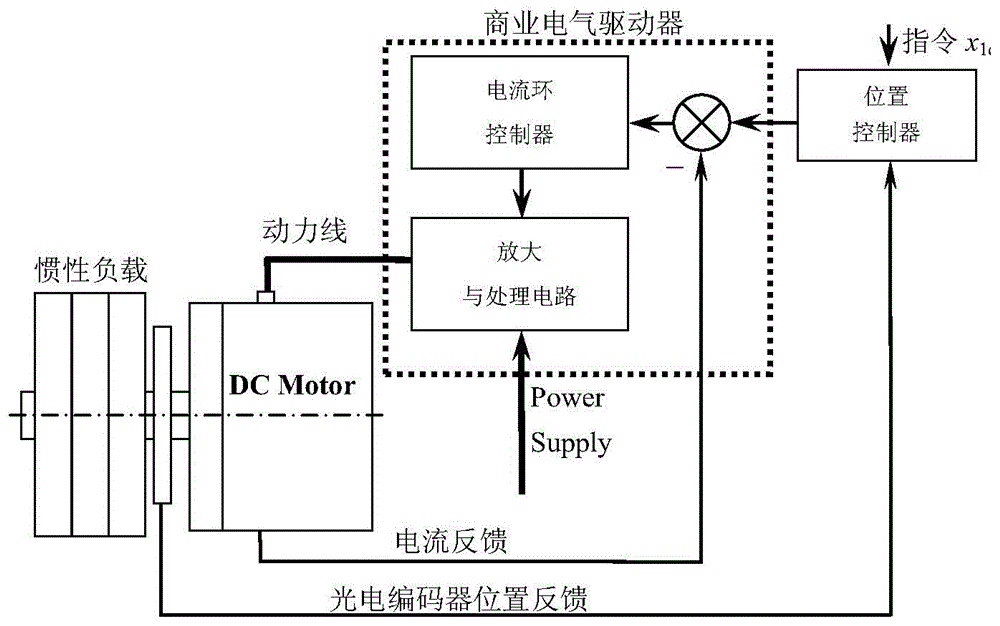
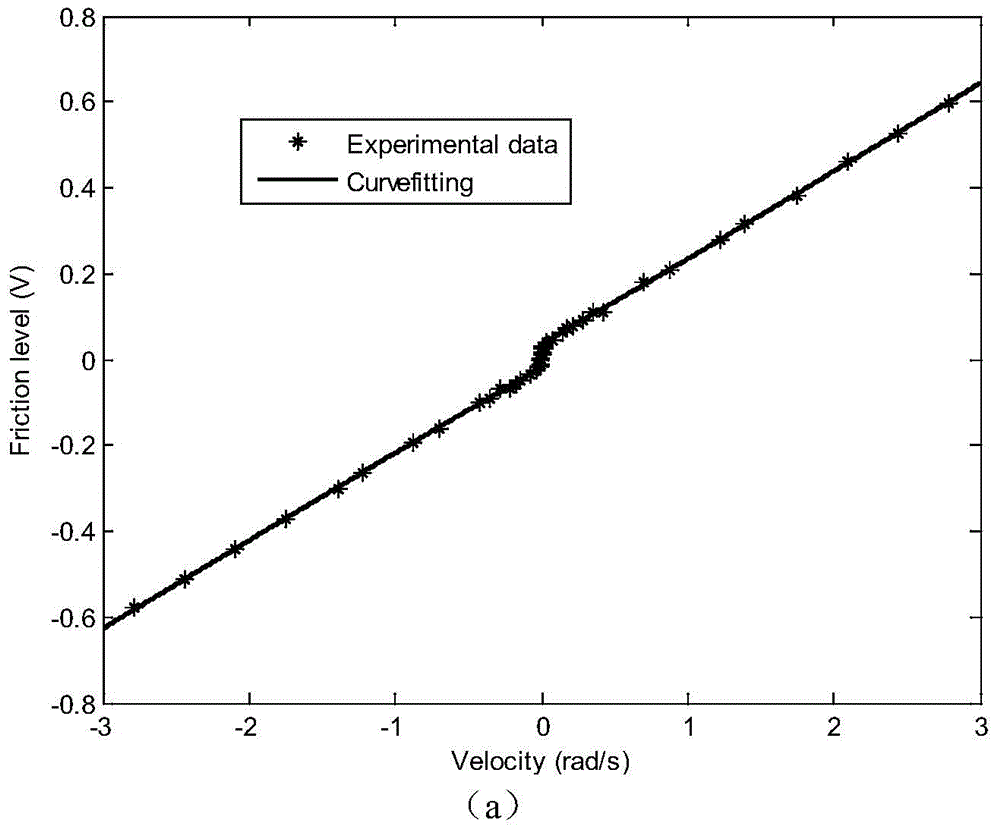
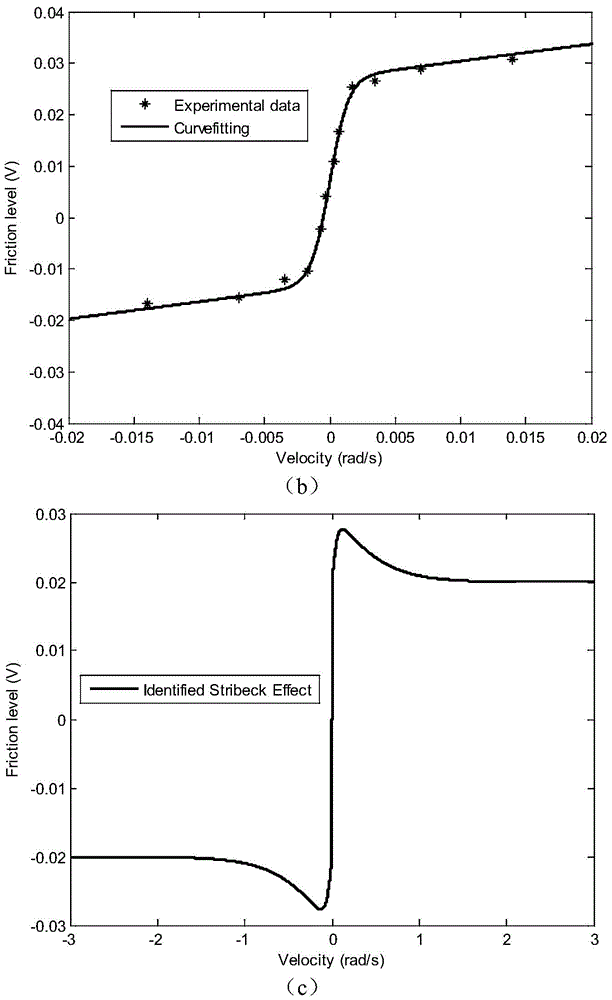
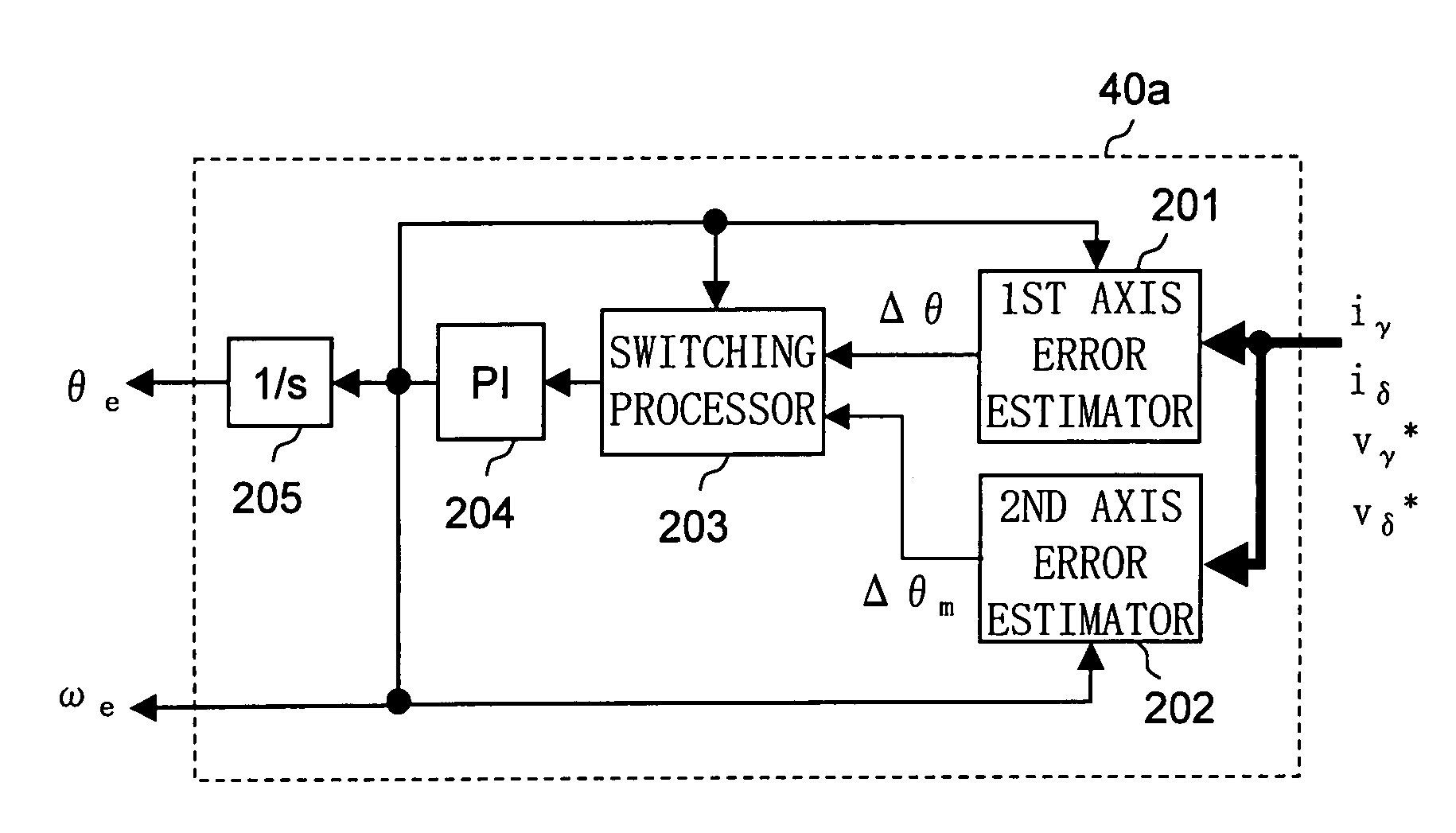
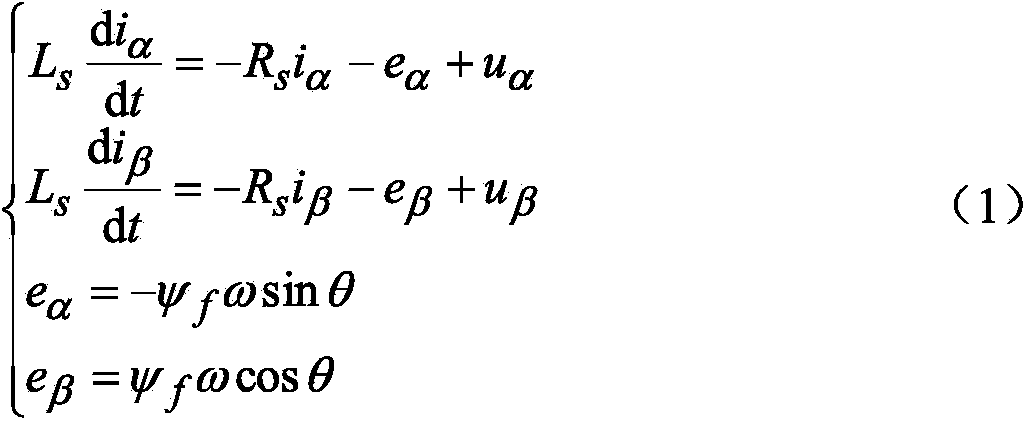Patents
Literature
630results about "Observer control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
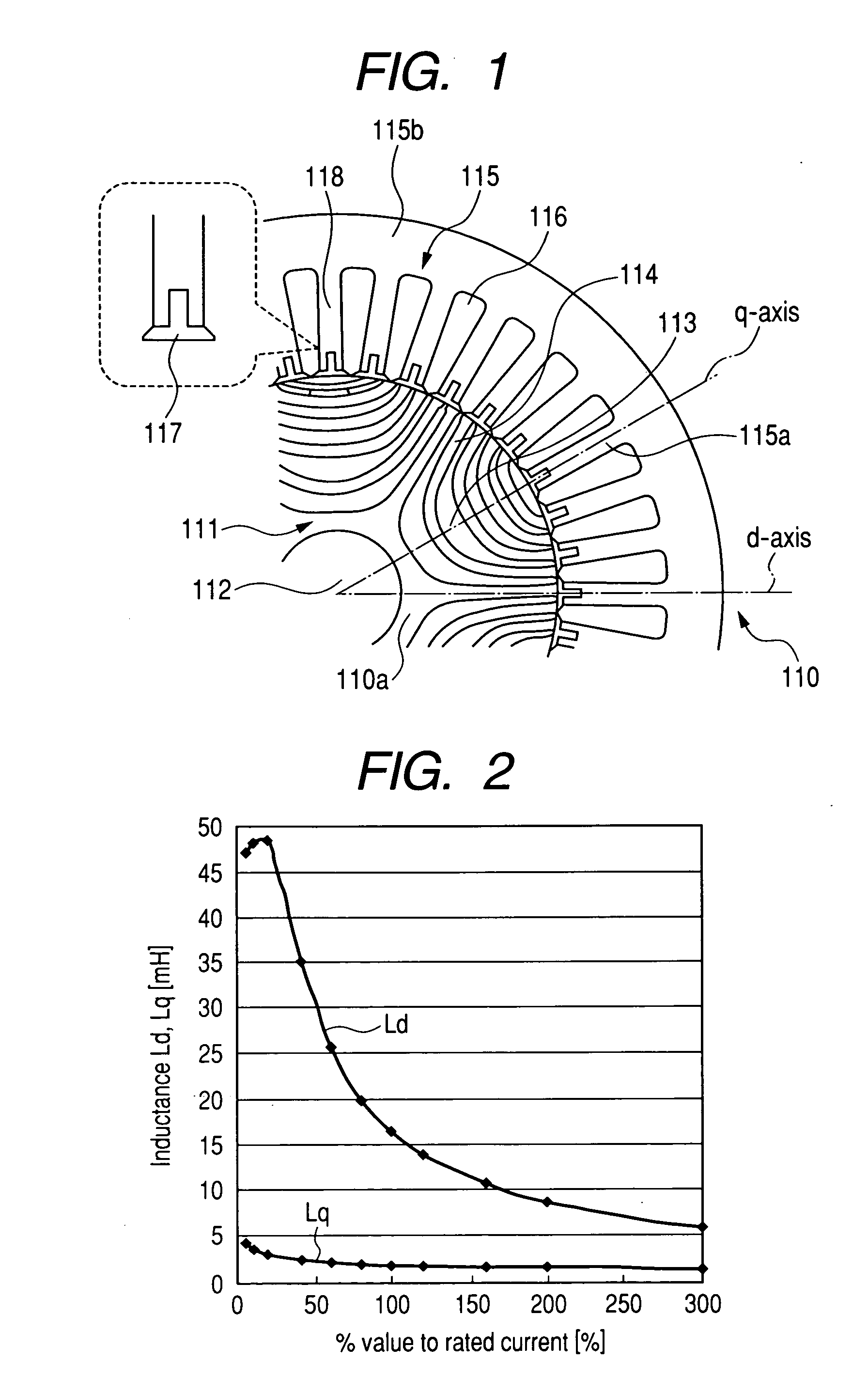
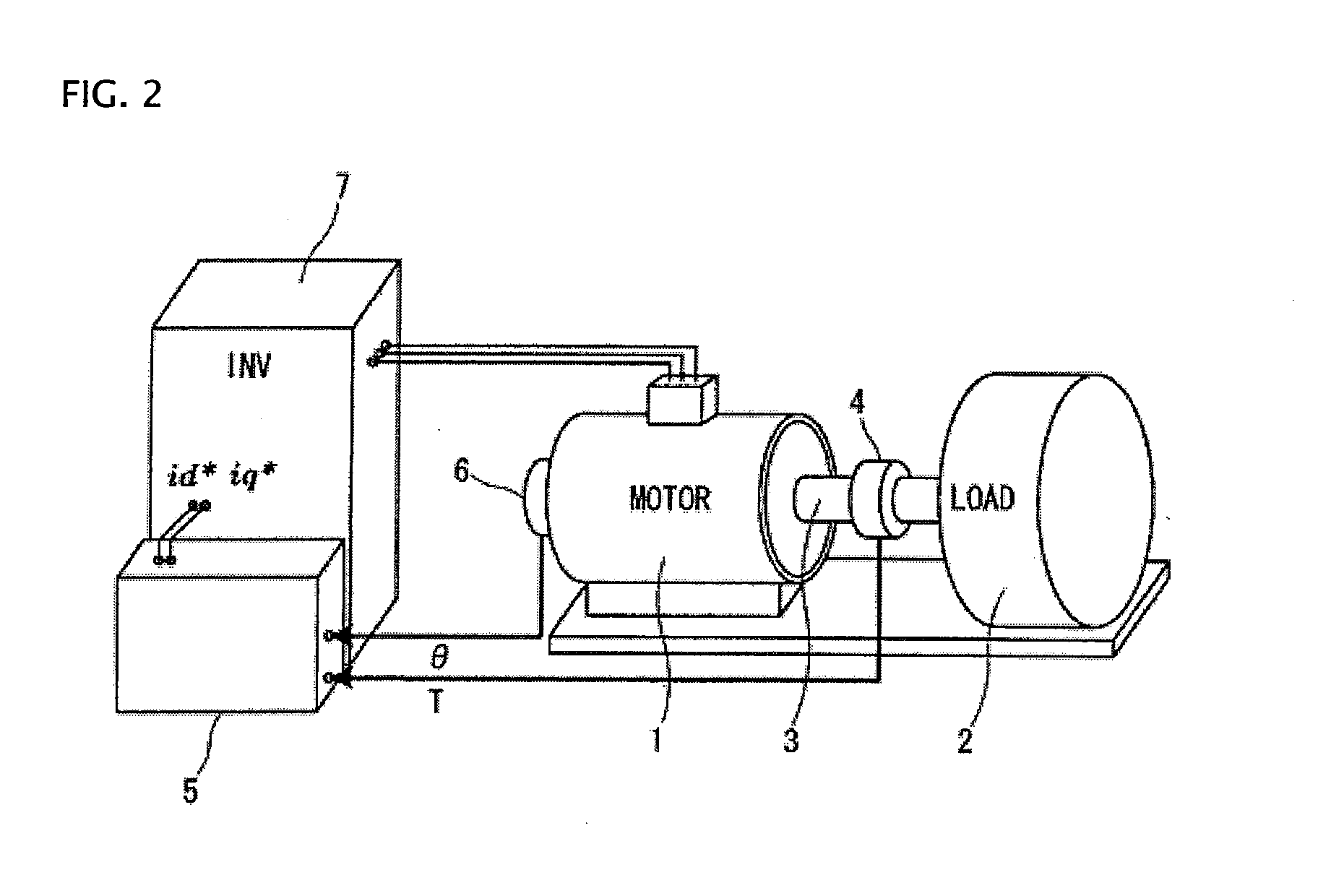
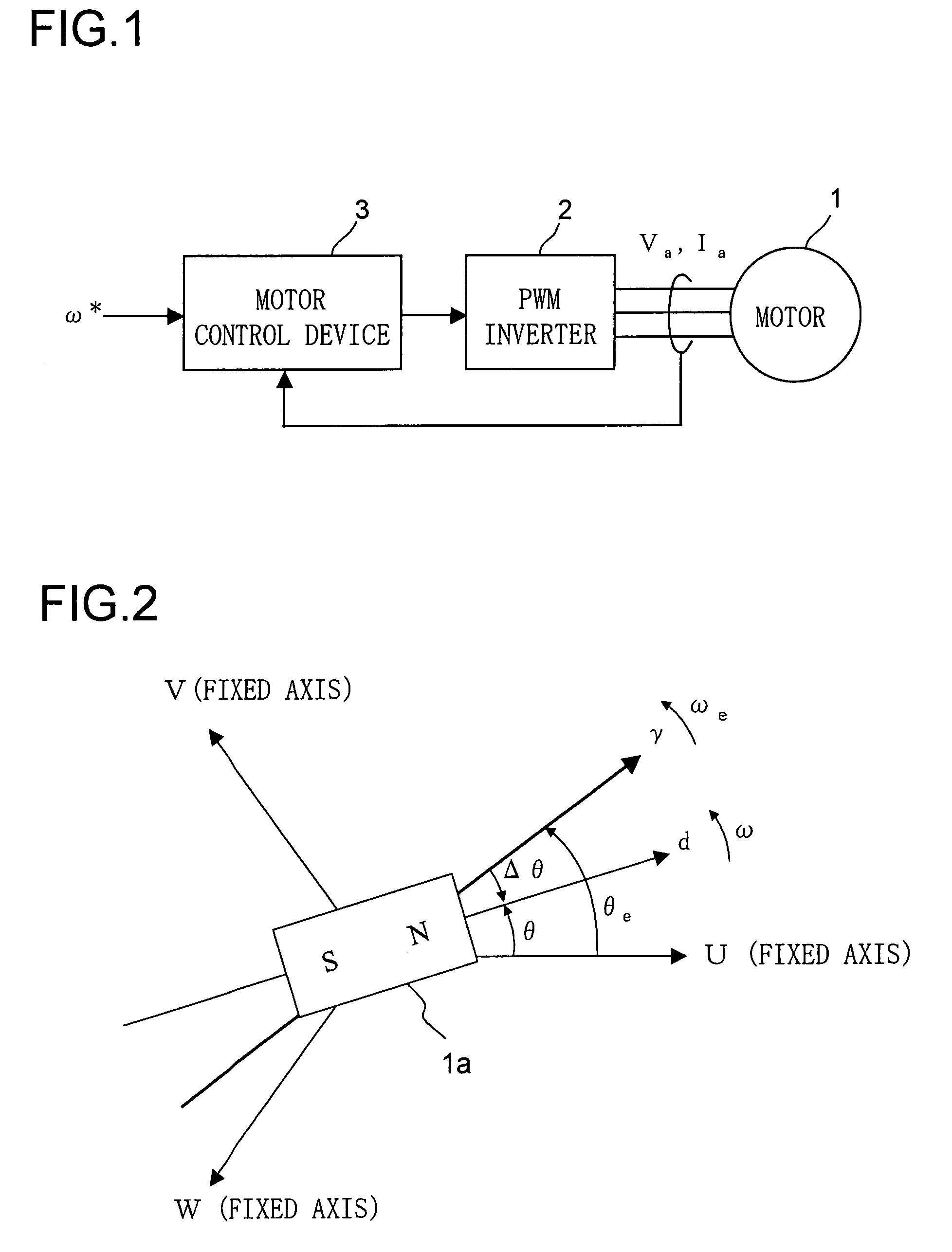
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS20060125439A1Efficient driveImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorPhase difference
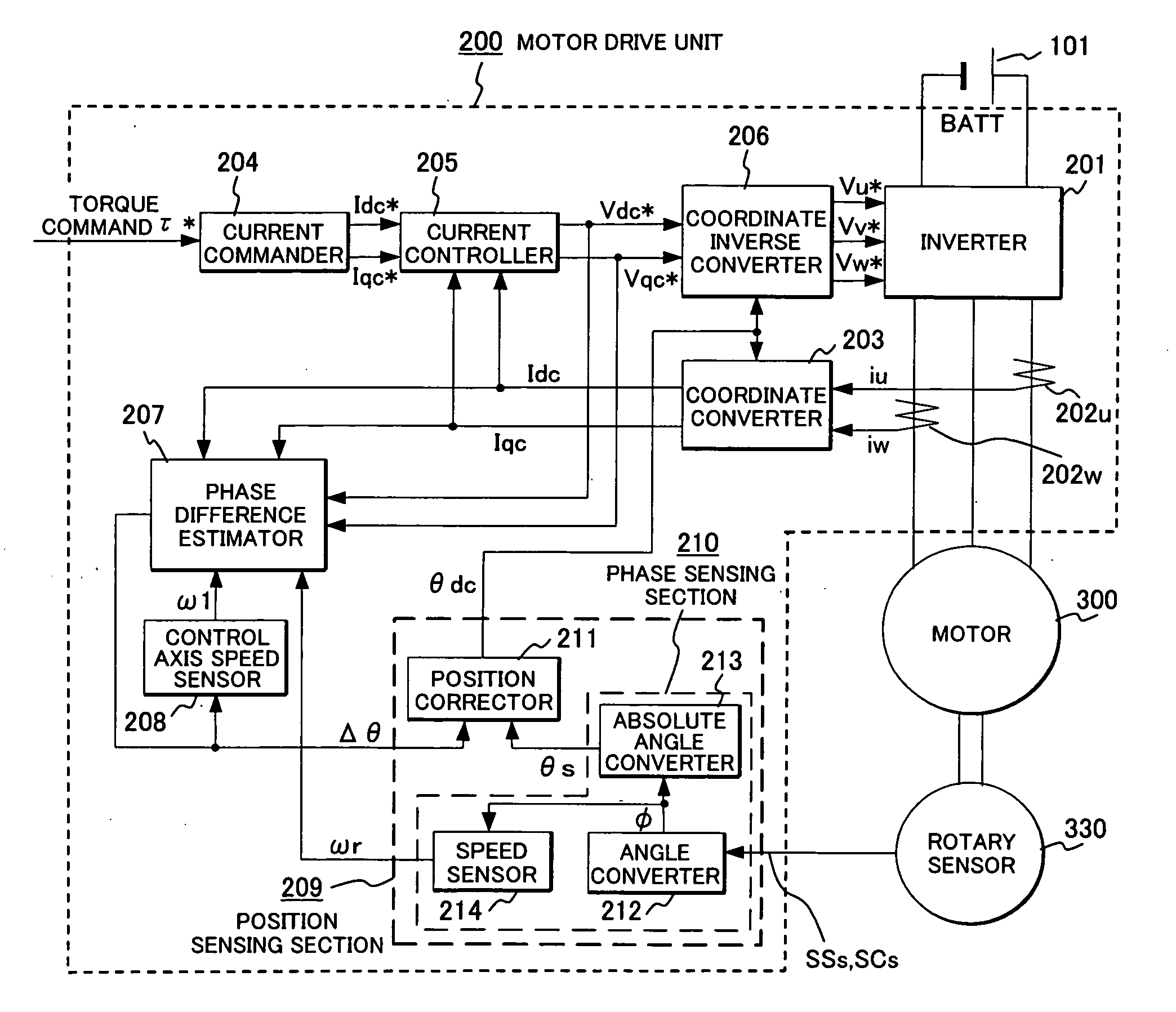
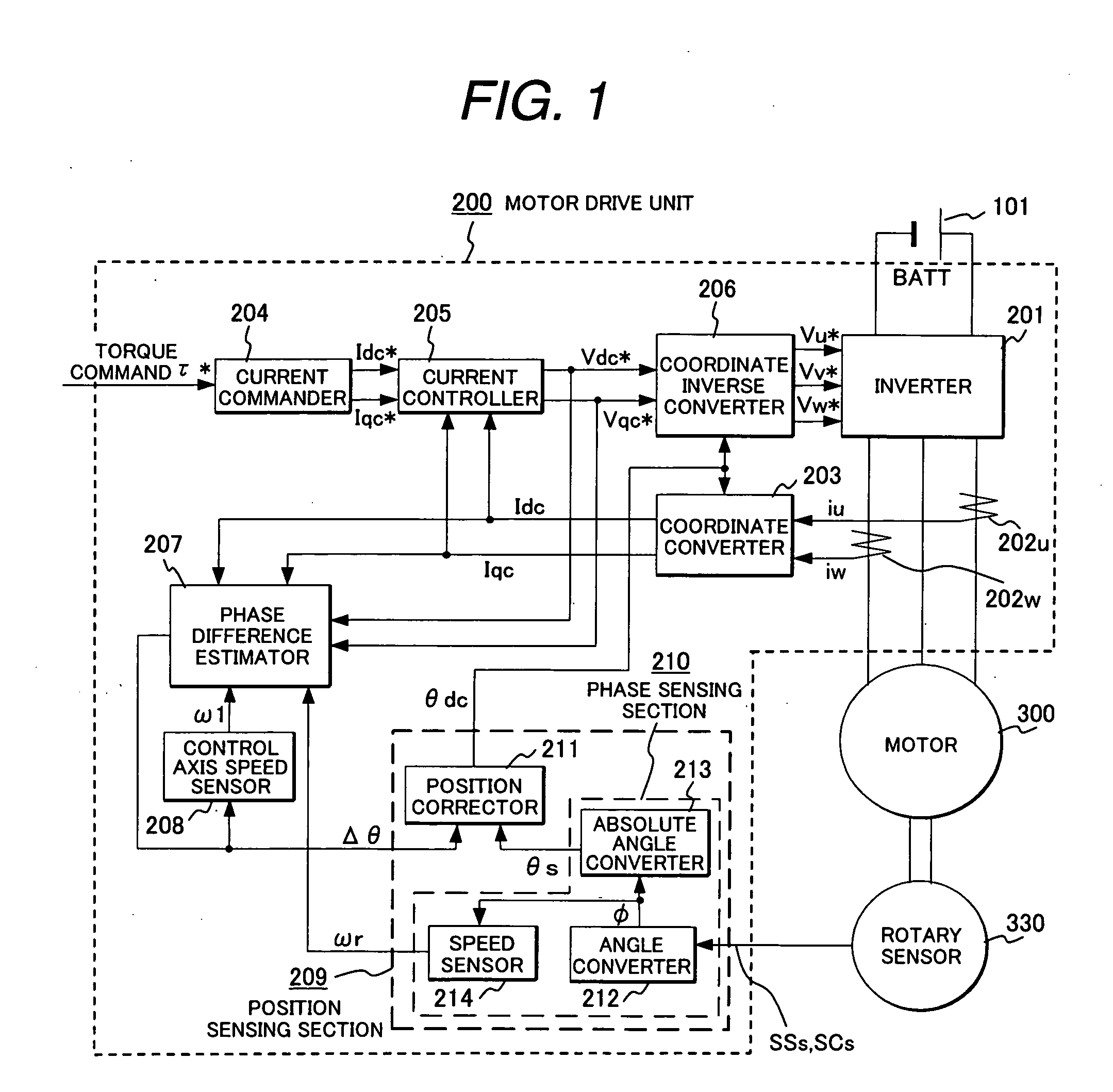
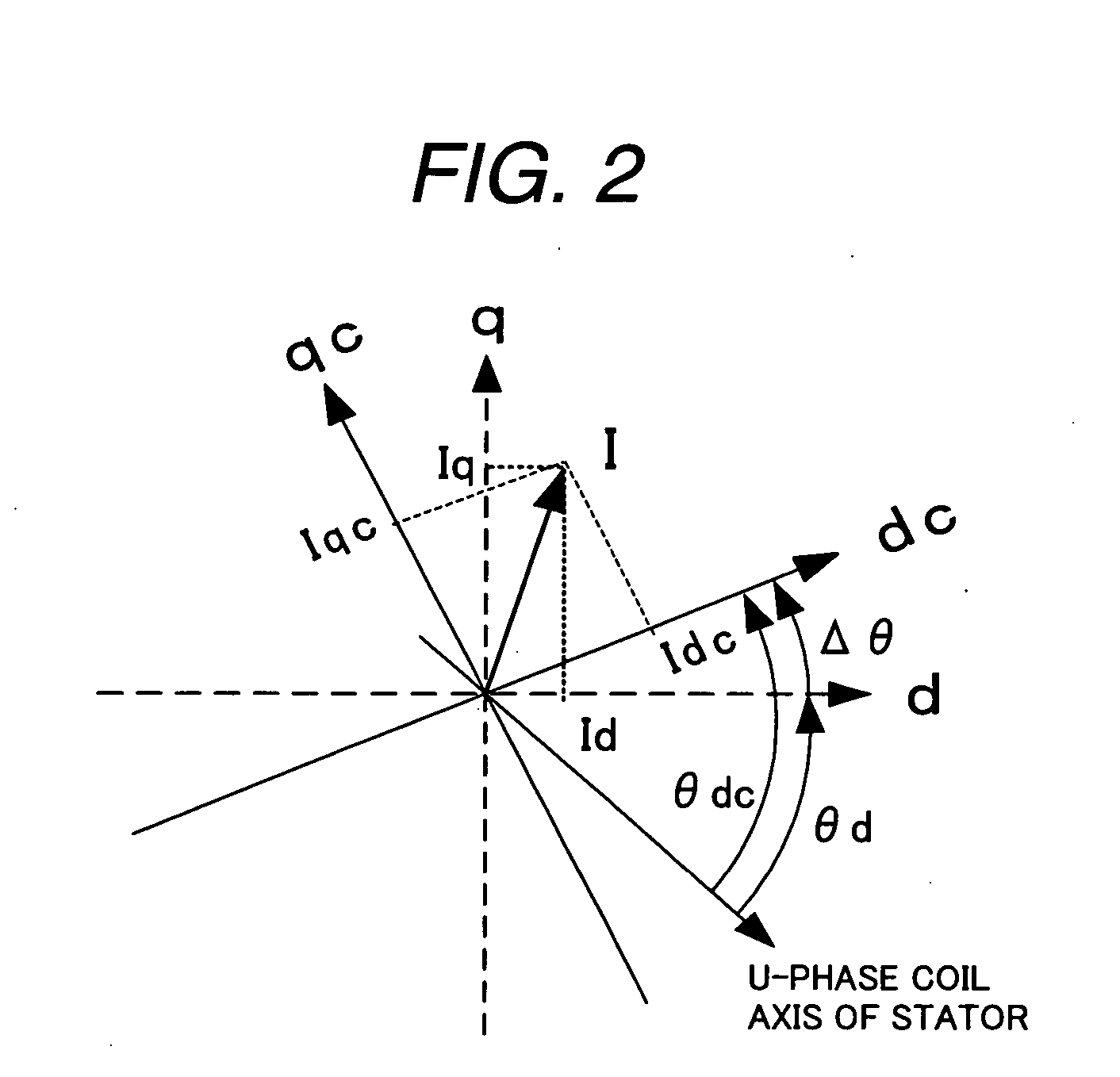
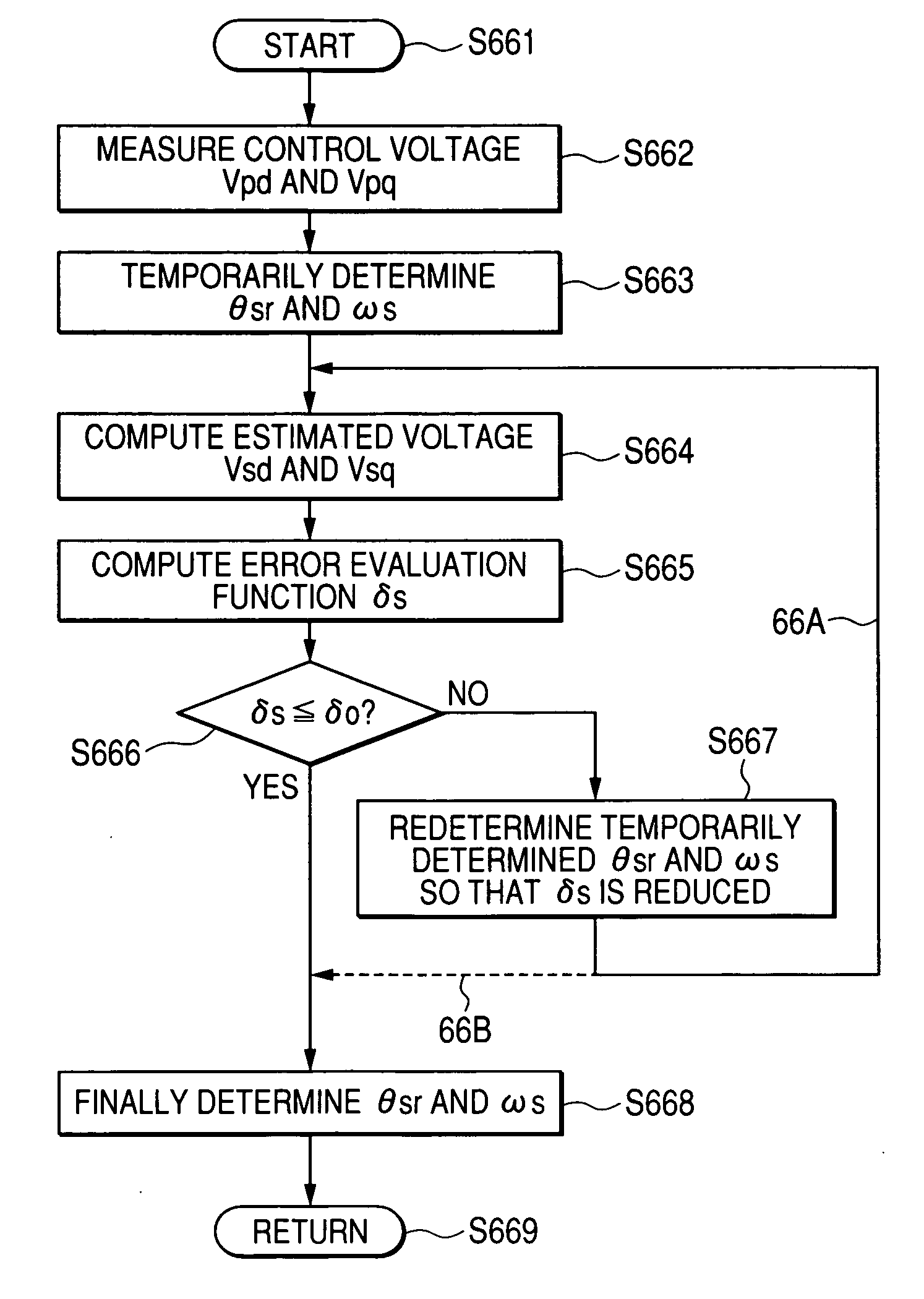
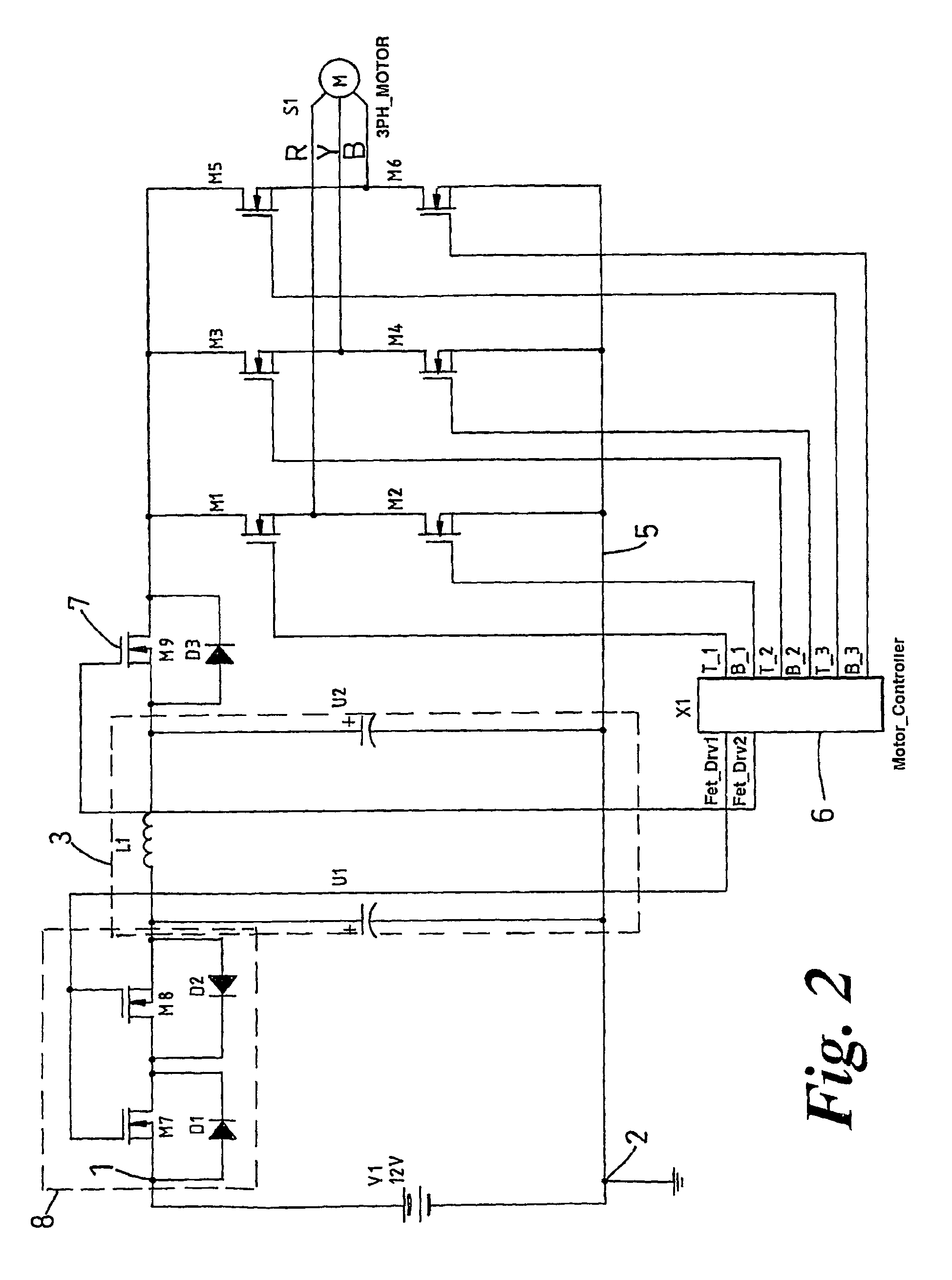
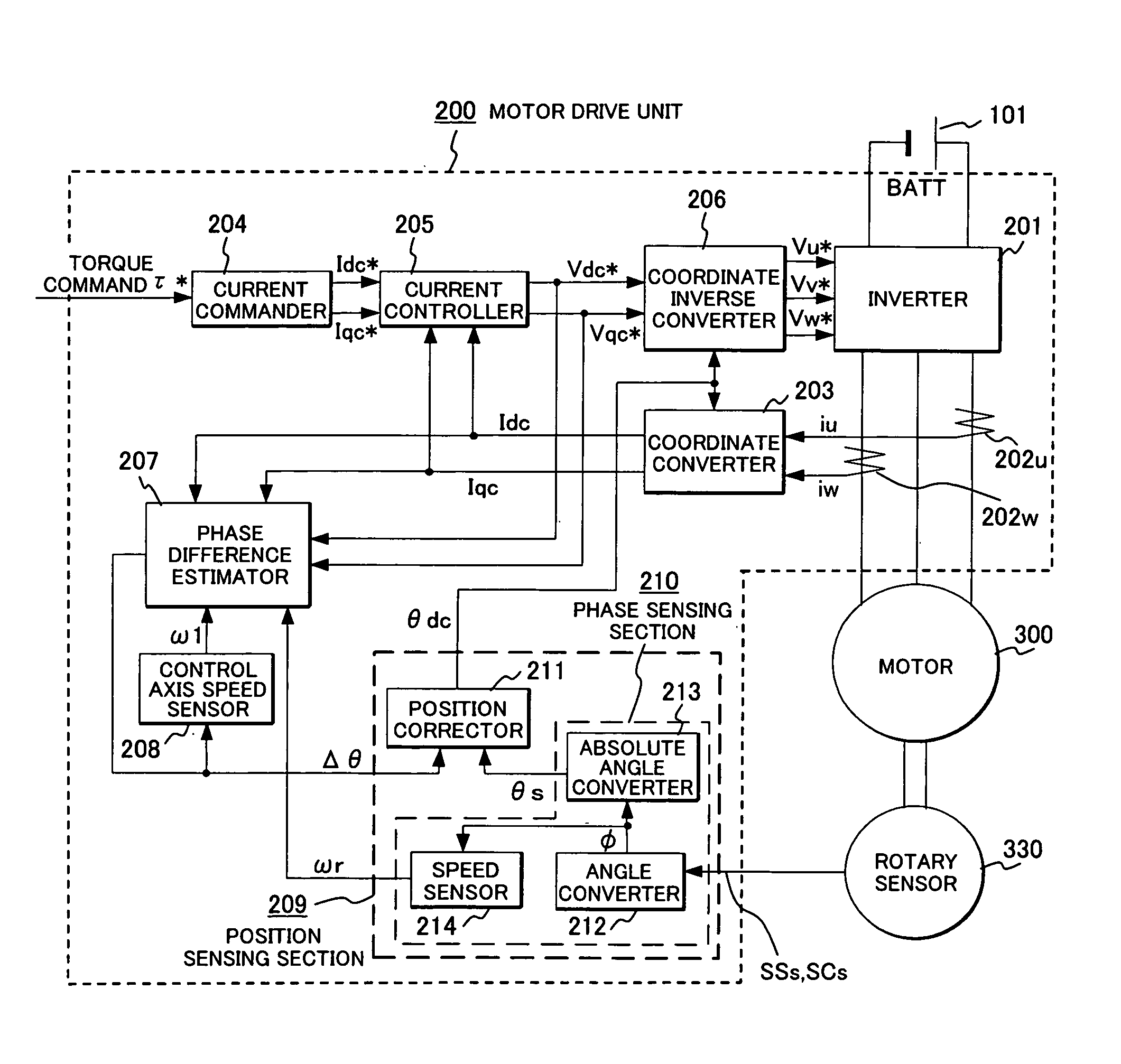
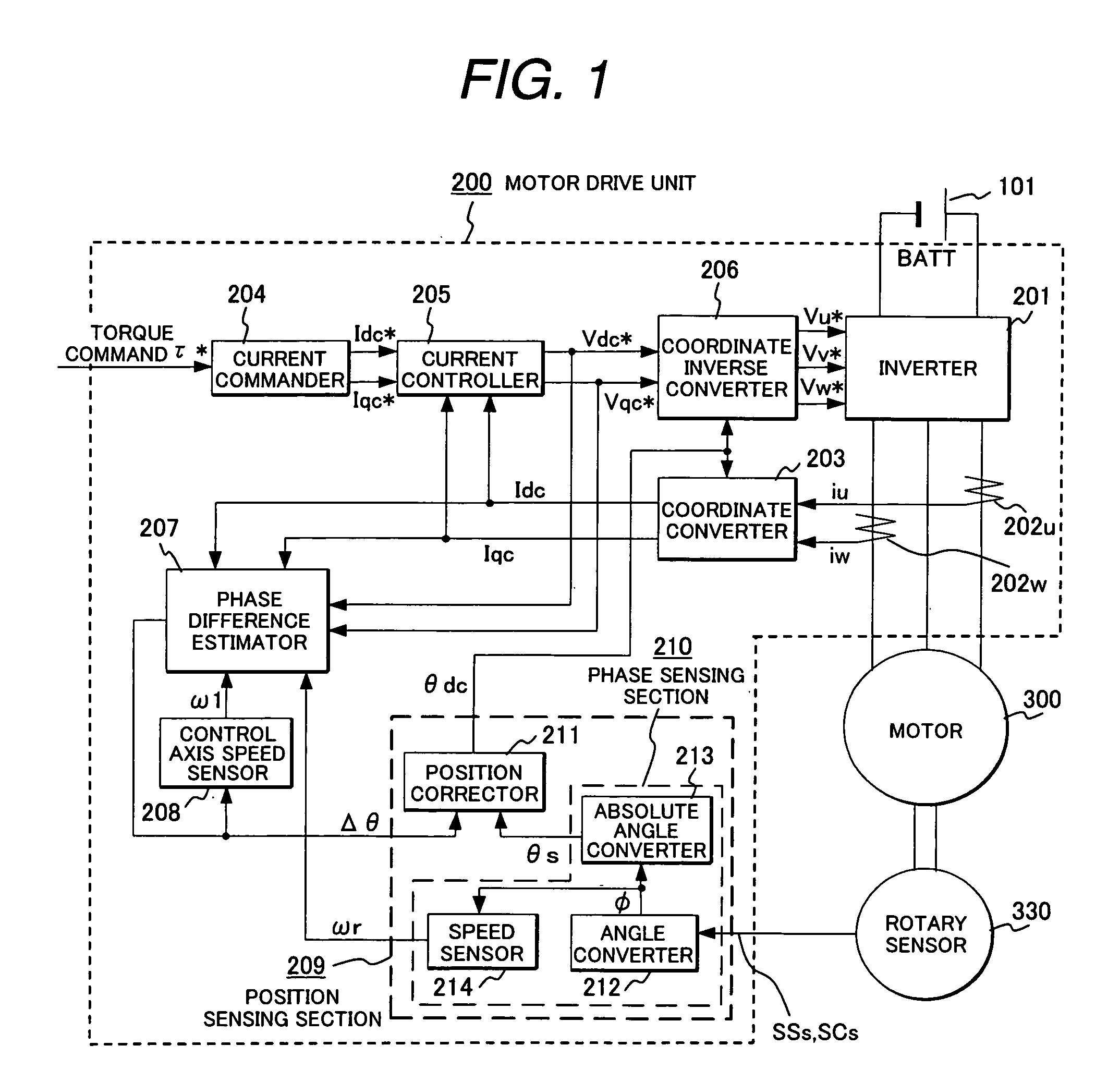
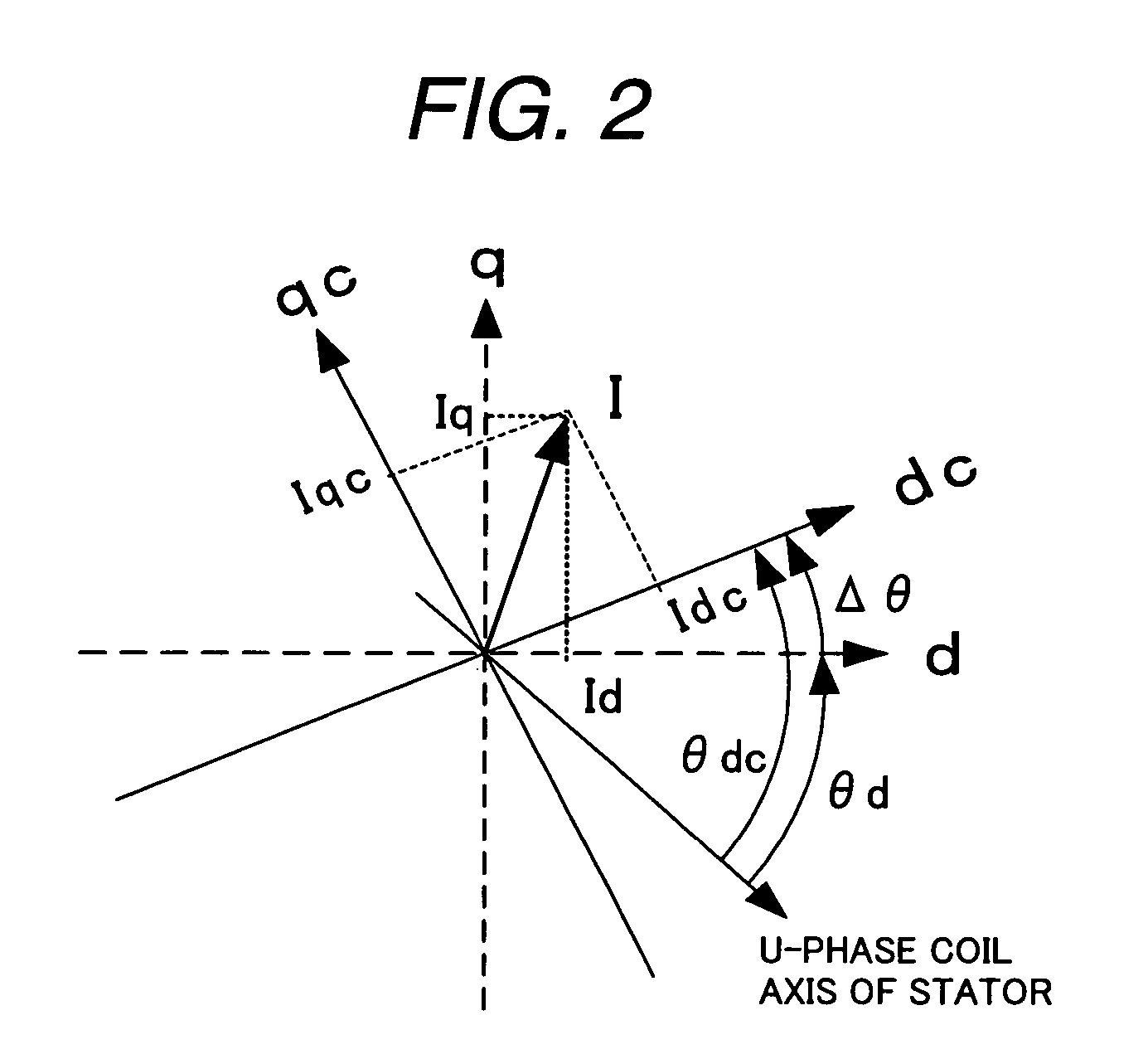
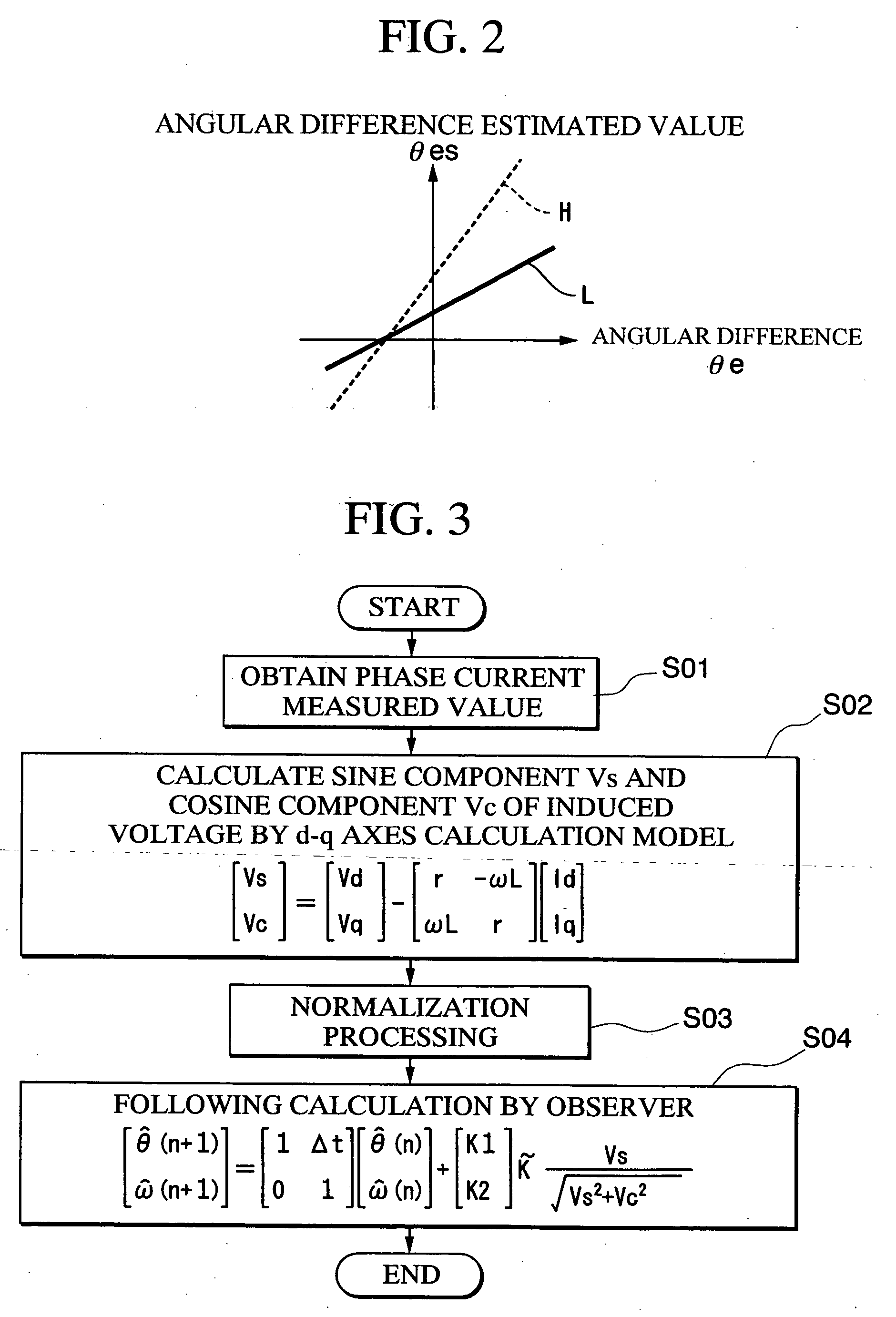
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position. A high-efficiency motor drive unit with improved maintainability of rotary sensor and improved accuracy of sensing the magnet pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor that accelerates and decelerates very quickly in a wide range of speed is realized.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS20080129243A1Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
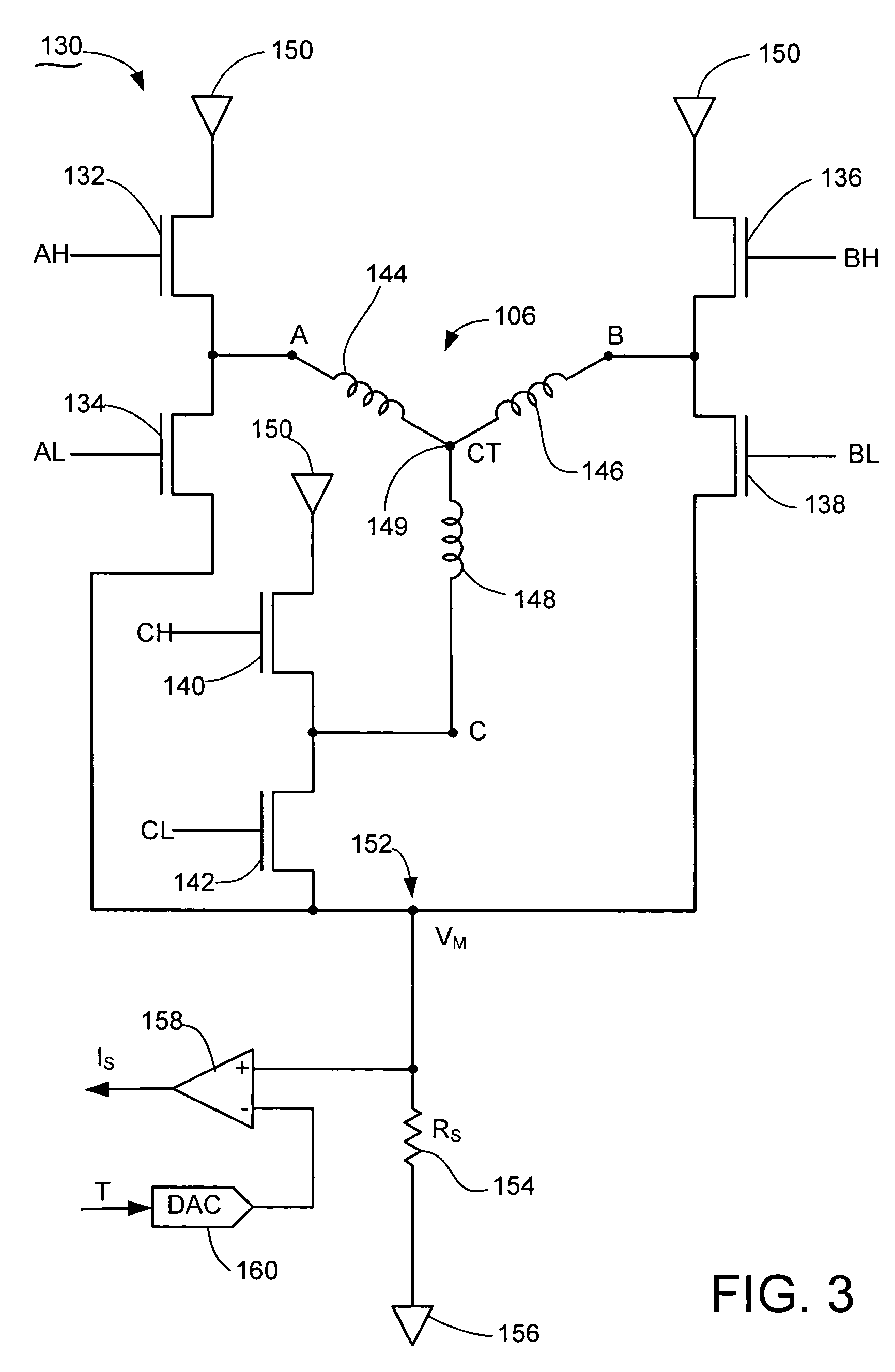
Motor drive circuit
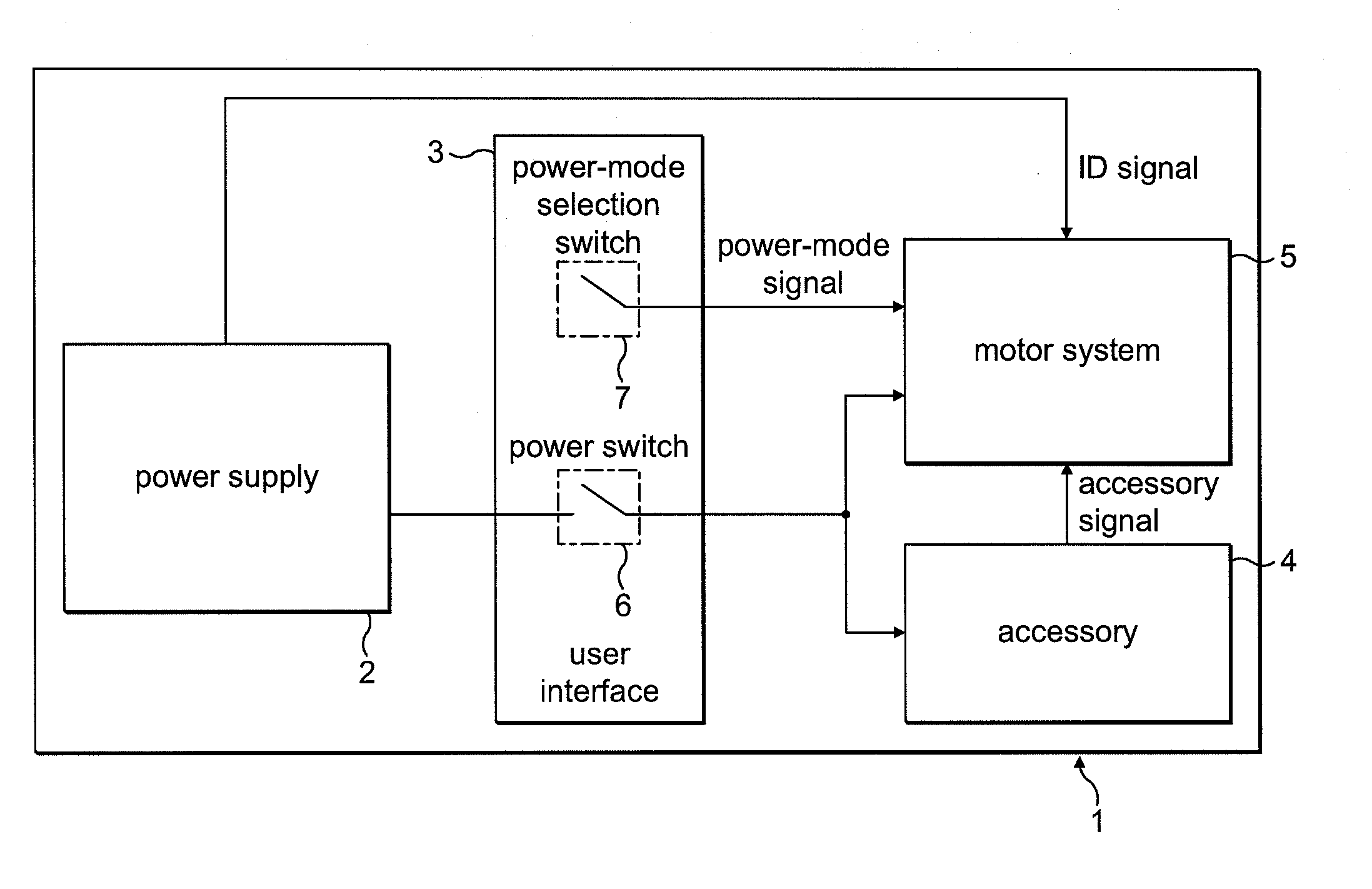
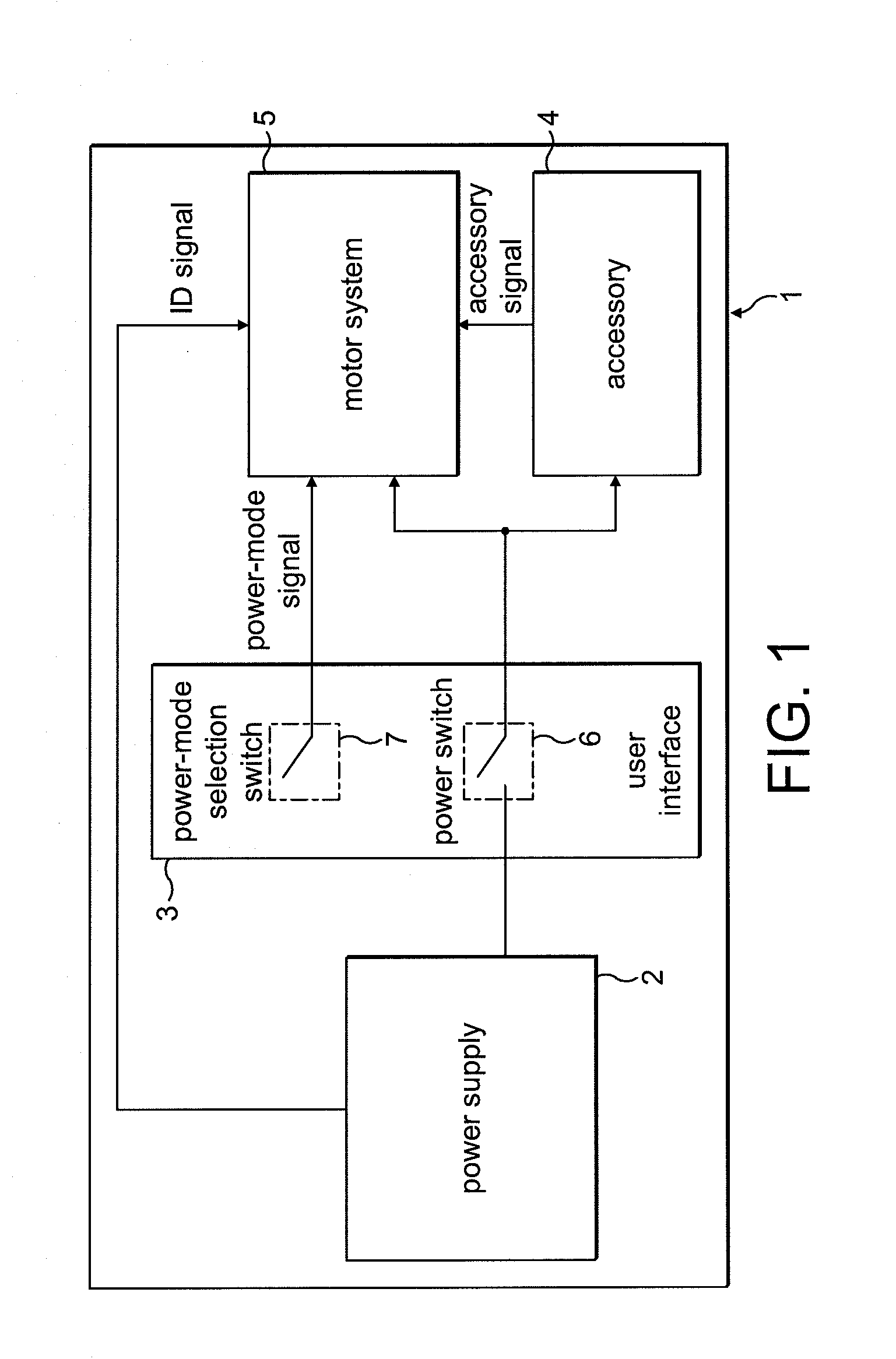
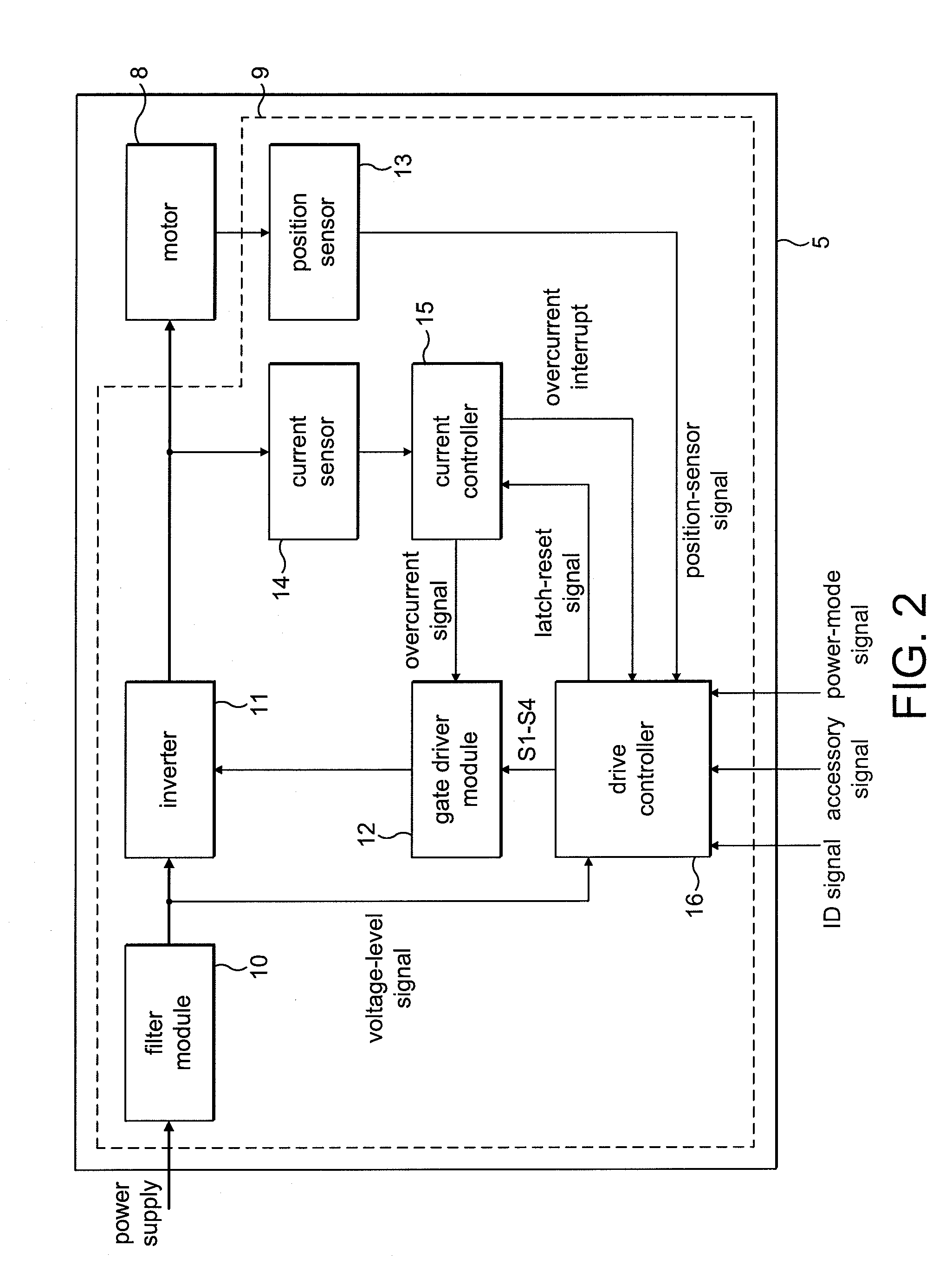
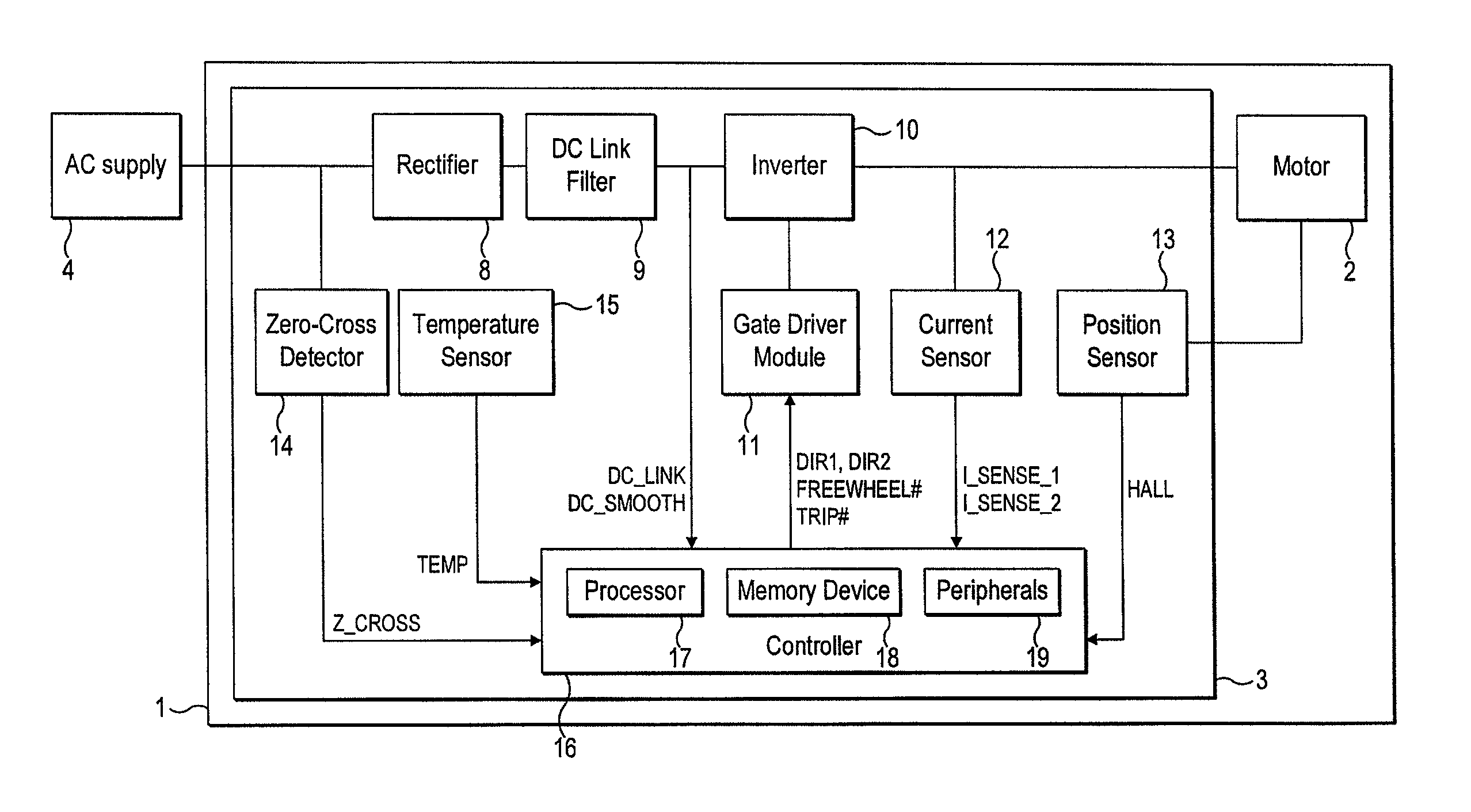
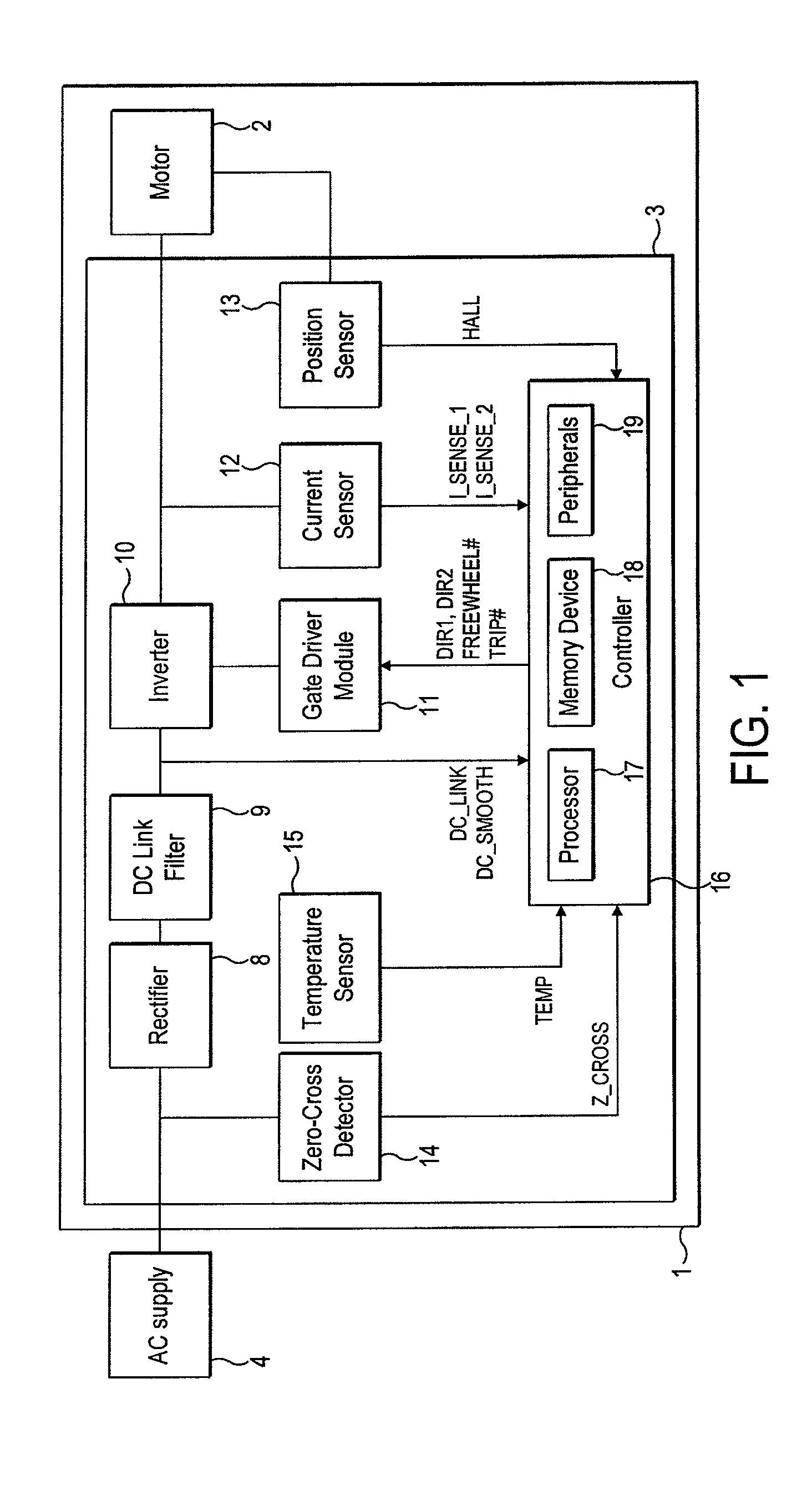
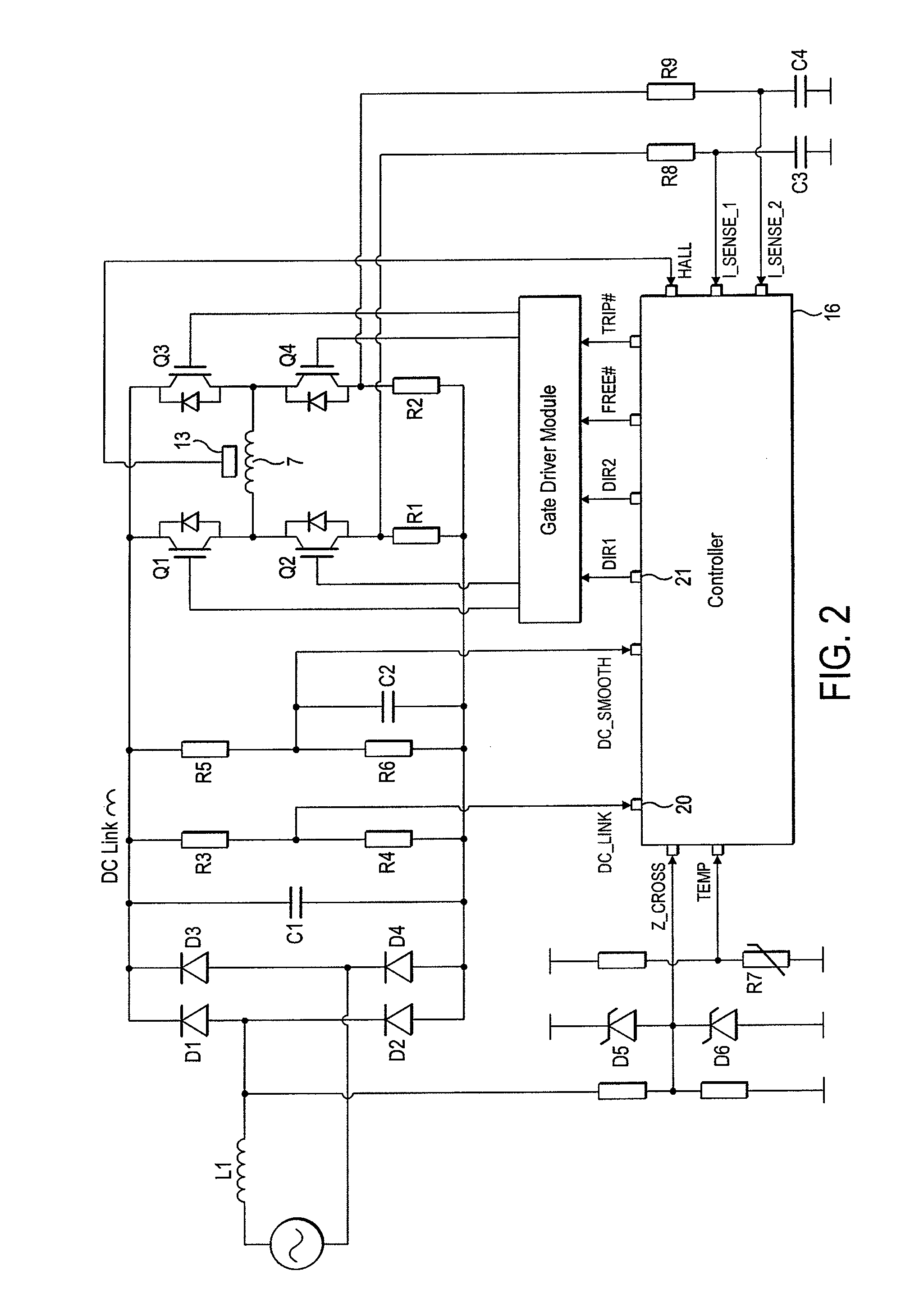
ActiveUS8049363B2Avoid catastrophic failureReduce the probability of failureDC motor speed/torque controlDc source parallel operationMotor driveElectric machine
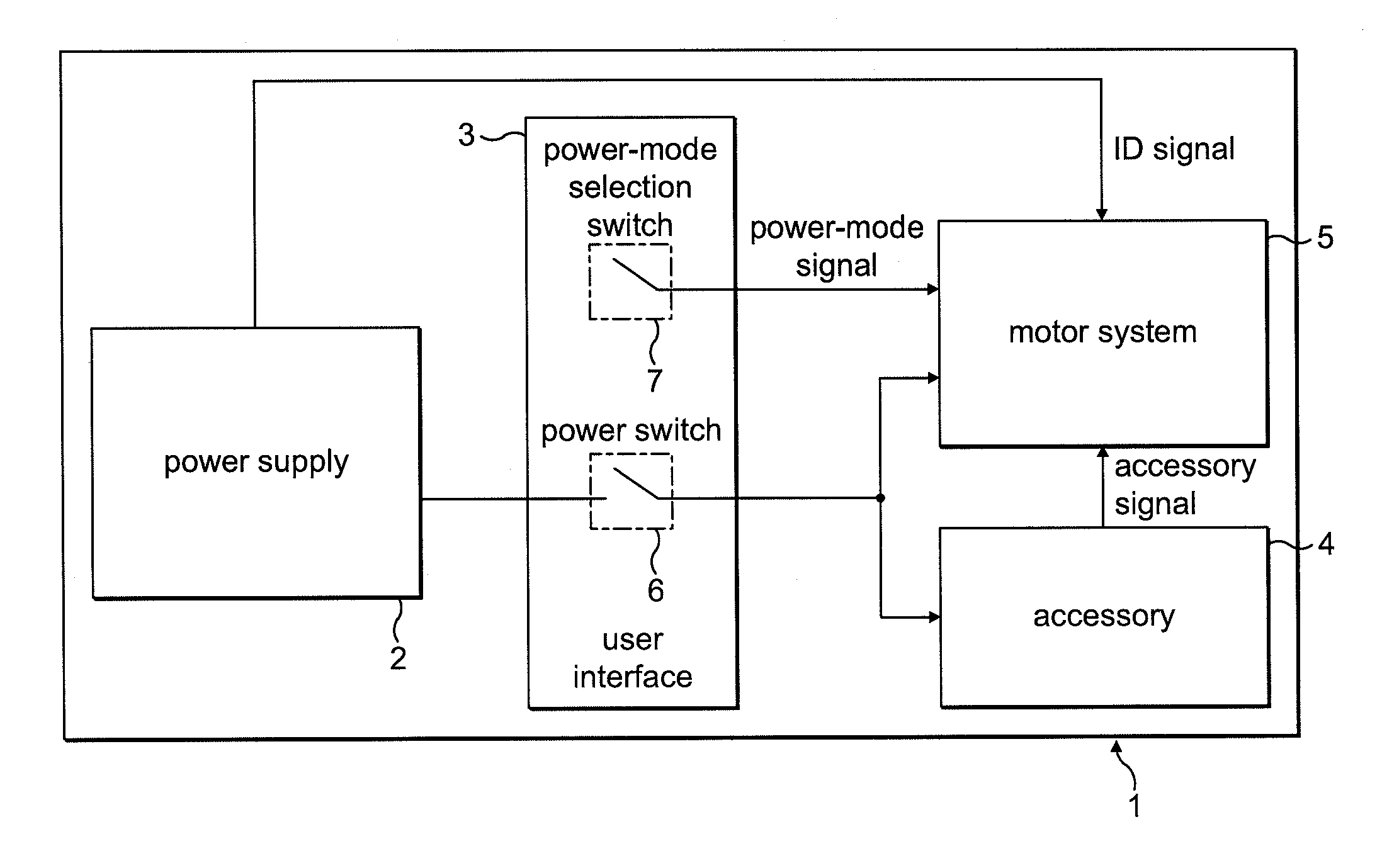
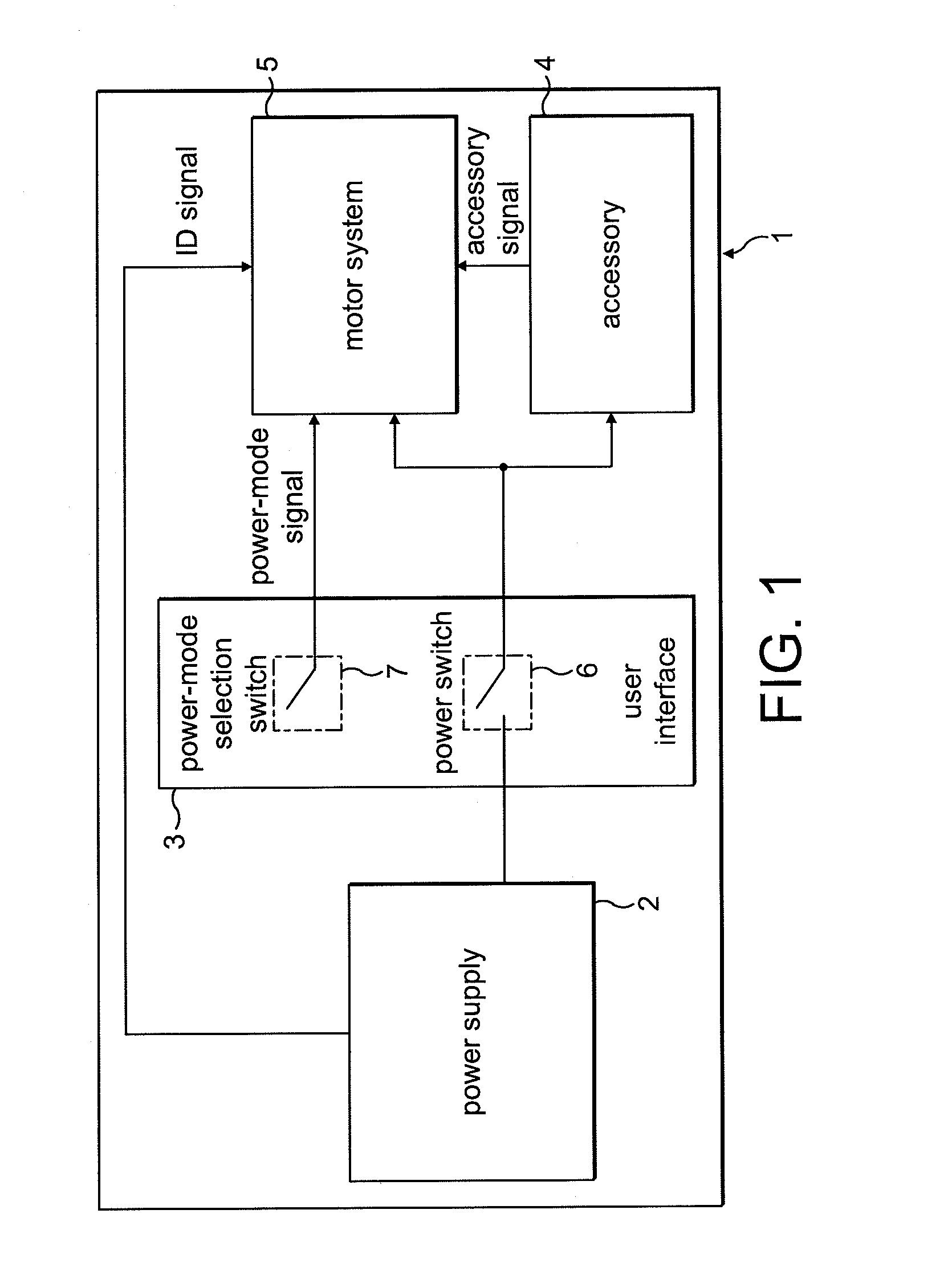
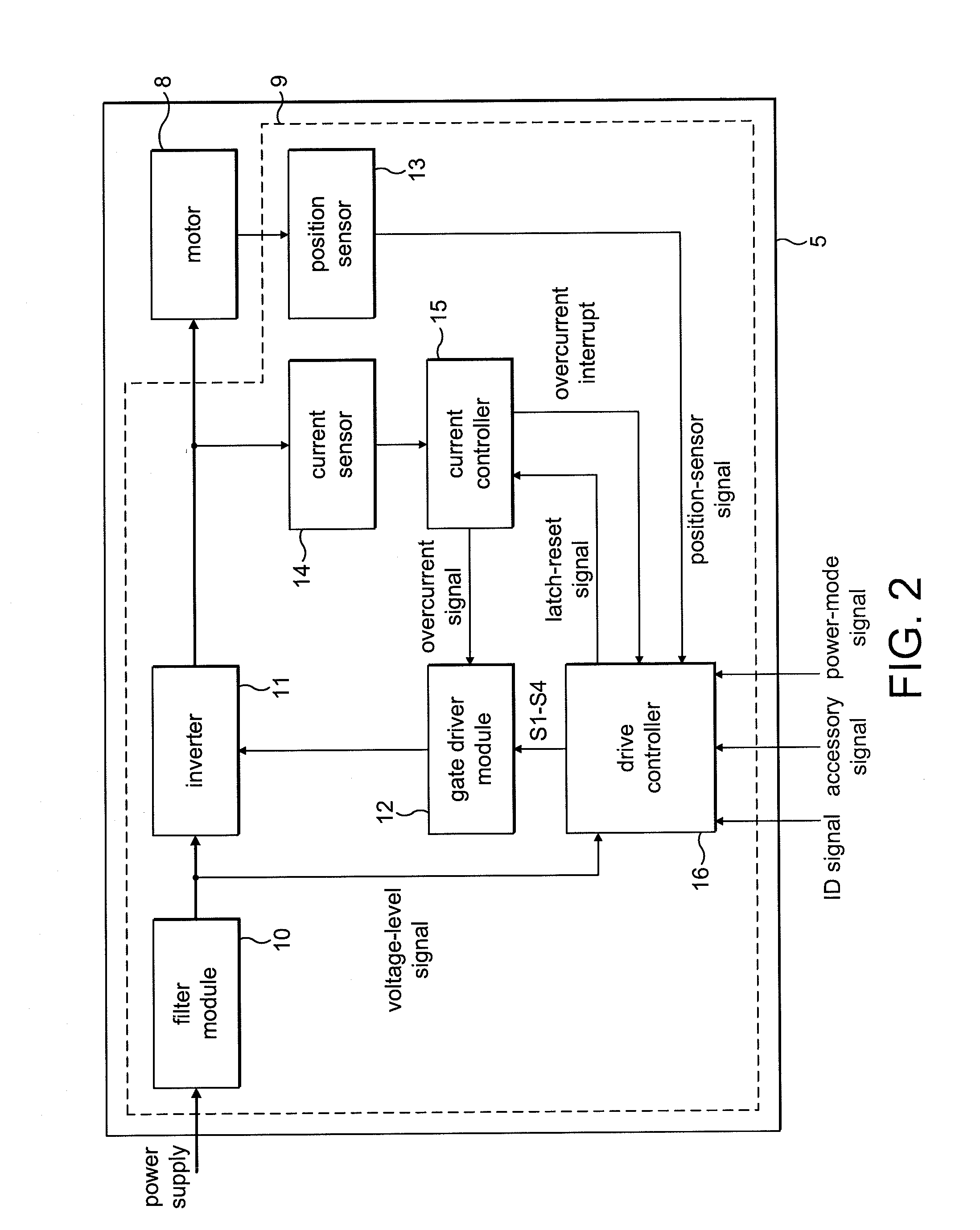
A motor drive circuit comprises positive and negative input terminals for connection of the motor circuit to a DC supply, a DC link filter connected between the input terminals: an electric motor having at least two phases, a plurality of motor drive sub-circuits, each connected to a respective phase of the electric motor and which each control the flow of current into or out of the respective phase of the motor that has been drawn from the supply through the DC link filter, and a switching means provided in the electrical path between the DC link filter and the electric motor drive sub-circuits, the switching means being movable between a closed position in which it connects the DC link filter to the motor drive sub-circuits, and an open position which isolates the DC link filter from the motor drive sub-circuits.
Owner:TRW LIMITED
Synchronous motor drive unit and a driving method thereof
InactiveUS7294988B2Improve sensing accuracyImprove maintainabilityAsynchronous induction motorsElectric energy vehiclesSynchronous motorEngineering
A rotary sensor that outputs two analog signals, such as one sine wave and one cosine wave and has multiple periods within one period of the electrical angle of a motor is employed. The motor is energized at each position for a specified length of time upon its startup by using multiple electrical angles corresponding to the multiple candidate absolute angles obtained from the rotary sensor signal as the initial position of the motor, and the electrical angle at which the motor acceleration becomes maximum is determined as the absolute angle. While the motor drive is in operation, on the other hand, the phase difference Δθ between the phase of the motor at the counter electromotive voltage and the control phase is directly computed from the parameters of the motor, sensed current, voltage command and angle speed so as to correct the shifted position.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Motor driving apparatus
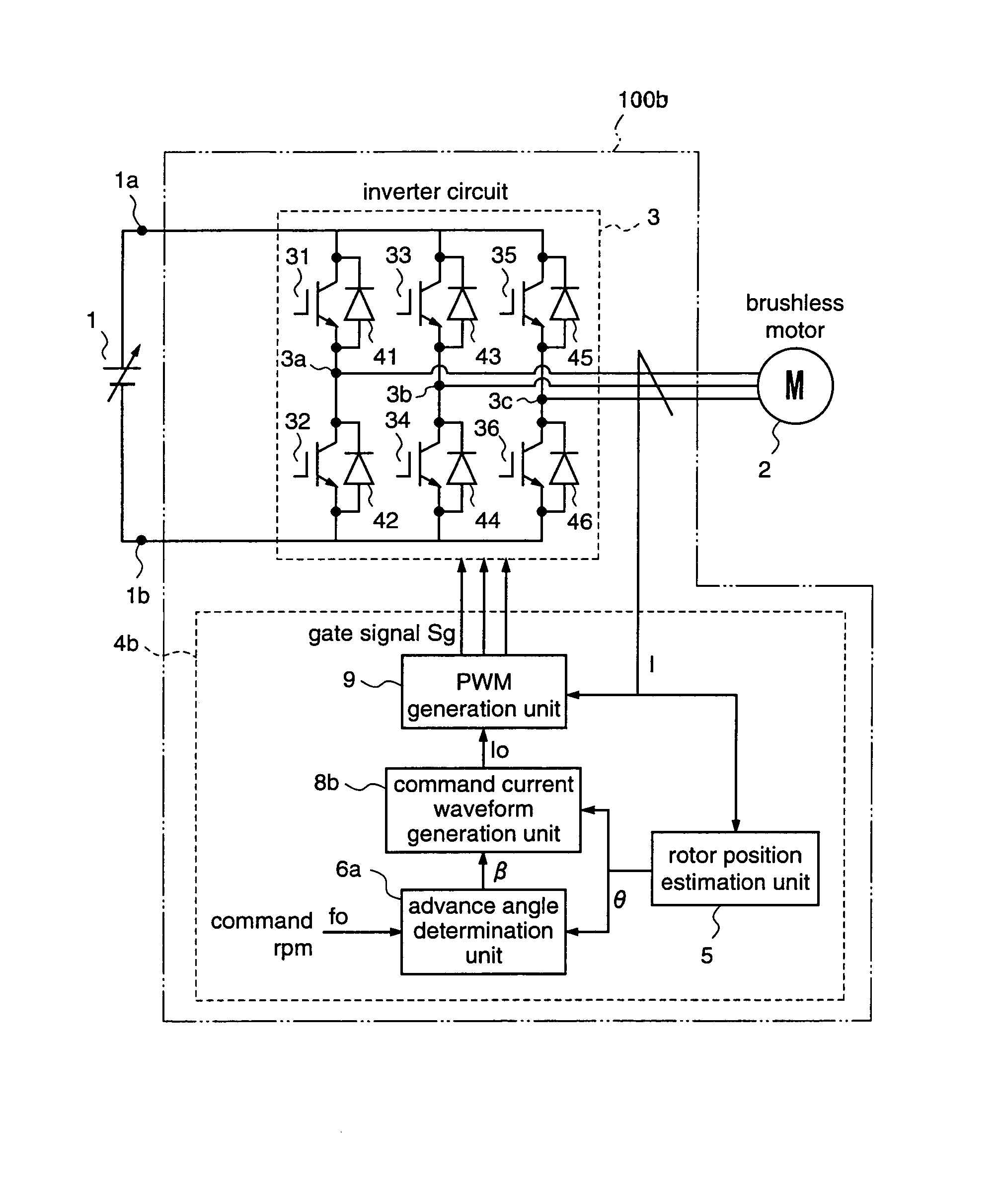
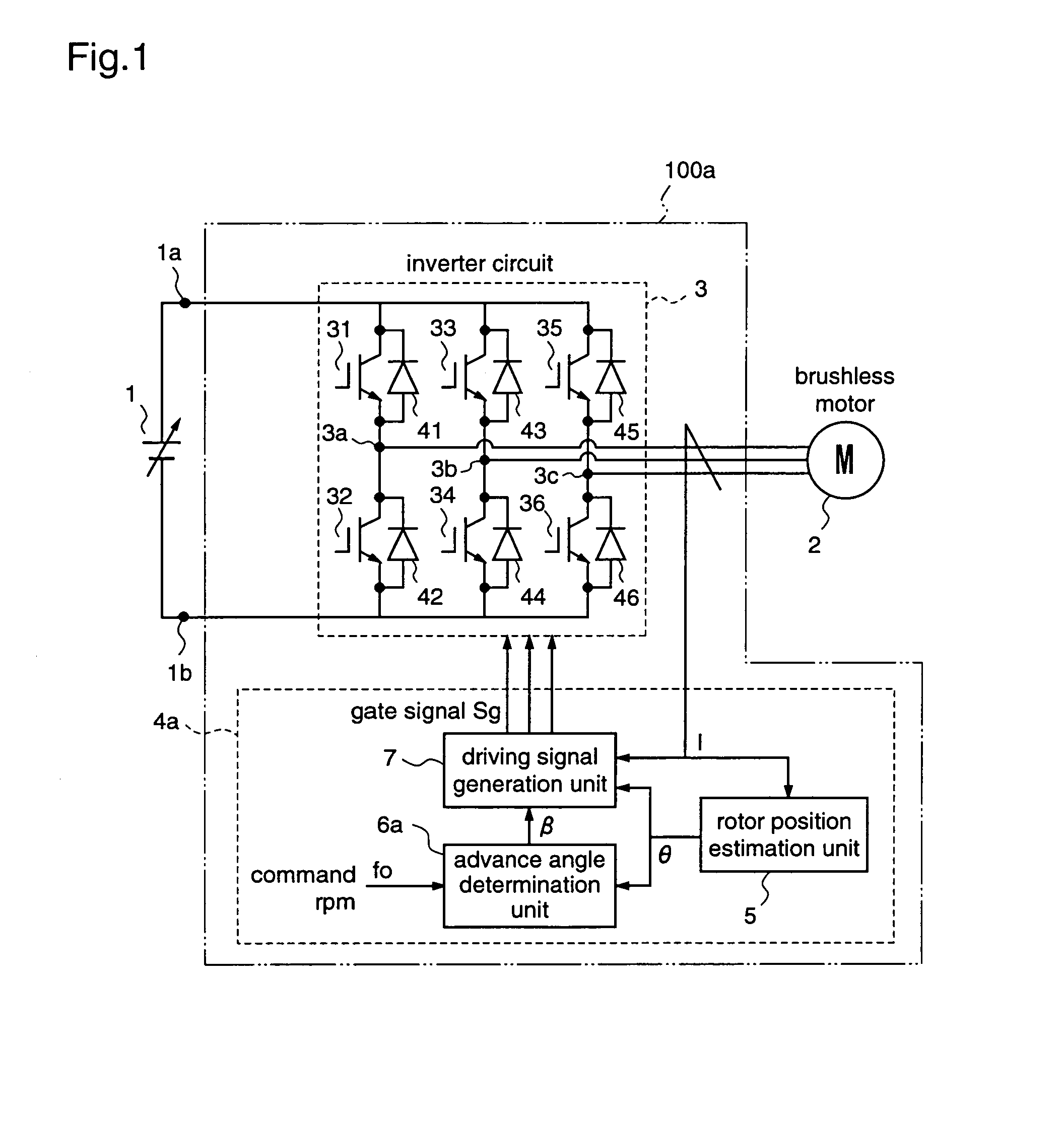
ActiveUS7176644B2Low costIncrease freedomSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsBrushless motorsMotor drive
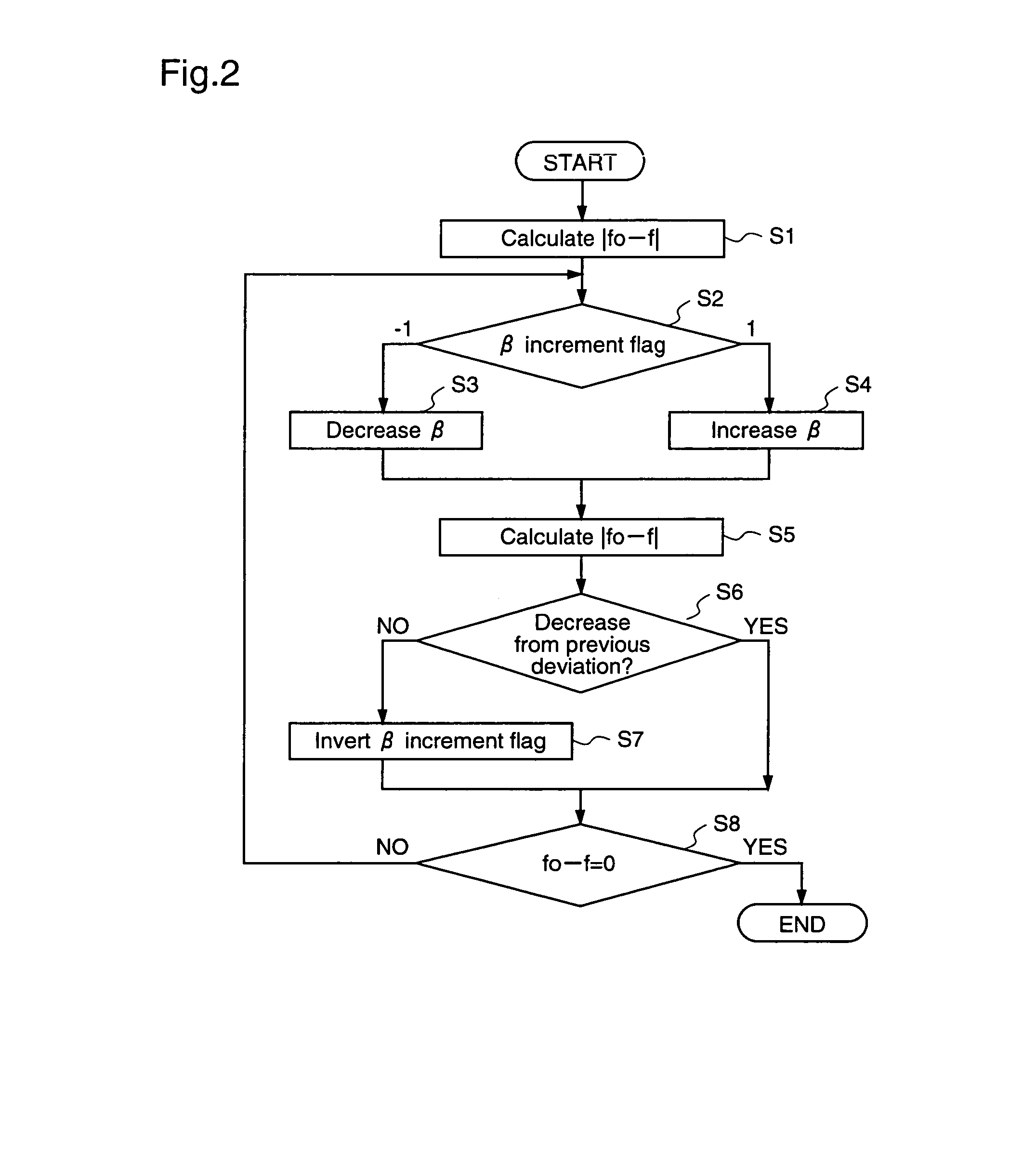
A motor driving apparatus includes an inverter circuit for converting an output voltage of a power supply into a three-phase AC and outputting the same to the brushless motor, a rotor position estimation unit for estimating a rotor position of the brushless motor, and an inverter control unit for controlling the inverter circuit so that the brushless motor is driven by a current based on the estimated rotor position. The inverter control unit determines an advance angle of the current supplied to the brushless motor with respect to the estimated rotor position so as to minimize a deviation between a command rpm and an actual rpm. Therefore, it is possible to perform stable weak field control for the brushless motor, independently from the input voltage of the inverter circuit, without using predetermined control variables such as table values.
Owner:III HLDG 7
Sensorless controller of AC motor and control method
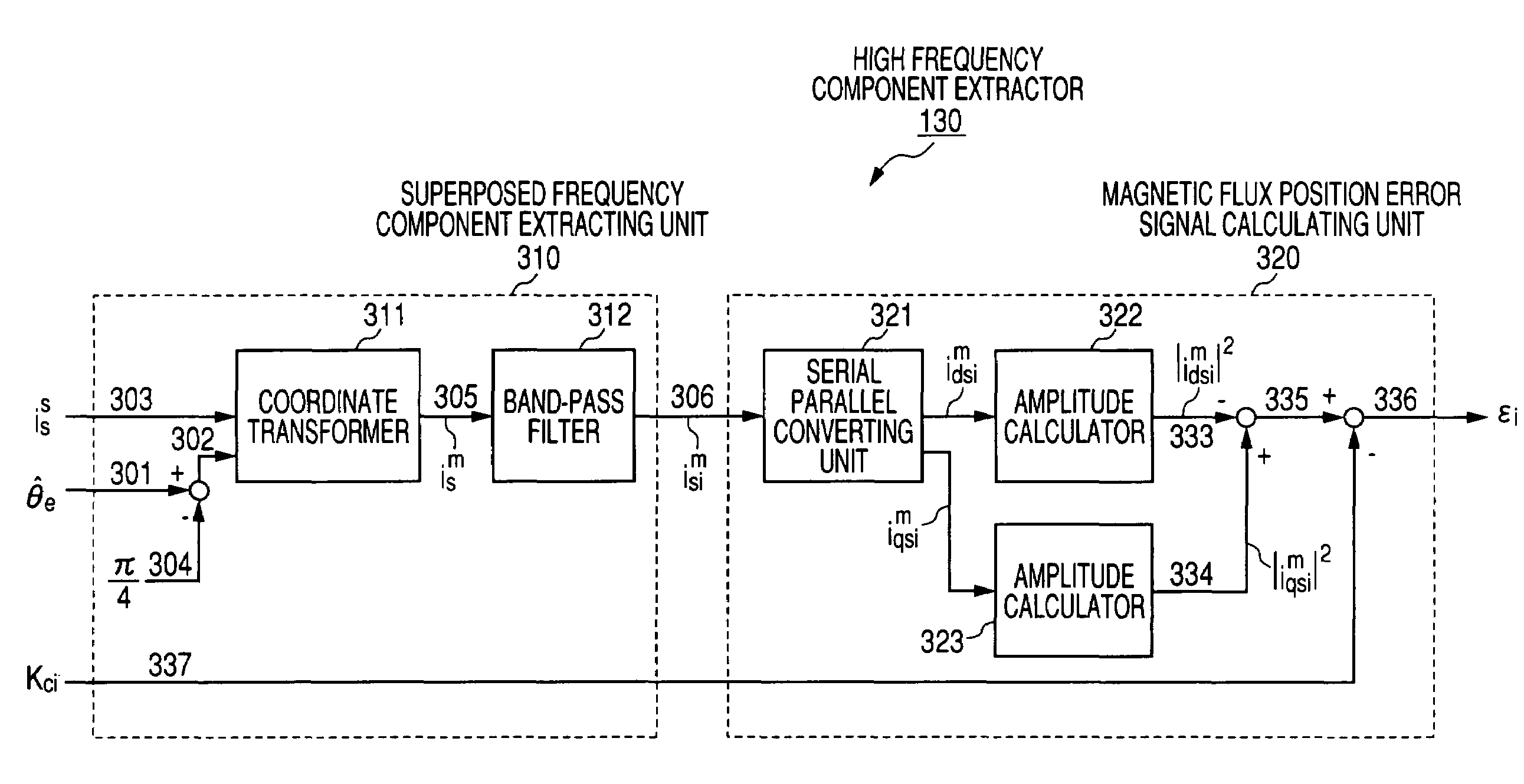
InactiveUS7045988B2Improve efficiencyMagnetic saliency at the high frequency is reducedVector control systemsSingle motor speed/torque controlLow speedSignal on
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Control apparatus for brushless DC motor
ActiveUS20050029972A1Improve estimation accuracySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsPhase currentsConductor Coil
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Initial rotor position detection for permanent magnet synchronous motors
ActiveUS20100181952A1High sensitivityAvoid uneven performanceMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFall timeVoltage vector
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253264A1Increase powerLess torqueTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersFreewheelControl system
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the speed of the electric machine. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
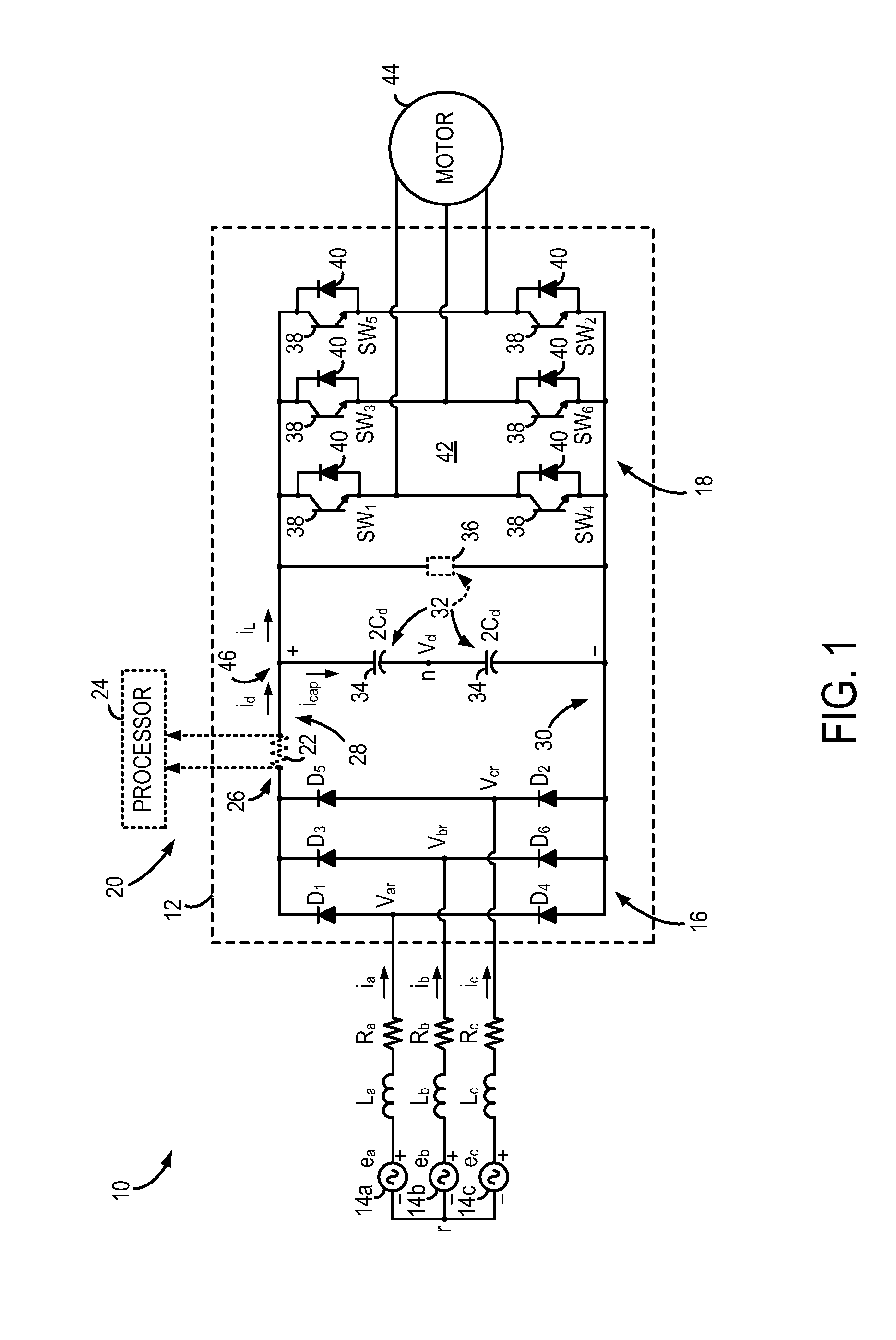
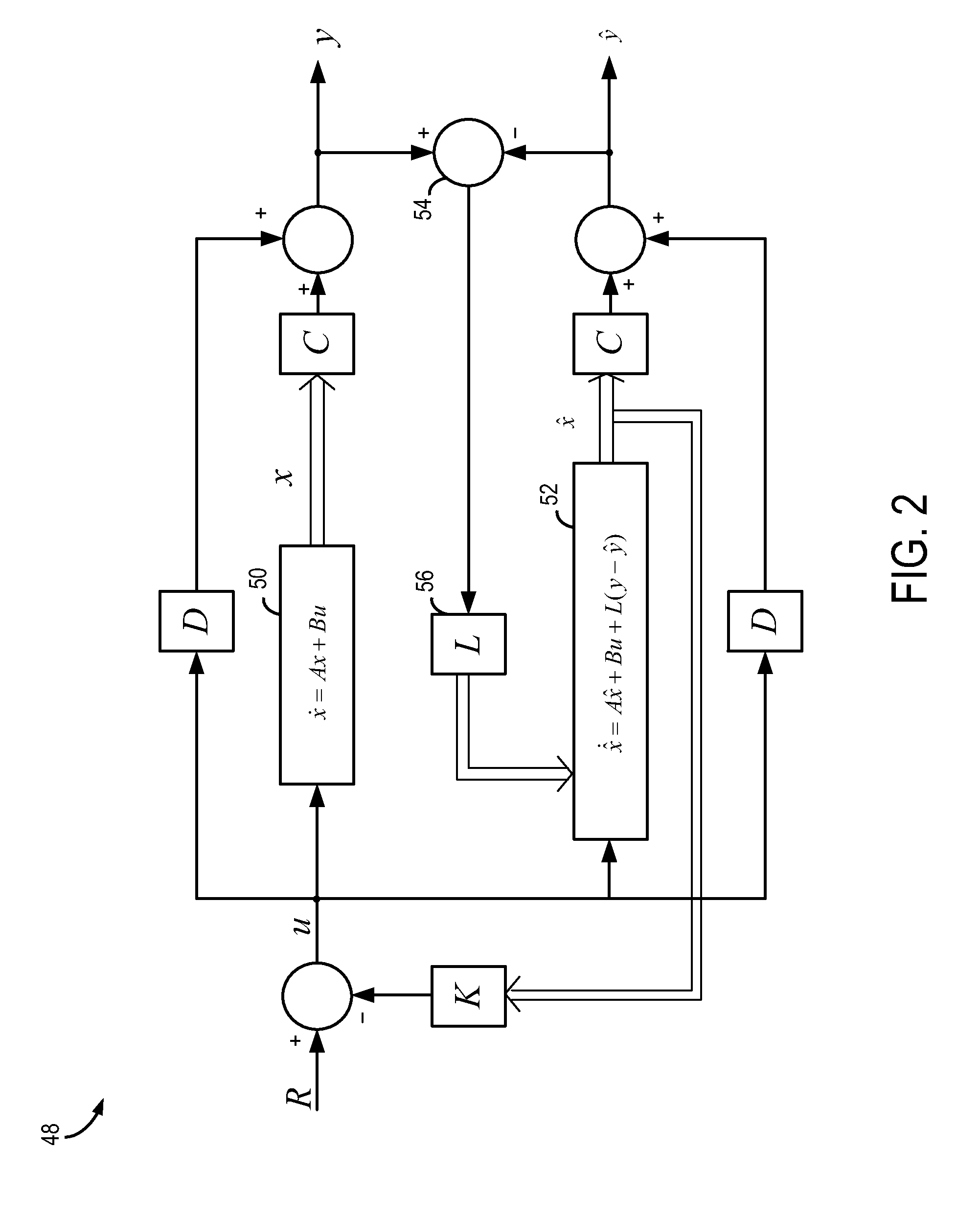
System and method for detecting phase loss and diagnosing DC link capacitor health in an adjustable speed drive
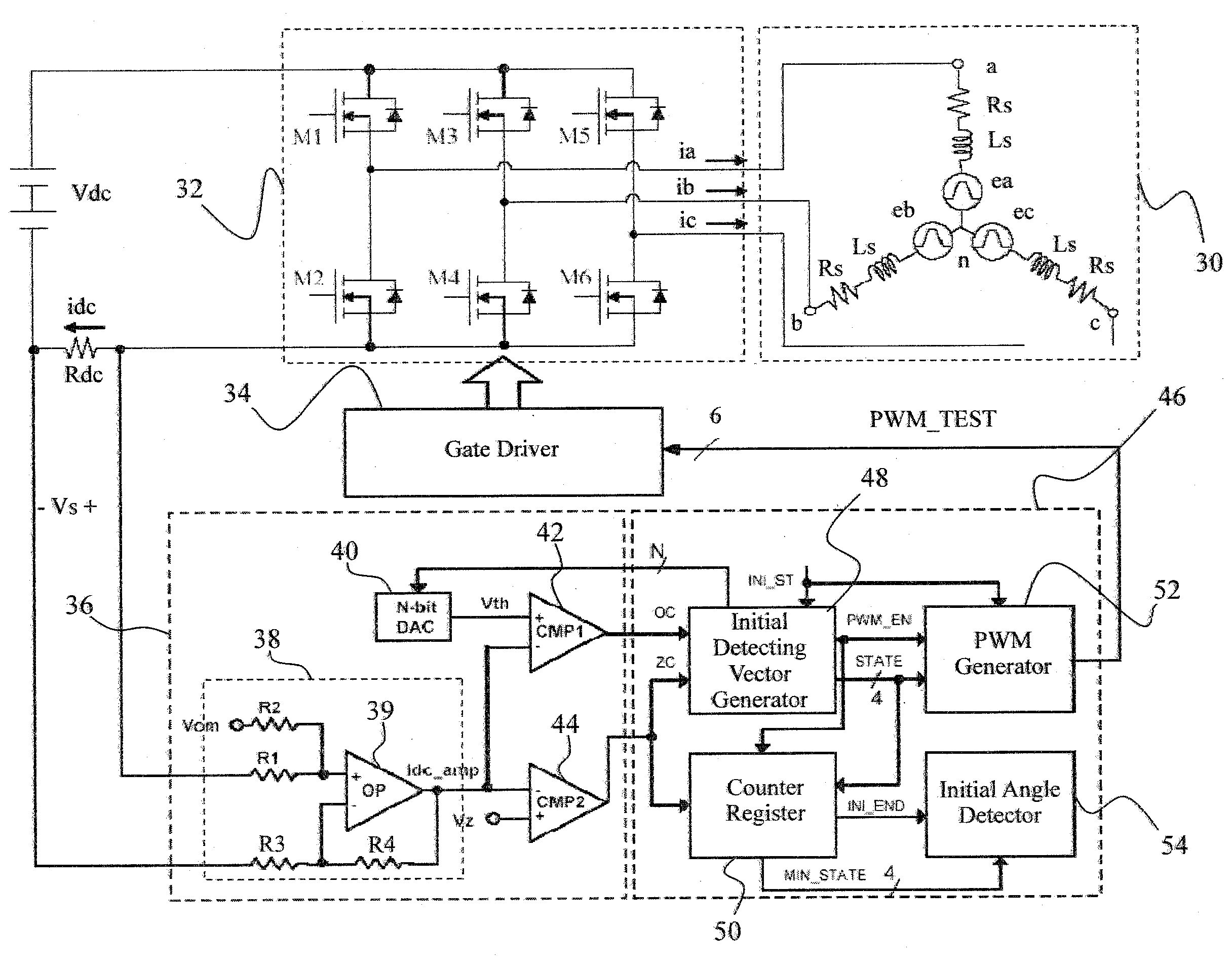
A system and method for detecting input phase loss in an adjustable speed drive (ASD) includes an input unit to detect operating data from the ASD. The operating data includes a DC link current of the ASD. The system also includes a state observer that is adapted to receive the operating data from the input unit and extract a DC link capacitor current of the ASD using the DC link current. The system also includes a controller programmed to compare the extracted DC link capacitor current to a predetermined fault range and generate a fault indication of an input phase loss if the extracted DC link capacitor current is within the predefined fault range. The controller is also programmed to calculate an estimated lifespan of the DC link capacitor based on the extracted DC link capacitor current.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
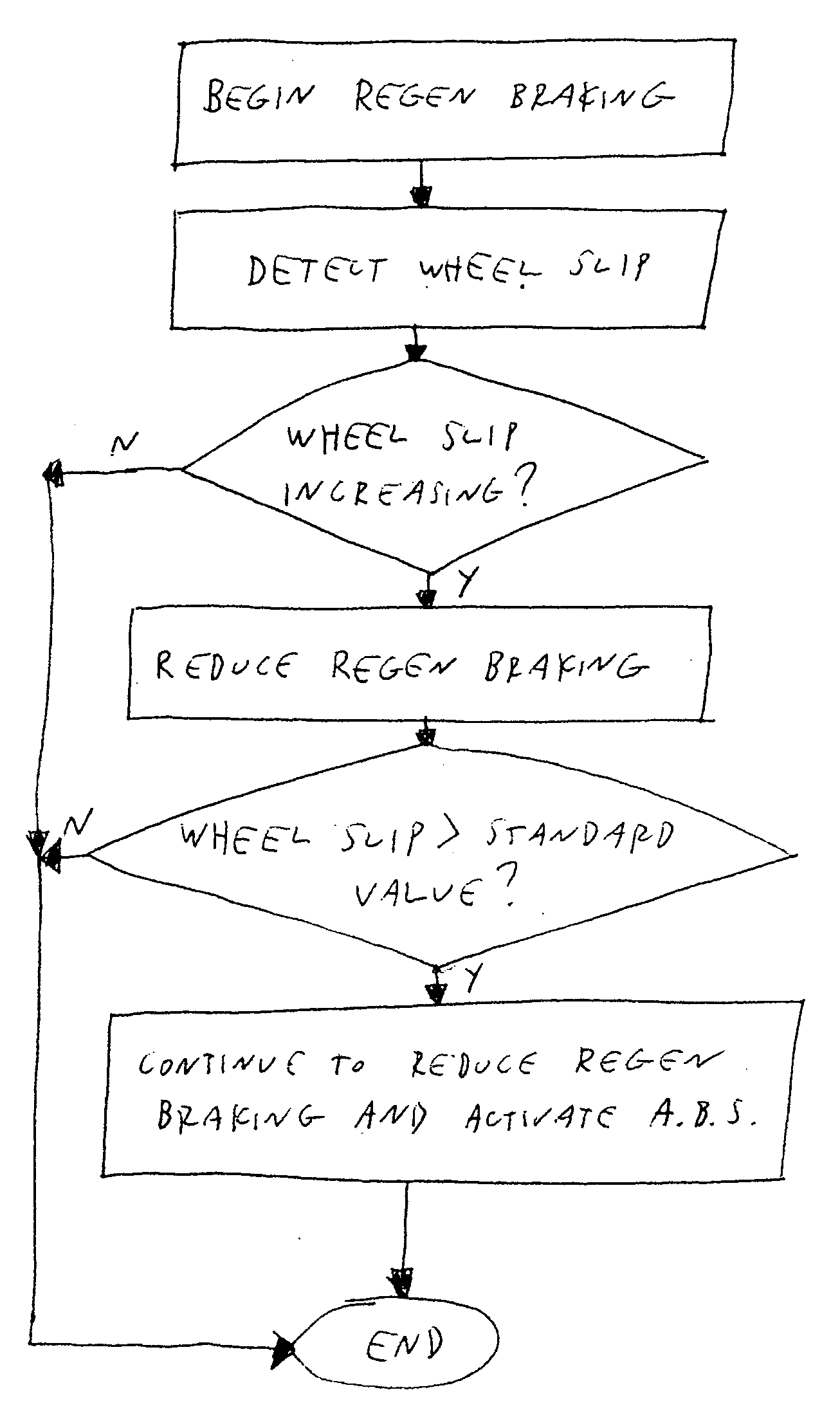
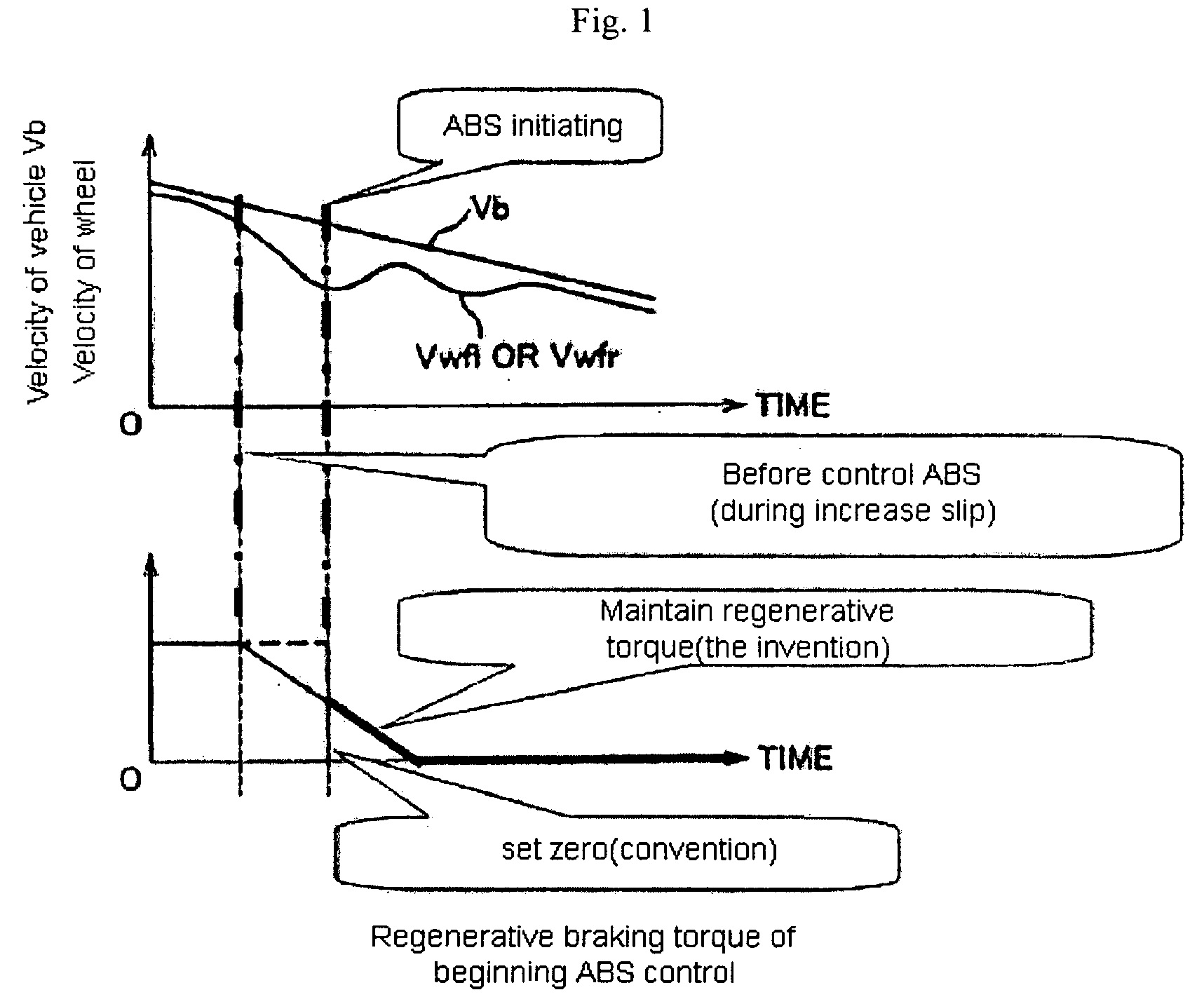
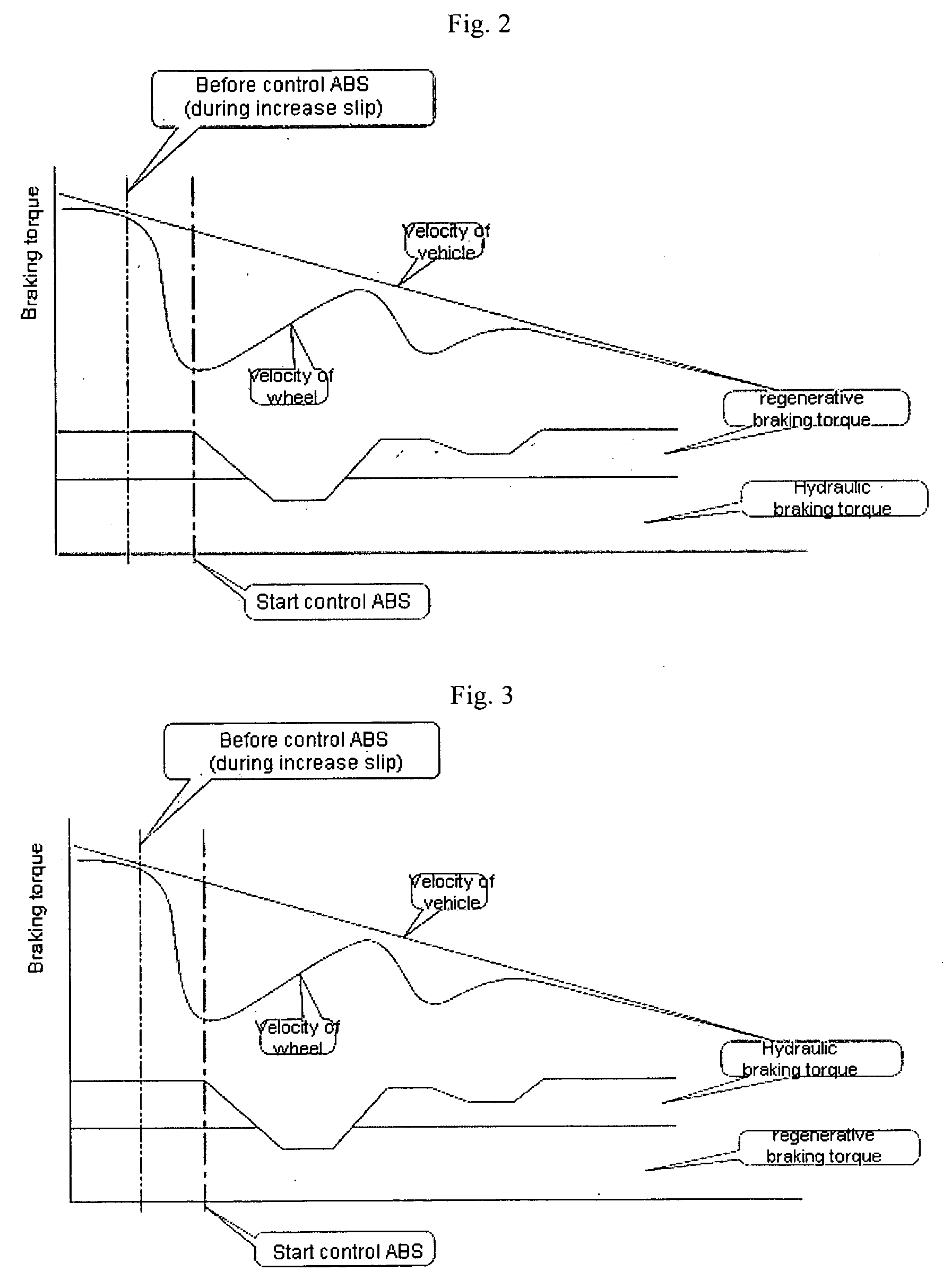
Method for control regenerative braking of electric vehicle
A method for controlling regenerative braking of a vehicle includes: initiating the regenerative braking; detecting an amount of slip of a wheel during the regenerative braking; if the amount of slip is increasing, reducing a regenerative braking torque; and if the amount of slip is greater than a set value, actuating an antilock brake system and reducing the regenerative braking torque or a hydraulic braking torque continuously until the vehicle is stopped. Alternatively, if the amount of slip is increasing, the regenerative braking torque is not reduced.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253265A1Good control over powerConvenient power controlSynchronous motors startersVacuum cleaner apparatusFreewheelElectric machine
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the voltage used to excite the winding. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Phase advance angle optimization for brushless motor control
InactiveUS7436139B2High degree of precision controllabilityMaximizes output torqueCommutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersBrushless motorsPhase currents
A control system for a multiphase permanent magnet motor having a controller for producing a control signal to energize each phase winding. The controller includes a current value calculator for determining a value of phase current advanced in phase with respect to back-EMF by a phase advance angle, and a phase advance optimization circuit for producing a value of the phase advance angle optimized so as to maximize output torque of the motor and mimimize the phase current. The phase advance optimization circuit determines the phase advance angle optimized for each phase of the motor.
Owner:MATRA MFG & SERVICES
Motor magnetic-pole-position estimating apparatus
InactiveUS20110175560A1Single-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersPower flowMagnetic poles
A motor magnetic-pole-position estimating apparatus includes a command voltage output device and a current detector. A model-current calculator is configured to calculate a model current corresponding to a voltage equation for a predetermined model of a motor based on a command voltage and an actual current. A current-difference calculator is configured to calculate a current difference between the model current and the actual current. Each of first and second magnetic-pole-position-difference calculators is configured to calculate a magnetic-pole-position difference between an actual magnetic-pole position of the motor and an estimated or designated magnetic-pole position based on the current difference depending on whether or not a rotation speed of the motor is lower than a predetermined value. A magnetic-pole-position calculation device is configured to calculate the magnetic-pole position of the motor based on the magnetic-pole-position difference calculated by the first or second magnetic-pole-position-difference calculator.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Torque ripple suppression control apparatus and torque ripple suppression control method for rotating electrical machine
ActiveUS20120306411A1Current disturbanceSuppress torque ripple accuratelySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsEngineeringDisturbance observer
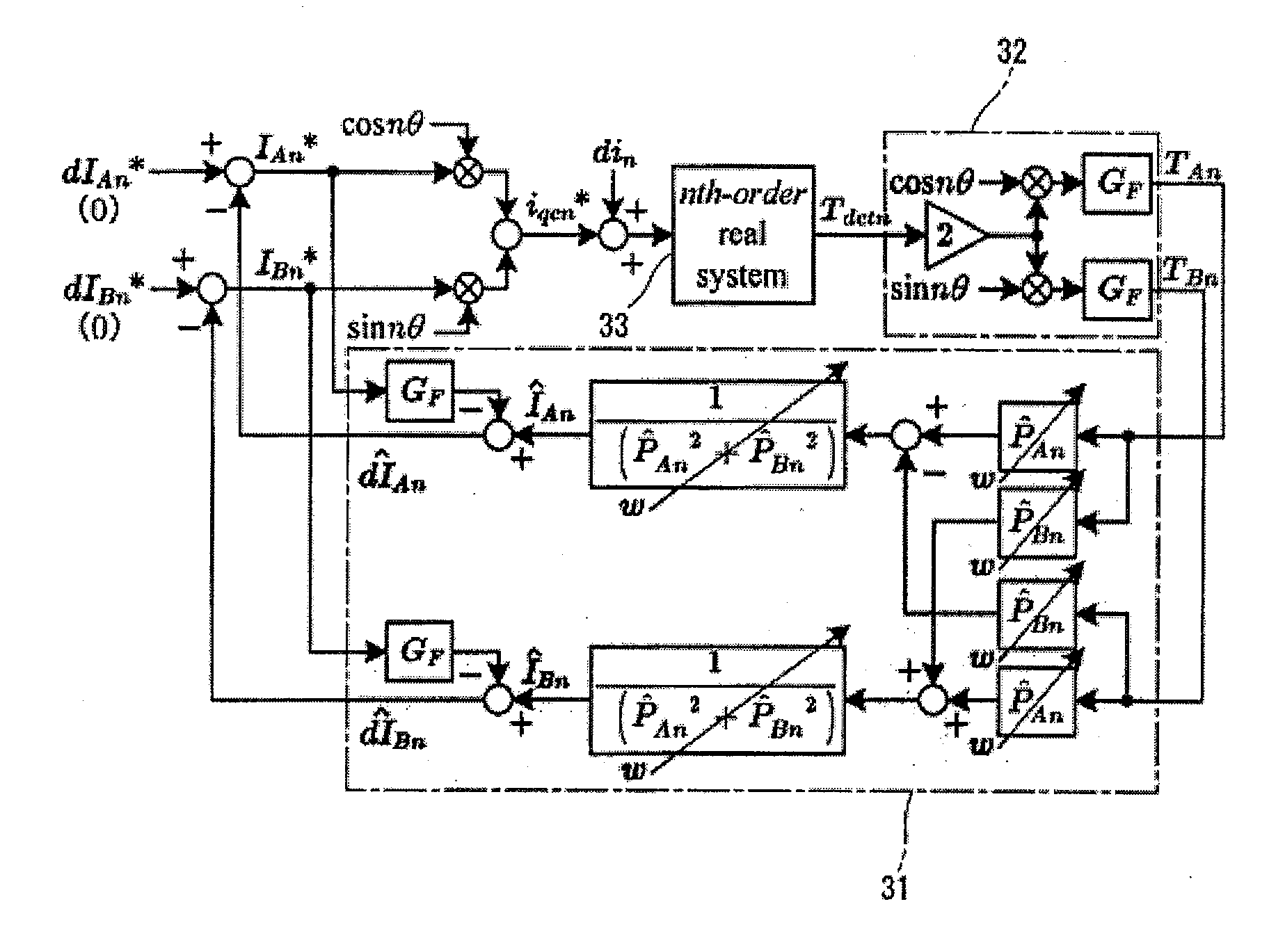
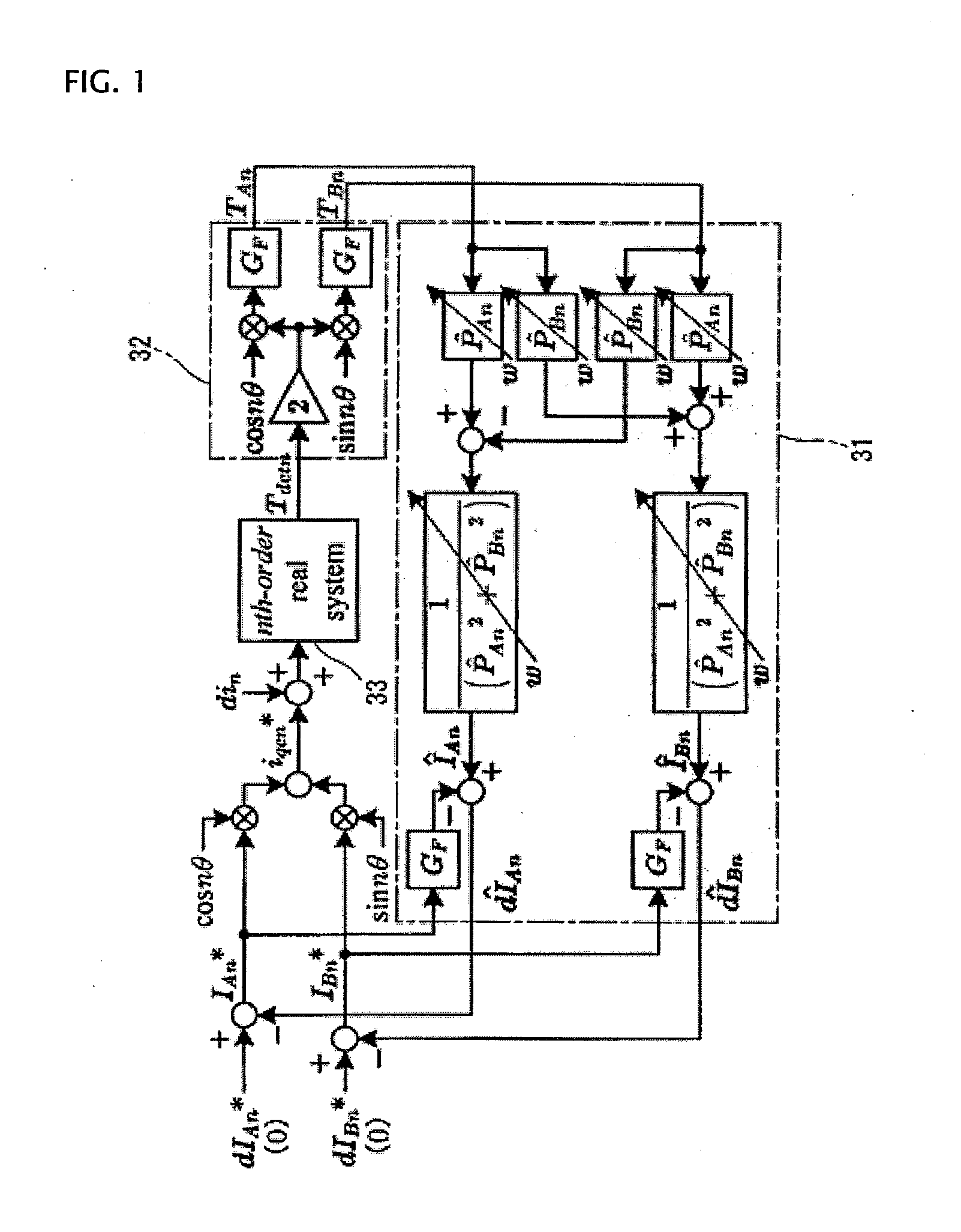
A periodic disturbance observer determines real part ÎAn and imaginary part ÎBn of an estimated current including a periodic disturbance, from value of identification identifying a system transfer function of an nth order torque ripple frequency component from a command torque to a detected torque value, with a one-dimensional complex vector having a real part P̂An and an imaginary part P̂Bn, a cosine coefficient TAn, a sine coefficient TBn, and the real part P̂An and imaginary part P̂Bn of the system transfer function; subtracts command compensating current IAn* and IBn* obtained through pulsation extracting filter GF, respectively, from the real part ÎAn and imaginary part ÎBn of the estimated current, and thereby determines estimated periodic disturbance current real part dÎAn and imaginary part dÎBn to cancel the periodic disturbance current.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
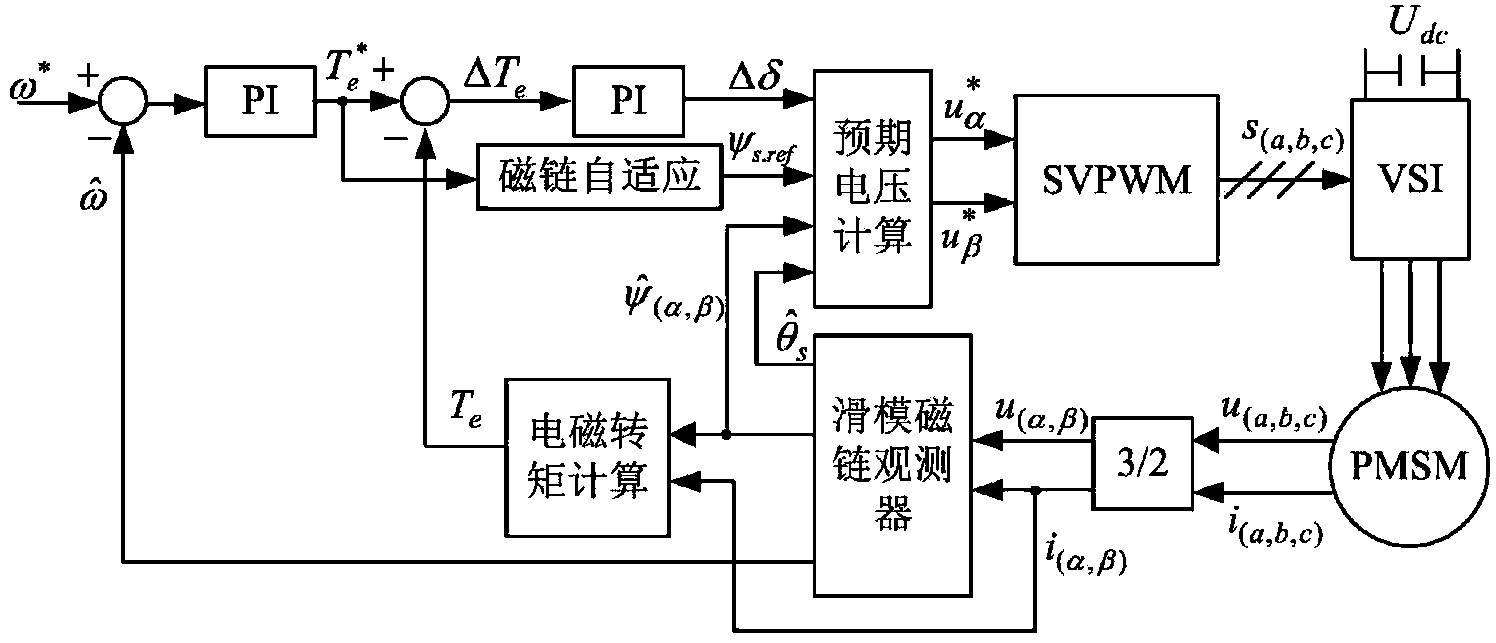
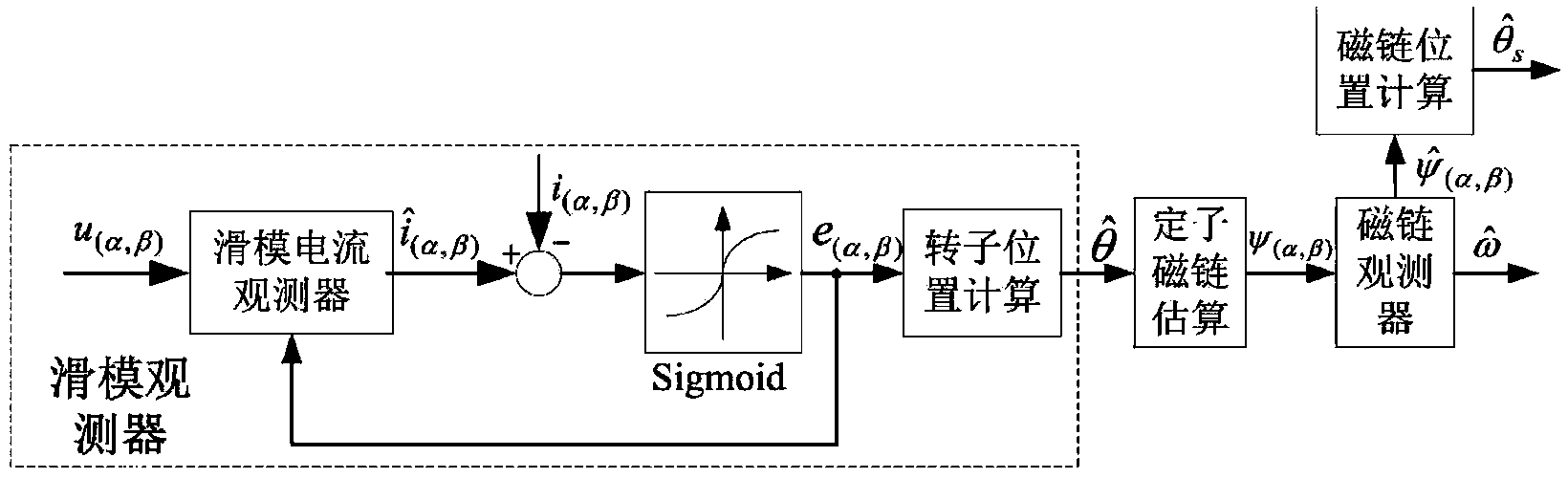
Permanent magnet synchronous motor torque control method based on sliding mode flux linkage observer
ActiveCN103872951AReal-time controlAchieving Direct Torque ControlTorque ripple controlSingle motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorVoltage reference
The invention discloses a permanent synchronization motor torque control method based on a sliding mode flux linkage observer. Direct torque control is performed on a permanent synchronization motor through a 3 / 2 coordinate conversion module, the sliding mode flux linkage observer, an electromagnetic torque calculation module, a rotating speed PI adjustor, a torque PI adjustor, a flux linkage self-adaptation module, an expected voltage calculation module, an SVPWM module and an inverter. The sliding mode flux linkage observer is adopted for estimating the size, phase and rotator speed of stator flux linkage, and set torque is processed through the flux linkage self-adaptation module to obtain a set value of the stator flux linkage. Expected voltage calculation is performed on size and phase estimation values and the set value of the stator flux linkage and the output quantity of the torque PI adjustor, so that two-phase alternating-current voltage reference values on a two-phase static coordinate system are obtained, and then through SVPWM conversion, a switching signal is obtained to drive the voltage source inverter to achieve direct torque control over the permanent synchronization motor.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for controlling output feedback of motor position servo system
ActiveCN104065322AImproved low speed servo performanceImprove noiseMotor parameters estimation/adaptationObserver controlLyapunov stabilityLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a method for controlling output feedback of a motor position servo system. The method comprises the following steps that a mathematic model of the motor position servo system is established; an extended state observer is designed, and the state of the system and interference in the mathematic model are observed; a second-order low-pass filter is designed so that an error system of the motor position servo system can be established, and an output feedback controller is designed according to the error system; stability certification is conducted on the motor position servo system according to the Lyapunov stability theory, and a result of the global asymptotic stability of the system is obtained according to the Barbalat lemma. According to the method for controlling output feedback of the motor position servo system, considering uncertainty such as external interference, the extended state observer conducts estimation, compensation is conducted during design of a controller, and therefore the robustness of the actual motor position servo system to external interference is improved; in this way, the problems of a high-frequency dynamic condition, measurement noise and the like caused by high-gain feedback are greatly relieved, so that the shadowing property of the system is improved, and the motor position servo system can be applied to practical engineering more conveniently.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
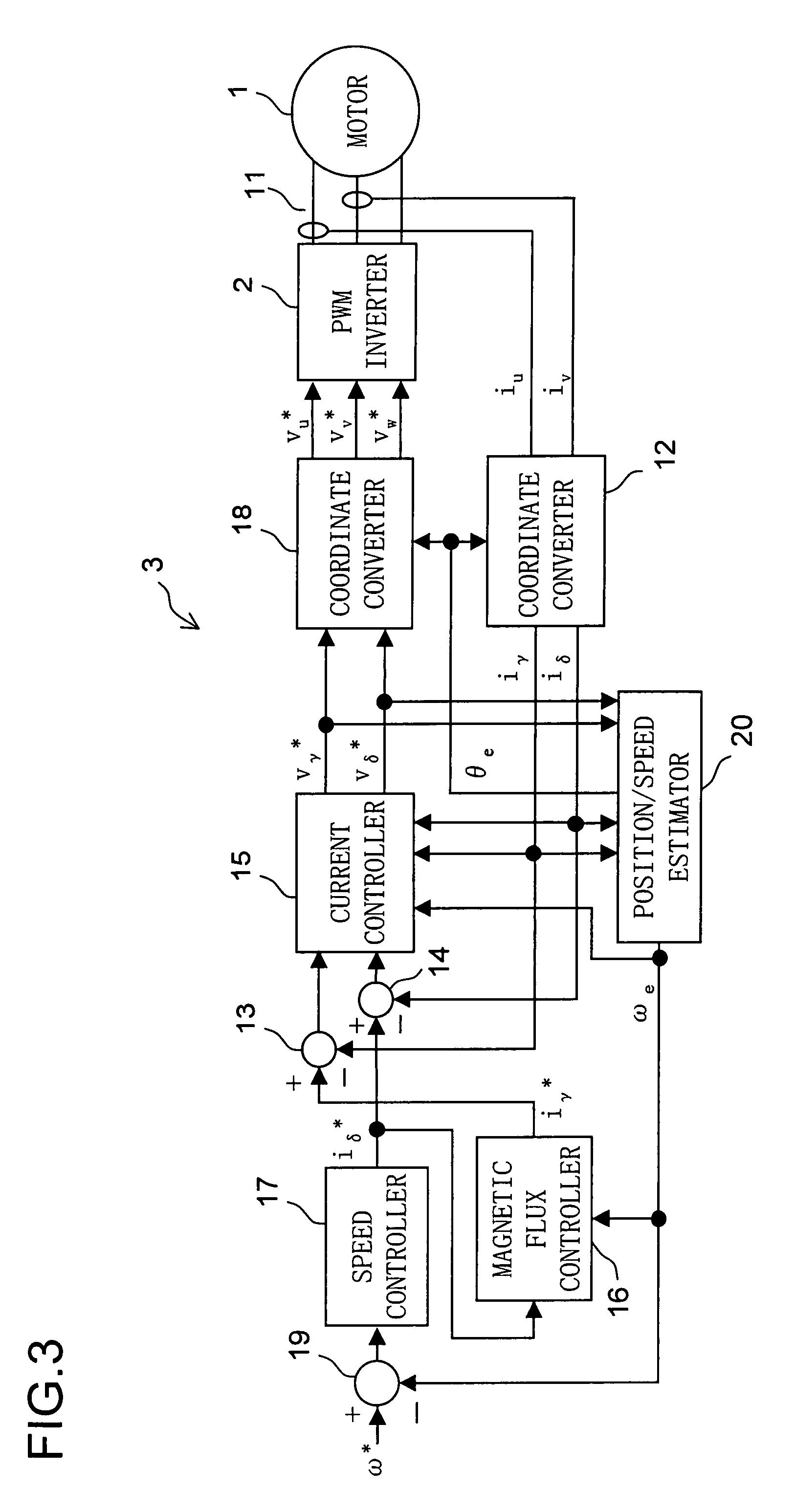
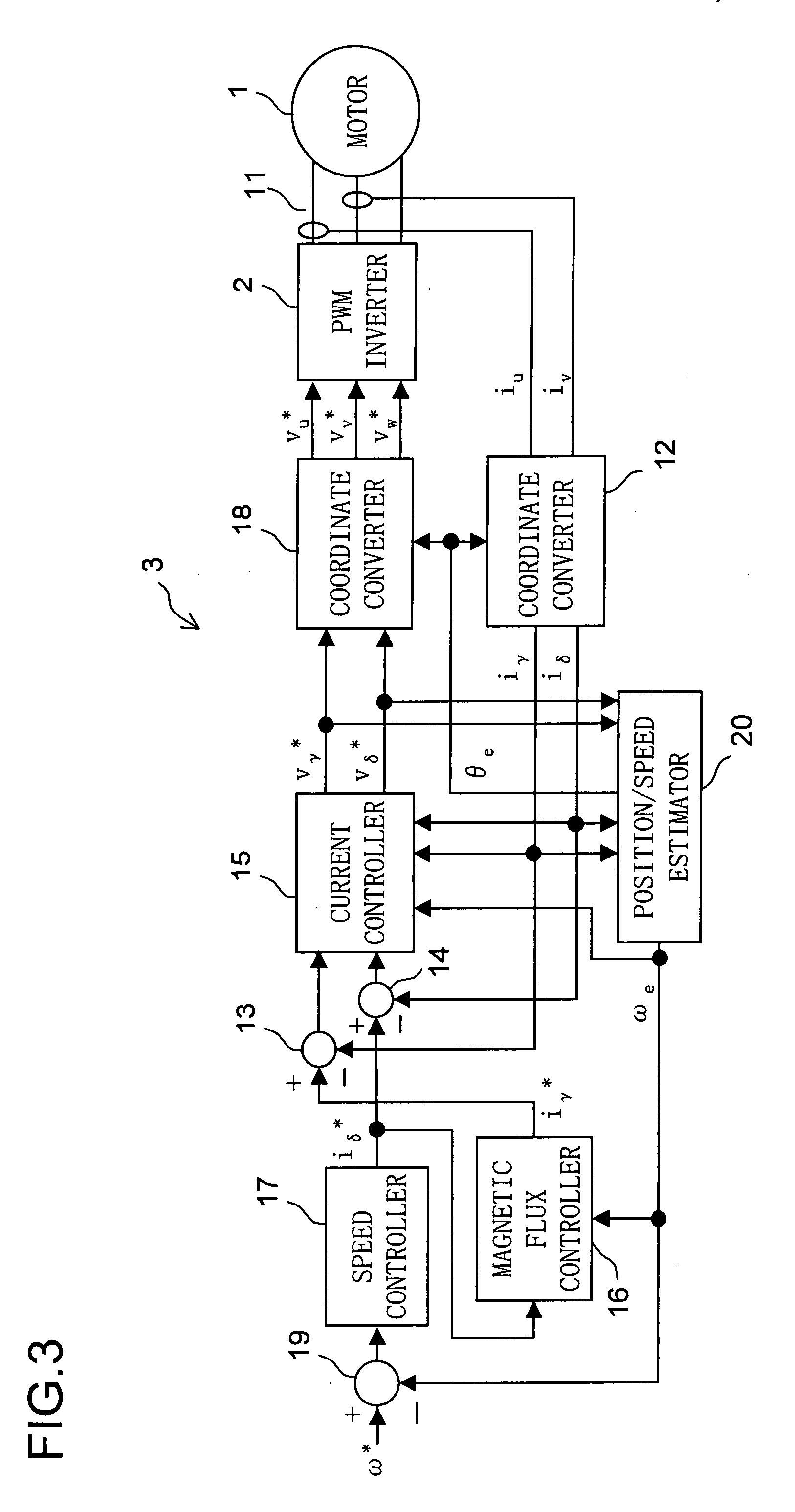
Motor control device
Let the rotating axis whose direction coincides with the direction of the current vector that achieves maximum torque control be called the qm-axis, and the rotating axis perpendicular to the qm-axis be called the dm-axis. A motor control device switches its operation between low-speed sensorless control and high-speed sensorless control according to the rotation speed of the rotor. In low-speed sensorless control, the magnetic salient pole of the motor is exploited, and the d-q axes are estimated by, for example, injection of a high-frequency rotating voltage. In high-speed sensorless control, the dm-qm axes are estimated based on, for example, the induction voltage produced by the rotation of the rotor. During high-speed sensorless control, the γ(dm)-axis current is kept at zero irrespective of the δ(qm)-axis current.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
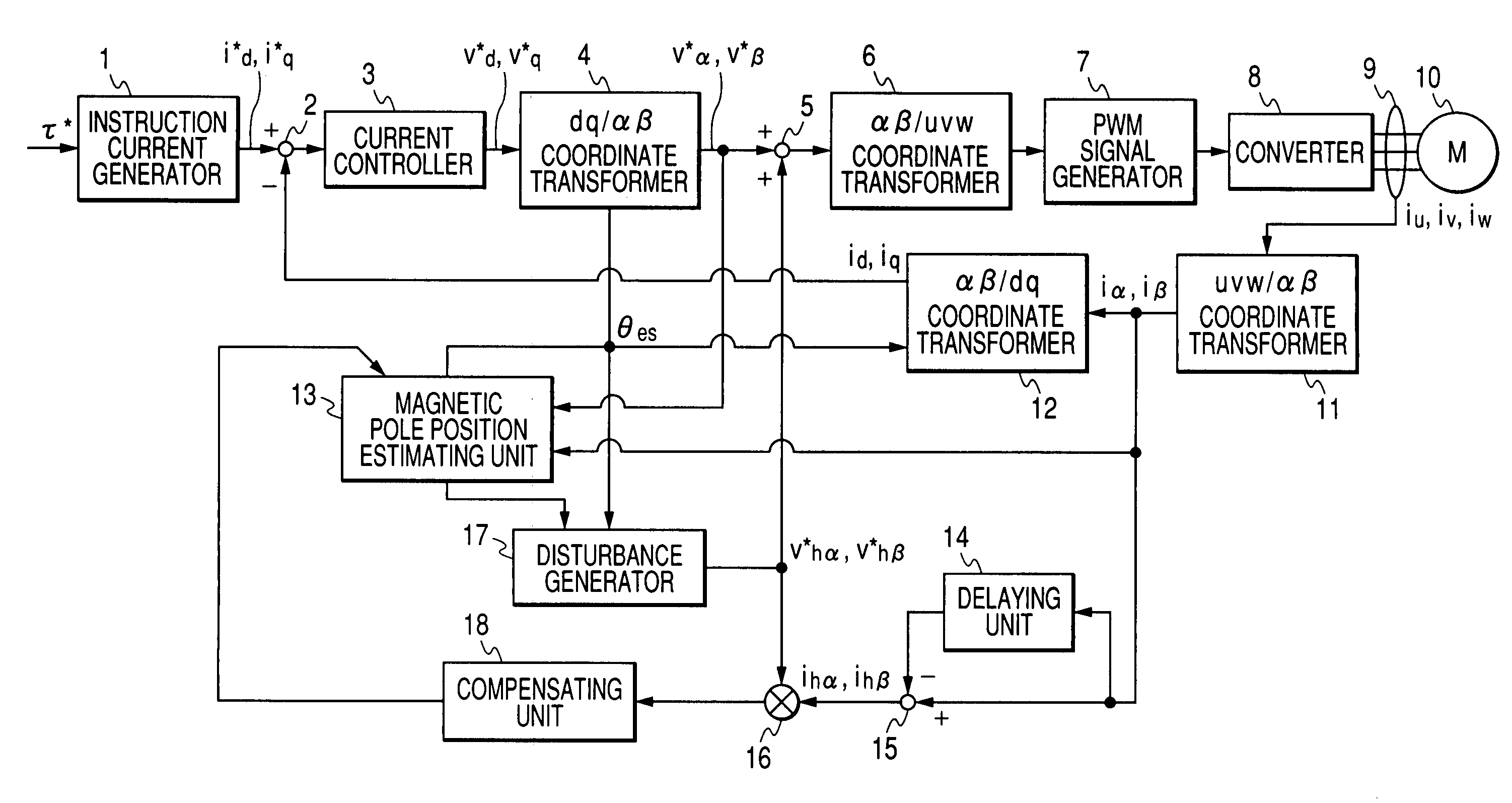
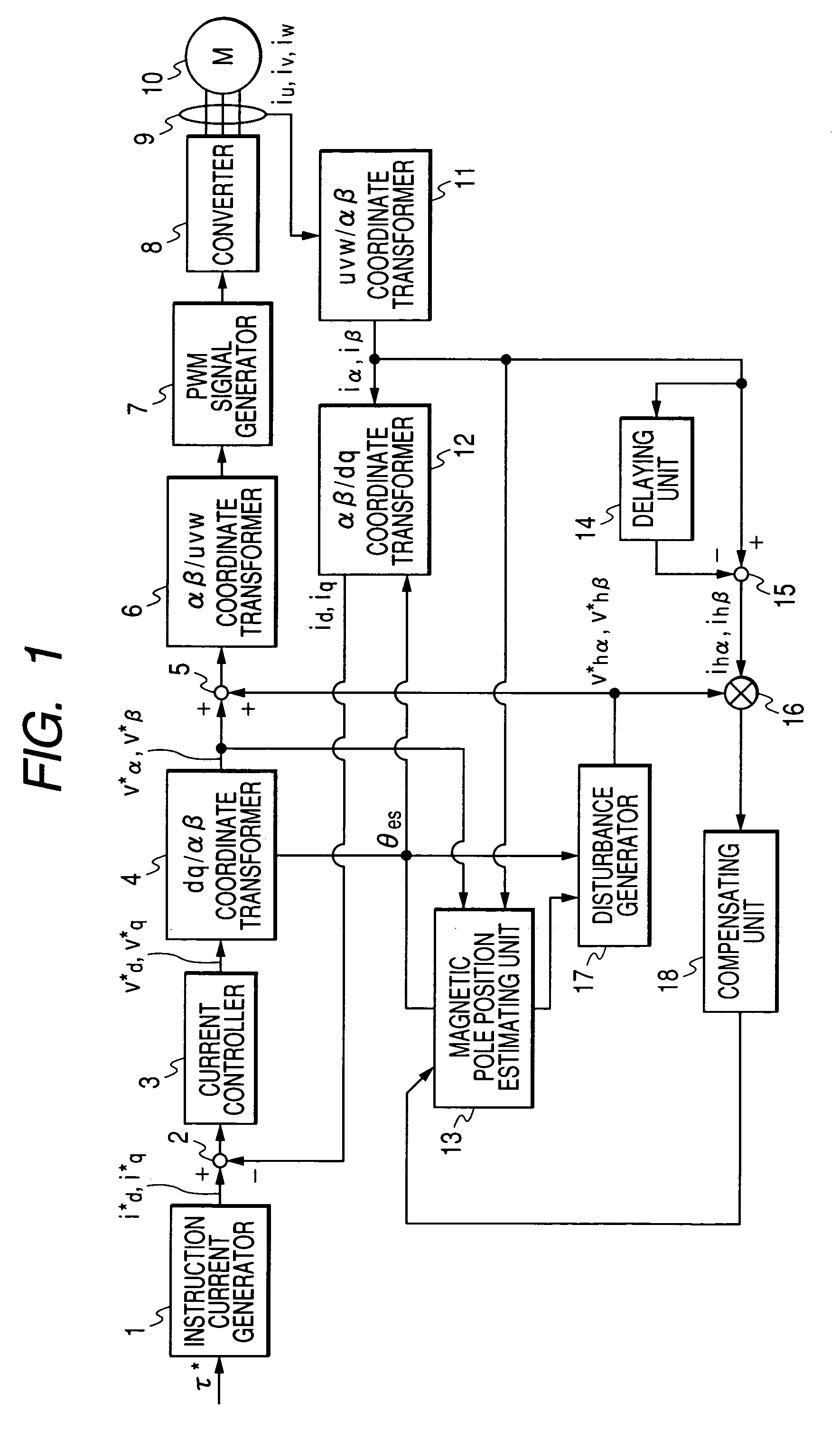
Method of estimating magnetic pole position in motor and apparatus of controlling the motor based on the estimated position
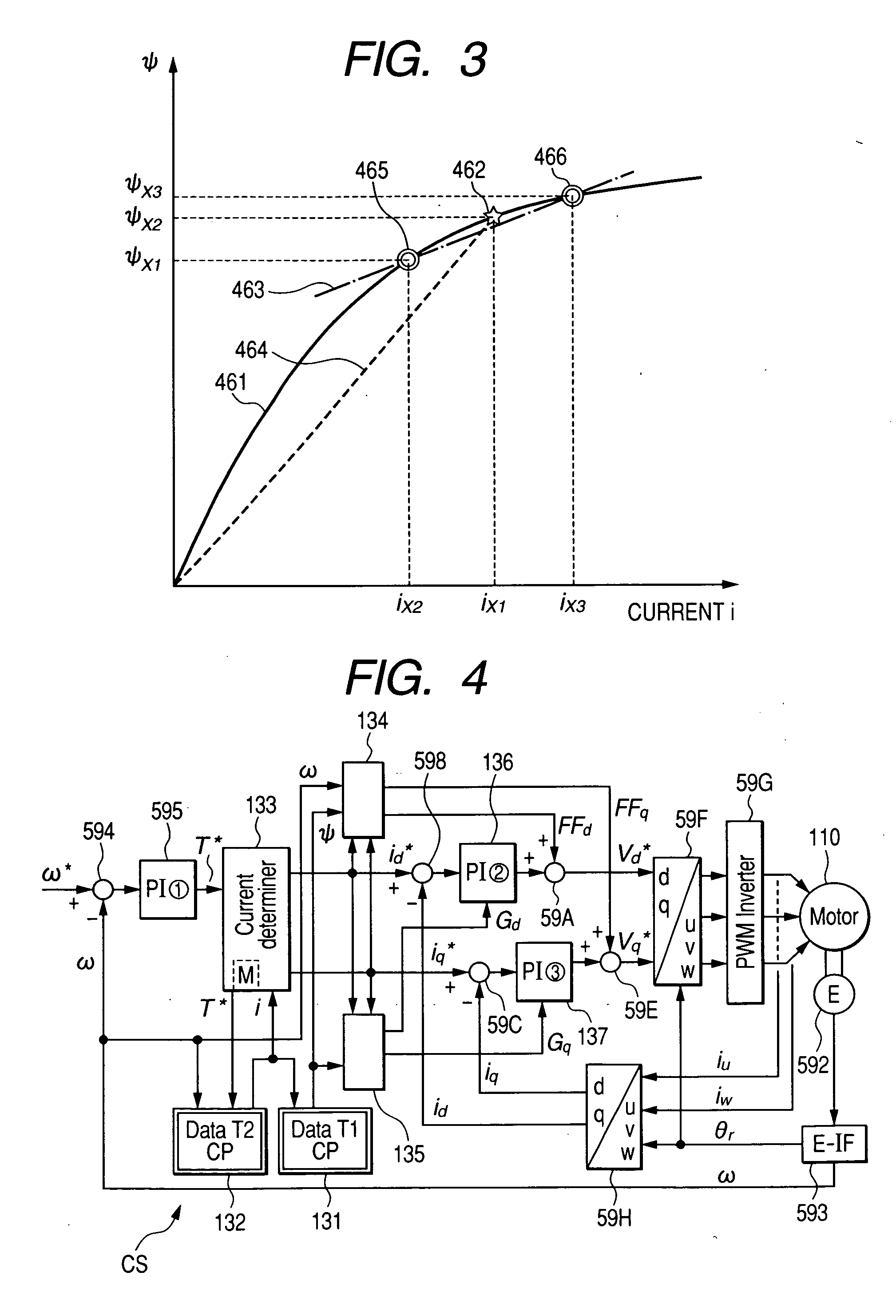
ActiveUS7352151B2Reduce the amount of calculationAccurate estimateSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsSynchronous motorPhase difference
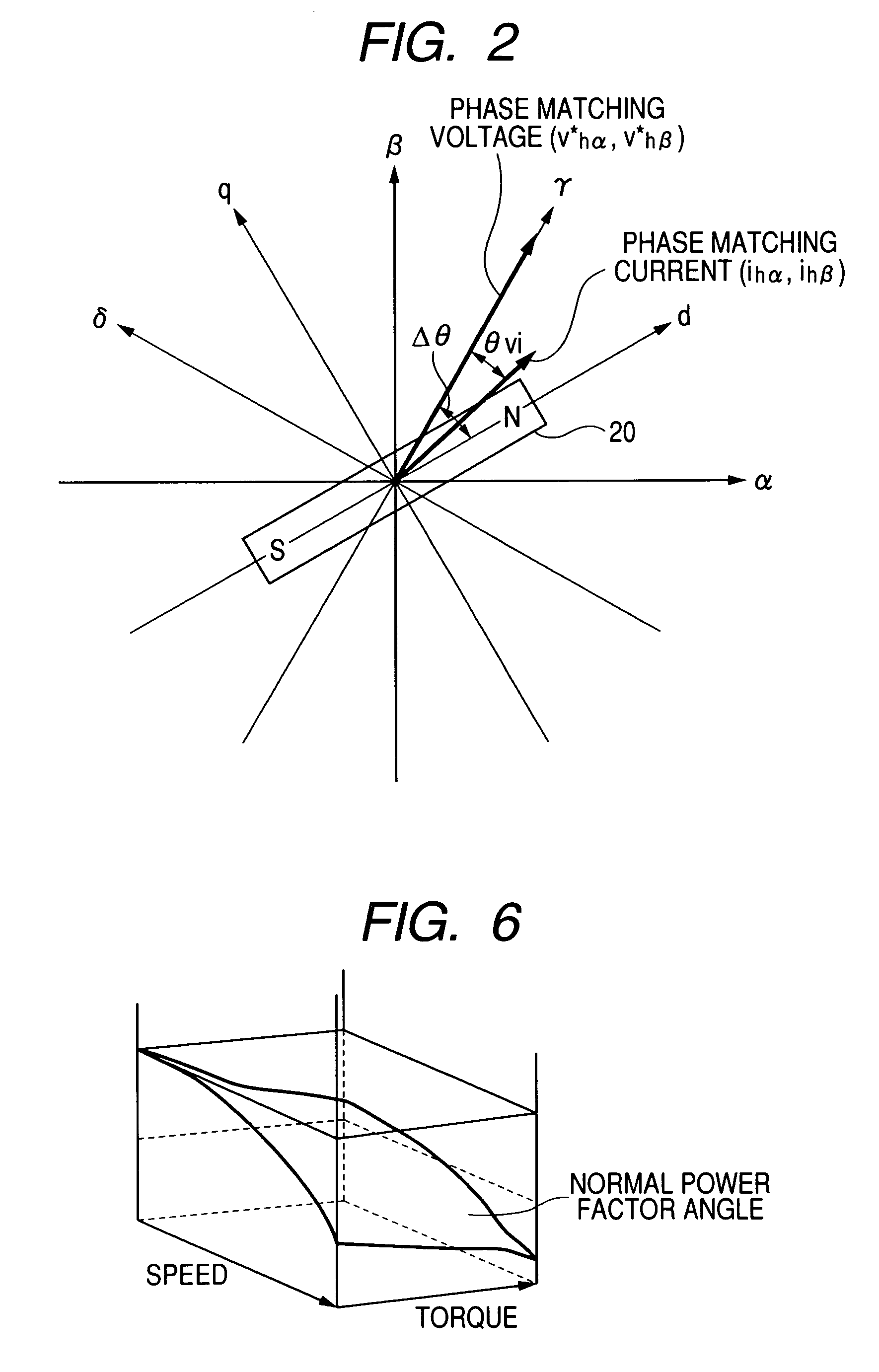
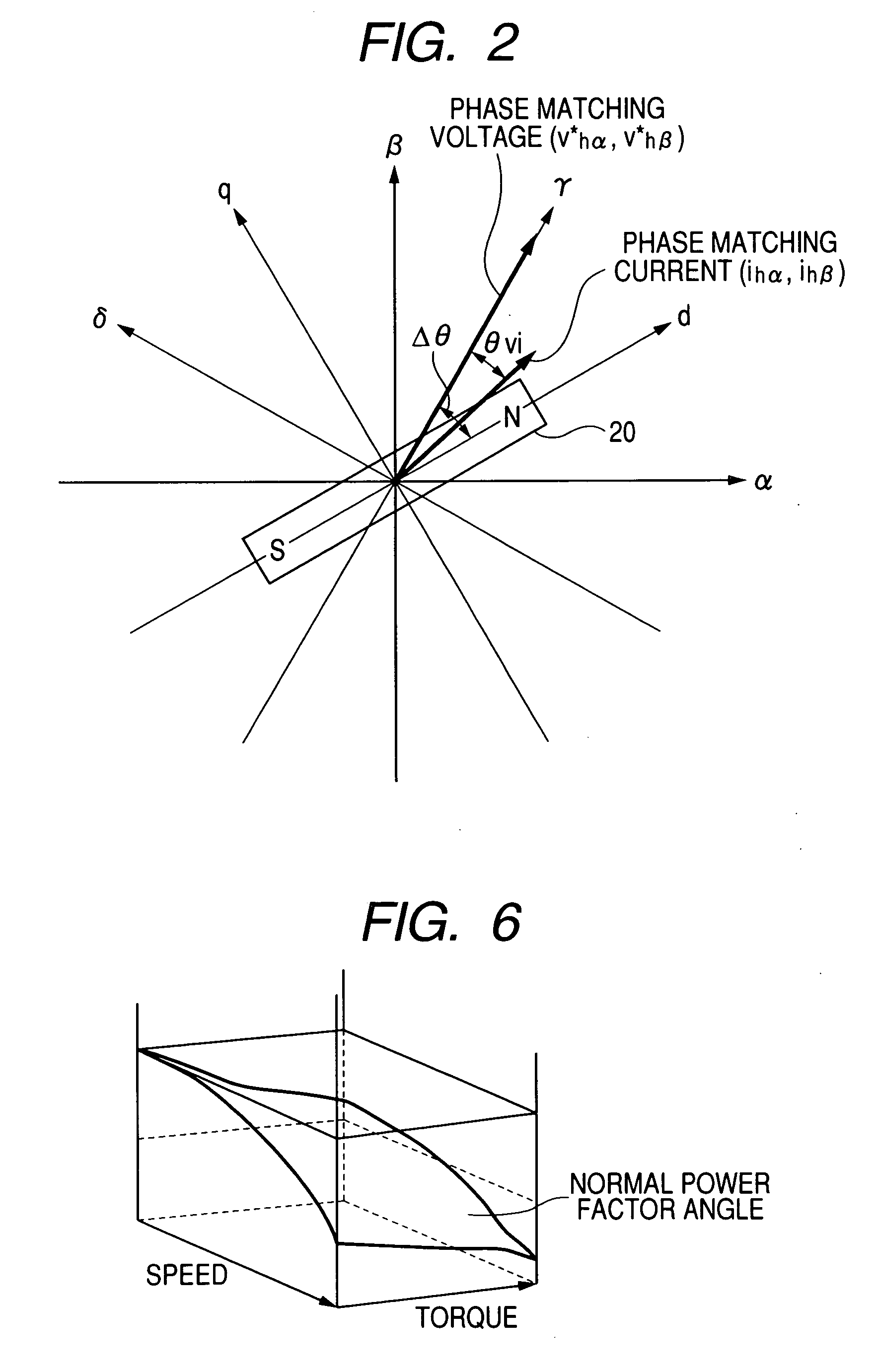
A magnetic pole position in a synchronous motor having salient poles is estimated from an instructed voltage applied to the motor, a current generated from the instructed voltage and parameters. To estimate the position substantially matching with a true magnetic pole position, a phase matching voltage having a phase matching with the estimated magnetic pole position previously obtained is applied to the motor. The phase matching voltage has a harmonic frequency higher than that of the instructed voltage. A phase matching current generated from the phase matching voltage is detected from the motor. A value of at least one of the parameters is corrected such that a difference in phase between the phase matching voltage and the phase matching current substantially becomes zero. An estimated magnetic pole position is calculated from the instructed voltage, the generated current and the parameter having the corrected value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor control device
Let the rotating axis whose direction coincides with the direction of the current vector that achieves maximum torque control be called the qm-axis, and the rotating axis perpendicular to the qm-axis be called the dm-axis. A motor control device switches its operation between low-speed sensorless control and high-speed sensorless control according to the rotation speed of the rotor. In low-speed sensorless control, the magnetic salient pole of the motor is exploited, and the d-q axes are estimated by, for example, injection of a high-frequency rotating voltage. In high-speed sensorless control, the dm-qm axes are estimated based on, for example, the induction voltage produced by the rotation of the rotor. During high-speed sensorless control, the γ(dm)-axis current is kept at zero irrespective of the δ(qm)-axis current.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
System and method for controlling motor using parameter associated with magnetic flux
InactiveUS7772790B2Reliably graspTorque ripple controlSynchronous motors startersDriving currentOperating point
A control method for a motor that rotates based on flux linkages to a winding member of the motor when the winding member is energized by a drive current is provided. The method includes storing magnetic-state information indicative of a relationship between each of a plurality of predetermined operating points of the drive current and a magnetic-state parameter associated with the flux linkages. The method includes obtaining at least one of command information associated with an operating state of the motor and detection information associated with the operating state of the motor. The method includes referencing the magnetic-state information with the use of the obtained at least one of the command information and detection information to obtain a value of the magnetic-state parameter based on a result of the reference. The method includes controlling an output of the motor based on the obtained value of the magnetic-state parameter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Control of a permanent-magnet motor
ActiveUS20100251511A1Less torqueEfficient processSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlControl systemPermanent magnet motor
A method of controlling a permanent-magnet motor that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the motor. The method includes varying the angle over which the winding is freewheeled in response to changes in speed of the motor. Additionally, a control system for a permanent-magnet motor, and a product incorporating the control system and motor.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Method of estimating magnetic pole position in motor and apparatus of controlling the motor based on the estimated position
ActiveUS20070085508A1Reduce the amount of calculationAccurate estimateSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsSynchronous motorPhase difference
A magnetic pole position in a synchronous motor having salient poles is estimated from an instructed voltage applied to the motor, a current generated from the instructed voltage and parameters. To estimate the position substantially matching with a true magnetic pole position, a phase matching voltage having a phase matching with the estimated magnetic pole position previously obtained is applied to the motor. The phase matching voltage has a harmonic frequency higher than that of the instructed voltage. A phase matching current generated from the phase matching voltage is detected from the motor. A value of at least one of the parameters is corrected such that a difference in phase between the phase matching voltage and the phase matching current substantially becomes zero. An estimated magnetic pole position is calculated from the instructed voltage, the generated current and the parameter having the corrected value.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor control device
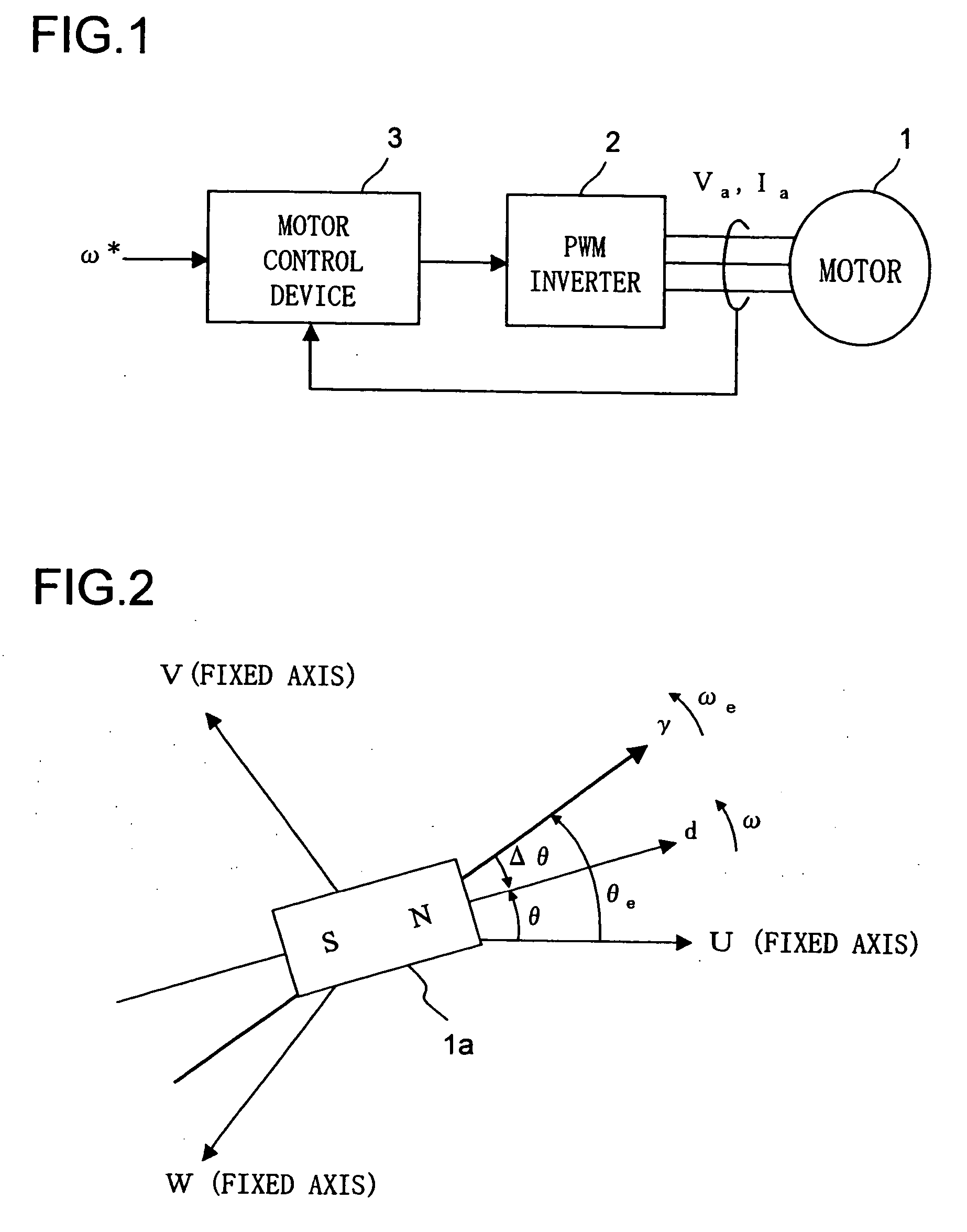
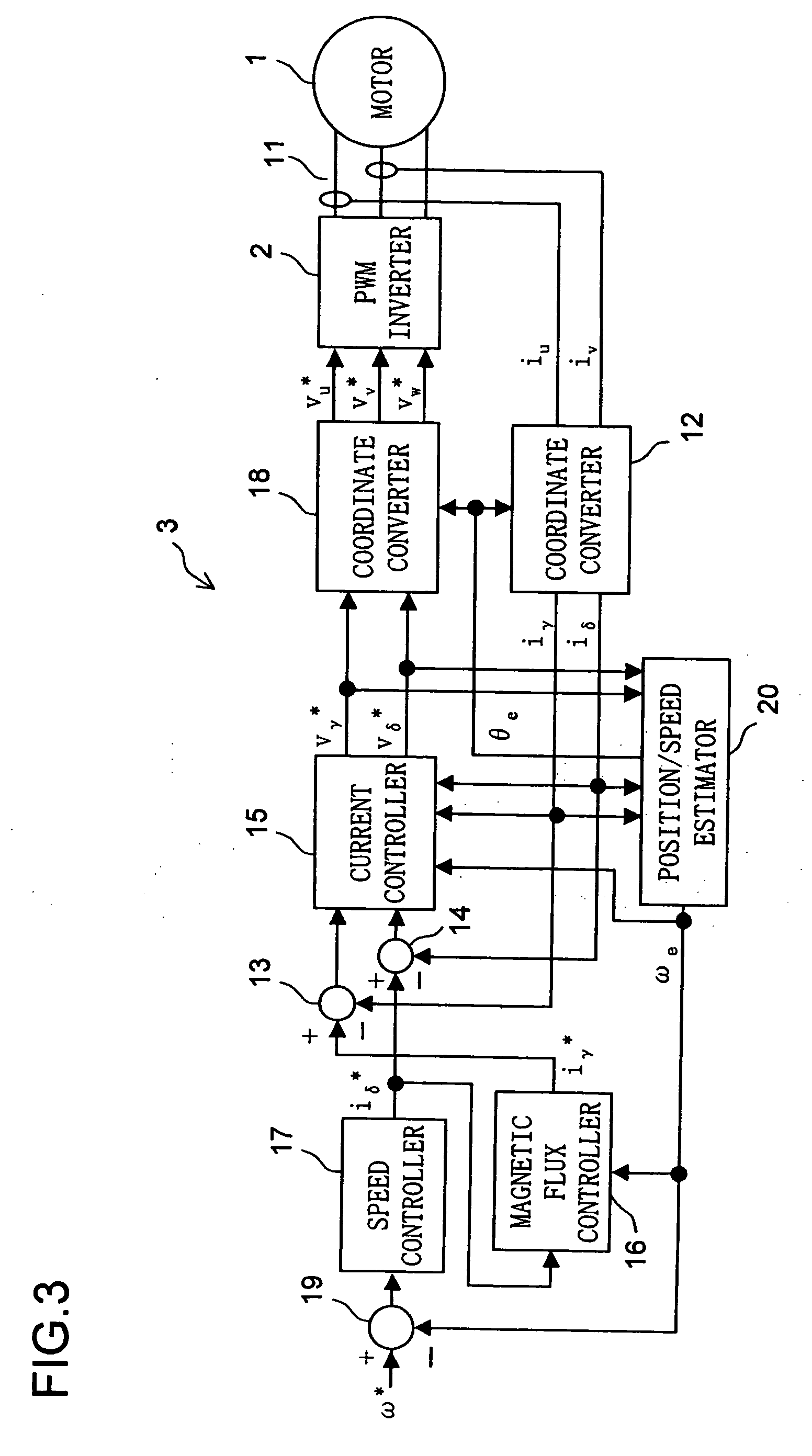
ActiveUS20070046249A1Reduce the amount of calculationEasy to adjustSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlMotor controlInductance
A motor control device includes an estimator for estimating a rotor position of a motor having a salient pole by using a value corresponding to a q-axis inductance of the motor as an operation parameter where an estimated axes for the control corresponding to d-q axes are γ-δ axes, and a controller for controlling the motor based on the estimated rotor position. The estimator generates a deviation between a d-axis and a γ-axis by performing the estimation of the rotor position based on a value between a real q-axis inductance and a real d-axis inductance of the motor adopted as the operation parameter. The controller controls the motor so that a γ-axis component of a motor current supplied to the motor is maintained to be a predetermined value of zero or close to zero regardless of a value of a δ-axis component of the motor current.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
High-speed electric system
ActiveUS20100251509A1Improve efficiencyConstant output powerSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlElectric machineControl system
An electric system that includes a single-phase permanent-magnet electric machine and a control system for driving the electric machine under load at speeds in excess of 60 krpm. Additionally, a product that includes the electric system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
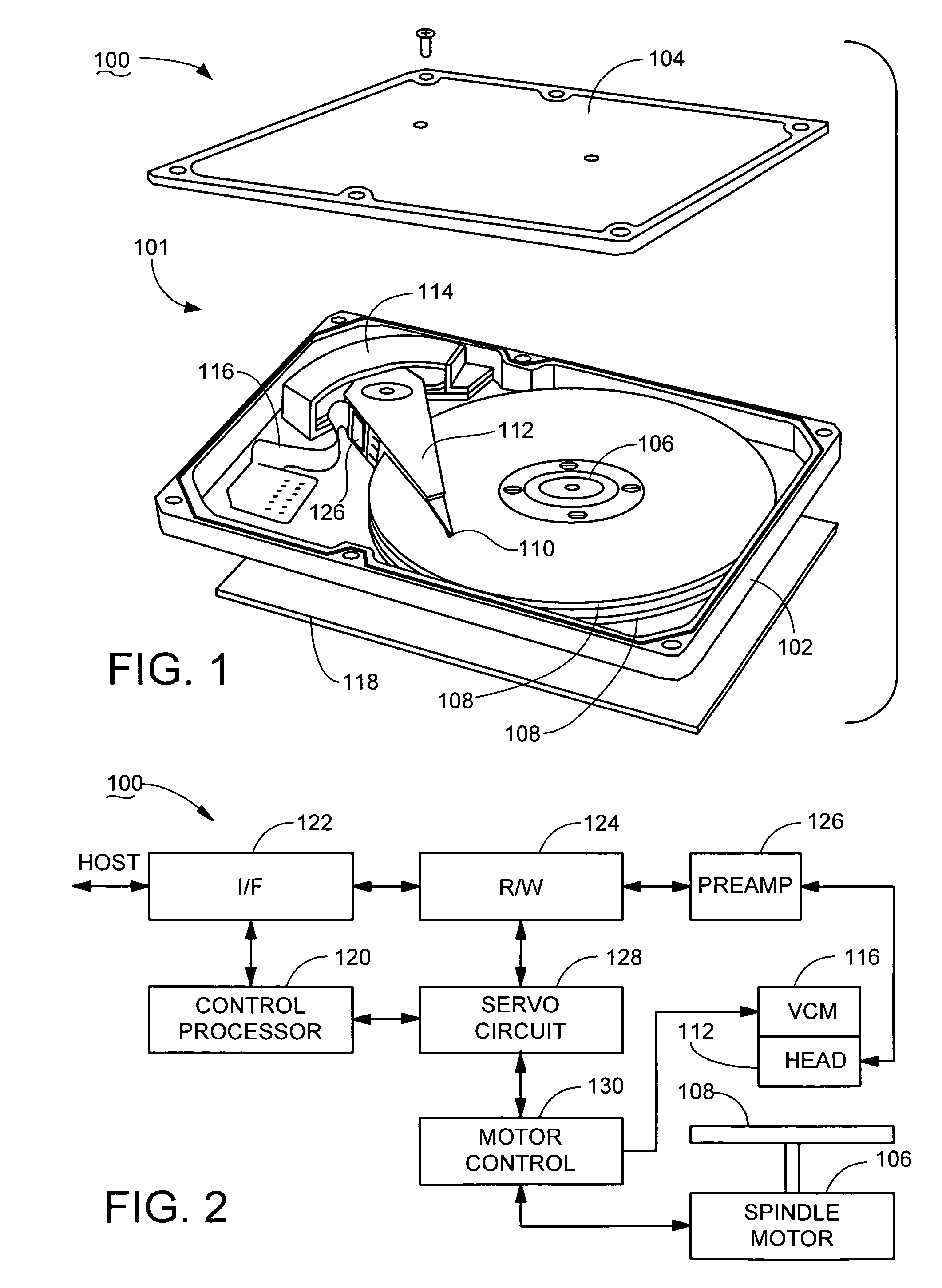
Closed-loop rotational control of a brushless dc motor
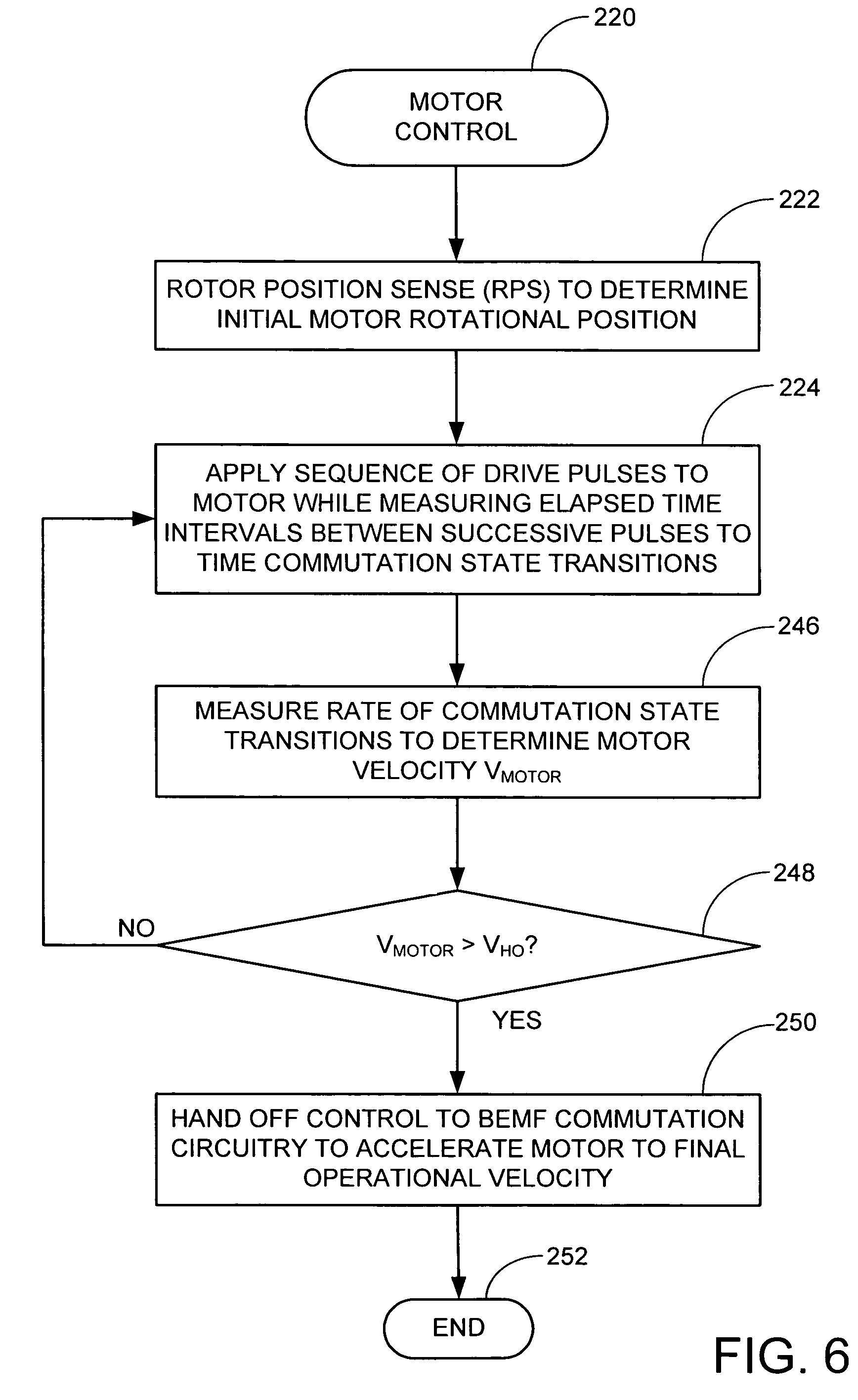
InactiveUS7432677B2Faster and efficient closed-loop accelerationReducing the potential for inadvertently rotating the motorMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersClosed loopPeak value
Method and apparatus for controlling a brushless dc motor, such as the type used in a data storage device to rotate data storage media. A sequence of drive pulses is applied to rotate the motor. The sequence is switched from first to second motor commutation states at a time determined in relation to changes in elapsed time between successive pulses in the sequence. Each drive pulse has a duration established in relation to an inductance of the motor, and is separated from adjacent pulses by an intermediate delay of predetermined value. A peak elapsed time interval between successive pulses is identified, and the next commutation state is switched in at a selected time after the peak time interval. The sequence preferably accelerates the motor from rest to an intermediate velocity, after which back electromotive force (bemf) commutation is used to accelerate the motor to a final operational velocity.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
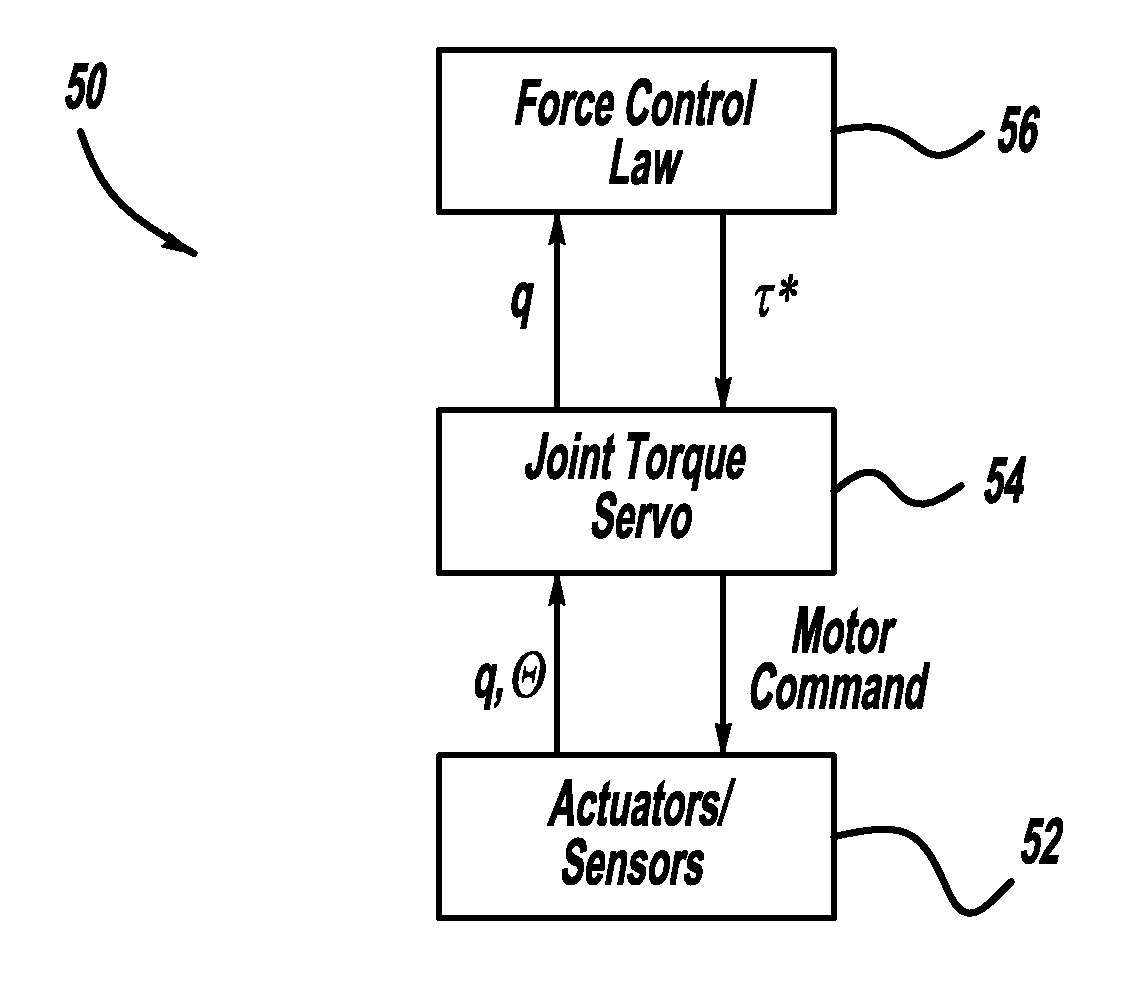
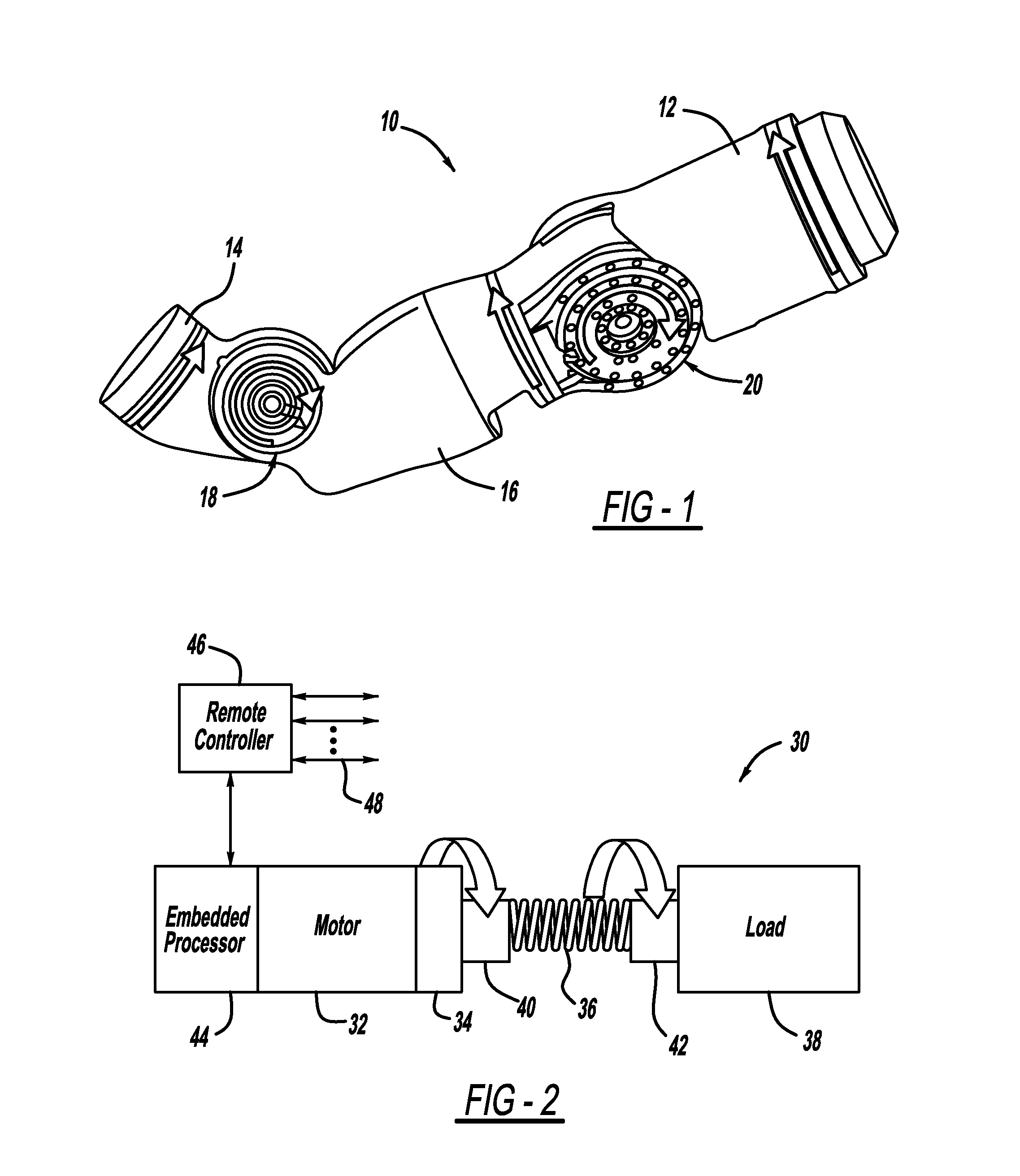
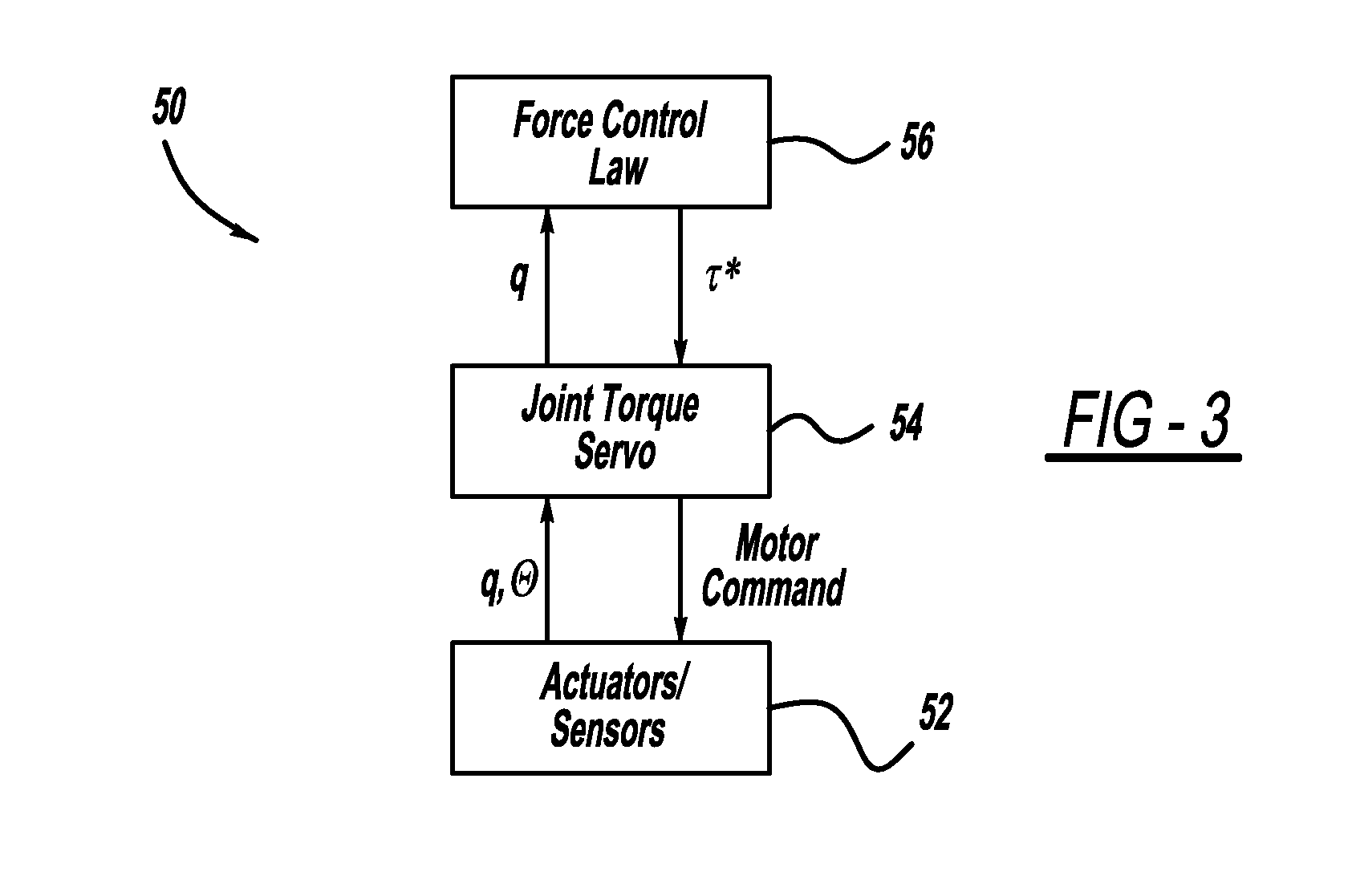
Architecture for robust force and impedance control of series elastic actuators
An SEA architecture for controlling the torque applied by an SEA that has particular application for controlling the position of a robot link. The SEA architecture includes a motor coupled to one end of an elastic spring and a load coupled to an opposite end of the elastic spring, where the motor drives the load through the spring. The orientation of the shaft of the motor and the load are measured by position sensors. Position signals from the position sensors are sent to an embedded processor that determines the orientation of the load relative to the motor shaft to determine the torque on the spring. The embedded processor receives reference torque signals from a remote controller, and the embedded processor operates a high-speed servo loop about the desired joint torque. The remote controller determines the desired joint torque based on higher order objectives by their impedance or positioning objectives.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC +1
Control of a brushless motor
ActiveUS8643319B2Reduce peak magnetic flux densityEfficient and small motorSingle-phase induction motor startersAc-dc conversion without reversalBrushless motorsMotor speed
A method of controlling a brushless motor that includes rectifying an alternating voltage to provide a rectified voltage, and exciting a winding of the motor with the rectified voltage. The winding is excited in advance of predetermined rotor positions by an advance period and is excited for a conduction period over each electrical half-cycle of the motor. The length the advance period and / or the conduction period is defined by a waveform that varies periodically with time. The method then includes adjusting the phase of the waveform relative to the alternating voltage in response to a change in one of motor speed and RMS value of the alternating voltage. Additionally, a control system that implements the method, and a motor system that incorporates the control system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Synchronous machine control apparatus
InactiveUS20130249448A1High precision temperatureElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMachine controlMagnetic flux
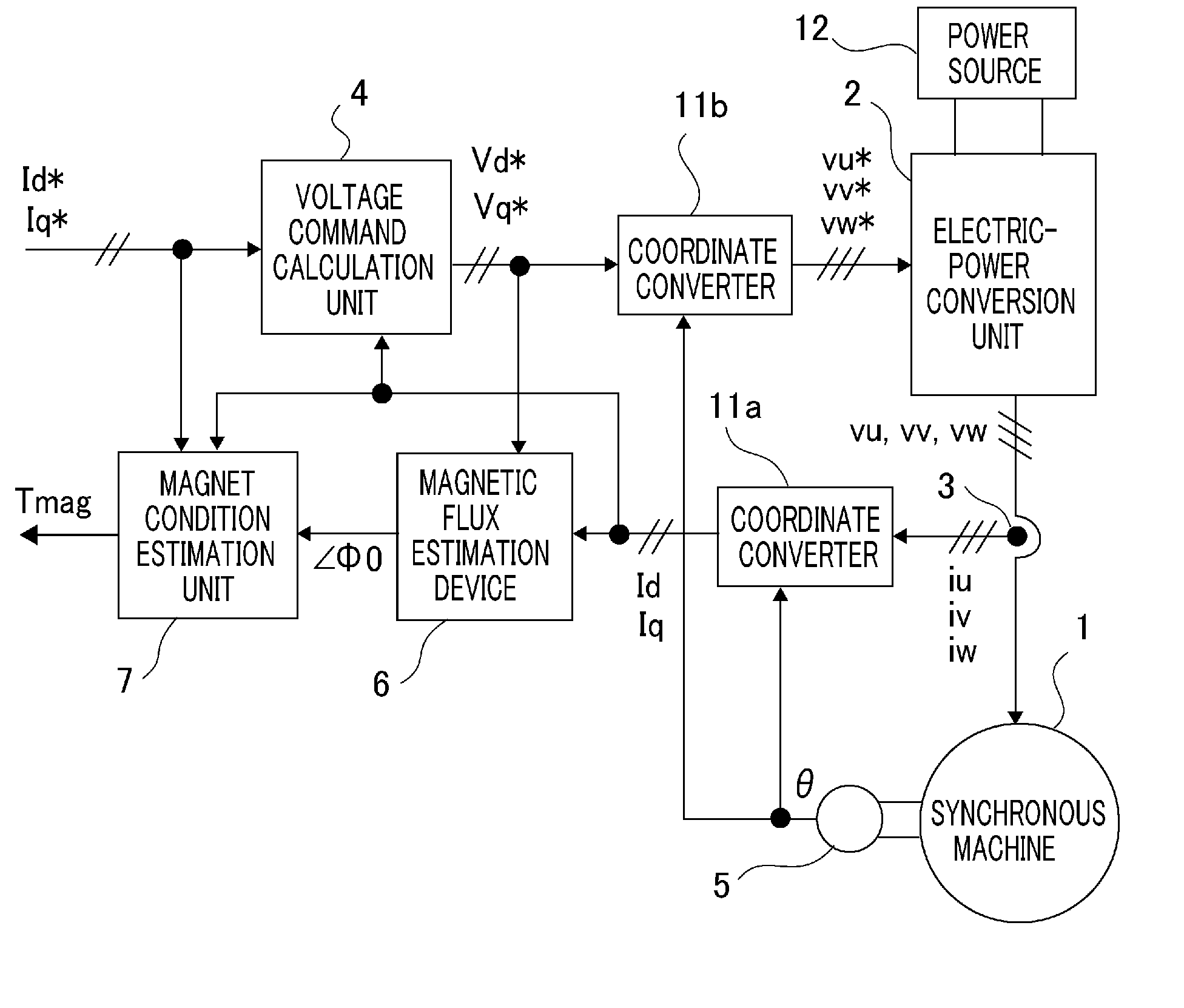
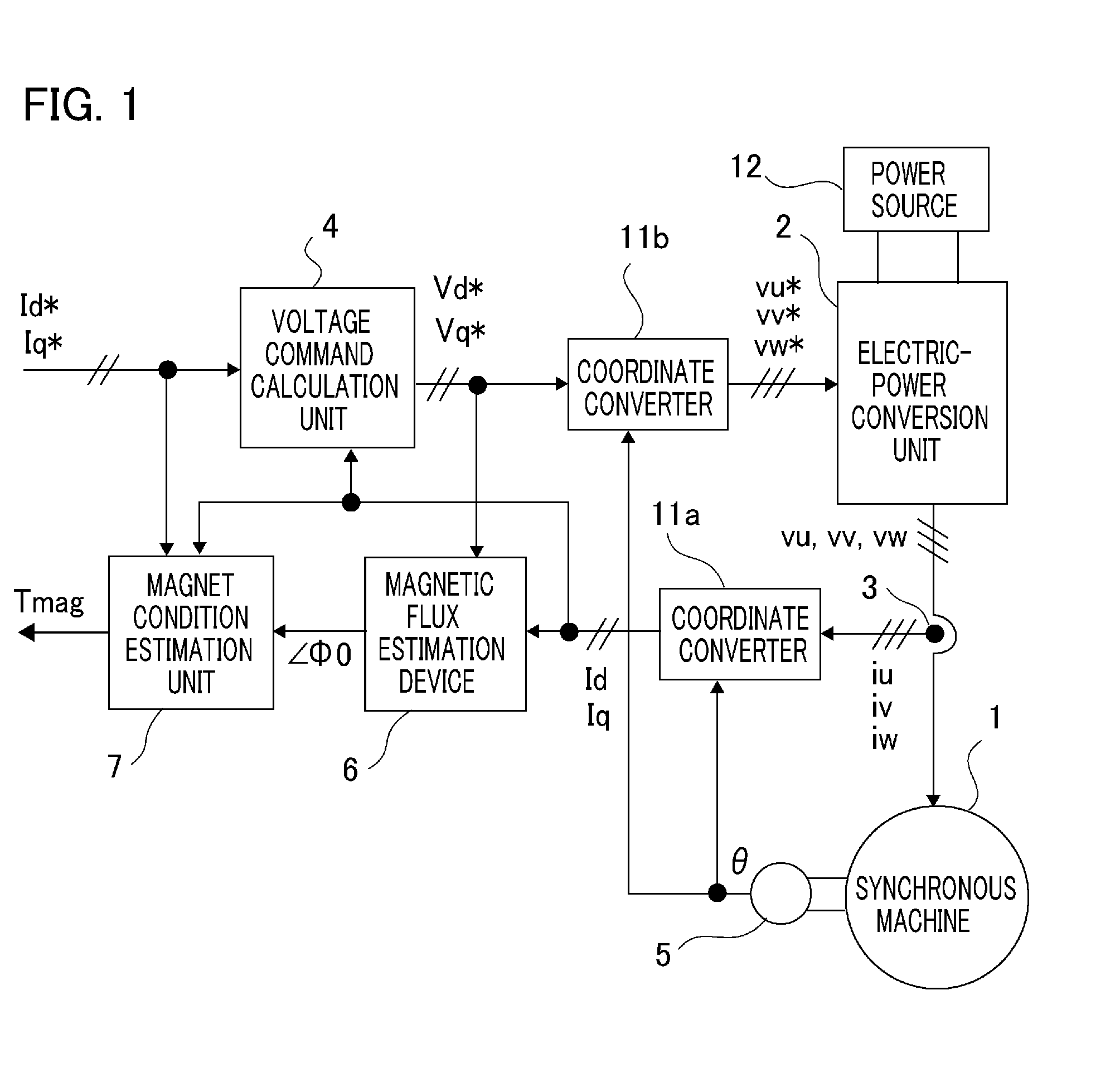
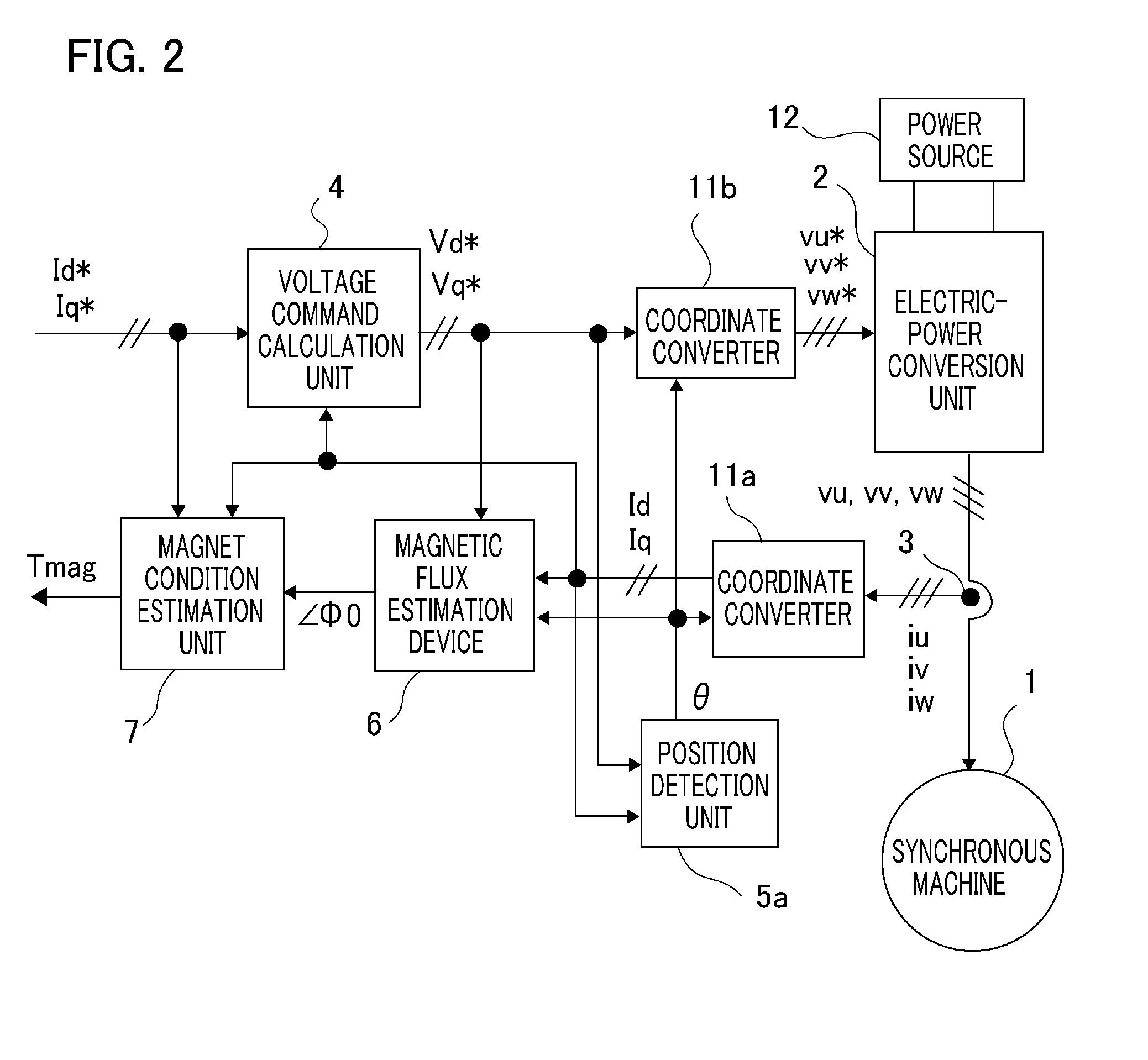
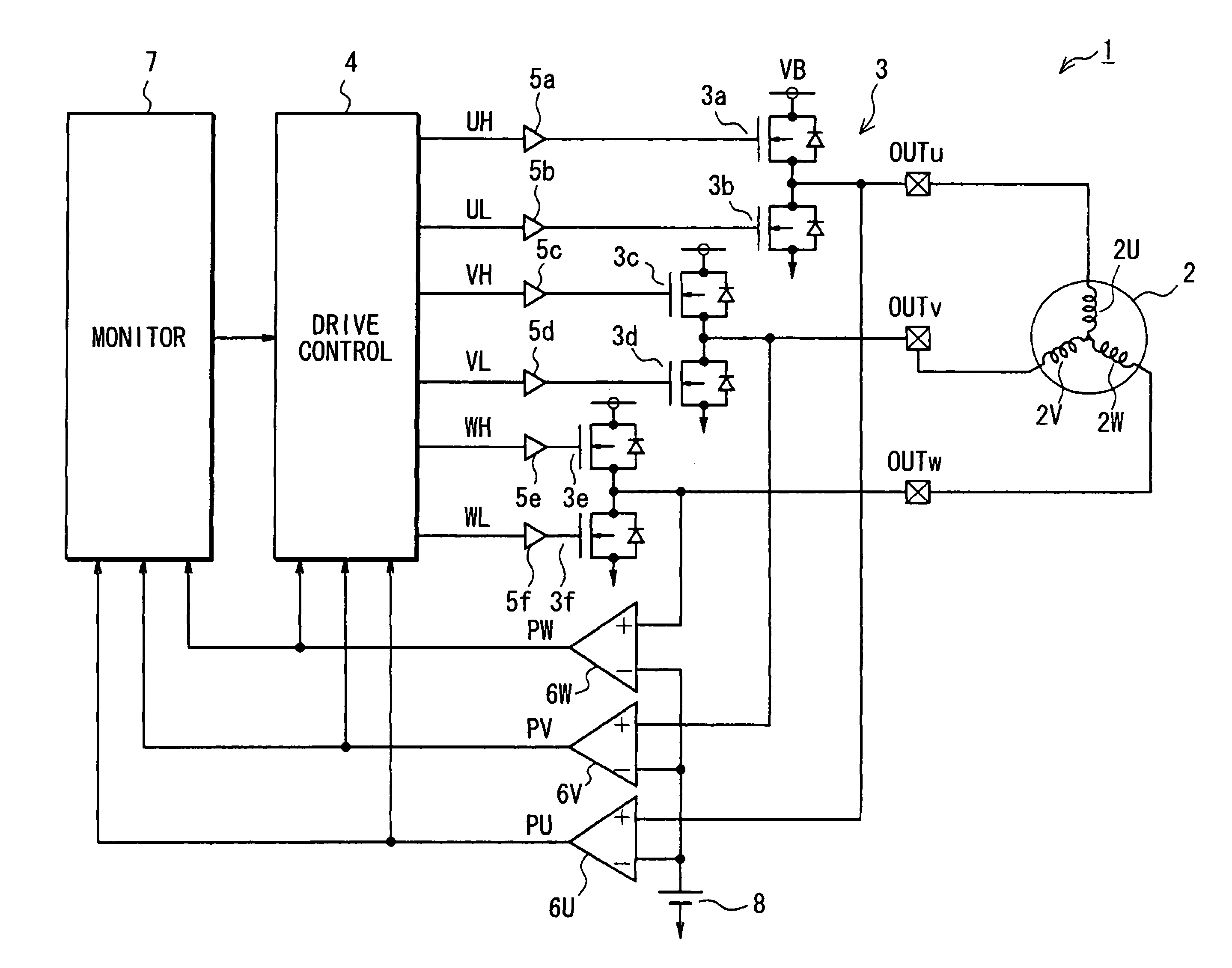
A synchronous machine control apparatus is characterized by including a magnet condition estimation unit (7, 7a) that estimates the temperature or the magnetic flux of a permanent magnet that forms the magnetic field of a synchronous machine (1), and is characterized in that the magnet condition estimation unit (7, 7a) coordinate-converts an armature current into currents on the γ-δ axis consisting of the γ axis and the δ axis that is perpendicular to the γ axis, based on the rotor position and the estimated γ axis, and estimates the temperature or the magnetic flux of the permanent magnet, based on the control command for the synchronous machine (1) and the γ-δ axis currents.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for driving rotary machine
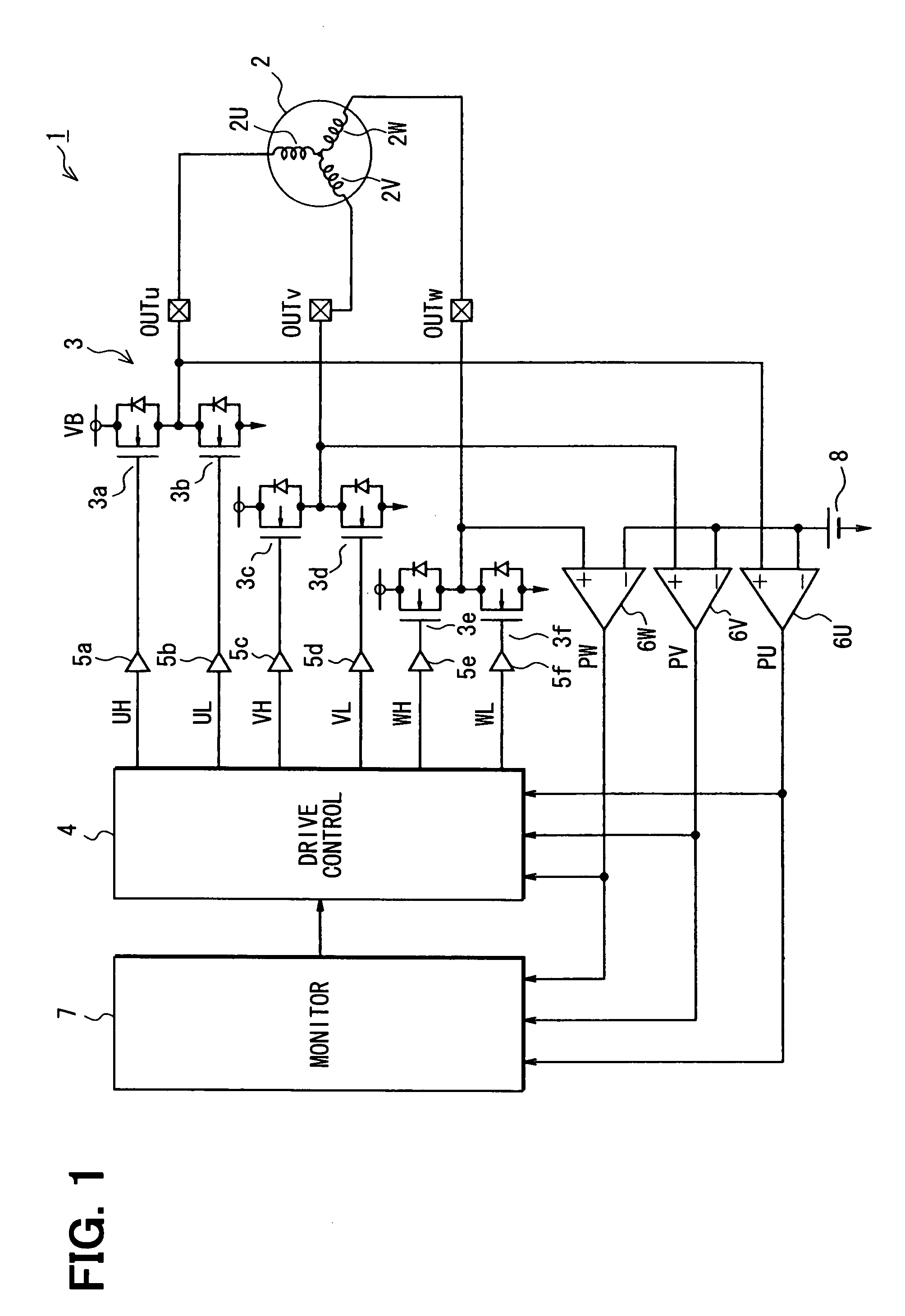
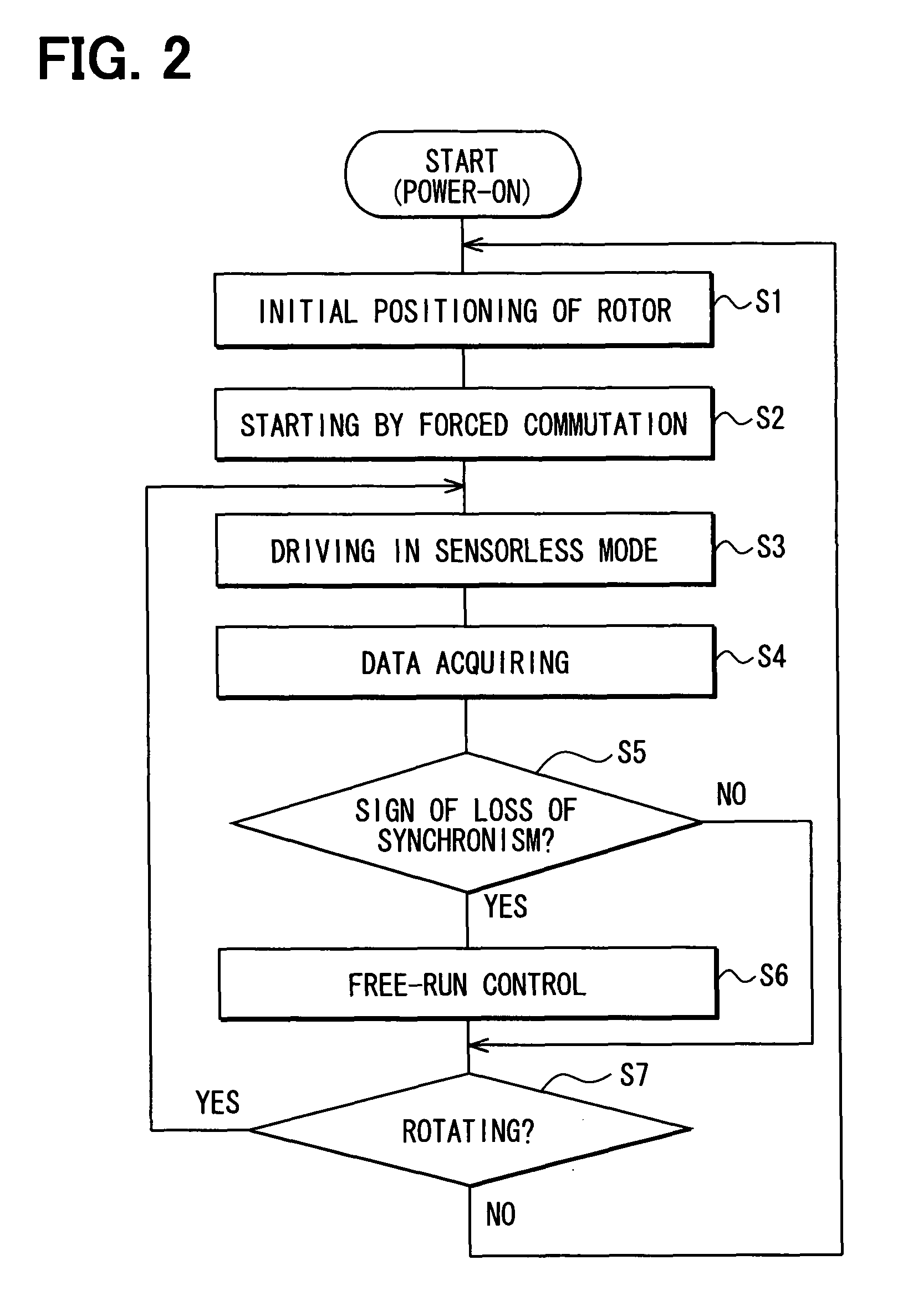
InactiveUS7893638B2Loss of stateShort timeMotor/generator/converter stoppersCommutation monitoringEngineeringControl switch
A motor driving apparatus has a loss-of-synchronism monitoring circuit that monitors the rotation of a rotary machine such as a brushless DC motor to detect a sign of transition to a state of loss of synchronism. When the sign is detected, an energization control circuit temporarily stops driving of the rotary machine to bring it into a free running state, and thereafter carries out control so as to resume driving of the rotary machine. Further, the motor driving apparatus has an inverter and a drive control circuit that controls switching operation of the inverter based on rotation of the rotary machine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com