Detecting fetal sub-chromosomal aneuploidies and copy number variations
A technology for copy number variation and chromosomes, applied in the fields of climate sustainability, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., which can solve the problems of difficult and reliable detection of copy number variation, insufficient sensitivity, limiting signal, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0479] Sequencing and preparation of primary and enriched sequencing libraries
[0480] a. Sequencing library preparation - abbreviated protocol (ABB)
[0481] All sequencing libraries, primary and enriched, were prepared from approximately 2 ng of purified cfDNA extracted from maternal plasma. Use as follows Library preparation was performed with reagents from the NEBNext™ DNA Sample Prep DNA Reagent Set 1 (Catalog No. E6000L; New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). Because cell-free plasma DNA fragments naturally, no further fragmentation by sonication or nebulization was performed on plasma DNA samples. according to The end repair module converts the overhangs of approximately 2 ng of purified cfDNA contained in 40 μl to phosphorylated blunt ends by incubating cfDNA with 5 μl 10X phosphorylation buffer, 2 μl deoxygenated nuclei in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube at 20 °C Nucleotide solution mixture (10 mM each dNTP), 1 μl of a 1:5 dilution of DNA polymerase I, 1 μl of T4 DNA...
Embodiment 2
[0490] Accurate aneuploidy detection in twin pregnancies
[0491] introduce
[0492]Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) of total cell-free DNA (cfDNA) using whole-genome massively parallel sequencing has been shown to be a very accurate and robust method for detecting fetal chromosomal aneuploidy. See, Bianchi DW, Platt LD, Goldberg JD, et al., Genome-wide fetal aneuploidy detection by maternal plasma DNA sequencing. Obstet Gynecol 2012;119:890- 901; Fan HC, Blumenfeld YJ, Chitkara U, Hudgins L, Quake SR. Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. blood).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:16266-71; Sehnert AJ, RheesB, Comstock D, et al. Optimal detection of fetal chromosomal abnormalities by massively parallel DNA sequencing of cell-free DNA from maternal blood ( Optimal detection of fetal chromosome abnormalities by massively parallel DNA sequencing of cell-free fetal DNA from maternal blood). Clin Chem 2011;57:1042-9. The test ...
Embodiment 3
[0514] Example 3: Syndrome-specific systematic bias removal pathway (SSS-BER)
[0515] introduction
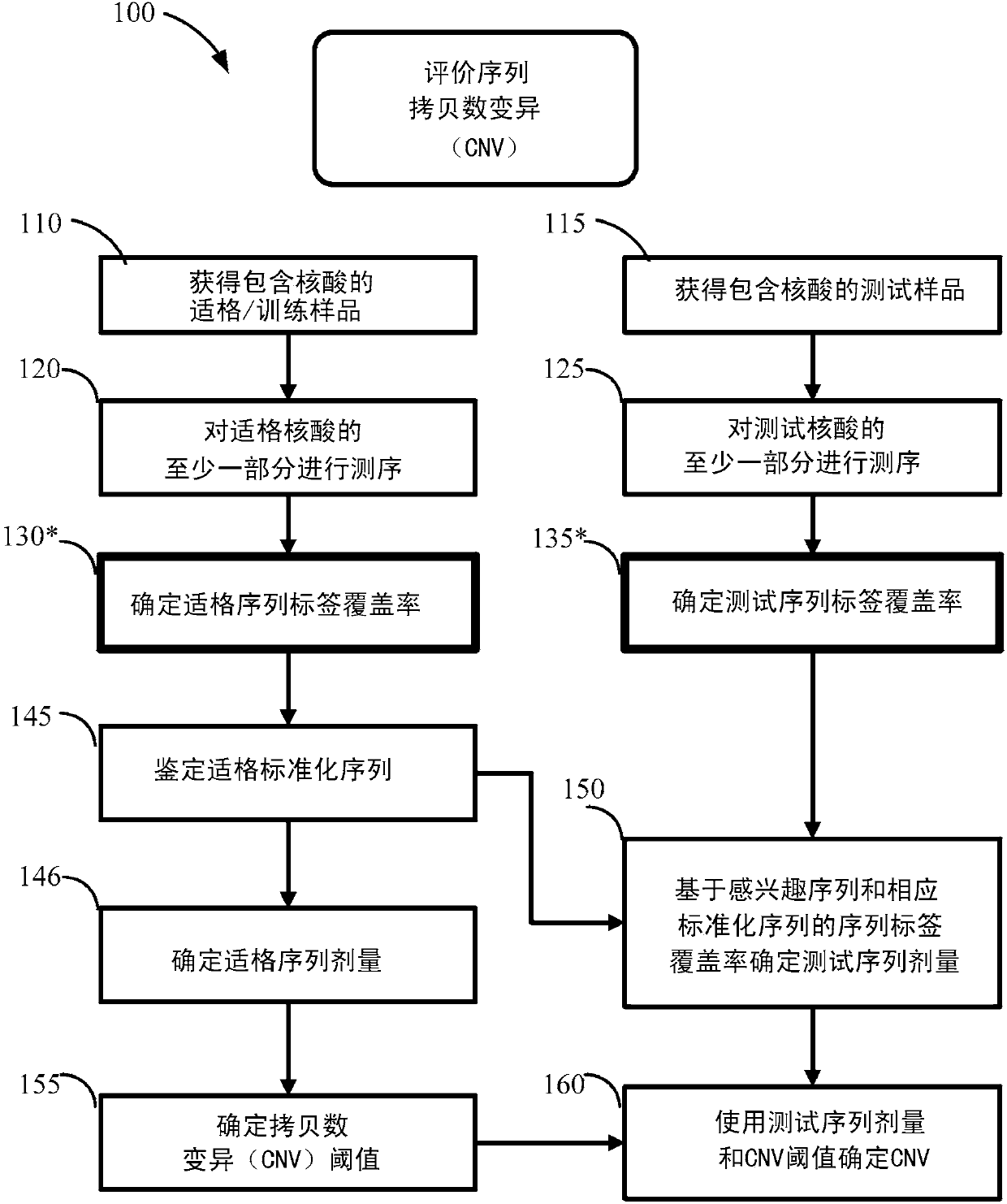
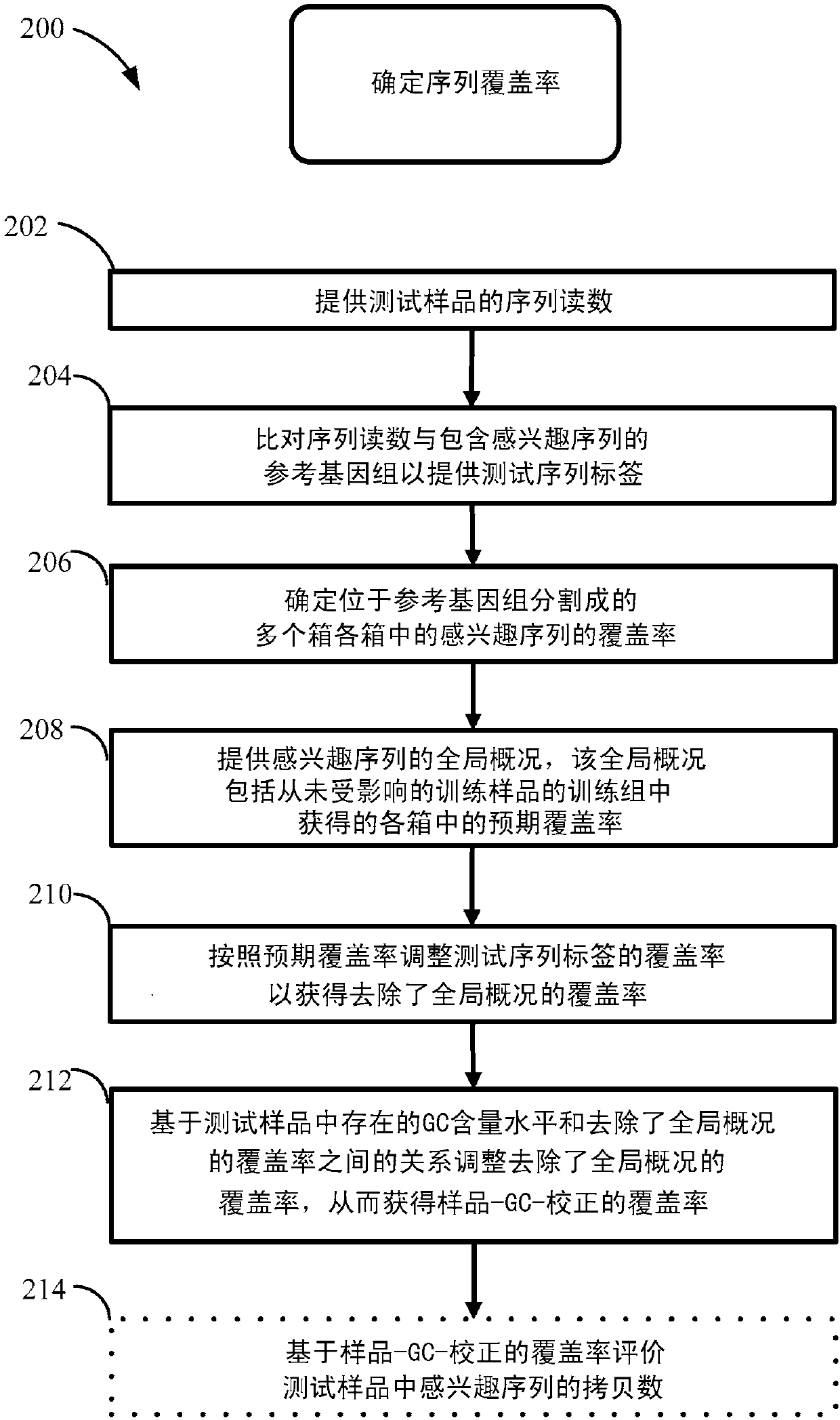
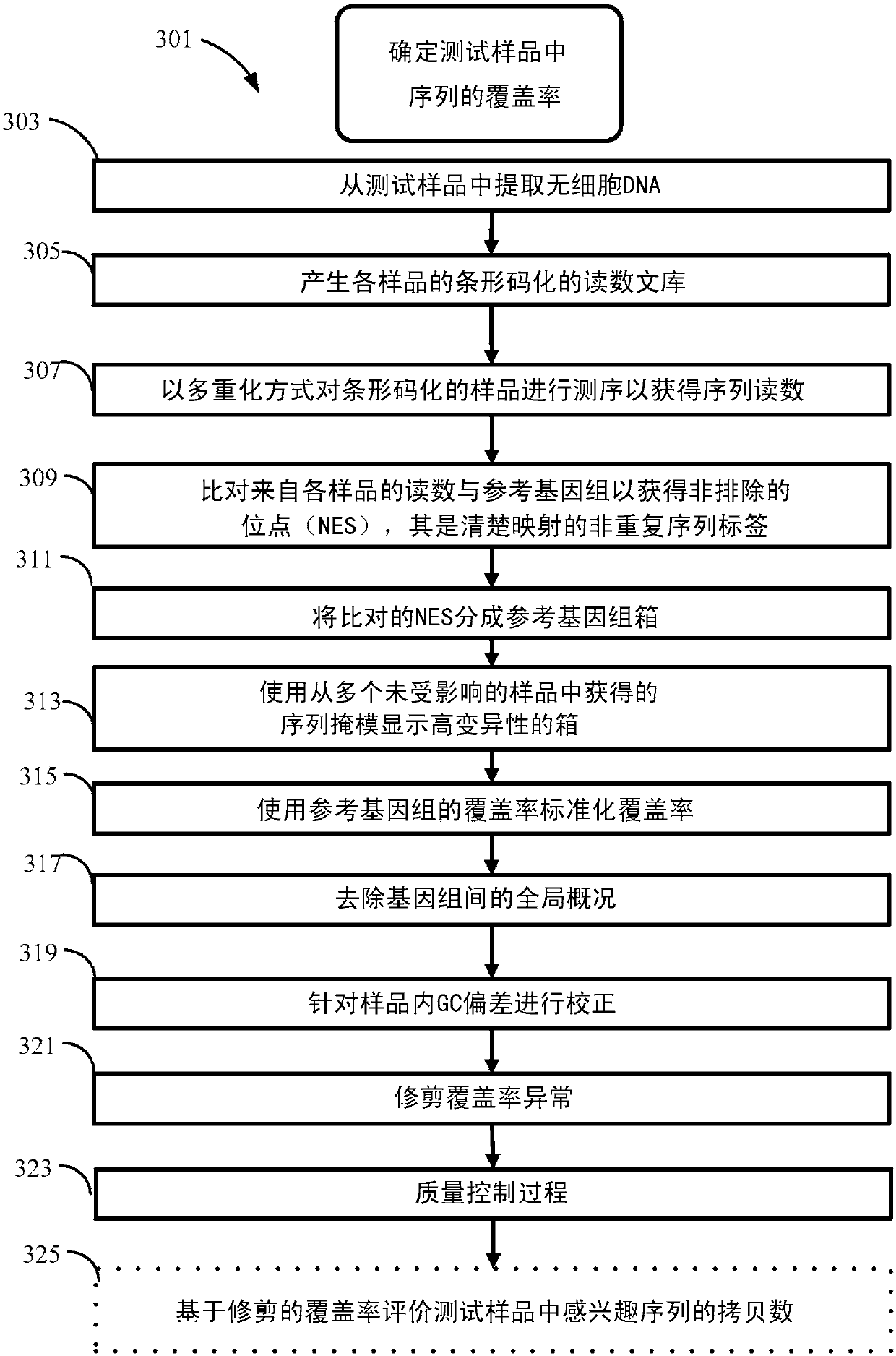
[0516] Various non-invasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD) methods employ fetal-derived cfDNA that is available in maternal body fluids such as peripheral blood. A number of NIPD methods extract, sequence, and compare cfDNA from the maternal periphery to determine whether fetal cfDNA from pregnant mothers contains copy number variations in genetic sequences associated with disease or phenotypes. Extracted and sequenced cfDNA provides sequence reads, which are then mapped to a reference genome. Sequence reads that map to unique locations or sites on a reference genome are called sequence tags. The number of sequence tags mapped to the sequence of interest can be used to determine the copy number or copy number variation of the sequence of interest.
[0517] The number of sequence labels that map to a sequence of interest is called coverage. Coverage of regions or bins of genetic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com