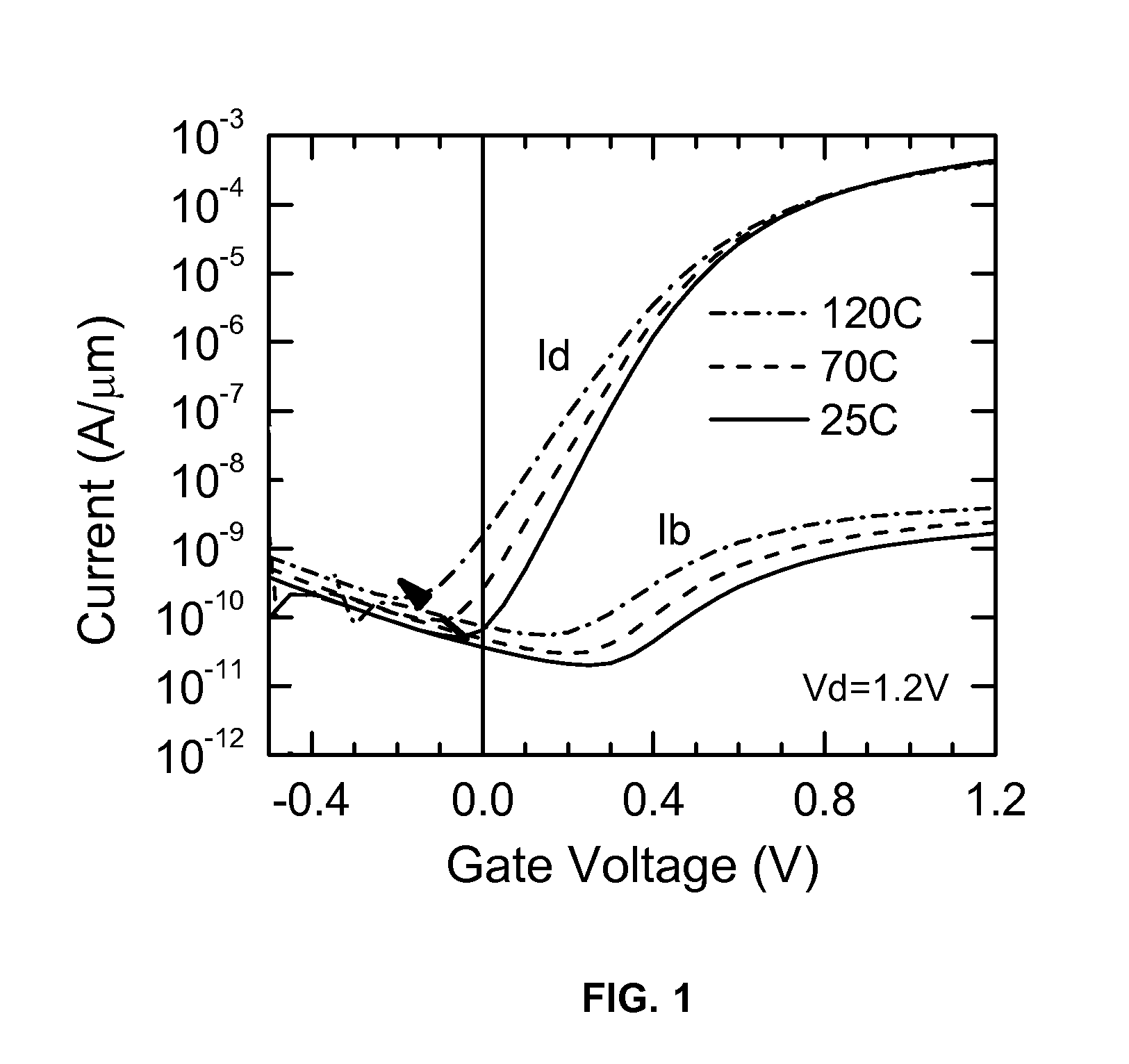
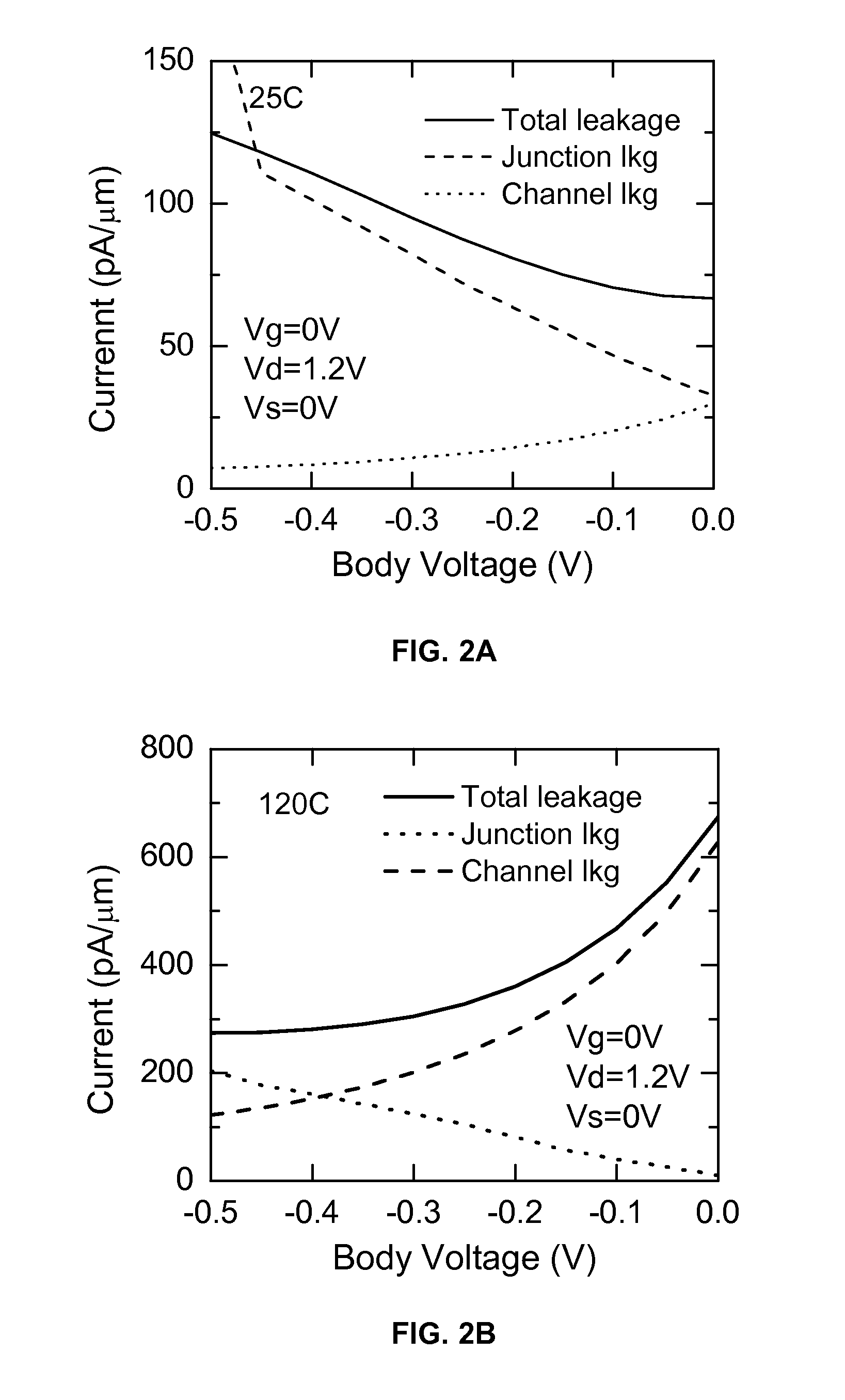
Patents
Literature
249results about "Voltage/temperature variation compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
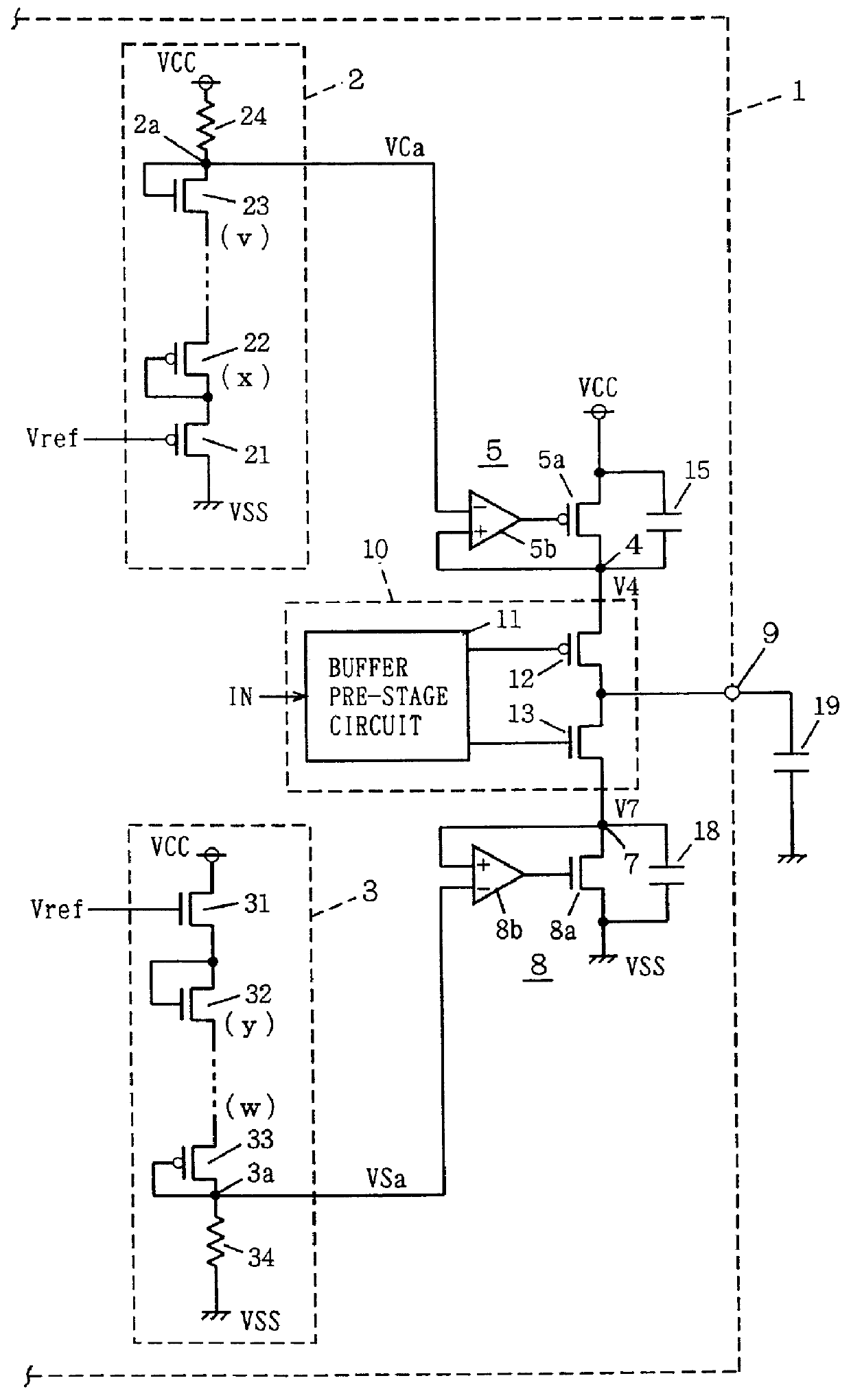
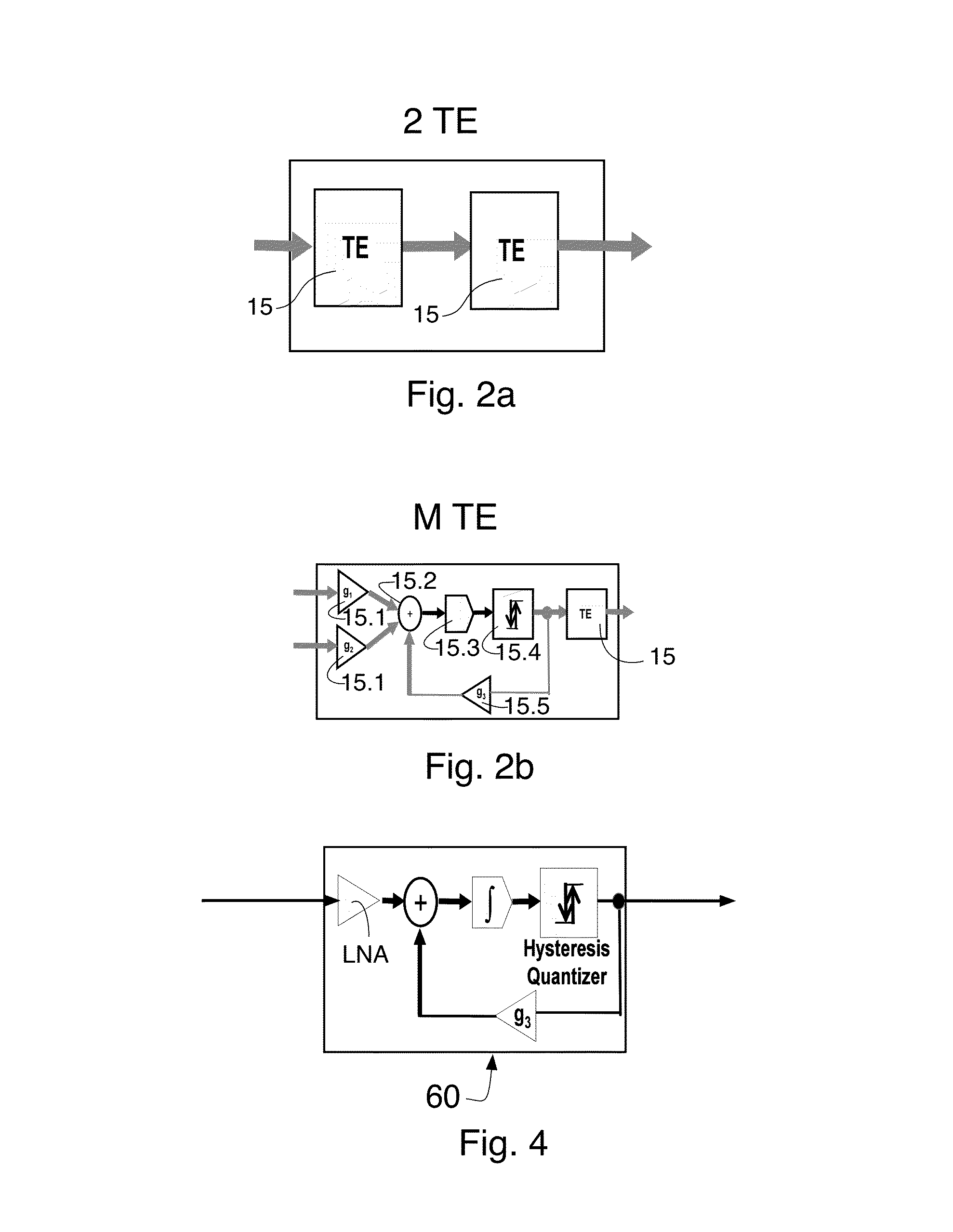
Semiconductor device allowing fast and stable transmission of signals
InactiveUS6087885AInput/output impedence modificationElectronic switchingPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
Internal power supply voltages at predetermined voltage levels are produced on output nodes of an output circuit in accordance with internal voltages generated by first and second voltage generating circuits which in receive a reference voltage on their inputs having high impedances. Stabilizing capacitors are connected to internal power supply nodes of this output circuit. The internal power supply voltage depends on MOS transistors operating in a source follower mode. During operation of the output circuit, charging and discharging currents are driven through the stabilizing capacitors, and an output signal having a limited amplitude can be reliably generated to an output node.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
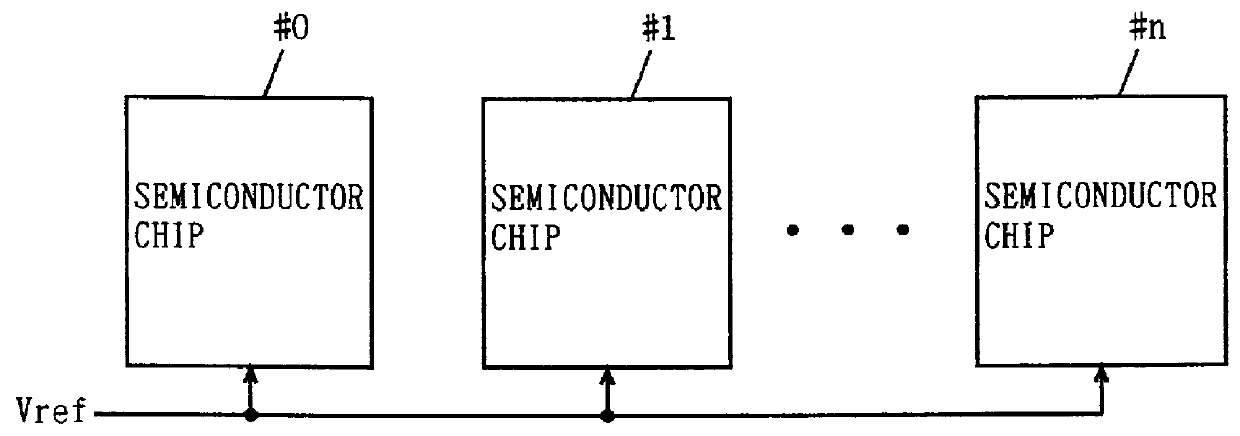
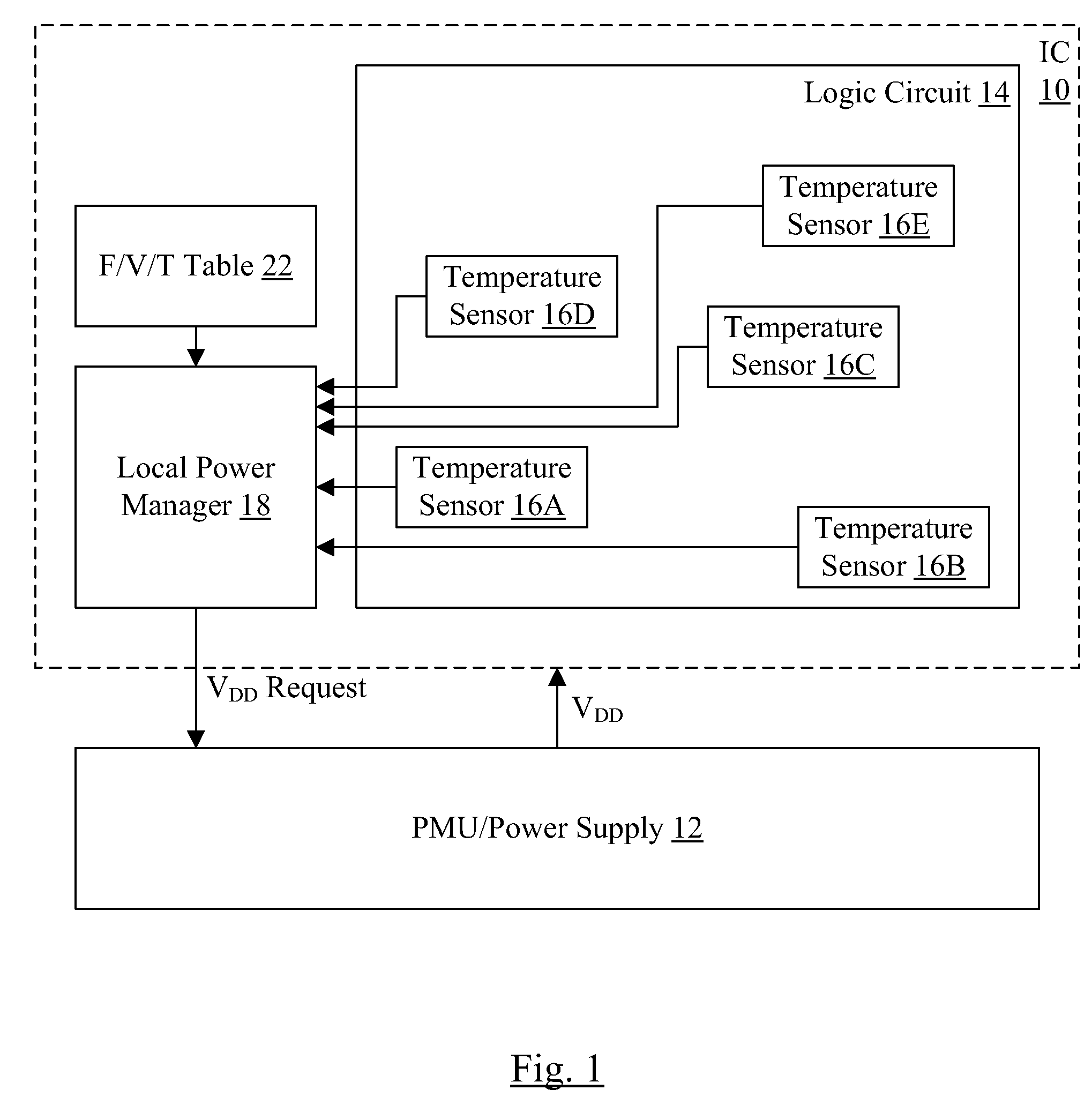
Temperature compensation in integrated circuit
ActiveUS20100213919A1Energy efficient ICTDc network circuit arrangementsLogic circuitryIntegrated circuit
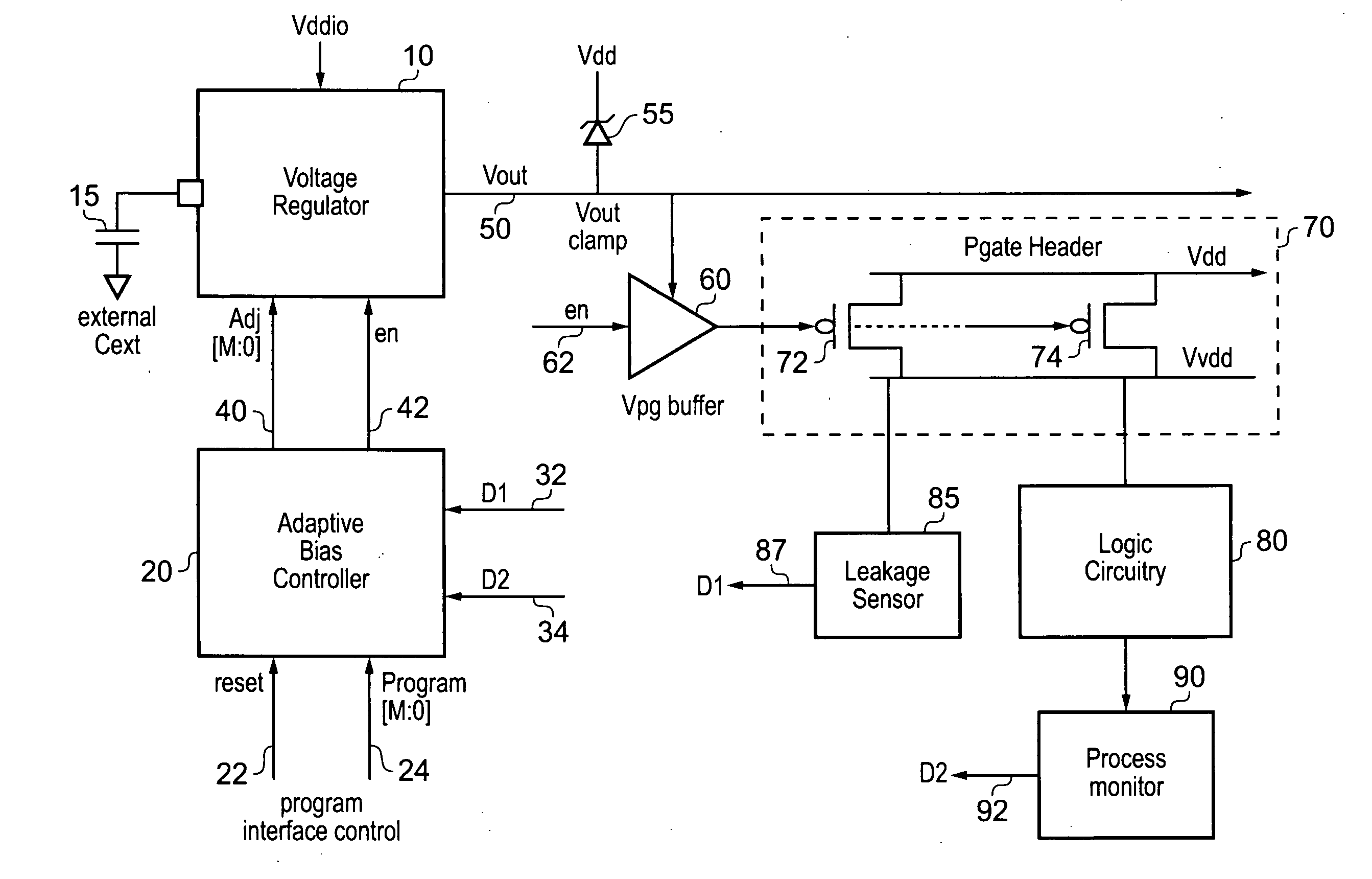
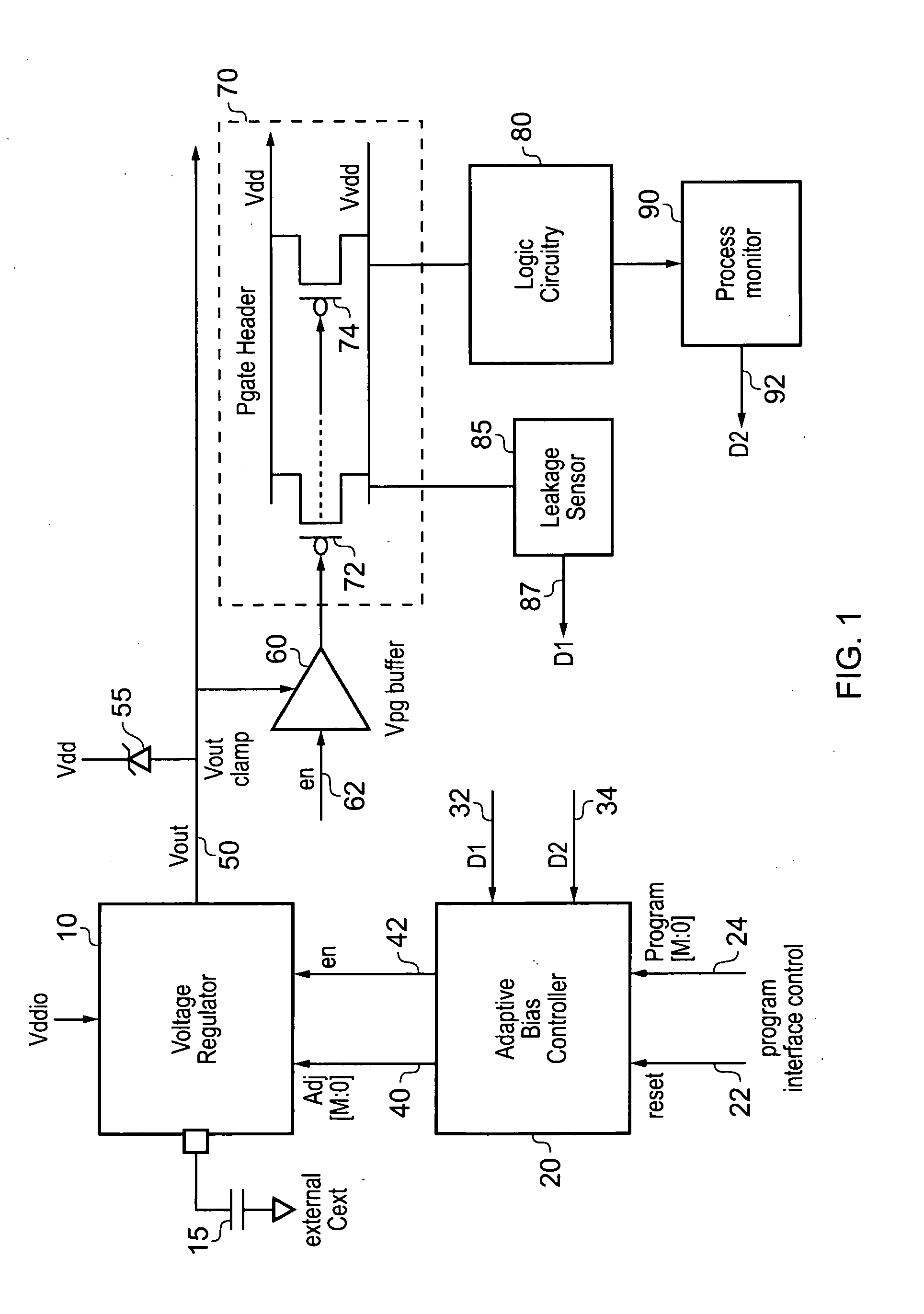
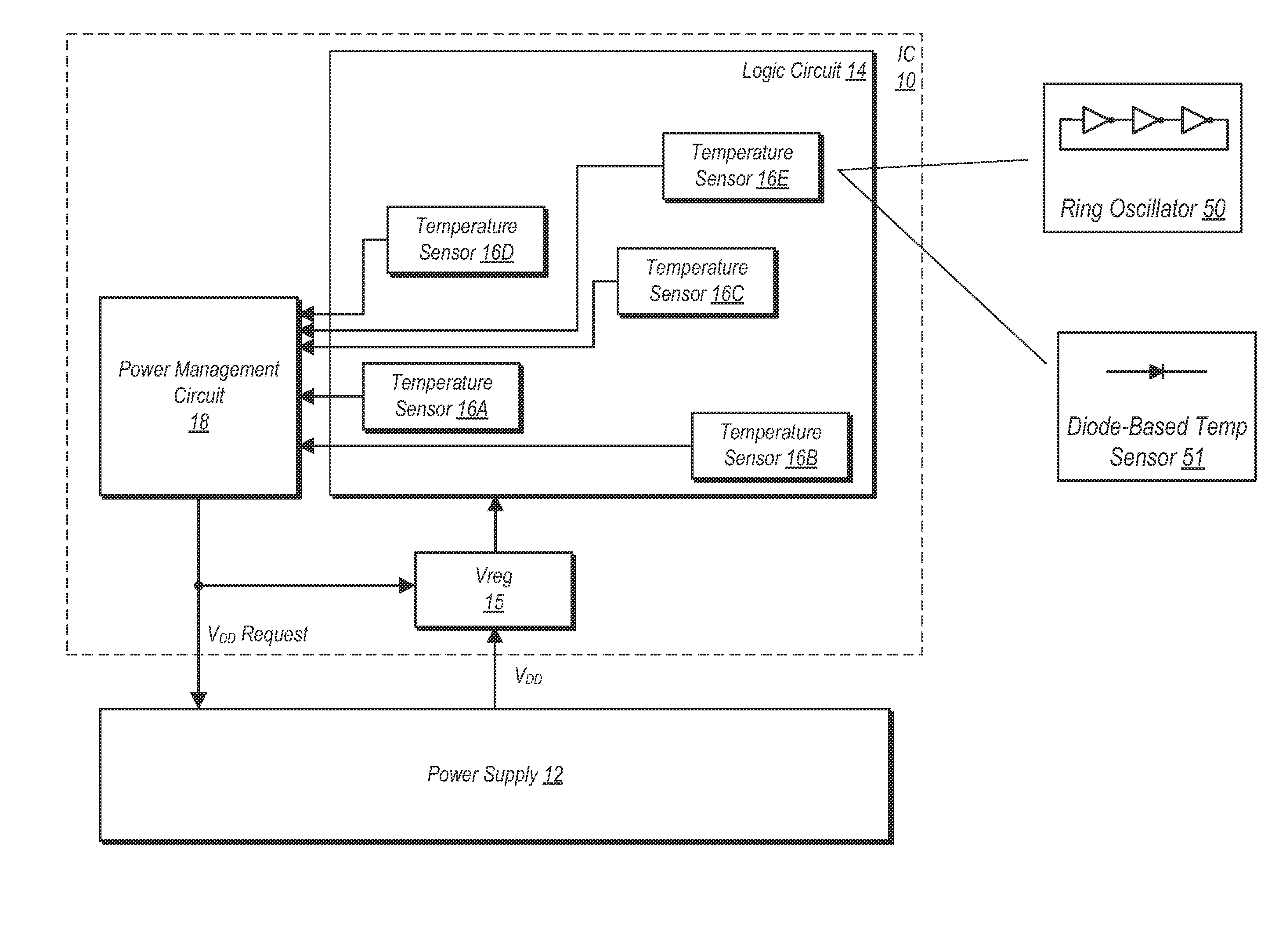
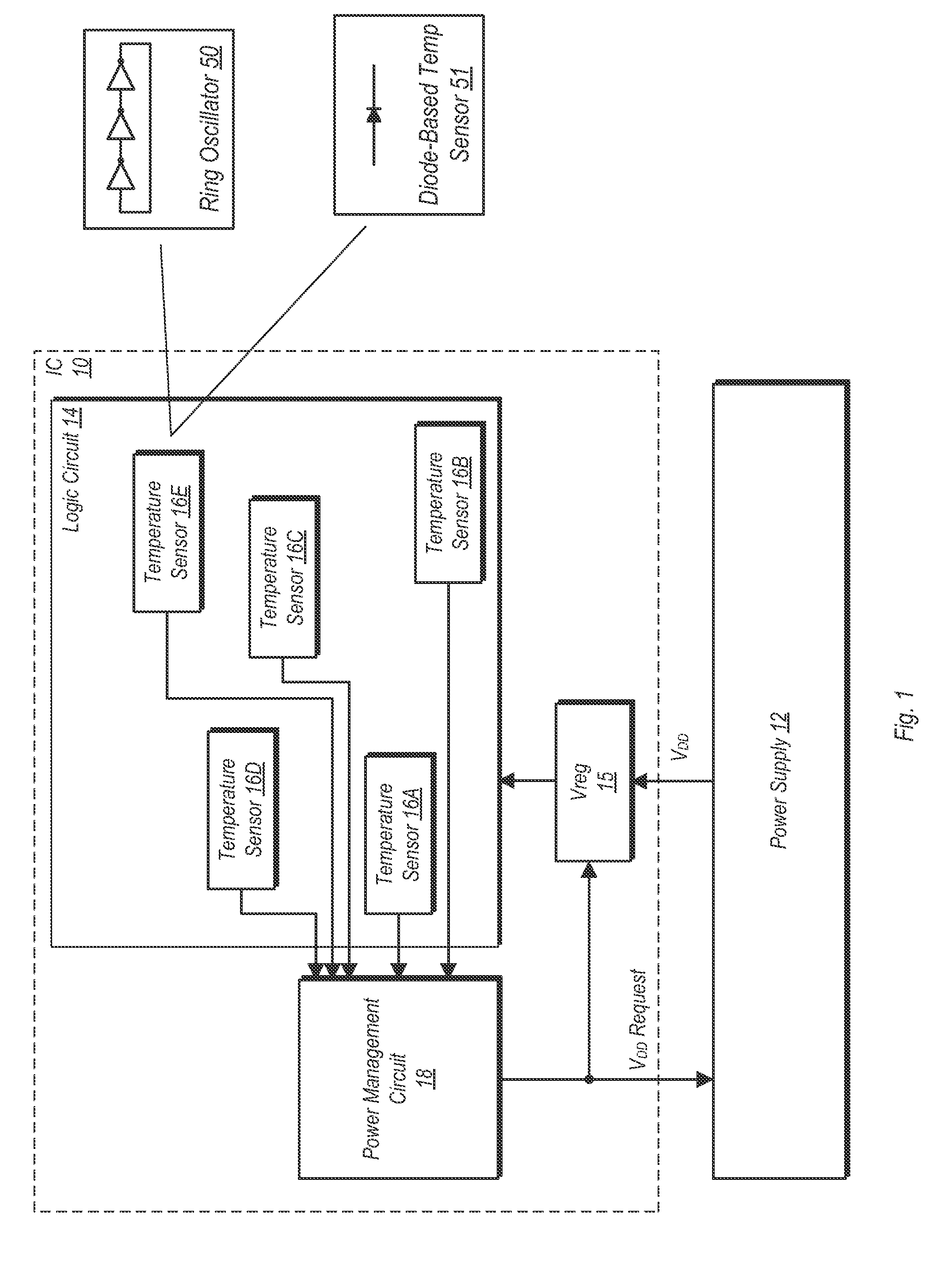
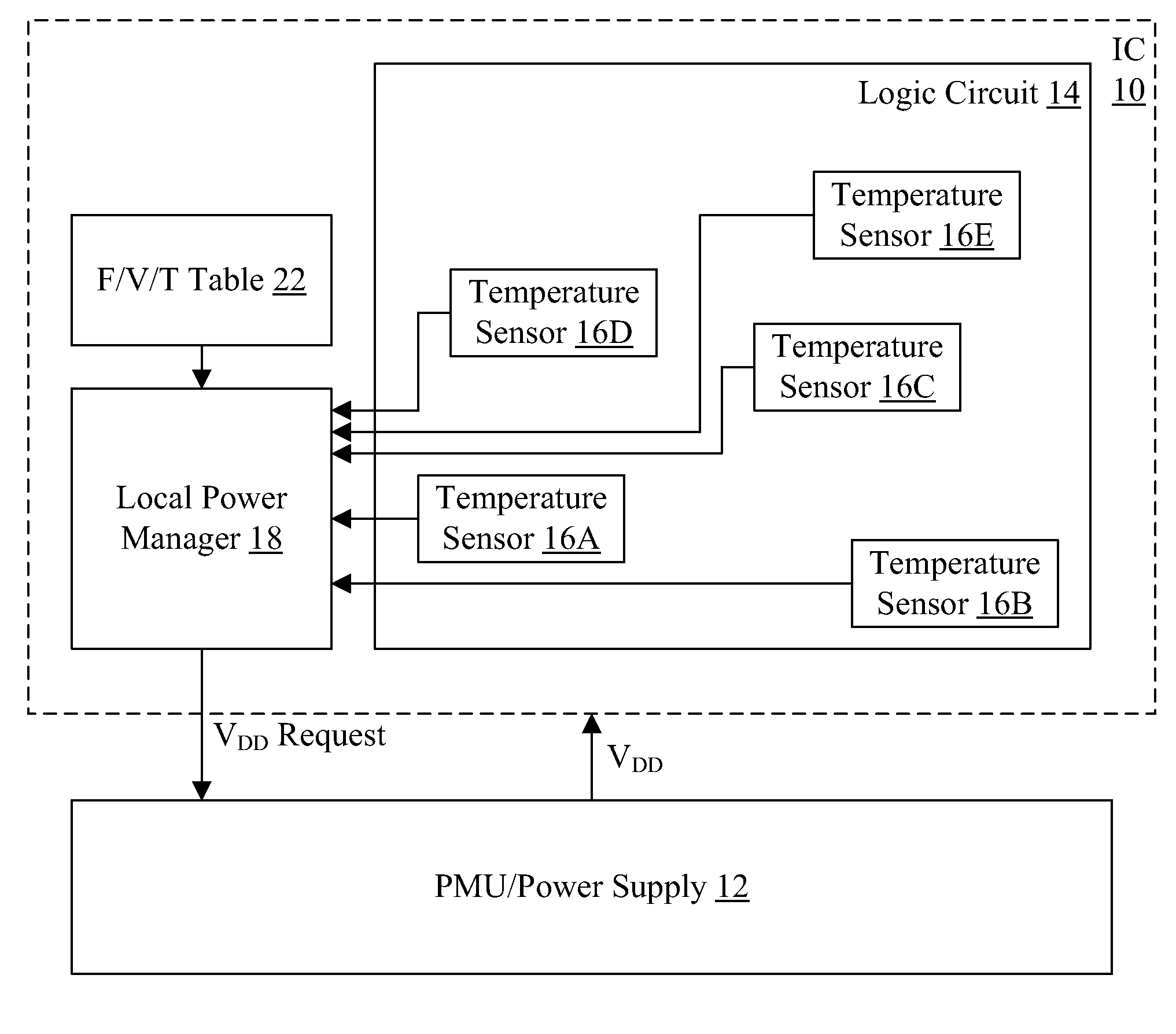
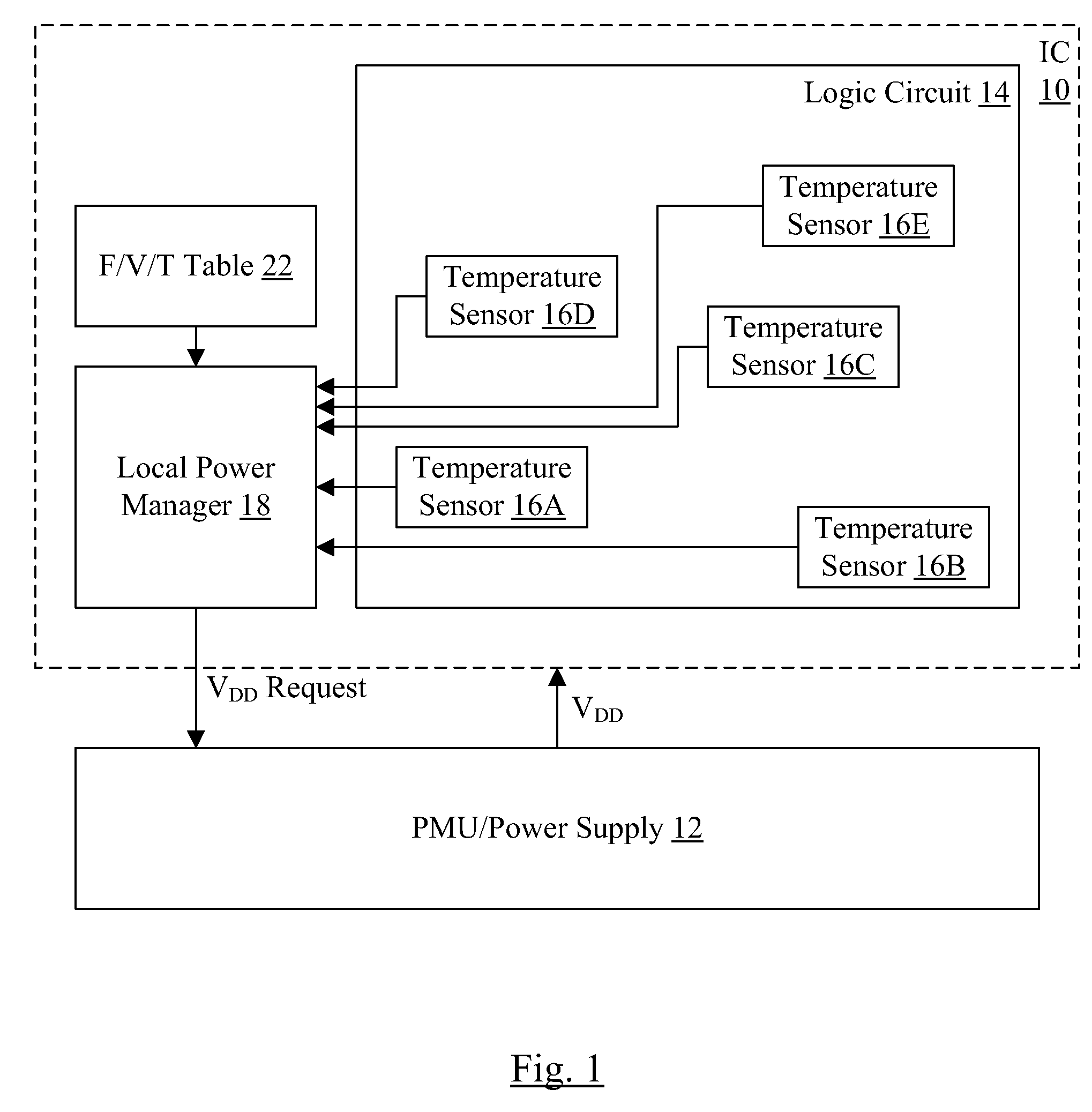
In an embodiment, an integrated circuit comprises a plurality of temperature sensors and a power manager coupled thereto. The temperature sensors are physically distributed over an area of the integrated circuit that is occupied by logic circuitry implementing the operations for which the integrated circuit is designed. The power manager is configured to transmit a power supply voltage request to an external power supply module, the power supply voltage request indicating a requested magnitude of the power supply voltage for the integrated circuit. The power manager is configured to modify the requested magnitude responsive to indications from each of the plurality of temperatures sensors that represent a temperature of the integrated circuit sensed by each of the plurality of temperature sensors.
Owner:APPLE INC
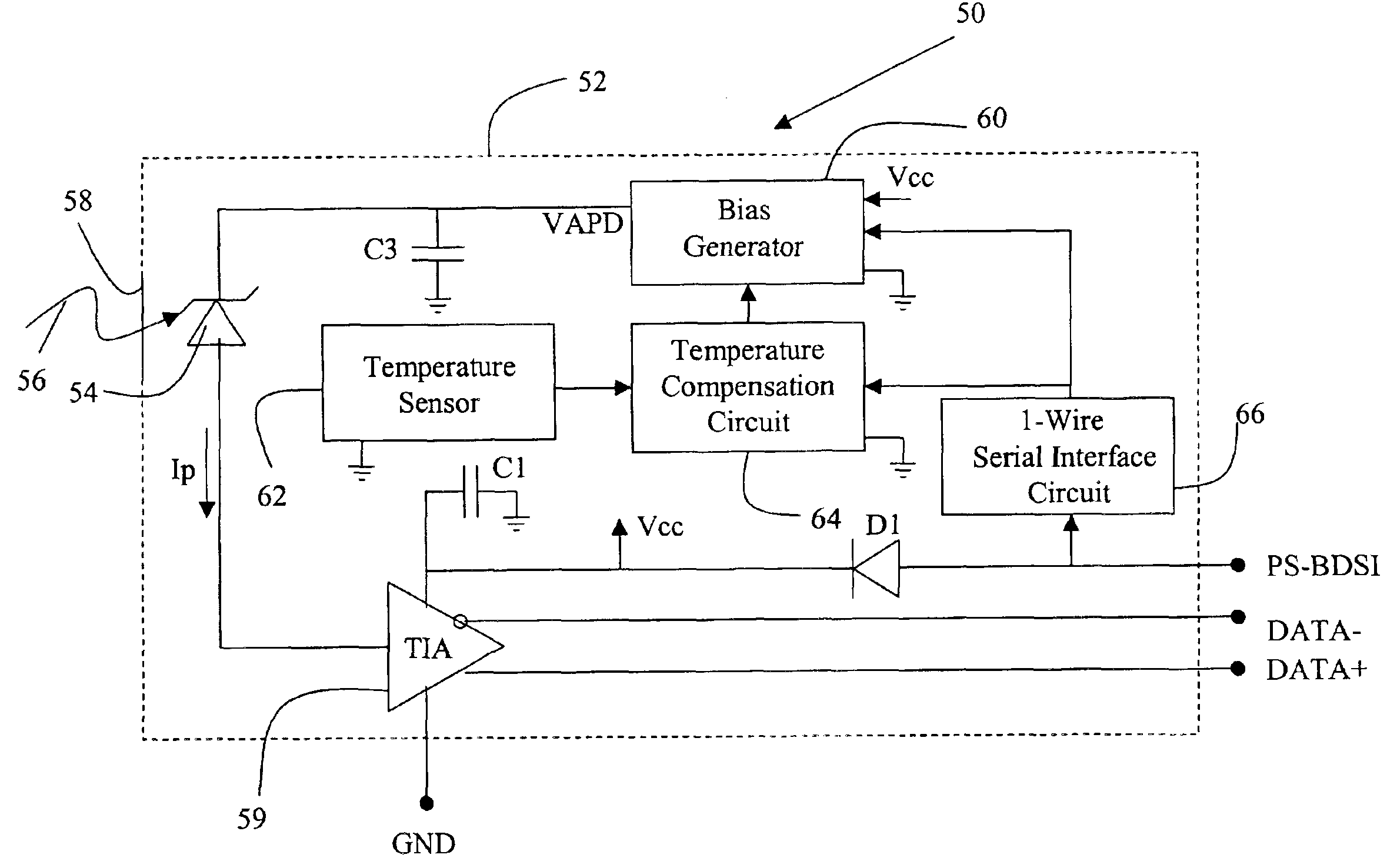
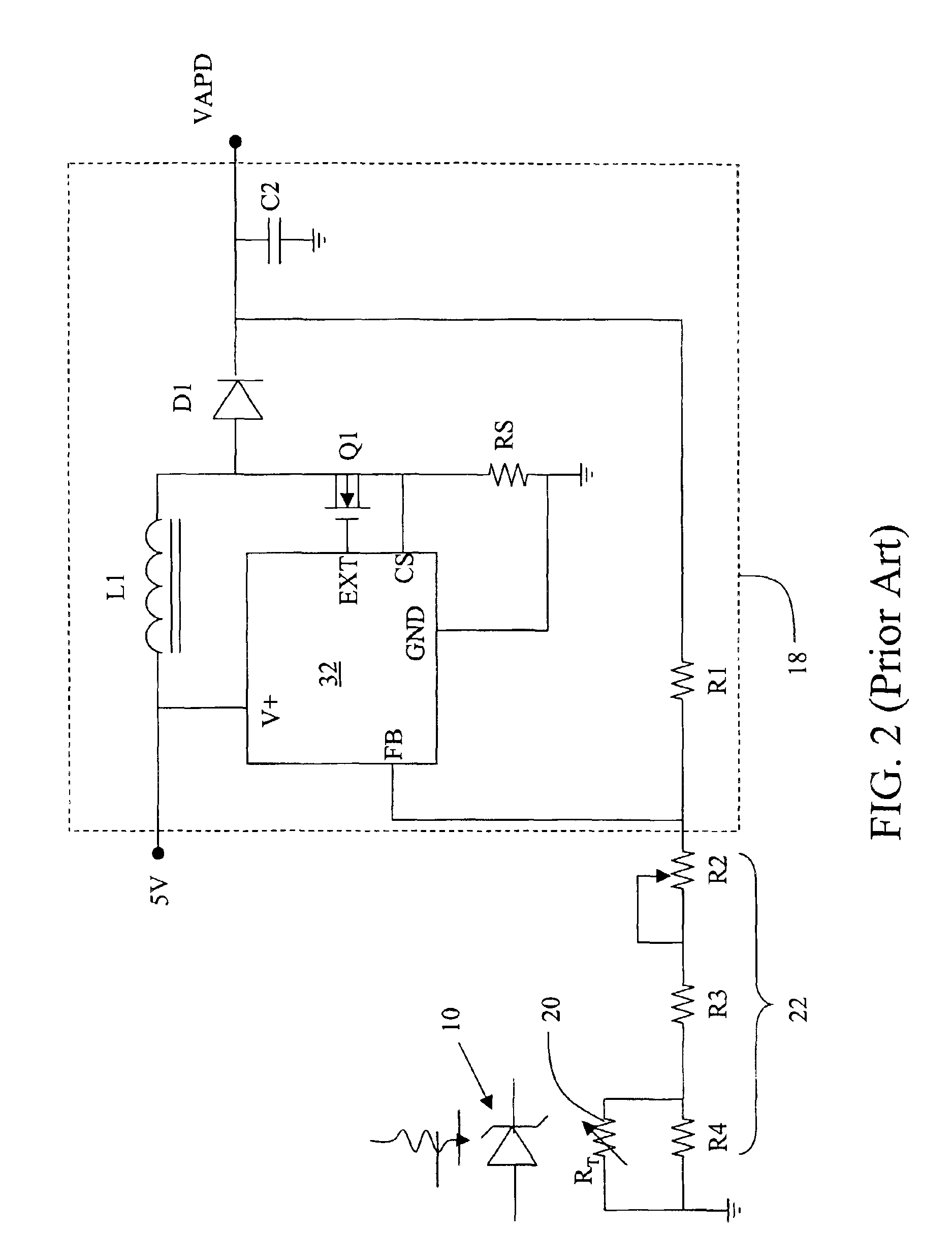
Single chip ASIC and compact packaging solution for an avalanche photodiode (APD) and bias circuit
ActiveUS6894266B2Few partsSmall sizeMultiplier circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringOperating frequency
A compact integrated APD device integrates the bias voltage and temperature compensation functions inside a standard 4-pin PIN package. The active components of the bias and temperature compensation circuits are integrated into a single ASIC using a high-voltage CMOS process and operated at frequencies of at least 1 MHz to greatly reduce the size of the passive components. To mount the relatively large ASIC chip inside the package with the APD chip, TIA chip and passives, the 4-pin package may be modified by either recessing the pins inside the can to facilitate surface mounting the ASIC or adding a spacer inside the can to facilitate three-dimensional packaging. Communication with the bias and temperature circuits is accomplished using a unique bi-directional 1-wire serial interface via the power supply pin. A clock signal is preferably embedded in the control data to synchronize the APD with an external controller.
Owner:OPLINK COMM
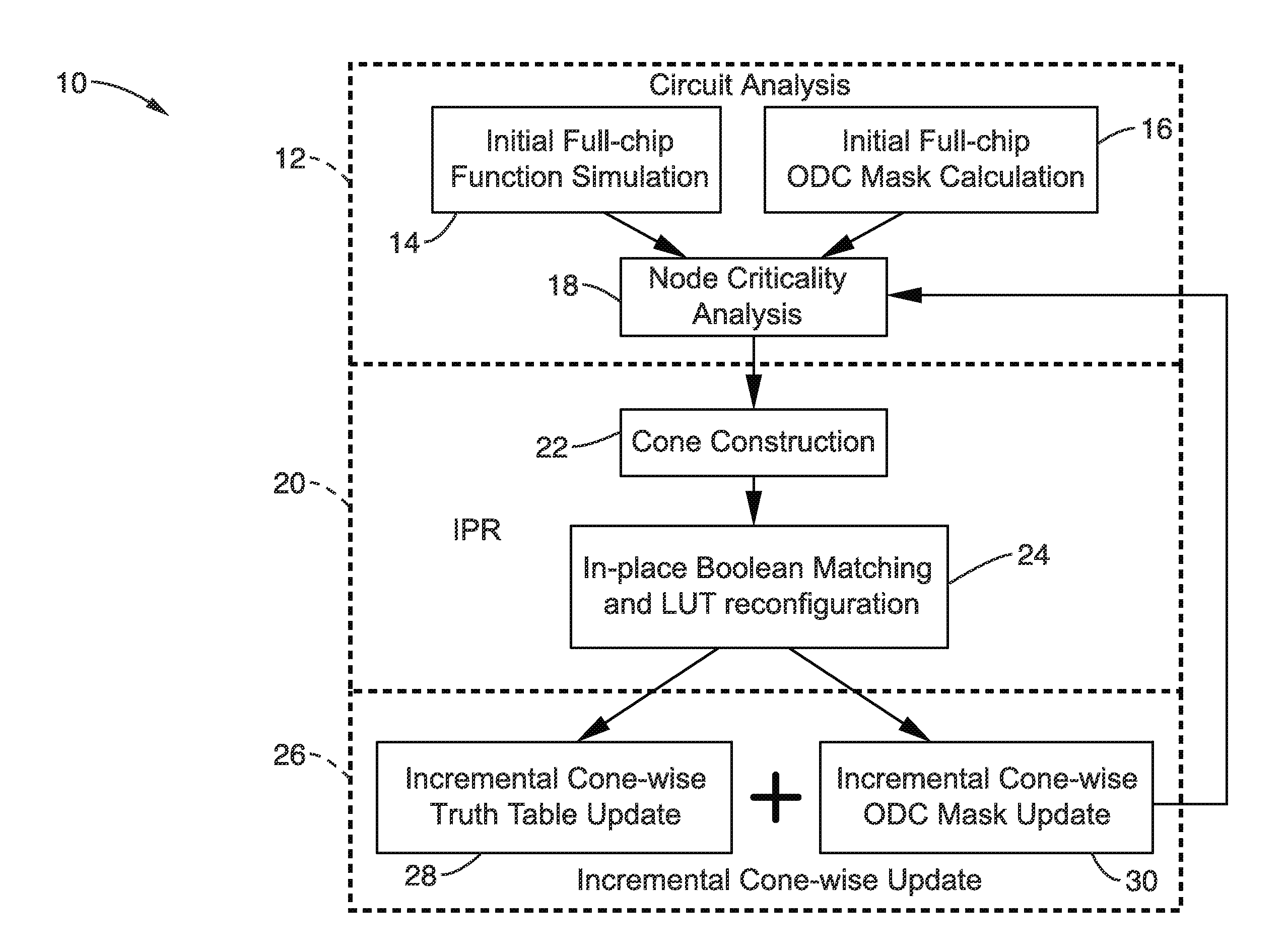
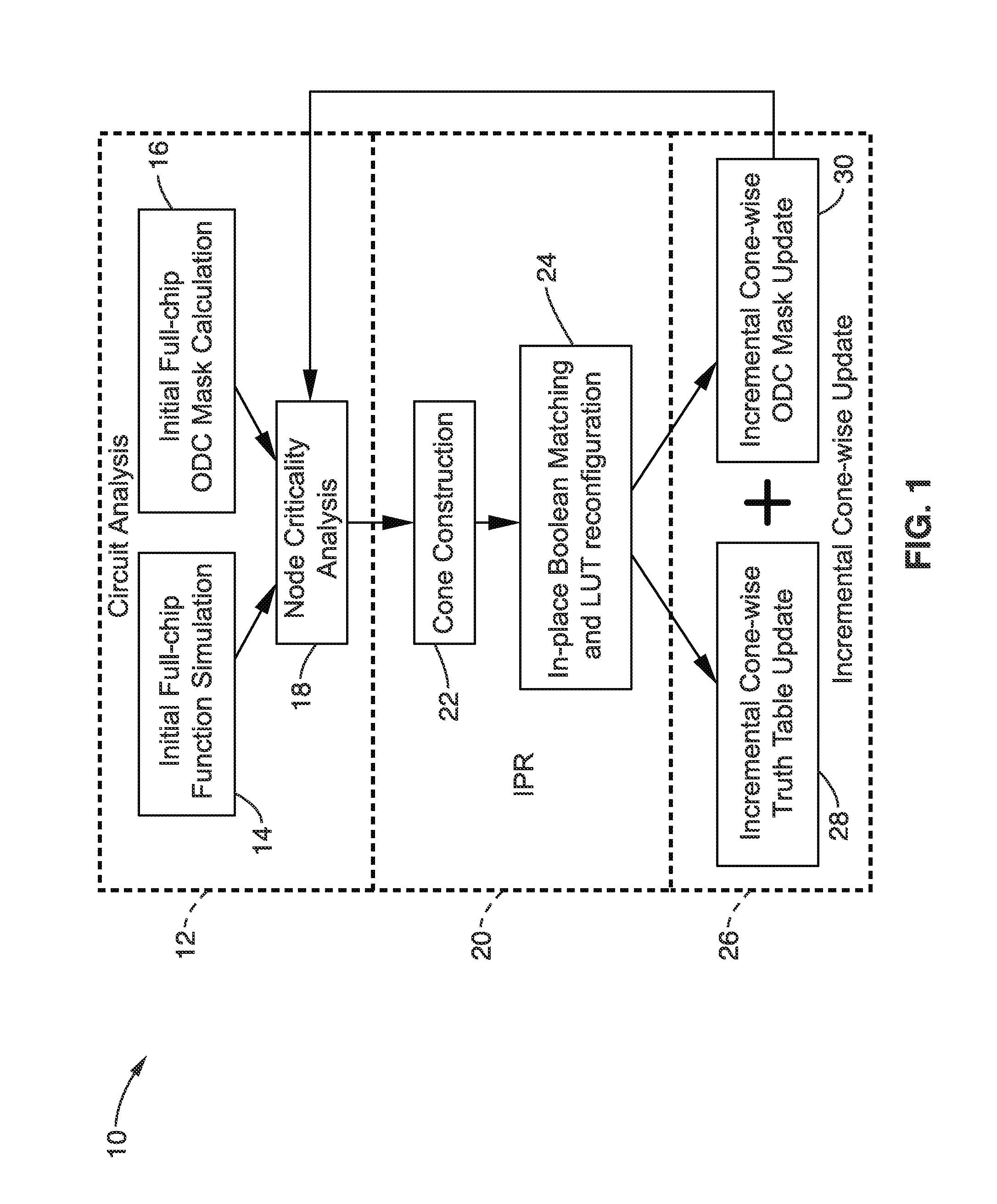
In-place resynthesis and remapping techniques for soft error mitigation in FPGA
InactiveUS20130305199A1Efficient and accurateImprove fault toleranceCAD circuit designRadiation hardeningFpga architectureDecomposition
In-place resynthesis for static memory (SRAM) based Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) toward reducing sensitivity to single event upsets (SEUs). Resynthesis and remapping are described which have a low overheard and improve FPGA designs without the need of rerouting LUTs of the FPGA. These methods include in-place reconfiguration (IPR), in-place X-filling (IPF), and in-place inversion (IPV), which reconfigure LUT functions only, and can be applied to any FPGA architecture. In addition, for FPGAs with a decomposable LUT architecture (e.g., dual-output LUTs) an in-place decomposition (IPD) method is described for remapping a LUT function into multiple smaller functions leveraging the unused outputs of the LUT, and making use of built-in hard macros in programmable-logic blocks (PLBs) such as carry chain or adder. Methods are applied in-place to mapped circuits before or after routing without affecting placement, routing, and design closure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
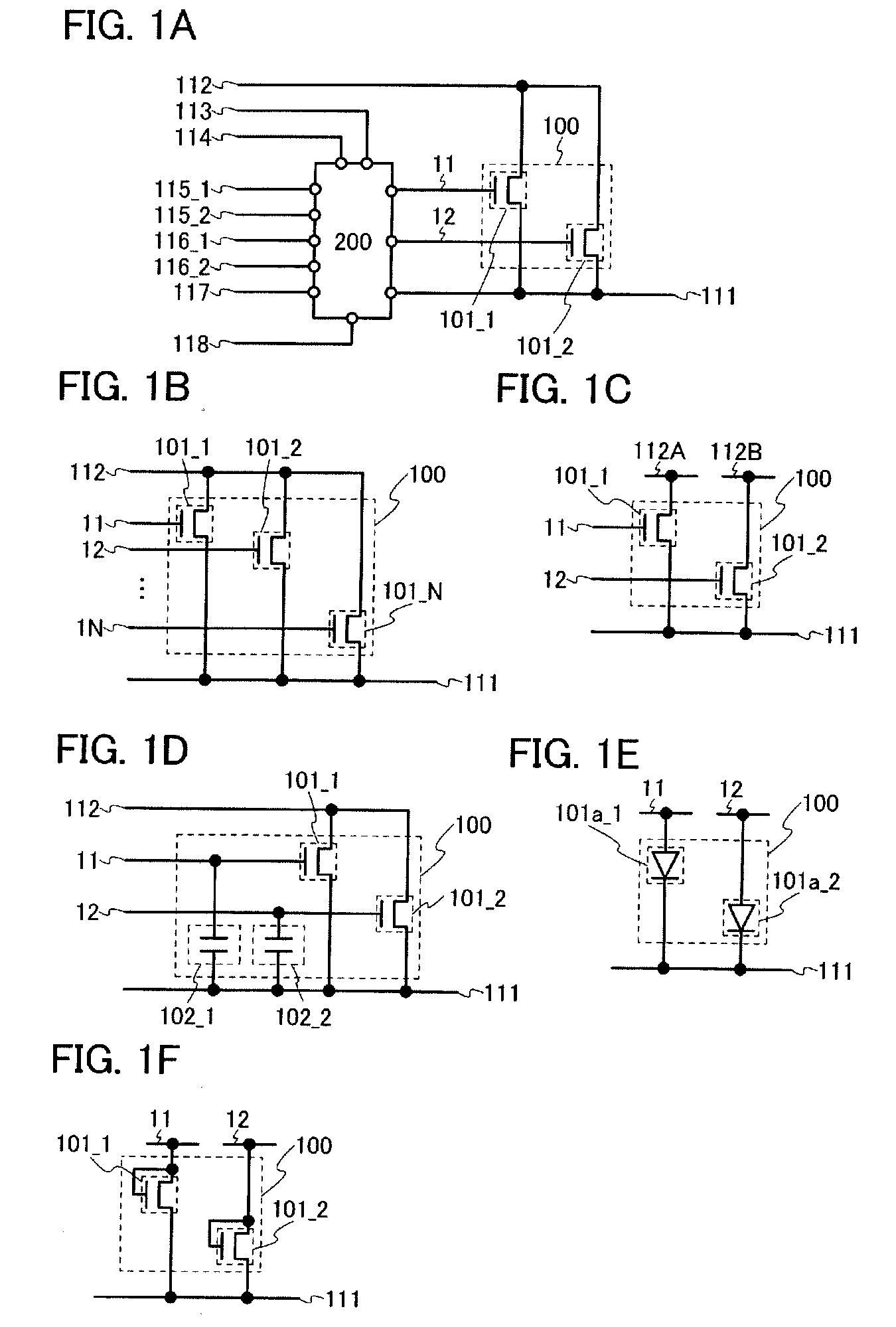
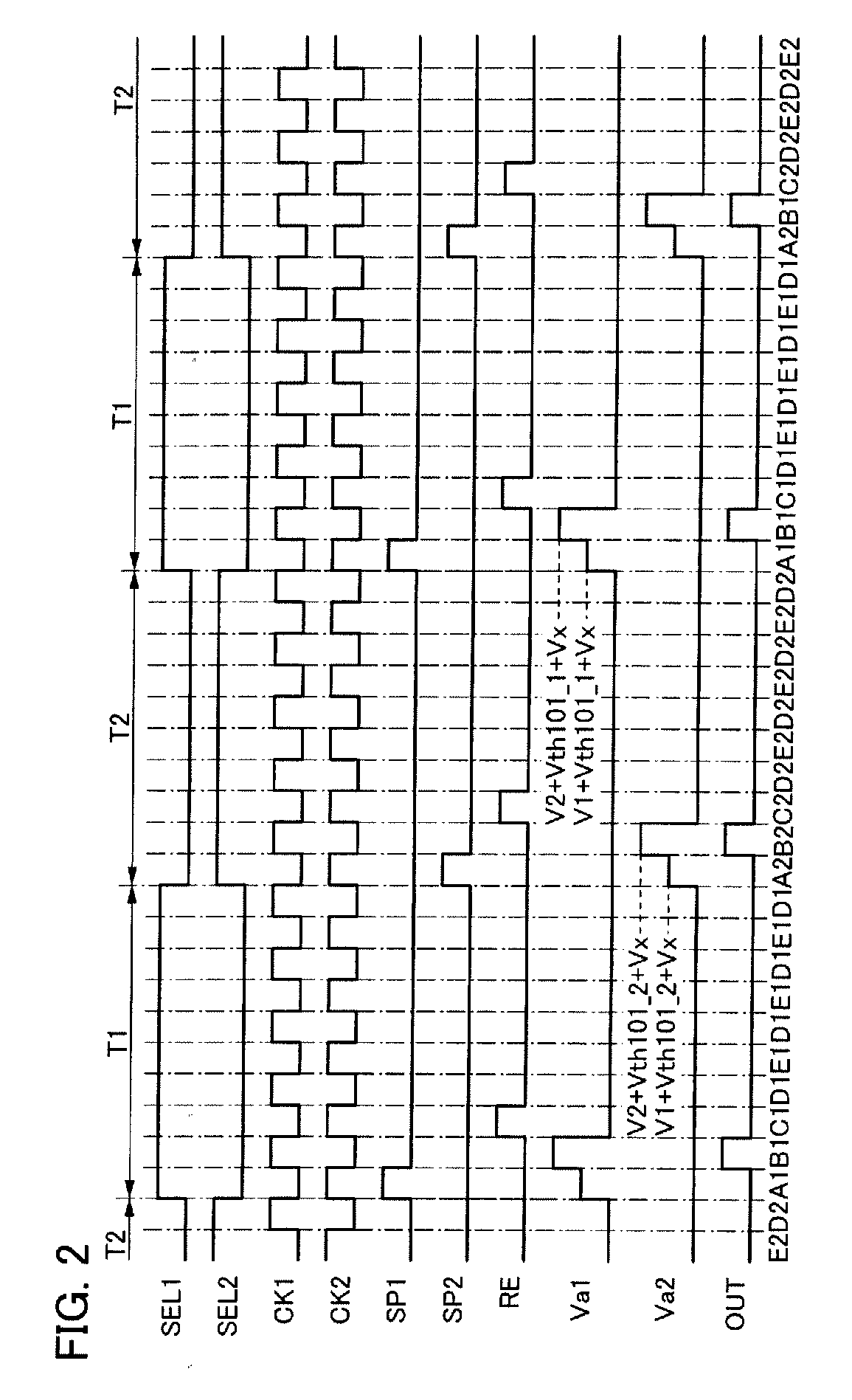
Semiconductor device, and display device and electronic device having the same
ActiveUS20130314139A1Threshold voltage shift can be suppressedSuppress noiseLogic circuits characterised by logic functionStatic indicating devicesShift registerDisplay device
An object is to provide a semiconductor device which can suppress characteristic deterioration in each transistor without destabilizing operation. In a non-selection period, a transistor is turned on at regular intervals, so that a power supply potential is supplied to an output terminal of a shift register circuit. A power supply potential is supplied to the output terminal of the shift register circuit through the transistor. Since the transistor is not always on in a non-selection period, a shift of the threshold voltage of the transistor is suppressed. In addition, a power supply potential is supplied to the output terminal of the shift register circuit through the transistor at regular intervals. Therefore, the shift register circuit can suppress noise which is generated in the output terminal.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Electronic Device Including Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20100246750A1Suppress characteristicImprove the shortageTransistorStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitEngineering
It is an object to suppress deterioration in characteristics of a transistor in a driver cricuit. A driver circuit includes a first transistor, a second transistor including a gate and one of a source and a drain to which a second signal is inputted, a third transistor whose gate is electrically connected to one of a source and a drain of the first transistor and which controls whether a voltage state of an output signal is set or not by being turned on / off, and a fourth transistor whose gate is electrically connected to the other of the source and the drain of the second transistor and which controls whether a voltage state of an output signal is set or not by being turned on / off.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
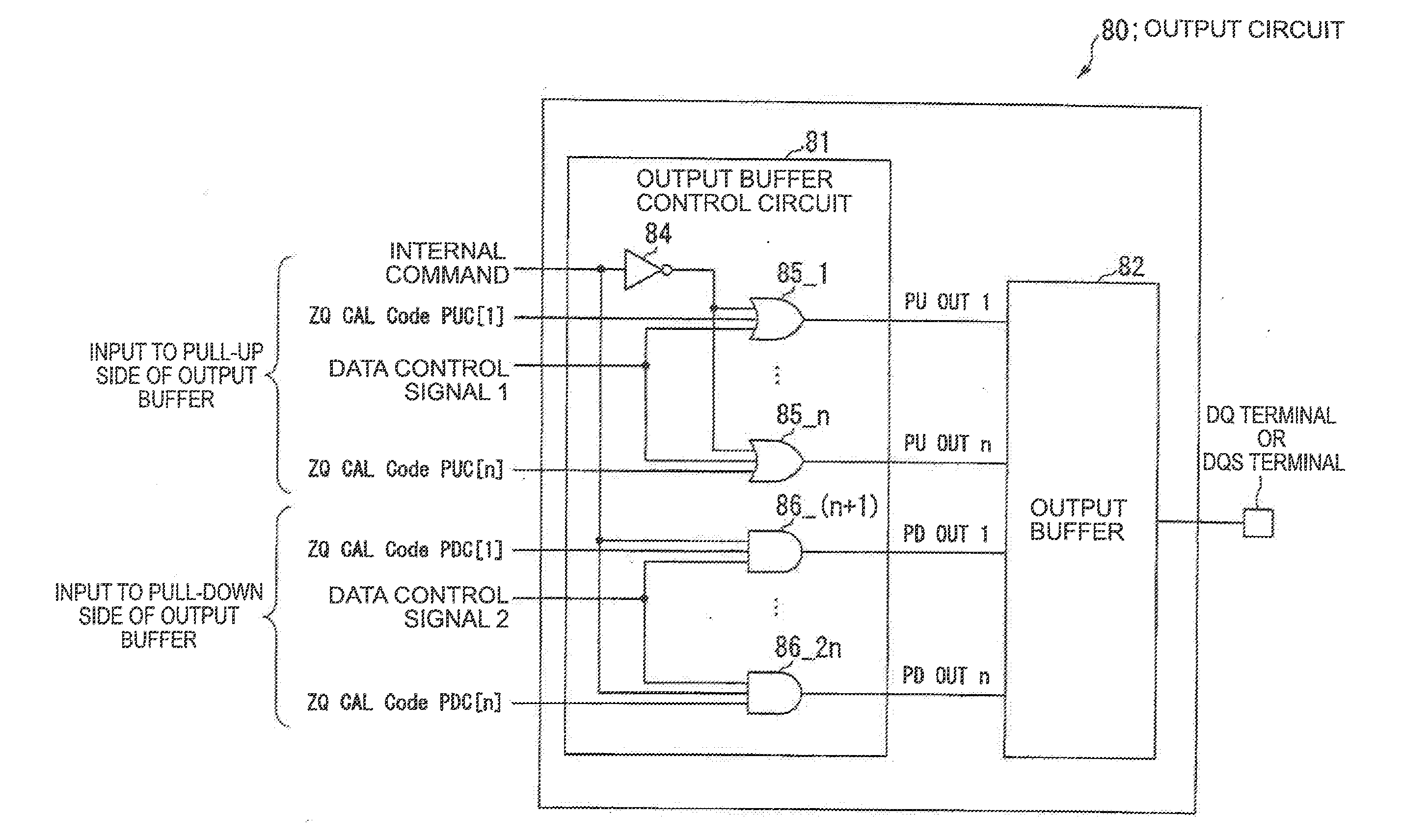
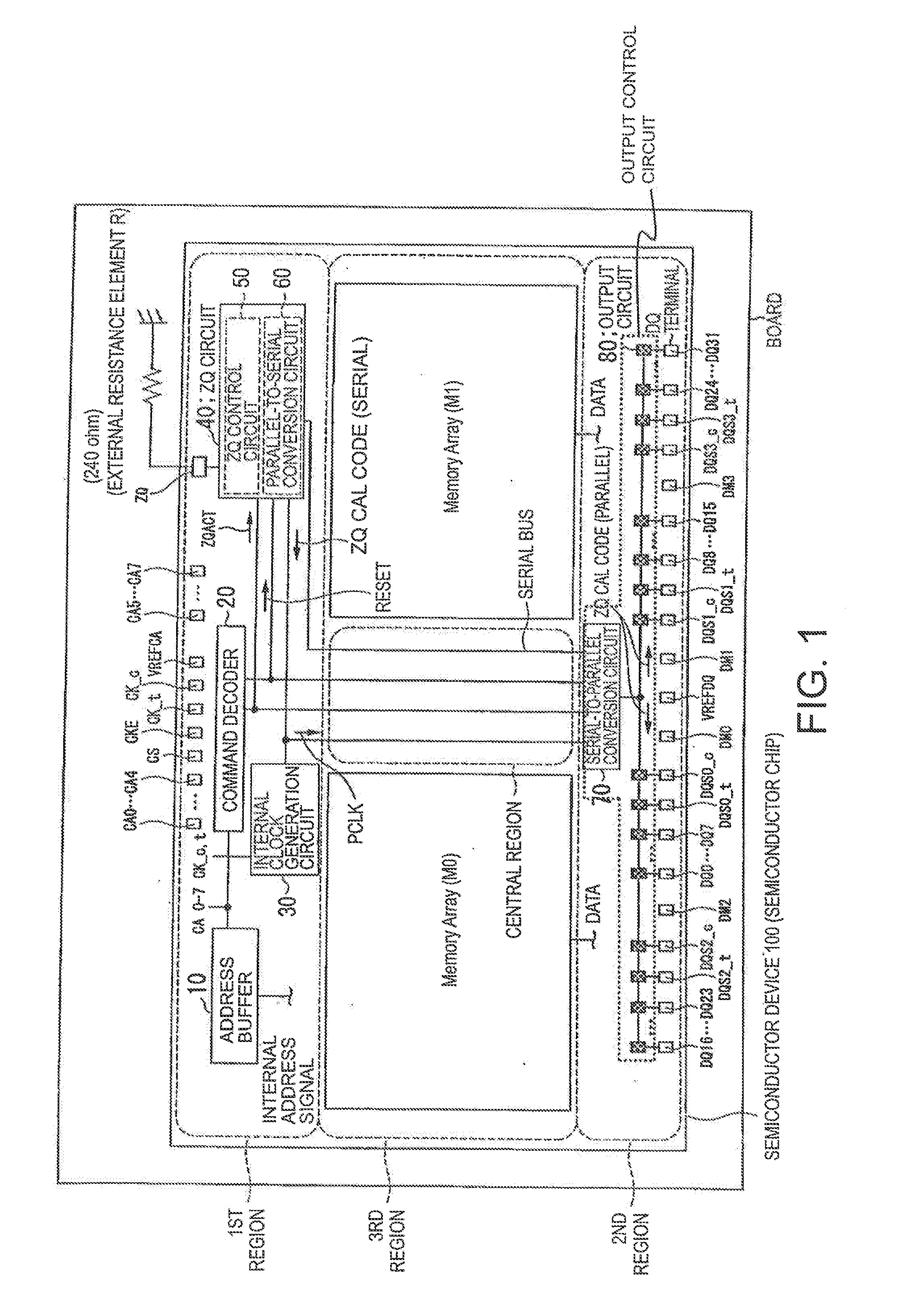
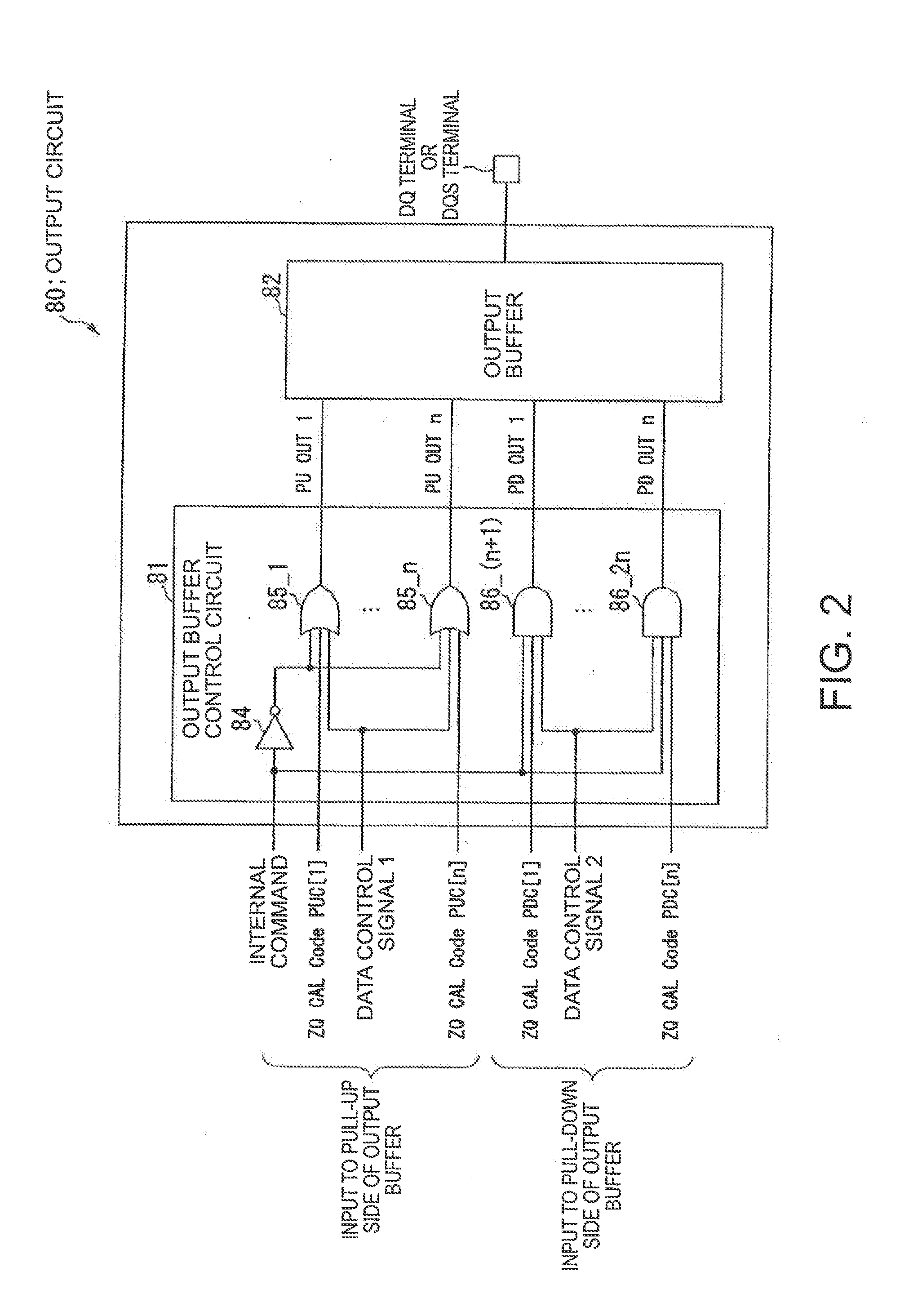
Semiconductor device and method of adjusting an impedance of an output buffer
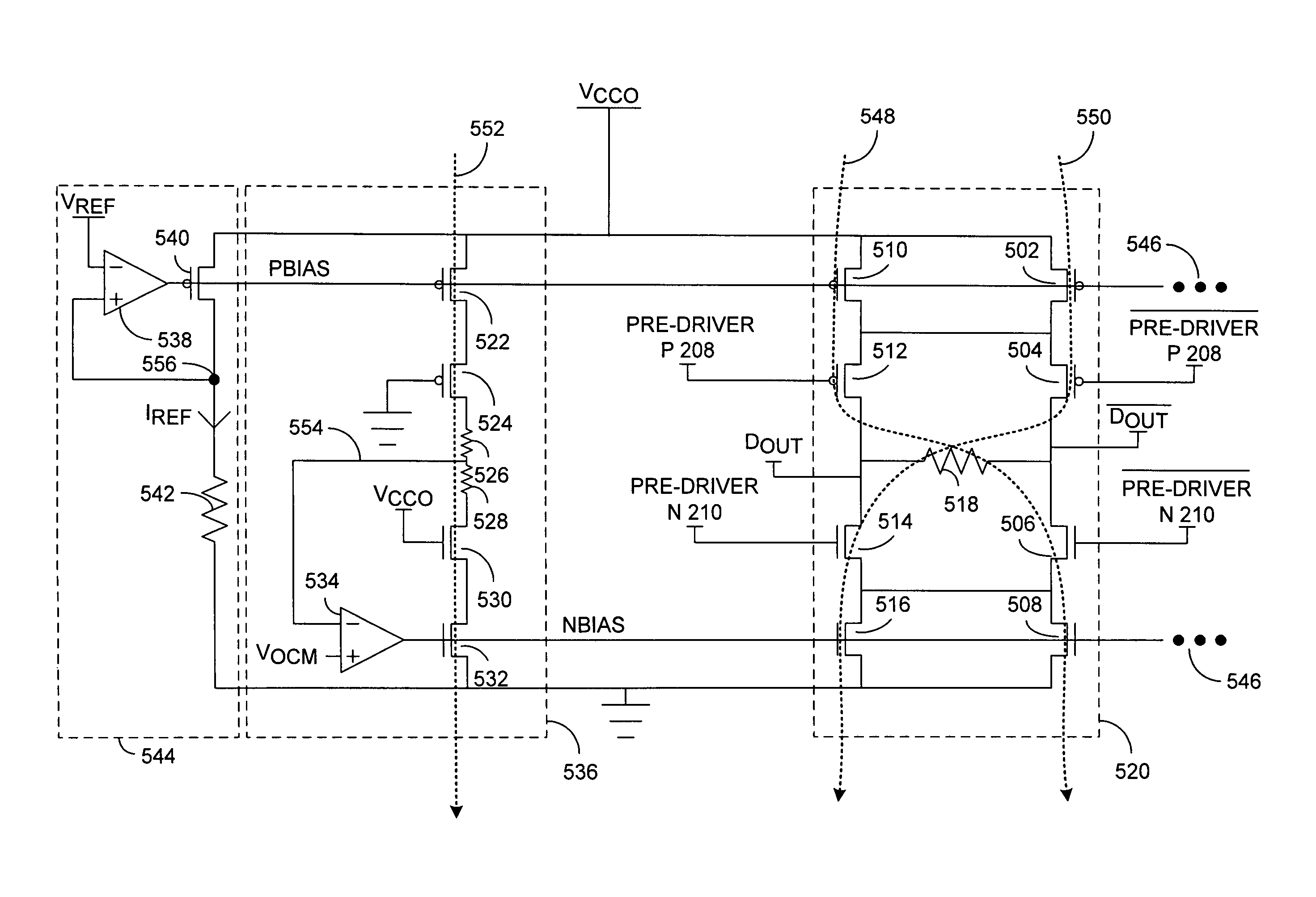
InactiveUS20130015880A1Increase in chip sizeIncrease wiring areaElectronic switchingVoltage/temperature variation compensationEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor device has a ZQ circuit (40) which generates impedance control information and an output buffer having an impedance controlled in response to the impedance control information. A plurality of control bits constituting the impedance control information are serially transferred from the ZQ circuit.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
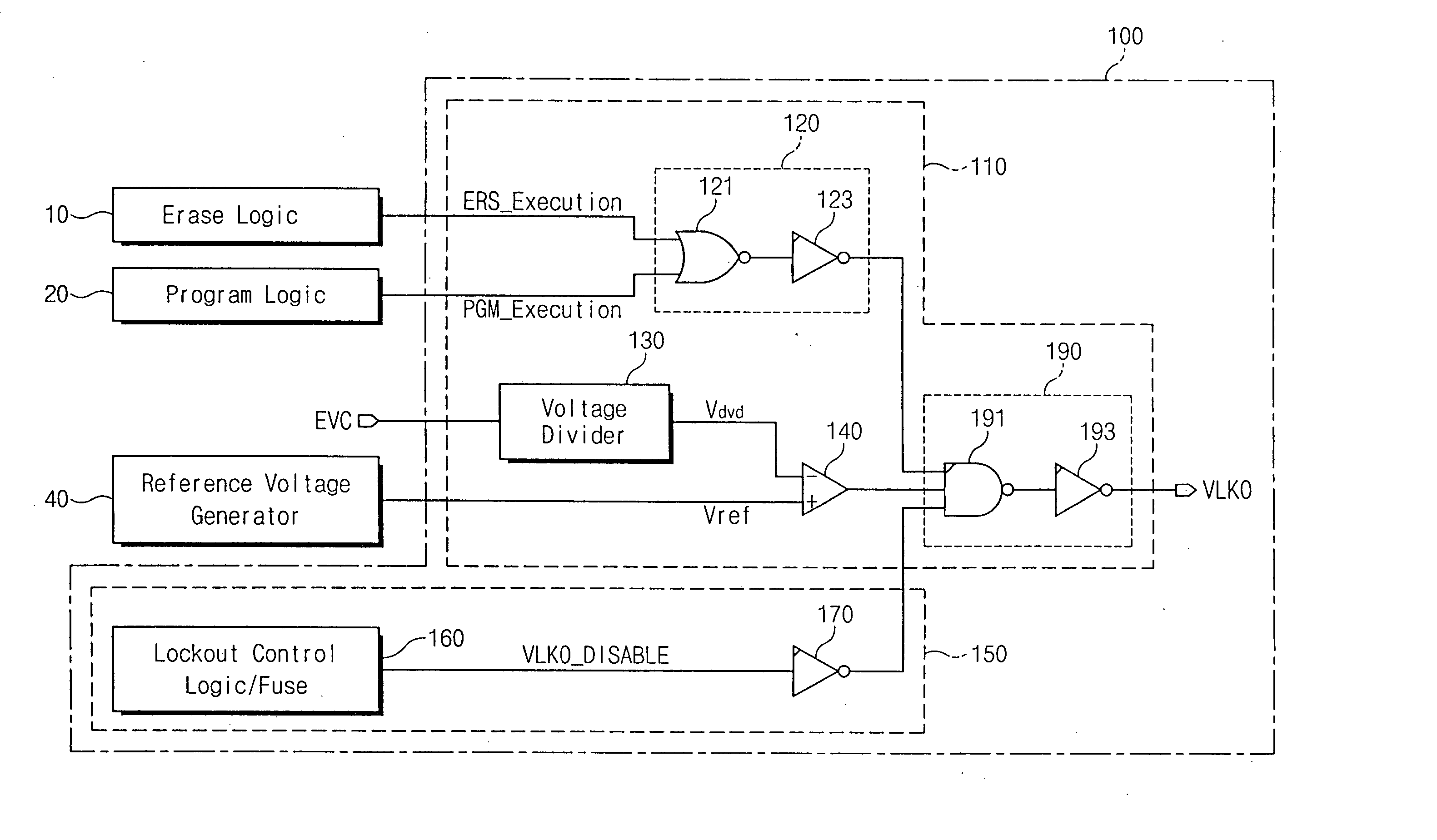
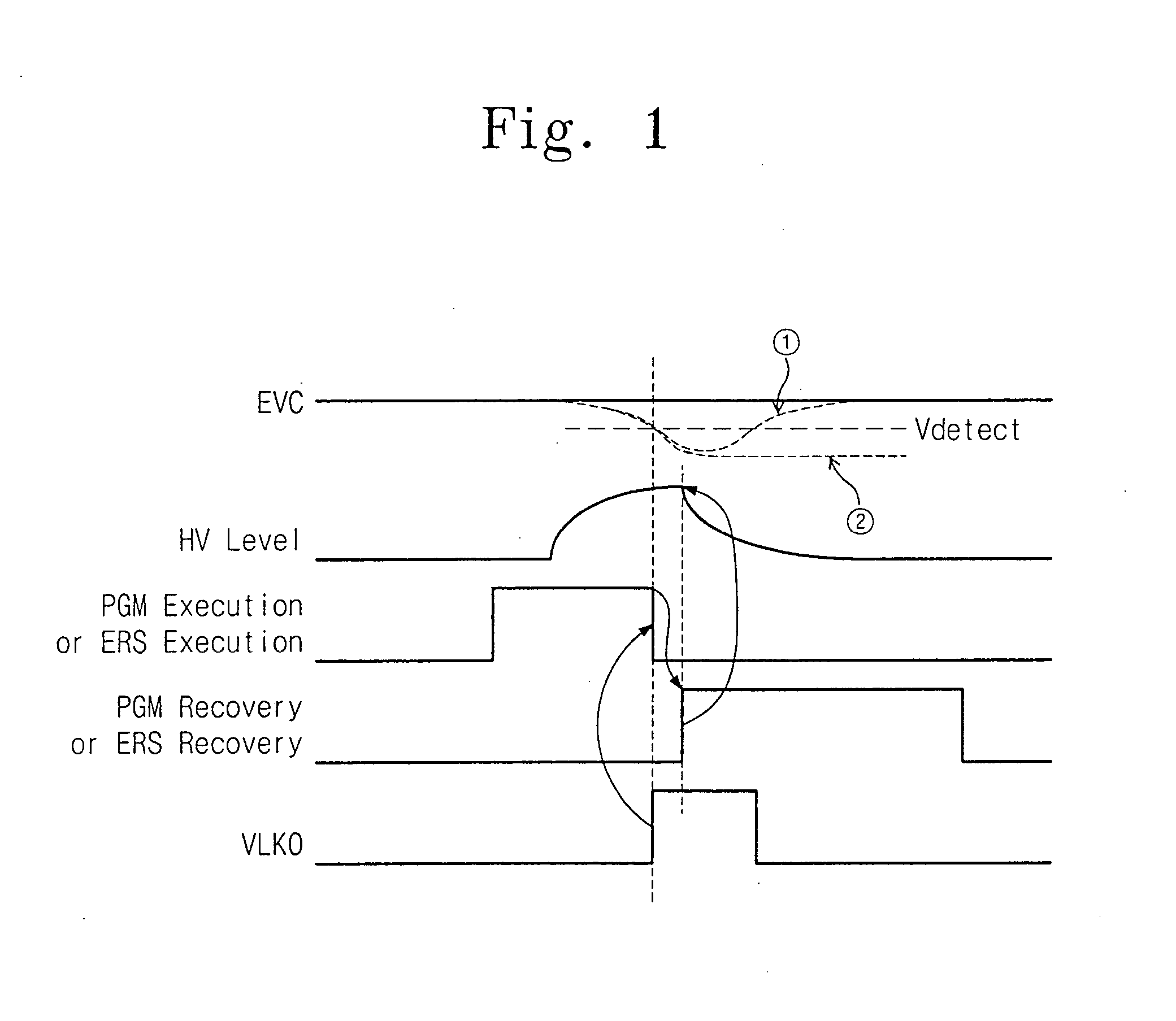
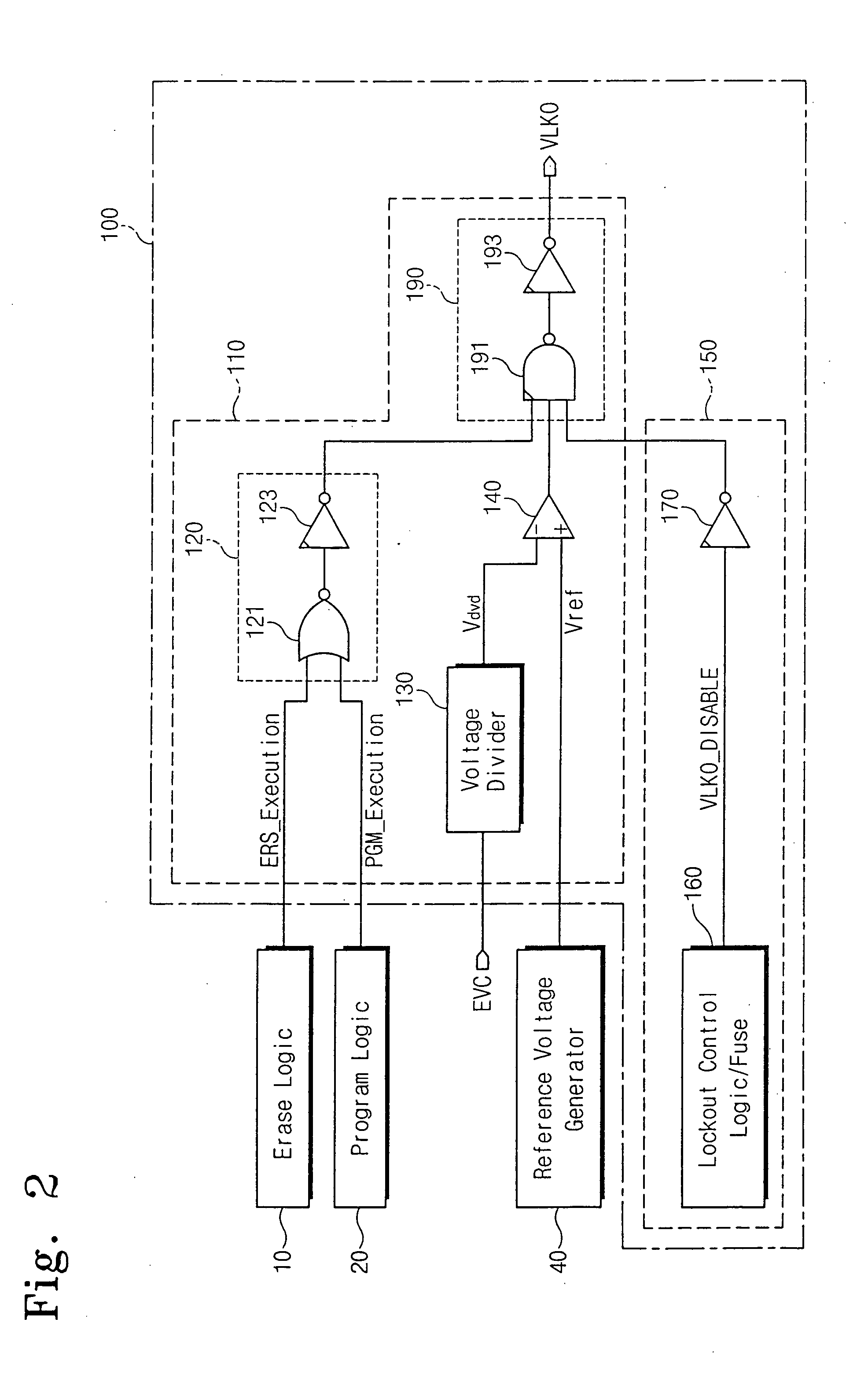
Method and apparatus for selectively performing lock-out function in integrated circuit device
A lock-out circuit is adapted to selectively perform a lock-out function in an integrated circuit device. The lock-out function cuts off the supply of an operating voltage to the integrated circuit device whenever a power supply voltage for the device falls below a predetermined detection voltage. However, the lock-out function is disabled whenever the integrated circuit device performs an operation requiring a power supply voltage lower than the predetermined detection voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
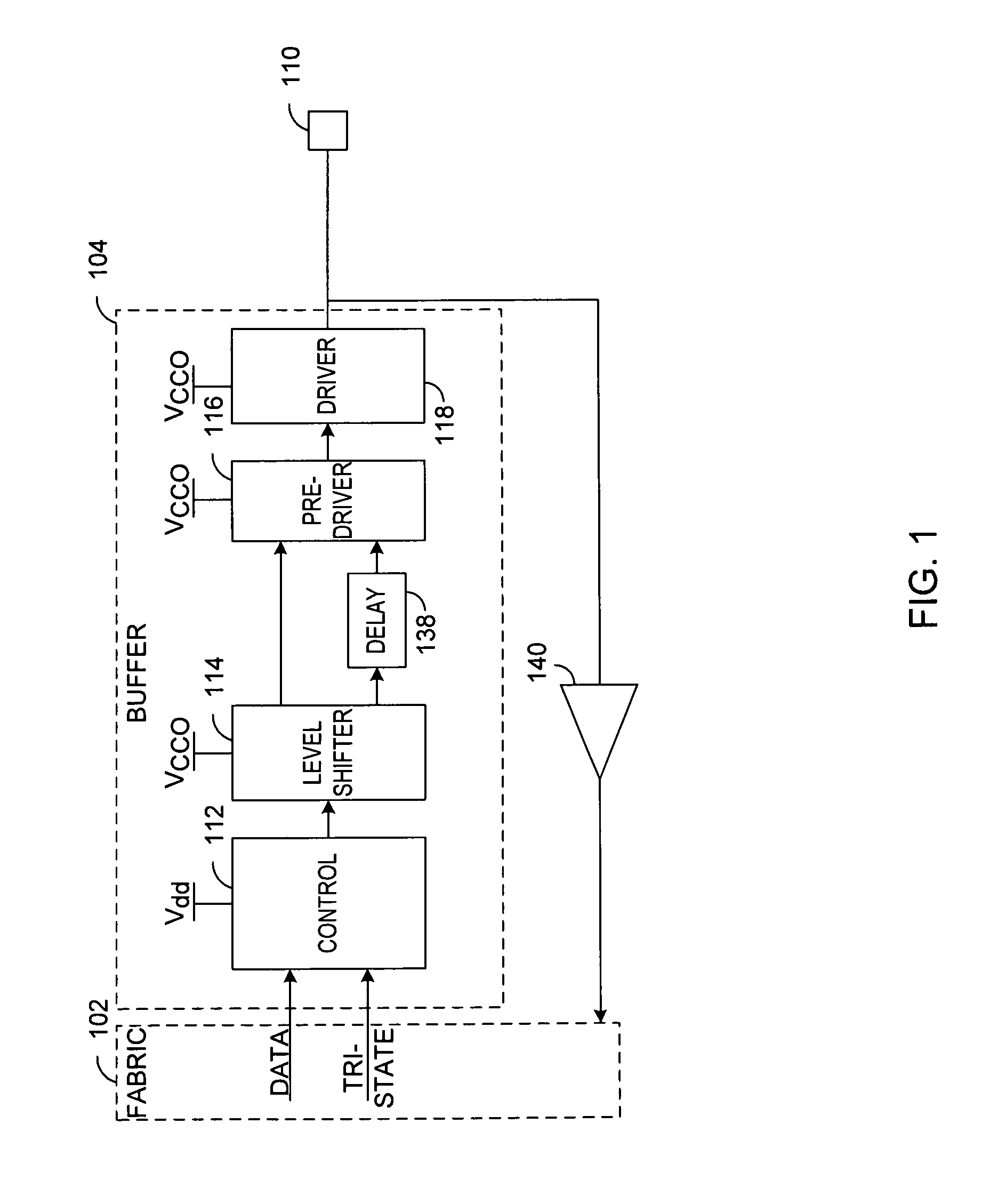
Apparatus and methods for altering the timing of a clock signal
Clock signal timing cells, clock signal timing circuits, clock circuits, memory devices, systems, and method for altering the timing of a clock signal are disclosed. An example method for altering the timing of an output signal provided responsive to an input clock signal includes adjusting a transition of an edge of the output signal from one voltage level to another based at least in part on a bias signal. An example clock signal timing cell includes an inverter and a bias controlled inverter coupled in parallel to the inverter. The bias controlled circuit is configured to provide an output signal wherein a transition of a clock edge of the output signal between first and second voltage levels is based at least in part on a bias signal.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Temperature compensating circuit and method and liquid crystal display
InactiveCN104361874ASmall amount of flickerImprove visual experienceStatic indicating devicesVoltage/temperature variation compensationLiquid-crystal displayGray level
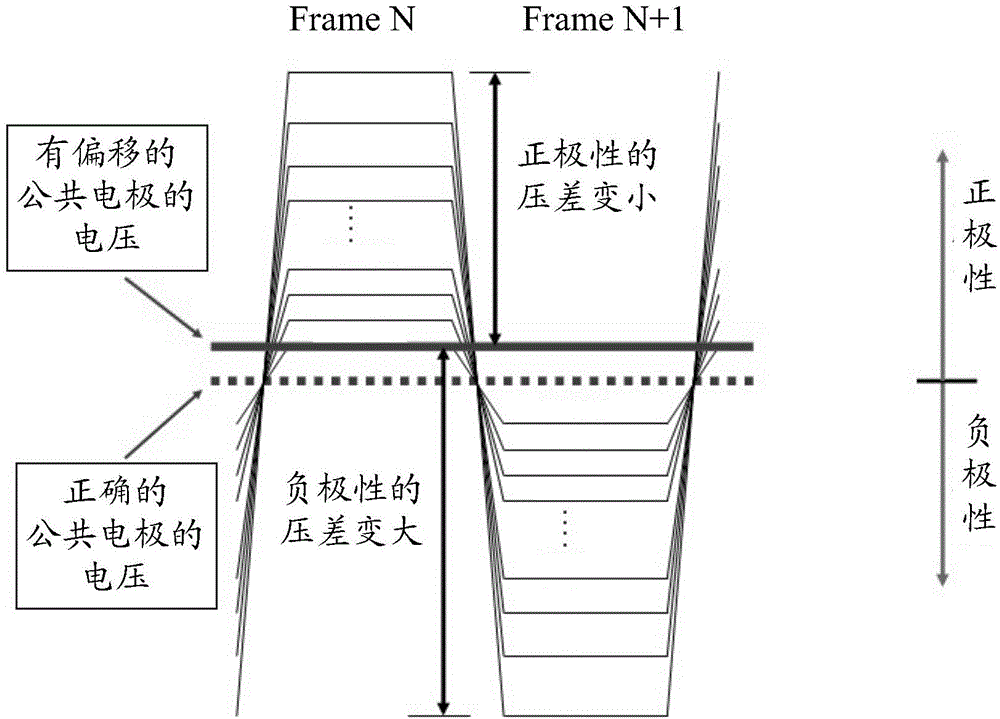
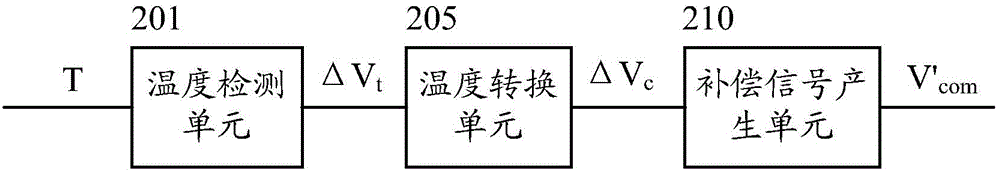
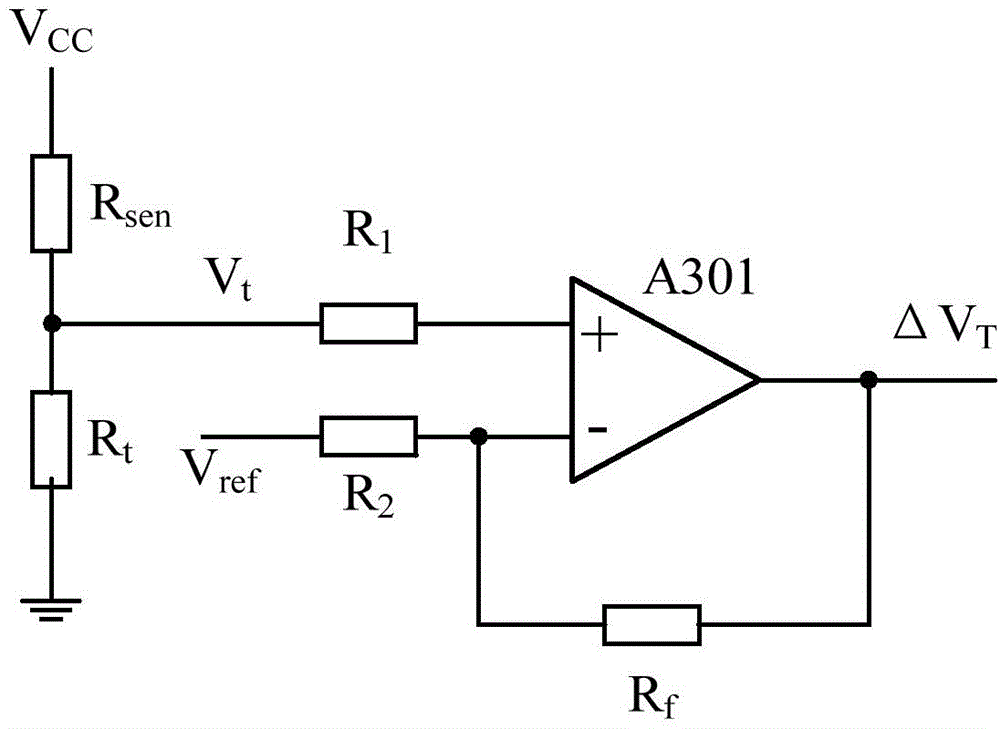
The invention discloses a temperature compensating circuit and method and a liquid crystal display. The temperature compensating circuit and method and the liquid crystal display are applied to a display panel. The temperature compensating circuit comprises a temperature detecting unit, a temperature converting unit and a compensating signal generating unit, wherein the temperature detecting unit is used for detecting a temperature variation, the temperature converting unit is used for converting the detected temperature variation into a voltage compensation variation, and the compensating signal generating unit is used for processing the voltage compensation variation so as to generate a compensating signal used for temperature compensation of the public electrode voltage of the display panel. According to the temperature compensating circuit and method, the public electrode voltage of the display panel can be adjusted in real time when the temperature changes, the public electrode voltage is made to be on the midpoint between positive gray scale change and negative gray scale change, in this way, the number of flickers generated when the polarity of the display panel is reversed is kept the smallest, an image can be displayed more stably, and the visual experience of a viewer is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
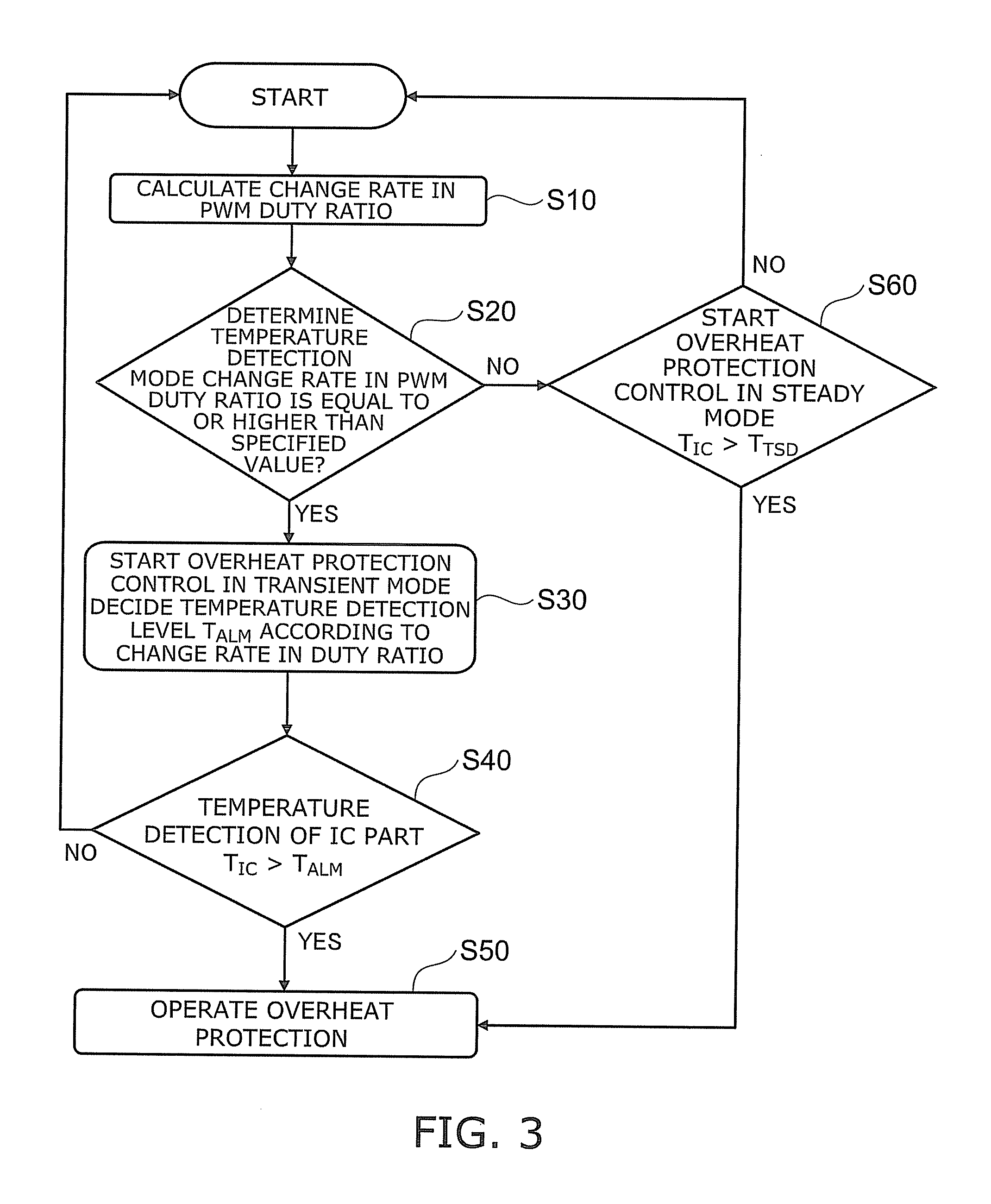
Power semiconductor system
InactiveUS20110298528A1Solid-state devicesElectronic switchingPower semiconductor deviceControl signal
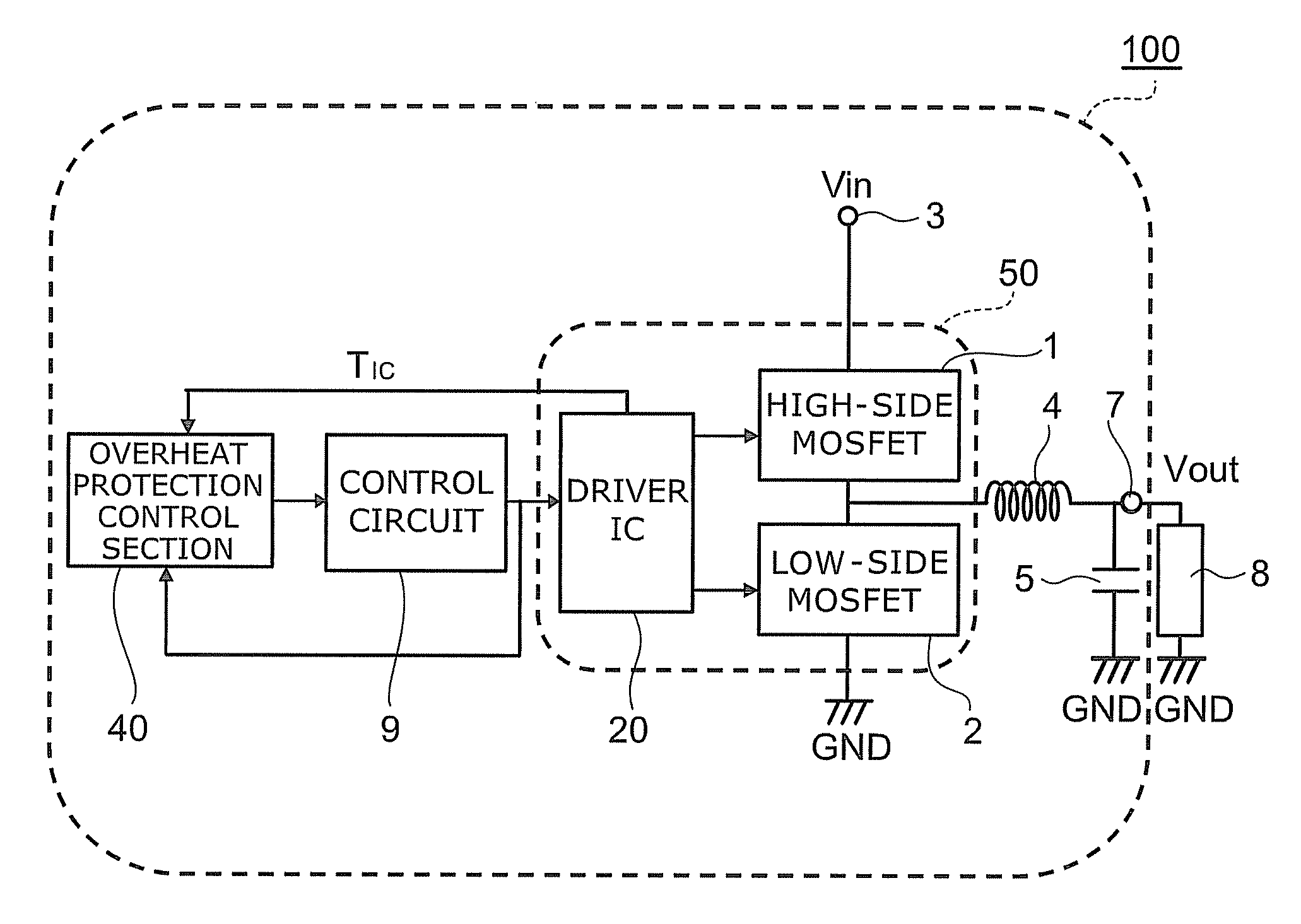
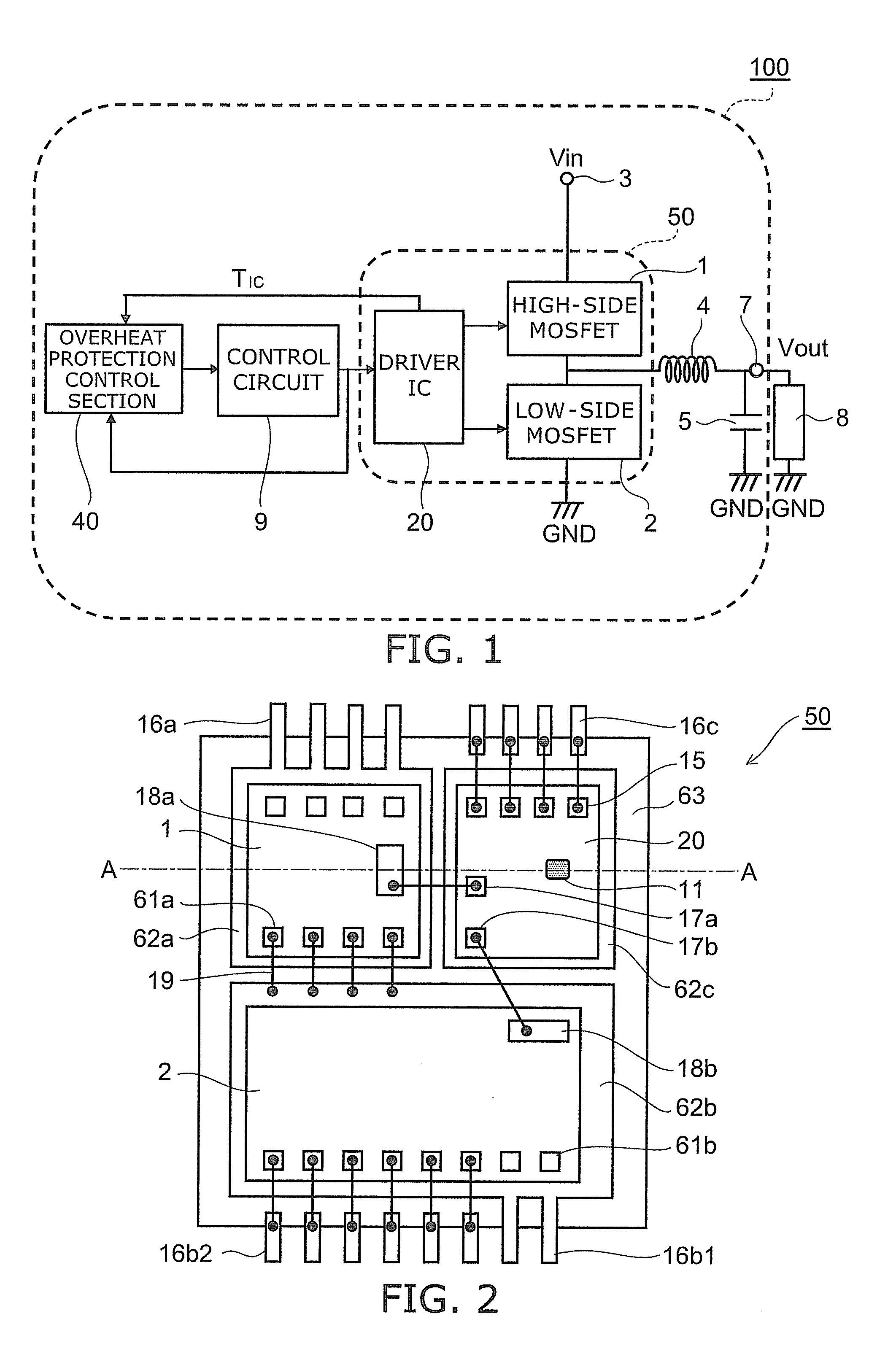
According to one embodiment, a power semiconductor system includes; a first power semiconductor element, a driver IC, a first temperature detection element, a control circuit and an overheat protection control section. The first power semiconductor element controls current flowing between a first electrode and a second electrode with a control electrode. The driver IC supplies a drive signal making the first power semiconductor element on and off. The first temperature detection element detects a temperature of the driver IC. The control circuit supplies a control signal for controlling operation of the driver IC to the driver IC. The overheat protection control section is configured to supply an overheat protection signal to the control circuit based on an output of the first temperature detection element. The control circuit performs overheat protection operation. The overheat protection control section supplies the overheat protection signal to the control circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
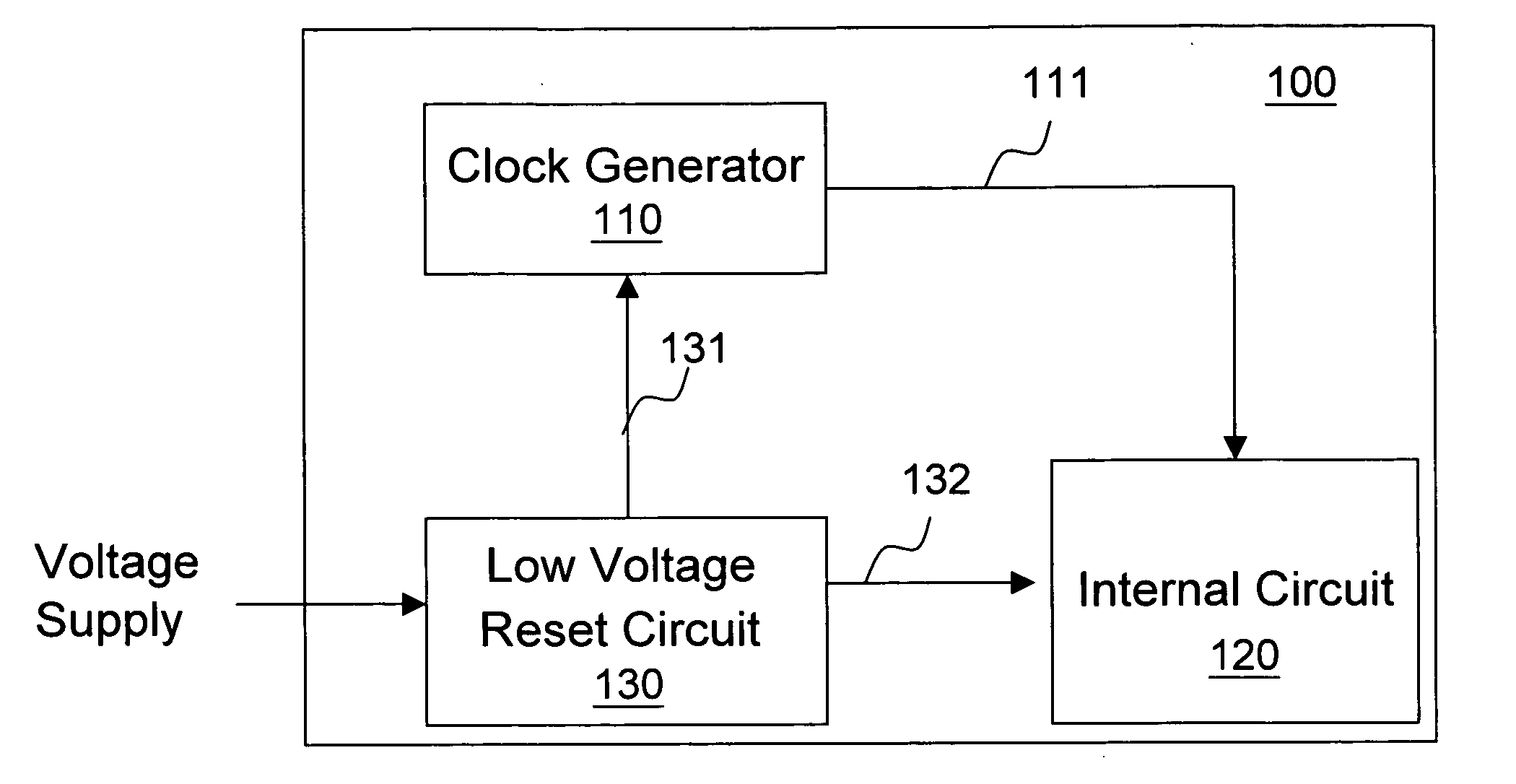
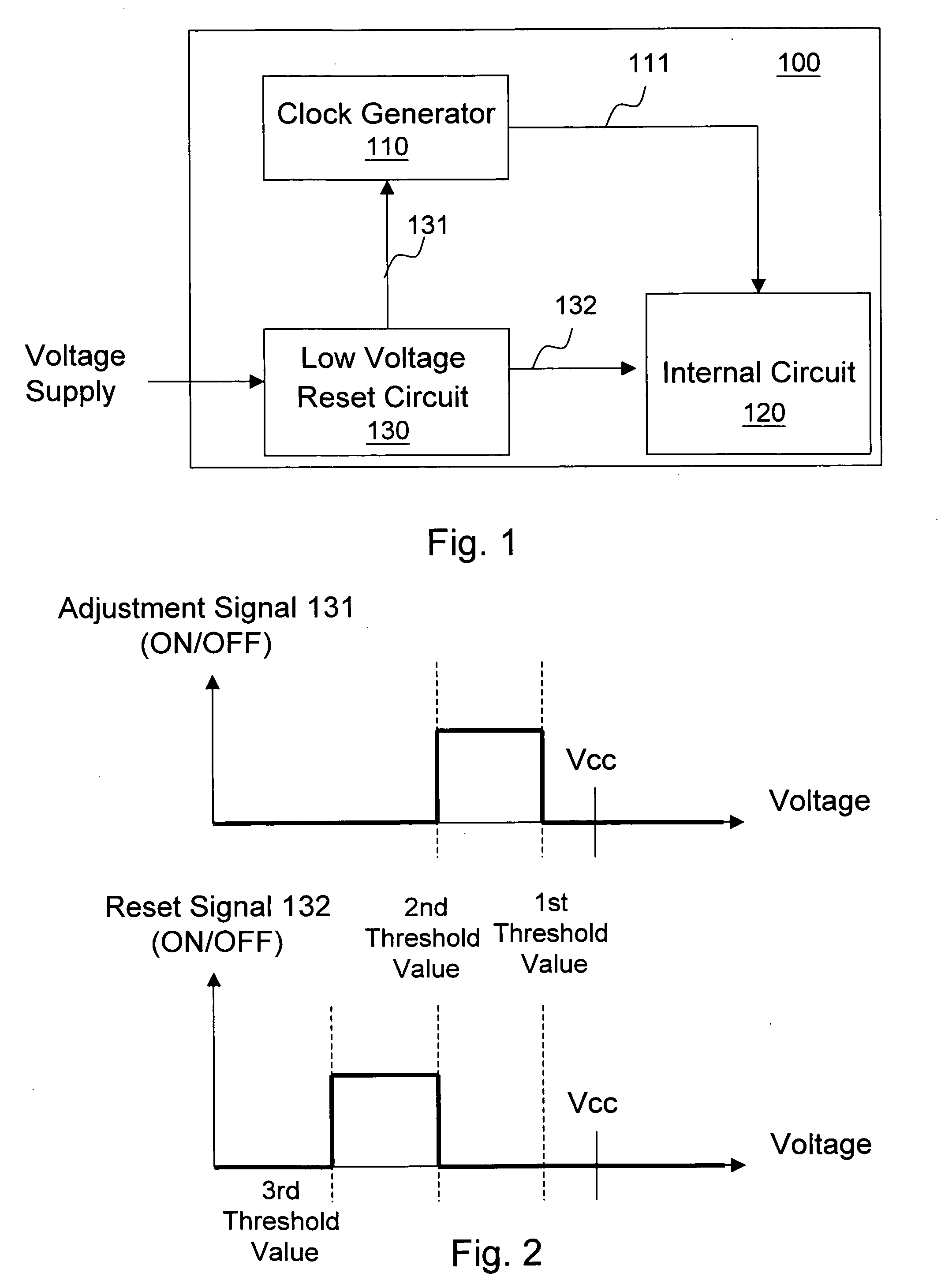
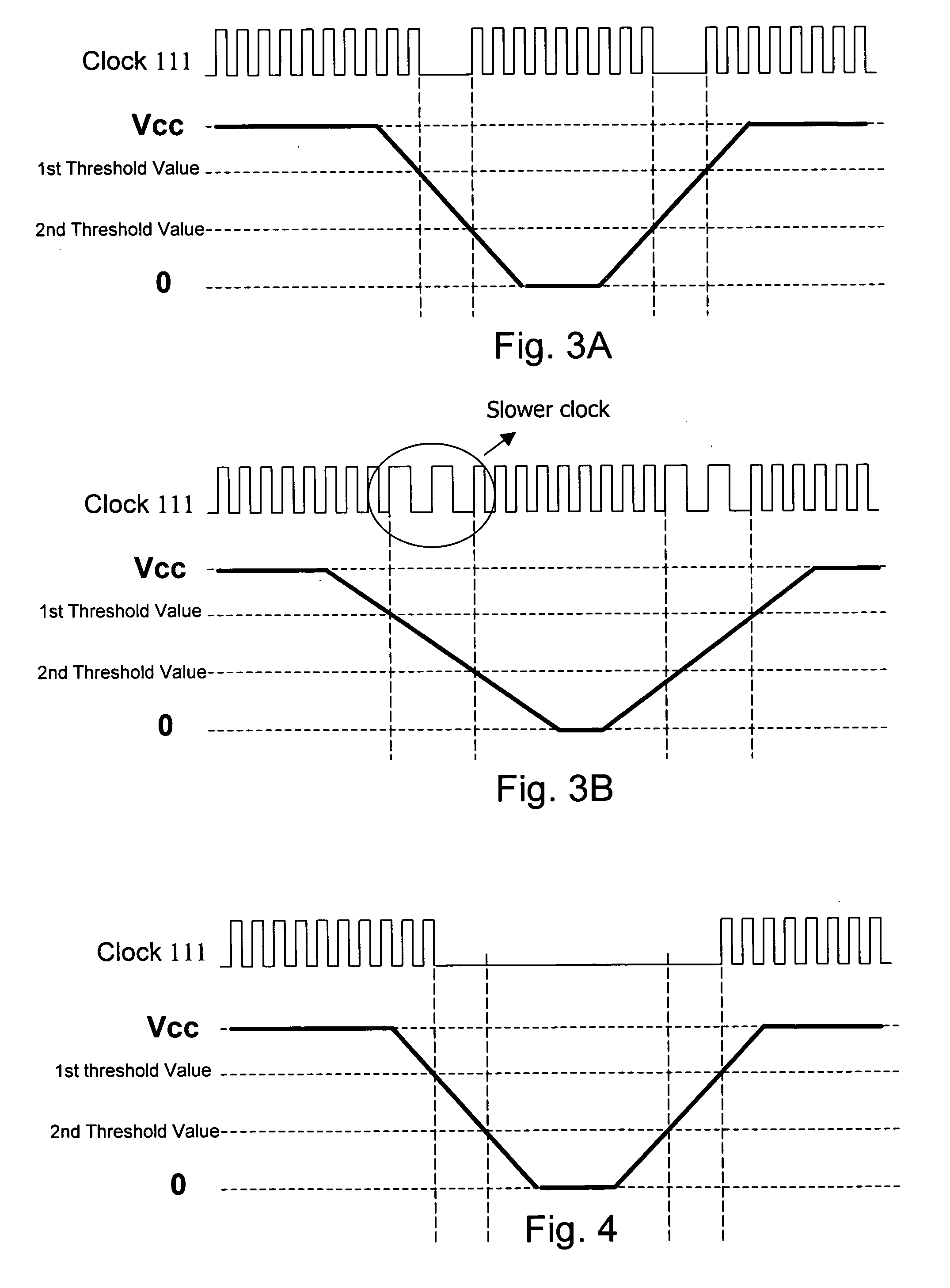
Circuit and method of adjusting system clock in low voltage detection, and low voltage reset circuit
ActiveUS20100090730A1Avoid repetitionAvoid failurePulse automatic controlData resettingLow voltageEngineering
The present invention discloses a circuit and a method of adjusting system clock in low voltage detection, and a low voltage reset circuit. The circuit of adjusting system clock in low voltage detection comprises: a clock generator for supplying a clock to at least one circuit in a system; and a low voltage reset circuit for generating an adjustment signal according to a detected voltage level, so that the clock generator adjusts or stops the clock supplied to the at least one circuit in the system.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Method and apparatus for a process, voltage, and temperature variation tolerant semiconductor device
ActiveUS8222954B1Reduce impactVoltage/temperature variation compensationElectric variable regulationElectricityReference current
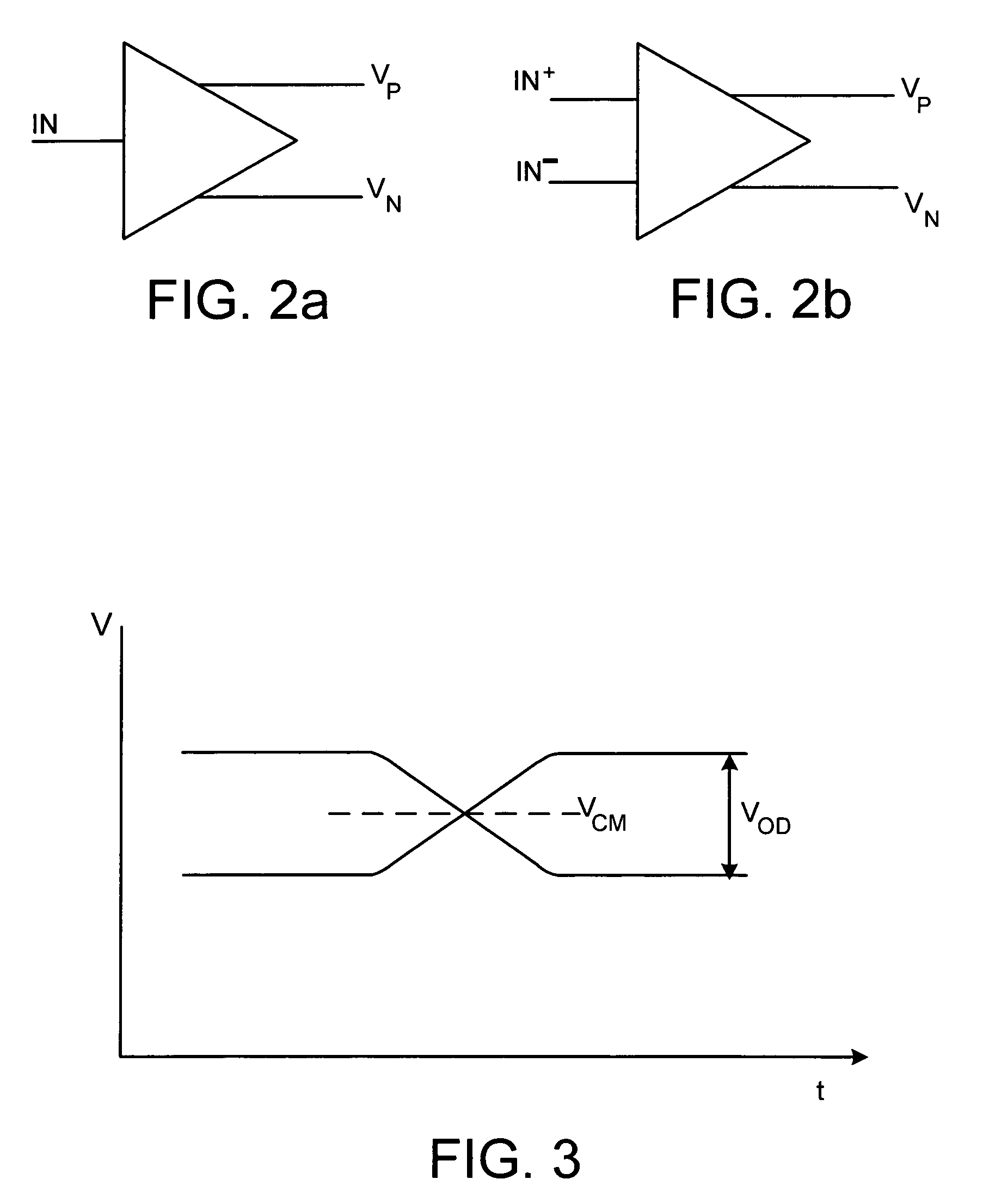
A method and apparatus to reduce the degradation in performance of semiconductor-based devices due to process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) and / or other causes of variation. Adaptive feedback mechanisms are employed to sense and correct performance degradation, while simultaneously facilitating configurability within integrated circuits (ICs) such as programmable logic devices (PLDs). A voltage-feedback mechanism is employed to detect PVT variation and mirrored current references are adaptively adjusted to track and substantially eliminate the PVT variation. More than one voltage-feedback mechanism may instead be utilized to detect PVT-based variations within a differential device, whereby a first voltage-feedback mechanism is utilized to detect common-mode voltage variation and a second voltage-feedback mechanism produces mirrored reference currents to substantially remove the common-mode voltage variation and facilitate symmetrical operation of the differential device.
Owner:XILINX INC
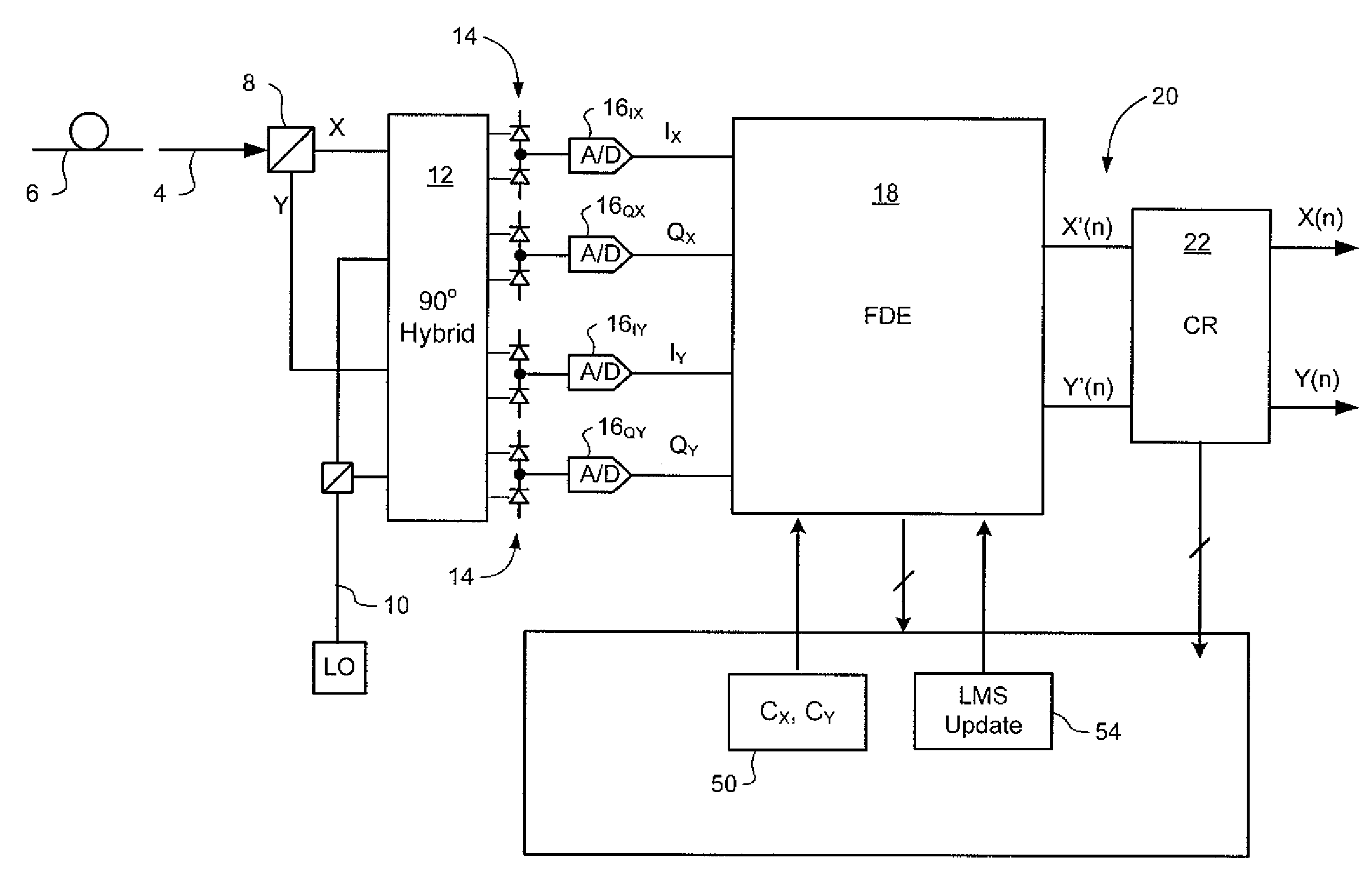
Soft thermal failure in a high capacity transmission system
InactiveUS20090256622A1Code conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresSignal processingEmbedded system
A method of managing operation of an Integrated Circuit (IC) designed to process a signal A temperature of the IC is detected, and signal processing performed by the IC adjusted based on the detected temperature.
Owner:CIENA
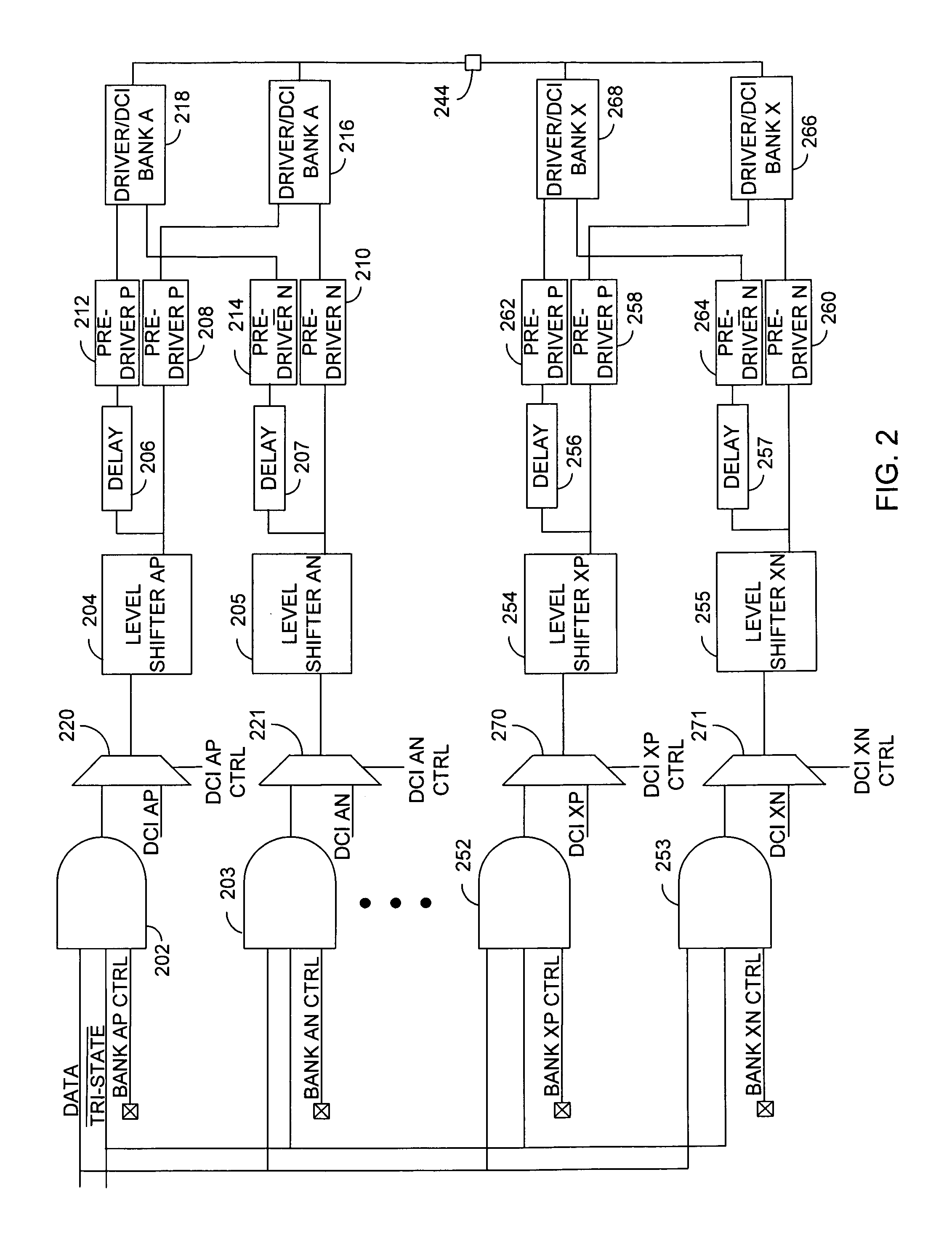
Dynamically-adjustable differential output drivers
InactiveUS7397270B1Increase productionReduce trafficLogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectronic switchingAutomatic controlProgrammable logic device
Systems and methods are provided using dynamically adjustable differential output drivers. Integrated circuits such as programmable logic devices may be provided with adjustable differential output drivers for transmitting high-speed data to other integrated circuits. The peak-to-peak output voltage and common-mode voltage of the output drivers may be adjusted. Dynamic control circuitry may be used to control the settings of current sources, programmable resistors, and voltage source circuitry in the adjustable differential output driver automatically in real time. The adjustable components in the differential output driver may be adjusted by the dynamic control circuitry based on feedback information received from the integrated circuit to which the data is transmitted.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
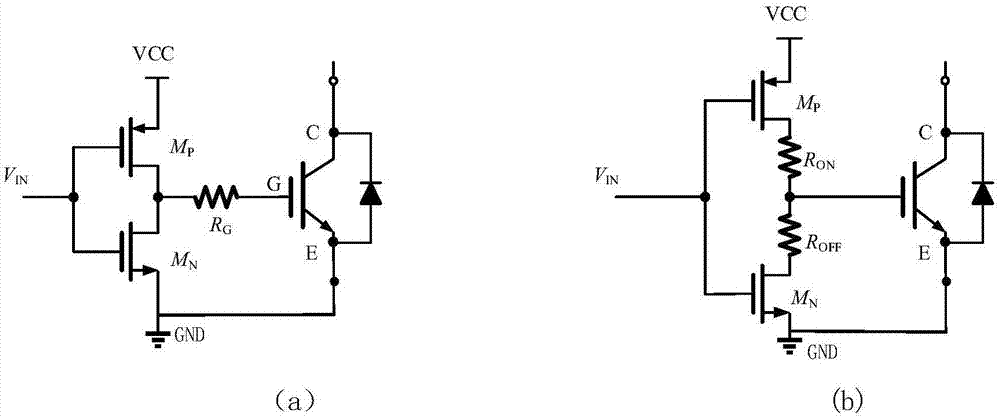
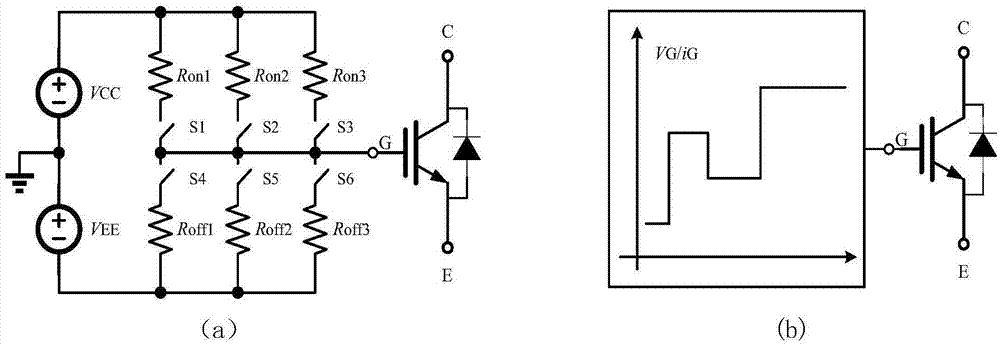
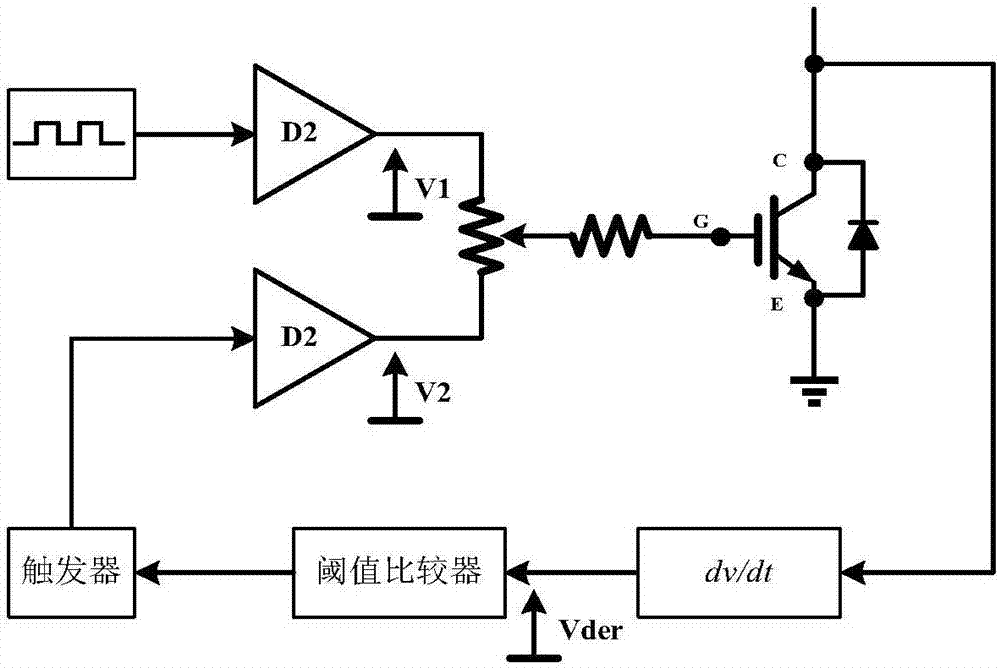
Silicon-based IGBT and silicon carbide Schottky diode hybrid grid driving system
ActiveCN107493095ASuppress current oscillationSpeed up decayElectronic switchingVoltage/temperature variation compensationEngineeringResistor
The invention provides a silicon-based IGBT and silicon carbide Schottky diode hybrid grid driving system. The grid driving system comprises a driving input stage, a logic enabling circuit, a current source circuit, an IGBT grid voltage-to-time change rate detection circuit, an IGBT collector current-to-time second-order differential change rate detection circuit, an IGBT, a Schottky diode D1 and a sampling resistor Rx. All stages of the IGBT starting process are mastered in real time by sampling and detecting the grid voltage VG of the IGBT, the change rate dVG / dt of the grid voltage and the second-order change rate d(dIc / dt) / dt of the collector current, after judgment of the logic enabling circuit and control over the current source circuit in the grid driving circuit, the size of the driving current in the IGBT starting process can be changed, and then the purposes of inhibiting current oscillation to reduce current overshoot and starting loss in the IGBT starting process are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Variable impedance sense architecture and method
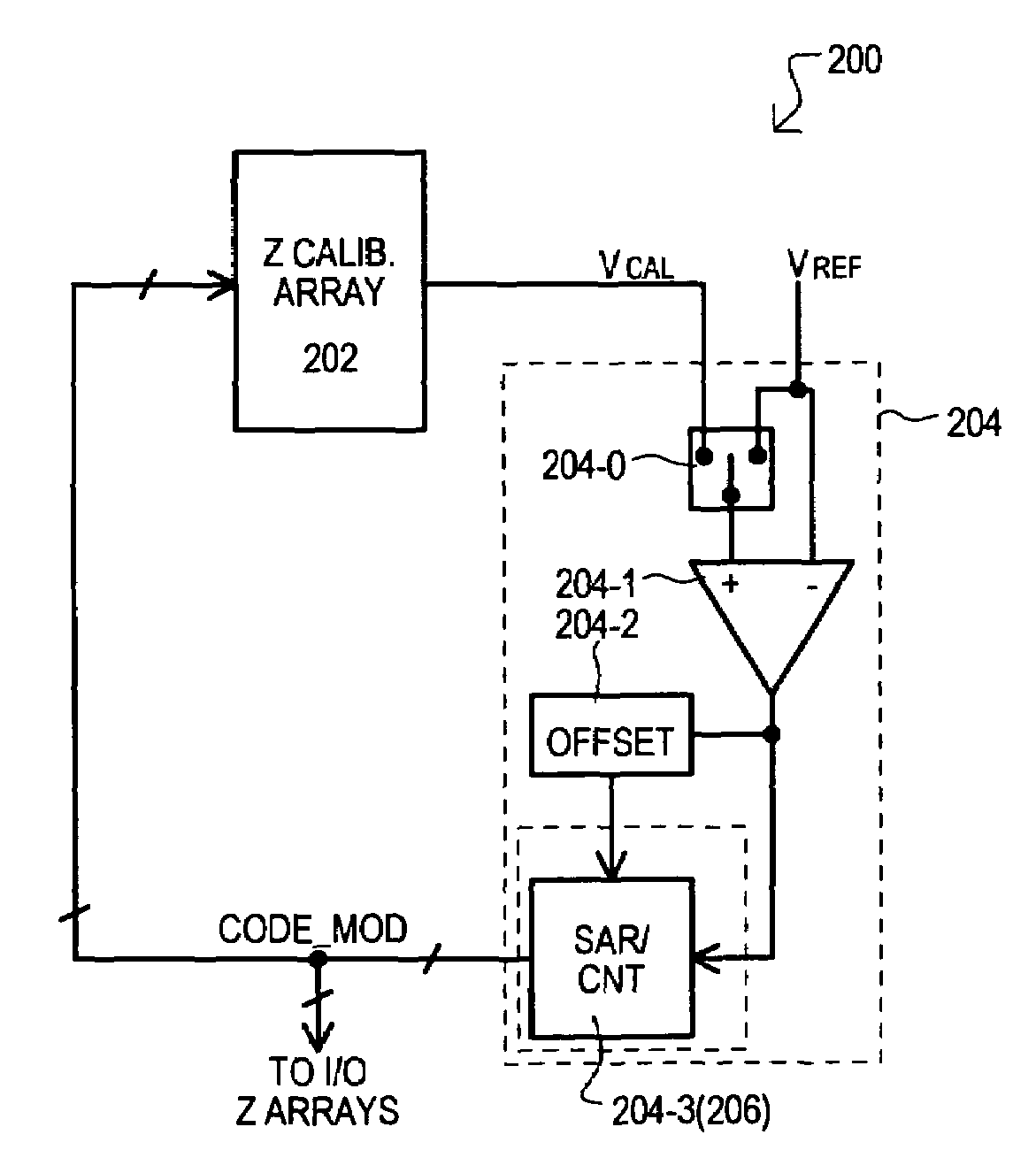
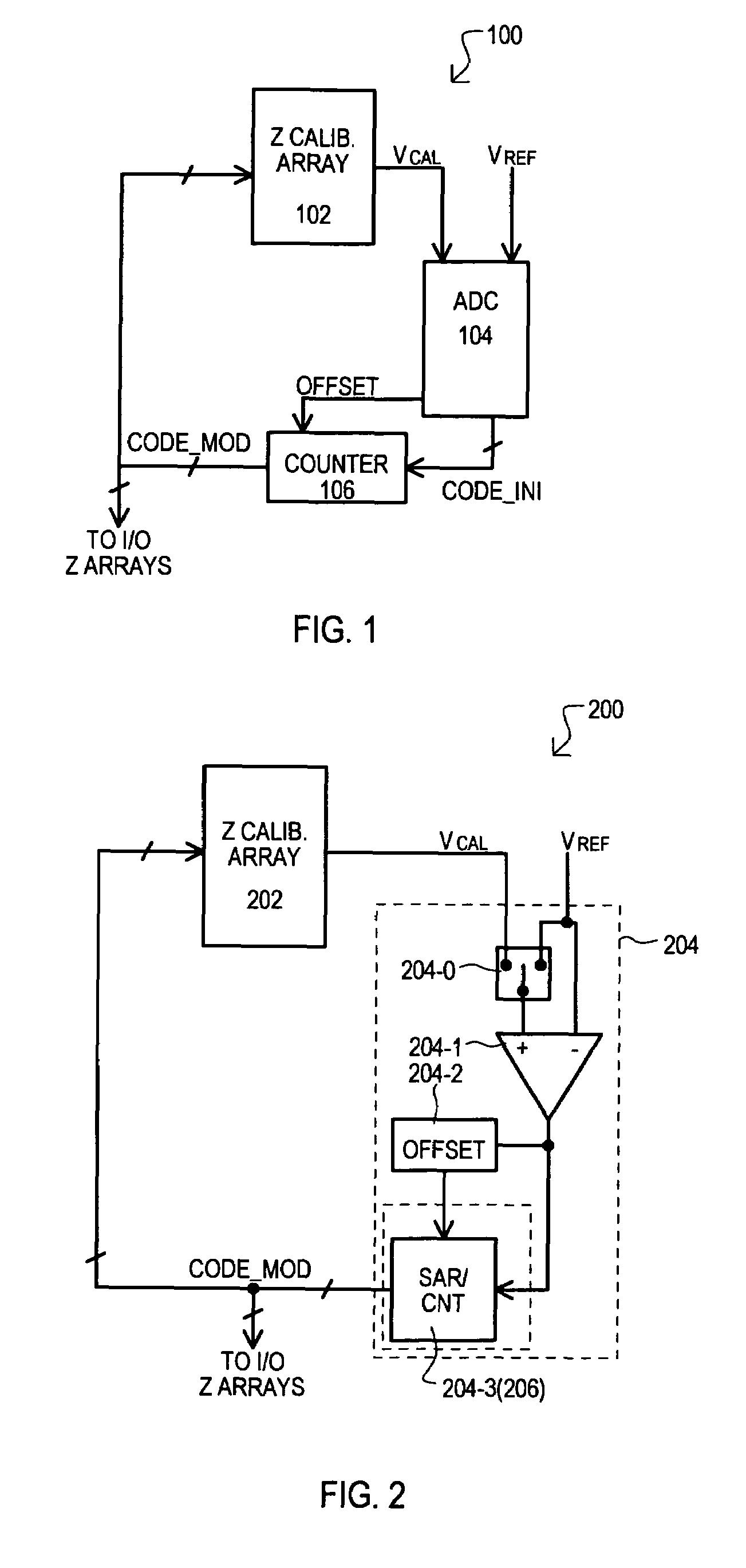
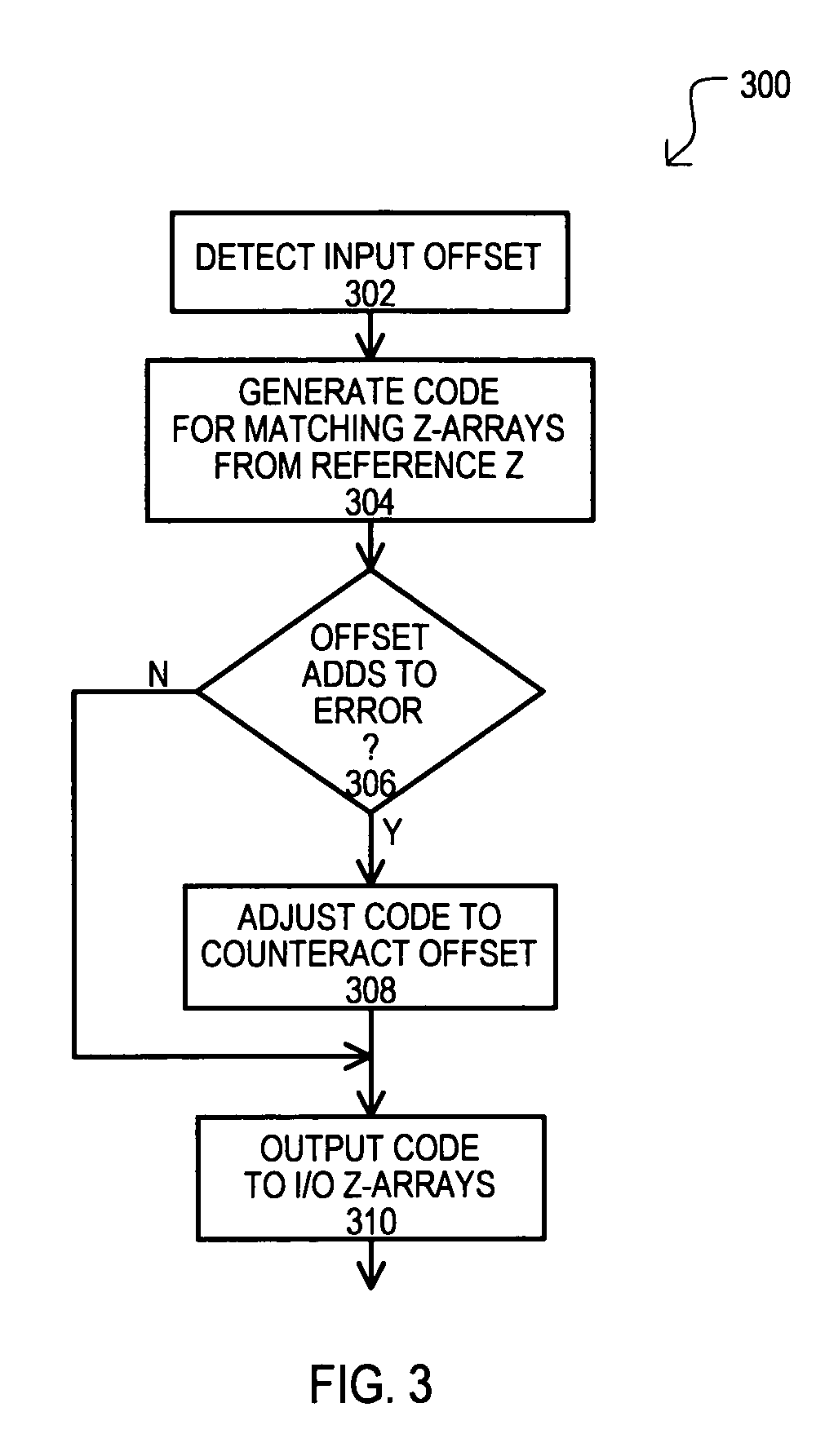
ActiveUS7479800B1Input/output impedence modificationElectronic switchingLeast significant bitImpedance matching
A variable impedance sense (VIS) circuit (600) can detect and store an input offset value inherent in a sensing loop (620 and / or 622). According to a detected input offset polarity, a resulting impedance matching binary code can be adjusted to compensate for error that can be introduced by the input offset. The binary code can also be adjusted to compensate for additional error that can be introduced by dropping a least significant bit (LSB) of the code to reduce noise effects caused by the switching of the LSB.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Semiconductor device having interconnected transistors and electronic device including semiconductor device
ActiveUS8319528B2Suppresses characteristic deteriorationReduce widthStatic indicating devicesDigital storagePower semiconductor deviceDriver circuit
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
PVT variation detection and compensation circuit
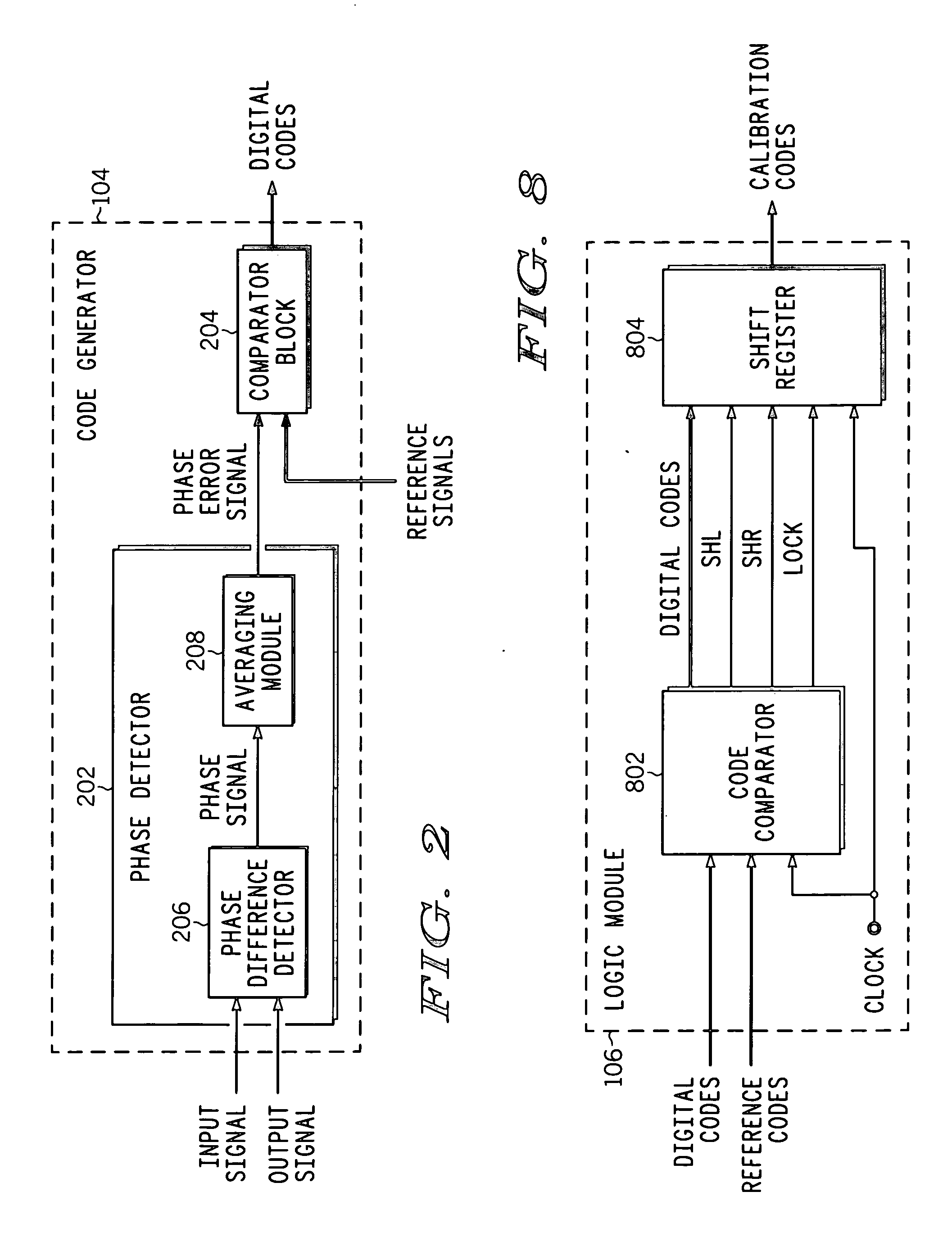
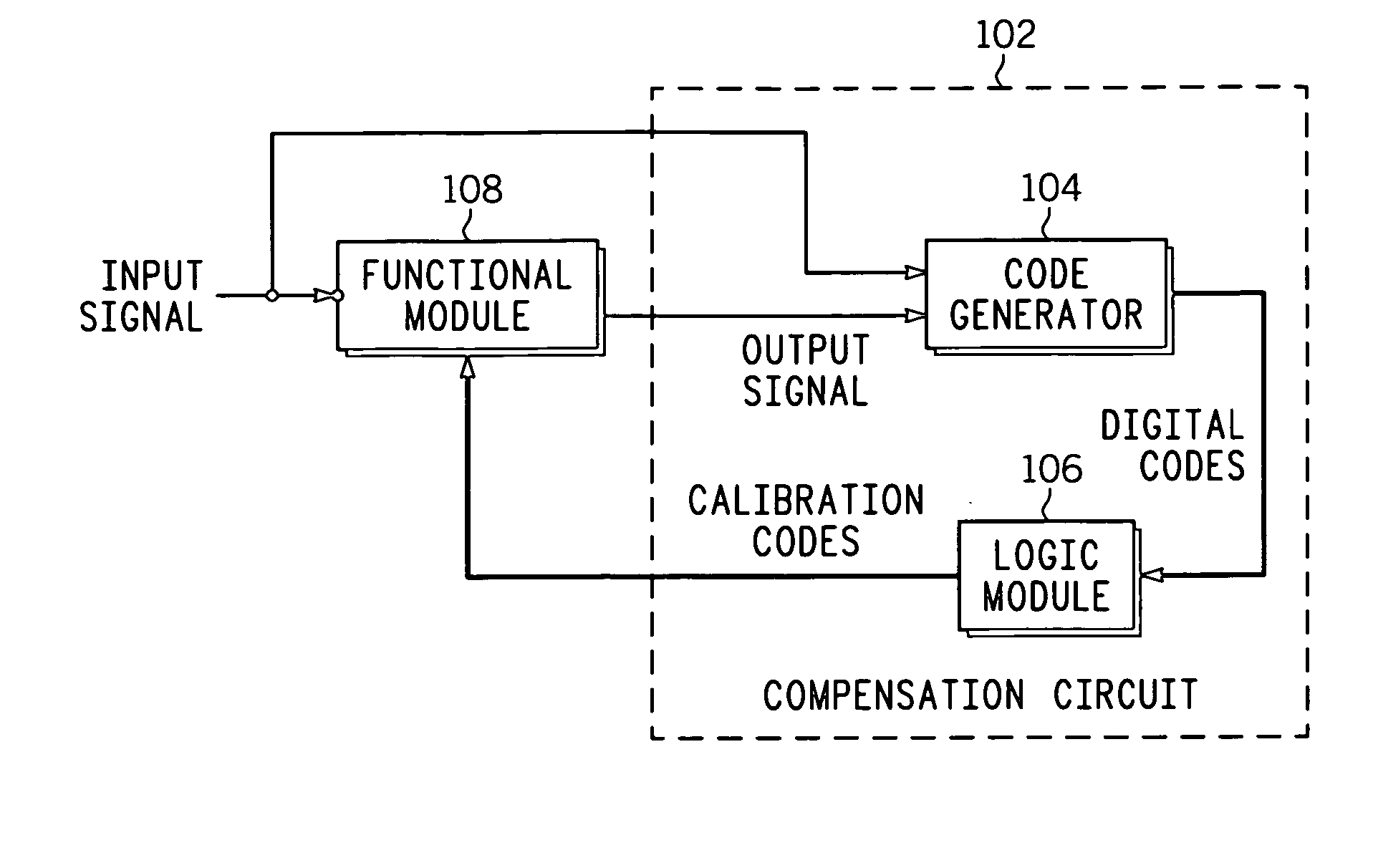
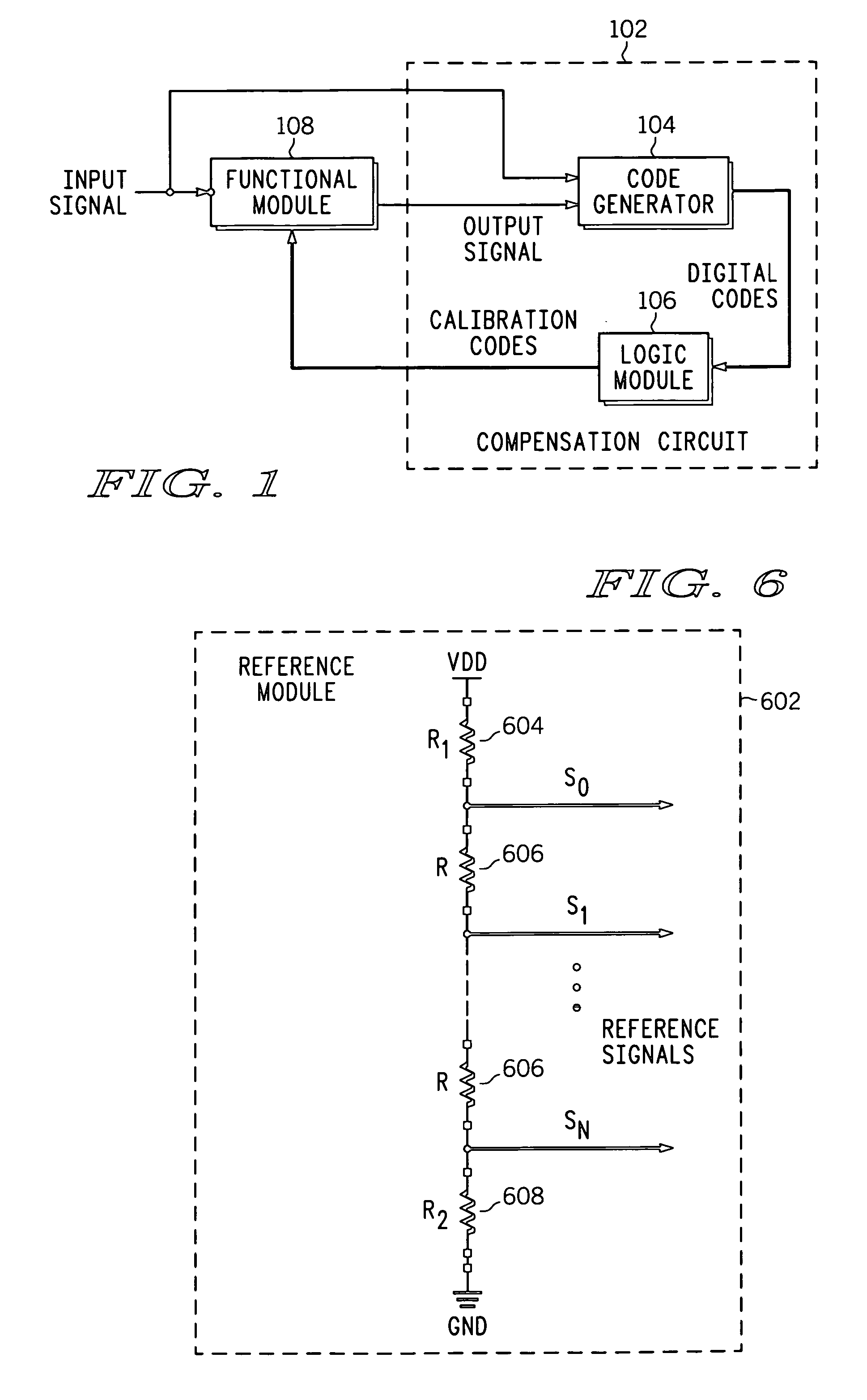
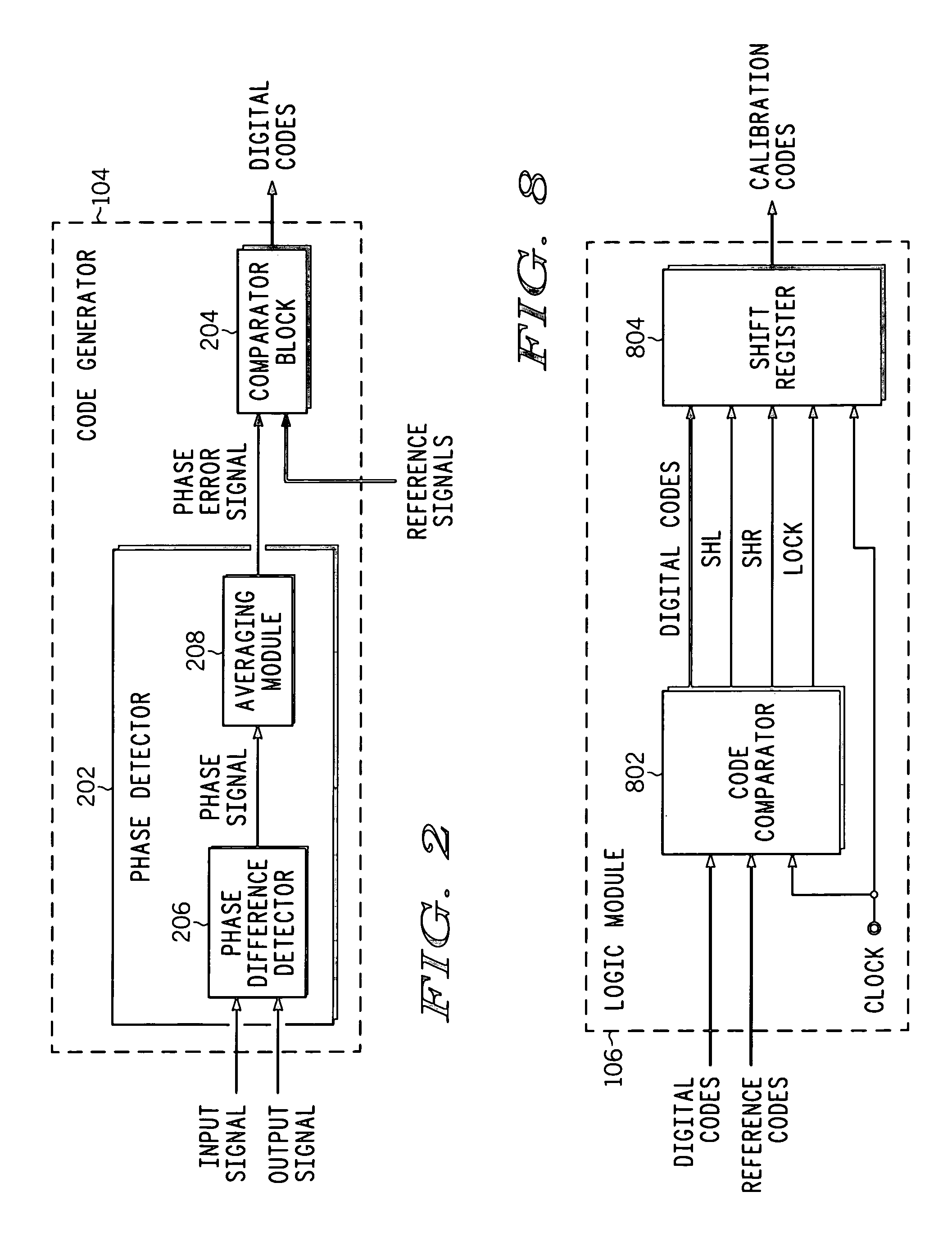
ActiveUS20070018712A1Electronic switchingPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesPhase differenceEngineering
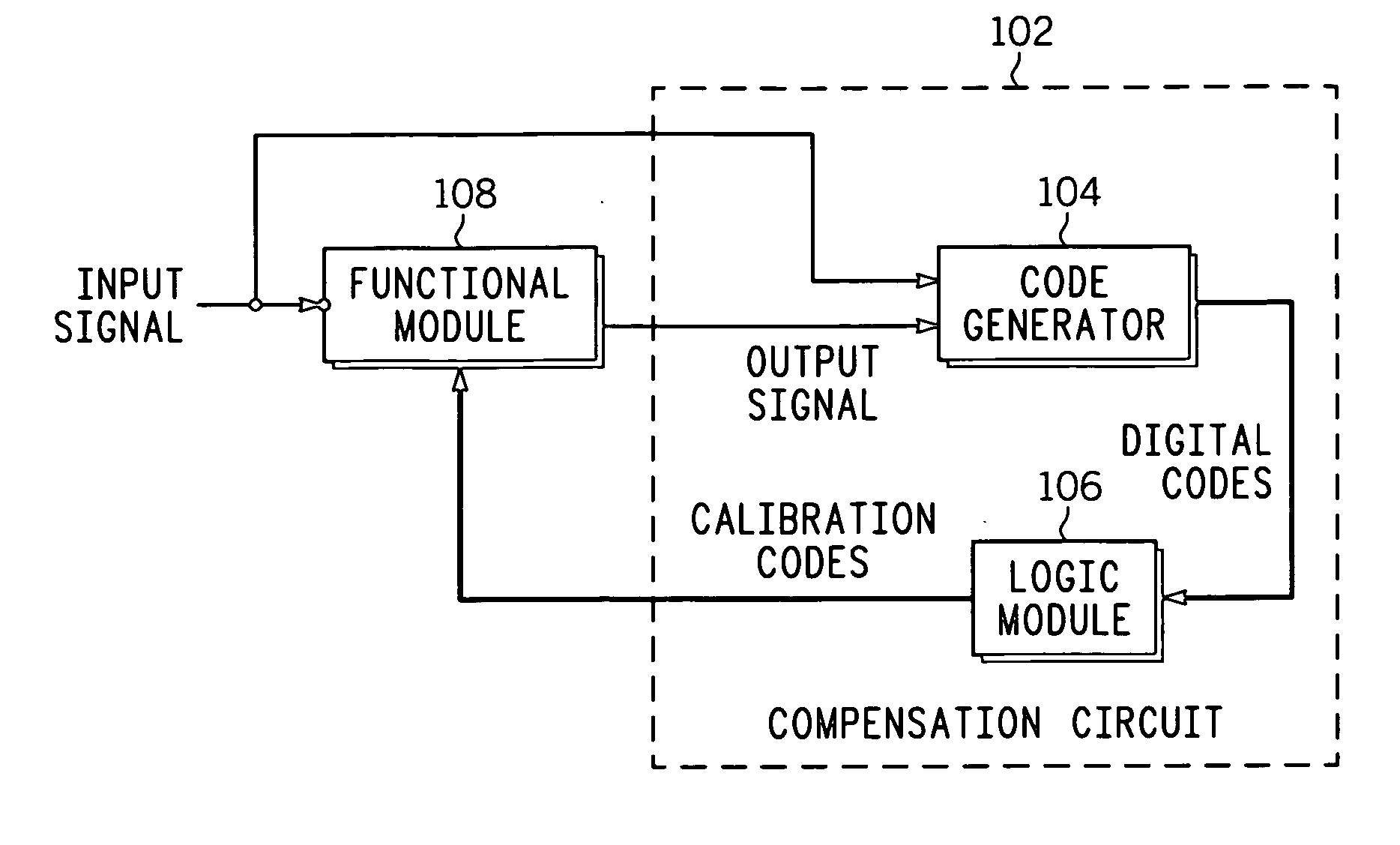
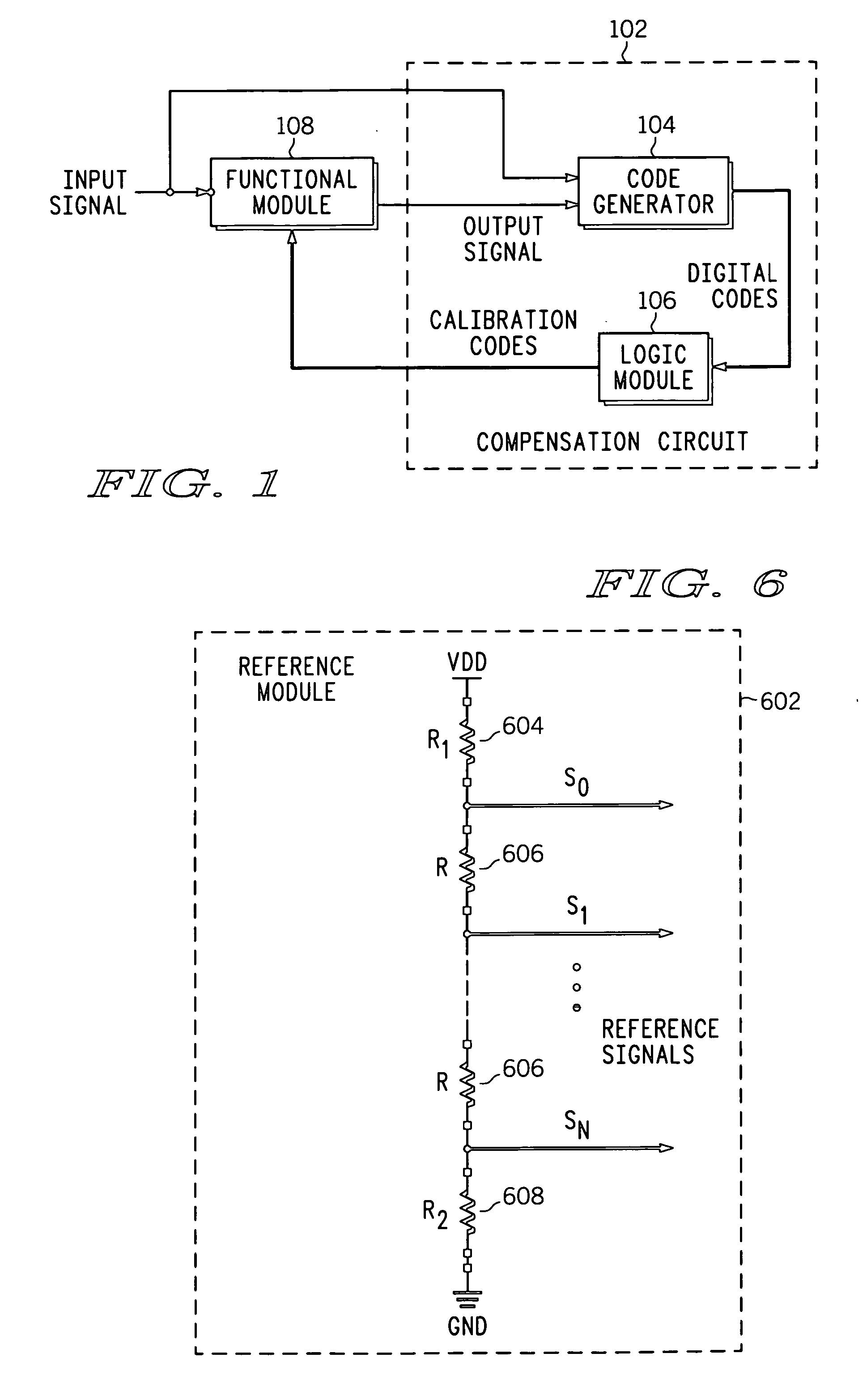
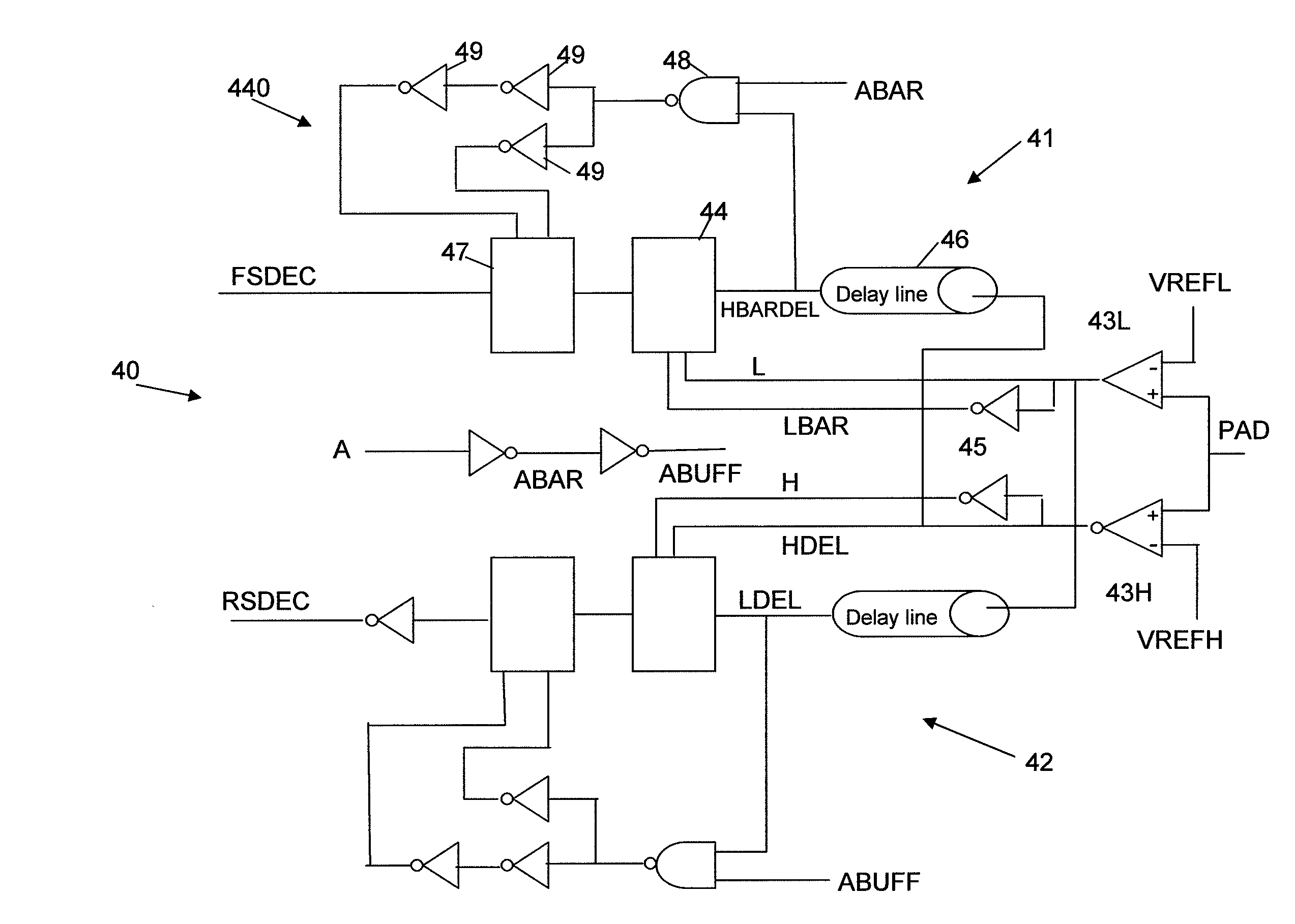
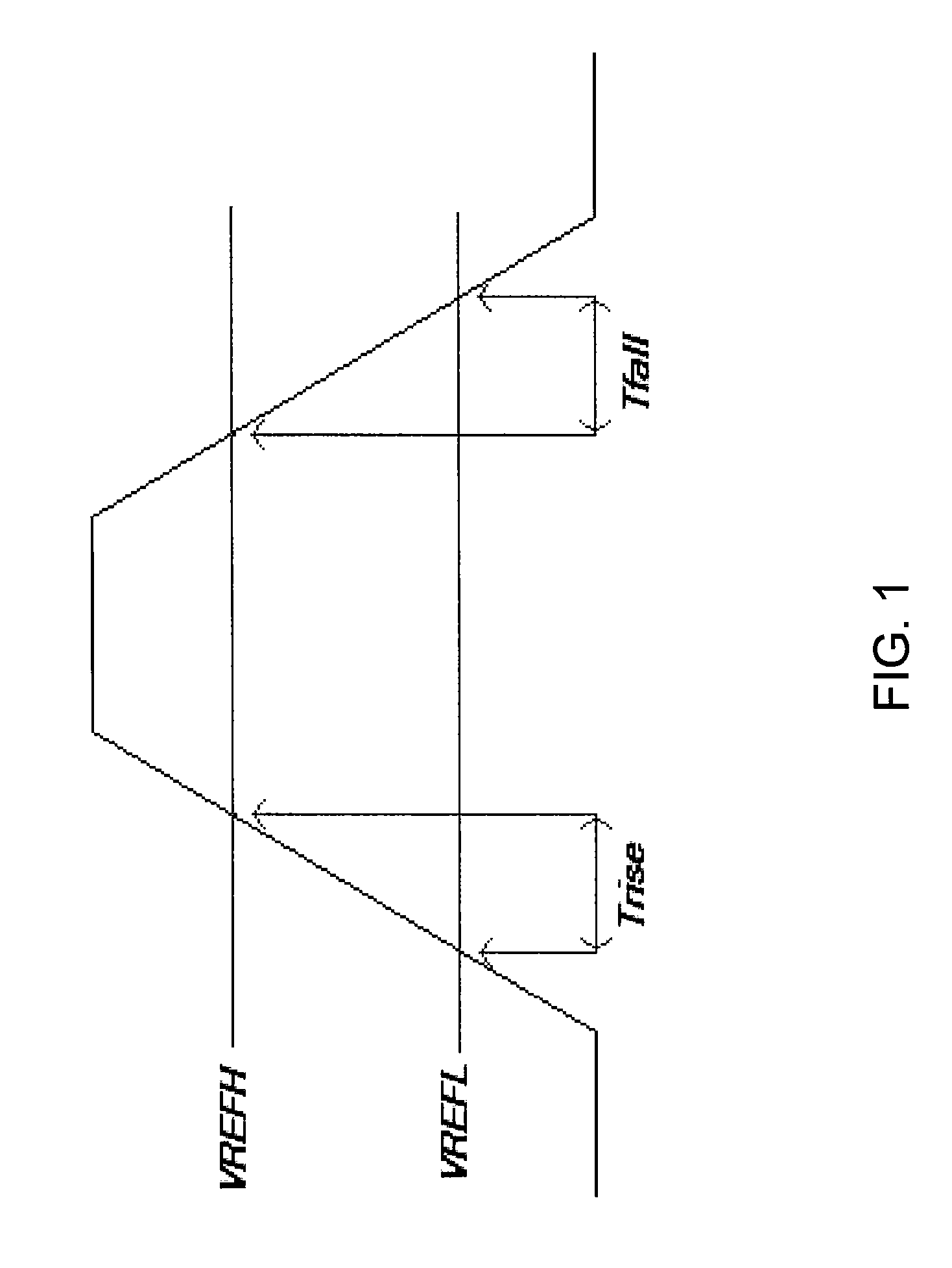
A compensation circuit and a method for compensating for process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations in an integrated circuit (IC). The IC includes several functional modules, each of which includes a set of functional units, and generates an output signal in response to an input signal. The compensation circuit includes a code generator and a logic module. The code generator generates a digital code for each functional unit. The digital codes are based on phase differences between the input signal and the output signal. The logic module generates calibration codes based on the digital codes. The calibration codes compensate for the PVT variations in the corresponding functional units.
Owner:NXP USA INC
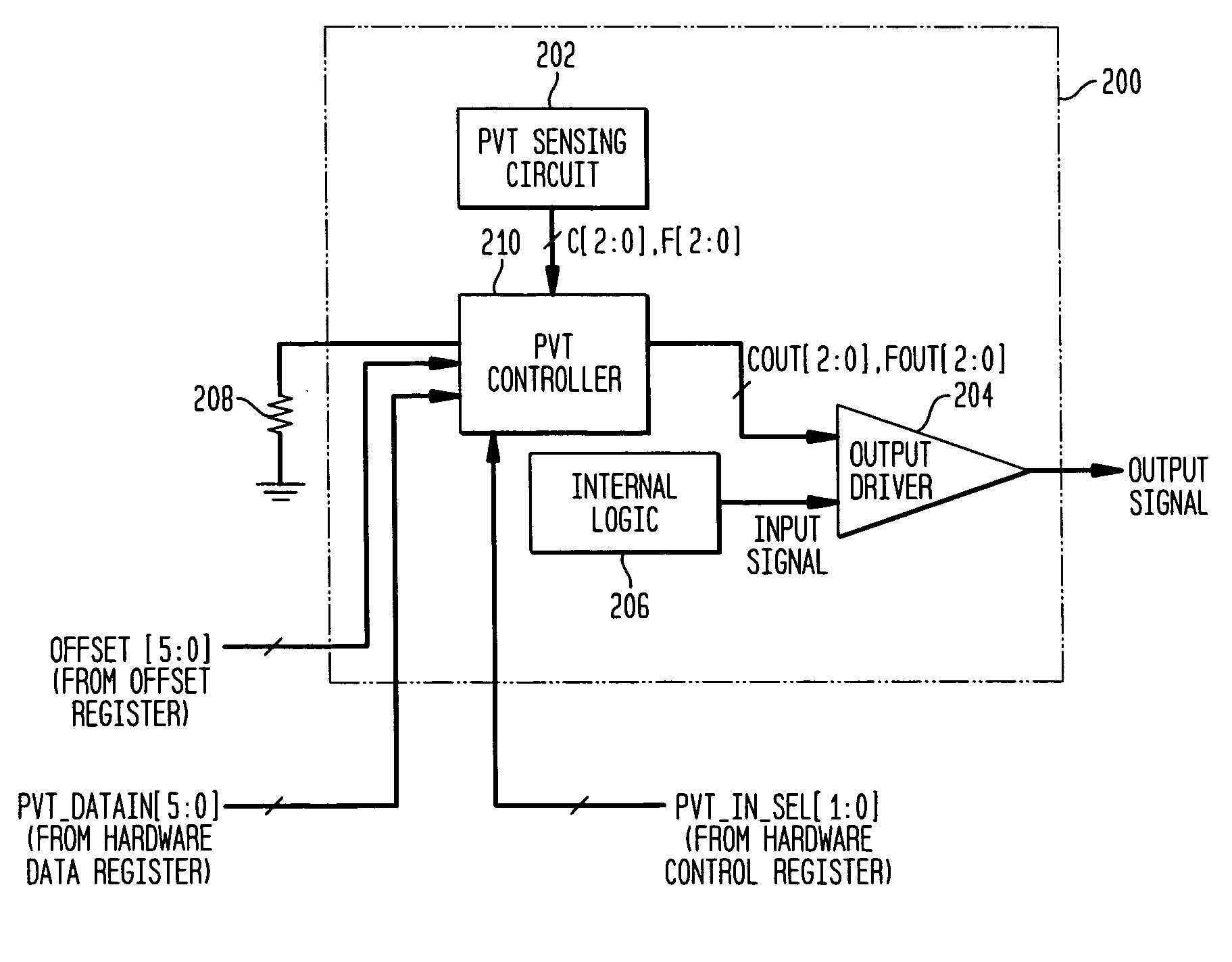
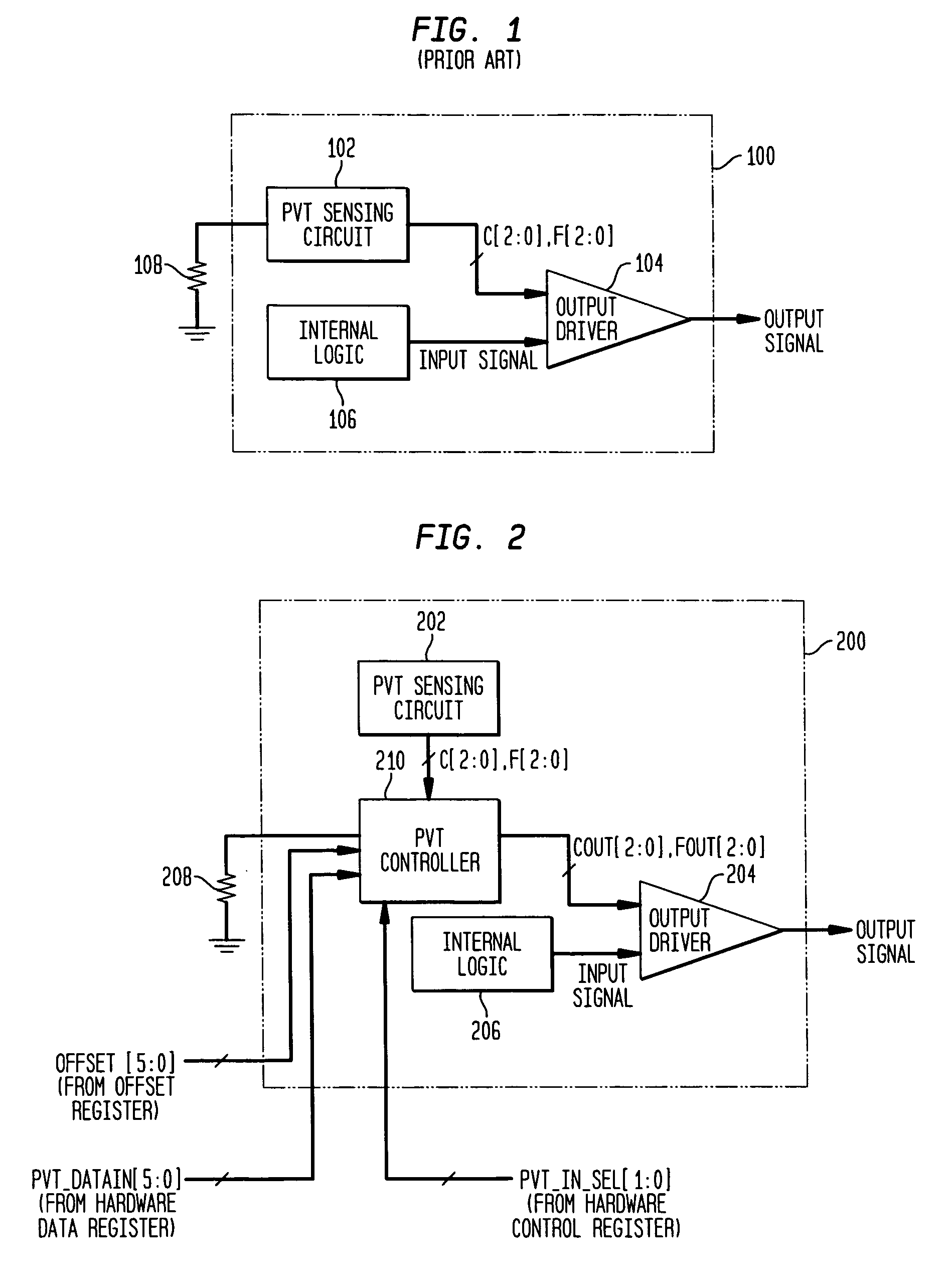
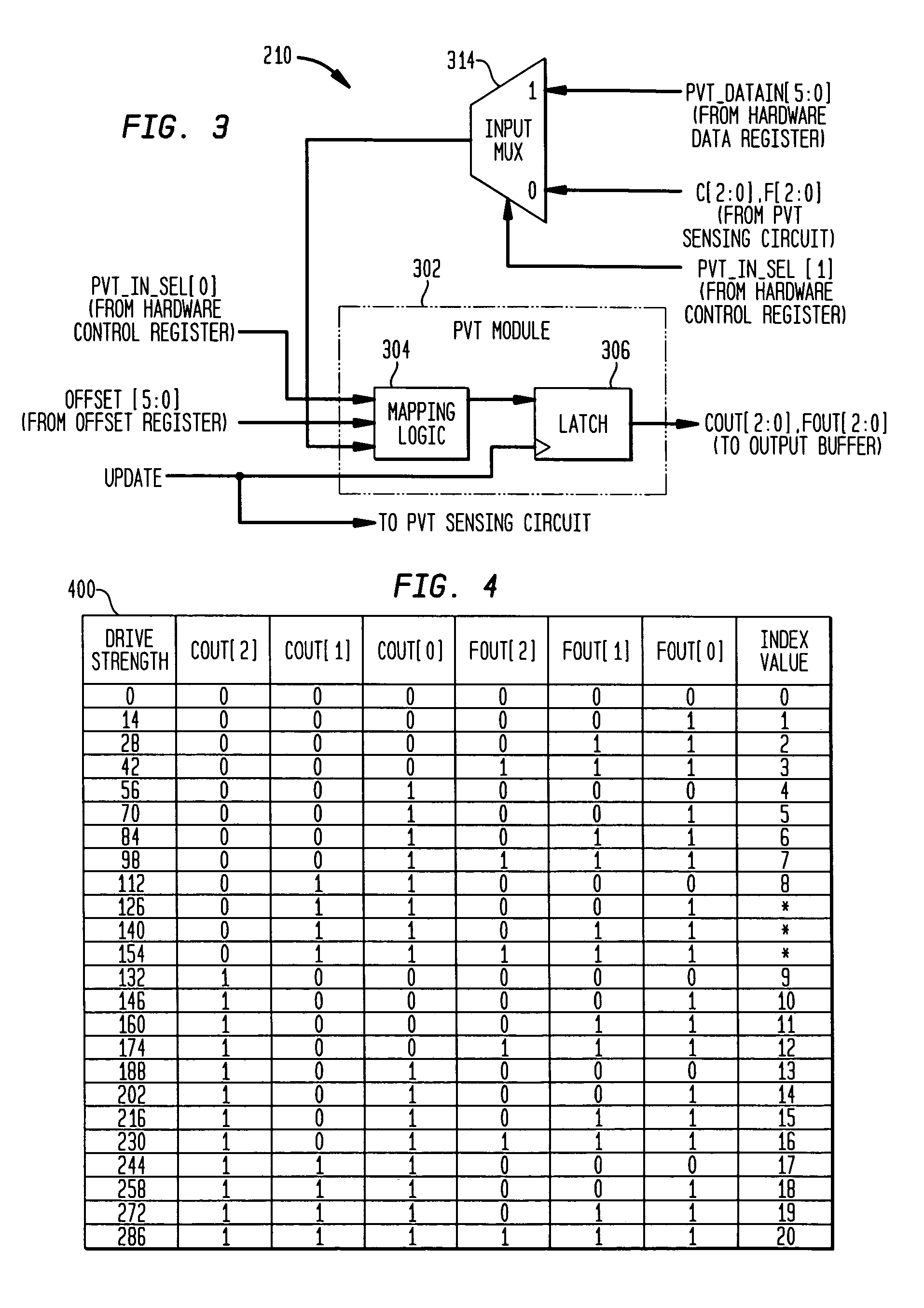
Adjusting settings of an I/O circuit for process, voltage, and/or temperature variations
A control circuit and method for controlling the electrical characteristics of an input / output (I / O) circuit such as an output driver to account for variations in fabrication process, supply voltage, and / or temperature (PVT) conditions includes a PVT controller having appropriate control logic to permit PVT compensation to be observed, tested, and selectively adjusted. The PVT controller permits selection between PVT sensing circuit-provided control signals and control signals stored in a hardware register for controlling drive strength. The PVT controller further provides the capability to offset the selected drive strength by a fixed amount and select whether or not the offset is applied and permits full testability and observability of the selected control signal, an offset value applied thereto, and the resulting output signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Apparatus and method for controlling power gating in an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20120126879A1Easy to convergeAvoid excessive wearPower consumption reductionElectronic switchingControl powerVoltage regulation
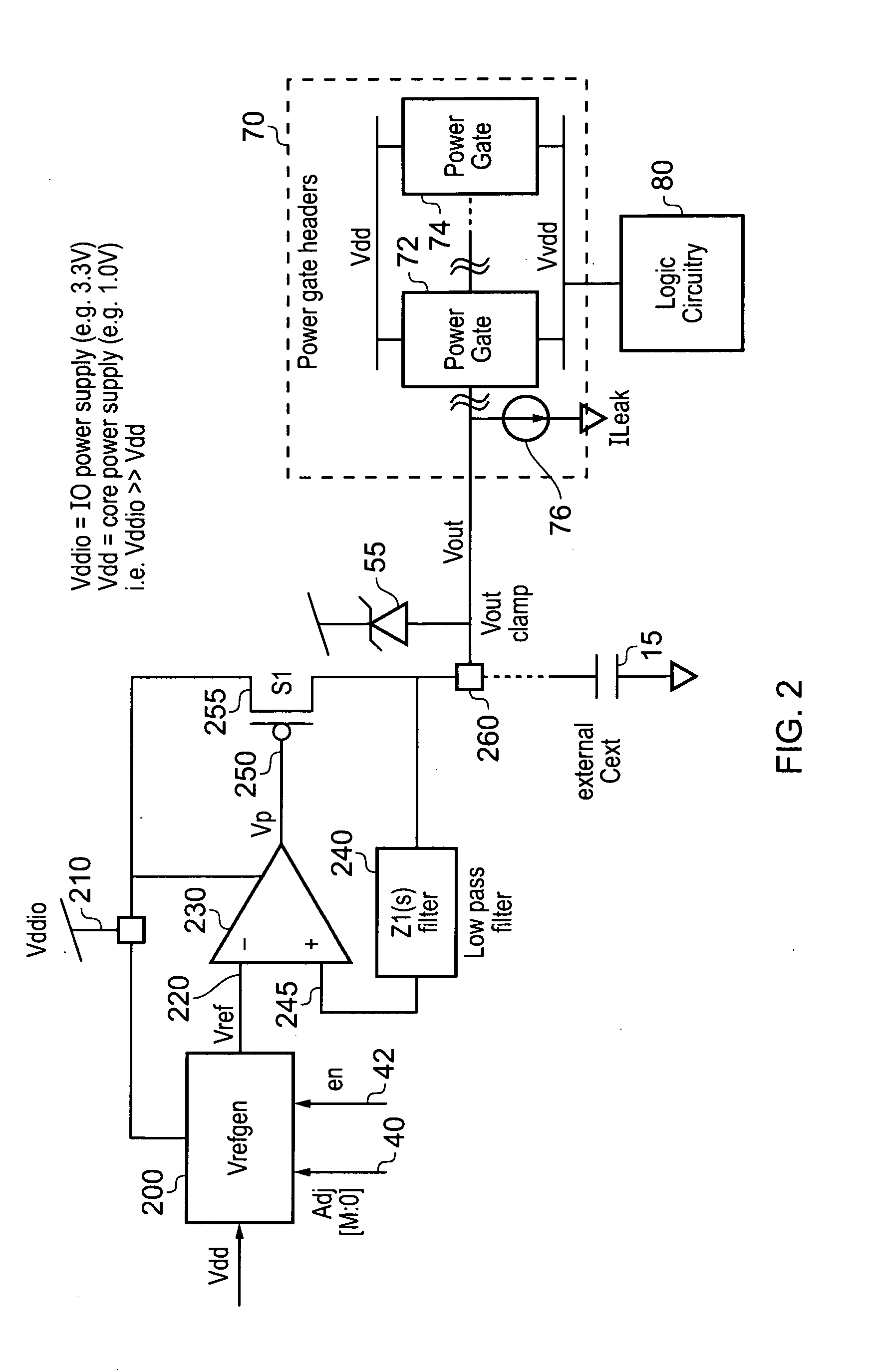
A technique for controlling power gating in an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises a block of components to be power gated, and power gating circuitry for selectively isolating the block of components from the source voltage supply in order to achieve such power gating. Voltage regulator circuitry is used to provide a control voltage to the power gating circuitry when performing such power gating operations, the control voltage being settable to any of a plurality of predetermined voltage levels. An adaptive controller receives operating parameter data from either or both of the block of components and the power gating circuitry, that operating parameter data being indicative of leakage current. The adaptive controller then issues a feedback control signal to the voltage regulator circuitry whose value is dependent on the received operating parameter data. The voltage regulator circuitry is then responsive to the feedback control signal to change the control voltage between the plurality of predetermined voltage levels, until the operating parameter data indicates that a desired leakage current has been obtained within the power gating circuitry. Such an approach enables a balance to be achieved between reducing leakage current and reducing wear out of the power gating circuitry.
Owner:ARM LTD
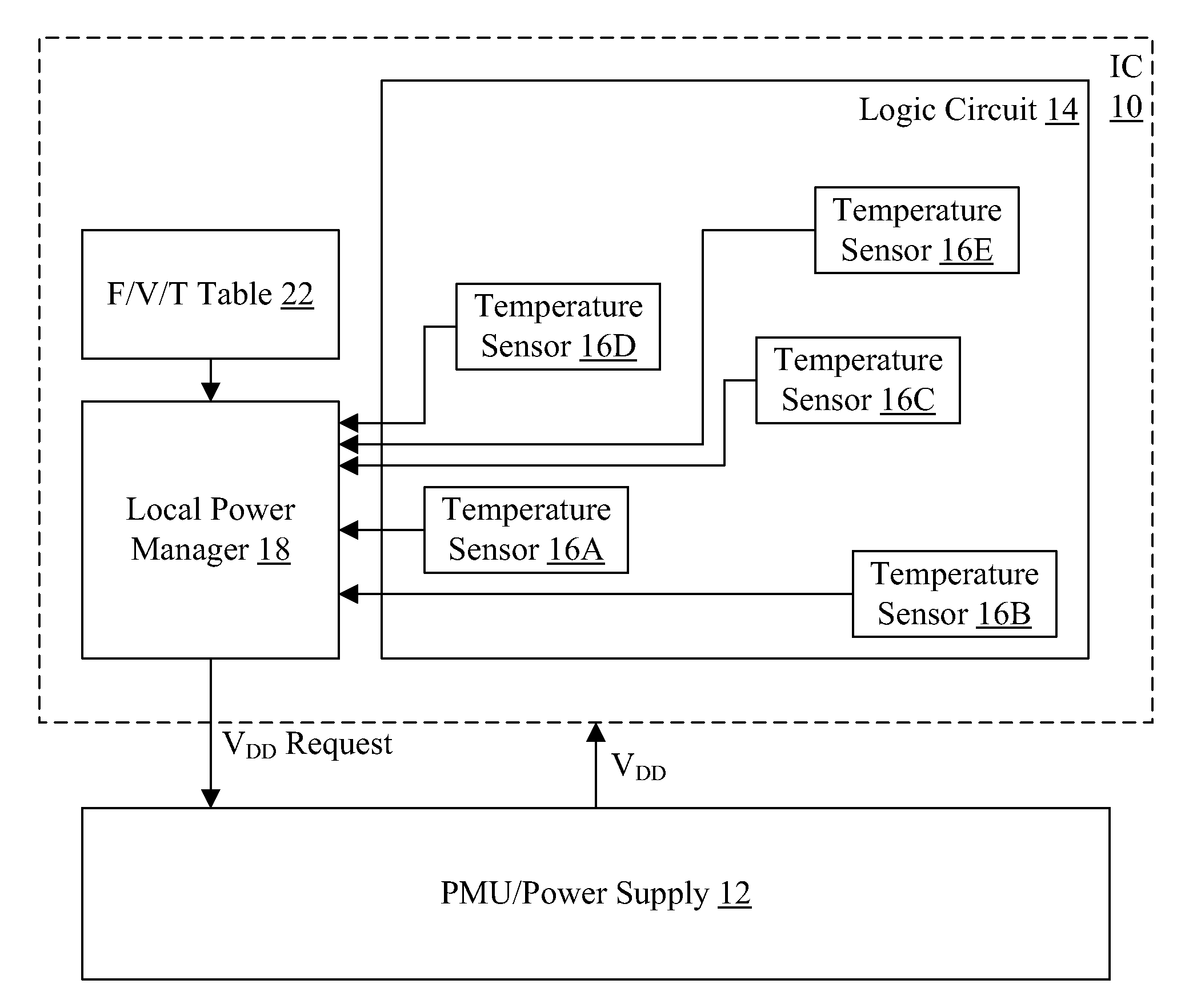
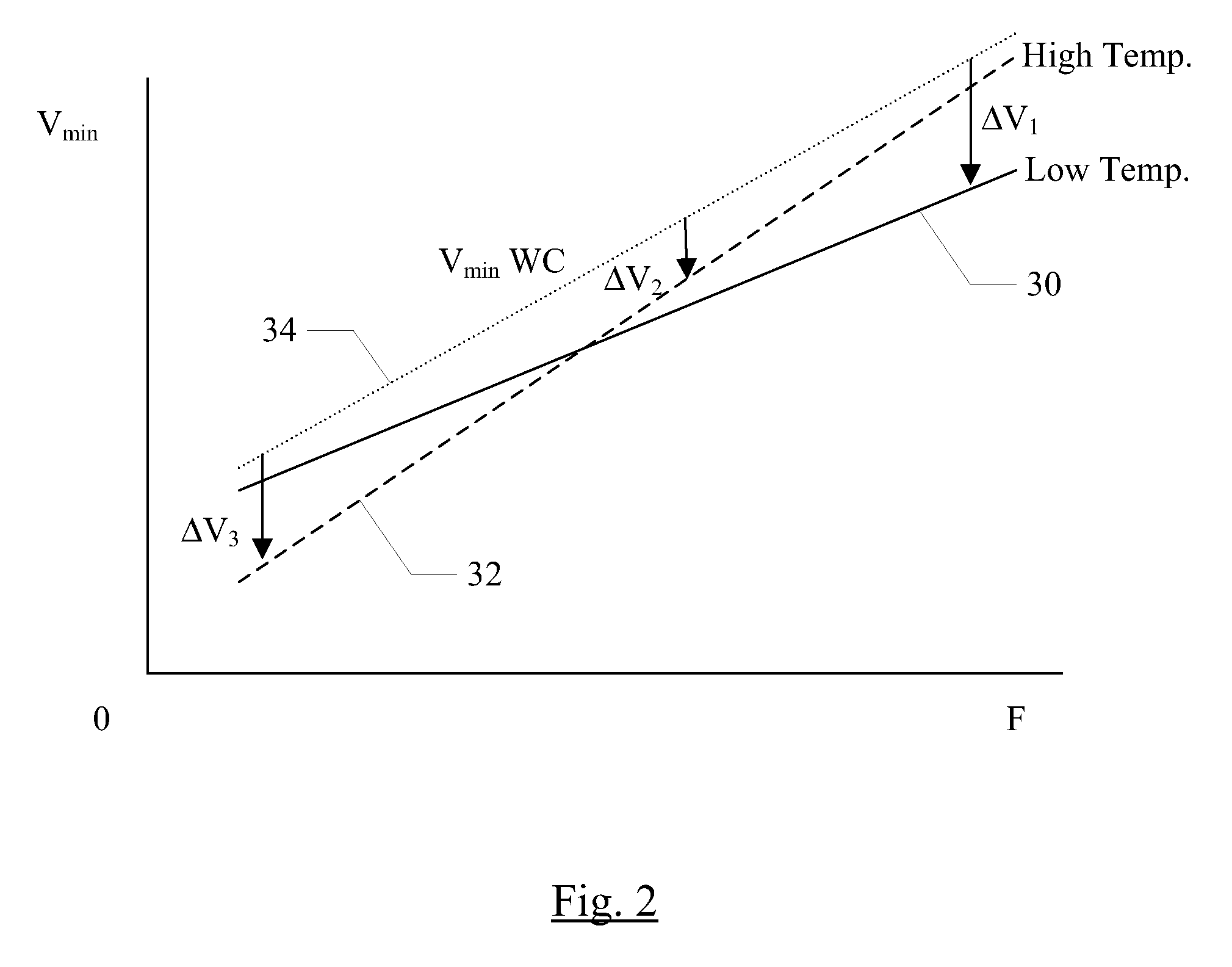
Adaptive voltage adjustment based on temperature value
ActiveUS8766704B2Simple designThermometer detailsEnergy efficient ICTThermal thresholdLogic circuitry
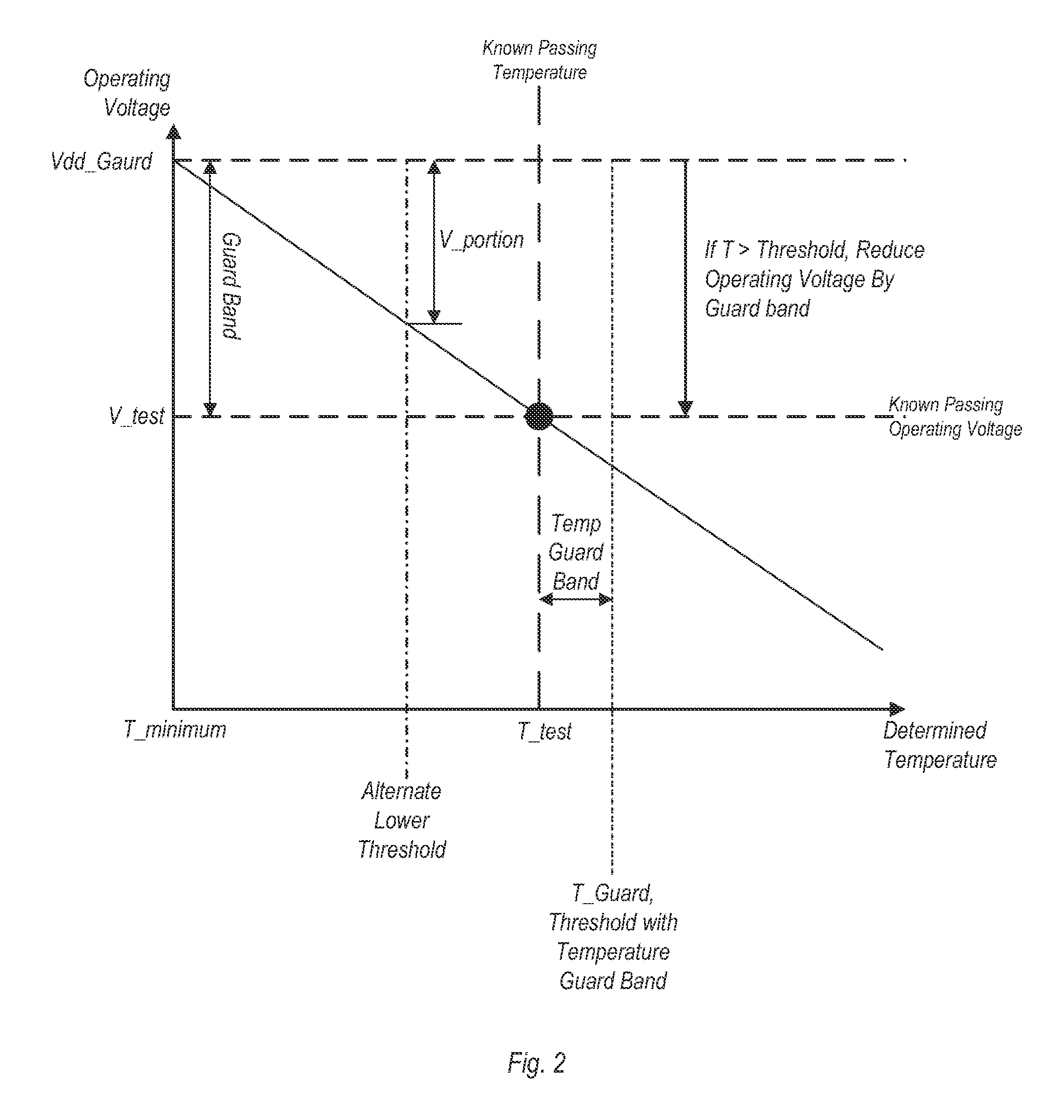
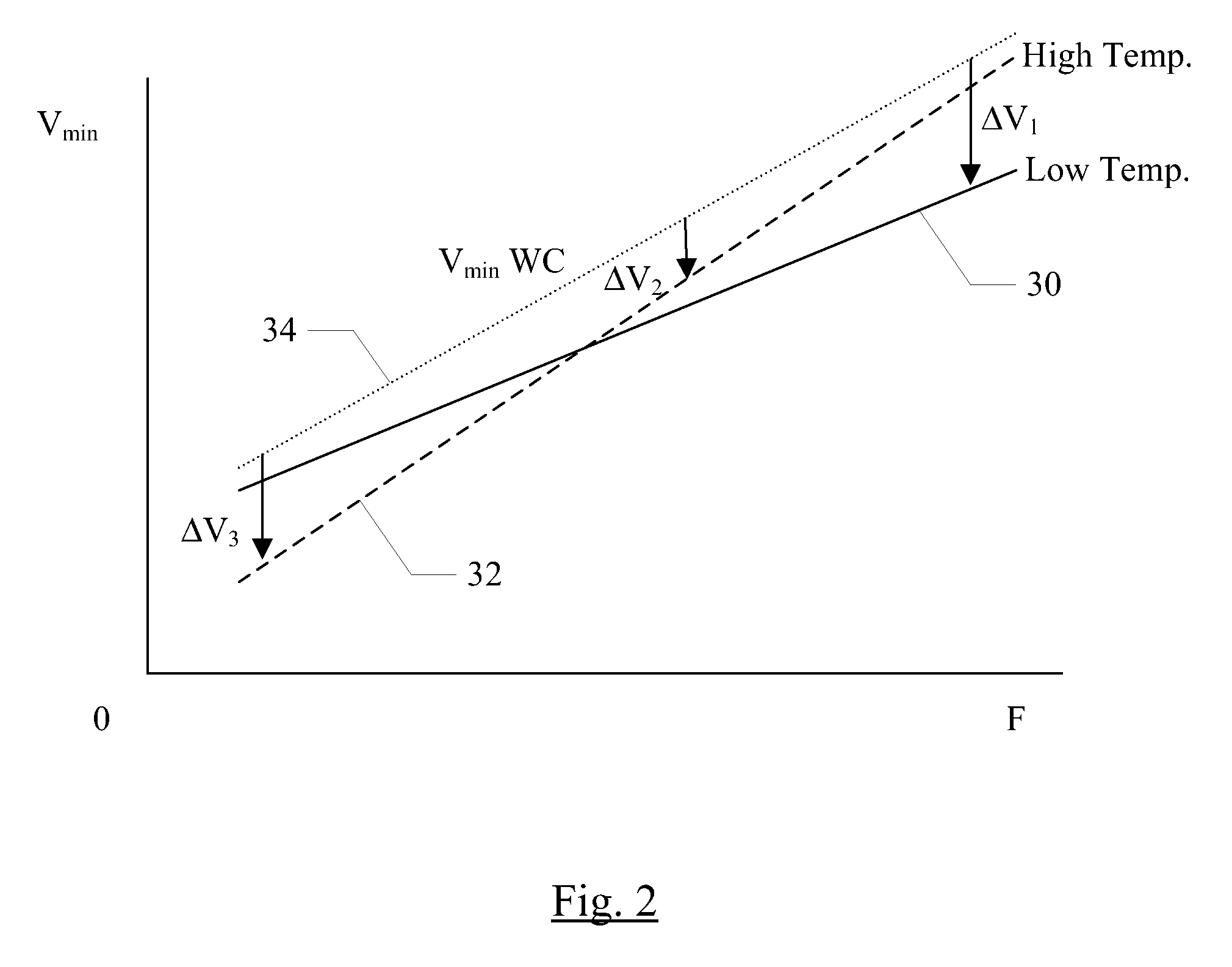
Various embodiments of a method and apparatus for performing adaptive voltage adjustment based on temperature value are disclosed. In one embodiment, and integrated circuit (IC) includes logic circuitry having at least one temperature sensor therein. The IC also includes a power management circuit coupled to receive temperature readings from the temperature sensor. The power management circuit is configured to determine a temperature of the IC based on a temperature reading received from the temperature sensor. The power management circuit may compare the determined temperature to a temperature threshold. If the temperature exceeds a temperature threshold value, the power management circuit may cause the operating voltage to be reduced by an amount equivalent to a voltage guard band.
Owner:APPLE INC
Time encoded circuits and methods and a time encoder based beamformer for use in receiving and transmitting applications
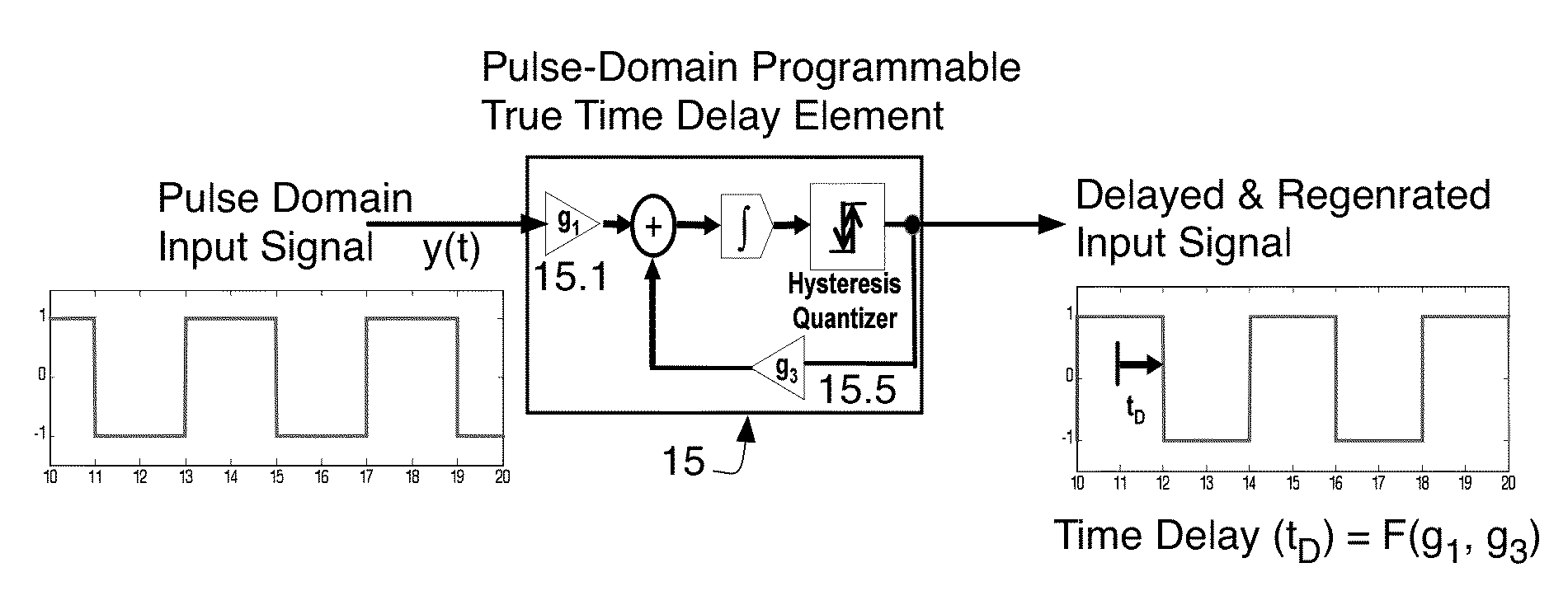
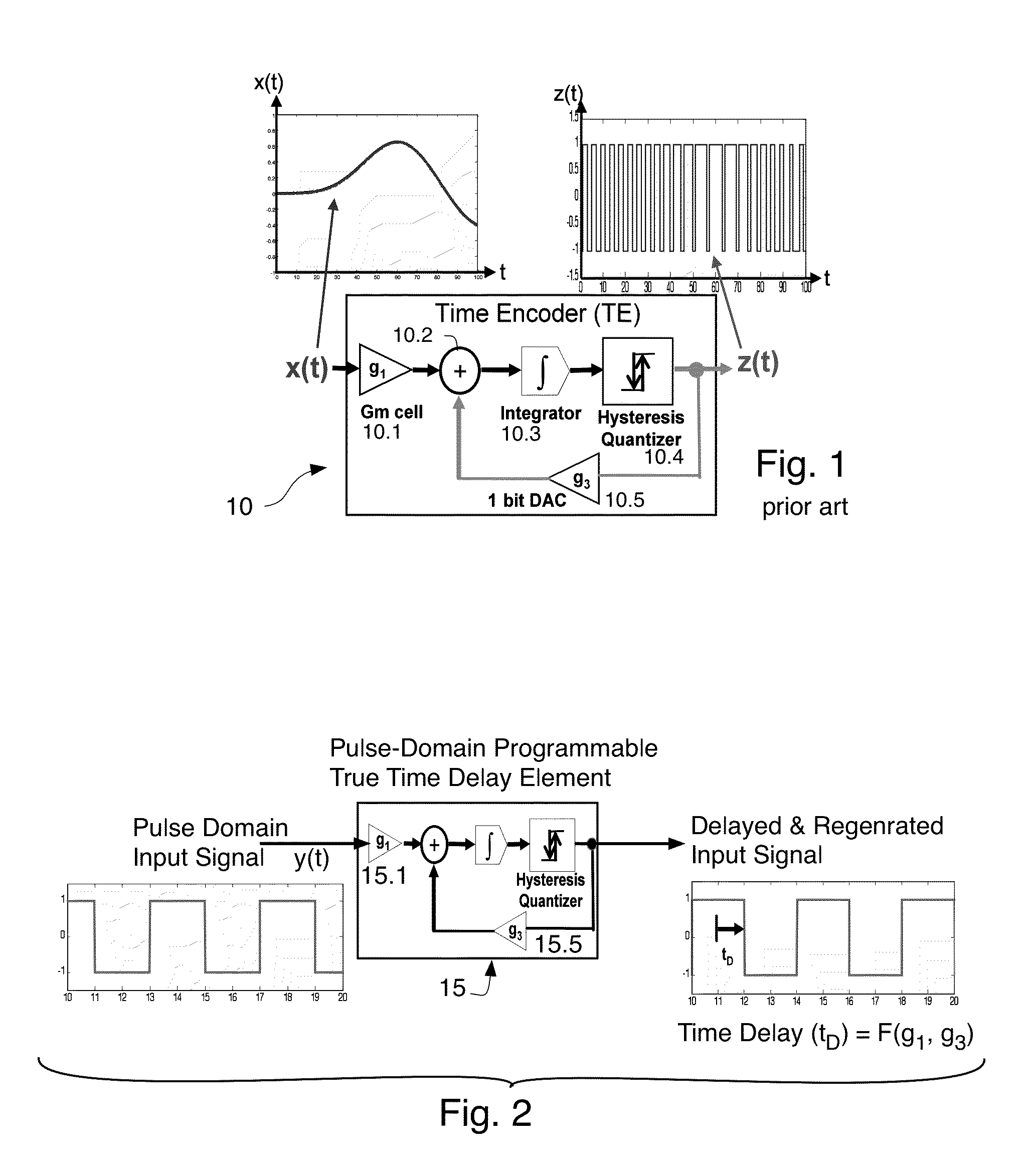
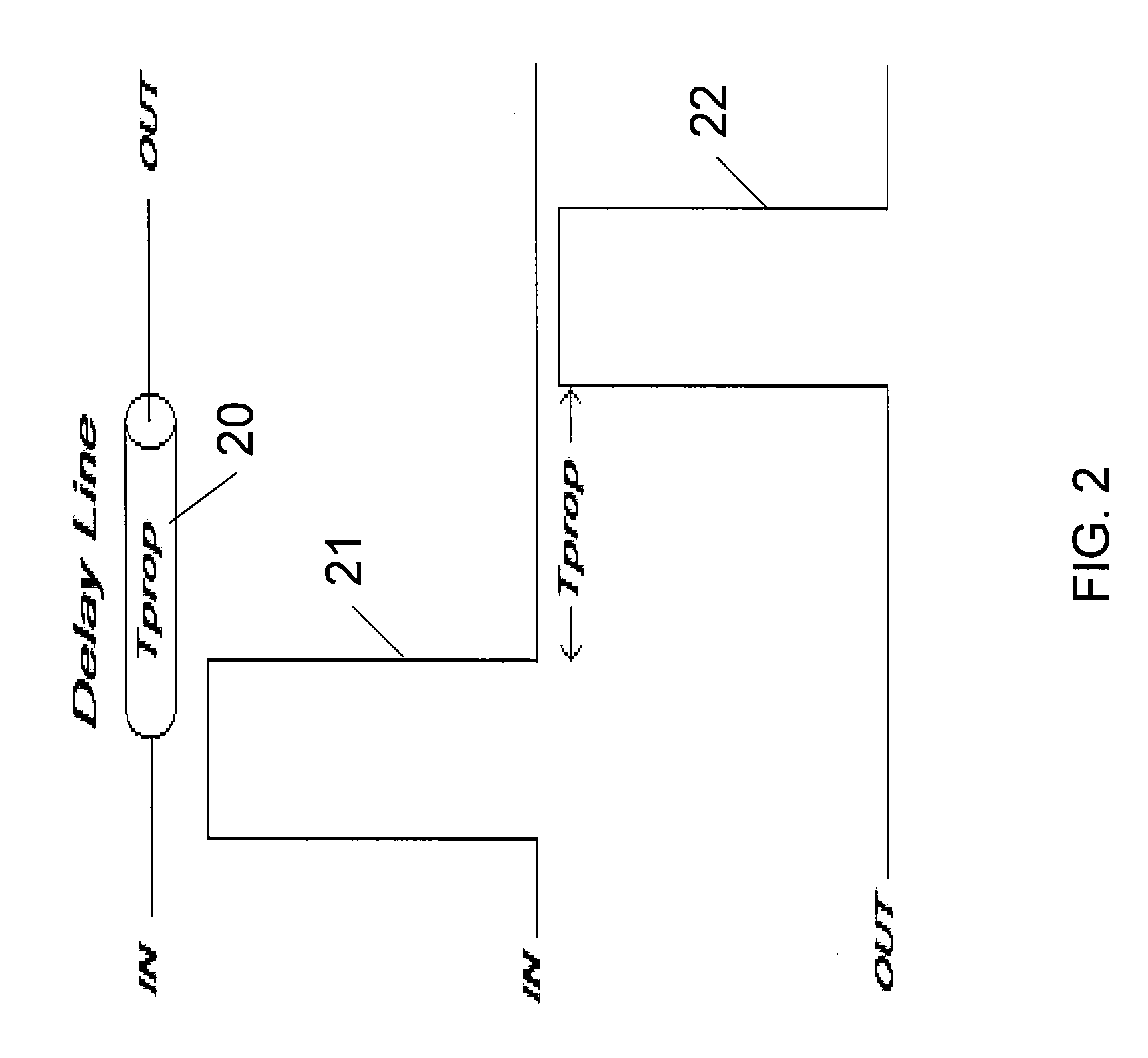
ActiveUS9154172B1Control delayDelay lines pulse generationPower reduction by control/clock signalComputer scienceEncoder
Owner:HRL LAB
PVT variation detection and compensation circuit
ActiveUS7388419B2Electronic switchingPulse generation by opto-electronic devicesPhase differenceLogic module
A compensation circuit and a method for compensating for process, voltage and temperature (PVT) variations in an integrated circuit (IC). The IC includes several functional modules, each of which includes a set of functional units, and generates an output signal in response to an input signal. The compensation circuit includes a code generator and a logic module. The code generator generates a digital code for each functional unit. The digital codes are based on phase differences between the input signal and the output signal. The logic module generates calibration codes based on the digital codes. The calibration codes compensate for the PVT variations in the corresponding functional units.
Owner:NXP USA INC
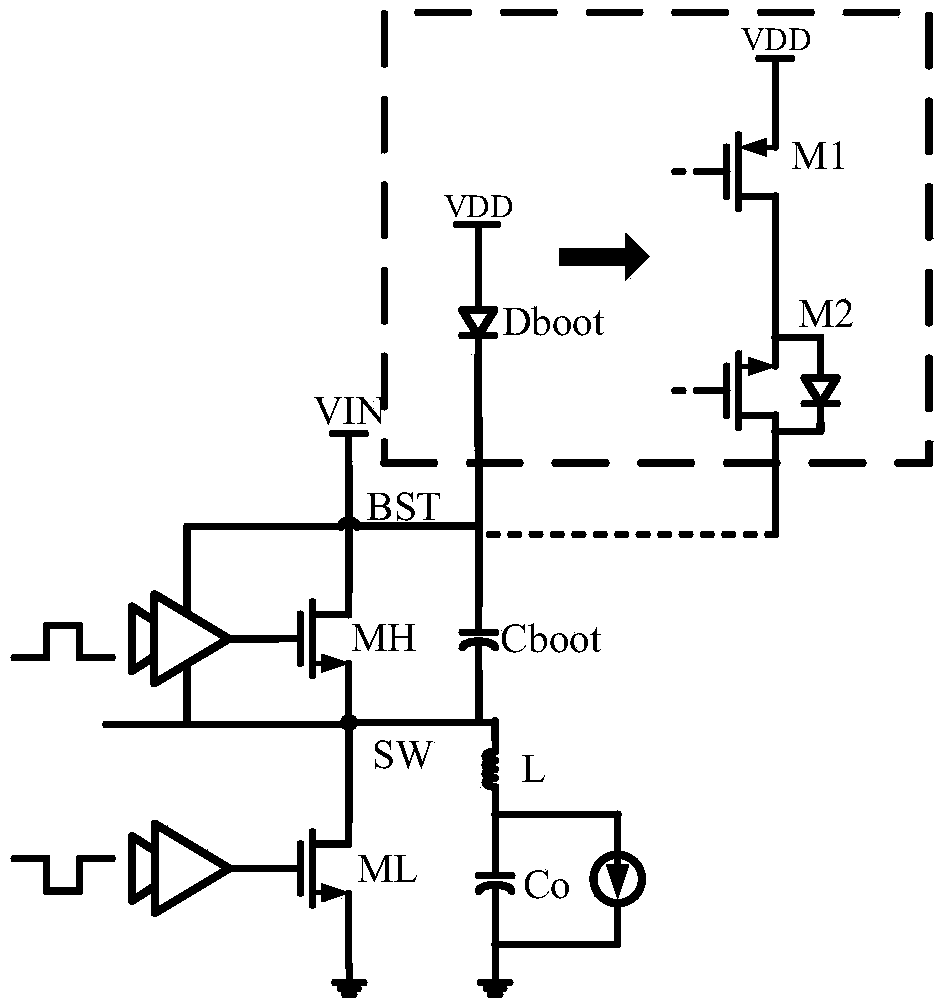
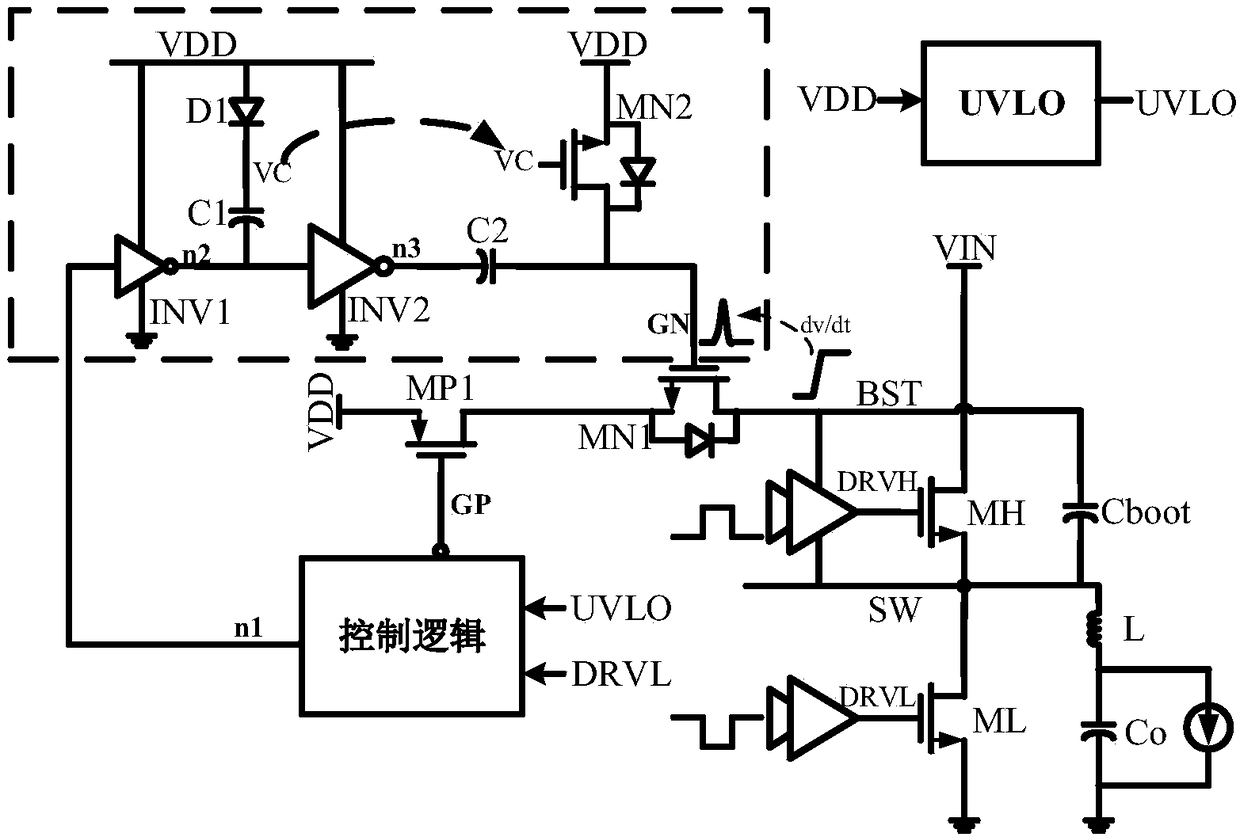
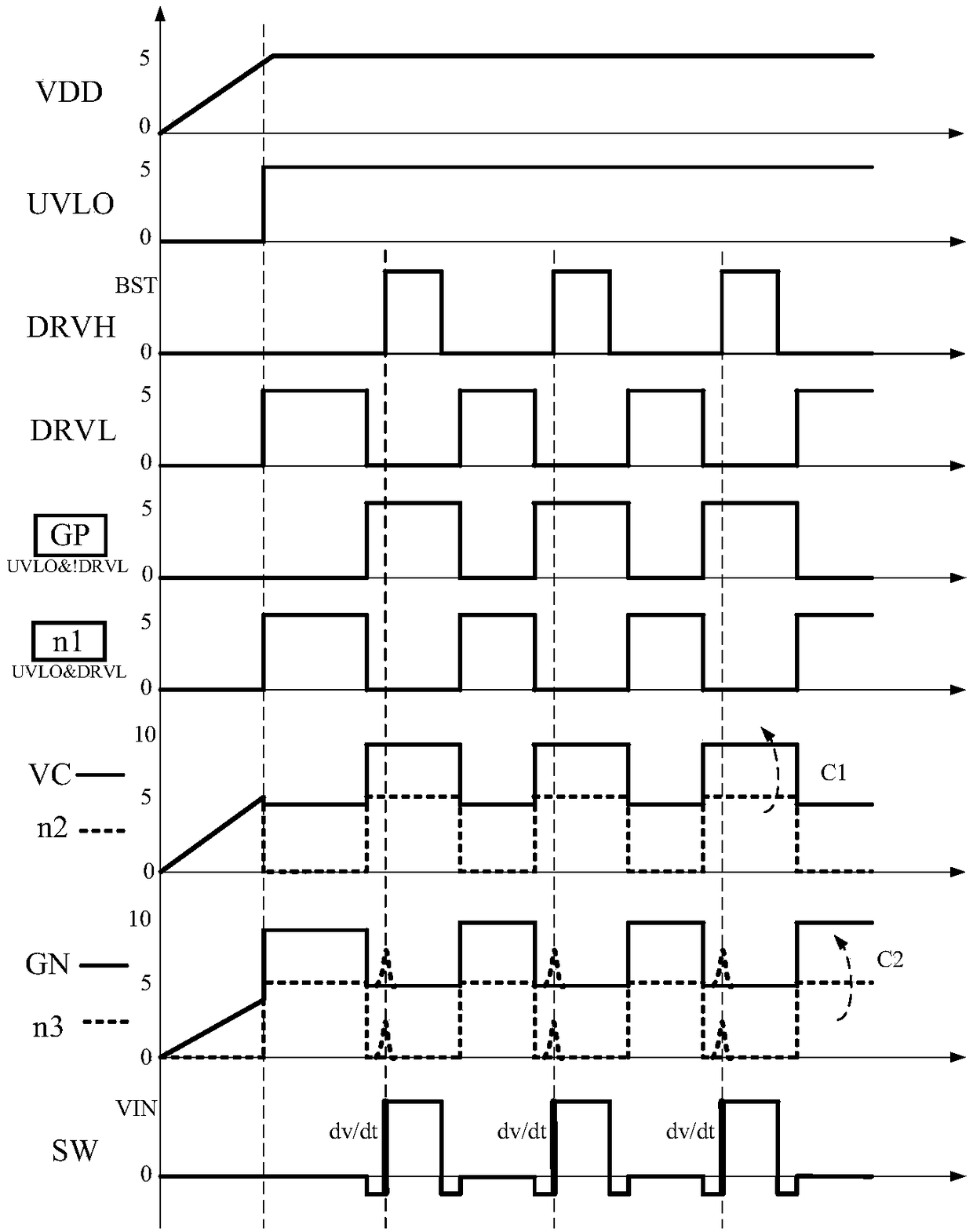
A switch bootstrap charging circuit suitable for high-speed gate driving of GaN power device
ActiveCN109004820ASimple structureLow costEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceControl signal
A switch bootstrap charging circuit suitable for high-speed gate driving of a GaN power device belongs to the technical field of power management. A control logic module generates a first control signal and a second control signal according to the undervoltage signal and the low-side gate driving signal. The gate electrode of the first PMOS transistor is connected to the second control signal, thesource electrode thereof is connected to the supply voltage, and the drain electrode thereof is connected to the source electrode of the first NMOS transistor. An input end of the first inverter is connected with a first control signal, an output end of the first inverter is connected with an input end of the second inverter and is connected with a cathode of the first diode and a gate electrodeof the second NMOS transistor through a first capacitor; The anode of the first diode and the source of the second NMOS transistor are connected to a supply voltage; The gate electrode of the first NMOS transistor is connected to the drain electrode of the second NMOS transistor and is connected to the output end of the second inverter through the second capacitor, and the drain electrode of the second NMOS transistor serves as the output end of the switch bootstrap charging circuit. The invention can prevent the voltage on the bootstrap capacitor from being too large when charging, can realize on-chip integration, and has a simple circuit structure and high reliability. It is especially suitable for GaN high-speed gate drive.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
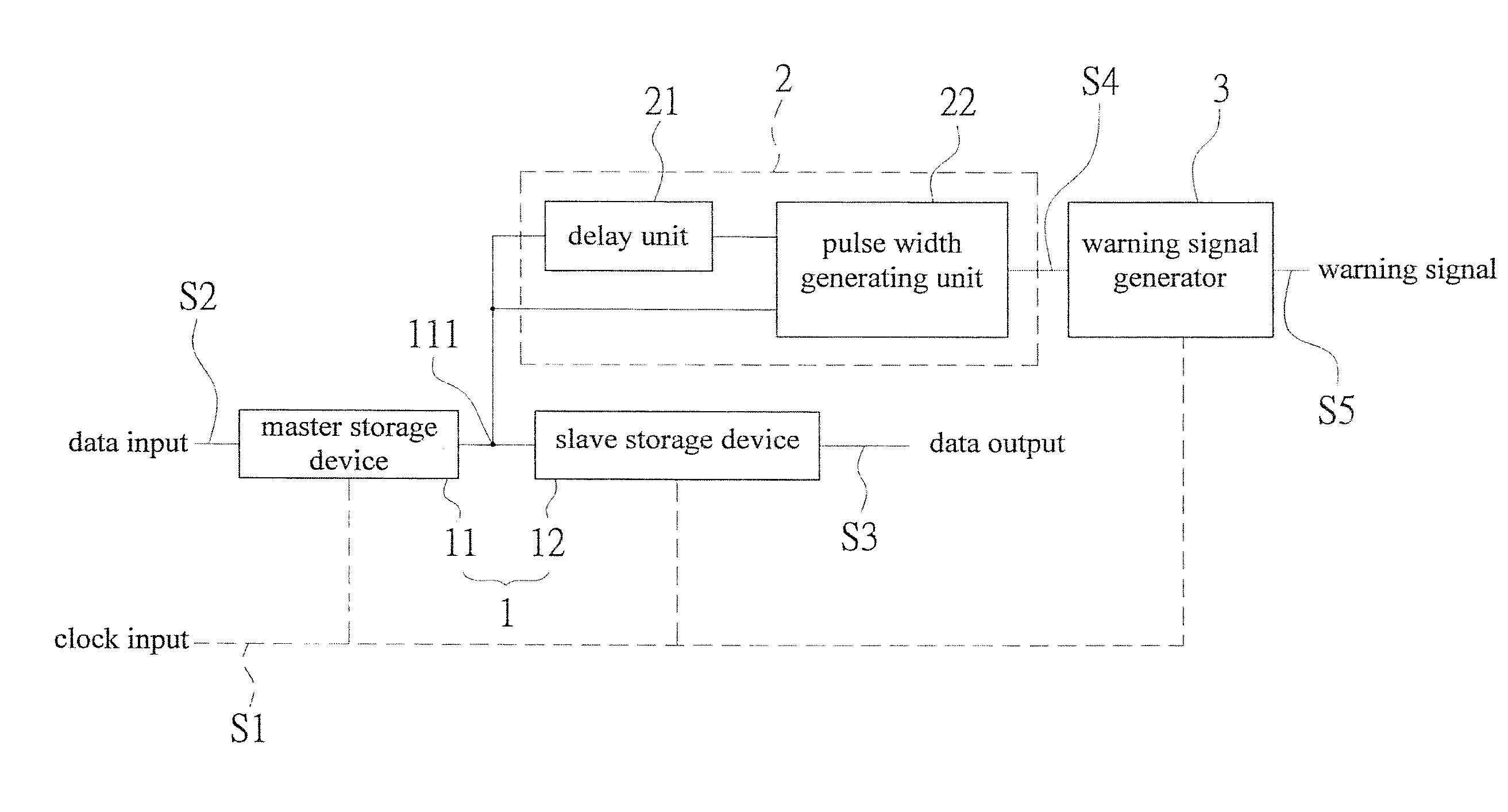
In situ pulse-based delay variation monitor predicting timing error caused by process and environmental variation
InactiveUS20140152344A1Increase the pulse widthSolve excessive overheadVoltage/temperature variation compensationElectricityElectrical connection
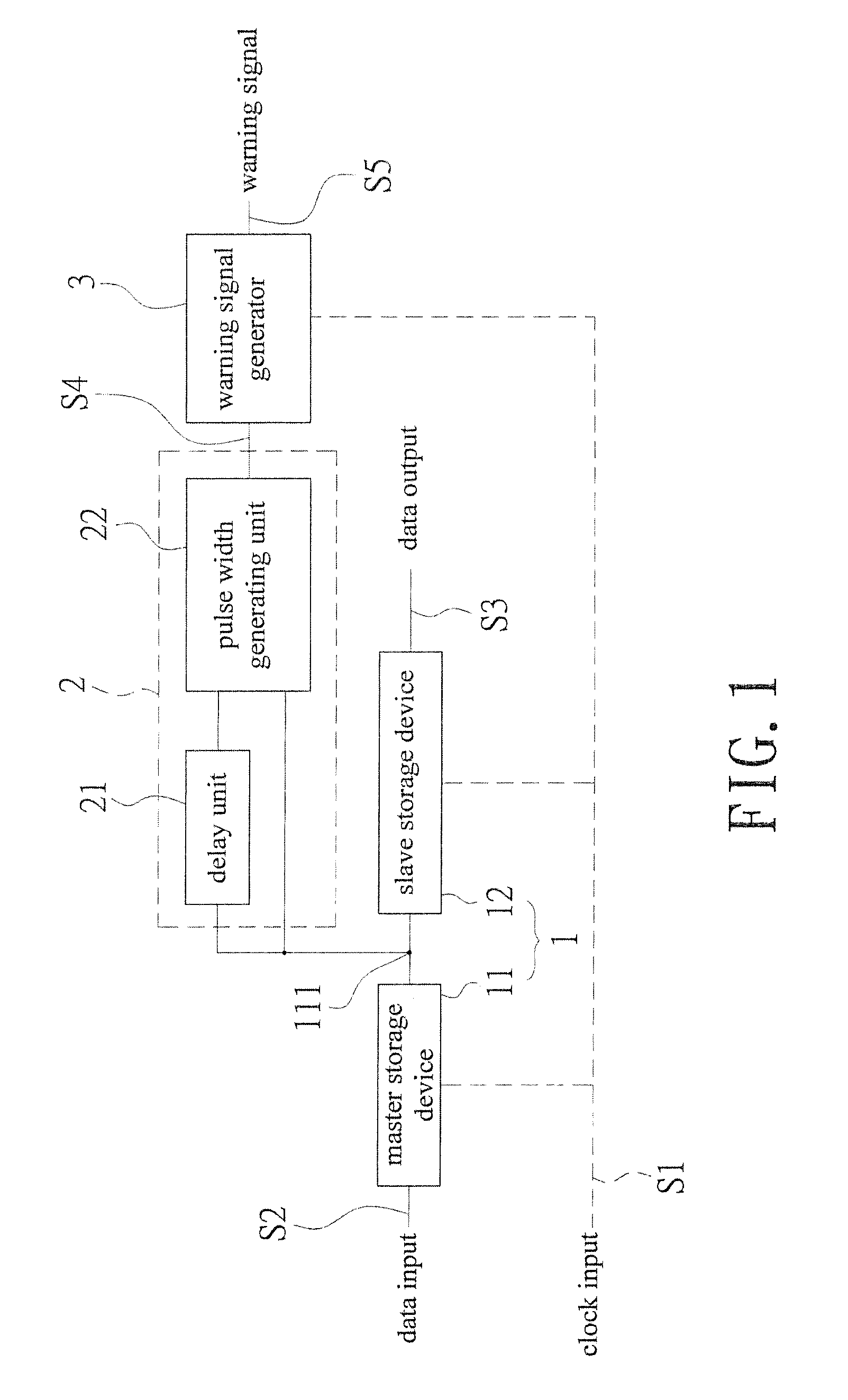
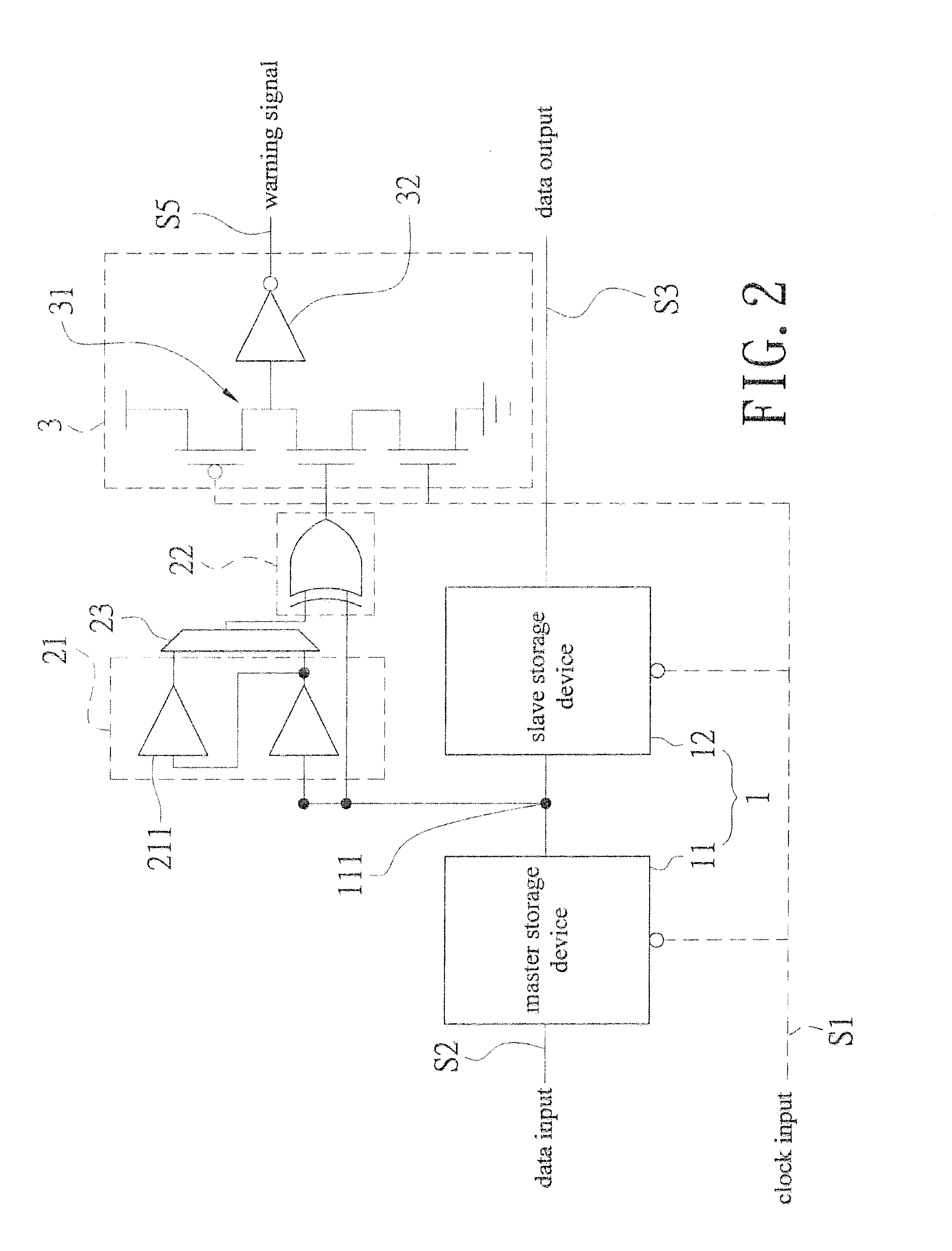
An in situ pulse-based delay variation monitor that predicts timing errors caused by process and environmental variations is revealed. The monitor includes a sequential storage device having a mater storage device and a slave storage device, a transition detector that is electrically connected to a node set on an electrical connection pathway from a master storage device to the slave storage device, and a warning signal generator electrically connected to the transition detector. The transition detector receives output of the master storage device to form a warning area by delay buffer, and generates a pulse width output correspondingly according to transition of the data input. Thus the warning signal generator generates a warning signal according to logic action at the pulse width and the clock input when the data input reaches the warning area. Thereby timing errors caused by static process variations and dynamic environmental variations are predicted.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Time Based Driver Output Transition (Slew) Rate Compensation
ActiveUS20080164924A1Programmable logic circuit arrangementsElectronic switchingDriver circuitPhase detector
Apparatus and method for controlling the driver output slew rate. The apparatus includes a driver circuit having an input signal and an output signal, where the driver circuit is structured and arranged to facilitate control of the slew rate of the output signal. A delay circuit having a time delay proportional to a desired transition time of the driver output signal is coupled to the output of the driver circuit. A first comparator detects when the driver output signal rises through a specified level, and a second comparator detects when the driver output falls through a second specified level. A phase detector is coupled to outputs of the first and second comparators and an output of the delay circuit for aligning the phases of the comparator outputs and the delayed comparator outputs by adjusting the driver output slew rate.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Temperature compensation in integrated circuit
In an embodiment, an integrated circuit comprises a plurality of temperature sensors and a power manager coupled thereto. The temperature sensors are physically distributed over an area of the integrated circuit that is occupied by logic circuitry implementing the operations for which the integrated circuit is designed. The power manager is configured to transmit a power supply voltage request to an external power supply module, the power supply voltage request indicating a requested magnitude of the power supply voltage for the integrated circuit. The power manager is configured to modify the requested magnitude responsive to indications from each of the plurality of temperatures sensors that represent a temperature of the integrated circuit sensed by each of the plurality of temperature sensors.
Owner:APPLE INC
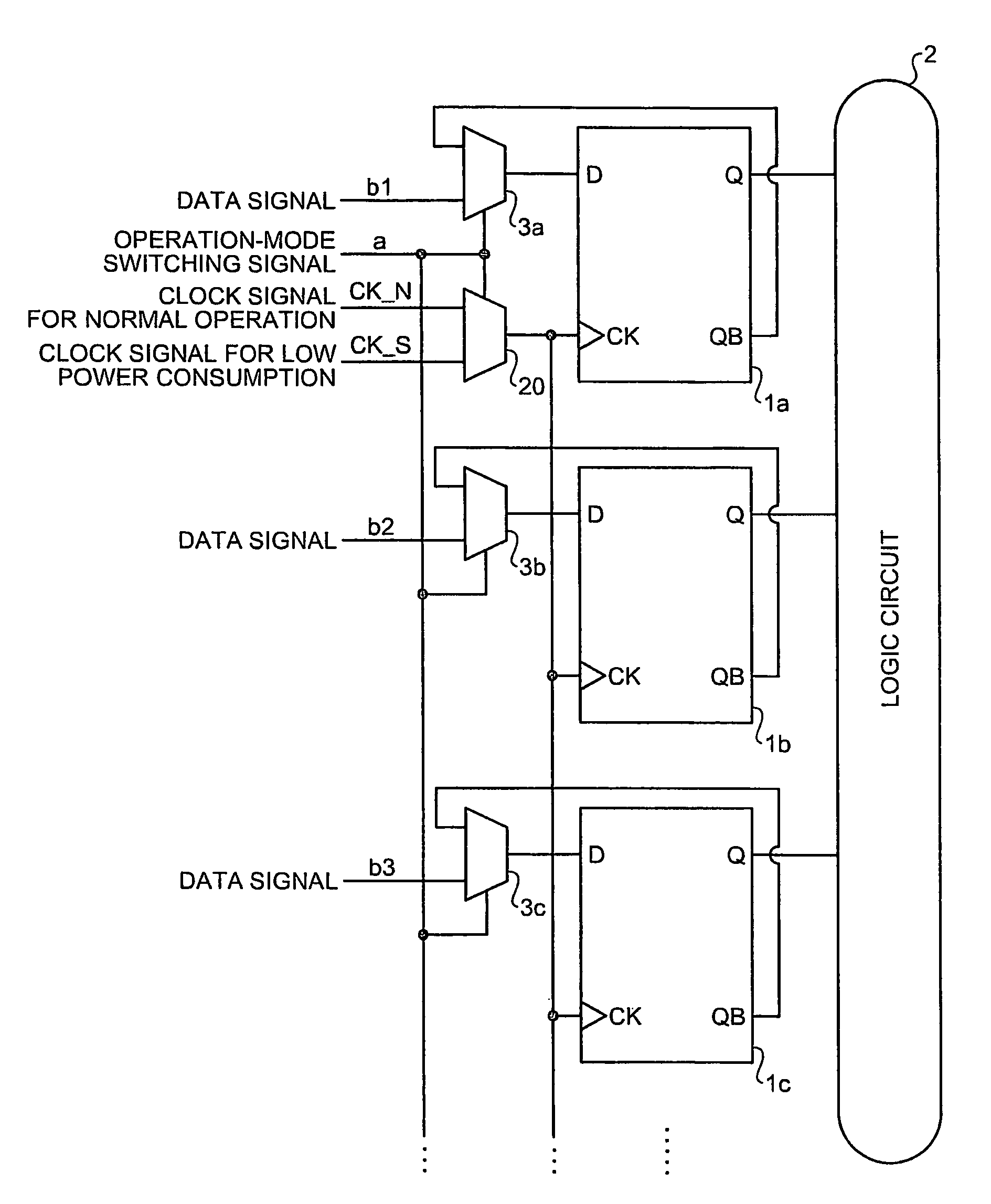
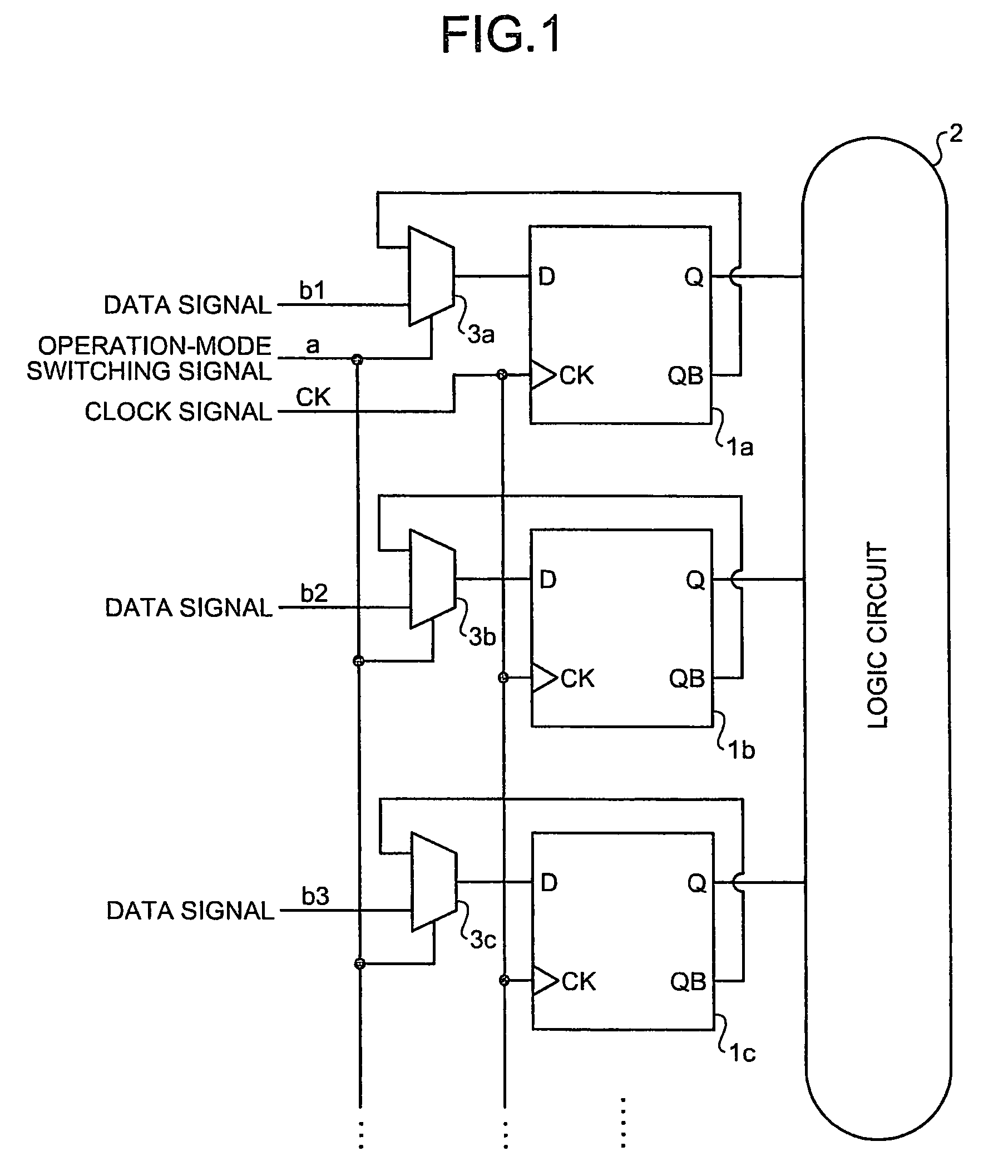
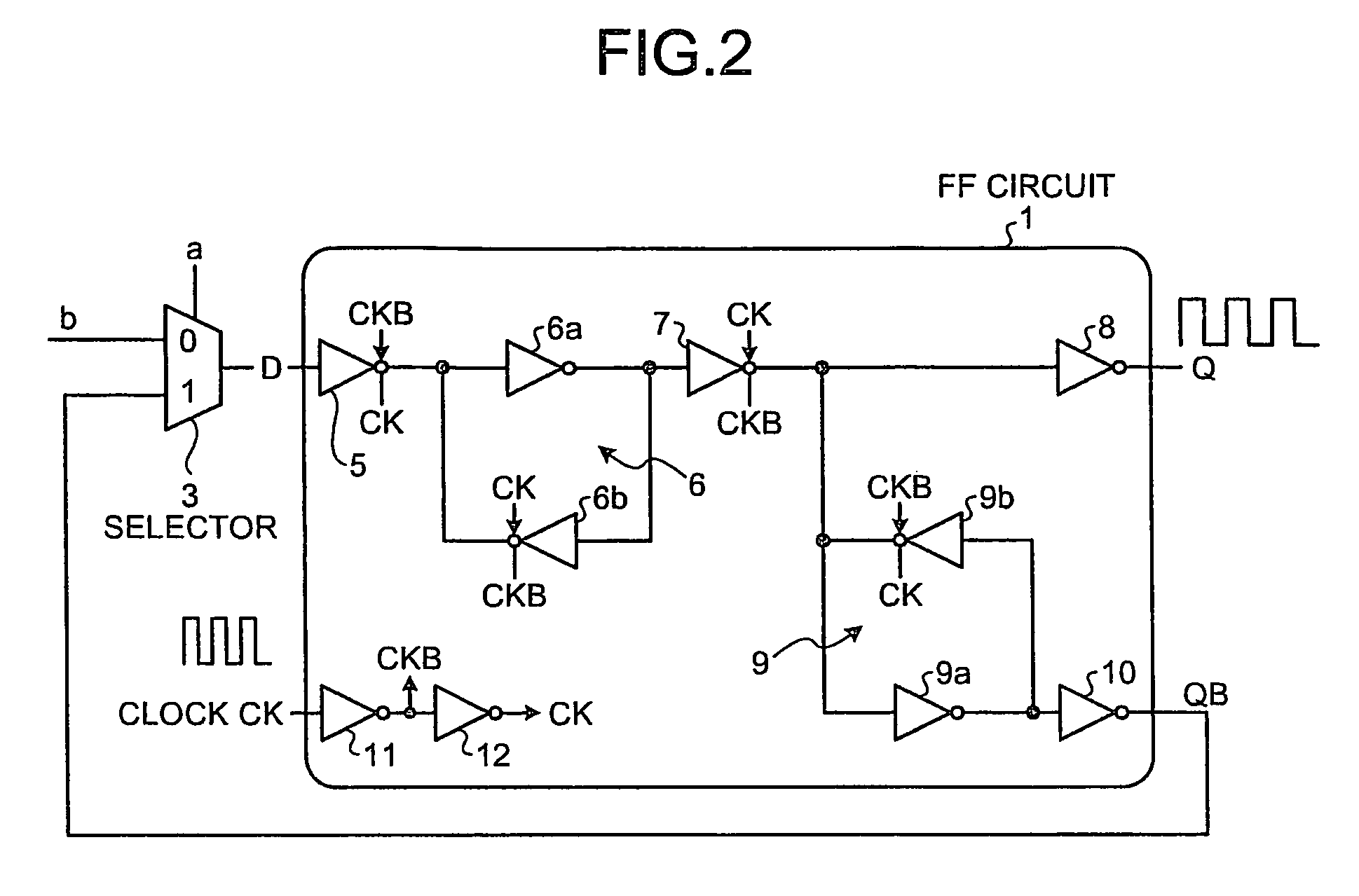
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and countermeasure method against NBTI degradation
A semiconductor integrated circuit device includes a target circuit of a low power consumption mode having at least one flip-flop circuit to which a clock signal is supplied in a normal operation mode and in a low power consumption mode, and a logic circuit to which each output of the at least one flip-flop circuit is input, wherein each of the flip-flop circuits includes a selector that selects a normal data signal in the normal operation mode, selects an inverted output of the flip-flop circuit in the low power consumption mode, based on an operation-mode switching signal that designates switching between the normal operation mode and the low power consumption mode, and inputs the selected signal to a data input terminal of the flip-flop circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Temperature Dependent Bias for Minimal Stand-by Power in CMOS Circuits
InactiveUS20090080276A1Reduce leakage currentDecrease temperature dependent leakage currentPower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic switchingCMOSSemiconductor chip
A circuit is disclosed which generates such a bias voltage that when this bias voltage is received by a large plurality of devices of a semiconductor chip, power consumption is reduced in the stand-by mode at any particular operating temperature. The disclosed circuit contains at least one monitor FET, which is kept in its off-state, and which has common properties with the large plurality of FET devices. The temperature dependent leakage current of the monitor FET is sensed, and used to generate the bias voltage in proportion to the leakage current. This bias voltage is received by the large plurality FET devices on their gate electrodes, or on their body terminals.
Owner:IBM CORP
Popular searches
Digital data processing details Welding electric supply Ignition automatic control Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnection Open-loop automatic control systems Energy efficient computing Ac network voltage adjustment Photoelectric discharge tubes Amplifiers controlled by light Logic circuits using opto-electronic devices
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com