Ground gravity unloading support method for large spatial reflector
A technology of gravity unloading and mirror, which is applied in the field of space optics, can solve problems such as the degradation of imaging quality of space optical remote sensors and the decrease of surface shape accuracy of mirrors, and achieve the best engineering implementability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
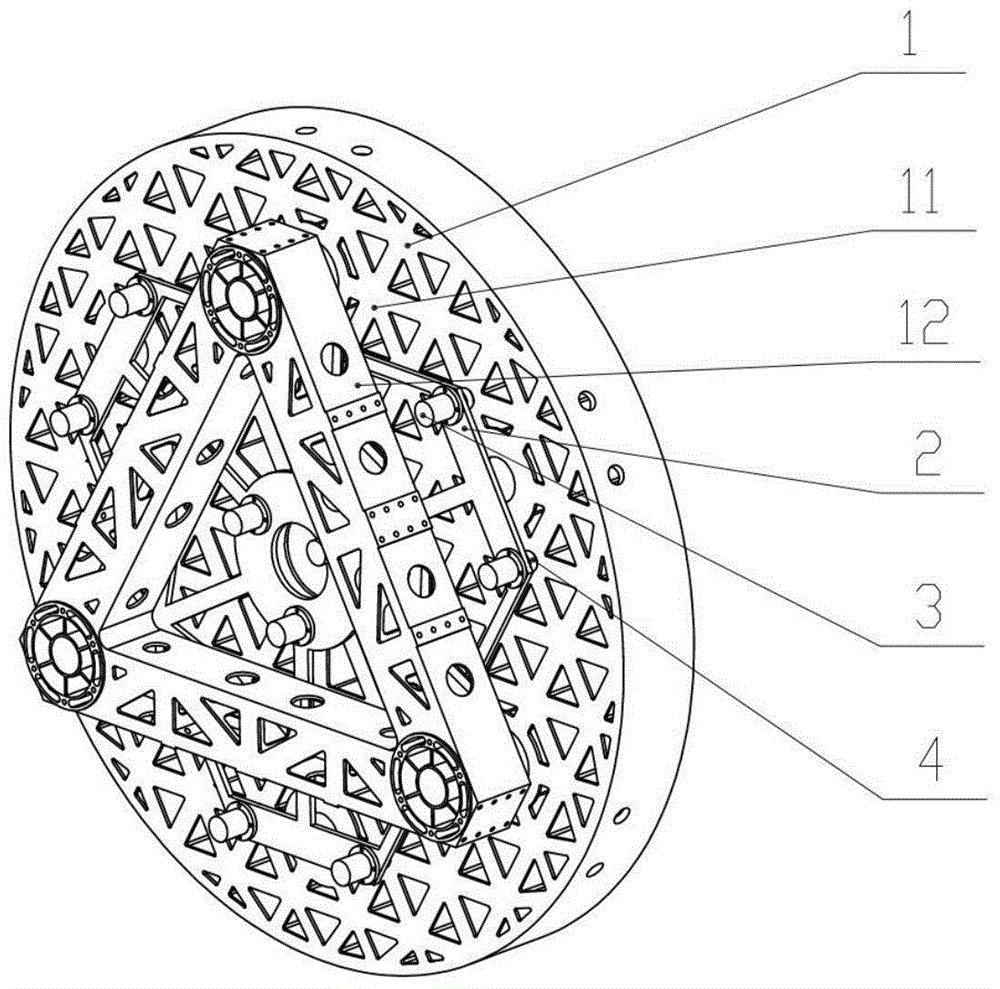
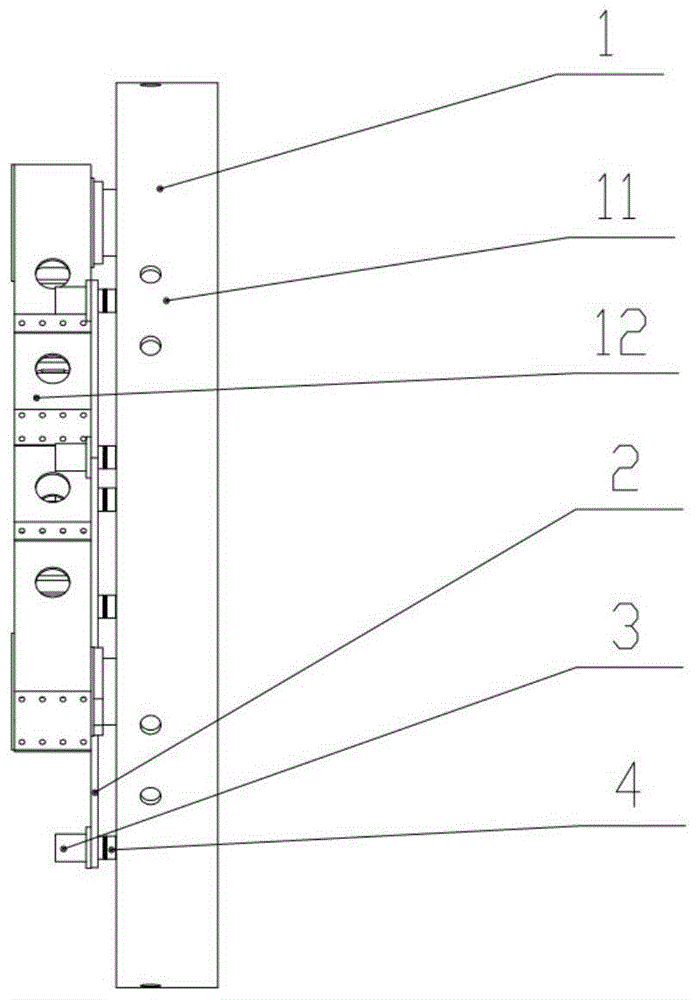
[0027] for a The gravity unloading method of the disk-shaped large-scale space mirror assembly 1 with a diameter of 1.4 m, a mirror thickness ratio of 1:9, and a lightweight ratio better than 70% is implemented as follows:
[0028] Step 1, use finite element analysis software to carry out finite element modeling on the space mirror assembly 1, and analyze the variation of the surface shape accuracy of the space mirror assembly 1 caused by gravity when the space mirror assembly 1 is placed horizontally.
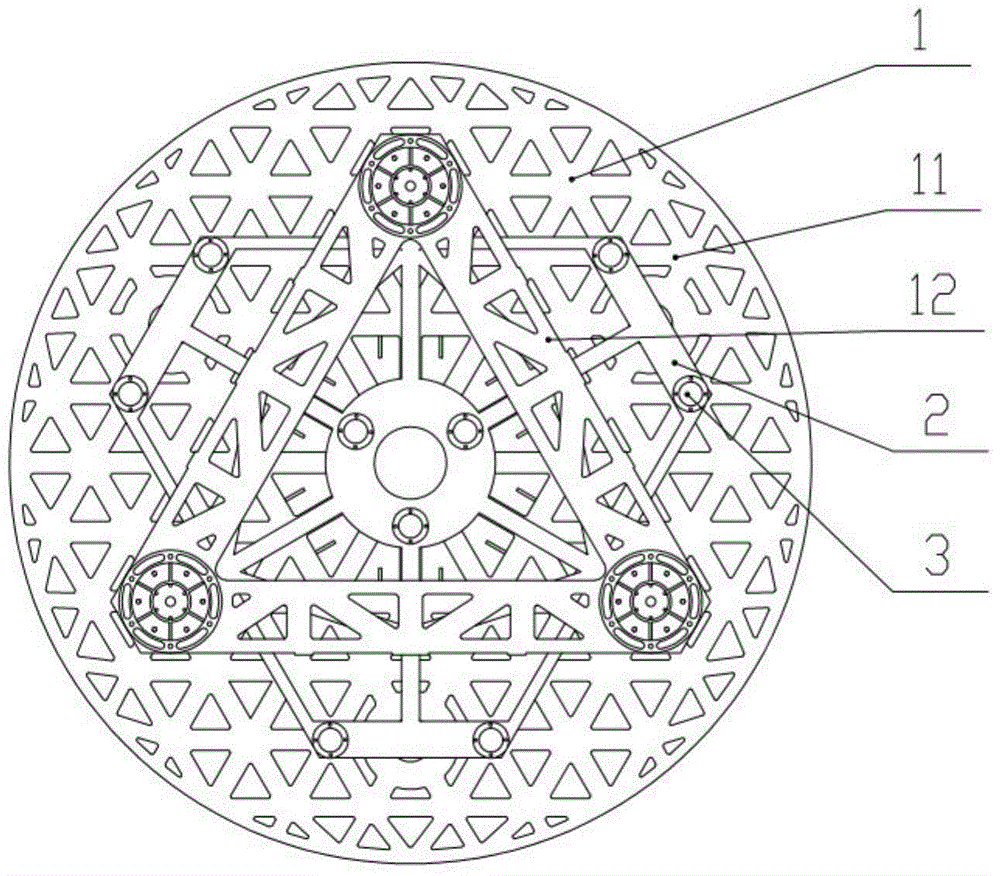
[0029] Step 2, according to the analysis results, it is determined to adopt the active support layout on the back of the space reflector 11 with 6 active support points distributed around the outer circle and 3 active support points distributed around the inner circle, as shown in image 3 shown.
[0030] Step 3, in the finite element software, apply a support force to the active support points on the back of the space mirror 11, and after multiple rounds of iterative calcul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com