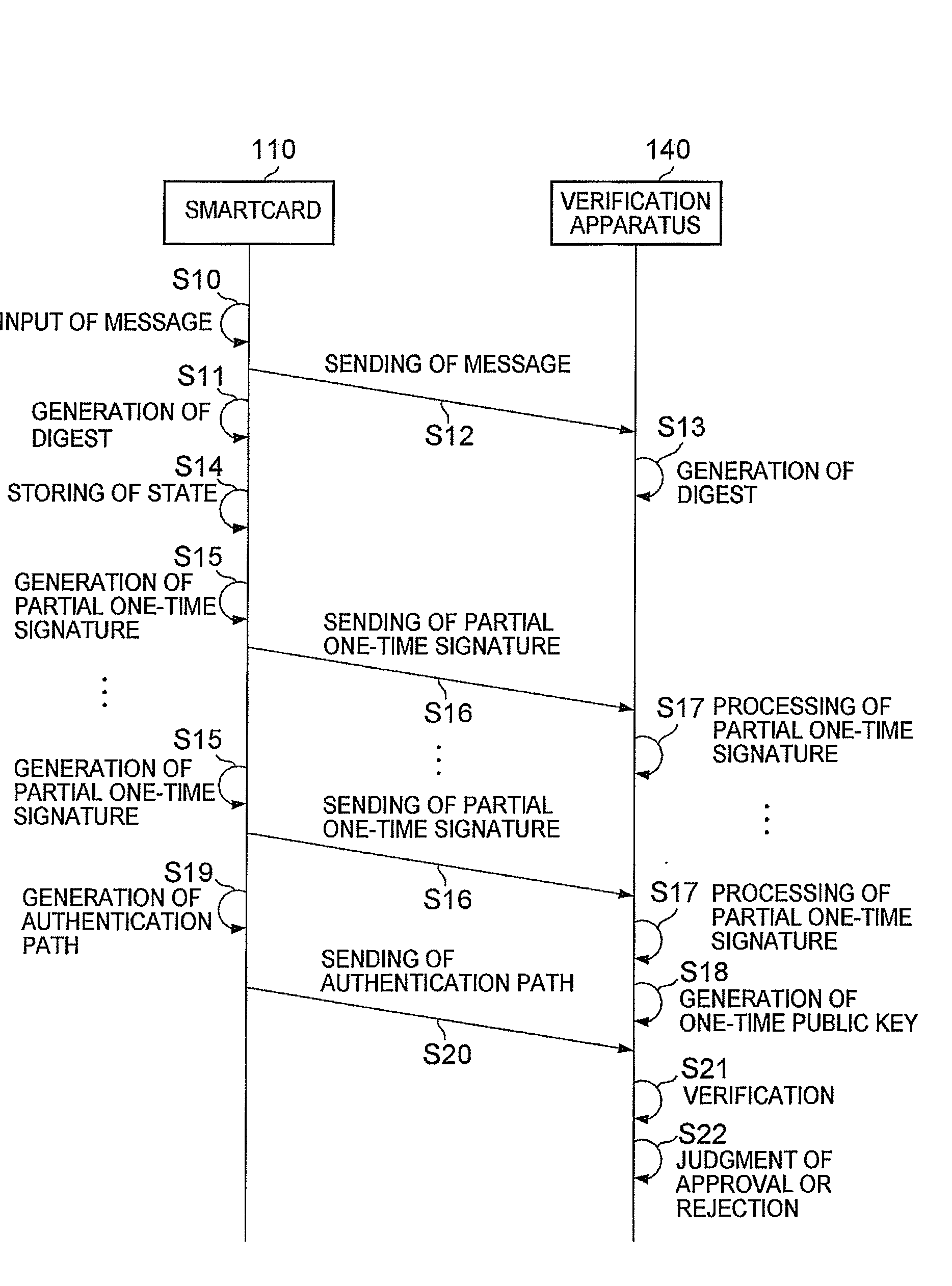
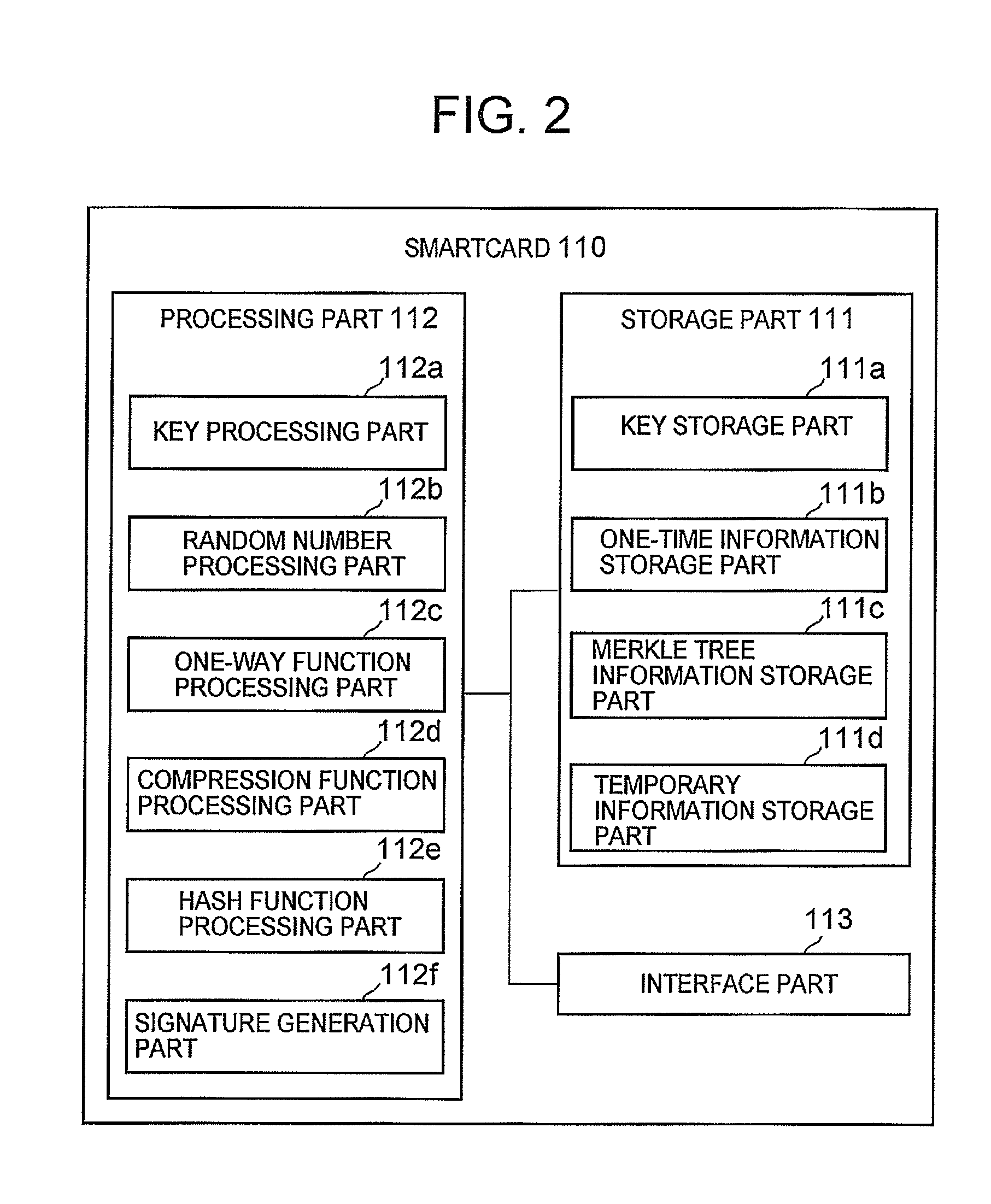
A signature system in which size of data to be transmitted is small and data can be processed efficiently in a Merkle signature system having high security. A processing part 112 of a smartcard 110 divides a message to be signed into groups of specific numbers of bits, starting from the first bit of the message. Then, respective partial one-time signatures of the groups are generated by encrypting each group by a one-way function processing part 112c. The partial one-time signatures are sequentially outputted to a verification apparatus through a interface part 113.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
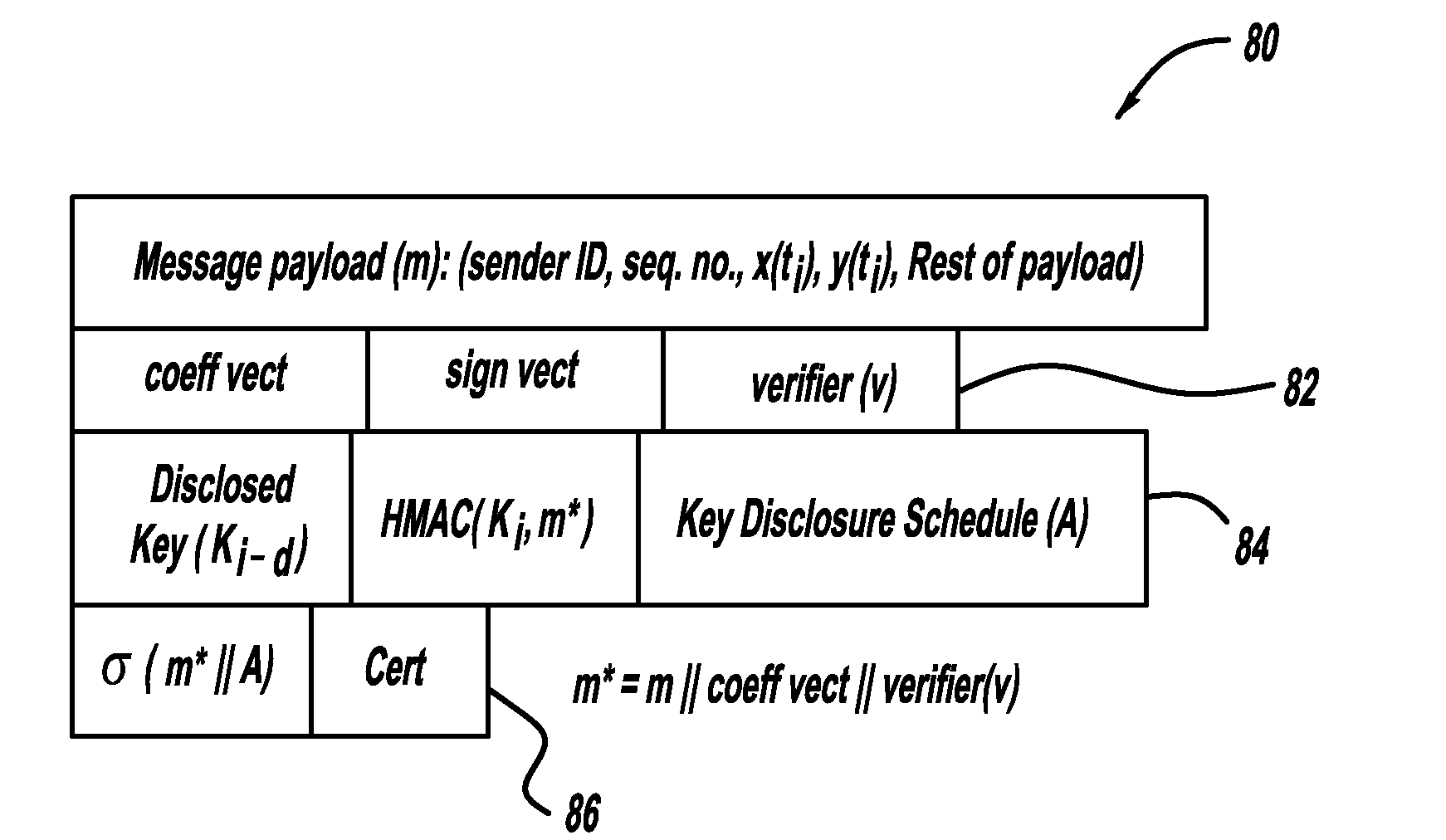
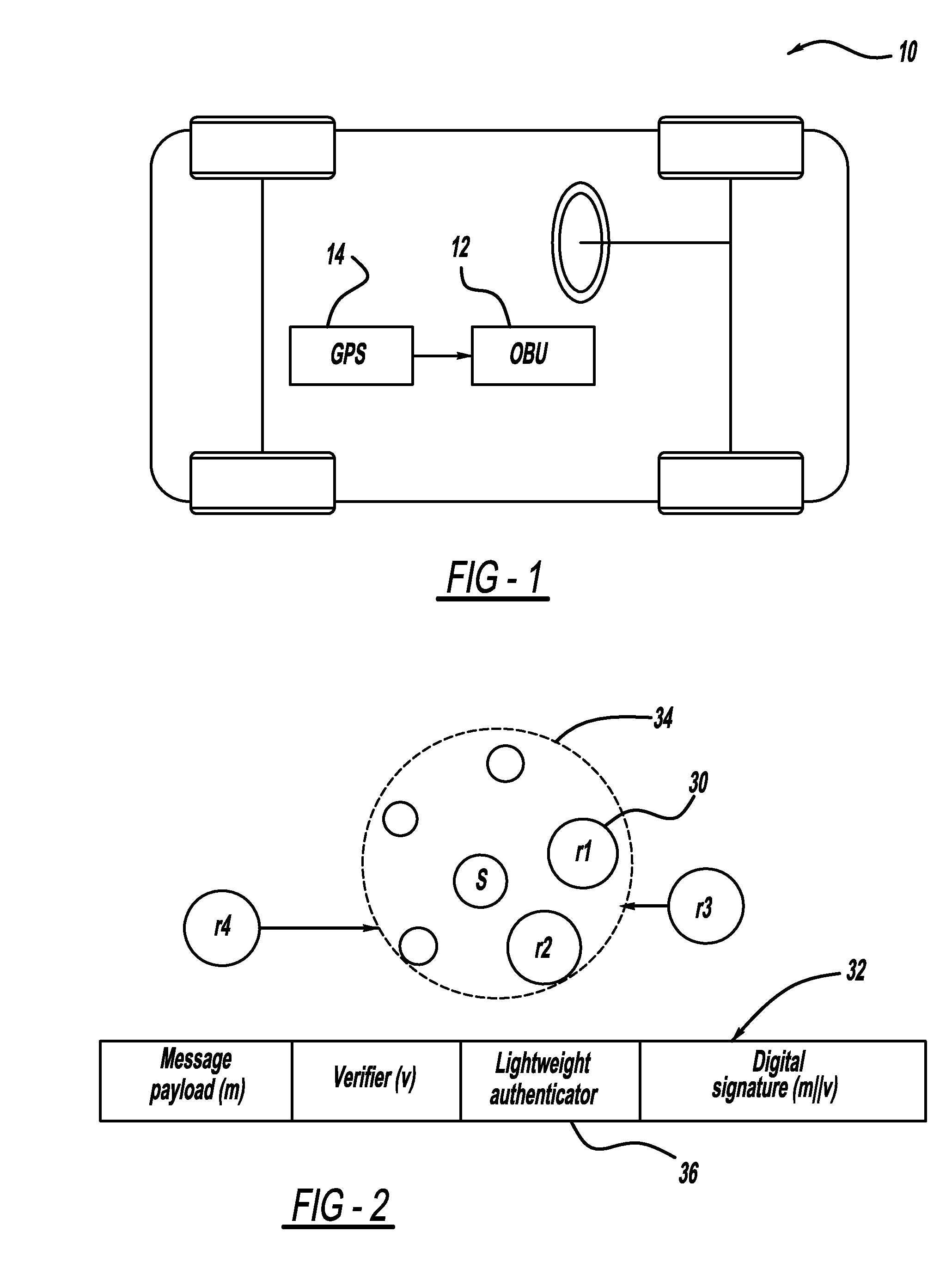
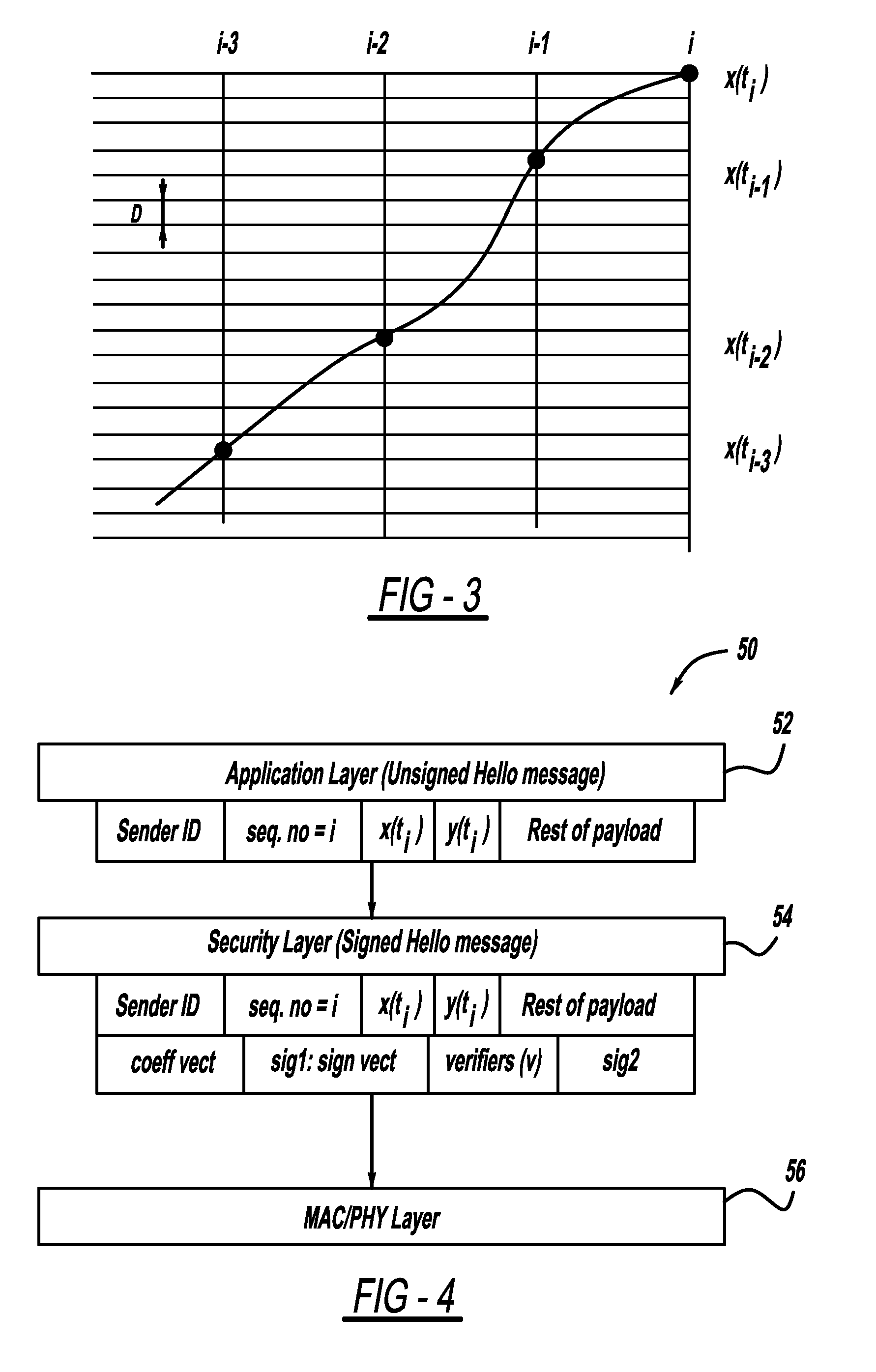
Lightweight geographic trajectory authentication via one-time signatures
InactiveUS20090254754A1User identity/authority verificationAnti-collision systemsActive safetyCommunications system
A system and method for a vehicle-to-vehicle communications system that provide active safety applications employing lightweight geographic authentication using one-time signatures. The system and method require each vehicle to construct a discretized representation of its trajectory, which captures its kinematical history to a tunable degree of accuracy and to a tunable extent in the past. This trajectory information is then signed using a one-time signature. Thus, with every periodic message, the sending vehicle transmits the usual application payload, a signed version of the trajectory as described, and the digital signature over all of the fields.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
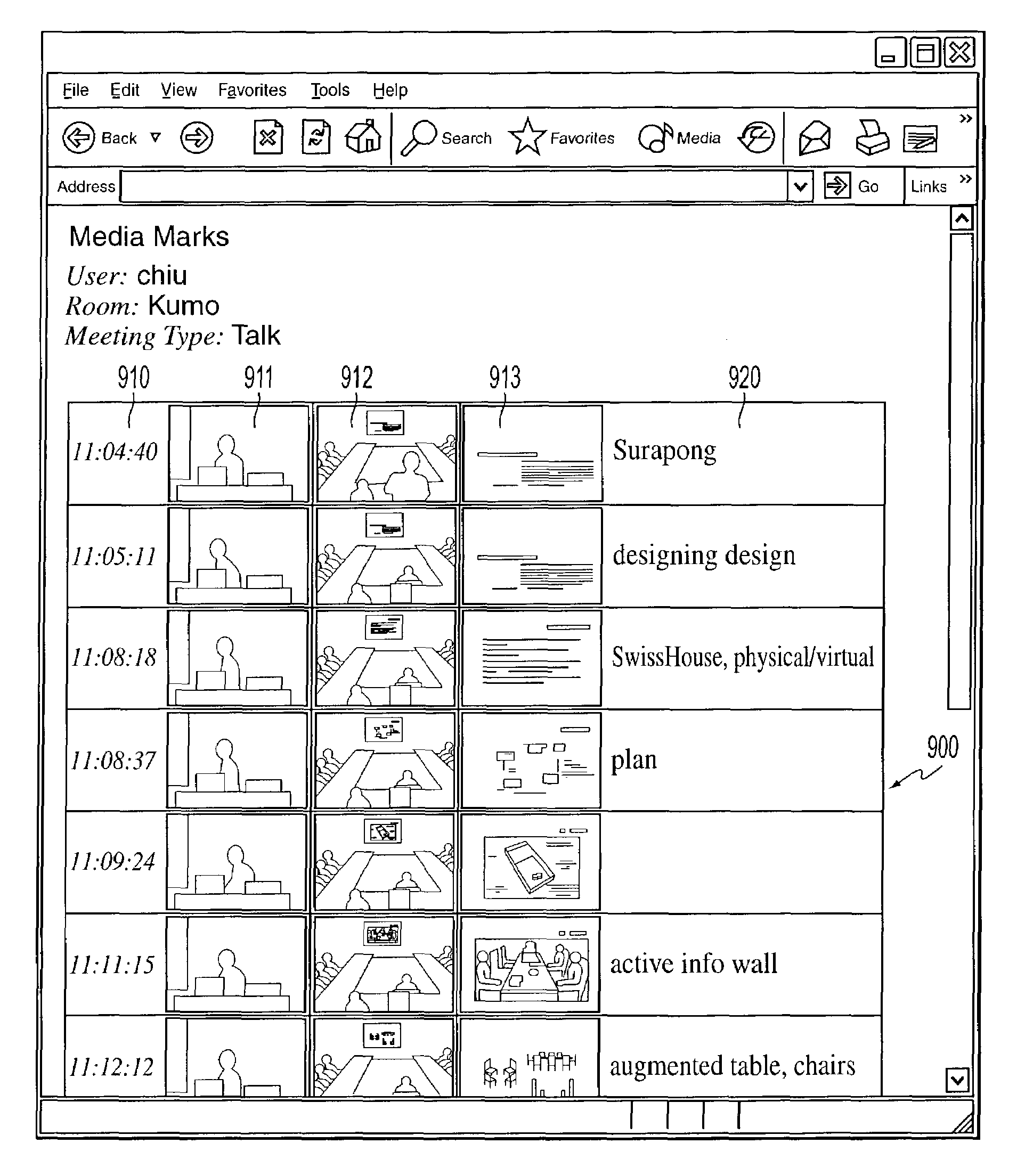
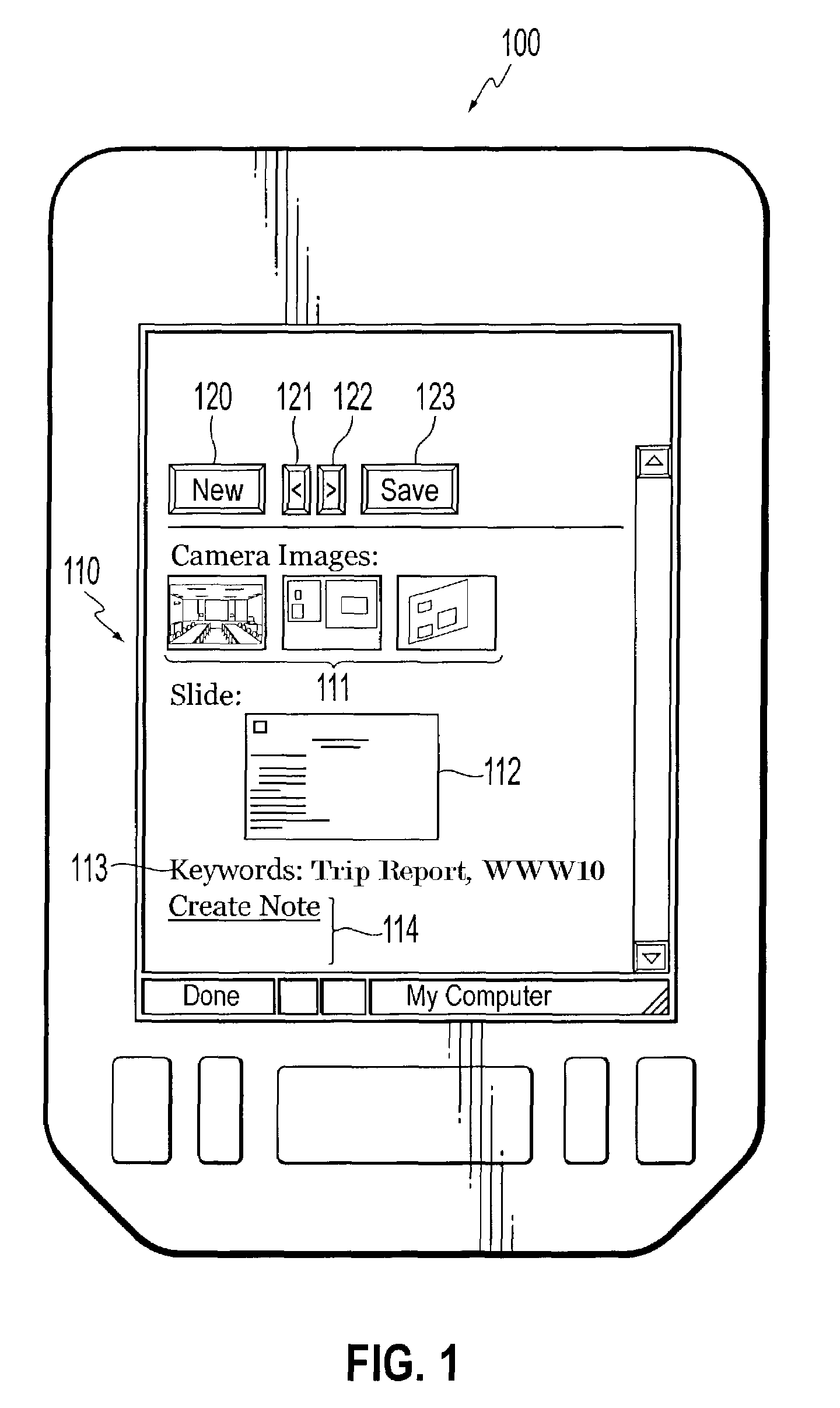
Systems and methods for bookmarking live and recorded multimedia documents
ActiveUS7730407B2Television conference systemsMetadata multimedia retrievalMultimedia streamsDocumentation
Systems and methods for bookmarking multimedia documents include displaying multiple multimedia streams, creating bookmarks comprising time signatures and snapshots of each multimedia stream based upon single action cues from a user, associating snapshots with portions of multimedia streams, displaying bookmarks and displaying portions of a multimedia stream associated with selected snapshots.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Measuring device and measuring method for determining distance and/or position
InactiveUS20070024845A1Simplifies control and adjustmentReduce divergenceAngle measurementOptical rangefindersMeasurement deviceSignal beam
A measuring device is provided with a signal generator and a signal receiver, which is located at a measurable distance from the signal generator. The signal generator is designed for the emission of at least two signal beams covering in given relationship to each other an area and the signal receiver is designed for the time-resolved reception of the signal beams in such a manner that the generator-receiver distance can be determined from the time signature of the signal beam reception.
Owner:ANDROTEC GMBH
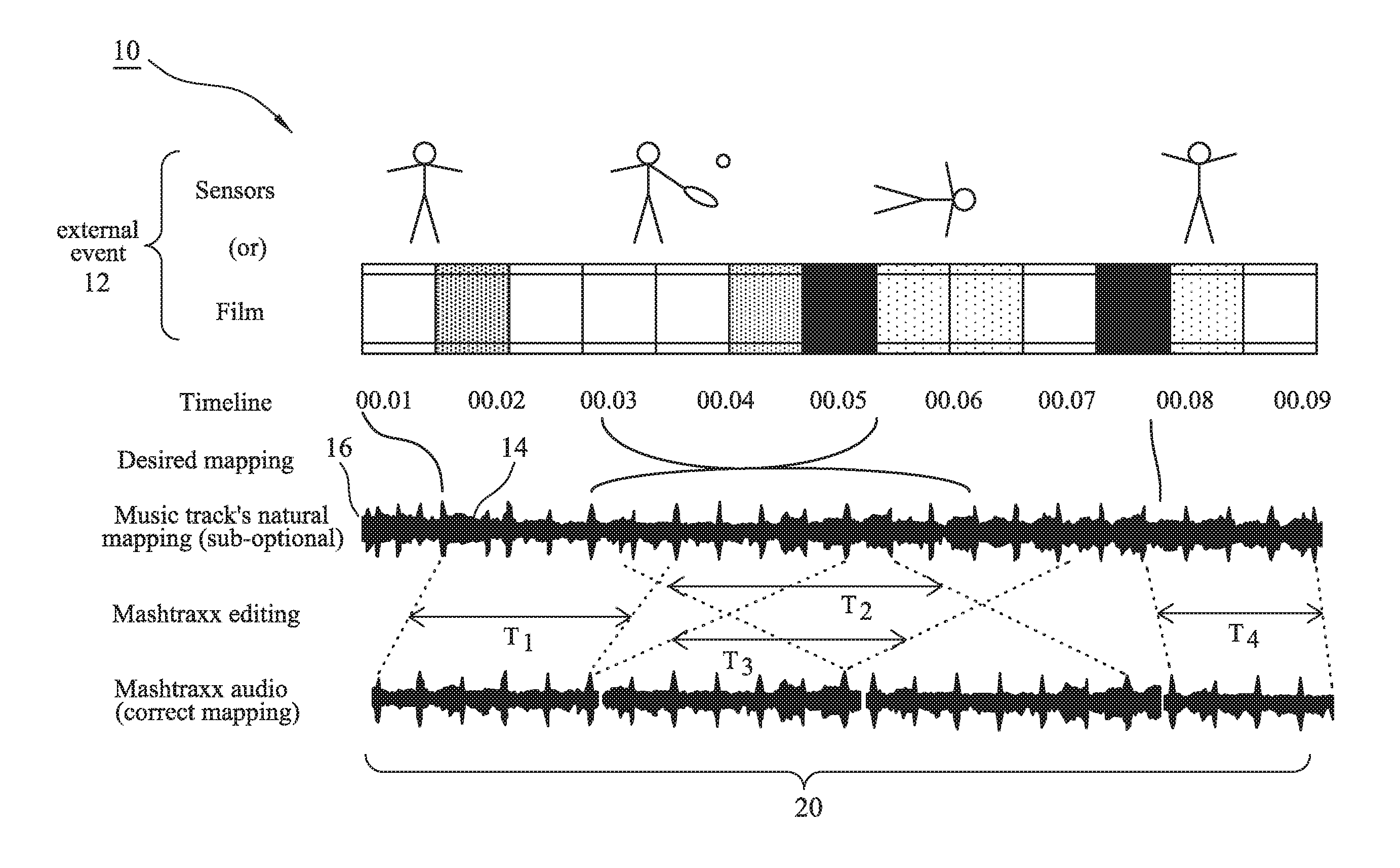
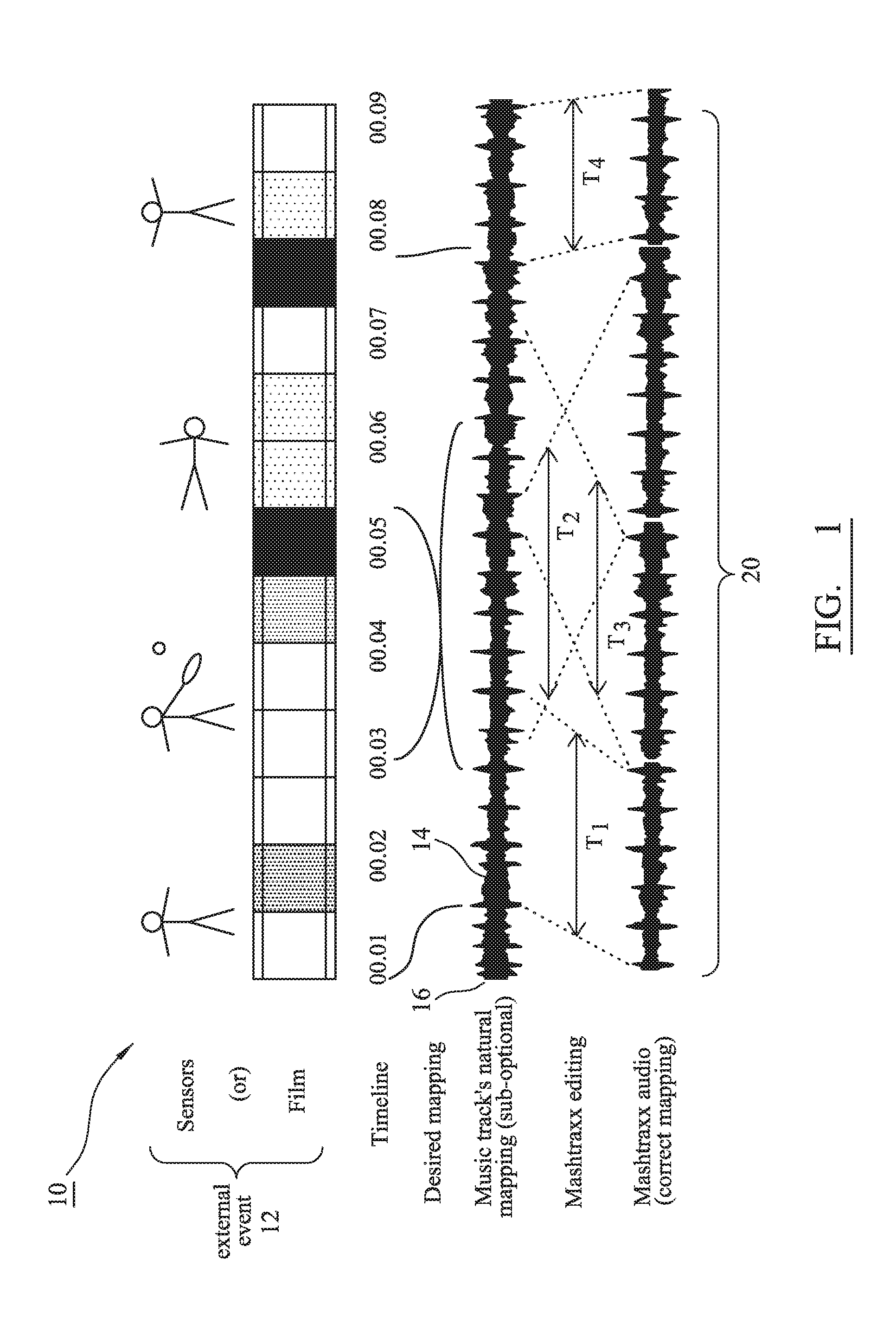
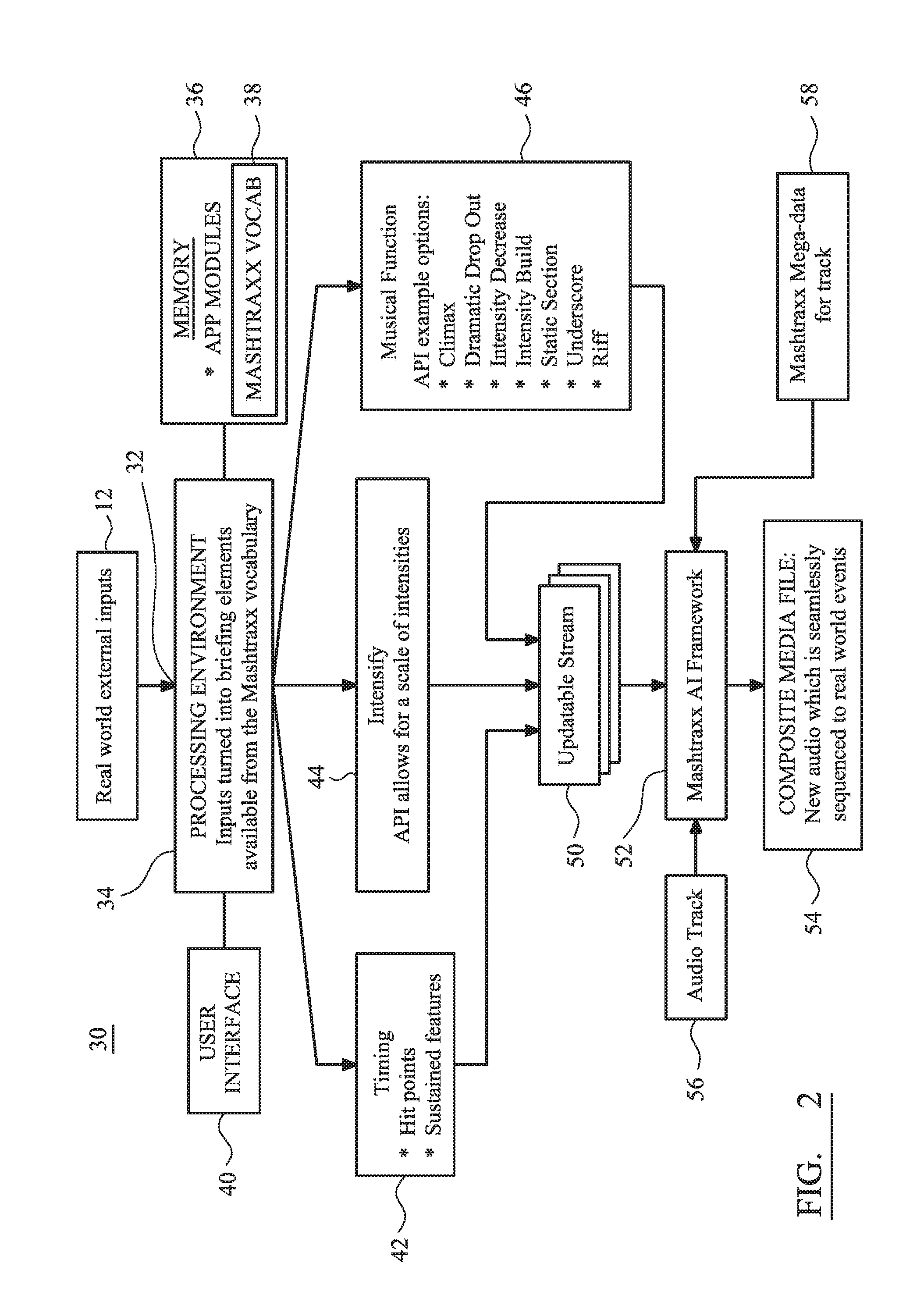
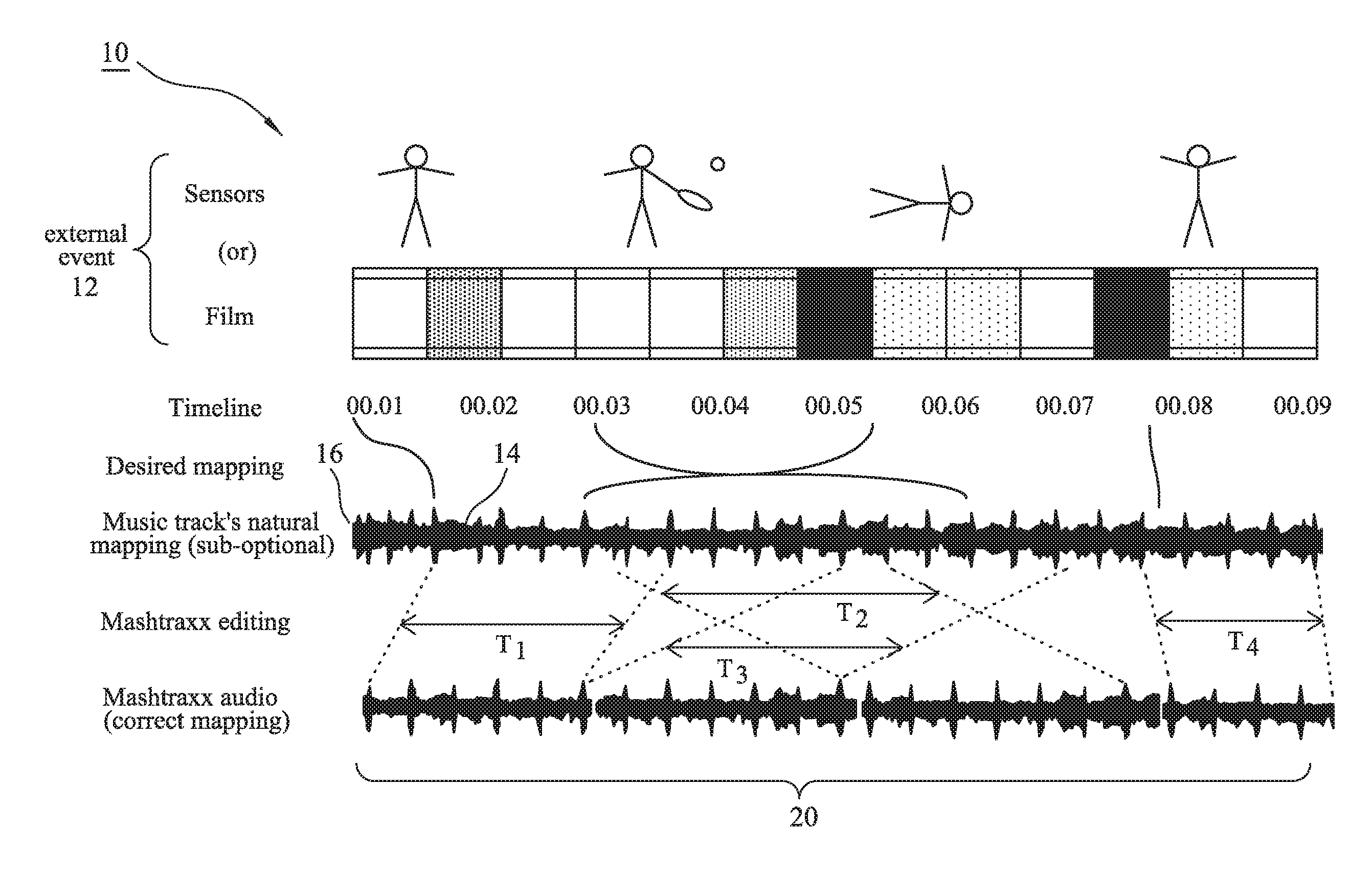
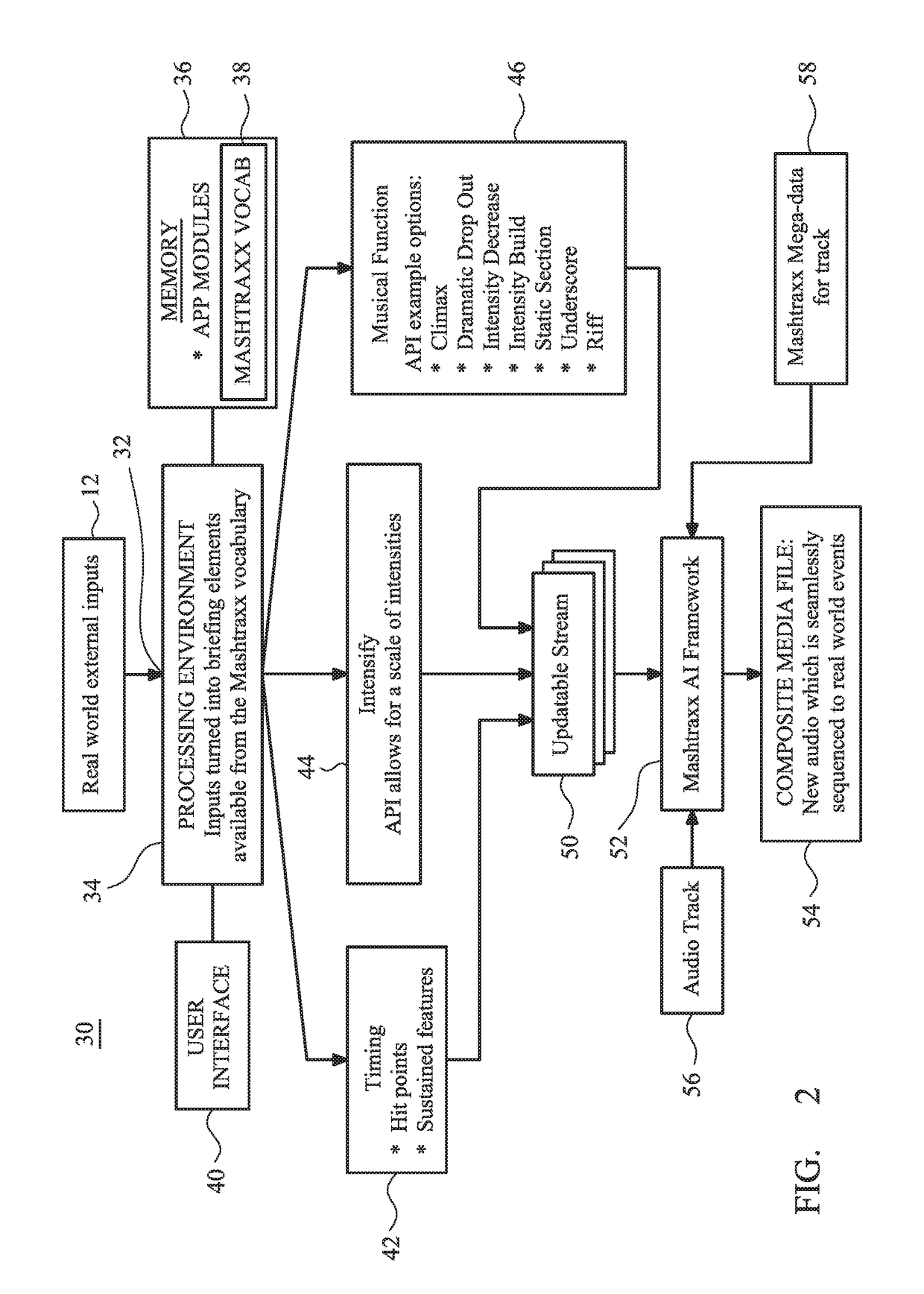
Music context system, audio track structure and method of real-time synchronization of musical content
ActiveUS20160372096A1Enhance sensory experienceIncrease intensityElectrophonic musical instrumentsData buffering arrangementsData synchronizationRecovery period
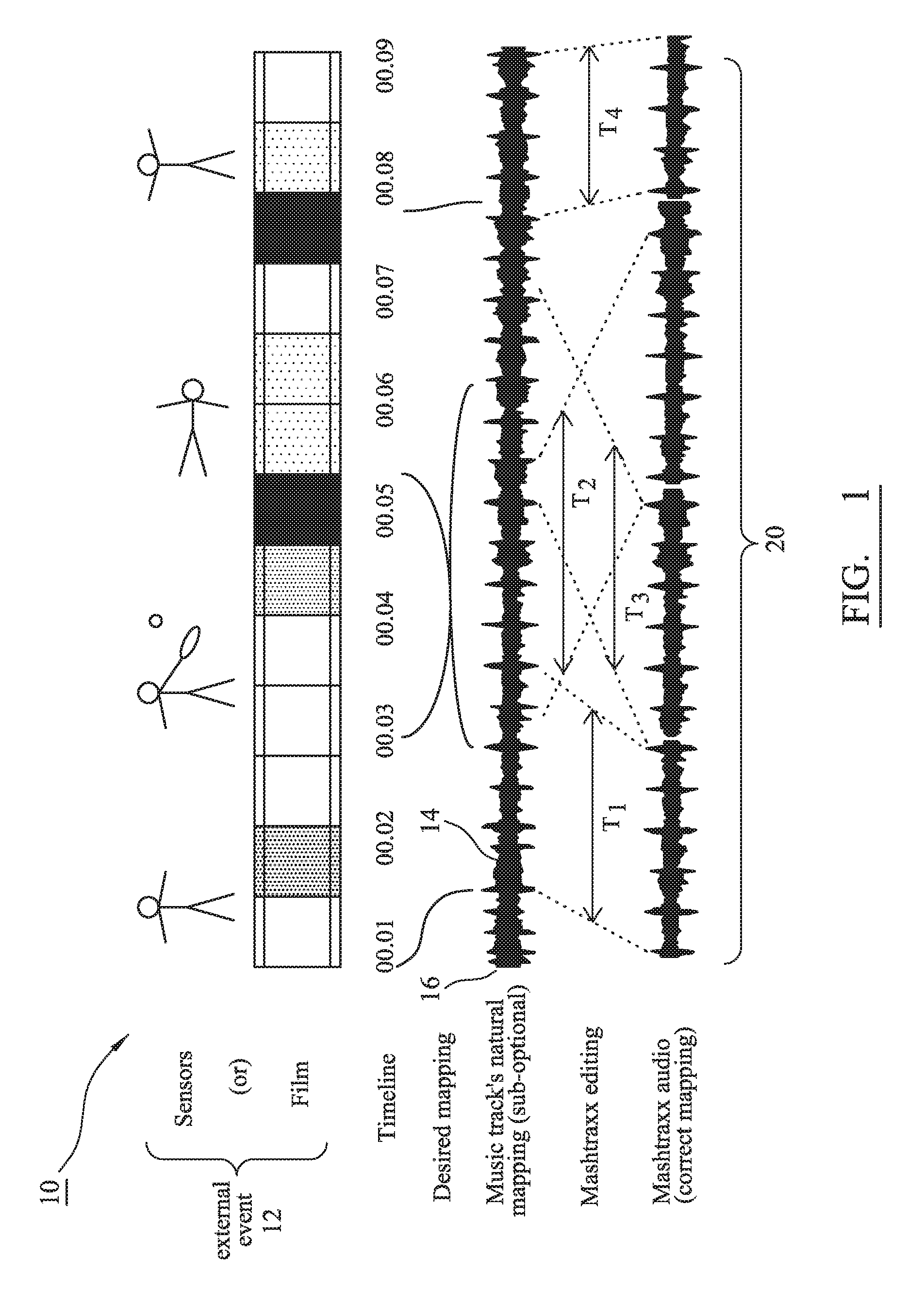
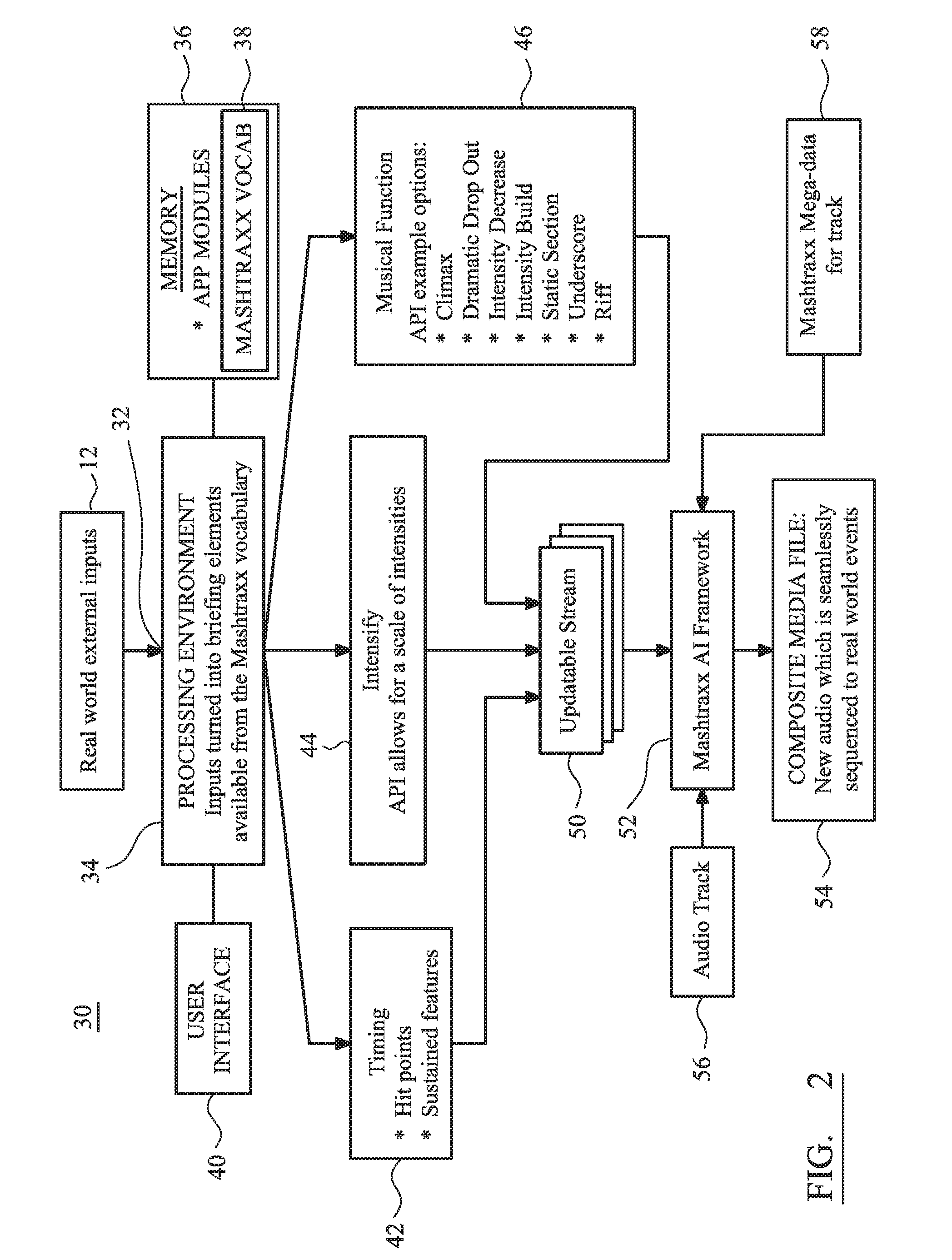
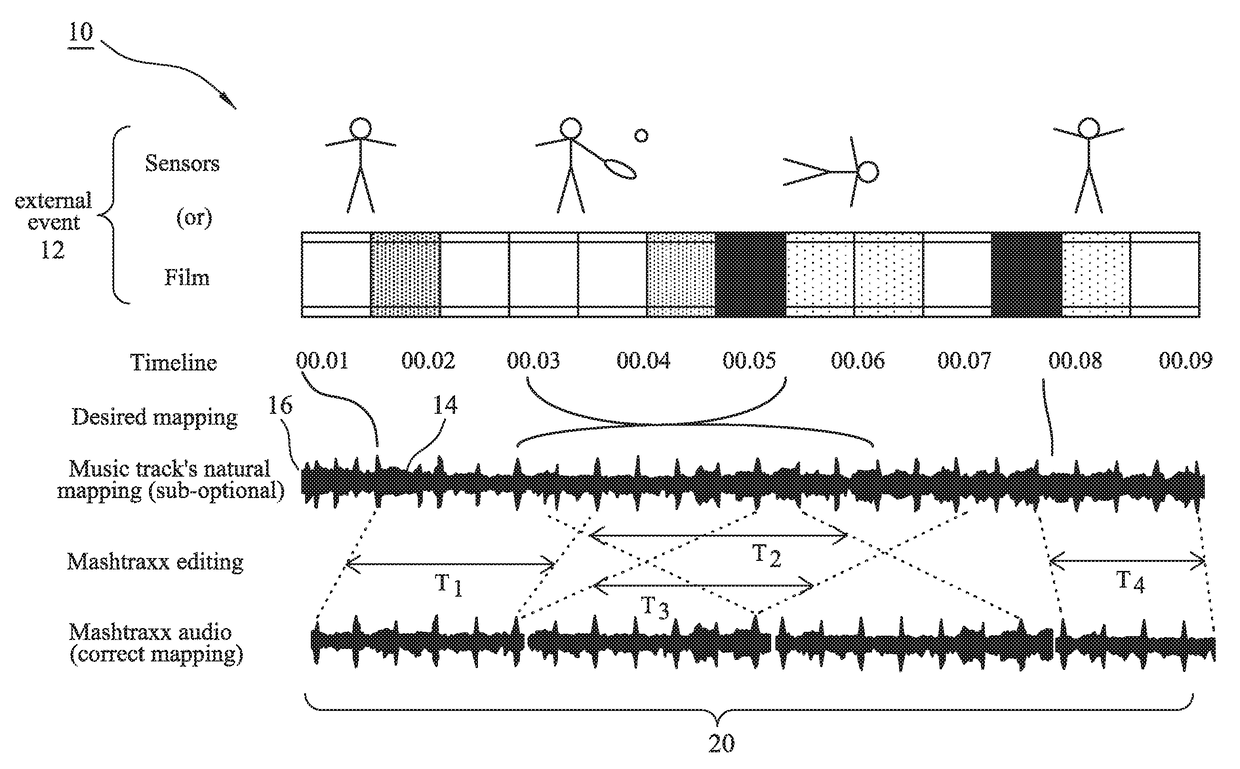
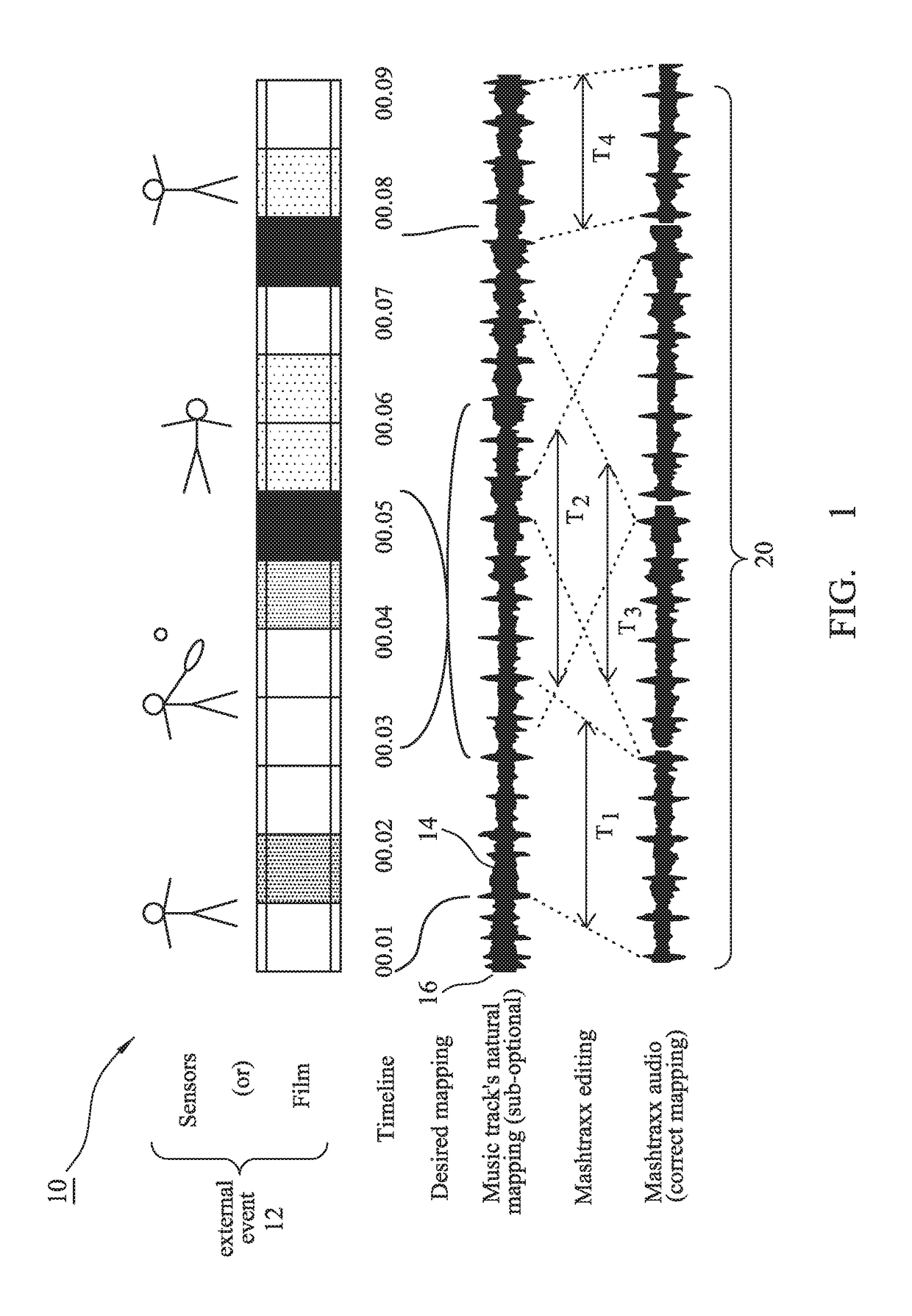
A system is described that permits identified musical phrases or themes to be synchronized and linked into changing real-world events. The achieved synchronization includes a seamless musical transition—achieved using a timing offset, such as relative advancement of an significant musical “onset”, that is inserted to align with a pre-existing but identified music signature, beat or timebase—between potentially disparate pre-identified musical phrases having different emotive themes defined by their respective time signatures, intensities, keys, musical rhythms and / or musical phrasing. The system operates to augment an overall sensory experience of a user in the real world by dynamically changing, re-ordering or repeating and then playing audio themes within the context of what is occurring in the surrounding physical environment, e.g. during different phases of a cardio workout in a step class the music rate and intensity increase during sprint periods and decrease during recovery periods.
Owner:MASHTRAXX LTD
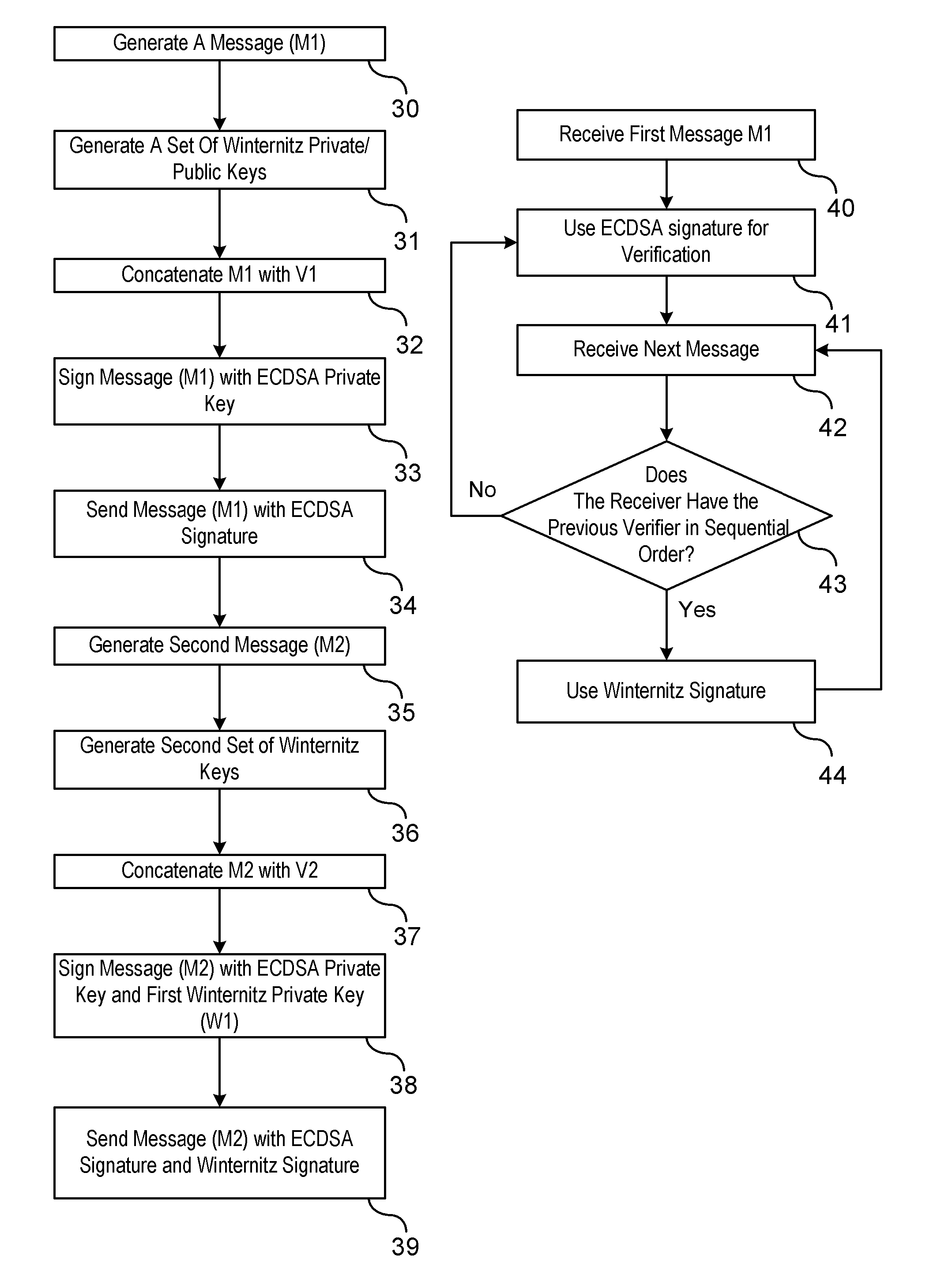
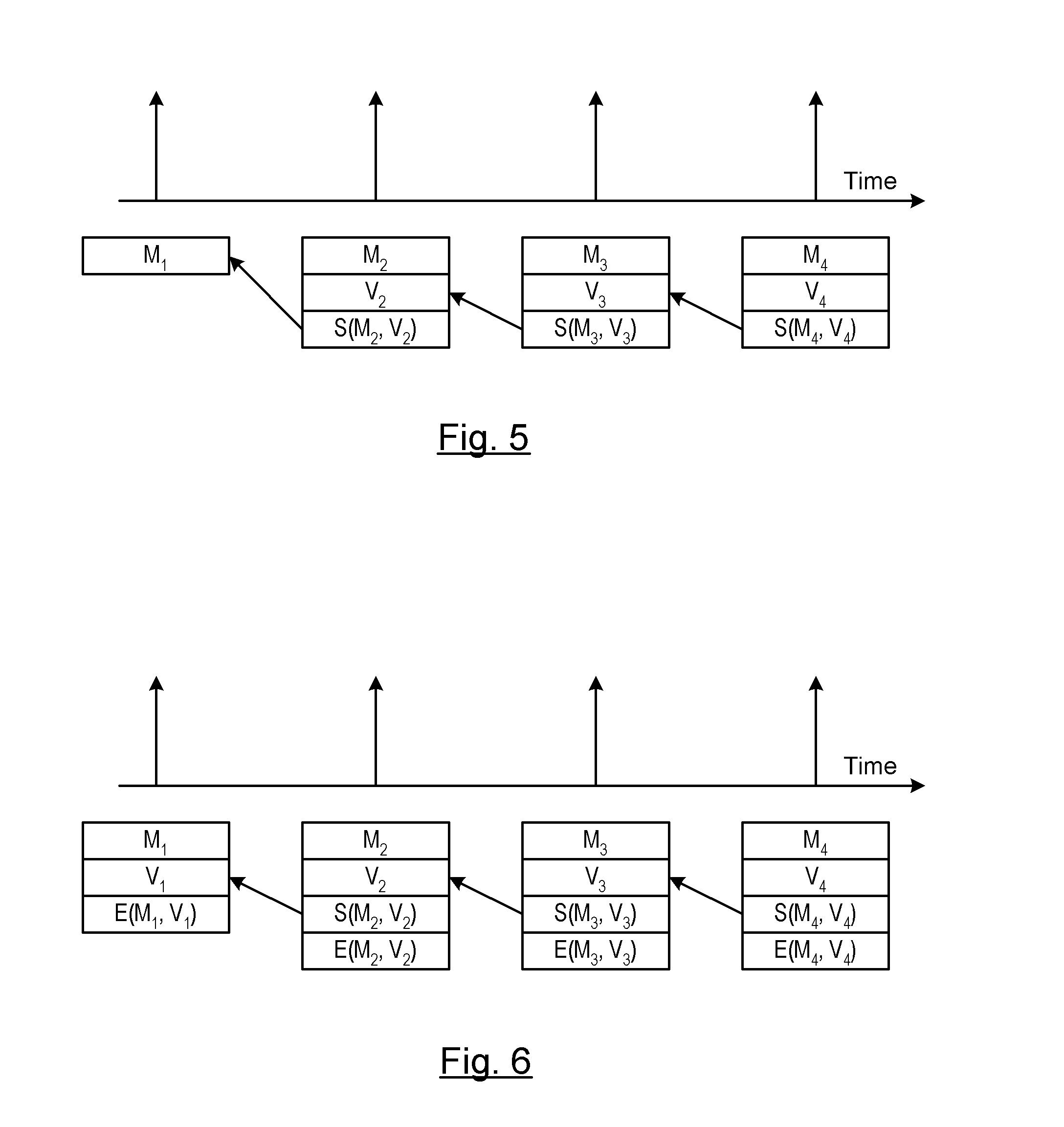
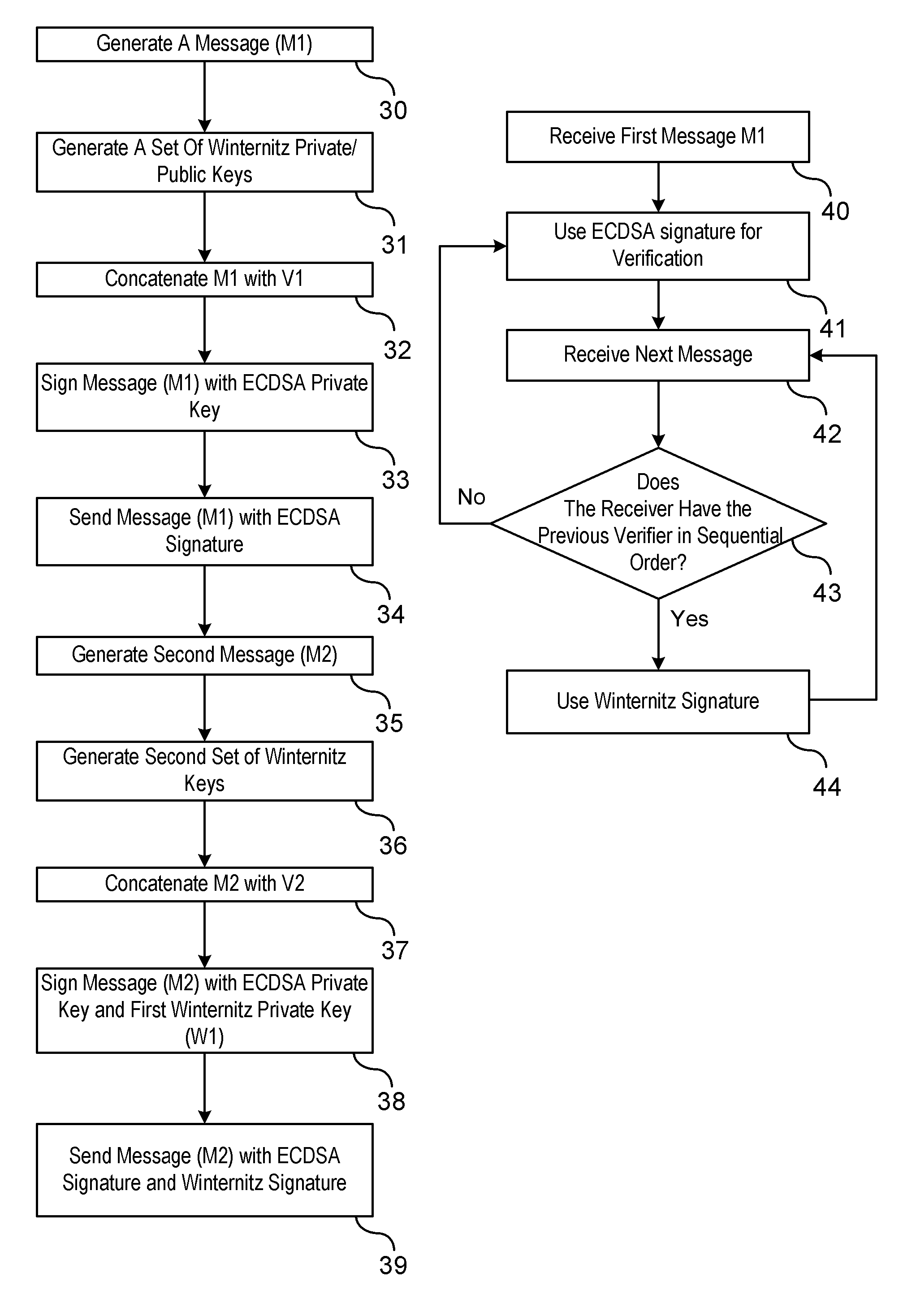
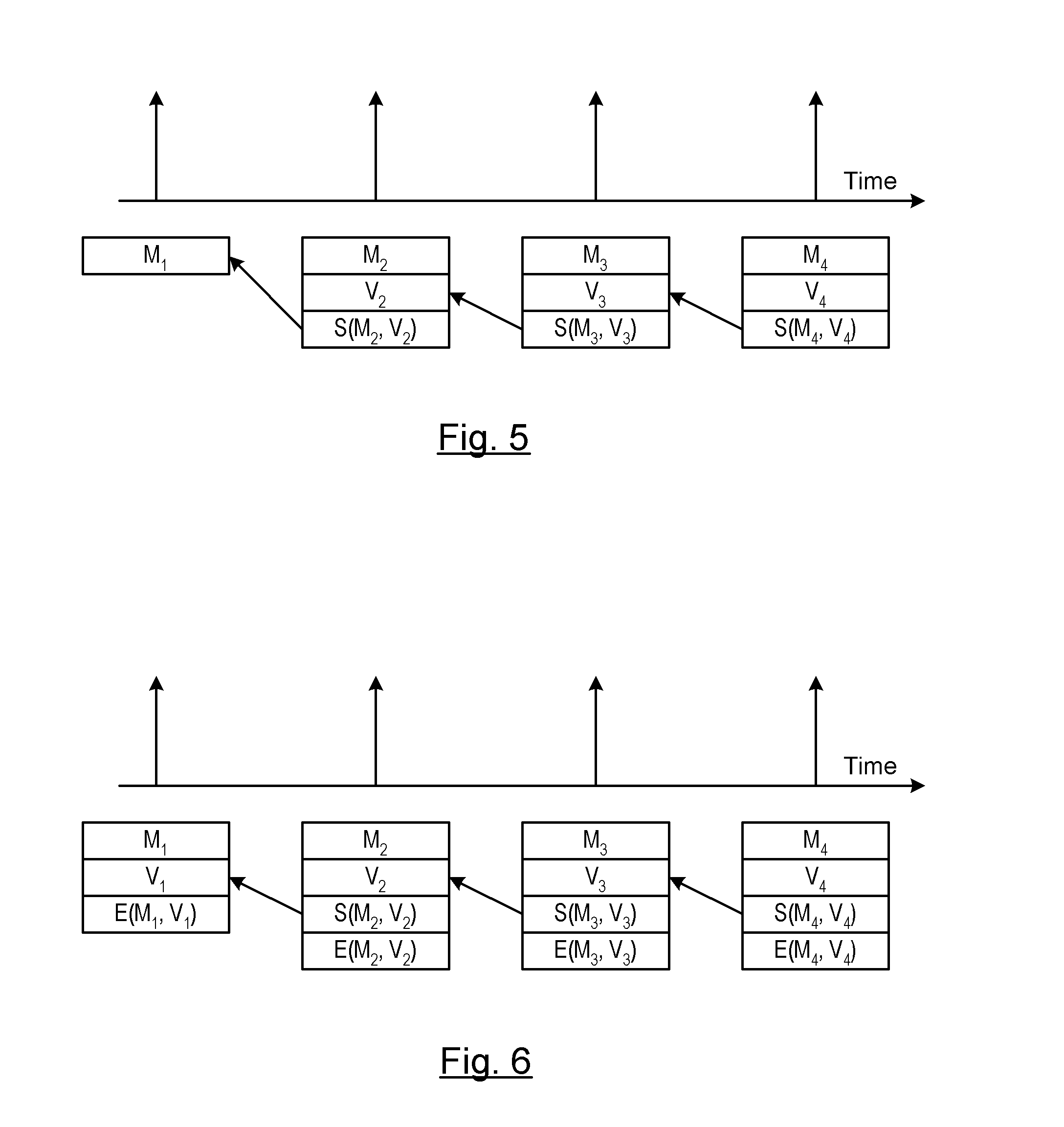
Method of Using ECDSA with Winternitz One Time Signature
ActiveUS20110208971A1Maintain robustnessRobustnessPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital Signature AlgorithmBroadcasting
A method is provided of authenticating a digitally signed message. A chain of messages is generated. A Winternitz pair of keys is generated for each respective message. A sequence number is assigned to each of the messages. Each of the sequence numbers cooperatively identify an order of Winternitz verifiers assigned to each of the messages. A signature to a first message in the chain of messages is signed using a digital signature algorithm private key. Signatures to each of the following messages in the chain of messages are signed using both Winternitz private keys and digital signature algorithm private keys. The signed messages are broadcast from a sender to a receiver. The first signed broadcast message is authenticated at the receiver by verifying the digital signature algorithm signature. At least some of the following signed broadcast messages are authenticated at the receiver by verifying only the Winternitz signature.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Music context system, audio track structure and method of real-time synchronization of musical content
ActiveUS20160372095A1Enhance sensory experienceIncrease intensityElectrophonic musical instrumentsData buffering arrangementsMusical toneData synchronization
A system is described that permits identified musical phrases or themes to be synchronized and linked into changing real-world events. The achieved synchronization includes a seamless musical transition—achieved using a timing offset, such as relative advancement of an significant musical “onset”, that is inserted to align with a pre-existing but identified music signature, beat or timebase—between potentially disparate pre-identified musical phrases having different emotive themes defined by their respective time signatures, intensities, keys, musical rhythms and / or musical phrasing. The system operates to augment an overall sensory experience of a user in the real world by dynamically changing, re-ordering or repeating and then playing audio themes within the context of what is occurring in the surrounding physical environment, e.g. during different phases of a cardio workout in a step class the music rate and intensity increase during sprint periods and decrease during recovery periods.
Owner:MASHTRAXX LTD
Security and ticketing system control and management
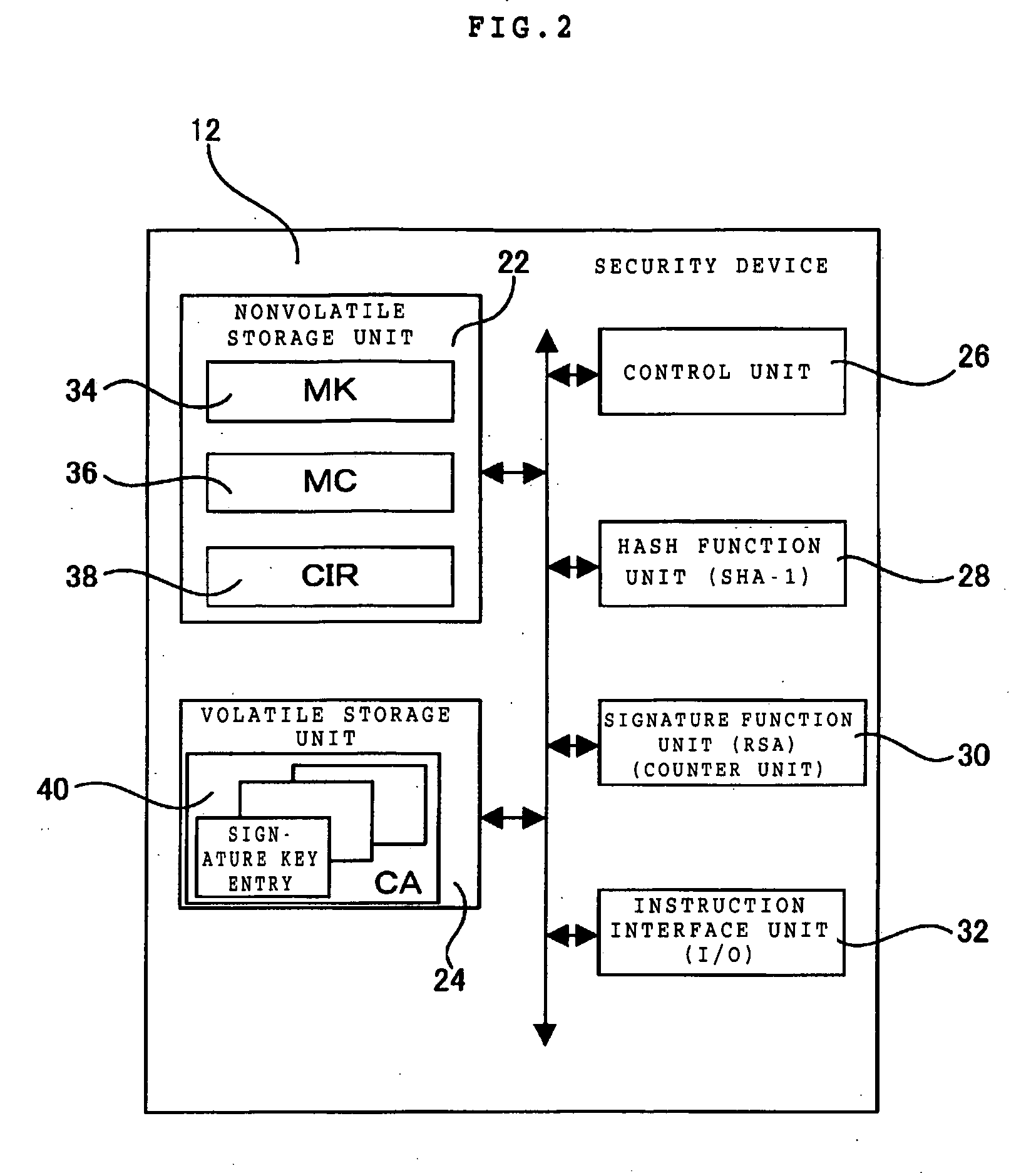
InactiveUS20050204140A1User identity/authority verificationPayment circuitsComputer hardwareHash function
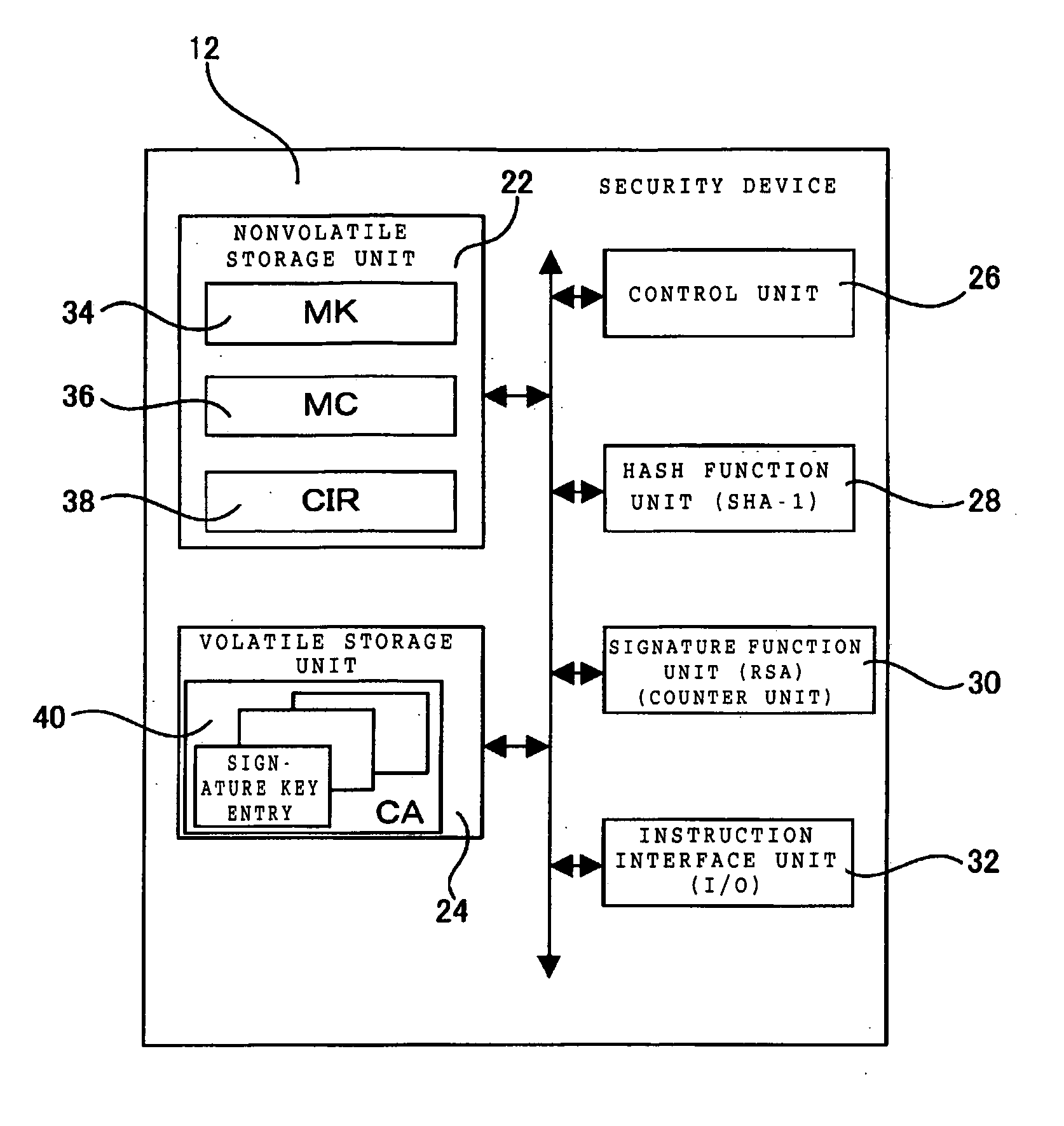
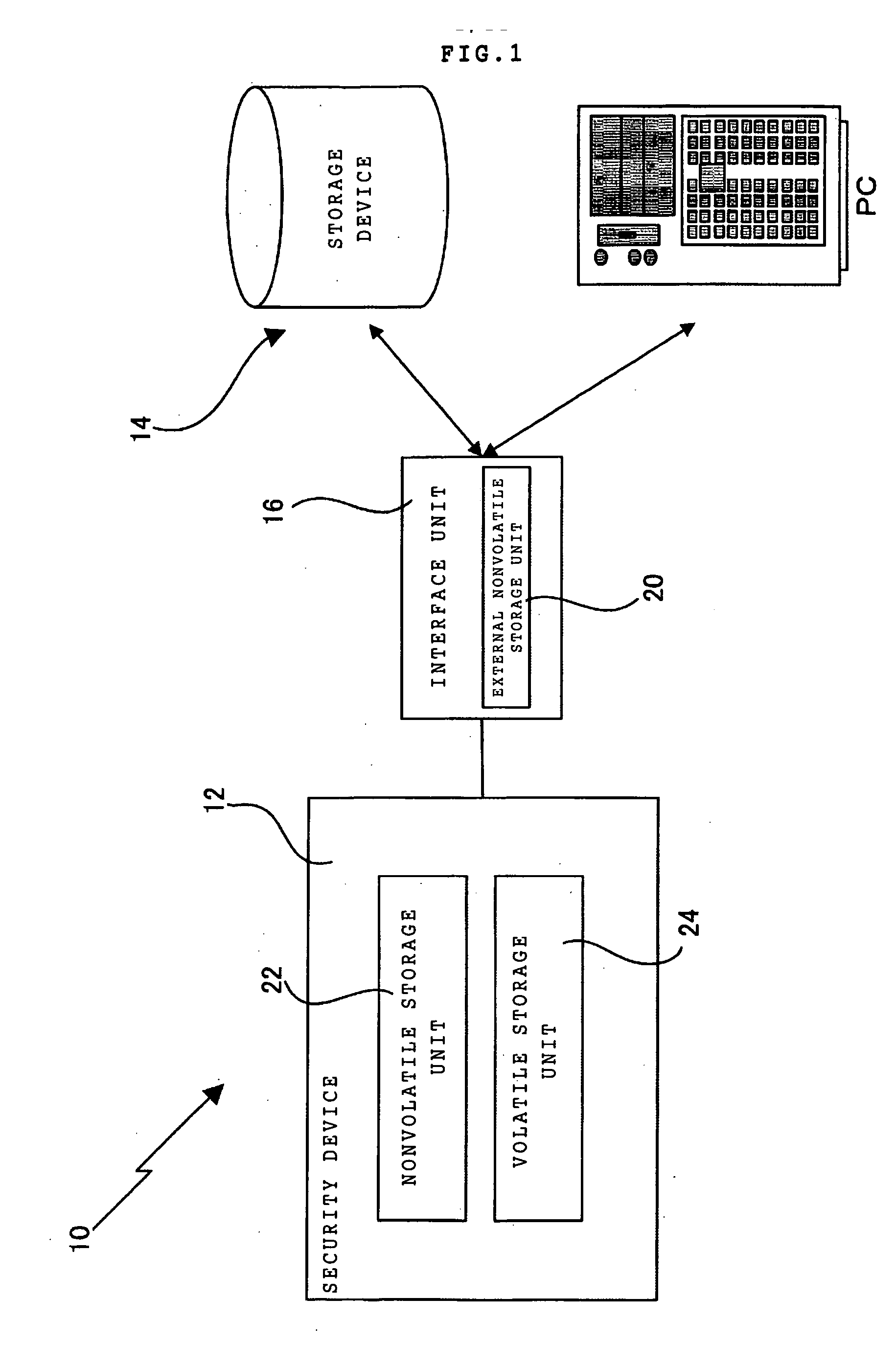
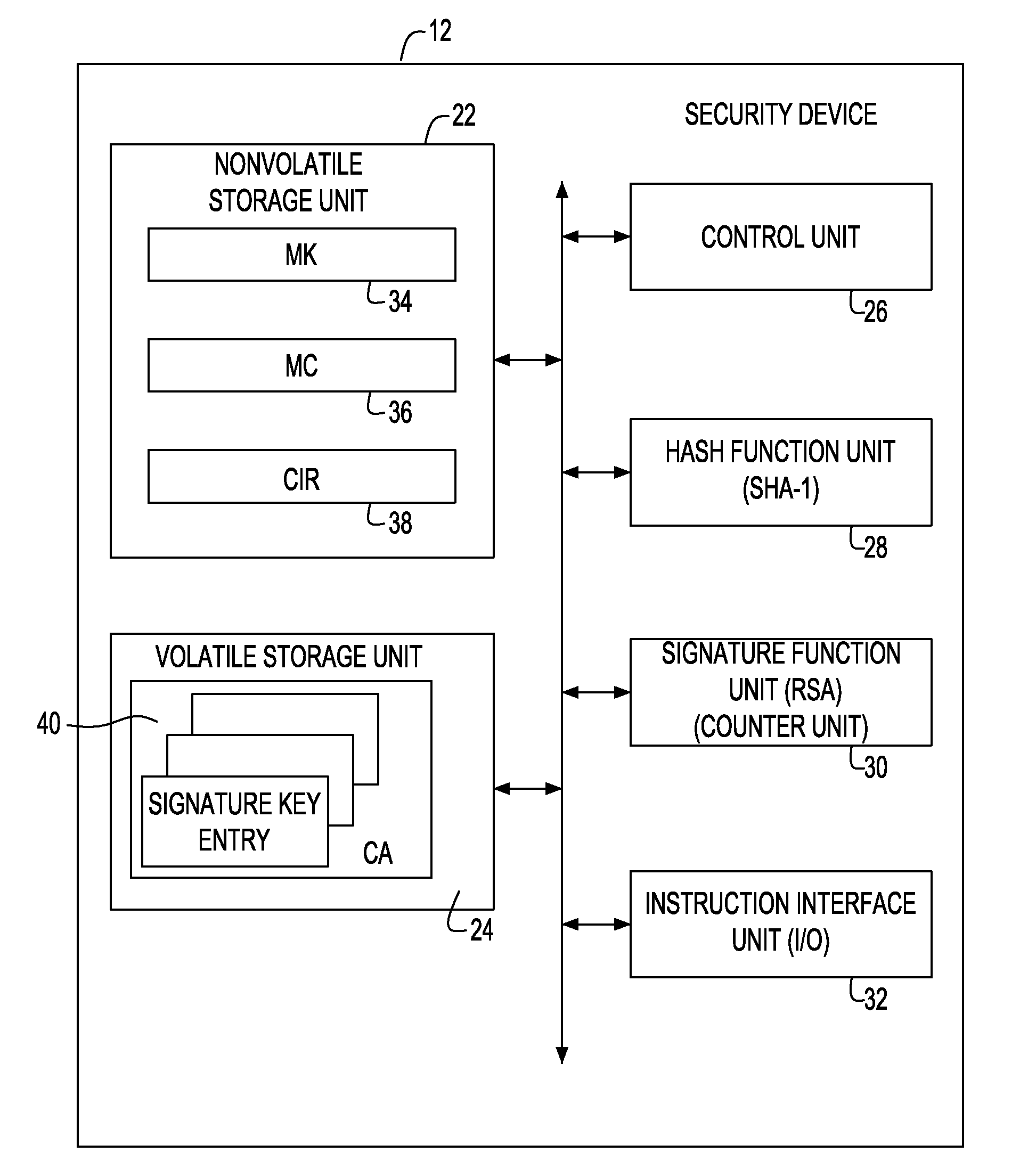
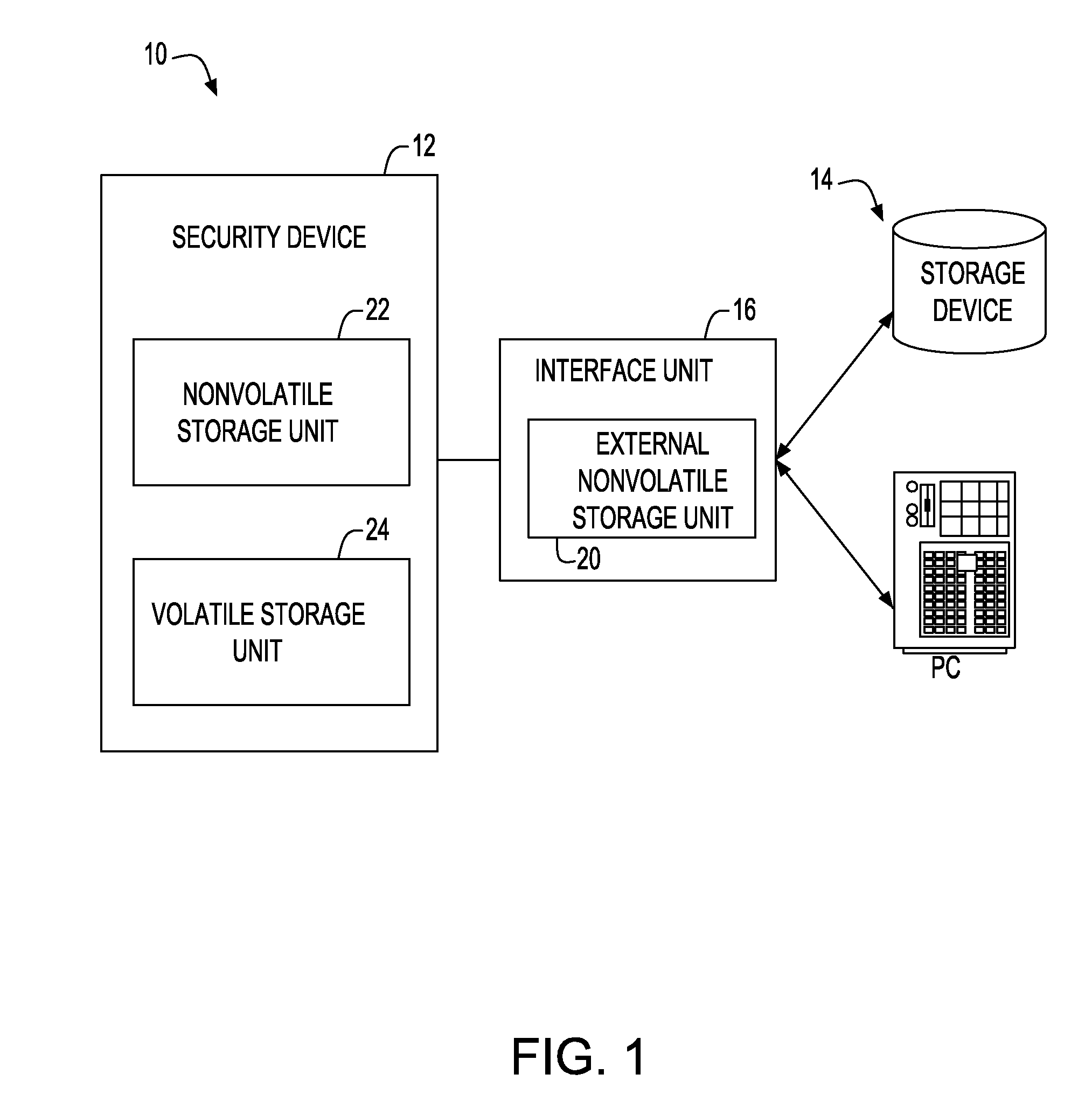
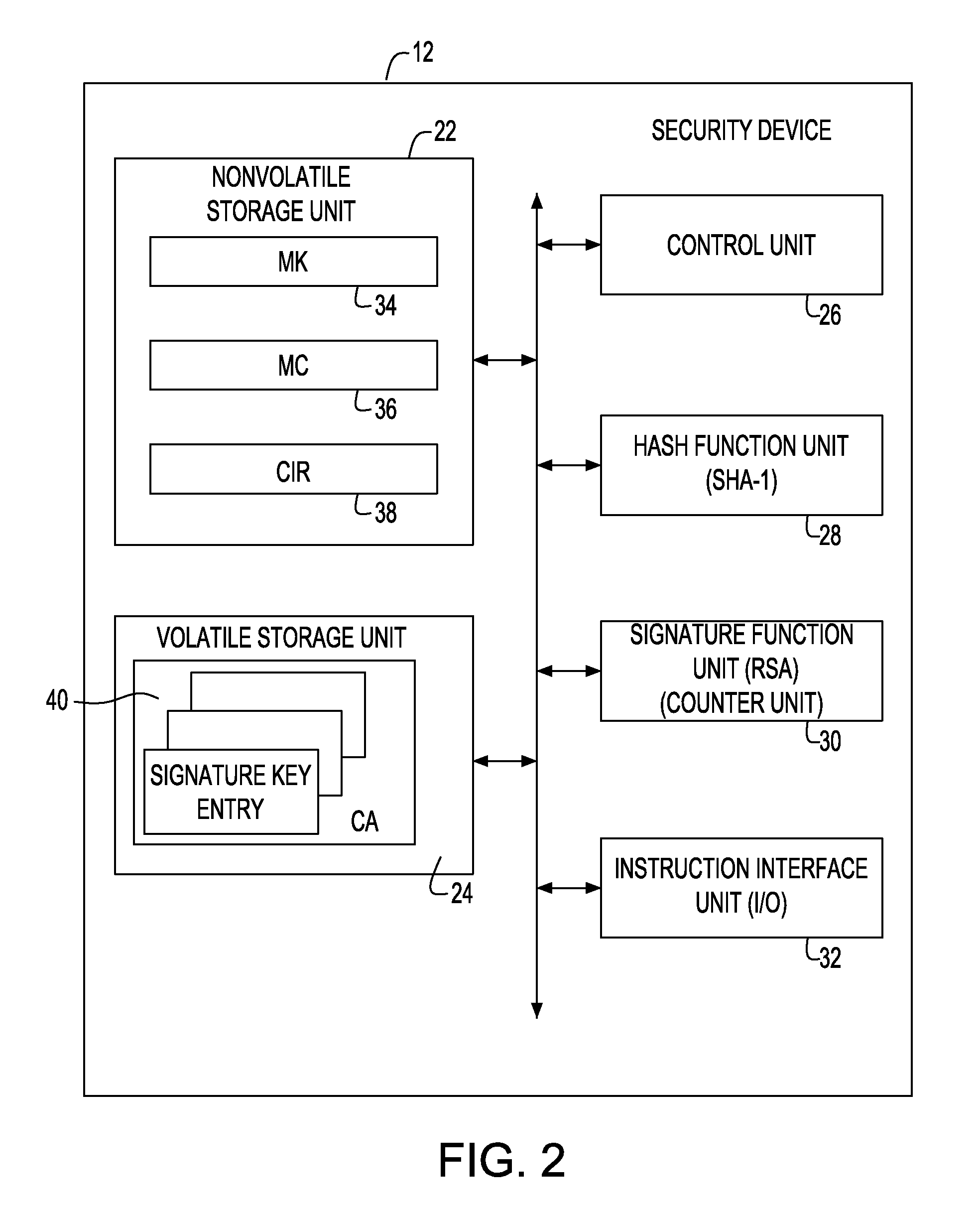
A security device of this invention includes a nonvolatile storage unit 22 for storing a validity check unit including a counter updated every time signature function means 30 is called up, a volatile storage unit 24 for reading and storing a counter array out of an external nonvolatile storage unit storing the counter array, in which the counter array is obtained by coupling a hash value generated for each signature key with a signature number counter for counting the number of signatures performed by use of the signature key, and a hash function unit 28 for reading the counter array out of the volatile storage unit 24, generating the hash value, and transferring the hash value to the validity check unit for a validity check.
Owner:IBM CORP
Symbian signature application authentication method and system
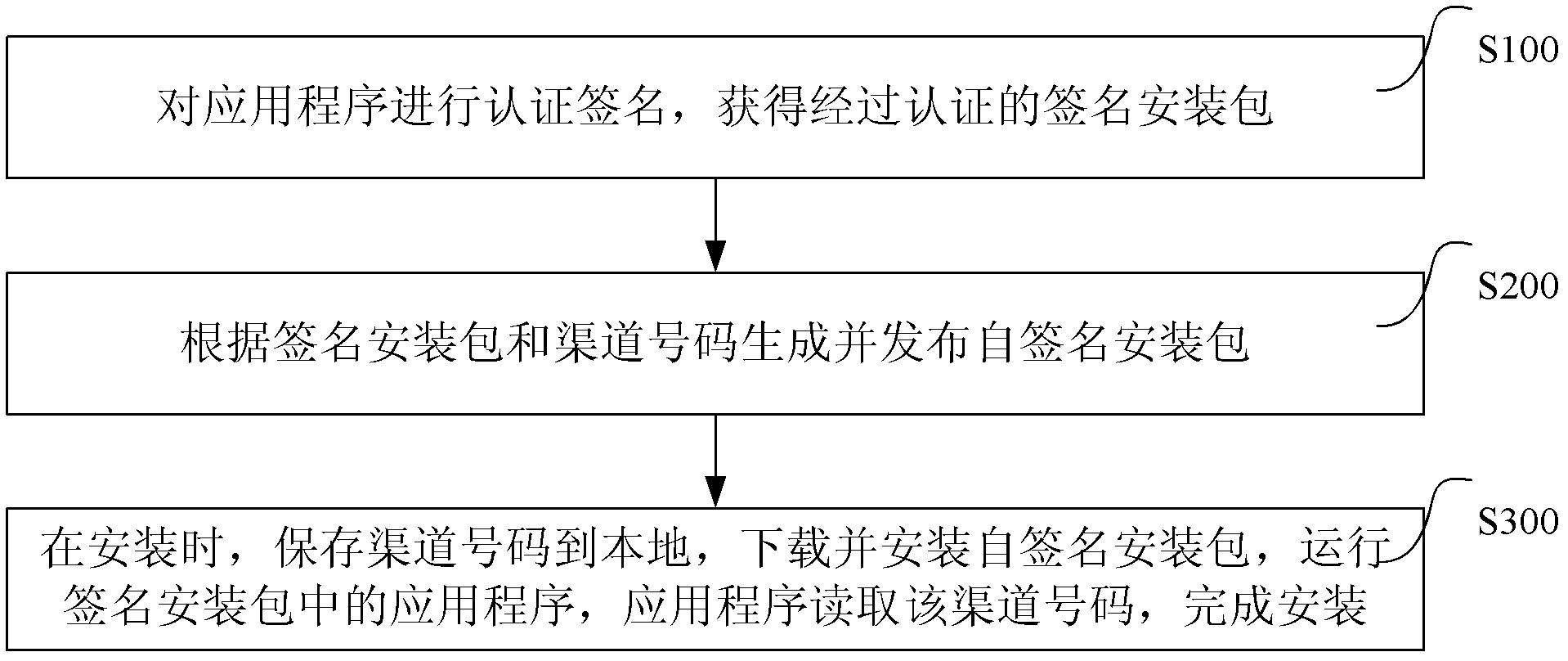
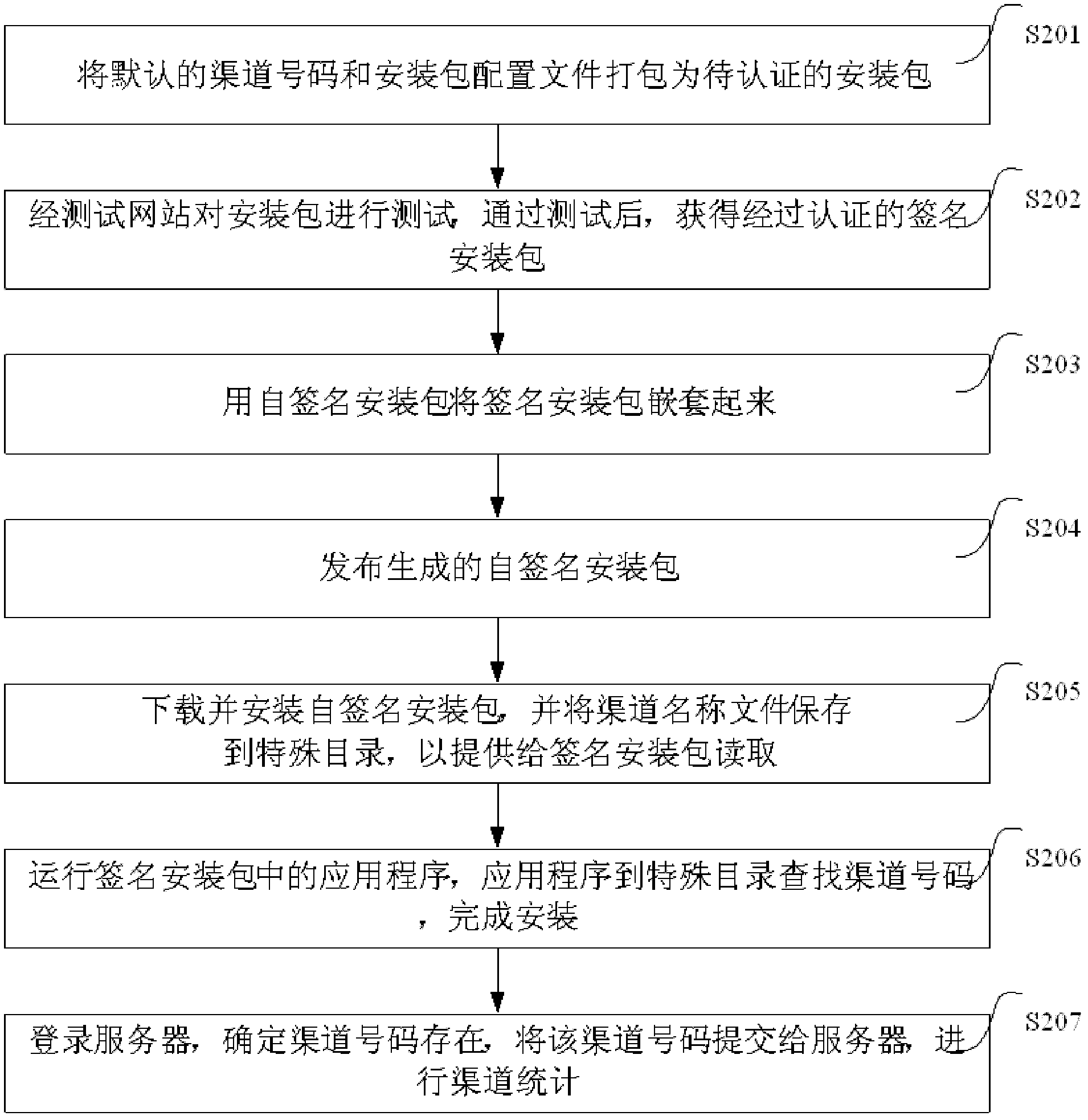
ActiveCN103036678AGuaranteed time accuracyRealize the statistical functionUser identity/authority verificationAuthenticationTime signature
The invention discloses a symbian signature application authentication method and system. The method comprises a first step of performing authentication signature on application programs and obtaining an authenticated signature installation package; a second step of generating a self-signature installation package according to the signature installation package and channel numbers, issuing the self-signature installation package, and enabling the self-signature installation package to comprise the signature installation package and the channel numbers; and a third step of saving the channel numbers locally in installation, downloading and installing the self-signature installation package, running the application programs in the signature installation package, enabling the application programs to read the channel numbers, and finishing installation. Packaging work of various channels can be finished by one-time signature, time accuracy of the signature is guaranteed, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING FEINNO COMM TECH
Detecting Musical Structures
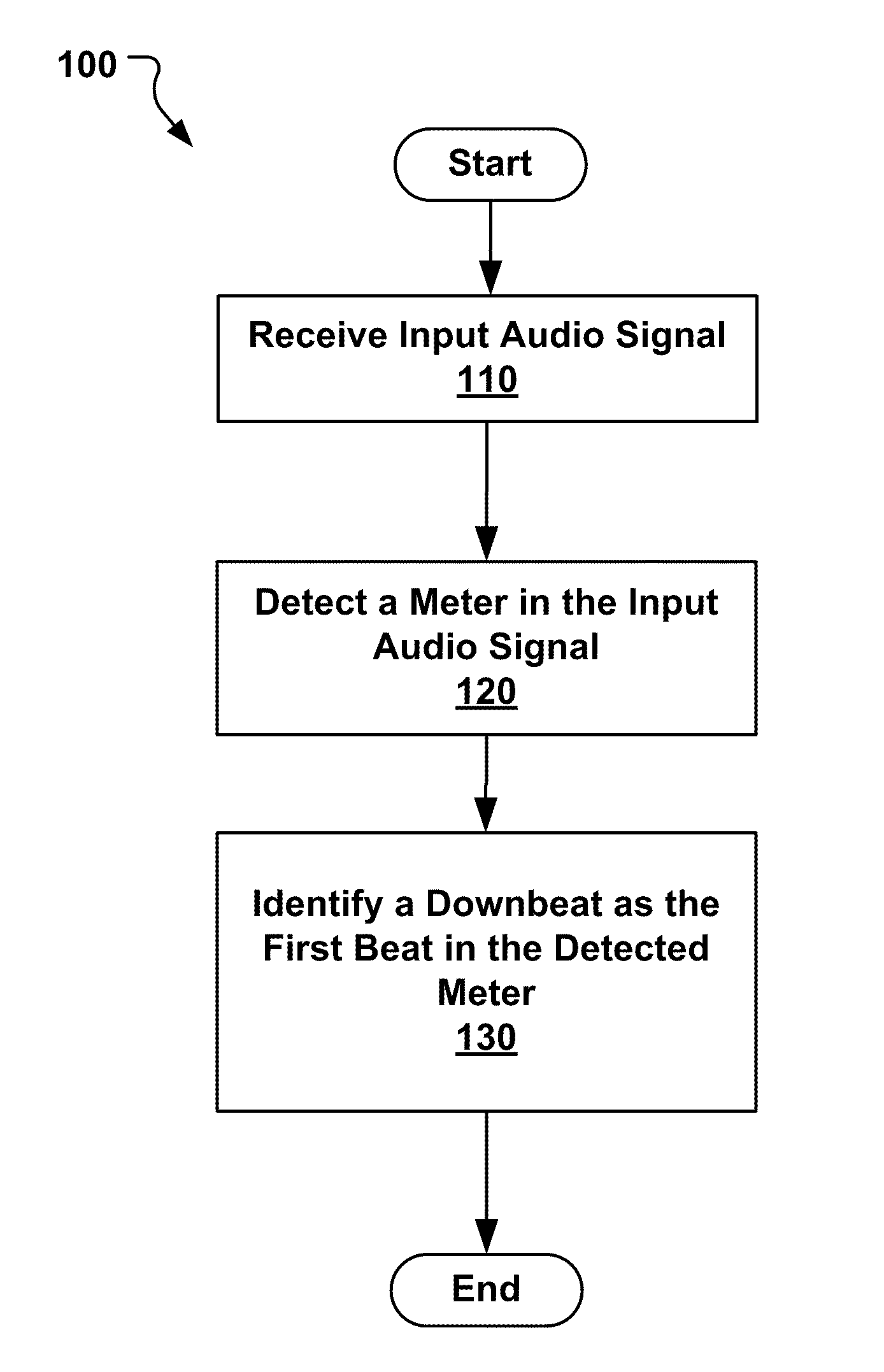
ActiveUS20110255700A1Reduce complexityDownsampling the generated envelopeElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic systemsComputer scienceAudio frequency
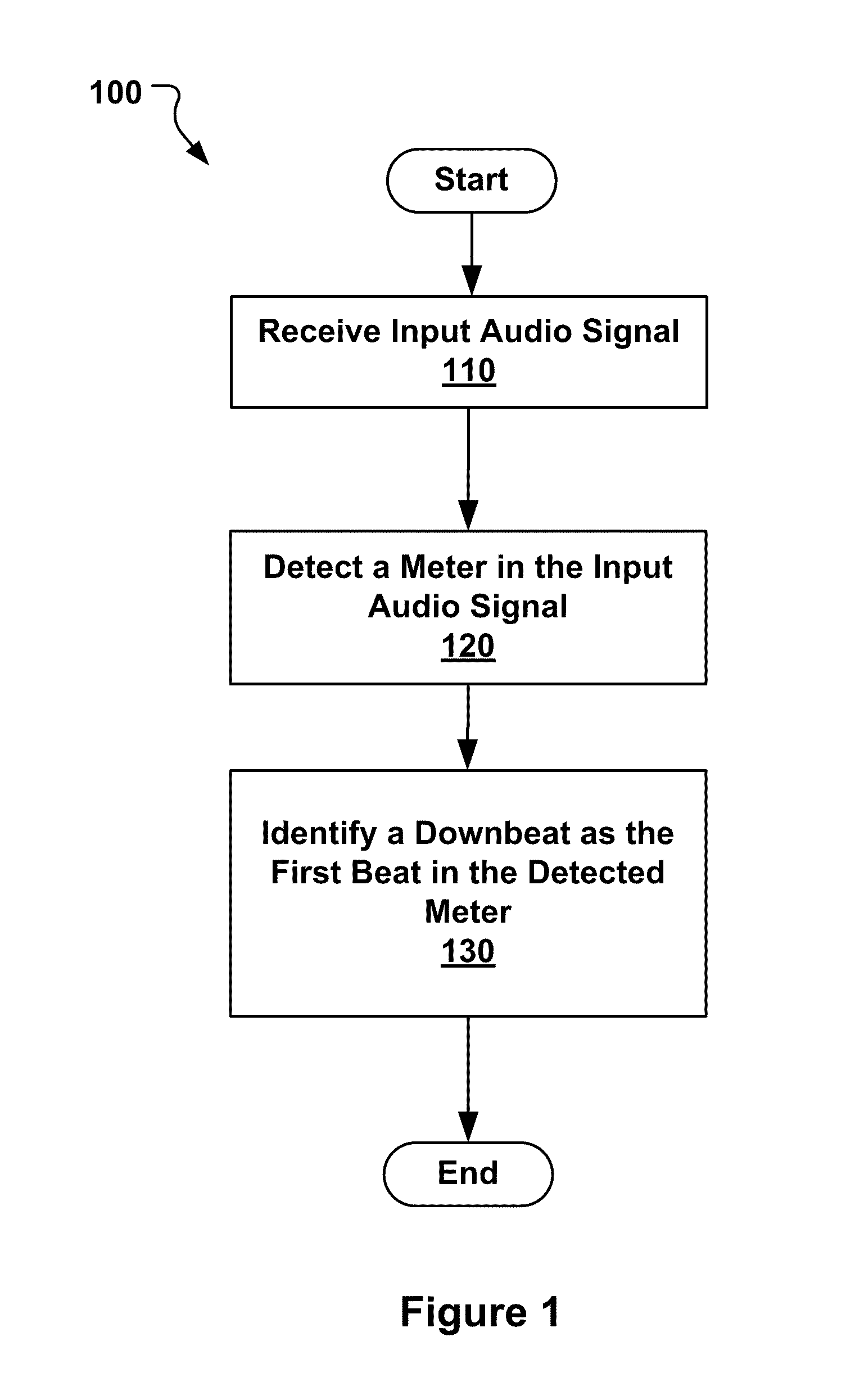
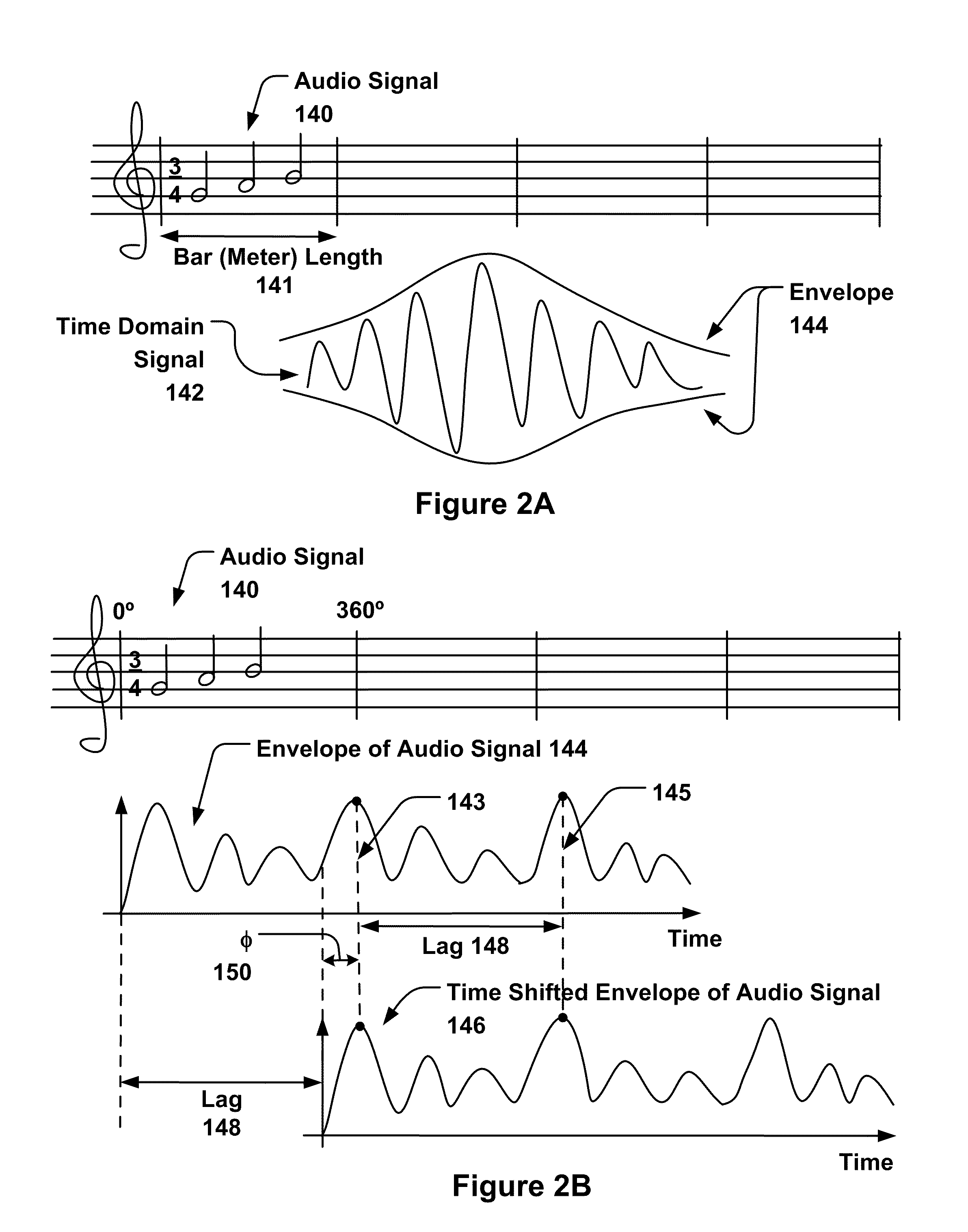
Among other things, techniques and systems are disclosed for detecting musical structures, such as downbeats. In one aspect, a method performed by a data processing device includes receiving an input audio signal. The method includes detecting a meter in the received audio signal. Detecting the meter includes generating an envelope of the received audio signal; generating an autocorrelation phase matrix having a two-dimensional array based on the generated envelope to identify a dominant periodicity in the received audio signal; and filtering both dimensions of the generated autocorrelation phase matrix to enhance peaks in the two-dimensional array. The meter represents a time signature of the input audio signal having multiple beats. Additionally, the method includes identifying a downbeat as a first beat in the detected meter.
Owner:APPLE INC
Music context system, audio track structure and method of real-time synchronization of musical content
ActiveUS9697813B2Enhance sensory experienceIncrease intensityElectrophonic musical instrumentsRecord information storageData synchronizationRecovery period
Owner:MASHTRAXX LTD
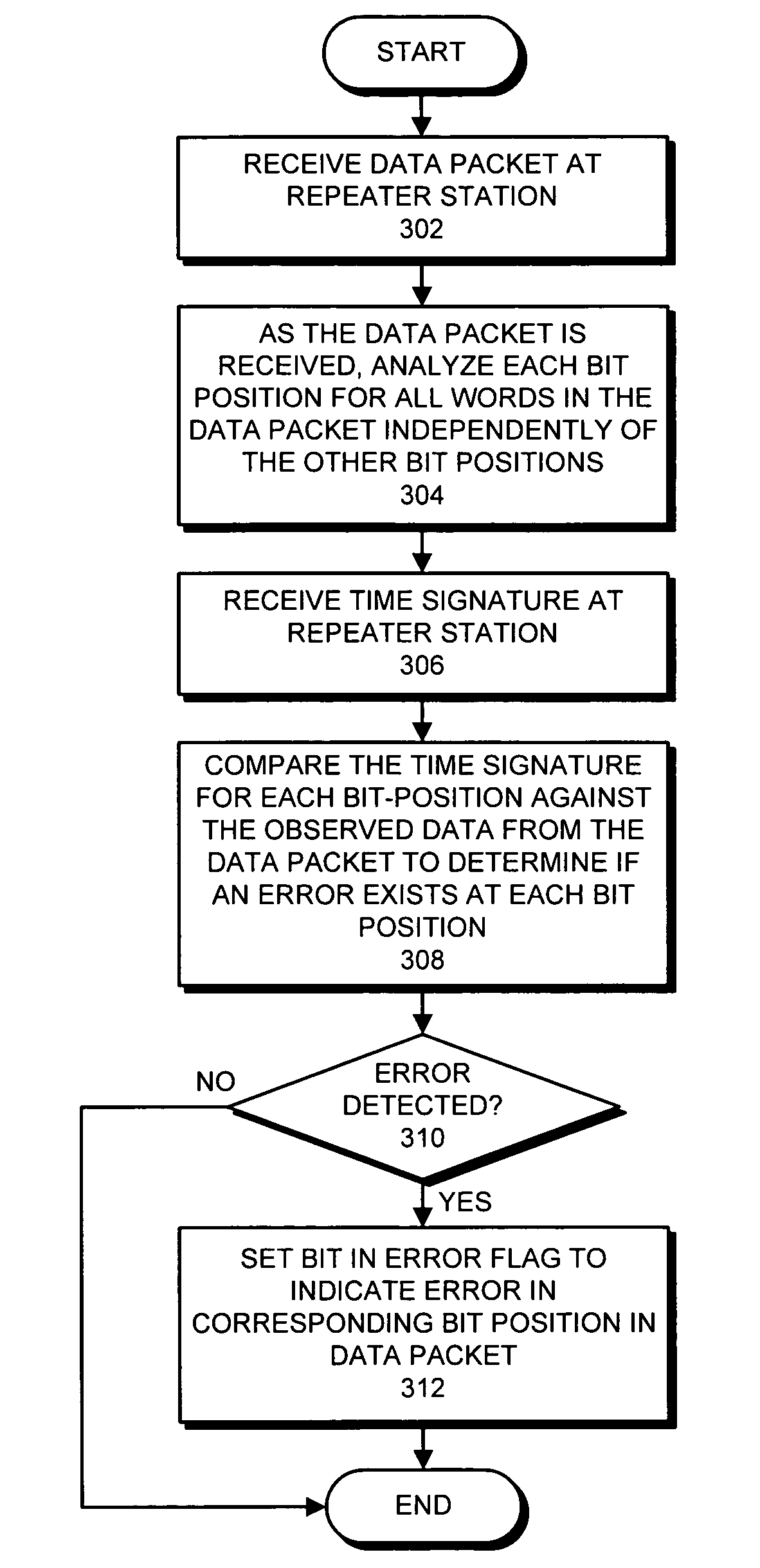
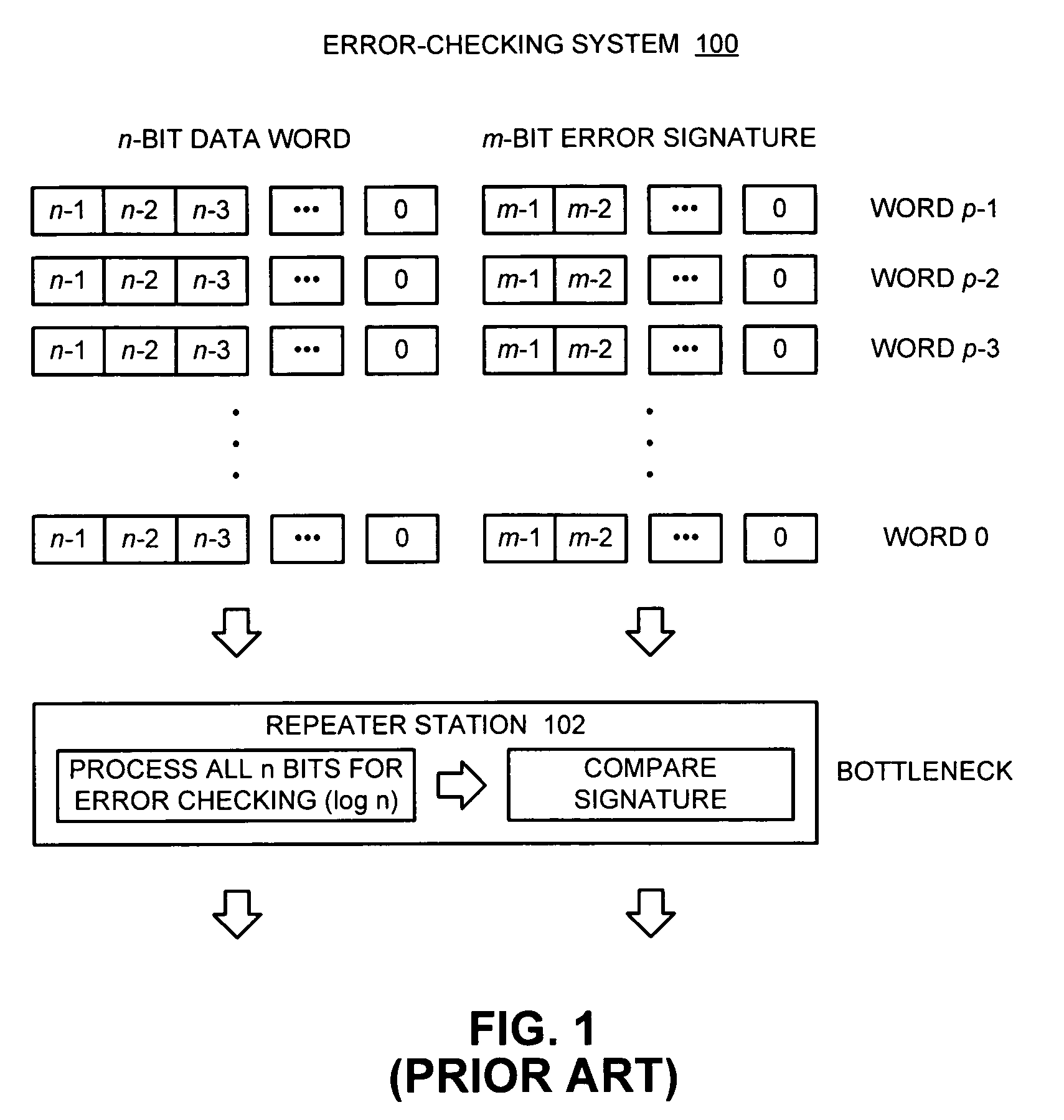
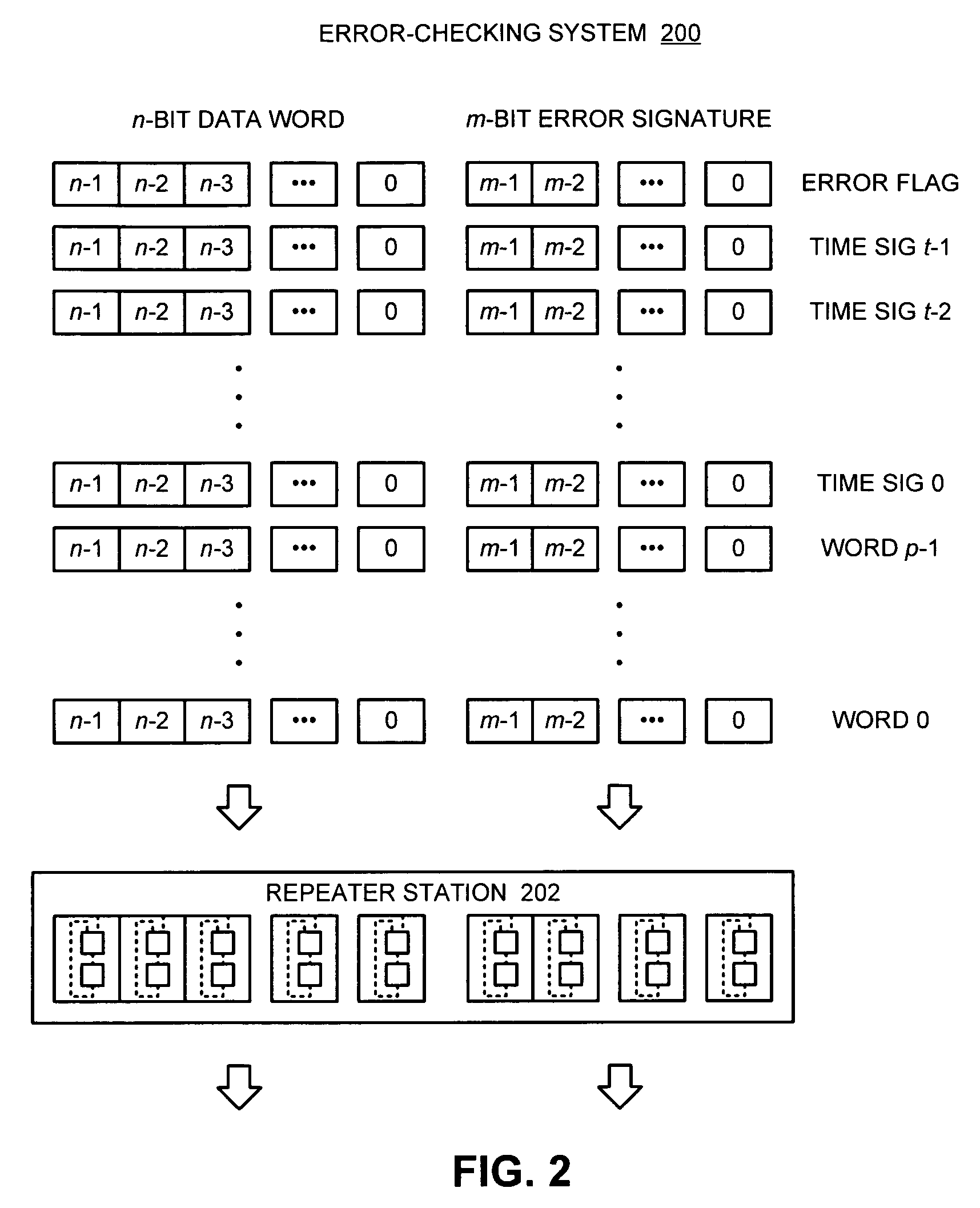
Method and apparatus for performing error-detection and error-correction
ActiveUS7395483B1Easy to detectFacilitates correcting errorOther decoding techniquesError detection/correctionNetwork packetData lines
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that facilitates detecting and correcting errors. The system operates by receiving a data packet comprised of p words on a communication pathway, wherein each bit of a word is received on a separate data line in a set of data lines that comprise the communication pathway. The system also receives a time signature t on the communication pathway, wherein t contains per-bit error information for the p words in the data packet. As the data packet is received, the system performs an error-detection operation on each data bit of the data packet in parallel, wherein the error-detection operation generates per-bit error information for each bit position across the p words in the data packet. Finally, the system compares the generated per-bit error-information with the corresponding per-bit error information in the time signature t to determine if there exists an error.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method of using ECDSA with winternitz one time signature
ActiveUS8386790B2Maintain robustnessOvercome deficienciesUser identity/authority verificationMechanically effected encryptionDigital Signature AlgorithmBroadcasting
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for teaching music
A system and method for teaching music both visually and tactilely. In one embodiment, the invention comprises blocks shaped to resemble musical symbols used to compose music, including time signatures, notes, rests, and dots. Each of the blocks are relative in thickness such that for a given time signature, the correct rhythm for a given measure can be determined by laying one or more of the notes, rests and dots one over the other to see if their combined thickness is equal to that of a preselected time signature. The thickness of the block shaped to resemble the time signature is such that it only allows the correct number of blocks shaped as notes, rests or dots to be of equal thickness to thereby determine the correct rhythm. In addition, the correct rhythm can be determined by simply reading the shaped blocks as one would read music. The use of the shaped blocks having relative thicknesses allows a student to learn rhythm by trial and error and does not necessarily require that the student understand complex music theory. In addition, the blocks can be used by the student when clapping the correct rhythms. Other musical notation can be represented by blocks as well such as bar lines and slurs.
Owner:HANINGTON DARLENE
Constant time signature methods for scalable and bandwidth-efficient multicast
ActiveUS7760732B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationTime efficientComputer science
A method, computer program product, system and apparatus are presented for reducing wasted bandwidth due to supercasting multicast cells through a router switch fabric. In one embodiment of the present invention, signatures of a switch fabric destination address are generated and compared. A signature is an information-rich representation of the fabric destination address that is generated using the fabric destination address. Therefore, supercasting can be minimized by combining fabric destination addresses with like signatures. Aspects of the present invention include generating the signatures using random permutation maps of the set of switch fabric ports or determining intersections of a fabric destination address with a selection of subsets of the switch fabric ports. Signature-based solutions for supercast minimization can be performed in a time-efficient manner and be implemented online, while solutions that can generate a more optimal solution but may take a longer time to perform, such as row-clustering, can be implemented off-line. A further aspect of the invention, incorporates an off-line row-clustering supercast minimization method with an on-line signature-based supercast minimization method.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Wireless router and mobile phone based attendance signature method
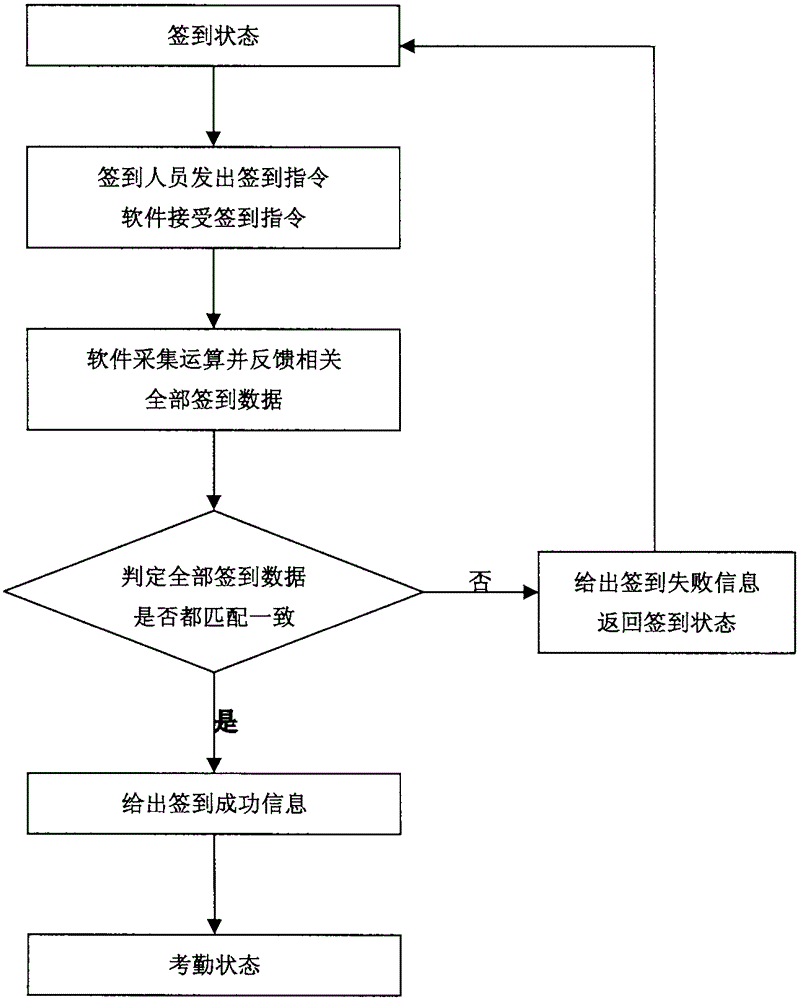
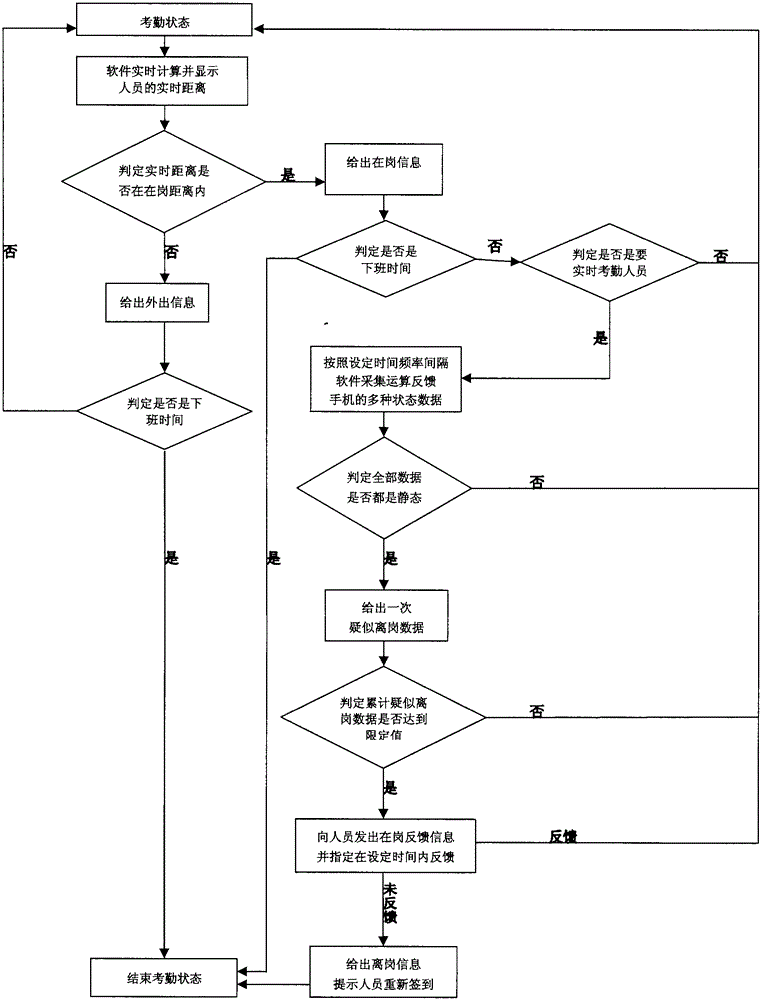
InactiveCN105225283AImprove work efficiencyImprove the quality of workRegistering/indicating time of eventsWireless routerMobile phone
The invention relates to a wireless router and mobile phone based attendance signature method. The wireless router and mobile phone based attendance signature method comprises the following steps that a wireless router conforming to attendance signature conditions is selected; related values of the wireless router, an address of an attendance signature place, limiting conditions of verifying a signature person, a zero coordinate using the address of the attendance signature place as a fixed reference coordinate, the on-duty distance range of the person, commuter time and other values are preset attendance signature software built in a mobile phone; a signature behavior is determined by judging whether three groups of real-time connected data including wireless router parameters and preset parameters, a real-time address and a preset address and real-time signature person verification mode and preset limiting conditions for signature person verification are matched and consistent or not; the attendance situations, such as outgoing, on-duty and off-duty are determined by calculating the real-time distance of the person holding the mobile phone and acquiring, computing and comparing multiple states feeding back the mobile phone at intervals of preset time frequency. By adoption of the new attendance signature method, real-time checking and supervision are achieved.
Owner:杨川林
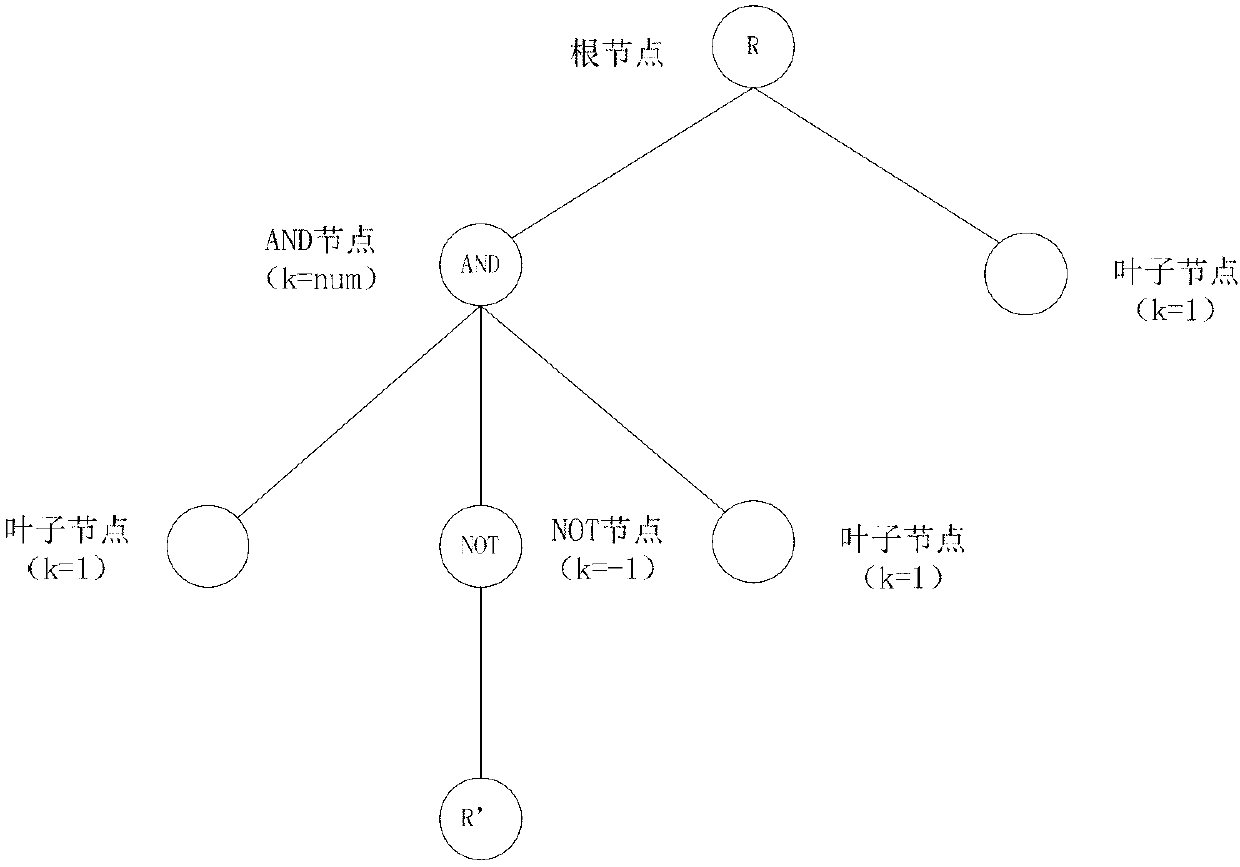
NOT operational character supported characteristic-based CP-ABE method having CCA security
The invention relates to a NOT operational character supported characteristic-based CP-ABE method having CCA security. An access control structure is an access control tree; a NOT node is added in the access control tree; and k is equal to -1. Meanwhile, according to regulation, a father node of the NOT node must be an ''AND'' node and only one intermediate node is hung under the NOT node; and thus the intermediate node is used as a root node to set a strategy tree and the strategy tree expresses a related strategy, set by an encryption party, of a NOT attribute. A high one-time signature technology is added to further enhance a security level of the method from a CPA security level to a CCA security level. Strategy expression based on an attribute encryption algorithm is enriched; security of the existing method is enhanced, thereby building the high access controlling capability; and moreover, the method has an encryption method with a provable security.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Single-pixel sensor
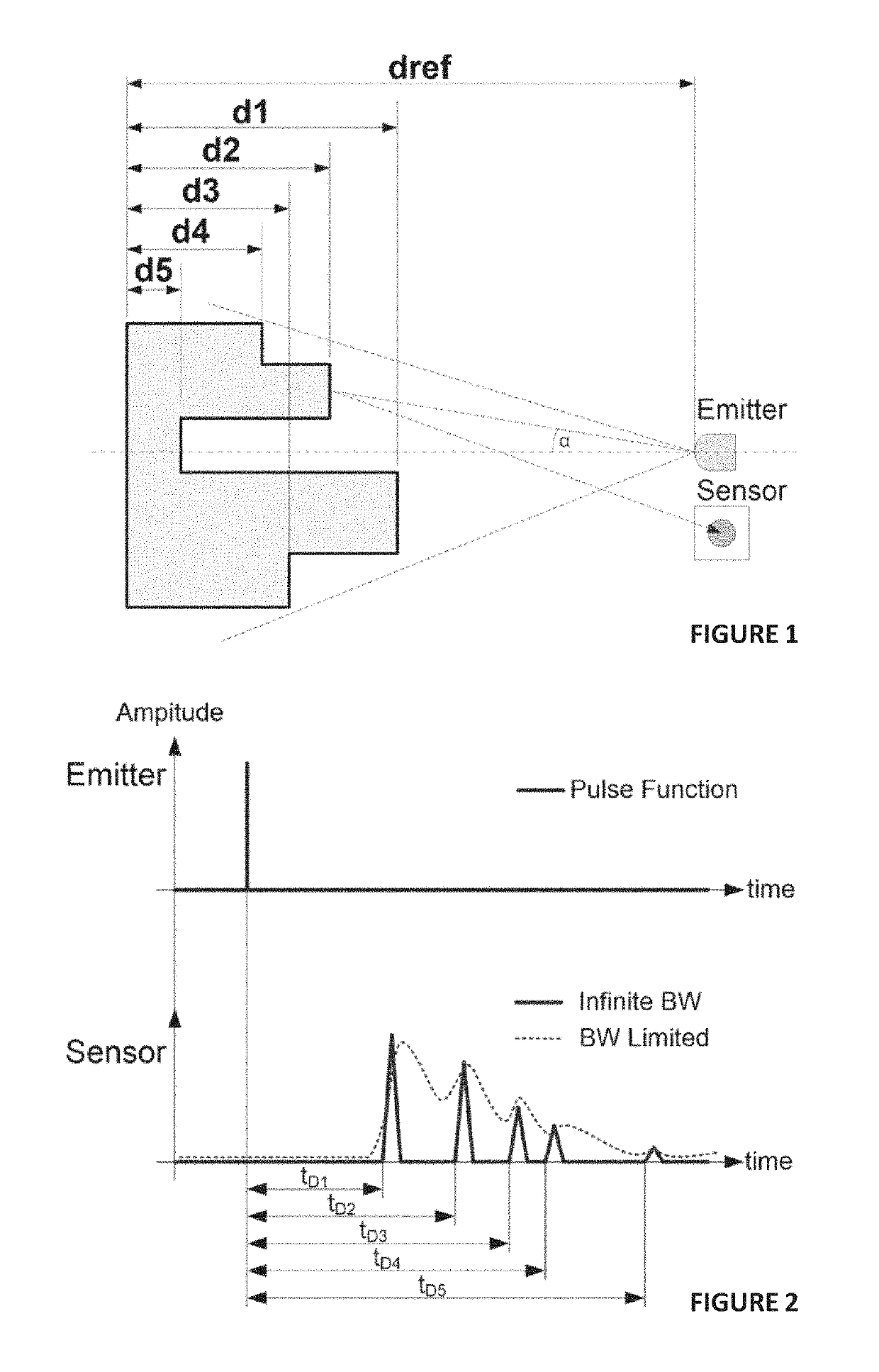
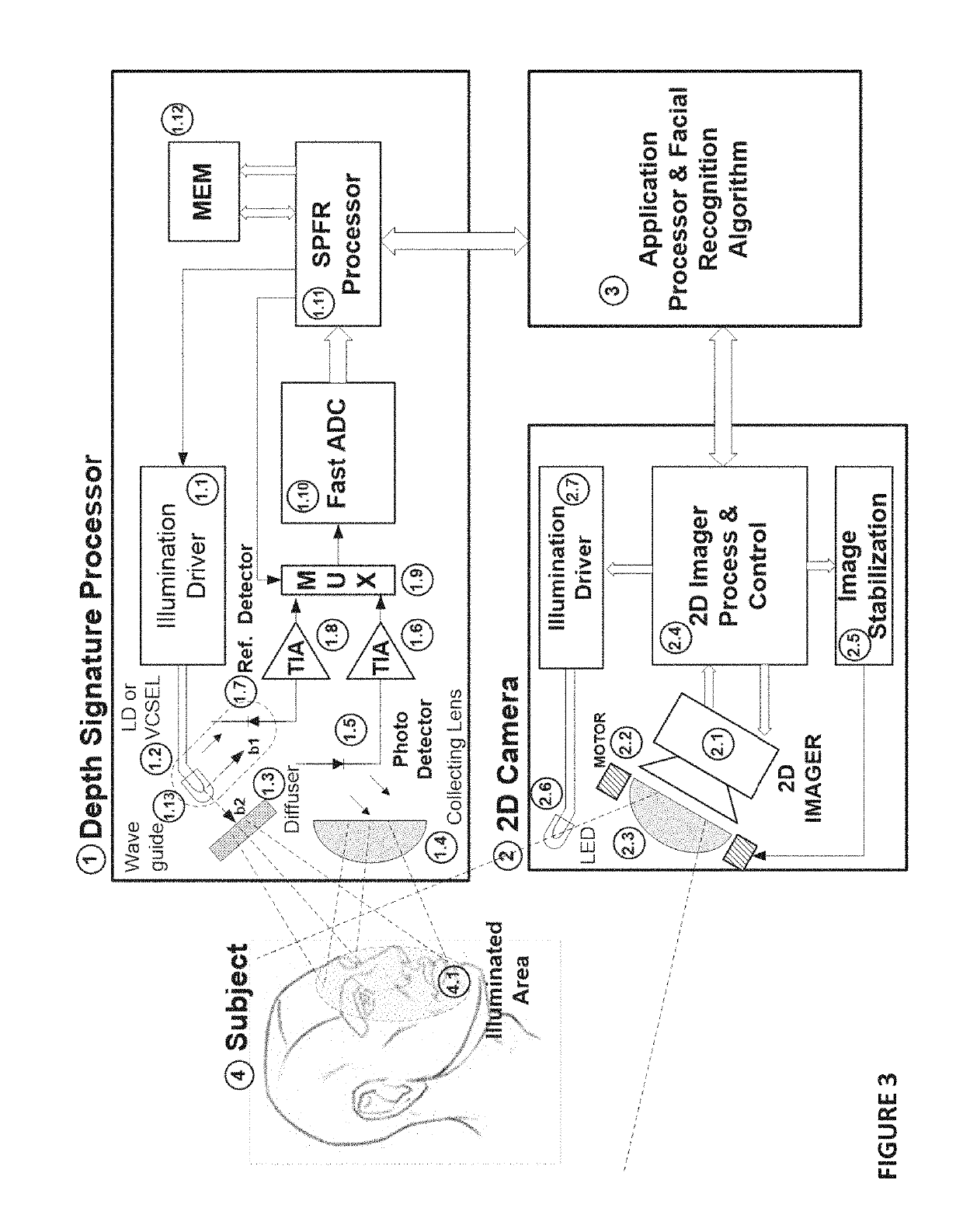
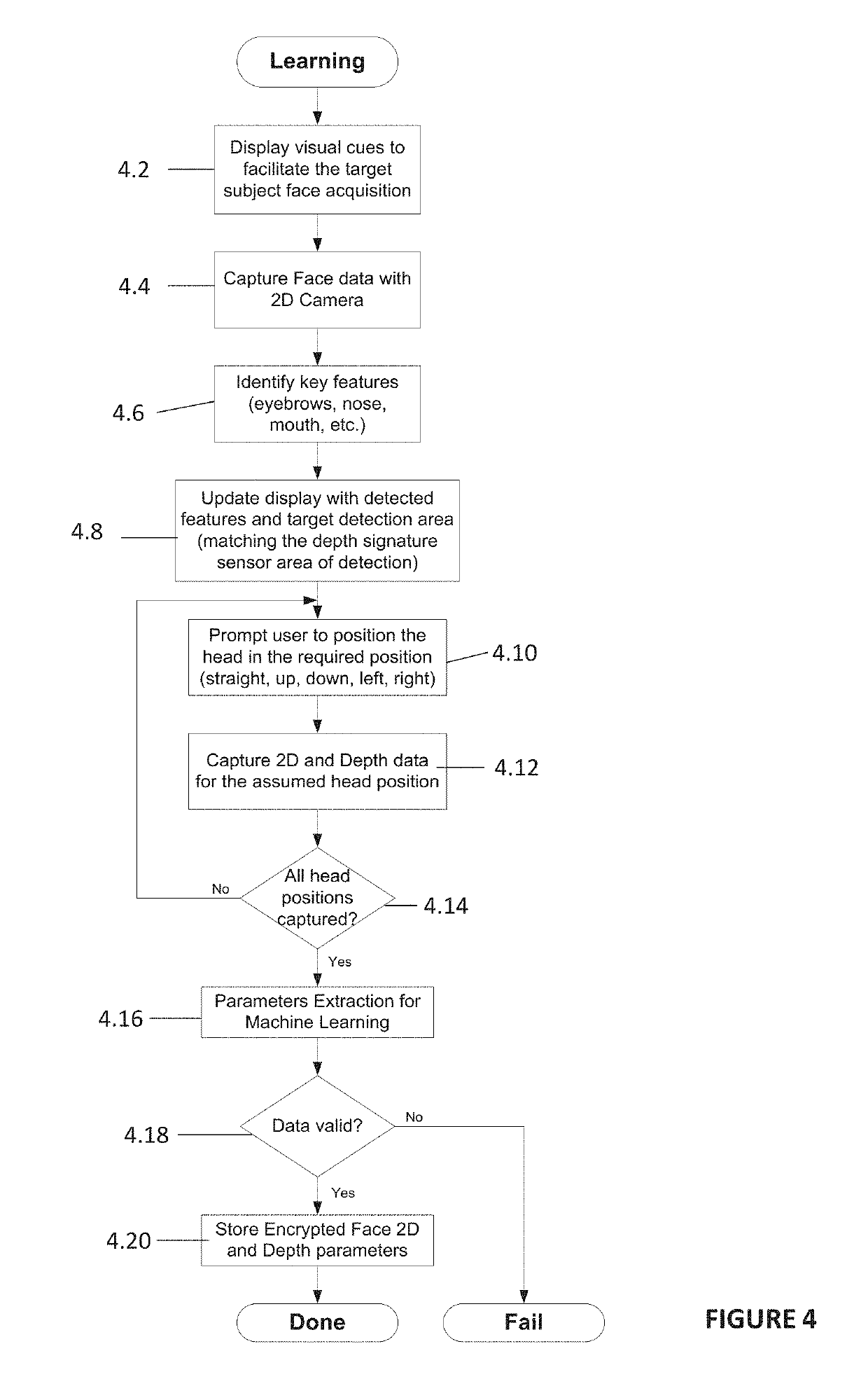
ActiveUS20190340418A1Easy to detectImprove performanceTelevision system detailsElectromagnetic wave reradiationPrincipal component analysisSubject matter
The present disclosure relates to performing facial recognition using a single-pixel sensor that measures the time signature of a light pulse reflected from a subjects face. Due to depth differences between the sensor position and different parts of the subject's face reflections of a short duration illumination pulse from the different parts of the subject's face will arrive back at the sensor at different times, thus providing a time-based one-dimensional signature unique to the individual subject. By analyzing the reflection signature using neural networks or principal component analysis (PCA), recognition of the subject can be obtained. In addition, the same system may also be used to recognize or discriminate between any other objects of known shape in addition to faces, for example manufactured products on a production line, or the like.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Music and math teaching system
A music and math teaching system teaches fraction computations utilizing musical note names and note values in the form of blocks with varying lengths while simultaneously teaching rhythmic topics of time signatures, beats, and tempo. A rhythm board is used to mount note blocks and beat blocks in the process and a blind is used to block the vision of a student working with the blocks.
Owner:SUGANUMA ALAN K
Multifunctional Bispectral Imaging Method and Device
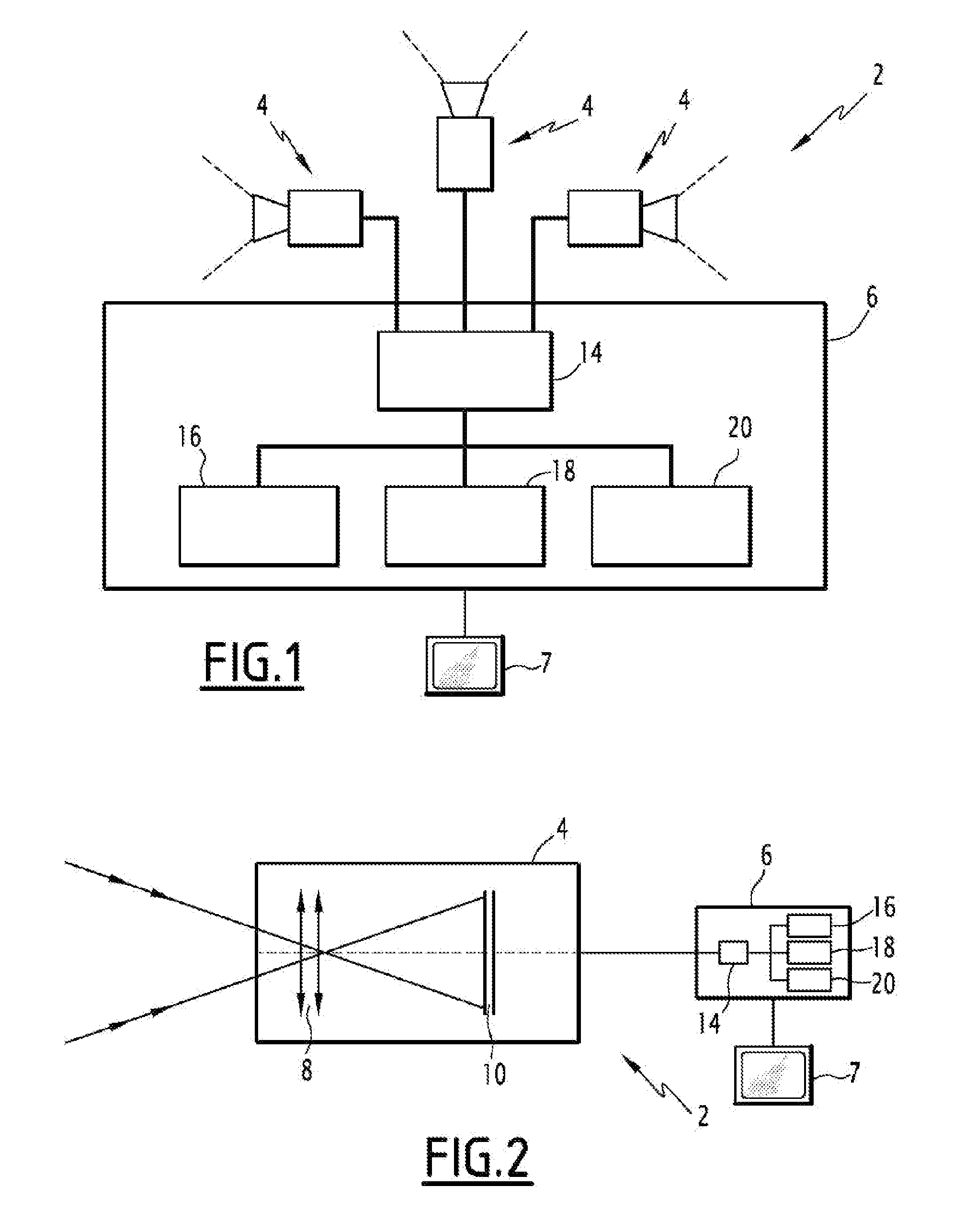
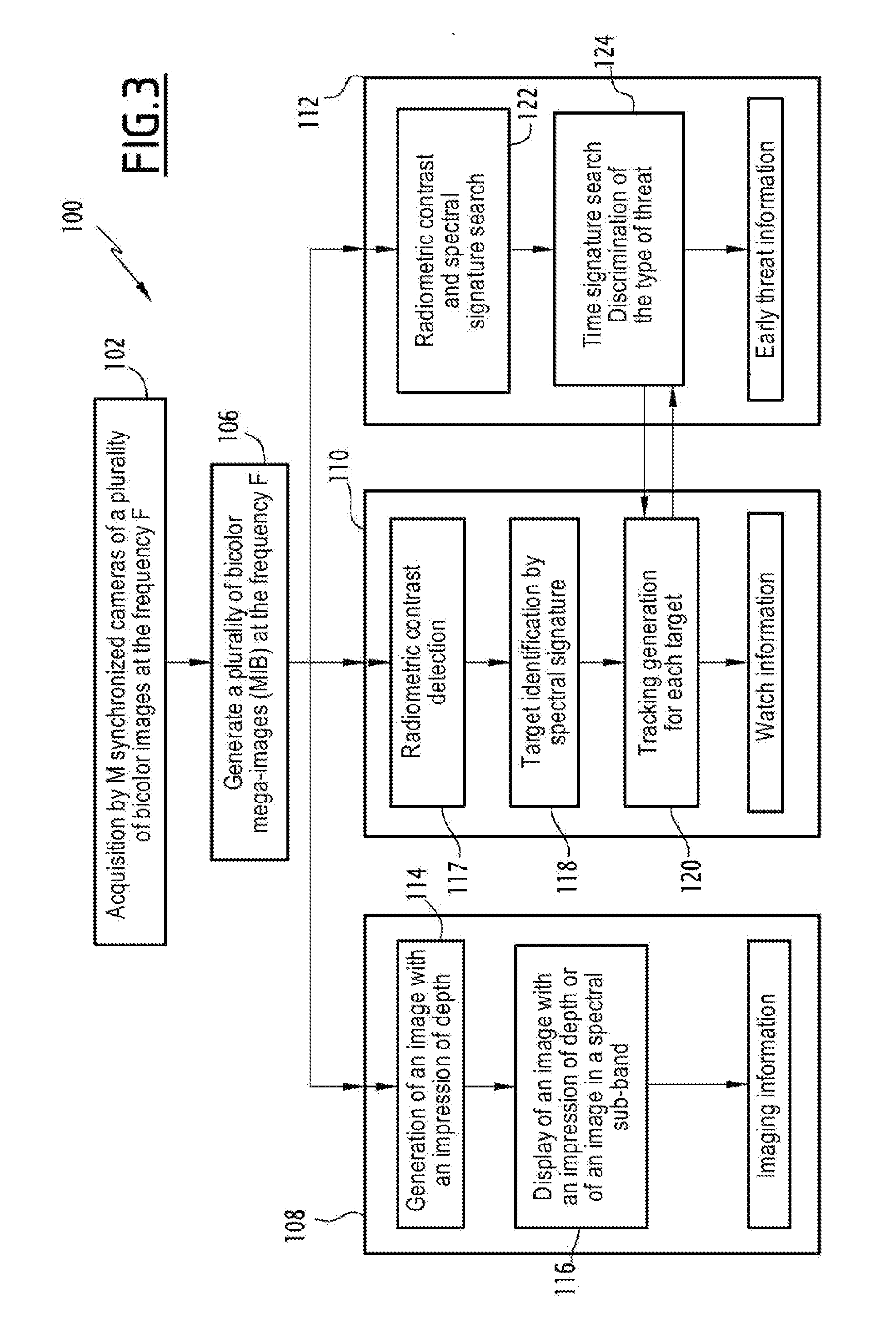
InactiveUS20130235211A1Easy to integrateLess bulkyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrequency spectrumSpectral bands
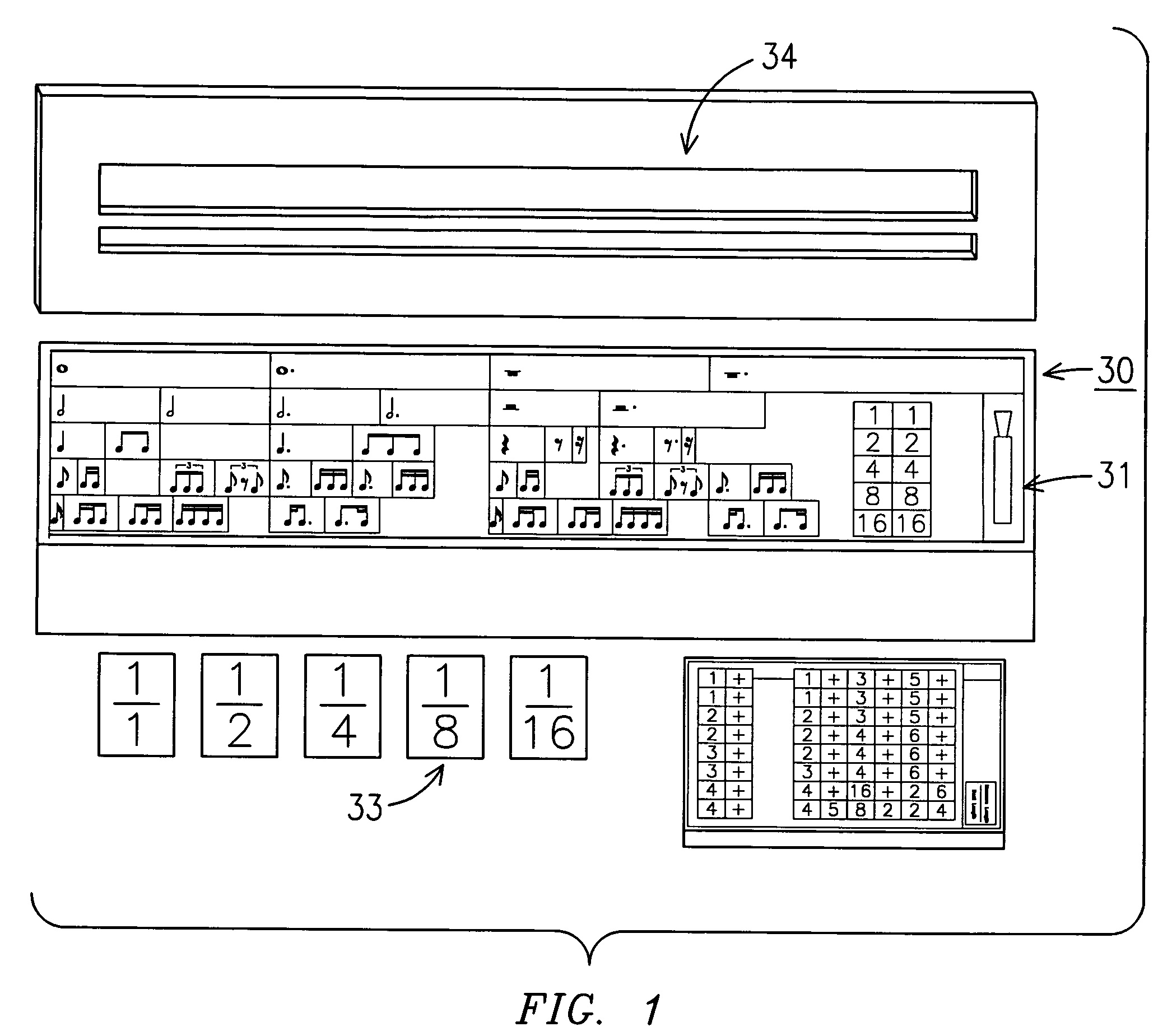
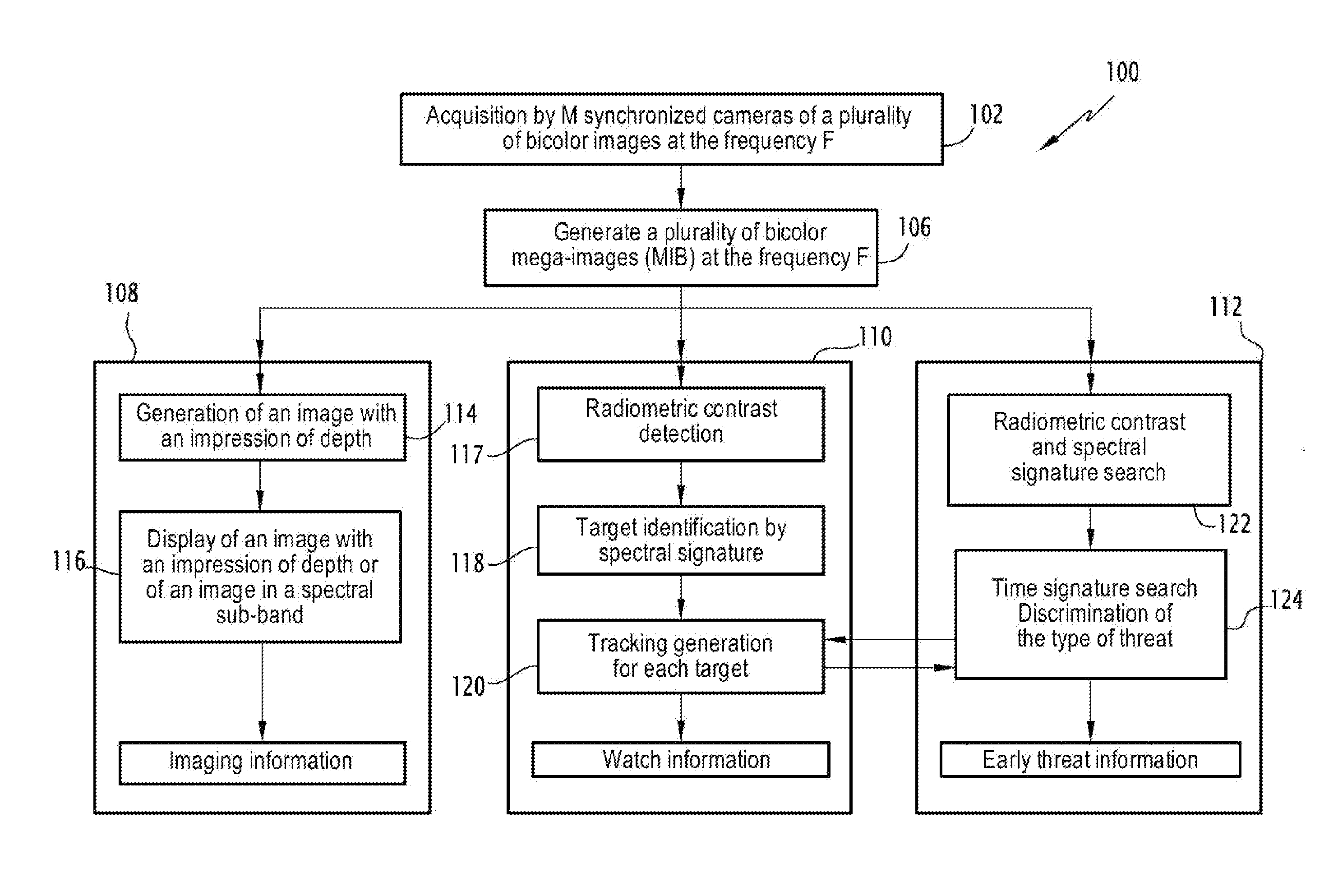
A multifunctional device and method for bispectral imaging are provided. The device and method include acquiring a plurality of bispectral images (IBM), each bispectral image being the combination of two acquired images (IM1, 1M2) in two different spectral bands, and generating a plurality of images, each of which gives an impression of depth by combining the two acquired images (IM1, 1M2) and forming imaging information. The method includes simultaneously processing the plurality of bispectral images in order to generate, in addition to the imaging information, watch information and / or early threat information, comprising the following steps: searching for specific spectrum and time signatures, associated with a particular threat, in the plurality of bispectral images; and detecting a specific object in each bispectral image, and generating a time-tracking of the position of the object in the plurality of images in each spectral band, and the detecting and the tracking of the object forming the watch information.
Owner:THALES SA
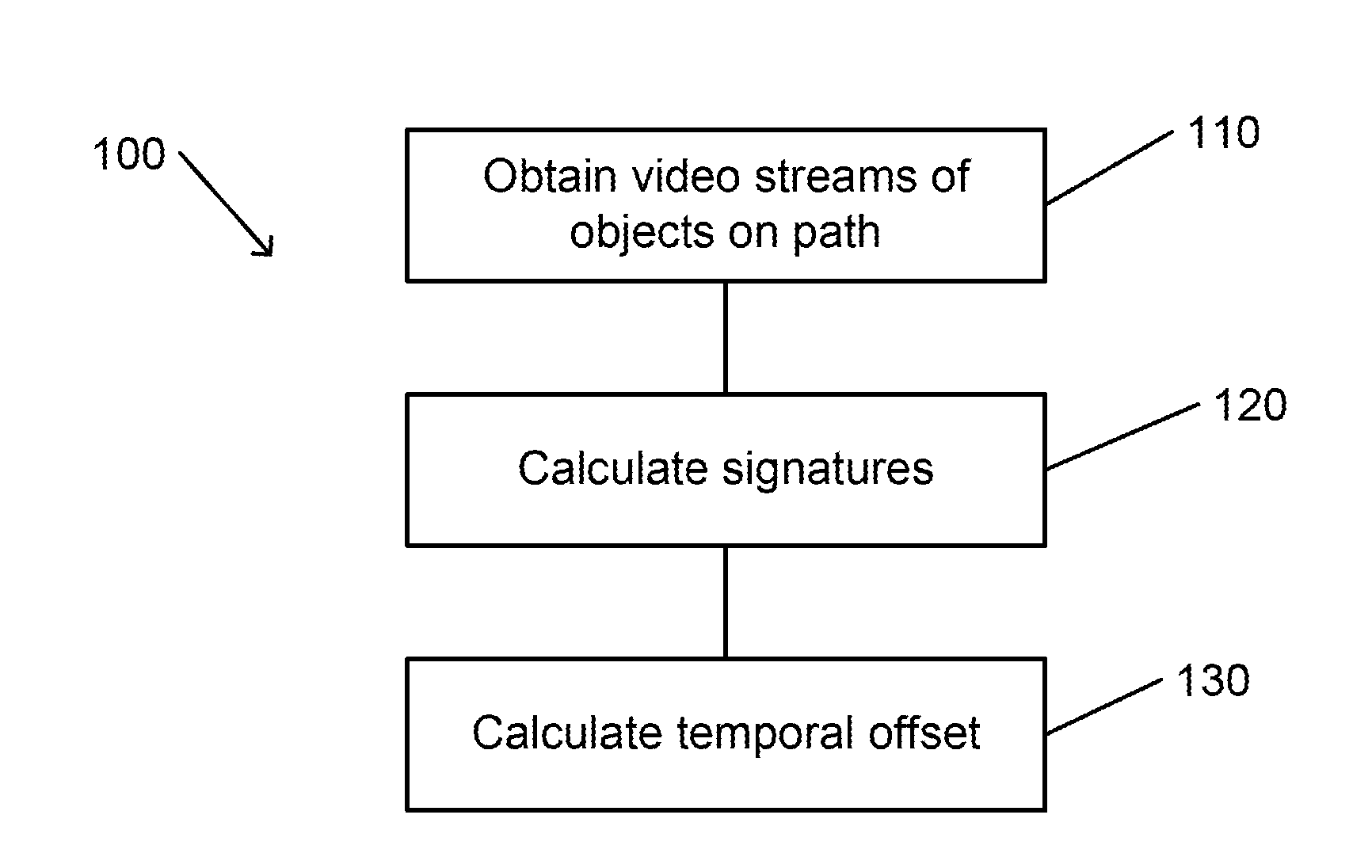
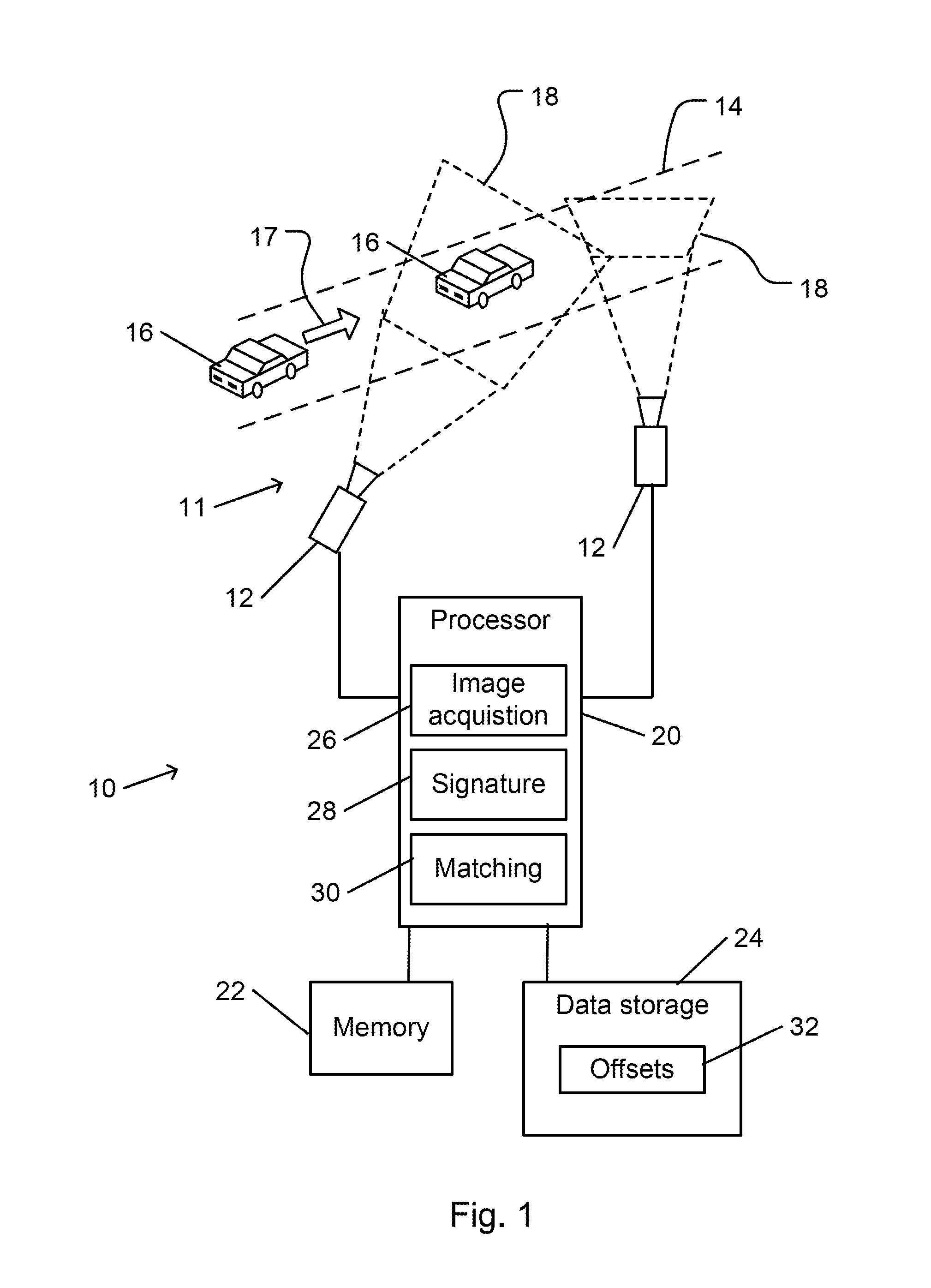
Automatic time signature-based video matching for a camera network
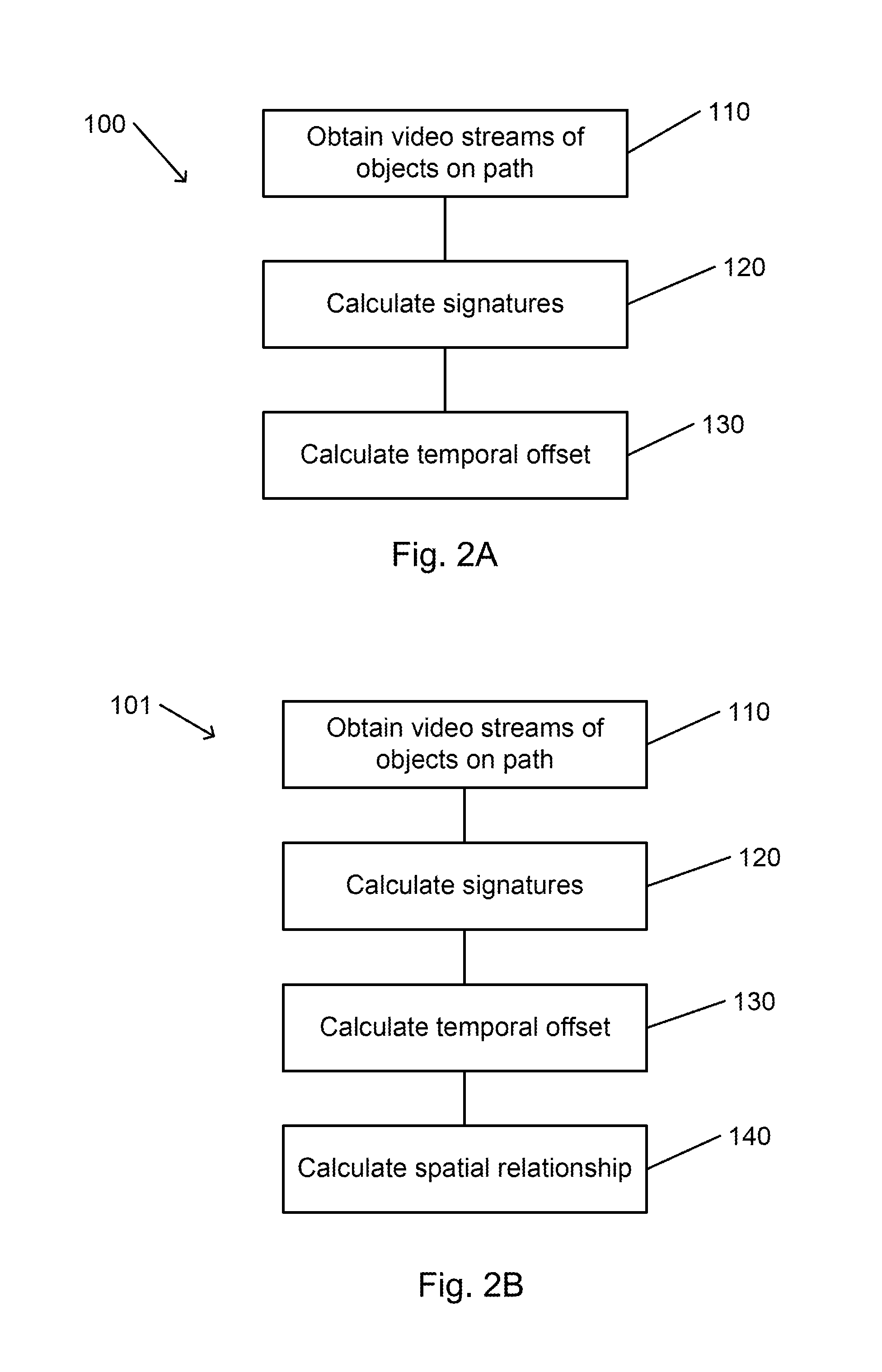
ActiveUS20160014305A1Maximizes correspondenceTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceTime signature
A method for automatically matching video streams from two cameras of a camera network includes obtaining a video stream of frames that are acquired by each of the cameras. Each video stream includes images of moving objects. A time signature for each of the video streams is calculated. Each time signature is indicative of a time at which an image of one the objects is located at a predetermined part of the frame. A temporal offset of one of the signatures relative to the other signature is calculated such that, when applied to one of the signatures, a correspondence between the signatures is maximized. The temporal offset is applicable to video streams that are acquired by the two cameras to determine if a moving object that is imaged by one of the cameras is identical to a moving object that is imaged by the other camera.
Owner:AGT INTERNATIONAL INC
Portable diagnostic apparatus for testing circuit breakers
InactiveUS9753088B2Earth resistance measurementsContact testing/inspectionEngineeringCircuit breaker
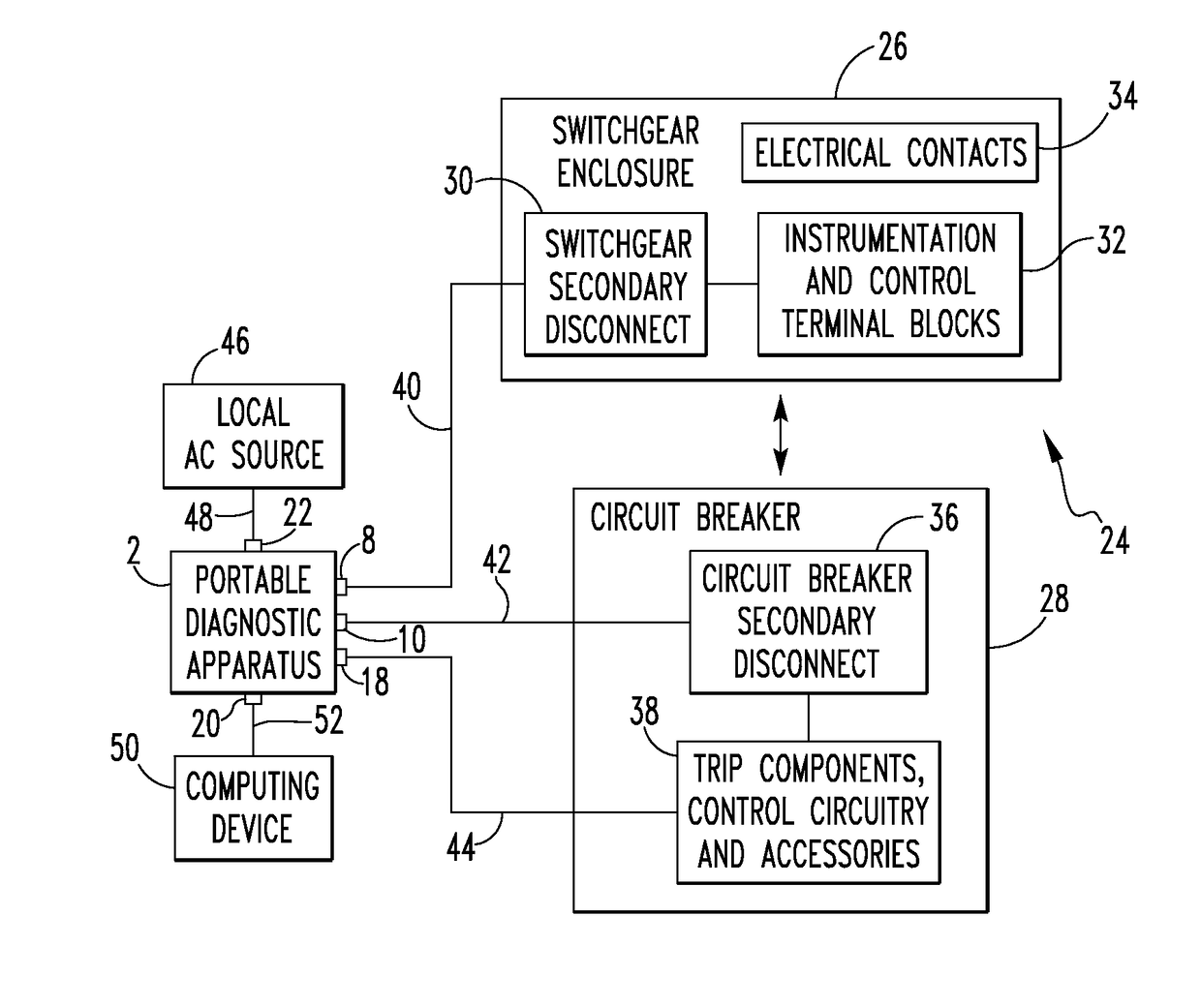
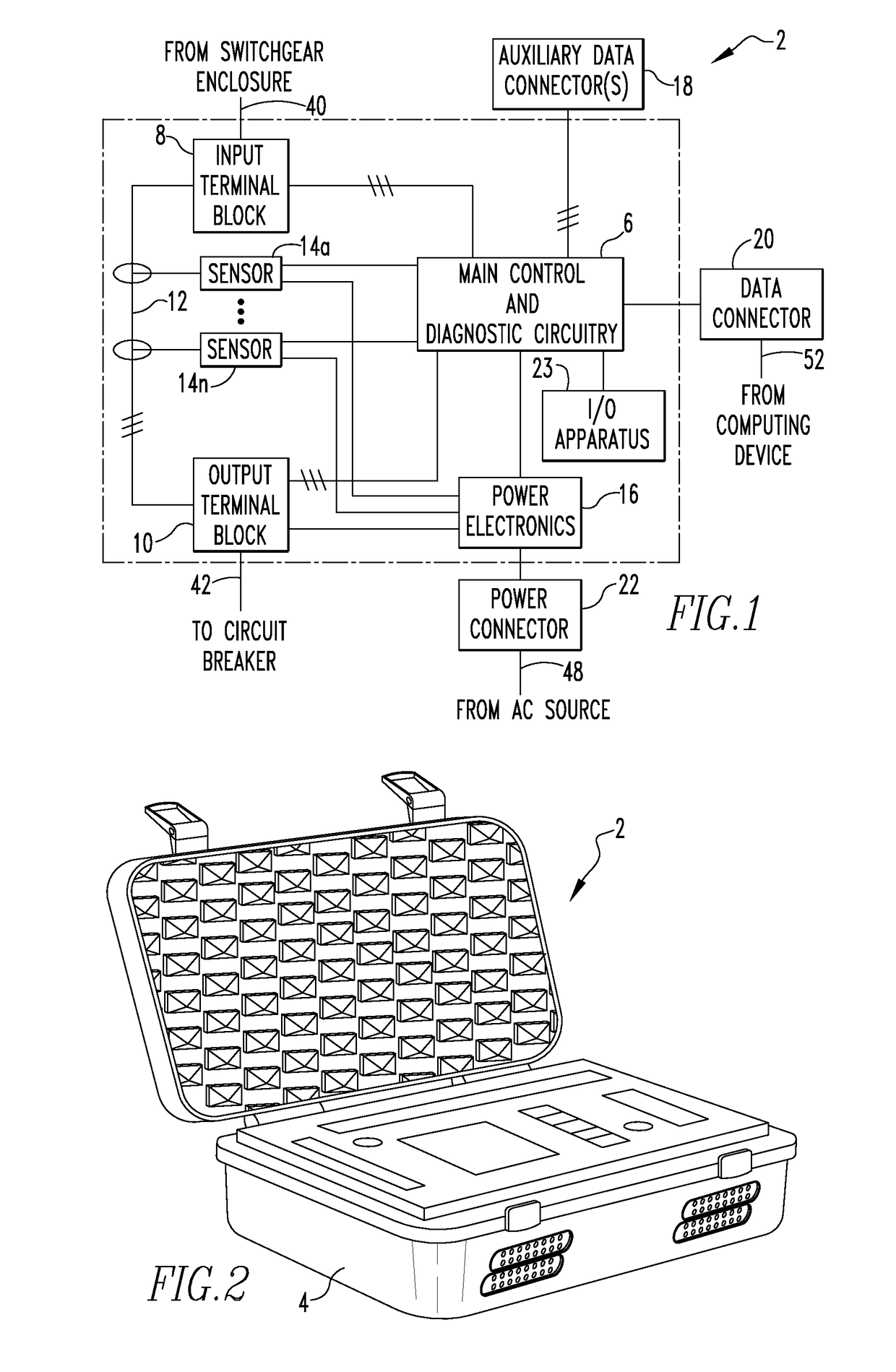
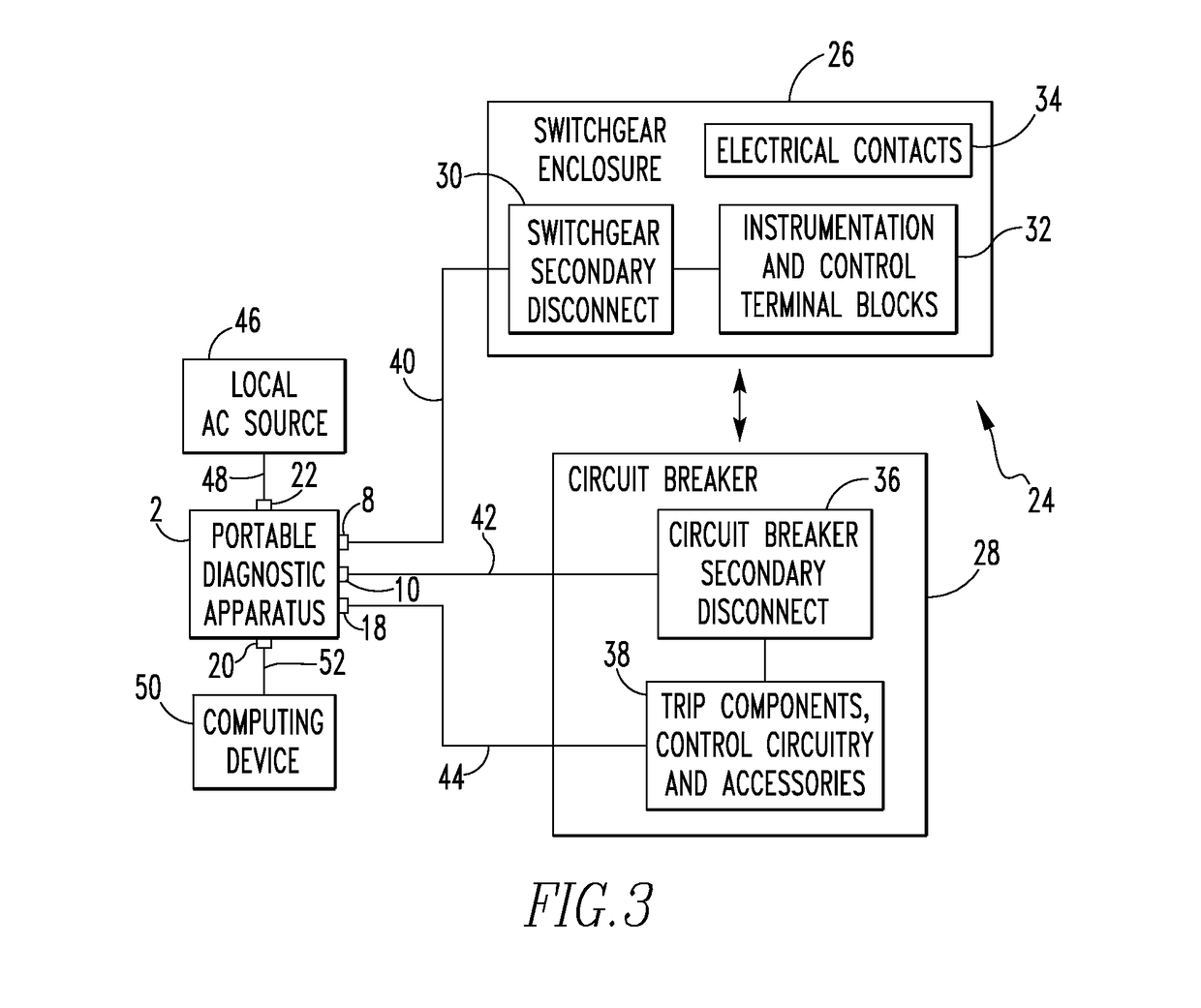
A portable diagnostic apparatus for performing diagnostic testing on a circuit breaker includes a number of sensor devices structured to generate a number of sensed parameter signals relating to operation of the circuit breaker during an operational sequence, a number of auxiliary input connectors structured to receive a number of auxiliary data signals from the circuit breaker, the number of auxiliary data signals relating to and being generated in response to the operation of the circuit breaker during the operational sequence, and control and diagnostic circuitry. The control and diagnostic circuitry is structured to control operation of the portable diagnostic apparatus, receive the number of sensed parameter signals and the number of auxiliary data signals, and generate a time signature based on the number of sensed parameter signals and the number of auxiliary data signals.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD
Security and ticketing system control and management
InactiveUS20100005304A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionNon-volatile memory
A security device of this invention includes a nonvolatile storage unit 22 for storing a validity check unit including a counter updated every time signature function means 30 is called up, a volatile storage unit 24 for reading and storing a counter array out of an external nonvolatile storage unit storing the counter array, in which the counter array is obtained by coupling a hash value generated for each signature key with a signature number counter for counting the number of signatures performed by use of the signature key, and a hash function unit 28 for reading the counter array out of the volatile storage unit 24, generating the hash value, and transferring the hash value to the validity check unit for a validity check.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Encryption method, decryption method and electronic equipment
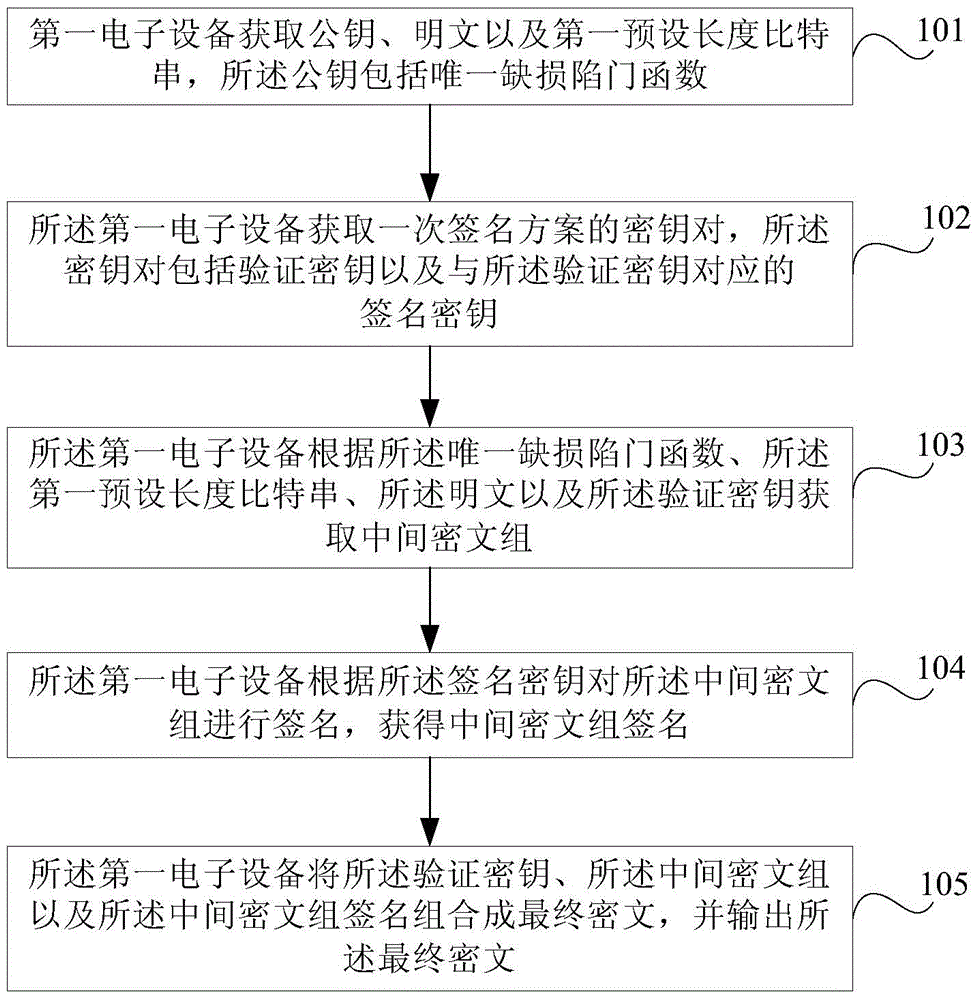
ActiveCN105227308AReduce the risk of being crackedUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextChosen-ciphertext attack
Embodiments of the invention provide an encryption method, a decryption method and electronic equipment. The method comprises steps of acquiring a public key, a plaintext and a first bit string of a preset length through first electronic equipment, wherein the public key comprises the only defect trapdoor function; acquiring a key pair of a one-time signature scheme by the first electronic equipment, wherein the public pair comprises a verification secret key and a signature secret key corresponding to the verification secret key; acquiring a middle cryptograph set according to the only defect trapdoor function, the first bit string of the preset length, the plaintext and the verification secret key; signing the middle cryptograph set by the first electronic equipment according to the signature secret key, and acquiring a signature of the middle cryptograph set; and forming a final cryptograph by combing the verification secret key, the middle cryptograph set and the signature of the middle cryptograph set, and outputting the final cryptograph. Therefore, anti-selection cryptograph attack is achieved.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
Method and equipment for detecting sealing deficiencies in drainage and vent systems for buildings
InactiveCN101553630ADifferent reflection coefficientsDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateTransient stateData acquisition
The method comprises the following steps - introducing a low amplitude air pressure transient into the drainage and vent system of a building in order to propagate a pressure wave from a fitting (6) into a stack (1) and the network of the drainage system; - recording the passage of said transient by means of an air pressure transducer (7) located near the fitting (6) or introduction area of the transient; - recording the successive pressure reflections of the transient from each drain pipe (2) of the network of the drainage system; - establishing a pressure versus time signature recorded by the pressure transducer (7) and sending those signals to a central data acquisition system; - the pressure transient is propagated throughout the network at an acoustic velocity and is reflected by each and every pipe termination of the network so as to establish a characteristic reflection coefficient for each pipe termination; - said characteristic reflection coefficient is compared with testing results performed initially in a perfect network with no dry trap defects or leakage's and in case a different signature of the pressure trace is recorded, the point of diversion will be determined at the time at which the reflection from the altered pipe end termination arrives at the air pressure transducer so that the comparison of this defect trace with the stored defect free signature yields that time and, as the wave speed is known, the determination of the distance from the pressure transducer to the defective trap or seal.
Owner:HERIOT WATT UNIV
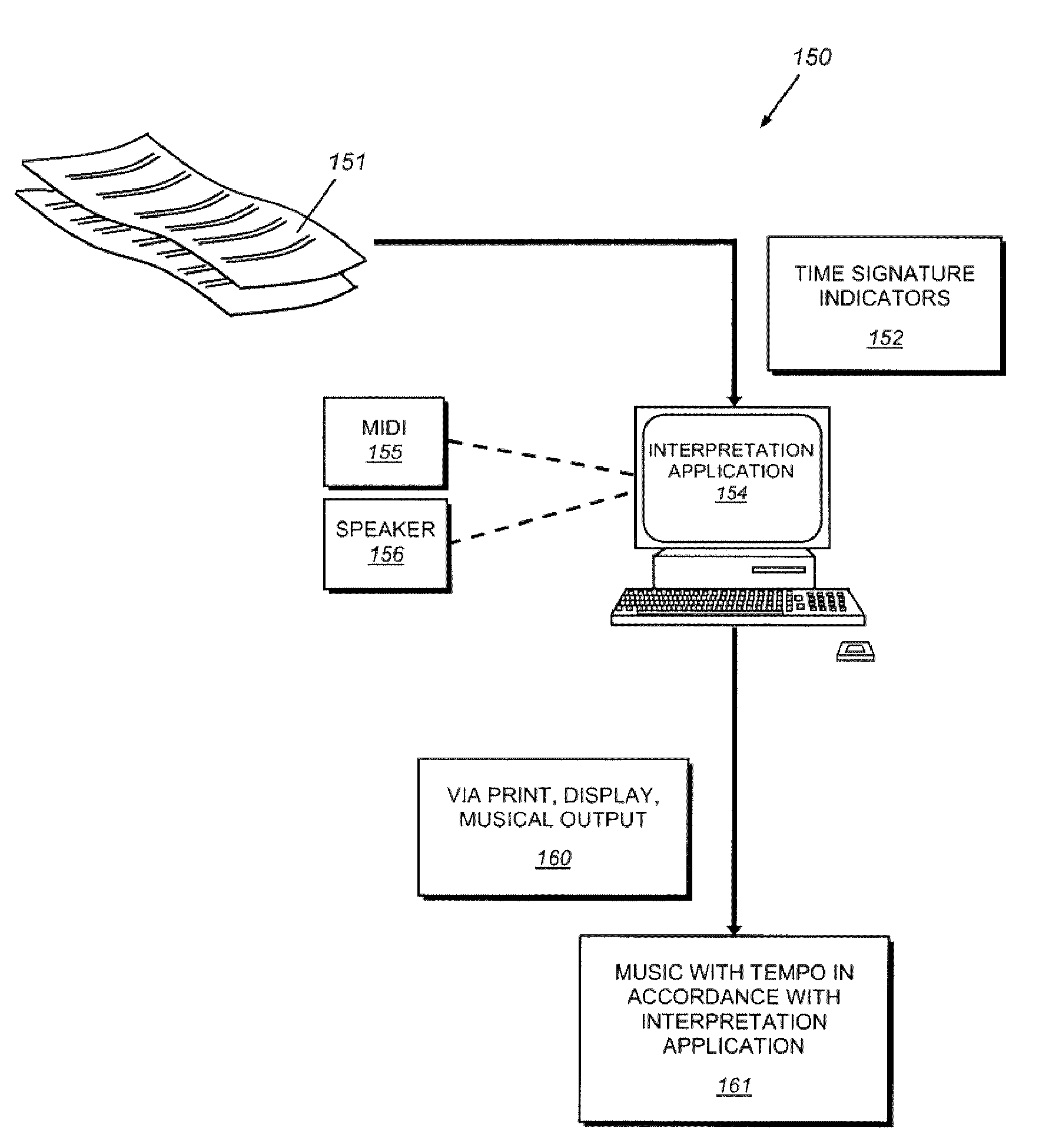
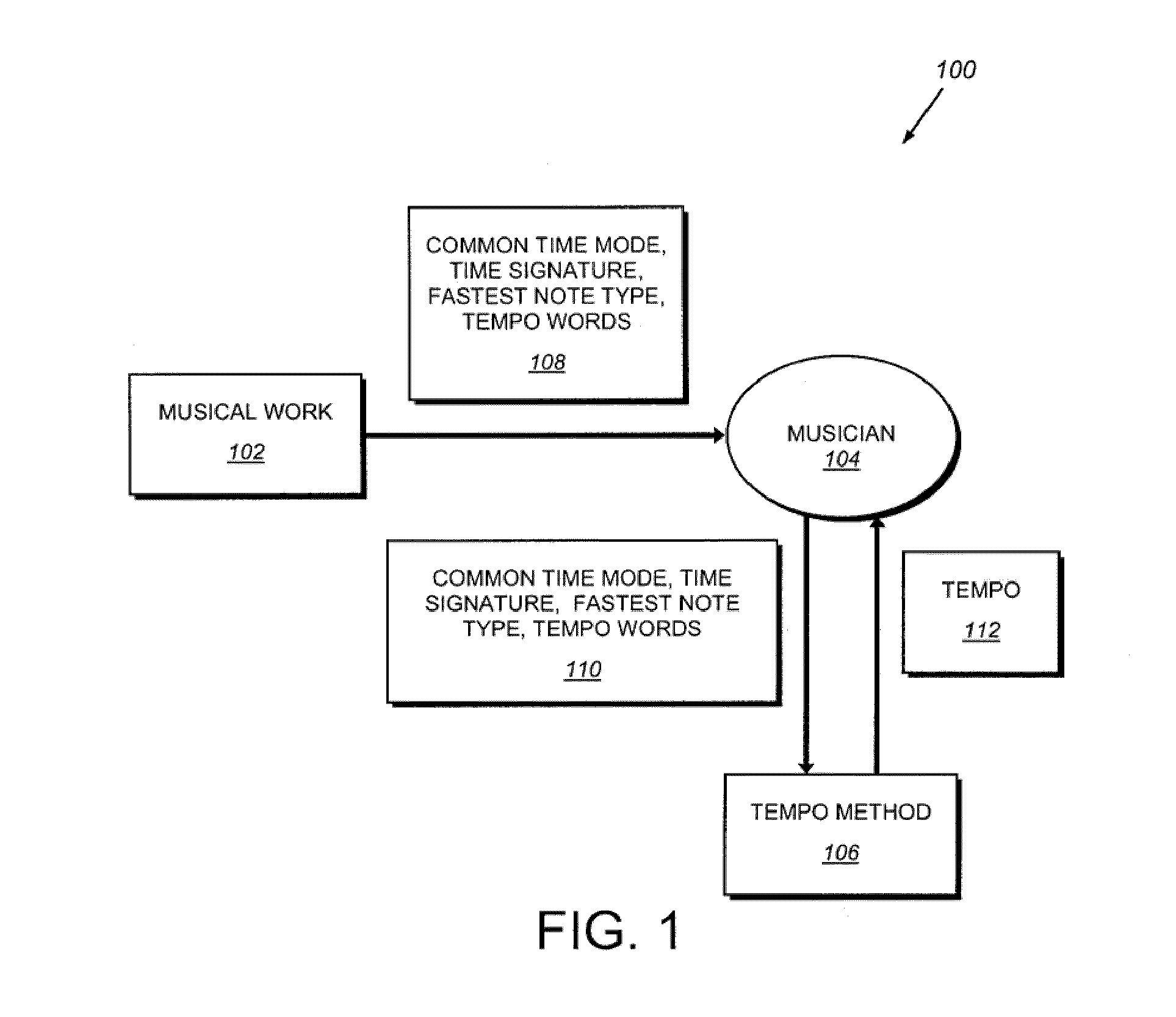
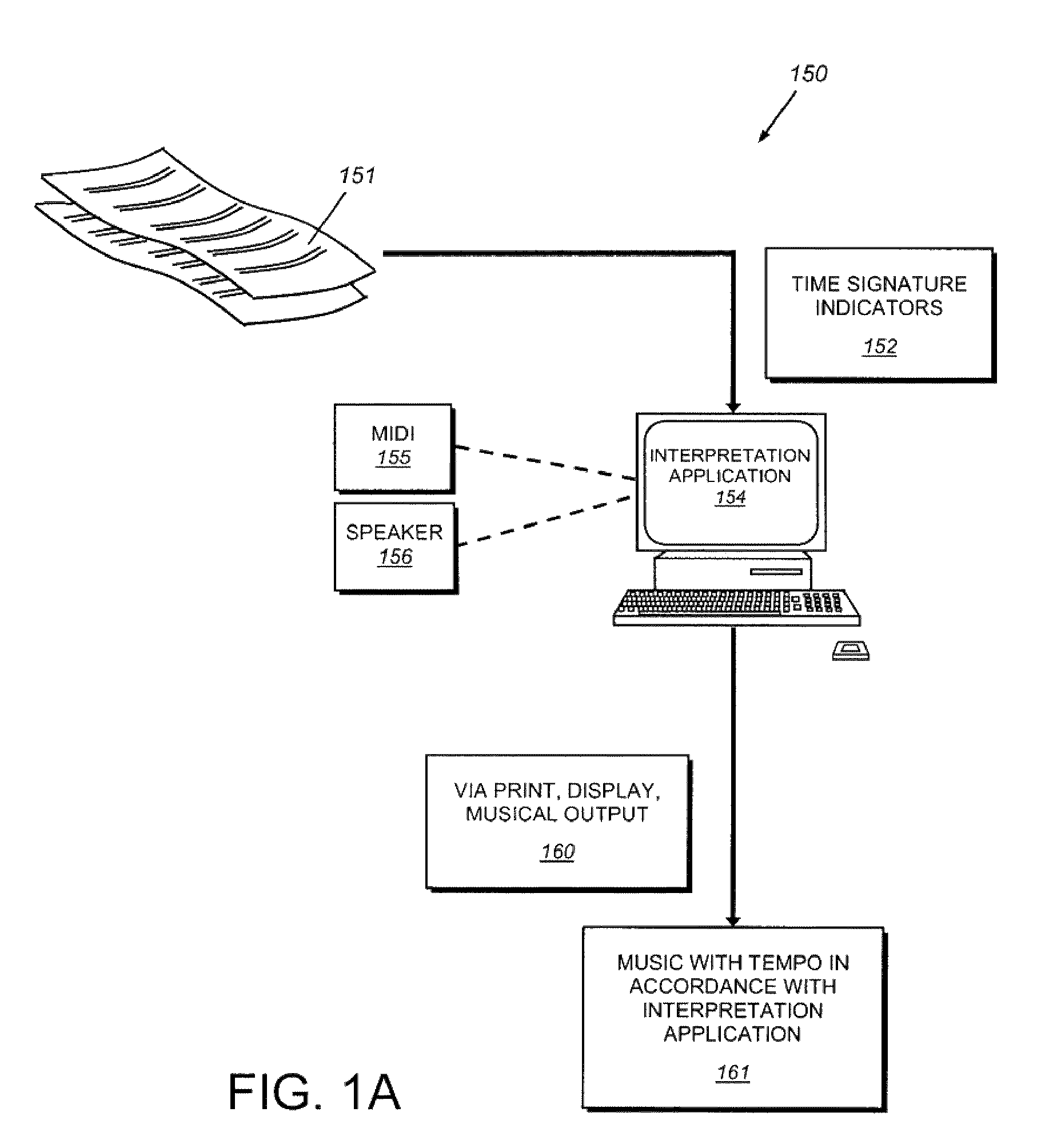
System and method for determining tempo in early music and for playing instruments in accordance with the same
A system and method for determining the appropriate tempo for early music, which may have originally lacked metronome-based time values, and for playing musical instruments according to the same. One example of such early music is the various piano works of Johann Sebastian Bach. The appropriate tempo is determined according to a number of indicators or parameters within the music score including the common time mode, the time signature, the fastest note type, and the absence or presence of any tempo words. Tempos are based around a common time beat value of 71 beats per minute and a cut-time beat value of 80. Other beats are derived using the parameters based on either of these two base values. An electronic device and / or software application may be provided for determining the appropriate tempo according to the illustrative system and displaying it according to an audio and / or visual queue.
Owner:KENNEY LESLIE M
Self-owned post quantum key distribution method
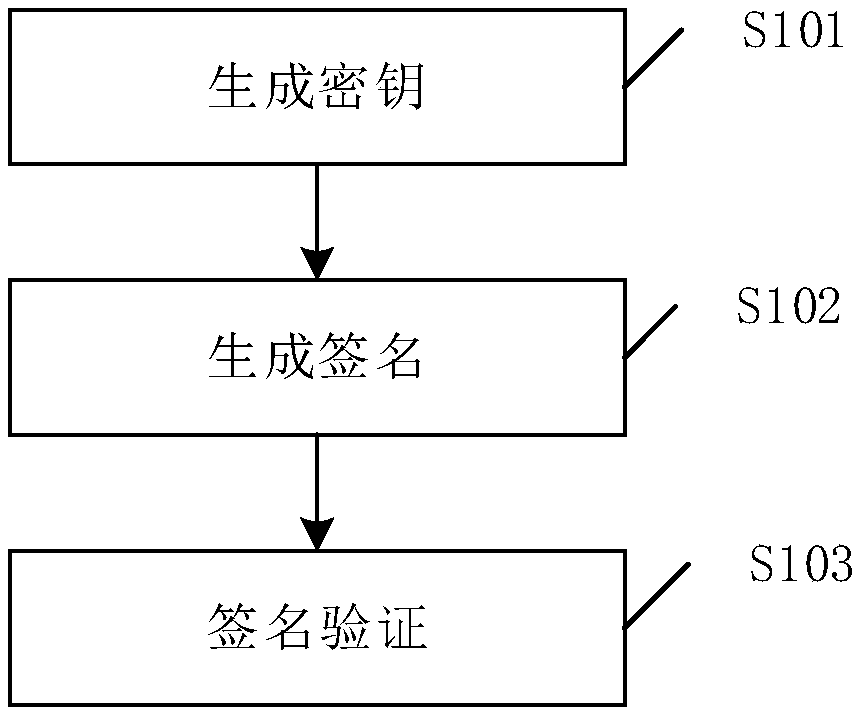
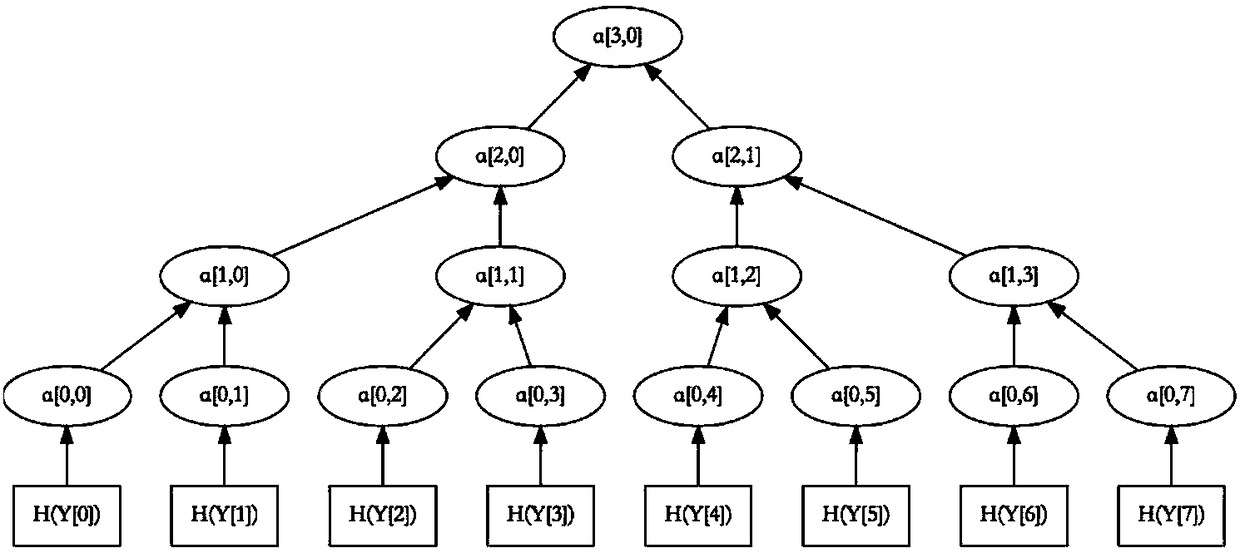
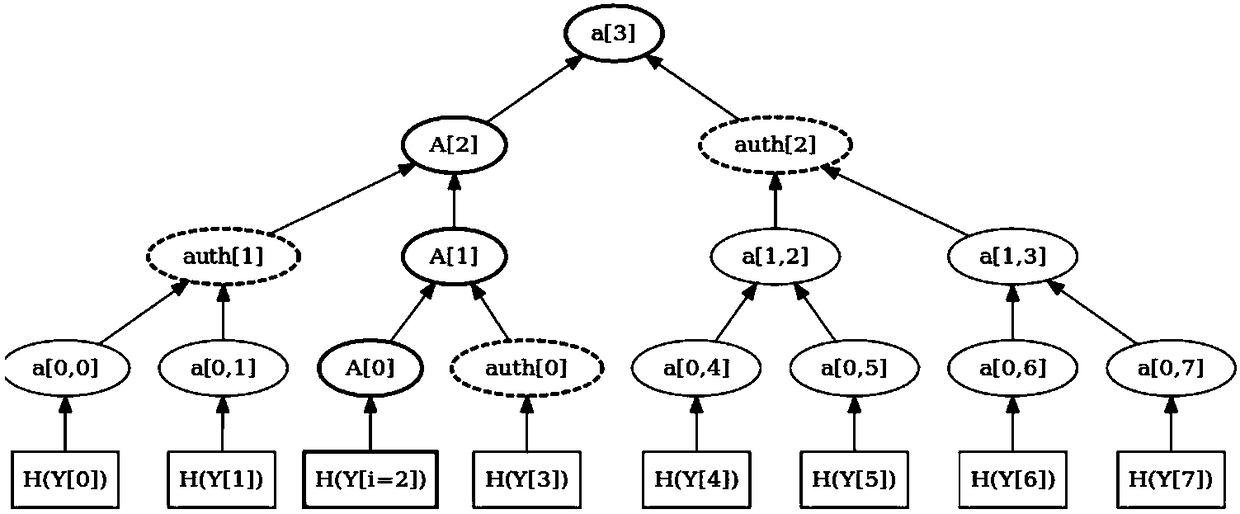
InactiveCN108173651AEnsure safetyReduce calculationKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesKey generationMerkle tree
The invention provides a self-owned post quantum key distribution method comprising the following steps: key generation: keys are generated by using a hash tree, and the hash tree calculates the initial hash value H(Yi) of a public key Yj and then calculates the hash value H(Yi-1) of a previous node until the hash value H(Y1) of the last node is left; signature generation: a signer selects a key pair (Xi, Yi), carries out Merkle signature on the key pair (Xi, Yi) through a one-time signature scheme, and sends additional information to Merkle to prove that Merkle is indeed a signed key; and signature verification: after receiving the Merkle-signed key pair (Xi, Yi), a receiver uses a public key Yi to verify whether the key pair (Xi, Yi) is signed by a one-time verification scheme. Computation can be reduced while the security of data is guaranteed. Therefore, the efficiency is improved.
Owner:陈柱
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com