Convex combination adaptive echo cancellation method for affine projection sign subband adaptive filter
A technique of affine projection and echo cancellation, applied in two-way sound reinforcement telephone systems, wired transmission systems, electrical components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
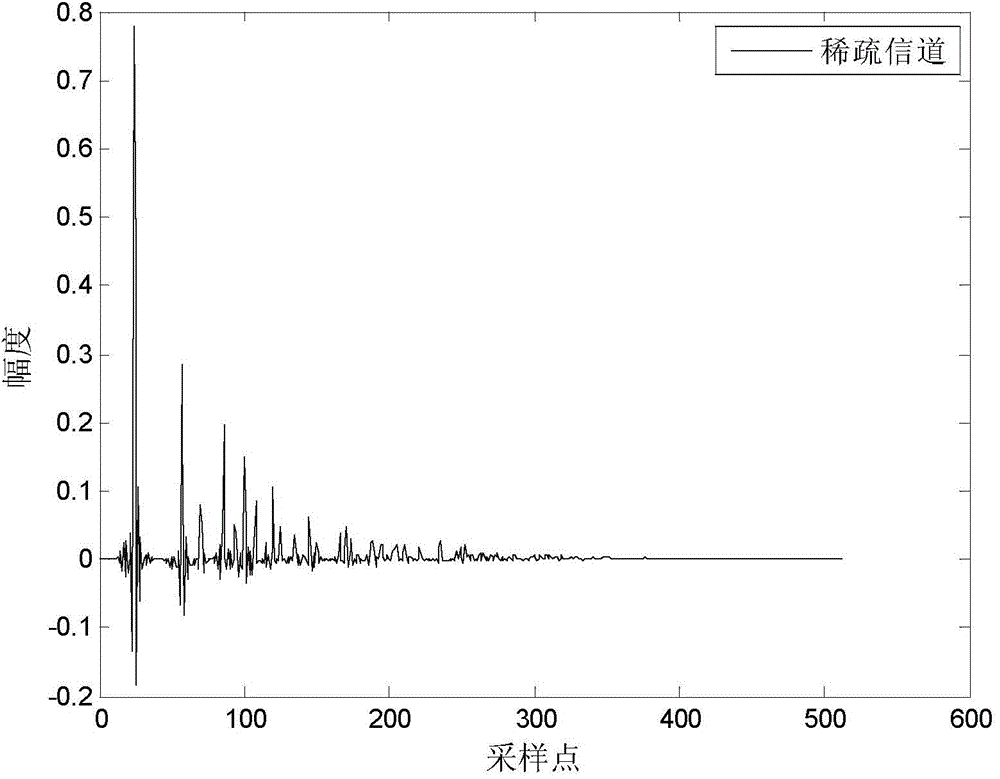
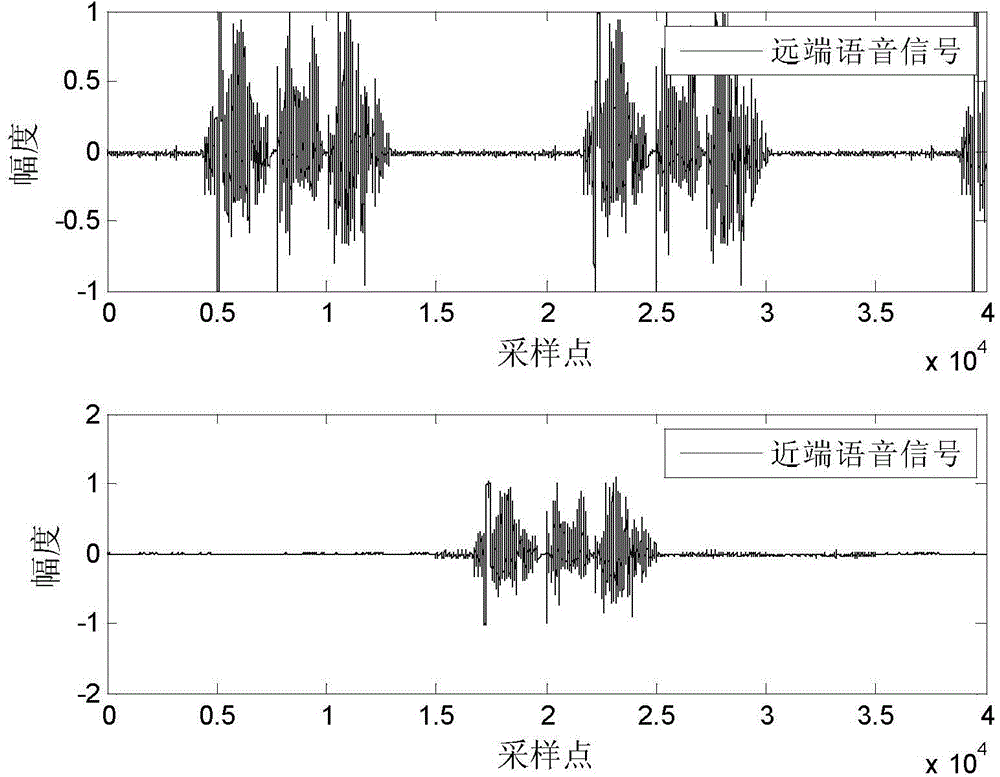
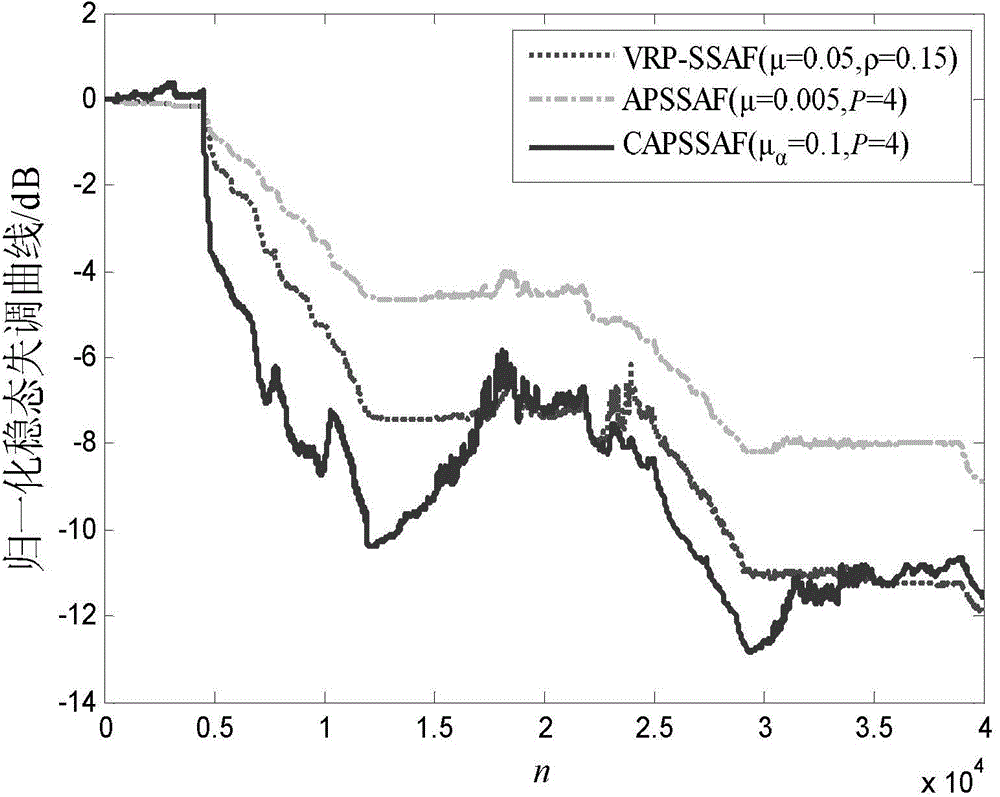
[0047] A specific embodiment of the present invention is an affine projection symbolic subband convex combination adaptive echo cancellation method, the steps of which are as follows:
[0048] A. Remote signal filtering
[0049] Sampling the remote signal from the far end to obtain the discrete value u(n) of the remote signal at the current time n, the discrete value u(n) of the remote signal at the current time n and the previous L-1 time, u( n-1)...,u(n-L+1), which constitutes the sub-band filter input vector U(n) at the current moment n, U(n)=[u(n),u(n-1) ...,u(n-L+1)] T ; Wherein L=512 is the number of filter taps, and the superscript T represents transposition;
[0050] Then combine the subband filter input vector U(n), U(n-1)...U(n-P+1) at the current time n and the previous P-1 time to obtain the subband filter affine projection input Vector G(n), G(n)=[U(n), U(n-1),...,U(n-P+1)], where P represents the order of affine projection, P=4 ,8,16;
[0051] Subsequently, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com