Operating a rotatable media storage device at multiple spin-speeds
a technology of rotatable media and storage devices, which is applied in the direction of digital signal error detection/correction, instruments, recording signal processing, etc., can solve the problems of head damage, data damage permanent, and damage to both disk surfaces and heads
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
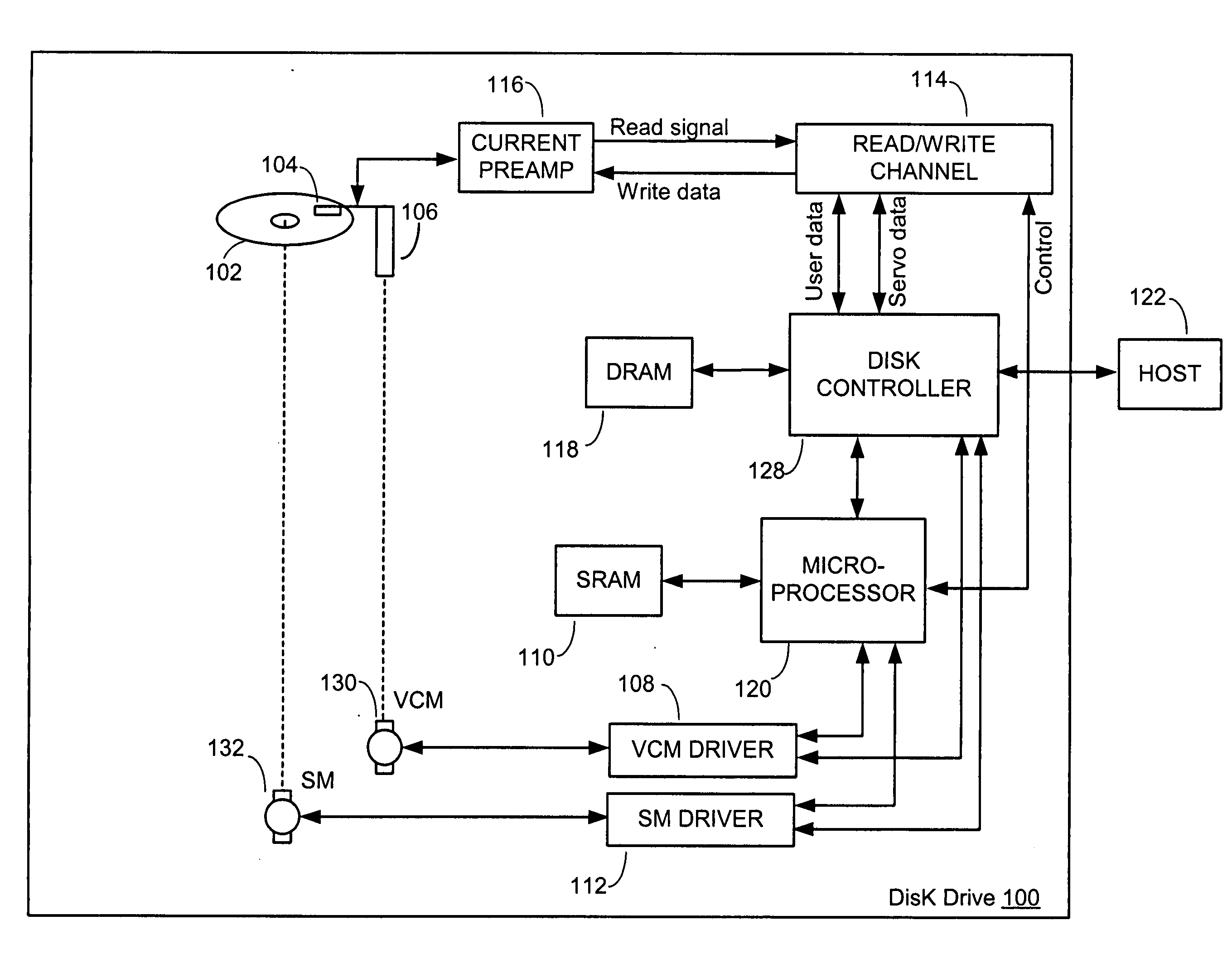
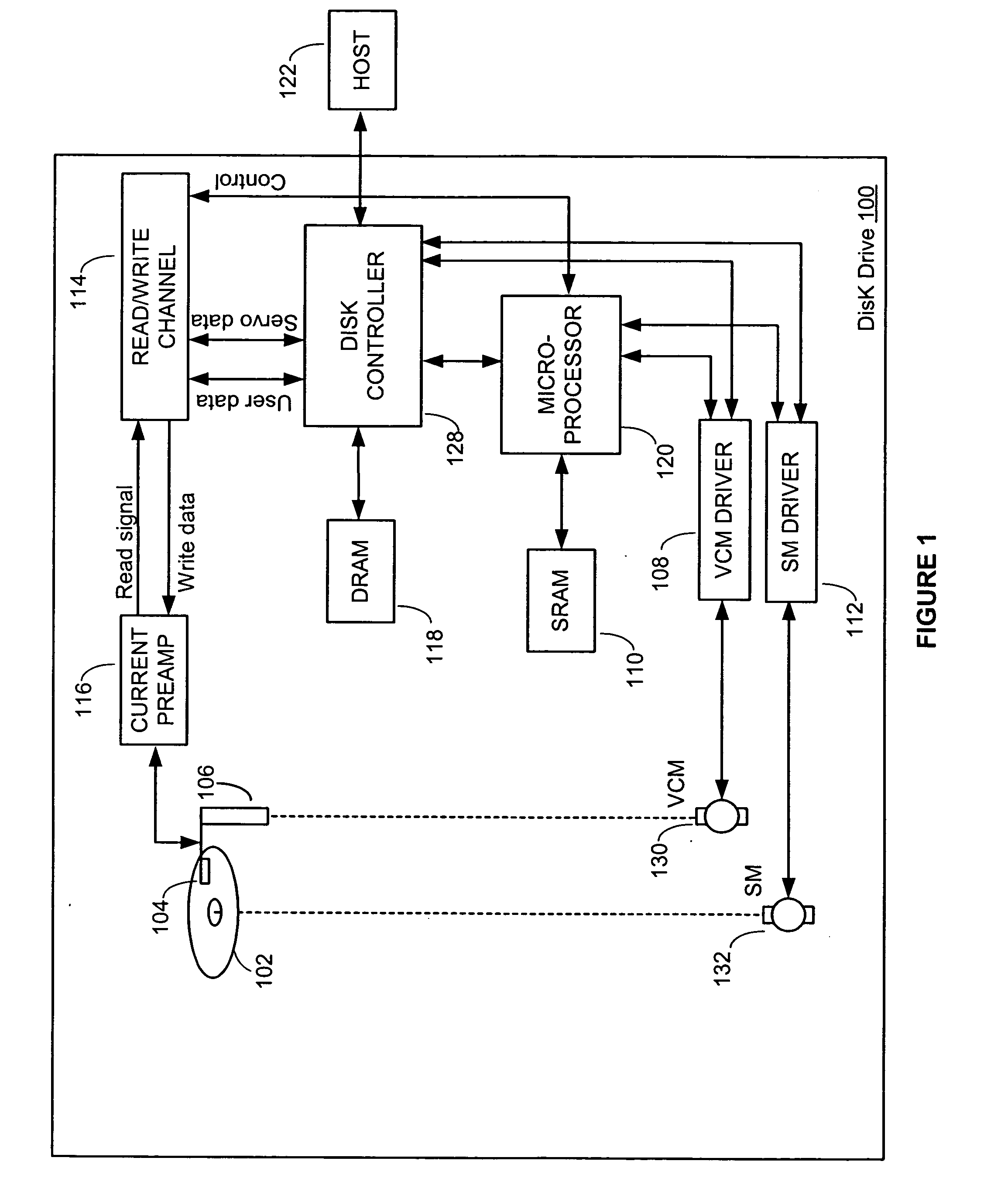
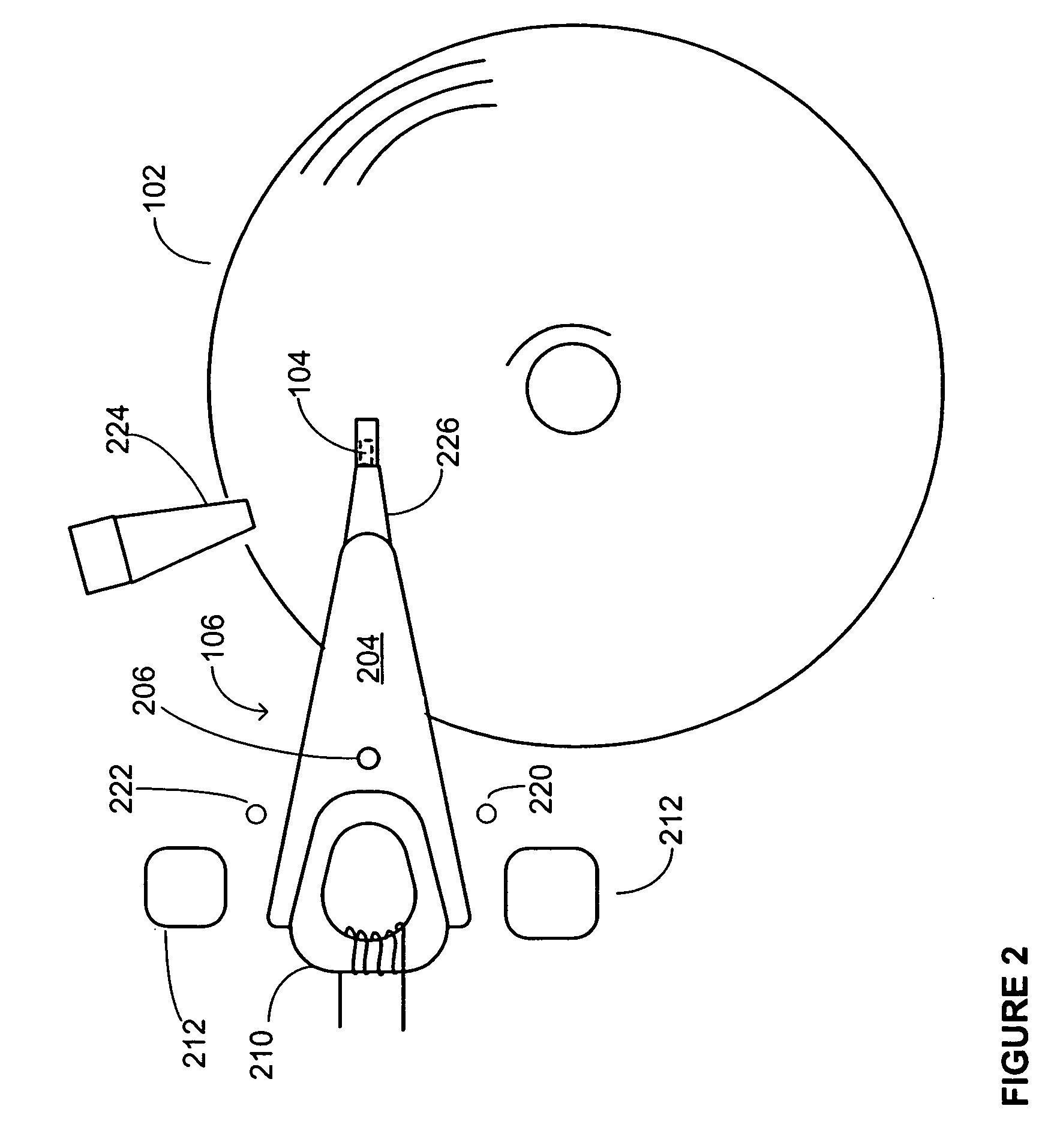
[0022] Embodiments of the present invention are useful for reducing the amount of time it takes for a head to begin reading from and / or writing to a disk, after an actuator assembly has been parked on a load / unload ramp and the disk has not been rotating. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a disk spin-speed is monitored as a disk spins up from rest. The disk may have been at rest, for example, because the drive had just been powered on, or because the drive had been in a power saving (e.g., idle) mode. In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, the drives “time-to-ready” is reduced by beginning a ramp load operation before the disk spin-speed reaches its nominal spin-speed, and in accordance with specific embodiments, even before the disk spin-speed achieves a minimum float spin-speed for causing the head to float over a surface of the disk. However, before explaining further details and embodiments of the present invention, it is first useful...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com