Patents
Literature
94 results about "Environmental variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environmental variation. the ability of an organism to alter greatly its PHENOTYPE depending upon environmental conditions. The phenomenon is seen most clearly in plants, perhaps because they are fixed in the ground. For example, a dandelion will produce an erect habit with long flower stalks if in a garden border with other plants.
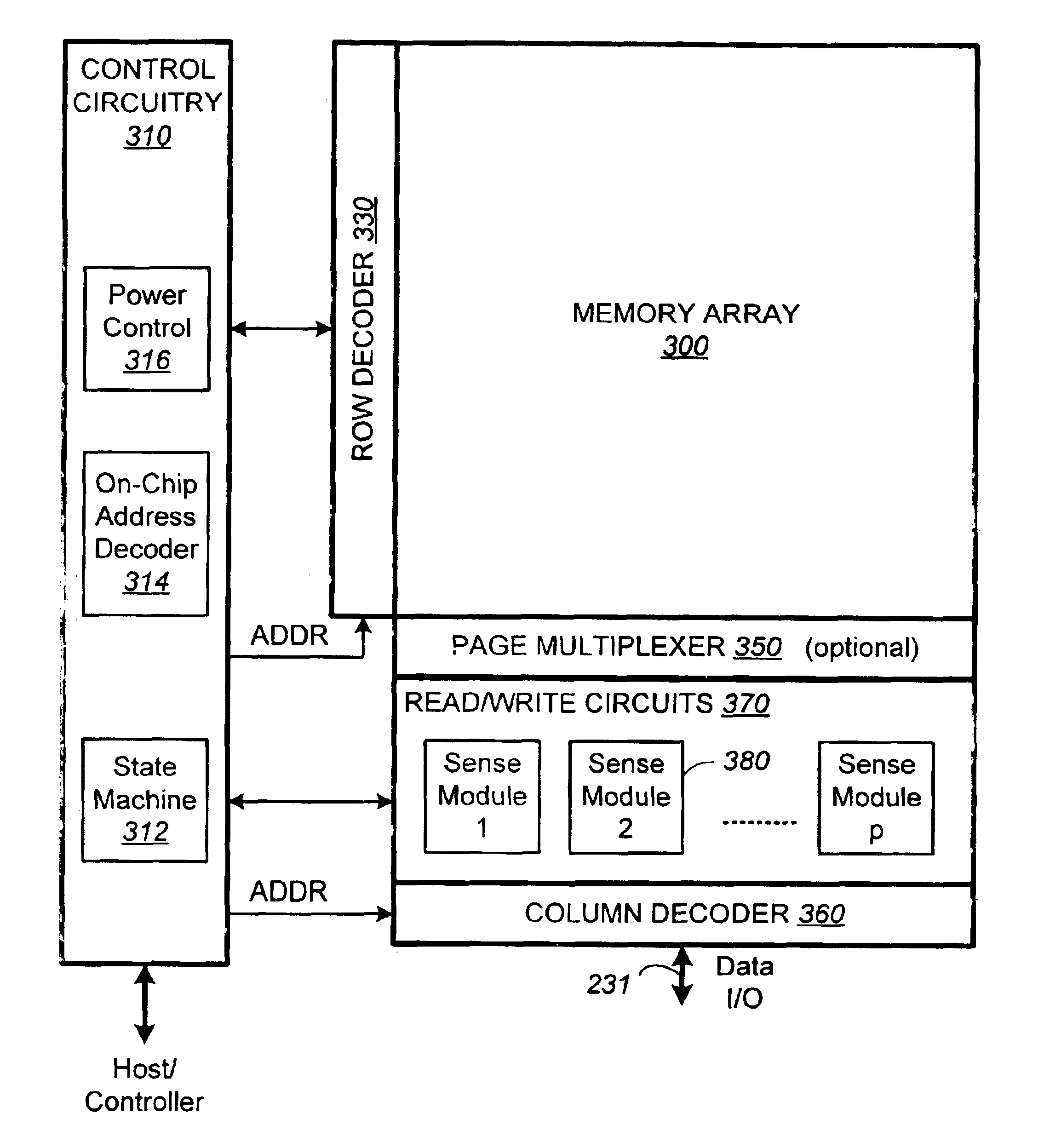
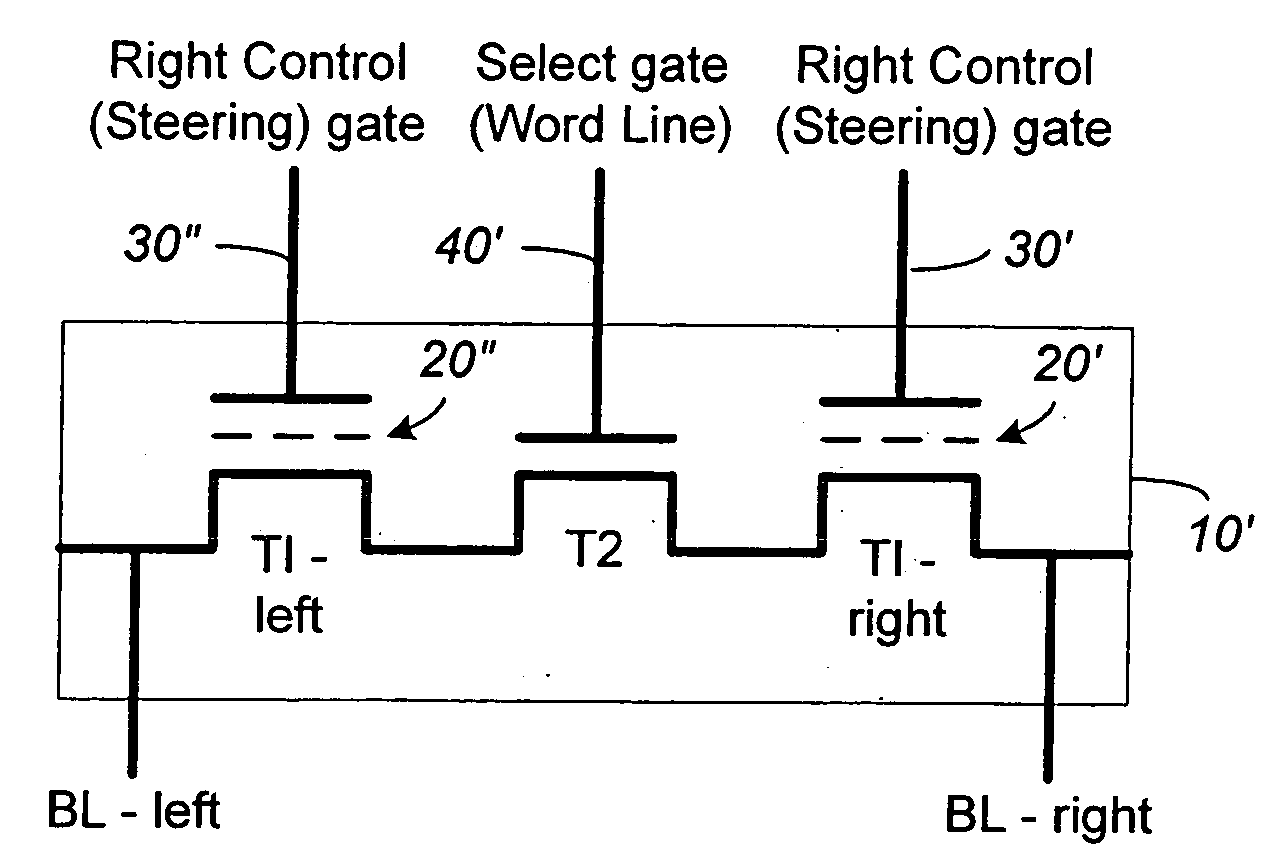
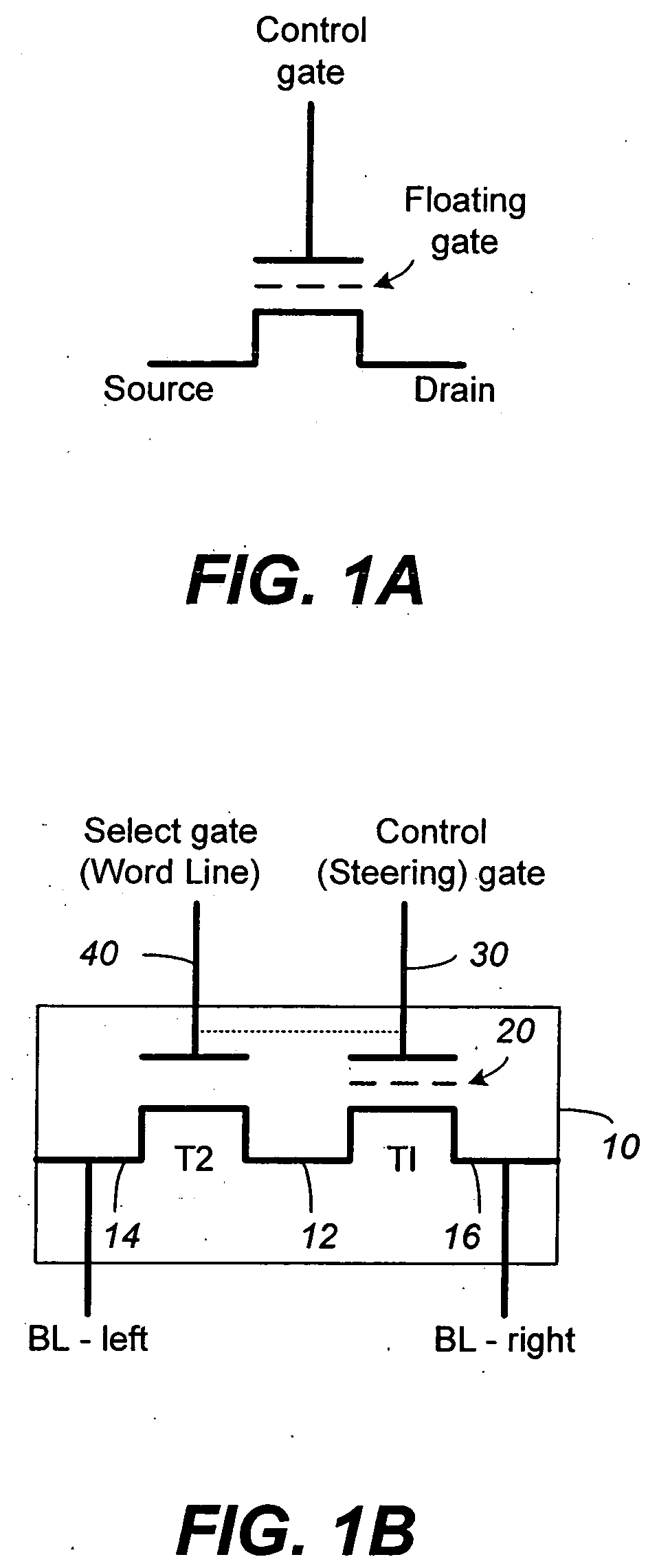
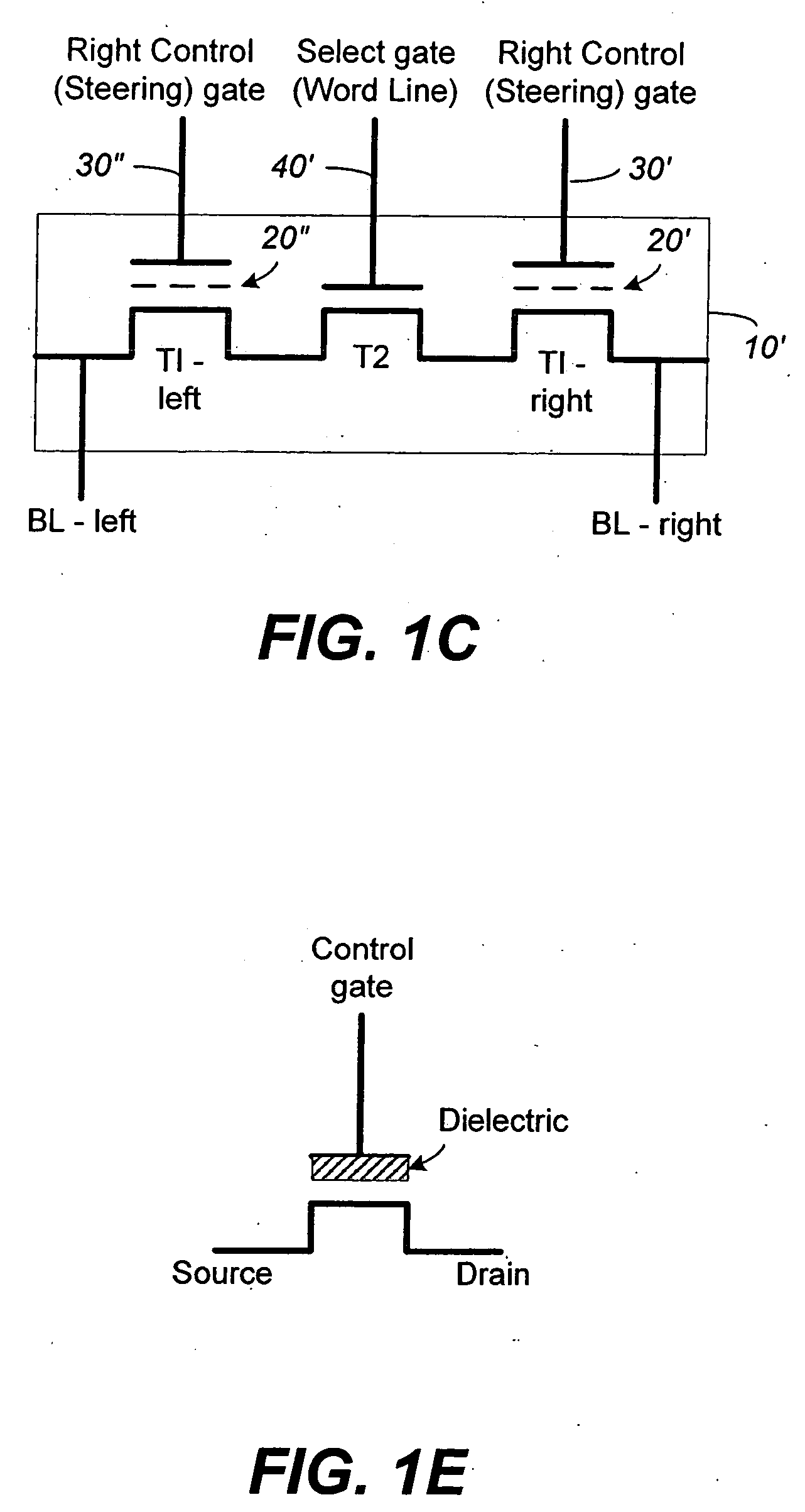
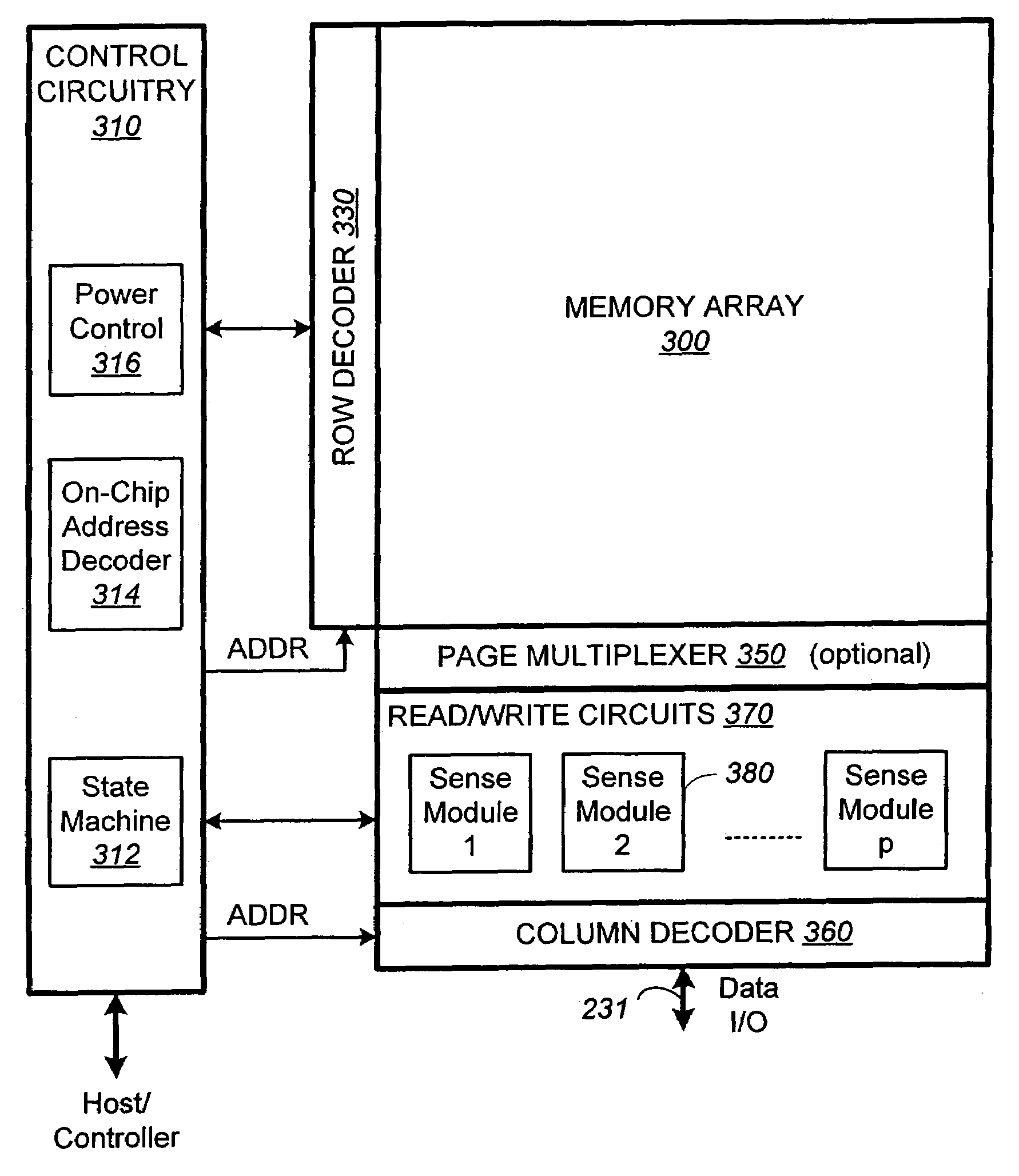
Non-volatile memory and method with improved sensing
InactiveUS7023736B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierMultiple pass
A method for reducing source line bias is accomplished by read / write circuits with features and techniques for multi-pass sensing. When a page of memory cells are being sensed in parallel, each pass helps to identify and shut down the memory cells with conduction current higher than a given demarcation current value. In particular, the identified memory cells are shut down after all sensing in the current pass have been completed. In this way the shutting down operation does not disturb the sensing operation. Sensing in subsequent passes will be less affected by source line bias since the total amount of current flow is significantly reduced by eliminating contributions from the higher current cells. In another aspect of sensing improvement, a reference sense amplifier is employed to control multiple sense amplifiers to reduce their dependence on power supply and environmental variations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
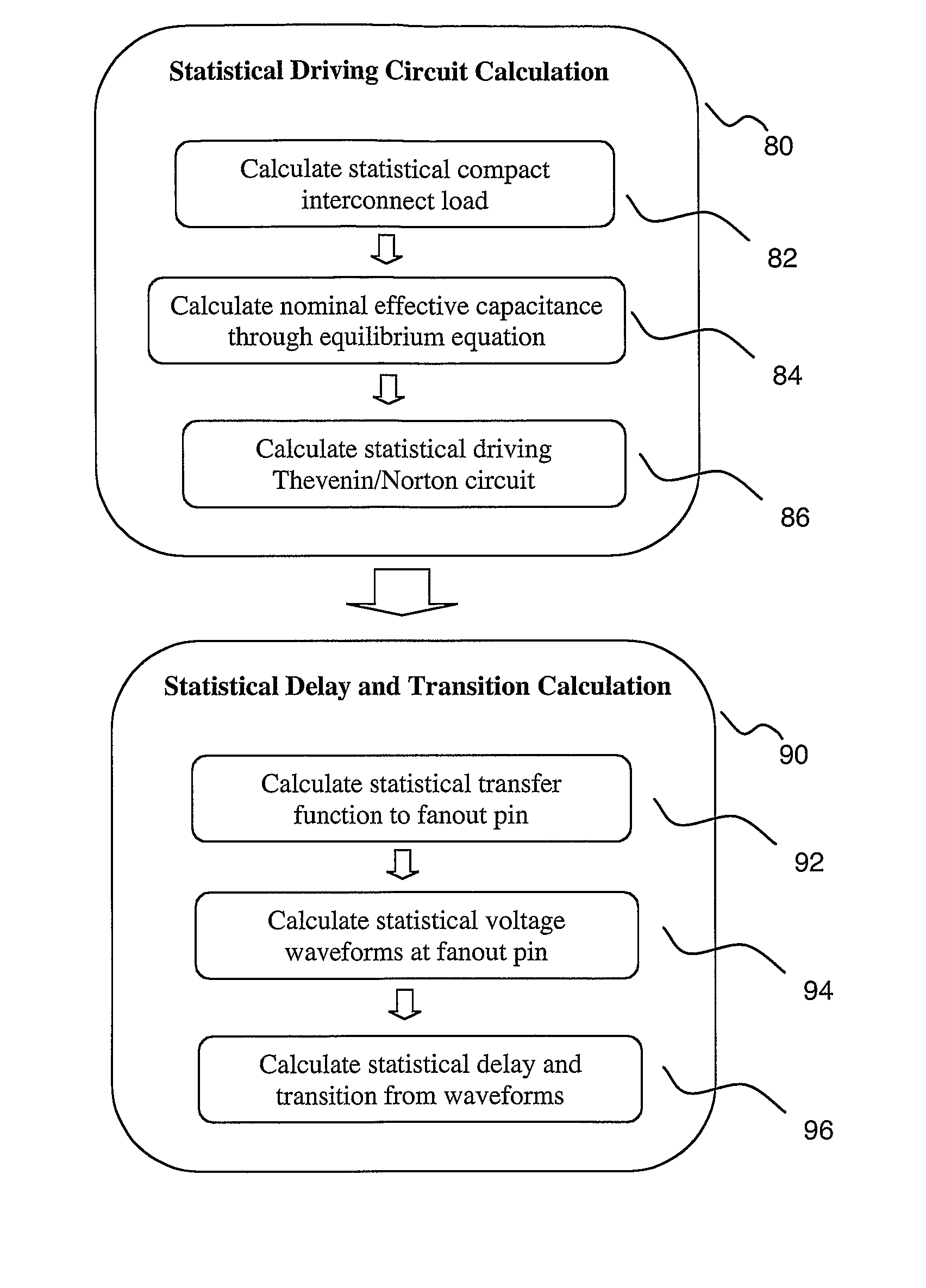
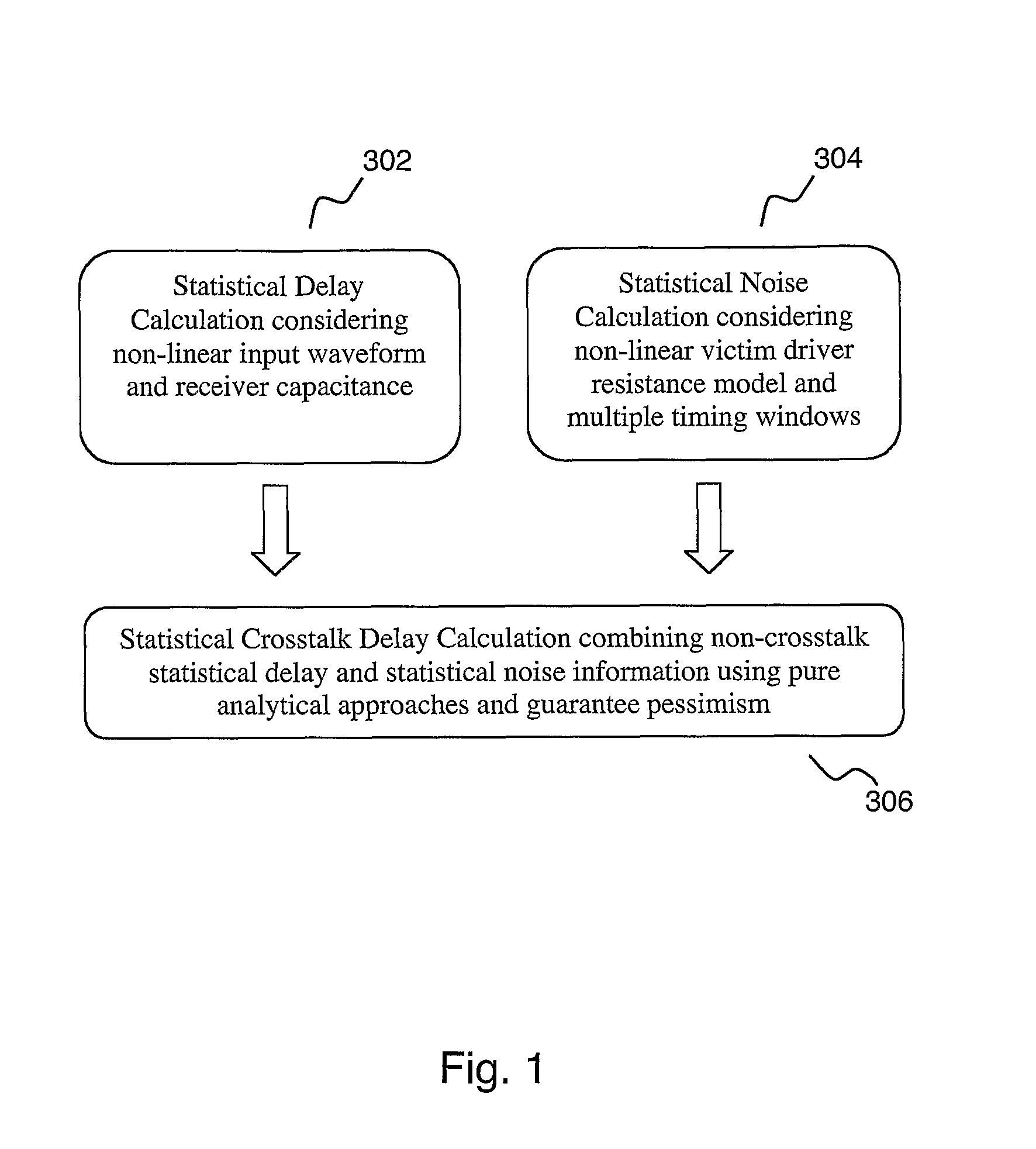
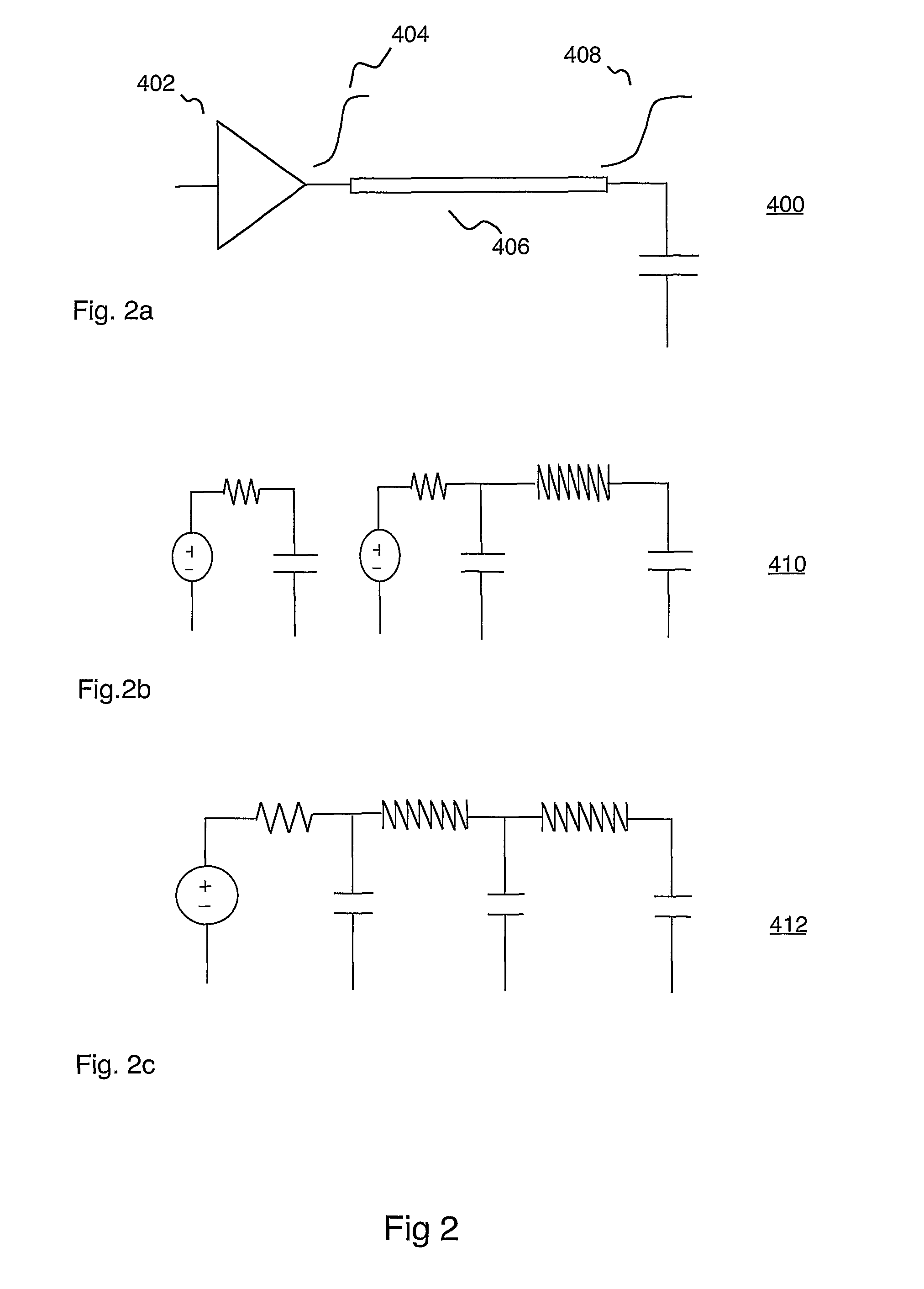
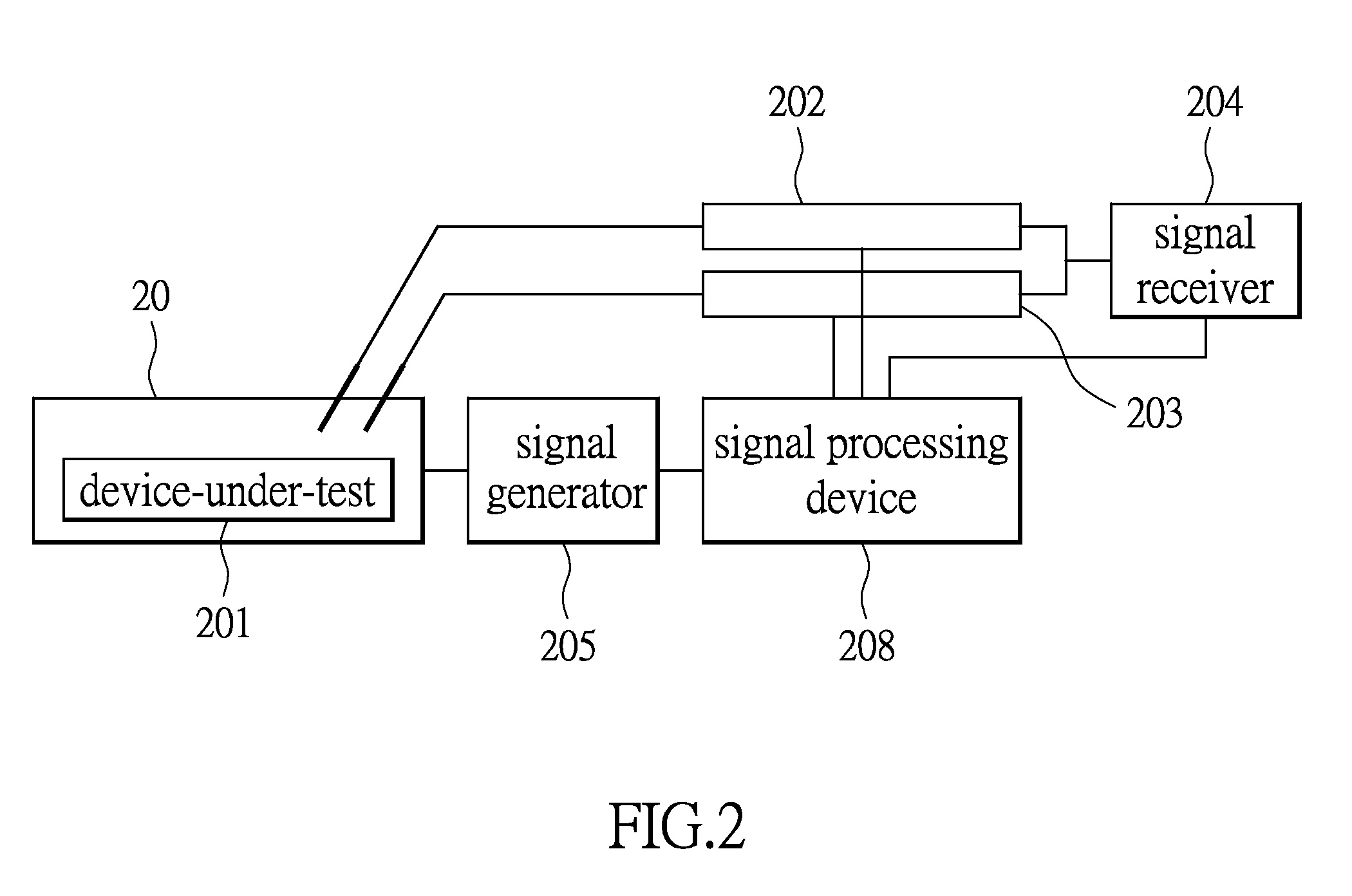
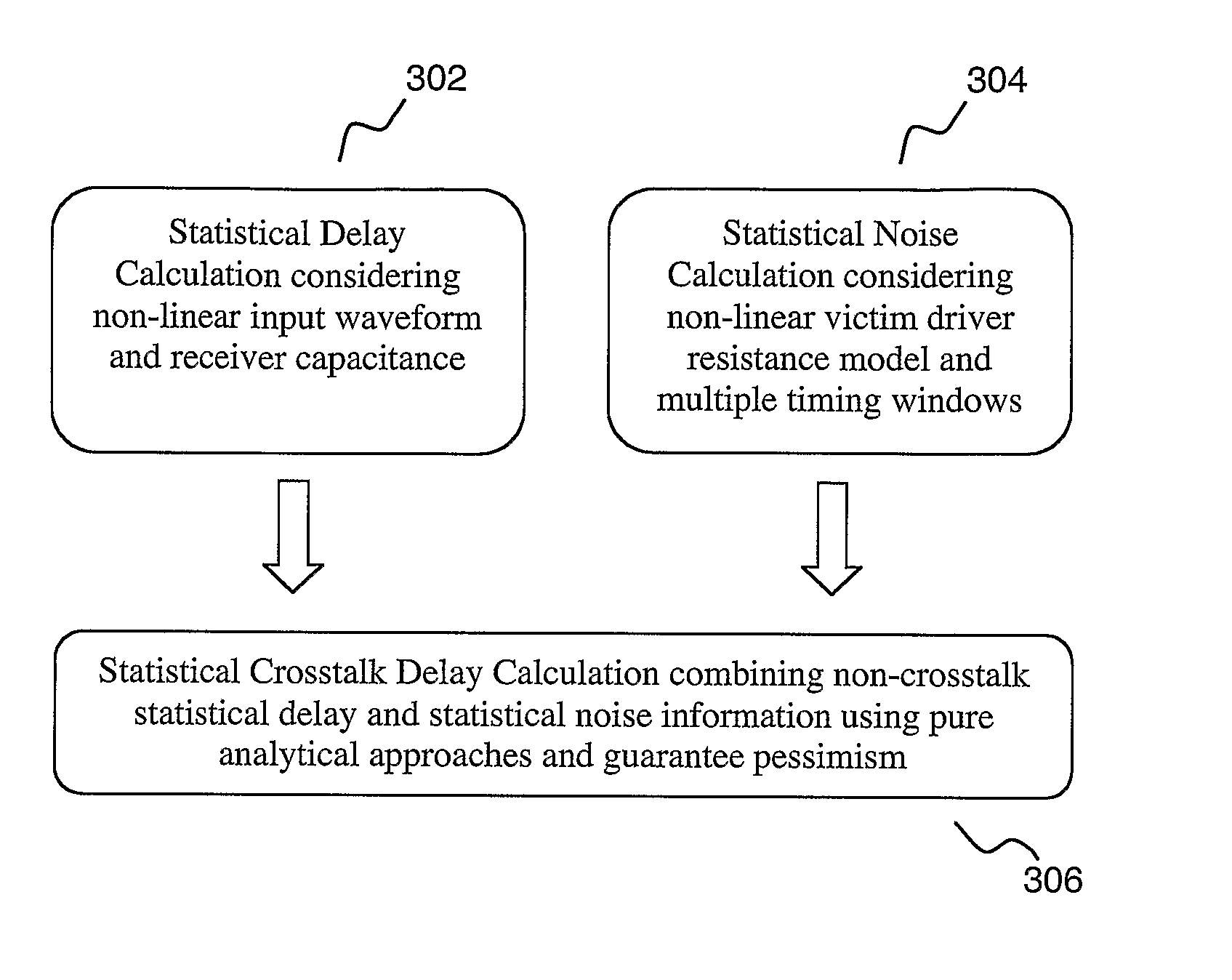
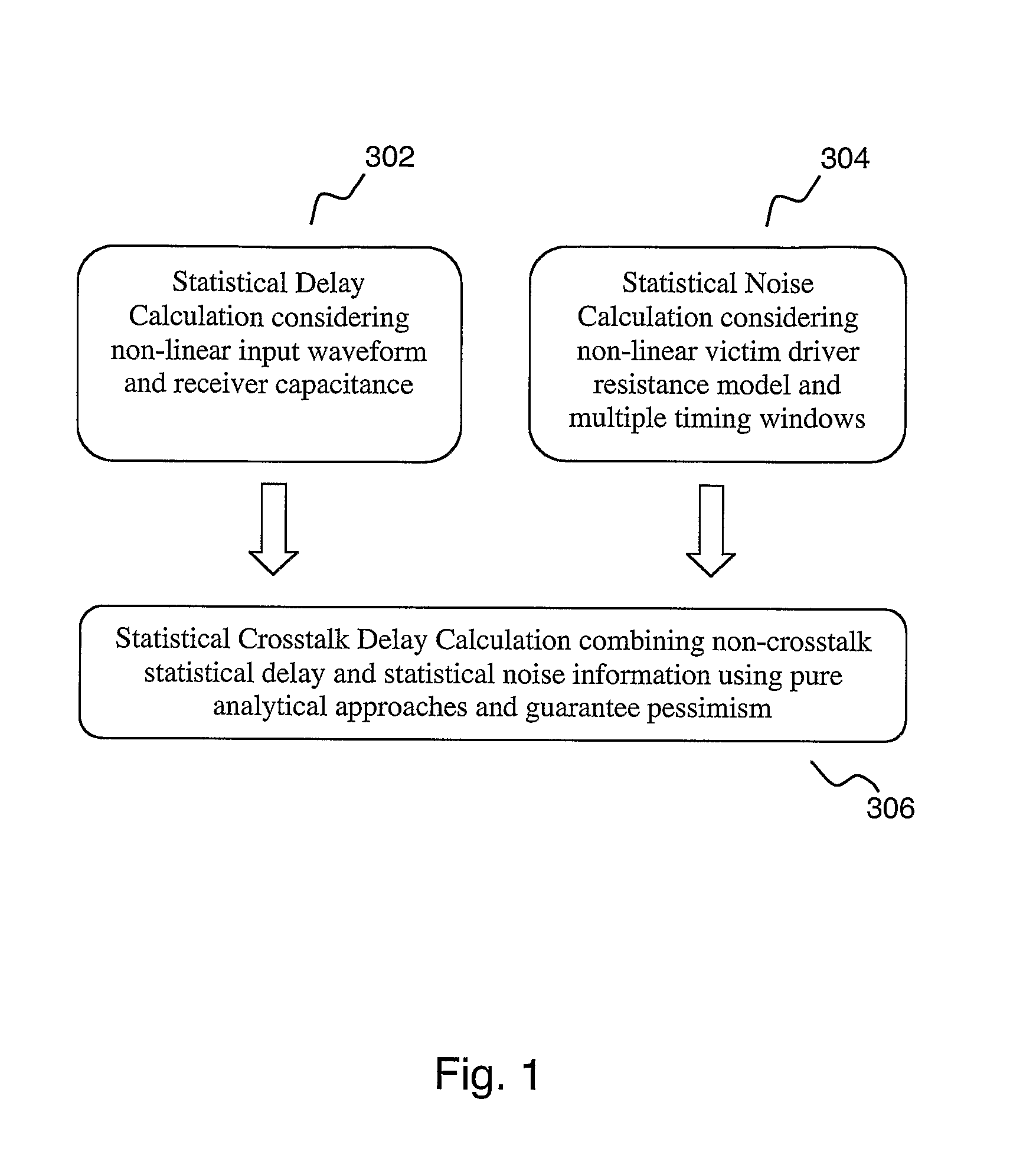
Statistical delay and noise calculation considering cell and interconnect variations
ActiveUS7890915B2Efficiently delayEfficiently sensitivityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationNumerical stabilityComputer science
The electrical circuit timing method provides accurate nominal delay together with the delay sensitivities with respect to different circuit elements {e.g., cells, interconnects, etc.) and variational parameters (e.g., process variations; environmental variations). All the sensitivity computations are based on closed-form formulas; as a consequence, the method provides rapidly and at low cost high accuracy and high numerical stability.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
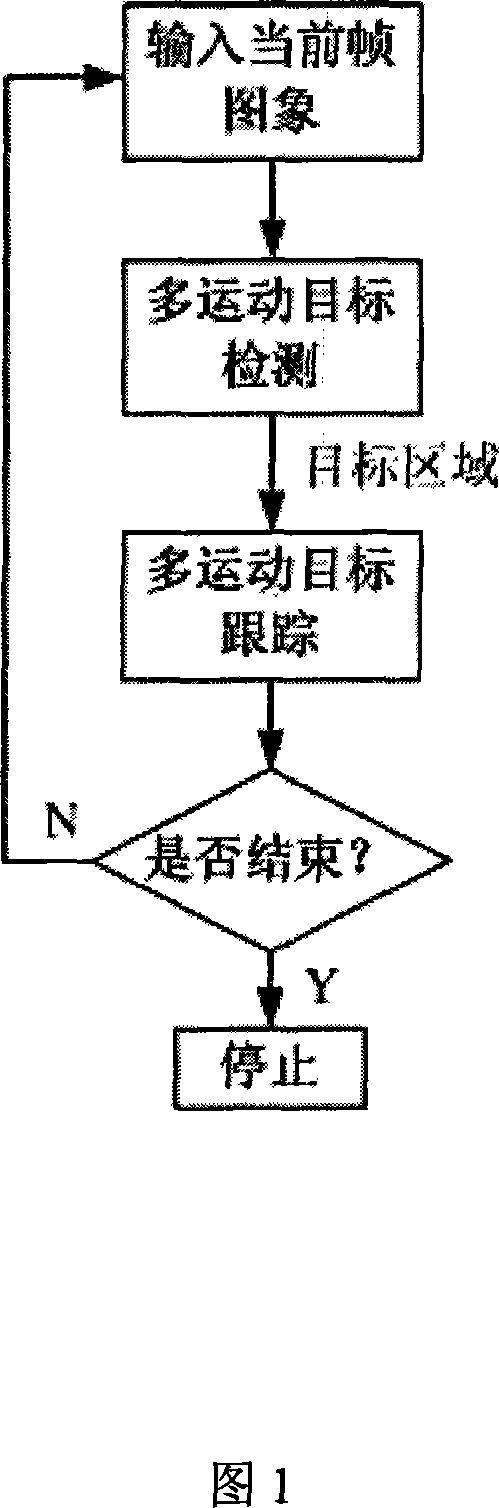
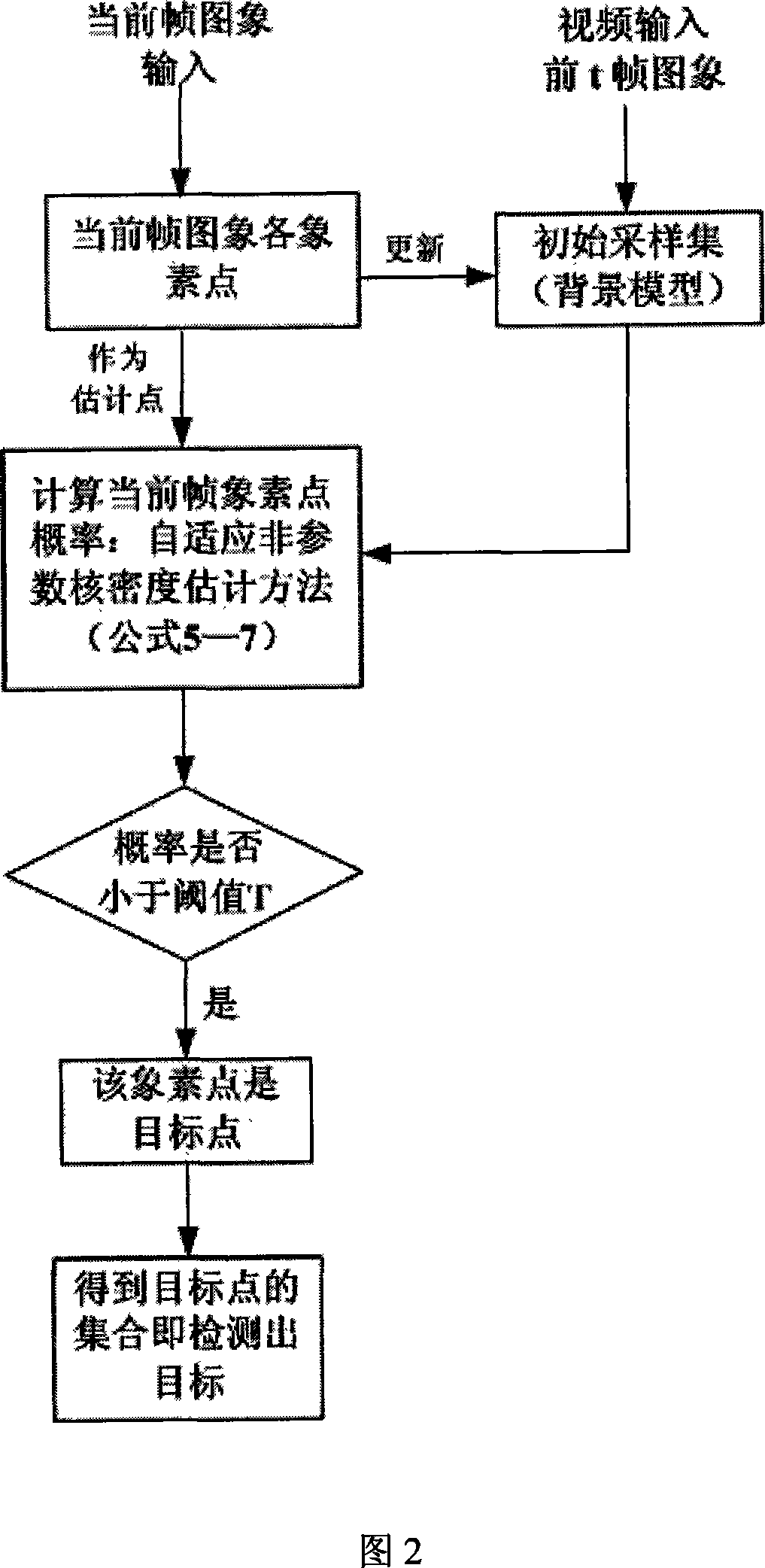
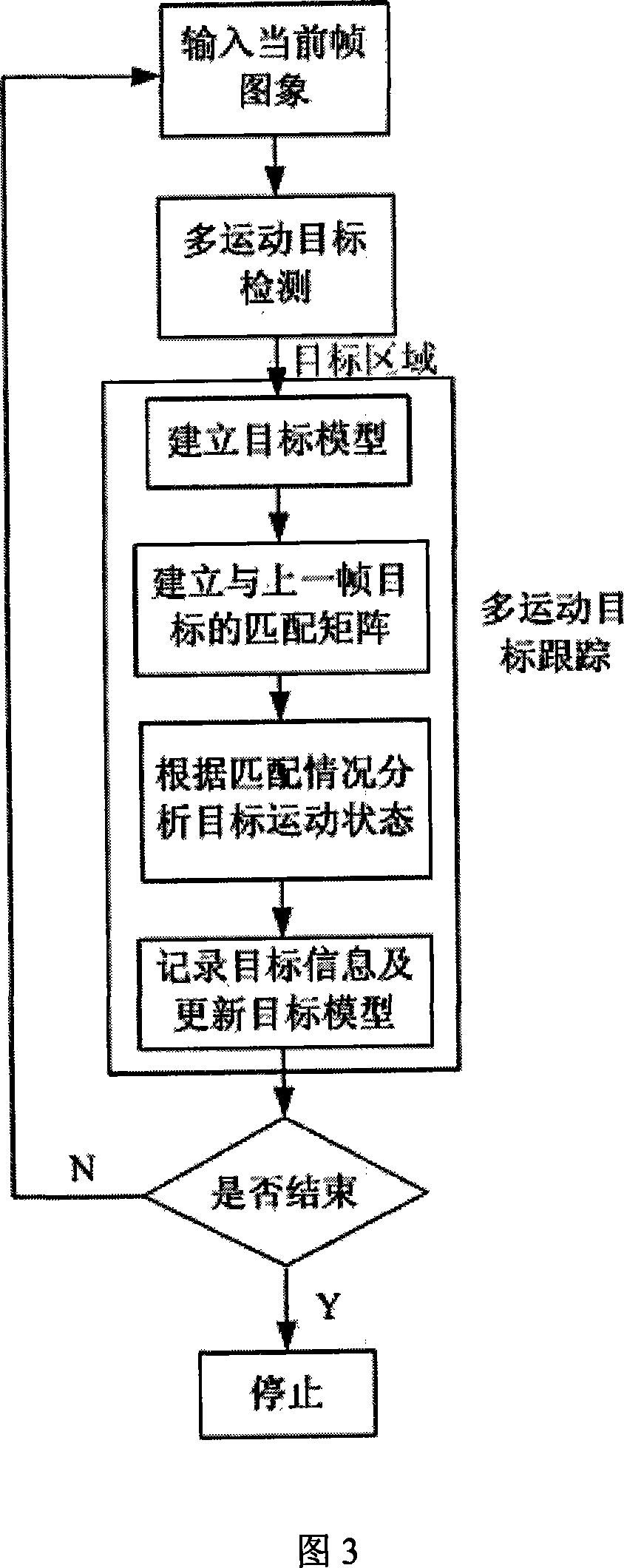
Moving object detecting and tracing method in complex scene
InactiveCN101141633AImprove accuracySuppress interferenceImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsObject motionVisual monitoring
The present invention discloses method for moving target detection and tracking in a complex scene. The method comprises two steps of multiple moving target detection and multiple moving target tracking: in the multiple moving target detection, a background model based on self adapting nonparametric kernel density estimation is established with the aim at the monitoring of the complex scene, therefore the disturbance of the movement of tiny objects can be effectively suppressed, the target shadow is eliminated, and the multiple moving target is detected; in the multiple moving target tracking, the target model is established, the moving state of the target is confirmed through ''matching matrix'', and corresponding tracking strategy is adopted according to the different movement condition of the target. Target information is ''recovered'' through the probabilistic reasoning method, and the target screening degree of the target is analyzed with the aim at the problem that multiple targets screen mutually. The algorithm of the present invention can well realize the moving target tracking, obtains the trace of the moving target, and has good real time and ability of adapting to the environmental variation. The present invention has wide application range and high accuracy, therefore being a core method for intelligent vision monitoring with versatility.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
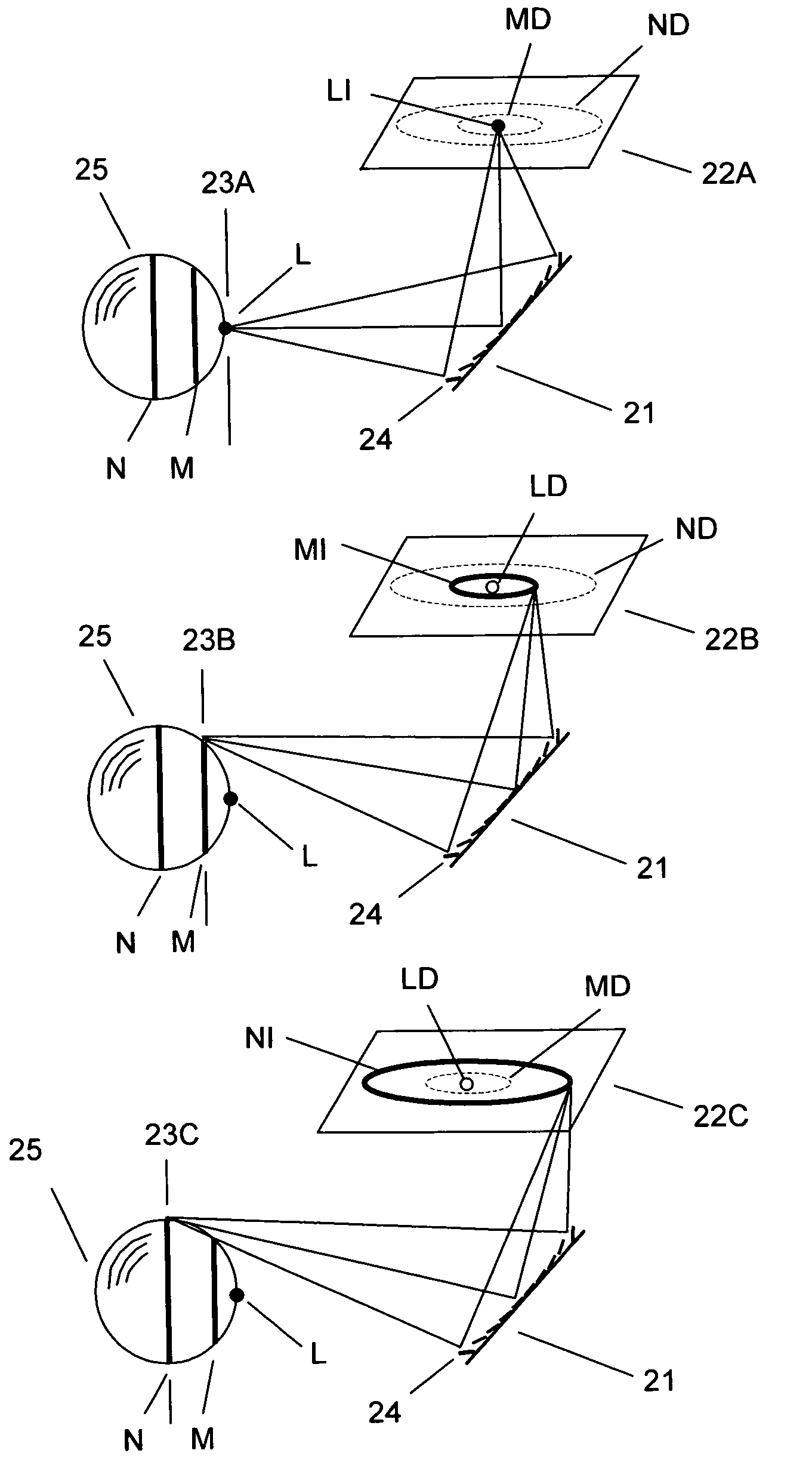
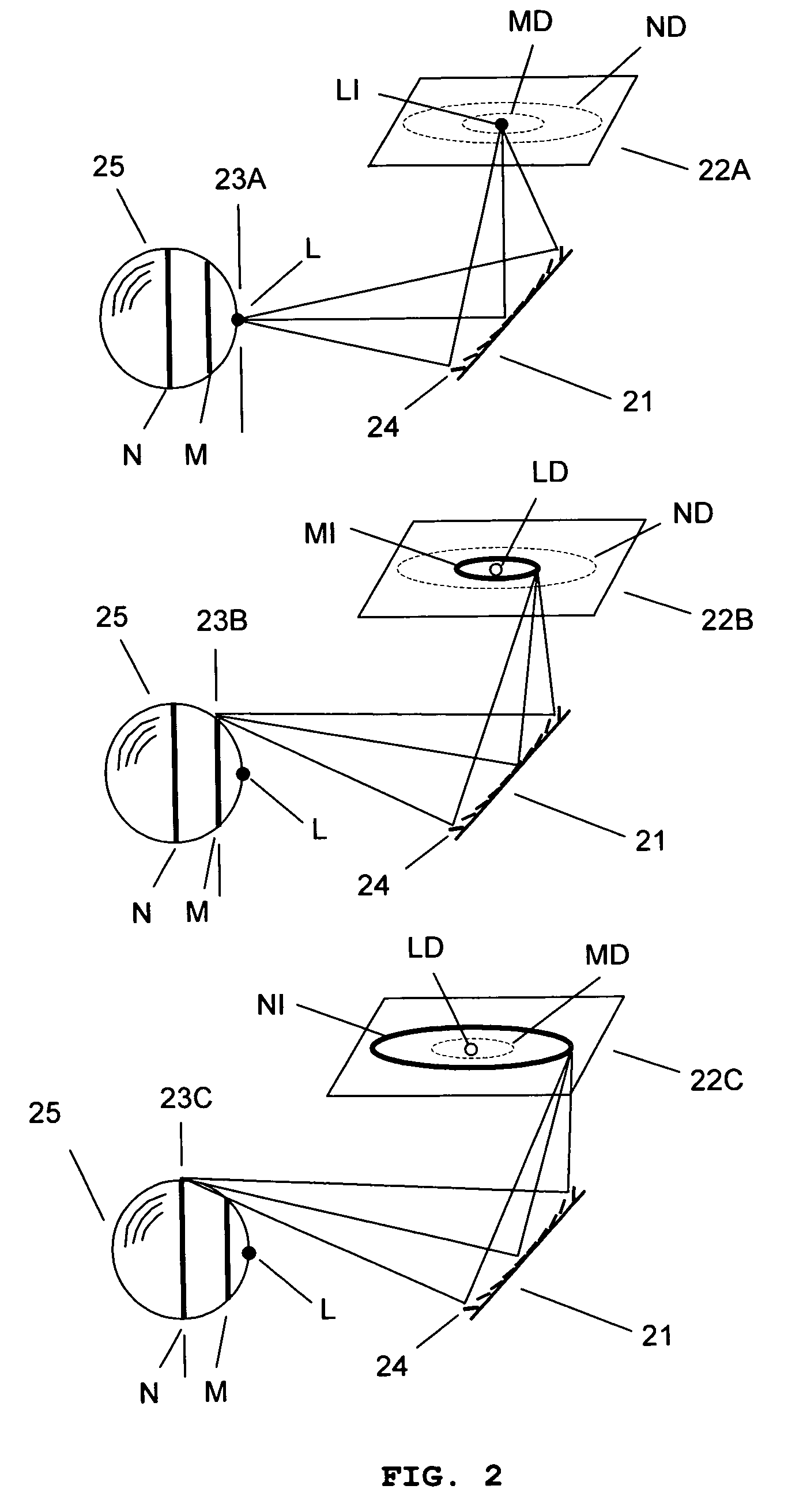
Three-dimensional imaging system for pattern recognition
ActiveUS7212330B2High depth resolutionFast acquisition timeCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansDepth of fieldMicromirror array
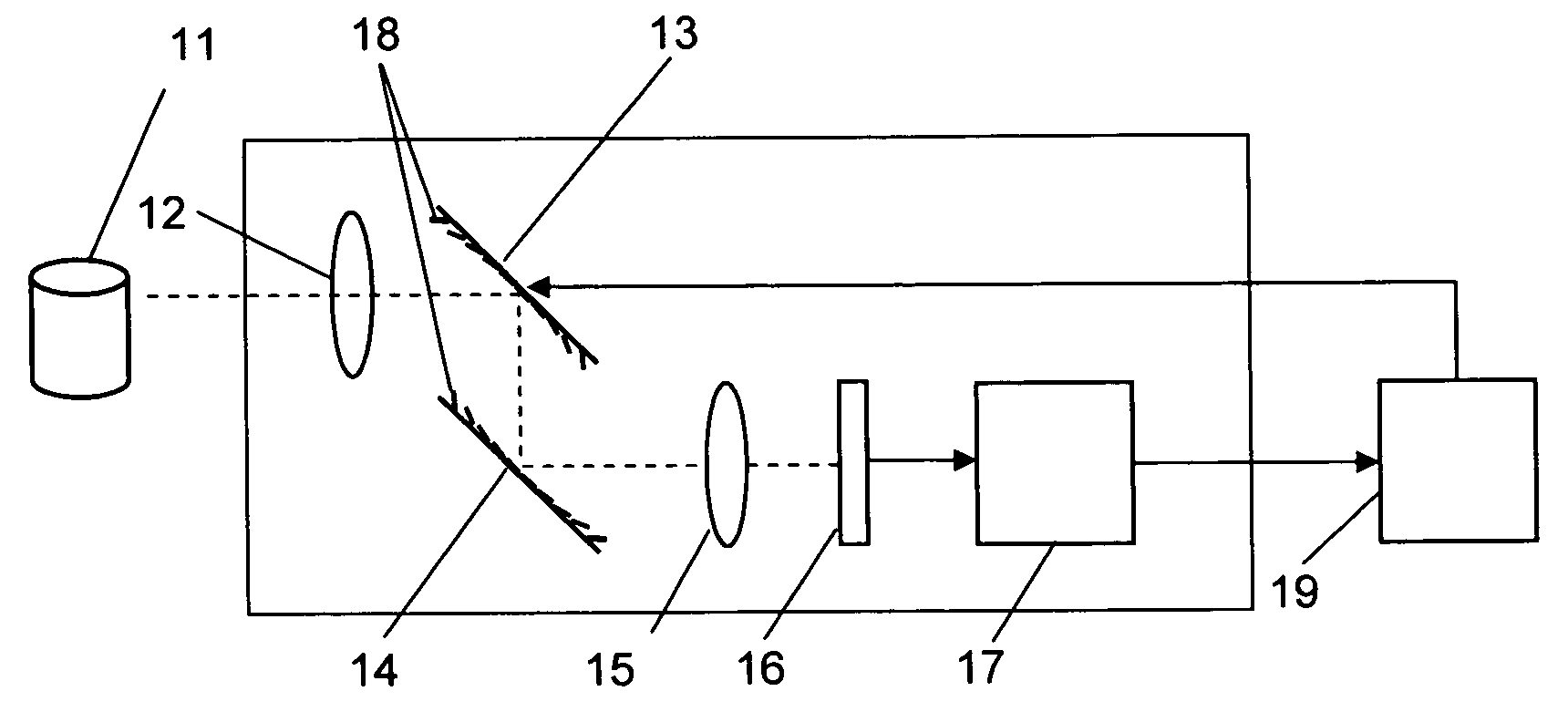
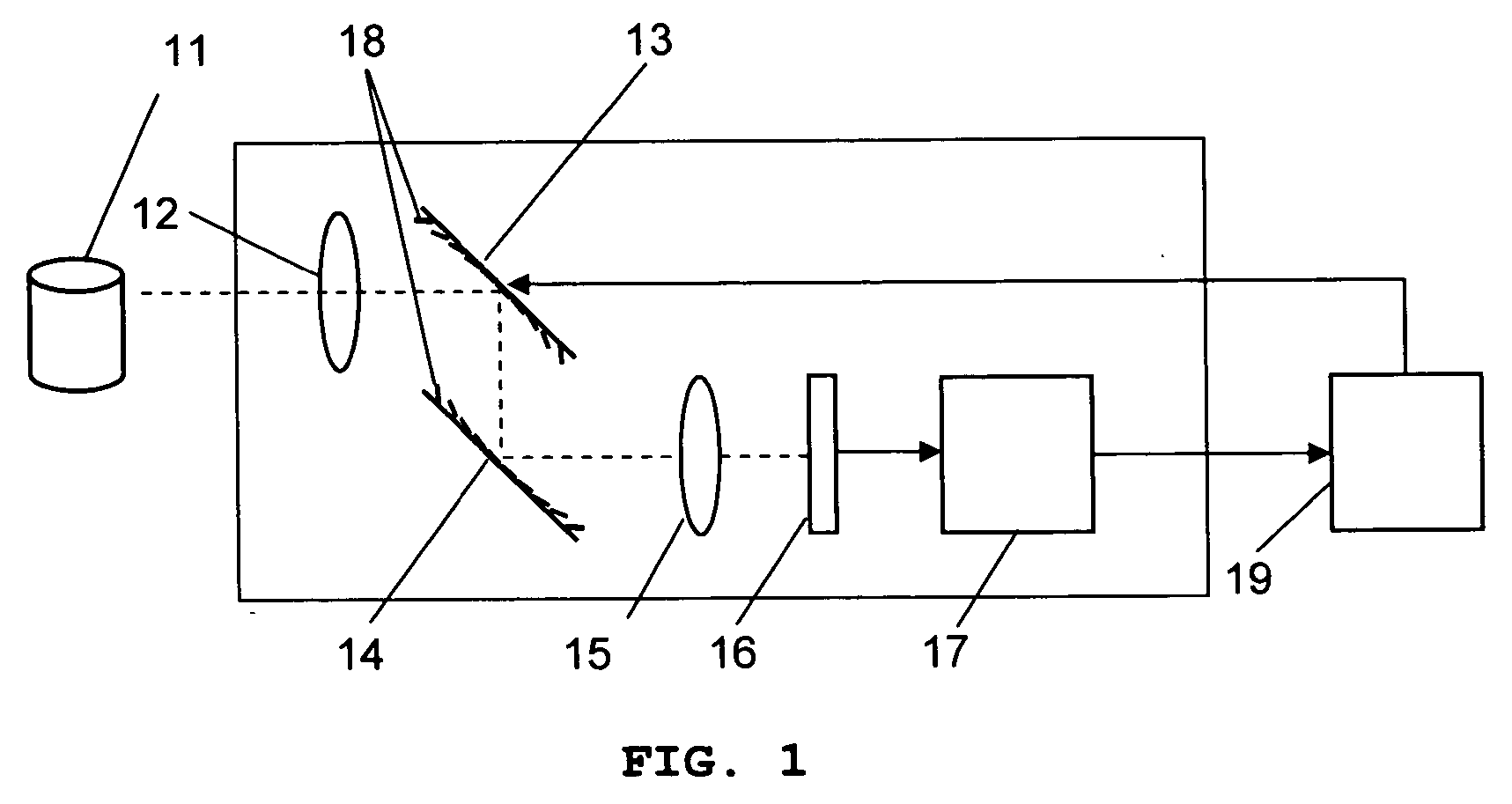
The present invention provides a real-time three-dimensional pattern recognition imaging system having a variable focal length, a wide depth of field, a high depth resolution, a fast acquisition time, a variable magnification, a variable optical axis for tracking, and capability of compensating various optical distortions and aberrations, which enables pattern recognition systems to be more accurate as well as more robust to environmental variation. The imaging system for pattern recognition comprises one or more camera system, each of which has at least one micromirror array lens(MMAL), a two-dimensional image senor, and an image processing unit. A MMAL has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable optical axis, and a variable magnification.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Three-dimensional imaging system for pattern recognition
ActiveUS20060098872A1Fast response timeLarge focal length variationCharacter and pattern recognitionDepth of fieldMicromirror array
The present invention provides a real-time three-dimensional pattern recognition imaging system having a variable focal length, a wide depth of field, a high depth resolution, a fast acquisition time, a variable magnification, a variable optical axis for tracking, and capability of compensating various optical distortions and aberrations, which enables pattern recognition systems to be more accurate as well as more robust to environmental variation. The imaging system for pattern recognition comprises one or more camera system, each of which has at least one micromirror array lens(MMAL), a two-dimensional image senor, and an image processing unit. A MMAL has unique features including a variable focal length, a variable optical axis, and a variable magnification.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
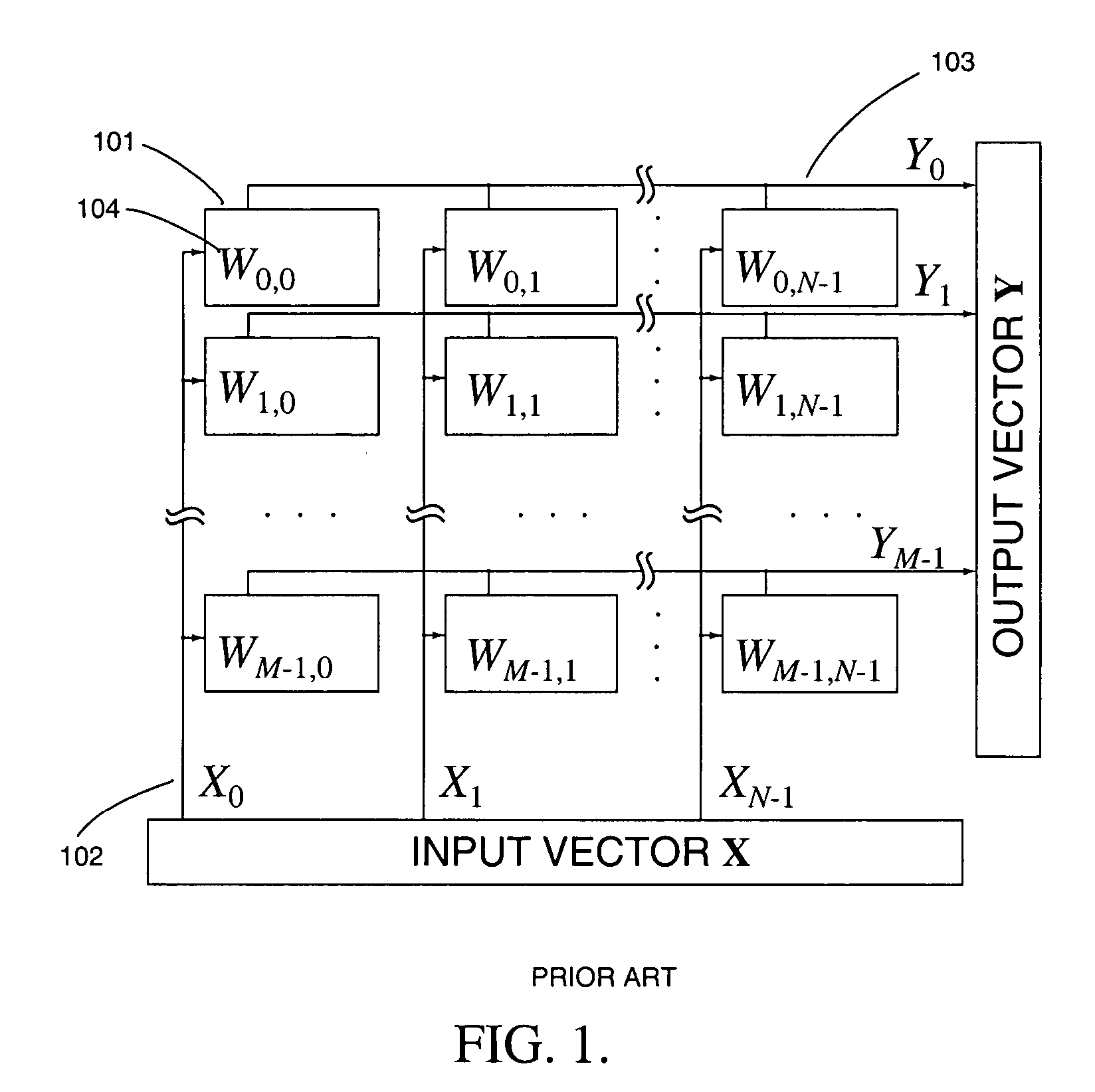
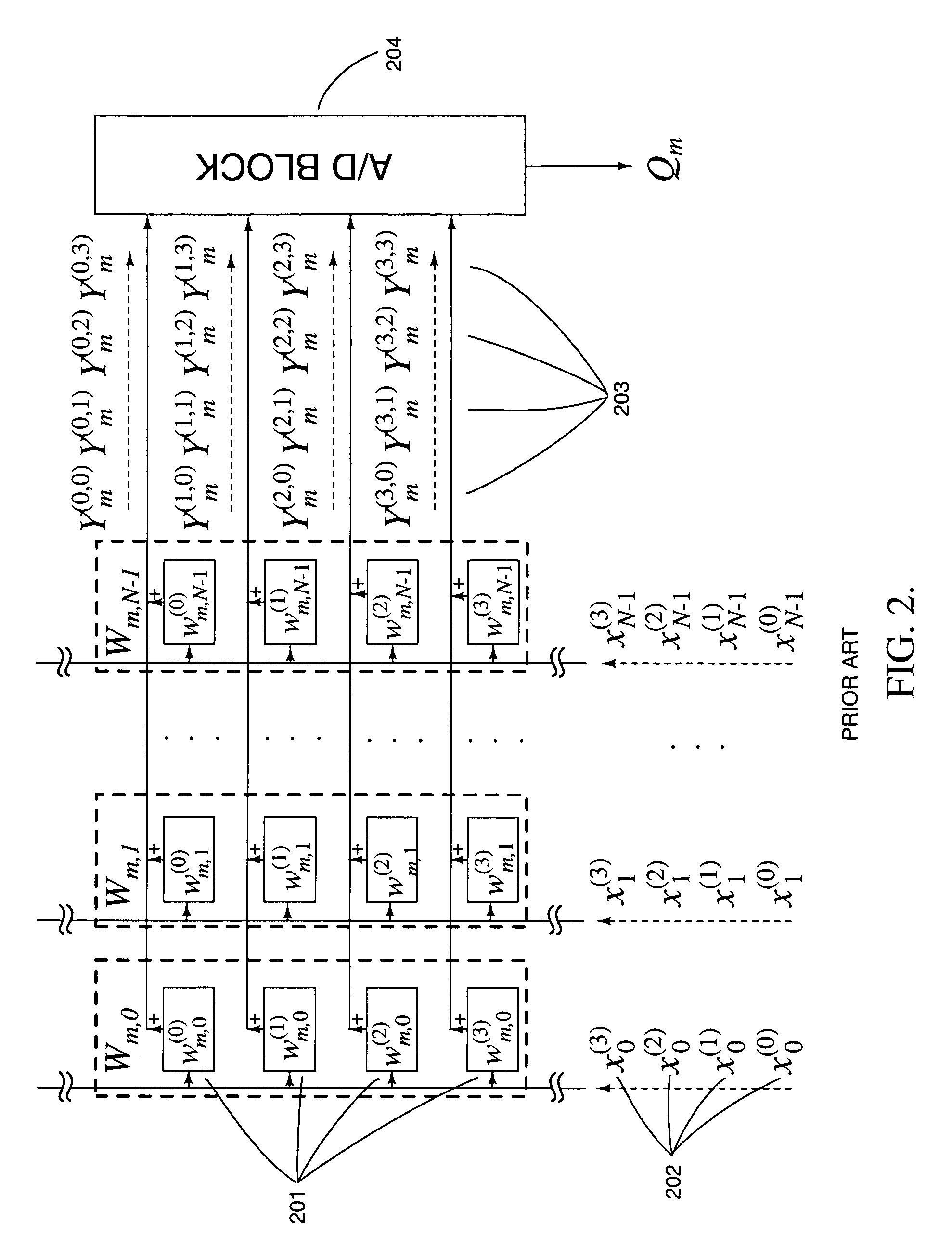
High-precision matrix-vector multiplication on a charge-mode array with embedded dynamic memory and stochastic method thereof
InactiveUS20050125477A1Efficient multiplicationIncrease cell densityComputation using non-contact making devicesPhysical realisationRandom methodReal time signal processing
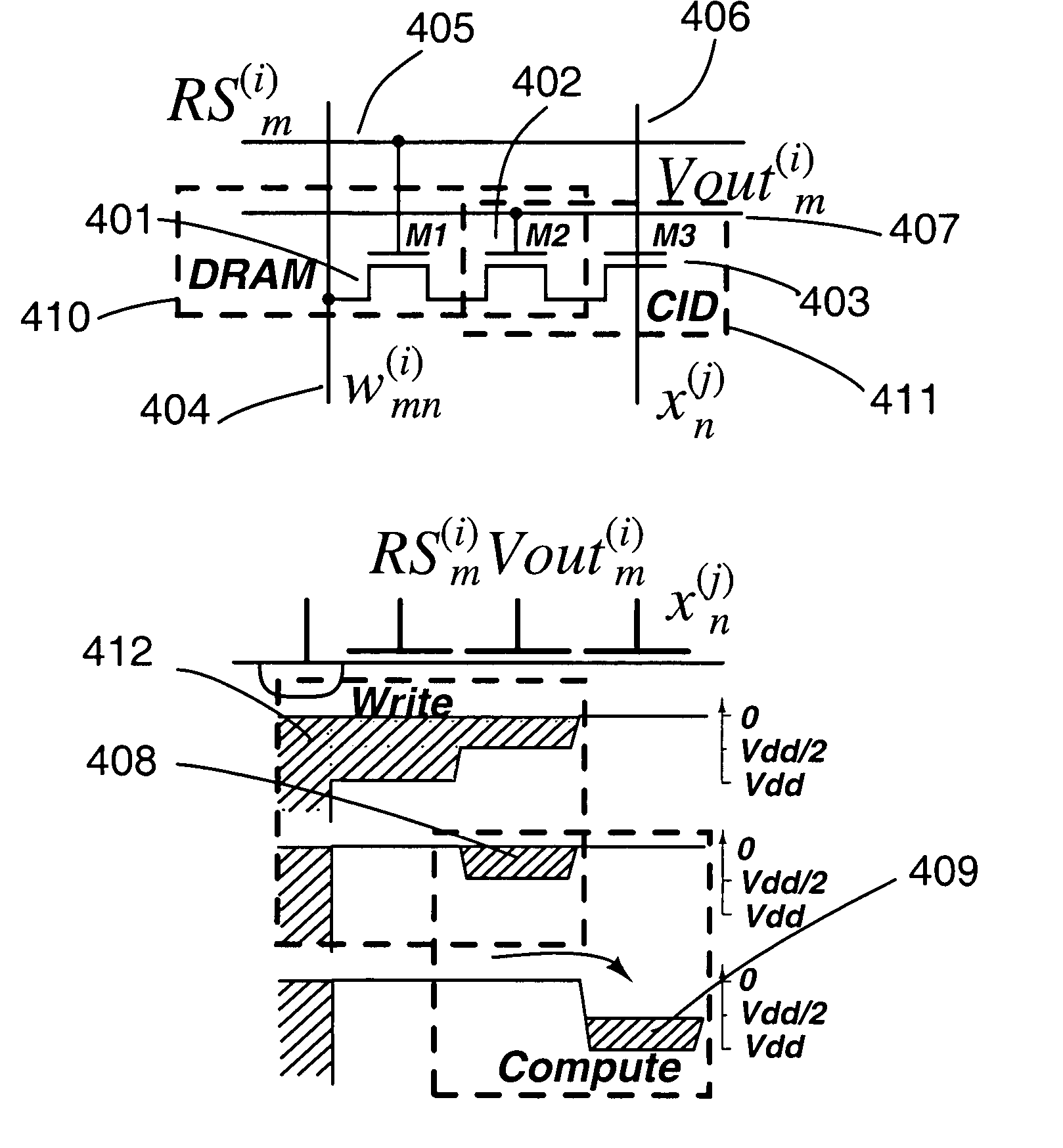
Analog computational arrays for matrix-vector multiplication offer very large integration density and throughput as, for instance, needed for real-time signal processing in video. Despite the success of adaptive algorithms and architectures in reducing the effect of analog component mismatch and noise on system performance, the precision and repeatability of analog VLSI computation under process and environmental variations is inadequate for some applications. Digital implementation offers absolute precision limited only by wordlength, but at the cost of significantly larger silicon area and power dissipation compared with dedicated, fine-grain parallel analog implementation. The present invention comprises a hybrid analog and digital technology for fast and accurate computing of a product of a long vector (thousands of dimensions) with a large matrix (thousands of rows and columns). At the core of the externally digital architecture is a high-density, low-power analog array performing binary-binary partial matrix-vector multiplication. Digital multiplication of variable resolution is obtained with bit-serial inputs and bit-parallel storage of matrix elements, by combining quantized outputs from one or more rows of cells over time. Full digital resolution is maintained even with low-resolution analog-to-digital conversion, owing to random statistics in the analog summation of binary products. A random modulation scheme produces near-Bernoulli statistics even for highly correlated inputs. The approach has been validated by electronic prototypes achieving computational efficiency (number of computations per unit time using unit power) and integration density (number of computations per unit time on a unit chip area) each a factor of 100 to 10,000 higher than that of existing signal processors making the invention highly suitable for inexpensive micropower implementations of high-data-rate real-time signal processors.
Owner:GENOV ROMAN A +1
Non-volatile memory and method with improved sensing
InactiveUS20060050562A1Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierVoltage drop
Source line bias is an error introduced by a non-zero resistance in the ground loop of the read / write circuits. During sensing the control gate voltage of a memory cell is erroneously biased by a voltage drop across the resistance. This error is minimized when the current flowing though the ground loop is reduced. A method for reducing source line bias is accomplished by read / write circuits with features and techniques for multi-pass sensing. When a page of memory cells are being sensed in parallel, each pass helps to identify and shut down the memory cells with conduction current higher than a given demarcation current value. In particular, the identified memory cells are shut down after all sensing in the current pass have been completed. In this way the shutting down operation does not disturb the sensing operation. Sensing in subsequent passes will be less affected by source line bias since the total amount of current flow is significantly reduced by eliminating contributions from the higher current cells. In another aspect of sensing improvement, a reference sense amplifier is employed to control multiple sense amplifiers to reduce their dependence on power supply and environmental variations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-volatile memory and method with improved sensing
InactiveUS7212445B2Large capacityImprove performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierEnvironmental variation
A method for reducing source line bias is accomplished by read / write circuits with features and techniques for multi-pass sensing. When a page of memory cells are being sensed in parallel, each pass helps to identify and shut down the memory cells with conduction current higher than a given demarcation current value. In particular, the identified memory cells are shut down after all sensing in the current pass have been completed. In this way the shutting down operation does not disturb the sensing operation. Sensing in subsequent passes will be less affected by source line bias since the total amount of current flow is significantly reduced by eliminating contributions from the higher current cells. In another aspect of sensing improvement, a reference sense amplifier is employed to control multiple sense amplifiers to reduce their dependence on power supply and environmental variations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
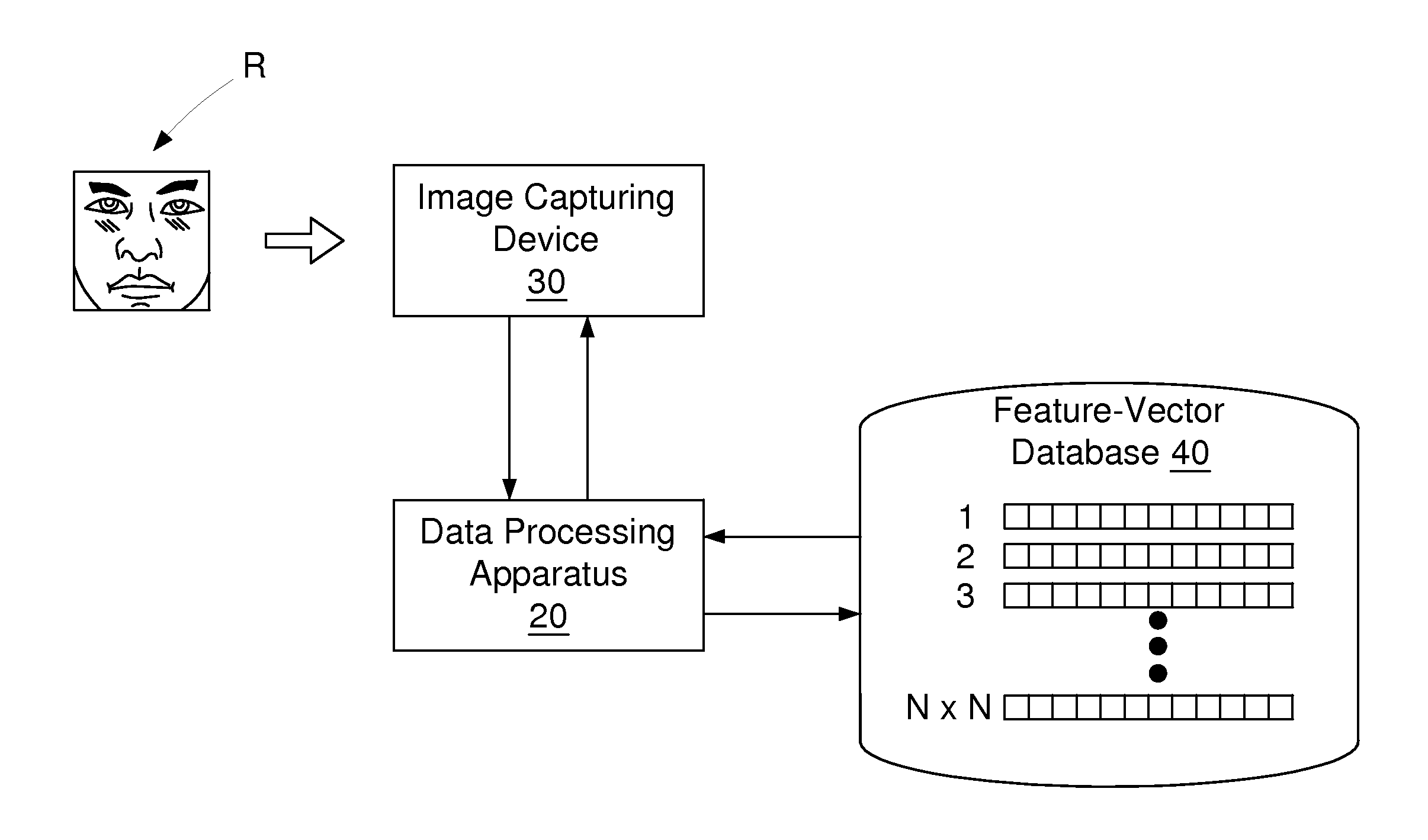
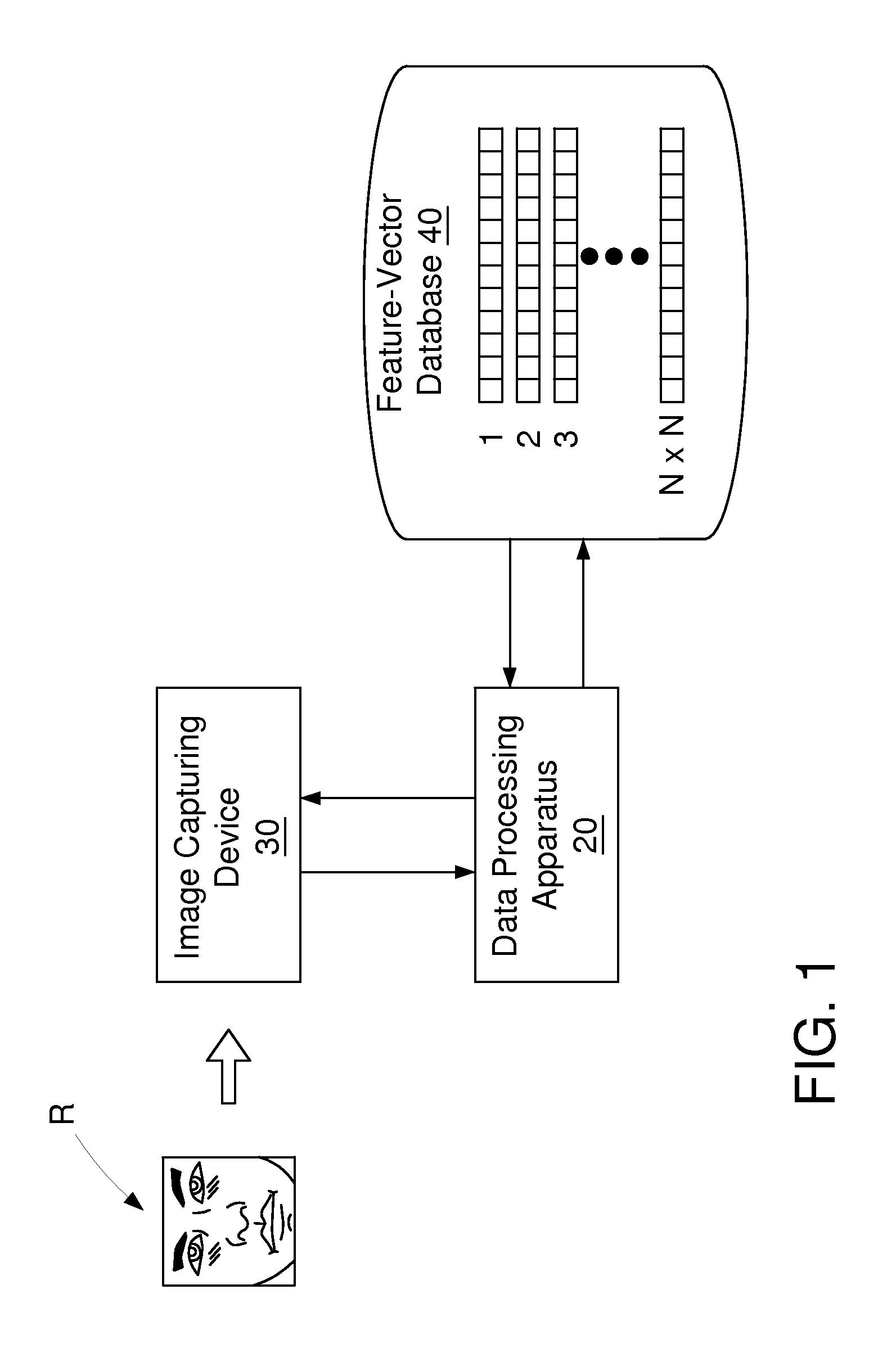
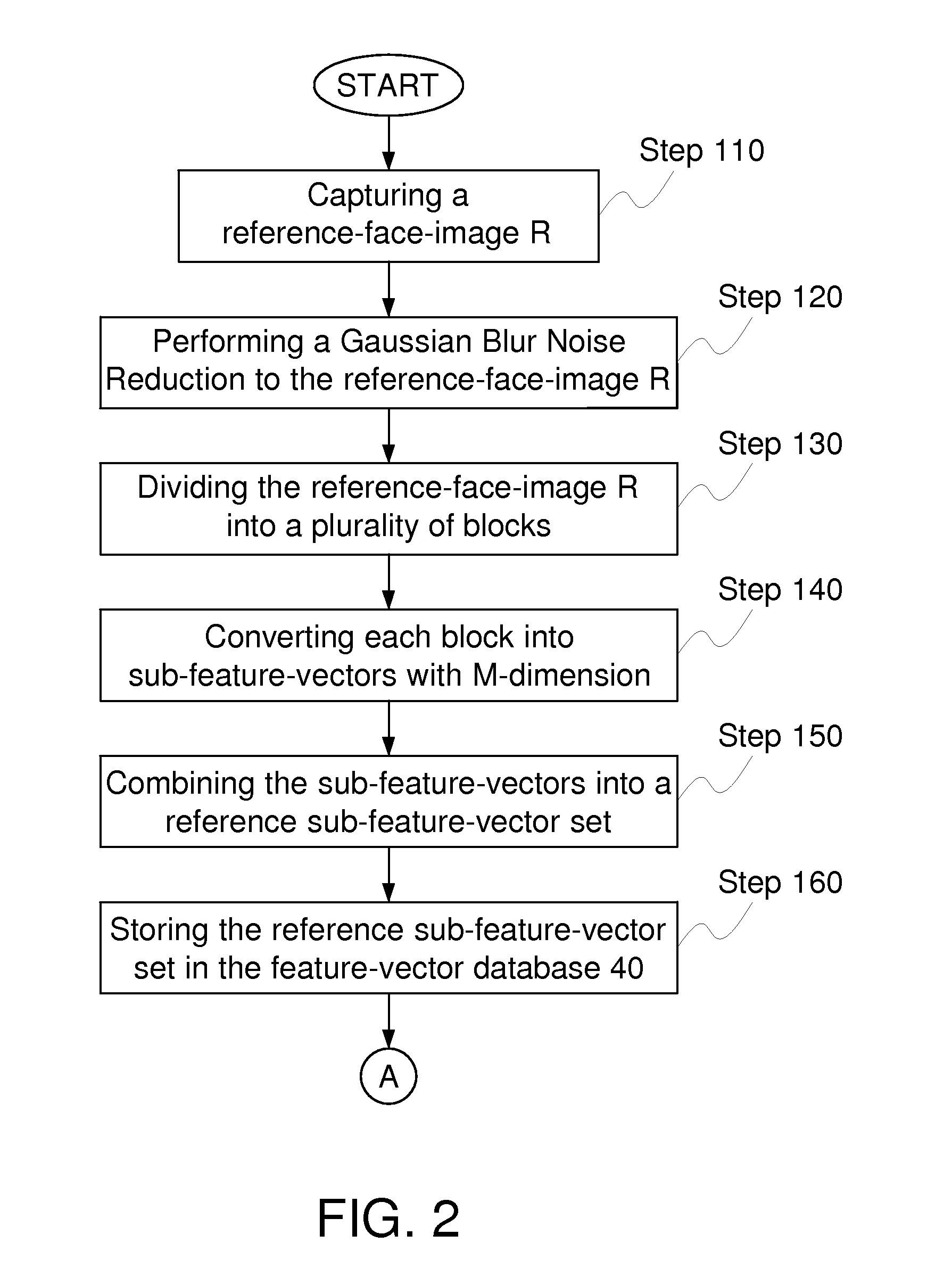
Facial recognition method for eliminating the effect of noise blur and environmental variations
ActiveUS20120087552A1Improve reliabilityReduce noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorFacial recognition system
A facial recognition method for eliminating the effect of noise blur and environmental variations is provided, applicable to a data processing apparatus, to determine whether a current-face-image matches a reference-face-image or not. According to the method, Gaussian Noise blur Reduction or another noise blur reduction method is performed on the current-face-image and the reference-face-image. Furthermore, the current-face-image and the reference-face-image are respectively divided into a plurality of blocks, so as to derive feature-vector sets representing the current-face-image and the reference-face-image. Finally a dynamic threshold value is determined according to environmental variations to be compared with the difference of the feature-vector sets, so as to determine whether a current-face-image matches a reference-face-image.
Owner:MSI COMP SHENZHEN
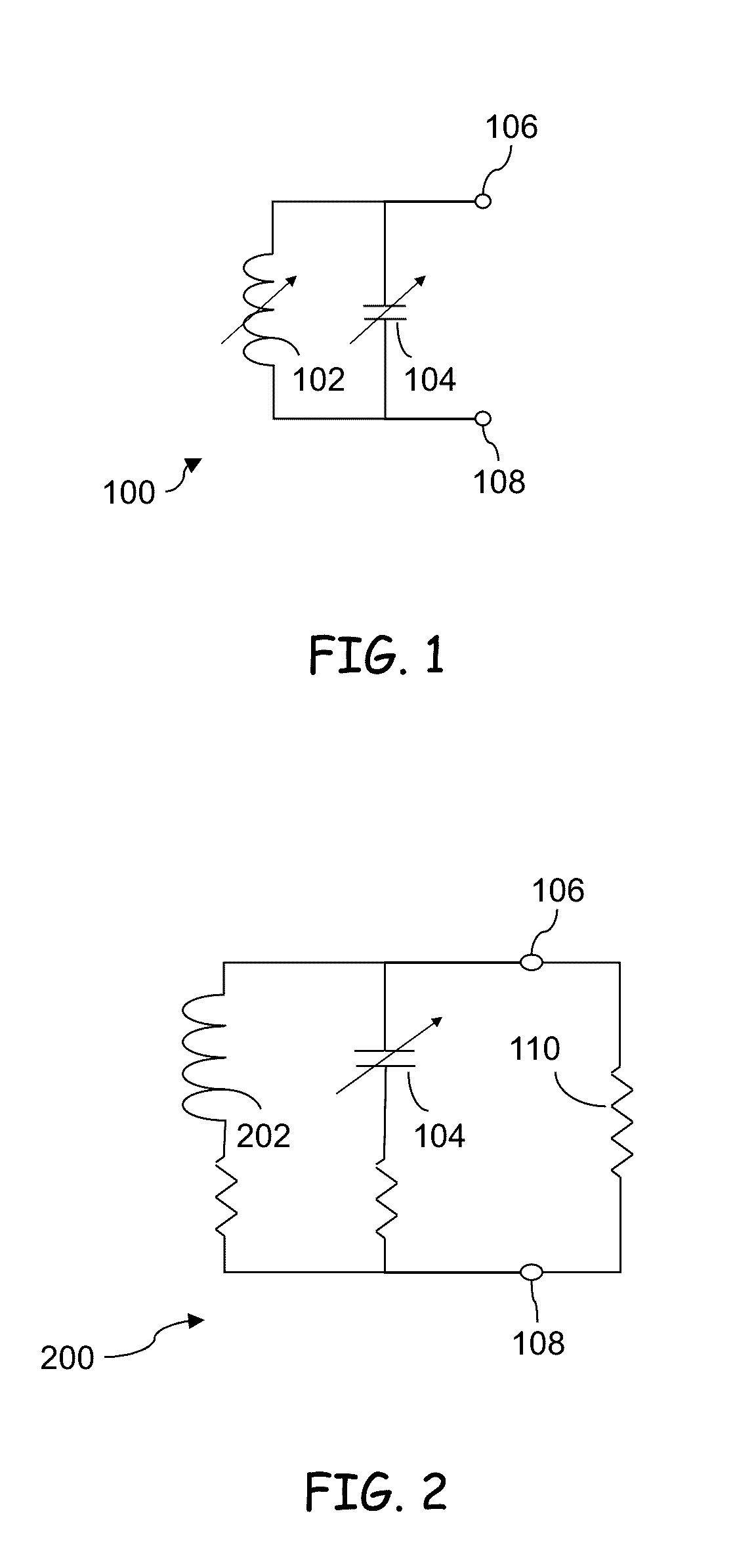
RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION (RFID) TAG(S) and SENSOR(S)
ActiveUS20160328584A1Increase flexibilityBroaden applicationSimultaneous aerial operationsRecord carriers used with machinesAntenna impedanceProcess module
A passive radio frequency identification (RFID) sensor is provided. This passive RFID sensor includes at least one antenna, at least one processing module, and a wireless communication module. The at least one antenna has an impedance that may vary with an environment in which the sensor is placed. Additionally, the antenna impedance might be permanently changed in response to an environmental variation or an event. The at least one processing module couples to the antenna and has a tuning module that may vary a reactive component impedance coupled to the antenna in order to change a system impedance. The system impedance includes both the antenna impedance and the reactive component impedance. The tuning module then produces an impedance value representative of the reactive component impedance. A memory module may store the impedance value which may then later be communicated to an RFID reader via the wireless communication module. The RFID reader may then exchange the impedance value representative of the reactive components of impedance with the RFID reader such that the RFID reader or another external processing unit may process the impedance value in order to determine environmental conditions at the inductive loop. These environmental conditions may include but are not limited to temperature, humidity, wetness, or proximity of the RFID reader to the passive RFID sensor.
Owner:RFMICRON
Method for detecting stress and strain of road surface
InactiveCN101696878AIn line with the actual situationCapture stress and strainForce measurementSimulationTechnology research
The invention discloses a method for detecting stress and strain of a road surface, belonging to the field of structure performance research of bituminous road surface. In the method, a bituminous layer strain sensor, a soil pressure case, a temperature sensor and a shaft sensor are embedded at the proper position of the road to be tested; and the data collected by a high-speed data collecting system is analyzed and processed to obtain the stress and strain of the road surface. The data measured by the method can reflect the actual situation of the road surface and has favorable values for promotion and application. The invention can be widely applied to the stress state, change rule and detection technology research inside the road surface under the action of traffic load and the coupling action of environmental variation.
Owner:山东省交通科学研究所
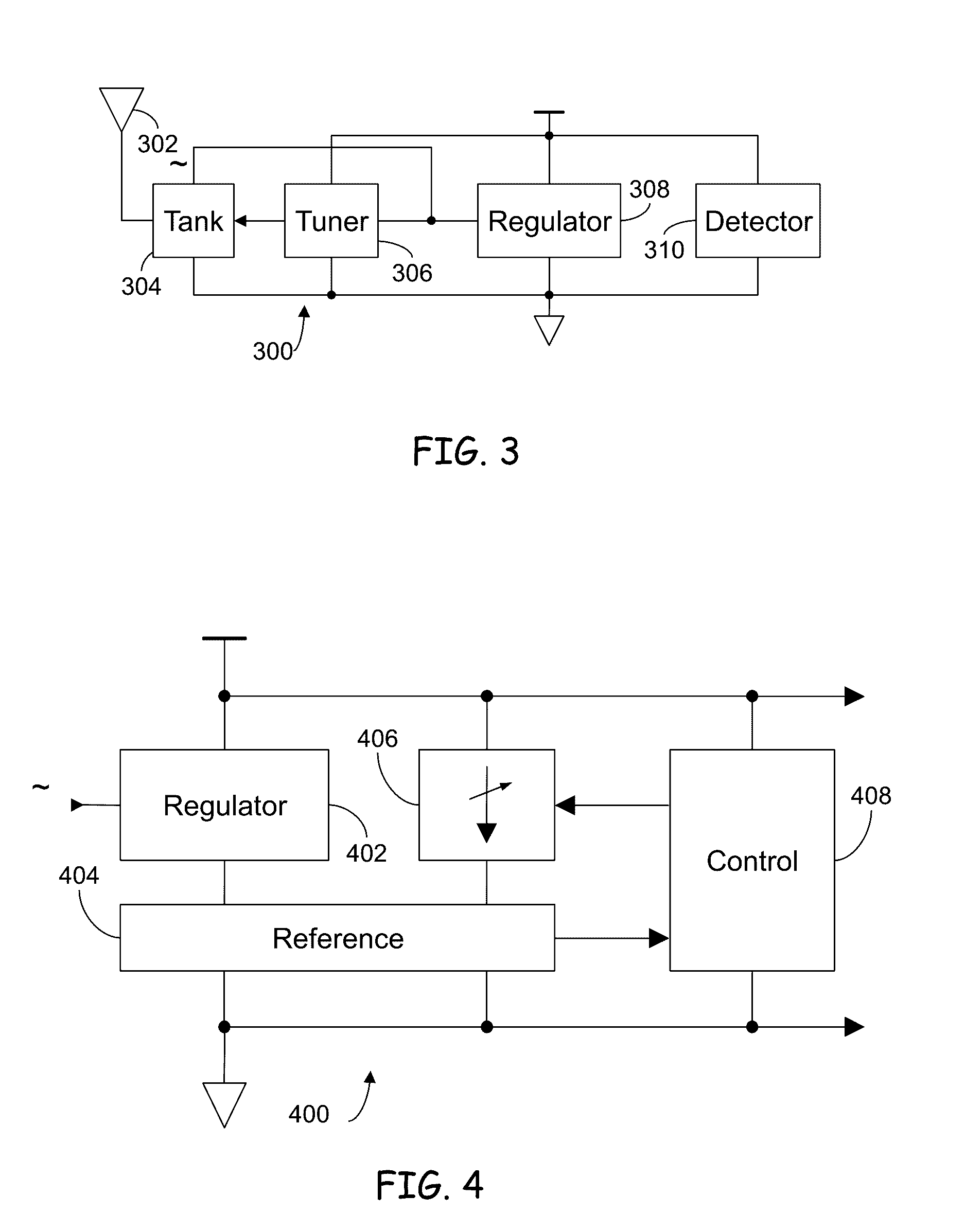
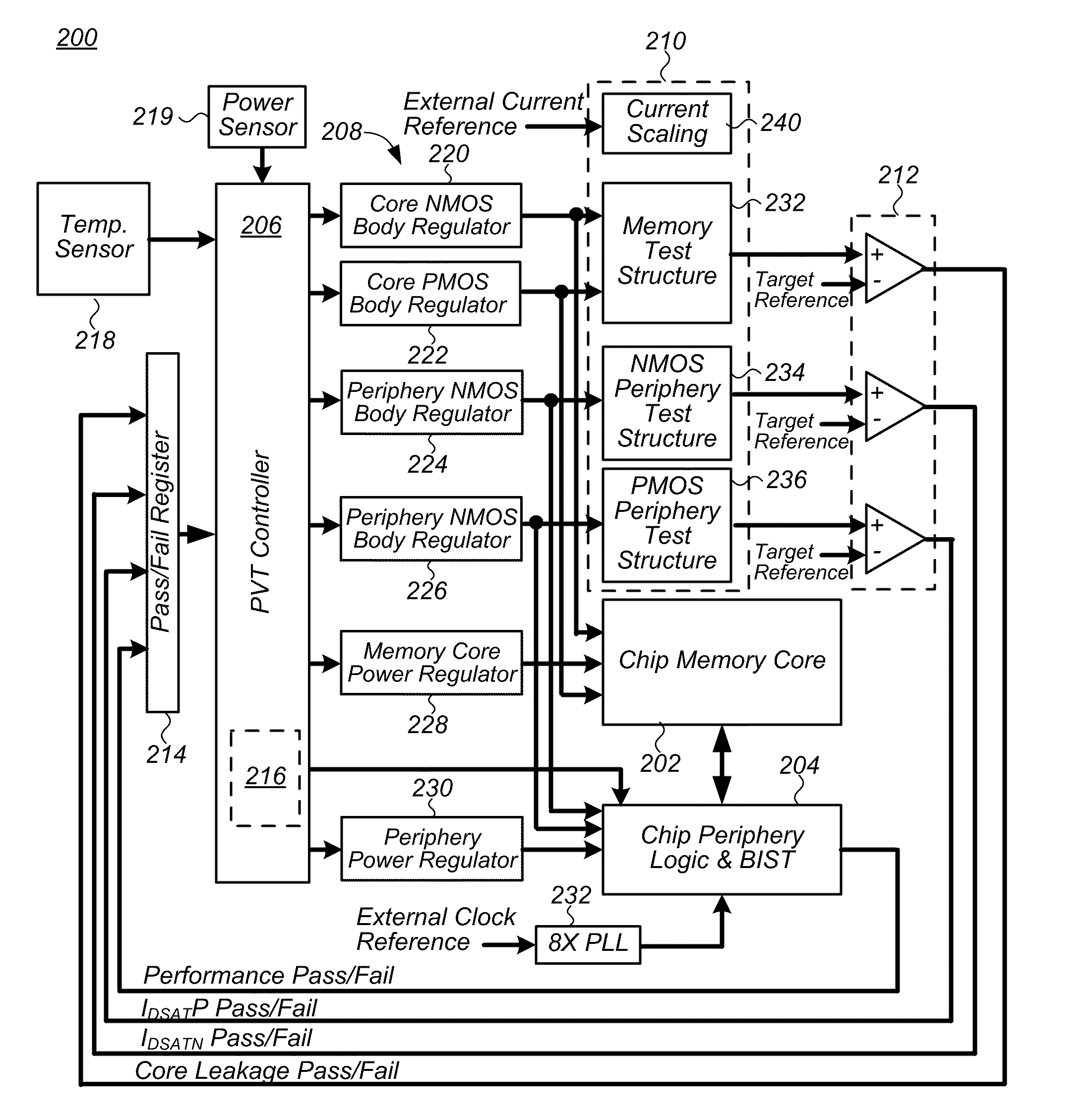
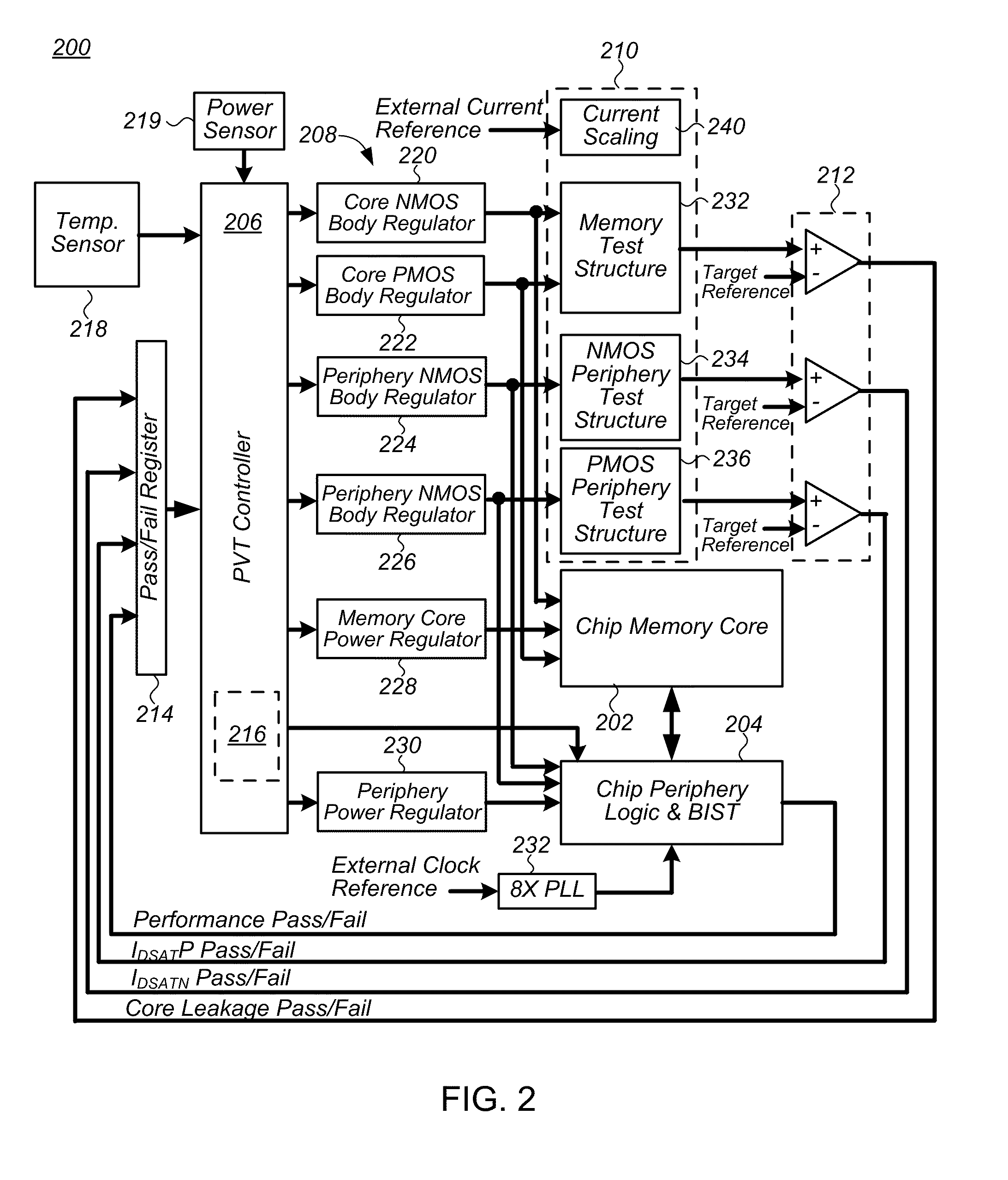
System and method to compensate for process and environmental variations in semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20110063937A1Improve data retentionIncrease frequencyImpedence convertorsElectronic switchingElectric forceDevice material
An integrated circuit (IC) including a controller integrally formed on a shared die with the IC and method of operating the same to compensate for process and environmental variations in the IC are provided. In one embodiment the IC is comprised of device and sub-circuits, and the method includes: receiving in the IC electrical power and information on at least one of one or more operational parameters of the IC; and adjusting one or more operating characteristics of at least one of the devices and sub-circuits in the IC based on the received information using a controller integrally formed on a shared die with the IC. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
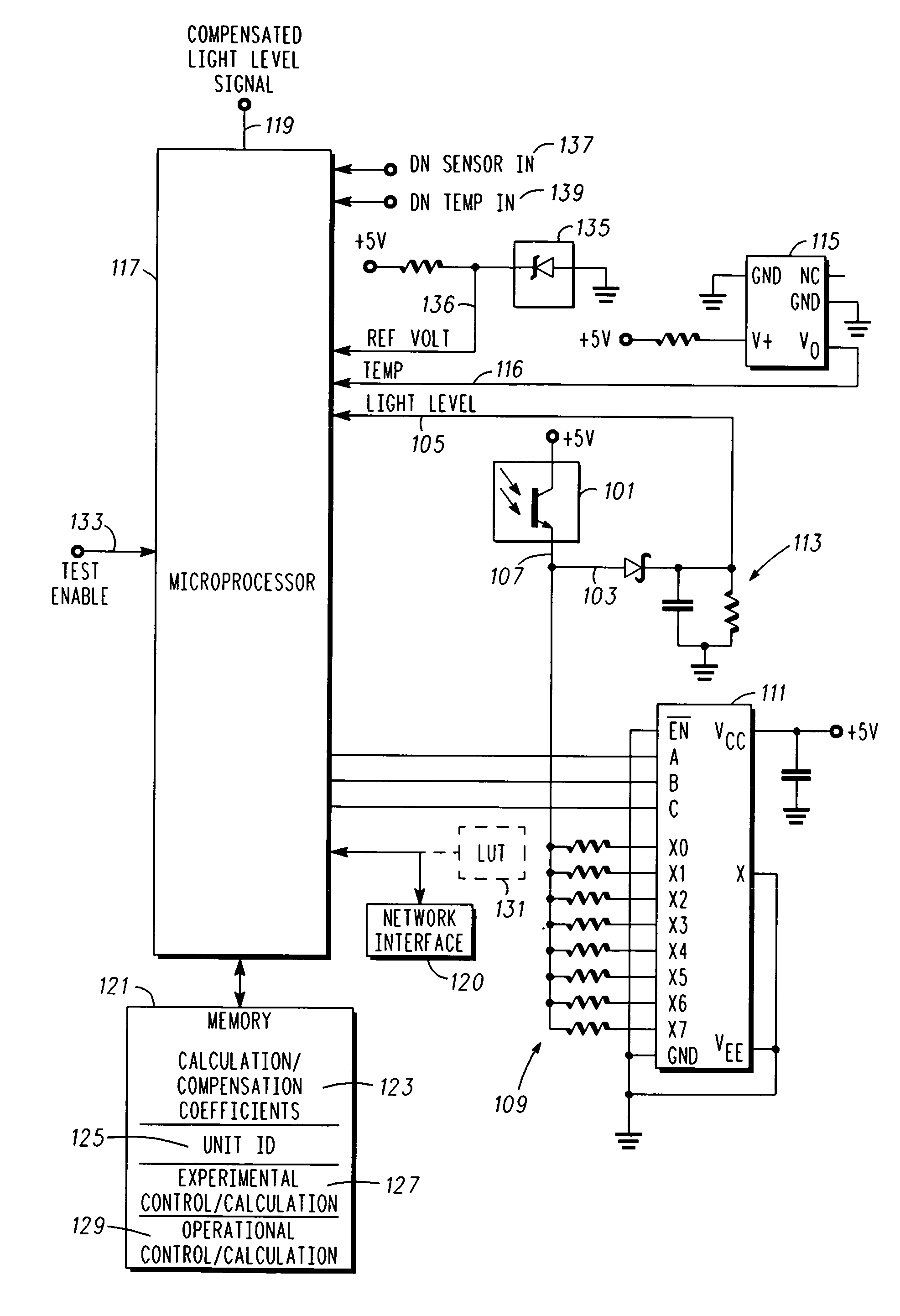
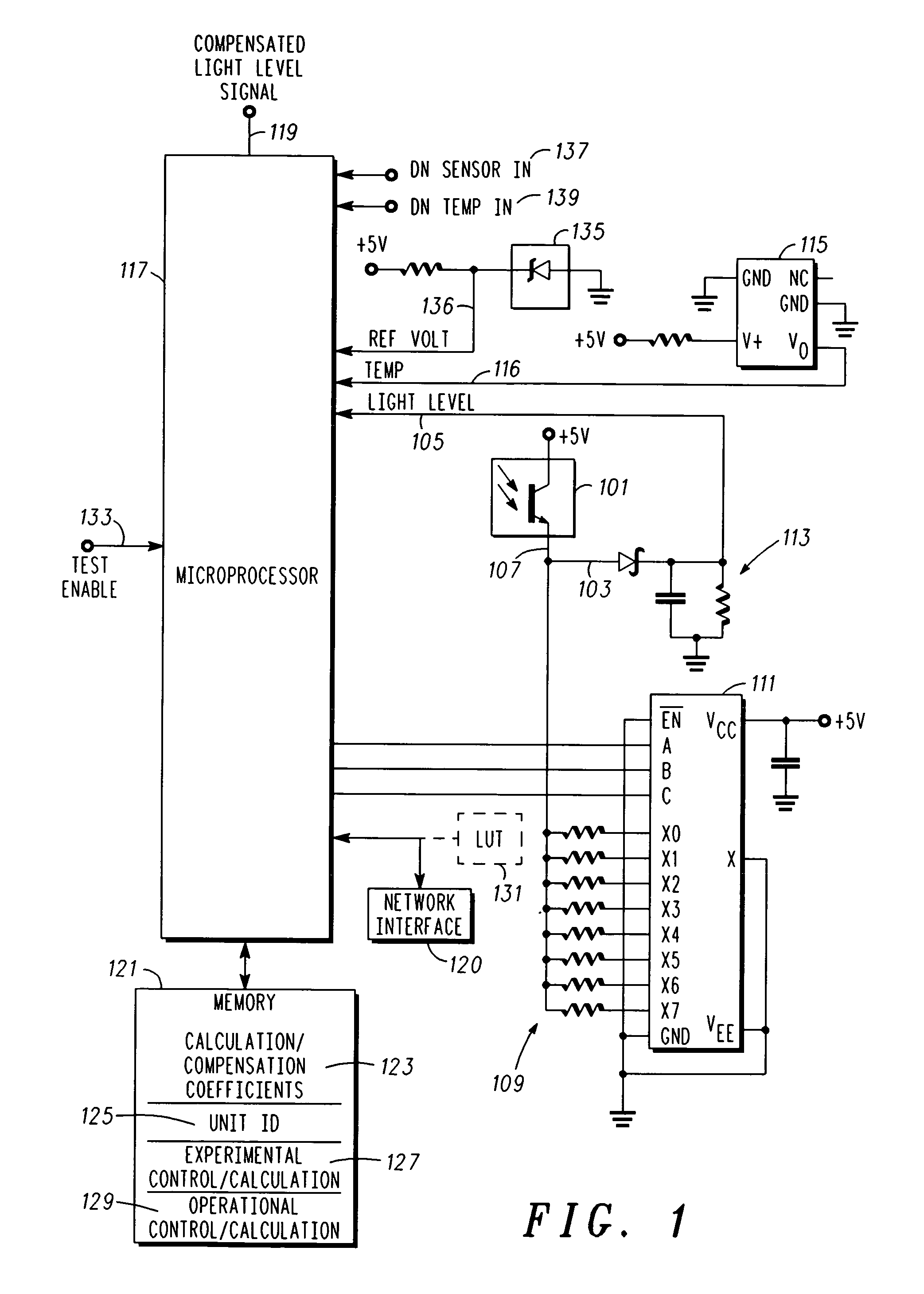
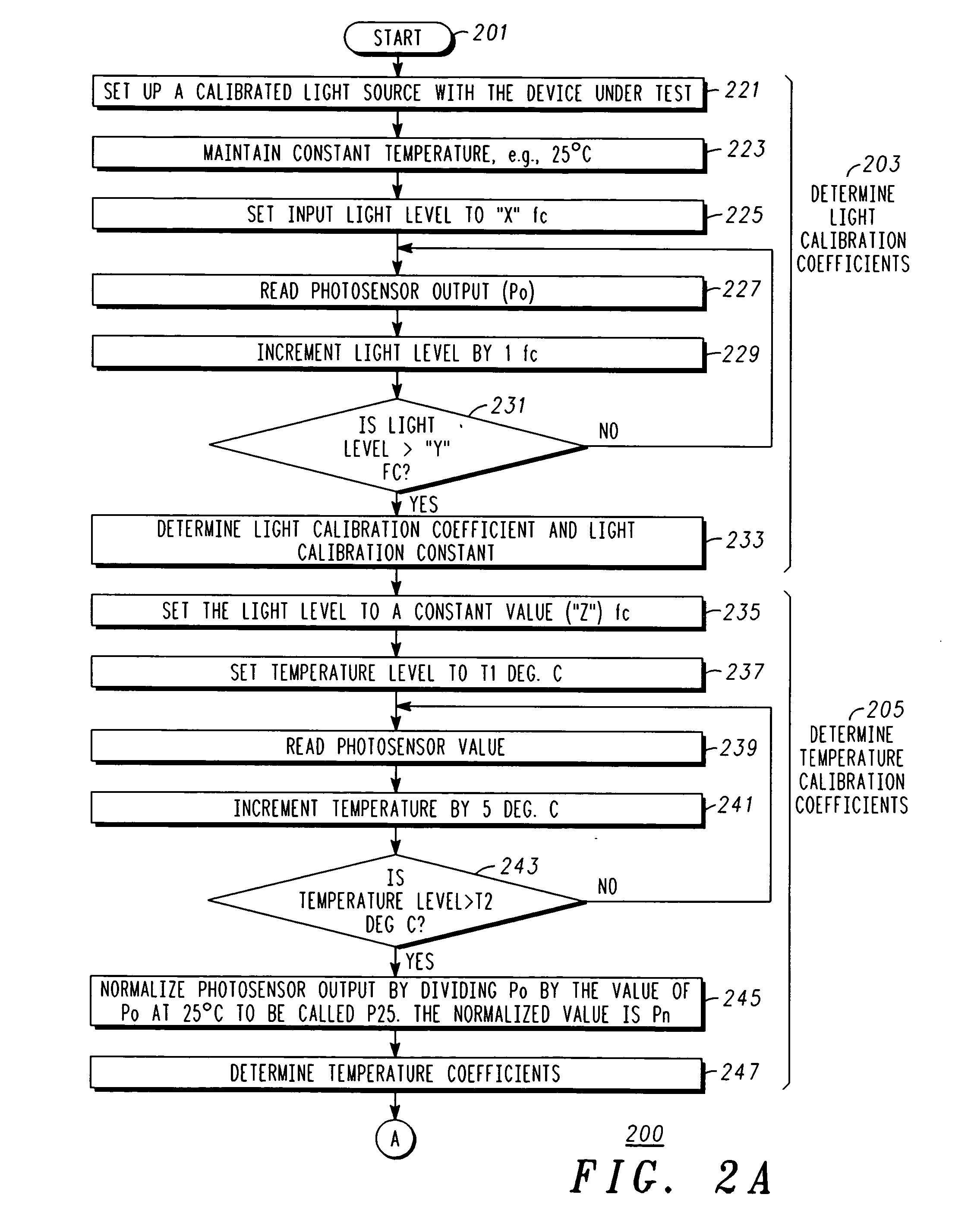
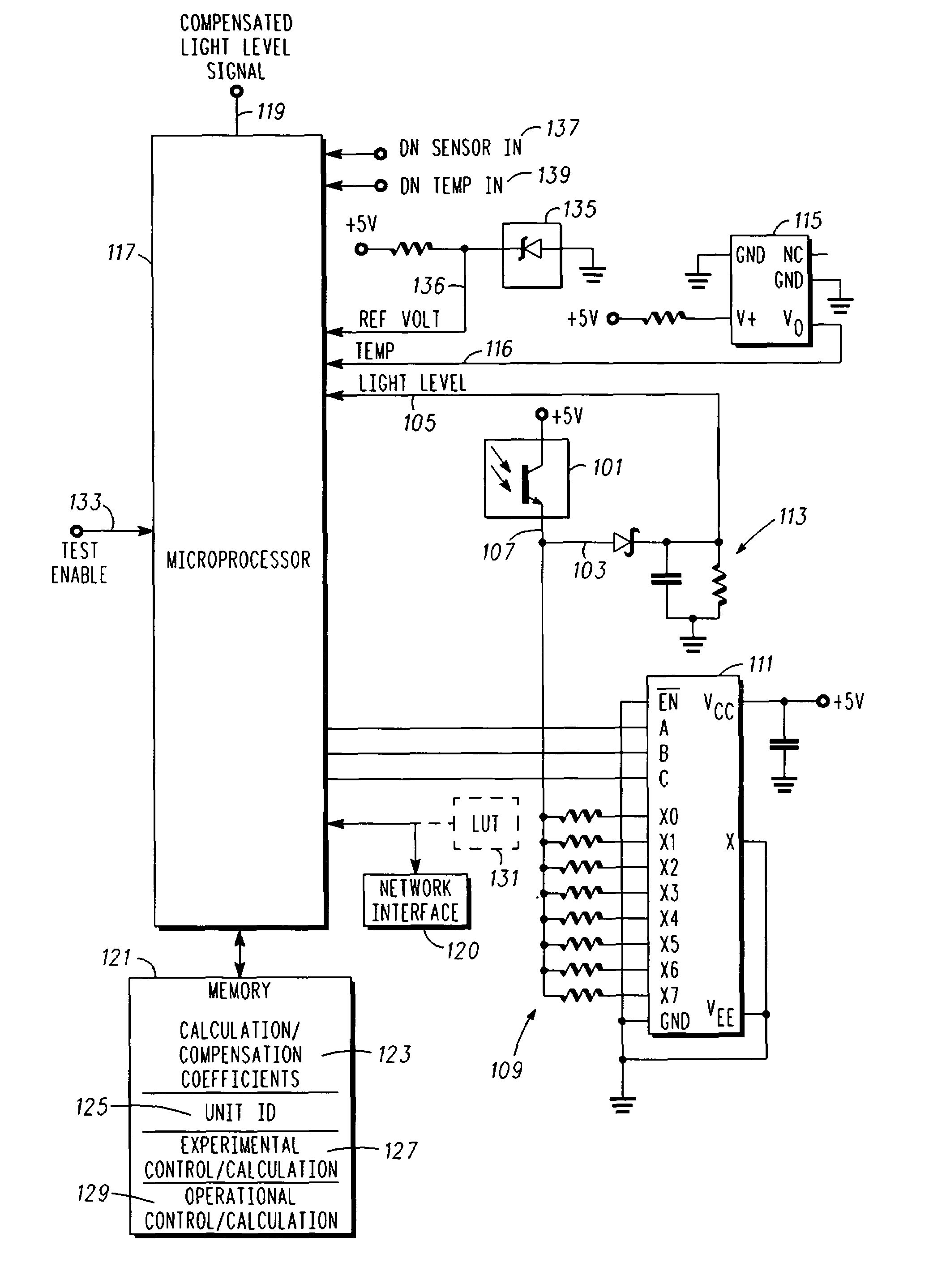
Compensation for photo sensor
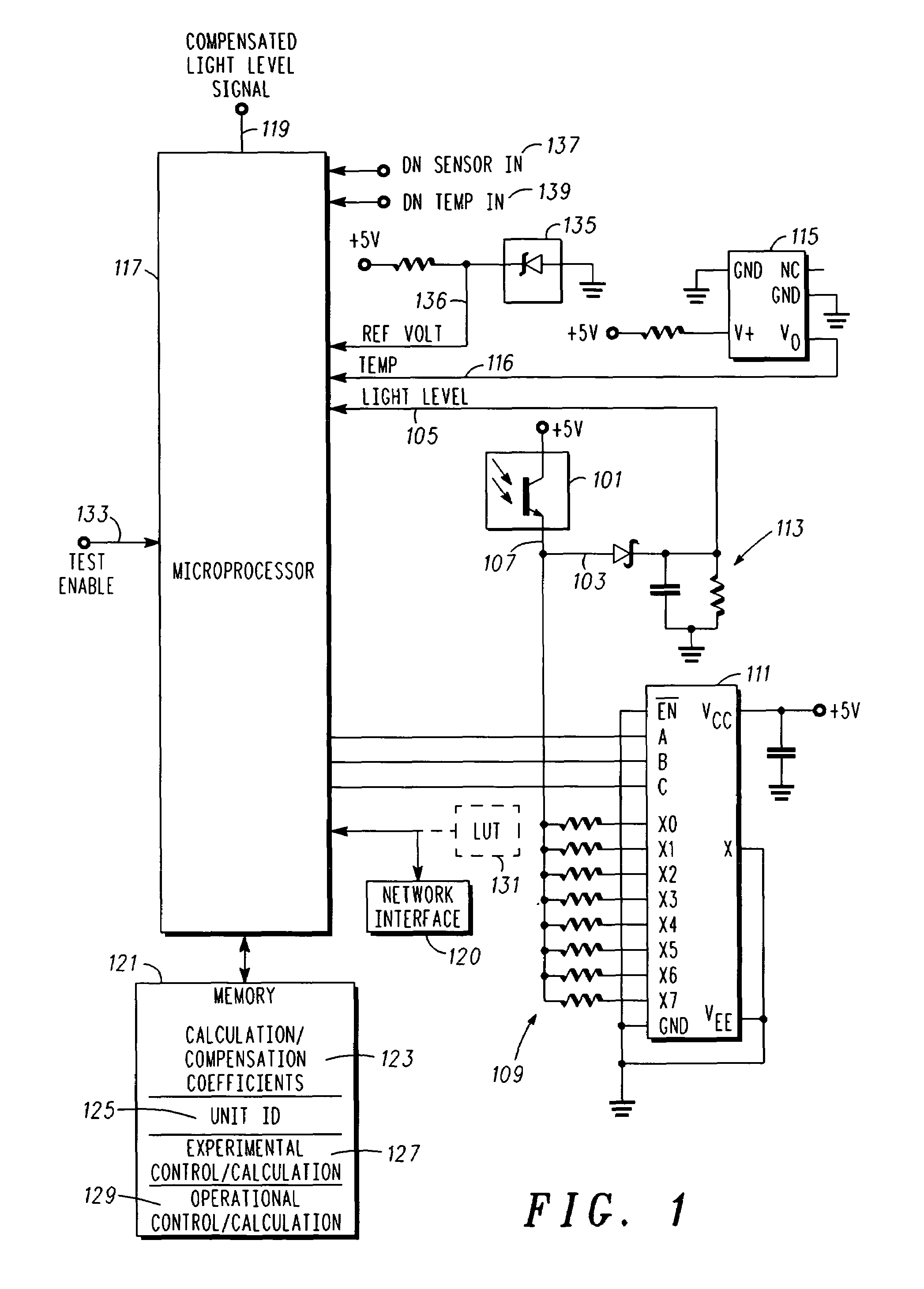
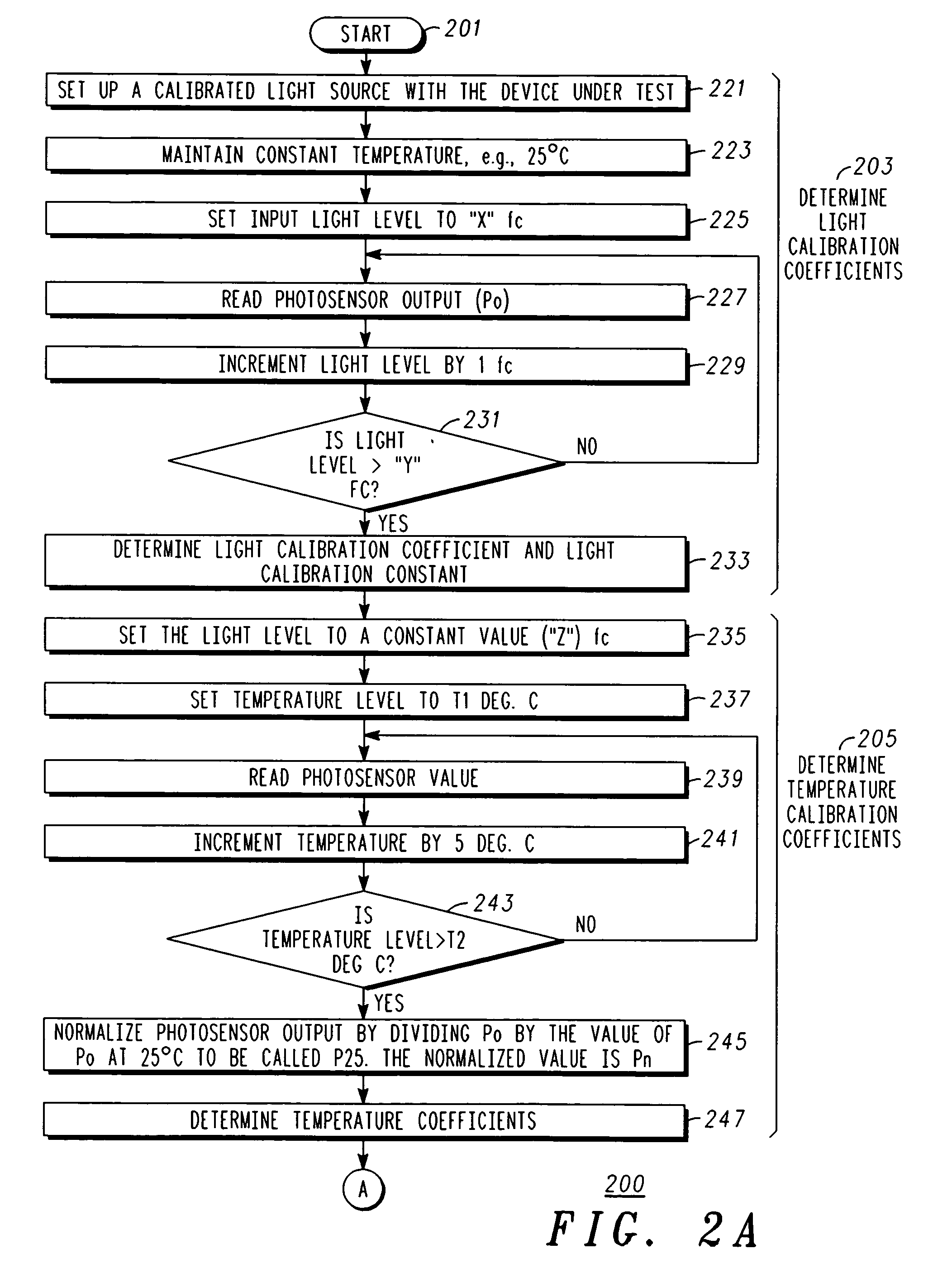
InactiveUS20070001833A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesEnvironmental variationPhysics
A method of compensating a photo sensor (and a corresponding photo sensor with compensation) insures the accuracy of the photo sensor, e.g., over environmental variations or photo cell variations. The method comprises: providing a first signal indicative of a light level; providing a second signal indicative of an environmental parameter, e.g., temperature; and calculating, responsive to the first signal and the second signal, a compensated signal that is indicative of an absolute light level. The calculating can be performed by a processor and utilize calibration and compensation information or parameters, which can be obtained experimentally.
Owner:LED ROADWAY LIGHTING +1
Photo detector with compensated output and method involving same
InactiveUS7608815B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotoelectric discharge tubesEnvironmental variationPhysics
A method of compensating a photo sensor (and a corresponding photo sensor with compensation) insures the accuracy of the photo sensor, e.g., over environmental variations or photo cell variations. The method comprises: providing a first signal indicative of a light level; providing a second signal indicative of an environmental parameter, e.g., temperature; and calculating, responsive to the first signal and the second signal, a compensated signal that is indicative of an absolute light level. The calculating can be performed by a processor and utilize calibration and compensation information or parameters, which can be obtained experimentally.
Owner:LED ROADWAY LIGHTING +1
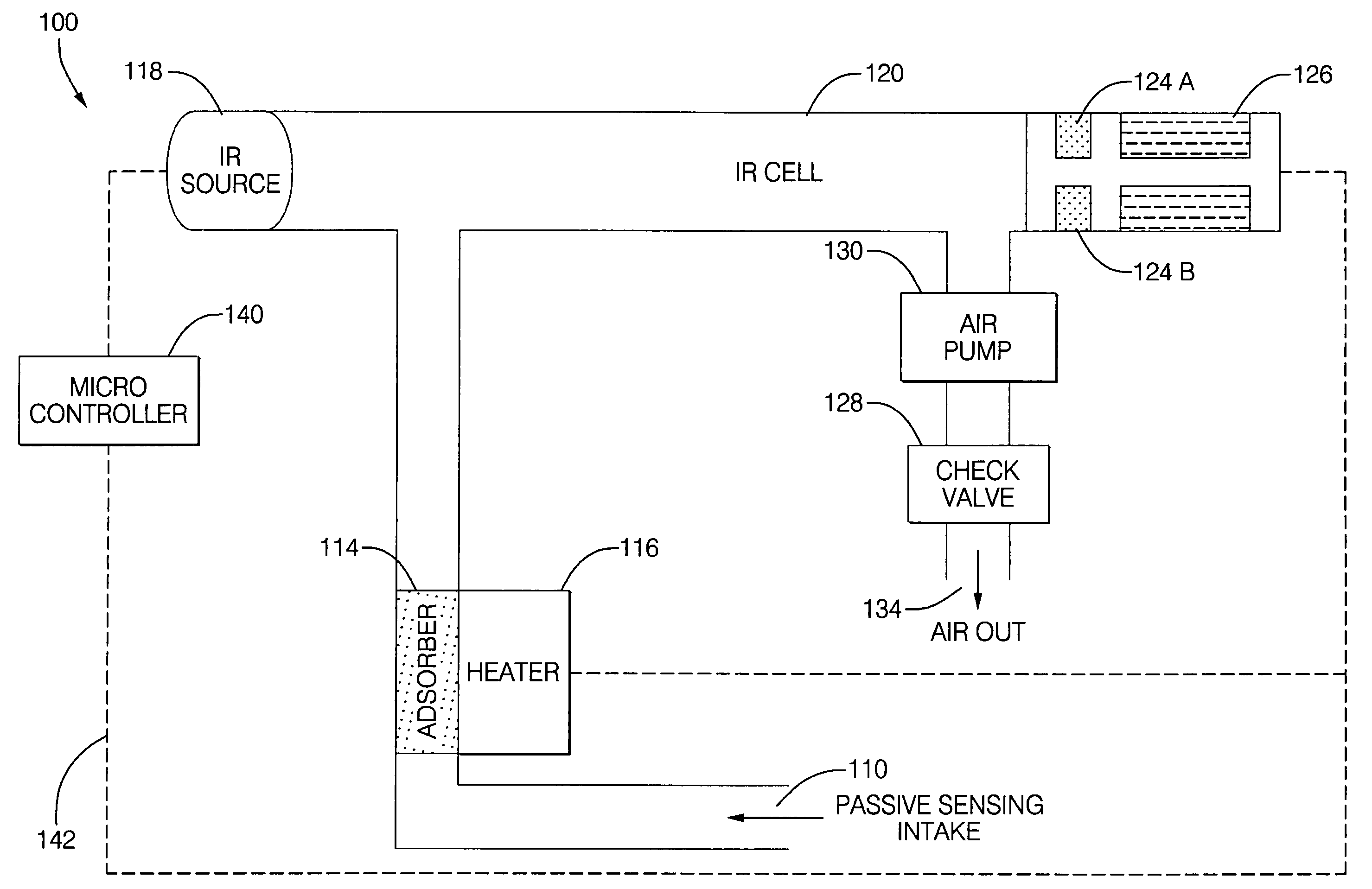
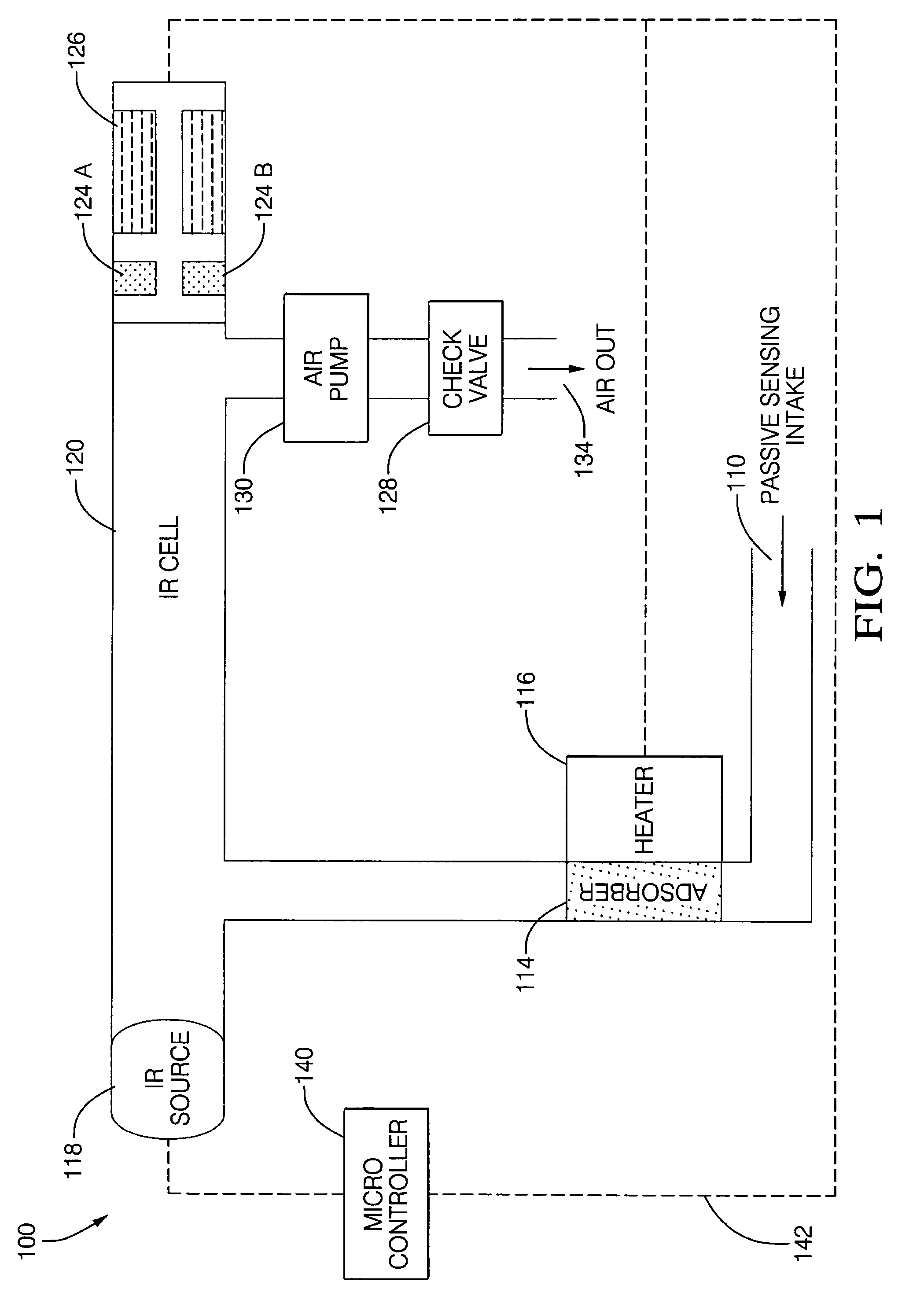
Tracer to compensate for environmental variations that influence a chemical vapor sensor measurement
ActiveUS7736903B2High sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityRadiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesChemical vaporsInfrared detector
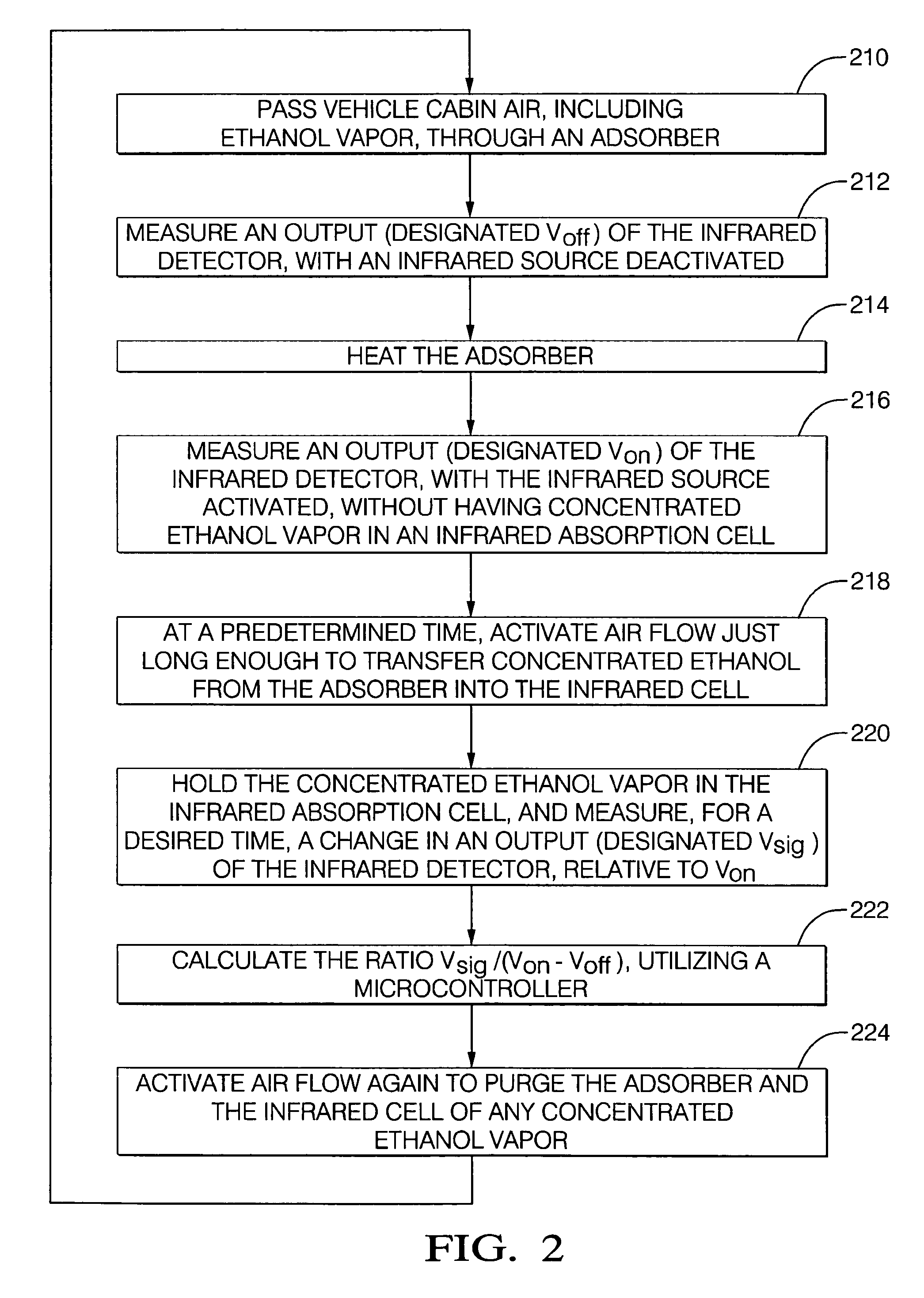
A chemical vapor sensor is provided that passively measures a suspect chemical species of interest with high sensitivity and chemical specificity, for use with safety systems. A vapor concentrator amplifies a suspect chemical vapor concentration to a detectible level, for use with an infrared detector. Compensation is provided for environmental variations that may influence the passive measurement of the chemical vapor sensor. Environmental variations may include extrinsic vapors in the surrounding air, or air currents that divert the sample vapor as it drifts from the suspect vapor source to a sampling intake. In an example, ethanol vapor is measured and carbon dioxide tracer measurements are used to calculate an ethanol vapor measurement that is adjusted for environmental variations. In an aspect, a time artifact filter sets the output of the carbon dioxide sensor to match the time dependence of the ethanol sensor, to calculate blood alcohol concentration.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Temperature-Robust MEMS Gyroscope with 2-DOF Sense-Mode Addressing the Tradeoff Between Bandwith and Gain
ActiveUS20100319451A1High gainHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMeasurement/indication equipmentsCapacitanceResonance
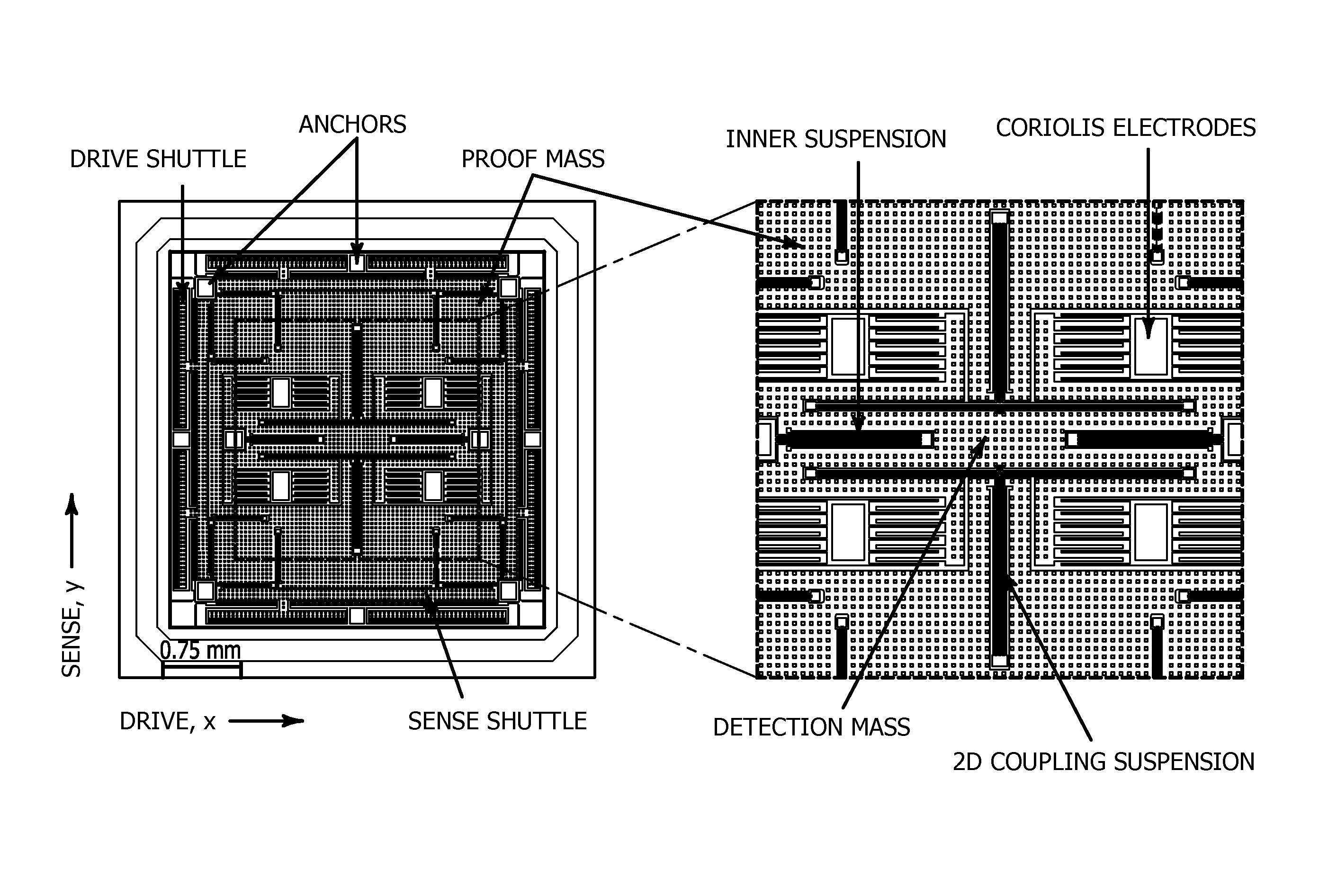
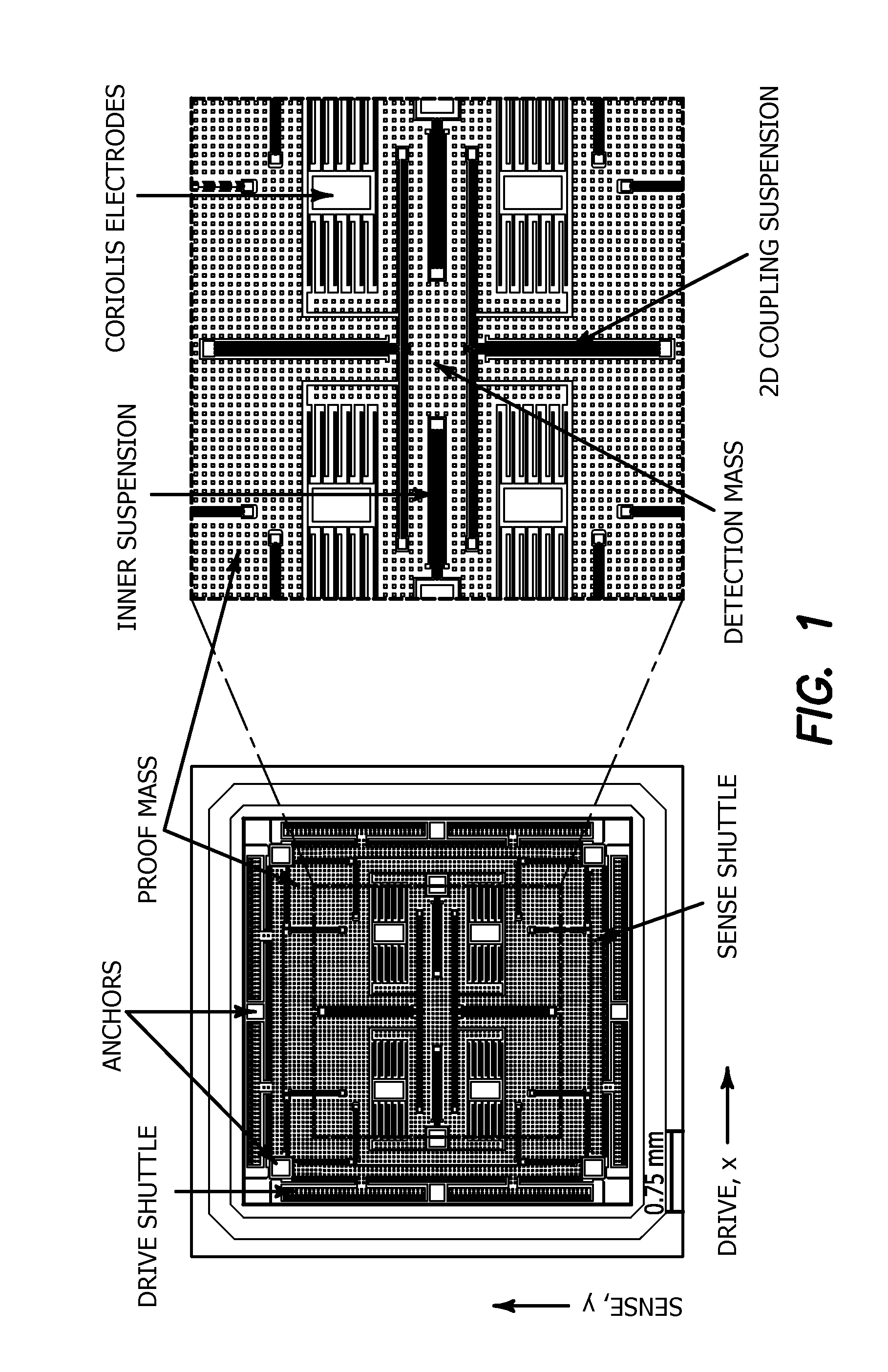
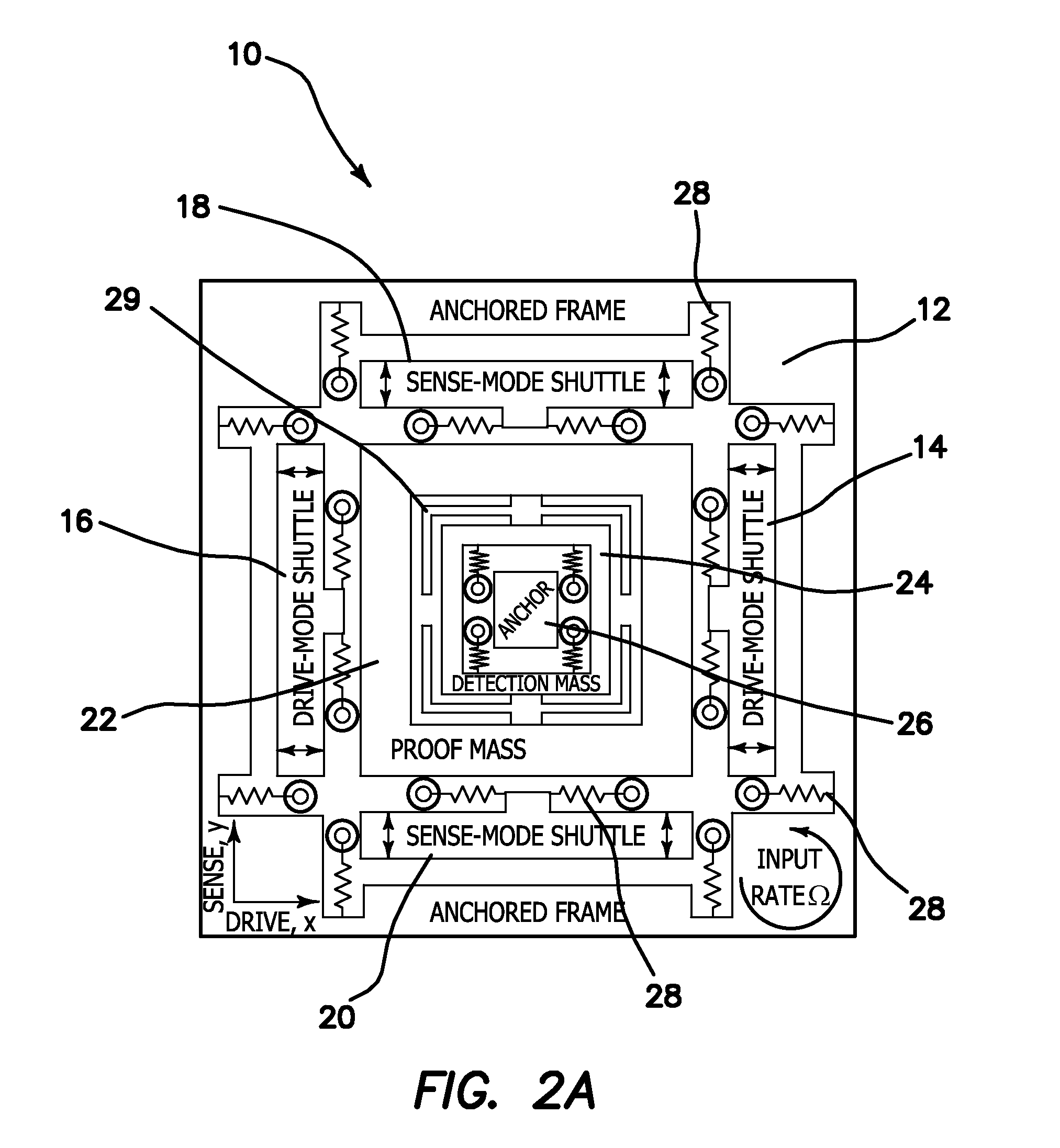
The current invention is a novel gyroscope design, which yields devices robust to fabrication and environmental variations, allows flexible selection of operational parameters, and provides increased bandwidth minimized sacrifice in gain regardless of the selected frequency of operation. The gyroscope has a single degree-of-freedom (DOF) drive-mode and a 2-DOF sense-mode. The drive-mode operational frequency and the sense-mode bandwidth can be selected arbitrarily in the proposed design, relaxing the tradeoff between the gain, die size, and detection capacitance. The symmetry of the structure ensures the optimal location of the drive-mode resonance relative to the sense-mode operational region, even in presence of fabrication imperfections.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
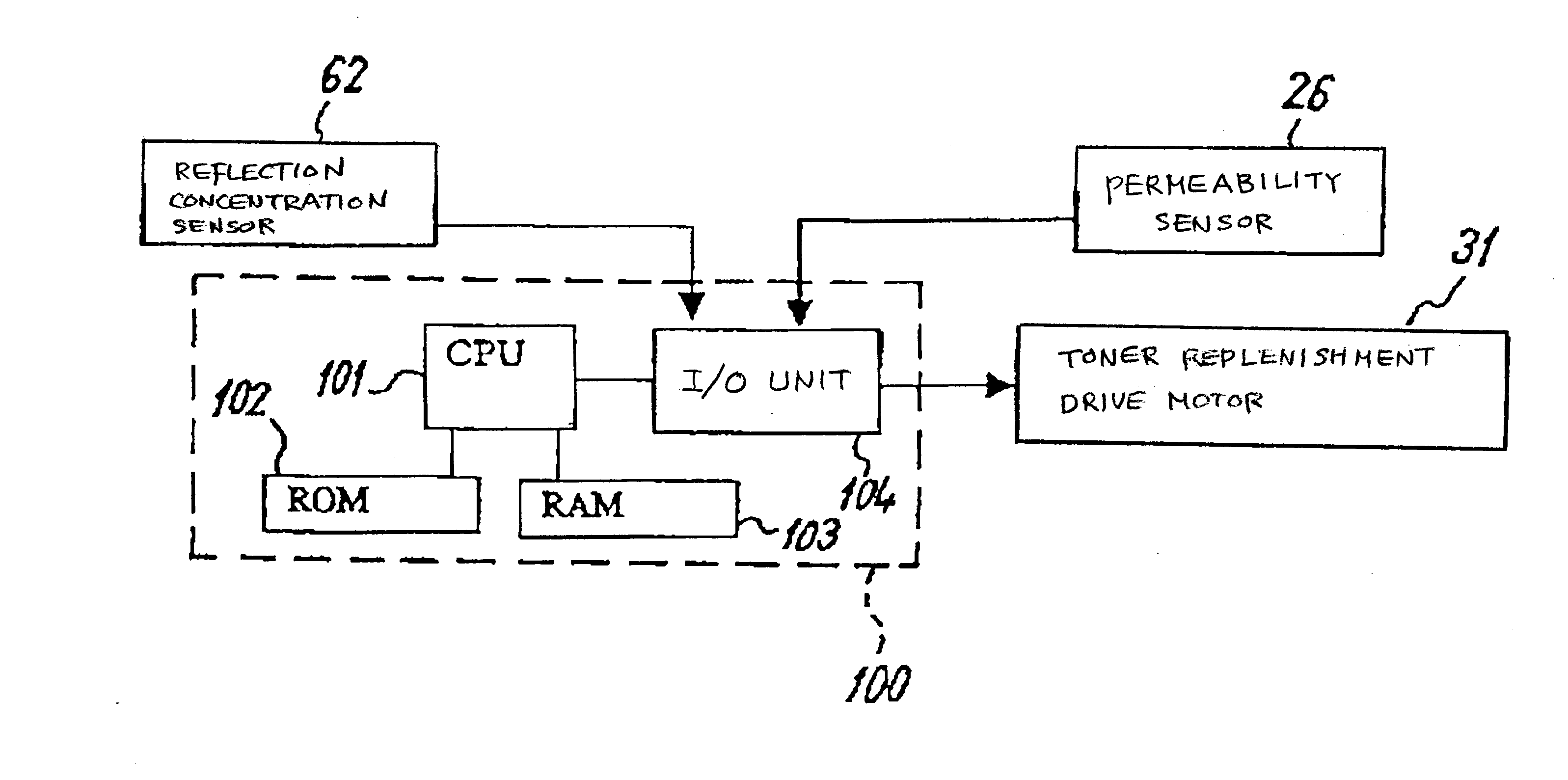
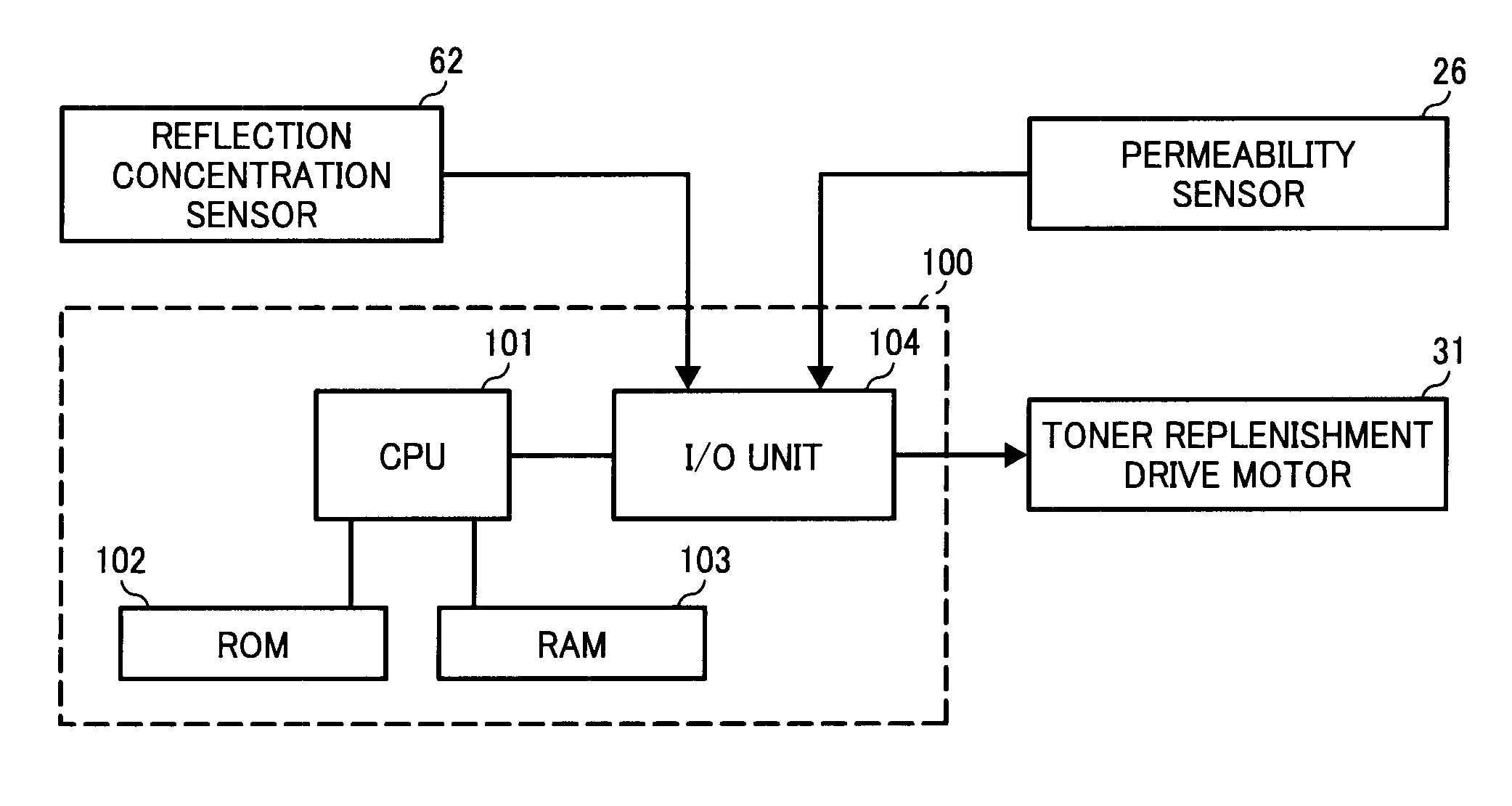
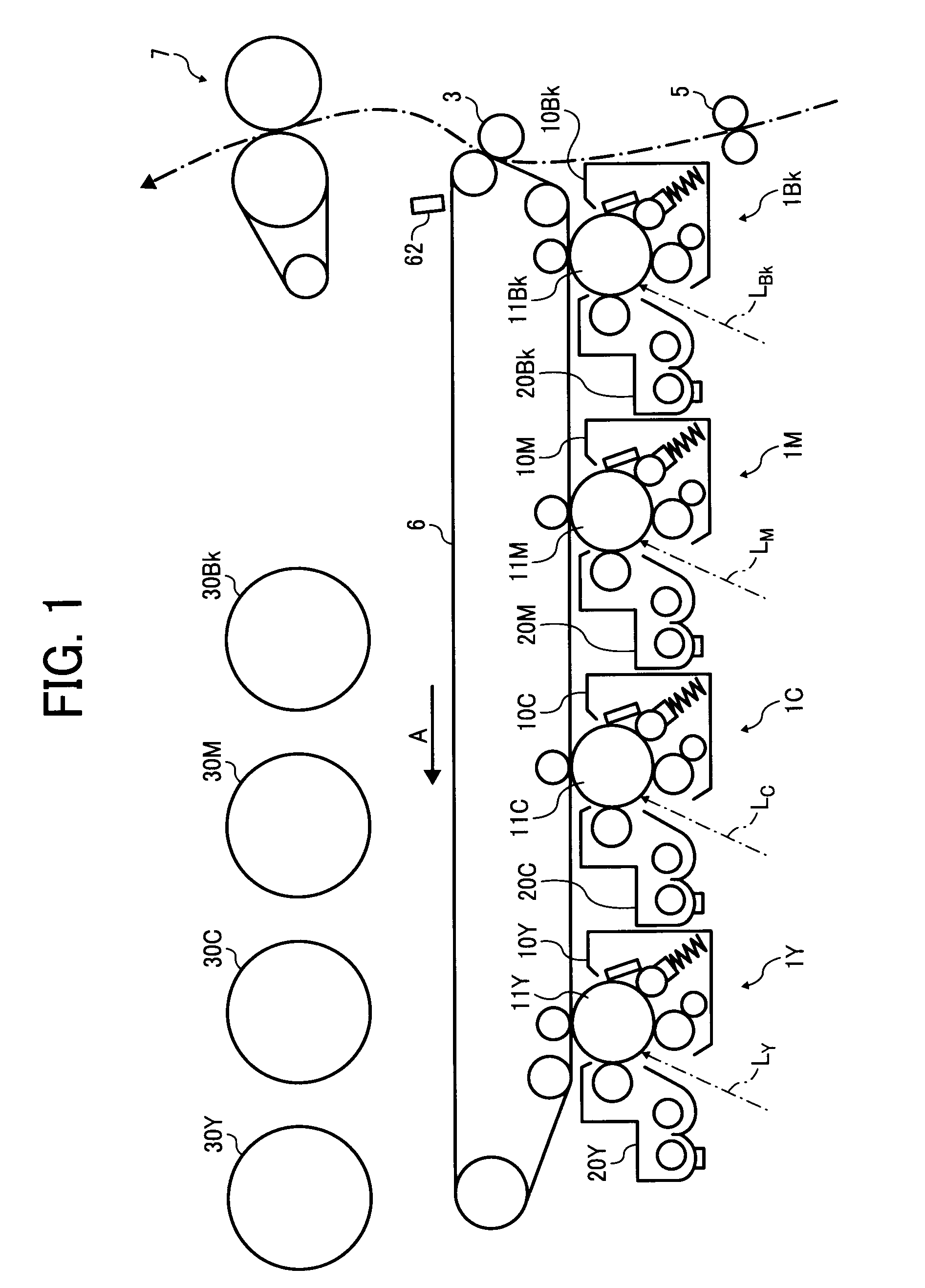
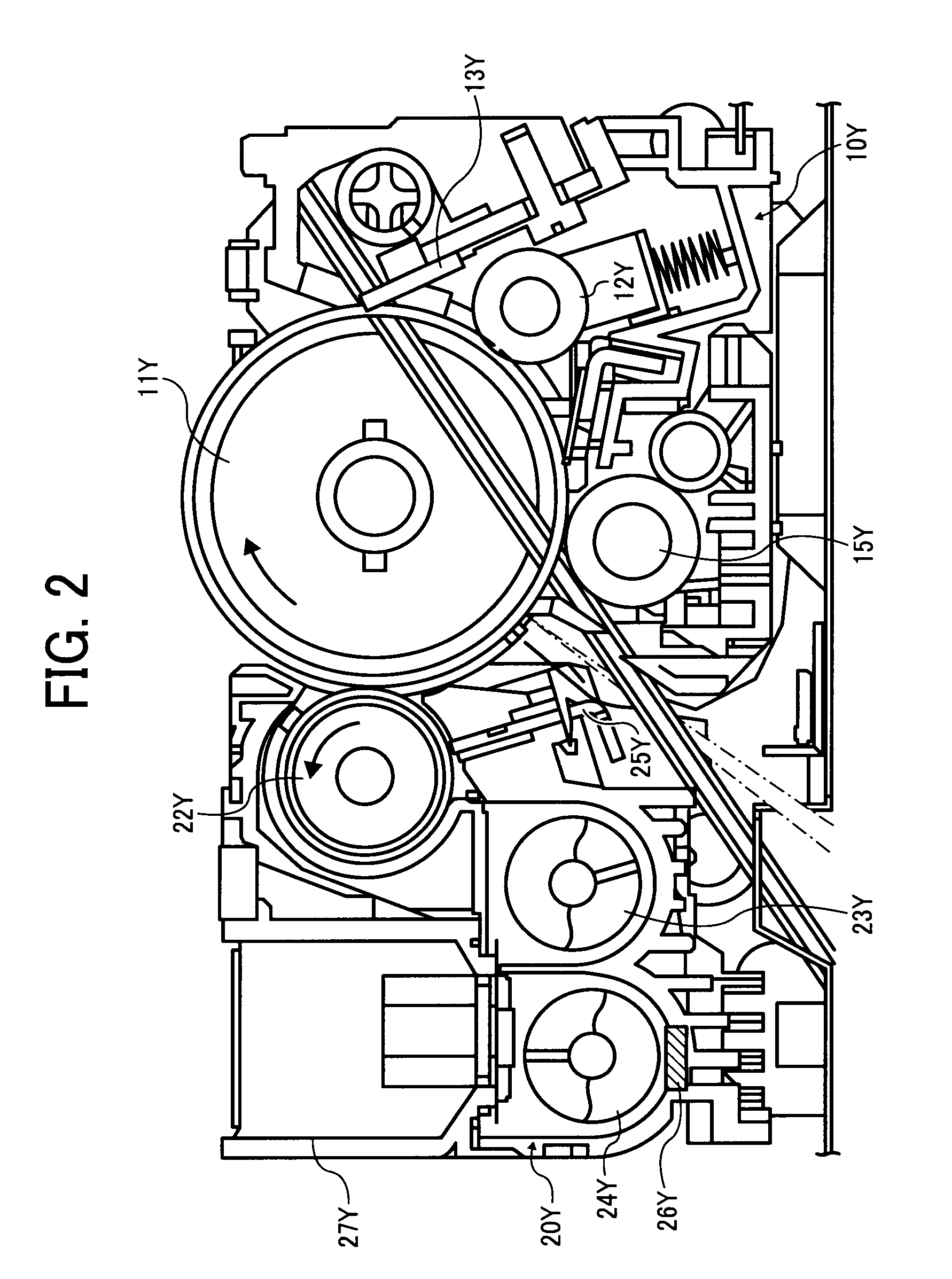
Image forming apparatus and image density control method
InactiveUS20080124107A1Suppression problemConstant image densityElectrographic process apparatusPattern detectionImage formation
In an image forming apparatus and an image density control method that are capable of suppressing the amount of toner consumed for a purpose other than image formation and responding to variation in the development ability of a development device due to environmental variation and the like such that a constant image density is obtained, the image density is maintained at a substantially fixed level by first target output value correcting means in accordance with a toner replacement amount and without consuming toner, and adjustment of the image density accompanying variation in the development ability due to environmental variation and the like is dealt with by second target output value correcting means in accordance with a toner pattern detection result. Hence, the frequency with which the toner pattern is detected in order to maintain the image density at a fixed level can be reduced in comparison with a case in which the image density is maintained at a fixed level on the basis of the toner pattern detection result alone, and as a result, the toner consumption amount can be suppressed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Ground gravity unloading support method for large spatial reflector
A ground gravity unloading support method for a large spatial reflector belongs to the technical field of space optics. In order to solve the problem that the gravity environmental variation of the large spatial reflector results in the decline of the surface shape precision of the reflector, a finite element analysis software is adopted to carry out finite element modeling on a spatial reflector assembly and analyze the variation of the reflector surface shape precision caused by gravity when the spatial reflector assembly is horizontally placed; the number and distribution of active support points at the back of the spatial reflector are primarily determined according to the size of the spatial reflector, the variation analysis result of the reflector surface shape precision and the layout condition of a support structure; after support force is applied on the active support points of the spatial reflector, the variation condition of the reflector surface shape precision caused by gravity when the spatial reflector assembly is horizontally placed is analyzed, the reflector surface shape precision result of the spatial reflector assembly is enabled to meet optical design requirements through analyzing and adjusting the size of the support force applied on the active support points and the number and distribution of the active support points, and the gravity unloading of the reflector is realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
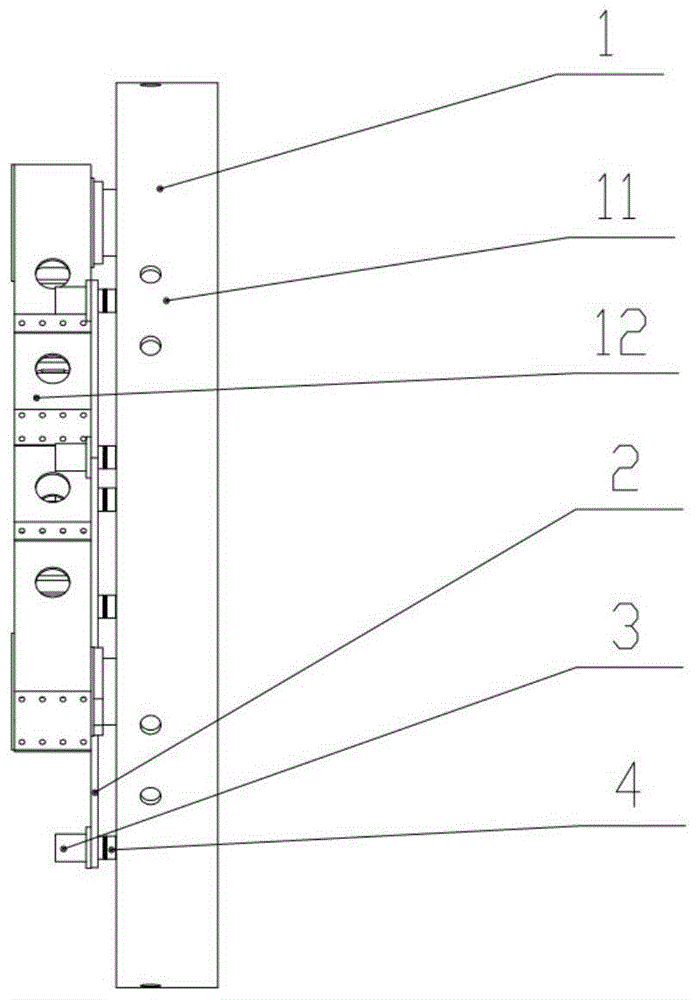
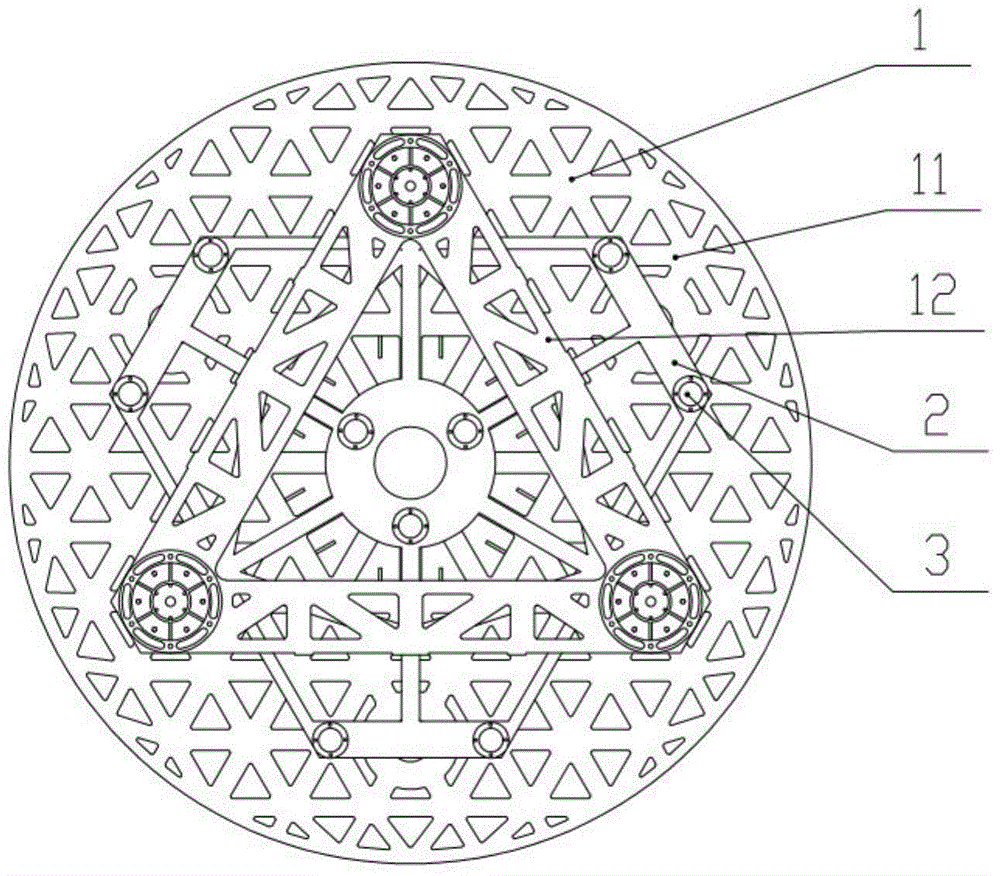
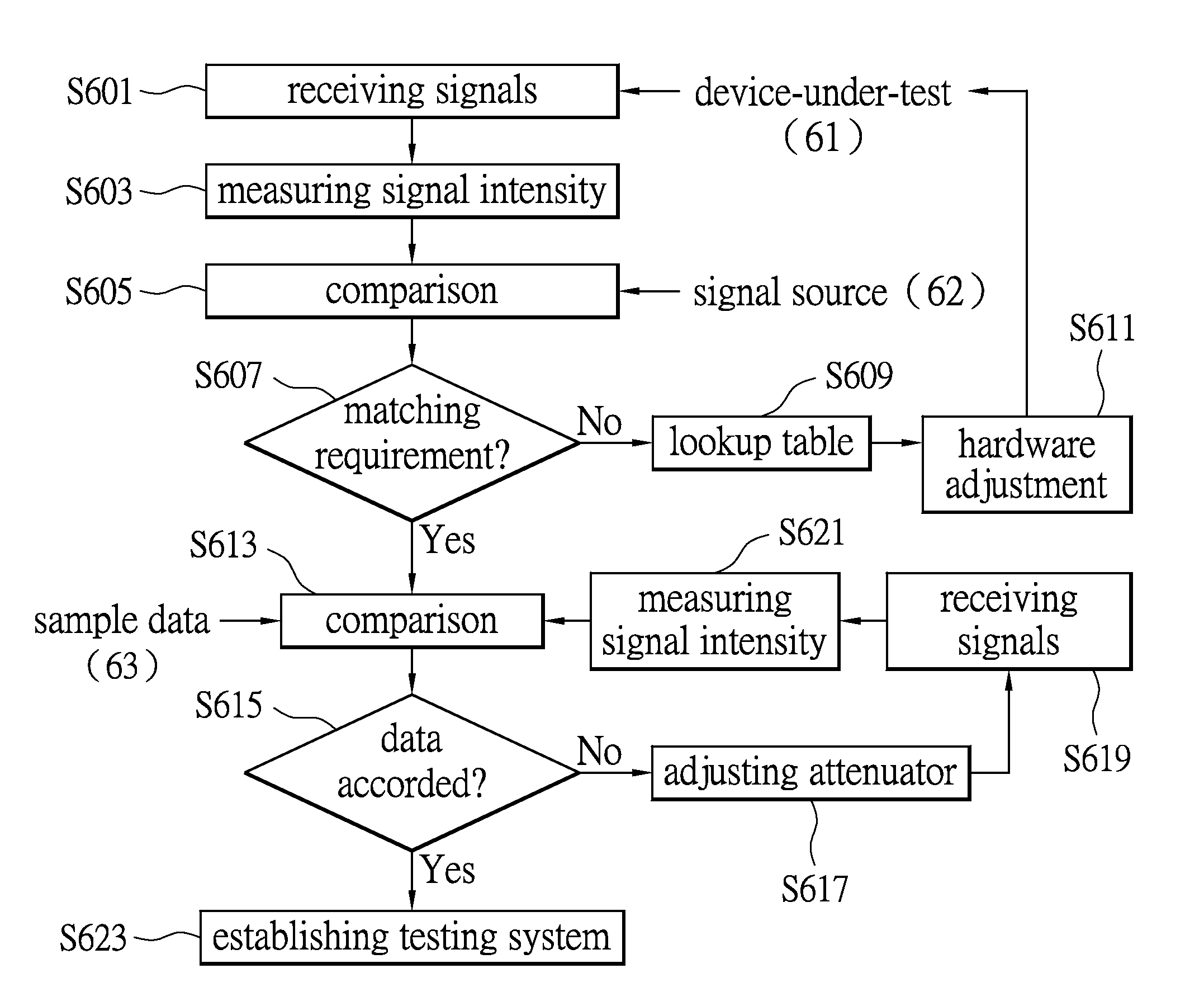
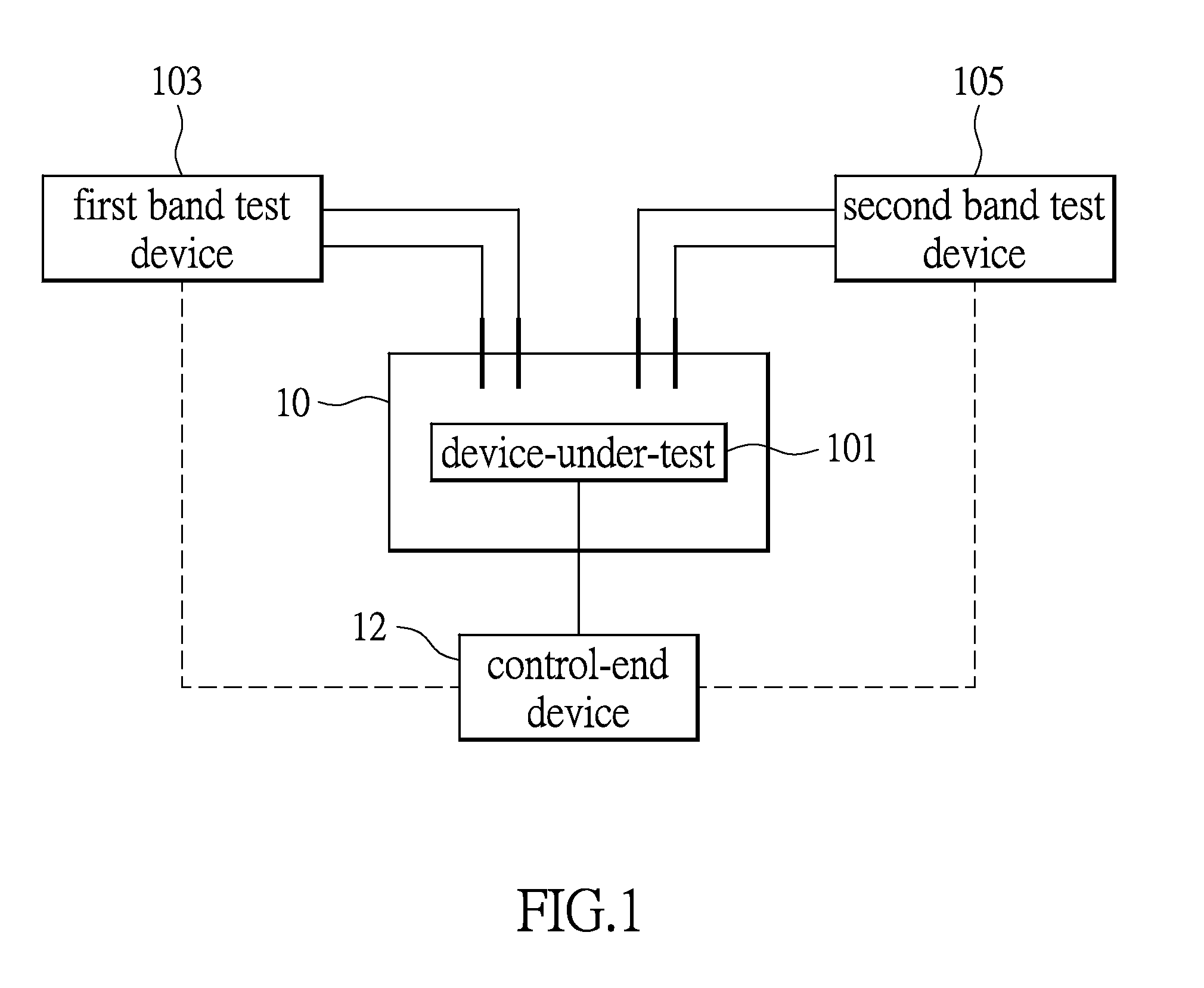
System for testing wireless signals and method for establishing the same
InactiveUS20140355457A1Stable and accurate testIncrease productionError preventionTransmission systemsUltrasound attenuationEngineering
Disclosure herein is related to a system for testing wireless signals and a method provided for establishing the system. One of the objectives is to establish one new testing system while the method effectively reduces the unstable problem caused by hardware or environmental variations. The testing system measures intensity of the wireless signals outputted from a device-under-test. While compared to a test signals, it is determined if the signal intensities there-between are balanced. Accordingly, the hardware of system is required to be adjusted. After that, the wireless signals are compared with sample signals for determining whether or not the test results are stable among the different testing system. An attenuation value may be introduced to adjusting the test result. A new testing system is therefore established.
Owner:ARCADYAN
Face recognition method based on template matching
ActiveCN1790374ACalculation speedImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionTemplate matchingTemplate based
The invention discloses a face identification method based on model matching, which comprises the following steps: transmitting the face to the changing region; doing LBP calculation of face image; extracting histogram from the LBP calculation result; accomplishing face identification through histogram matching. The invention improves the calculation speed, which reduces the sensitive degree of gesture, light, appearance and environmental variation.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Statistical delay and noise calculation considering cell and interconnect variations
ActiveUS20090288050A1Efficiently delayEfficiently sensitivityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputation using non-denominational number representationNumerical stabilityEnvironmental variation
The electrical circuit timing method provides accurate nominal delay together with the delay sensitivities with respect to different circuit elements {e.g., cells, interconnects, etc.) and variational parameters (e.g., process variations; environmental variations). All the sensitivity computations are based on closed-form formulas; as a consequence, the method provides rapidly and at low cost high accuracy and high numerical stability.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
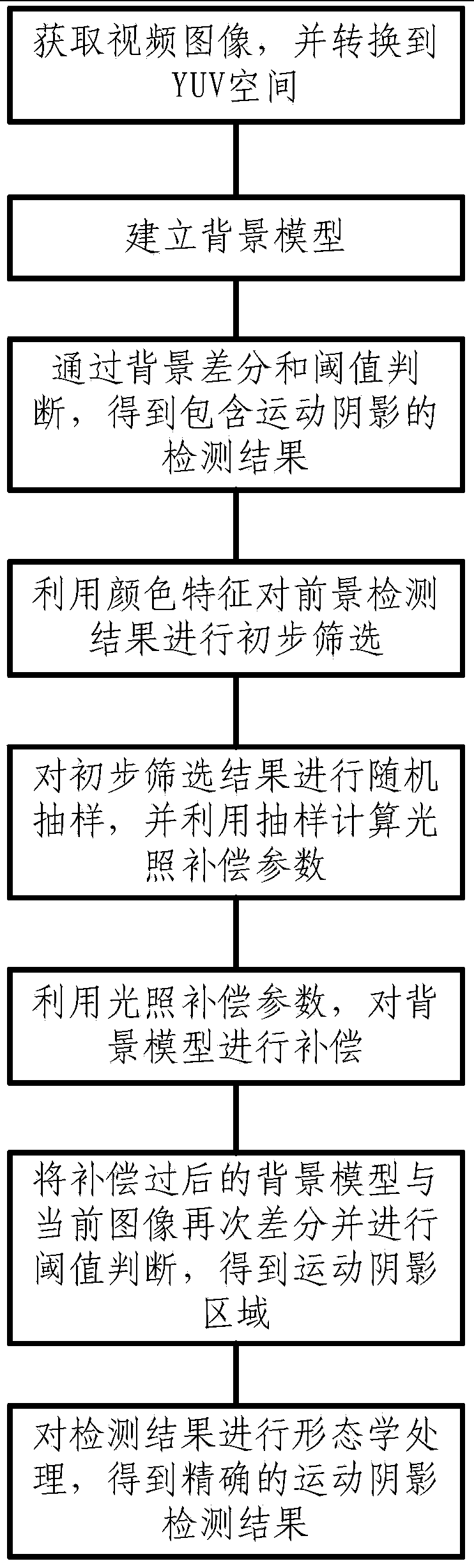
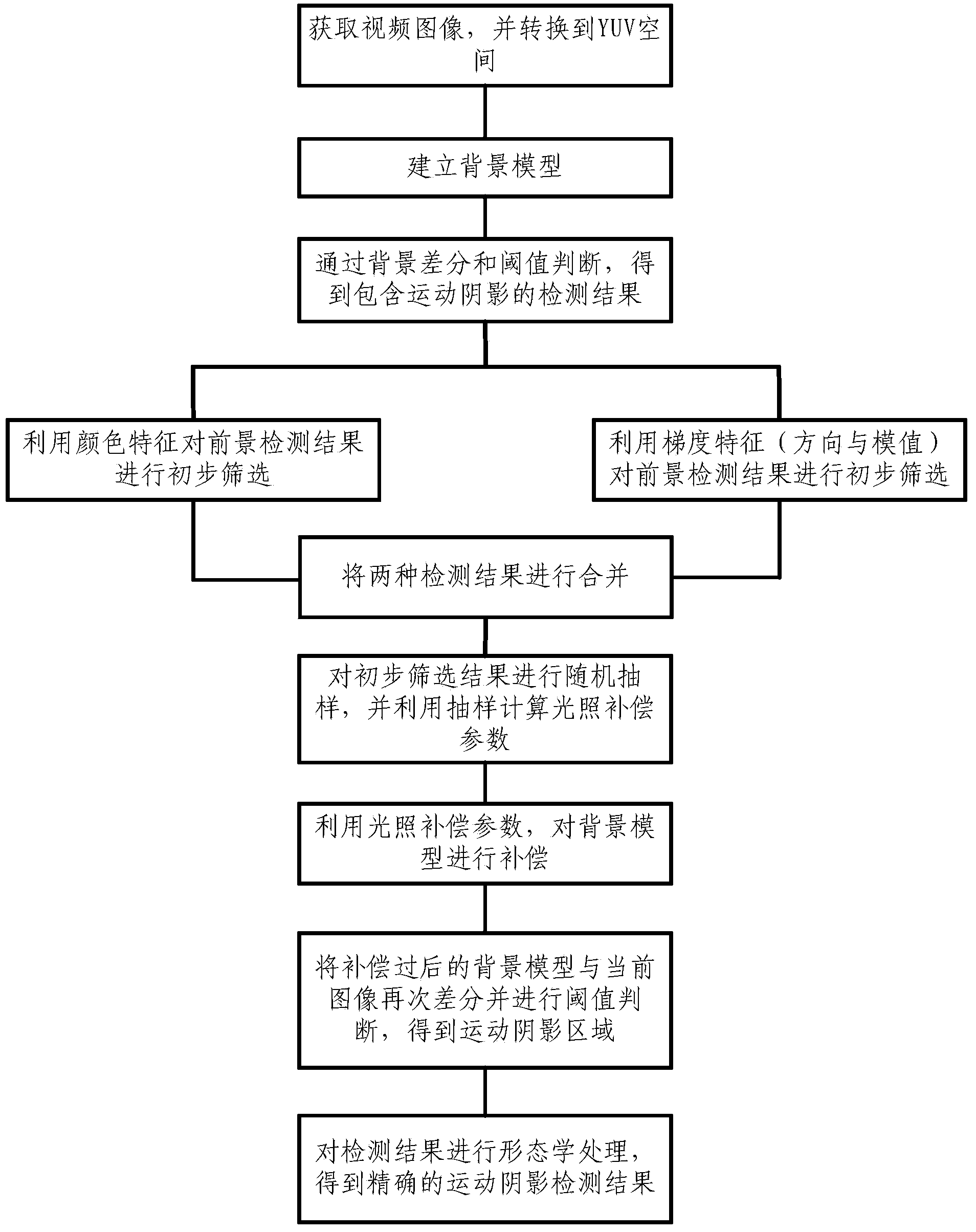
Video motion shadow detecting method based on lighting compensation
InactiveCN103679704AAutomatic filterImprove detection accuracyImage analysisEnvironmental variationMulti feature
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
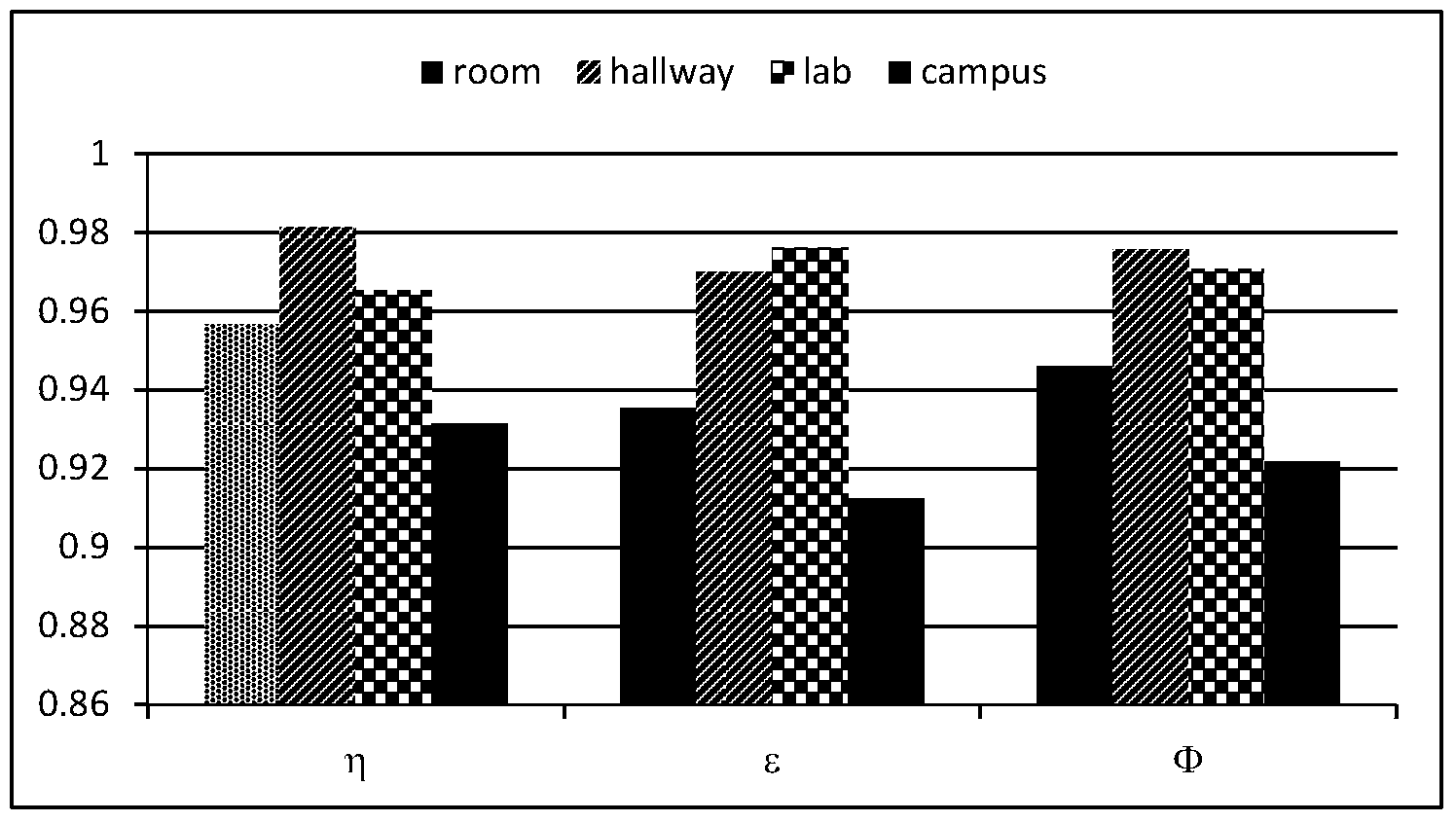
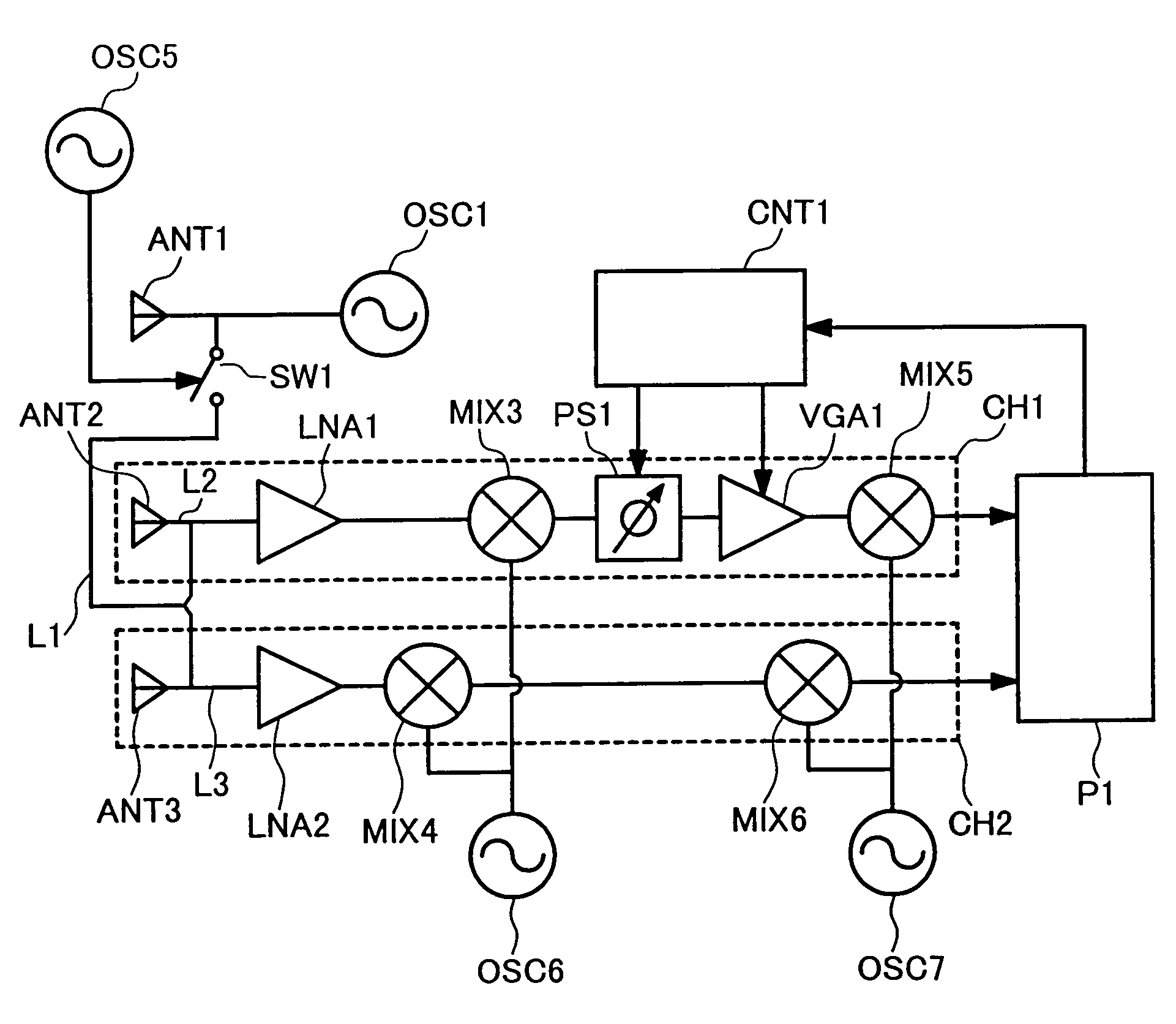
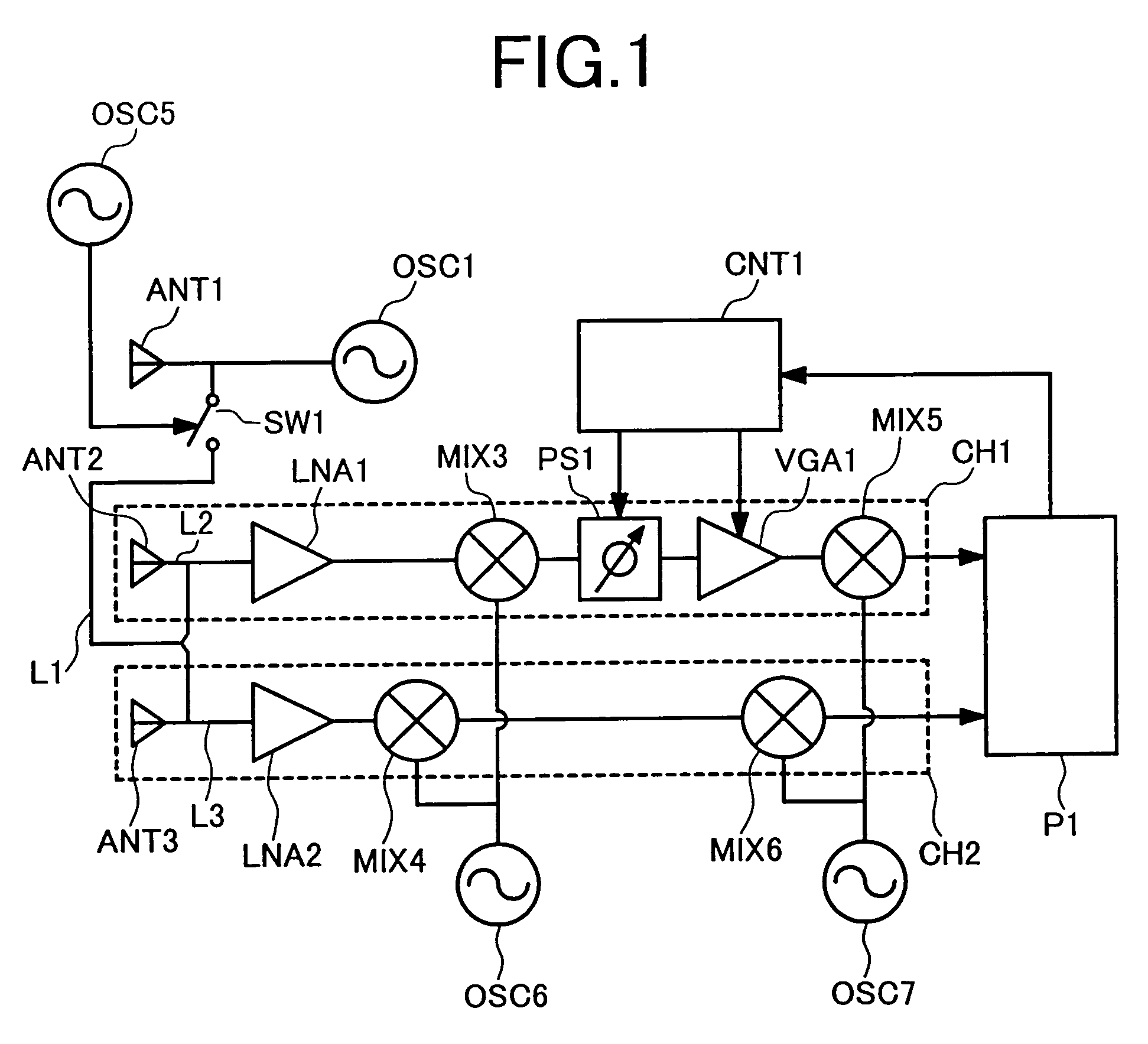
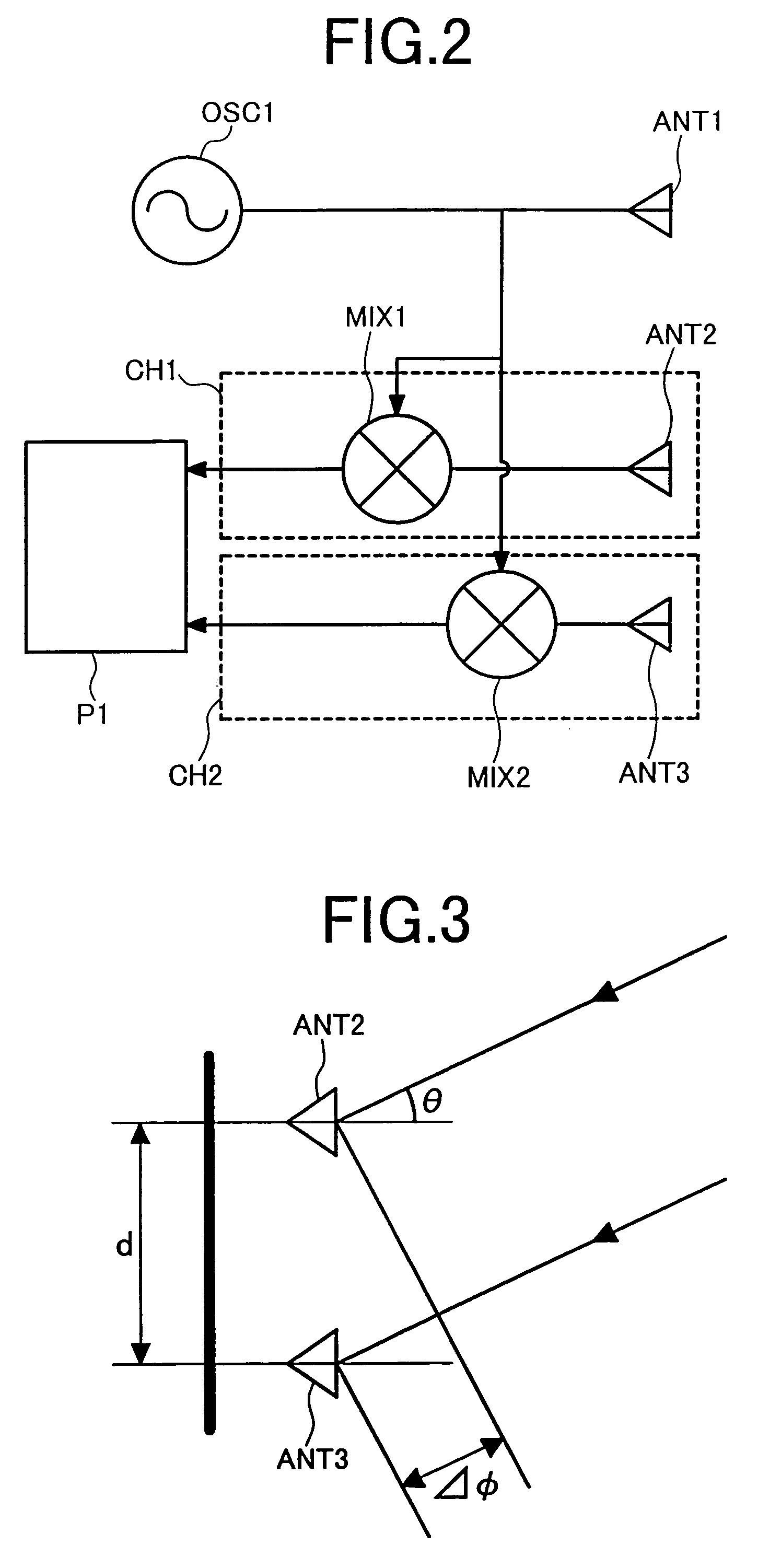
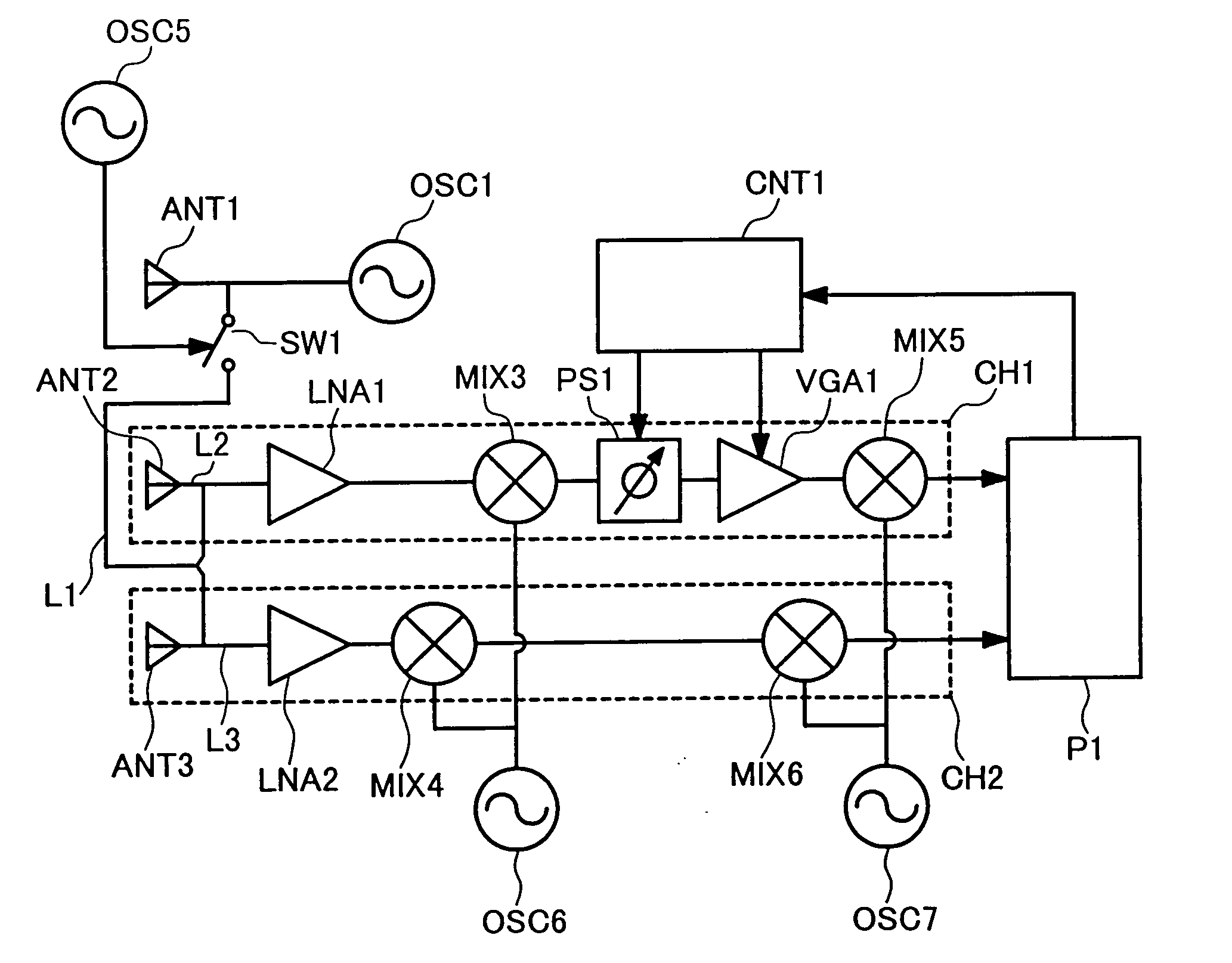
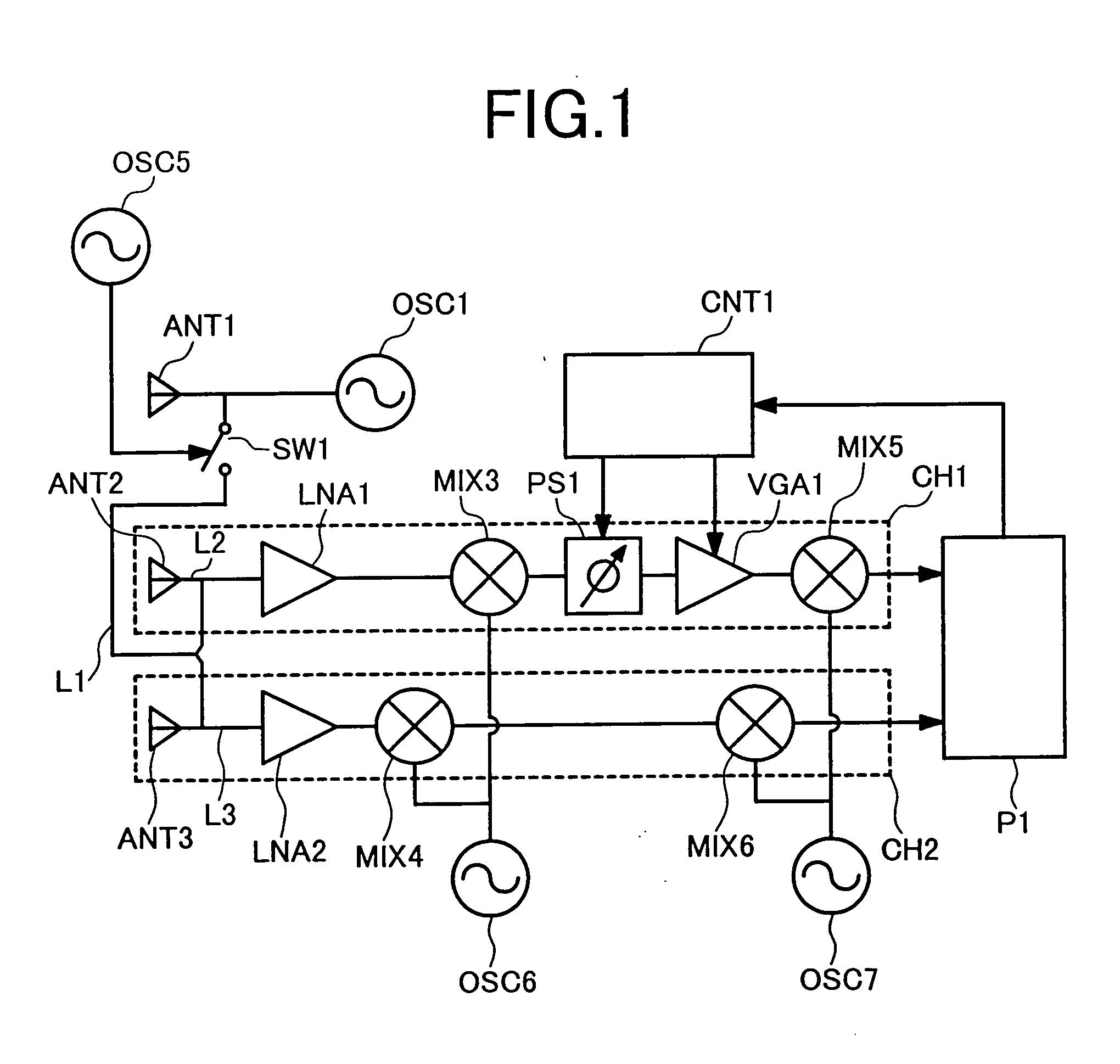
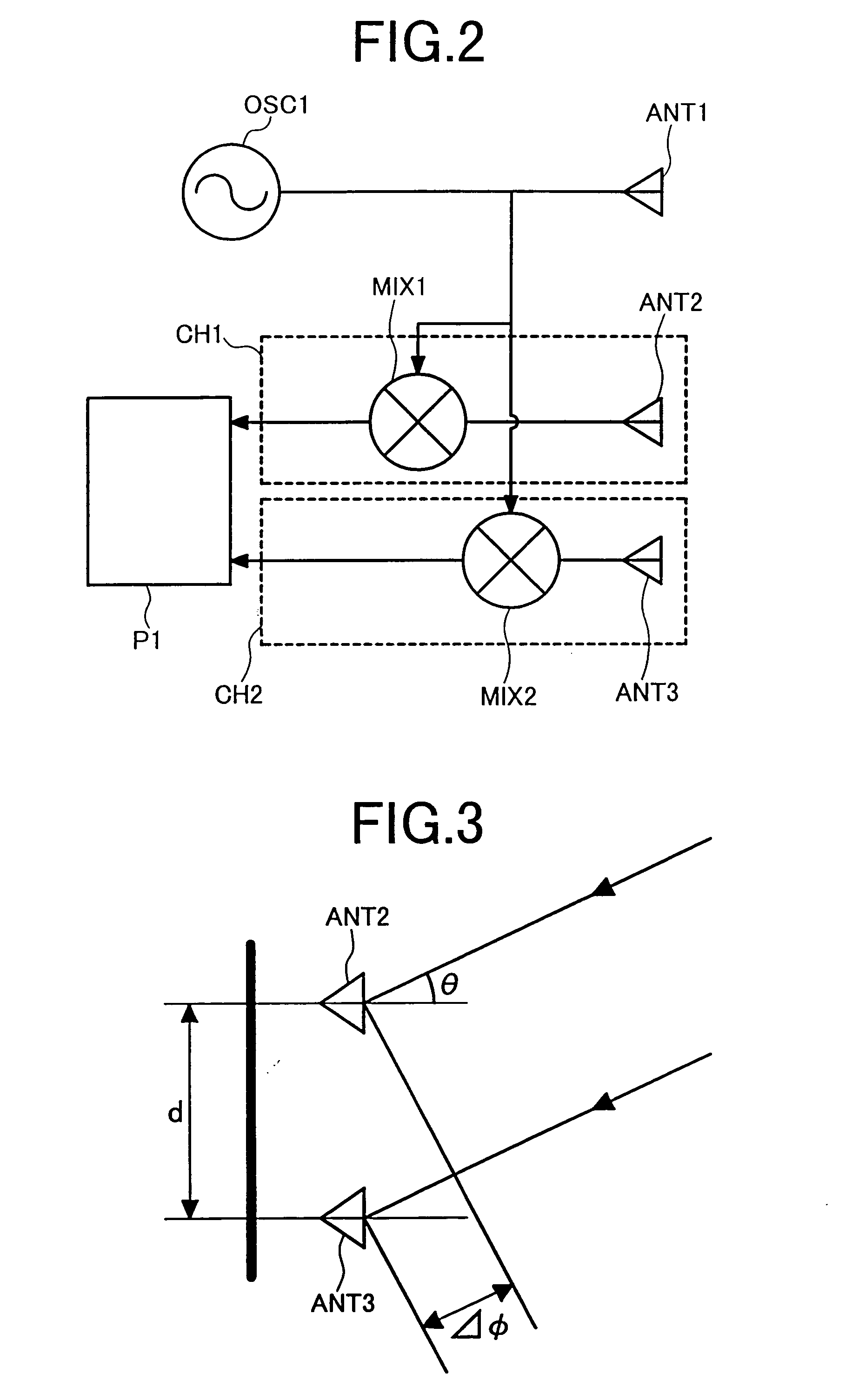
Monopulse radar system
InactiveUS7212152B2Accuracy of the angle detected by the monopulse radarMaintain accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
The present invention provides that a monopulse radar system to correct an amplitude error and a phase error developed between receiving channels and improve the accuracy of a detected angle. A part of a transmit signal is supplied to respective channels on the receiving side through a signal transmission line for calibration. At this time, the gains of a variable phase shifter and a variable gain amplifier are adjusted so that an azimuth angle of a pseudo target, based on a signal for calibration, which is calculated by signal processing means, reaches a predetermined angle. In the monopulse radar system of the present invention, calibration work is simplified and an angular correction can be automated. The present monopulse radar system of the present invention is capable of coping even with variations in characteristic after product shipment due to environmental variations and time variations in parts characteristic.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Reliability enhancement methods for physically unclonable function bitstring generation
ActiveUS20170364709A1Reduce errorsCryptographic strength can be increasedDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionVoltage regulationPhysical unclonable function
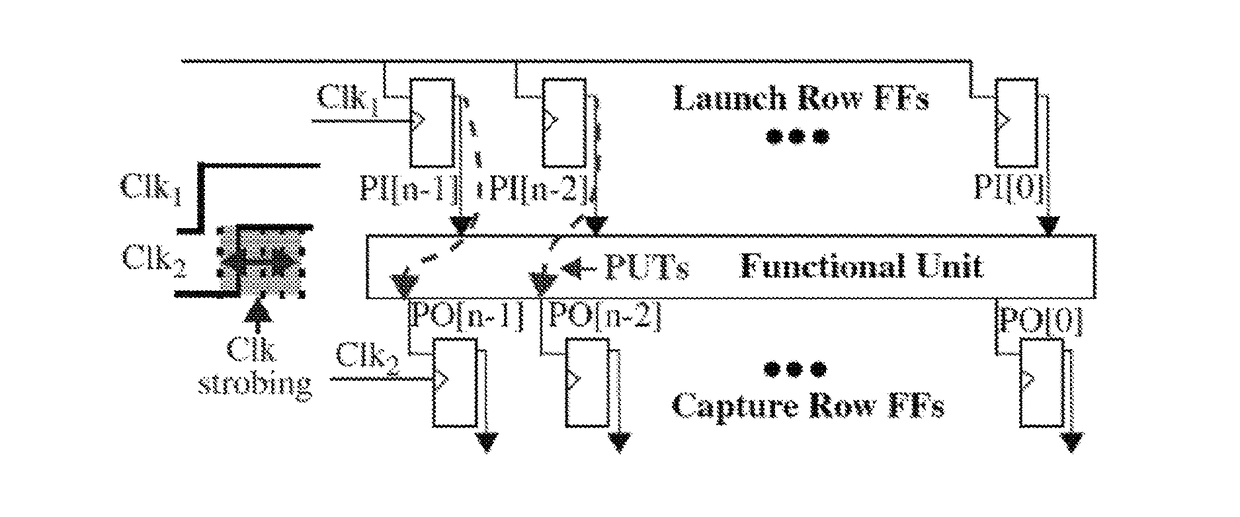
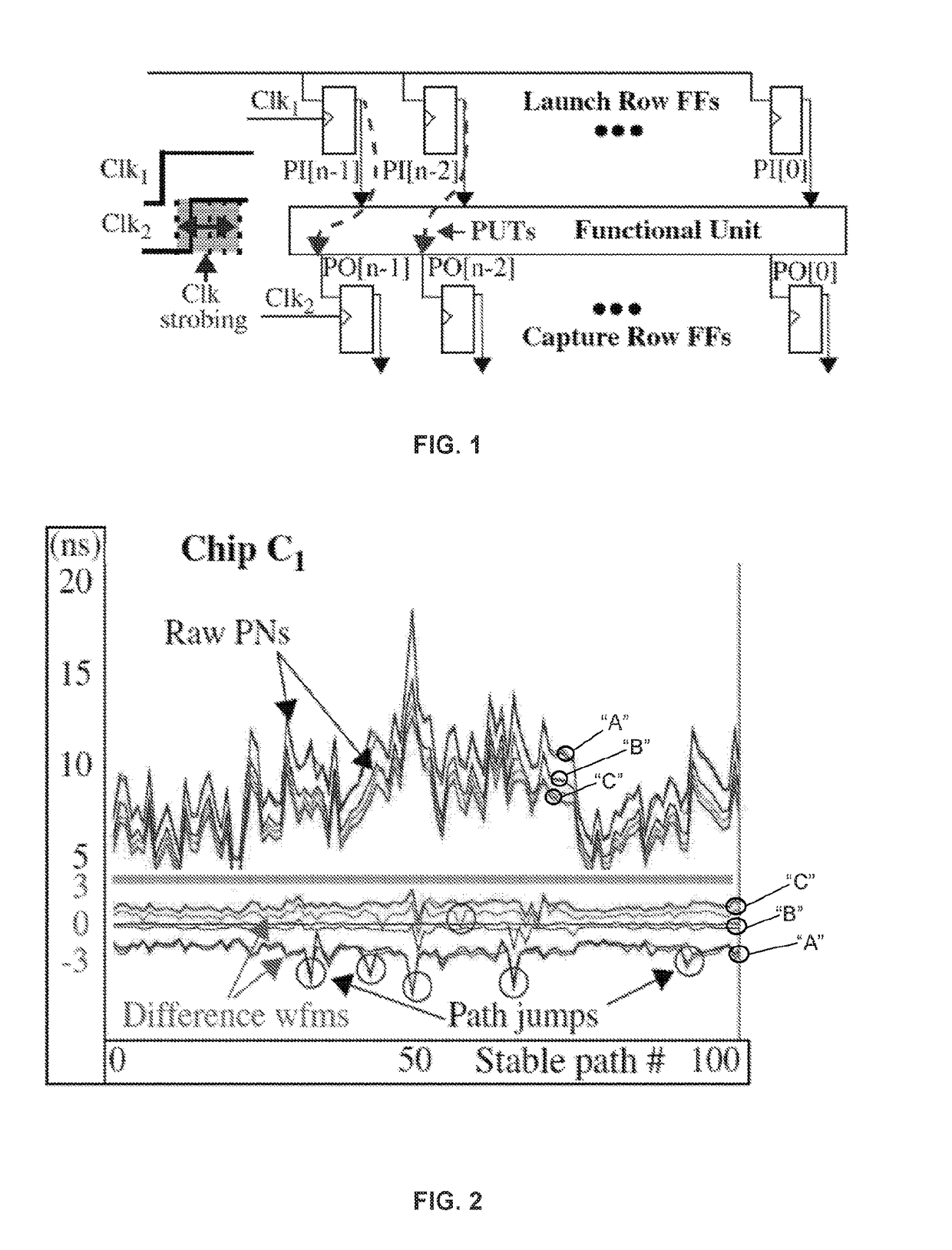
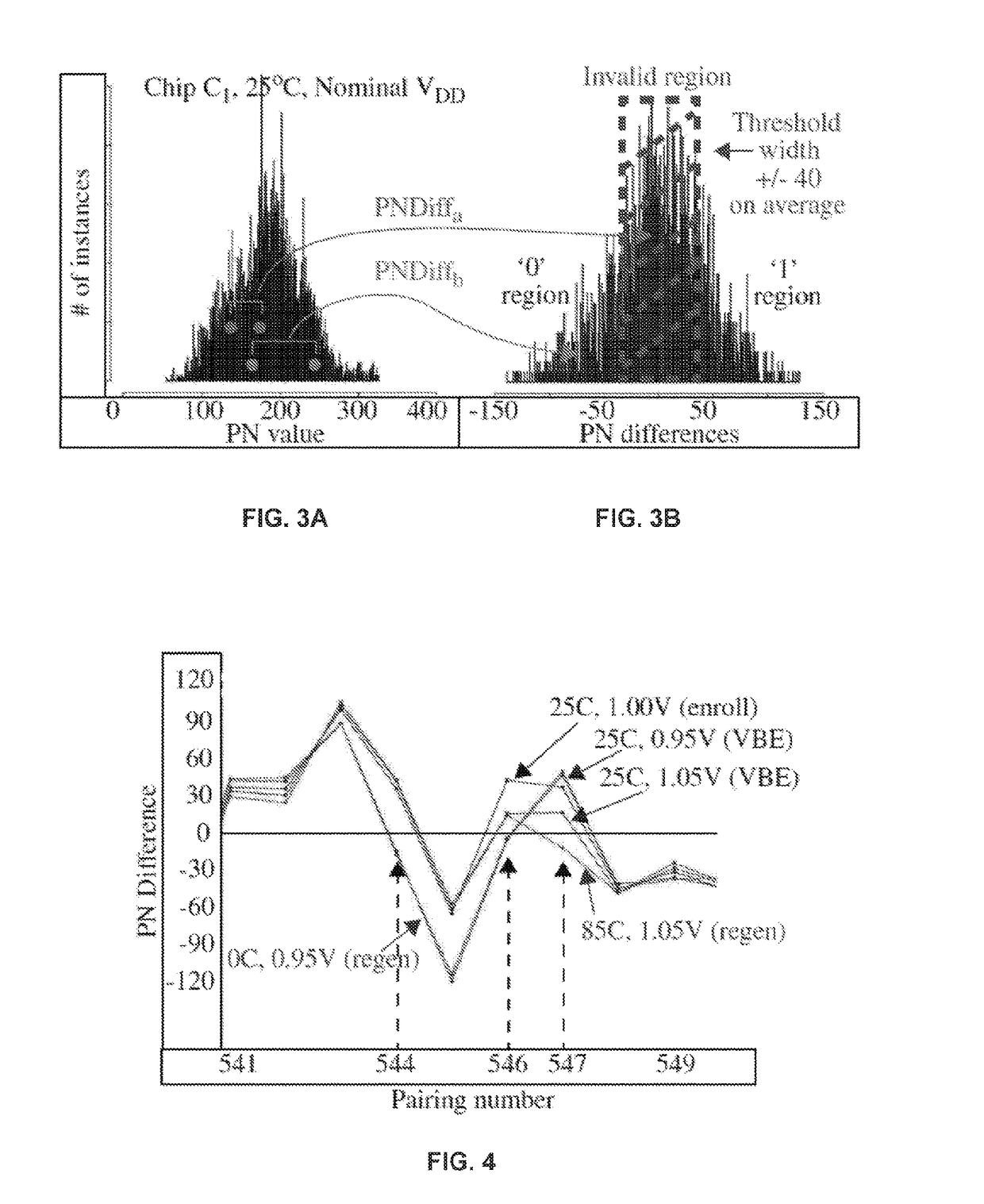
A Hardware-Embedded Delay Physical Unclonable Function (“HELP PUF”) leverages entropy by monitoring path stability and measuring path delays from core logic macros. Reliability and security enhancing techniques for the HELP PUF reduce bit flip errors during regeneration of the bitstring across environmental variations and improve cryptographic strength along with the corresponding difficulty of carrying out model building attacks. A voltage-based enrollment process screens unstable paths on normally synthesized (glitchy) functional units and reduces bit flip errors by carrying out enrollment at multiple supply voltages controlled using on-chip voltage regulators.
Owner:STC UNM
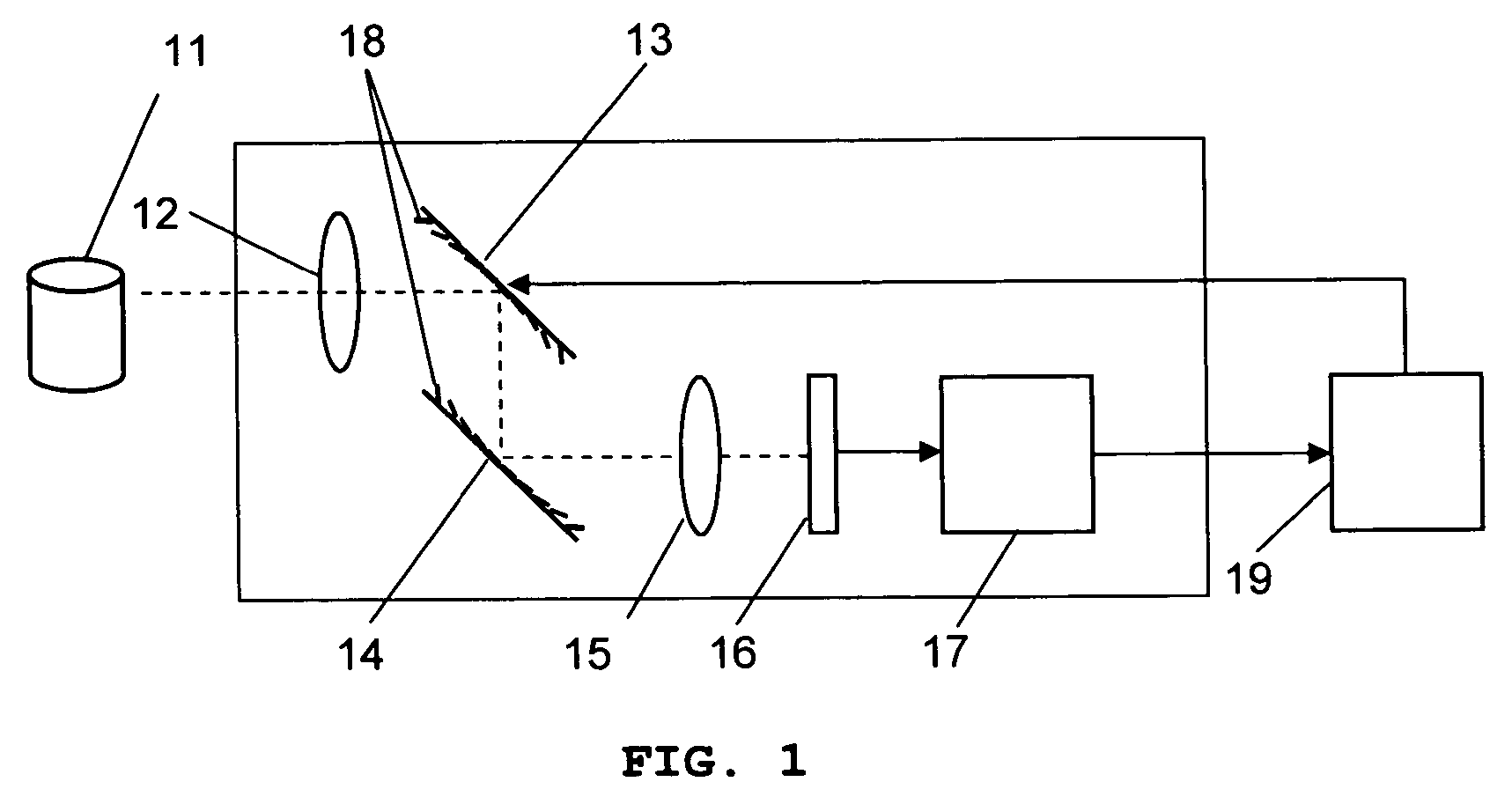
Lens device and lens barrel
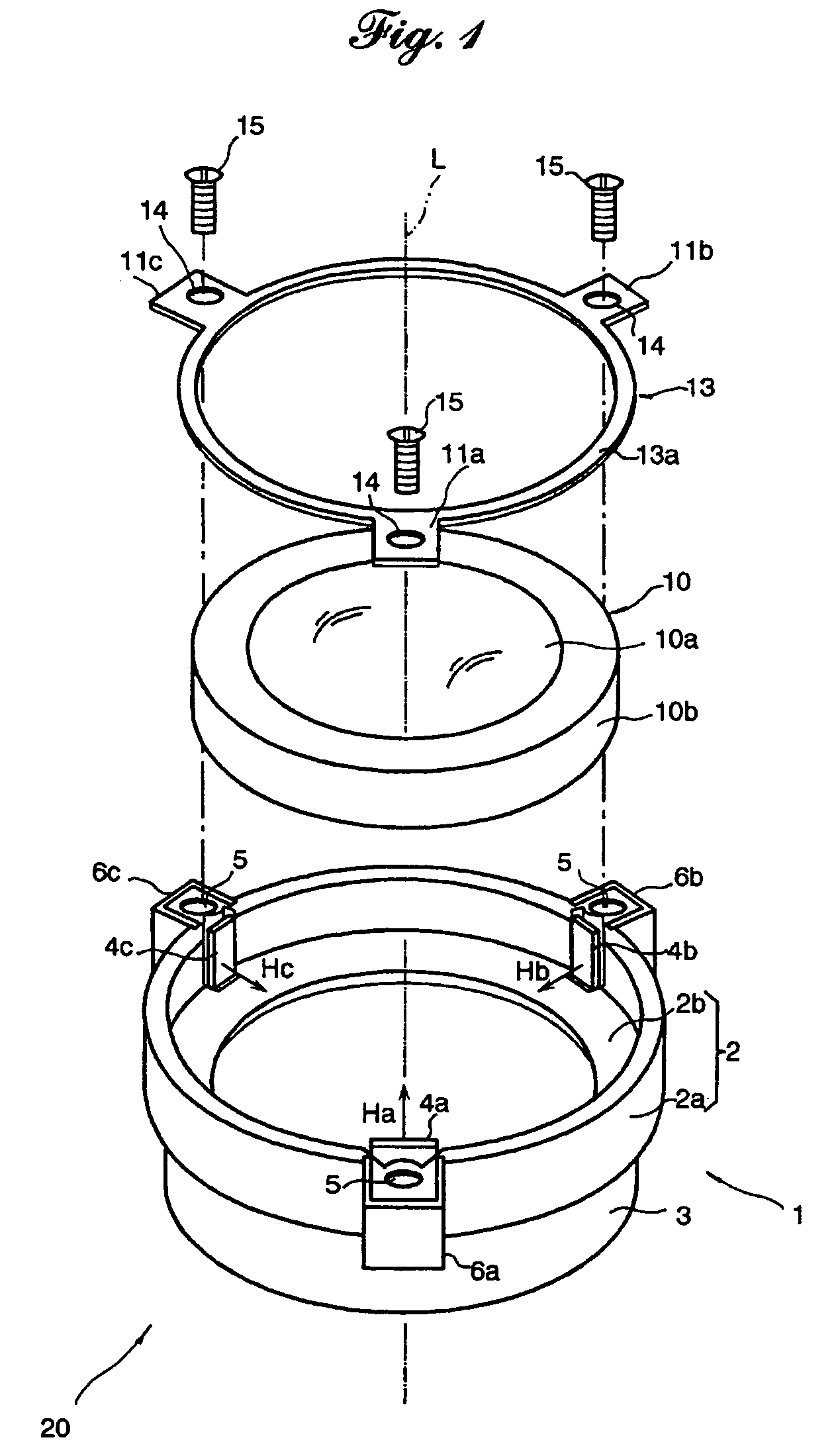
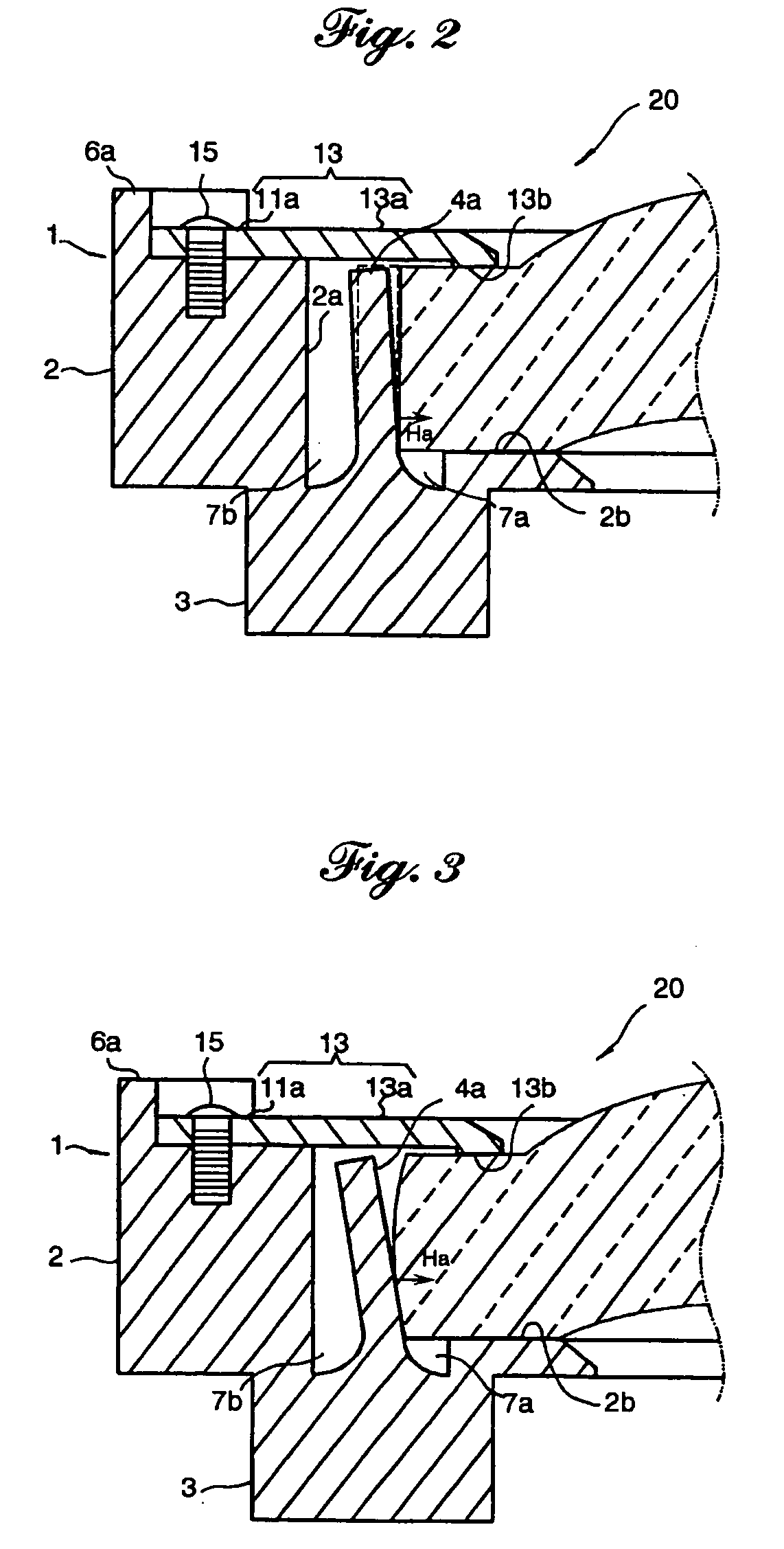
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
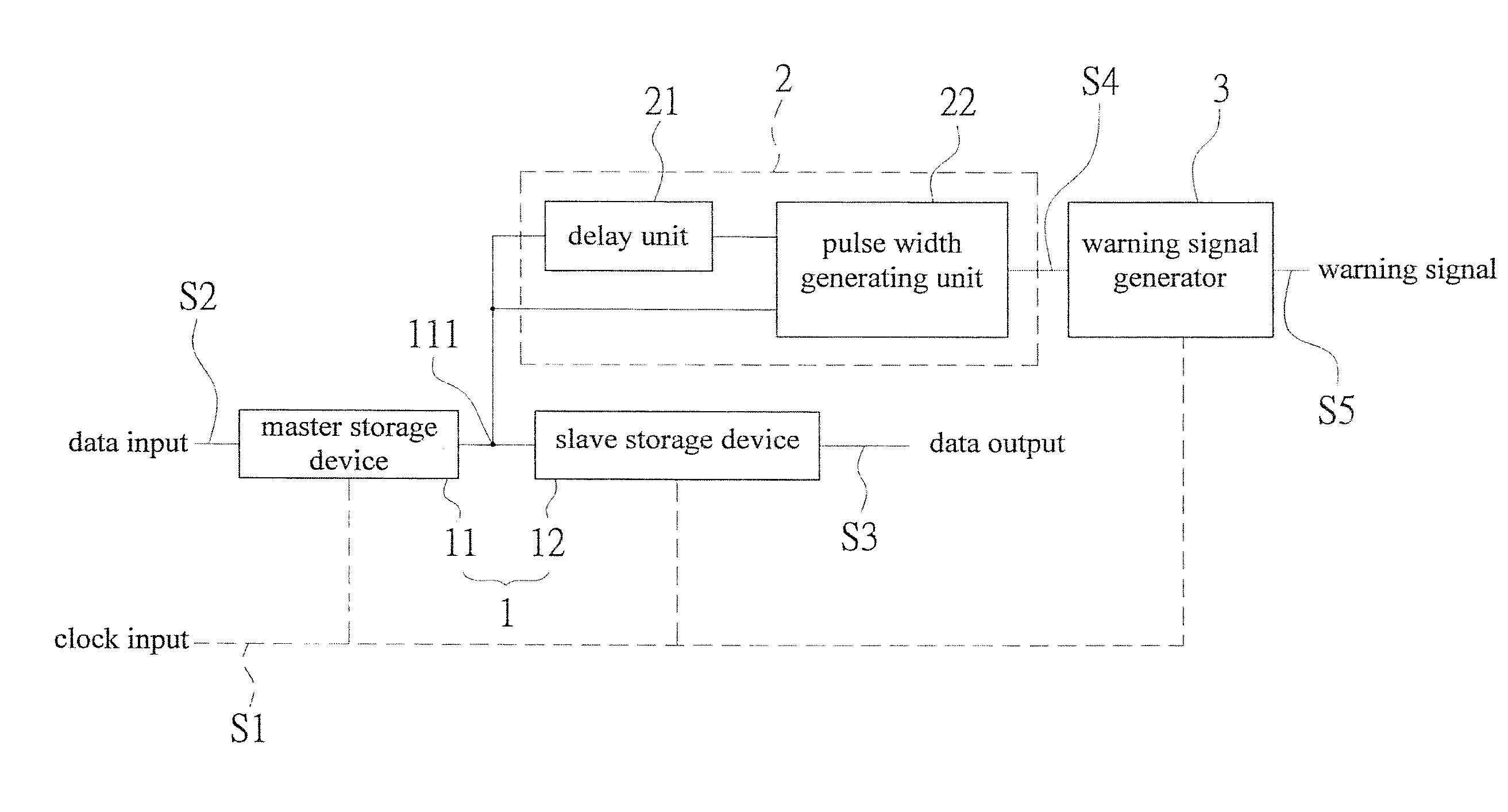
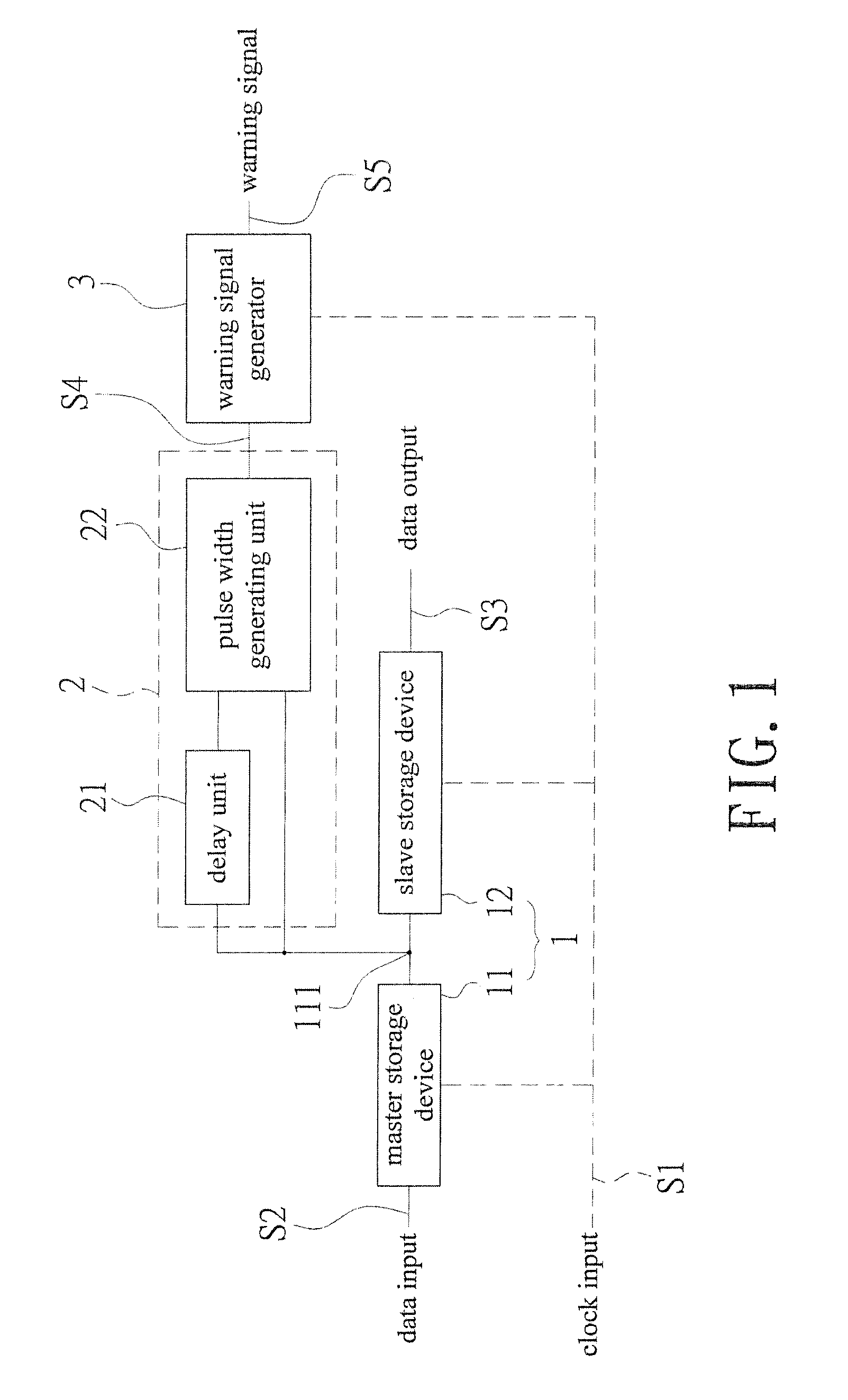
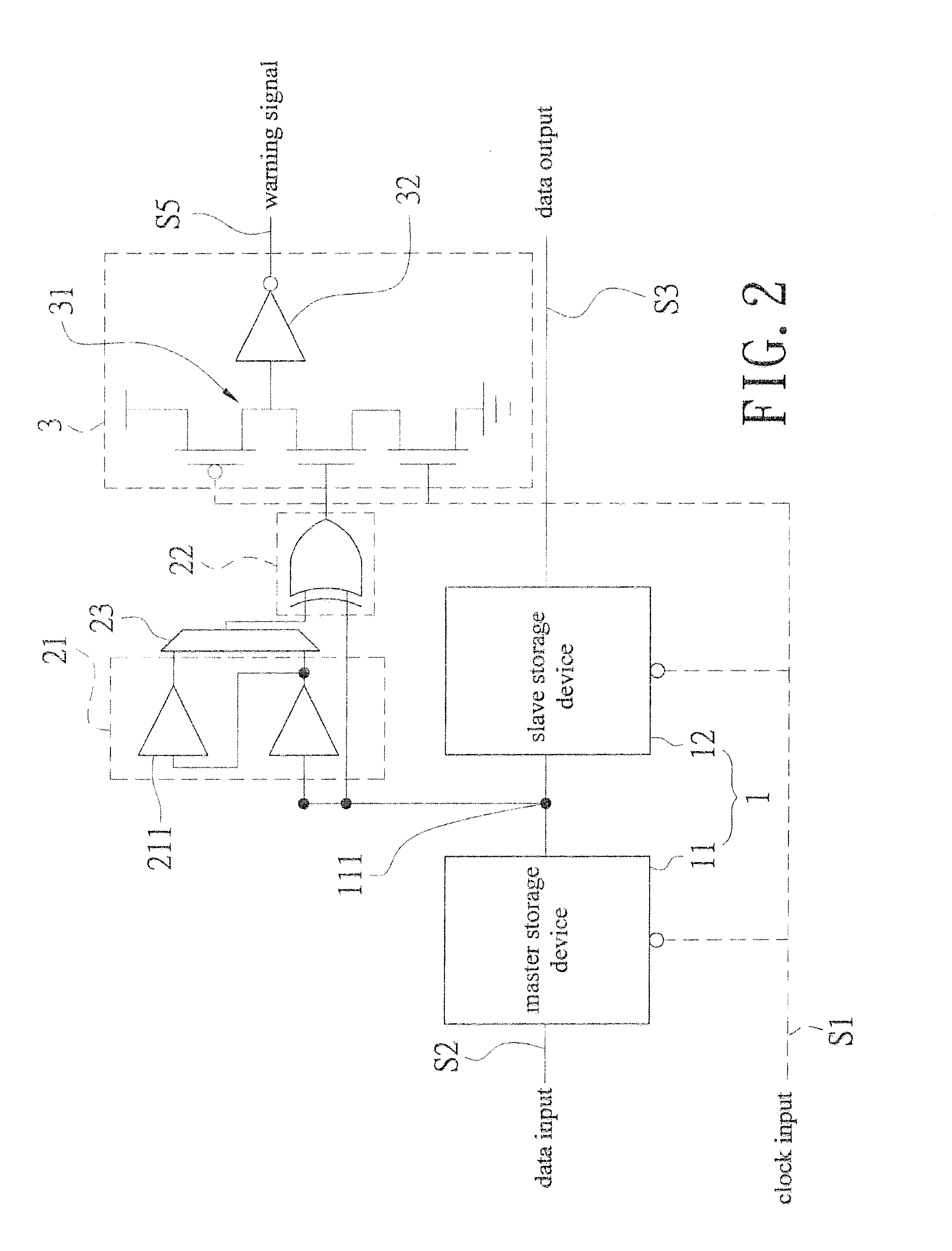
In situ pulse-based delay variation monitor predicting timing error caused by process and environmental variation
InactiveUS20140152344A1Increase the pulse widthSolve excessive overheadVoltage/temperature variation compensationElectricityElectrical connection
An in situ pulse-based delay variation monitor that predicts timing errors caused by process and environmental variations is revealed. The monitor includes a sequential storage device having a mater storage device and a slave storage device, a transition detector that is electrically connected to a node set on an electrical connection pathway from a master storage device to the slave storage device, and a warning signal generator electrically connected to the transition detector. The transition detector receives output of the master storage device to form a warning area by delay buffer, and generates a pulse width output correspondingly according to transition of the data input. Thus the warning signal generator generates a warning signal according to logic action at the pulse width and the clock input when the data input reaches the warning area. Thereby timing errors caused by static process variations and dynamic environmental variations are predicted.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
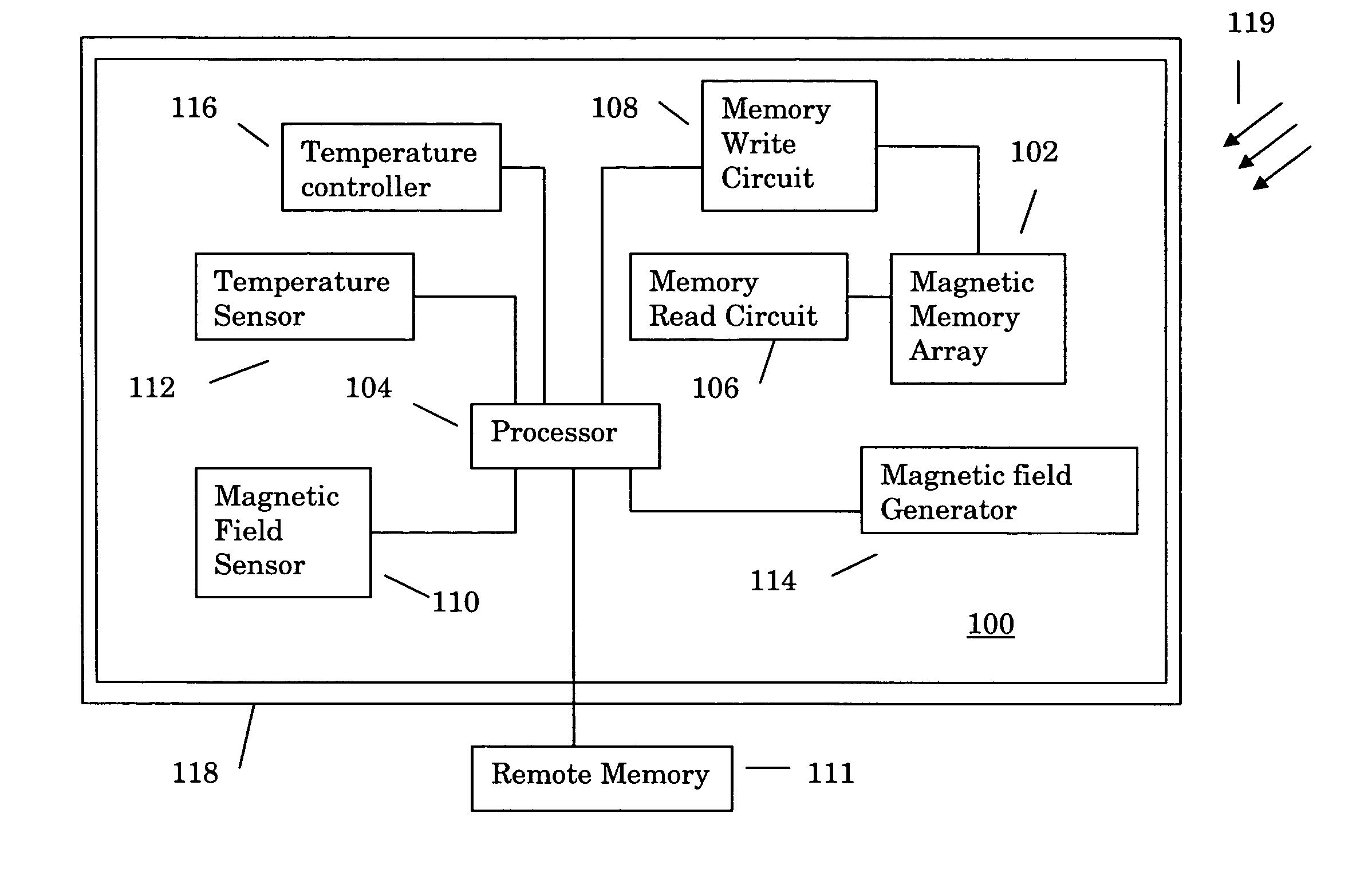
Sensor compensation for environmental variations for magnetic random access memory
A compensation system for an array of magnetic memory cells measures local operating conditions and compensates for changes in the operating characteristics of the magnetic memory cells in the array that result from the changes in the operating conditions. The magnetic field strength near the magnetic memory array is measured. If the magnetic field strength rises above, or falls below certain predetermined threshold values, the write current used to alter the orientation of the magnetic fields in the magnetic memory cells is altered based upon the predetermined operating characteristics of the memory cells. A solenoid or similar type magnetic field generator may also be used to substantially compensate for variations in the sensed magnetic fields. In addition, the temperature of the environment in which the magnetic memory cells are operating is sensed and appropriate changes made in the write current. Temperature control means may also be used to compensate for sensed changes in the local operating environment.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Monopulse radar system
InactiveUS20050190099A1Accurate calibration can notGuaranteed current efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A monopulse radar system aims to correct an amplitude error and a phase error developed between receiving channels and improve the accuracy of a detected angle. To achieve the above aim, part of a transmit signal is supplied to respective channels on the receiving side through a signal transmission line for calibration. At this time, the gains of a variable phase shifter and a variable gain amplifier are adjusted so that an azimuth angle of a pseudo target, based on a signal for calibration, which is calculated by signal processing means, reaches a predetermined angle. Therefore, calibration work is simplified and an angular correction can be automated. Therefore, the present monopulse radar system is capable of coping even with variations in characteristic after product shipment due to environmental variations and time variations in parts characteristic.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Image forming apparatus and image density control method
InactiveUS7881629B2Suppression amountConstant densityElectrographic process apparatusPattern detectionImage formation
In an image forming apparatus and an image density control method that are capable of suppressing the amount of toner consumed for a purpose other than image formation and responding to variation in the development ability of a development device due to environmental variation and the like such that a constant image density is obtained, the image density is maintained at a substantially fixed level by first target output value correcting means in accordance with a toner replacement amount and without consuming toner, and adjustment of the image density accompanying variation in the development ability due to environmental variation and the like is dealt with by second target output value correcting means in accordance with a toner pattern detection result. Hence, the frequency with which the toner pattern is detected in order to maintain the image density at a fixed level can be reduced in comparison with a case in which the image density is maintained at a fixed level on the basis of the toner pattern detection result alone, and as a result, the toner consumption amount can be suppressed.
Owner:RICOH KK
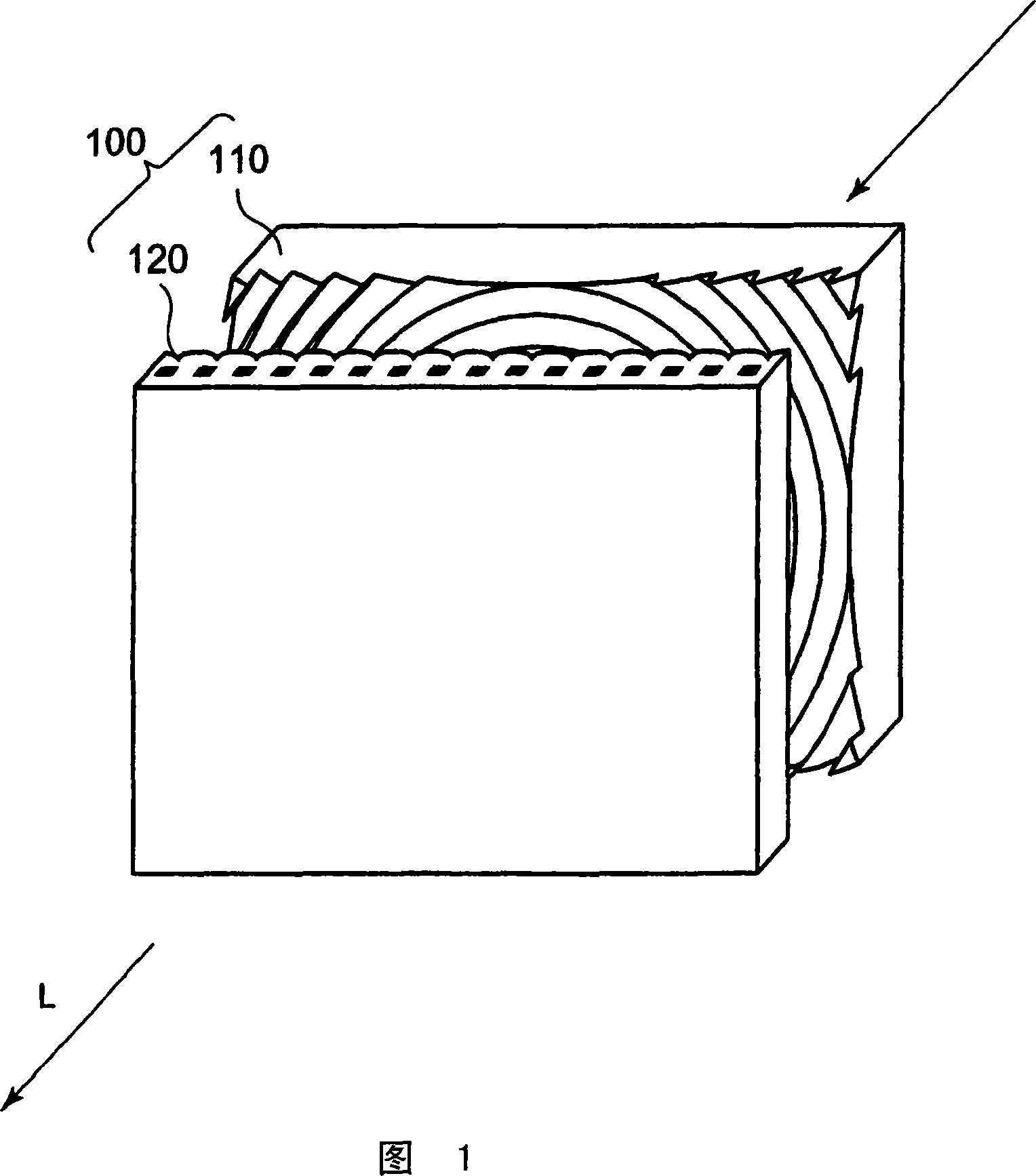
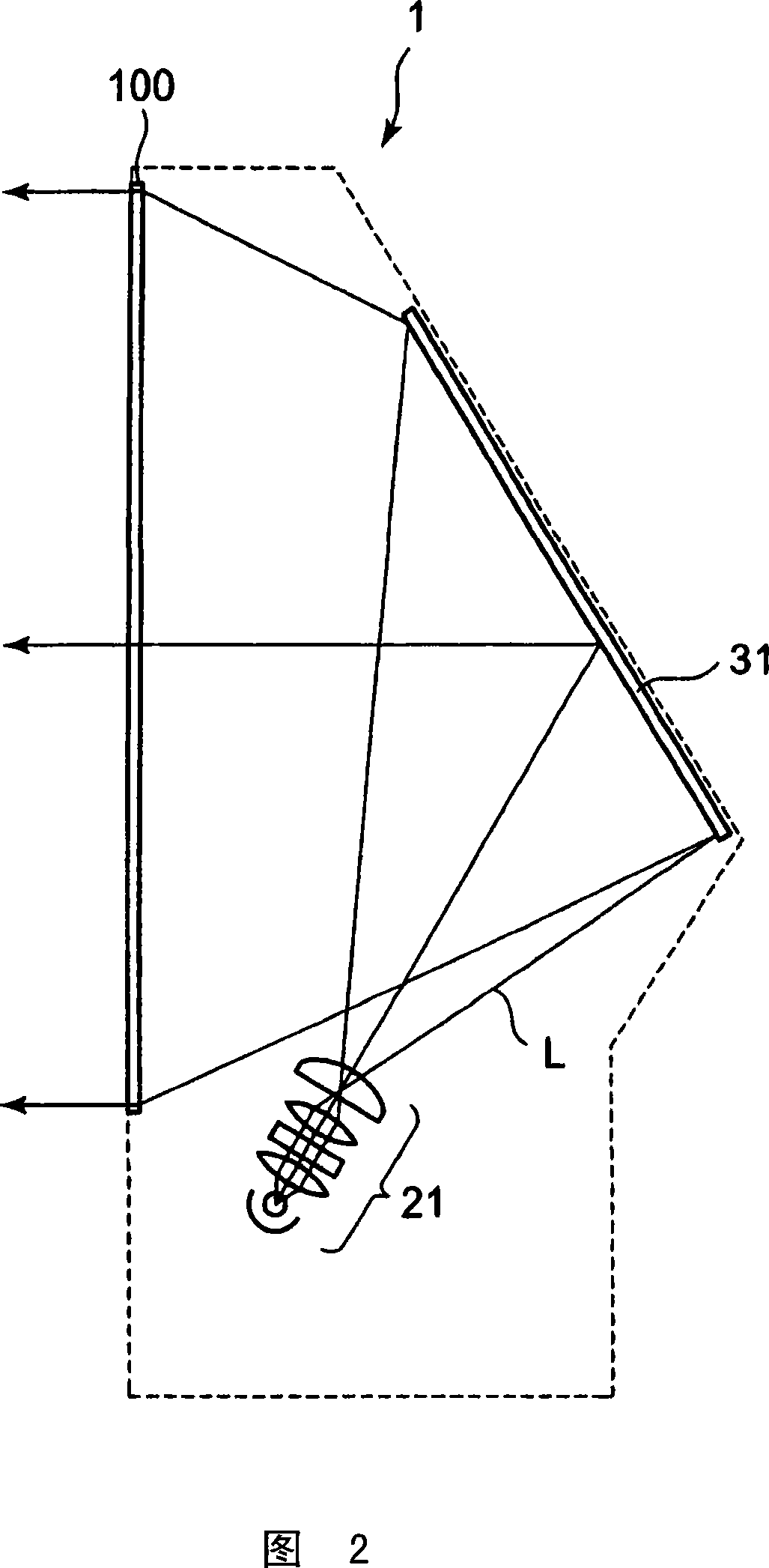
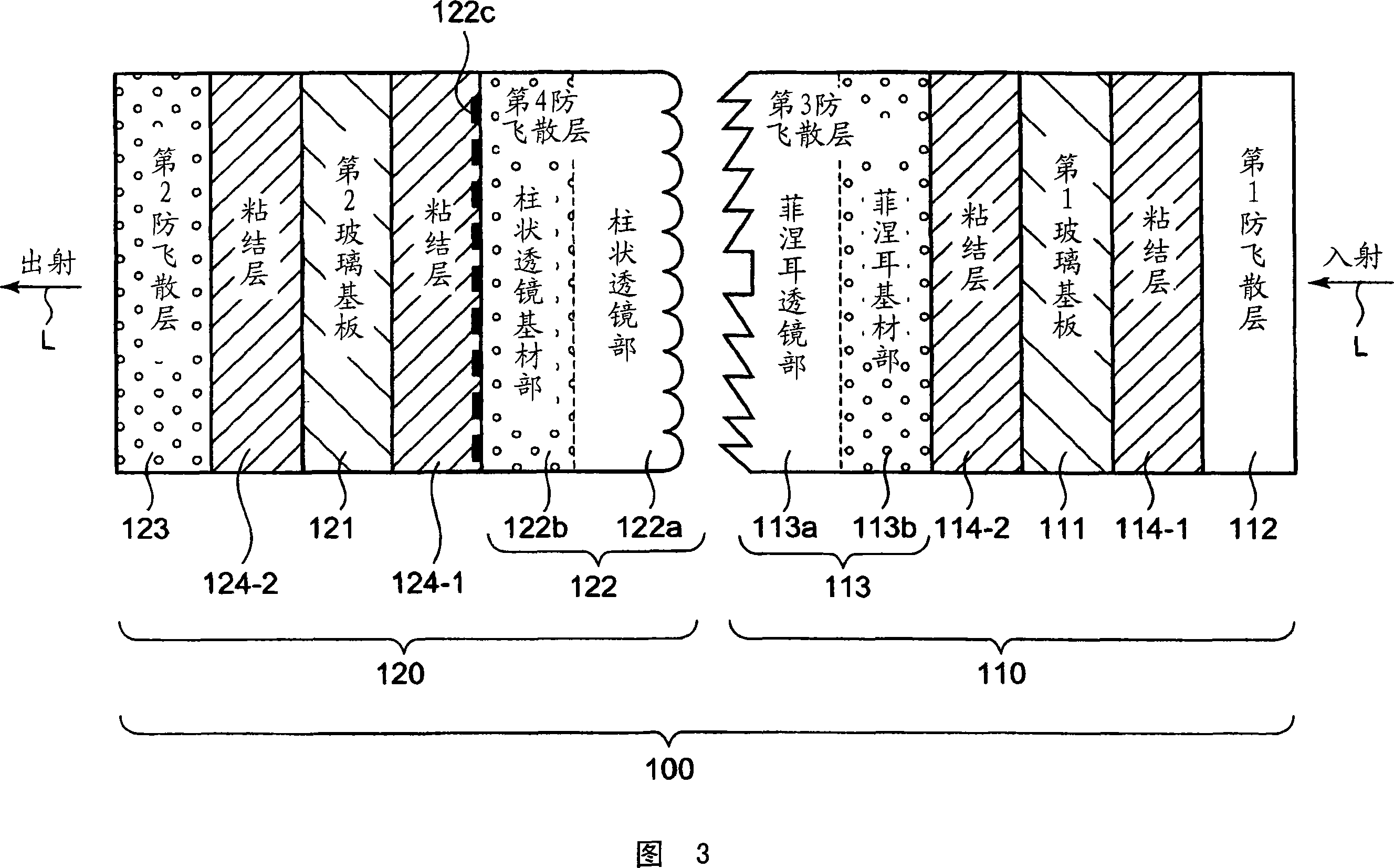
Diffusion optical sheet, deflection optical sheet, and transmission screen
A diffusion optical sheet in which the image quality can be prevented from deteriorating because of warp caused by environmental variation, and fragments can be prevented from scattering even if a substrate is damaged due to failure or the like. The diffusion optical sheet (120) is employed in a transmission screen where video light projected from the incoming side exits to the outgoing side. The diffusion optical sheet (120) comprises a high-rigidity light-transmitting substrate layer (121) and a plurality of layers formed on the high-rigidity substrate layer. The plurality of layers include at least a pair of layers arranged on both sides of the high-rigidity substrate layer and preventing scattering thereof. At least any one of the two or more layers has a diffusion optical element for diffusing video light.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com