Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Soft error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
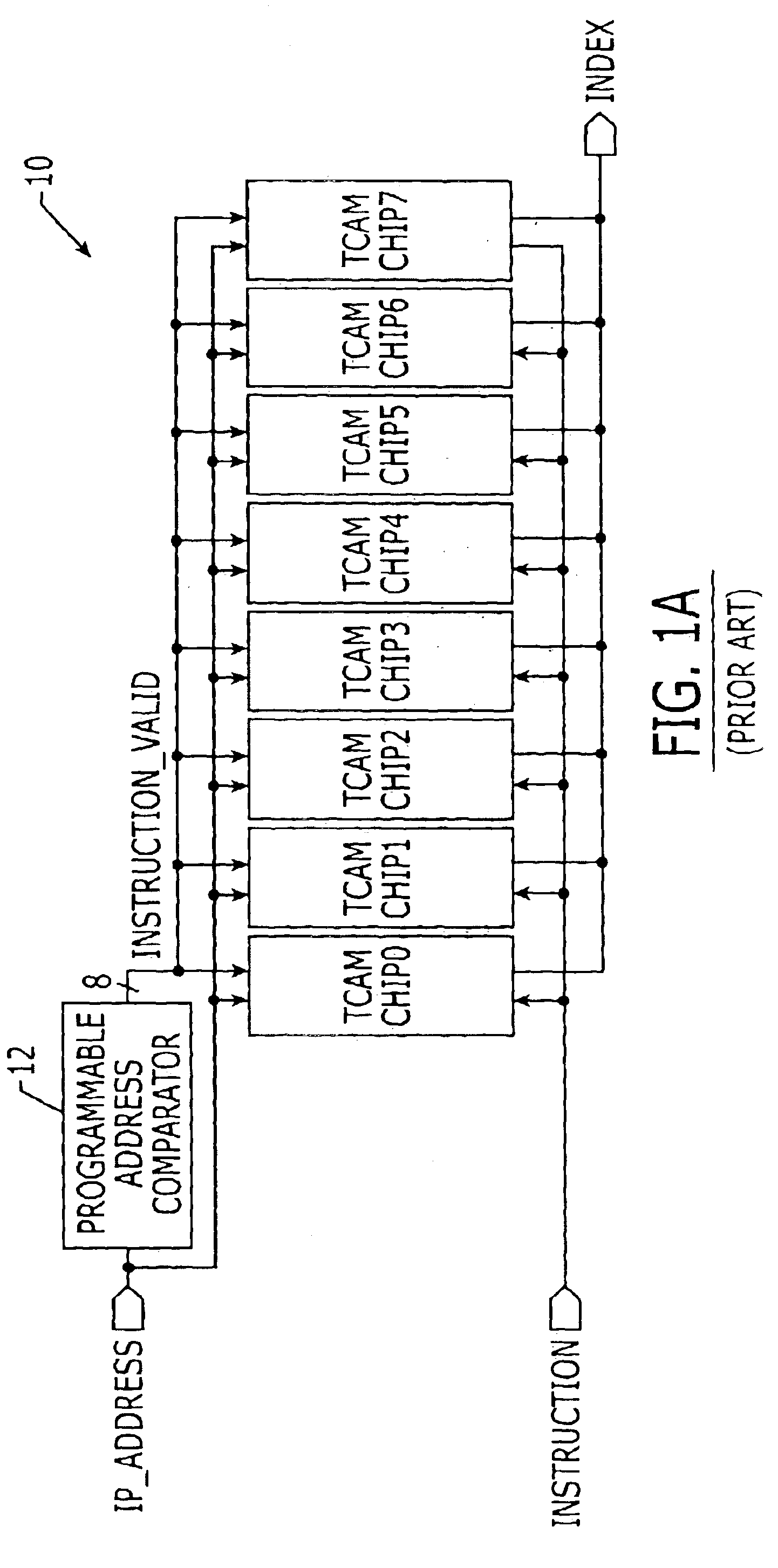
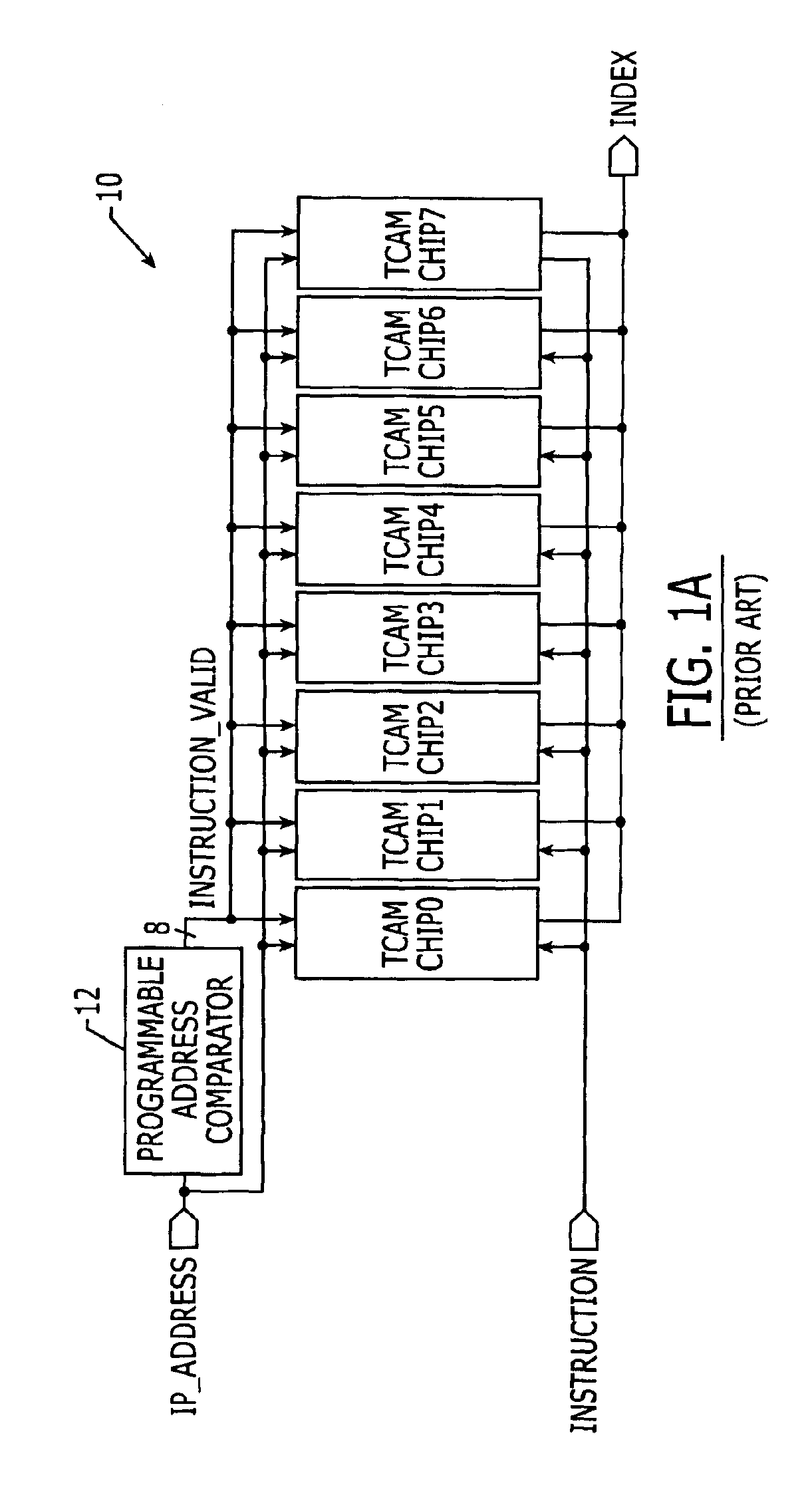
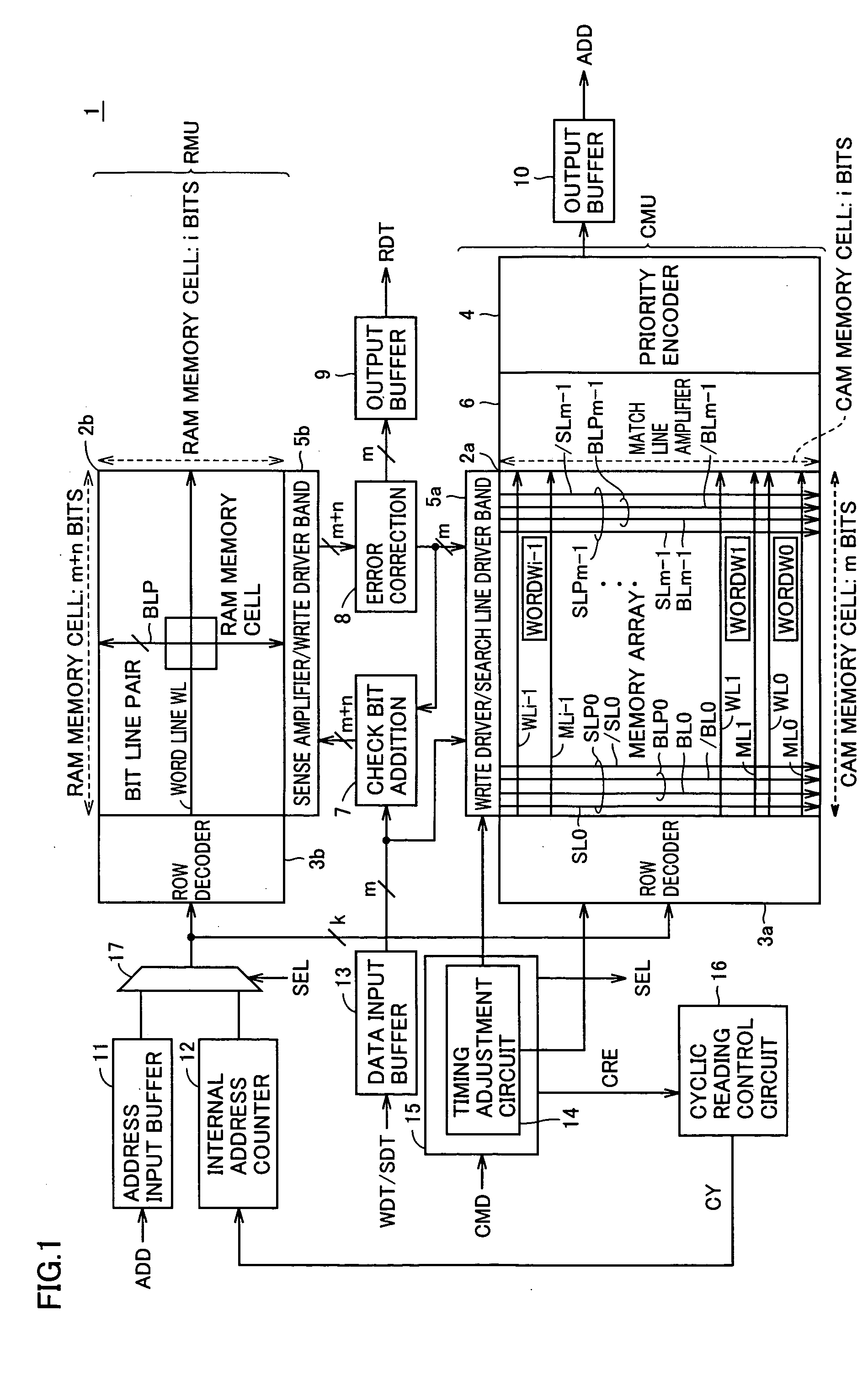
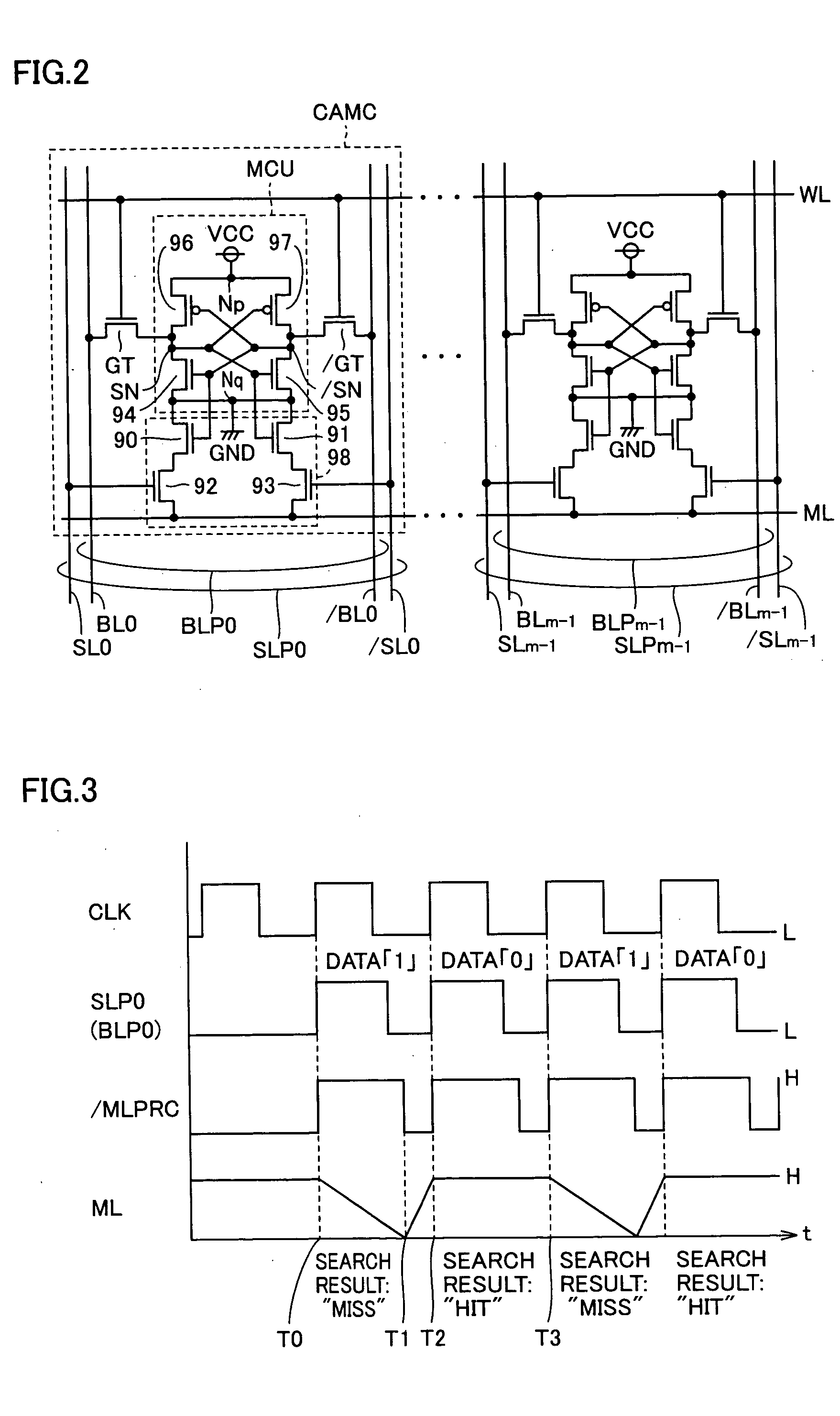
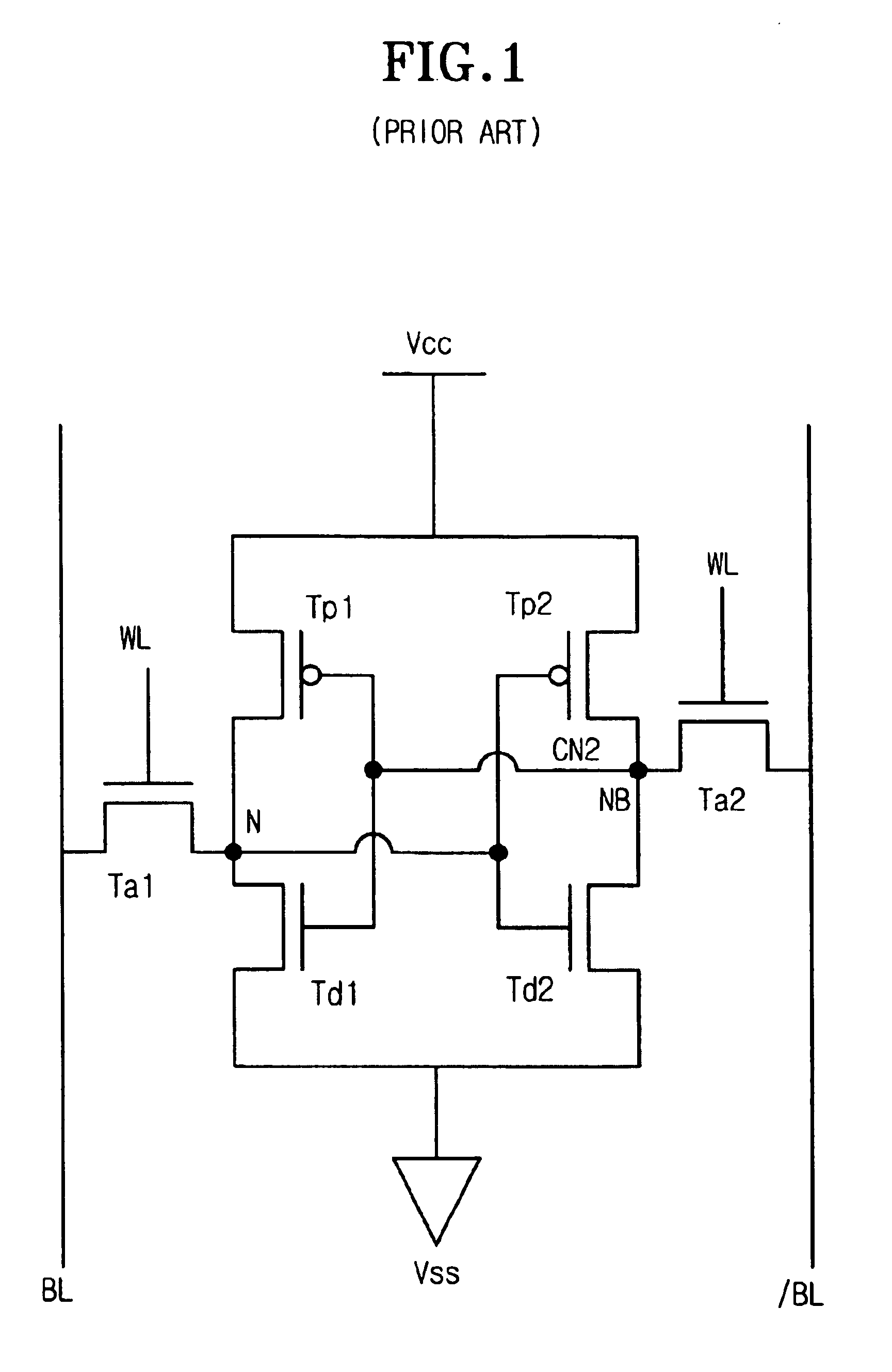
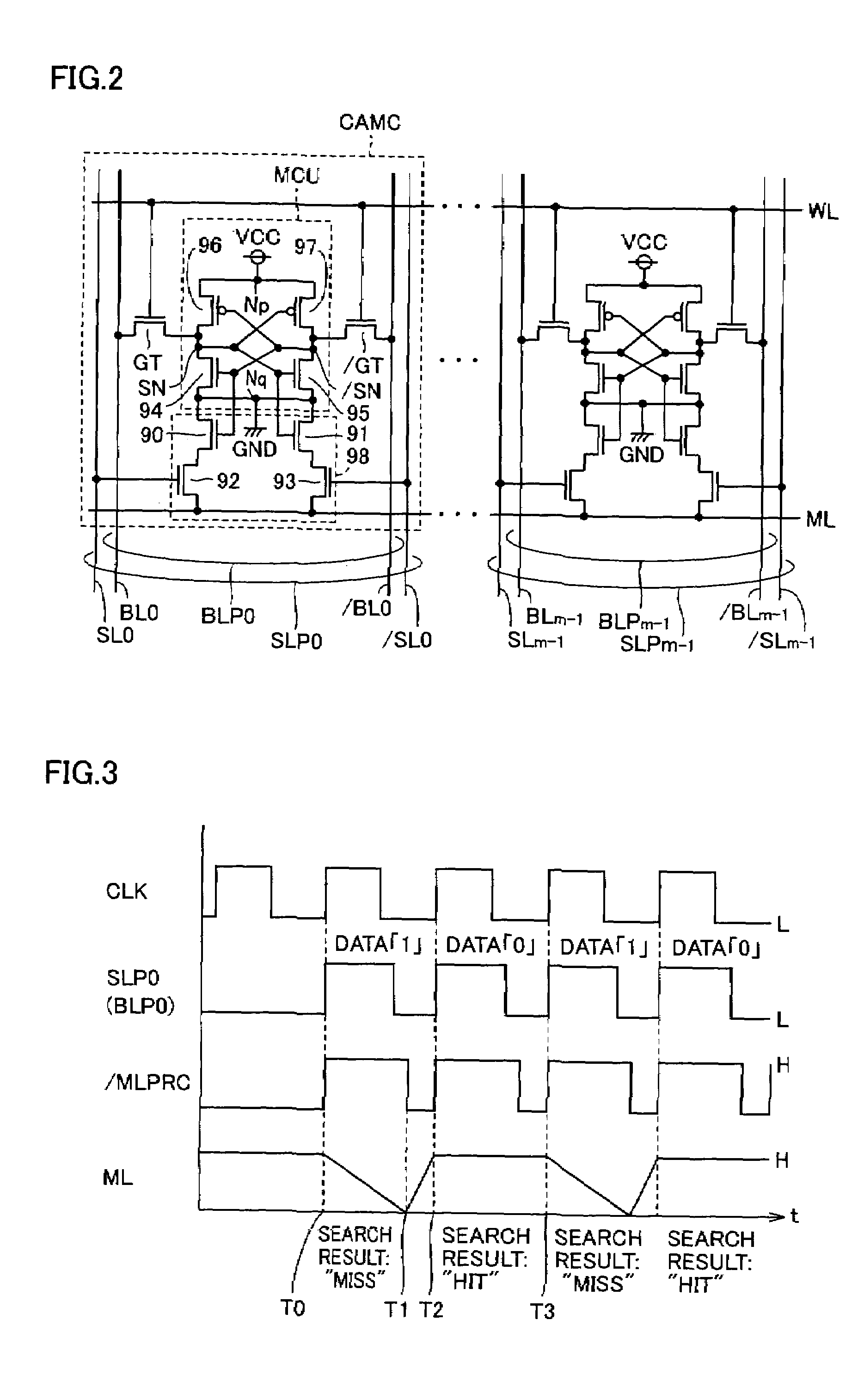
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices with dual-function check bit cells that support column redundancy and check bit cells with reduced susceptibility to soft errors
ActiveUS6870749B1Great degreeSoft errorDigital storageRedundant data error correctionEmbedded systemReduced susceptibility
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices include dual-function check bit cells that can operate as check bit cells to support error detection and correction (EDC) operations or as redundant CAM cells that support column redundancy. Dedicated check bit cells are also provided that have a reduced susceptibility to soft errors relative to adjacent CAM cells. The dedicated check bit cells may also be provided within a global mask cell sub-array to support correction of soft errors within global masks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
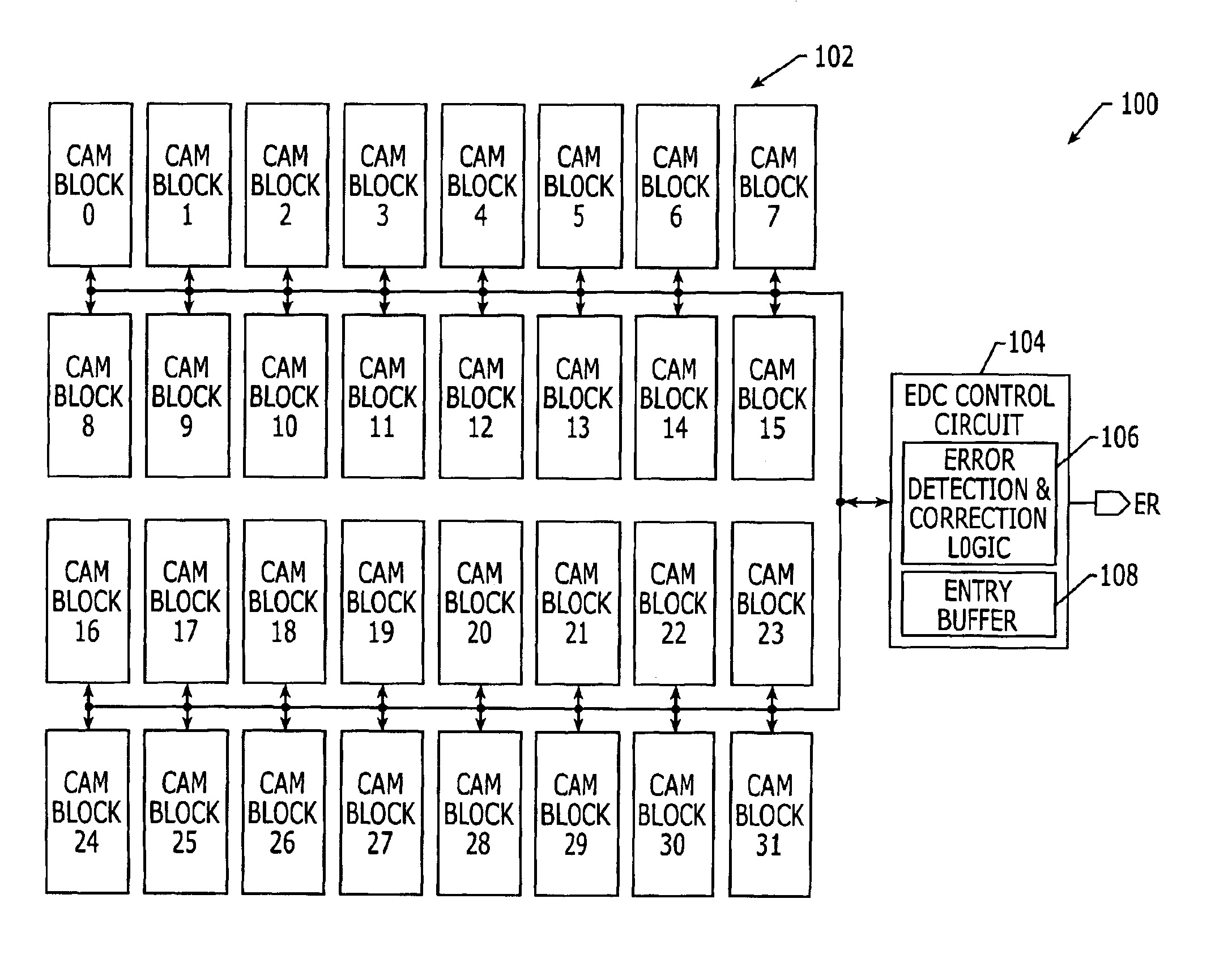
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices having error detection and correction control circuits therein and methods of operating same
Content addressable memory (CAM) devices include error detection and correction (EDC) control circuits therein. The EDC control circuit operates to correct soft errors in entries within a plurality of internal CAM array blocks with, at most, limited interruption to other operations performed by the CAM device. The EDC control circuit utilizes a multi-bit check word associated with each entry to detect a soft error and perform one-bit error correction on the entry. The EDC control circuit is configured to be active during a background mode of operation when the CAM array blocks are undergoing search operations in a foreground mode of operation. A CAM array block may also include a column of dual-function check bit cells that are configured to operate as a column of CAM cells when necessary to replace a defective column of CAM cells.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Duplicated double checking production rule set for fault-tolerant electronics
InactiveUS20070016823A1Reduce soft errorsEliminating soft errorReliability increasing modificationsError detection/correctionElectronic systemsHemt circuits
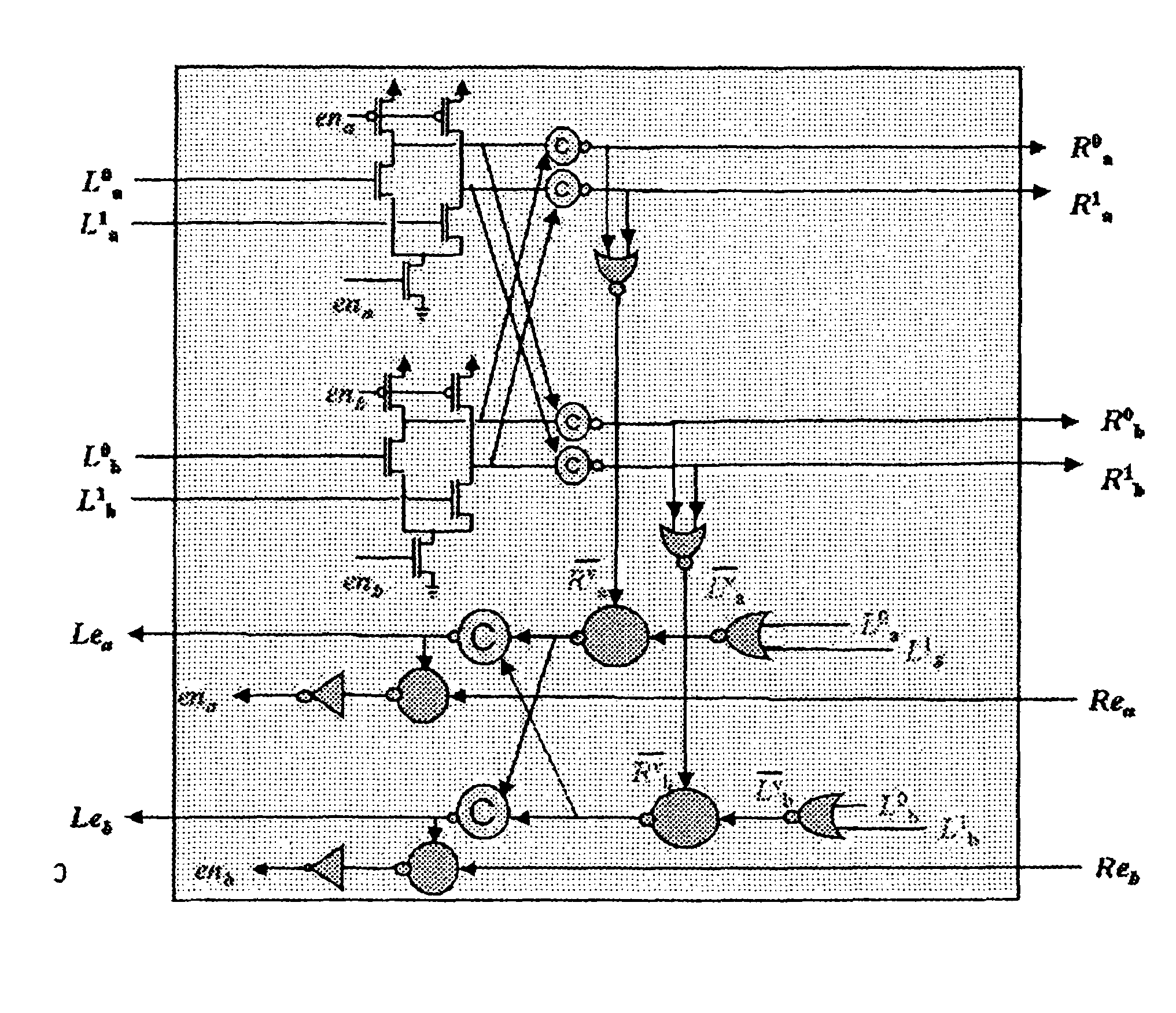
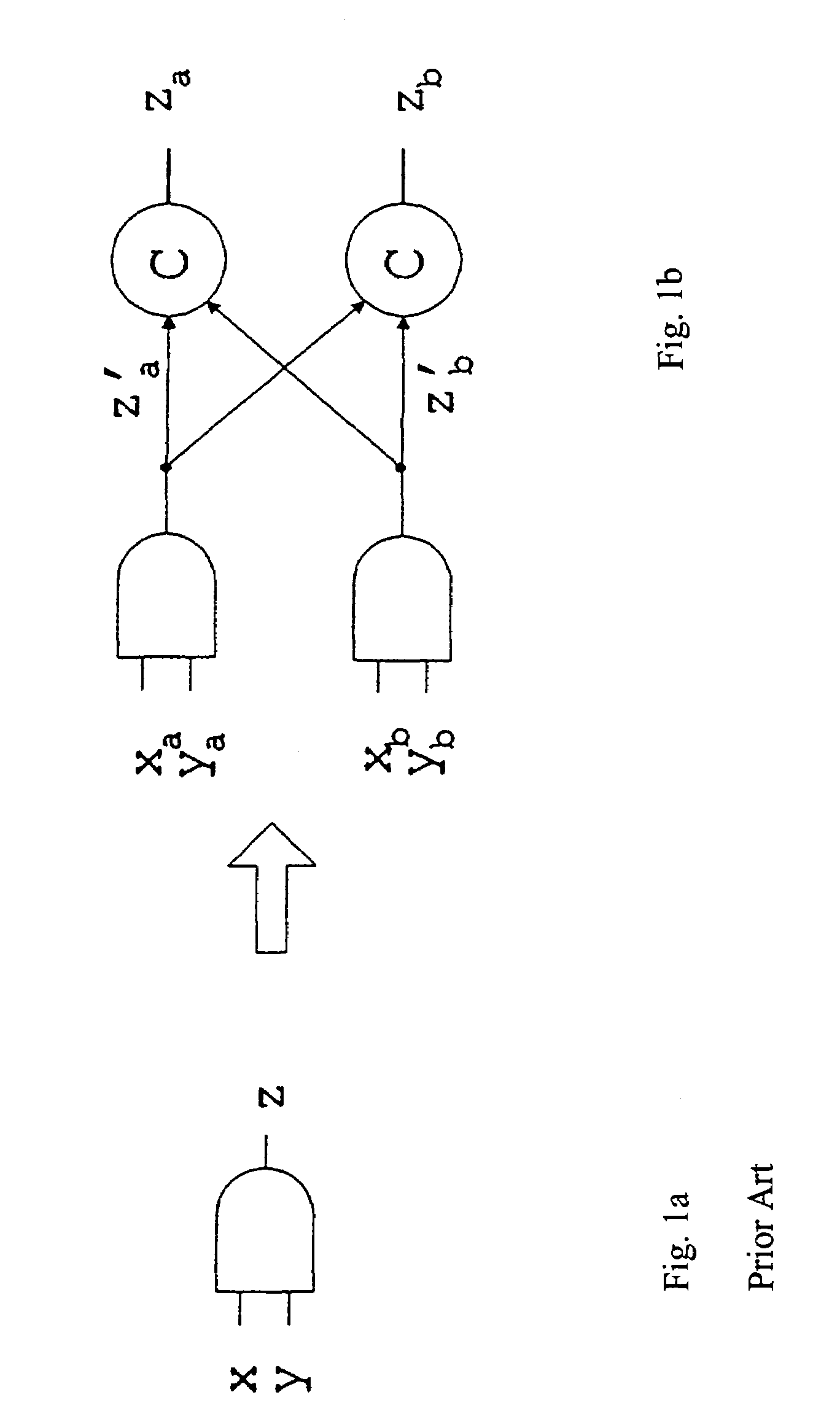
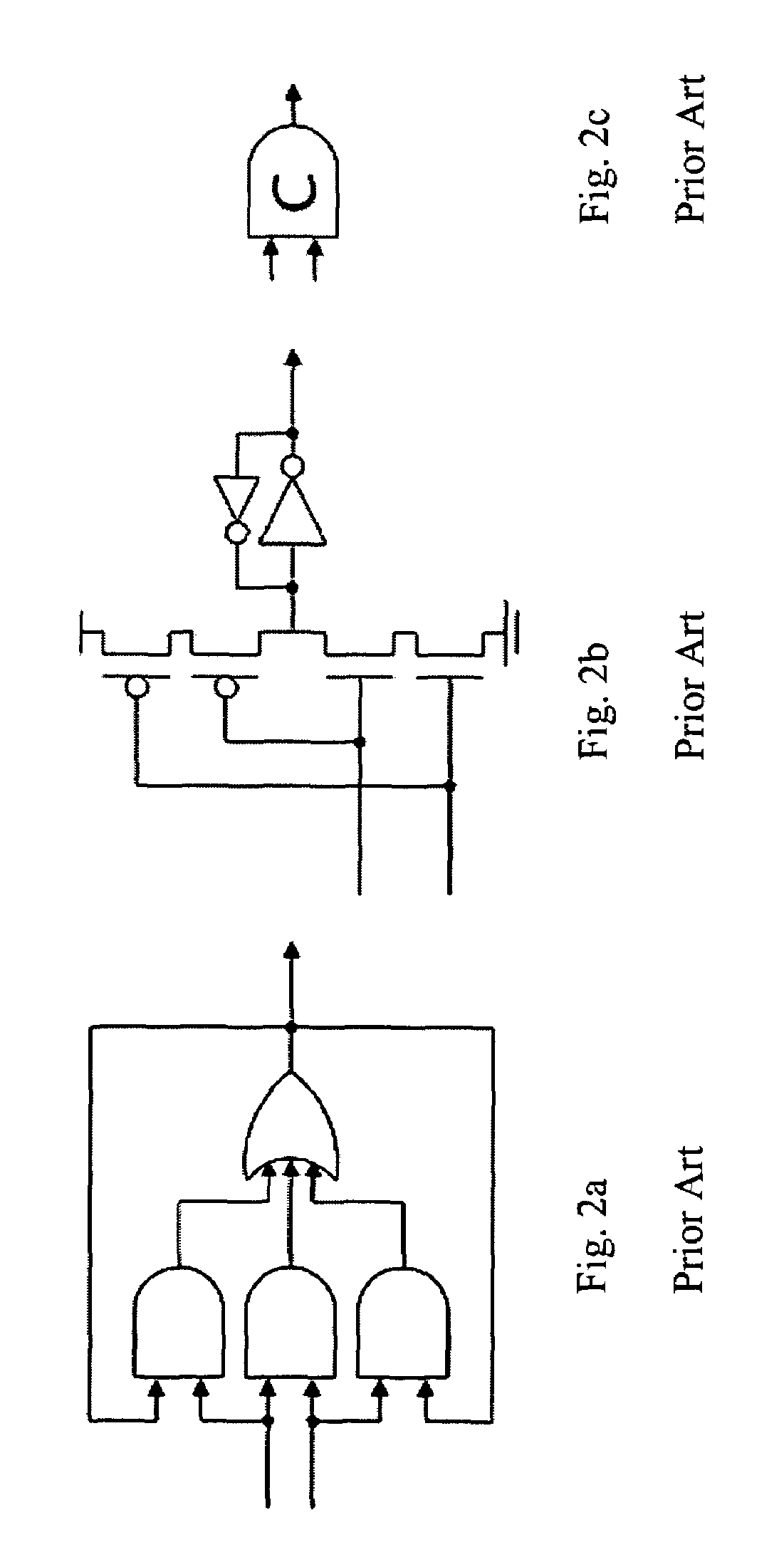
Systems and methods for mitigating the effects of soft errors in asynchronous digital circuits. Circuits are constructed using stages comprising doubled logic elements which are connected to c-elements that compare the output states of the double logic elements. The inputs of logic elements in a stage are inhibited from changing until the outputs of the c-elements of that stage are enabled. The c-elements inhibit the propagation of a soft error by halting the operation of the circuit until the temporary effects of the soft error pass.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
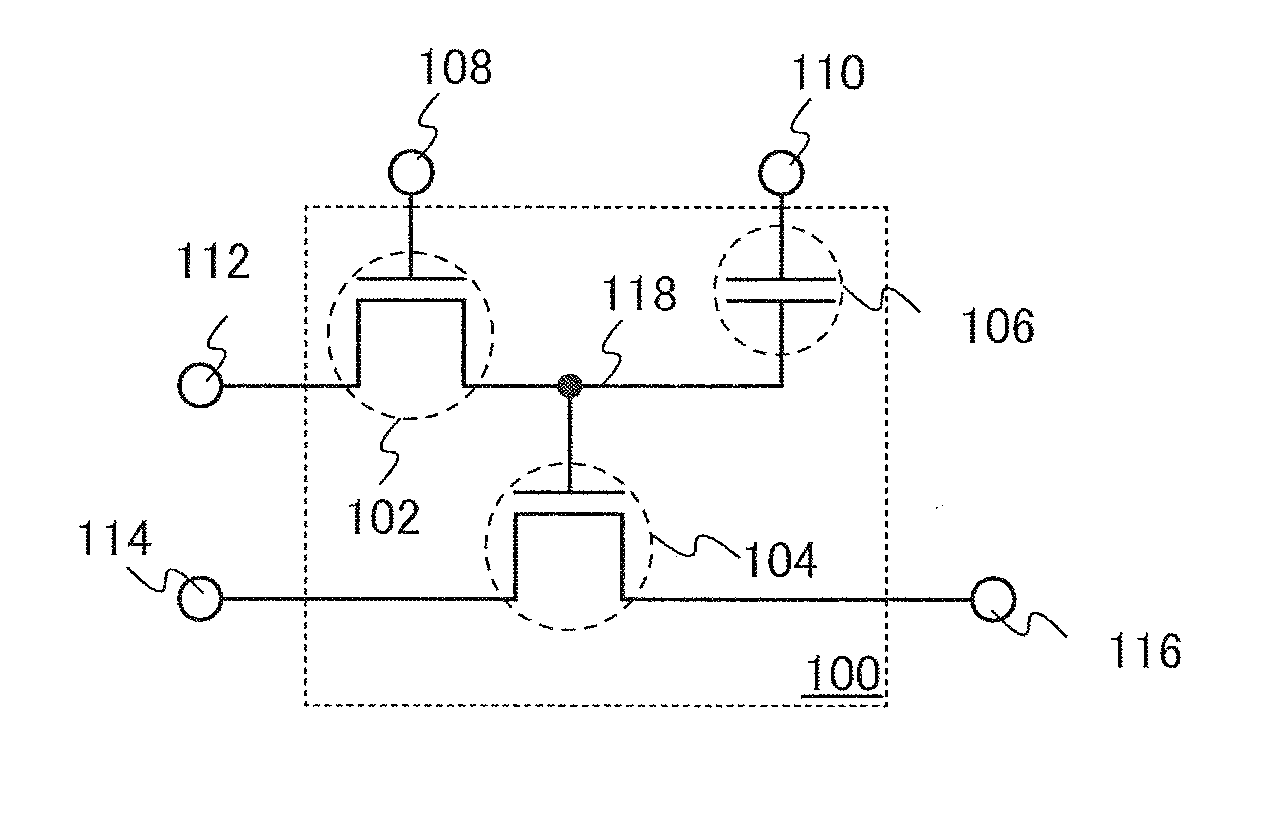
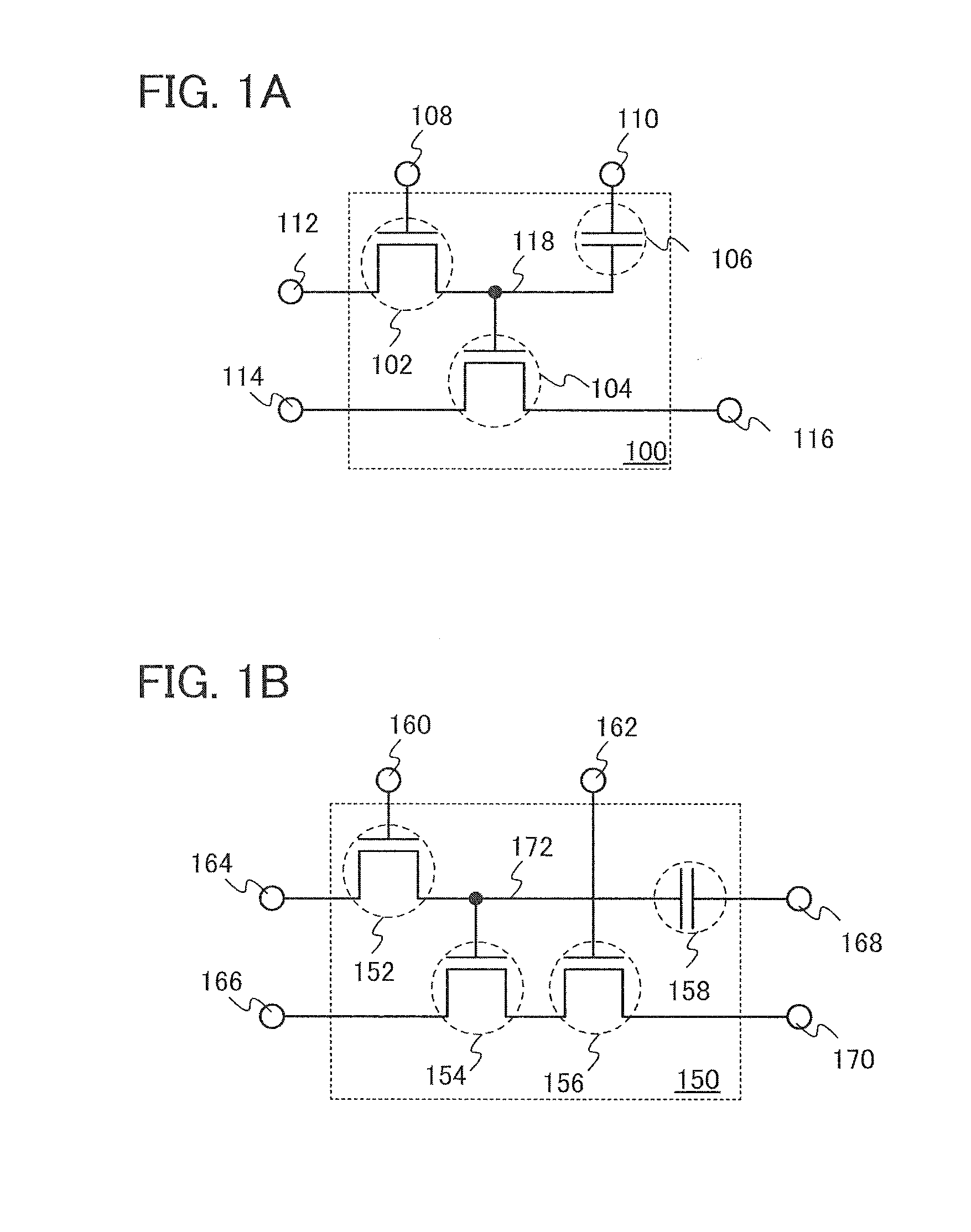
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
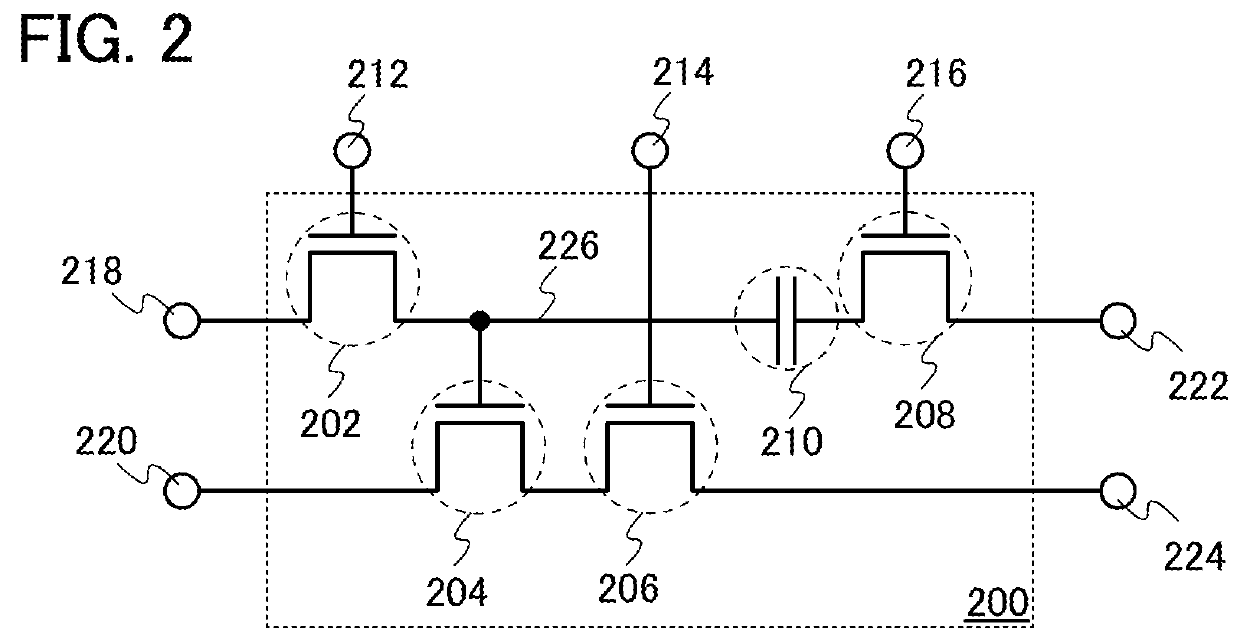
ActiveUS20130286757A1Improve accuracySoft errorError detection/correctionSolid-state devicesComputer hardwareCapacitor
An error of stored data is detected with high accuracy. Data (e.g., a remainder in a CRC) used for detecting an error is stored in a memory in which an error is unlikely to occur. Specifically, the following semiconductor device is used: a memory element including a plurality of transistors, a capacitor, and a data storage portion is provided in a matrix; the data storage portion includes one of a source and a drain of one of the plurality of transistors, a gate of another one of the plurality of transistors, and one electrode of the capacitor; a semiconductor layer including a channel of the transistor, the one of the source and the drain of which is connected to the data storage portion, has a band gap of 2.8 eV or more, or 3.2 eV or more; and the data storage portion stores data for detecting an error.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
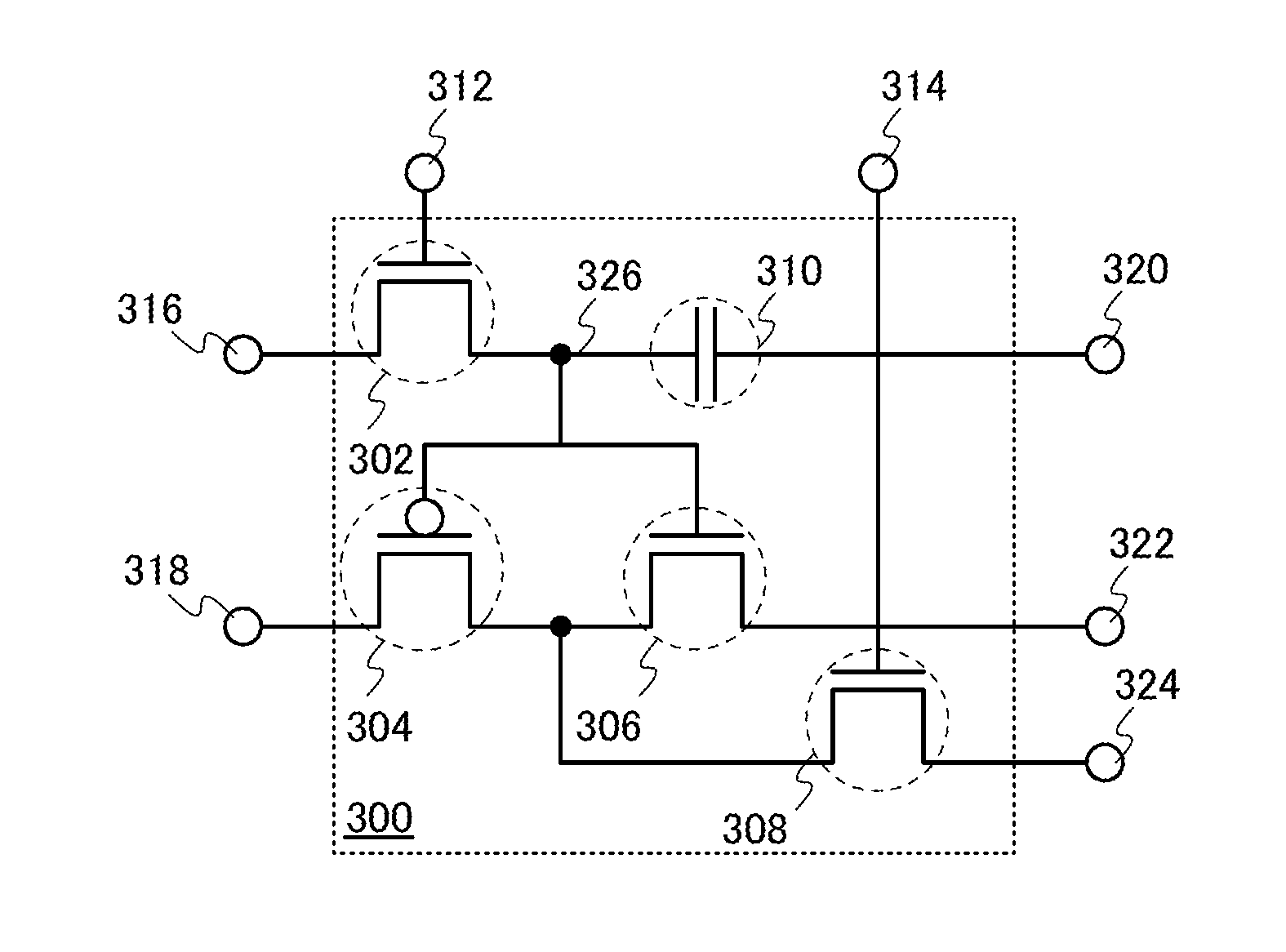
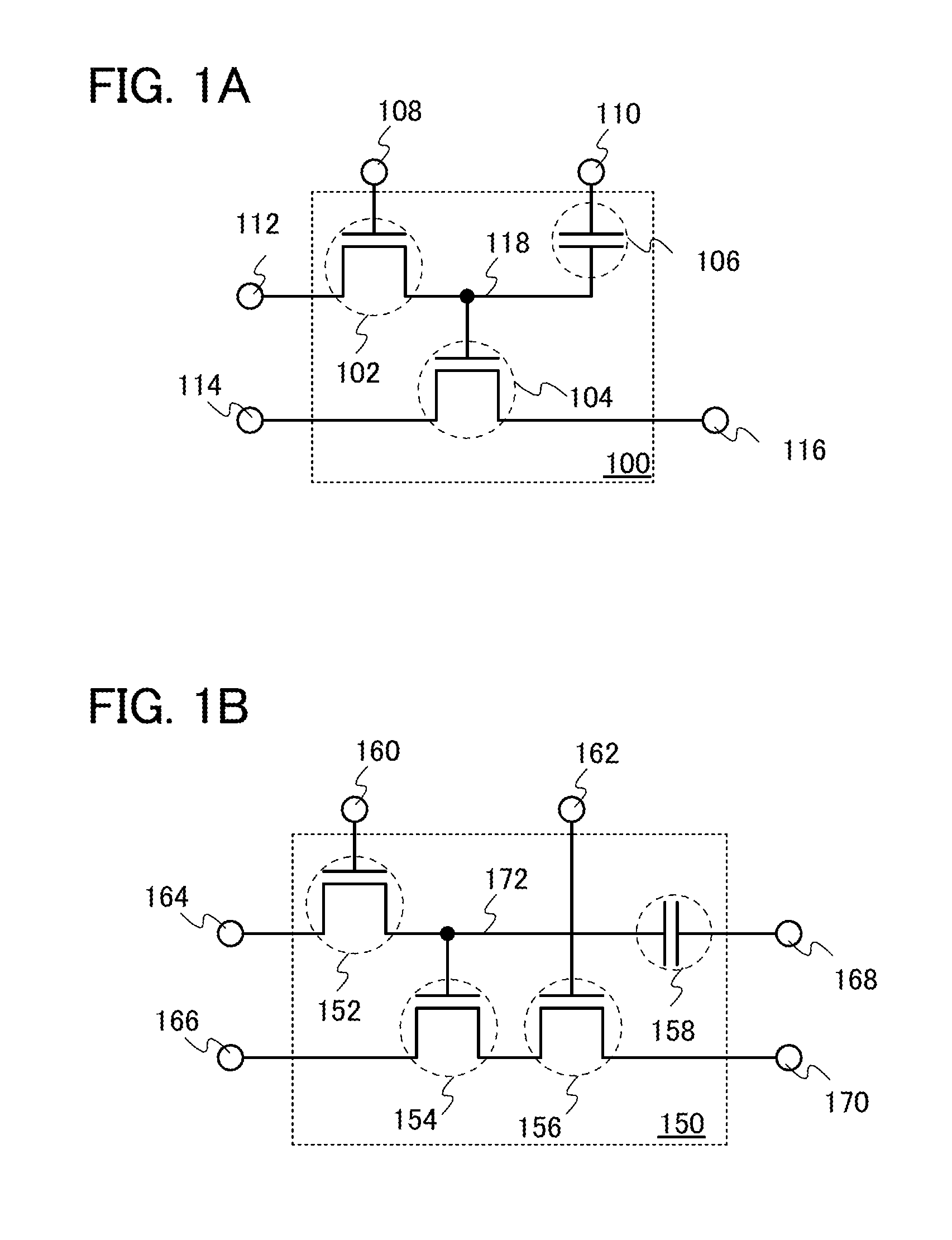
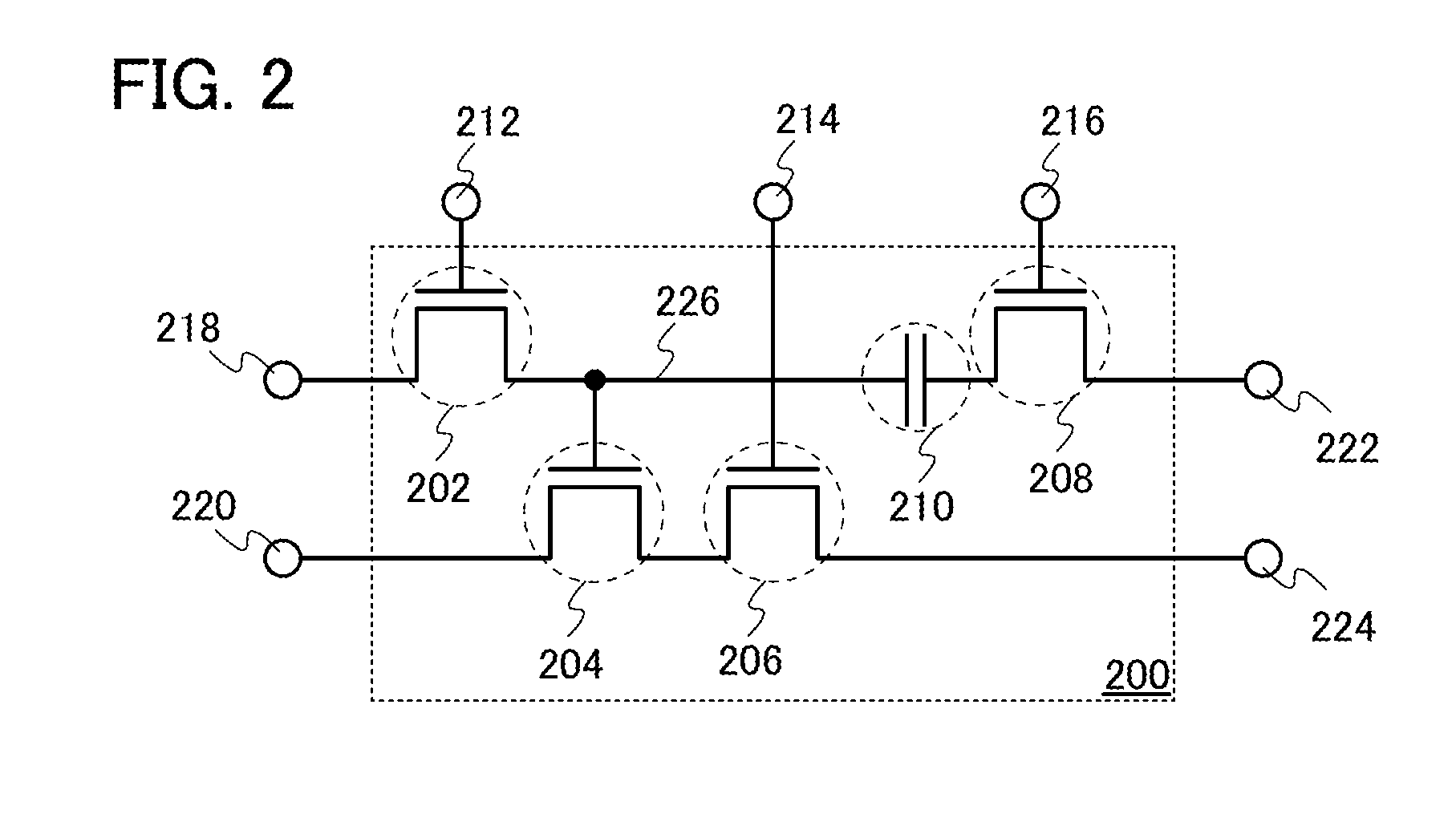
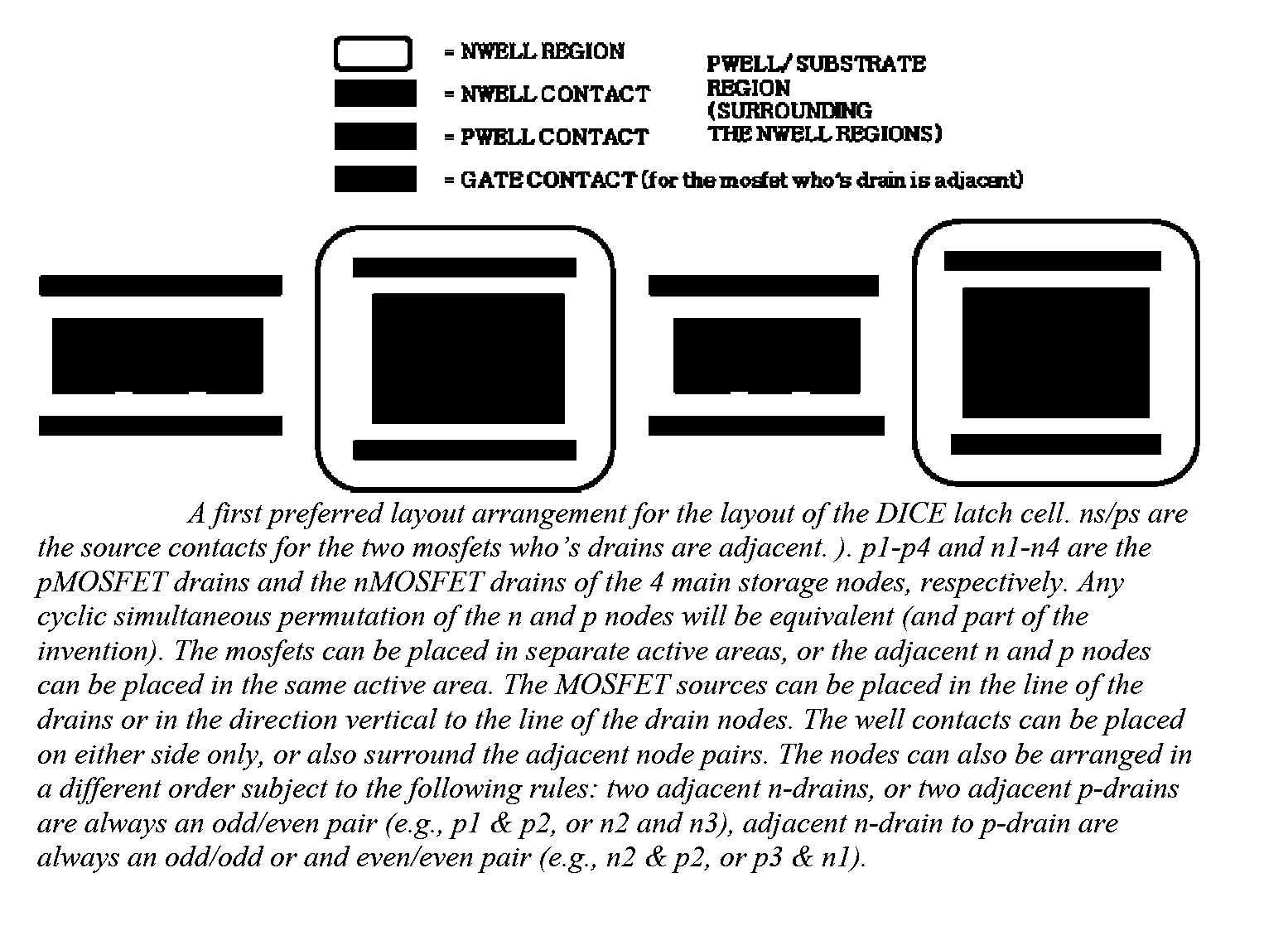
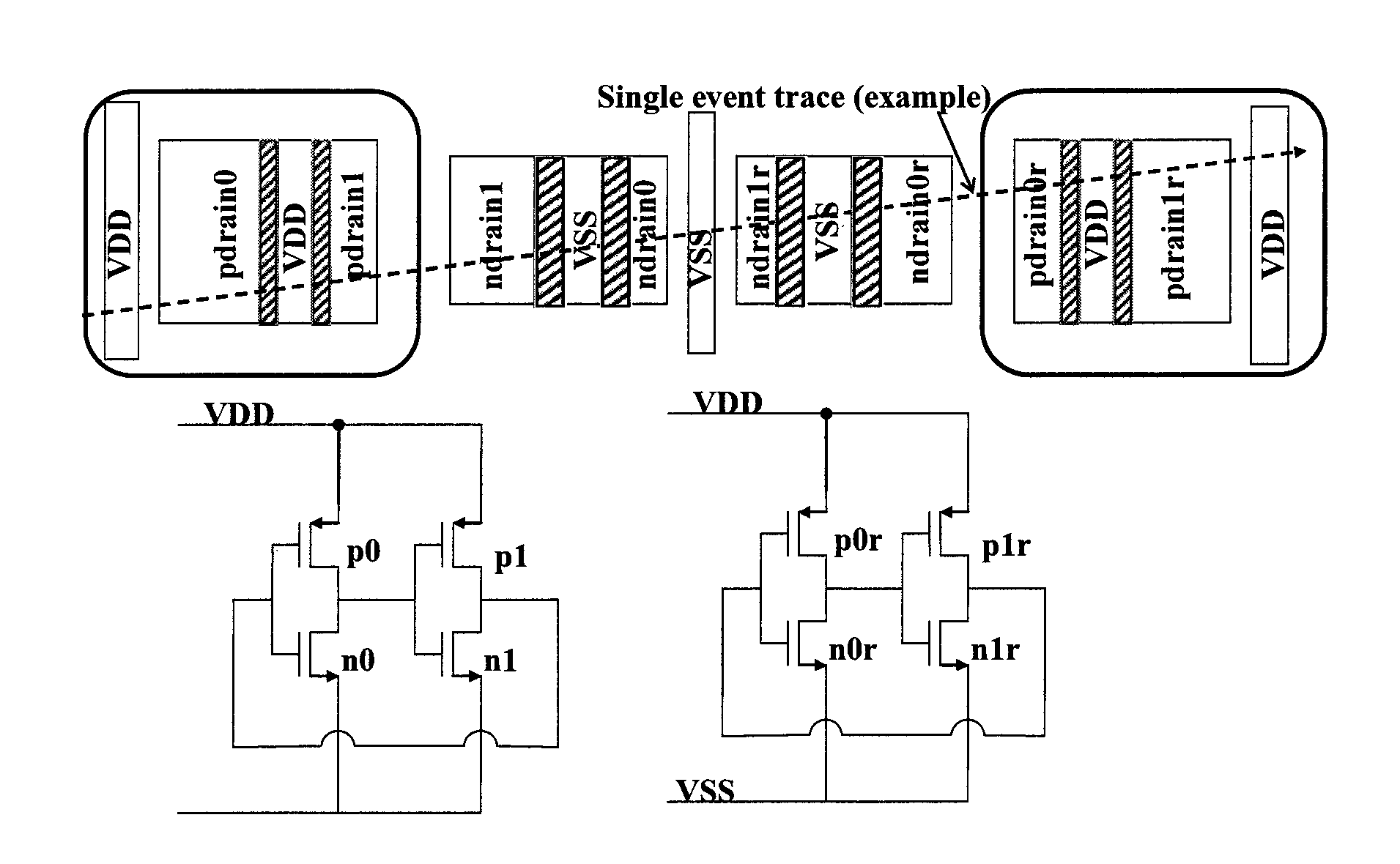
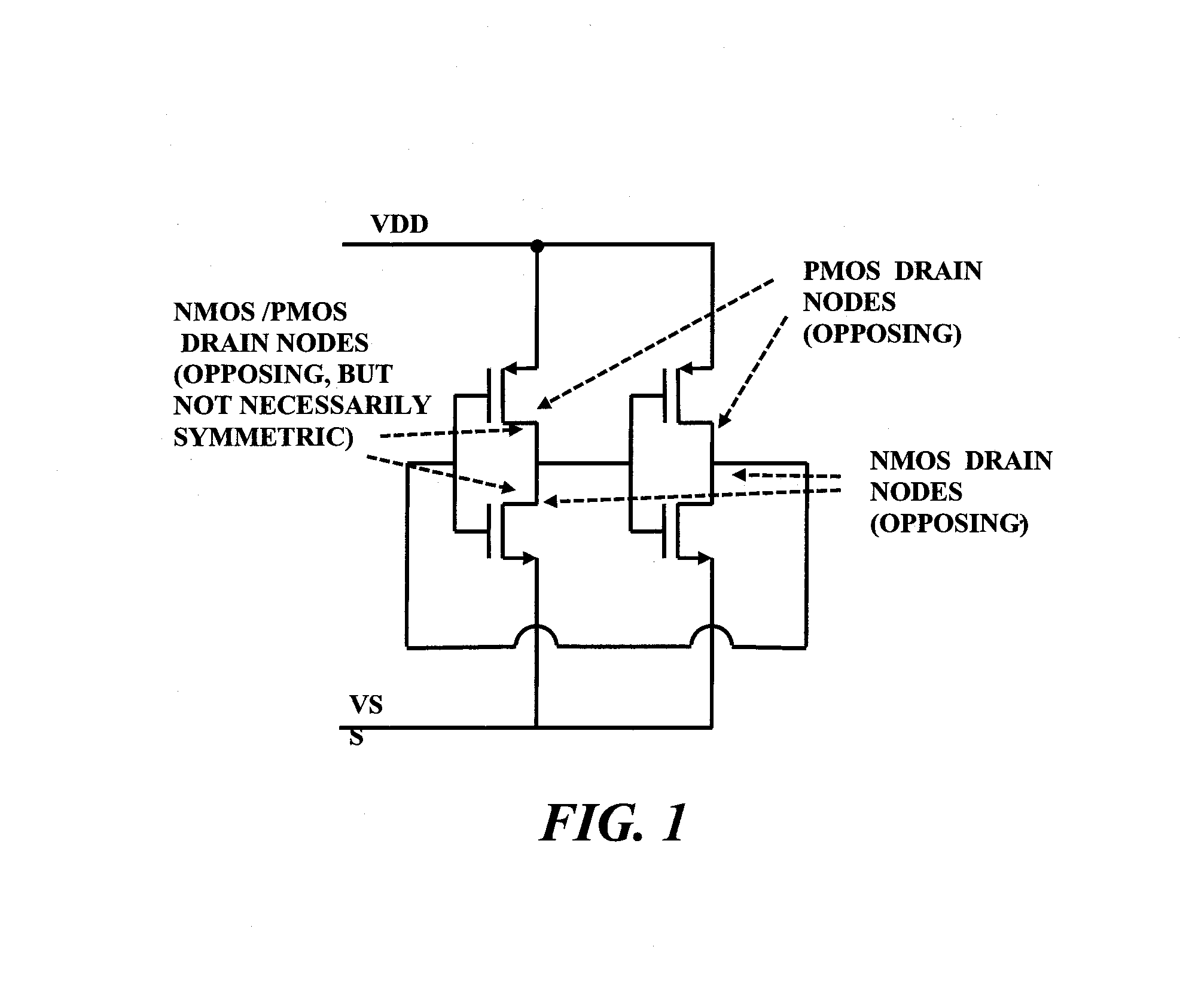
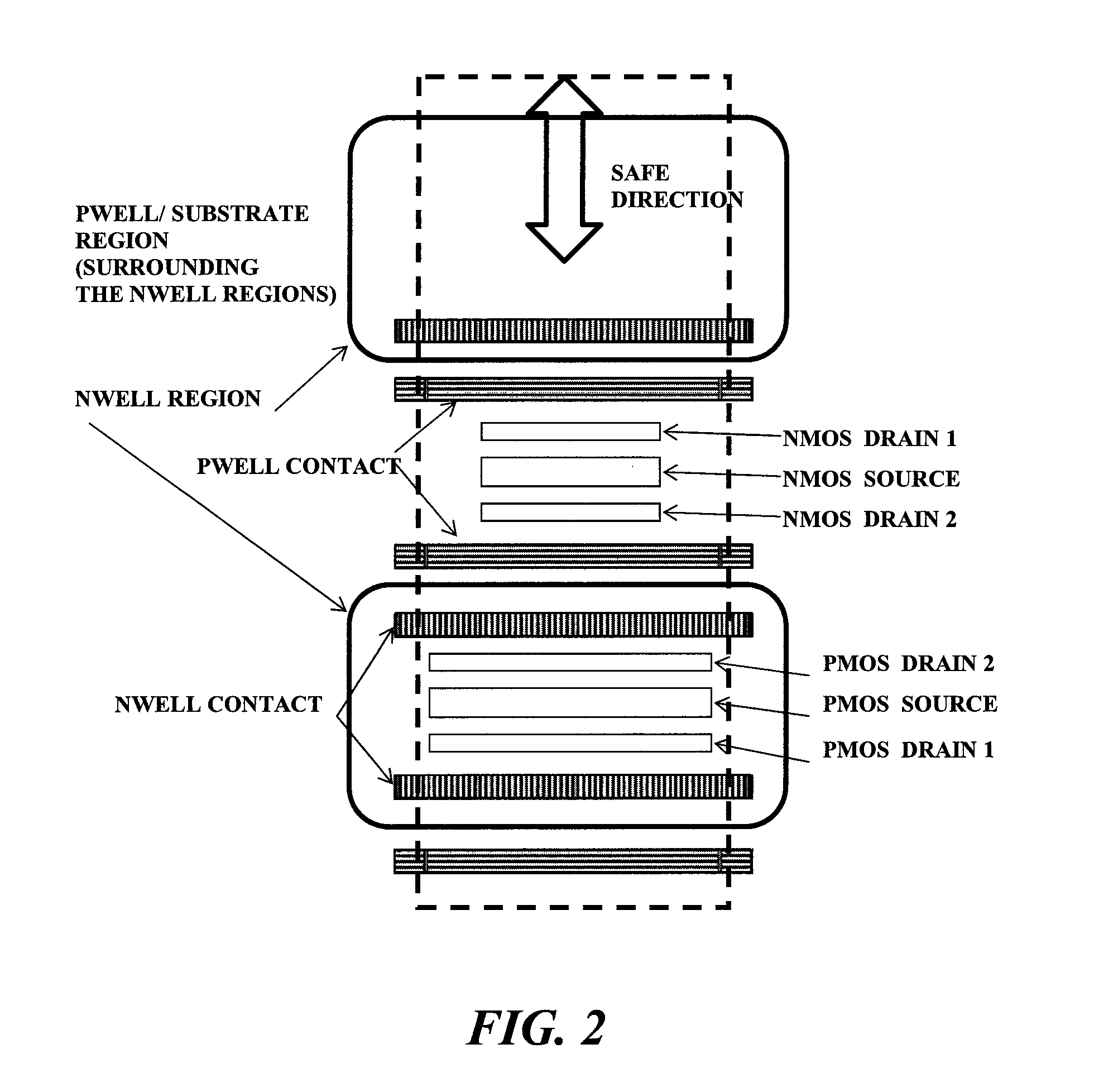
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
InactiveUS20090184733A1Protected against soft errorReduce the impactLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSolid-state devicesModem deviceElectron
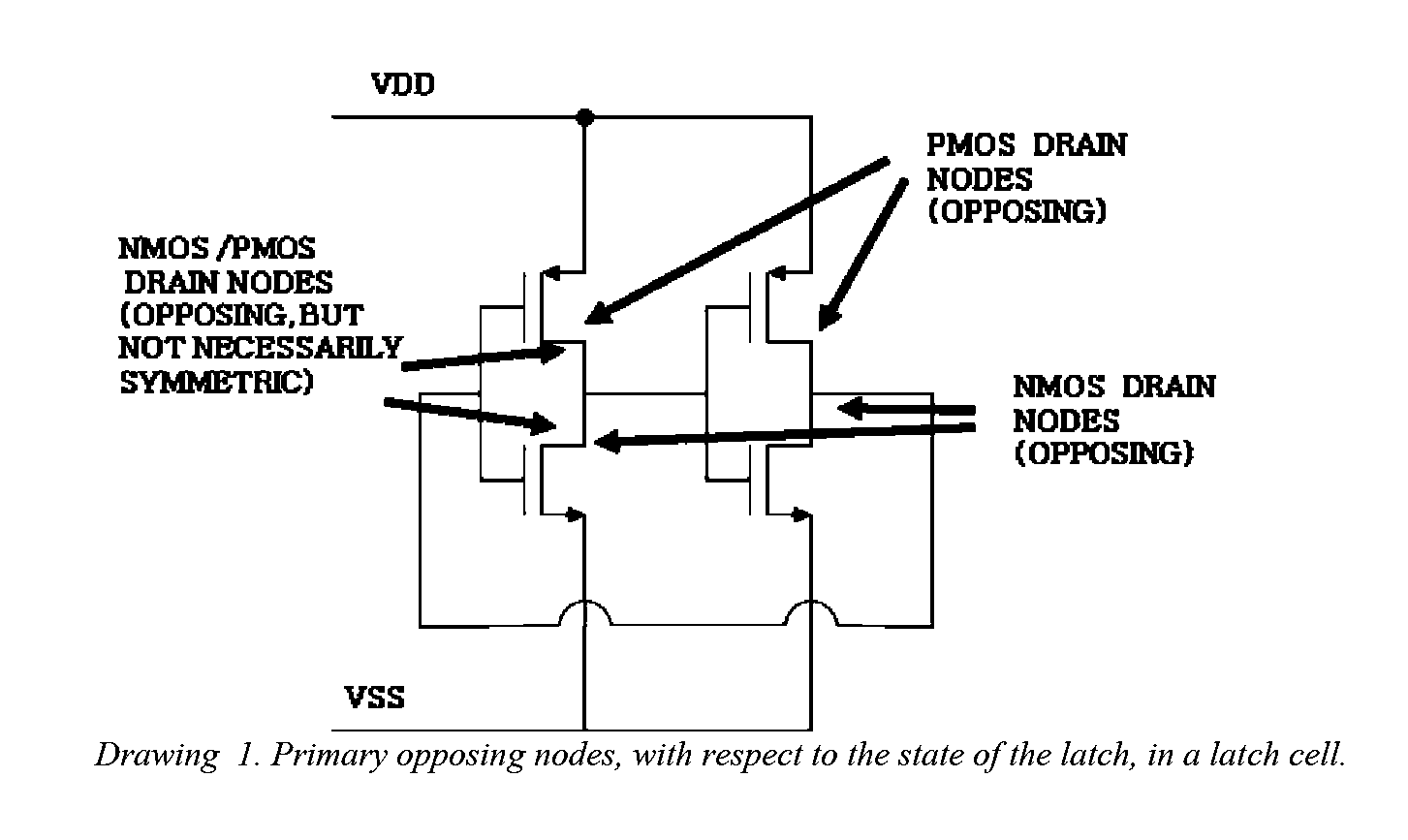
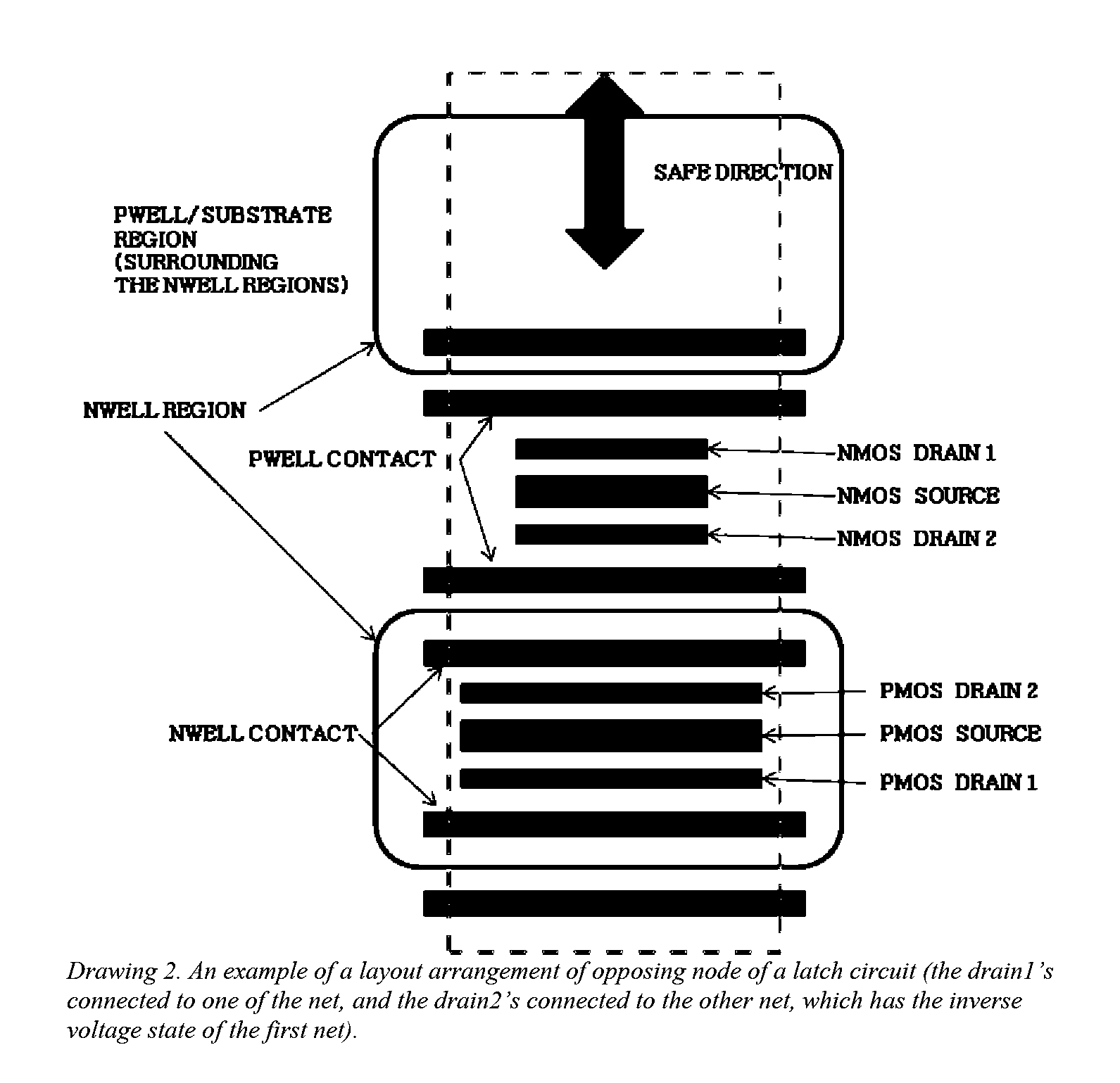
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect logic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, with layout, which are protected against soft errors. In particular, the method protects against cases where multiple nodes in circuit are affected by a single event. These events lead to multiple errors in the circuit, and while several methods exist to deal with single node errors, multiple node errors are very hard to deal with using any currently existing protection methods. The method is particularly useful for CMOS based logic circuits in modem technologies (≦90 nm), where the occurrence of multiple node pulses becomes high (due to the high integration level). It uses a unique layout configuration, which makes the circuits protected against single event generated soft-errors.
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
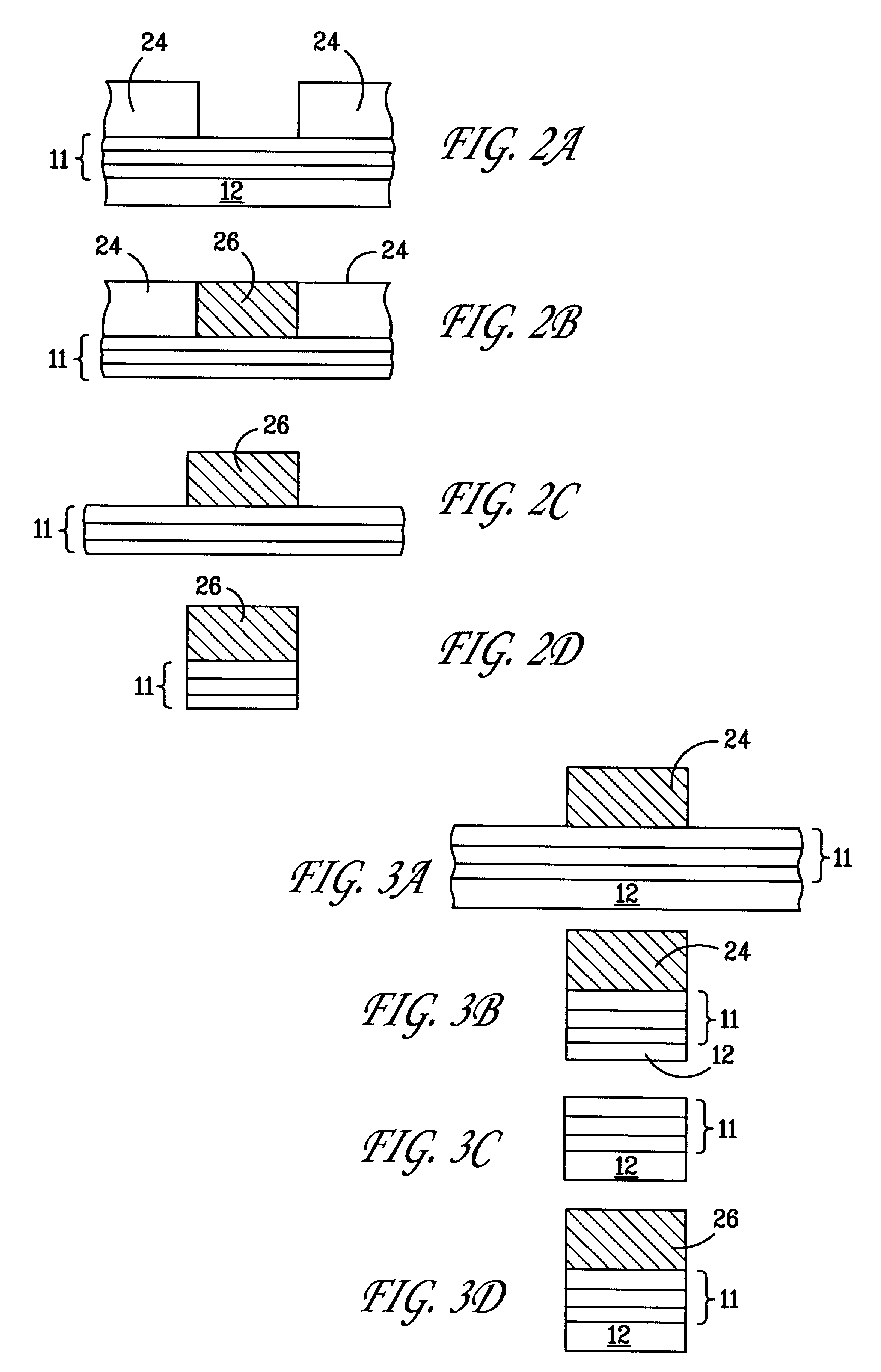
Interconnections for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having improved reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS20080157395A1Soft errorCost-effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballSolder wetting
An interconnection structure suitable for flip-chip attachment of microelectronic device chips to packages, comprising a two, three or four layer ball-limiting metallurgy including an adhesion / reaction barrier layer, and having a solder wettable layer reactive with components of a tin-containing lead free solder, so that the solderable layer can be totally consumed during soldering, but a barrier layer remains after being placed in contact with the lead free solder during soldering. One or more lead-free solder balls is selectively situated on the solder wetting layer, the lead-free solder balls comprising tin as a predominant component and one or more alloying components.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
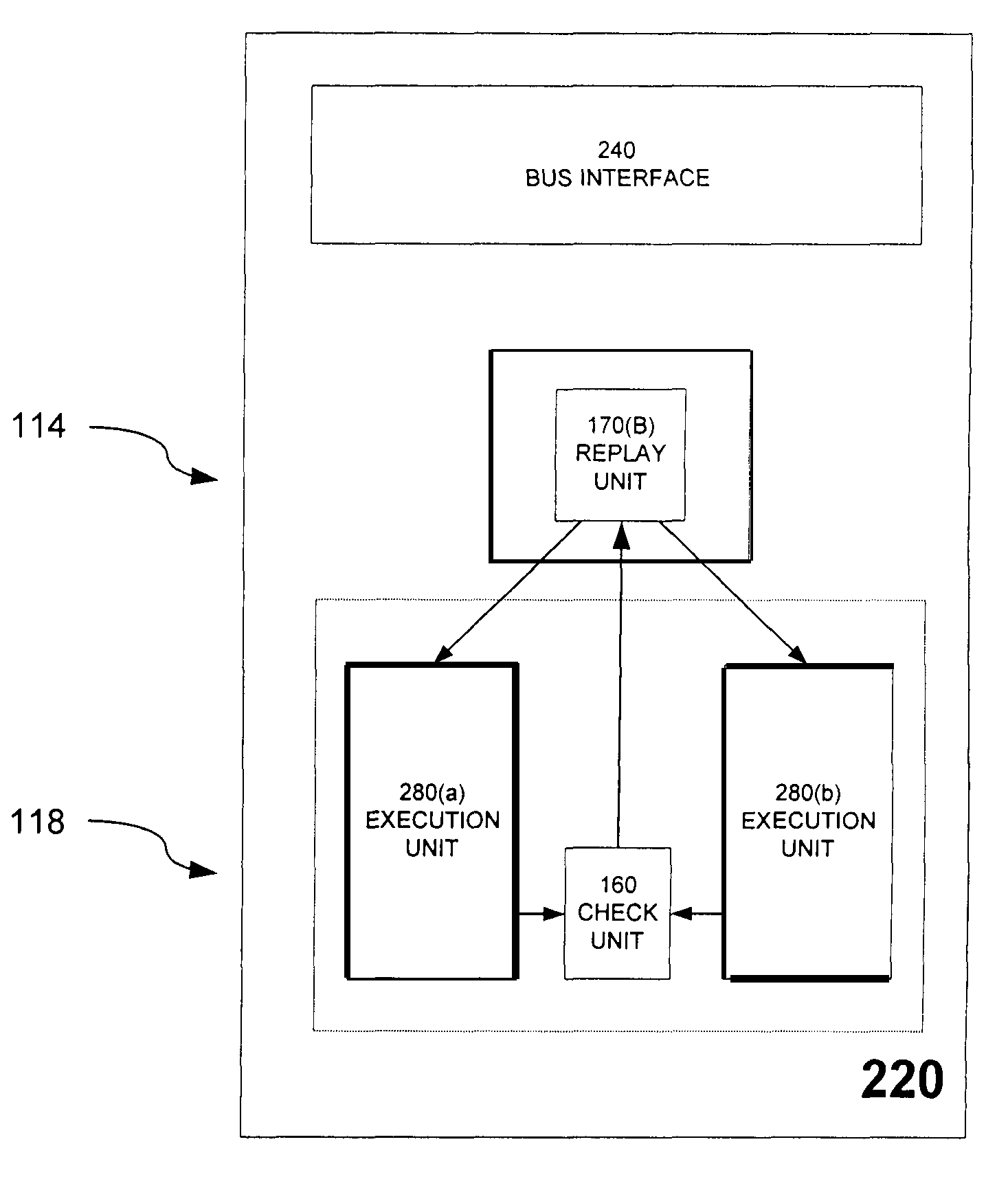
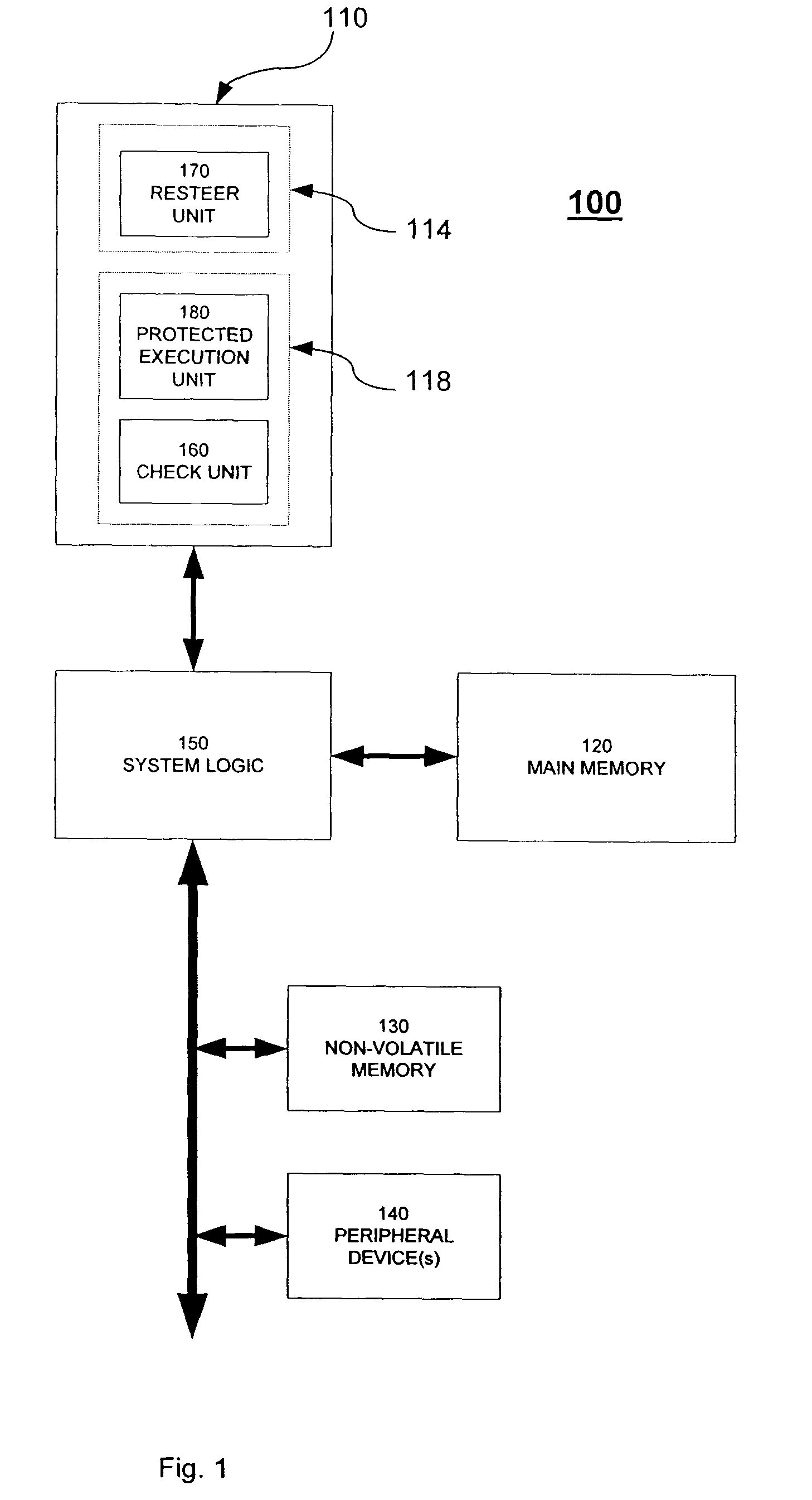
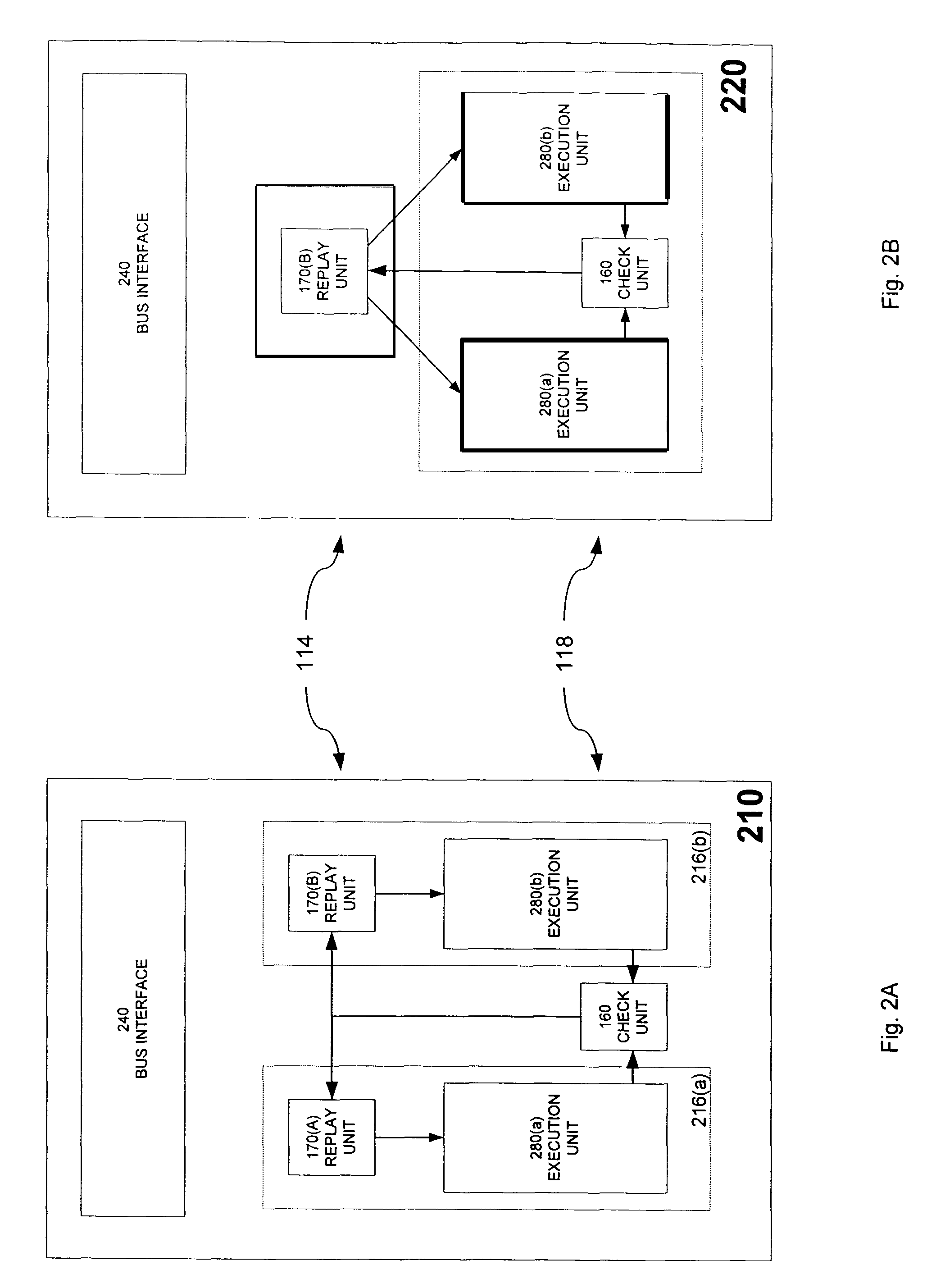
Replay mechanism for correcting soft errors
InactiveUS7340643B2Soft errorOperational speed enhancementError detection/correctionSoft errorParallel computing
A processor is provided that implements a replay mechanism to recover from soft errors. The processor includes a protected execution unit, a check unit to detect errors in results generated by the protected execution unit, and a replay unit to track selected instructions issued to the protected execution unit. When the check unit detects an error, it triggers the replay unit to reissue the selected instructions to the protected execution unit. One embodiment of the replay unit provides an instruction buffer that includes pointers to track issue and retirement status of in-flight instructions. When the check unit indicates an error, the replay unit resets a pointer to reissue the instruction for which the error was detected.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Duplicated double checking production rule set for fault-tolerant electronics
InactiveUS7301362B2Reduce soft errorsEliminating soft errorReliability increasing modificationsFail-safe circuitsElectronic systemsHemt circuits
Systems and methods for mitigating the effects of soft errors in asynchronous digital circuits. Circuits are constructed using stages comprising doubled logic elements which are connected to c-elements that compare the output states of the double logic elements. The inputs of logic elements in a stage are inhibited from changing until the outputs of the c-elements of that stage are enabled. The c-elements inhibit the propagation of a soft error by halting the operation of the circuit until the temporary effects of the soft error pass.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Flip-flop with additional state storage in the event of turn-off
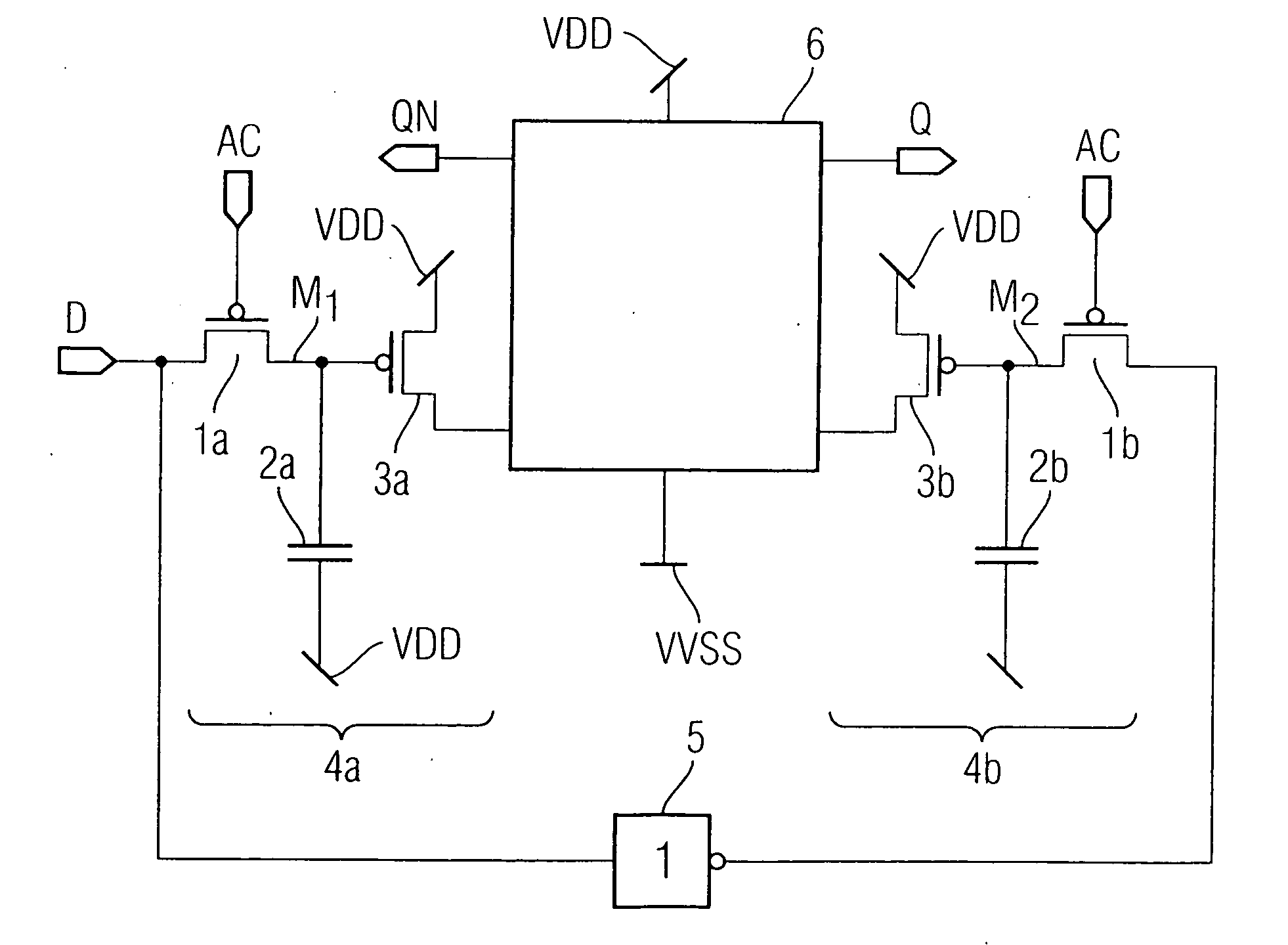
InactiveUS20060119406A1Unintentional activationImprove leakage currentDigital storageElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLogic state
The flip-flop according to the invention serves for storing an item of logic state information and has at least one data input and at least one data output. The flip-flop comprises at least one latch stage for storing the state information if the flip-flop is switched on. Furthermore, the flip-flop according to the invention comprises at least one memory cell having a capacitance as storage element. In this case, the at least one memory cell serves for storing the state information if the flip-flop is switched off.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
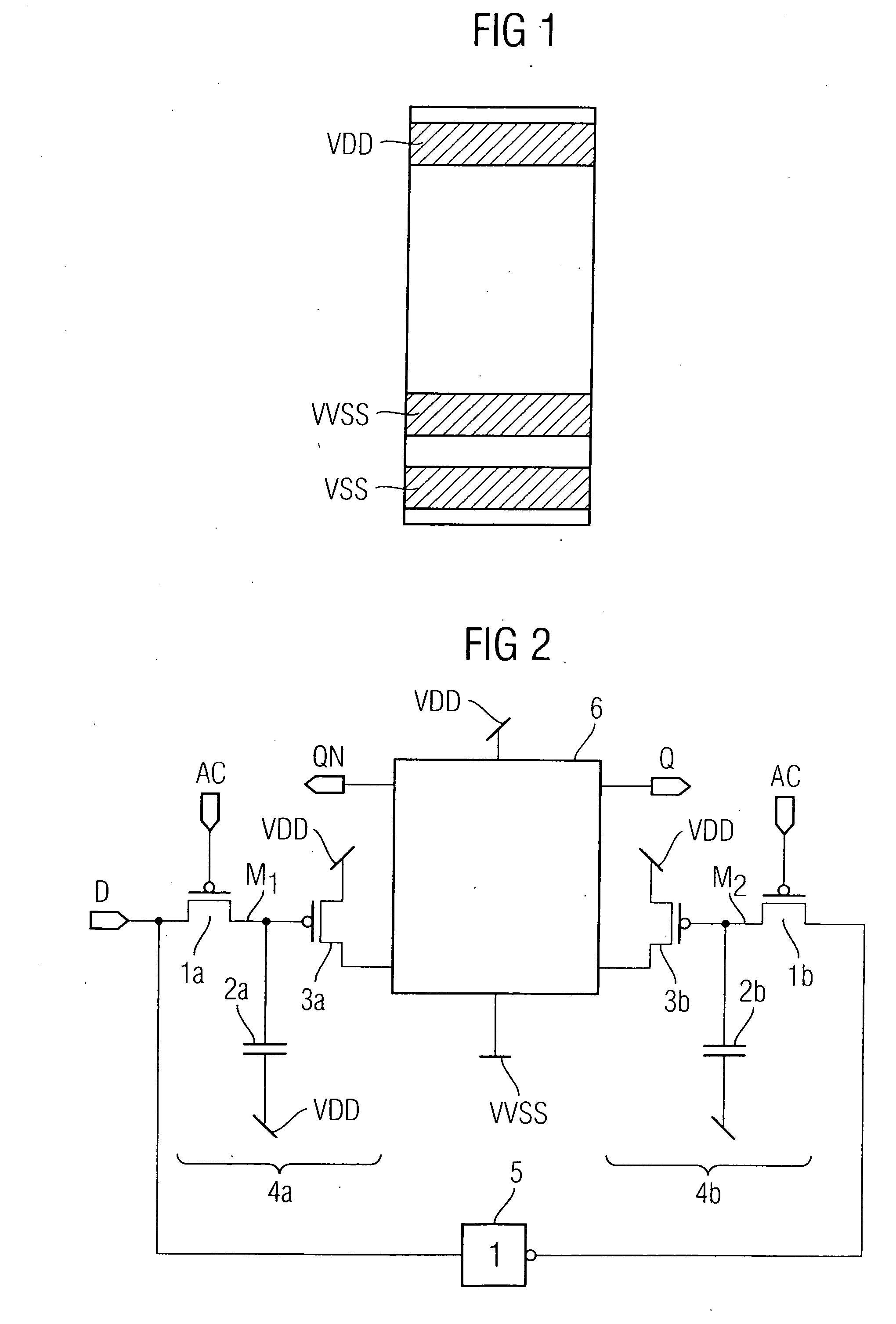
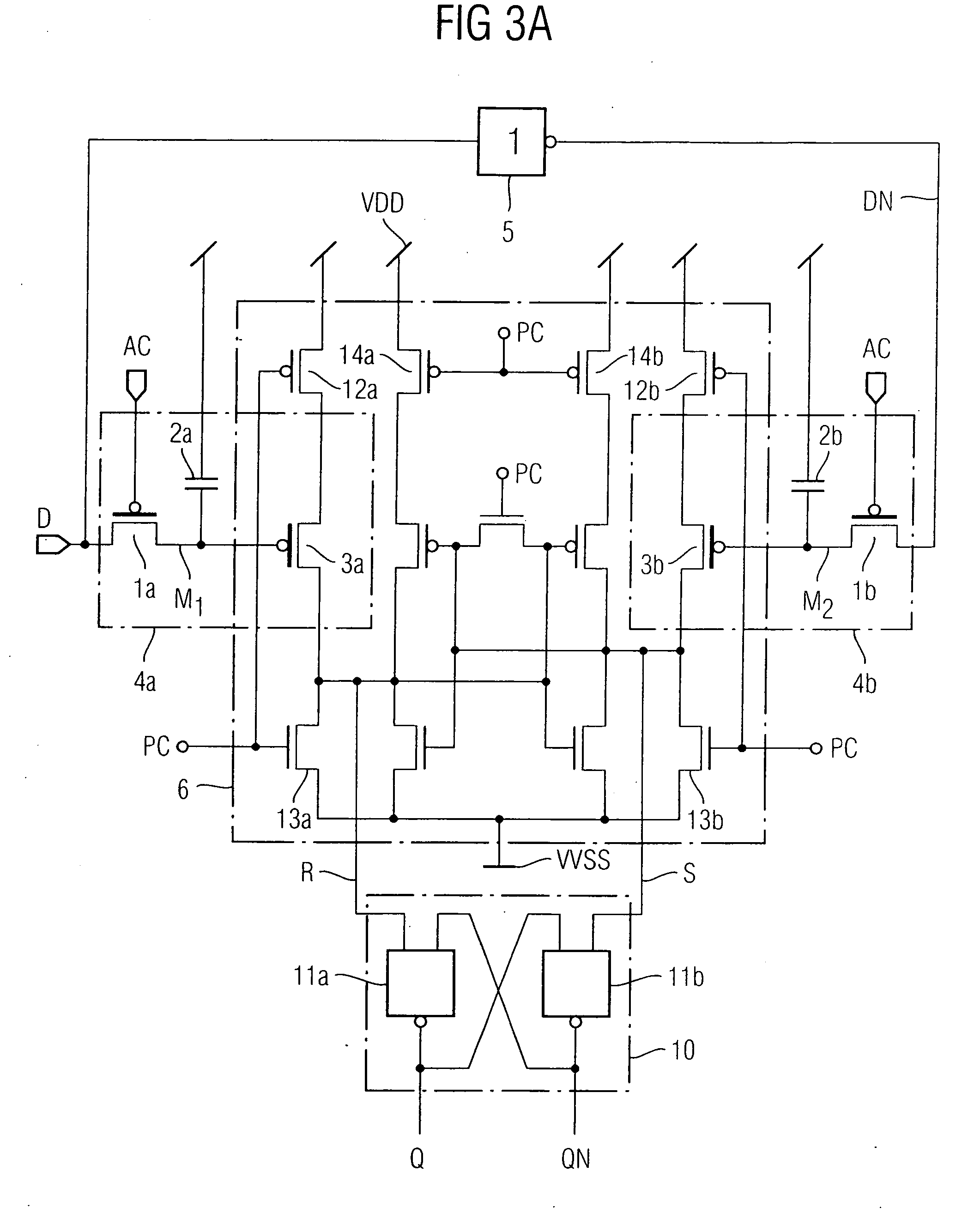
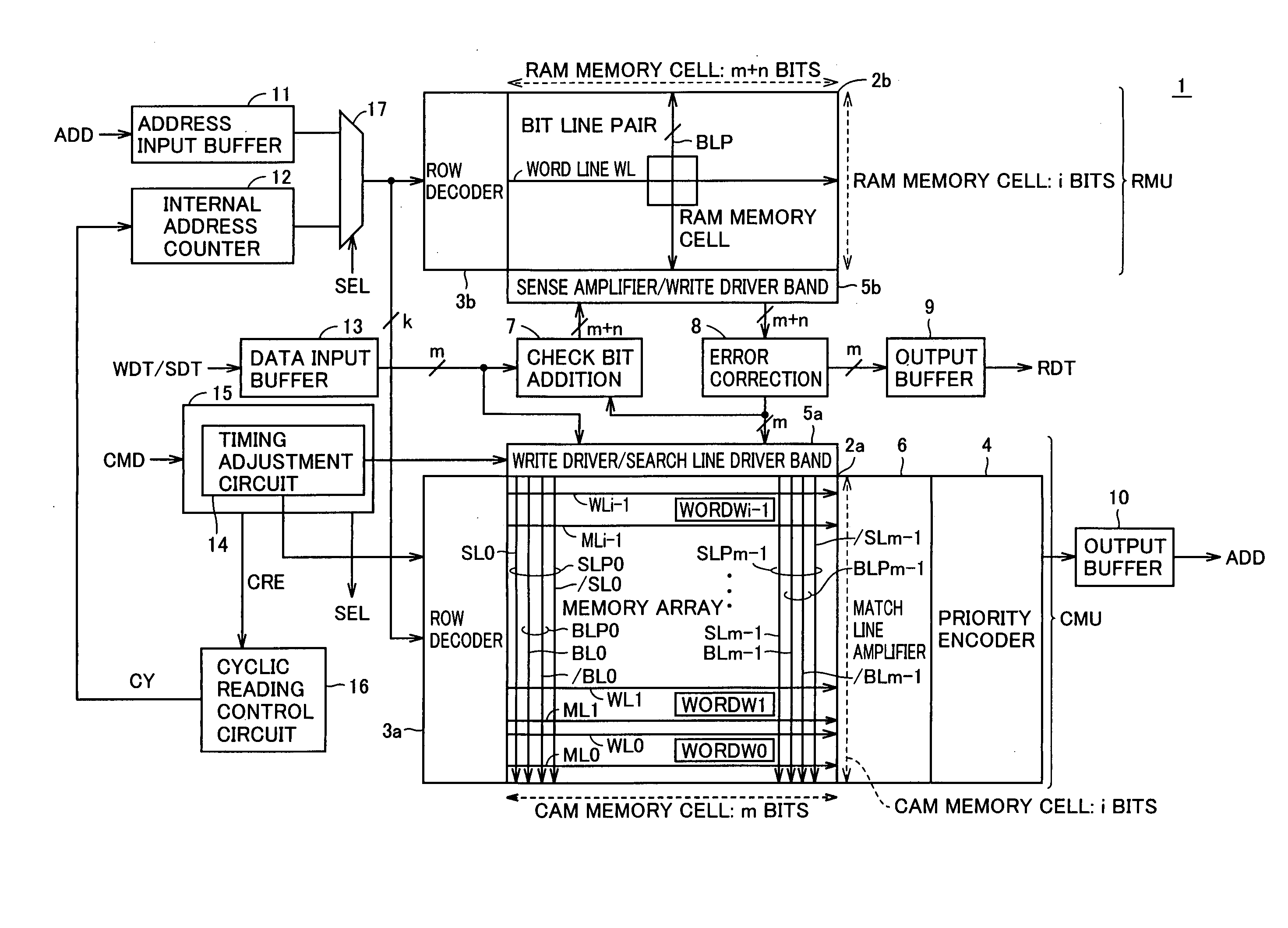
Associative memory capable of searching for data while keeping high data reliability
InactiveUS20050289407A1High data reliabilityImprove the immunityError detection/correctionCode conversionDependabilityData reliability
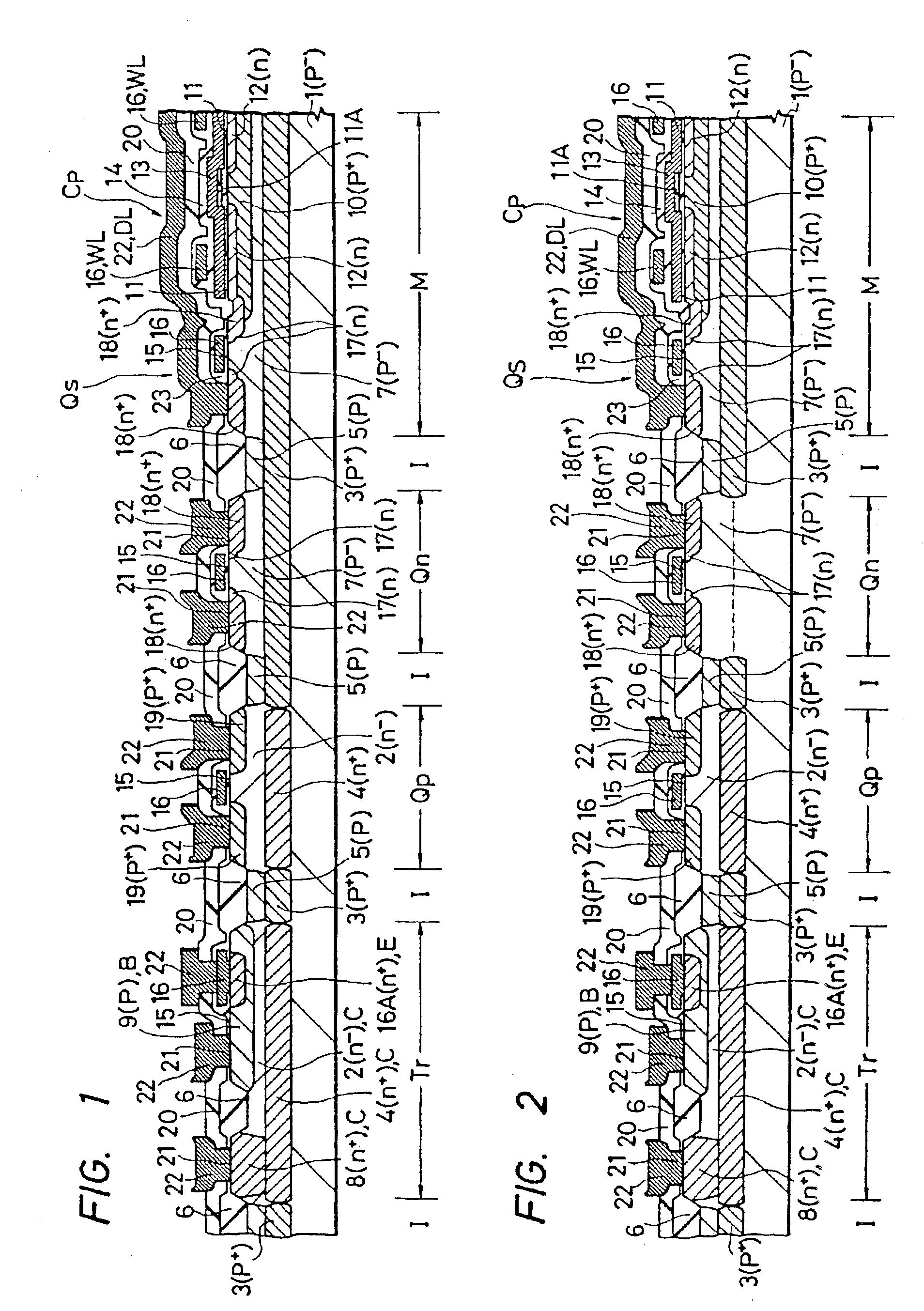
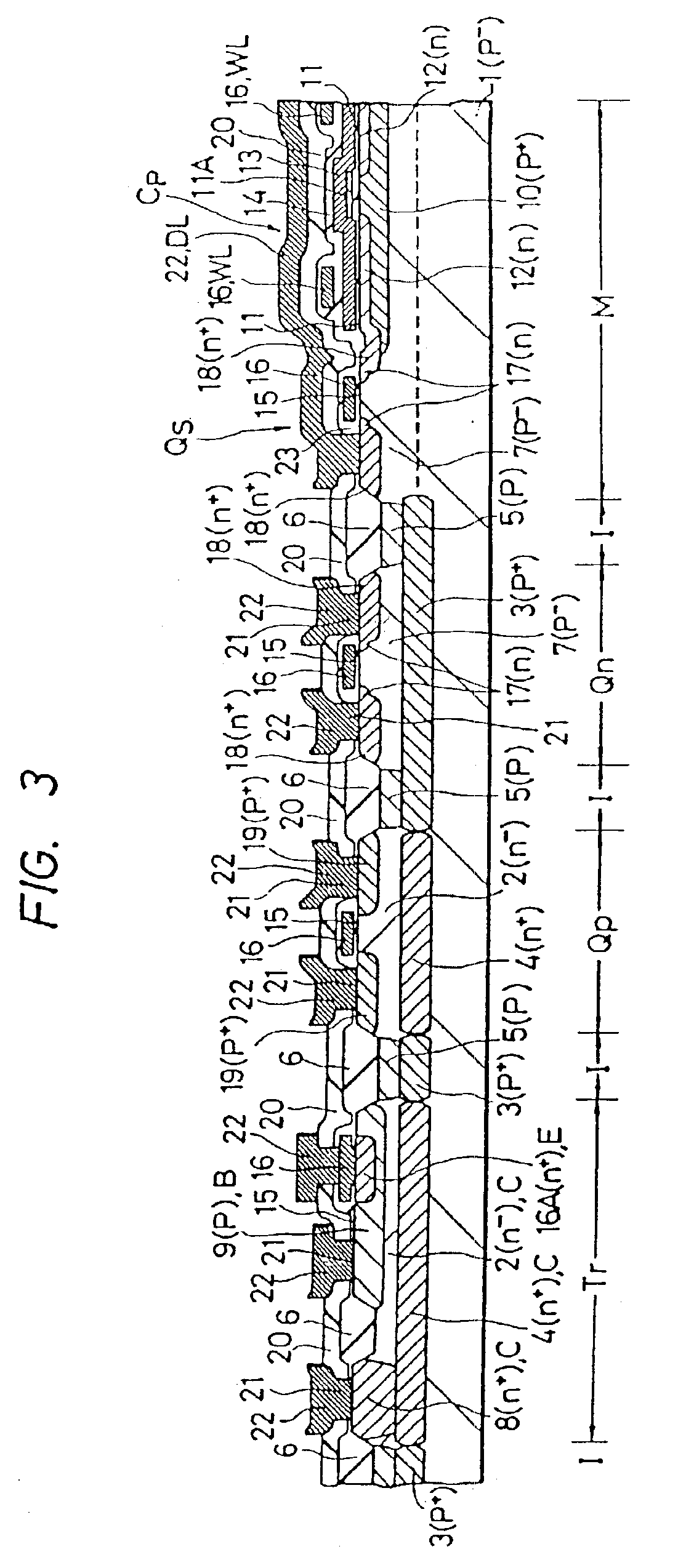
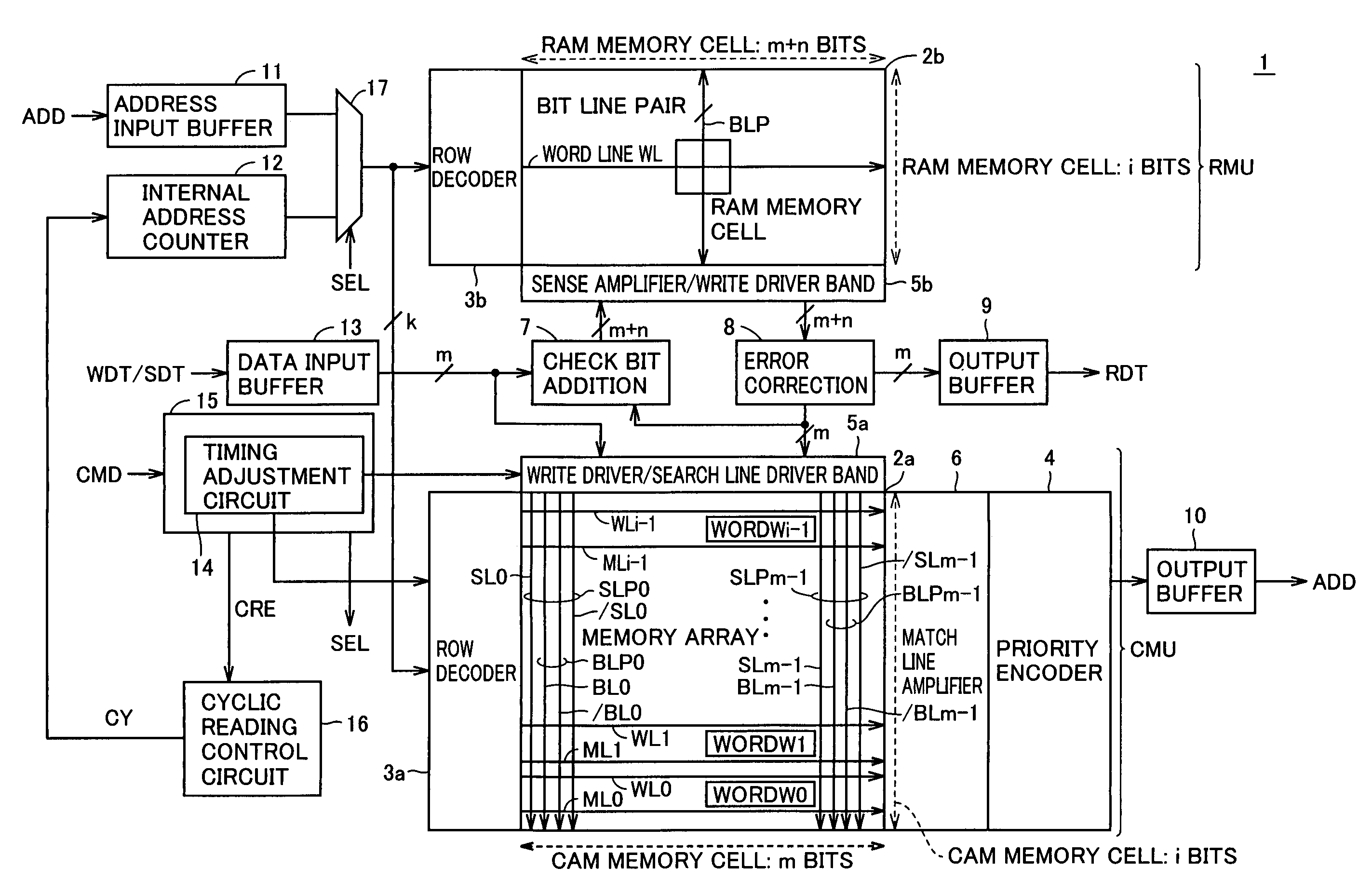
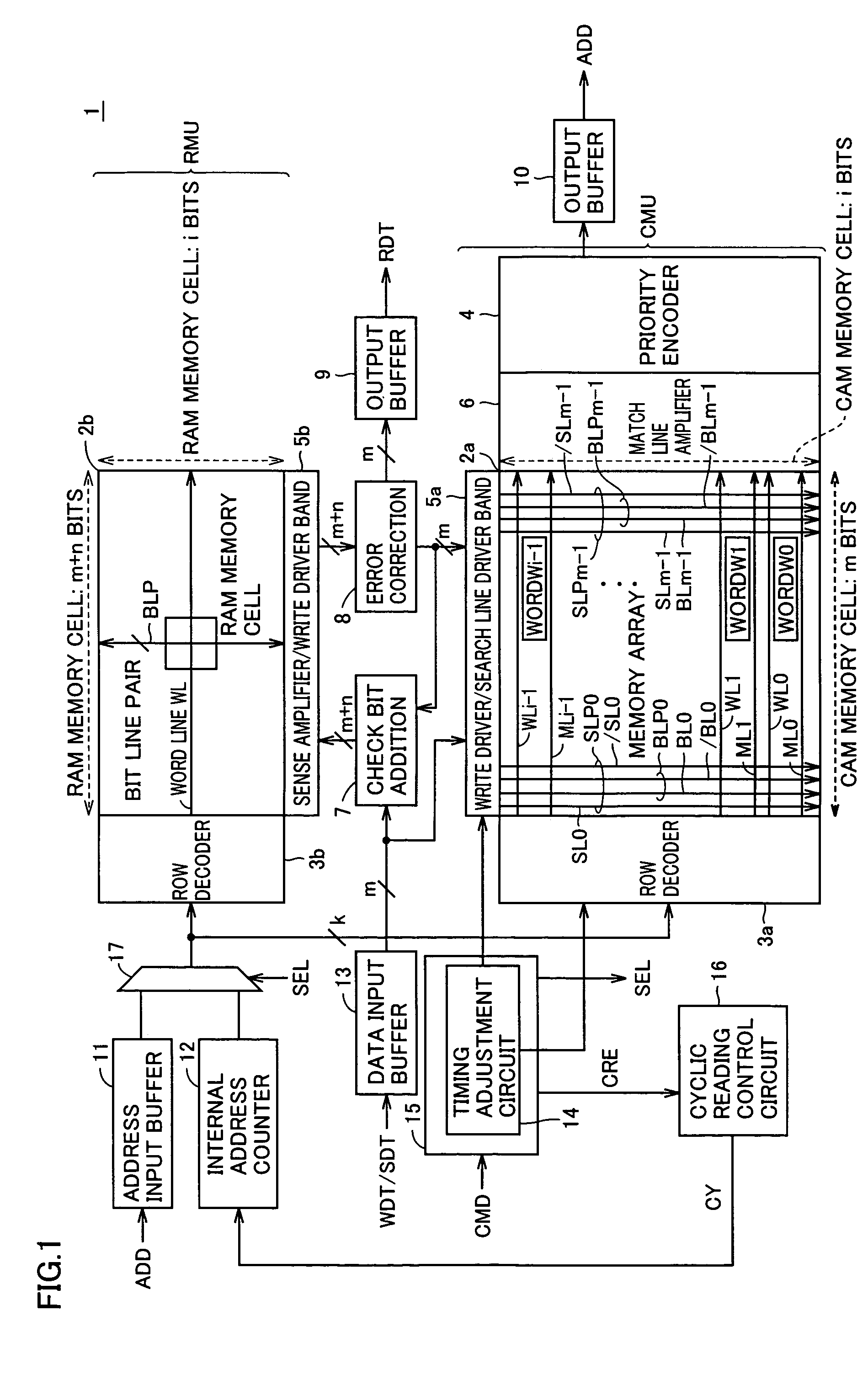
A CAM unit has a memory array for storing storage data, and a RAM unit has a memory array for storing the same storage data and check bits added thereto for determining whether the storage data in its memory array has an error. An error correction circuit uses the check bits to correct any error of data read from the memory array of the RAM unit and rewrite the error-corrected data to the memory arrays. Even if a soft error occurs in the storage data, the check bits can be used to correct the error in the data and rewrite the error-corrected data. Thus, a matching comparison can be performed on the storage data with high reliability.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
ActiveUS8566770B2Reduce impactSoft errorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionFail-safe circuitsCMOSLogic cell
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
Interconnections for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS7410833B2Soft errorCost-effectivePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder wettingSolder ball
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
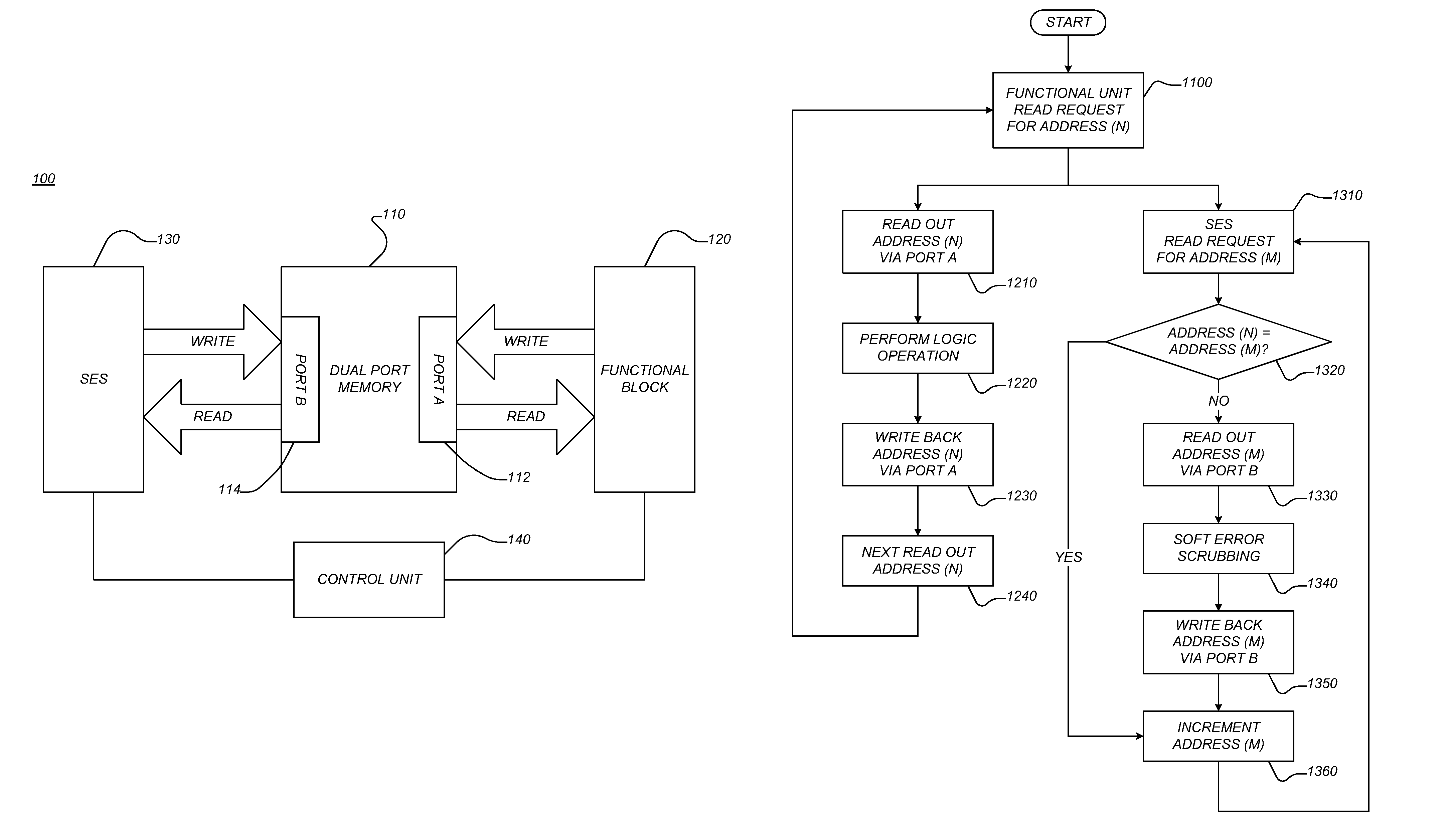
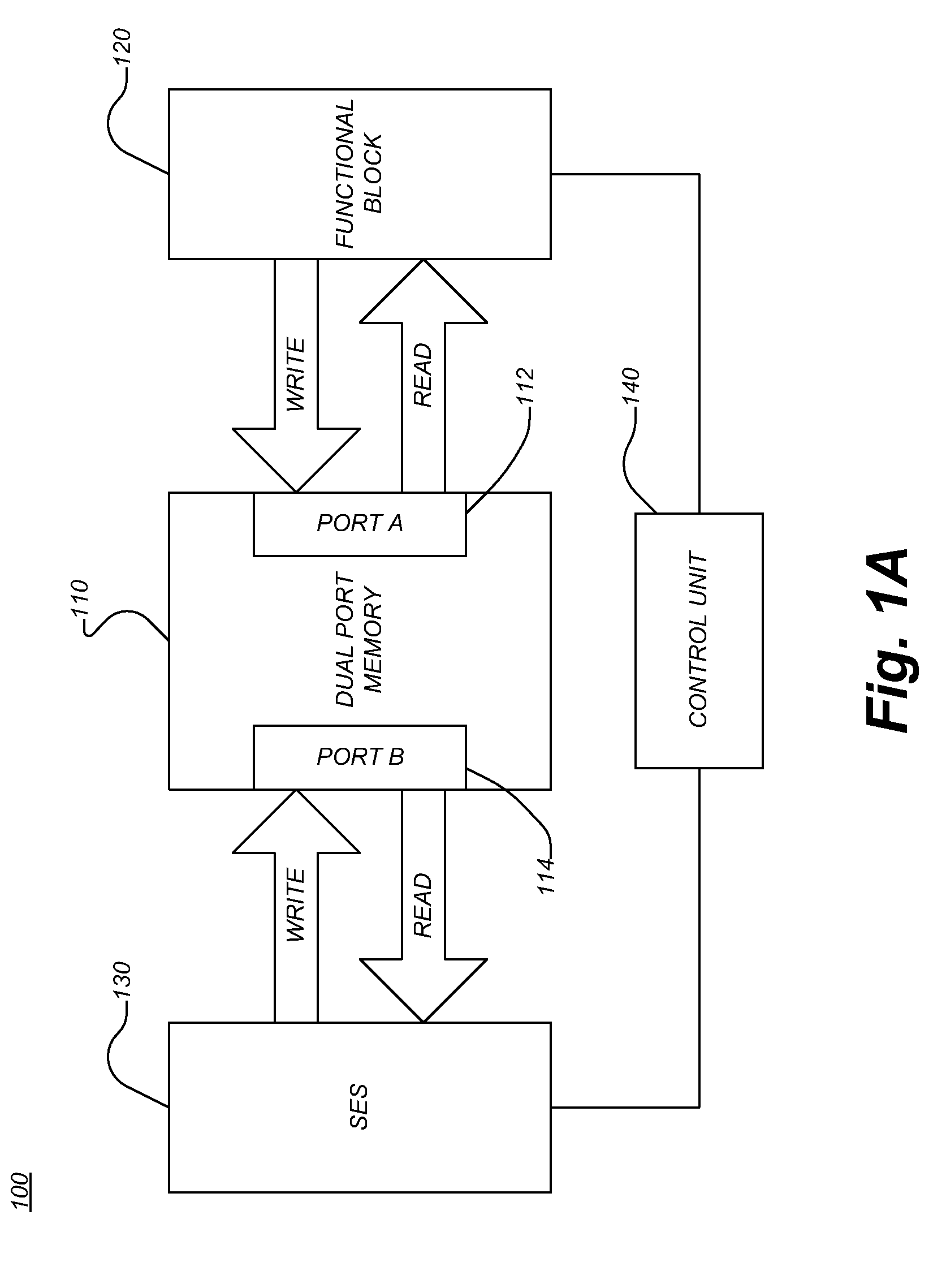
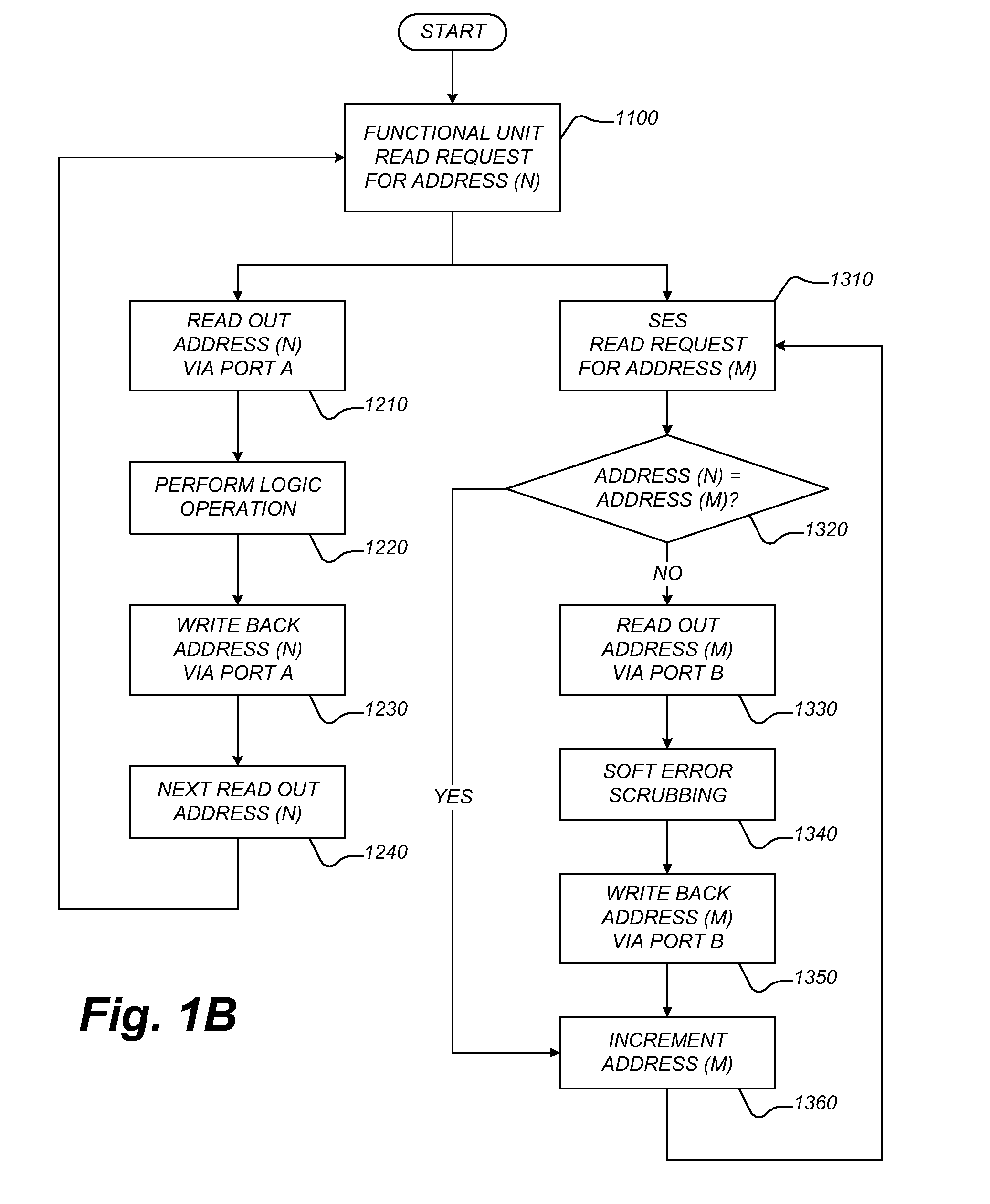
System and method for soft error scrubbing
A data processing system includes a memory configured to store data in a plurality of addressable storage spaces thereof, wherein the memory includes a first data port and a second data port, a first functional block configured to access the memory via the first data port to perform a logic operation, and a second functional block configured to access the memory via the second data port to perform soft error scrubbing in the data stored in the memory.
Owner:MARVELL ISRAEL MISL
Interconnection for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having improved reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS20100062597A1Soft errorCost-effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballSolder wetting
An interconnection structure suitable for flip-chip attachment of microelectronic device chips to packages, comprising a two, three or four layer ball-limiting metallurgy including an adhesion / reaction barrier layer, and having a solder wettable layer reactive with components of a tin-containing lead free solder, so that the solderable layer can be totally consumed during soldering, but a barrier layer remains after being placed in contact with the lead free solder during soldering. One or more lead-free solder balls is selectively situated on the solder wetting layer, the lead-free solder balls comprising tin as a predominant component and one or more alloying components.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Low power and soft error hardened dual edge triggered flip flop
ActiveUS20100052756A1Avoid signalingReduce power consumptionElectric pulse generatorComputer scienceThroughput
A dual edge triggered flip flop can pass data values on a clock rising or falling edge. The dual edge triggered flip flop can be operated at half the clock speed of a single edge triggered flip flop and produce substantially the same throughput. The dual edge triggered flip flop may use less power than a single edge triggered flip flop due at least in part to the construction of an intermediate gate as a data interlock gate. The dual edge triggered flip flop may contain a plurality of master nodes, and is soft error hardened compared to a single edge triggered flip flop.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
SRAM cell and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS6902963B2Increase battery capacityReduce errorsTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceInterconnection
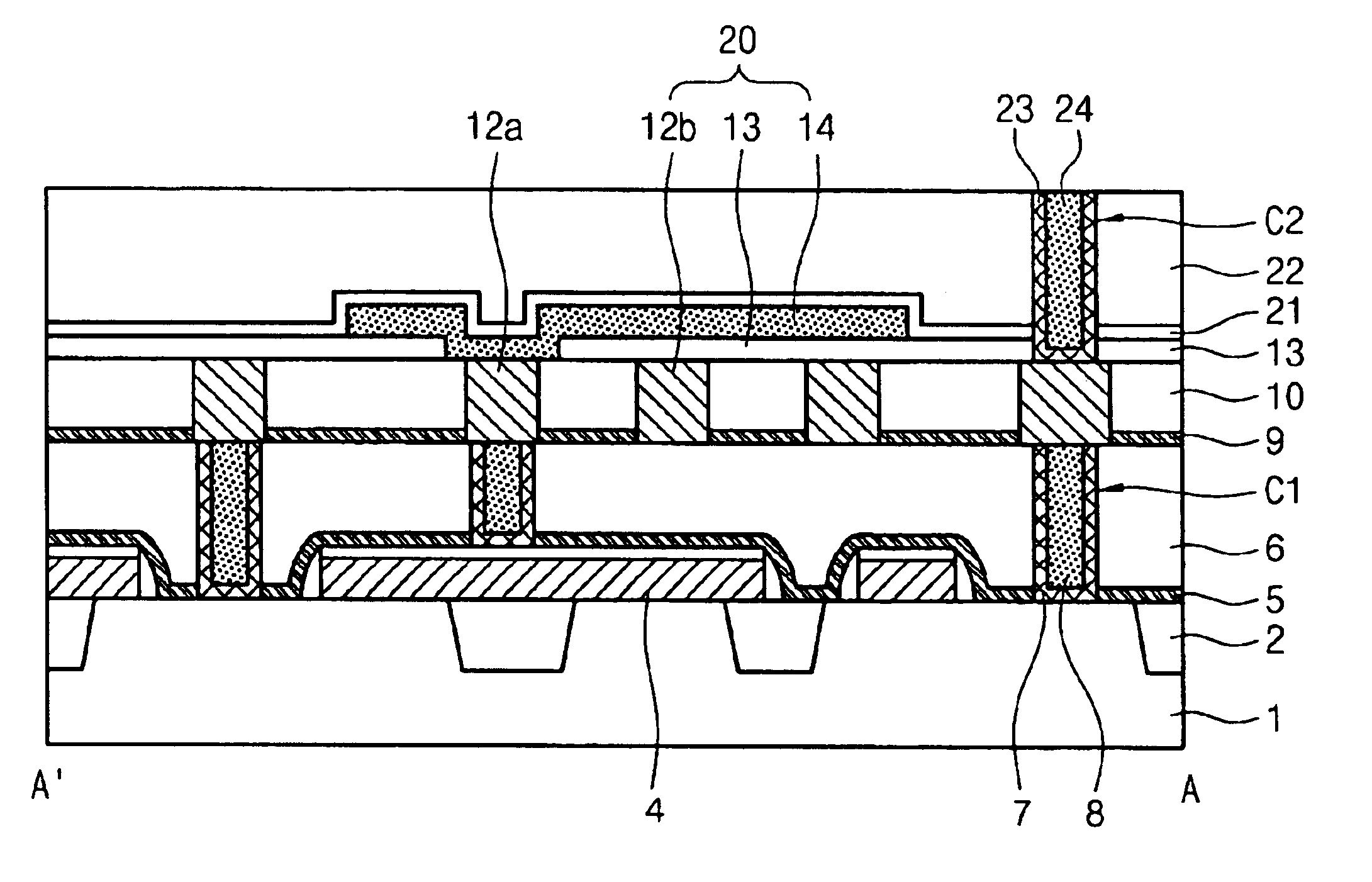
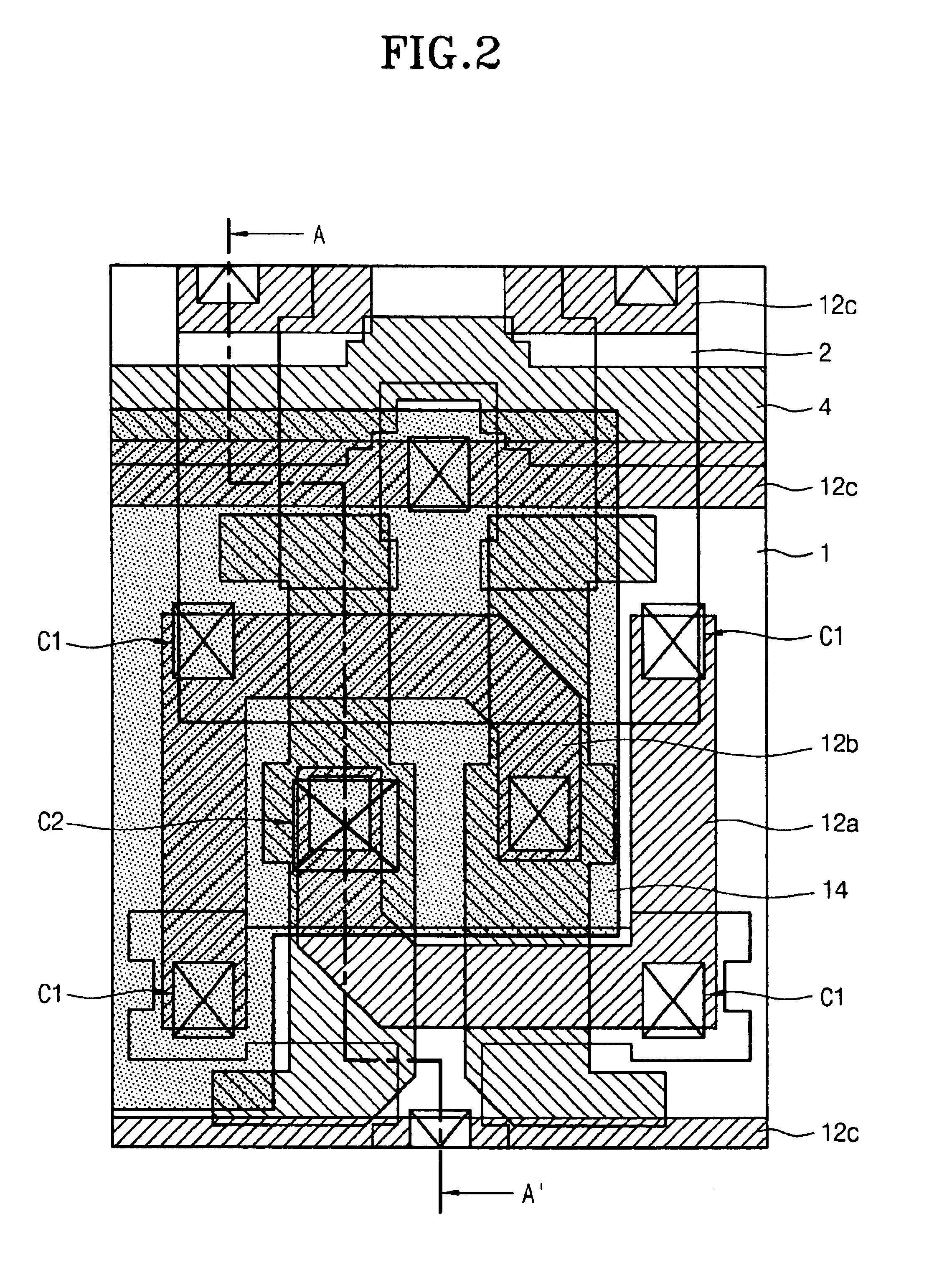
Disclosed is a SRAM cell and a method of manufacturing the same. The SRAM cell comprises: a pair of access devices; a pair of pull-up devices; a pair of pull-down devices; and at least one metal plate formed on metal interconnection lines in contact with a substrate, having a dielectric film interposed between the metal plate and the metal interconnection lines, so as to increase a cell capacitance, thereby reducing a soft error rate. Herein, one metal plate may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plate overlaps with a first one of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with a second one of the metal interconnection lines of the node side and the node bar side. Also, two metal plates may be included in each cell. In this case, the metal plates overlap, respectively, with one metal interconnection line of metal interconnection lines of a node side and a node bar side, while being in contact with another metal interconnection line of the node side or the node bar side, respectively. Therefore, capacitance is additionally formed to increase cell capacitance, so that variation of the electric potentials of cell nodes, which is caused by generated electrons, is prevented, and thereby soft error can be efficiently reduced.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS6864559B2High integration densityHigh speed operationTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringVoltage
Disclosed is a semiconductor device, such as a semiconductor memory device, having structure wherein invasion of minority carriers from the semiconductor substrate into components of the device, formed on the substrate, can be avoided. The semiconductor memory device can be an SRAM or DRAM, for example, and includes a memory array and peripheral circuit on a substrate. In one aspect of the present invention, a buried layer of the same conductivity type as that of the substrate, but with a higher impurity concentration than that of the substrate, is provided beneath at least one of the peripheral circuit and memory array. A further region can extend from the buried layer, for example, to the surface of the semiconductor substrate, the buried layer and further region in combination acting as a shield to prevent minority carriers from penetrating to the device elements. As a second aspect of the present invention, first carrier absorbing areas (to absorb minority carriers) are located between the memory array and the switching circuit of the peripheral circuit, and second carrier absorbing areas are provided to surround input protective elements of the device. As a third embodiment of the present invention, a plurality of isolation regions of the same conductivity type are provided, with unequal voltages applied to these isolation regions, or unequal voltages applied to the substrate, on the one hand, and to these isolation regions, on the other.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Associative memory capable of searching for data while keeping high data reliability
InactiveUS7277306B2Improve the immunityHigh data reliabilityError detection/correctionCode conversionDependabilityData reliability
A CAM unit has a memory array for storing storage data, and a RAM unit has a memory array for storing the same storage data and check bits added thereto for determining whether the storage data in its memory array has an error. An error correction circuit uses the check bits to correct any error of data read from the memory array of the RAM unit and rewrite the error-corrected data to the memory arrays. Even if a soft error occurs in the storage data, the check bits can be used to correct the error in the data and rewrite the error-corrected data. Thus, a matching comparison can be performed on the storage data with high reliability.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Layout method for soft-error hard electronics, and radiation hardened logic cell
ActiveUS20120185816A1Reduce impactSoft errorLogic circuits characterised by logic functionFail-safe circuitsCMOSNon destructive
This invention comprises a layout method to effectively protect logic circuits against soft errors (non-destructive errors) and circuit cells, with layout, which are protected against soft errors. In particular, the method protects against cases where multiple nodes in circuit are affected by a single event. These events lead to multiple errors in the circuit, and while several methods exist to deal with single node errors, multiple node errors are very hard to deal with using any currently existing protection methods. The method is particularly useful for CMOS based logic circuits in modern technologies (.ltoreq.90 nm), where the occurrence of multiple node pulses becomes high (due to the high integration level). It uses a unique layout configuration, which makes the circuits protected against single event generated soft-errors.
Owner:LILJA KLAS OLOF
Error management within a data processing system
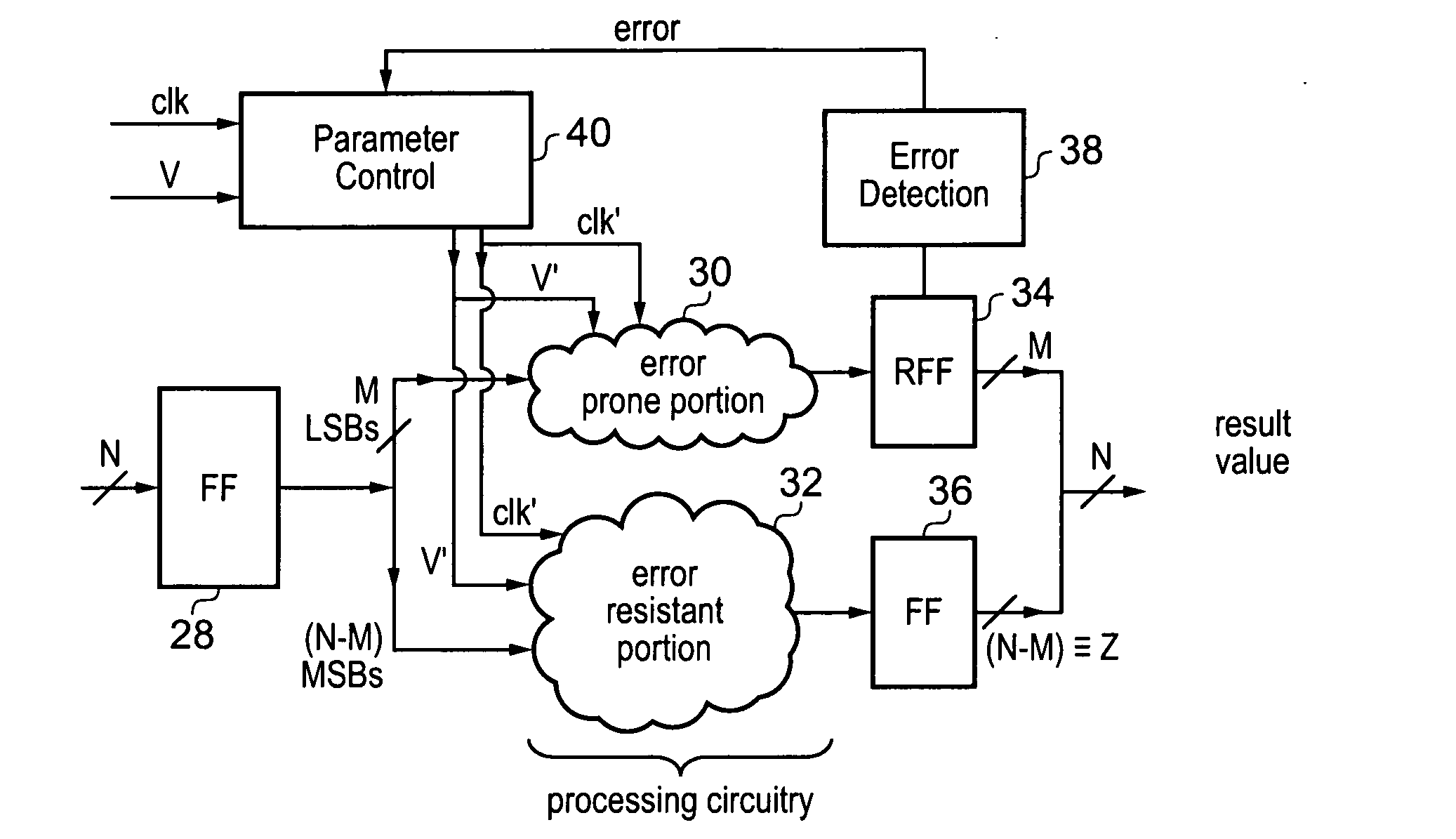
ActiveUS8639975B2Easy to operateLow priorityError detection/correctionError detection onlyData processing systemParameter control
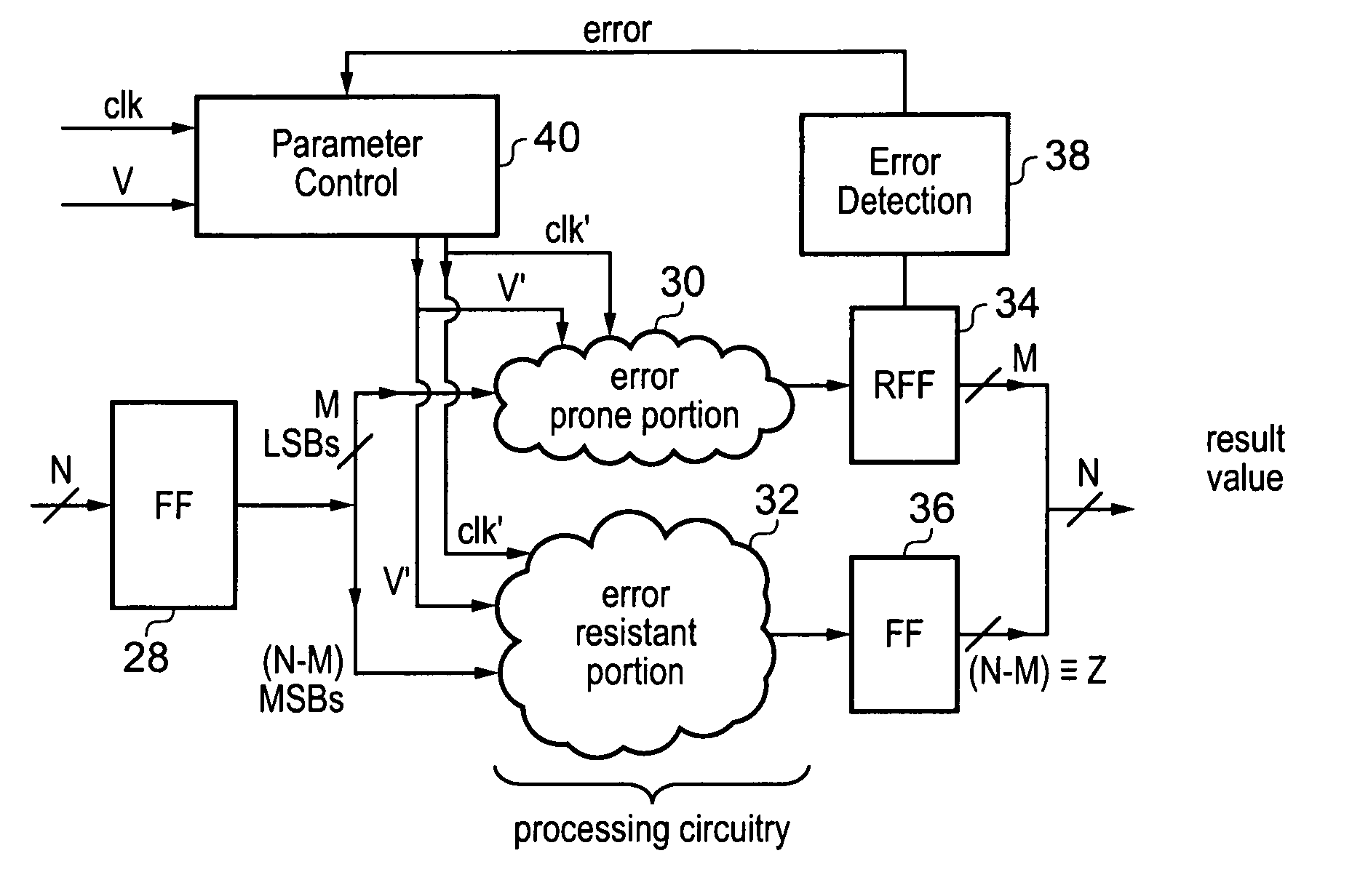
A data processing system 2 is used to perform processing operations to generate a result value. The processing circuitry which generates the result value has an error resistant portion 32 and an error prone portion 30. The probability of an error in operation of the error prone portion for a given set of operating parameters (clk, V) is greater than the probability of an error for that same set of operating parameters within the error resistant portion. Error detection circuitry 38 detects any errors arising in the error prone portion. Parameter control circuitry 40 responds to detected errors to adjust the set of operating parameters to maintain a non-zero error rate in the errors detected by the error detection circuitry. Errors within the one or more bits generated by the error prone portion are not corrected as the apparatus is tolerant to errors occurring within such bit values of the result value.
Owner:ARM LTD
Interconnections for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS20080202792A1Soft errorCost-effectivePrinted circuit assemblingNon-insulated conductorsSolder wettingSolder ball
Owner:FOGEL KEITH E +7
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
ActiveUS9230683B2Improve accuracySoft errorSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer hardwareSemiconductor
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Error management within a data processing system
ActiveUS20120124421A1Easy to operateLow priorityFault responseError detection onlyData processing systemParameter control
A data processing system 2 is used to perform processing operations to generate a result value. The processing circuitry which generates the result value has an error resistant portion 32 and an error prone portion 30. The probability of an error in operation of the error prone portion for a given set of operating parameters (clk, V) is greater than the probability of an error for that same set of operating parameters within the error resistant portion. Error detection circuitry 38 detects any errors arising in the error prone portion. Parameter control circuitry 40 responds to detected errors to adjust the set of operating parameters to maintain a non-zero error rate in the errors detected by the error detection circuitry. Errors within the one or more bits generated by the error prone portion are not corrected as the apparatus is tolerant to errors occurring within such bit values of the result value.
Owner:ARM LTD
Circuit arrangement
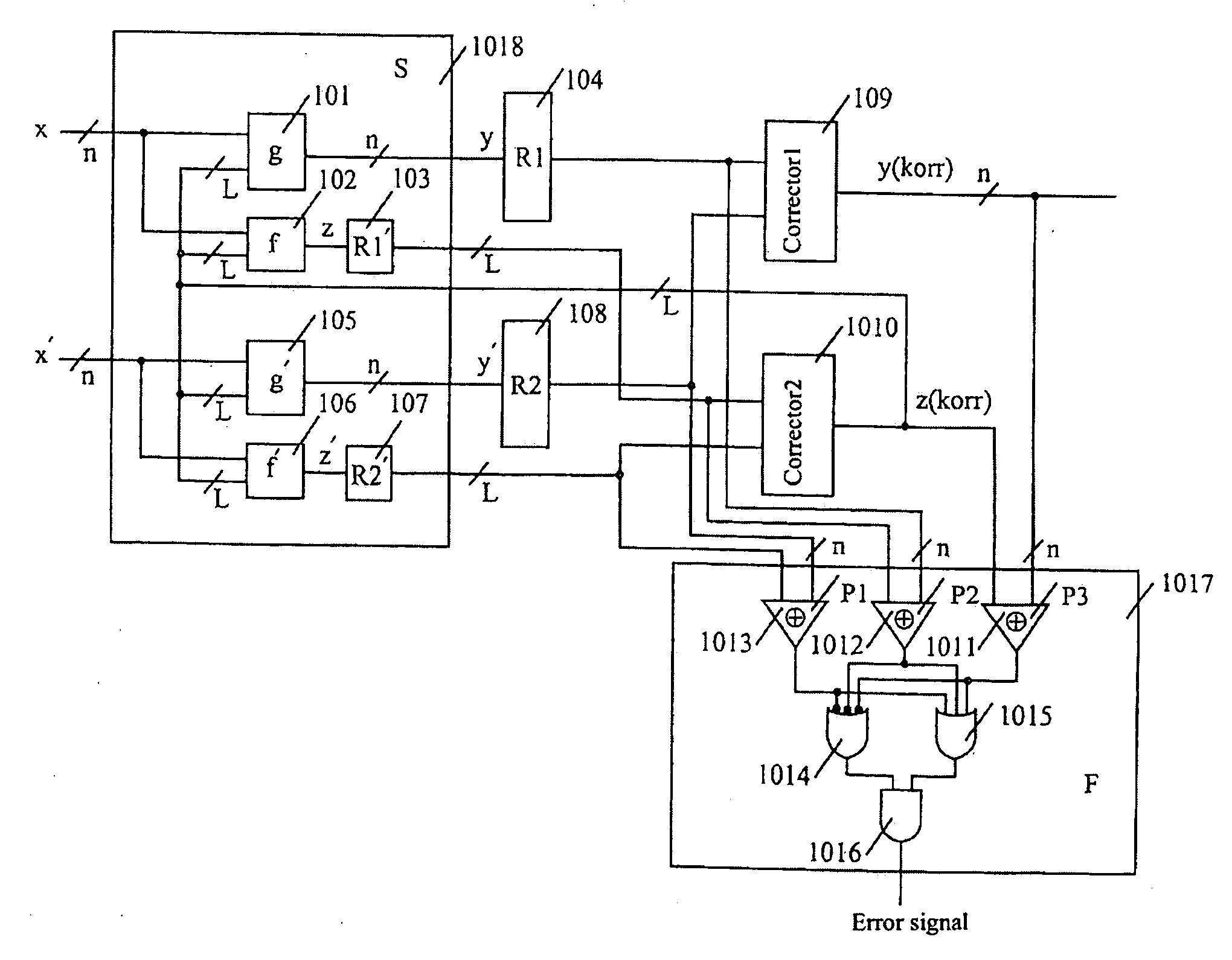
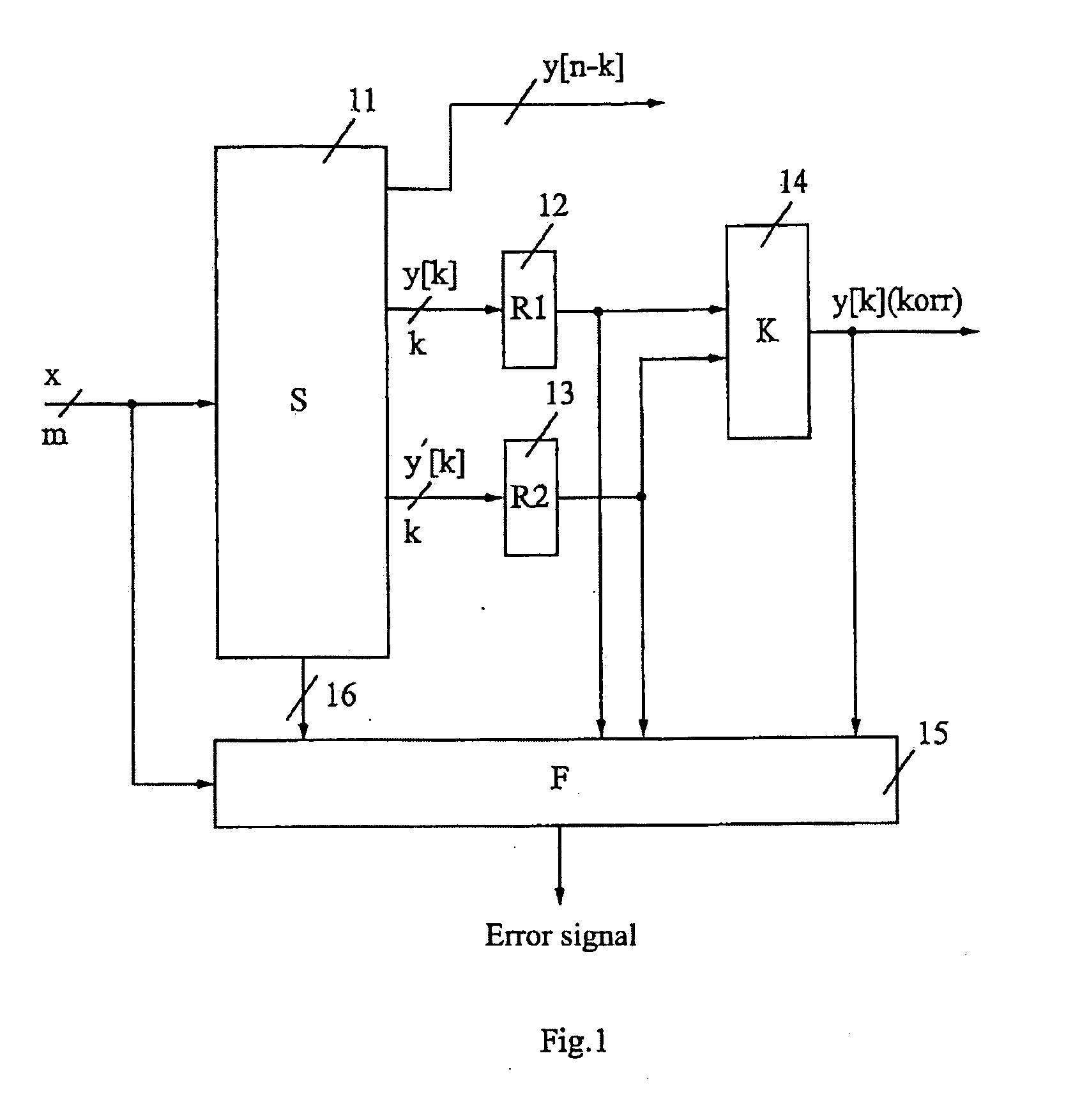
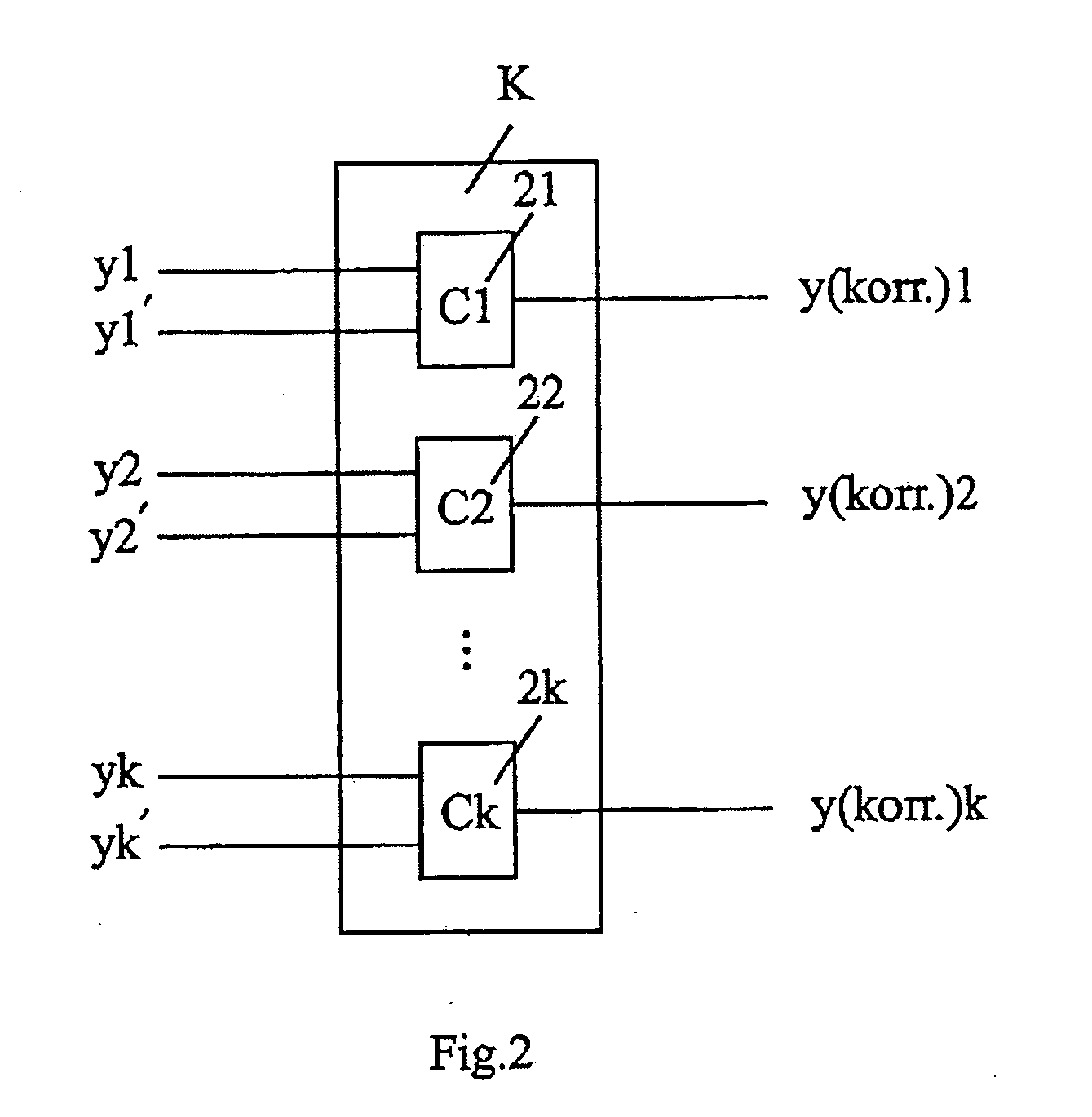
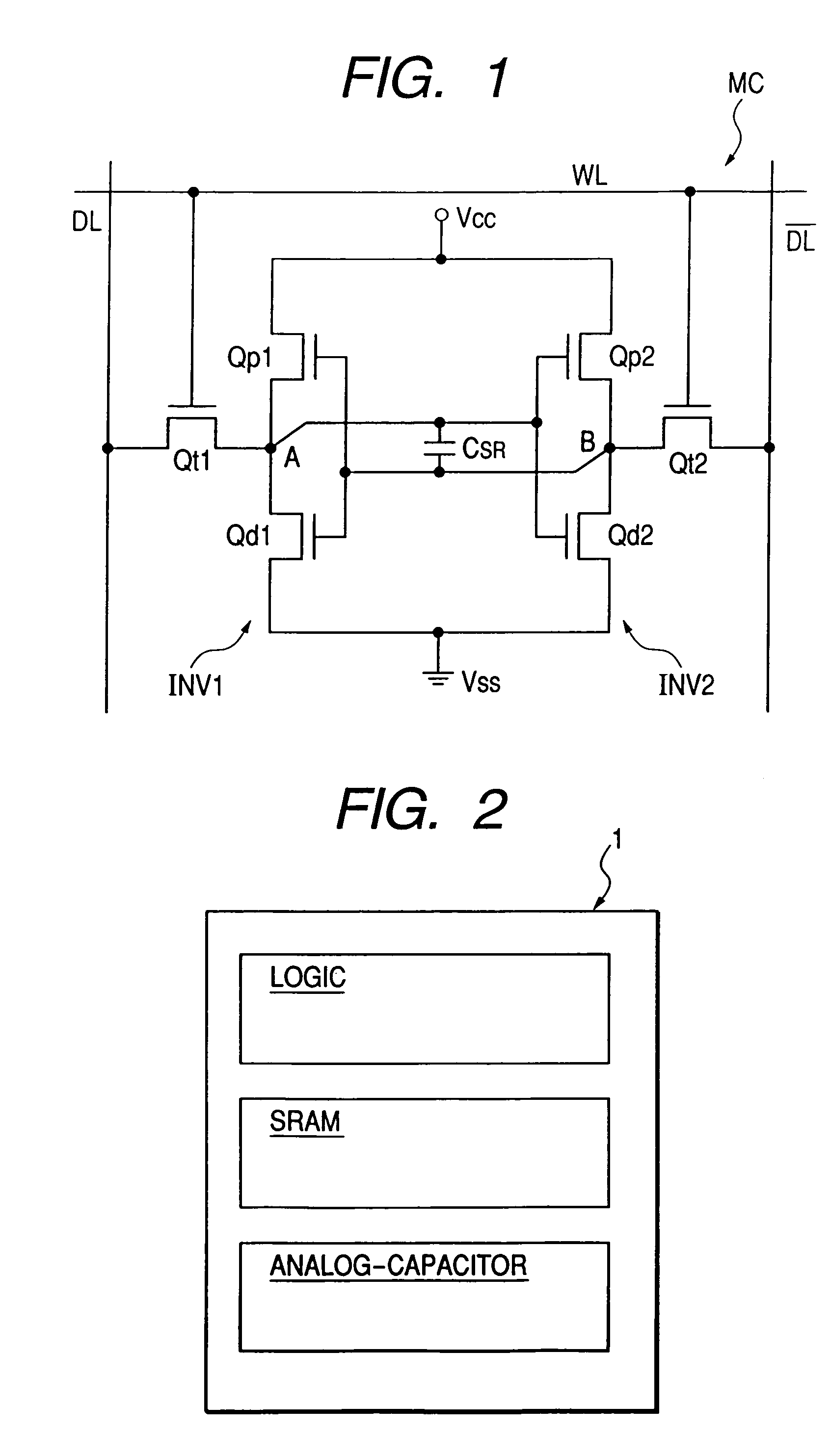
The invention relates to a circuit arrangement, comprising: a functional circuit with m (m=1, 2, . . . ) data inputs and n (n=1, 2, . . . ) data outputs for processing at least one m-dimensional binary data input (x1, . . . , xm) to form an n-dimensional data output (y1, . . . , yn), wherein the functional circuit comprises at least one combinatorial circuit part, at least two registers with a word length k (k=1, 2, . . . ; k≦n) which are coupled to at least some of the n data outputs of the functional circuit in order to store output values (y=y1, . . . , yk; y′=y′1, . . . , y′k) which are duplicated with respect to one another or are duplicated with bit-by-bit inversion with respect to one another, said output values being derived from the n-dimensional data output (y1, . . . , yn) of the functional circuit, at least one corrector with an input word length 2k and an output word length k, which is coupled to data outputs of the at least two registers and supplies a k-dimensional corrected data output (y[k](korr)=y1(korr), . . . , yk(korr)), and an error detection circuit for detecting errors during operation of at least one of the aforementioned circuit elements: the functional circuit, the at least two registers and the corrector.
Owner:UNIV POSTDAM
Interconnections for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS20080203585A1Soft errorCost-effectivePrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder wettingSolder ball
An interconnection structure suitable for flip-chip attachment of microelectronic device chips to packages, comprising a two, three or four layer ball-limiting composition including an adhesion / reaction barrier layer, and having a solder wettable layer reactive with components of a tin-containing lead free solder, so that the solderable layer can be totally consumed during soldering, but a barrier layer remains after being placed in contact with the lead free solder during soldering. One or more lead-free solder balls is selectively situated on the solder wetting layer, the lead-free solder balls comprising tin as a predominant component and one or more alloying components.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
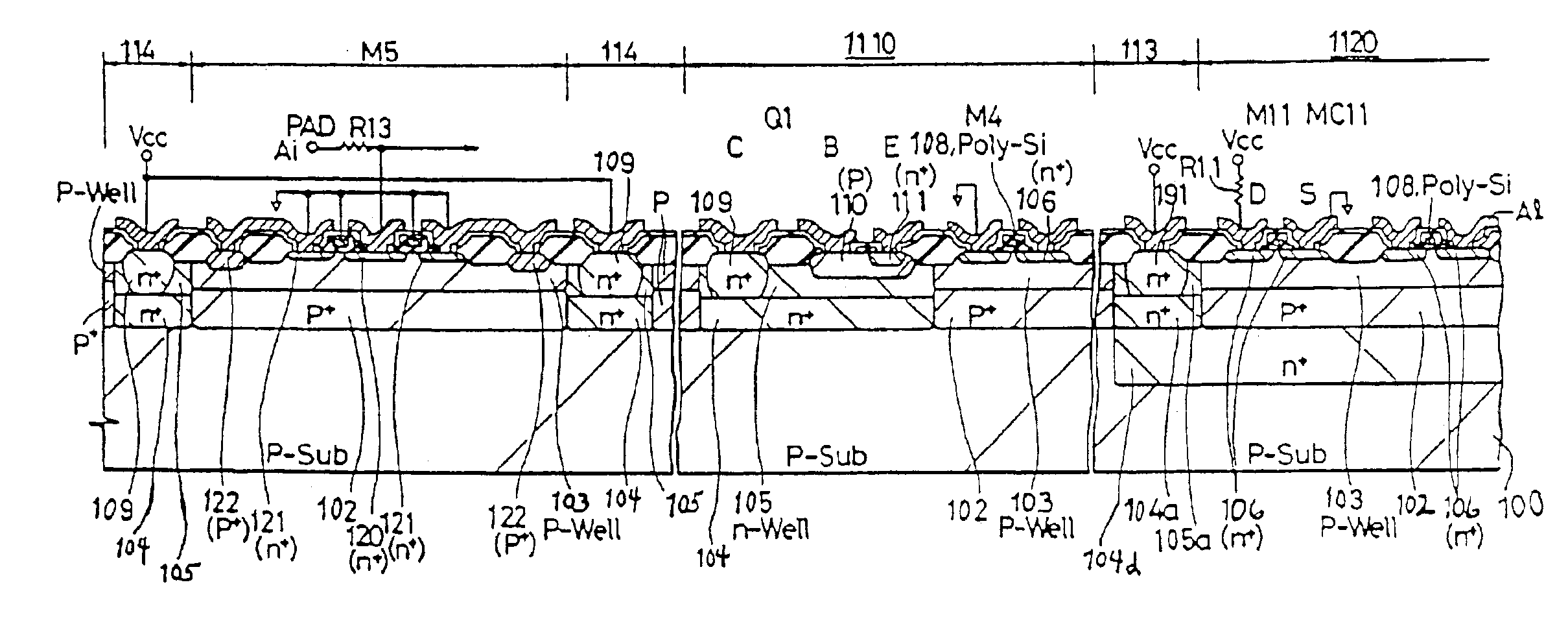
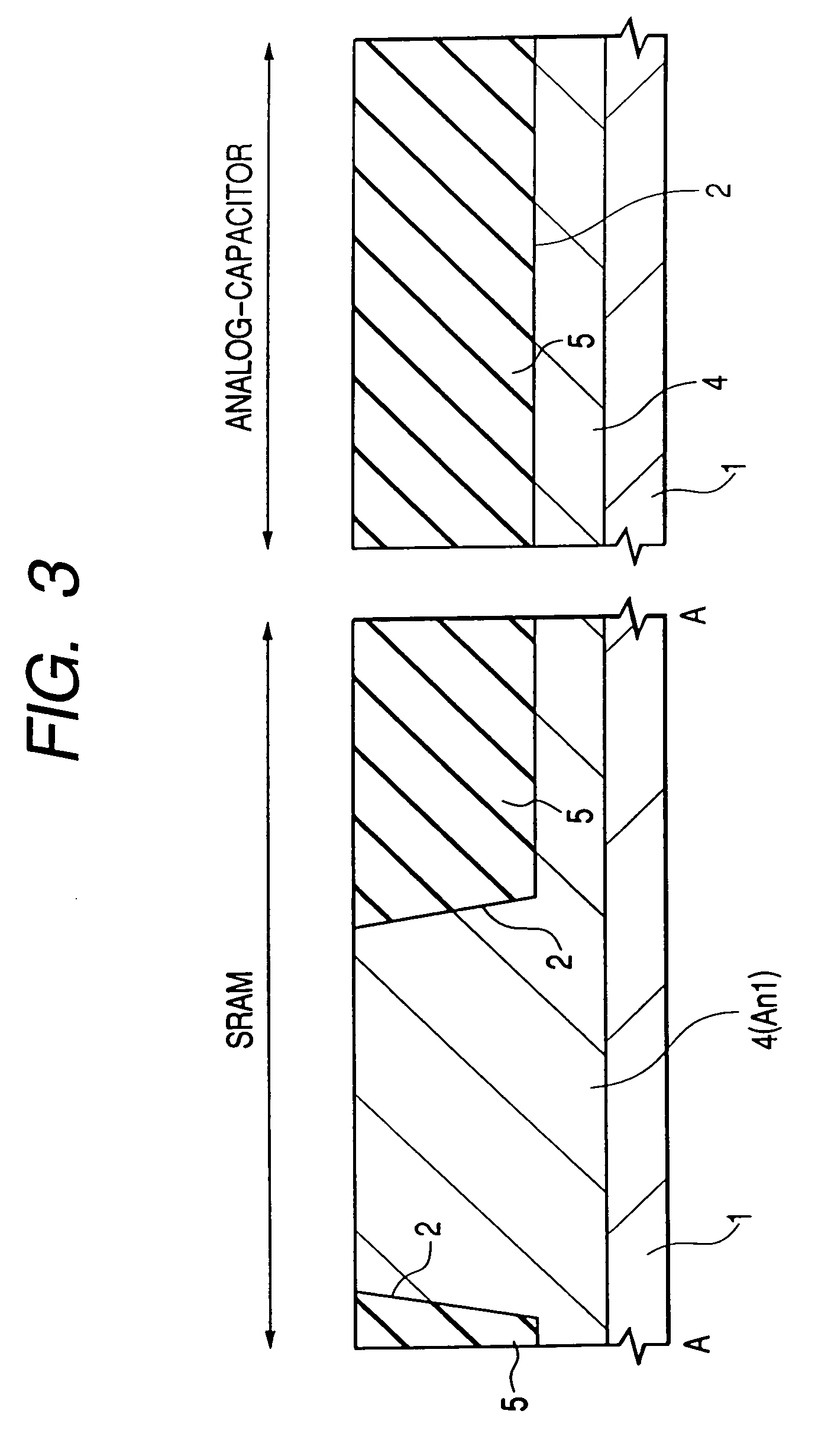
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and a method of manufacturing the same
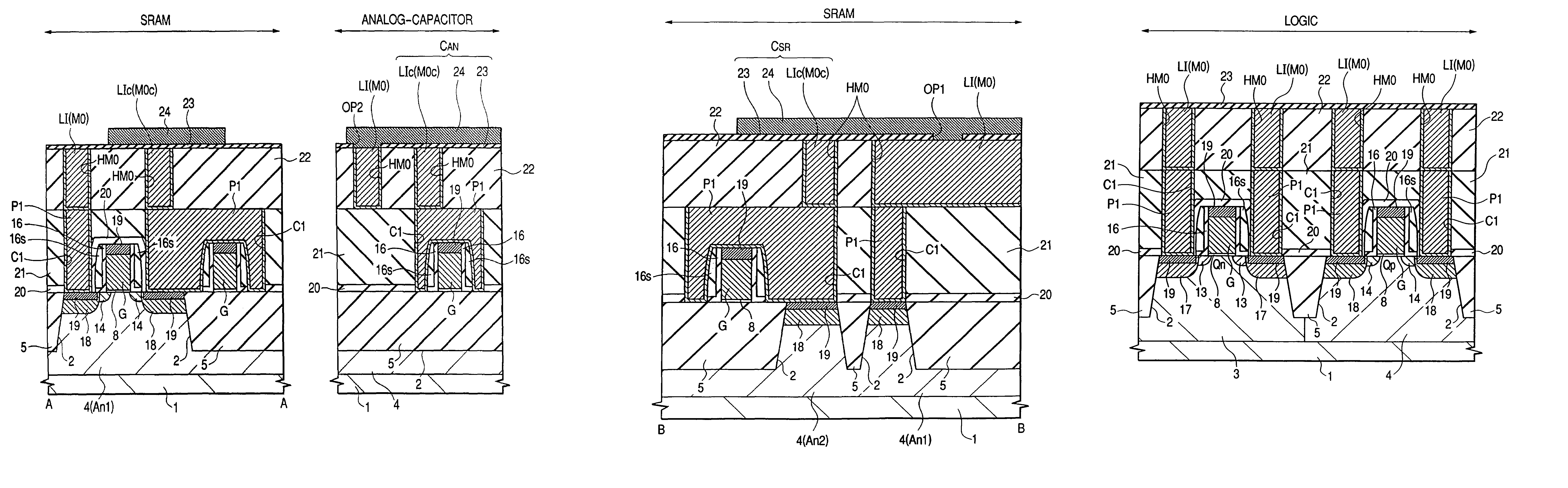
In order to improve the performance of a semiconductor integrated circuit device wherein a capacitor provided between storage nodes of an SRAM and a device having an analog capacitor are formed on a single substrate, a plug is formed in a silicon oxide film on a pair of n channel type MISFETs in a memory cell forming area, and a local wiring LIc for connecting respective gate electrodes and drains of the pair of n channel type MISFETs is formed over the silicon oxide film and the plug. Thereafter, a capacitive insulating film and an upper electrode are further formed over the local wiring LIc. According to the same process step as the local wiring, capacitive insulating film and upper electrode formed in the memory cell forming area, a local wiring LIc, a capacitive insulating film and an upper electrode are formed over a silicon oxide film in an analog capacitor forming area and a plug in the silicon oxide film.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
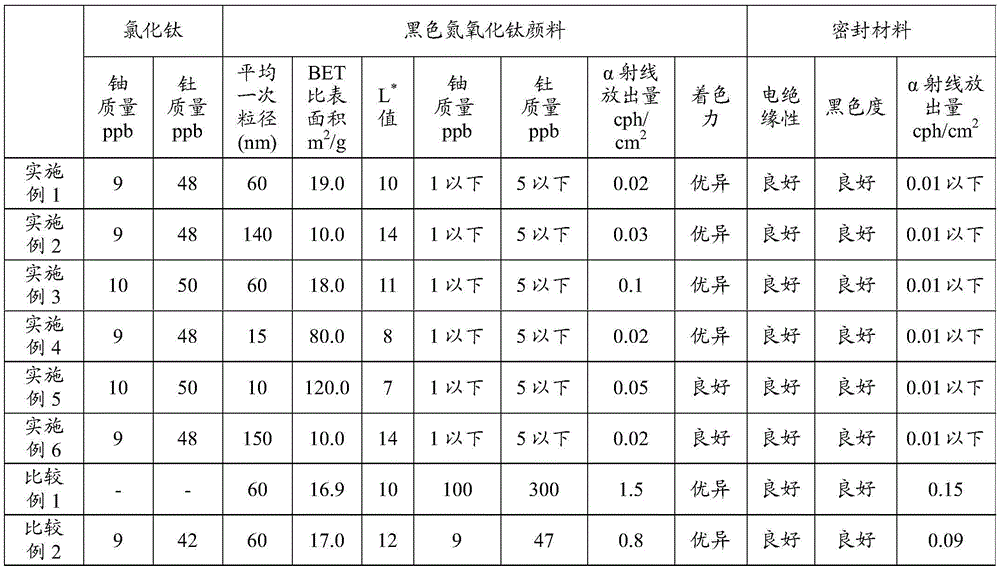
Black titanium oxynitride pigment, method for producing same, and semiconductor-sealing resin compound using black titanium oxynitride pigment
Owner:MITSUBISHI MATERIALS ELECTRONICS CHEM CO LTD
Semiconductor device and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20160132386A1Improve accuracySoft errorInput/output to record carriersSolid-state devicesComputer hardwareSemiconductor
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low α-dose tin or tin alloy, and method for producing same
ActiveUS9394590B2Improve compactnessReduce capacityPhotography auxillary processesWelding/cutting media/materialsSemiconductor chipAlloy
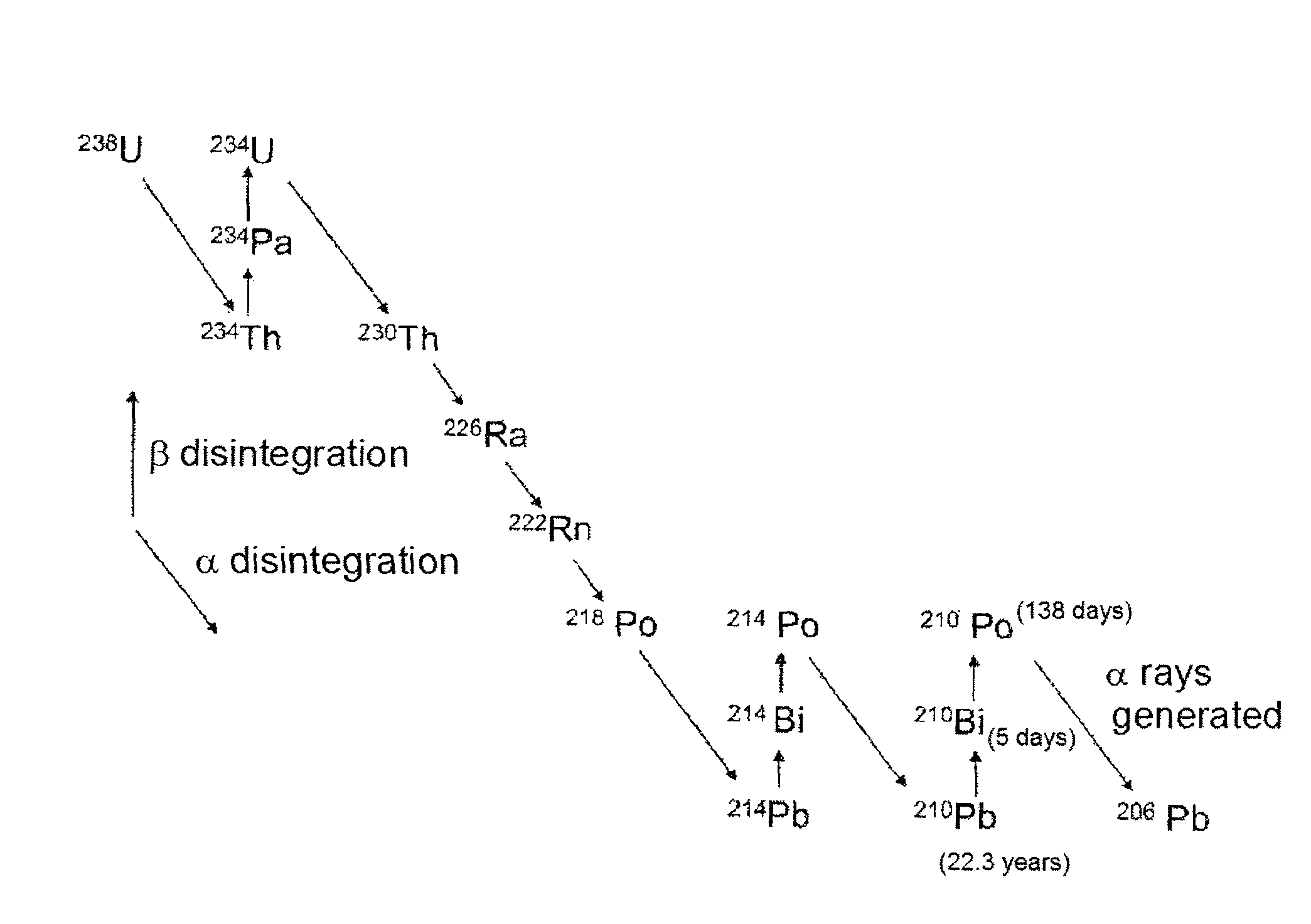
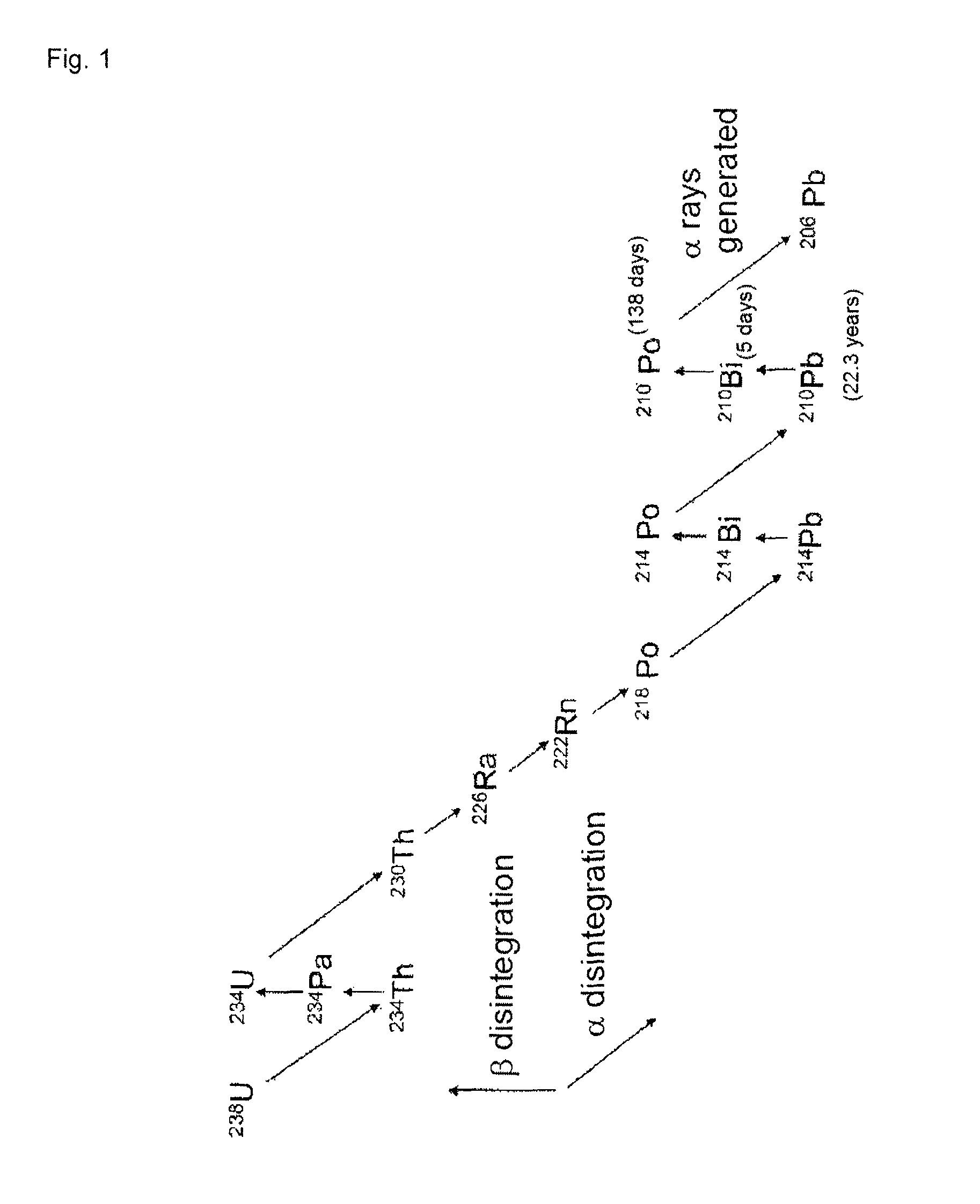
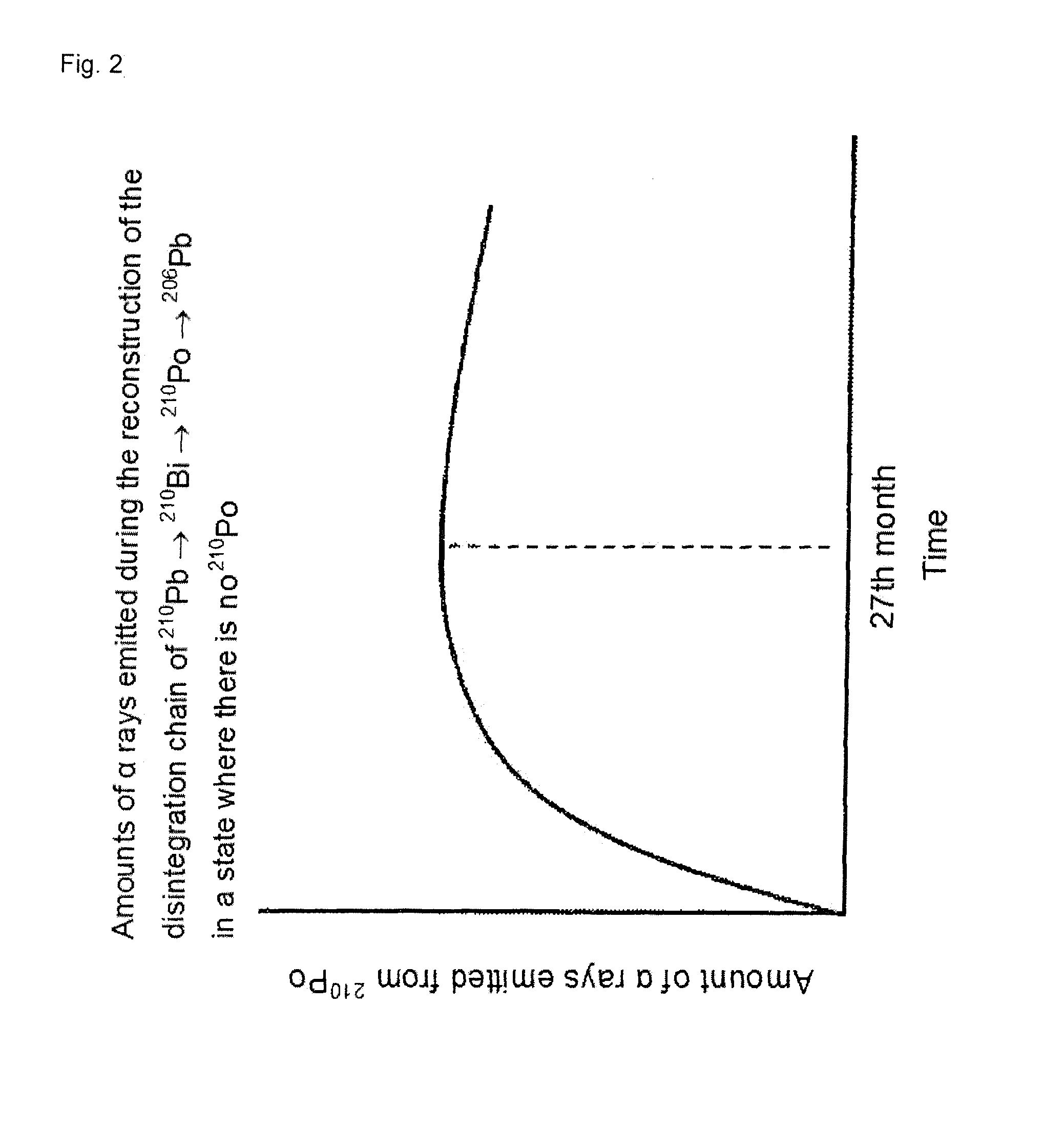
Disclosed is tin characterized in that a sample of the tin after melting and casting has an α dose of less than 0.0005 cph / cm2. Since recent semiconductor devices are highly densified and of high capacity, there is an increasing risk of soft errors caused by the influence of α rays emitted from materials in the vicinity of semiconductor chips. In particular, there are strong demands for high purification of solder materials and tin for use in the vicinity of semiconductor devices, and demands for materials with lower α rays. Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to clarify the phenomenon of the generation of α rays in tin and tin alloys, and to obtain high-purity tin, in which the α dose has been reduced, suitable for the required materials, as well as a method for producing the same.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
Interconnection for flip-chip using lead-free solders and having improved reaction barrier layers
InactiveUS7932169B2Soft errorCost-effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder wettingSolder ball
An interconnection structure suitable for flip-chip attachment of microelectronic device chips to packages, comprising a two, three or four layer ball-limiting metallurgy including an adhesion / reaction barrier layer, and having a solder wettable layer reactive with components of a tin-containing lead free solder, so that the solderable layer can be totally consumed during soldering, but a barrier layer remains after being placed in contact with the lead free solder during soldering. One or more lead-free solder balls is selectively situated on the solder wetting layer, the lead-free solder balls comprising tin as a predominant component and one or more alloying components.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com