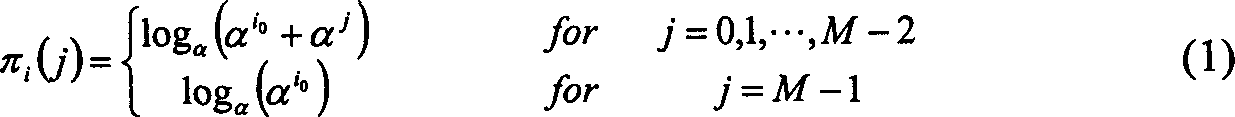Patents
Literature
119 results about "Bit inversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
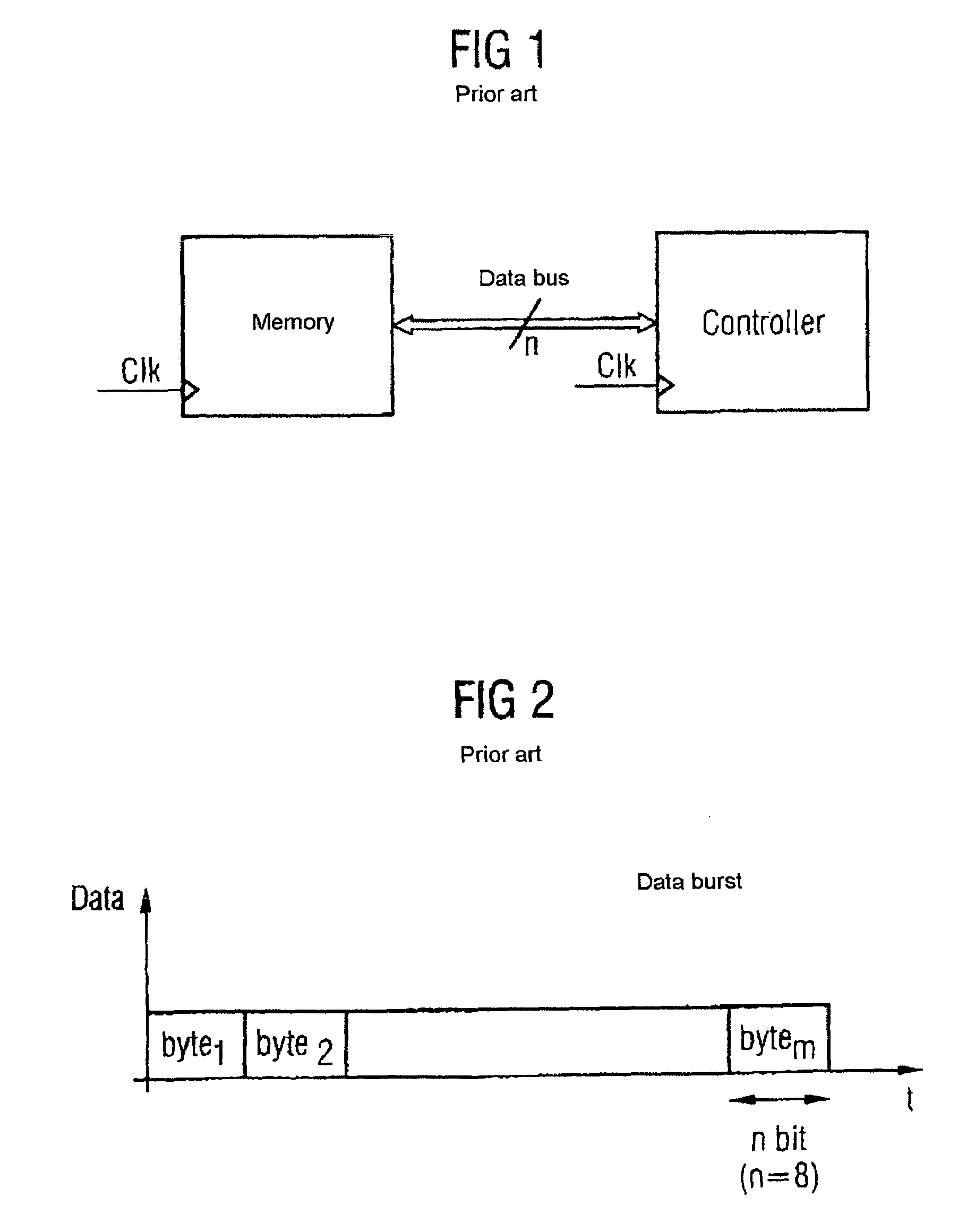
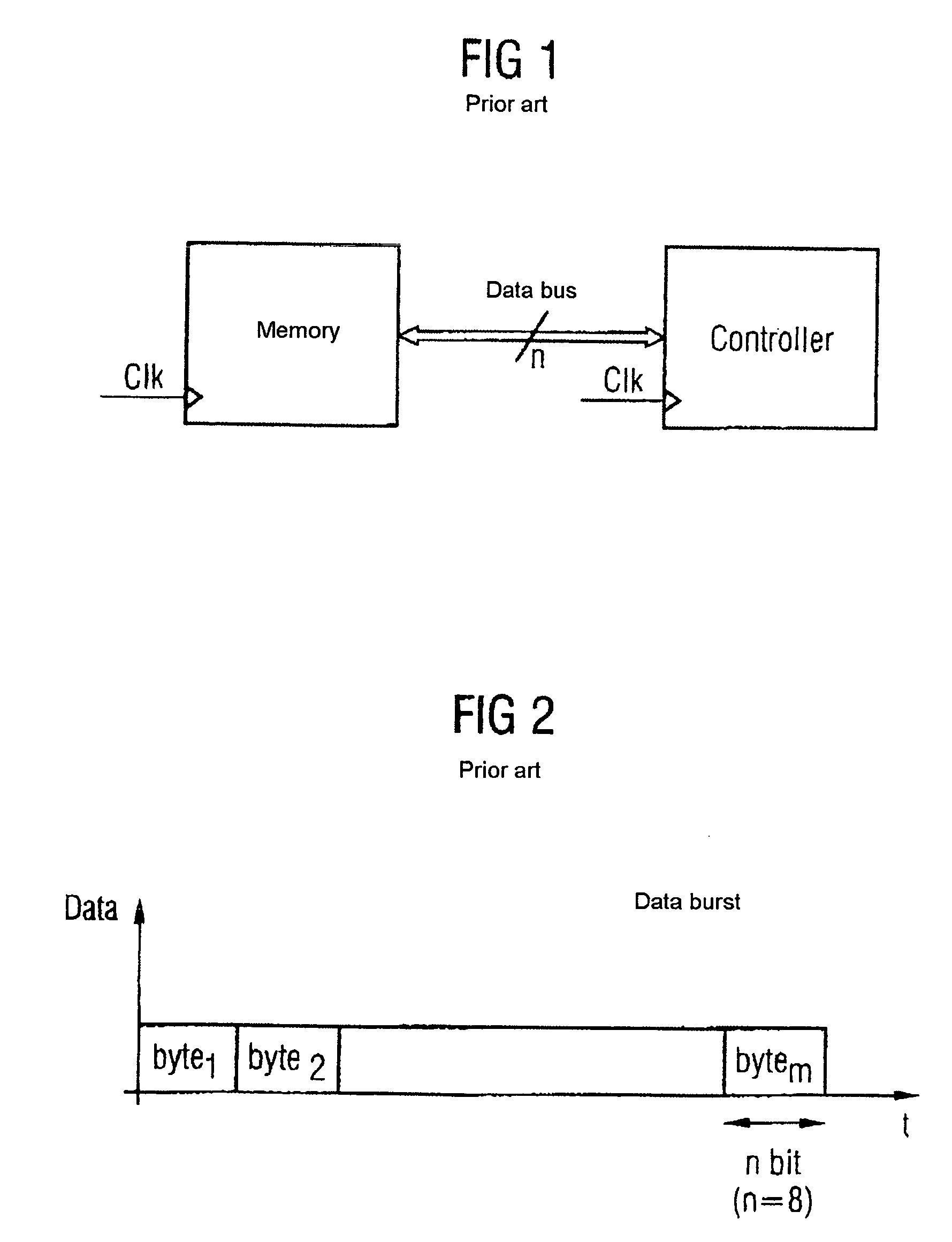
In telecommunications, bit inversion means the changing of the state of a bit to the opposite state, i.e. the changing of a 0 bit to 1 or of a 1 bit to 0. It also refers to the changing of a state representing a given bit to the opposite state.
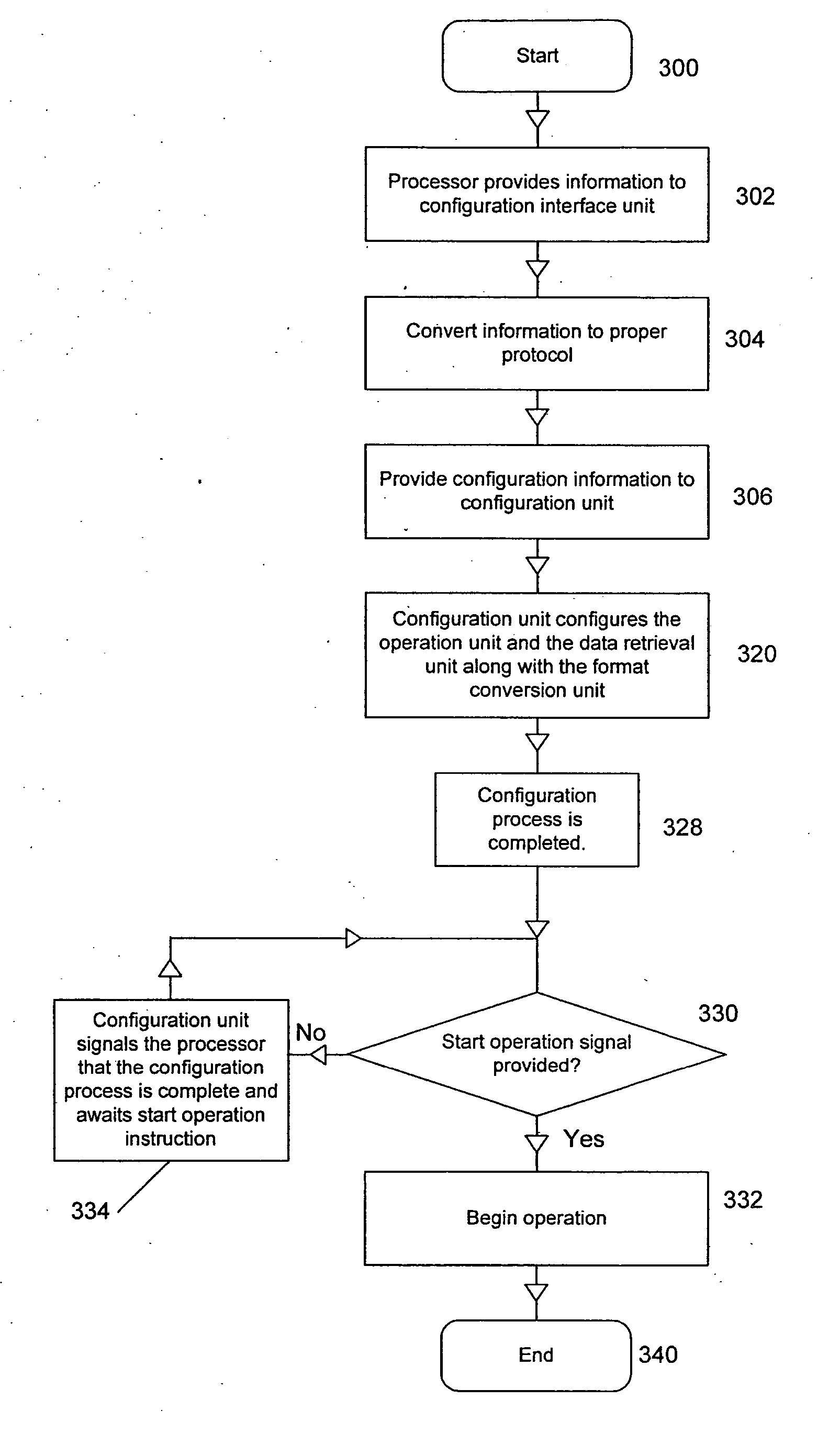
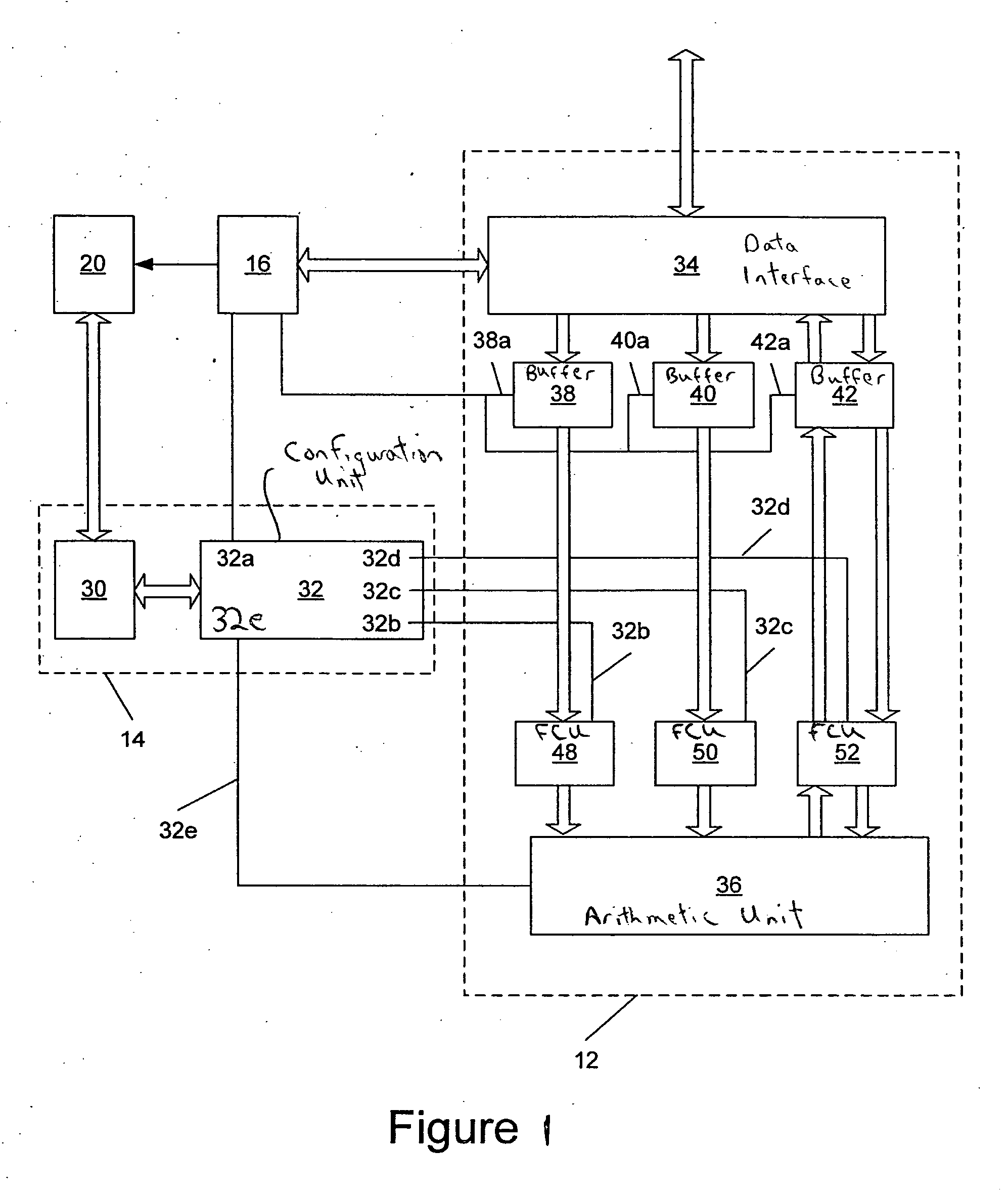
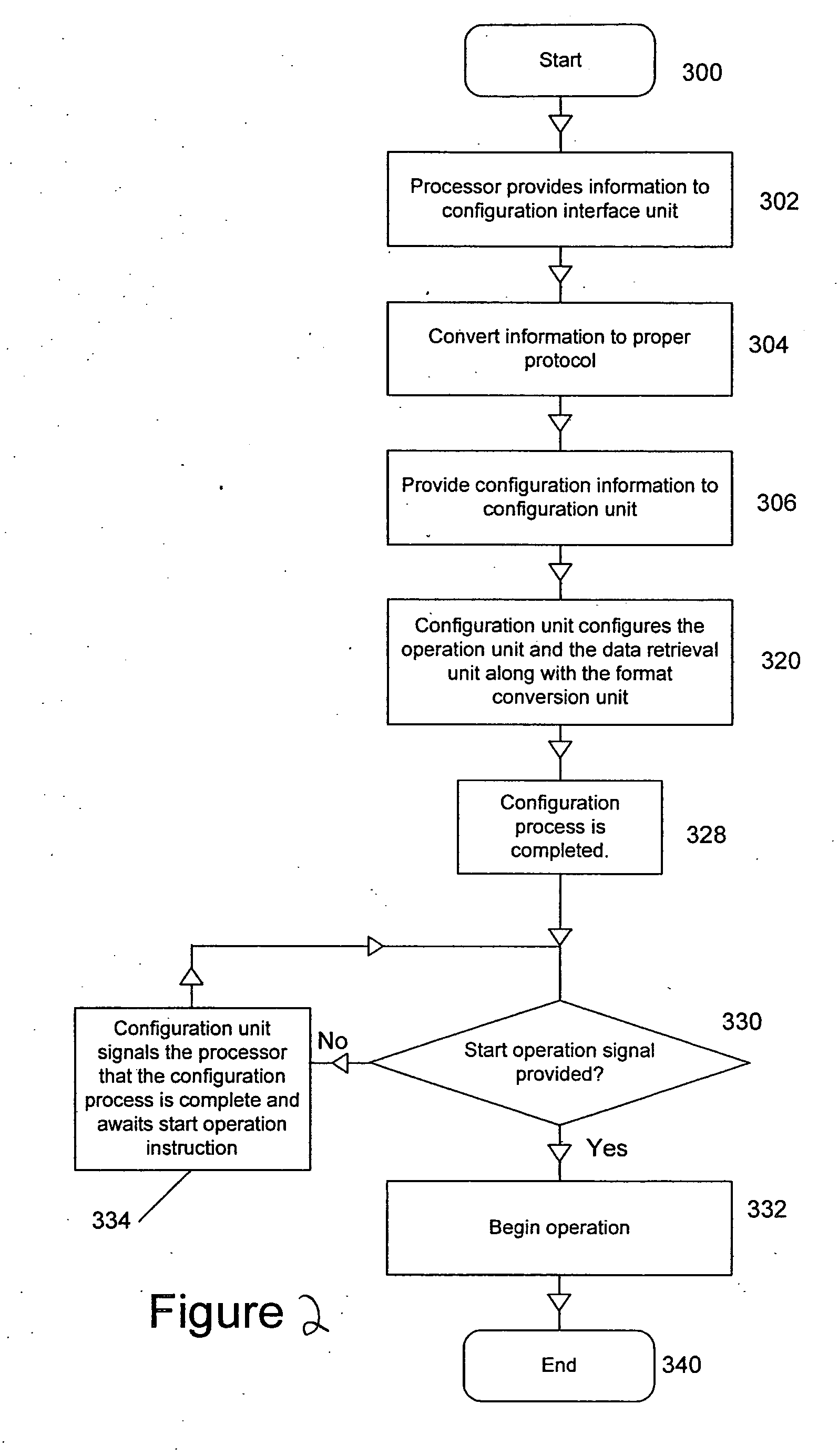
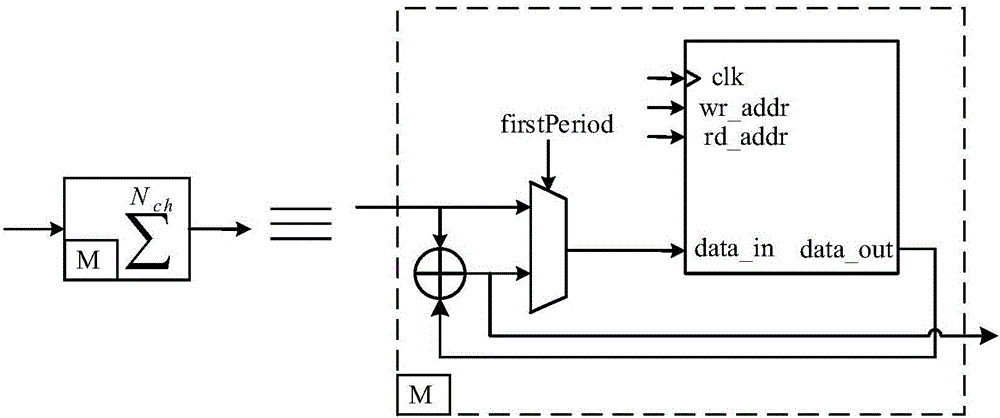
Configurable system for performing repetitive actions and method for configuring and operating same
ActiveUS20070078661A1Efficient executionHigh power consumptionSpeech analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemOperand
In some embodiments, a data processing system including an operation unit including circuitry configurable to perform any selected one of a number of operations on data (e.g., audio data) and a configuration unit configured to assert configuration information to configure the operation unit to perform the selected operation. When the operation includes matrix multiplication of a data vector and a matrix whose coefficients exhibit symmetry, the configuration information preferably includes bits that determine signs of all but magnitudes of only a subset of the coefficients. When the operation includes successive addition and subtraction operations on operand pairs, the configuration information preferably includes bits that configure the operation unit to operate in an alternating addition / subtraction mode to perform successive addition and subtraction operations on each pair of data values of a sequence of data value pairs. In some embodiments, the configuration information includes bits that configure the operation unit to operate in a non-consecutive (e.g., butterfly or bit-reversed) addressing mode to access memory locations having consecutive addresses in a predetermined non-consecutive sequence. Other aspects are audio encoders and decoders including any embodiment of, and configuration units and operation units for use in, any embodiment of the system, and methods performed during operation of any embodiment of the system or configuration or operation unit thereof.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
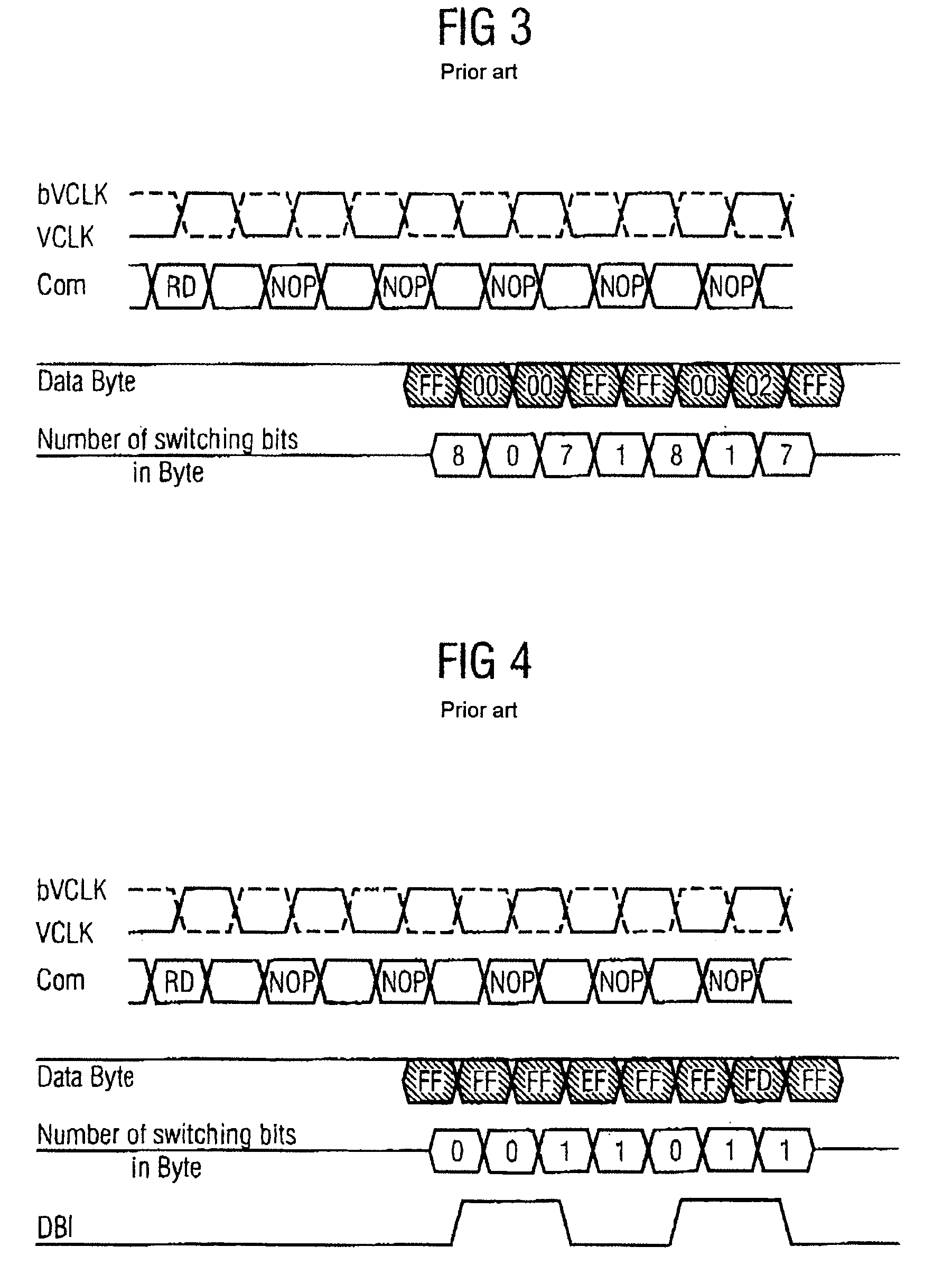
Circuit for producing a data bit inversion flag
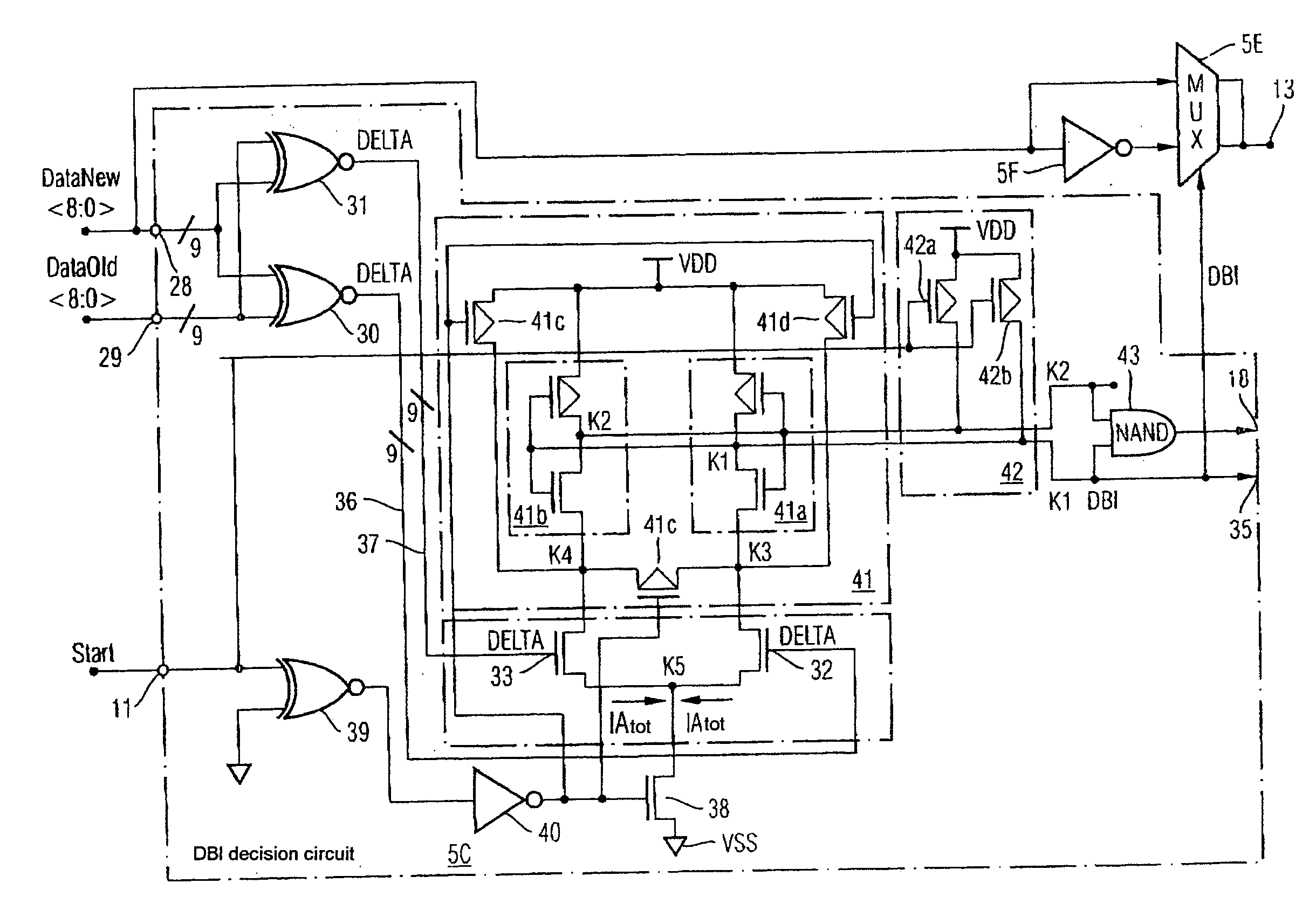
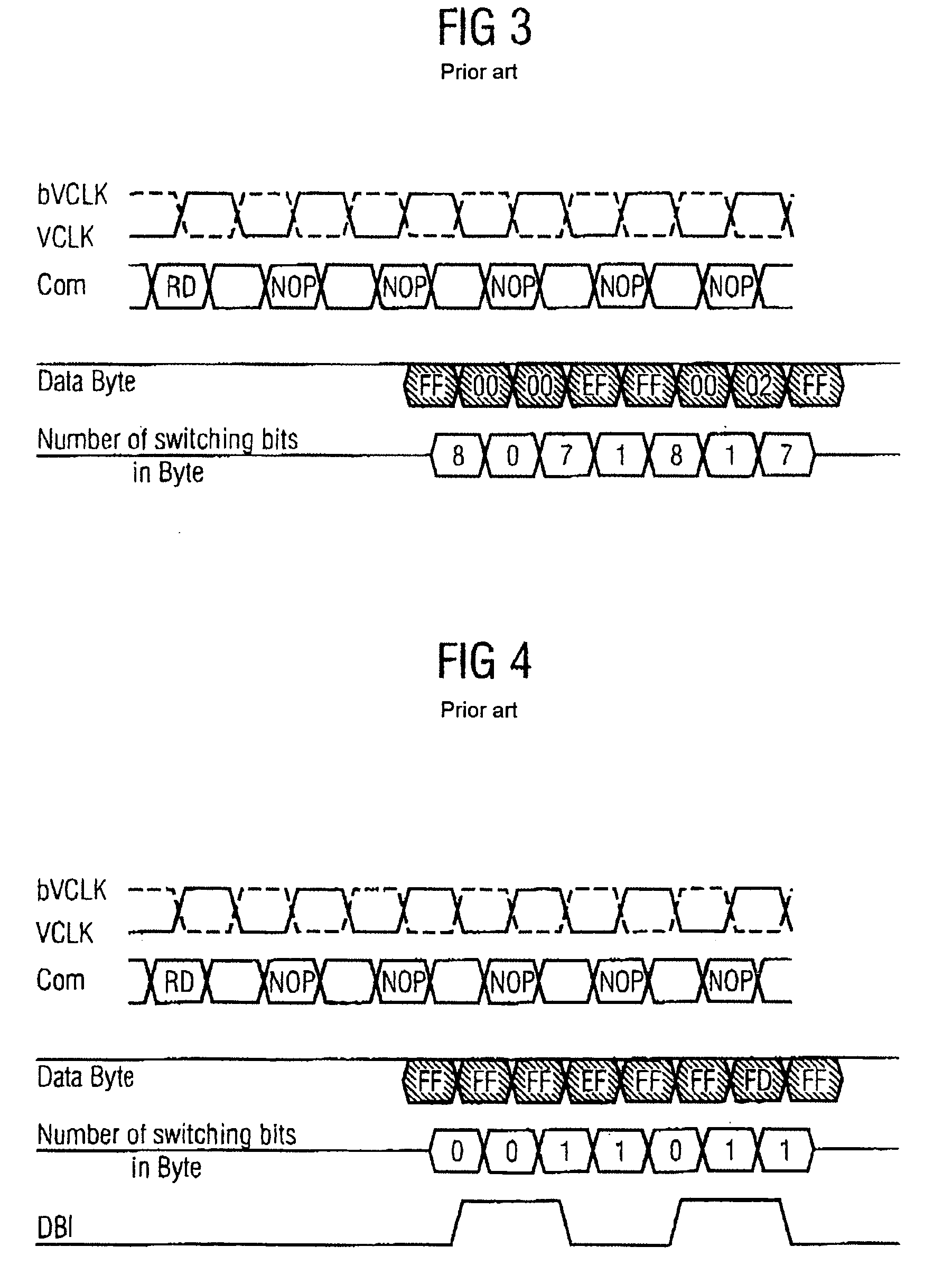
ActiveUS7221292B2Electric signal transmission systemsElement comparisonBit inversionComputer science
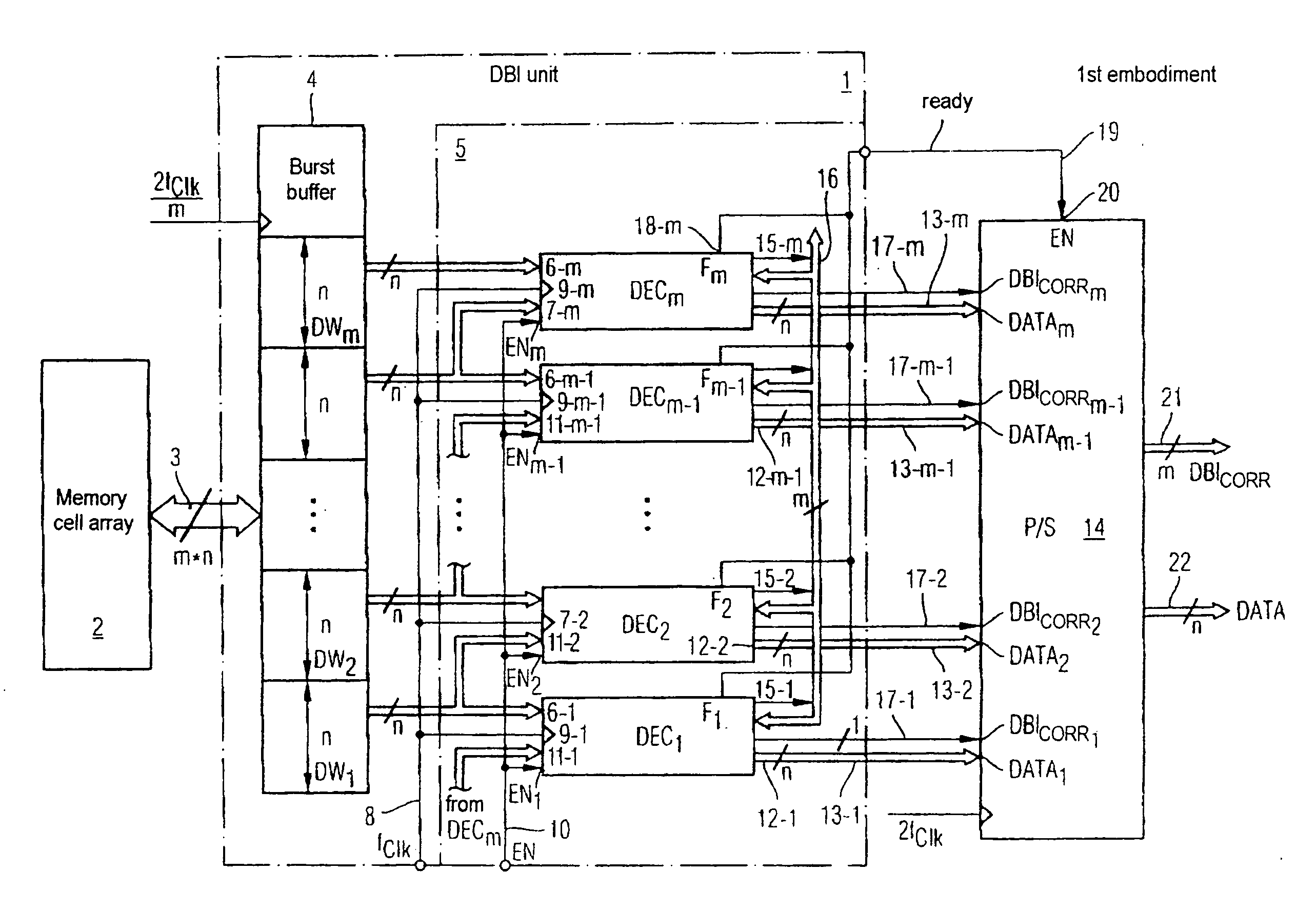
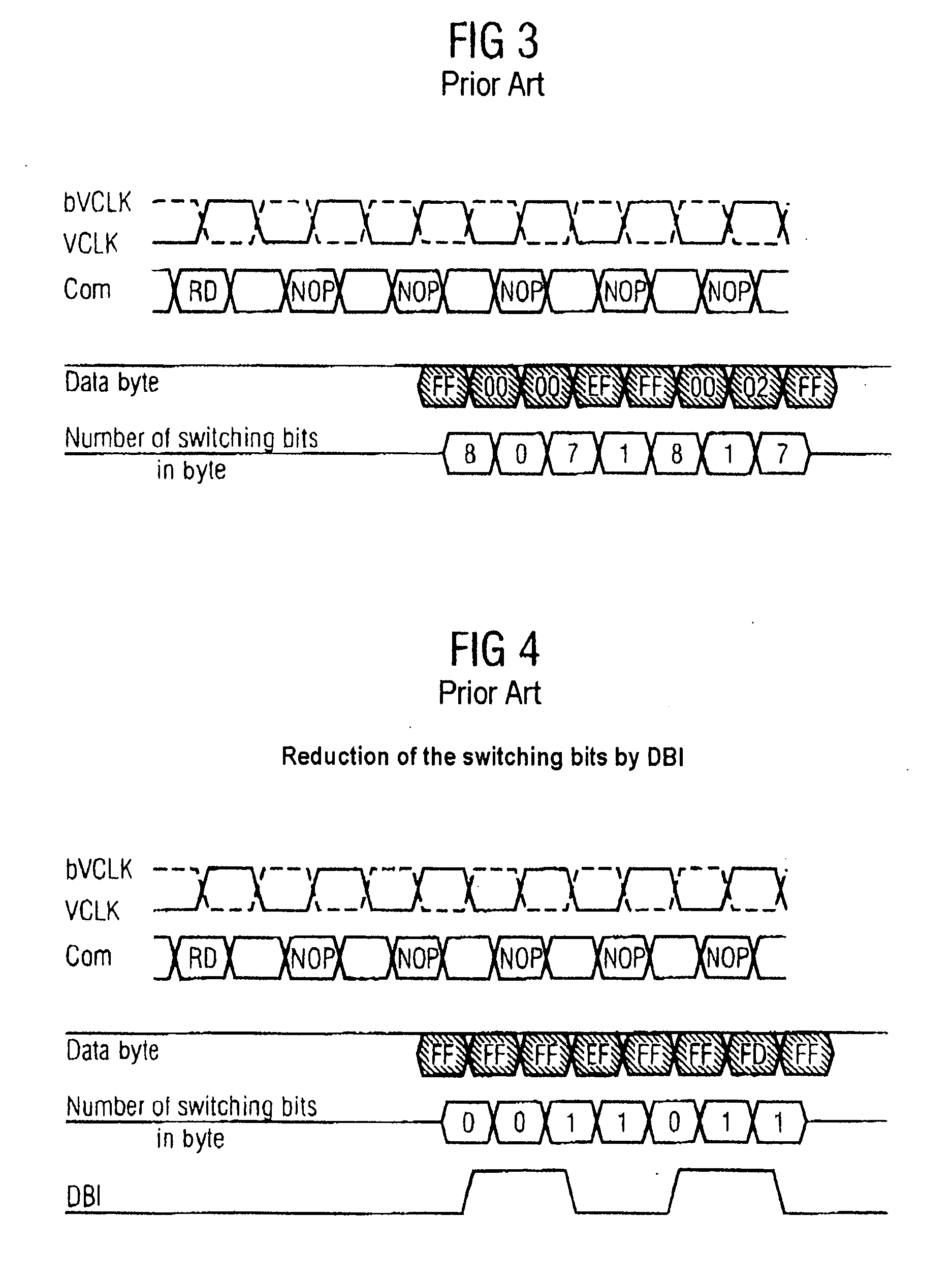
A circuit for producing a data bit inversion flag comprises a first summed-current production unit for producing a first summed current, whose amplitude is proportional to the number of different data bits in two adjacent data words in a data burst, a second summed-current production unit for producing a second summed current, whose amplitude is proportional to the number of identical data bits in the two adjacent data words, and a current comparator comparing the first with the second summed current and producing a data bit inversion flag if the first summed current is greater than the second summed current.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
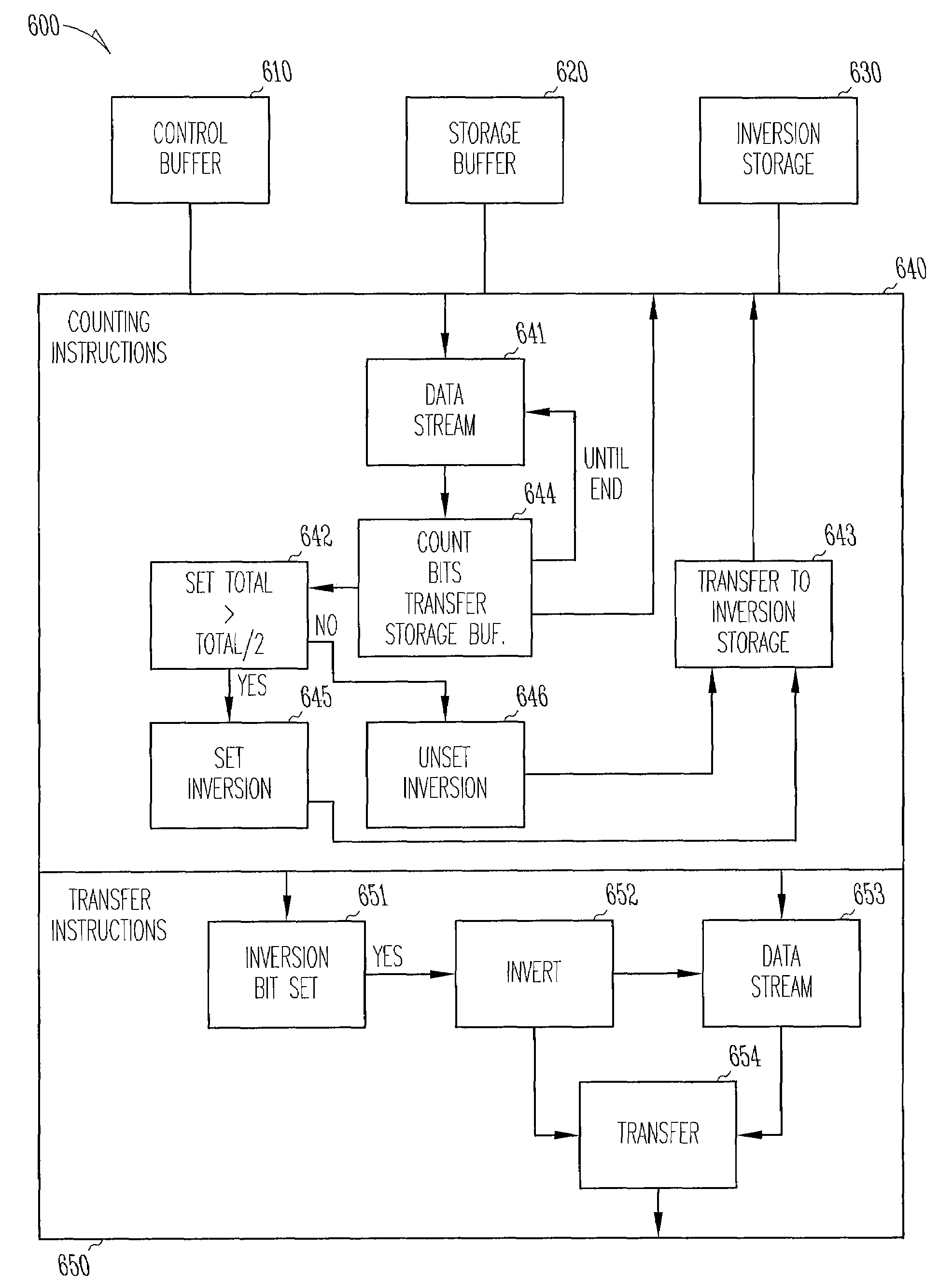
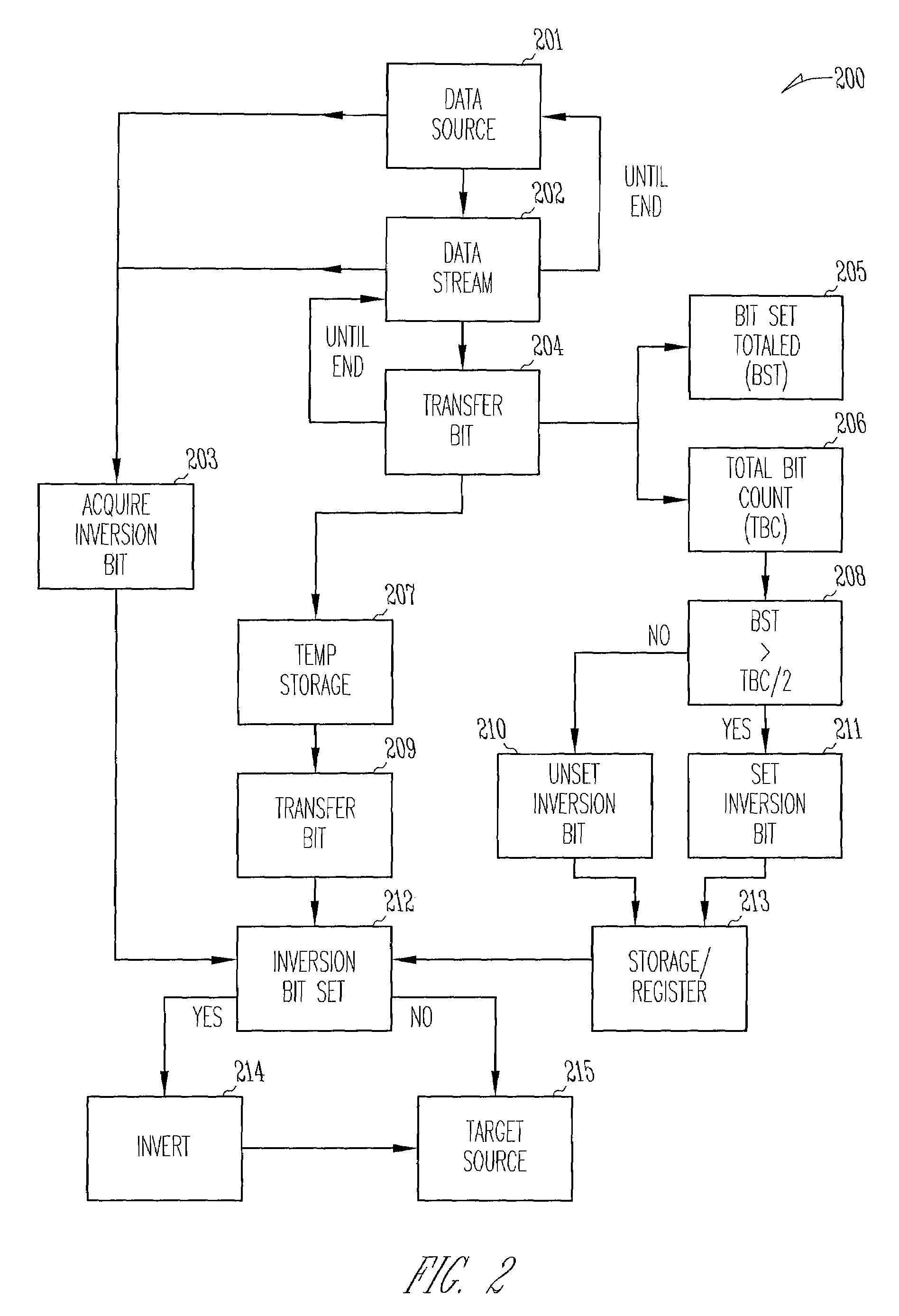
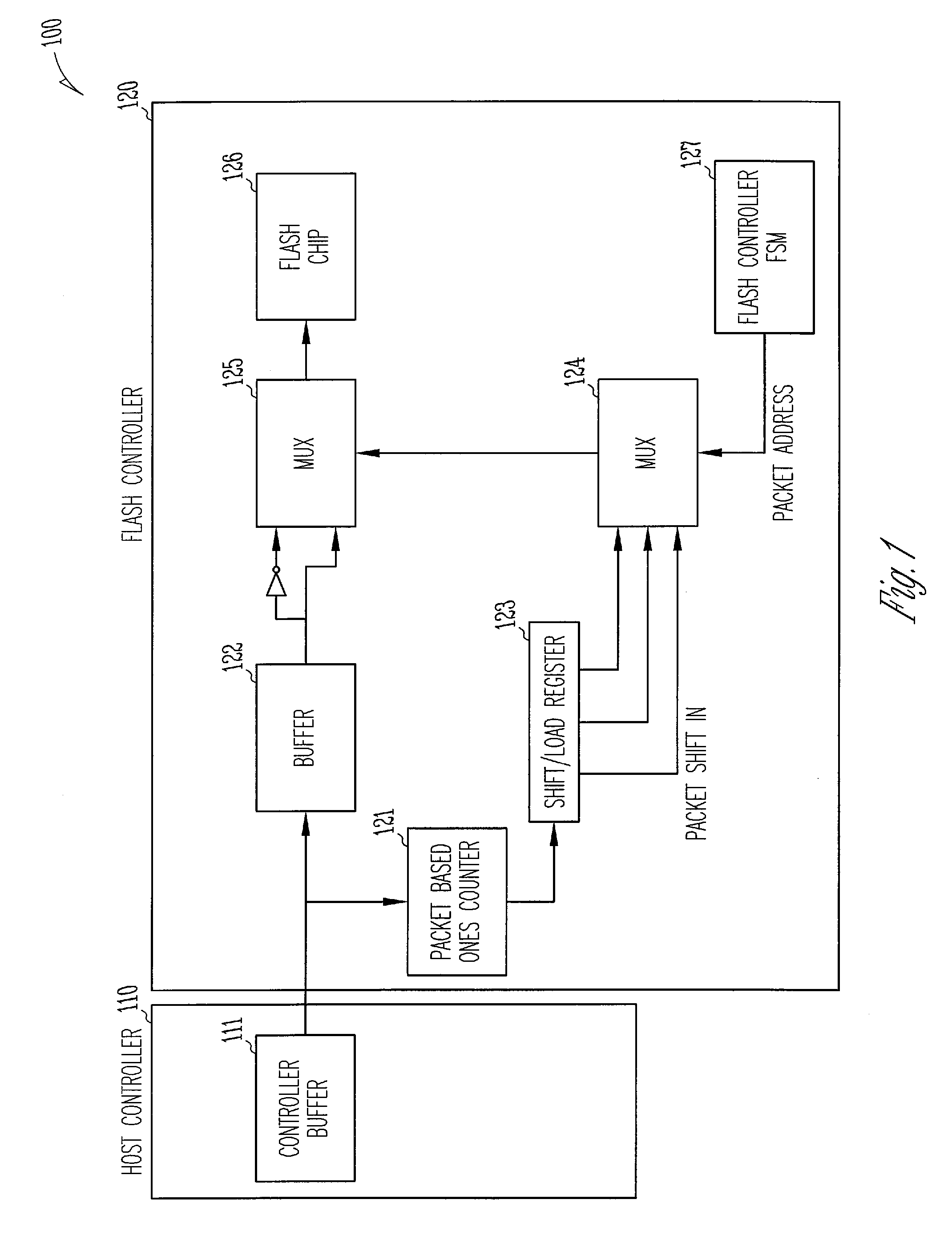
Bit inversion in memory devices
Bit inversions occurring in memory systems and apparatus are provided. Data is acquired from a source destined for a target. As the data is acquired from the source, the set bits associated with data are tabulated. If the total number of set bits exceeds more than half of the total bits, then an inversion flag is set. When the data is transferred to the target, the bits are inverted during the transfer if the inversion flag is set.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
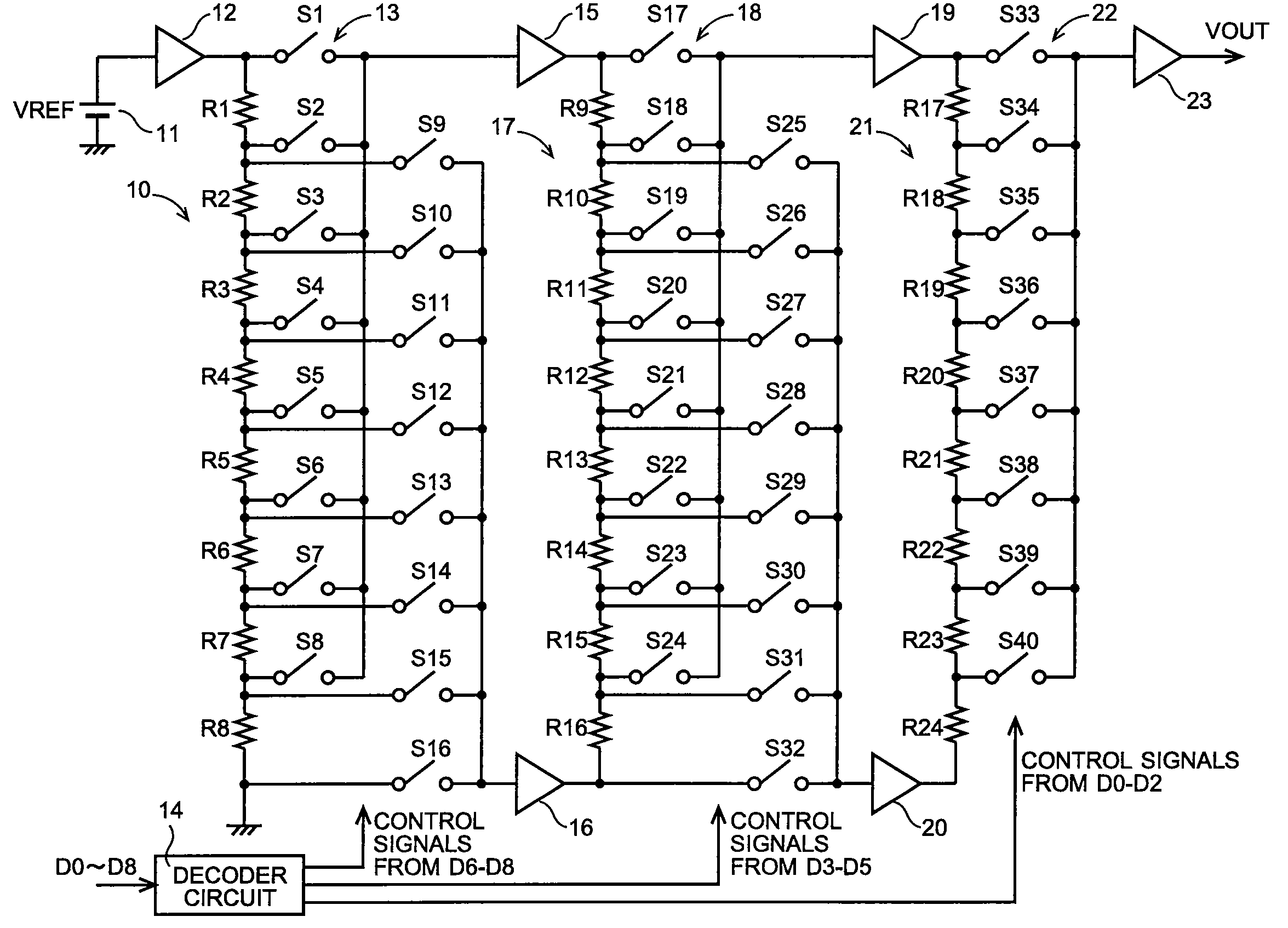
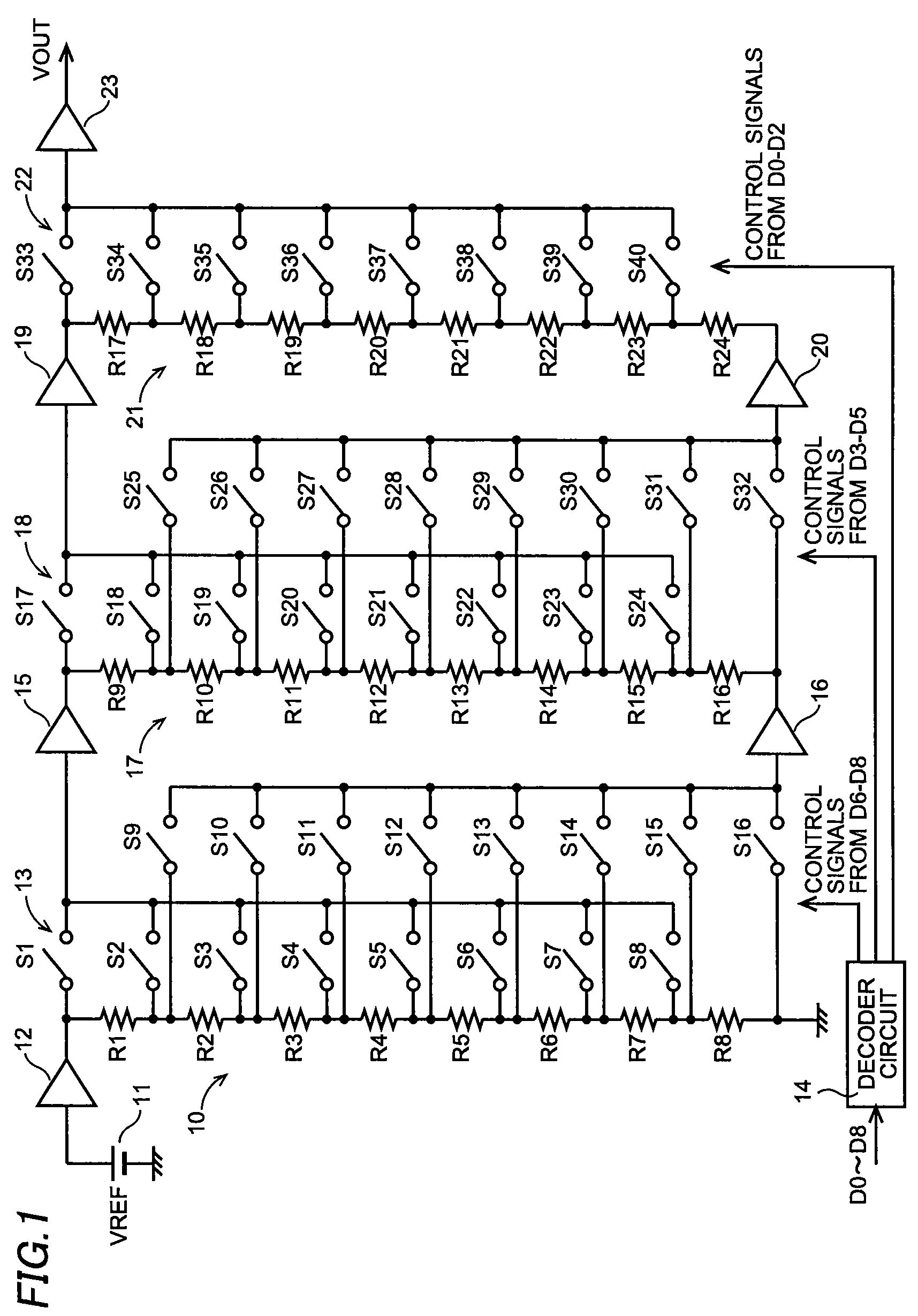
D/A converter circuit
ActiveUS7639166B2Reduce layout areaPrevent reversalElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersBit inversionResistor
A multi-bit D / A converter circuit that prevents a bit inversion and requires a reduced layout area is offered. A first switching circuit is provided in order to select a pair of analog voltages generated across one of resistors in a first resistor string. The selected pair of analog voltages is provided as reference voltages to a second resistor string. A second switching circuit is provided in order to select a pair of analog voltages generated across one of the resistors in the second resistor string. The selected pair of analog voltages is provided as reference voltages to a third resistor string. A third switching circuit is provided in order to select one of analog voltages generated in the third resistor string.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Circuit for data bit inversion
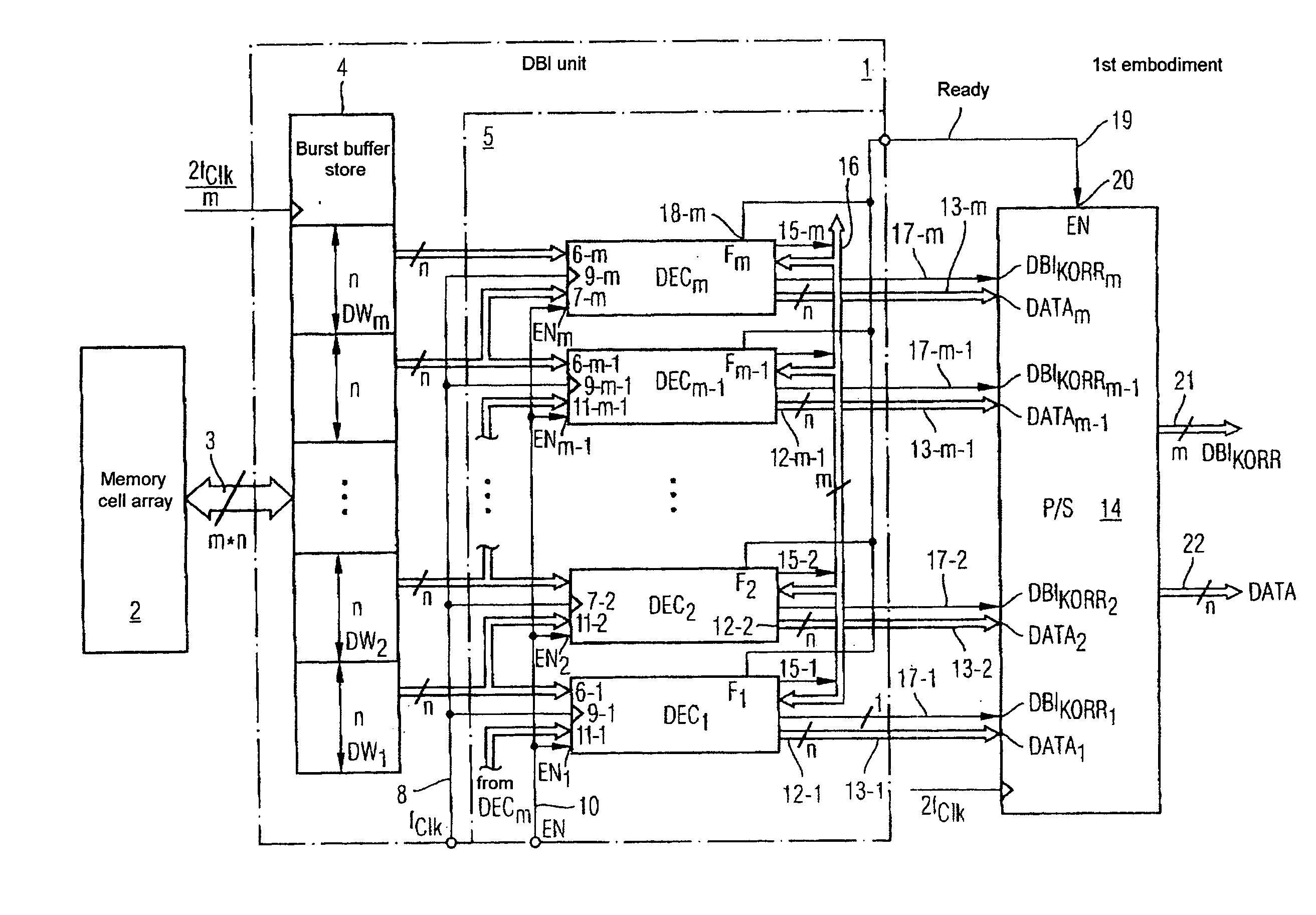
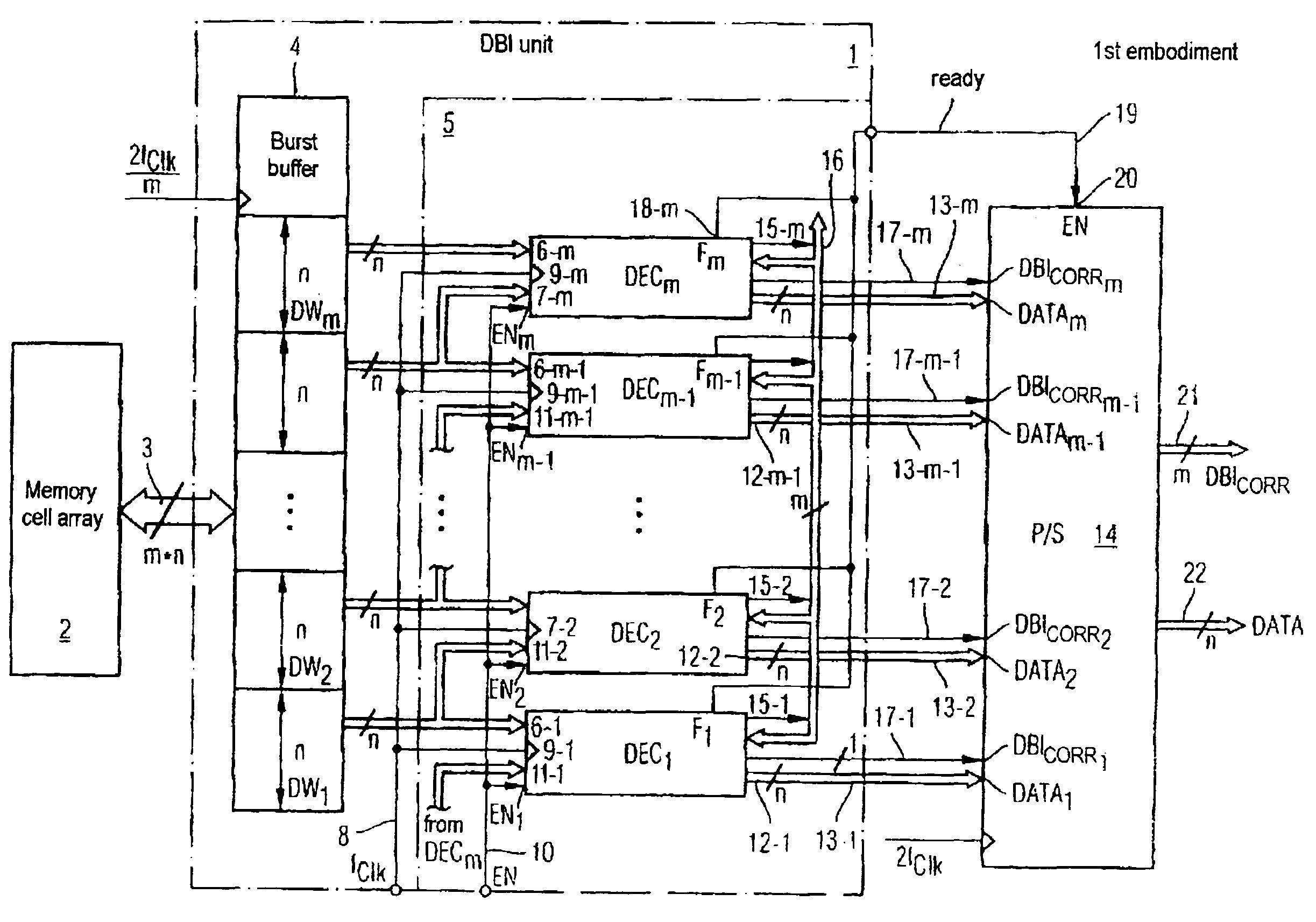
InactiveUS7405981B2Memory access timeDigital storageRedundant data error correctionBit inversionComputer science
An electric circuit for inverting a data bit of a data burst read out from a memory module comprises a buffer for buffering a data burst being comprised of at least two data words, a decoder device comprised of at least two parallel-connected decoders, each comparing bitwise and simultaneously two neighbouring data words of the data words buffered in the buffer and generating an inversion flag, if the number of different data bits of the two neighbouring data words exceeds half the number of data bits of a data word, a correction device for generating a corrected inversion flag for a specific decoder of the decoders by inverting or not inverting the inversion flag of the specific decoder dependent on the inversion flag generated by the specific decoder and the inversion flags generated by the remaining of the decoders, and an inversion device comprised of a plurality of inverters, each inverting or not inverting a present of the data words of an associated of the decoders dependent on the corrected inversion flag of the associated decoder.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
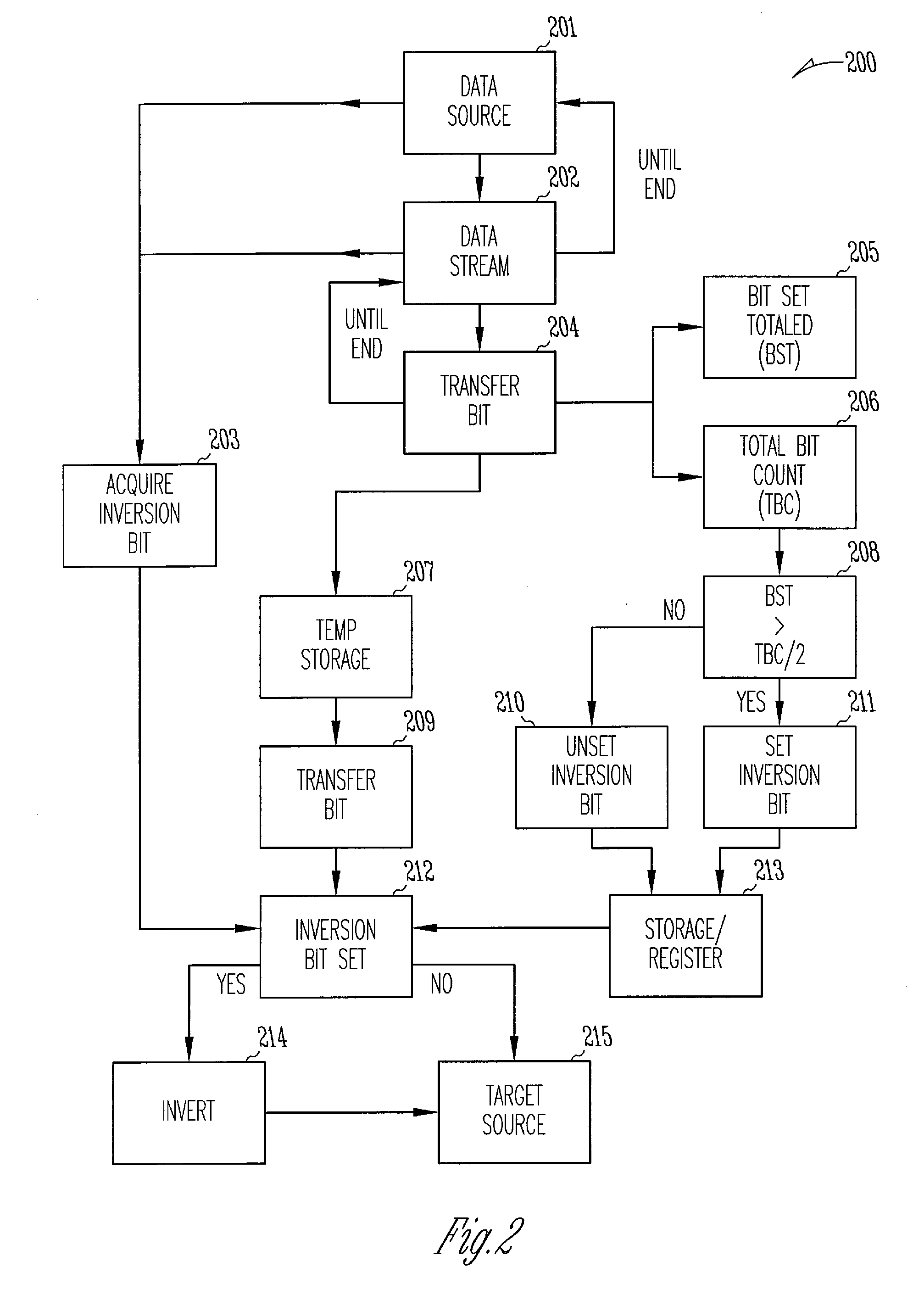
Bit inversion in memory devices
Bit inversions occurring in memory systems and apparatus are provided. Data is acquired from a source destined for a target. As the data is acquired from the source, the set bits associated with data are tabulated. If the total number of set bits exceeds more than half of the total bits, then an inversion flag is set. When the data is transferred to the target, the bits are inverted during the transfer if the inversion flag is set. Alternatively, an acquired data stream includes an association with an inversion bit. The inversion bit is acquired and stored separately from the data stream. As the data stream is transferred, if the inversion bit is set then the stream is inverted during the transfer of the stream to a target.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
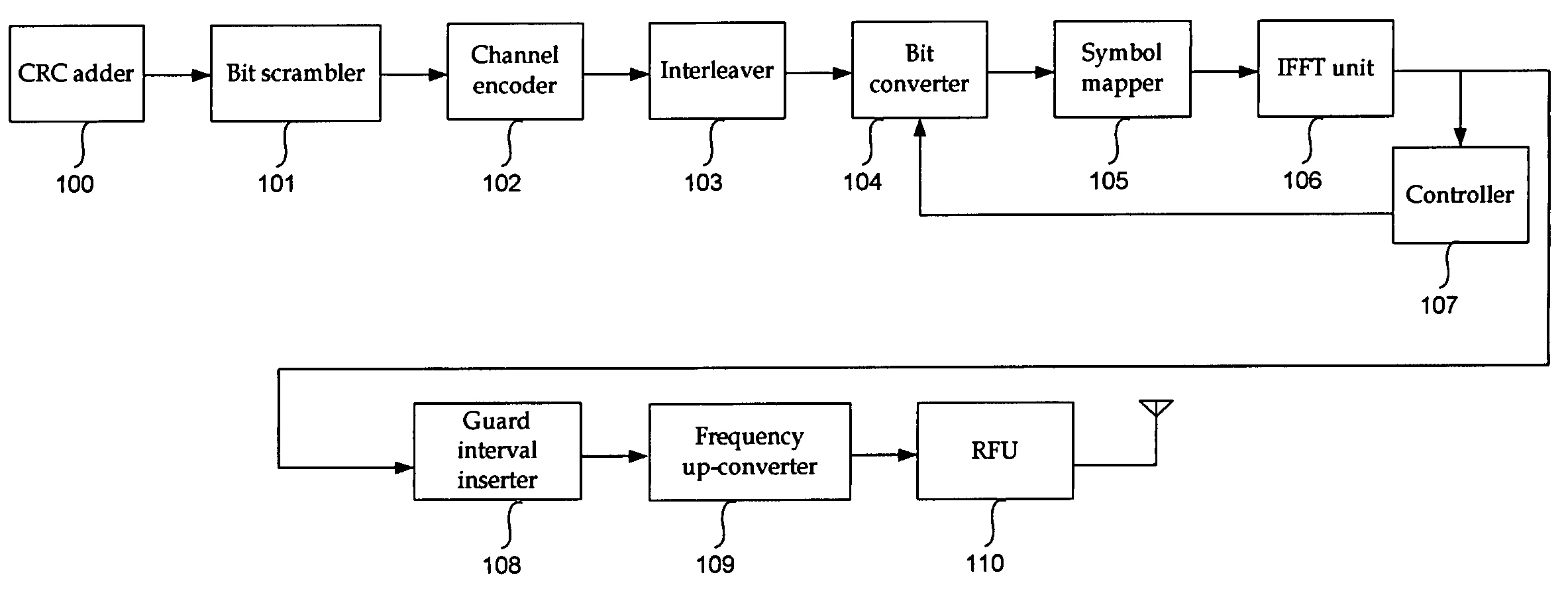
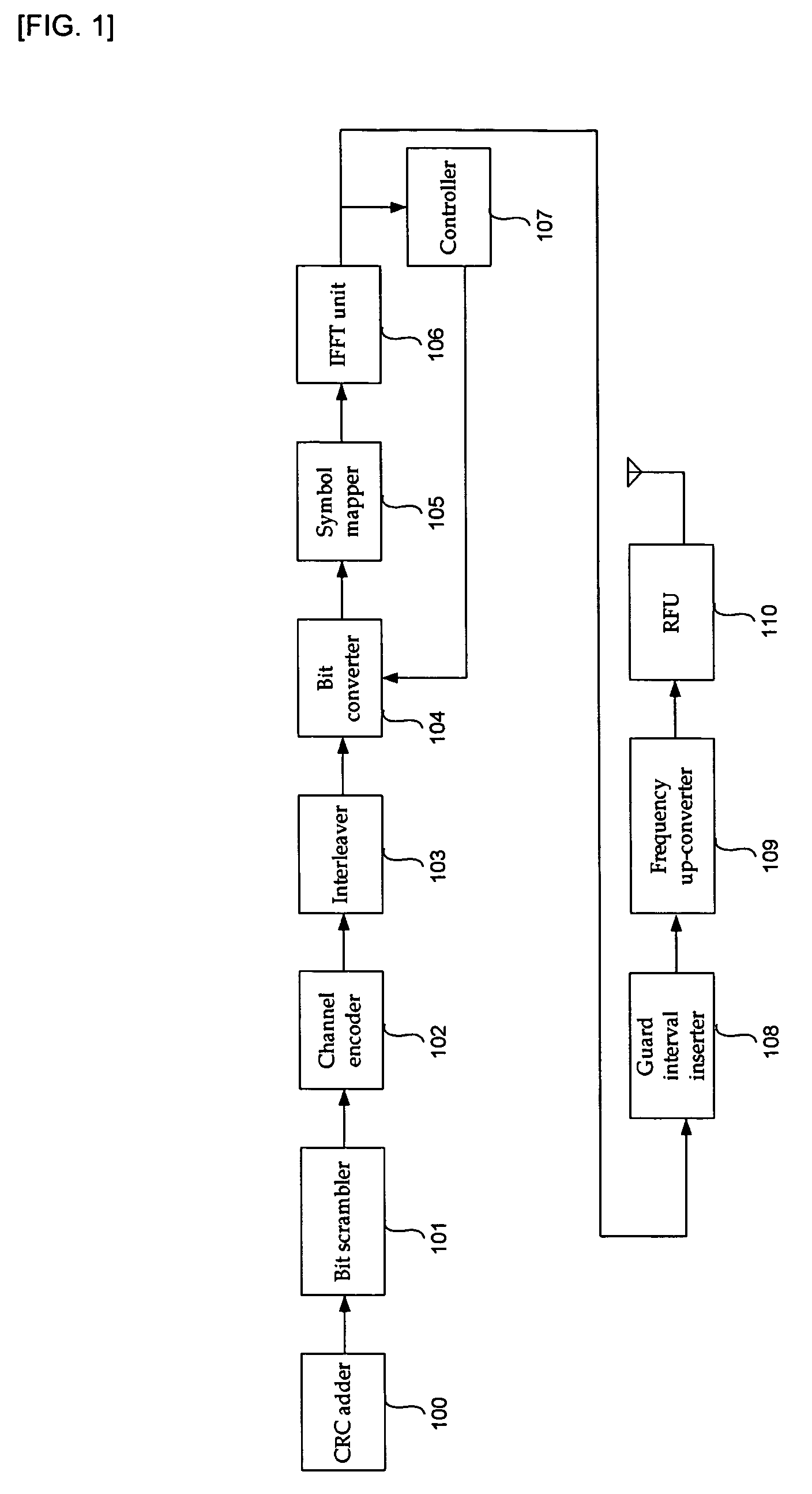
Transmitting apparatus of OFDM system and method thereof
InactiveUS7652978B2Enhanced signalReduce the ratioSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsRadio channelData transmission
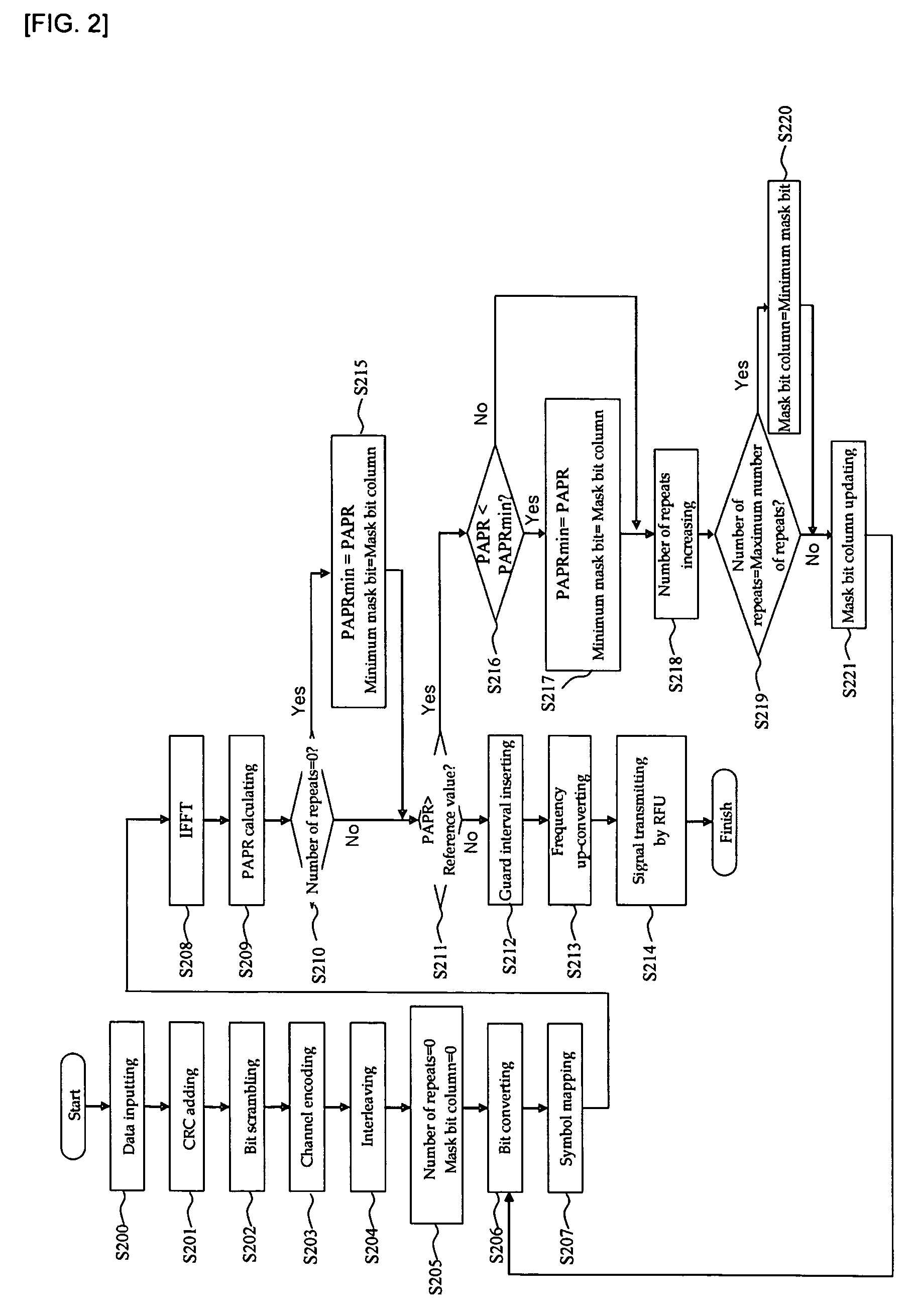
The present invention relates to a transmitter in an OFDM system for improving the PAPR, and a method thereof. According to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention, channel encoding is performed in order to correct a data transmission error of a radio channel, a predetermined bit of the channel encoded data is bit-inverted by using a mask bit or a mask bit sequence, and a PAPR of the signal is reduced. Accordingly, reduction of transmission efficiency which has been generated in block coding and DSI methods is not generated when the signal is transmitted because an additional bit is not required.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Pruned bit-reversal interleaver
InactiveCN101124731ACode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesConvolutional codeLow density
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
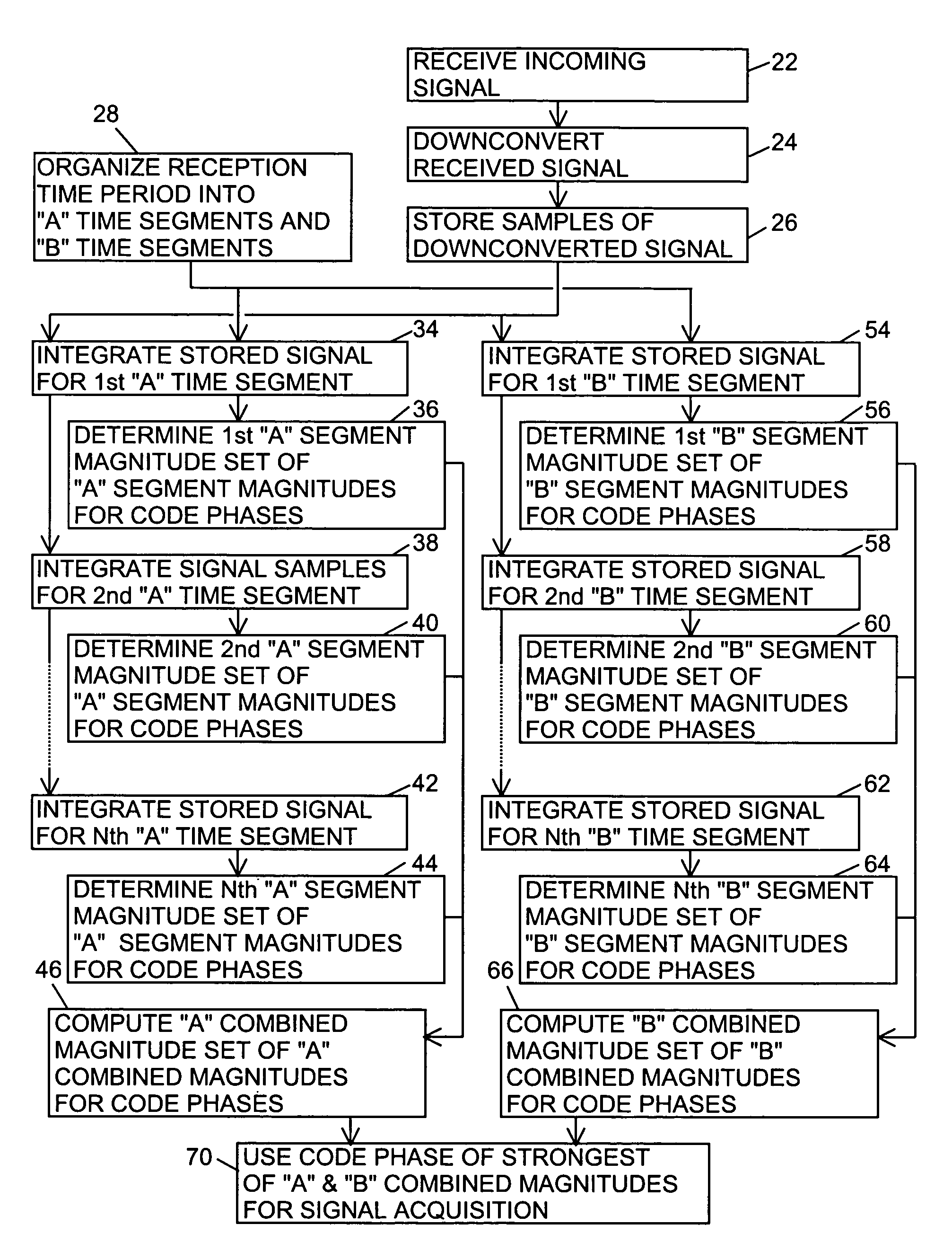
Signal receiver for integrating and combining integrations in alternating time segments for signal acquisition at low signal strength
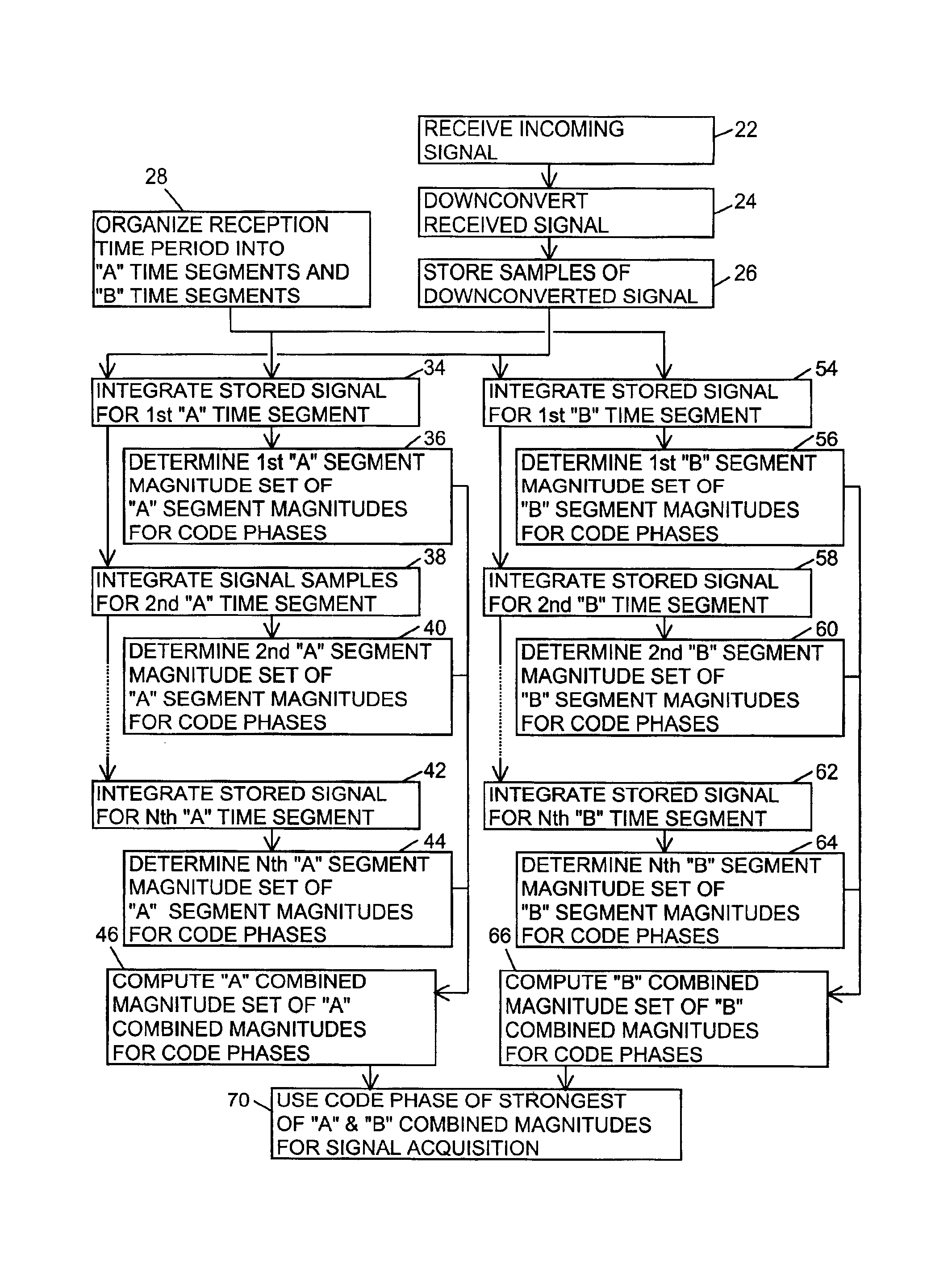
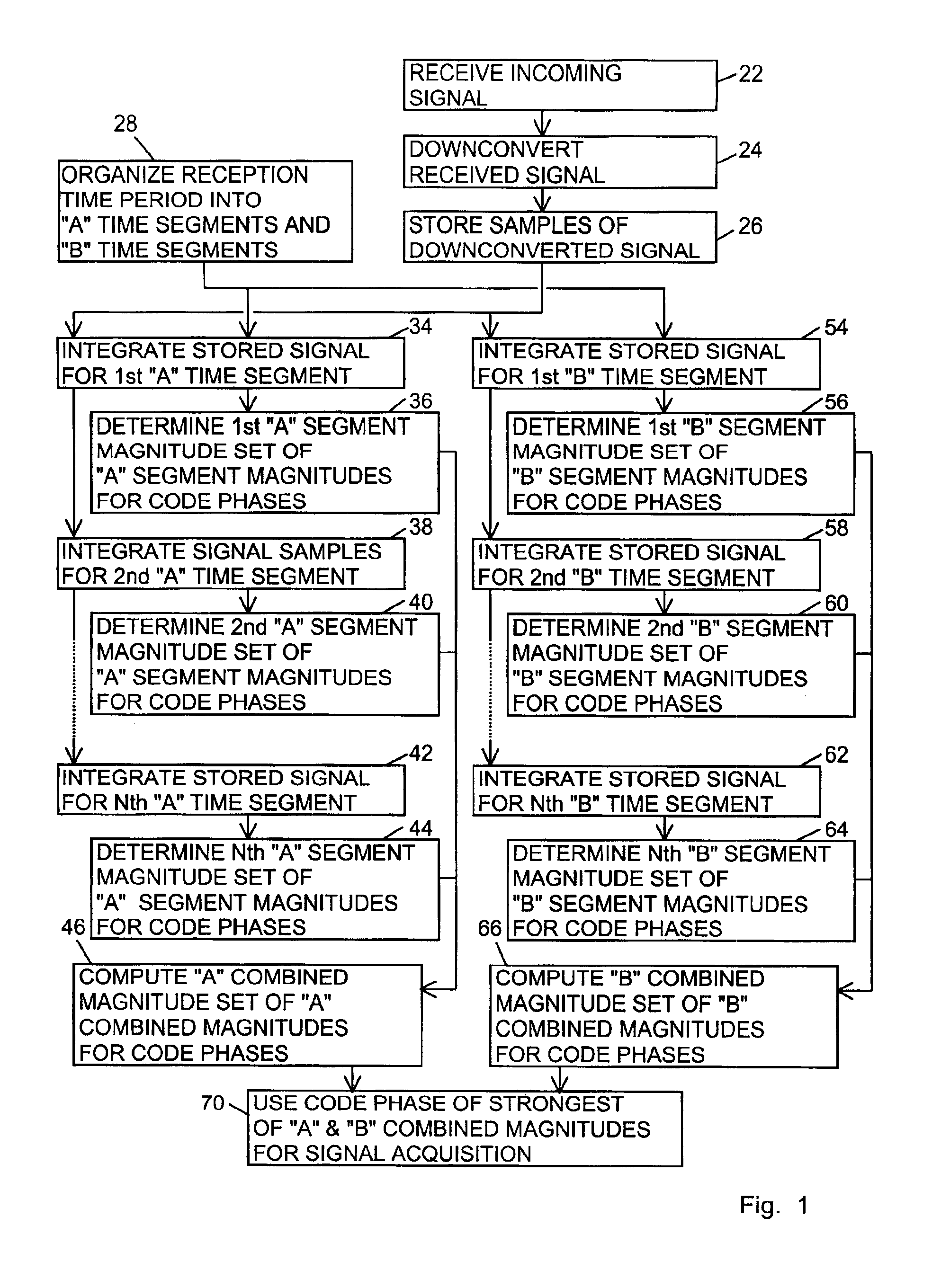
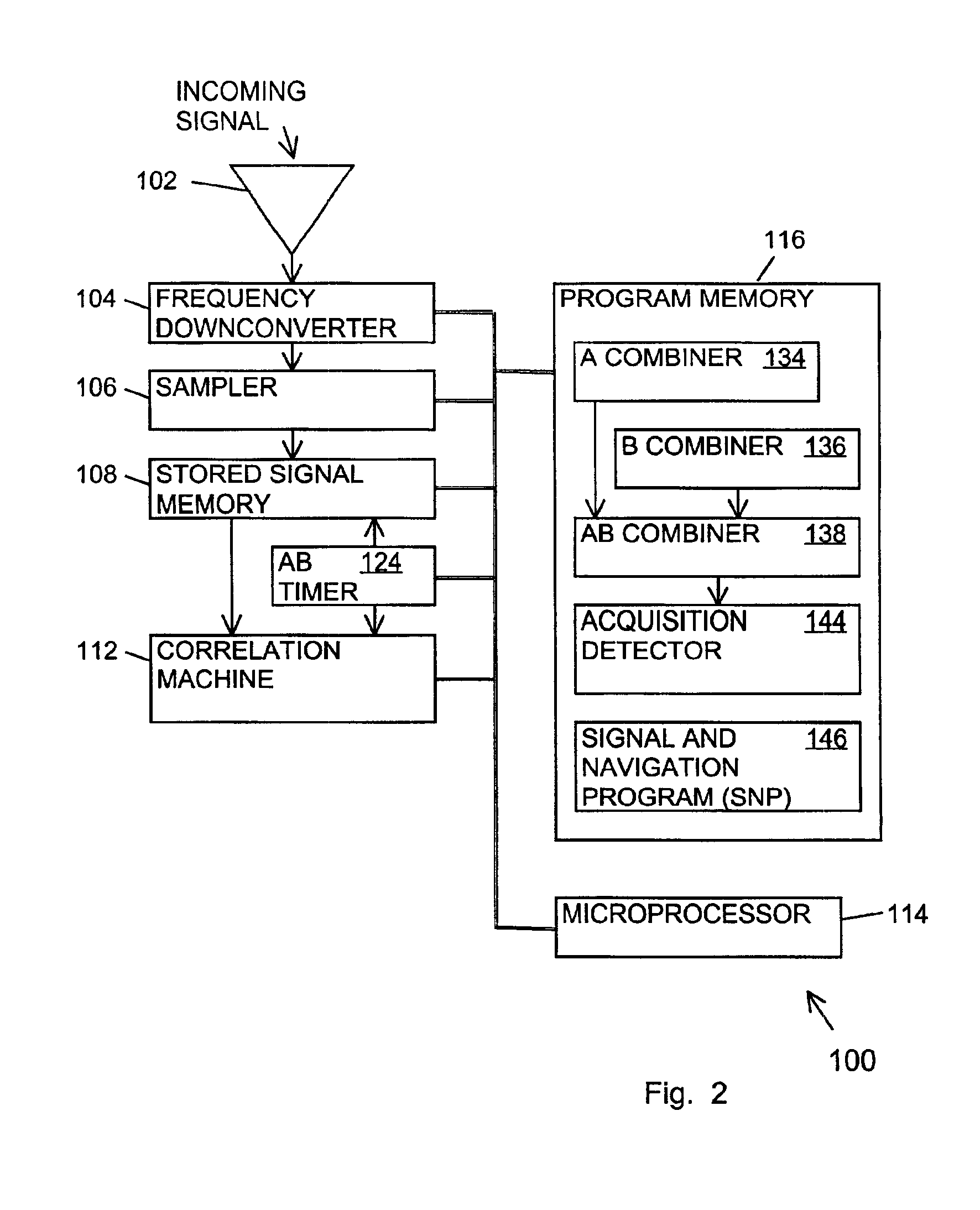
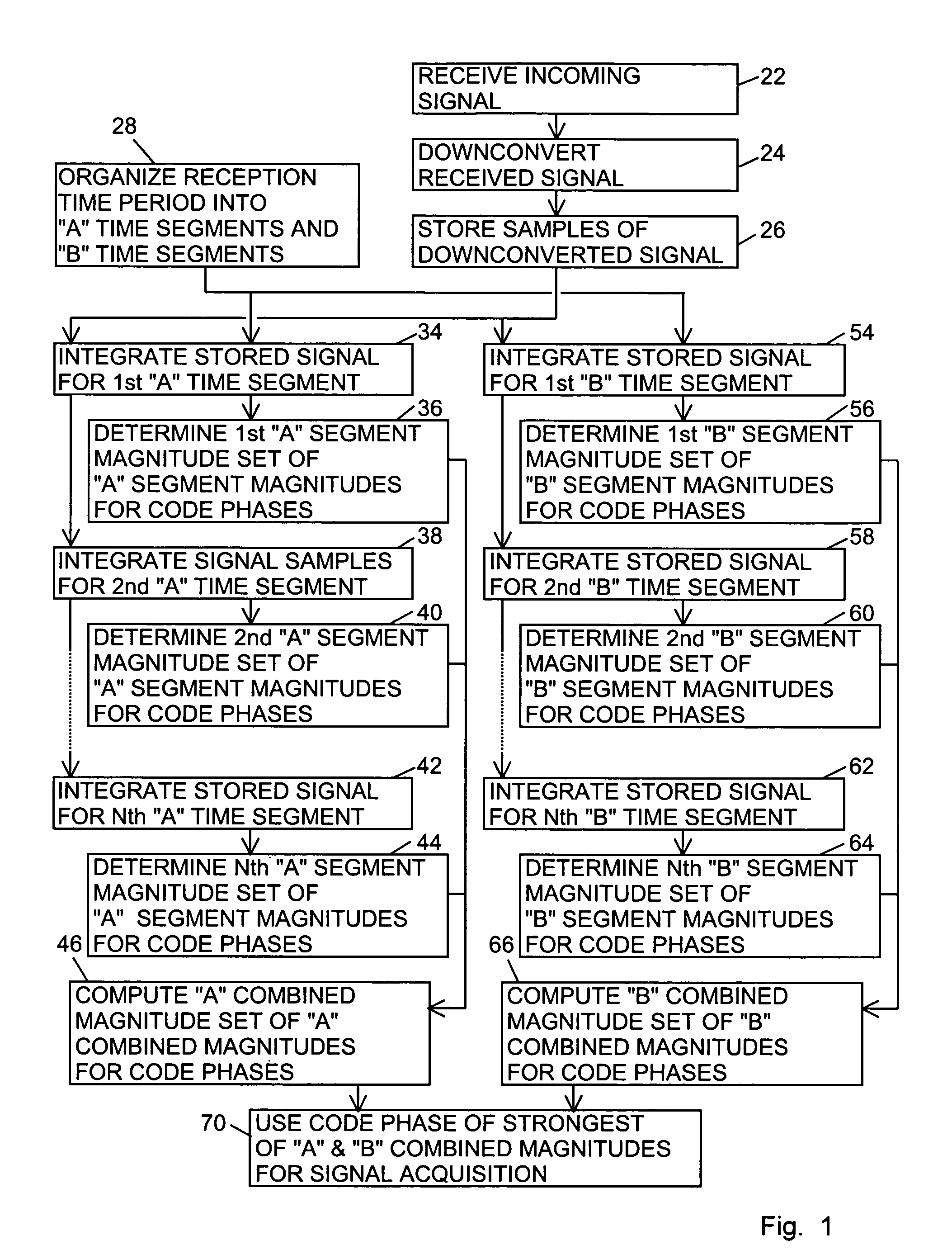
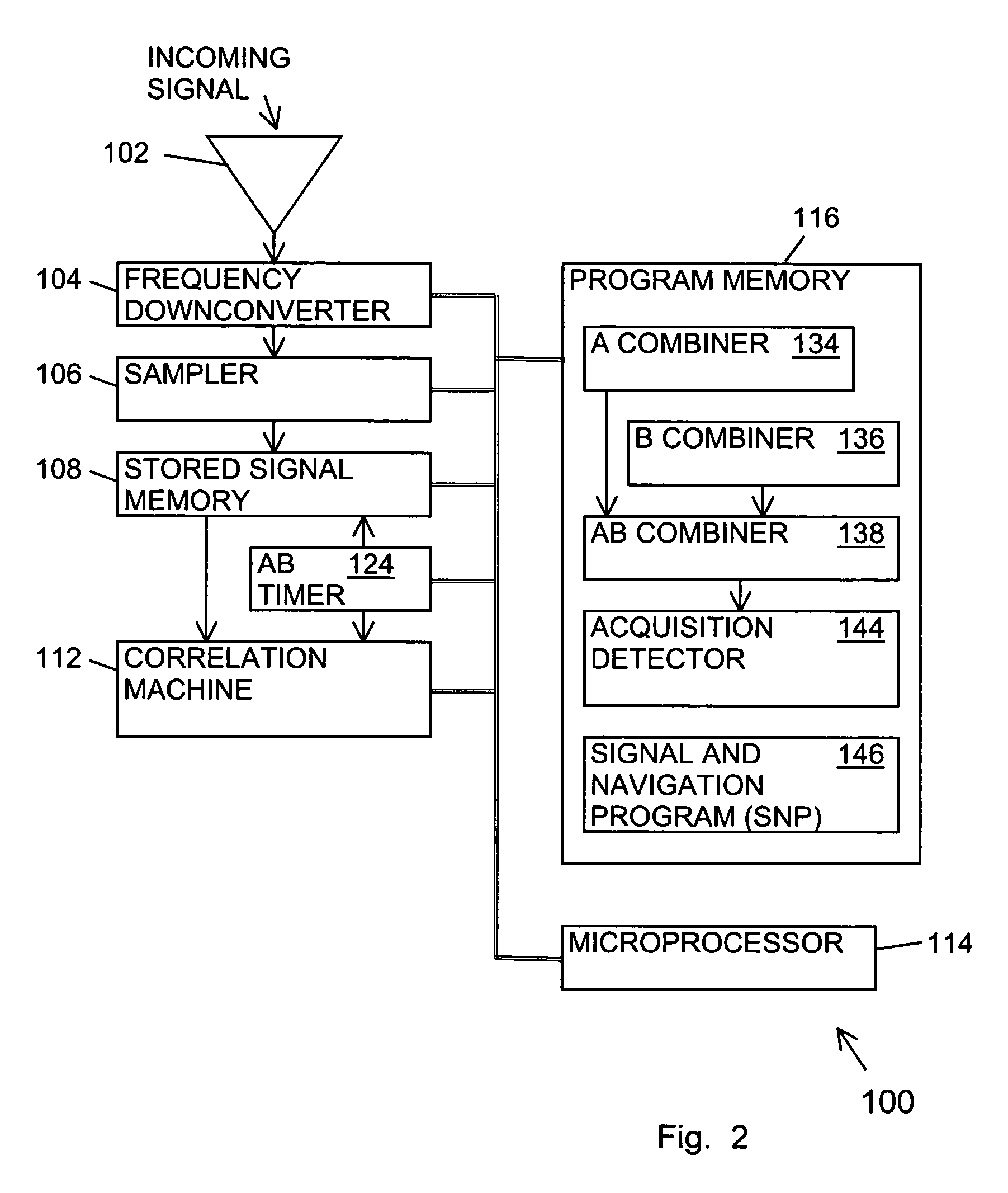
ActiveUS6898234B1Large signal processing gainIncrease probabilityBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingTime segmentGps receiver
A GPS receiver for integrating a GPS signal separately in a series of “A” type and “B” type time segments, the “A” segments alternating with the “B” time segments; combining the squares of the magnitudes of “A” time segment integrations corresponding to code phases for forming “A” type combined magnitudes; combining the squares of the magnitudes of the “B” time segment integrations corresponding to code phases for forming “B” type combined magnitudes; and determining an acquisition code phase of the signal from the strongest of the “A” or “B” combined magnitudes. The “A” time segments and the “B” time segments are one-half the period of the data bits of the signal, thereby ensuring that either the “A” time segments or the “B” time segments avoid the nullifying effect of data bit inversions.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
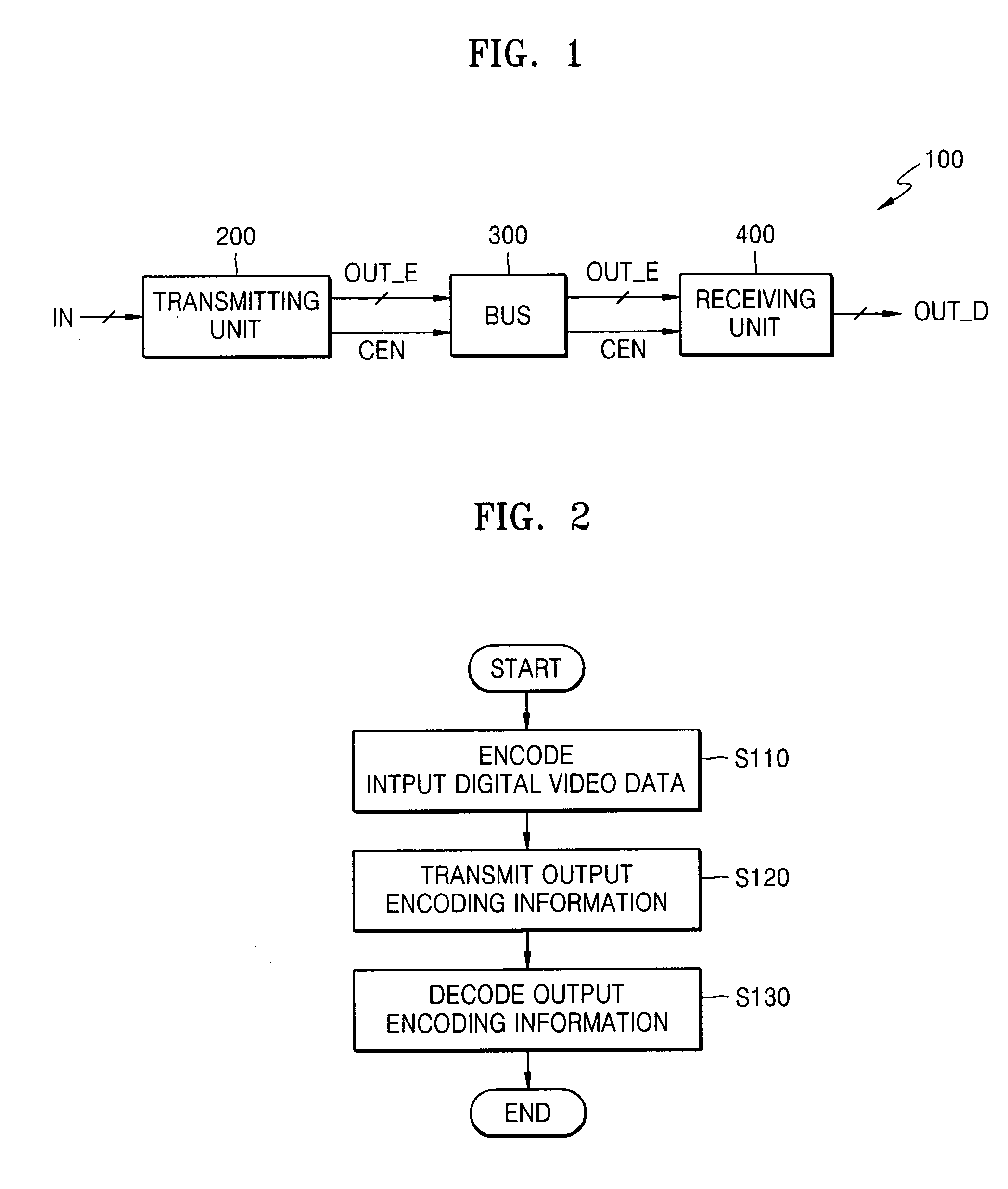
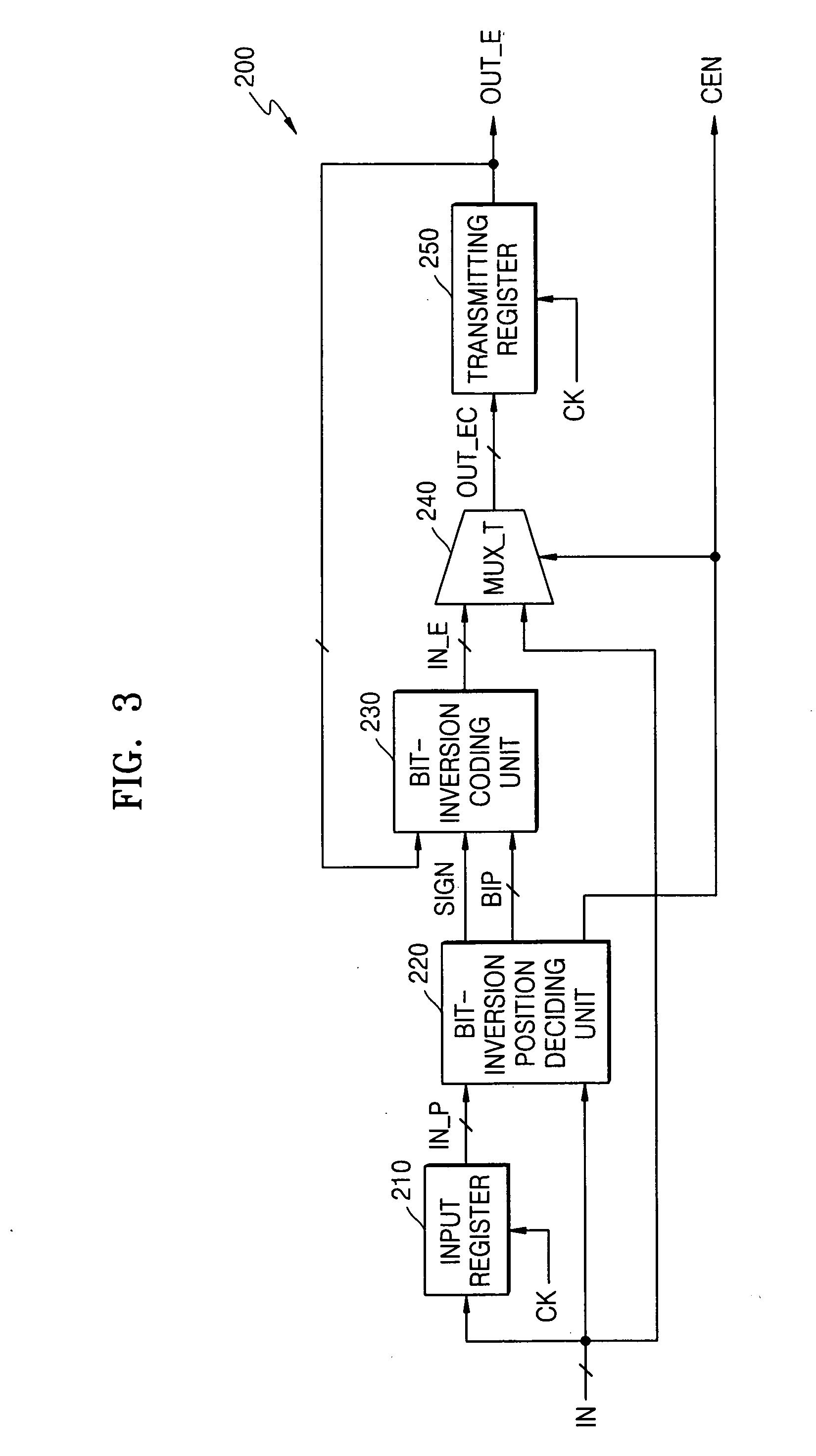
Digital video data transmission system and method
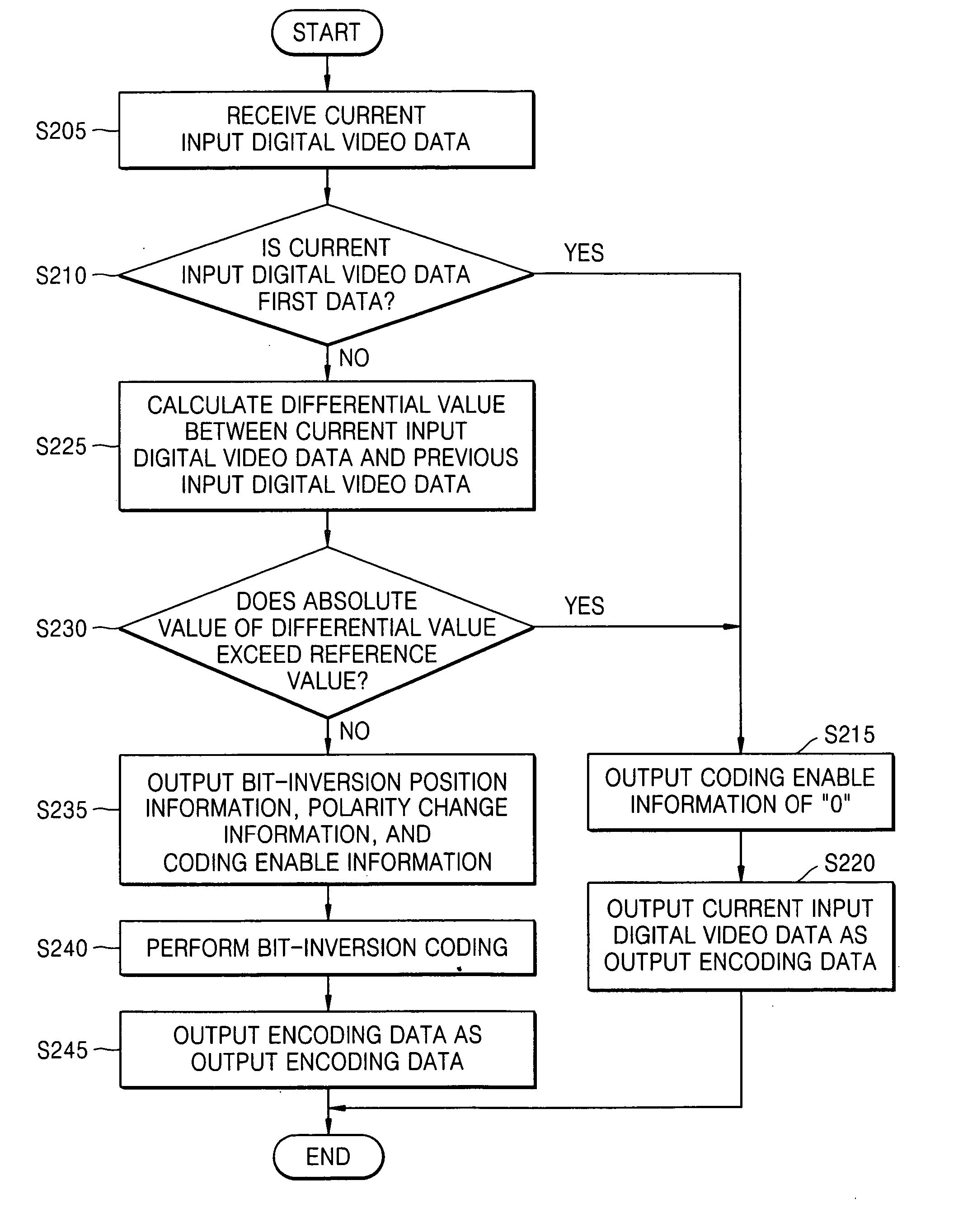
InactiveUS20060098731A1Reduce Hamming distanceReduce electromagnetic interferenceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoTransfer system
Provided are a digital video data transmission system and digital video data transmission method. The digital video data transmission system includes a transmitting unit transmitting valid first data in input digital video data having spatial locality to a bus as output encoding information without bit-inversion coding the first data, bit-inversion coding previous data of output encoding data corresponding to the input digital video data based on differential values of adjacent digital video data, and transmitting the bit-inversion coded value to the bus as the output encoding information; and a receiving unit not decoding output encoding information transmitted in parallel through the bus, i.e., the first data, but decoding output encoding information transmitted in parallel through the bus based on the differential values. The output encoding information includes the output encoding data and coding enable information that indicates whether to bit-inversion encode previous data of the output encoding data. The digital video data transmission system and digital video data transmission method can reduce the number of transitions of bits included in the digital video data transmitted through the bus, thereby reducing power consumption and electromagnetic interference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
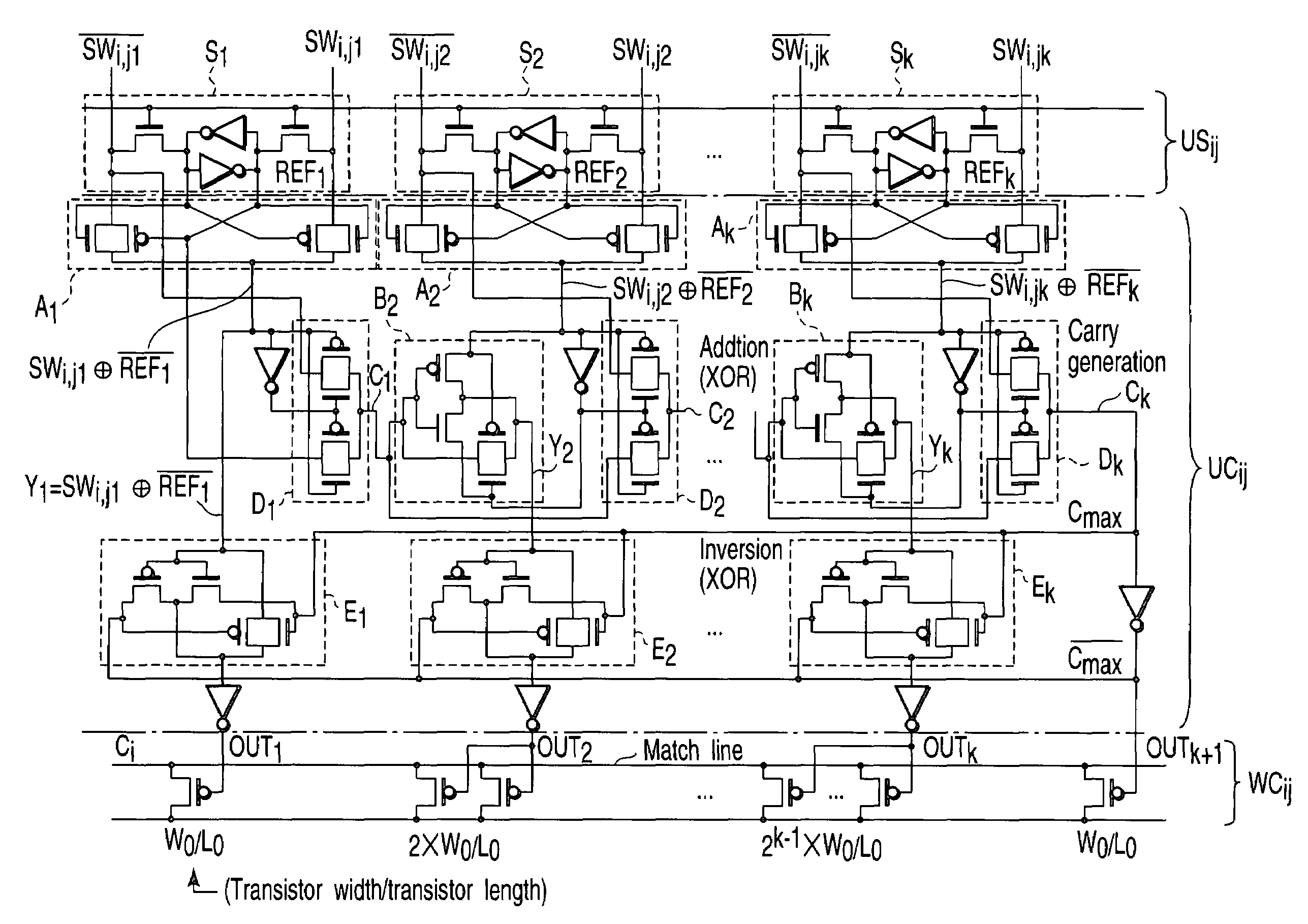
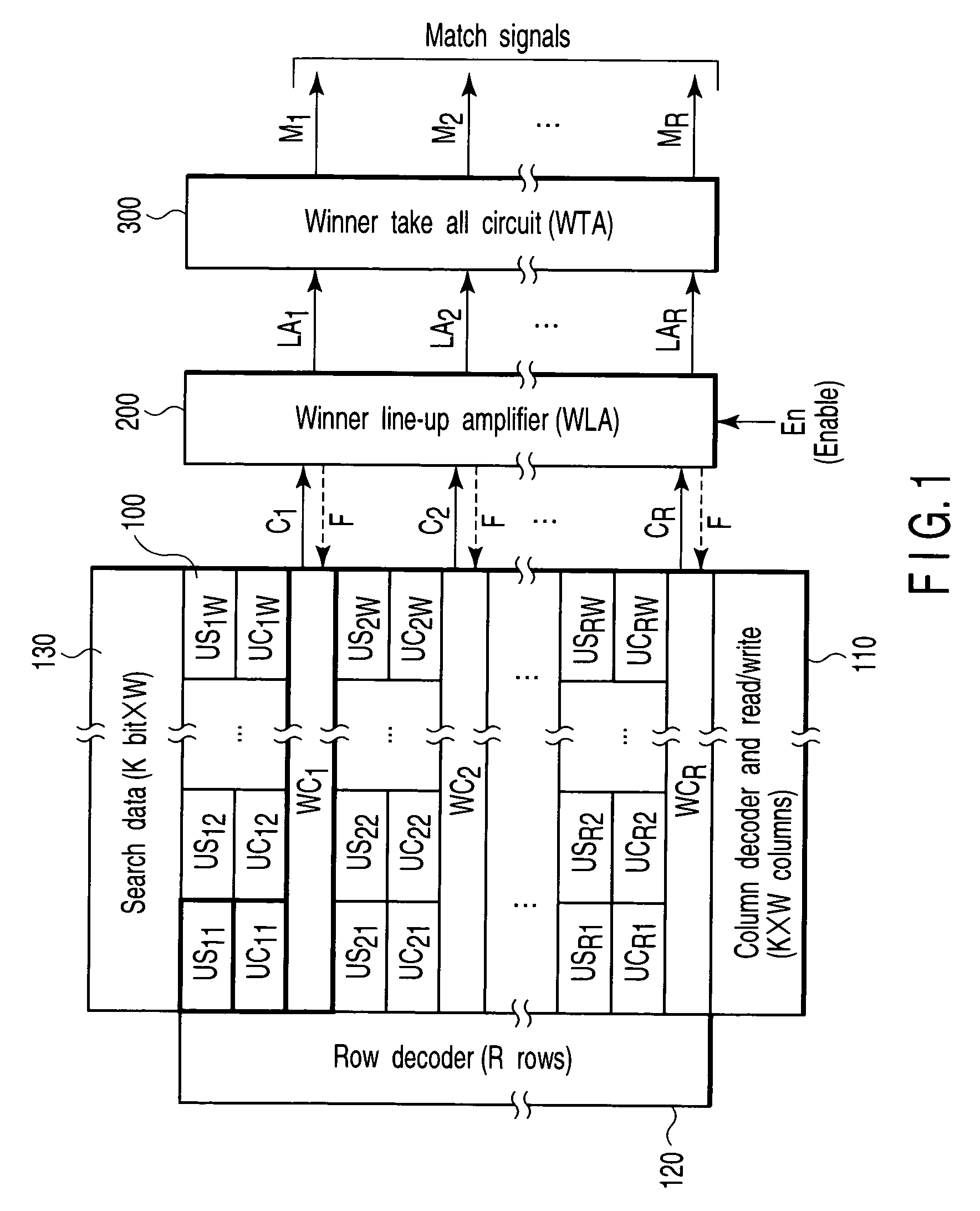
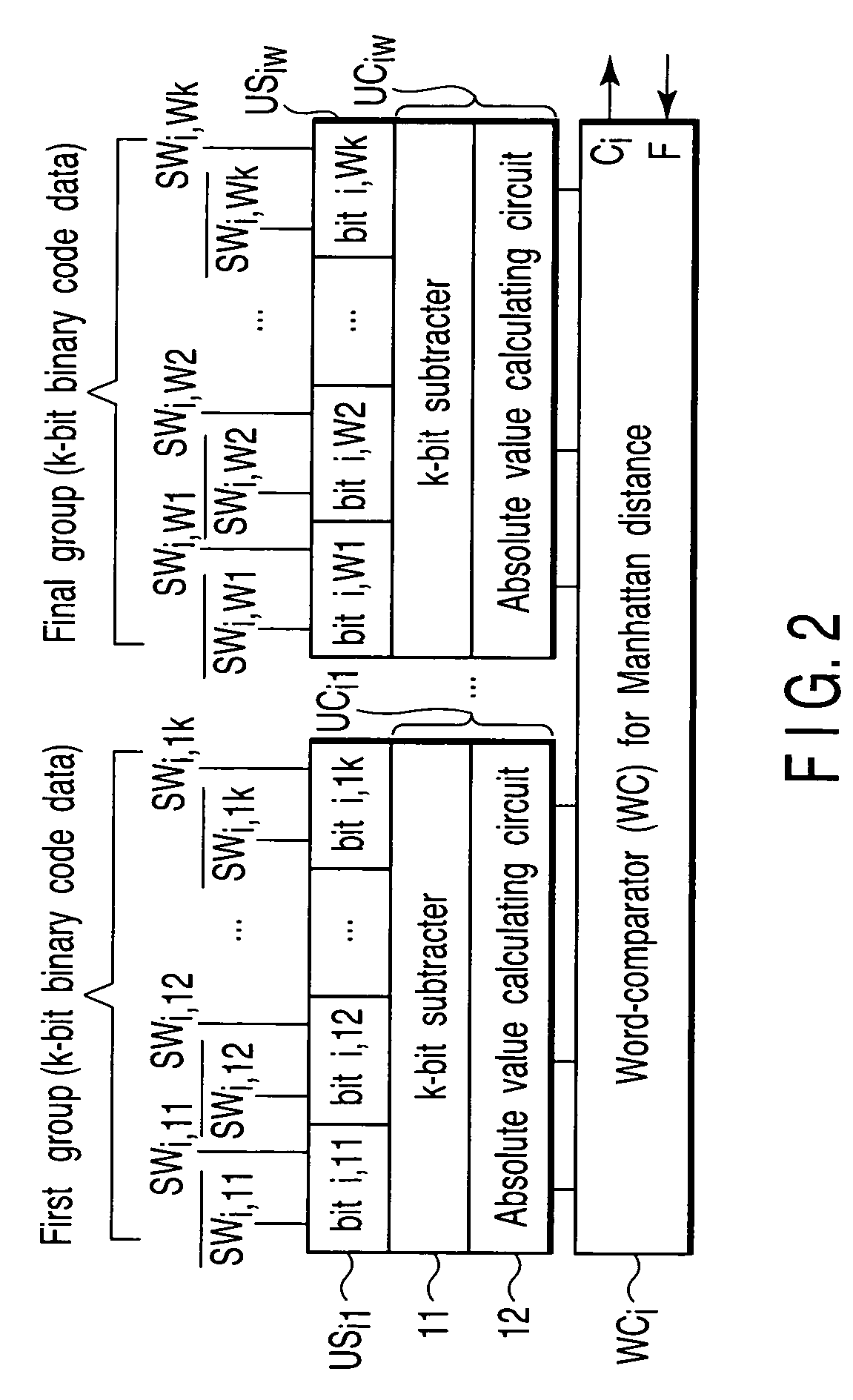
Associative memory apparatus for searching data in which manhattan distance is minimum
InactiveUS7113416B2Increase speedMinimum distanceImage analysisDigital storageBit inversionComputer science
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
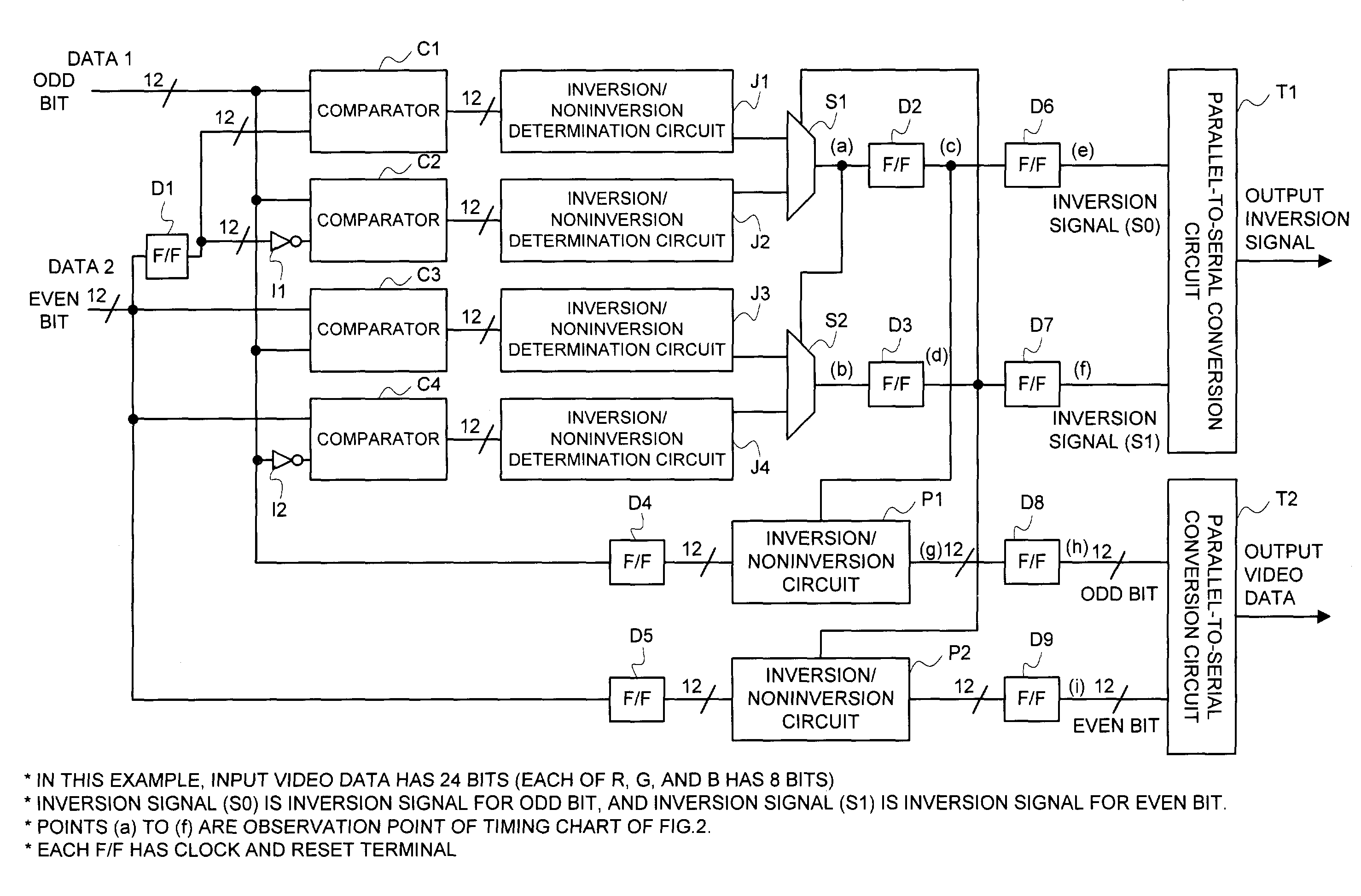
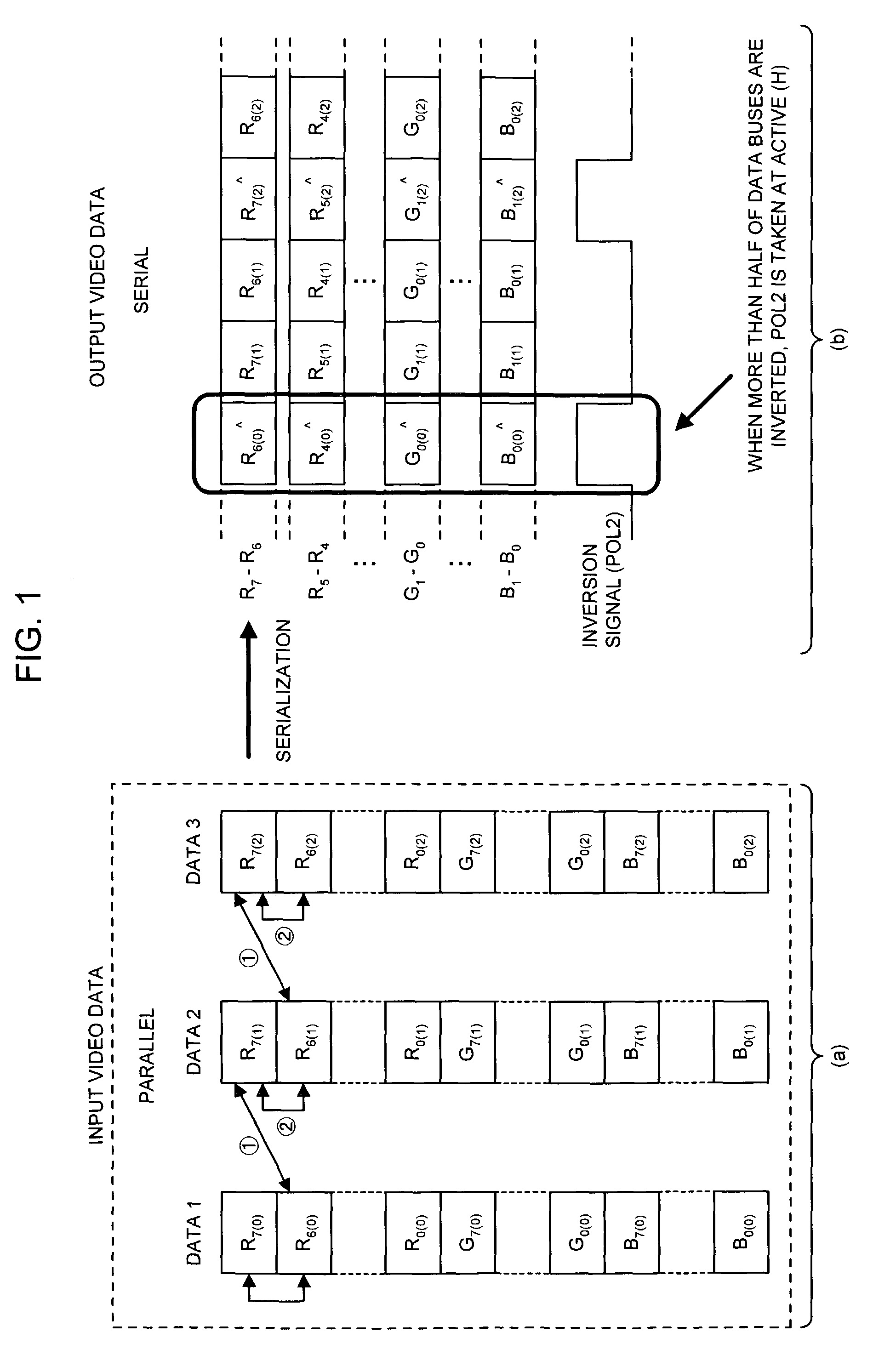
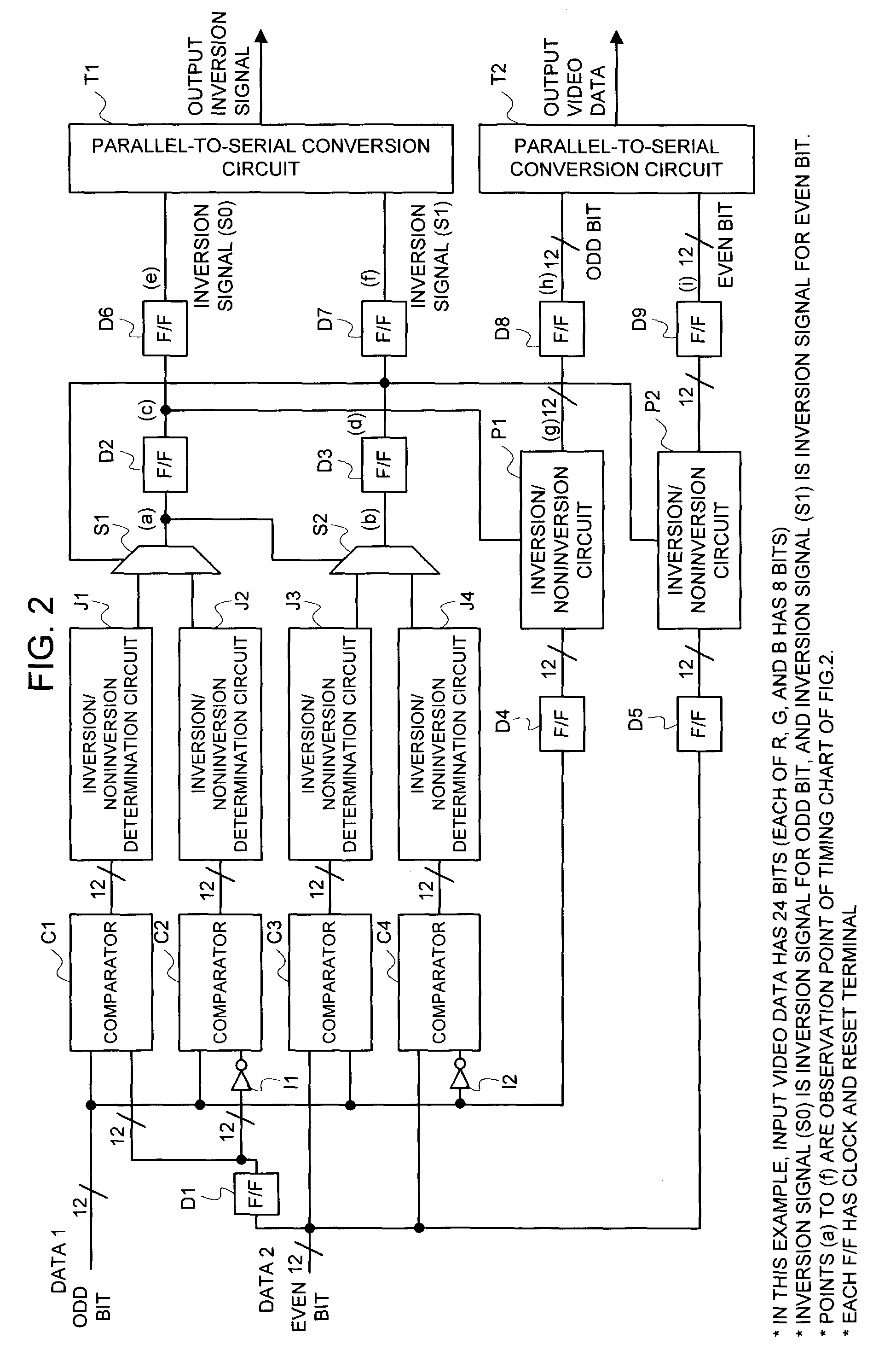
Video data transfer method, display control circuit, and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS7307613B2Increase computing speedAvoid electromagnetic interferenceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displaySerialization
In a technique of partially serializing video data to transfer it from a display control circuit to a signal-line driving circuit such as a source driver, data comparisons ① and ② in the data order after serialization are made sequentially in a stage of parallel data prior to making a parallel-to-serial conversion of the video data, and determination is made as to whether or not the bit inversion number of the data is more than half to take a control of an inversion / noninversion for the transfer data. An operational speed of a comparator, an inversion / noninversion determination circuit, etc. can be reduced as compared with the case in which a control is taken of the inversion / noninversion for the data of which an operation speed became high by partially serializing the video data.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Circuit for data bit inversion
InactiveUS20060215473A1Memory access timeDigital storageRedundant data error correctionBit inversionComputer science
An electric circuit for inverting a data bit of a data burst read out from a memory module comprises a buffer for buffering a data burst being comprised of at least two data words, a decoder device comprised of at least two parallel-connected decoders, each comparing bitwise and simultaneously two neighbouring data words of the data words buffered in the buffer and generating an inversion flag, if the number of different data bits of the two neighbouring data words exceeds half the number of data bits of a data word, a correction device for generating a corrected inversion flag for a specific decoder of the decoders by inverting or not inverting the inversion flag of the specific decoder dependent on the inversion flag generated by the specific decoder and the inversion flags generated by the remaining of the decoders, and an inversion device comprised of a plurality of inverters, each inverting or not inverting a present of the data words of an associated of the decoders dependent on the corrected inversion flag of the associated decoder.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
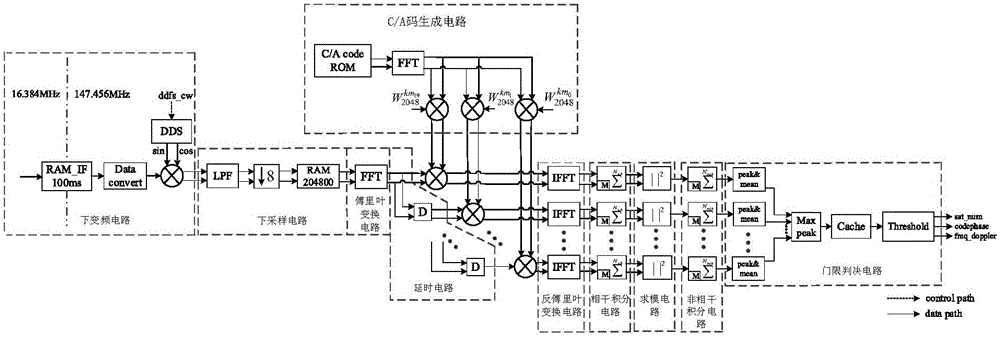
GPS capture circuit based on optimization parallel code phase search
InactiveCN106093981AReduce consumptionImprove capture speedSatellite radio beaconingFast Fourier transformDecision circuit
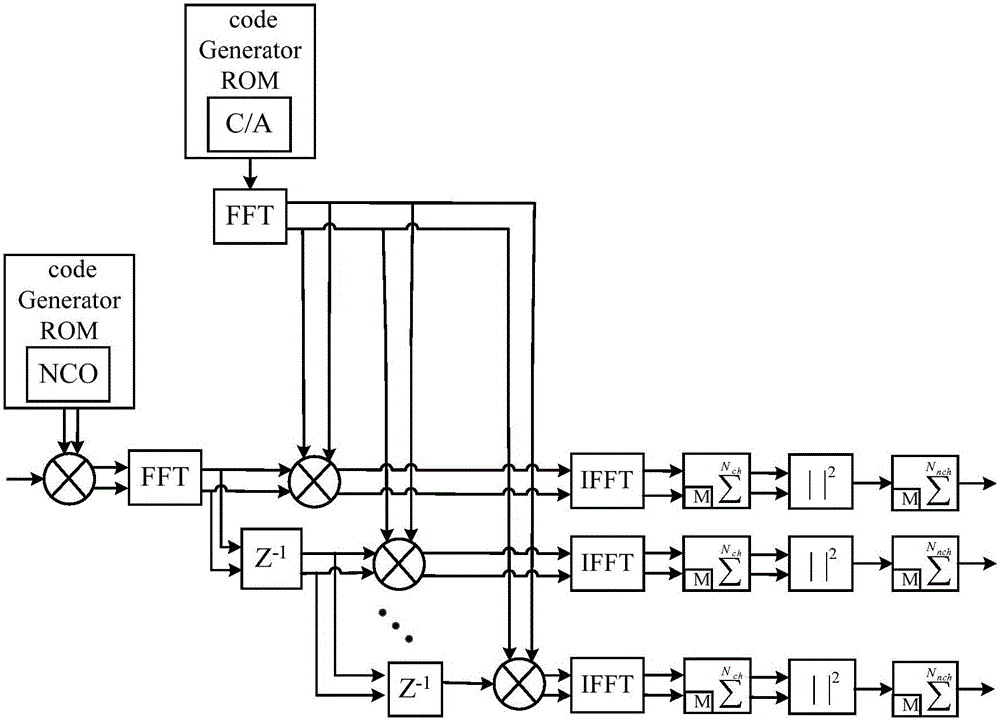
The invention discloses a GPS capture circuit based on optimization parallel code phase search. The GPS capture circuit comprises a down conversion circuit, a down sampling circuit, a fast Fourier transform circuit, a delay circuit, a C / A code generating circuit, an inverse Fourier transform circuit, a coherent integration circuit, a modulus circuit, a non-coherent integration circuit and a threshold decision circuit. In IFFT operation, output data reordering is prevented, and ultimately position bit inversion is simply carried out on the position of the maximum peak-to-average ratio to acquire the received signal C / A code phase. The memory consumption in an IFFT module is saved. According to the invention, the GPS capture circuit can be used to capture any GPS satellite signal; in the case of abundant hardware resources, the capture speed is doubled without changing the frequency search step; the cold start capture time is 1.17 seconds; the hot start capture time is less than 0.5 second; the capture sensitivity can reach -145dBm; and capture can be completed when signals are very weak.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
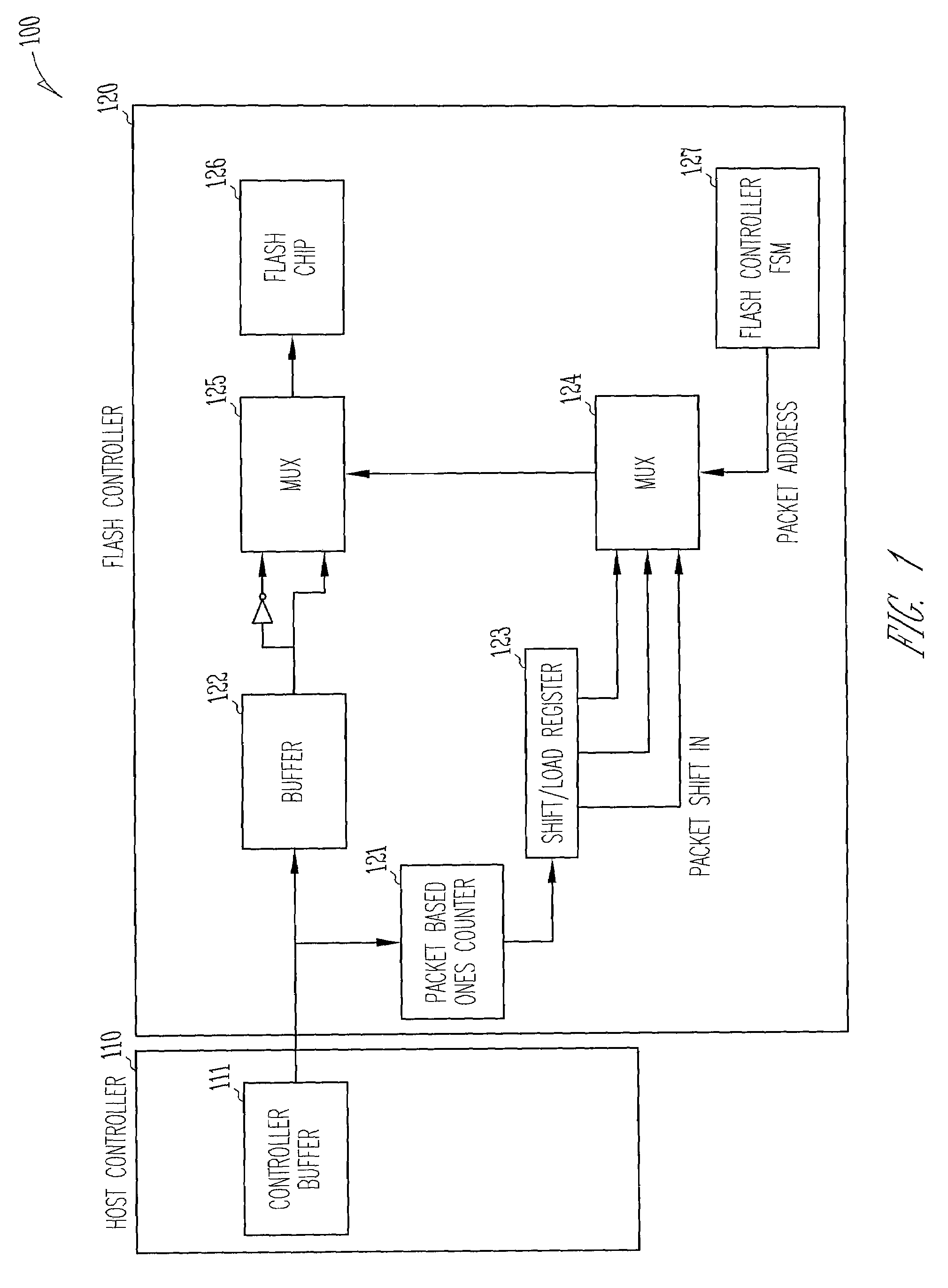
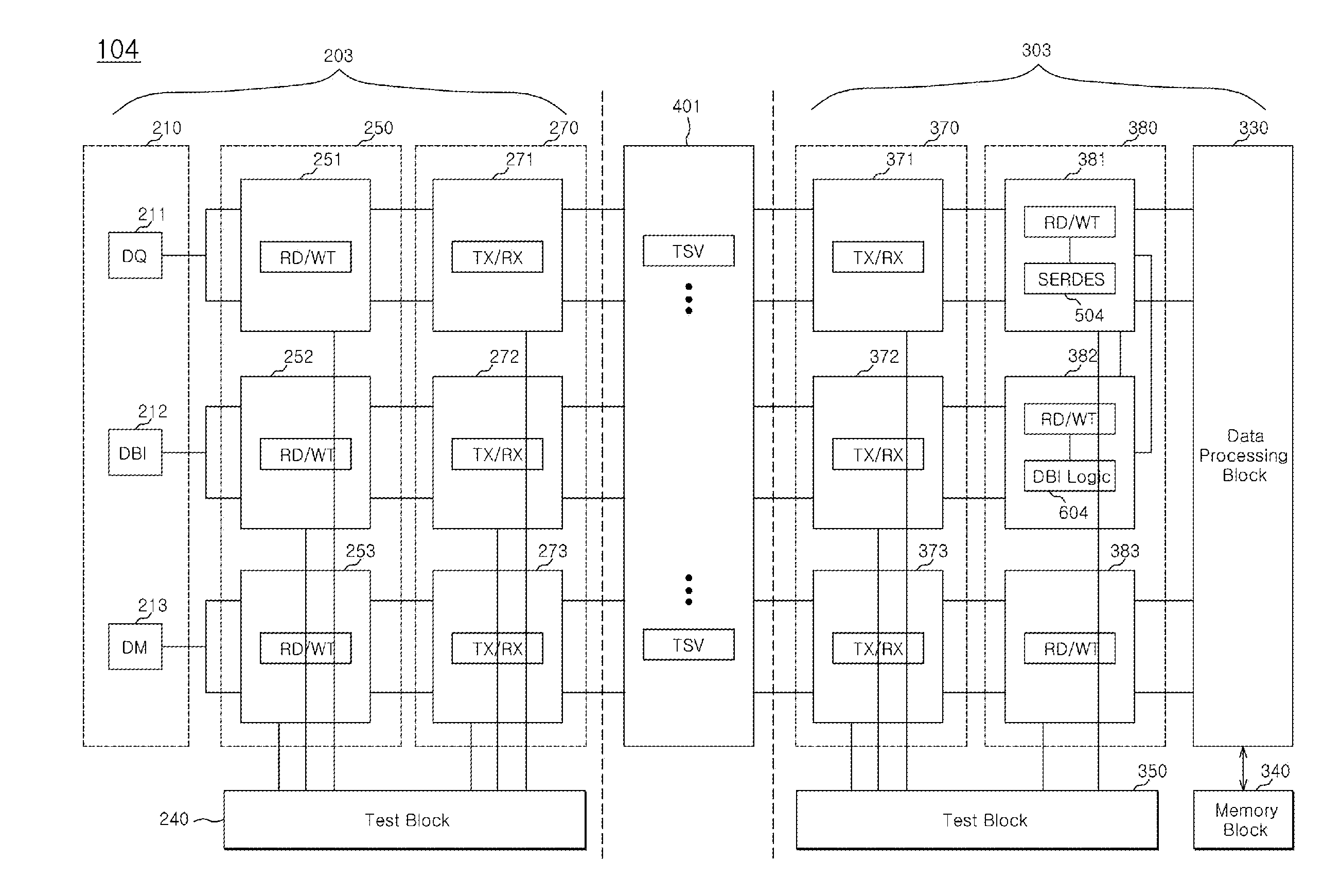
Semiconductor apparatus and data bit inversion
A semiconductor apparatus may include a first semiconductor chip; and a second semiconductor chip configured to transmit / receive signals to / from the first semiconductor chip. Further, a serializer / deserializer (SERDES) configured to serialize / deserialize input / output signals and a data bit inversion (DBI) logic electrically coupled to the SERDES and configured to perform a data inversion function on input / output data of the SERDES may be arranged in a preset region of any one of the first and second semiconductor chips.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
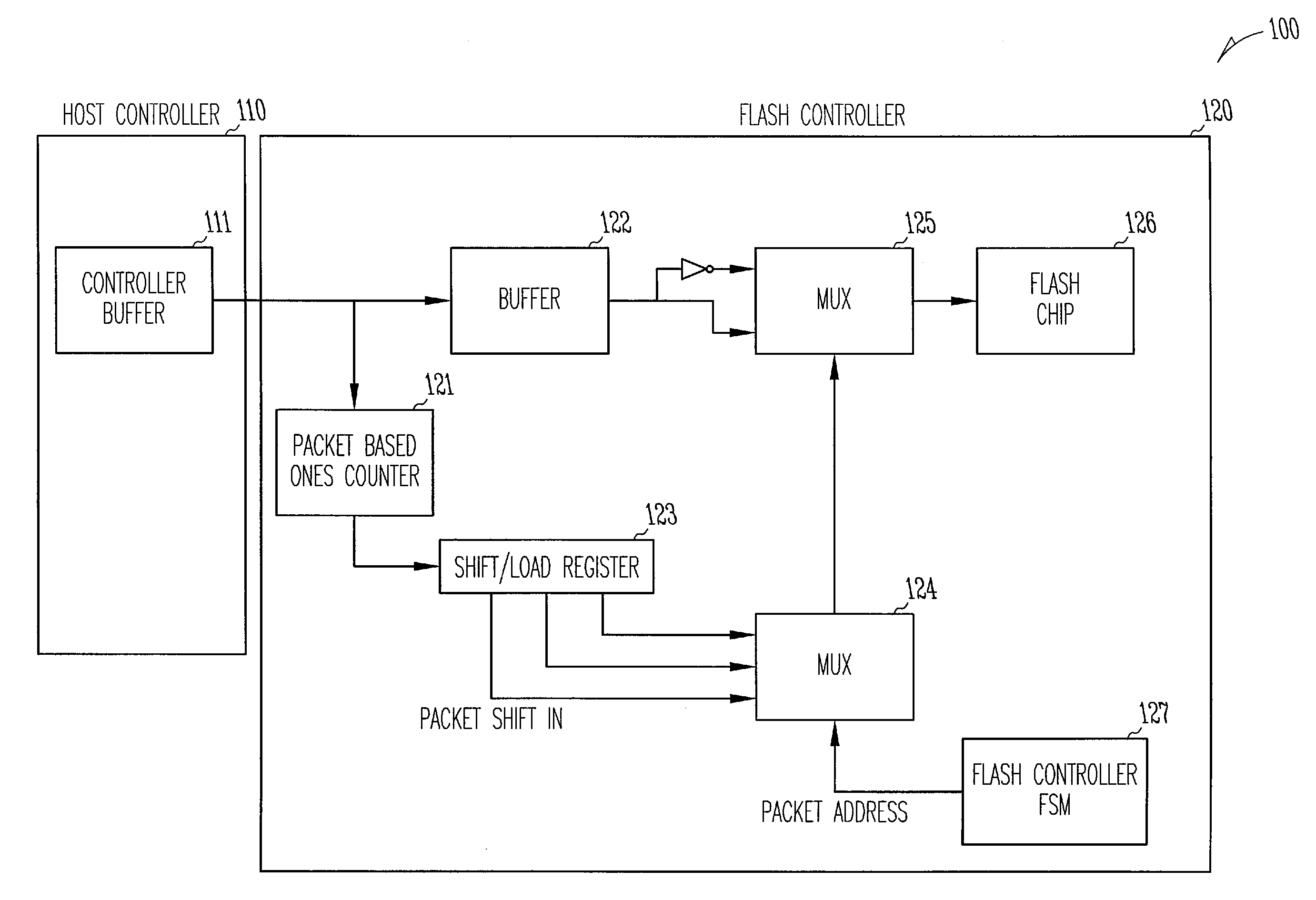
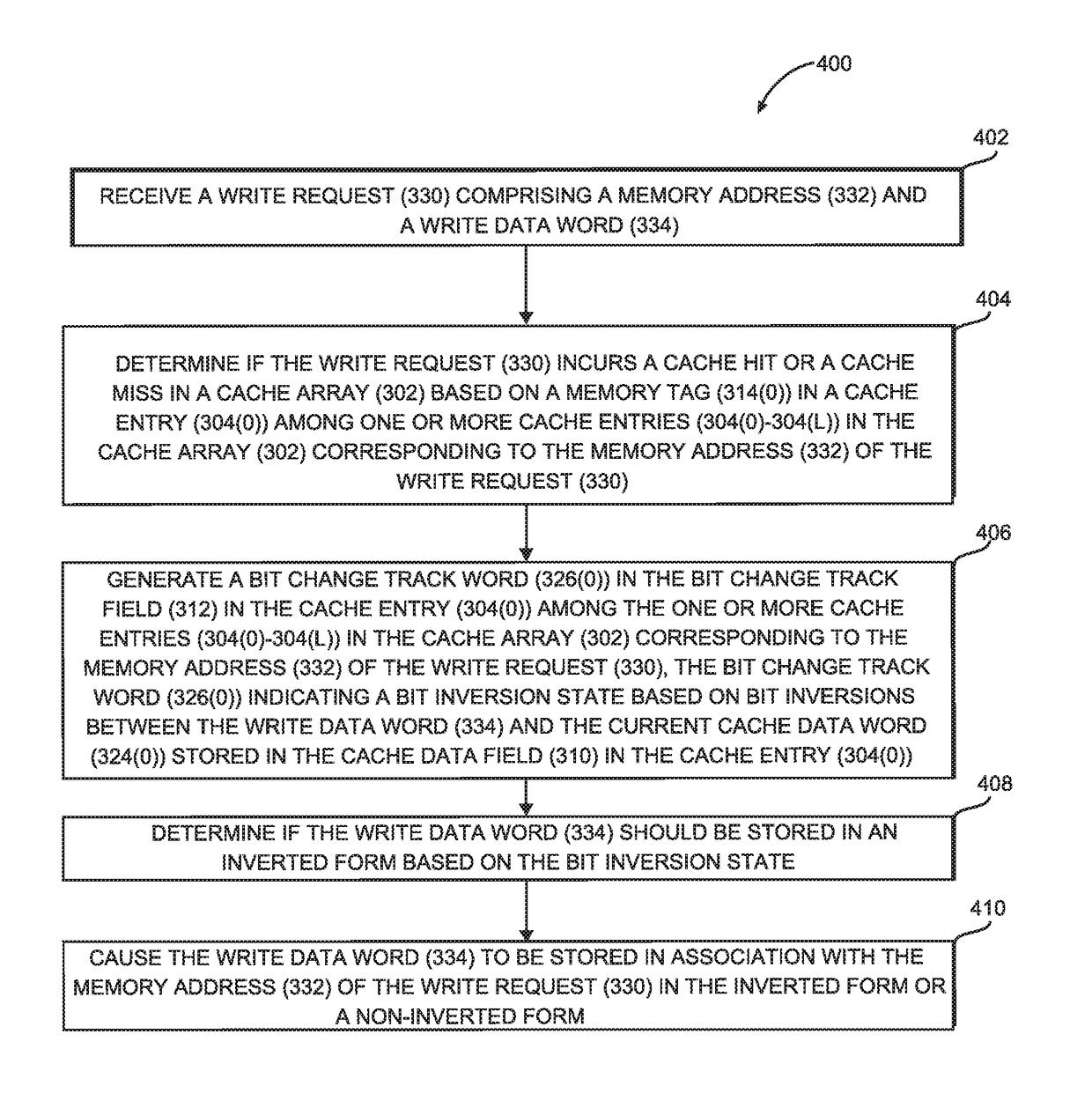
Data bit inversion tracking in cache memory to reduce data bits written for write operations
ActiveUS10115444B1Reduce the amount of dataReduce power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationCode conversionParallel computingData field
Data bit inversion tracking in cache memory to reduce data bits written for write operations is disclosed. In one aspect, a cache memory including a cache controller and a cache array is provided. The cache array includes one or more cache entries, each of which includes a cache data field and a bit change track field. The cache controller compares a current cache data word to a new data word to be written and stores a bit track change word representing the difference (i.e., inverted bits) between the current cache data word and the new data word in the bit change track field. By using the bit track change word stored in the bit change track field to determine whether fewer bit writes are required to write data in an inverted or a non-inverted form, power consumption can be reduced for write operations through reduced bit write operations.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Circuit for producing a data bit inversion flag
ActiveUS20060261929A1Electric signal transmission systemsElement comparisonBit inversionComputer science
A circuit for producing a data bit inversion flag comprises a first summed-current production unit for producing a first summed current, whose amplitude is proportional to the number of different data bits in two adjacent data words in a data burst, a second summed-current production unit for producing a second summed current, whose amplitude is proportional to the number of identical data bits in the two adjacent data words, and a current comparator comparing the first with the second summed current and producing a data bit inversion flag if the first summed current is greater than the second summed current.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Data encryption method and decryption method and device
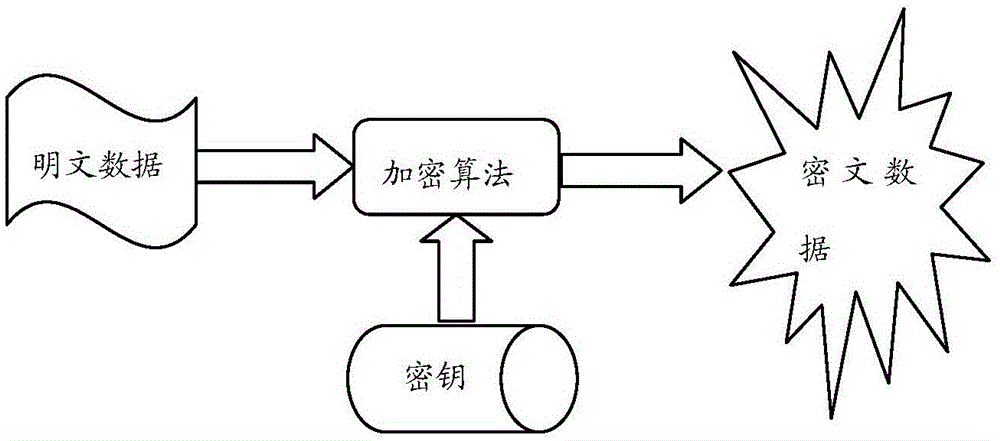
ActiveCN106301759ASolve confidentialityFix security issuesEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCiphertextConfidentiality
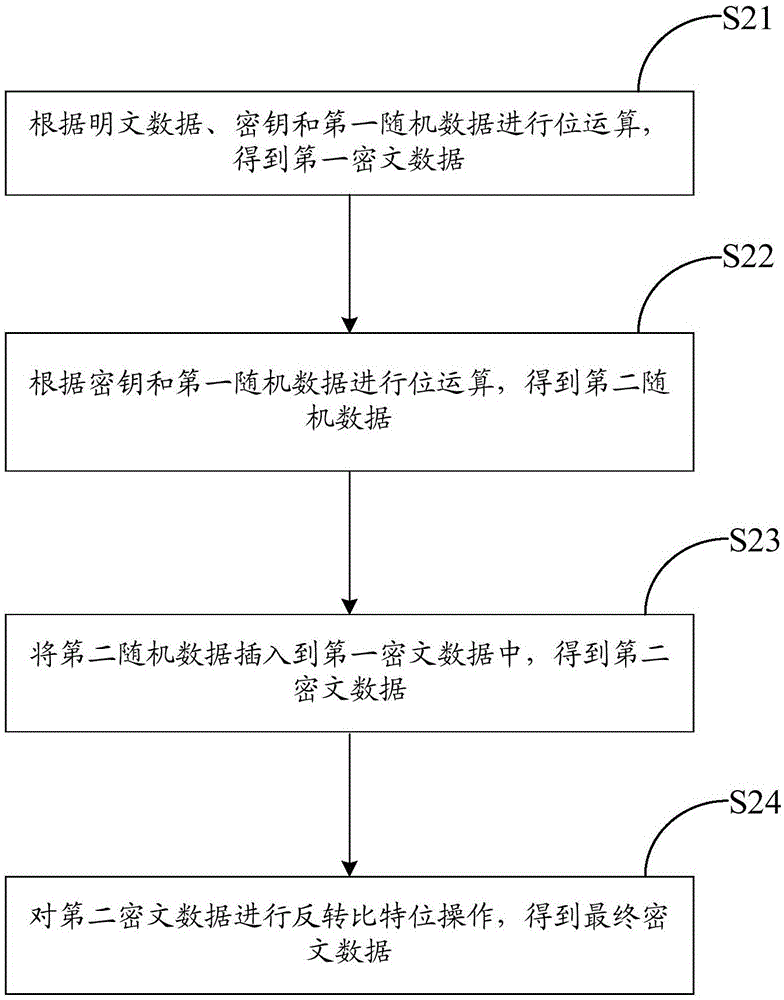
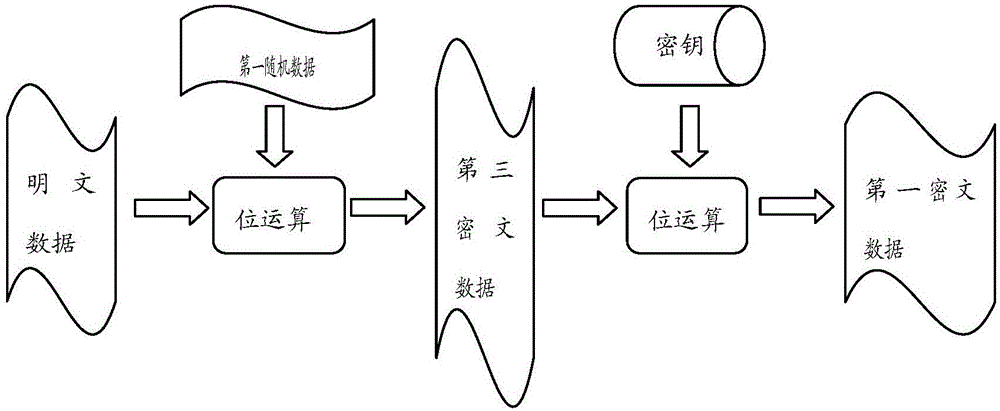
The embodiment of the invention provides a data encryption method and decryption method and device. The data encryption method comprises the steps that bit operation is performed according to plaintext data, a secret key and first random data so that first ciphertext data are obtained; bit operation is performed according to the secret key and the first random data so that second random data are obtained; the second random data are inserted in the first ciphertext data so that second ciphertext data are obtained; and bit inversion operation is performed on the second ciphertext data so that final ciphertext data are obtained. The algorithm is simple and the encryption efficiency is high so that the decoding difficulty can be greatly increased and thus the confidentiality and the security of information can be increased.
Owner:ZTE CORP
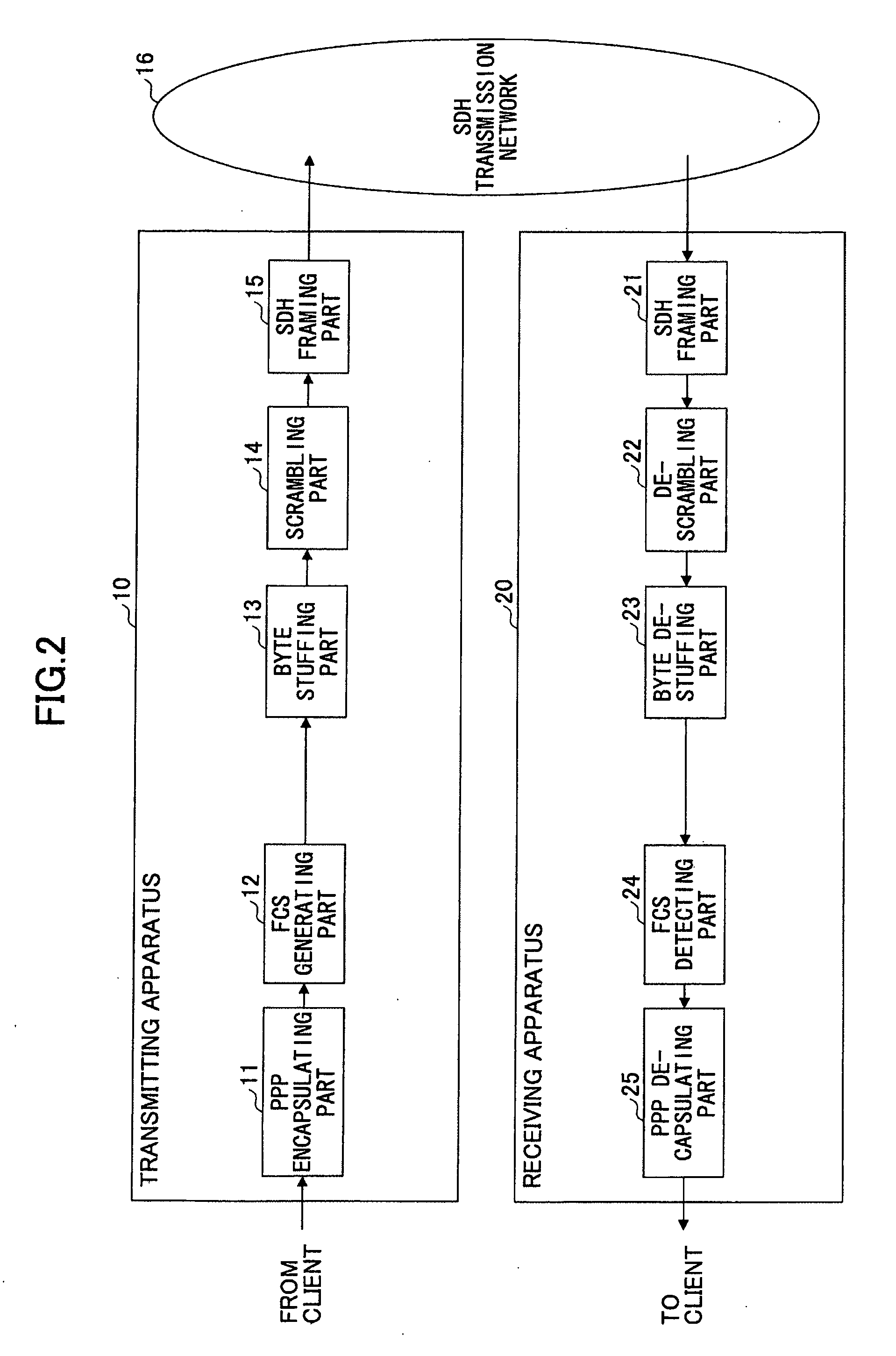
Method and apparatus for transmitting data from asynchronous network via synchronous network
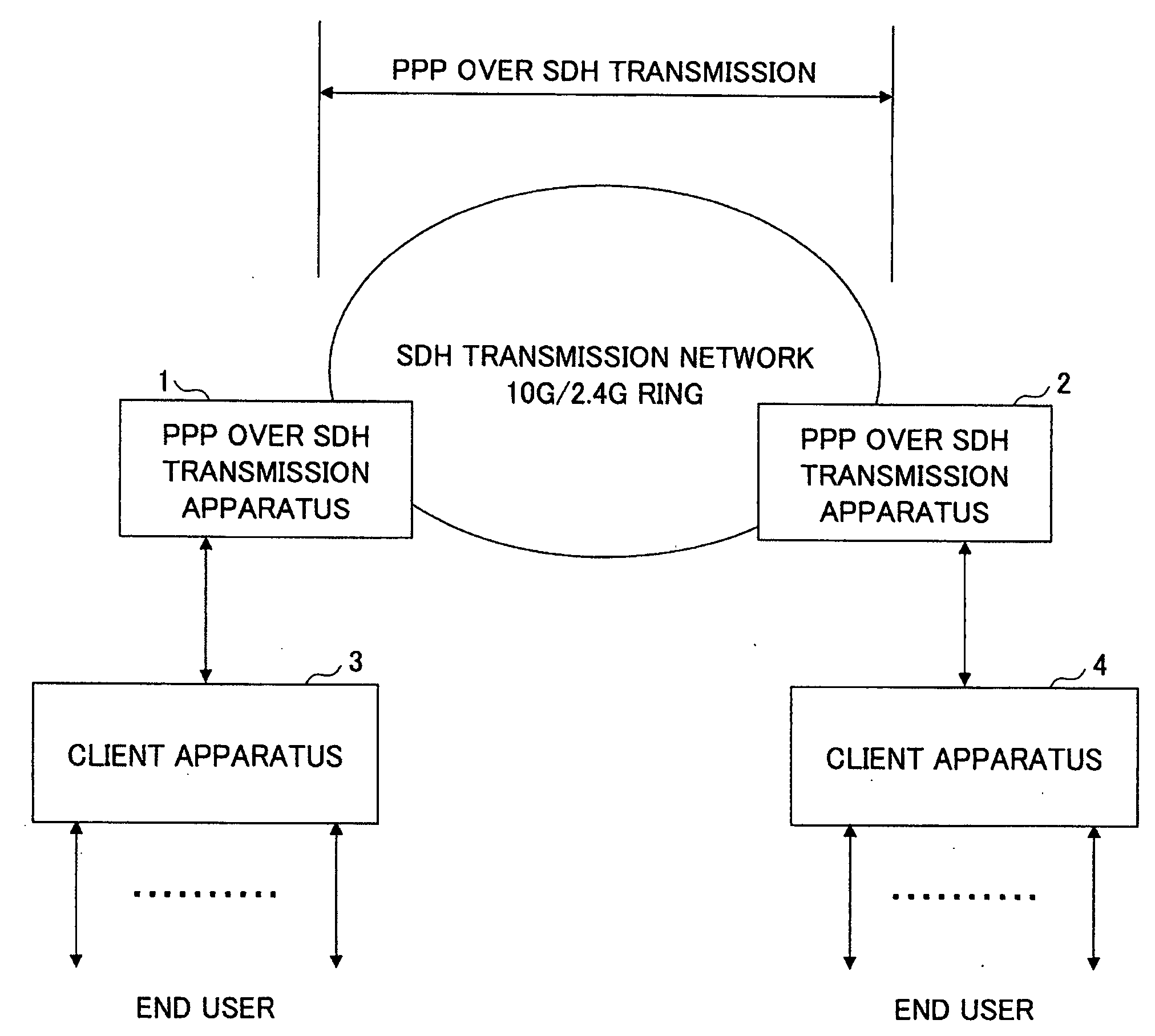
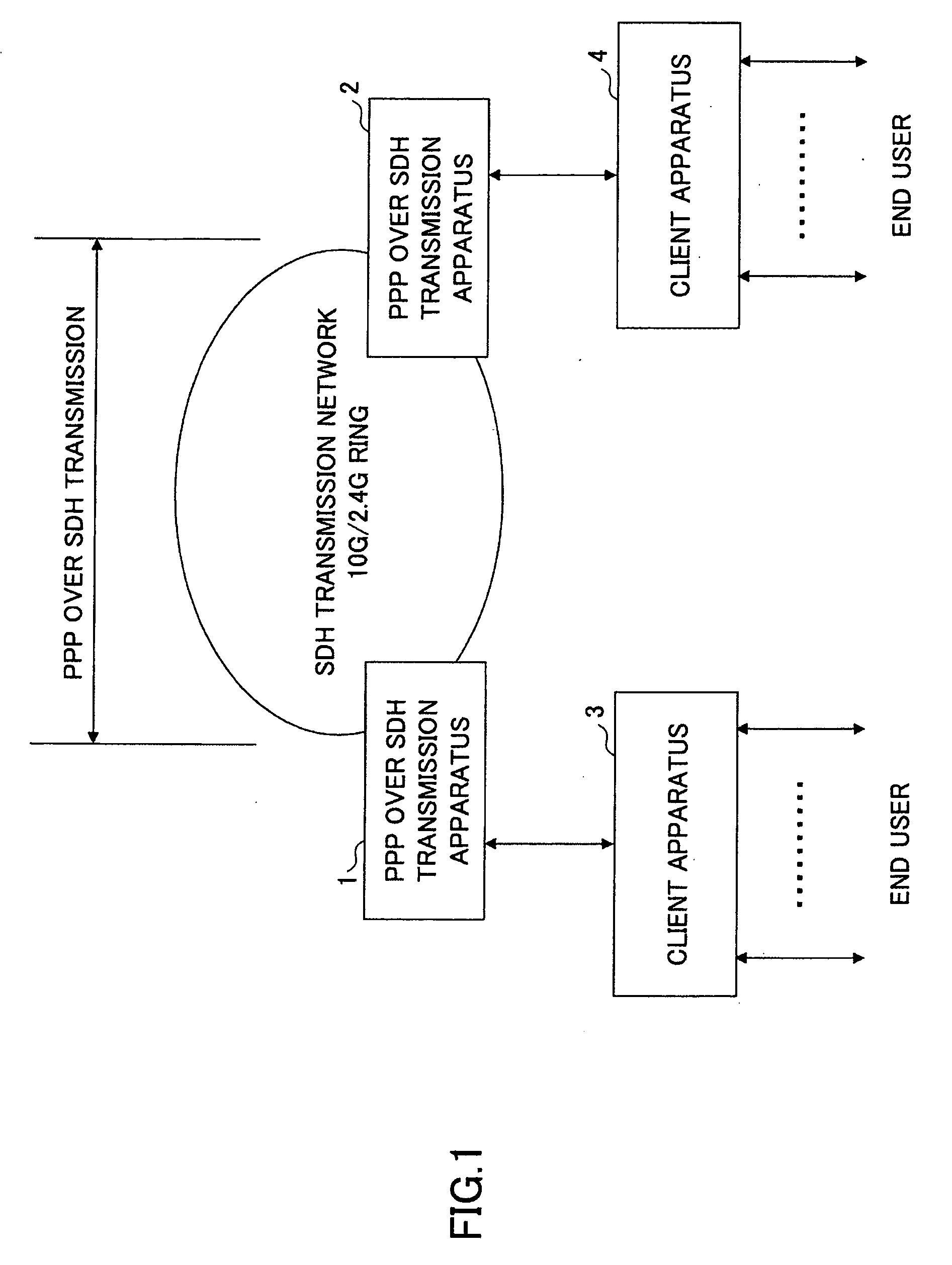
A transmitting apparatus for encapsulating data received from an asynchronous network to a frame of a specified format and transmitting the received data as a synchronous frame to a synchronous network, includes a code generating part configured to generate an error detection code for detecting an error in the received data and add the error detection code to the received data, an inverting part configured to perform bit inversion in which the received data added with the error detection code are converted to bit inverted received data, a selecting part configured to select either the received data or the bit inverted received data according to the number of bit patterns included in the received data and the bit inverted received data, and a transmitting part configured to transmit either the received data added with the error detection code or the bit inverted received data selected by the selecting part.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Real-time method for bit-reversal of large size arrays
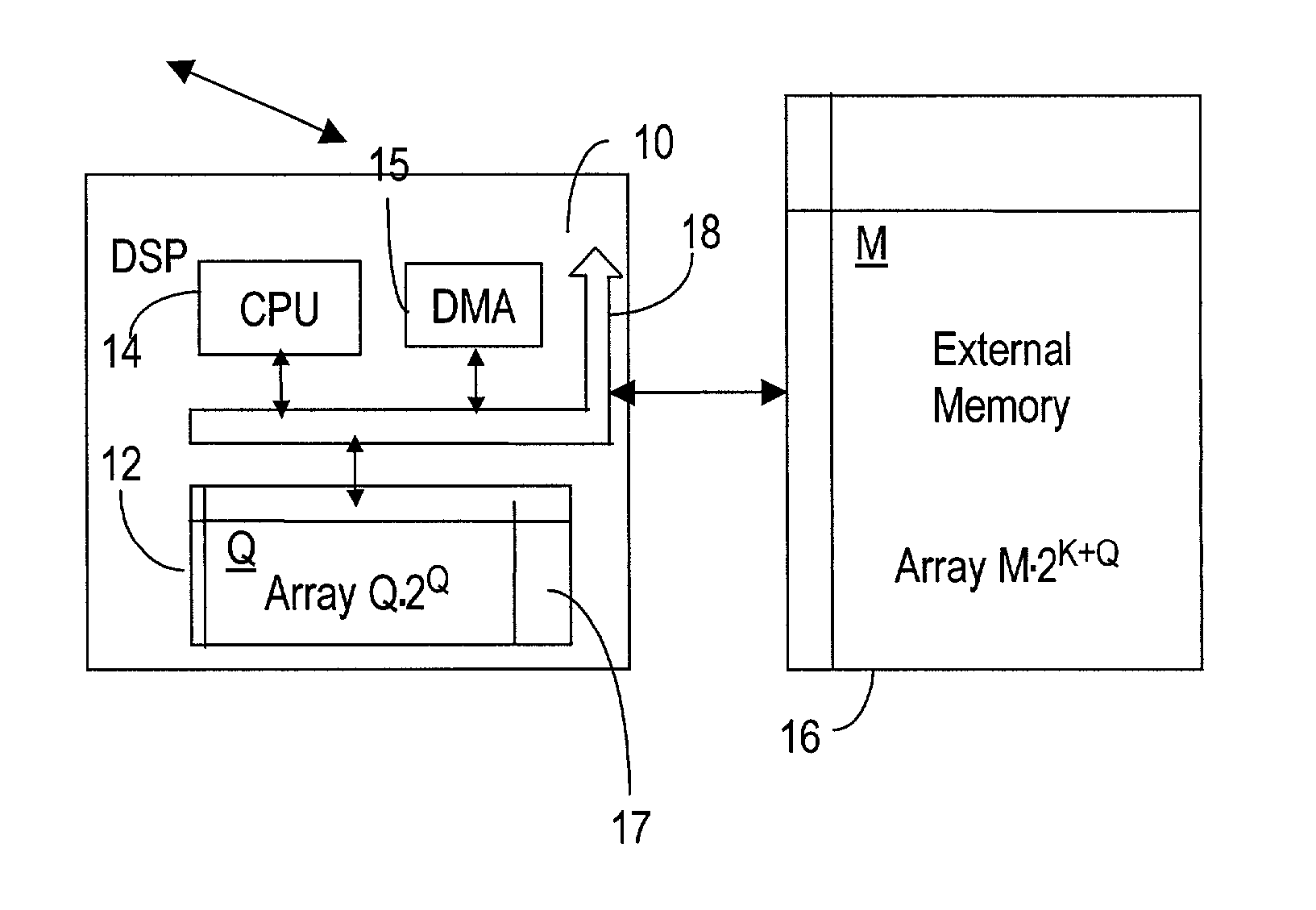
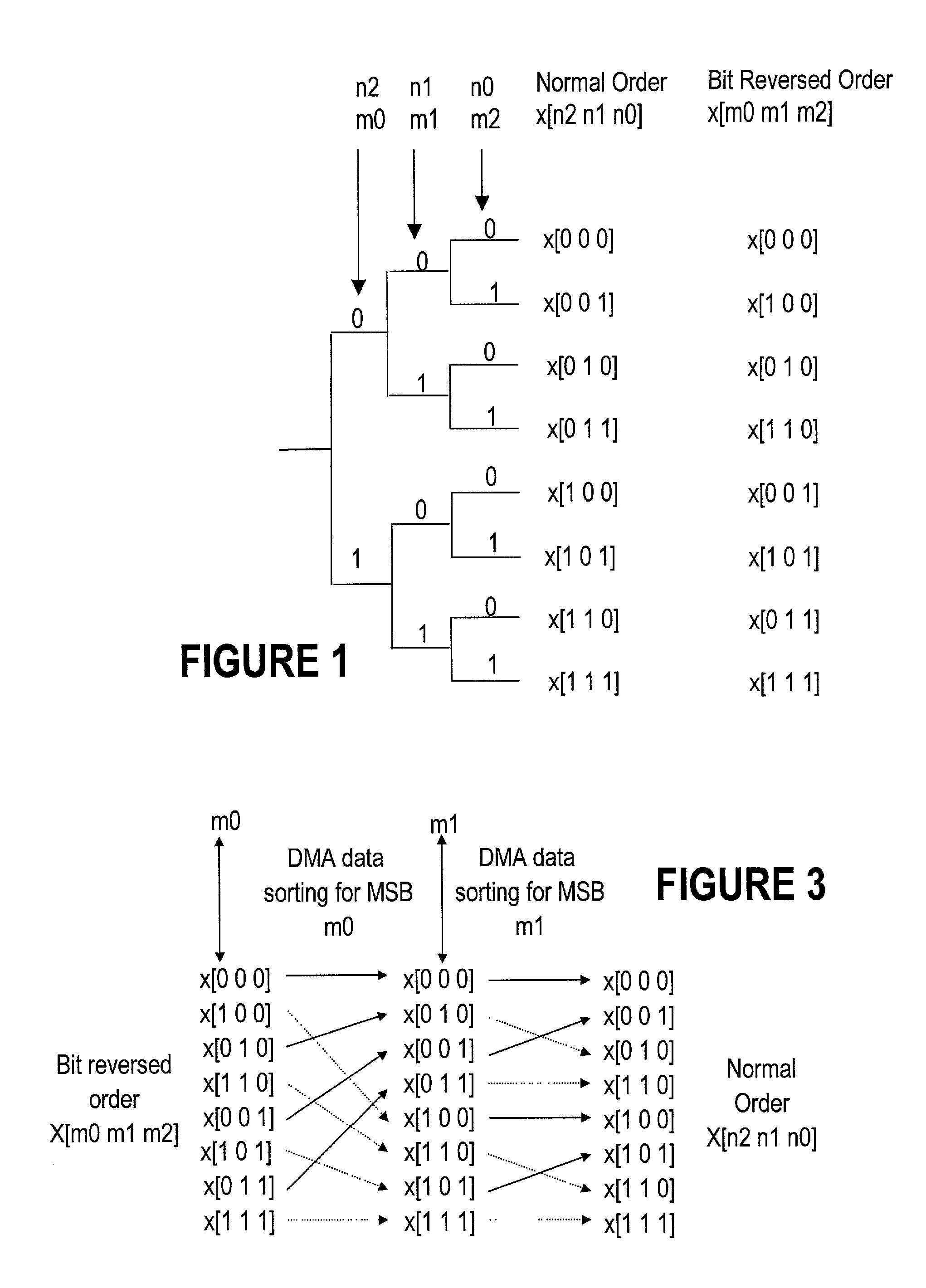
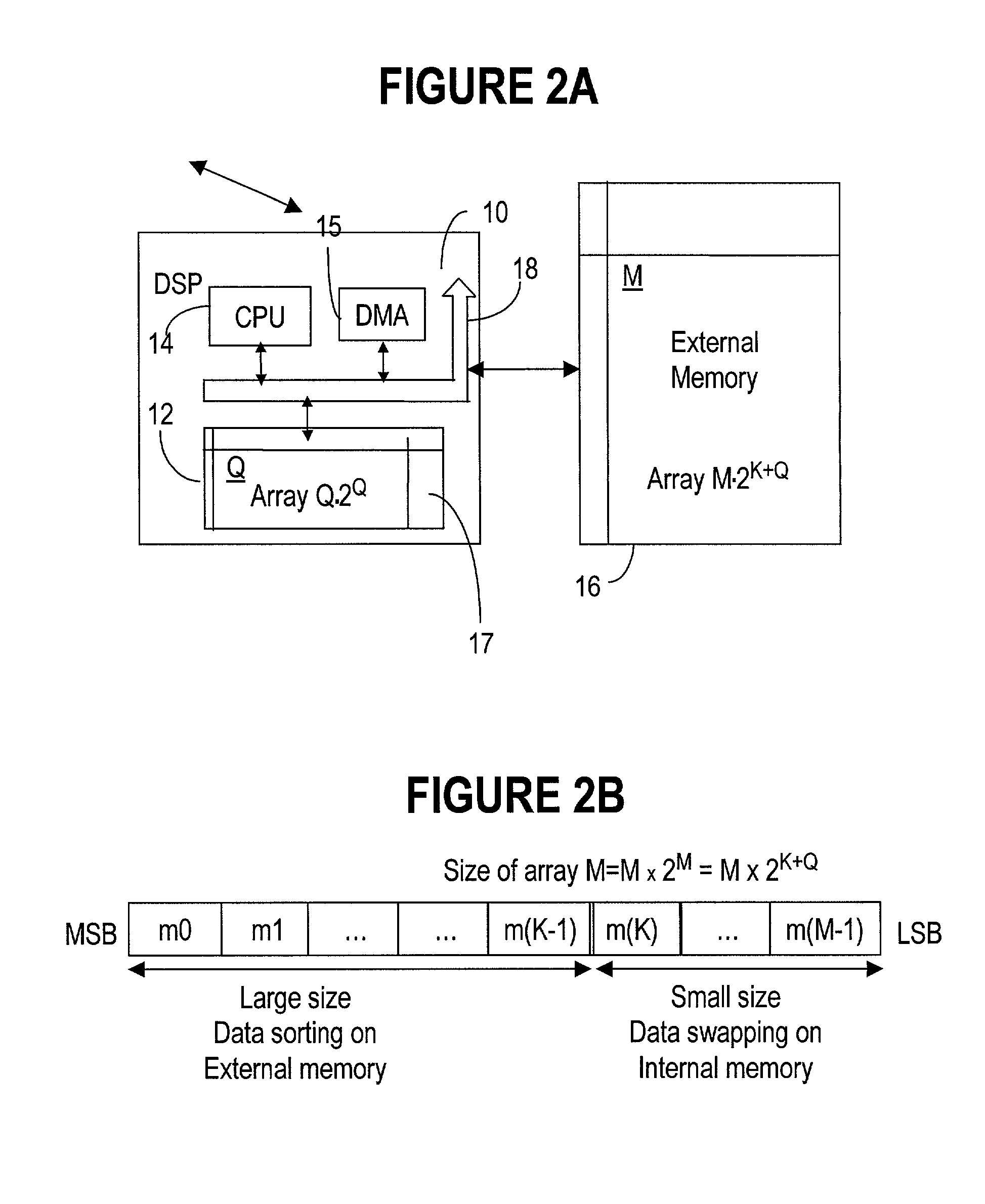
InactiveUS20030028571A1Digital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsInternal memoryExternal storage
A digital signal processor DSP for bit-reversal of a large data array of a size has a direct memory access (DMA) controller for performing in-place bit reversal routines on an external memory during a first stage, and a central processing unit (CPU) for swapping small sub-arrays on internal memory in a second stage. The two stage method according to the invention importantly reduces the real-time implementation for sorting large size data arrays on uni-processor DSP platforms, by extensively using the external memory and avoiding a random access to the internal memory. As well, the invention provides for improved dense integration and reduced costs when used in dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) systems.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT CANADA +1
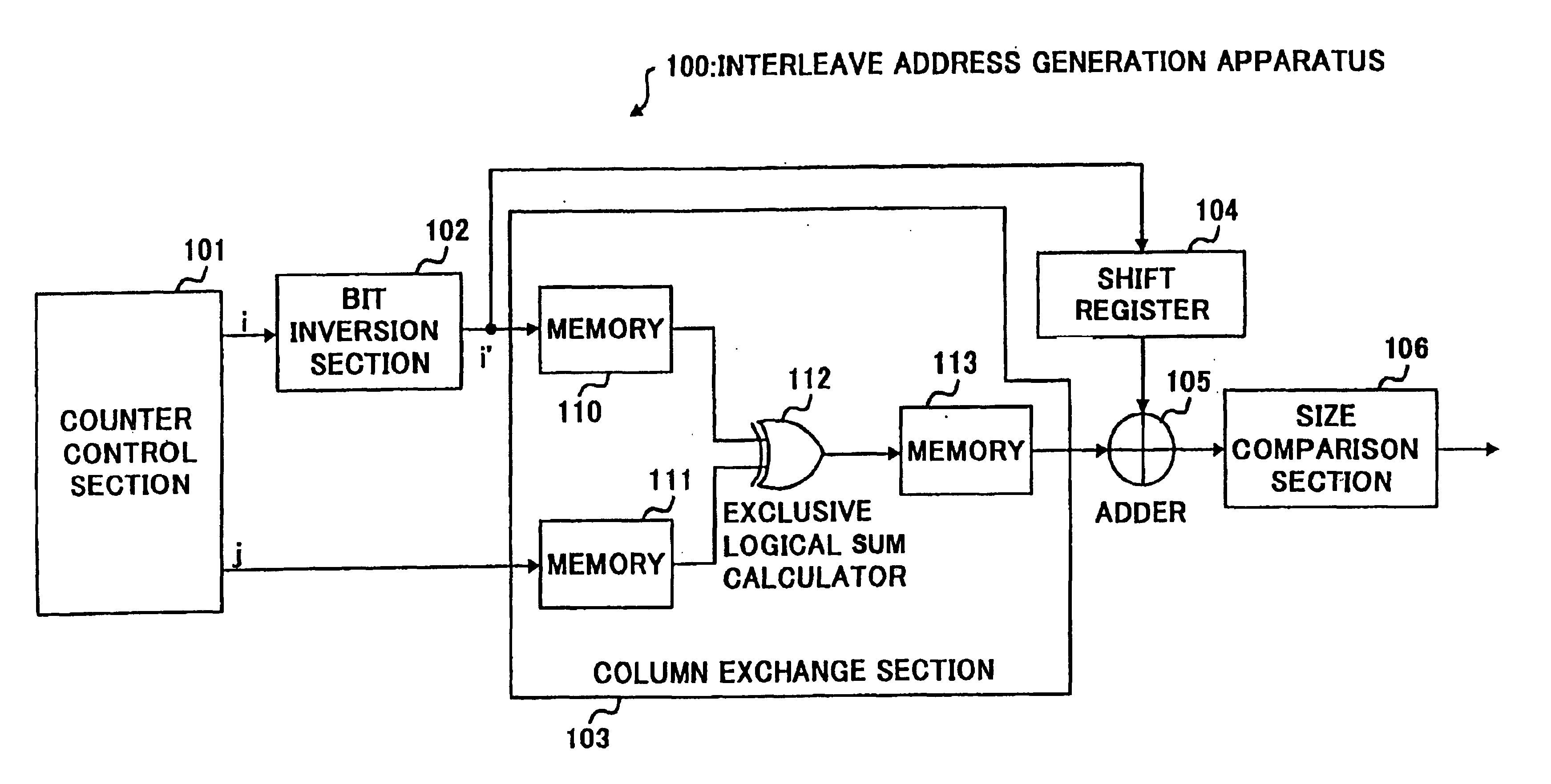
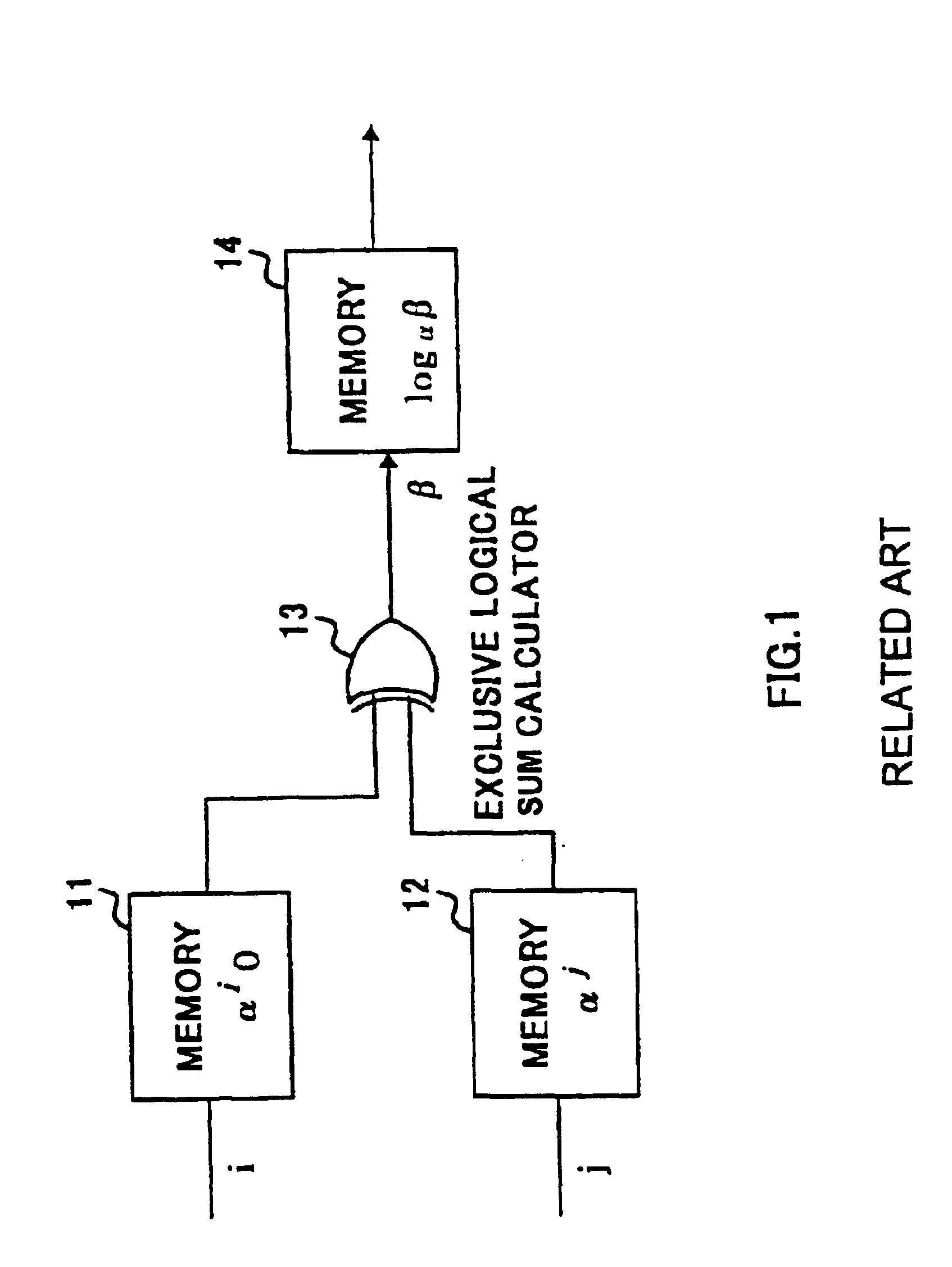
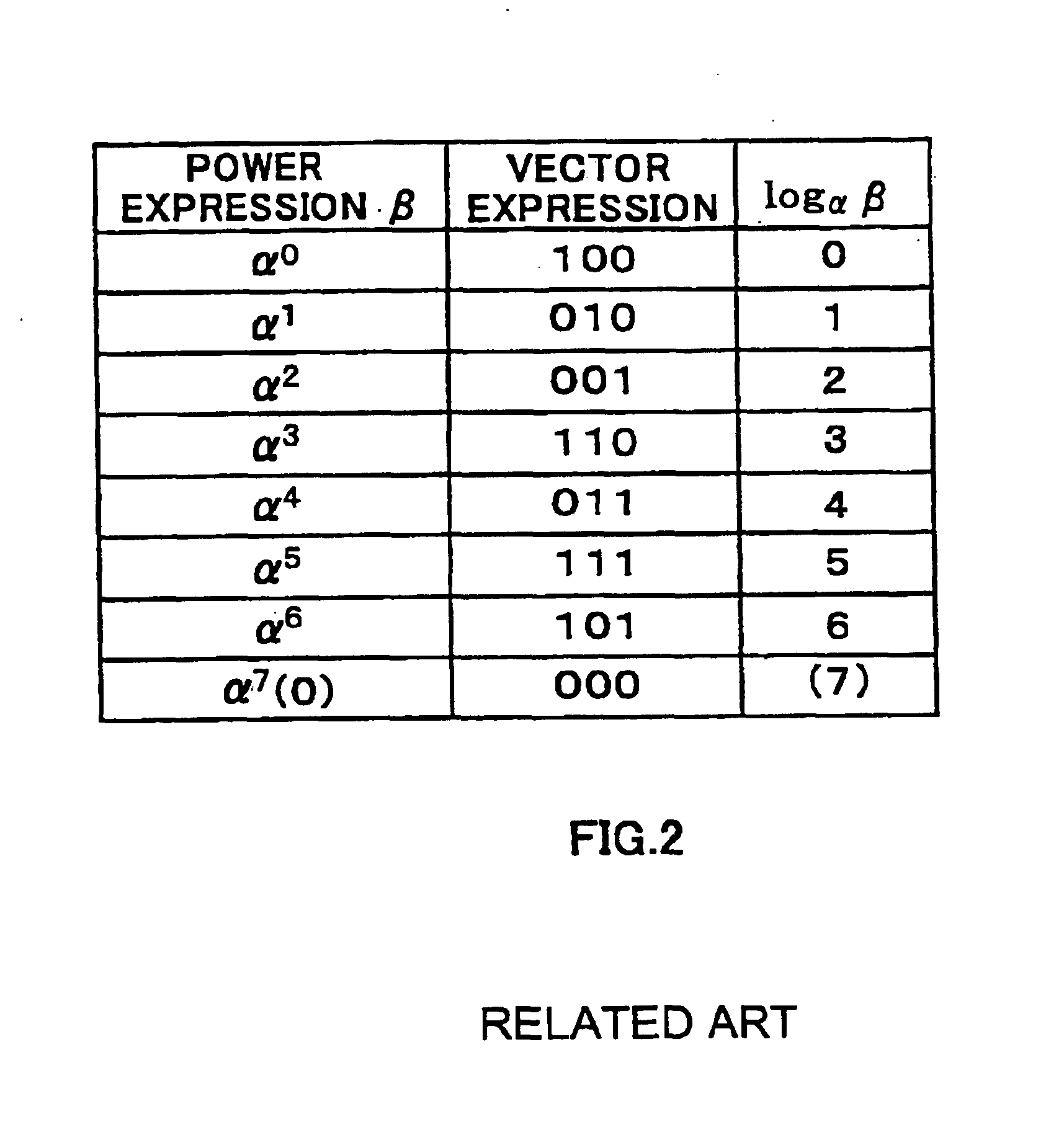
Interleave address generating device and interleave address generating method
InactiveCN1327634ACode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesShift registerBit inversion
In the counter control unit 101, the block represented by the matrix two-dimensional array is interleaved, the row number and the column number of the two-dimensional array are incremented, and output as a read address value, and in the bit inverting device 102, the read address value is The address value is used as an input to perform bit inversion. In the column conversion device 103, the address value corresponding to the bit inversion output value and the column number from the counter control unit 101 is output as a column conversion value. In the register 104, the output value of the bit inversion device 102 is shifted and output as an address offset value, and in the adder 105, the address offset value and the column exchange value are added, and in the size comparison unit 106 , compare the added value with the interleave size, and output the data within the interleave size as an address value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Radix-2 fast Fourier transform hardware design method based on an FPGA
ActiveCN110765709AReduce in quantityLess shift-add operationsCAD circuit designEnergy efficient computingFast Fourier transformShift register
The invention relates to a radix-2 fast Fourier transform hardware design method based on an FPGA. The method is composed of four levels of similar butterfly-shaped units, a twiddle factor multipliermodule, a positive sequence output module and a control module. A circuit structure and a working mode of each level of butterfly-shaped unit are similar, and only the depths of shift registers in thebutterfly-shaped units decrease progressively in sequence according to a geometric progression mode. Each butterfly unitis used for performing addition and subtraction operation on a real part and animaginary part of input data. An operation result enters a subsequent twiddle factor multiplier unit to realize a function of multiplying data by a twiddle factor, odd stages enter a simple twiddle factor multiplier unit, even stages enter a universal twiddle factor multiplier unit, and the twiddle factor after the fourth-stage operation is 1; and the positive sequence output module rearranges the final data result in a bit inversion mode, so that the final data result is output according to a correct sequence.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
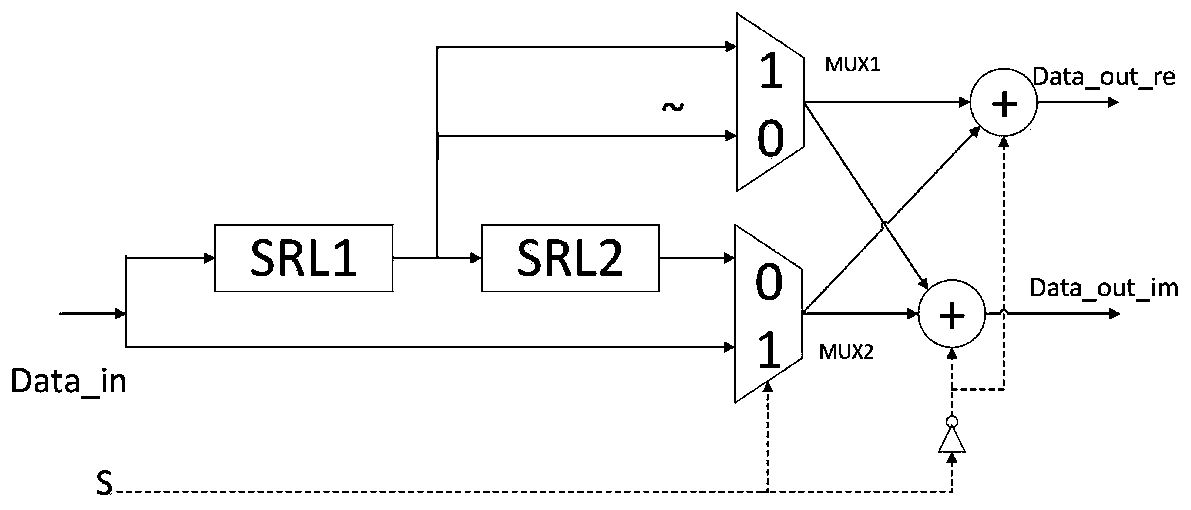
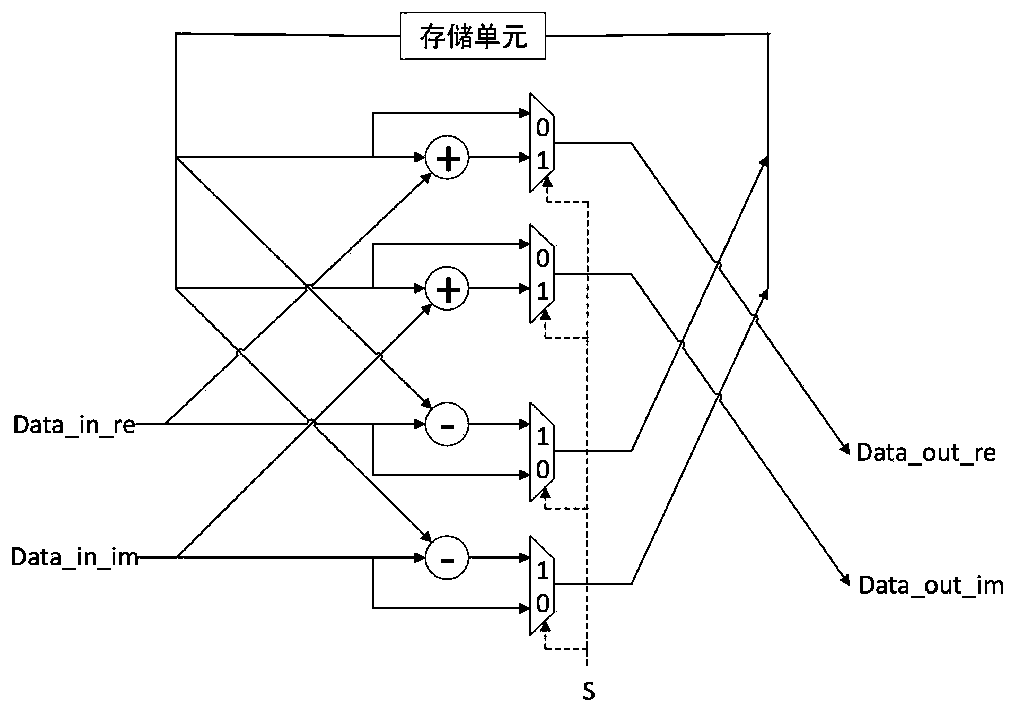
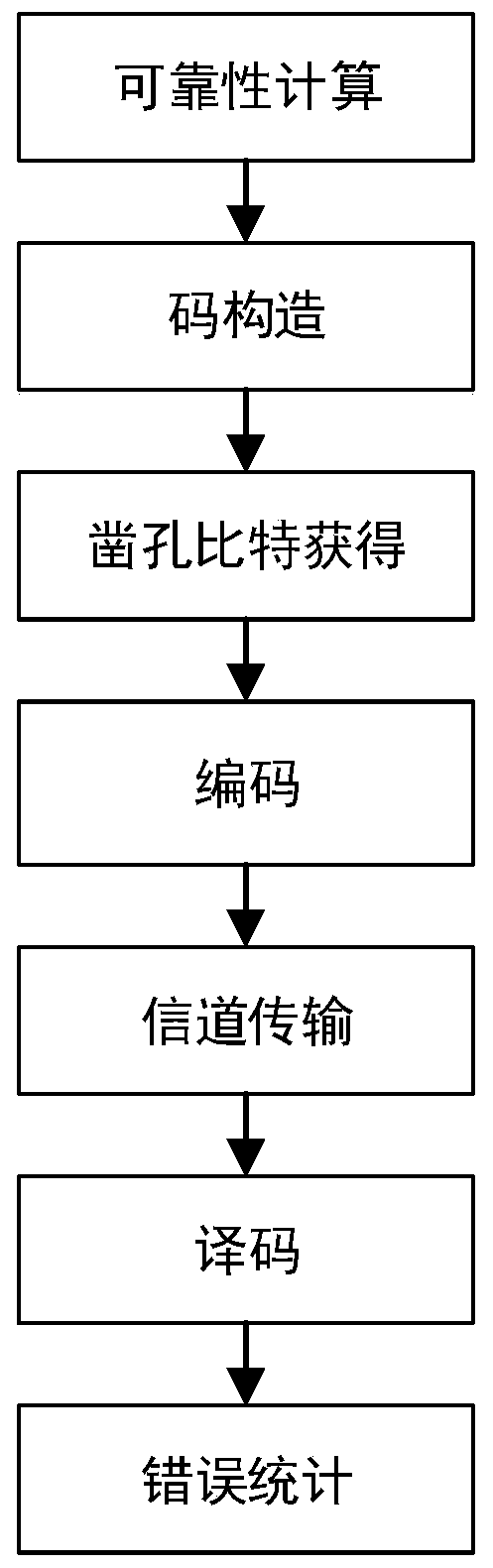
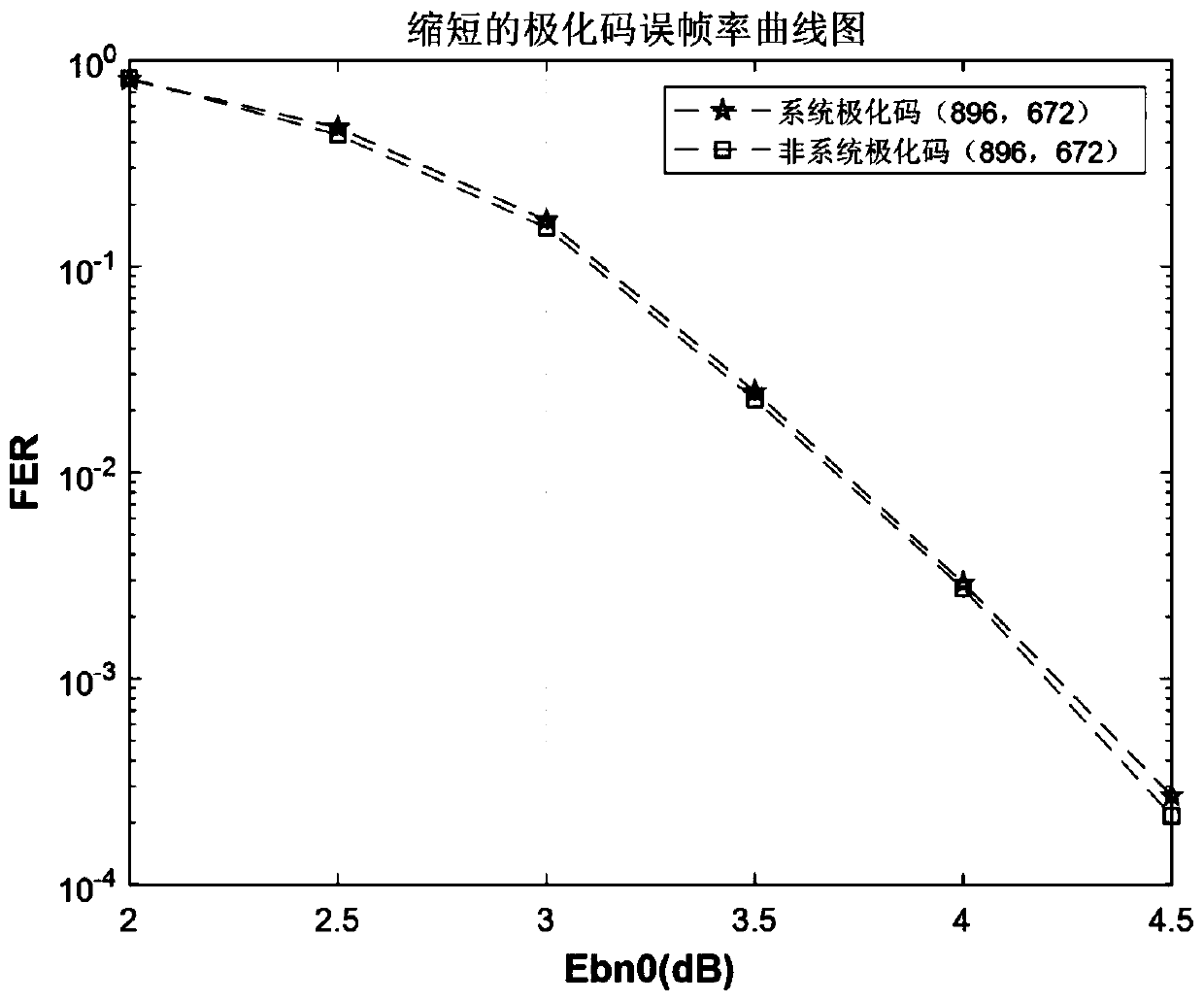
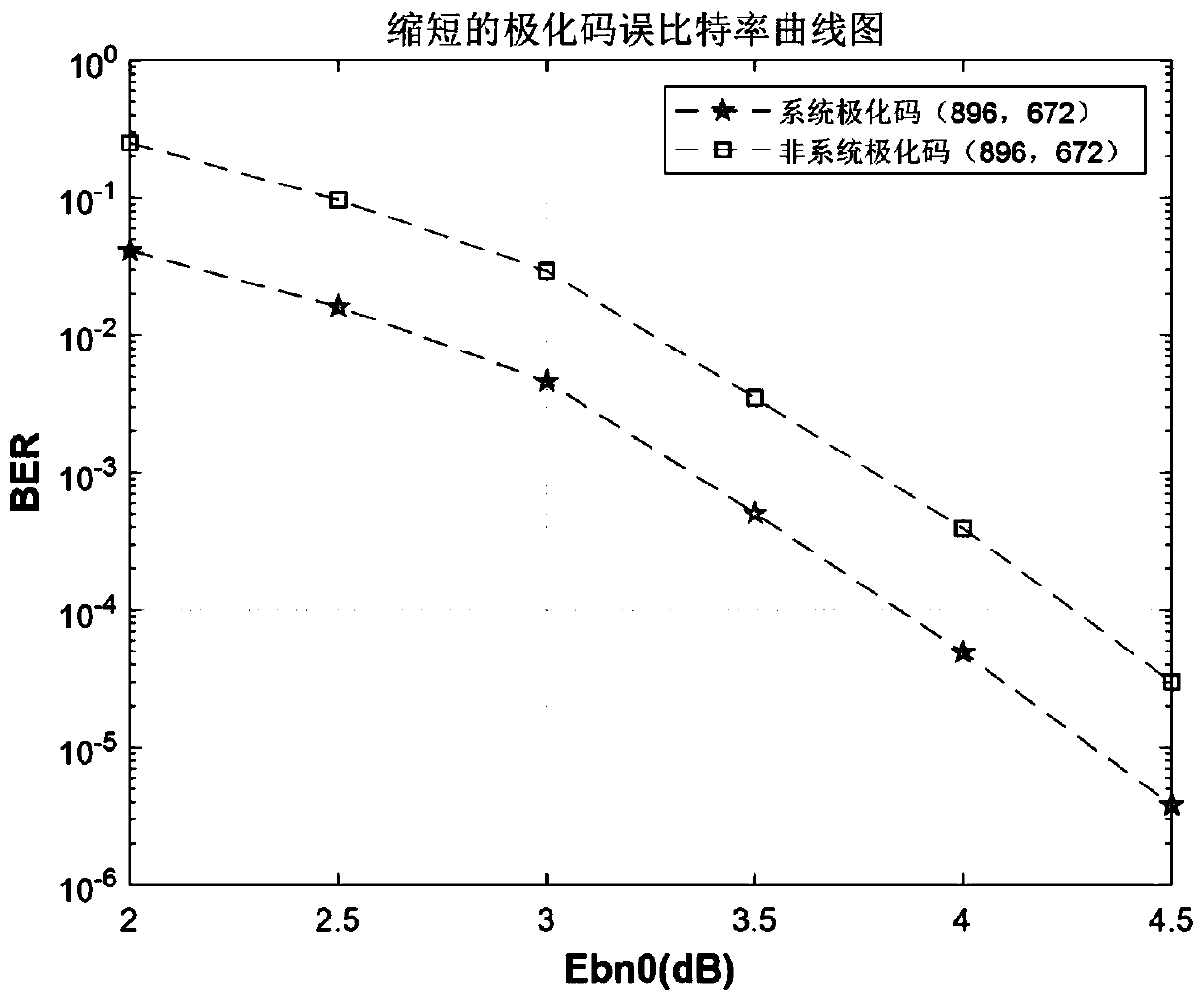
Reliability-based system polarization code puncturing method and system
PendingCN111200444ARealize code length adaptationSolve the problem of inflexible code lengthError preventionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresDependabilityBit inversion
The invention discloses a system polarization code puncturing method and system based on reliability. The method comprises the steps of performing reliability calculation on a system polarization codewith a code length of N; assuming that an L bit needs to be shortened, firstly selecting the last L sub-channel as a first part of a frozen bit, taking the K sub-channel with the highest reliabilitymetric value as an information bit from the remaining (N to L) sub-channels, and taking the remaining sub-channels as a second part of the frozen bit; performing bit inversion replacement on the indexvalue of the first part of the frozen bit to obtain a codeword end punching vector index s; encoding the system polarization code; deleting codeword bits at corresponding positions according to the punching vector index s; transmitting the punctured system polarization code through a Gaussian channel; initializing a log-likelihood ratio corresponding to the punching index vector s to be infiniteat a decoding end; and evaluating the puncturing method. According to the invention, the system polarization code can adapt to different code lengths on the premise of not changing the basic structureof the system polarization code.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Interleave address generation device and interleave address generation method
InactiveUS6957310B1Little memory spaceShort processing timeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCode conversionShift registerBit inversion
Counter control section 101 increments a row number and column number on a two-dimensional array for a block interleave expressed by a matrix two-dimensional array, outputs the incremented numbers as the read address values, bit inversion apparatus 102 performs bit inversion using the read address values as inputs, column conversion section 103 outputs the address values corresponding to the bit inversion output values and the column numbers from counter control section 101 as the column conversion values, shift register 104 bit-shifts the output values of bit inversion apparatus 102 and outputs as the address offset values, adder 106 adds up the address offset values and column conversion values and size comparison section 106 compares the addition value with the interleave size and outputs data which is not greater than the interleave size as address values.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
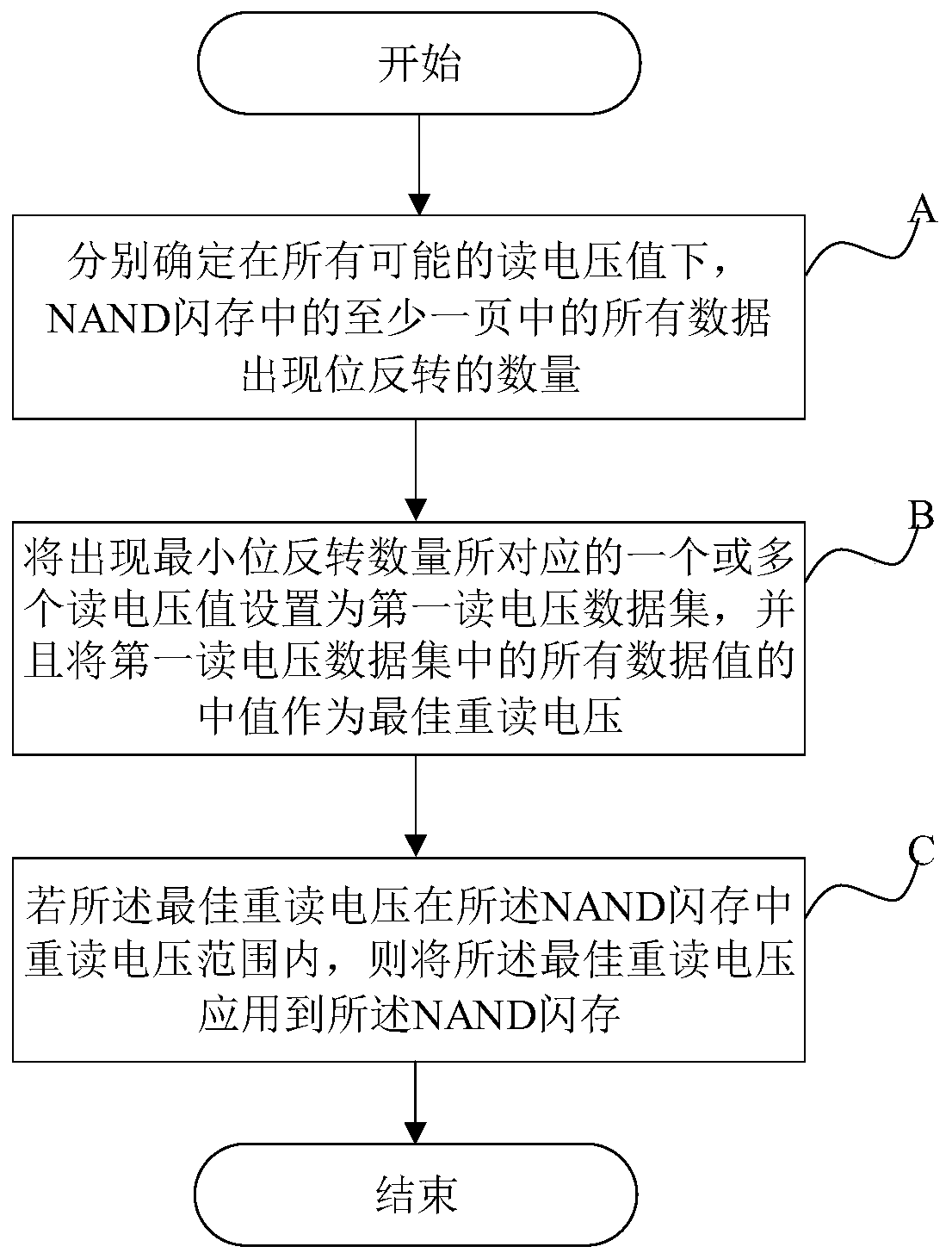
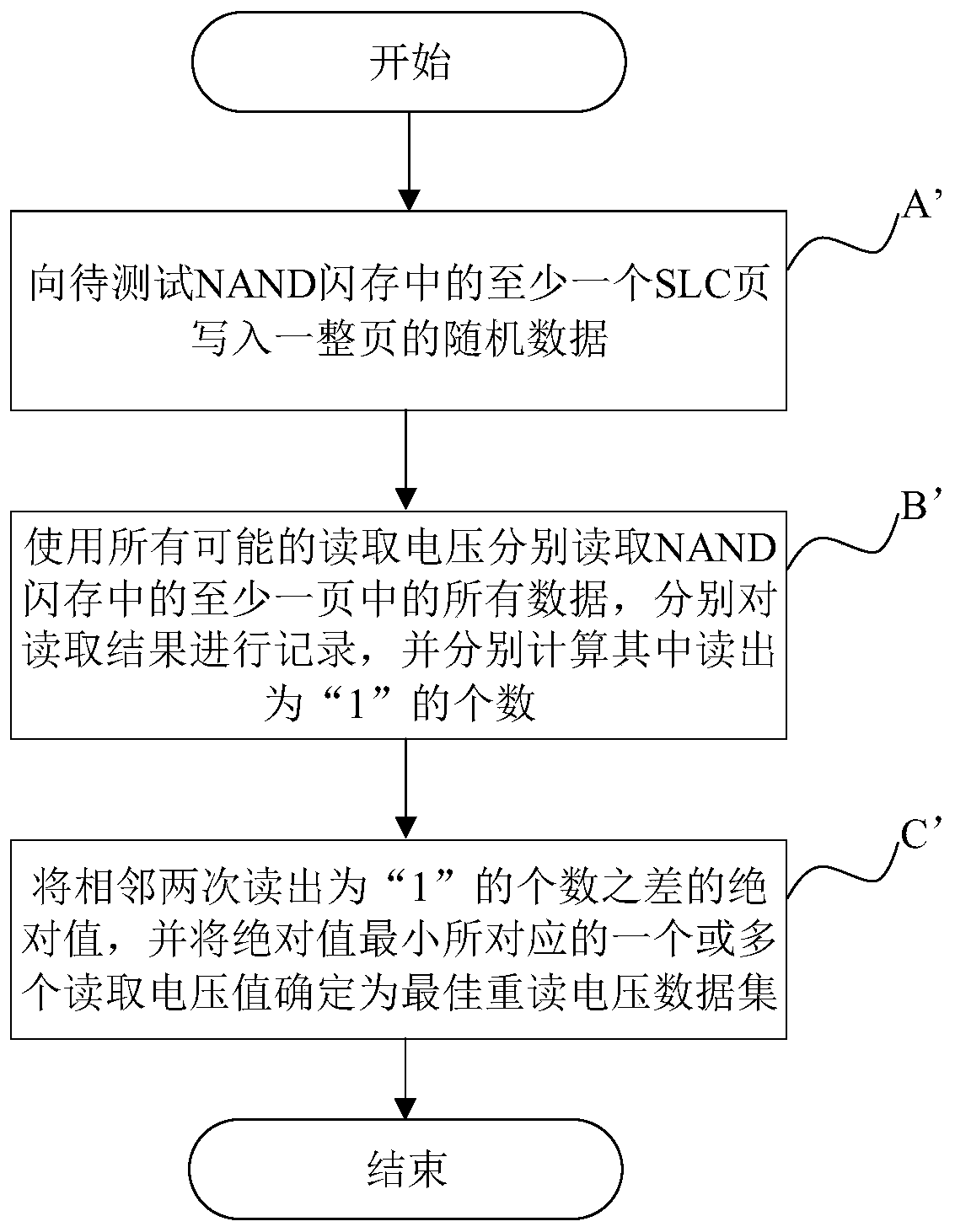
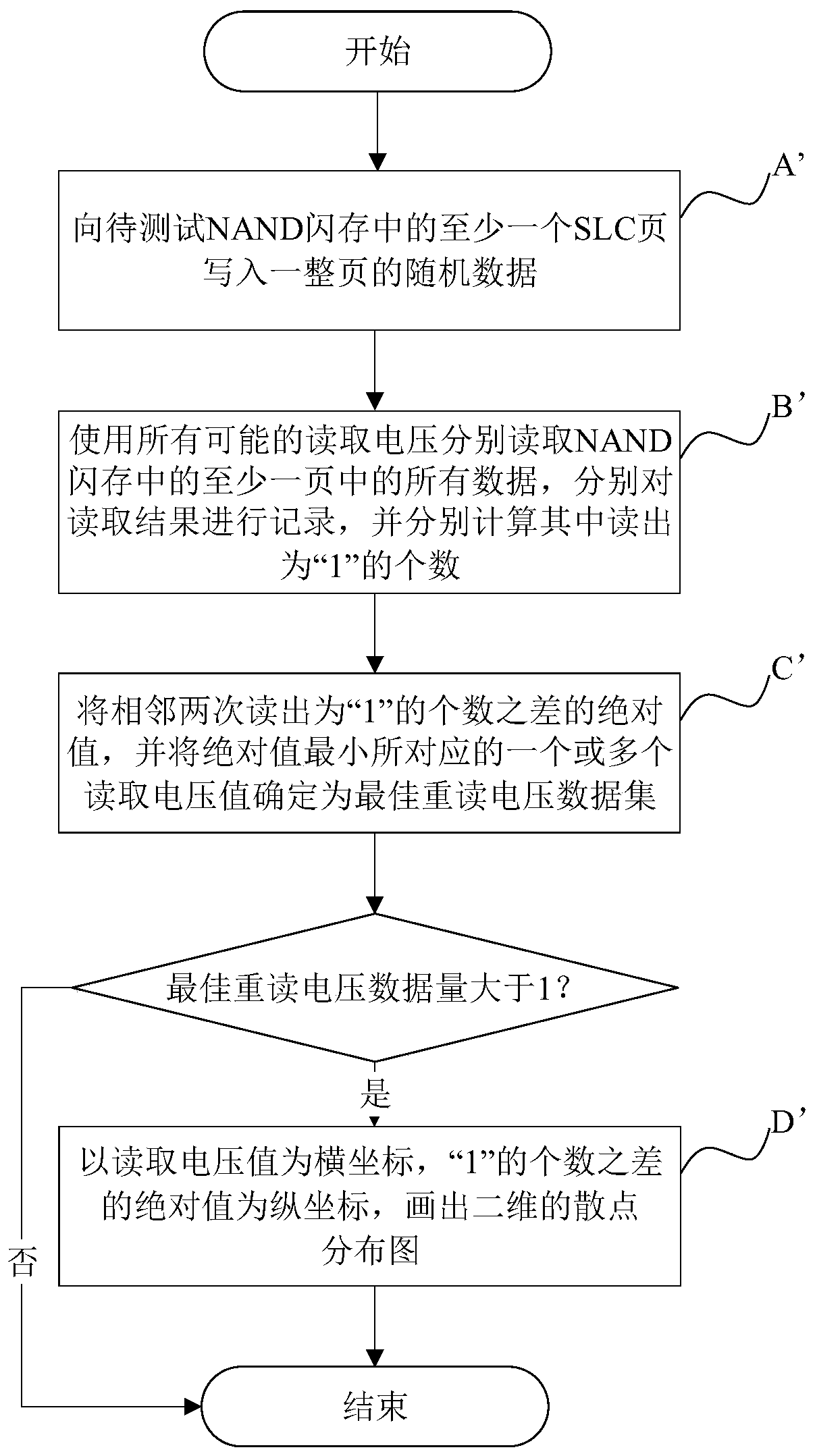
Method for quickly searching optimal reread voltage of NAND flash memory
The invention provides a method for quickly searching the optimal reread voltage of an NAND flash memory. The method comprises the following steps: A, respectively determining the quantity of bit inversion of all data in at least one page of the NAND flash memory under all possible read voltage values; B, setting one or more read voltage values corresponding to the minimum bit inversion number asa first read voltage data set, and taking the median of all data values in the first read voltage data set as the optimal reread voltage; and C, if the optimal reread voltage is within the reread voltage range in the NAND flash memory, applying the optimal reread voltage to the NAND flash memory.
Owner:广州匠芯创科技有限公司
Signal receiver for integrating and combining integrations in alternating time segments for signal acquisition at low signal strength
InactiveUS7480325B1Increase processing gainEasy to followAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBeacon systemsTime segmentGps receiver
A GPS receiver for integrating a GPS signal separately in a series of “A” type and “B” type time segments, the “A” segments alternating with the “B” time segments; combining the squares of the magnitudes of “A” time segment integrations corresponding to code phases for forming “A” type combined magnitudes; combining the squares of the magnitudes of the “B” time segment integrations corresponding to code phases for forming “B” type combined magnitudes; and determining an acquisition code phase of the signal from the strongest of the “A” or “B” combined magnitudes. The “A” time segments and the “B” time segments are one-half the period of the data bits of the signal, thereby ensuring that either the “A” time segments or the “B” time segments avoid the nullifying effect of data bit inversions.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Data processing apparatus and data processing method
ActiveUS20120308149A1Character and pattern recognitionImage codingParallel computingTransducing Unit
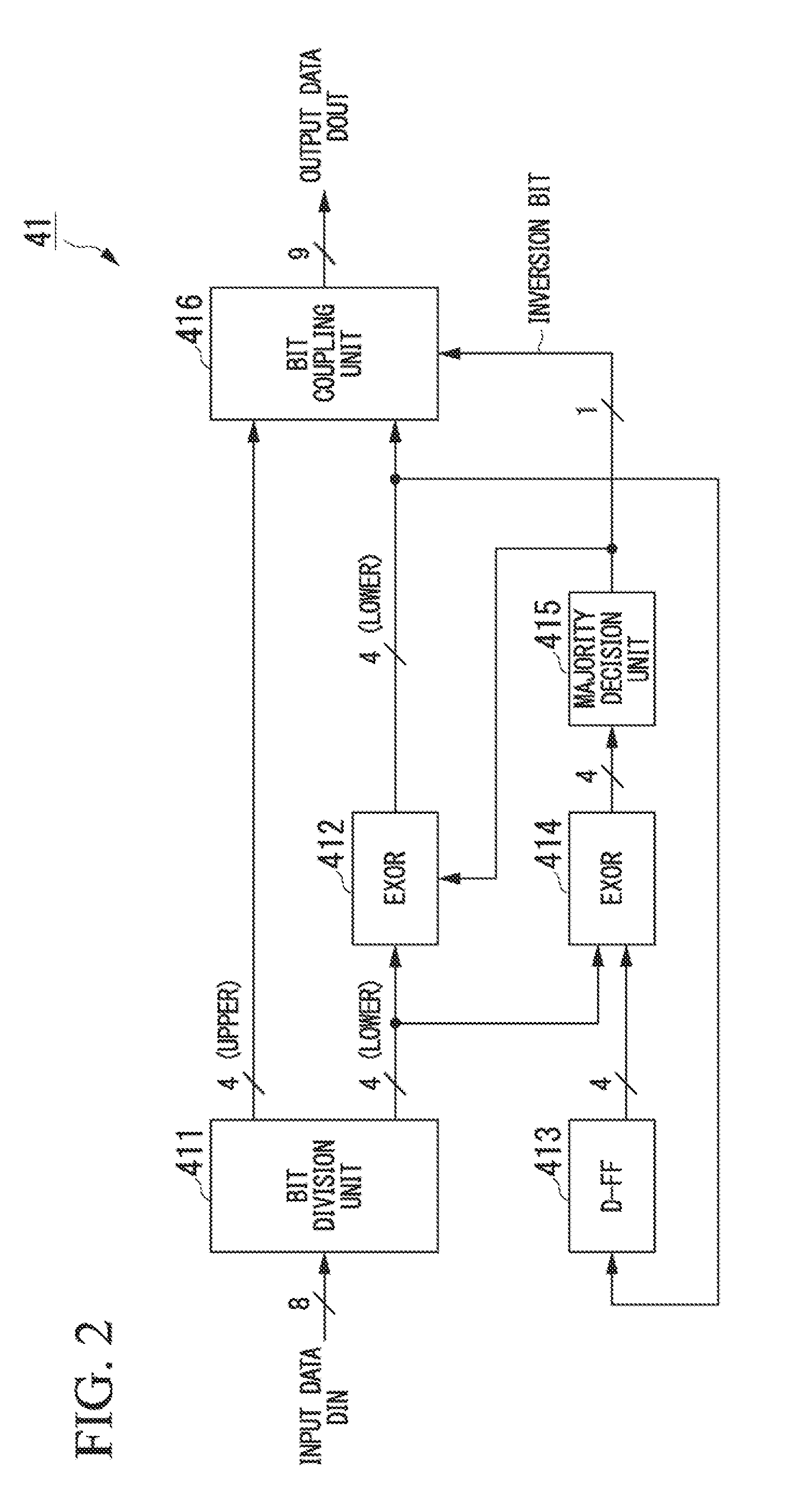
A data processing apparatus includes a data conversion unit for converting a plurality of sequentially input data into transfer data and sequentially transferring the transfer data, arranging the input data in each conversion unit using one transfer data as one transfer unit and a prescribed number of transfer units as one conversion unit, and the data conversion unit includes a first bit division unit for dividing the input data into first and second divided data, a bit comparison unit for comparing first divided data of an n-th time (n is a natural number equal to or more than 1) and an (n+1)-th time, a bit determination unit for determining whether the first divided data is to be inverted based on the determination result to output inversion information, a first bit inversion unit for outputting data selected based on the inversion information, and a first bit coupling unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Low power consumption compact digital decimation filter for CMOS image sensor
ActiveCN108156401AReduce in quantityReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCMOSProcessor register
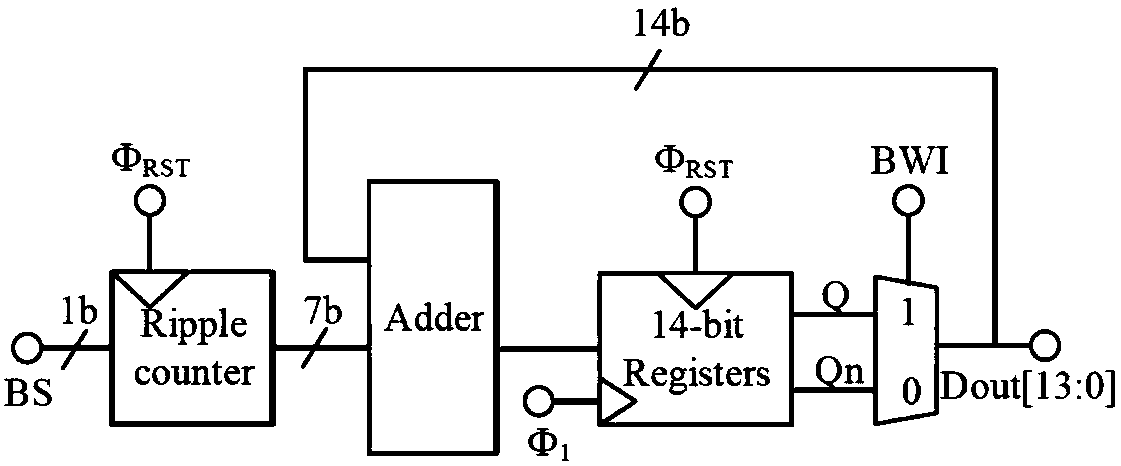
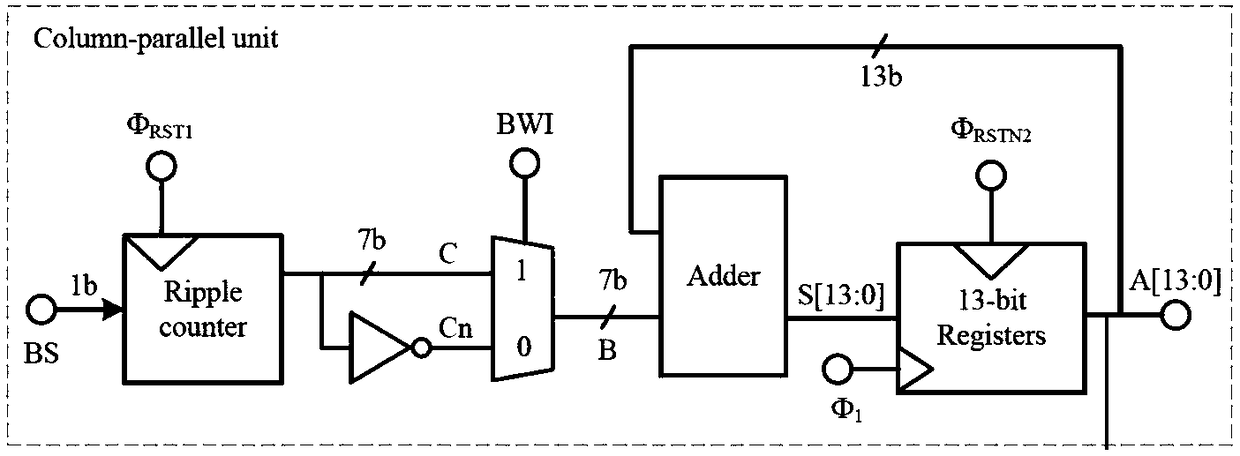
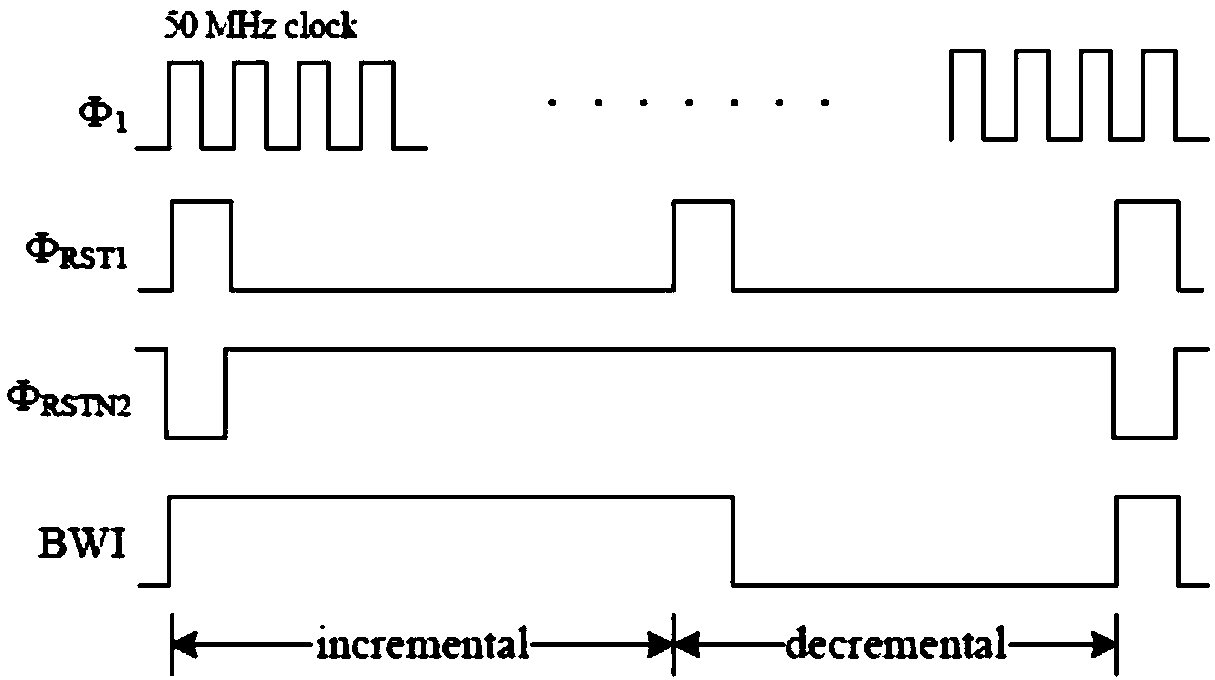
The invention discloses a low power consumption compact digital decimation filter for a CMOS image sensor. The low power consumption compact digital decimation filter comprises a ripple counter, a bit-by-bit inversion module BWI, an adder and a 13-bit register, and an inverter and the bit-by-bit inversion module BWI are arranged in front of the adder, the output data bit width of the ripple counter is 7 bit and is half of the output data bit width of the register; an meanwhile, the register only needs 13 bits to realize a 13-bit dynamic range. In practice, since the output data bit width of the ripple counter is 7 bit and is half of the output data bit width of the register, the number of inverters and selectors is reduced by half compared to the original. Meanwhile, the structure guarantees that the register data will not have the problem of data overflow, so the register only needs 13 bits to realize the 13-bit dynamic range without overflowing the data bit register. The low power consumption compact digital decimation filter disclosed by the invention adopts a special structure of pre-BWI, which greatly reduces the number of filter transistors, reduces the power consumption andreduces the cost.
Owner:重庆湃芯创智微电子有限公司
Data transformation for the reduction of power and noise in CMOS structures
InactiveUS6938172B2Reduce in quantityVolume/mass flow measurementComputation using non-contact making devicesCMOSData transformation
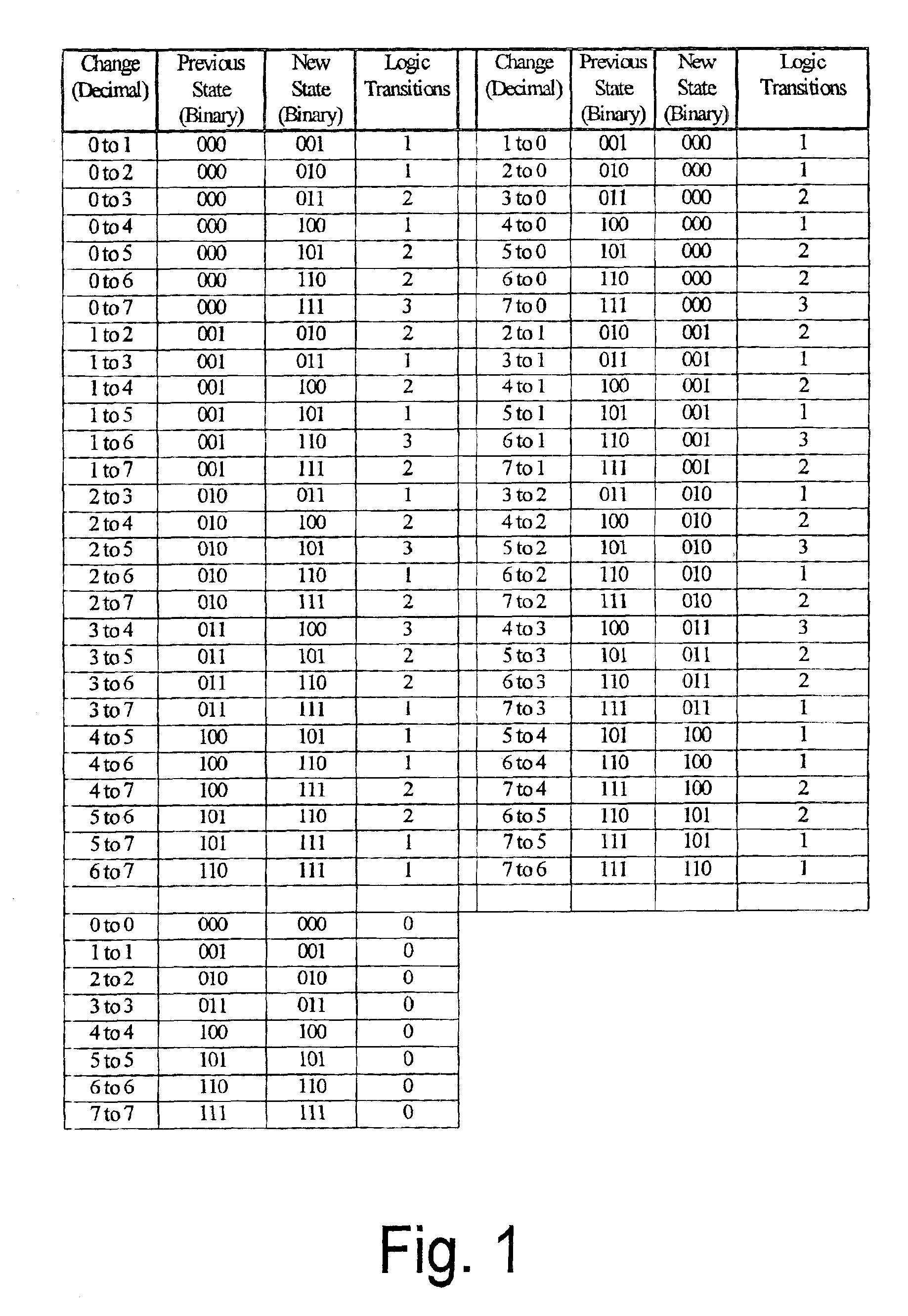
A data transformation algorithm is selectively applied to each data vector as it enters the pipelined structure. In a selection step, the algorithm compares the bit value of the new data vector with the corresponding bit values of the preceding data vector, and sums the number of logic transitions. The transformation algorithm is applied to the new data vector only if it would reduce the resulting number of transitions, otherwise the data vector is propagated unmodified. Bit inversion is a data transformation algorithm according to the present invention that provides up to a 50% reduction in the number of logic transitions.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Control method of information processing device and information processing device
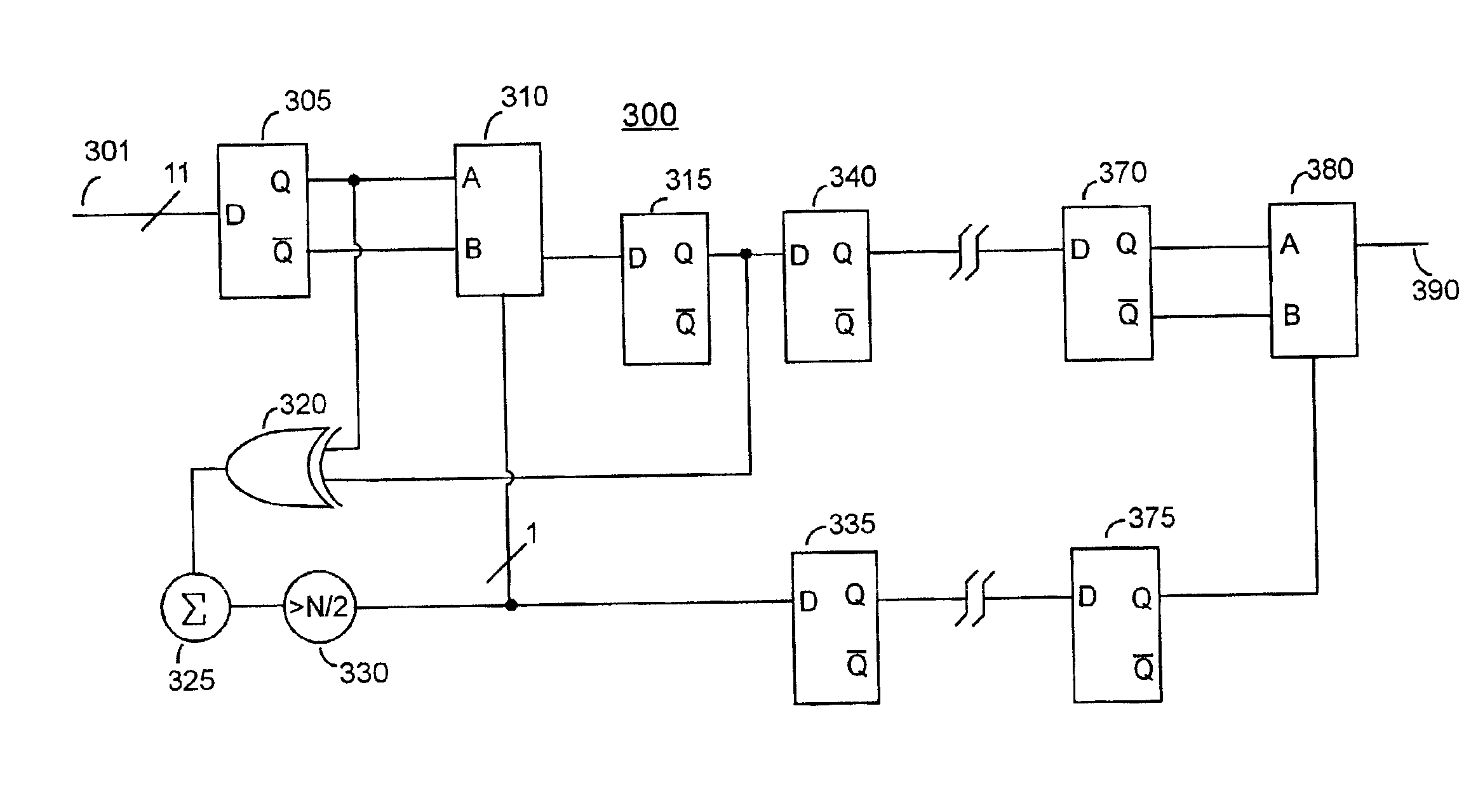
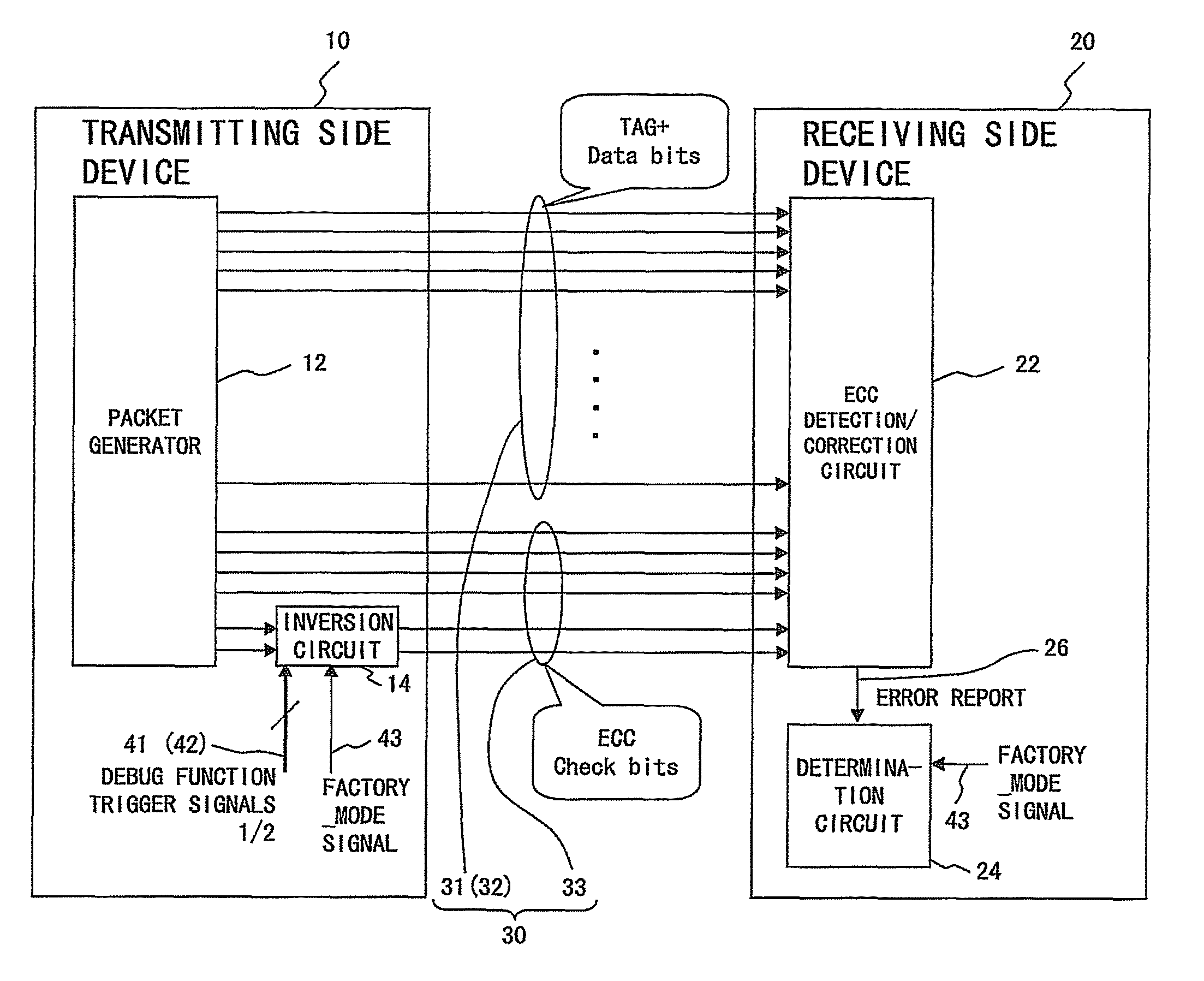
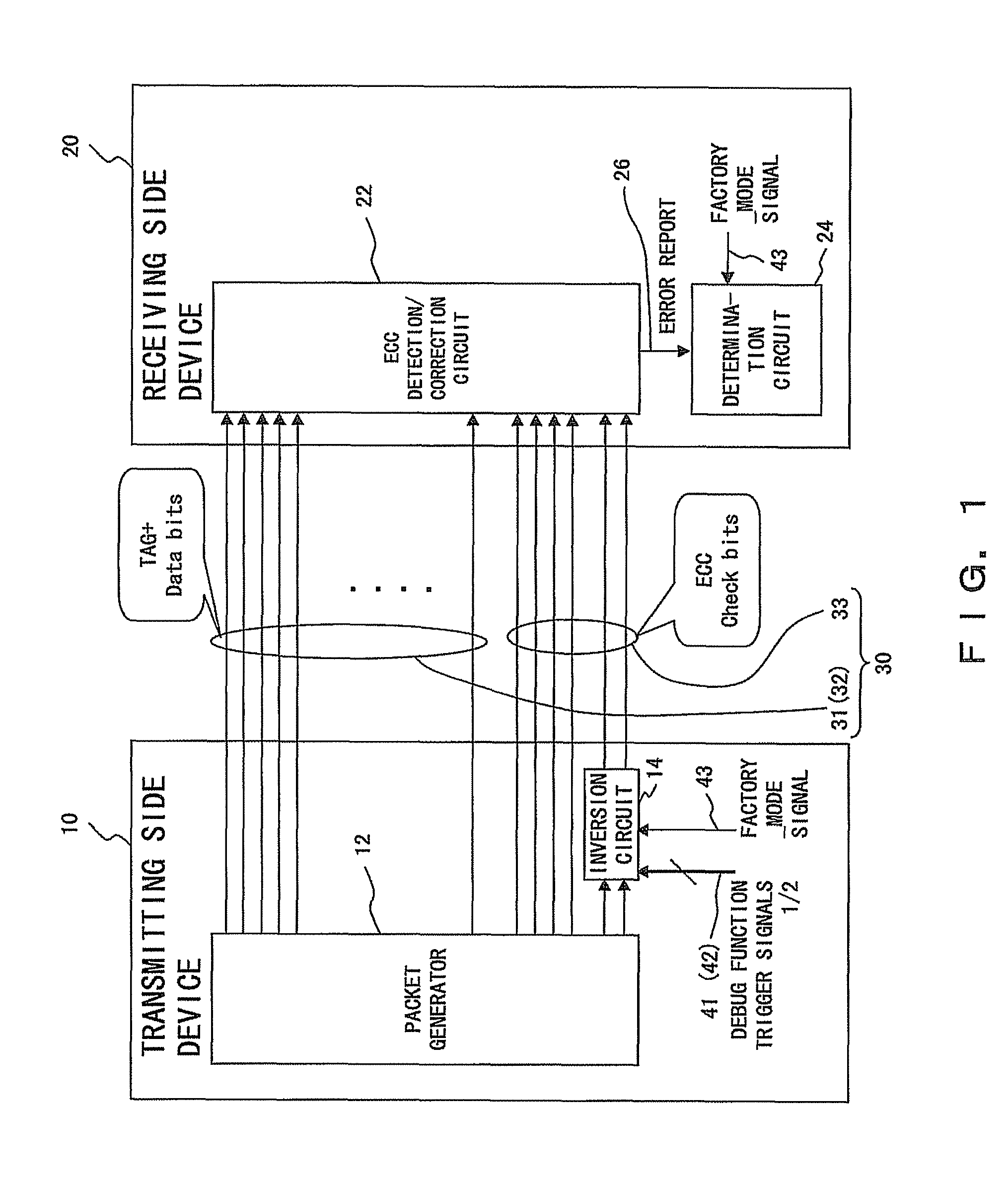
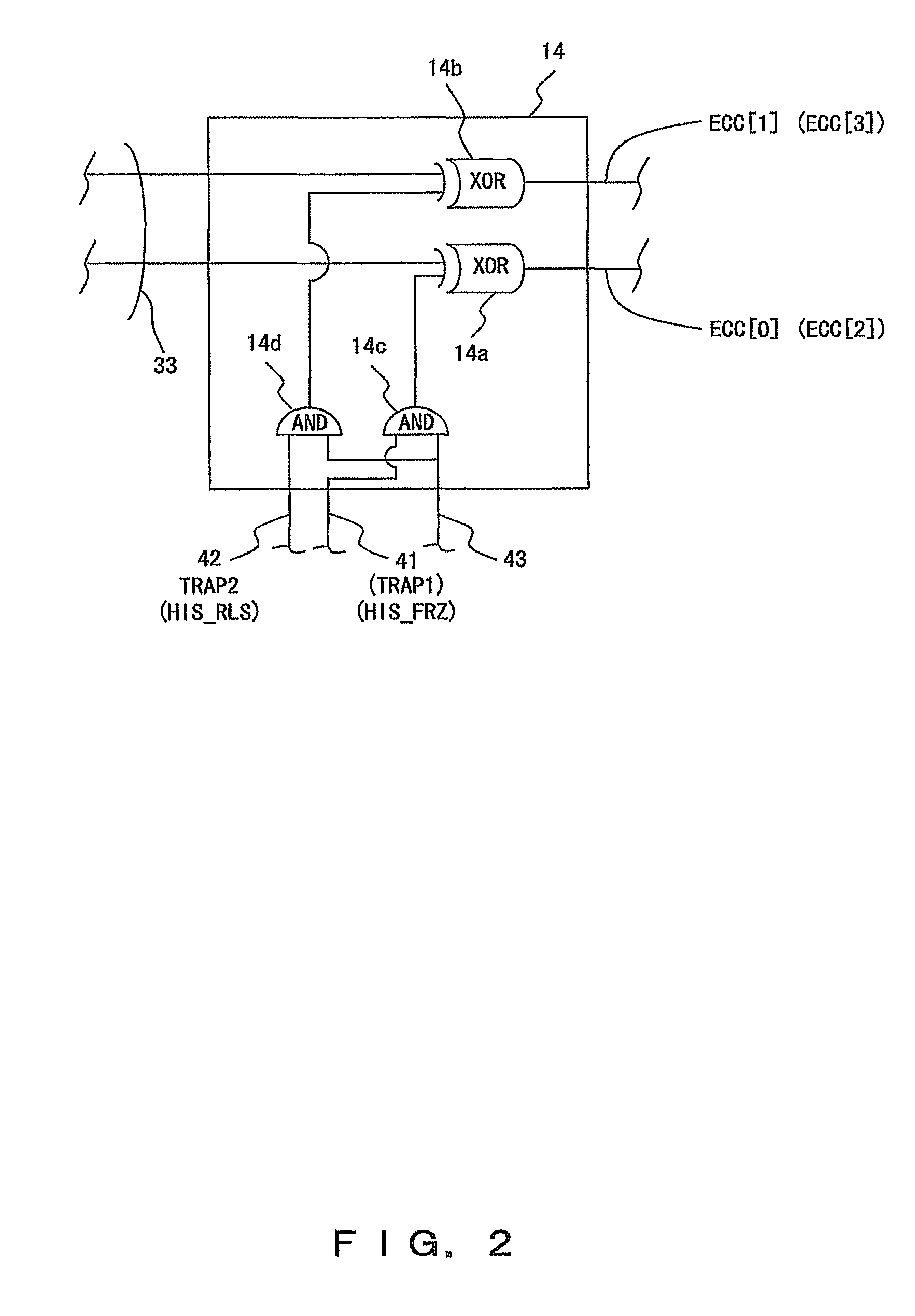
InactiveUS8301969B2Increasing costRealizing the debug of system behavior highlyError preventionTransmission systemsInformation processingBit inversion
A transmitting side device (10) and a receiving side device (20) are connected to each other via a bus (30) comprising TAG bits (31), data bits (32) and error detection / correction ECC bits (33). The transmitting side device (10) uses a redundant bit inversion circuit (14) to invert different bits of the ECC bits (33) corresponding to trigger signals (41&42). In the receiving side device (20), a determination circuit (24), which has received an error report signal (26) from an error detection / correction circuit (22), determines, from the position of an error bit in the ECC bits (33), which one of the trigger signals (41&42) has been transmitted from the transmitting side device (10).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com