Patents
Literature
95results about "Radiation hardening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
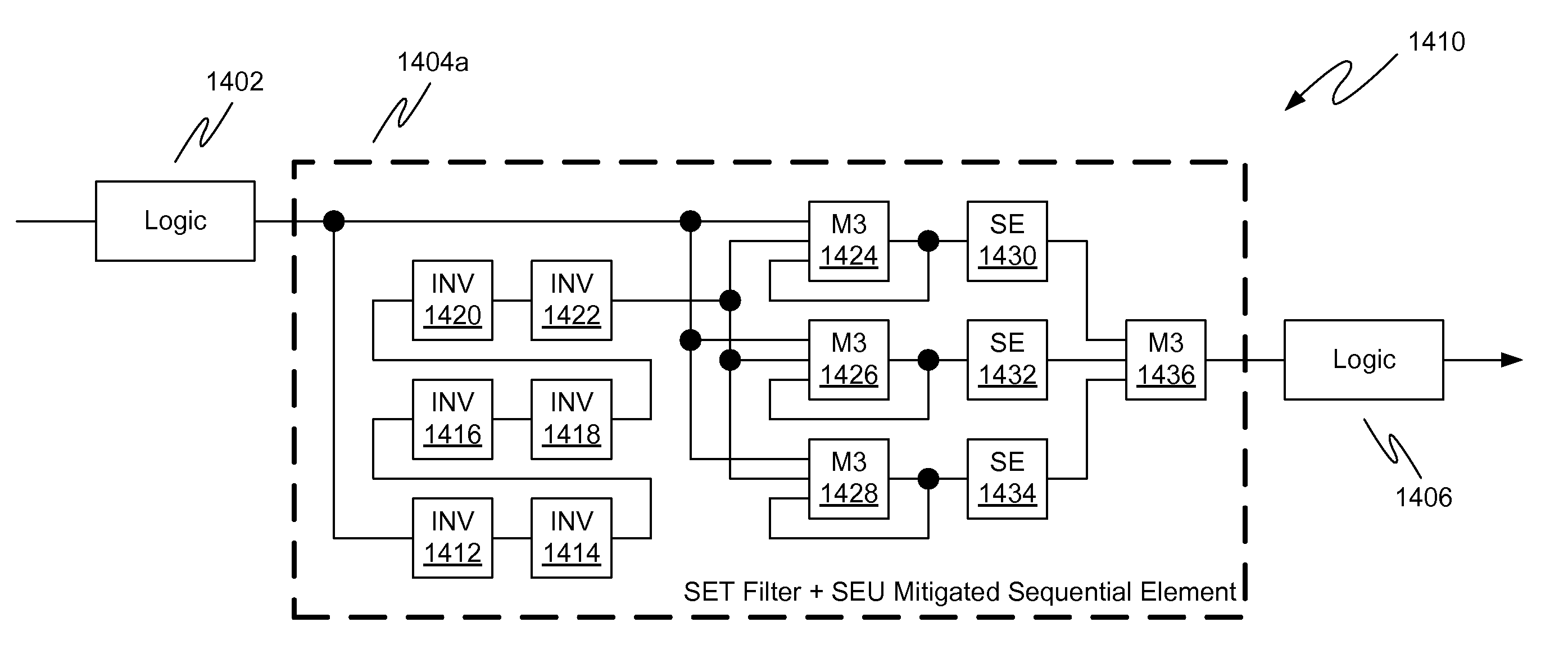
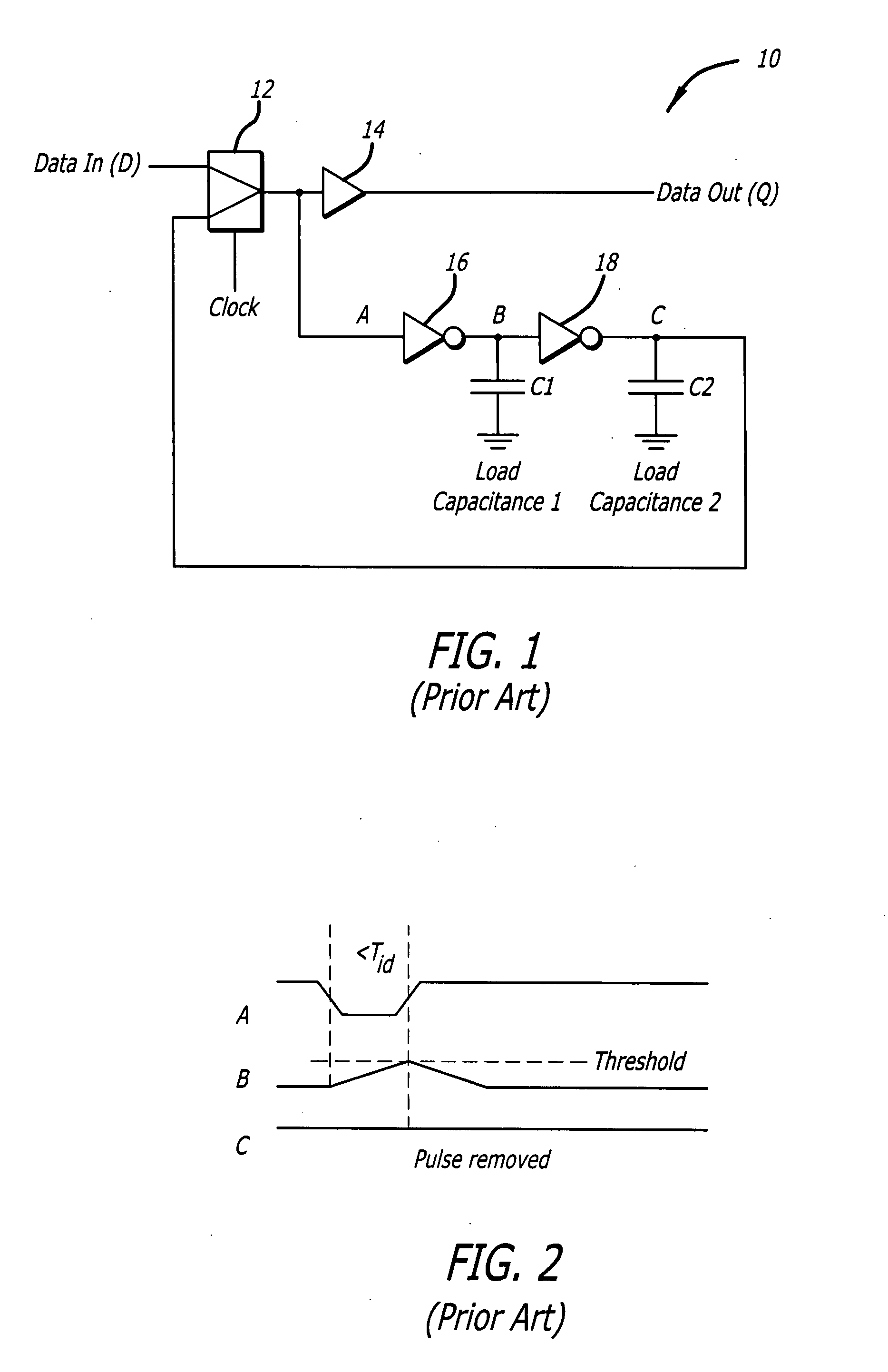
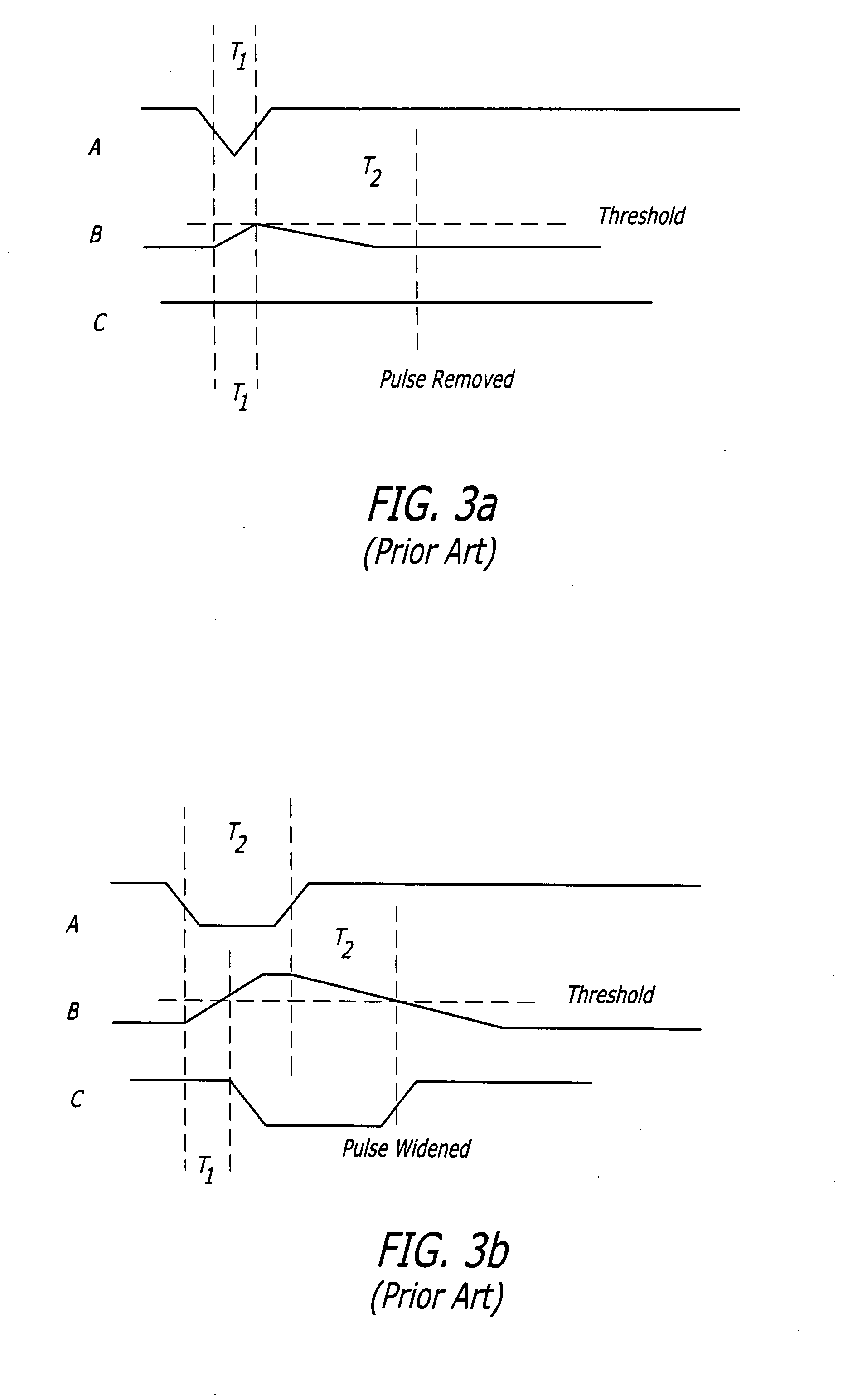
Single event transient mitigation and measurement in integrated circuits
ActiveUS20090204933A1Fail-safe circuitsDetecting faulty computer hardwareIntegrated circuit layoutComputer science
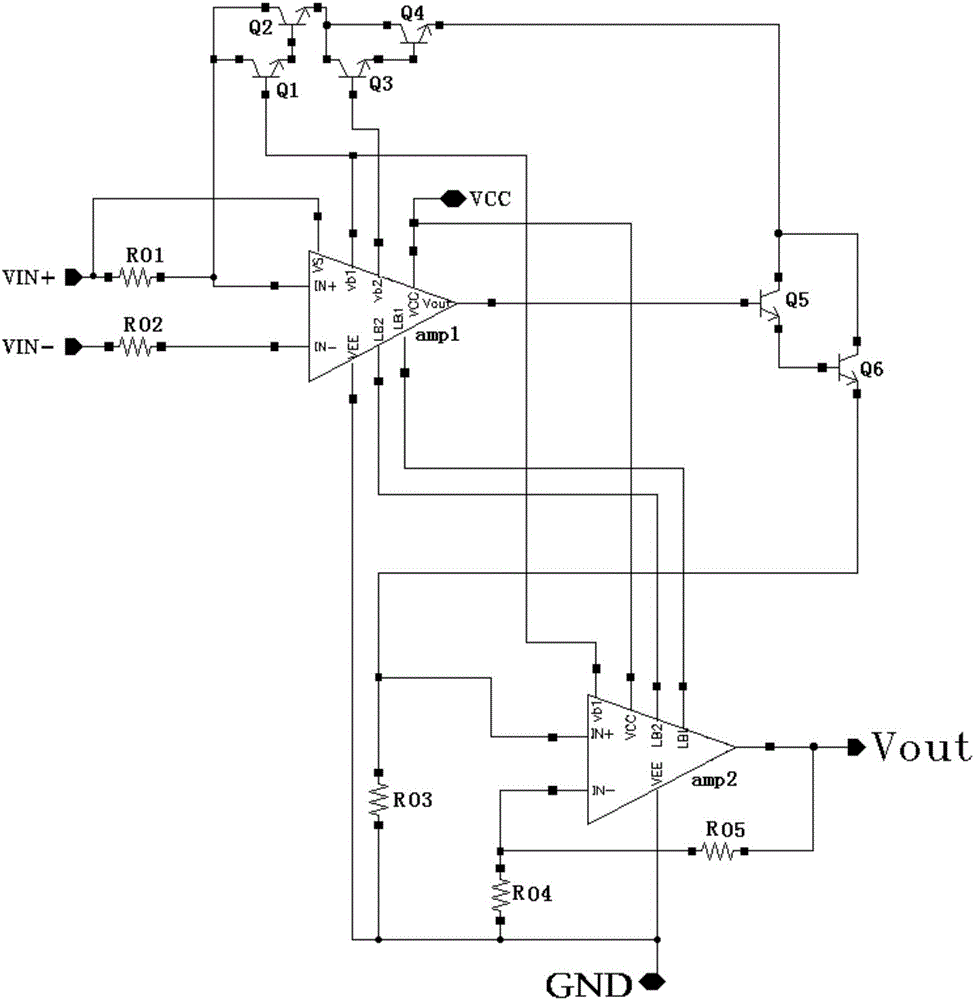
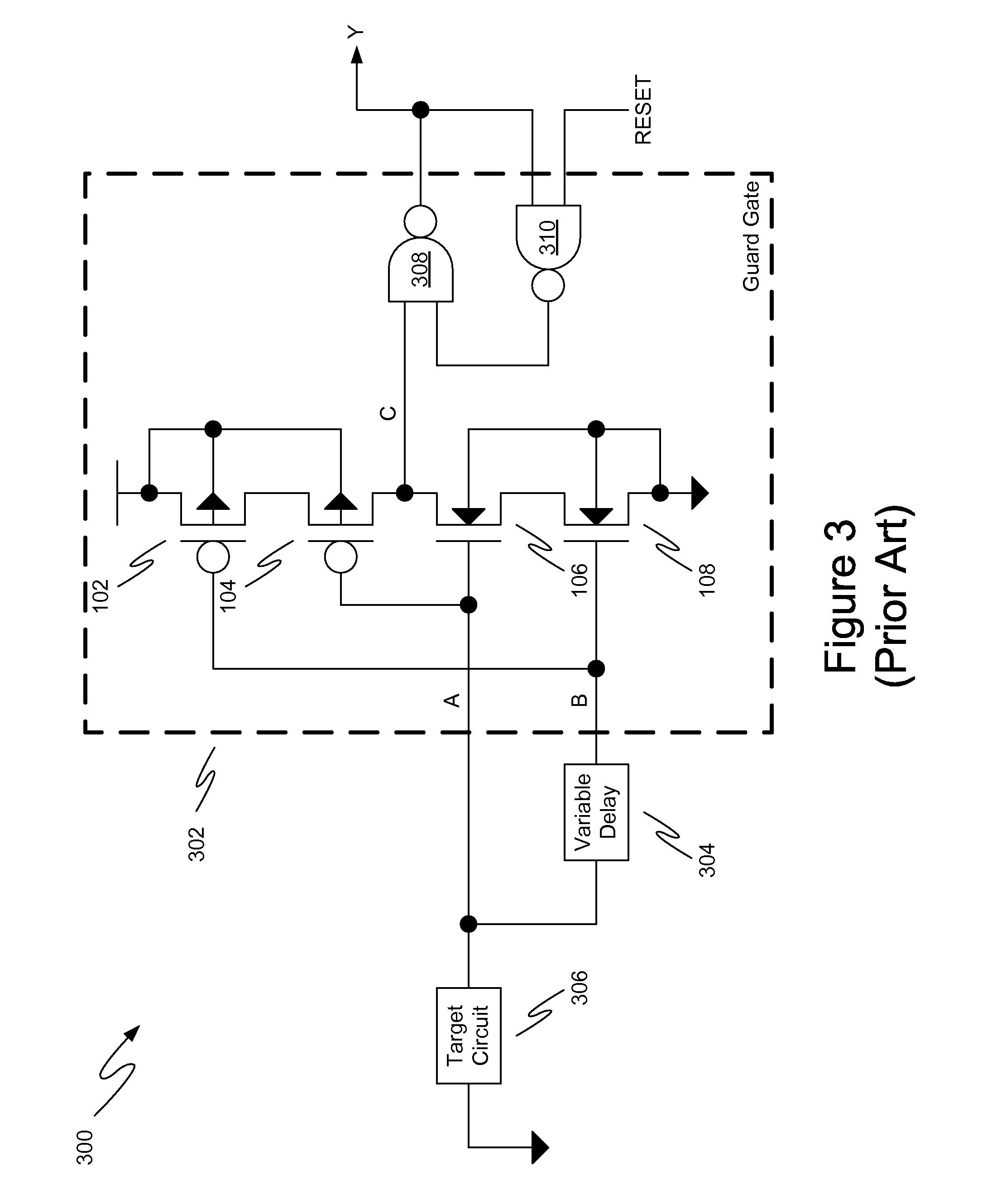
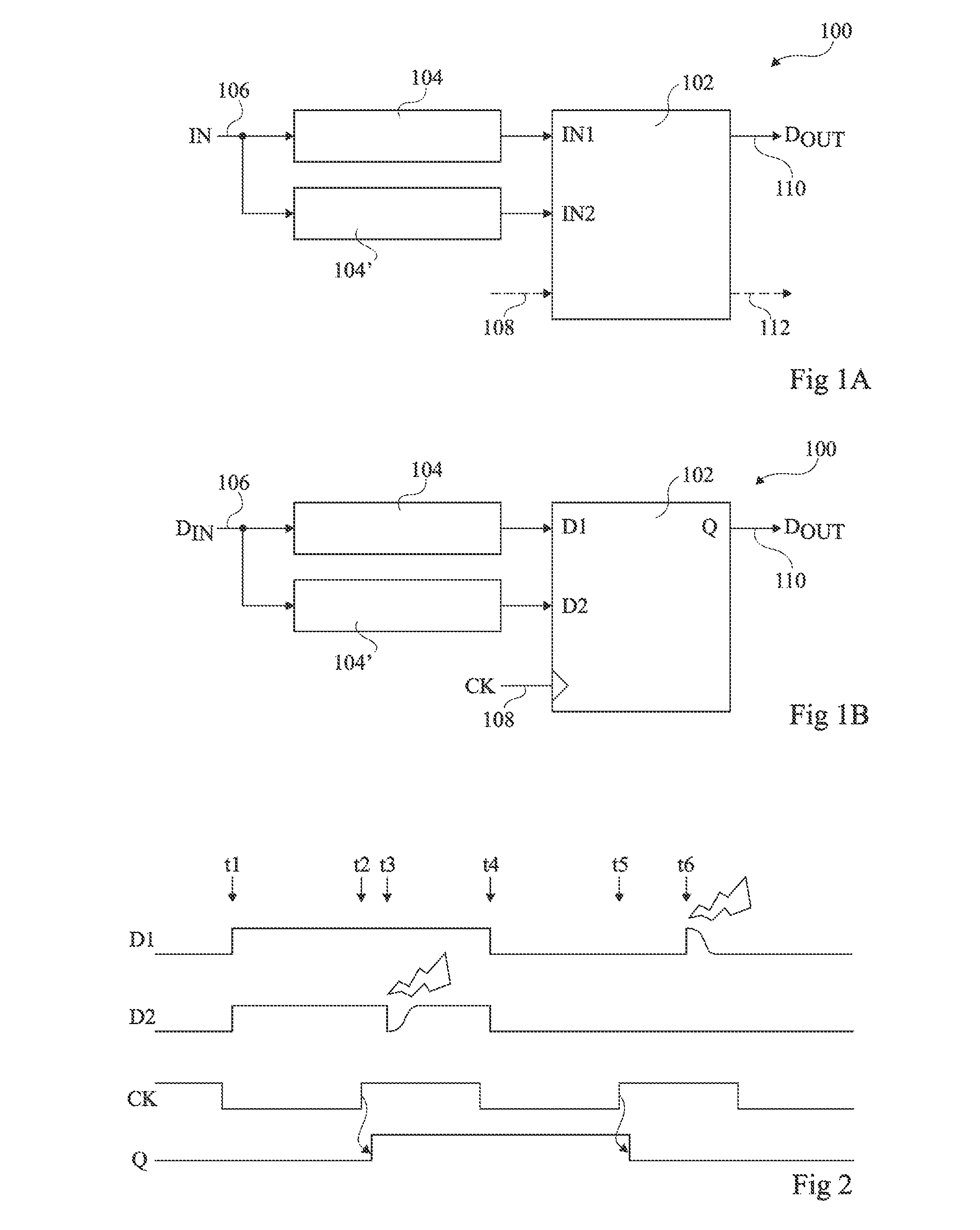
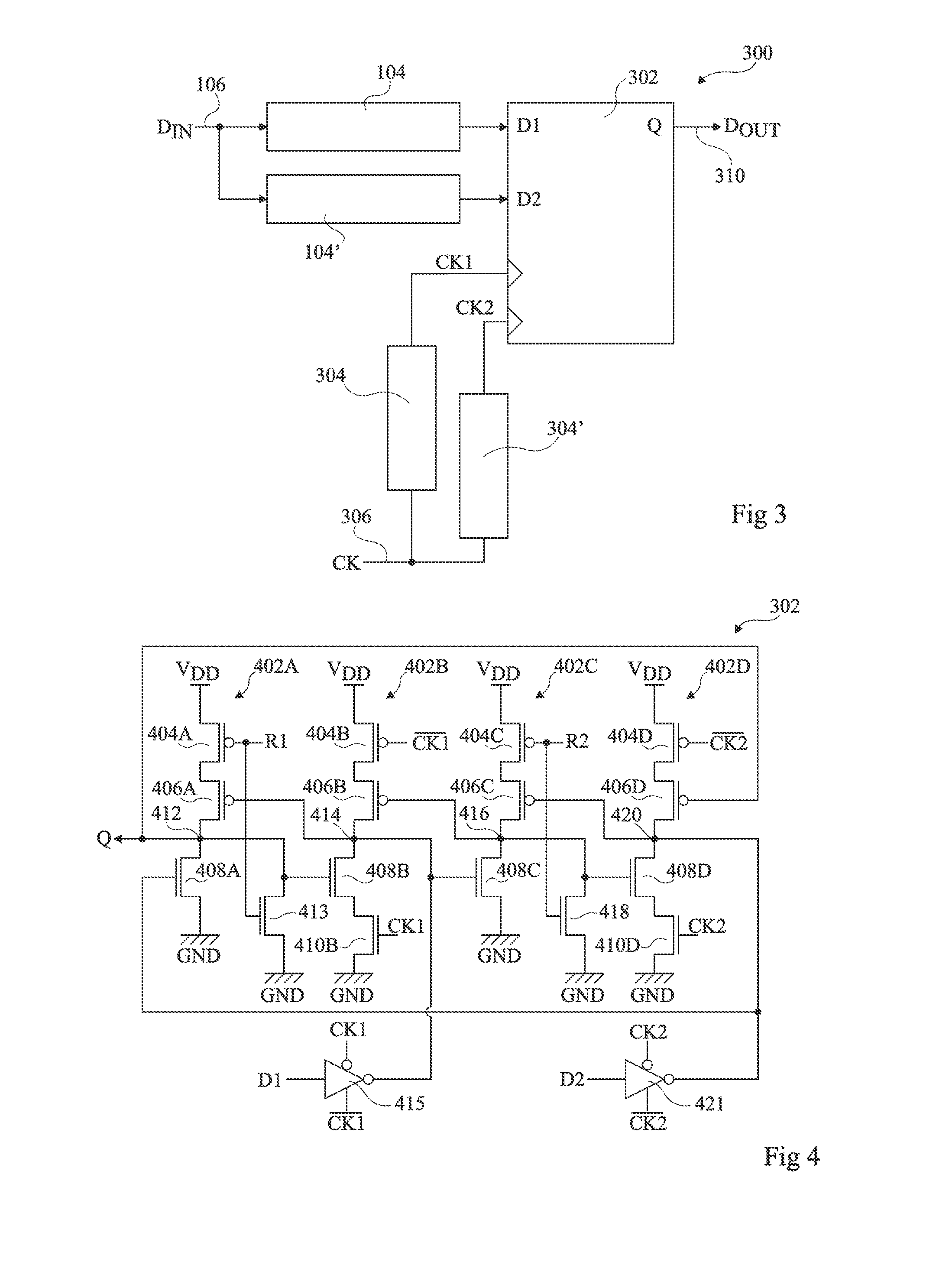
A method for single event transient filtering in an integrated circuit device is described. The device comprises three sequential elements, each having a data input and a data output with each of the three data outputs coupled to one of three inputs of a voting gate. The method comprises generating first and second nominally equivalent logic signals in first and second SET domains, converting the first and second nominally equivalent logic signals into first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels, and transmitting the first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels to the data inputs of the first, second and third sequential elements. Provision is made for applying the method to logic designs implemented in programmable logic integrated circuit devices.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
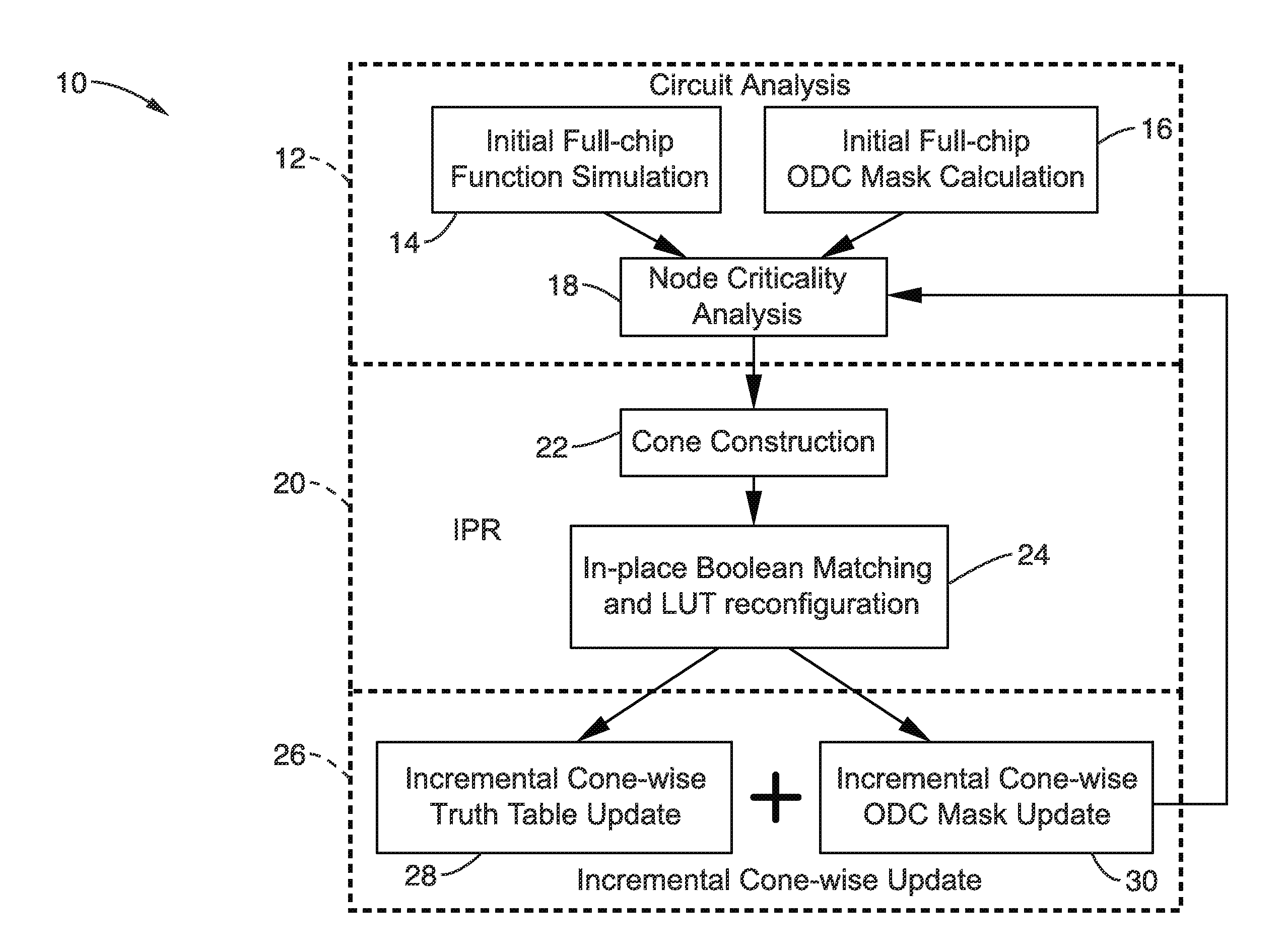
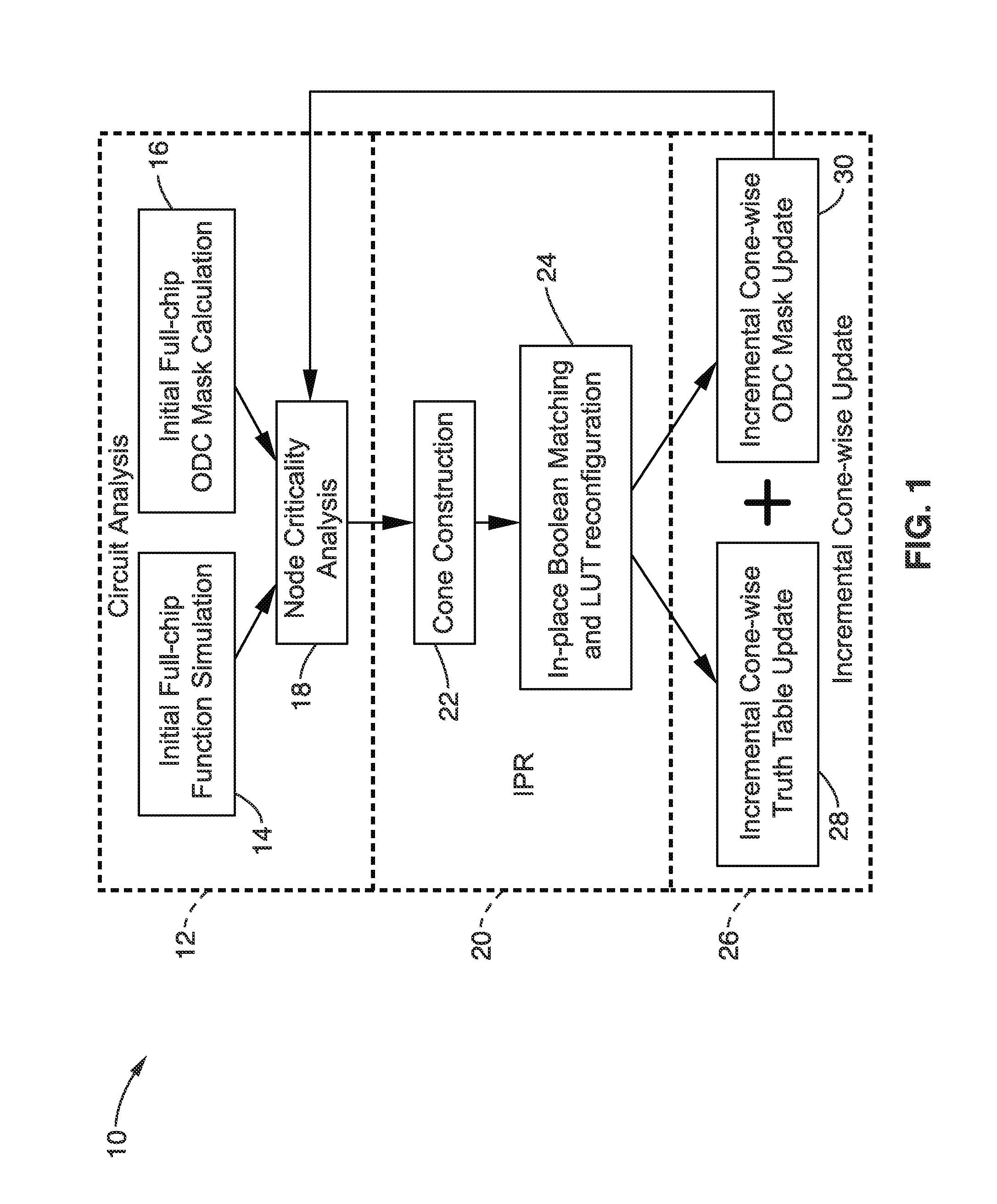
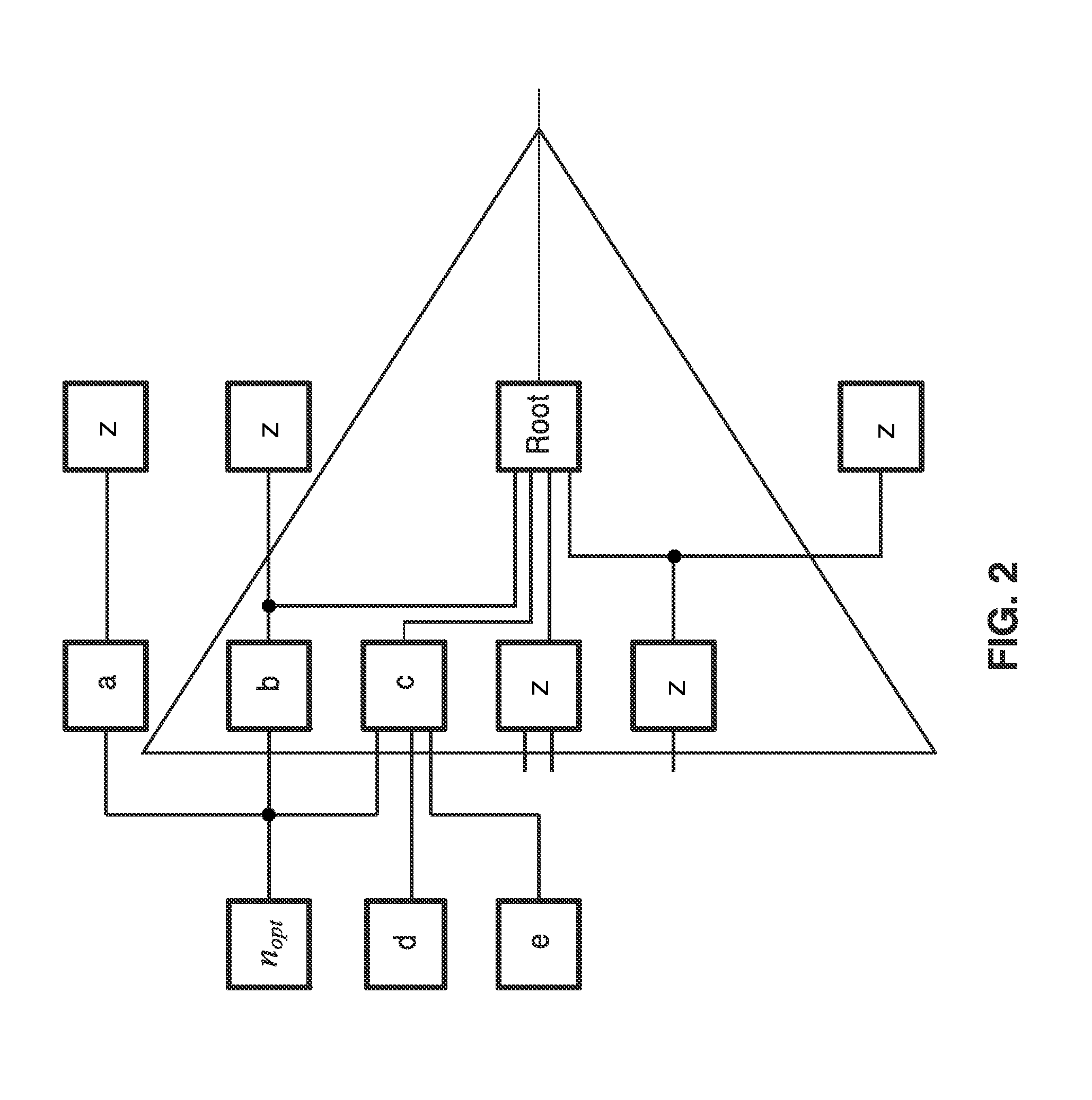
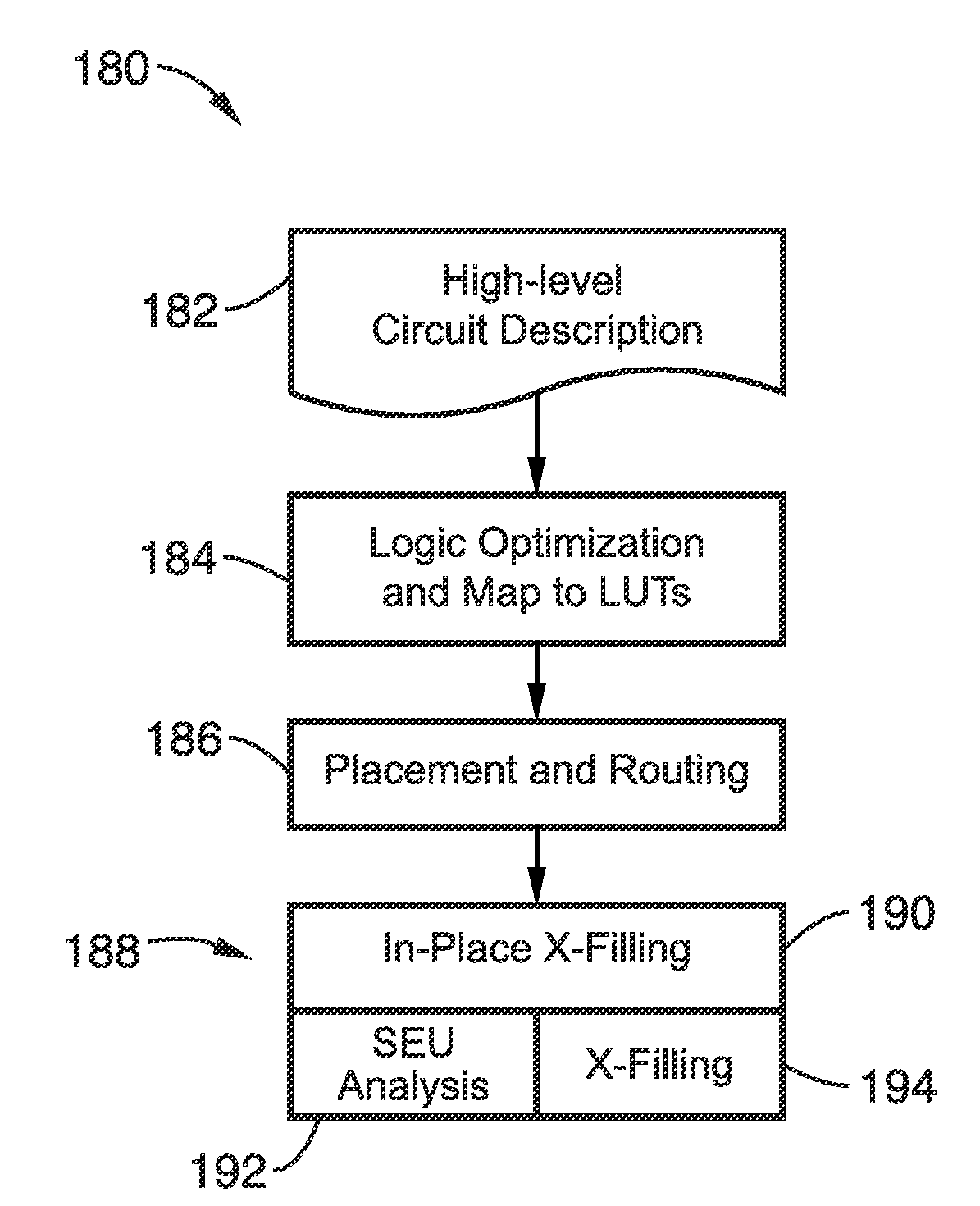
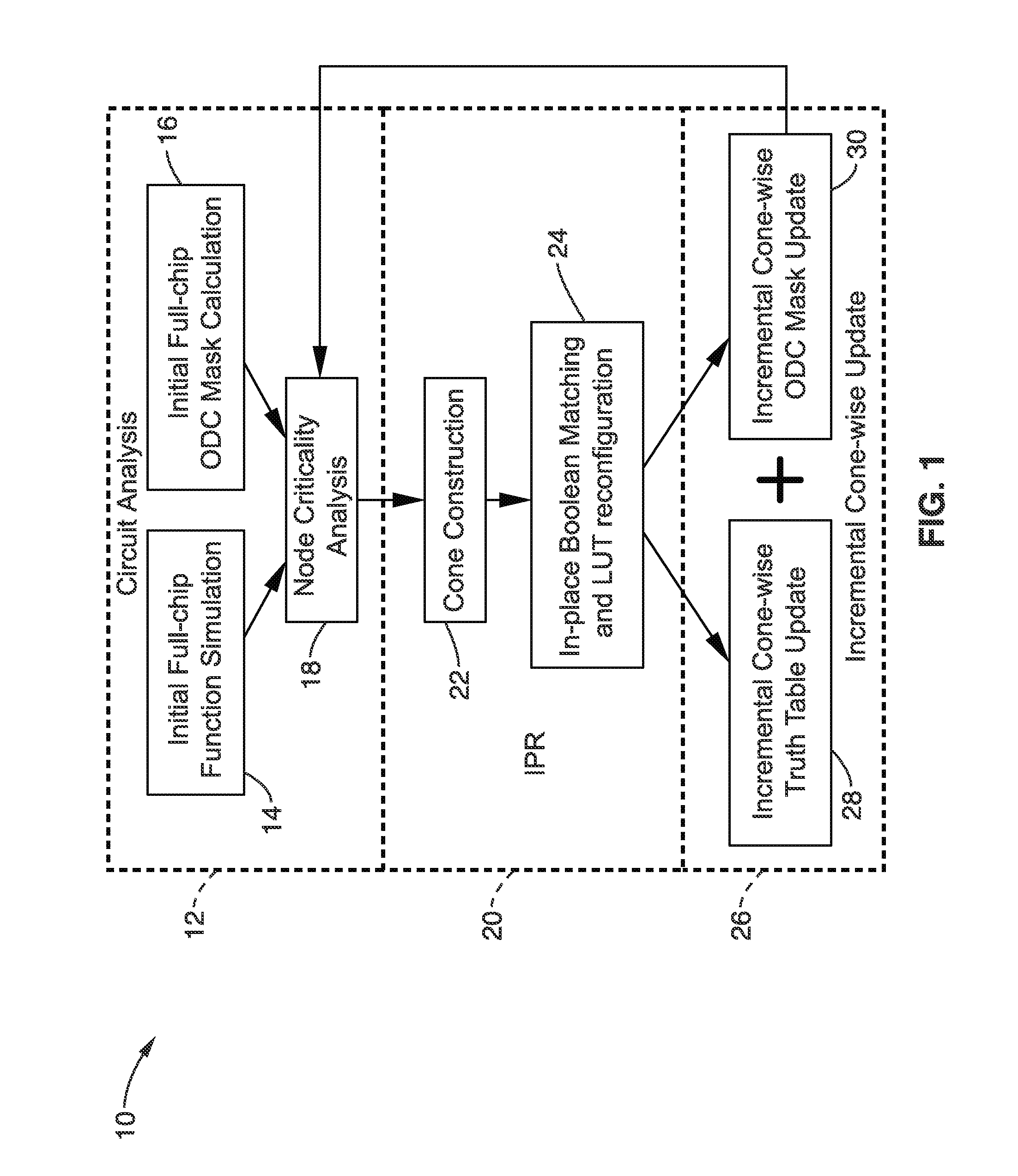
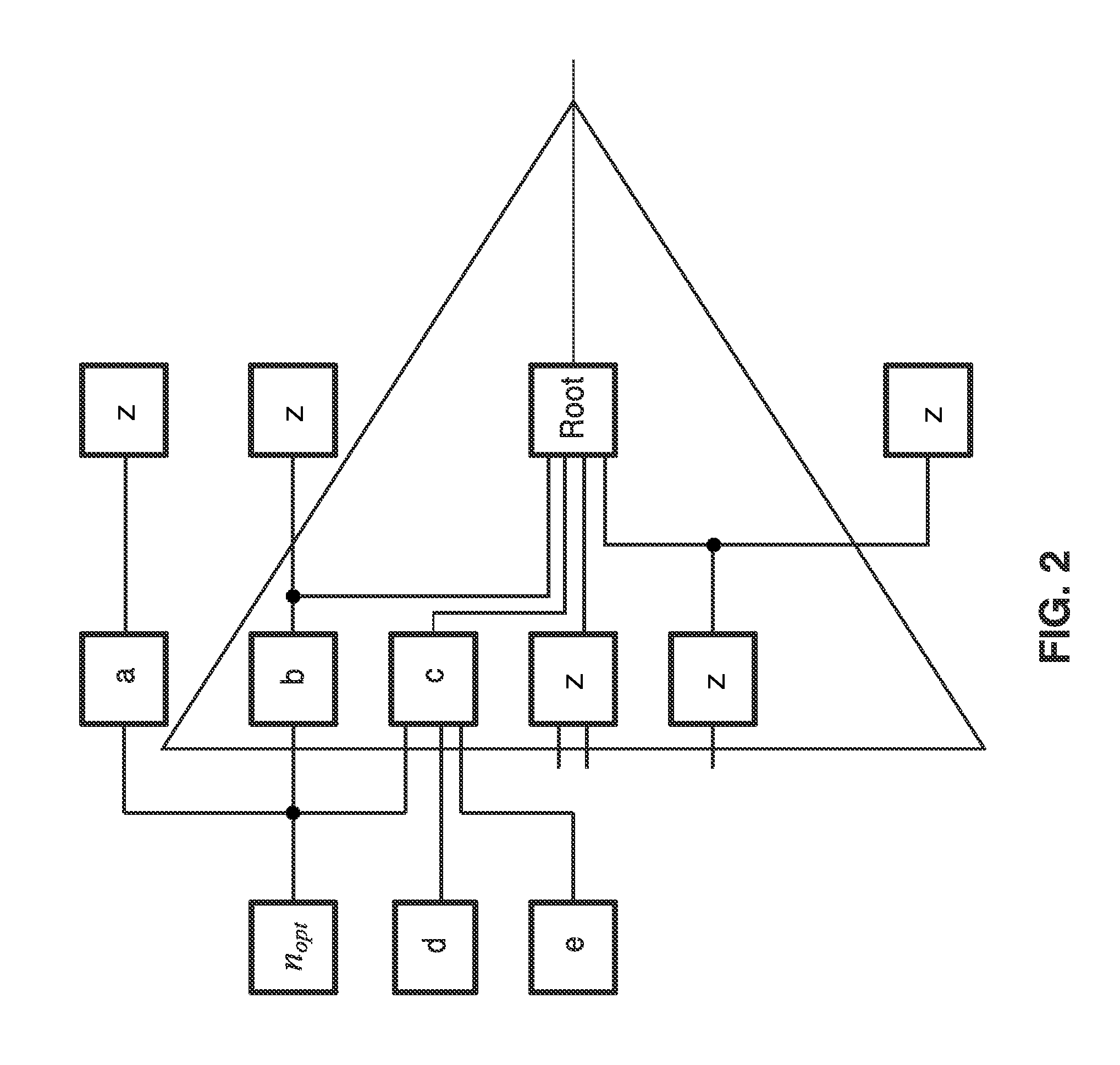
In-place resynthesis and remapping techniques for soft error mitigation in FPGA
InactiveUS20130305199A1Efficient and accurateImprove fault toleranceCAD circuit designRadiation hardeningFpga architectureDecomposition
In-place resynthesis for static memory (SRAM) based Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) toward reducing sensitivity to single event upsets (SEUs). Resynthesis and remapping are described which have a low overheard and improve FPGA designs without the need of rerouting LUTs of the FPGA. These methods include in-place reconfiguration (IPR), in-place X-filling (IPF), and in-place inversion (IPV), which reconfigure LUT functions only, and can be applied to any FPGA architecture. In addition, for FPGAs with a decomposable LUT architecture (e.g., dual-output LUTs) an in-place decomposition (IPD) method is described for remapping a LUT function into multiple smaller functions leveraging the unused outputs of the LUT, and making use of built-in hard macros in programmable-logic blocks (PLBs) such as carry chain or adder. Methods are applied in-place to mapped circuits before or after routing without affecting placement, routing, and design closure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
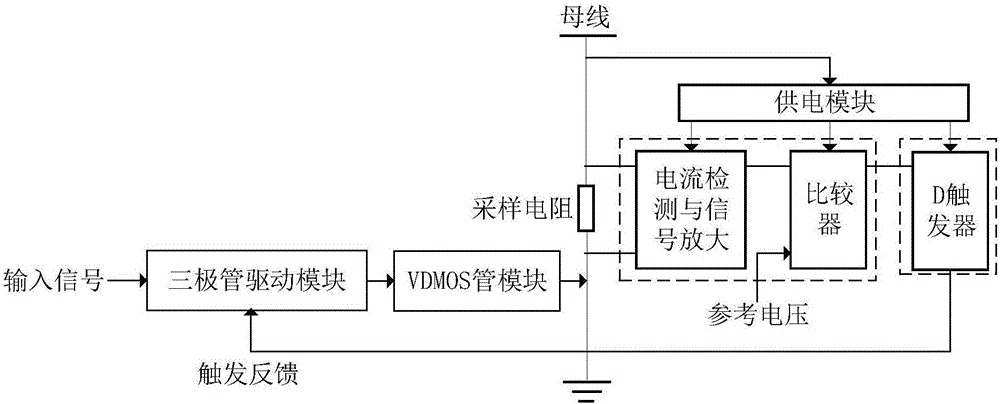
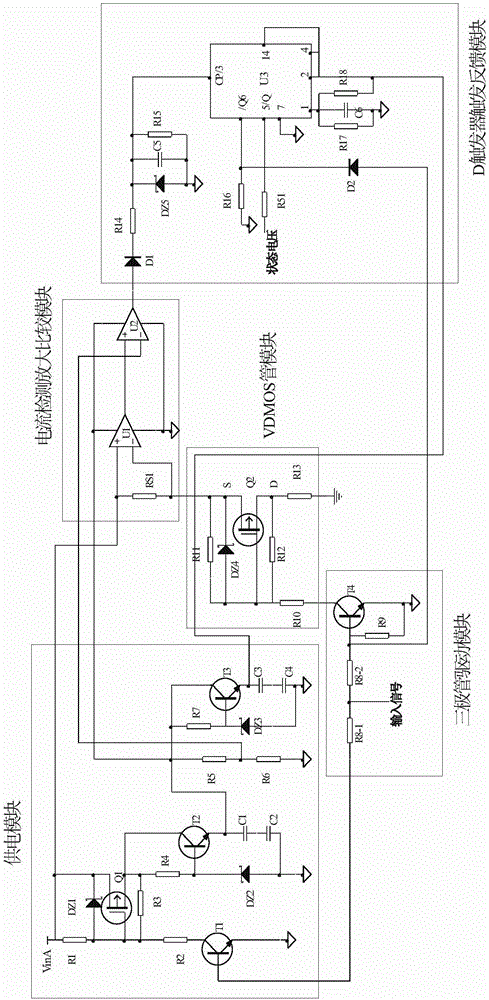
Radiation-proof self-recovery over-current/short-circuit protection circuit for satellite
ActiveCN106486963AReduce weightReduce volumeCurrent/voltage measurementRadiation hardeningSelf recoveryShort circuit protection
The invention relates to a radiation-proof self-recovery over-current / short-circuit protection circuit for a satellite. On the basis of a line structure, the self-recovery over-current / short-circuit protection function is realized. Moreover, the circuit has advantages of reasonable design, small size, and light weight. The radiation-proof self-restoring over-current / short-circuit protection circuit is composed of a power supply module, a triode driver module, a VDMOS tube module including a VDMOS tube Q2, a current detection, amplifier and comparator module, a trigger feedback module having a D trigger U3, and a precision sampling resistor RS1 connected in series to a bus. The power supply module is used for providing power for the current detection, amplifier and comparator module and the trigger feedback module through buses. The input terminal of the triode driver module is connected with an input signal of the control circuit and the output terminal is connected with a gate terminal of the VDMOS tube Q2; and a source end of the VDMOS tube Q2 is connected with the bus by the precision sampling resistor RS1 and a drain end is grounded by a resistor R13. The current detection, amplifier and comparator module consists of a current detection chip U1 for current detection and signal amplification and a comparator U2.
Owner:XIAN MICROELECTRONICS TECH INST
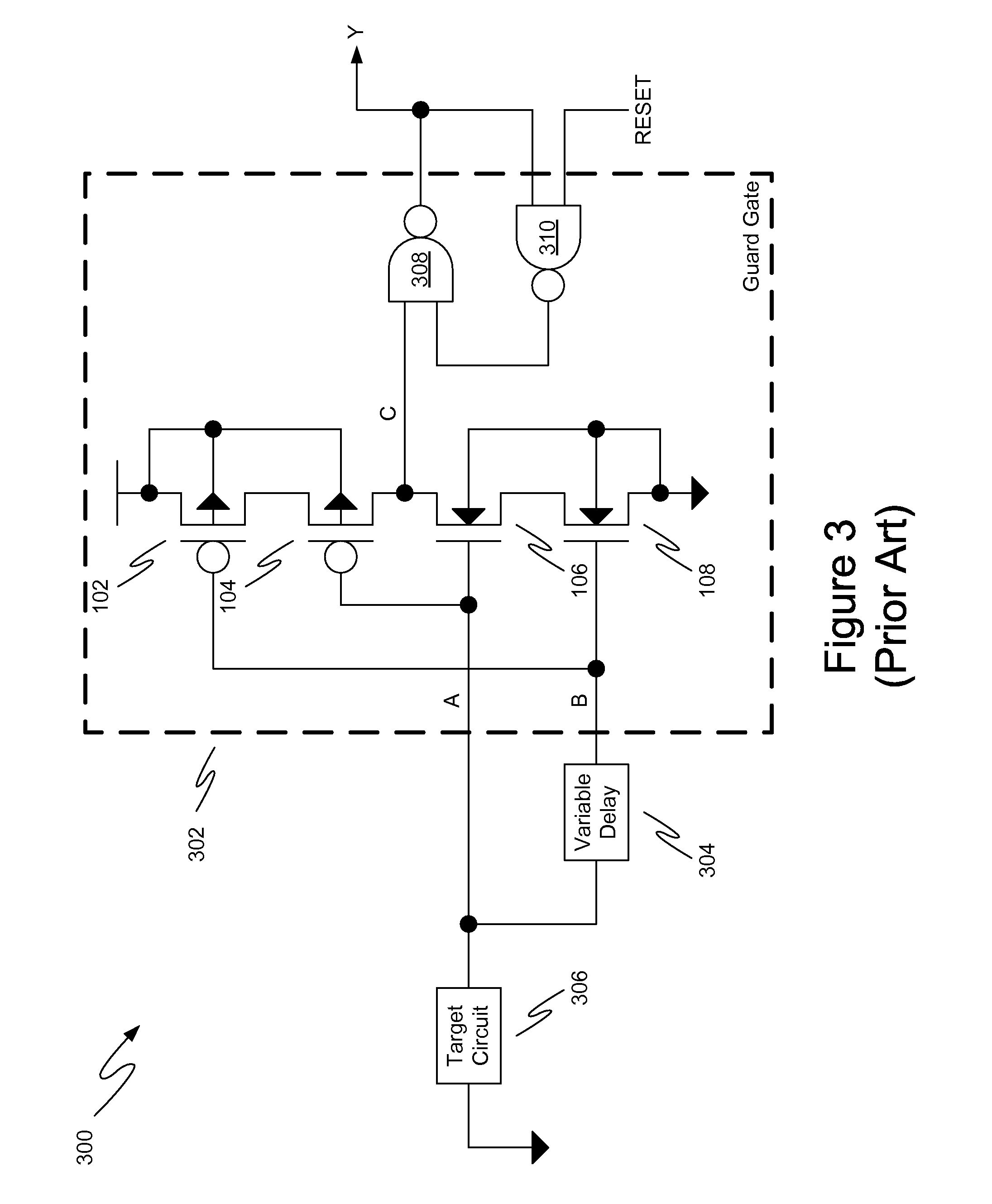
Methods and circuitry for reconfigurable SEU/SET tolerance
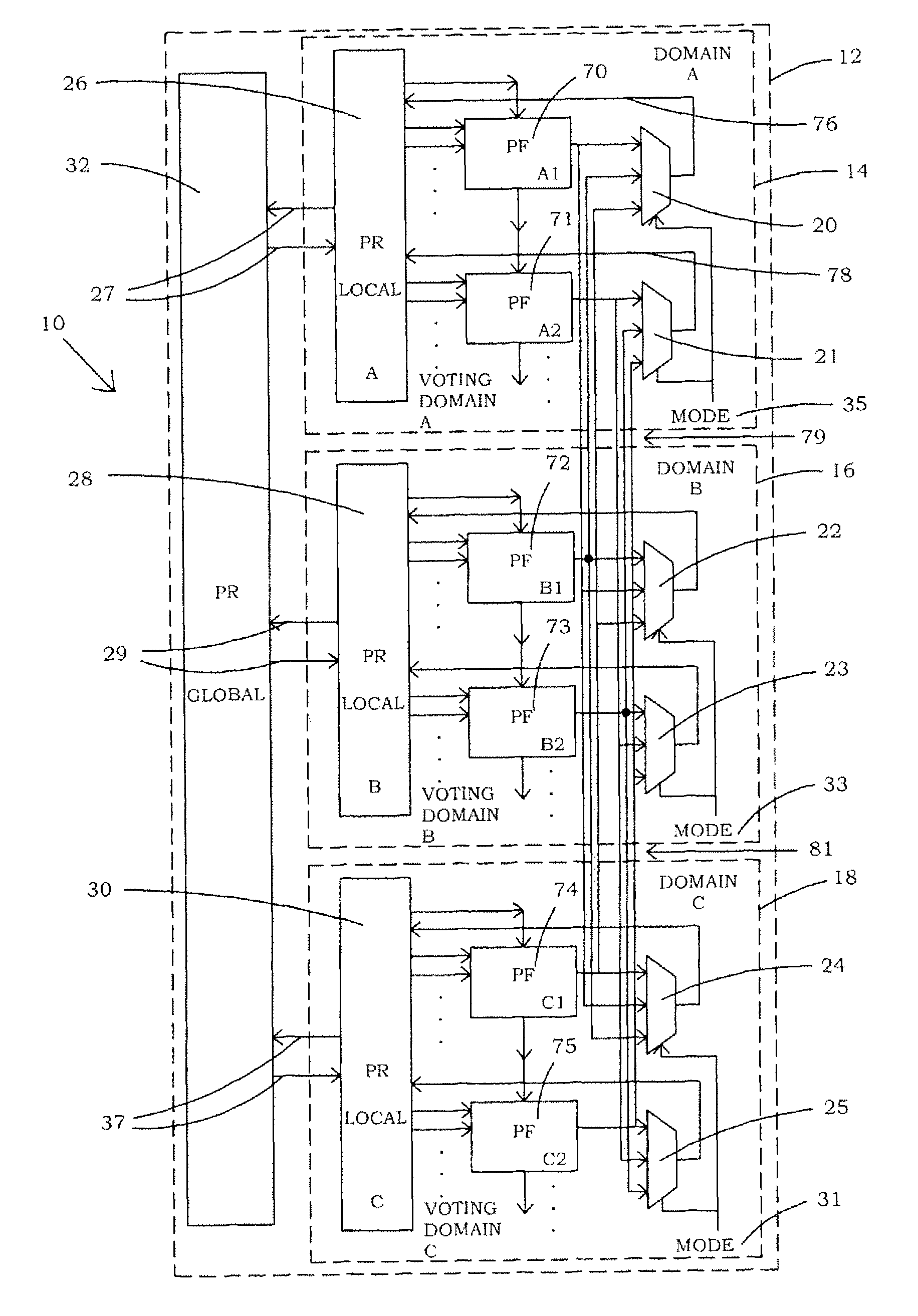
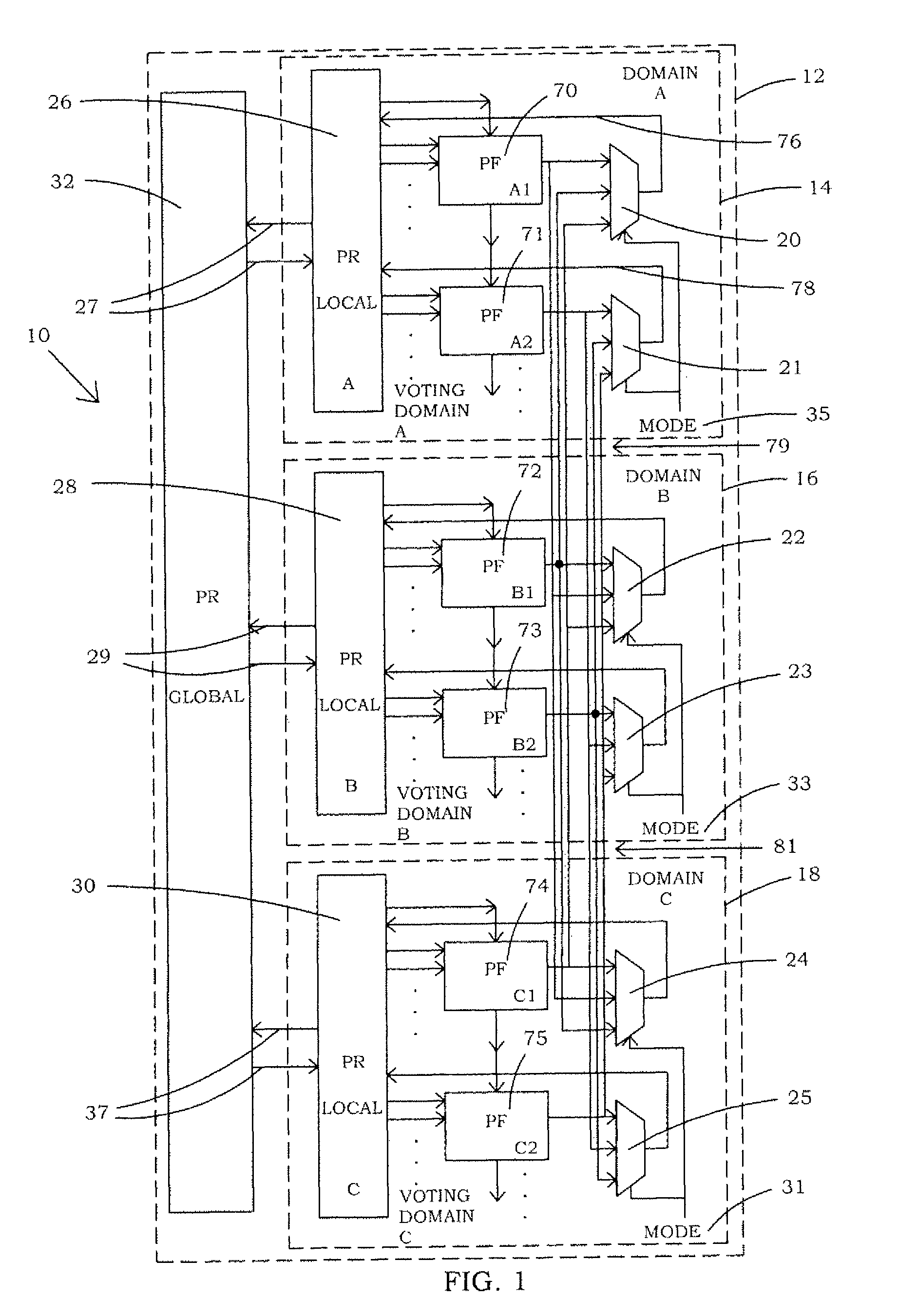
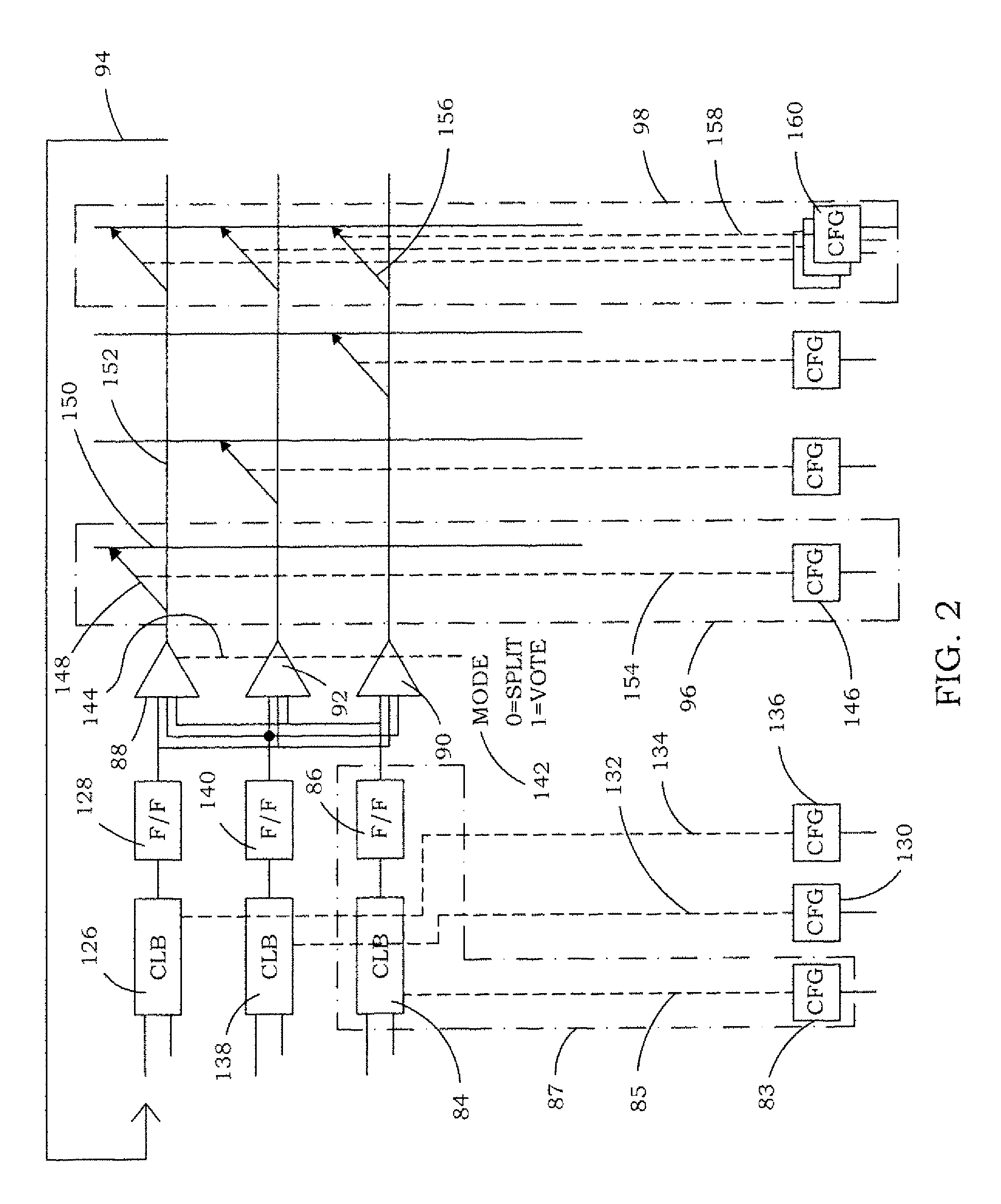
InactiveUS7859292B1Large capacityQuicklyMajority/minority circuitsWave amplification devicesComputer scienceMajority voter
Owner:NASA
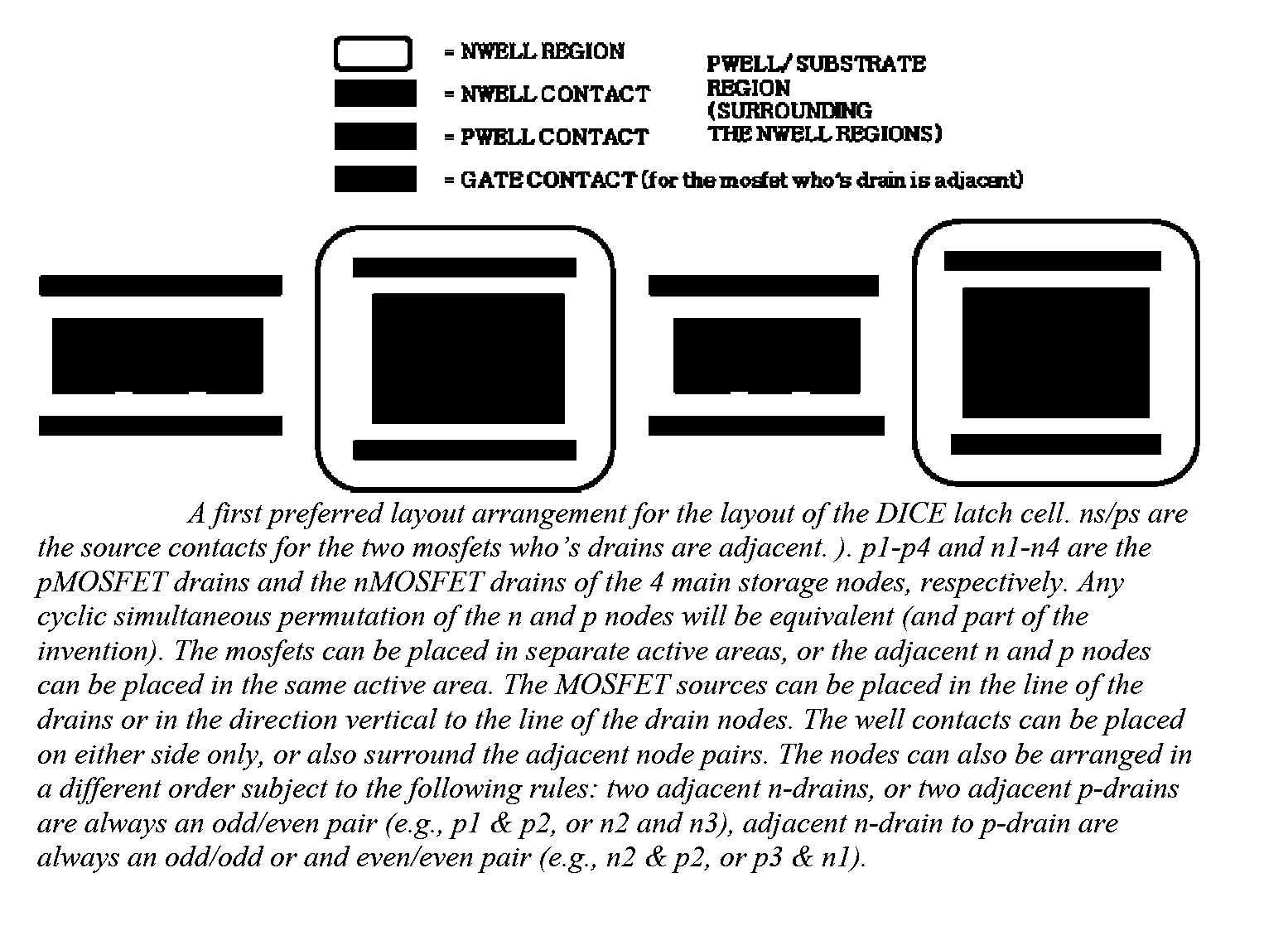
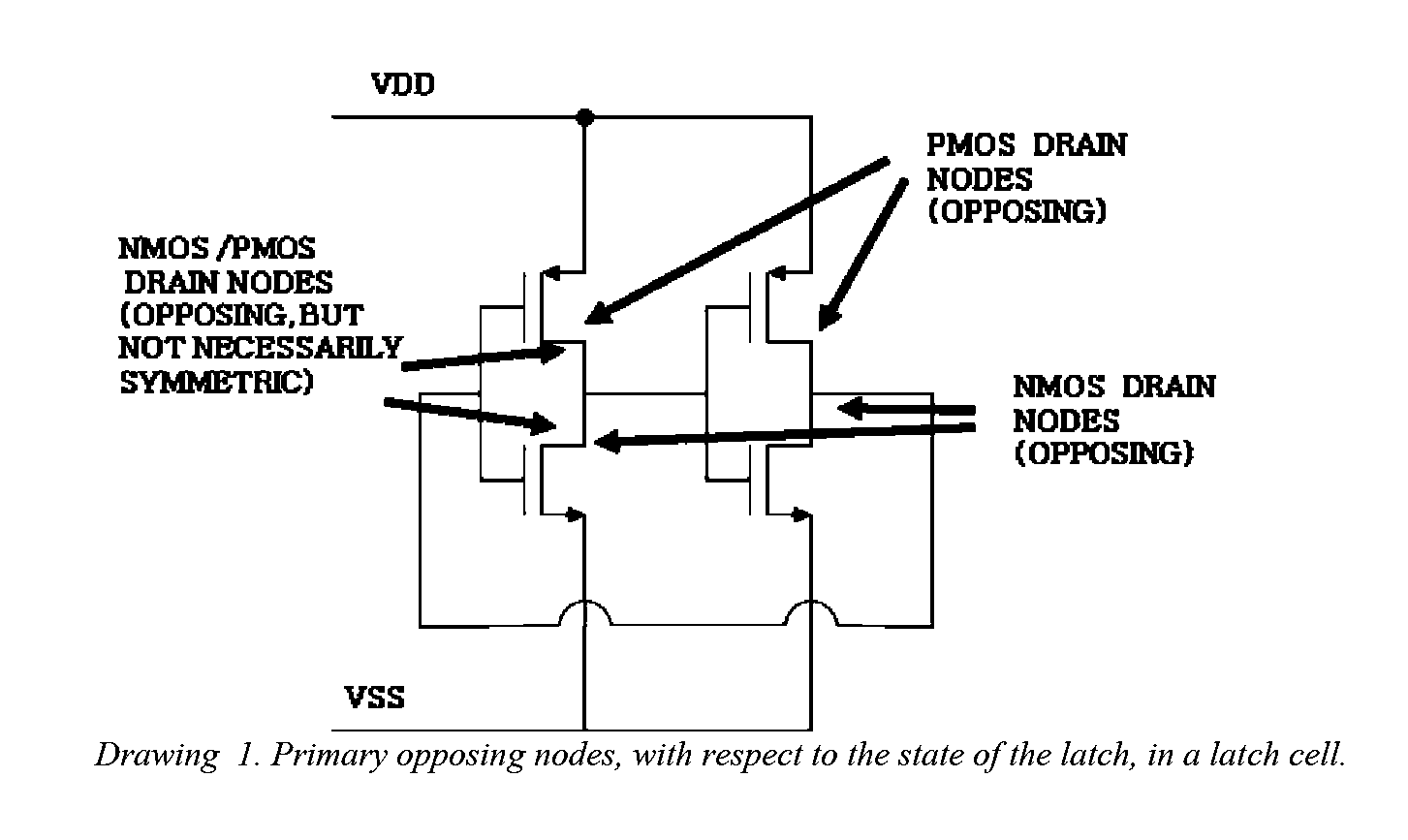
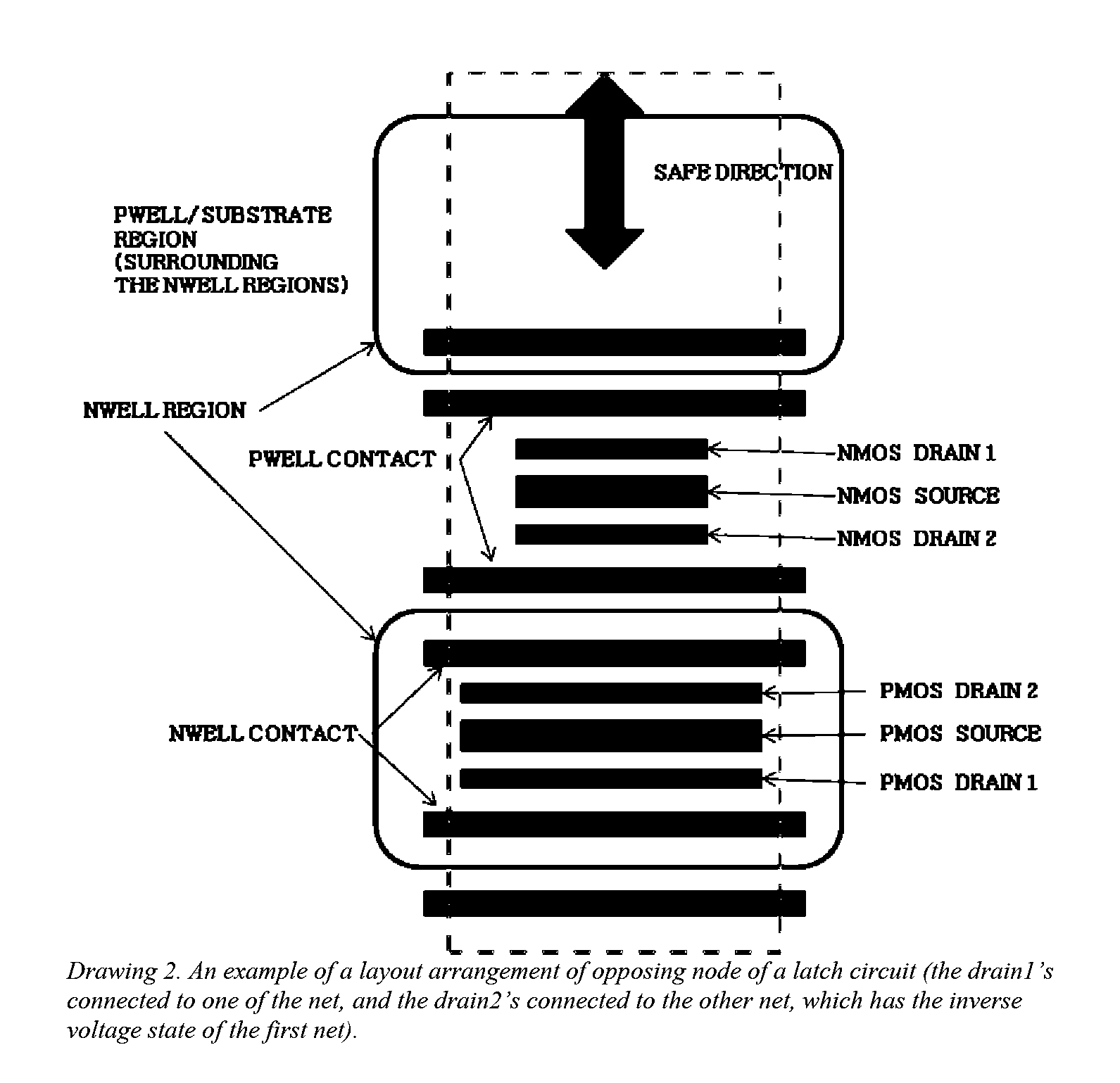
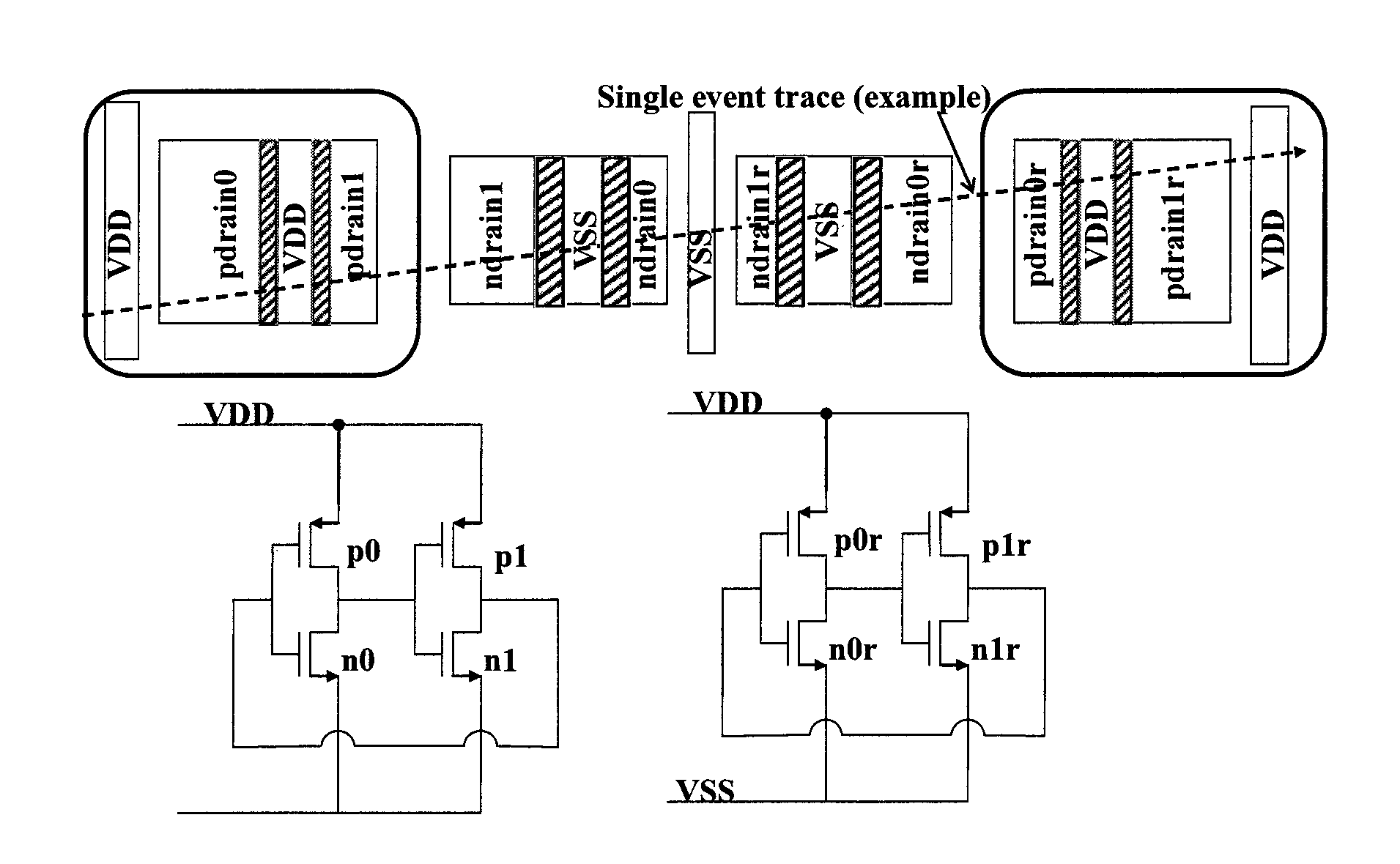
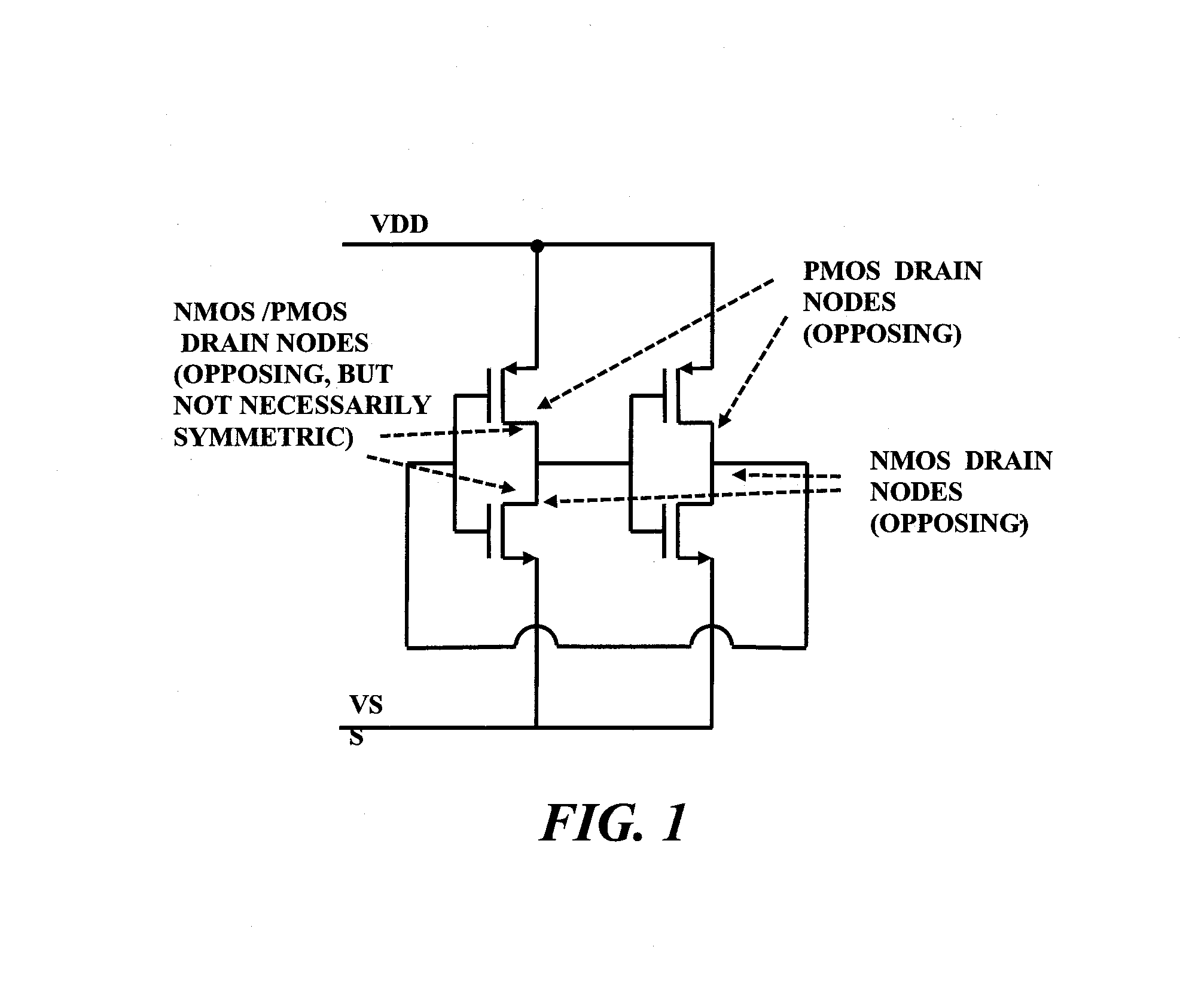
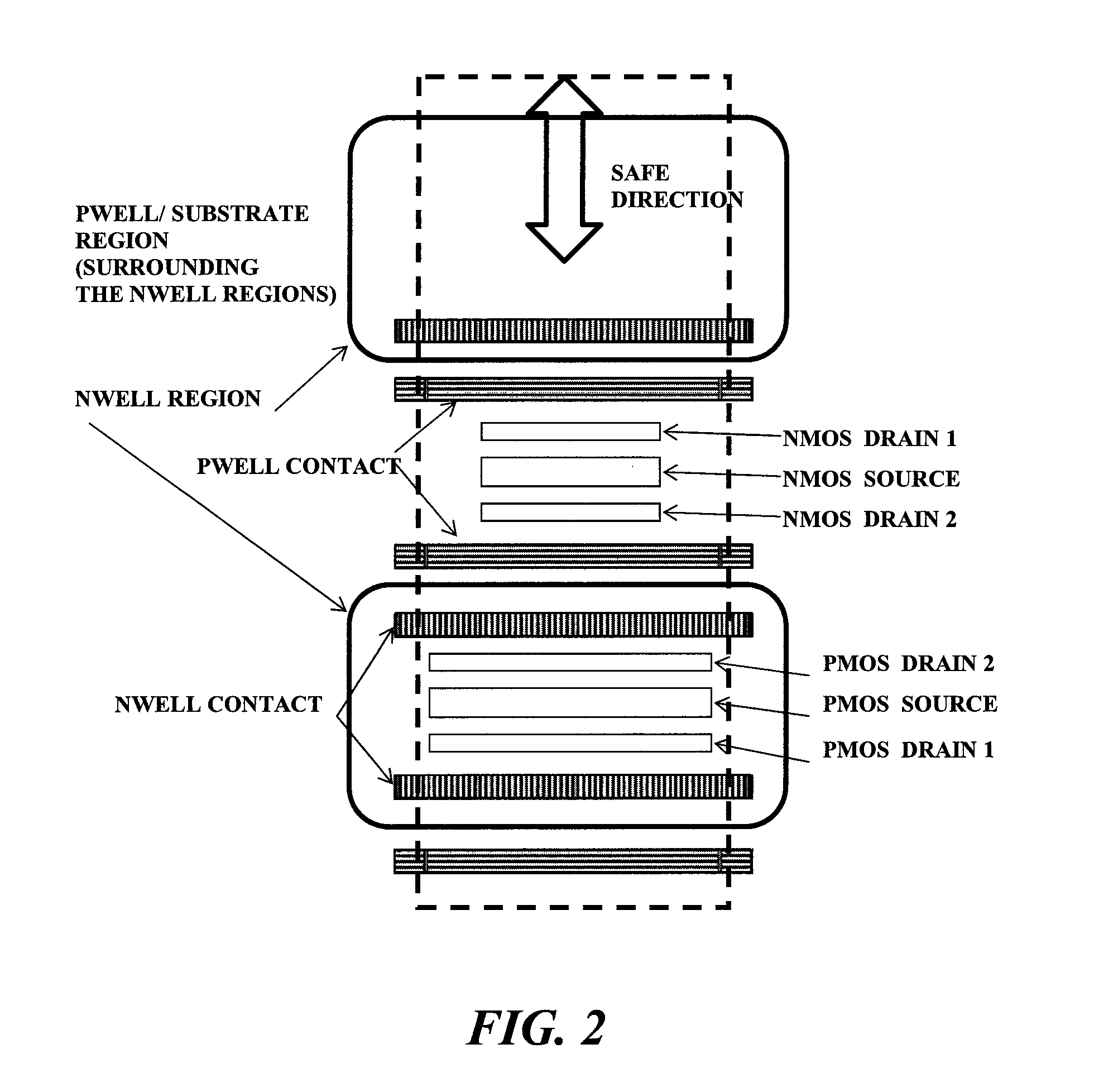
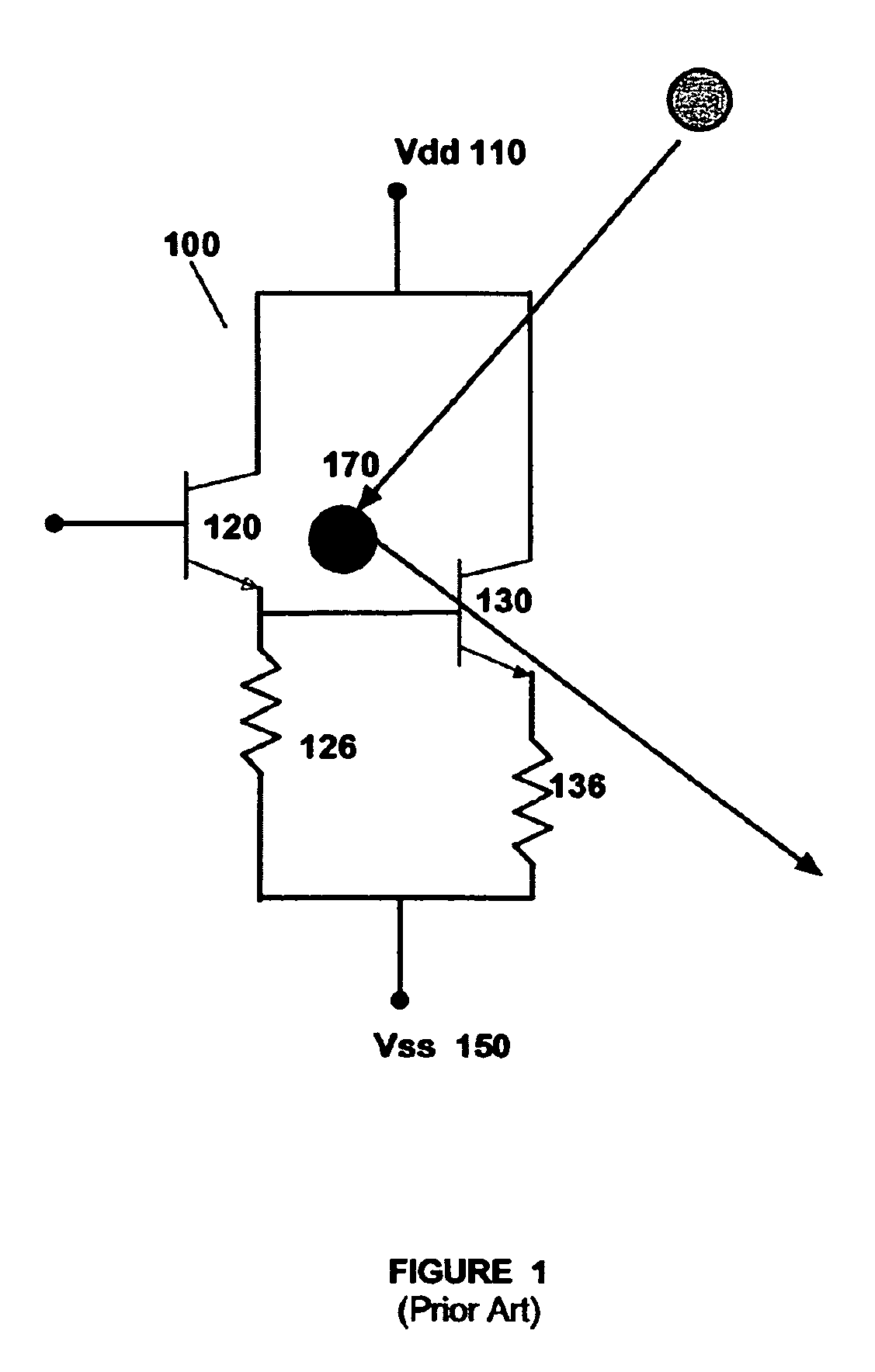
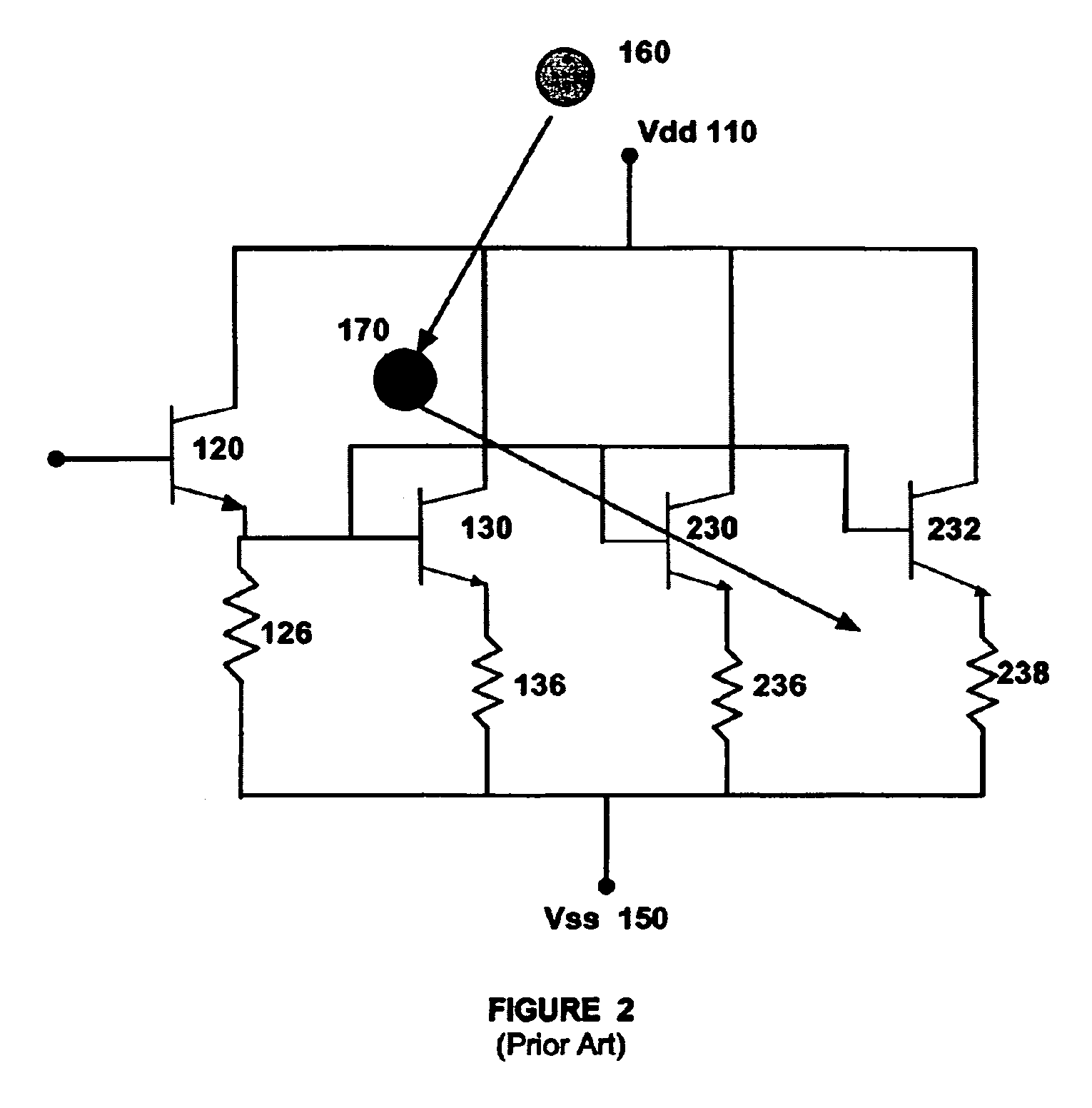
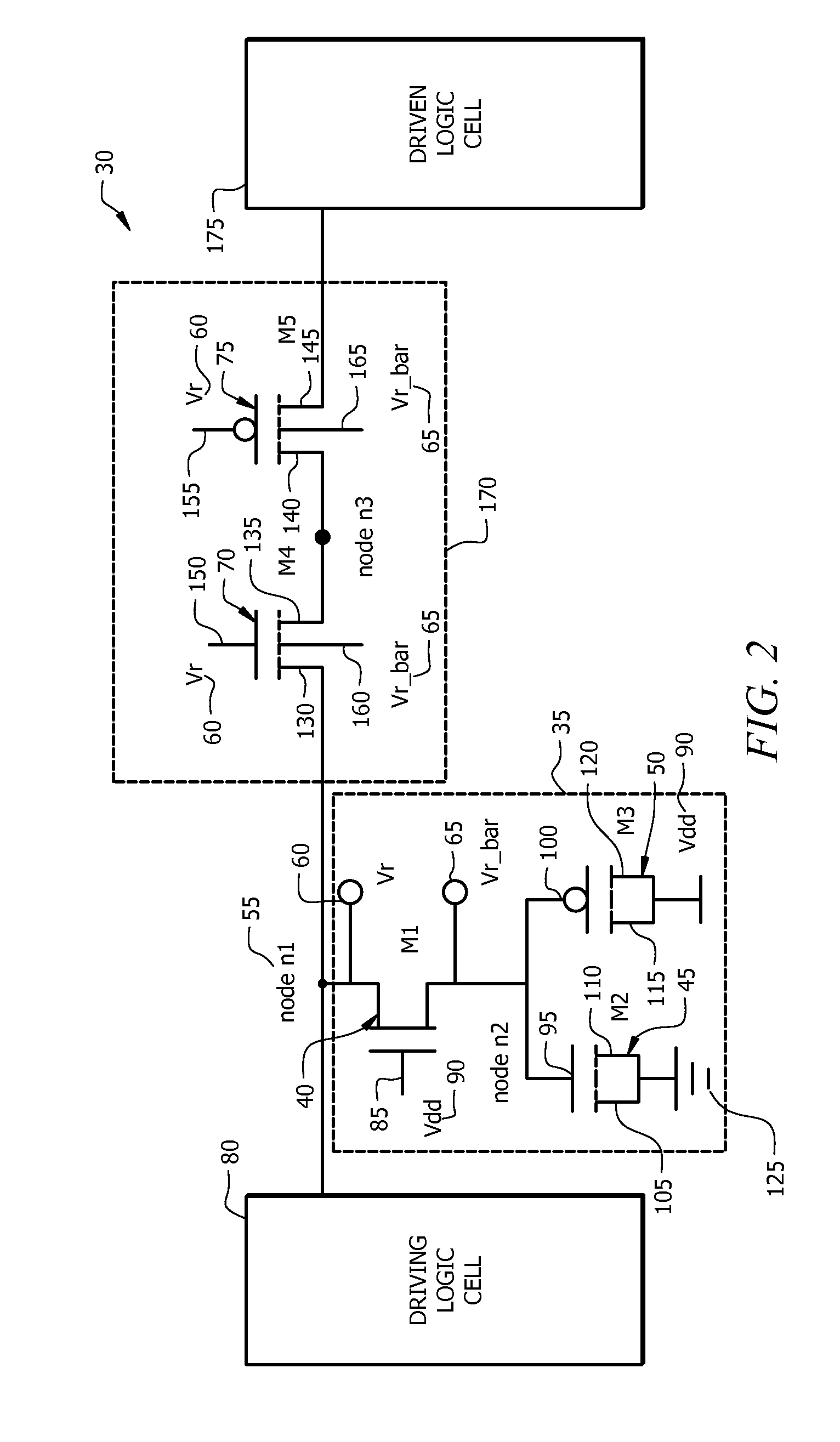
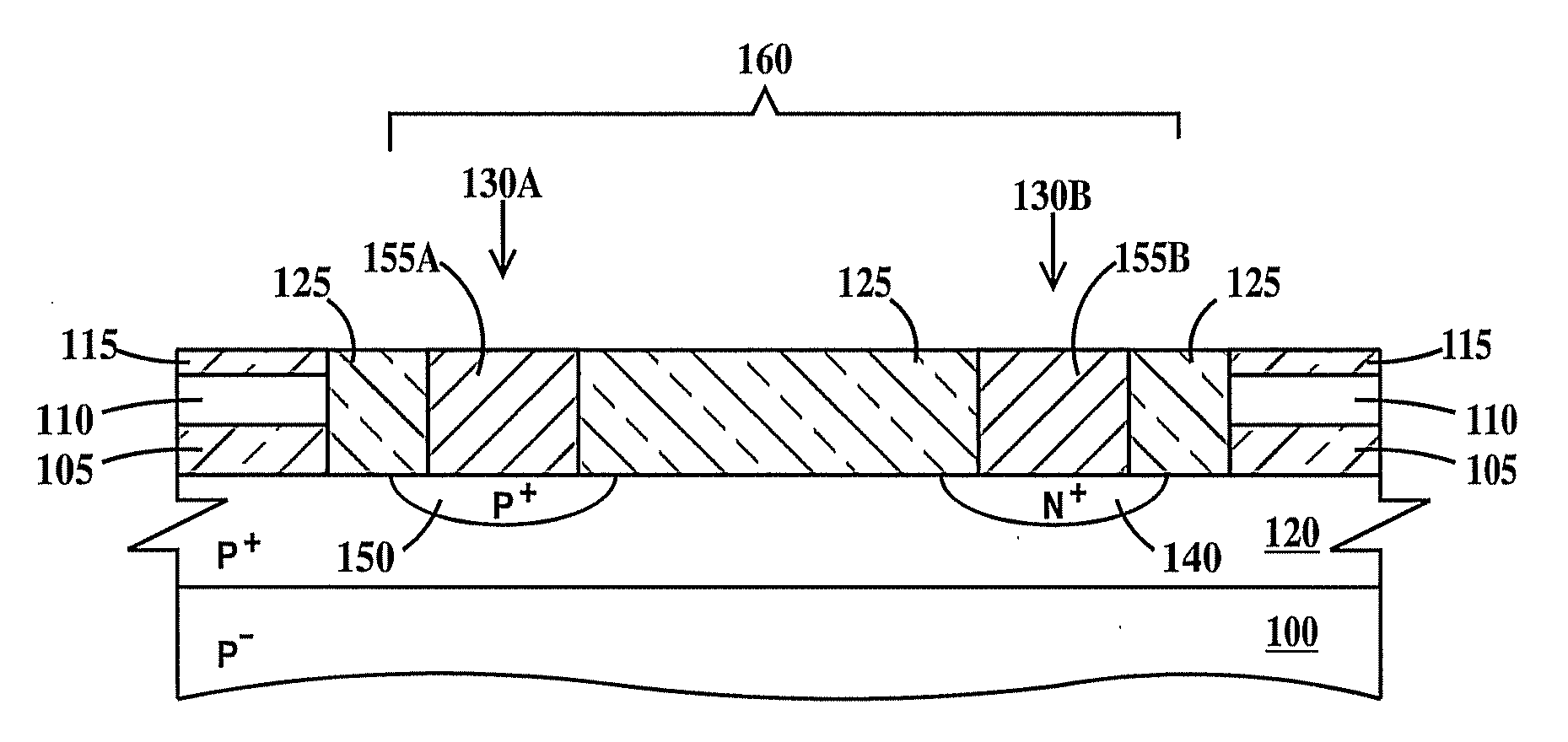
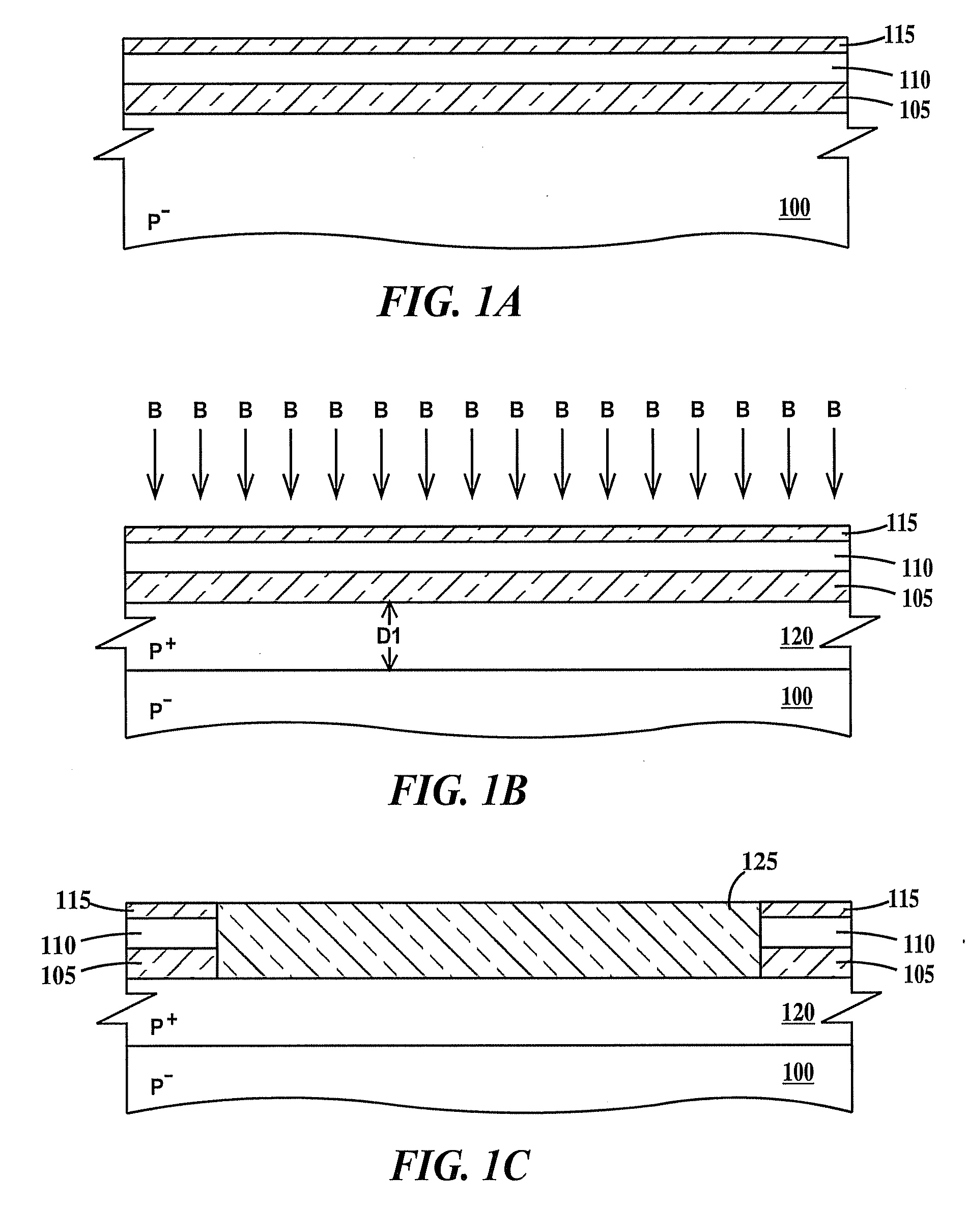
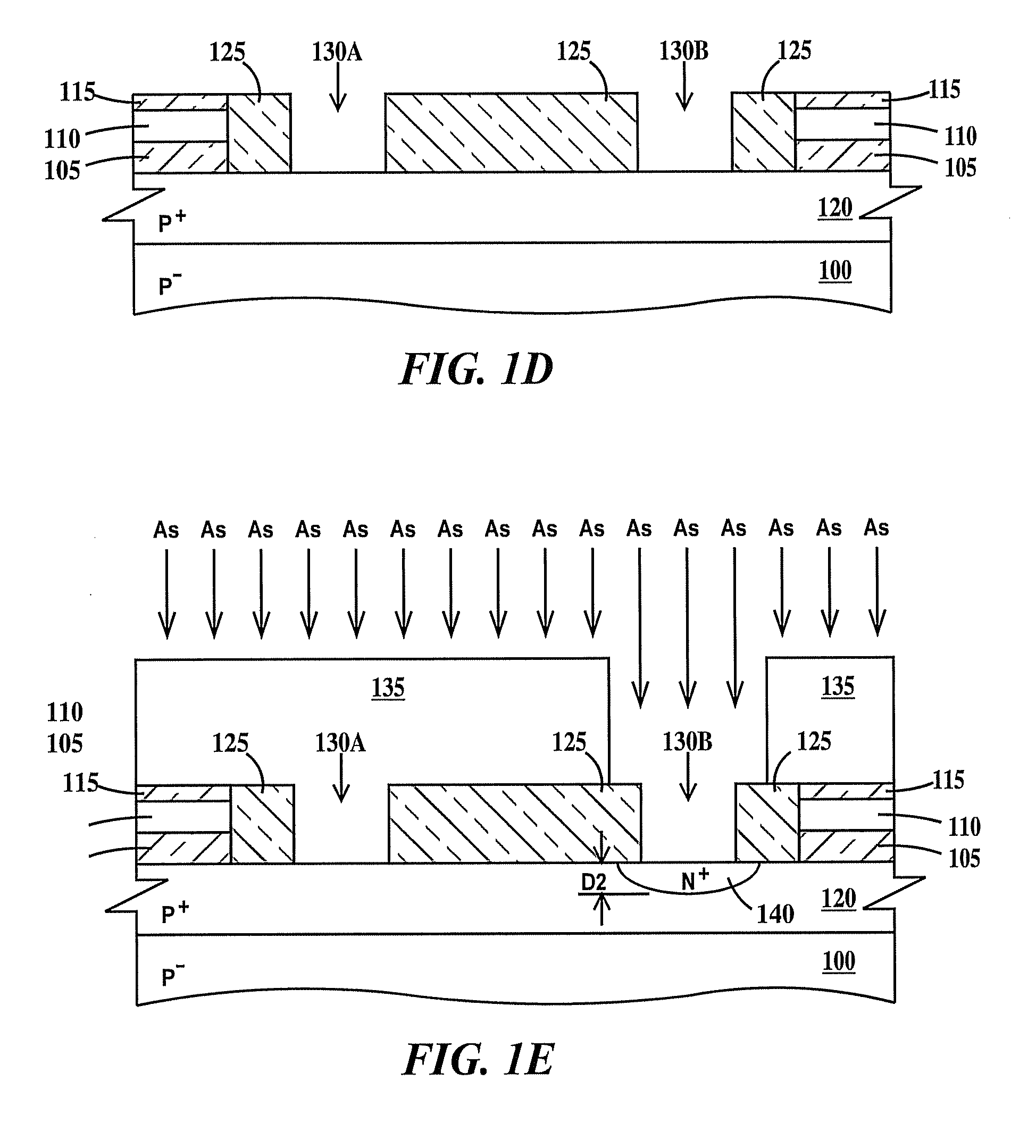
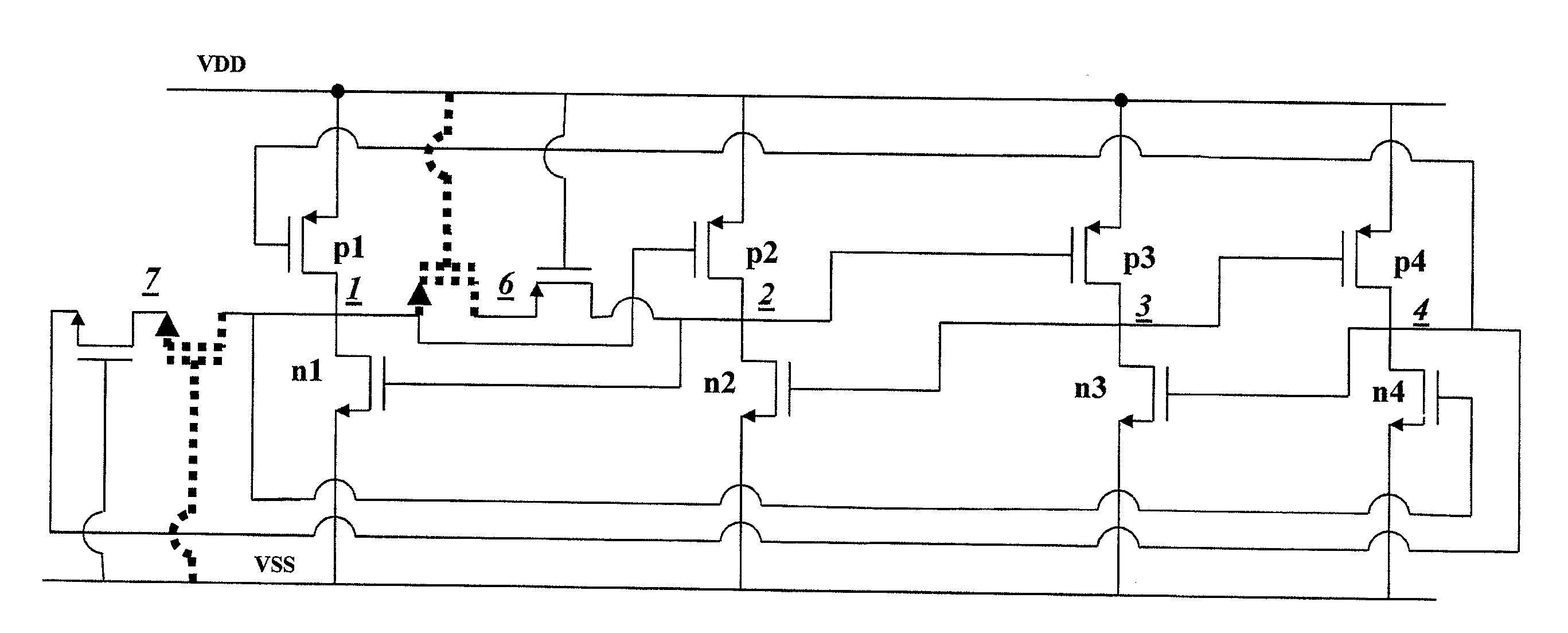
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
InactiveUS20090184733A1Protected against soft errorReduce the impactLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSolid-state devicesModem deviceElectron
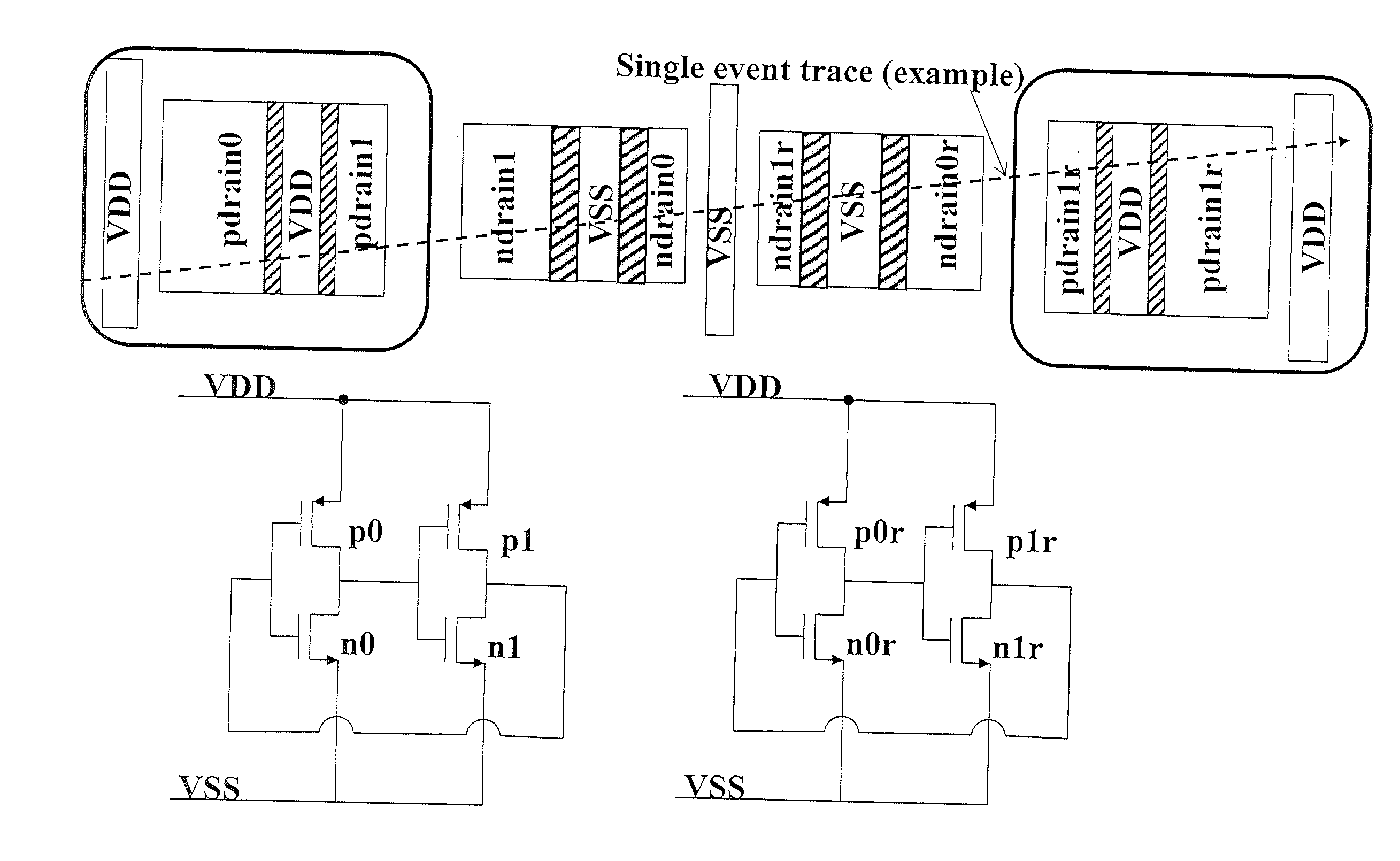
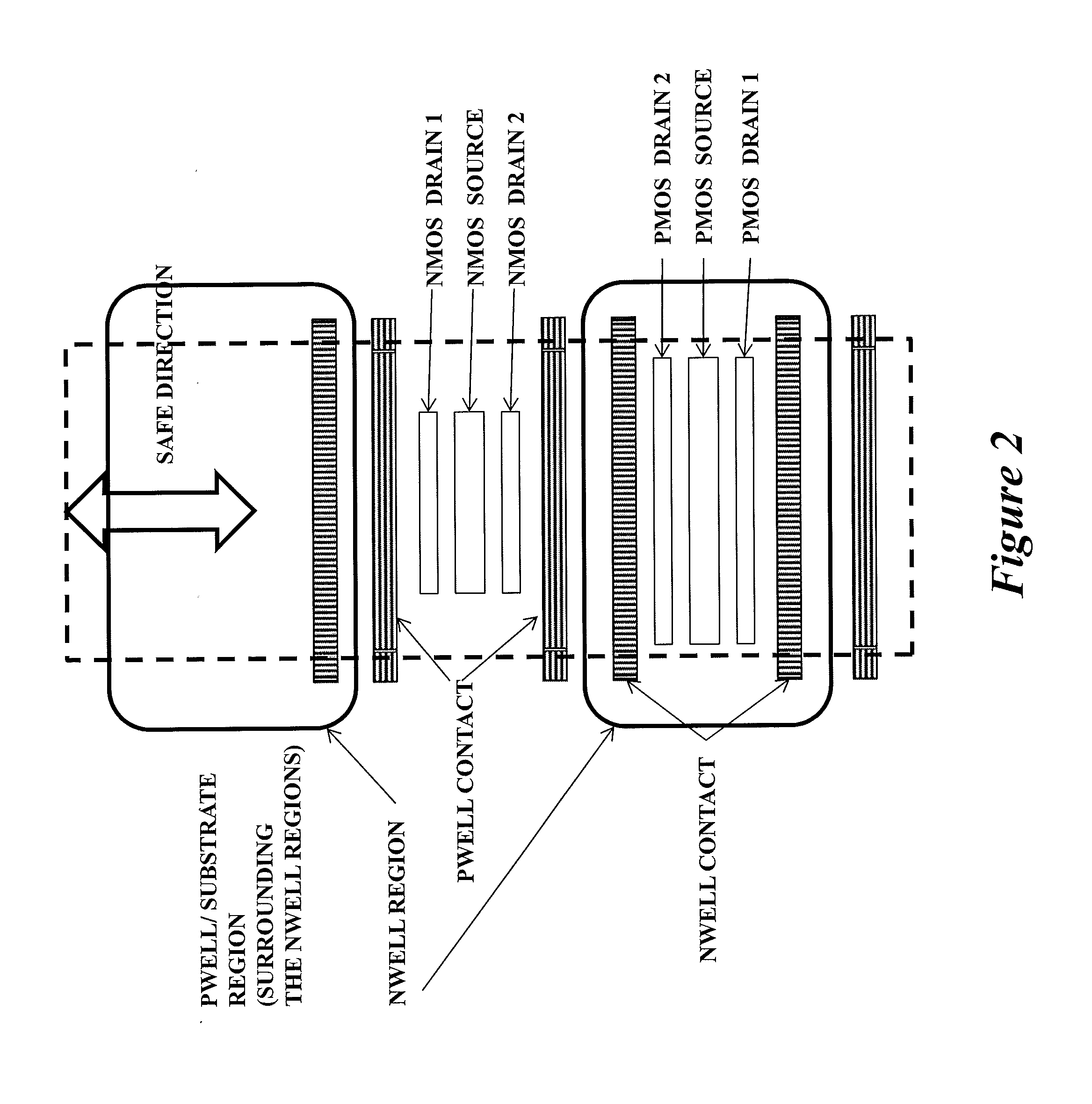
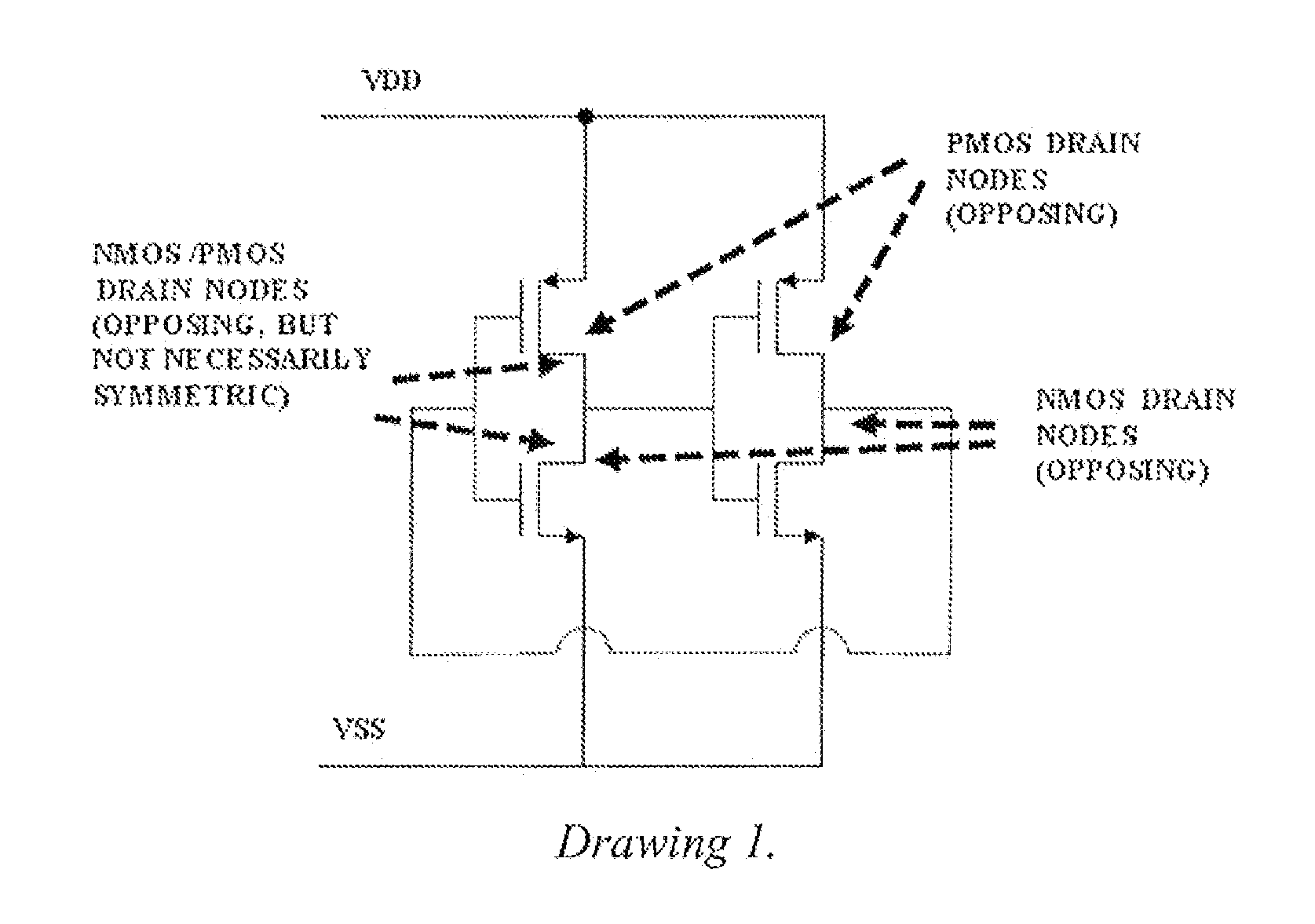
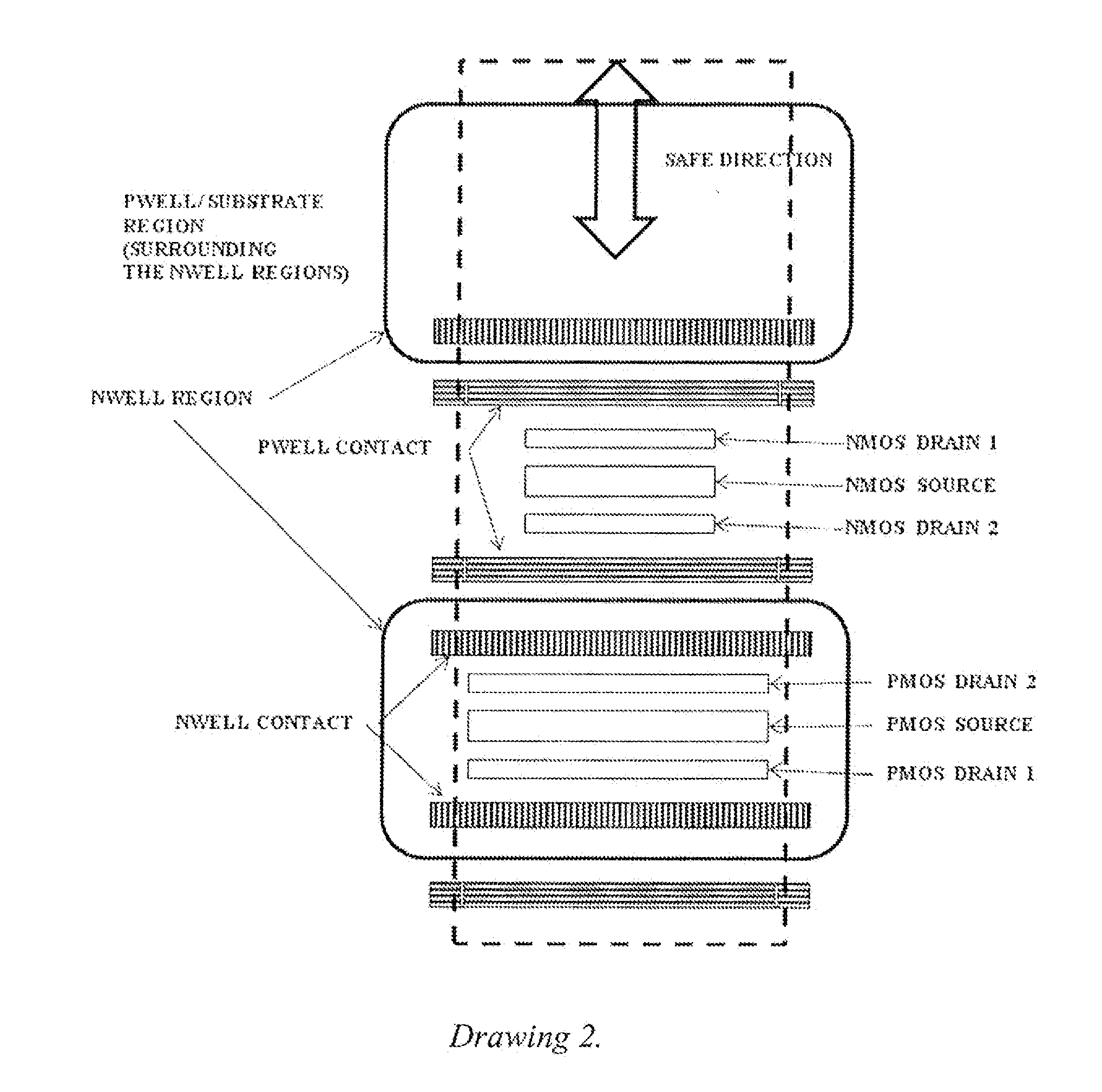
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect logic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, with layout, which are protected against soft errors. In particular, the method protects against cases where multiple nodes in circuit are affected by a single event. These events lead to multiple errors in the circuit, and while several methods exist to deal with single node errors, multiple node errors are very hard to deal with using any currently existing protection methods. The method is particularly useful for CMOS based logic circuits in modem technologies (≦90 nm), where the occurrence of multiple node pulses becomes high (due to the high integration level). It uses a unique layout configuration, which makes the circuits protected against single event generated soft-errors.
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
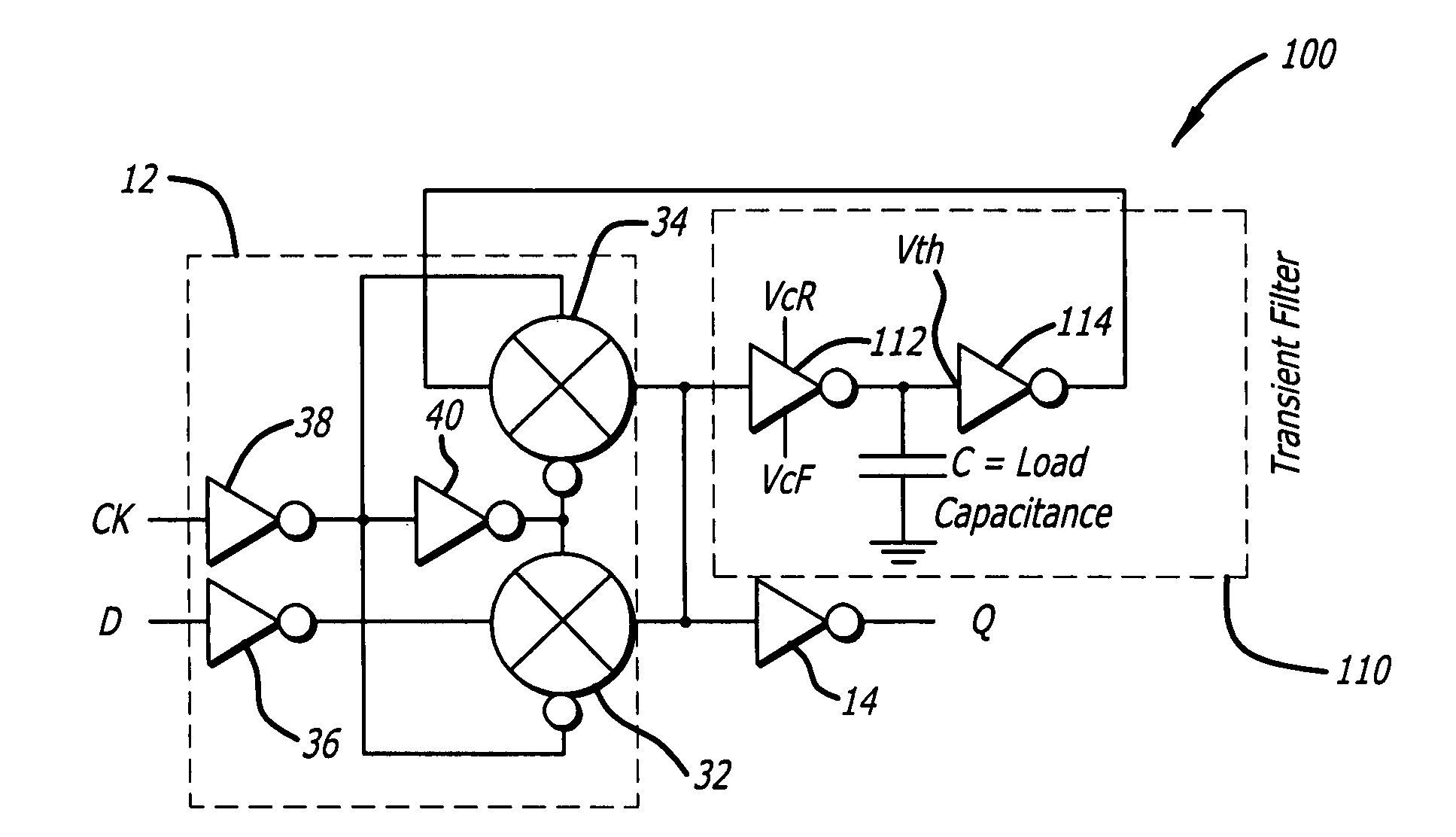
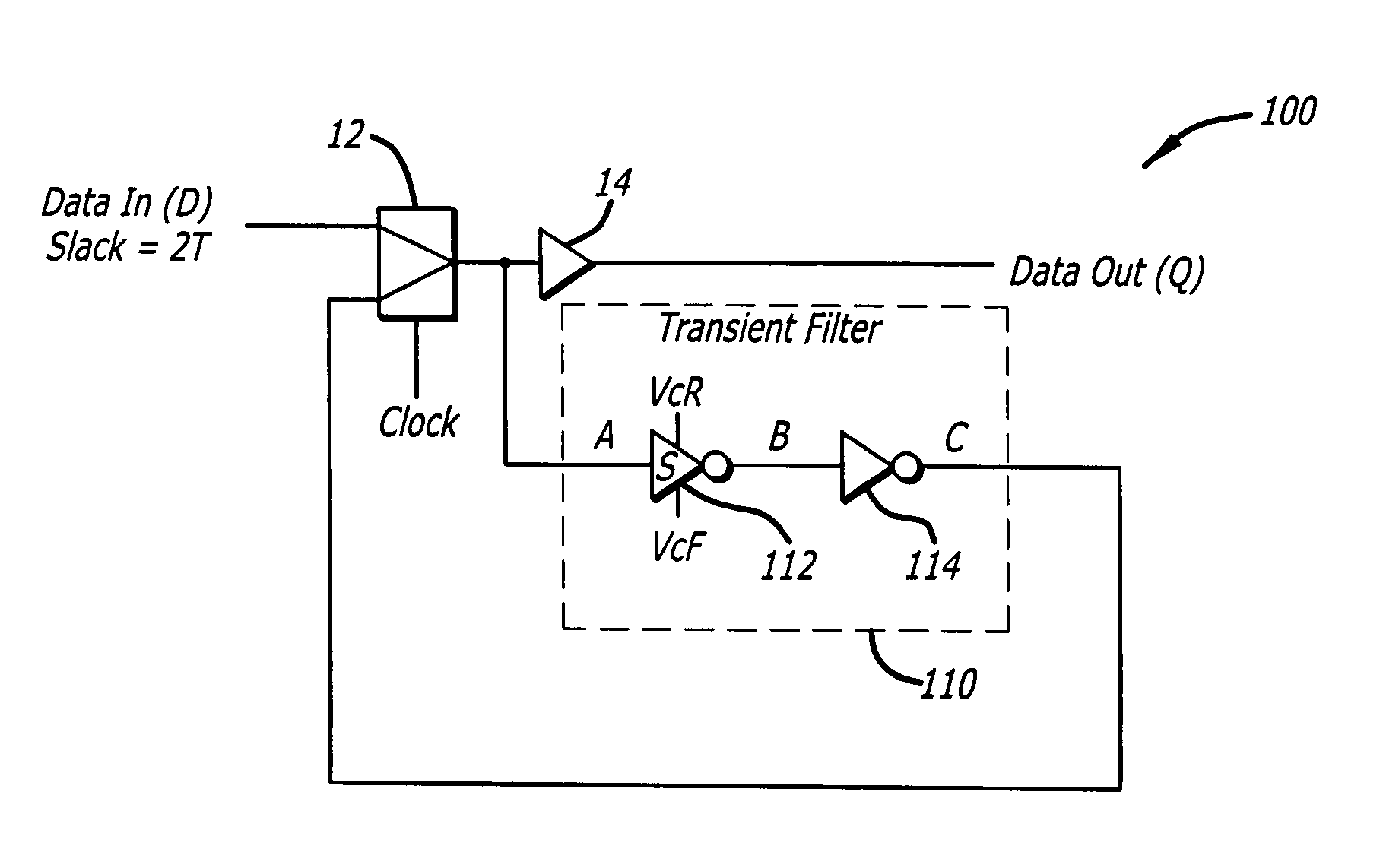
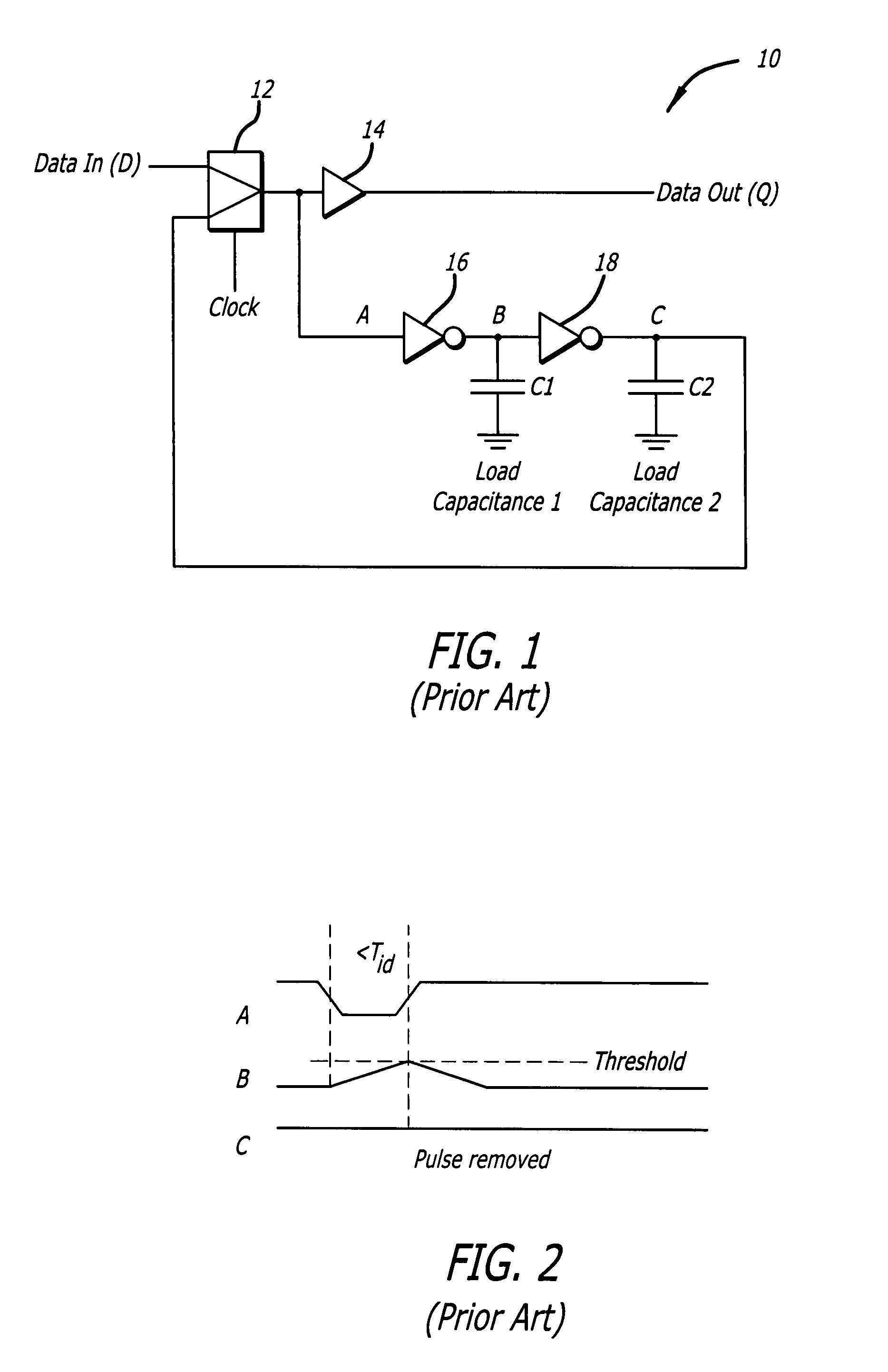
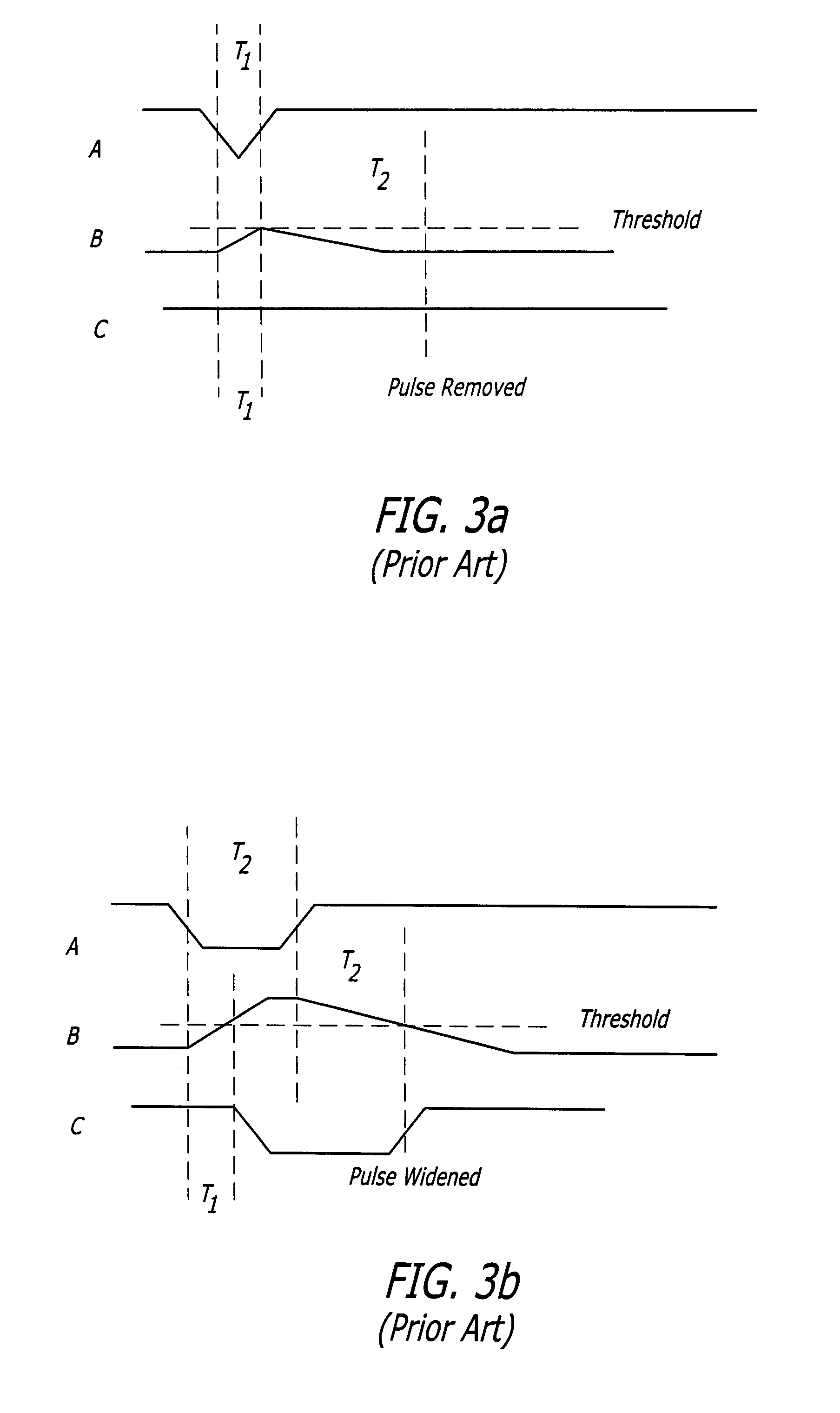
Digital circuits with adaptive resistance to single event upset
ActiveUS20090045834A1Easy to controlElectronic switchingDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationFall timeSingle event upset
A digital circuit with adaptive resistance to single event upset. A novel transient filter is placed within the feedback loop of each latch in the digital circuit to reject pulses having a width less than T, where T is the longest anticipated duration of transients. The transient filter includes a first logic element having a controllable inertial delay and a second logic element coupled to an output of the first logic element. A first controller provides a control voltage VcR to each first logic element to control a rise time of the first logic element to be equal to T. A second controller provides a control voltage VcF to each first logic element to control a fall time of the first logic element to be equal to T.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Single event transient mitigation and measurement in integrated circuits
ActiveUS8191021B2Fail-safe circuitsDetecting faulty computer hardwareIntegrated circuit layoutComputer science
A method for single event transient filtering in an integrated circuit device is described. The device comprises three sequential elements, each having a data input and a data output with each of the three data outputs coupled to one of three inputs of a voting gate. The method comprises generating first and second nominally equivalent logic signals in first and second SET domains, converting the first and second nominally equivalent logic signals into first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels, and transmitting the first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels to the data inputs of the first, second and third sequential elements. Provision is made for applying the method to logic designs implemented in programmable logic integrated circuit devices.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Methods and circuitry for reconfigurable seu/set tolerance
InactiveUS20110012638A1Large capacityQuicklyMajority/minority circuitsWave amplification devicesReconfigurable antennaComputer science
Owner:NASA
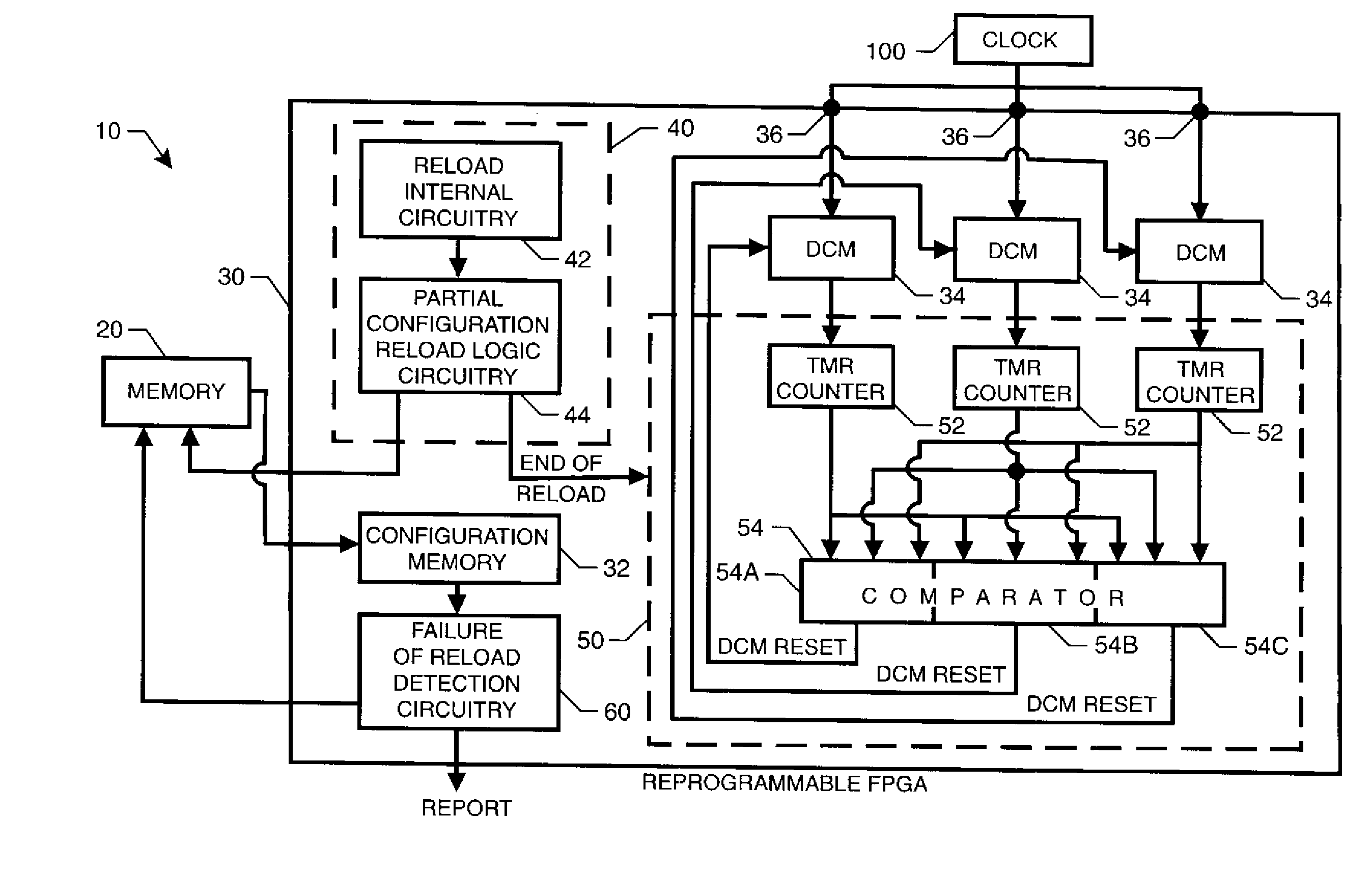
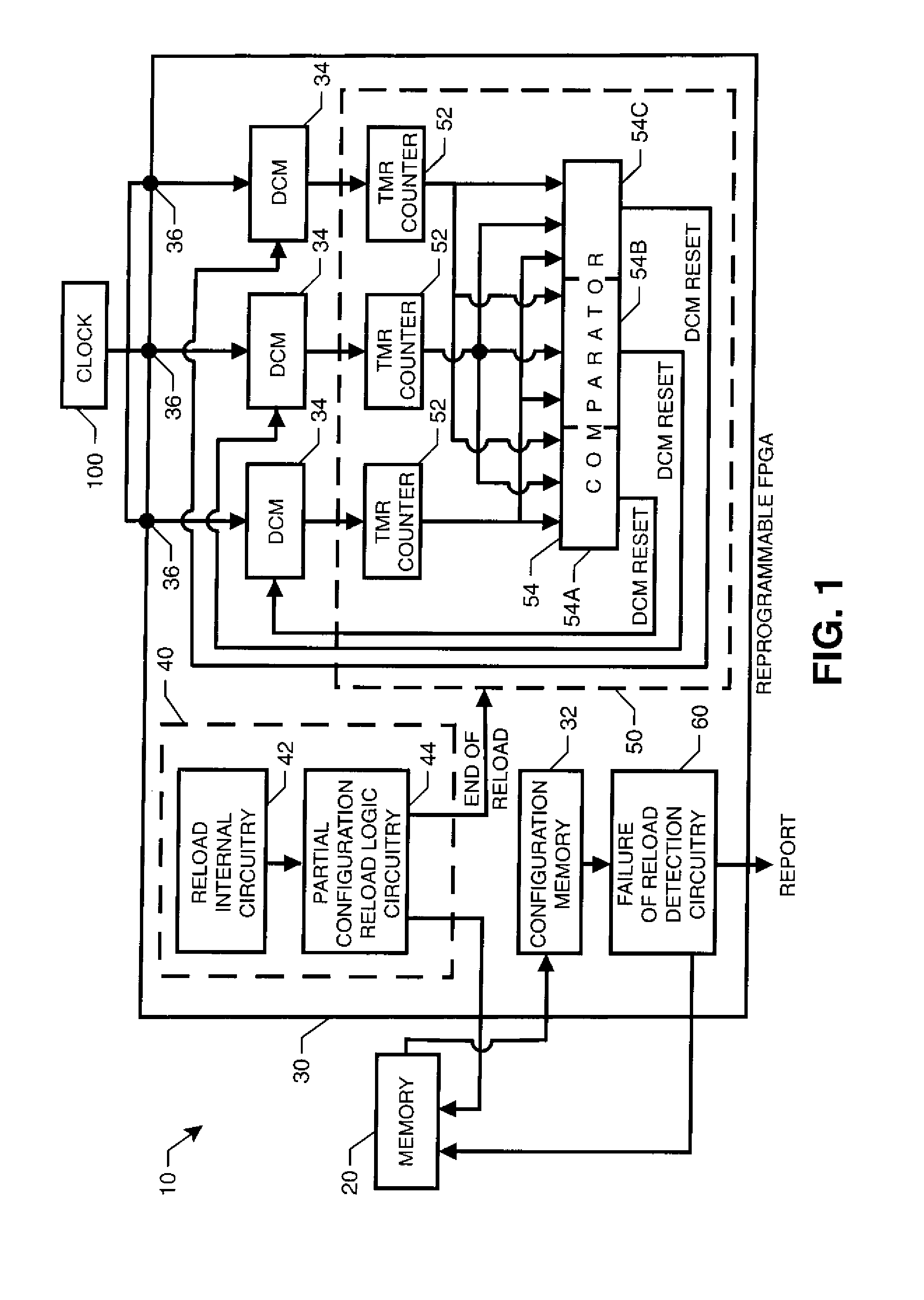
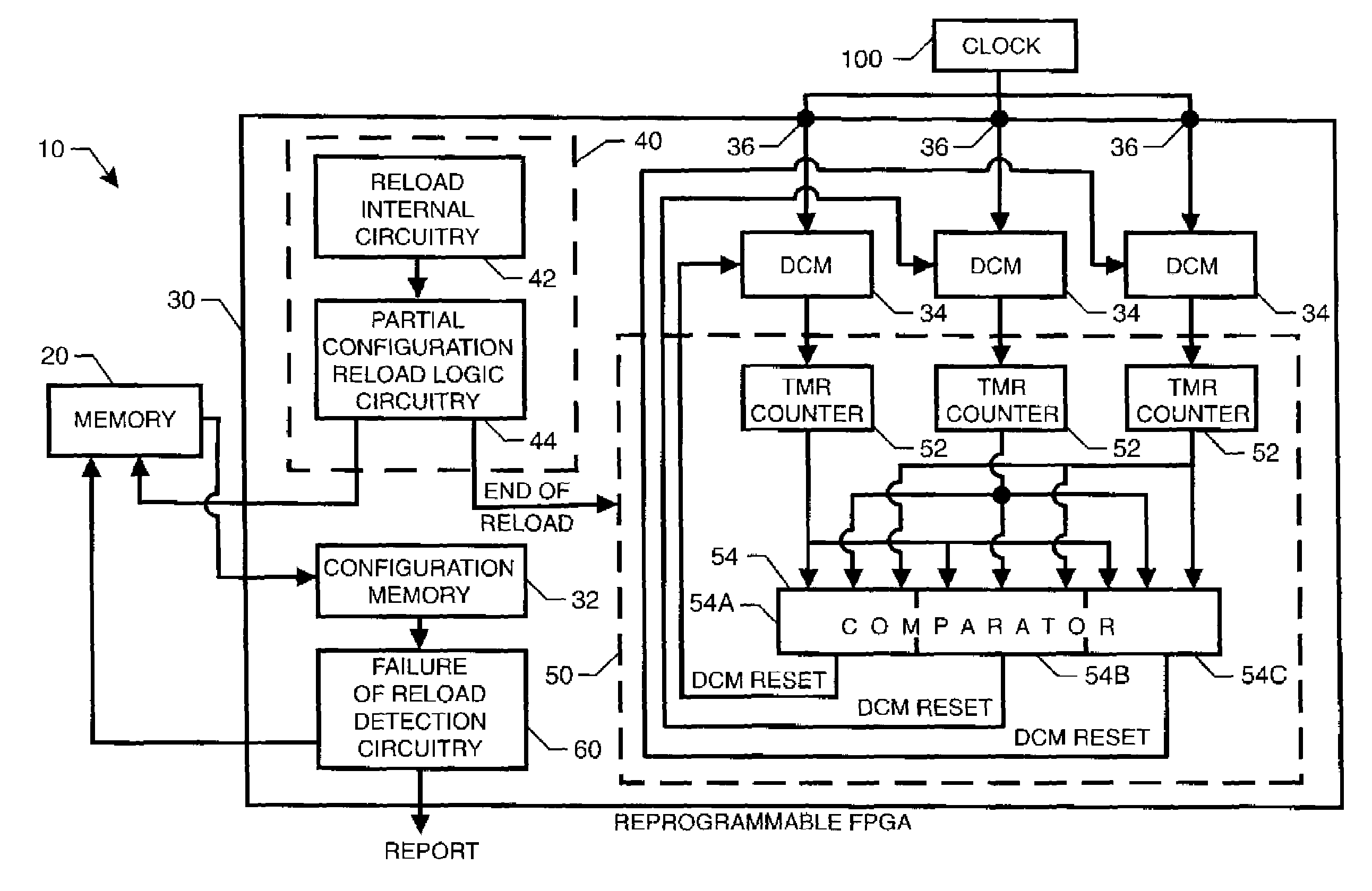
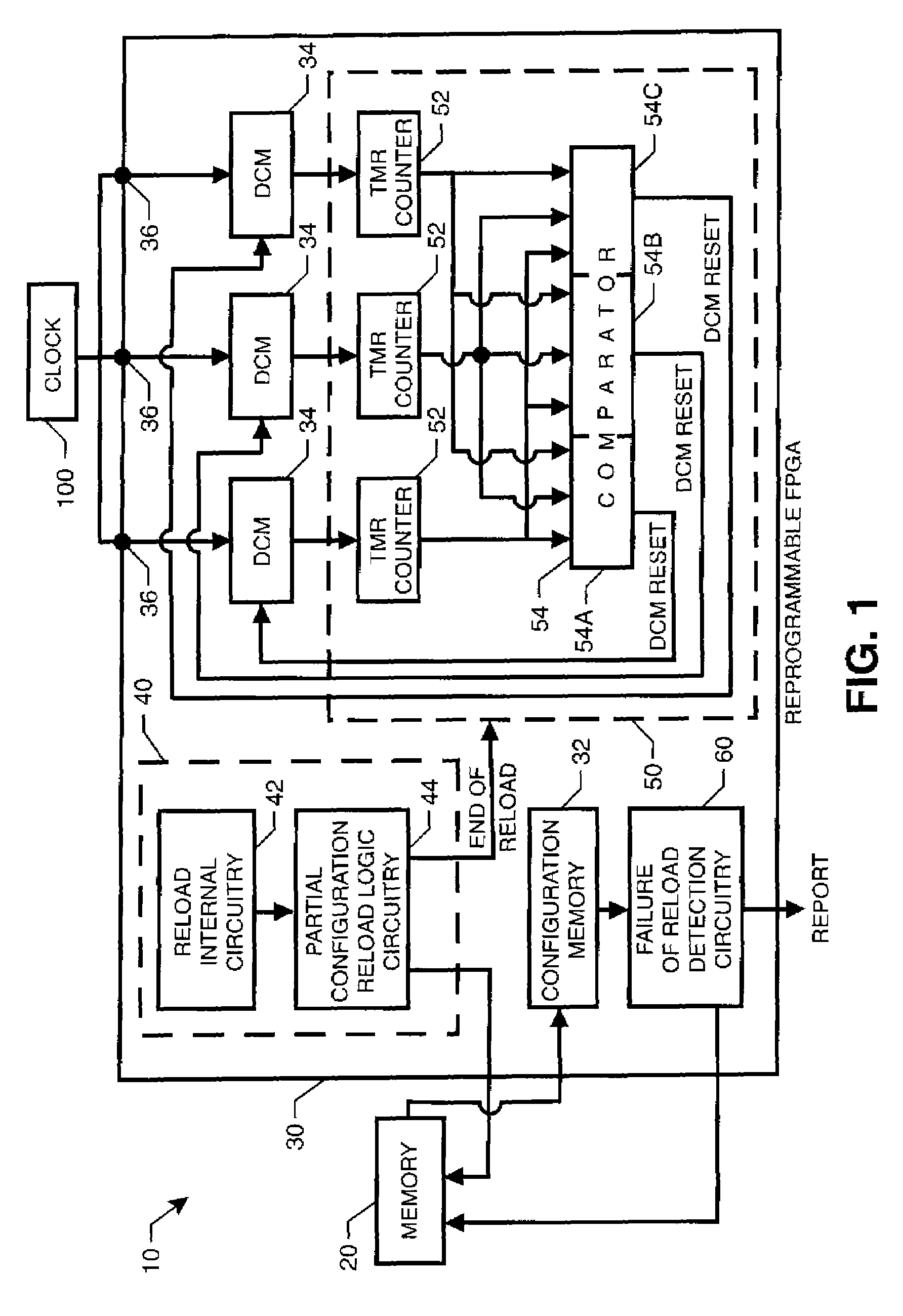
Reprogrammable field programmable gate array with integrated system for mitigating effects of single event upsets
InactiveUS20070176627A1Reduce the impactReduce impactError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsDigital clockDigital clock manager
An integrated system mitigates the effects of a single event upset (SEU) on a reprogrammable field programmable gate array (RFPGA). The system includes (i) a RFPGA having an internal configuration memory, and (ii) a memory for storing a configuration associated with the RFPGA. Logic circuitry programmed into the RFPGA and coupled to the memory reloads a portion of the configuration from the memory into the RFPGA's internal configuration memory at predetermined times. Additional SEU mitigation can be provided by logic circuitry on the RFPGA that monitors and maintains synchronized operation of the RFPGA's digital clock managers.
Owner:NASA
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
ActiveUS8566770B2Reduce impactSoft errorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionFail-safe circuitsCMOSLogic cell
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
Digital circuits with adaptive resistance to single event upset
ActiveUS7795927B2Electronic switchingDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationFall timeEngineering
A digital circuit with adaptive resistance to single event upset. A novel transient filter is placed within the feedback loop of each latch in the digital circuit to reject pulses having a width less than T, where T is the longest anticipated duration of transients. The transient filter includes a first logic element having a controllable inertial delay and a second logic element coupled to an output of the first logic element. A first controller provides a control voltage VcR to each first logic element to control a rise time of the first logic element to be equal to T. A second controller provides a control voltage VcF to each first logic element to control a fall time of the first logic element to be equal to T.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
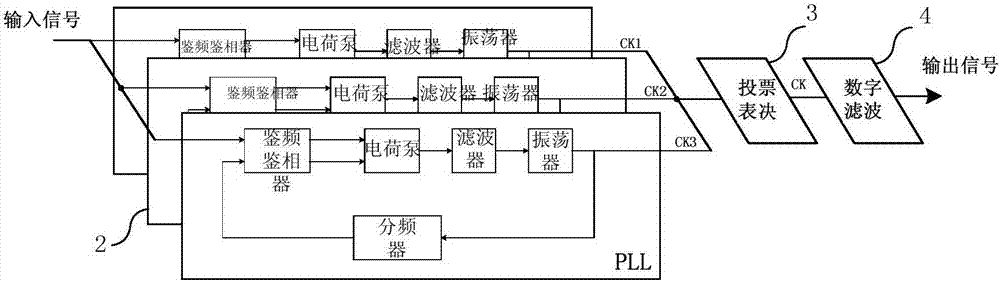
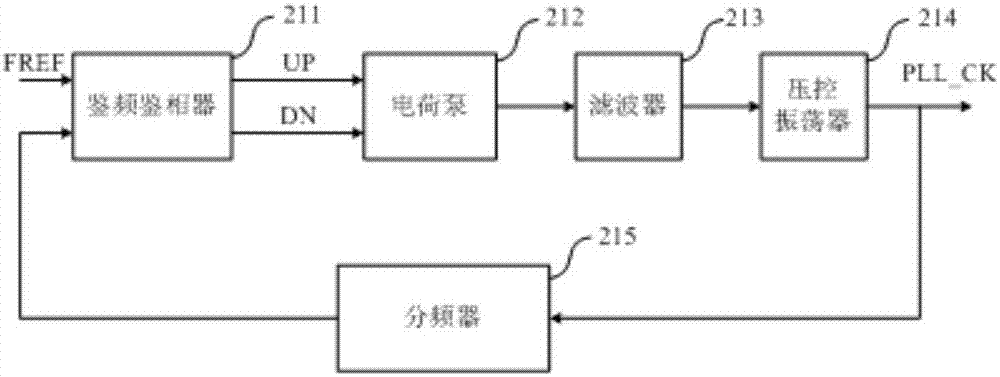
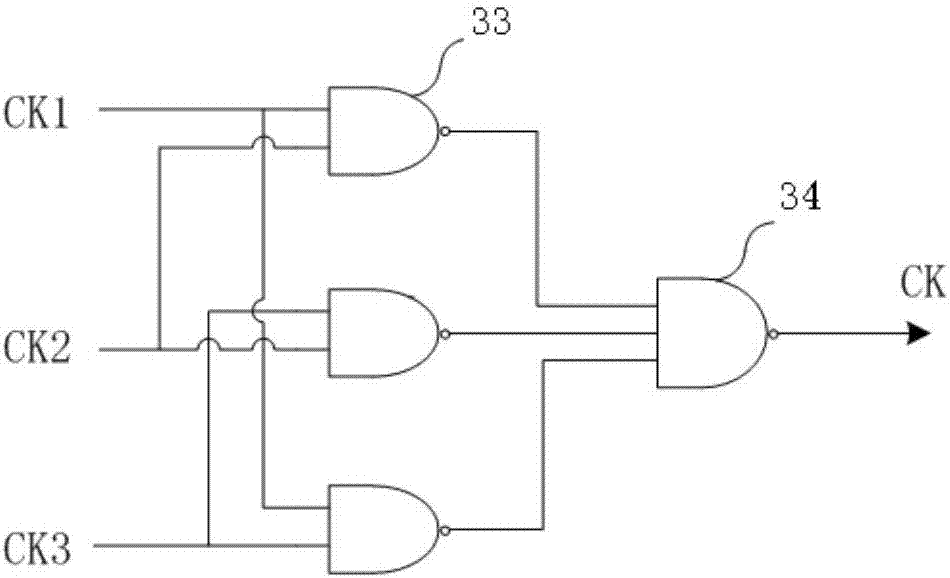
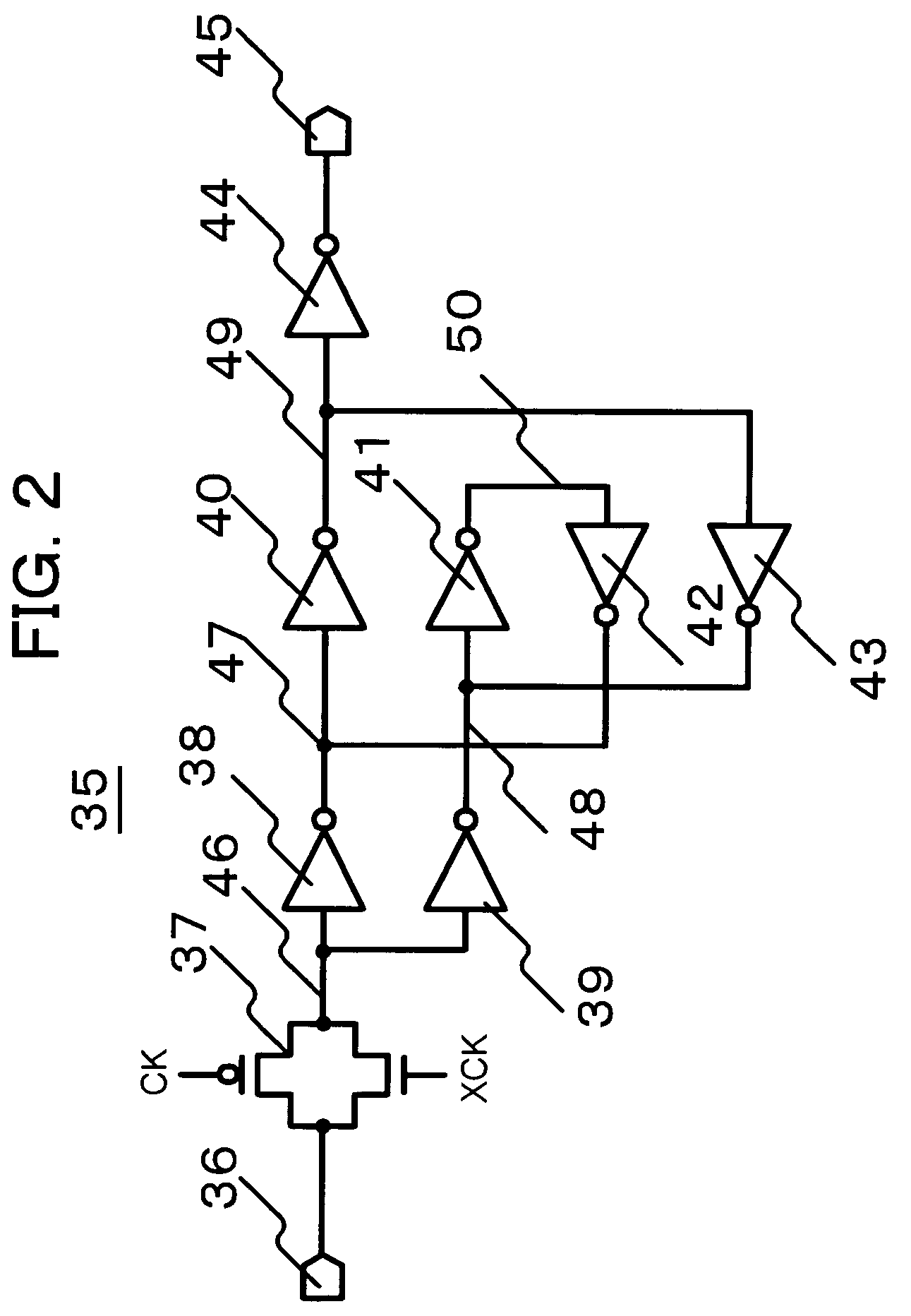
Triple-modular-redundancy anti-radiation reinforced clock generation circuit based on phase-locked loops
InactiveCN106936426AImprove immunityExcellent resistance to single event transientsPulse automatic controlRadiation hardeningTransient stateDigital filter
The invention discloses a triple-modular-redundancy anti-radiation reinforced clock generation circuit based on phase-locked loops. The circuit comprises three independent phase-locked loops in parallel connection, a voting unit and a digital filtering unit; when at least two of CK1, CK2 and CK2 are the same in level, the at least two signals CK of the same level are transmitted to the digital filtering unit via voting, the digital filtering processes the signals CK obtained by voting, and the signals are output after removing burrs if there are burrs; and the signals are output directly if there are no burrs. According to the invention, a triple-modular-redundancy structure of a phase-locked loop structure is used, final output of the system is not influenced if abnormity occurs in any one of the three phase-locked loops, immunity against single-particle transient state is high, and the immunity against single-particle transient state is higher than that of a manner that only sensitive nodes in the phase-locked loops are reinforced.
Owner:BEIJING MXTRONICS CORP +1
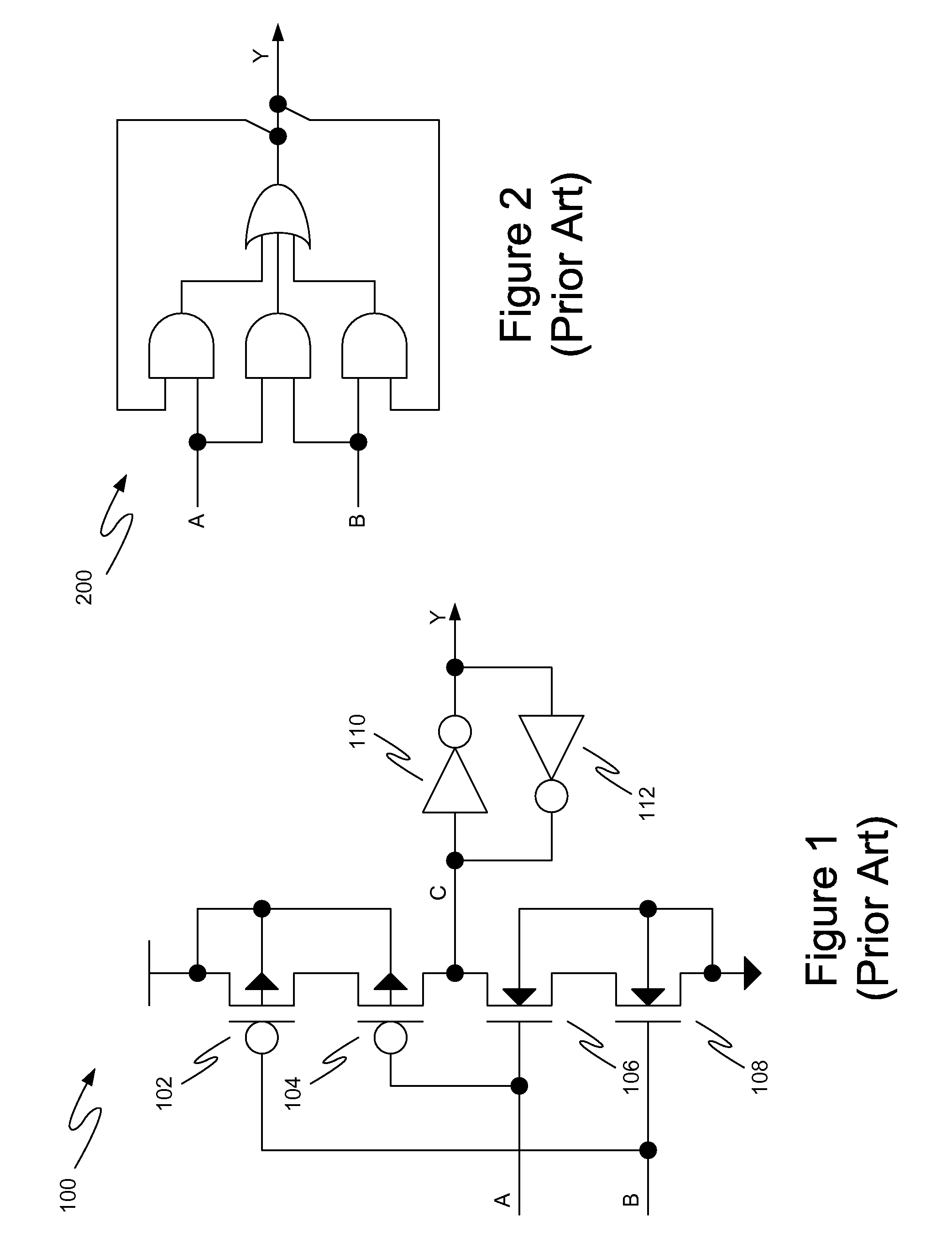
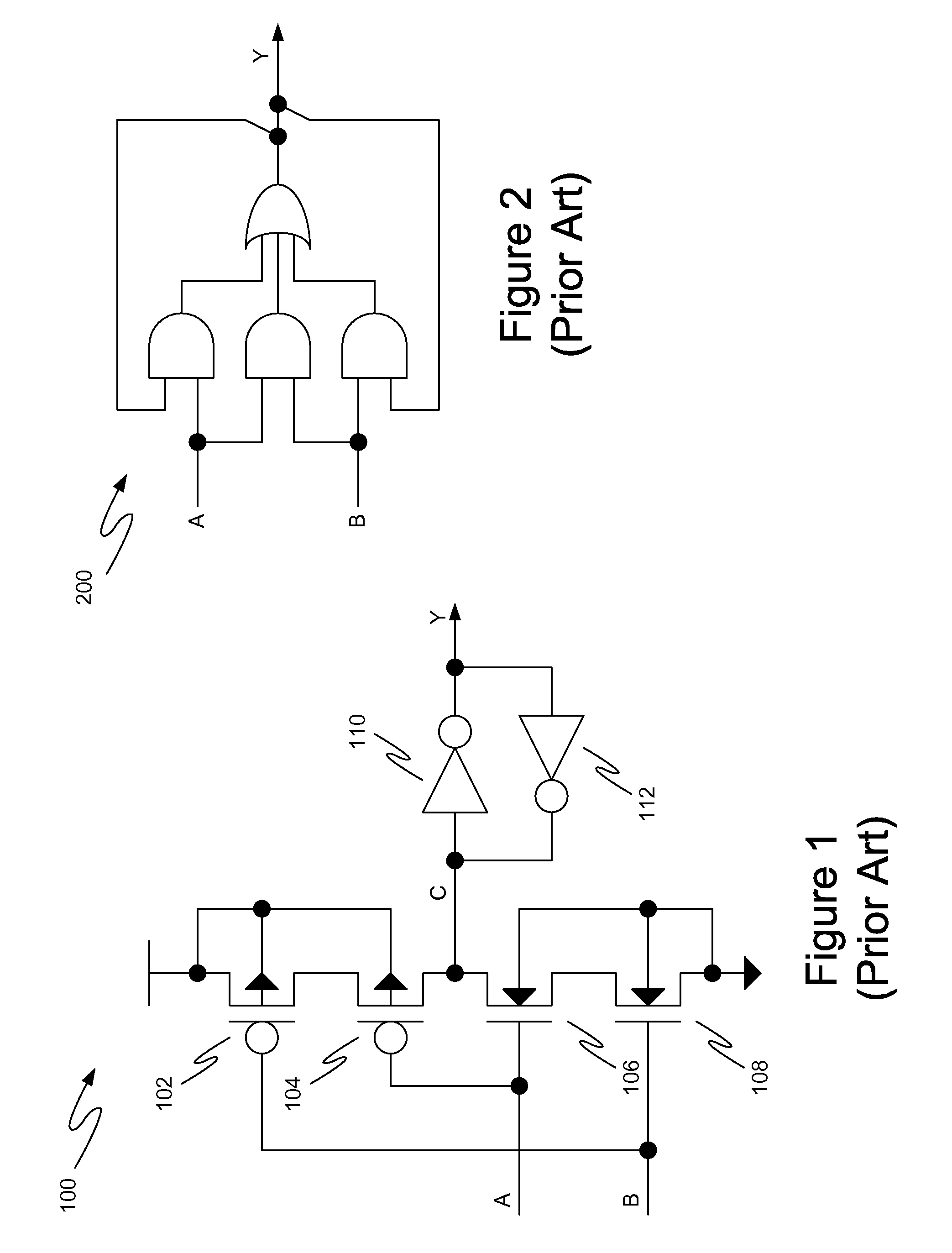
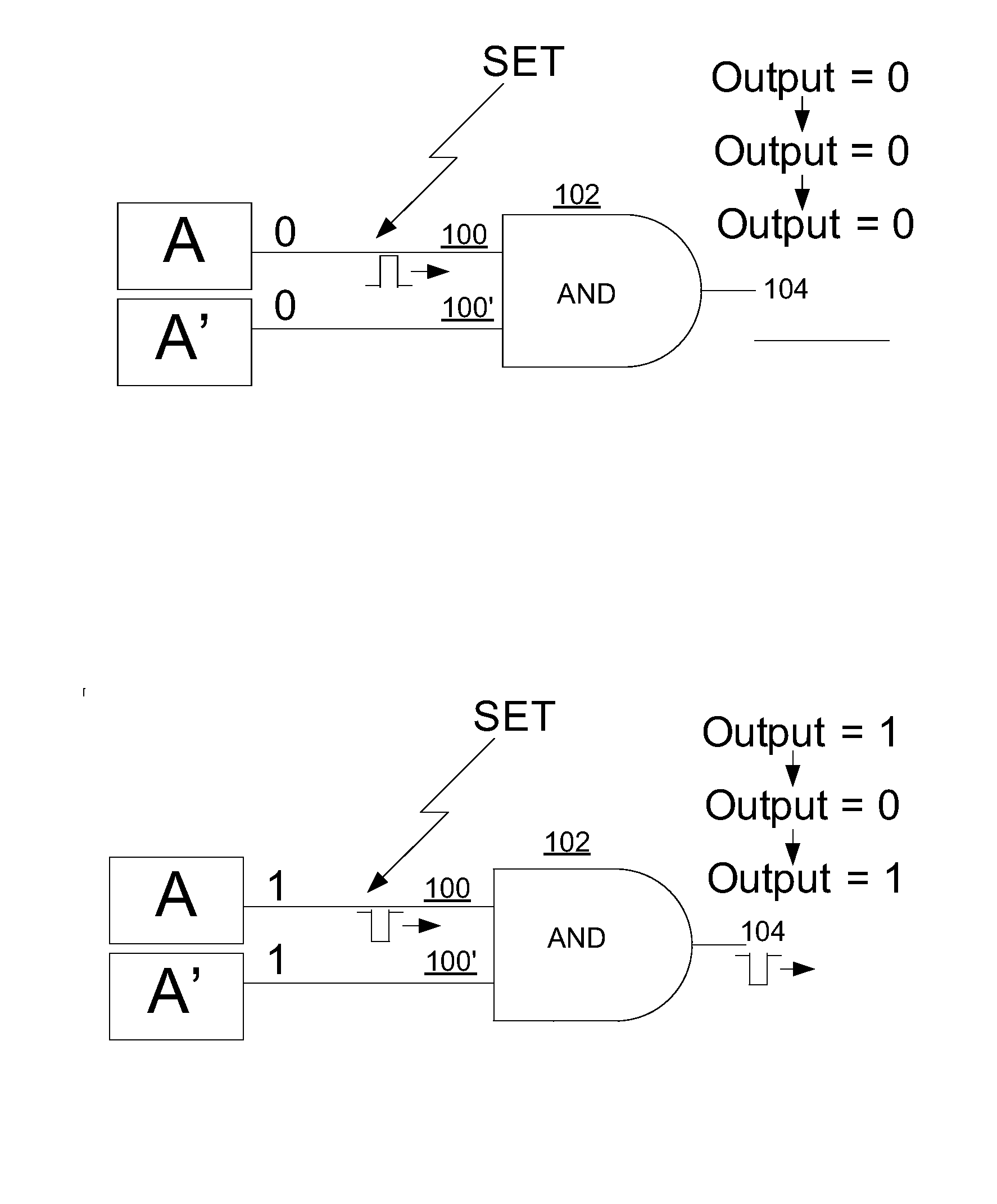
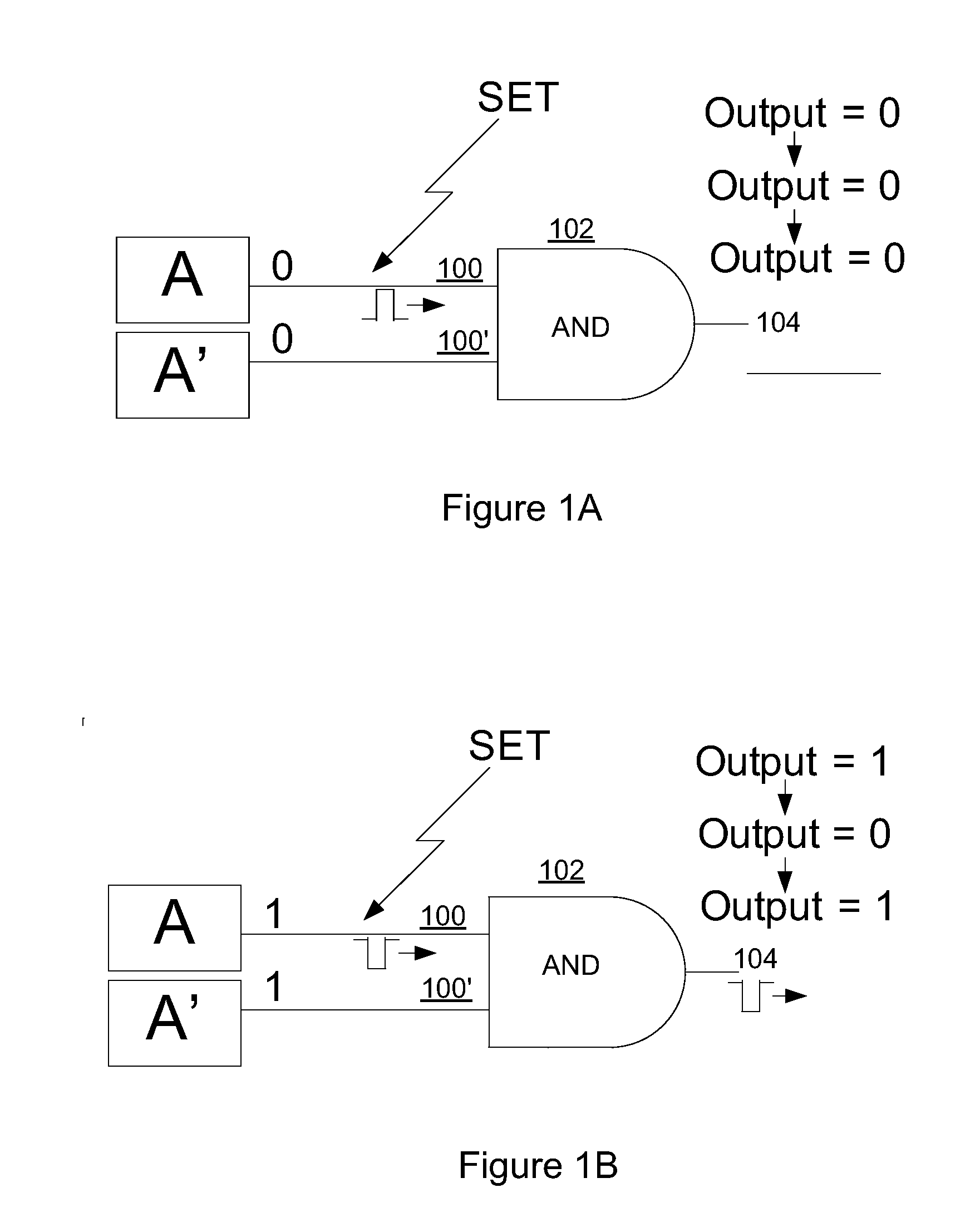
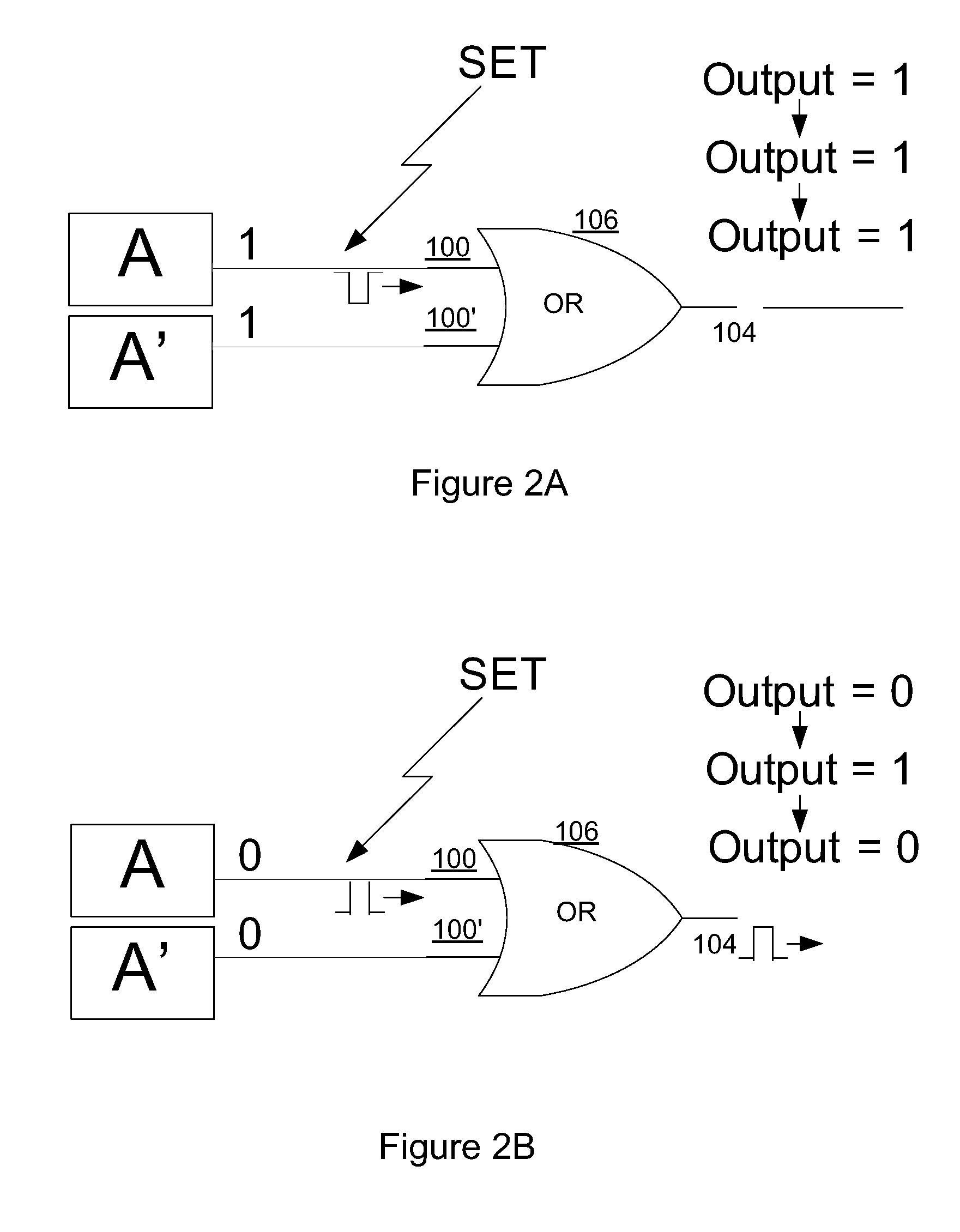
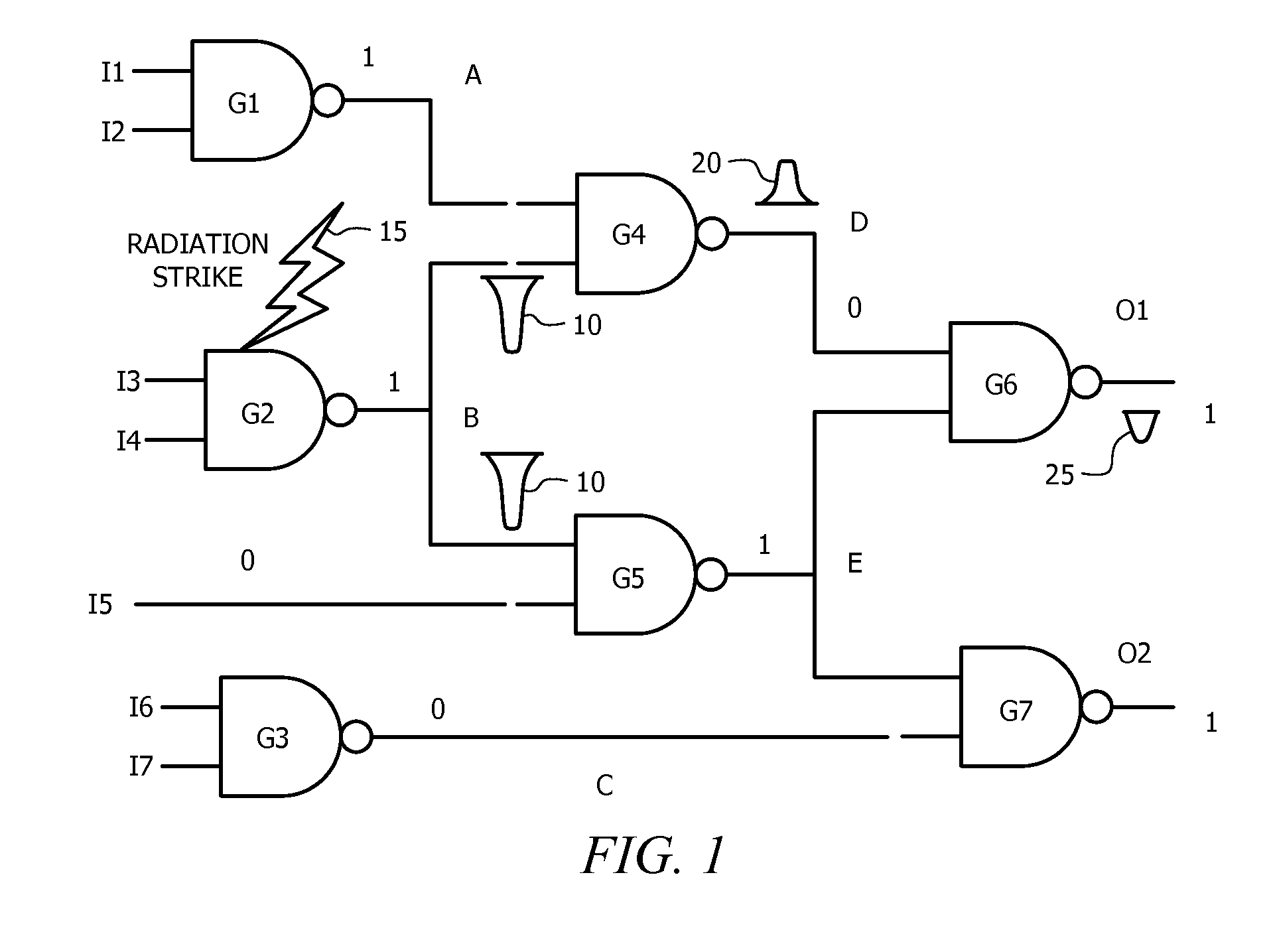
Method and circuit structure for suppressing single event transients or glitches in digital electronic circuits
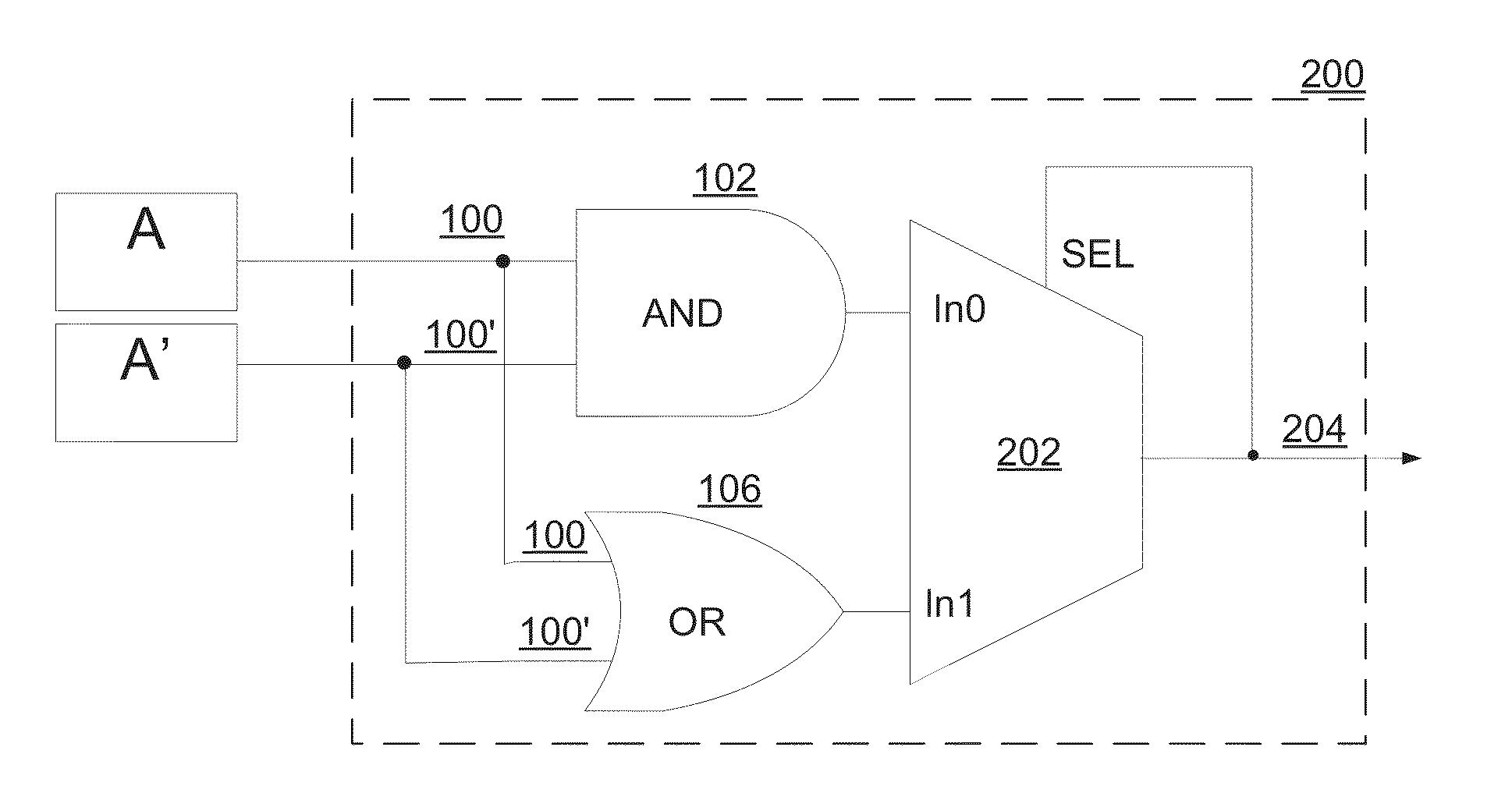
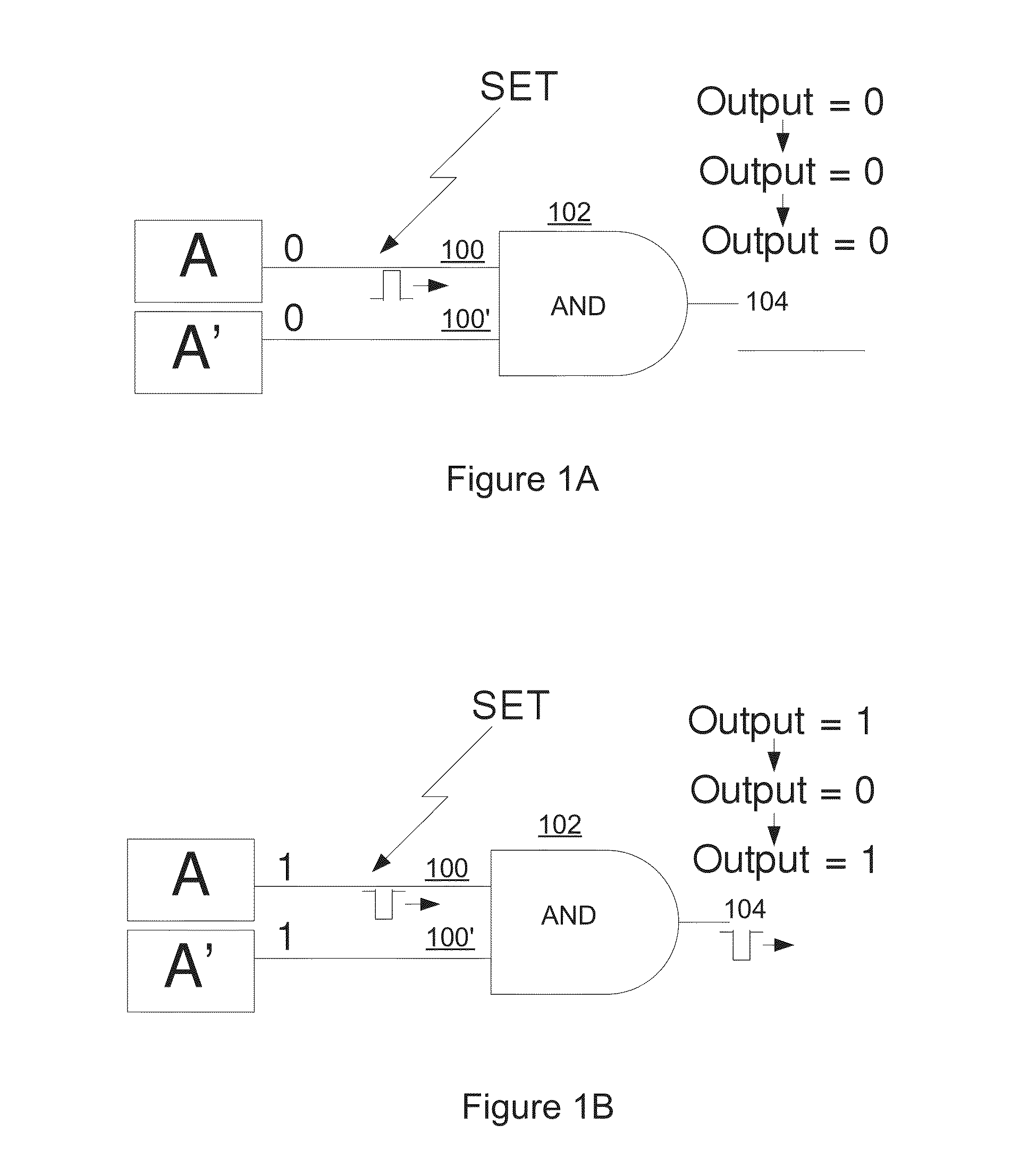
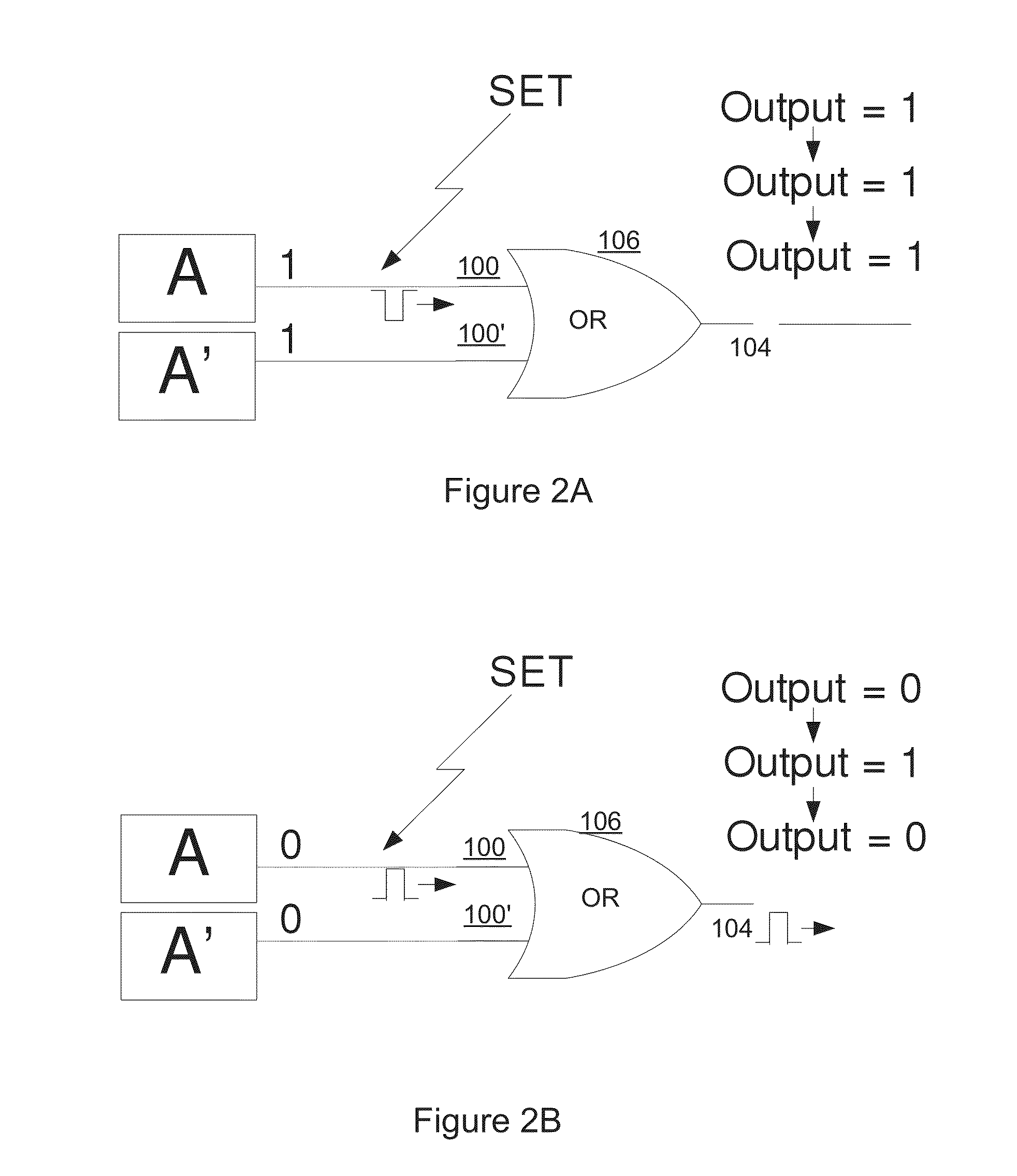
A circuit structure (200) for suppressing single event transients (SETs) or glitches in digital electronic circuits is provided. The circuit structure includes a first input (100) which receives an output of a digital electronic circuit (A), a second input (100′) which receives a redundant or duplicated output of the digital electronic circuit (A′), and two sub-circuits (102, 106) that each receive the inputs and have one output. One of the sub-circuits is insensitive to a change in the value of one of its inputs when the inputs are in a first logic state and the other sub-circuit is insensitive to a change in the value of one of the inputs when the inputs are in a second, inverted logic state. The sub-circuit outputs are input into a two-input multiplexer (202) which has its output (204) connected to its selection port (SEL), and the sub-circuits are arranged so that the sub-circuit which is insensitive to a change in the value of one of its inputs is selected whenever the output of the multiplexer changes. The multiplexer output (204) is provided as a final output in which SETs and glitches have been suppressed.
Owner:NELSON MANDELA METROPOLITAN UNIV
Reprogrammable field programmable gate array with integrated system for mitigating effects of single event upsets
InactiveUS7647543B2Reduce impactEliminate the effects ofError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsDigital clockDigital clock manager
An integrated system mitigates the effects of a single event upset (SEU) on a reprogrammable field programmable gate array (RFPGA). The system includes (i) a RFPGA having an internal configuration memory, and (ii) a memory for storing a configuration associated with the RFPGA. Logic circuitry programmed into the RFPGA and coupled to the memory reloads a portion of the configuration from the memory into the RFPGA's internal configuration memory at predetermined times. Additional SEU mitigation can be provided by logic circuitry on the RFPGA that monitors and maintains synchronized operation of the RFPGA's digital clock managers.
Owner:NASA
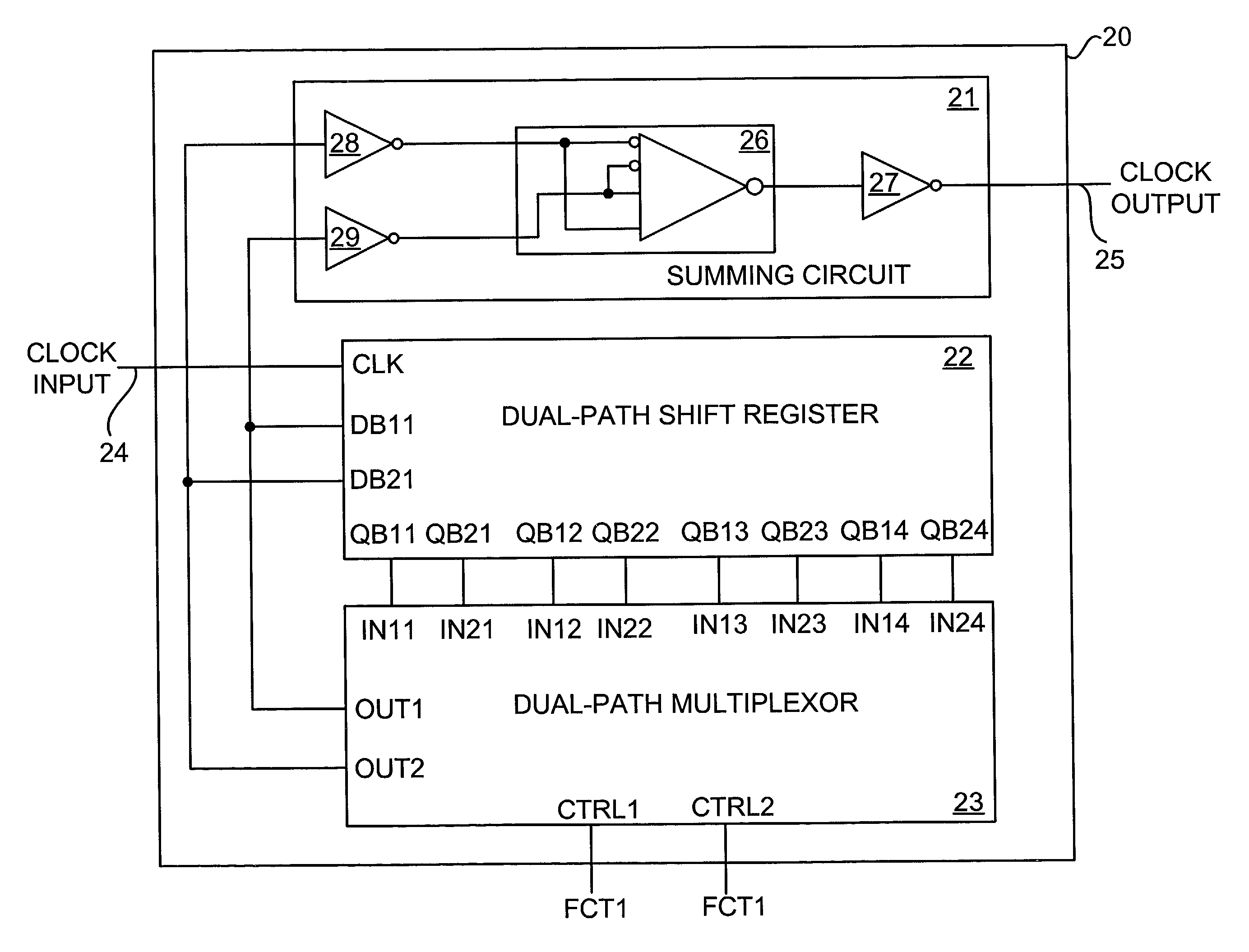
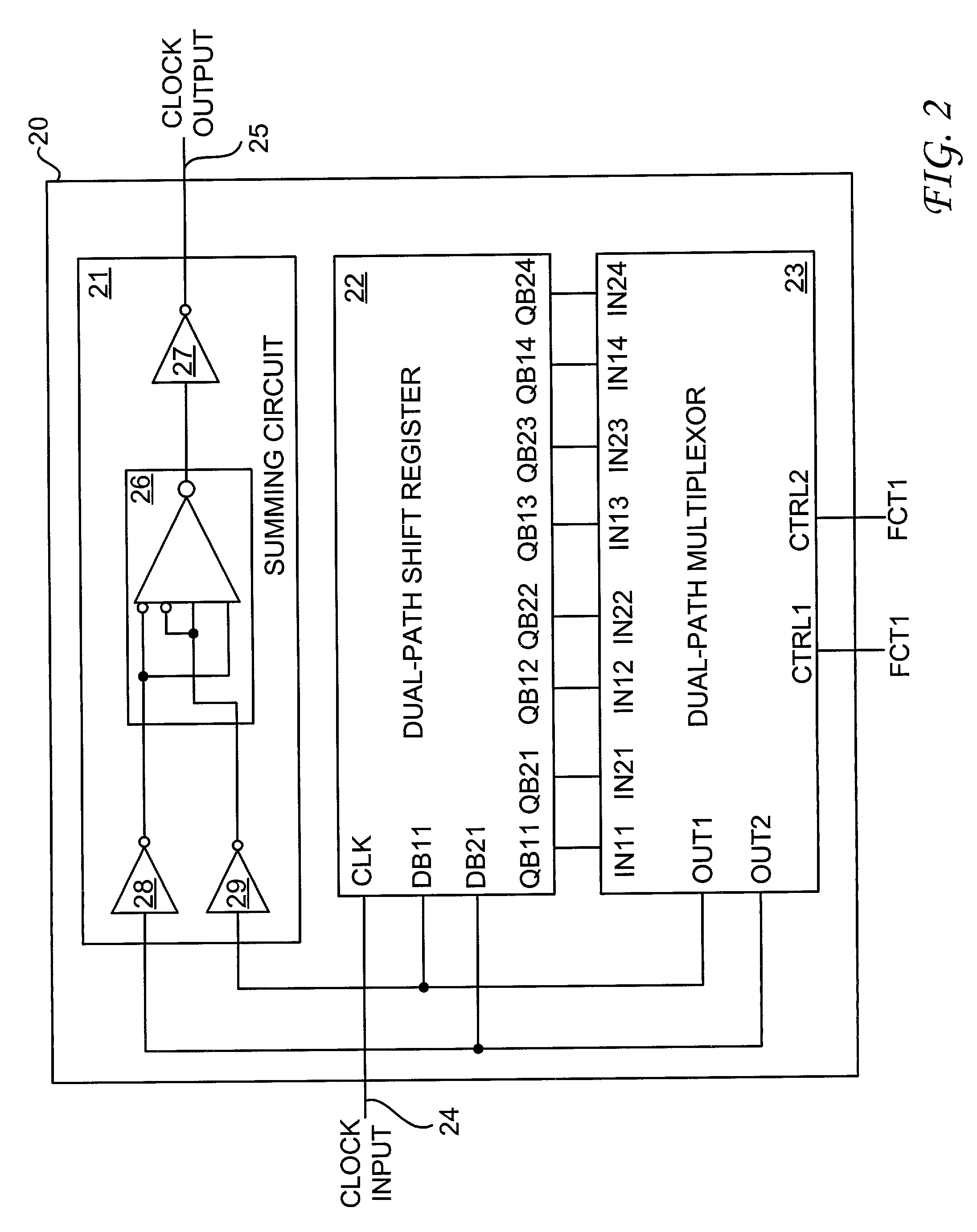
Single-event upset immune frequency divider circuit
InactiveUS20040017233A1Counting chain pulse countersPulse counters with static storageShift registerProcessor register
A single-event upset immune frequency divider circuit is disclosed. The single-event upset immune frequency divider circuit includes a dual-path shift register, a dual-path multiplexor, and a summing circuit. The dual-path shift register has a clock input, one signal input pair and multiple signal output pairs. The dual-path multiplexor has multiple signal input pairs and one output pair. The signal input pairs of the dual-path multiplexor are respectively connected to the signal output pairs of the dual-input shift register. The dual-path multiplexor selects one of the signal output pairs of the dual-path shift register for feeding back into the signal input pair of the dual-path shift register. The summing circuit then sums the signal input pair of the dual-path shift register to generate an output clock signal that is a fraction of the frequency of an input clock signal at the clock input of the dual-path shift register.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Radiation tolerant electrostatic discharge protection networks
Realizing that rather than protect electronic circuitry, electrostatic discharge networks when hit by cosmic rays and charged particles, can actually cause the electronic circuitry in satellites and other space applications to fail, the inventor created an ESD network having a redundant voltage clamping element in series with a first voltage clamping element between two voltage pads. The ESD network may be connected to a power voltage pad or a signal voltage pad either directly or through a dummy voltage pad. The voltage clamping elements may further comprise an array of unit cells wherein the array is electrically equivalent to single large transistors currently used in ESD networks. By creating an ESD network as an array of unit cells, benefits greater than those obtained by using a single transistor as a clamping or a trigger element are realized—such as increased ballast resistance and less overall damage to the circuitry resulting from cosmic rays and particles.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methodology and Apparatus for Reduction of Soft Errors in Logic Circuits
InactiveUS20090309627A1Hinders its propagationLogic circuits characterised by logic functionFail-safe circuitsDifferentiatorLogic cell
The present invention includes a circuit-level system and method for preventing the propagation of soft errors in logic cells. A radiation jammer circuit in accordance with the present invention, including an RC differentiator and a depletion mode MOS circuit, when inserted at the output of a logic cell, significantly reduces the propagation of transient glitches. The radiation jammer circuit is a novel transistor-level optimization technique, which has been used to reduce soft errors in a logic circuit. A method to insert radiation jammer cells on selective nodes in a logic circuit for low overheads in terms of delay, power, and area is also introduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Monitoring ionizing radiation in silicon-on insulator integrated circuits
InactiveUS20090113357A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareDigital storageIonizationSilicon on insulator
A method, device and system for monitoring ionizing radiation, and design structures for ionizing radiation monitoring devices. The method including: collecting an ionizing radiation induced charge collected by the depletion region of a diode formed in a silicon layer below an oxide layer buried below a surface of a silicon substrate; and coupling a cathode of the diode to a precharged node of a clocked logic circuit such that the ionizing radiation induced charge collected by a depletion region of the diode will discharge the precharged node and change an output state of the clocked logic circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
InactiveUS20130038348A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionCAD circuit designNon destructiveCMOS
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect logic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, with layout, which are protected against soft errors. In particular, the method protects against cases where multiple nodes in circuit are affected by a single event. These events lead to multiple errors in the circuit, and while several methods exist to deal with single node errors, multiple node errors are very hard to deal with using any currently existing protection methods. The method is particularly useful for CMOS based logic circuits in modem technologies (.ltoreq.90 nm), where the occurrence of multiple node pulses becomes high (due to the high integration level). It uses a unique layout configuration, which makes the circuits protected against single event generated soft-errors.
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
Latch circuit
ActiveUS7474116B2Minimized increasePrevent decrease in circuit response speedElectric pulse generatorReliability increase in field effect transistorsFeedback circuitsPositive feedback
A latch circuit includes a feedback circuit having inverter circuits and at least two input terminals and an input circuit for inputting input signals or signals having the same phase as the input signals to the input terminals of the feedback circuit in synchronization with a clock signal. In the feedback circuit section, only when the input signals or the signals having the same phase as the input signals are input to the at least two input terminals at the same time, positive feedback using a predetermined number of amplification stages is applied to the input terminals.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
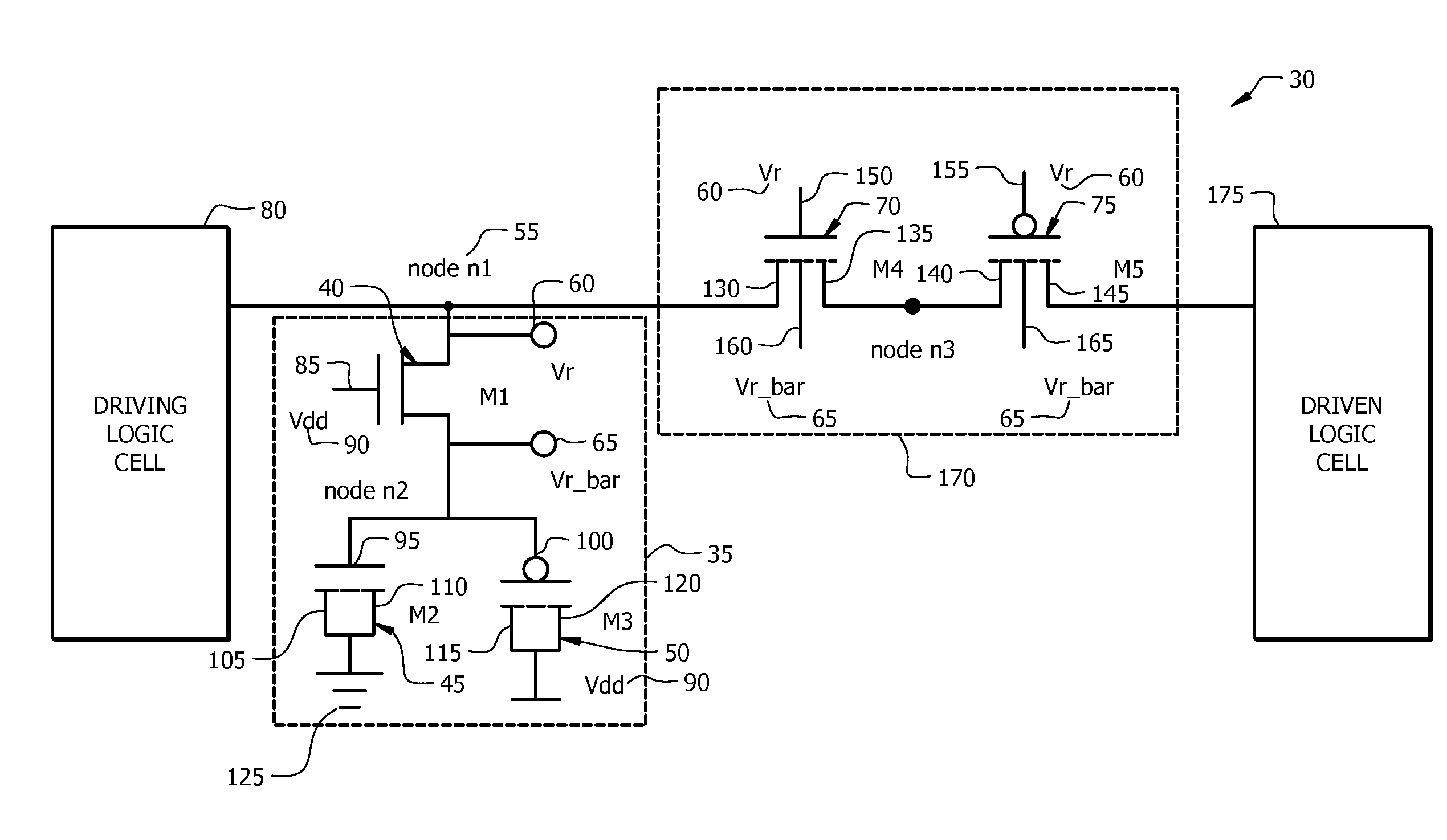
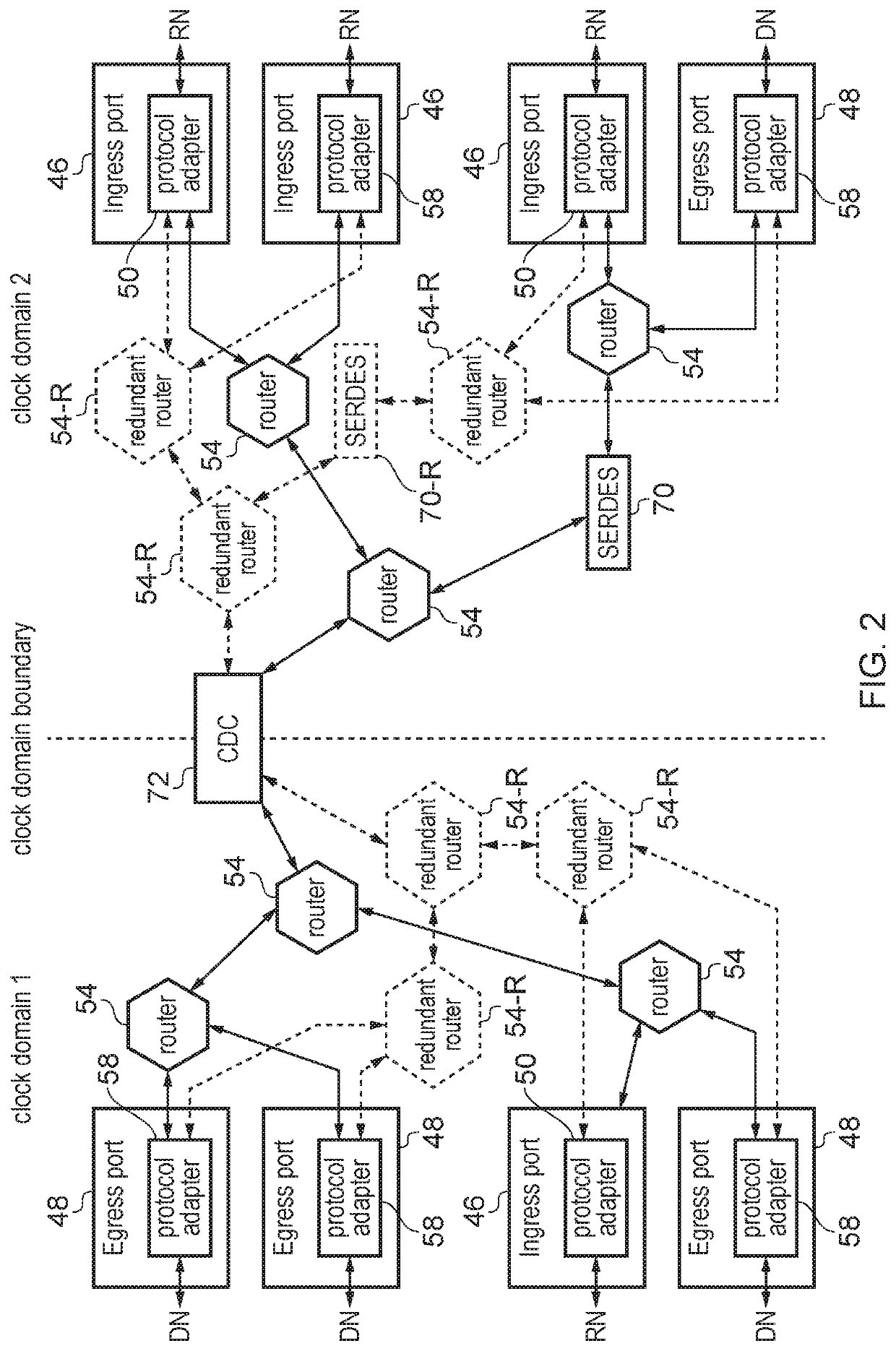
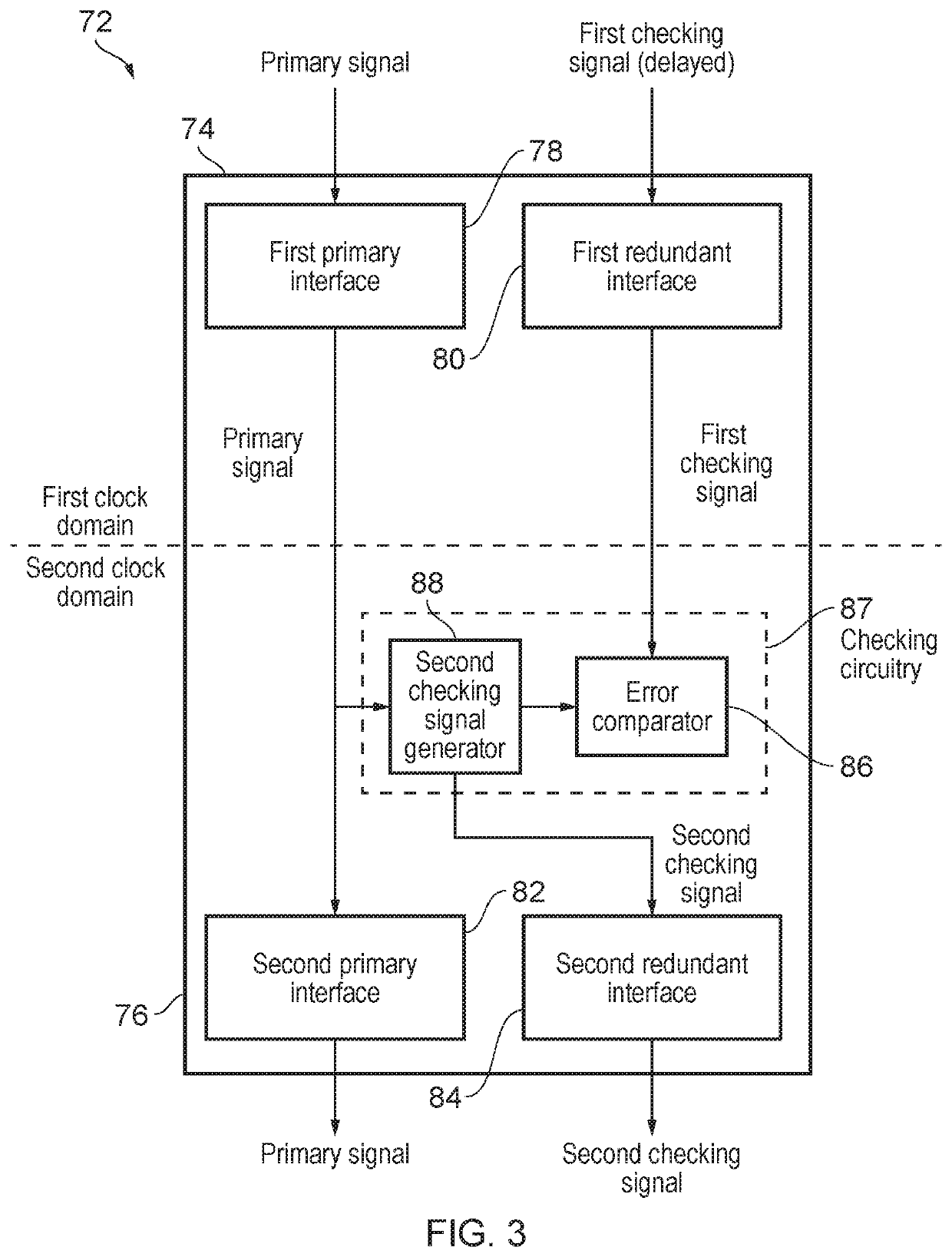
Error checking for primary signal transmitted between first and second clock domains
An apparatus and method for transmitting signals between two clock domains in which at least one of a phase and a frequency of clock signals in the two clock domains is misaligned. The apparatus includes a first primary interface and a first redundant interface in the first clock domain for receiving a primary signal and a first checking signal respectively, and a second primary interface and second redundant interface in the second clock domain for outputting the primary signal and a second redundant signal respectively. The primary signal and the checking signals are separated by a predetermined time delay and the second checking signal is generated in the second clock domain based on the primary signal. Checking circuitry is provided in the second clock domain to perform an error checking procedure based on the two checking signals and to provide the second checking signal to the second redundant interface.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method and circuit structure for suppressing single event transients or glitches in digital electronic circuits
Owner:NELSON MANDELA METROPOLITAN UNIV
SRAM-type FPGA device single-particle inversion detection and error correction circuit
ActiveCN106301334AIncrease the areaRealize anti-SEU functionRadiation hardeningEnergy efficient computingShift registerProcessor register
The present invention discloses an SRAM-type FPGA device single-particle inversion detection and error correction circuit. The SRAM-type FPGA device comprises an SRAM, a programming control module, an address pointer shift register block module and a data shift register block module. The address pointer shift register block module and the data shift register block module are connected with the SRAM; the address pointer shift register block module and the data shift register block module are connected with the programming control module; the programming control module is provided with an address counter and adds an single-particle inversion detection work mode at the programming control module; and a verification detection module is arranged on the loop of the data shift register block module and the programming control module. Through adoption of the existing FPGA programming circuit and based on the SEU detection and error correction circuit, the SRAM-type FPGA device single-particle inversion detection and error correction circuit can effectively realize the anti-SEU function on the basis of increasing little chip area and cost. The speed of the error correction time is fast in the third mode so as to greatly reduce the single-particle inversion influence on the normal work of the device.
Owner:GOWIN SEMICON CORP LTD
Radiation tolerant electrostatic discharge protection networks
InactiveUS20070075373A1Improve protectionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrical ballast
Realizing that rather than protect electronic circuitry, electrostatic discharge networks when hit by cosmic rays and charged particles, can actually cause the electronic circuitry in satellites and other space applications to fail, the inventor created an ESD network having a redundant voltage clamping element in series with a first voltage clamping element between two voltage pads. The ESD network may be connected to a power voltage pad or a signal voltage pad either directly or through a dummy voltage pad. The voltage clamping elements may further comprise an array of unit cells wherein the array is electrically equivalent to single large transistors currently used in ESD networks. By creating an ESD network as an array of unit cells, benefits greater than those obtained by using a single transistor as a clamping or a trigger element are realized—such as increased ballast resistance and less overall damage to the circuitry resulting from cosmic rays and particles.
Owner:IBM CORP
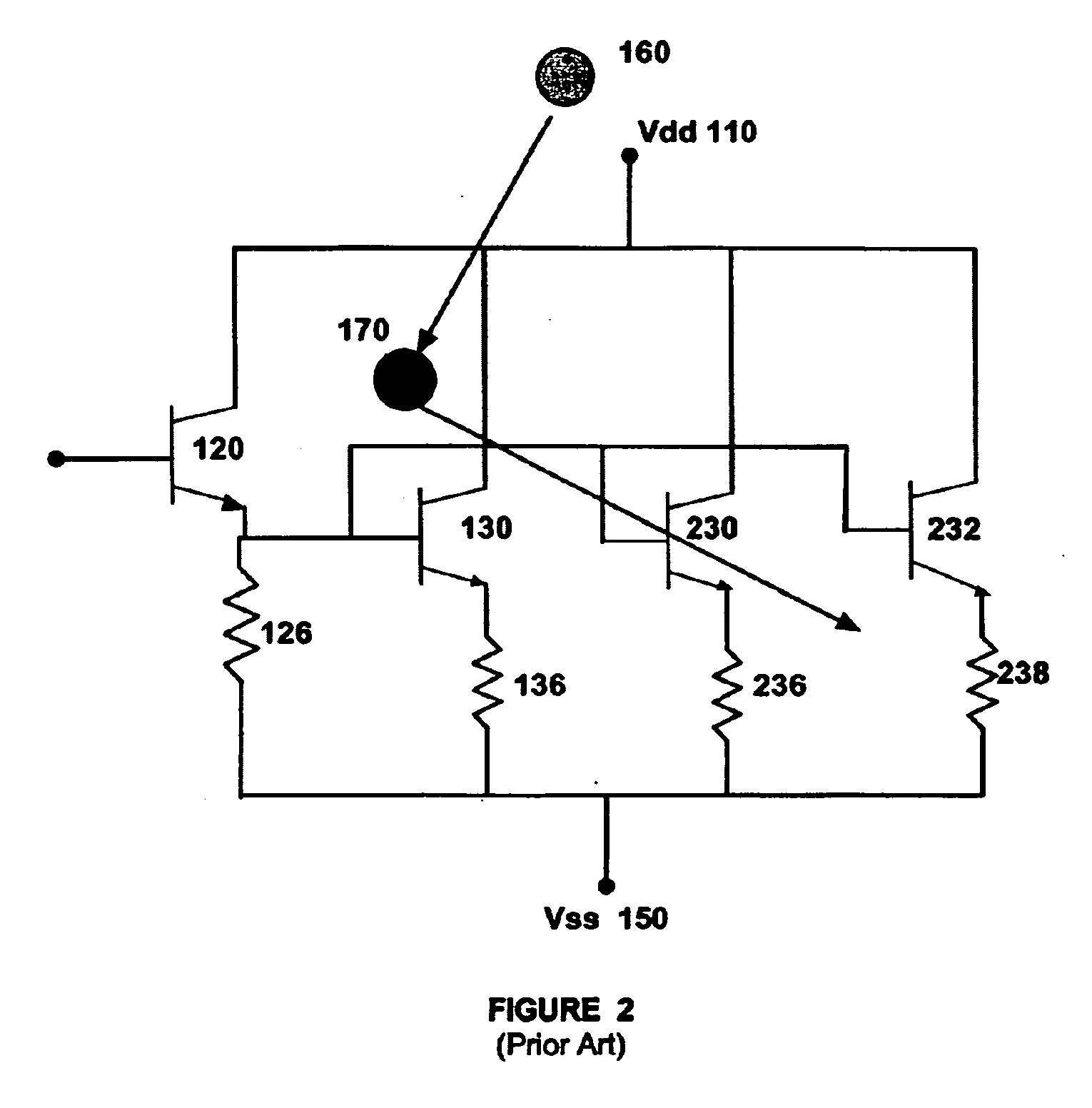
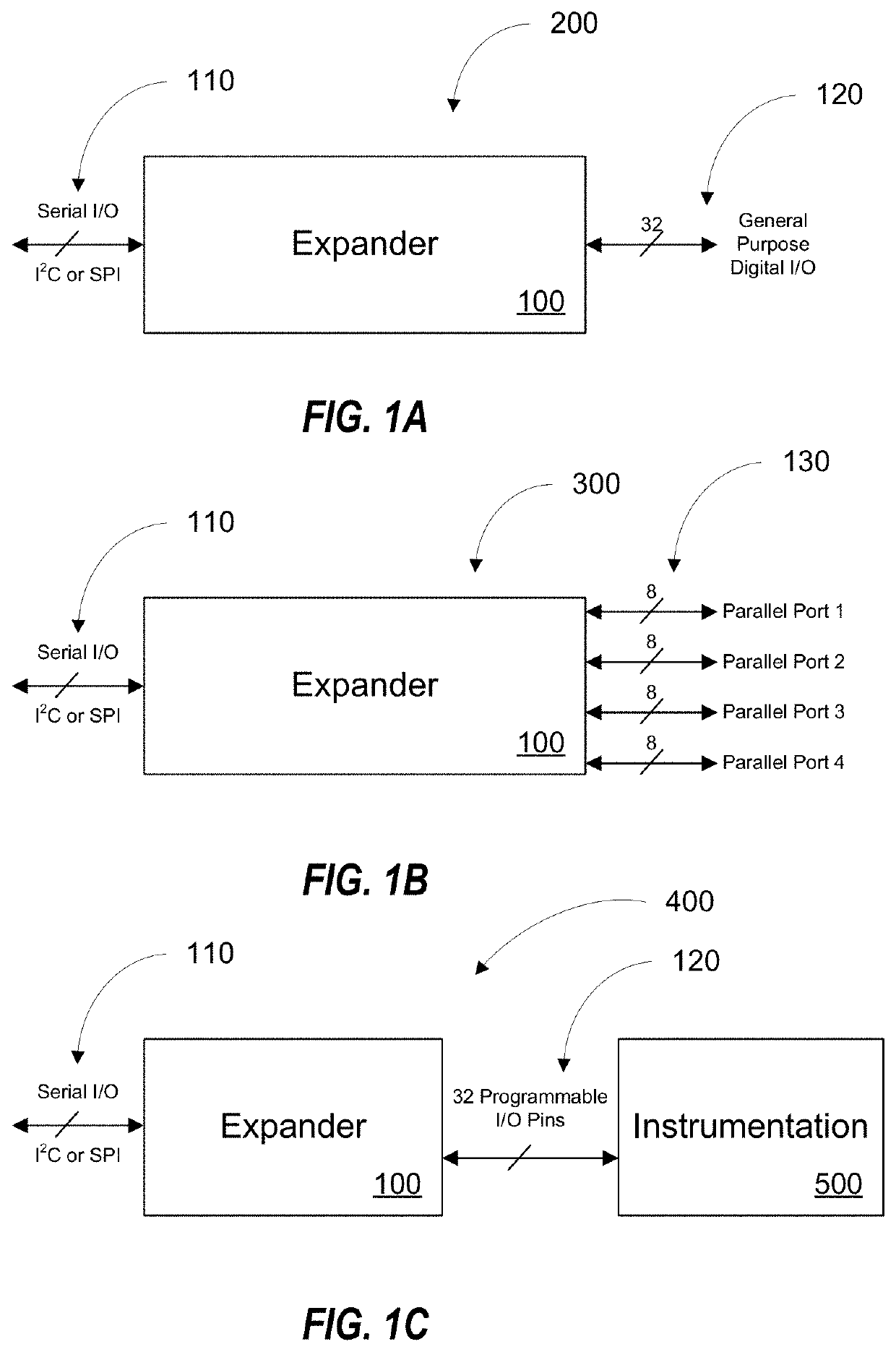
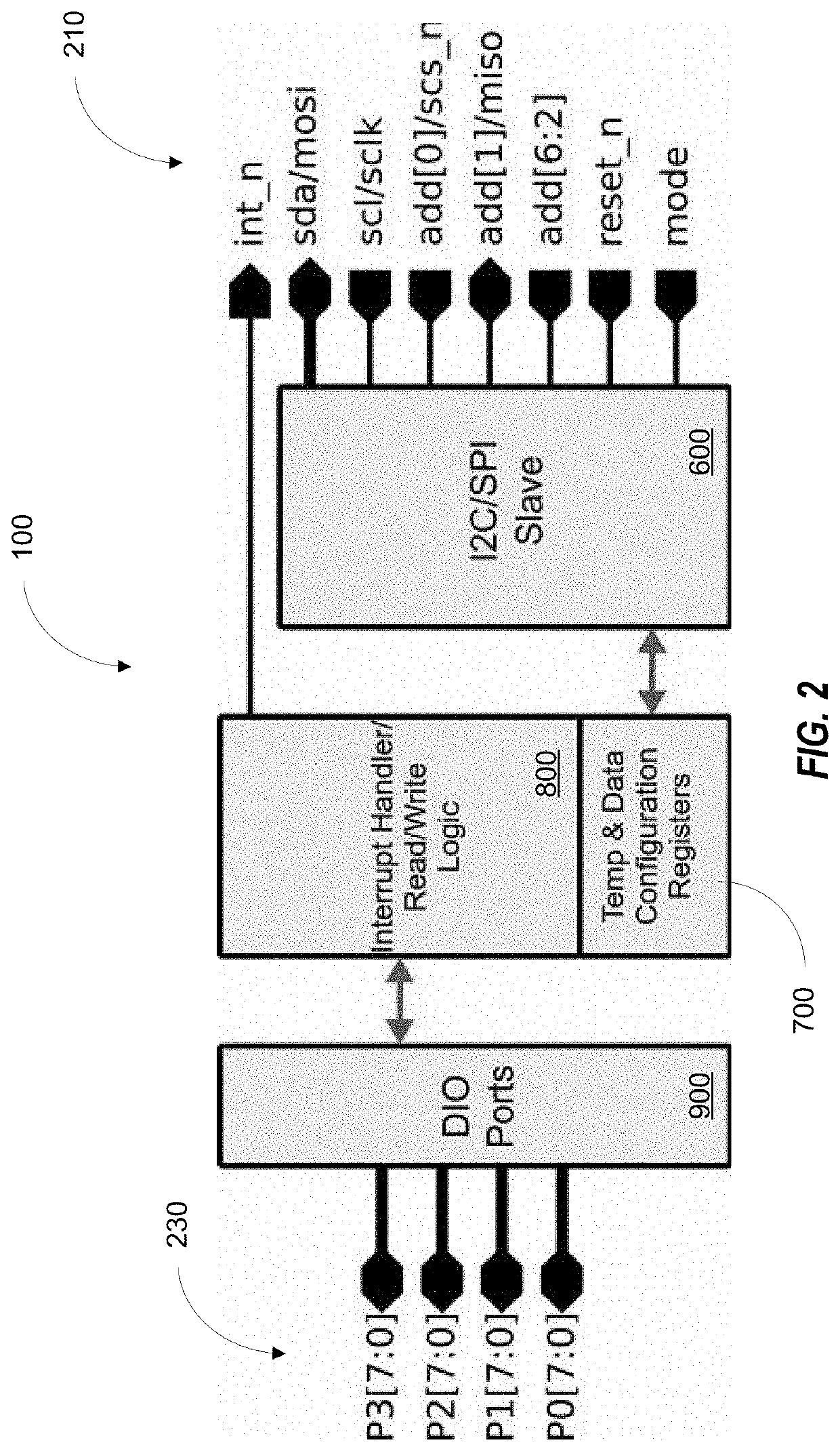
Radiation hardened input/output expander with I2C and SPI serial interfaces
ActiveUS10649949B1Easy to solveRadiation hardeningElectric digital data processingMicrocontrollerGeneral purpose
The invention is a microcircuit configured as a compact, radiation hardened, low-power general purpose I / O expander. The expander may be controlled by an external microcontroller or central processing unit through a serial interface. The expander provides a simple solution to miniaturize static parallel I / O signals using a simplified serial interface such as I2C or SPI.
Owner:NASA
In-place resynthesis and remapping techniques for soft error mitigation in FPGA
InactiveUS9047429B2Improve fault toleranceReliable circuitCAD circuit designRadiation hardeningFpga architectureDecomposition
In-place resynthesis for static memory (SRAM) based Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) toward reducing sensitivity to single event upsets (SEUs). Resynthesis and remapping are described which have a low overheard and improve FPGA designs without the need of rerouting LUTs of the FPGA. These methods include in-place reconfiguration (IPR), in-place X-filling (IPF), and in-place inversion (IPV), which reconfigure LUT functions only, and can be applied to any FPGA architecture. In addition, for FPGAs with a decomposable LUT architecture (e.g., dual-output LUTs) an in-place decomposition (IPD) method is described for remapping a LUT function into multiple smaller functions leveraging the unused outputs of the LUT, and making use of built-in hard macros in programmable-logic blocks (PLBs) such as carry chain or adder. Methods are applied in-place to mapped circuits before or after routing without affecting placement, routing, and design closure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
ActiveUS20120185816A1Reduce impactSoft errorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionFail-safe circuitsCMOSNon destructive
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect logic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, with layout, which are protected against soft errors. In particular, the method protects against cases where multiple nodes in circuit are affected by a single event. These events lead to multiple errors in the circuit, and while several methods exist to deal with single node errors, multiple node errors are very hard to deal with using any currently existing protection methods. The method is particularly useful for CMOS based logic circuits in modern technologies (.ltoreq.90 nm), where the occurrence of multiple node pulses becomes high (due to the high integration level). It uses a unique layout configuration, which makes the circuits protected against single event generated soft-errors.
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
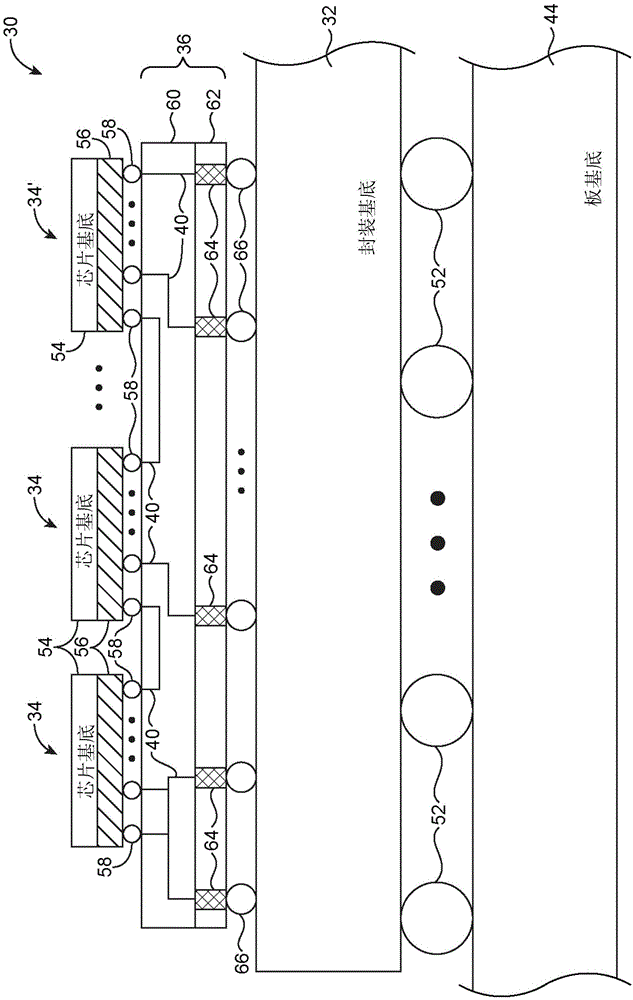
Error resilient packaged components
A packaged component may include an interposer and integrated circuit dies mounted on the interposer. At least one of the dies may be a radiation-hardened integrated circuit die, whereas the remaining dies may be non-radiation-hardened dies. If desired, the interposer may be a radiation-hardened interposer whereas the integrated circuit dies may be non-radiation-hardened dies. The radiation-hardened die or the radiation-hardened interposer may include monitor circuitry that is used to test non-radiation-hardened circuitry of the packaged component. Test results may be stored in a database at the monitor circuitry or transmitted to external devices such as a server. The monitor circuitry may be used to reconfigure failed circuitry or may control multiplexing circuitry in the interposer to functionally replace the failed circuitry. If desired, the monitor circuitry may adjust power consumption of non-radiation-hardened circuitry based on the test results.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
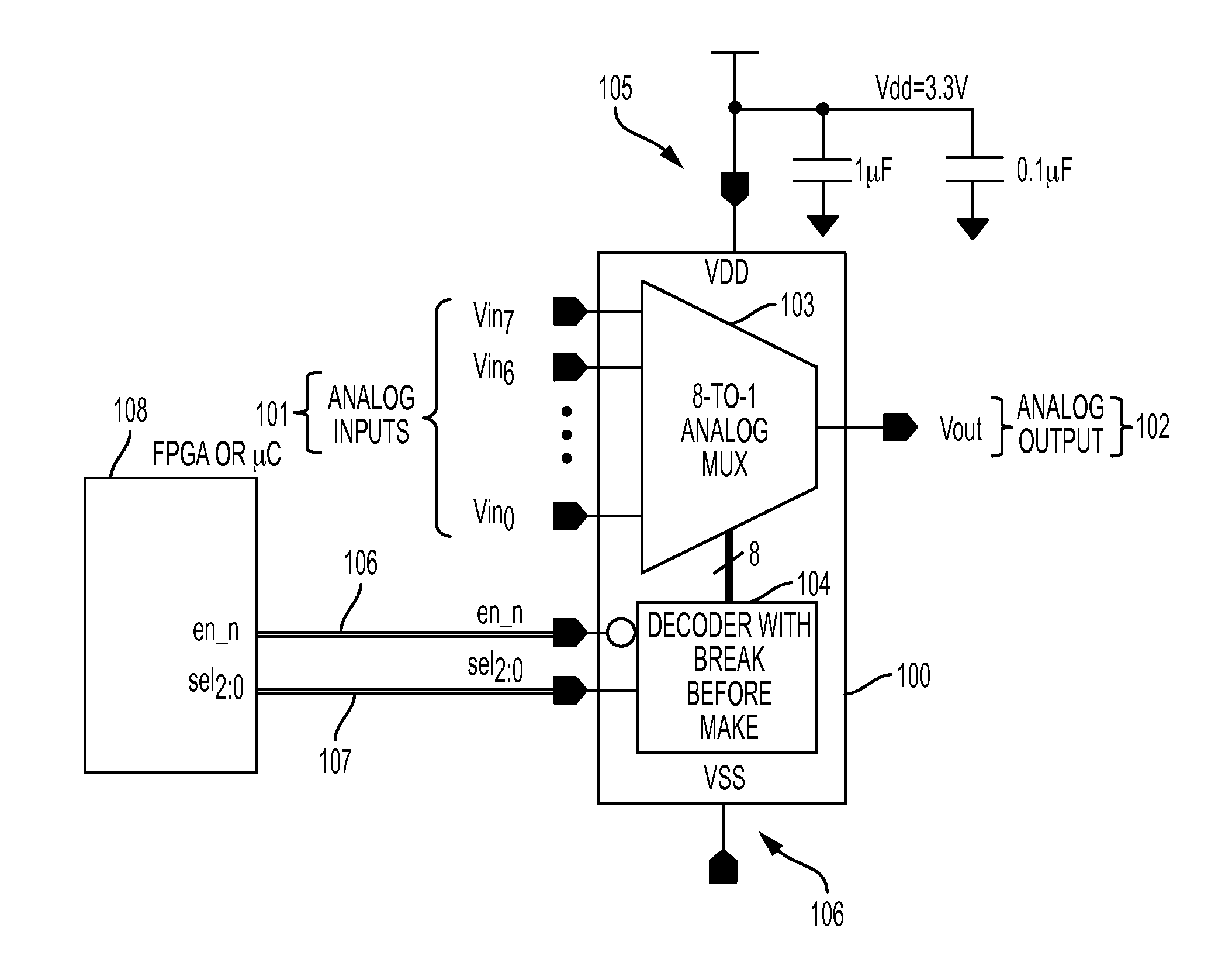
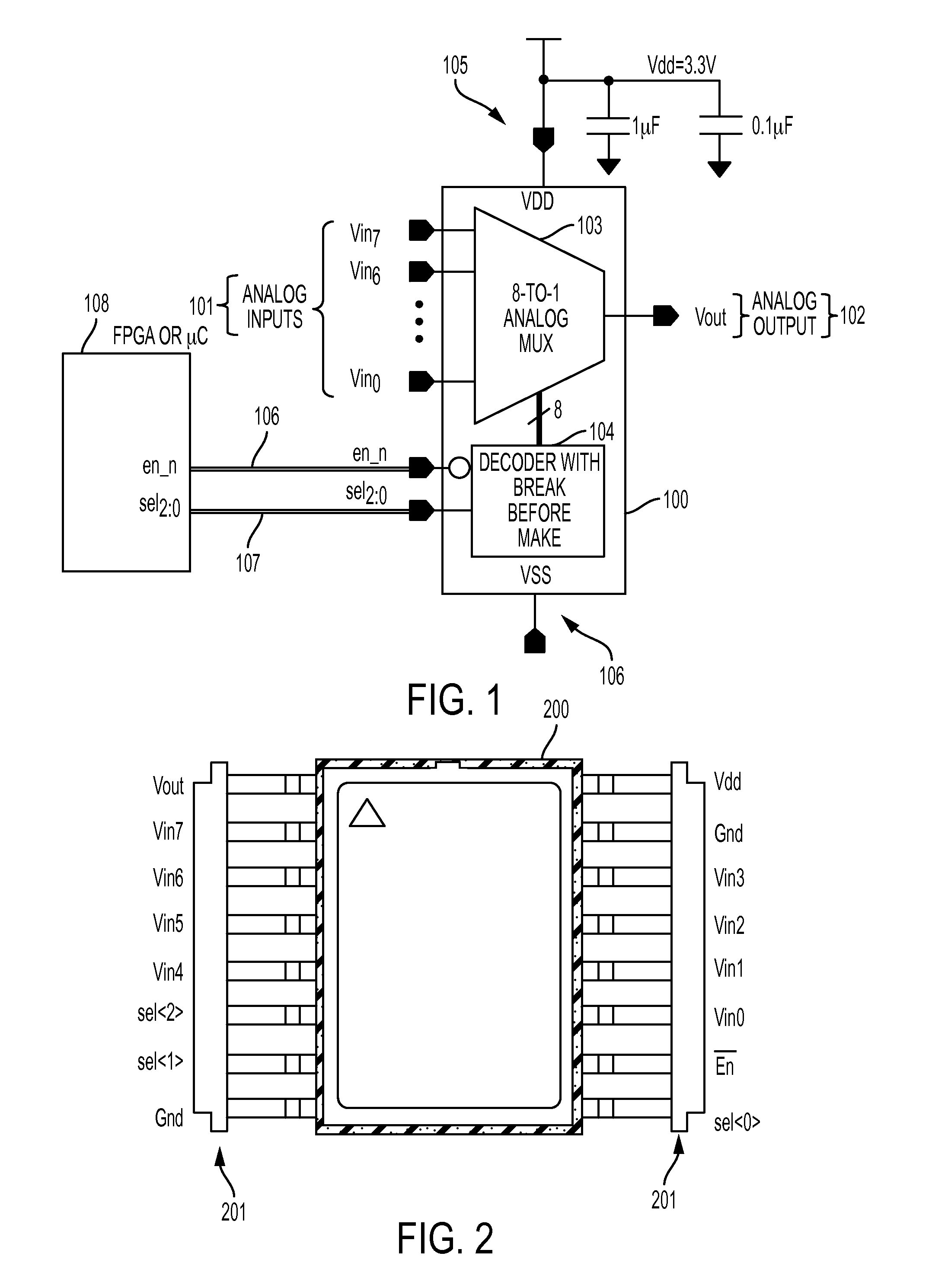
Multiplexer
The present invention relates to a compact, low power, radiation-hardened-by-design 8-channel analog multiplexer ASIC, a 0.25 μm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS); a 500 krad total ionization dose and single event latchup which is greater than the linear energy transfer (LET) 120 MeV-sq. cm / mg; eight channels for 8-to-1 multiplexing; a three nanosecond break-before-make decoder; an active low enable pin; and an on-resistance of less than 500 ohms from input to output pads.
Owner:NASA
Radiation hardened circuit
InactiveUS20140340133A1Avoid radiationPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorComputer scienceTransistor
A circuit including a data storage element; first and second input circuitry coupled respectively to first and second inputs of the data storage element and each including a plurality of components adapted to generate, as a function of an initial signal, first and second input signals respectively provided to the first and second inputs; wherein the data storage element includes a first storage node and is configured such that a voltage state stored at the first storage node is protected from a change in only one of the first and second input signals by being determined by the conduction state of a first transistor coupled to the first storage node and controlled based on the first input signal and by the conduction state of a second transistor coupled to the first storage node and controlled based on the second input signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (CROLLES 2) SAS +1
Popular searches
Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Special data processing applications Memory systems Voltage/temperature variation compensation Arrangements responsive to excess current Redundant data error correction Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit components Computation using denominational number representation Total factory control Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com