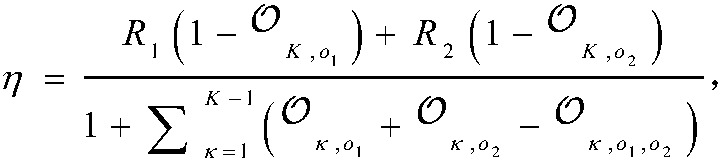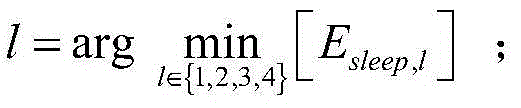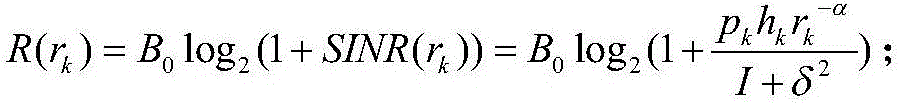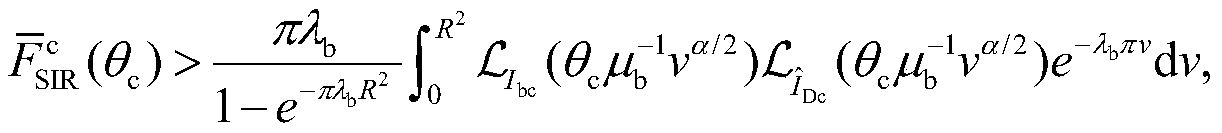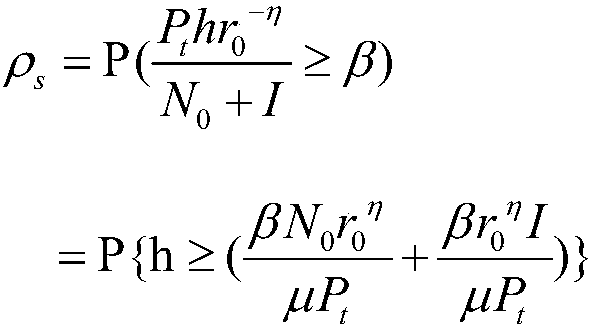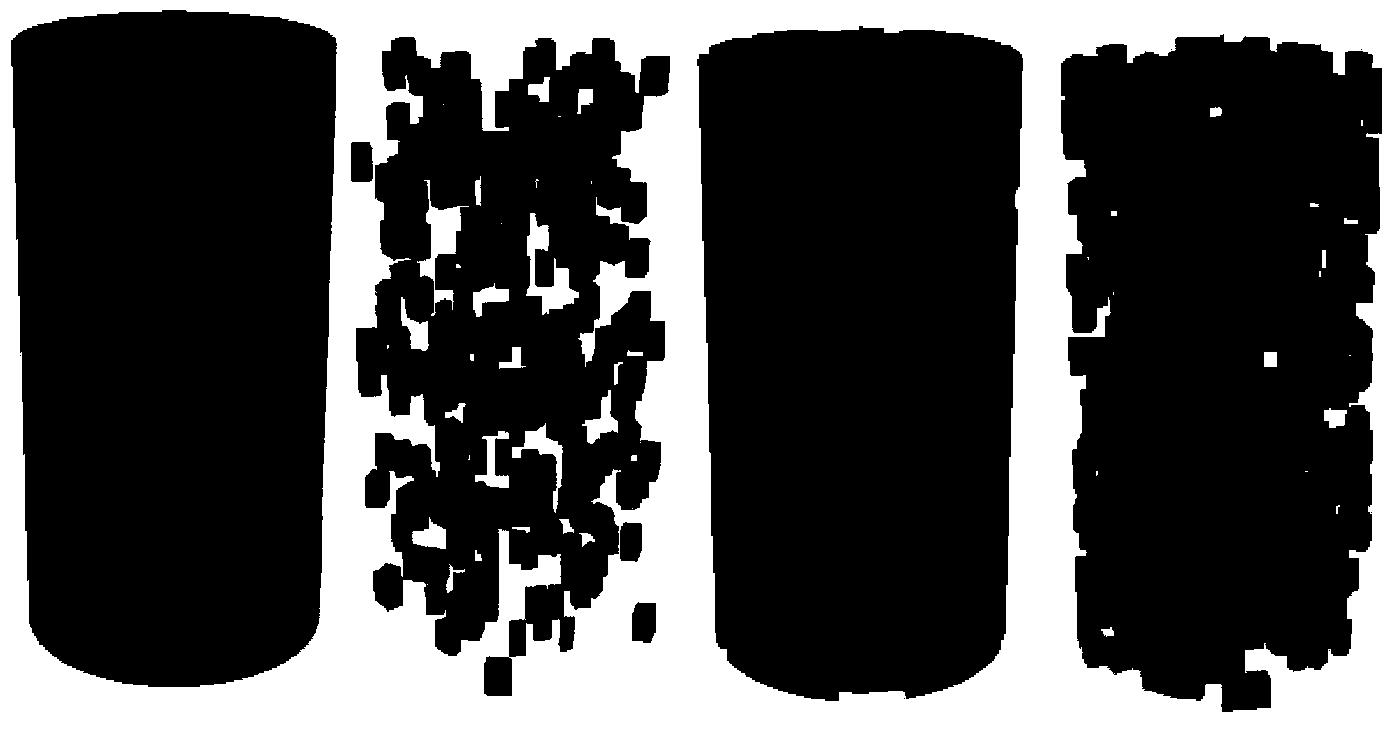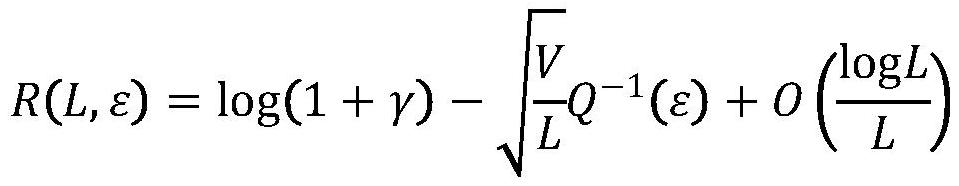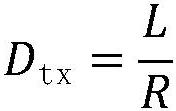Patents
Literature
74 results about "Stochastic geometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
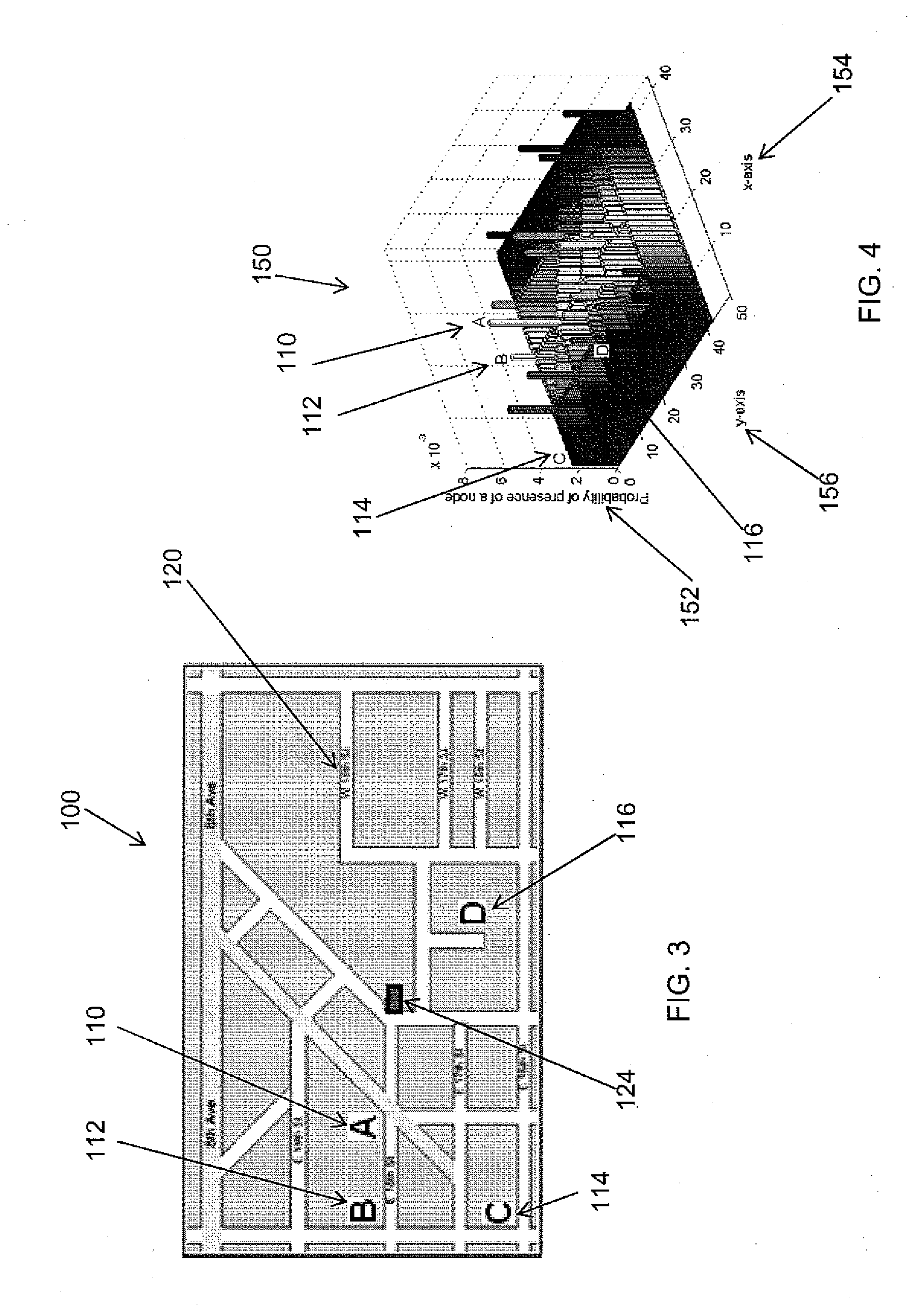
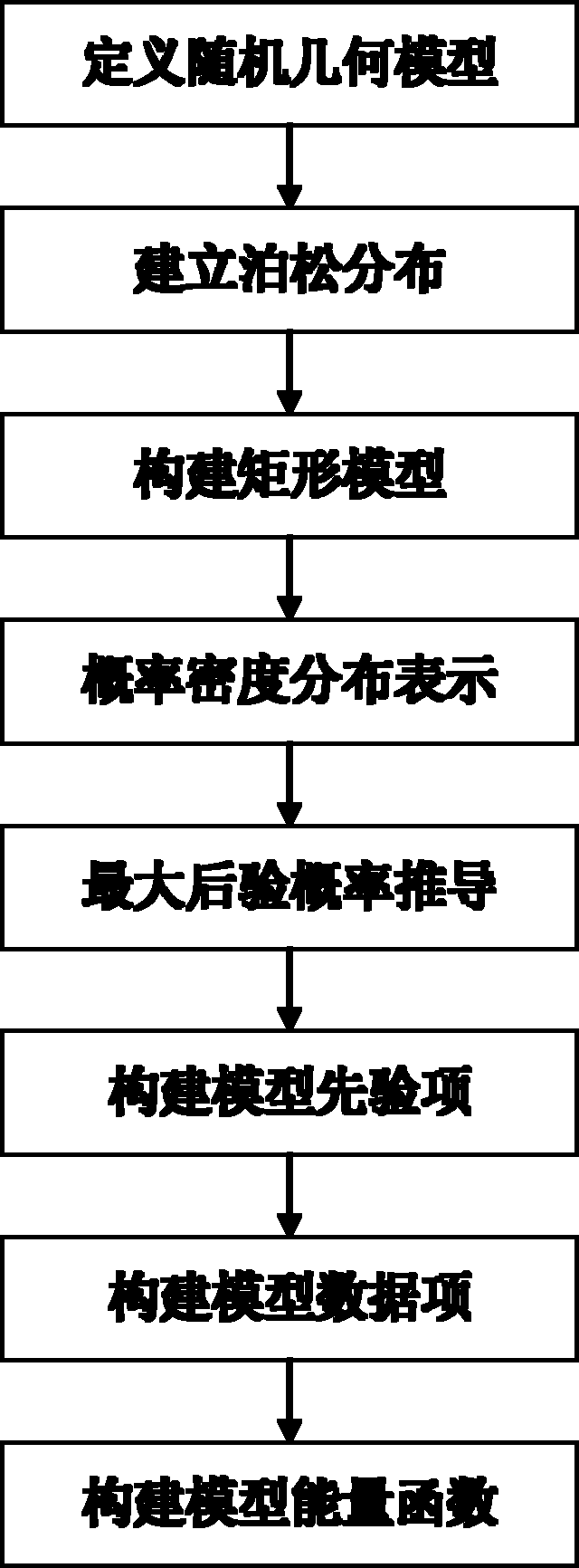
In mathematics, stochastic geometry is the study of random spatial patterns. At the heart of the subject lies the study of random point patterns. This leads to the theory of spatial point processes, hence notions of Palm conditioning, which extend to the more abstract setting of random measures.
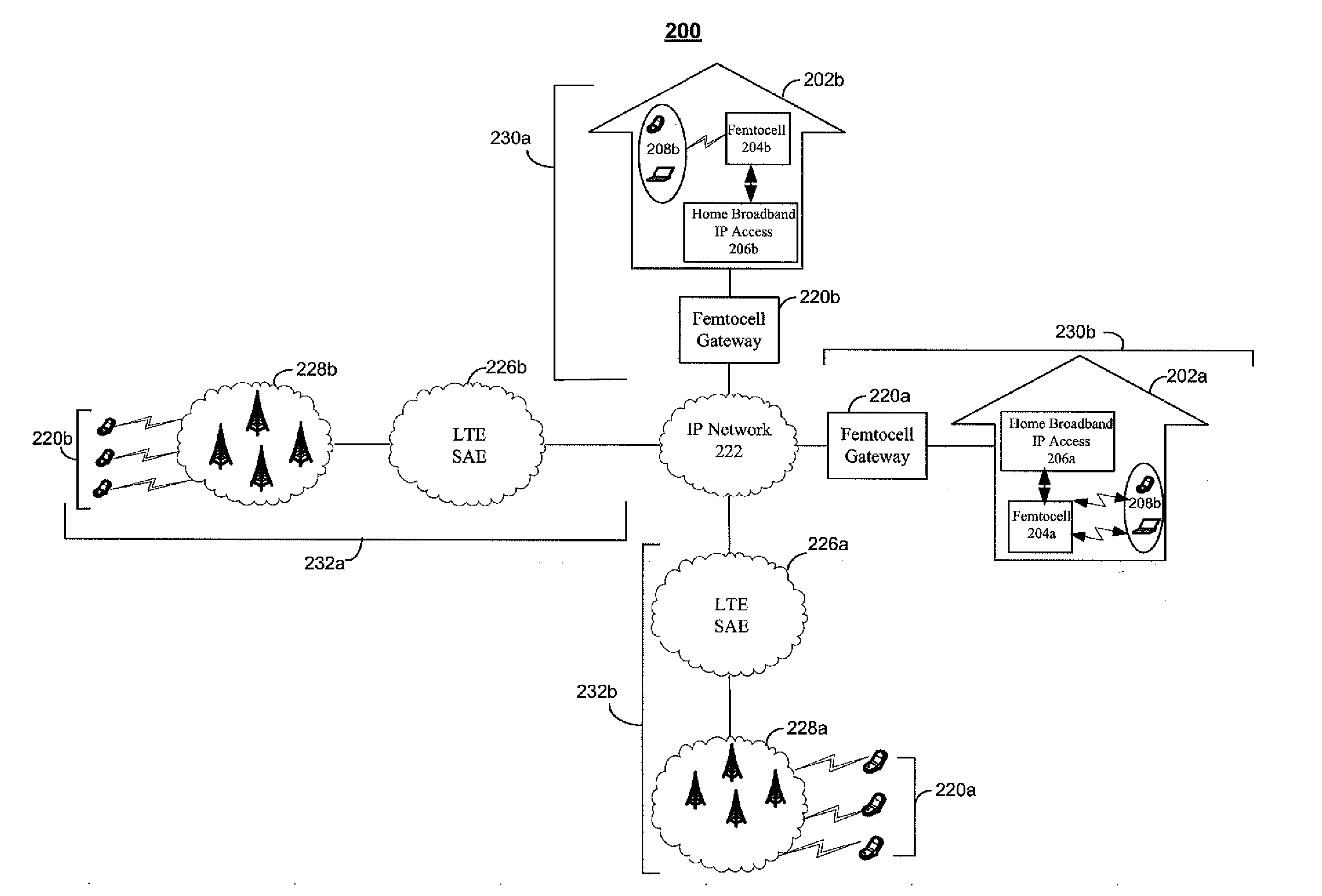
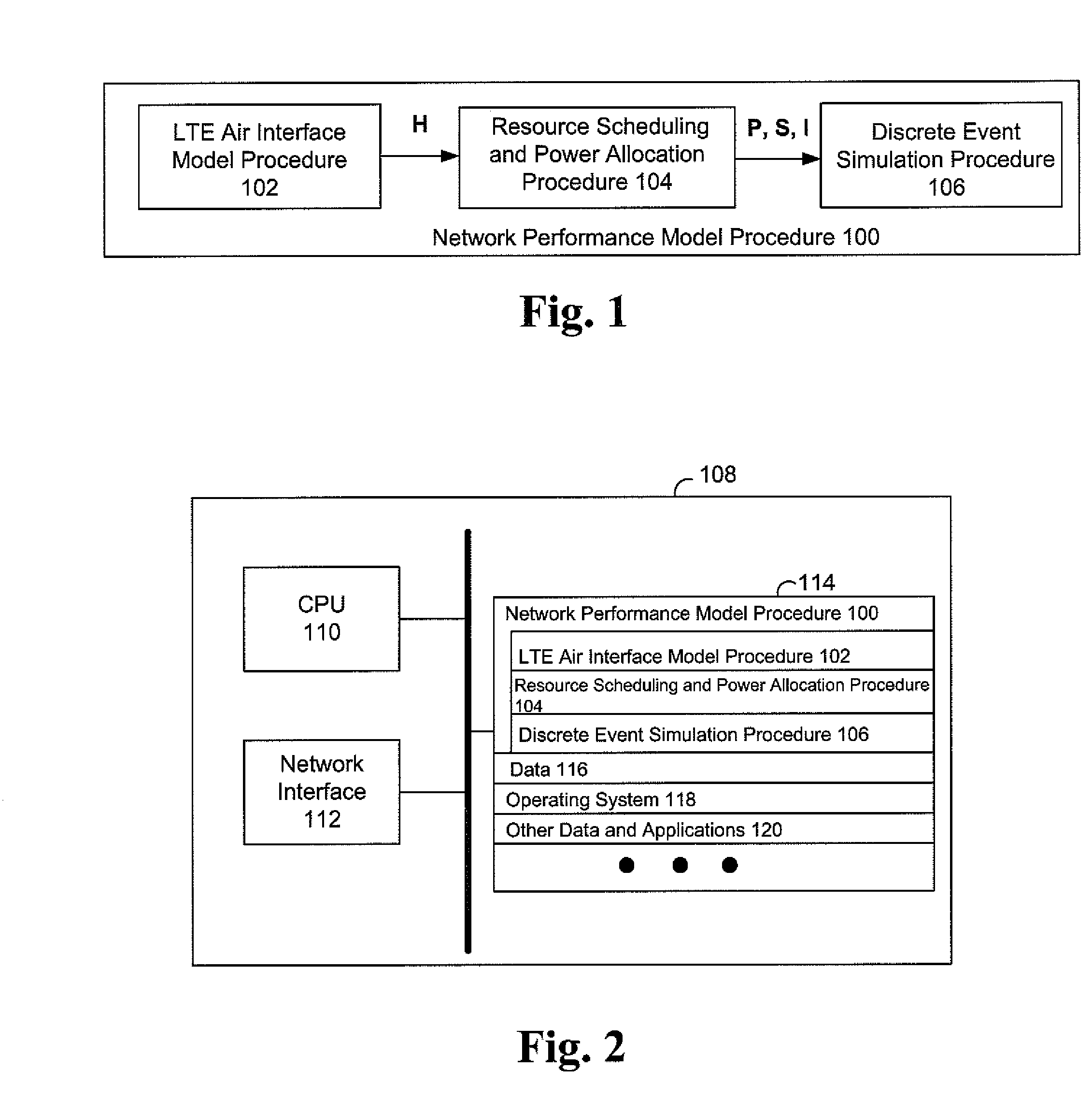
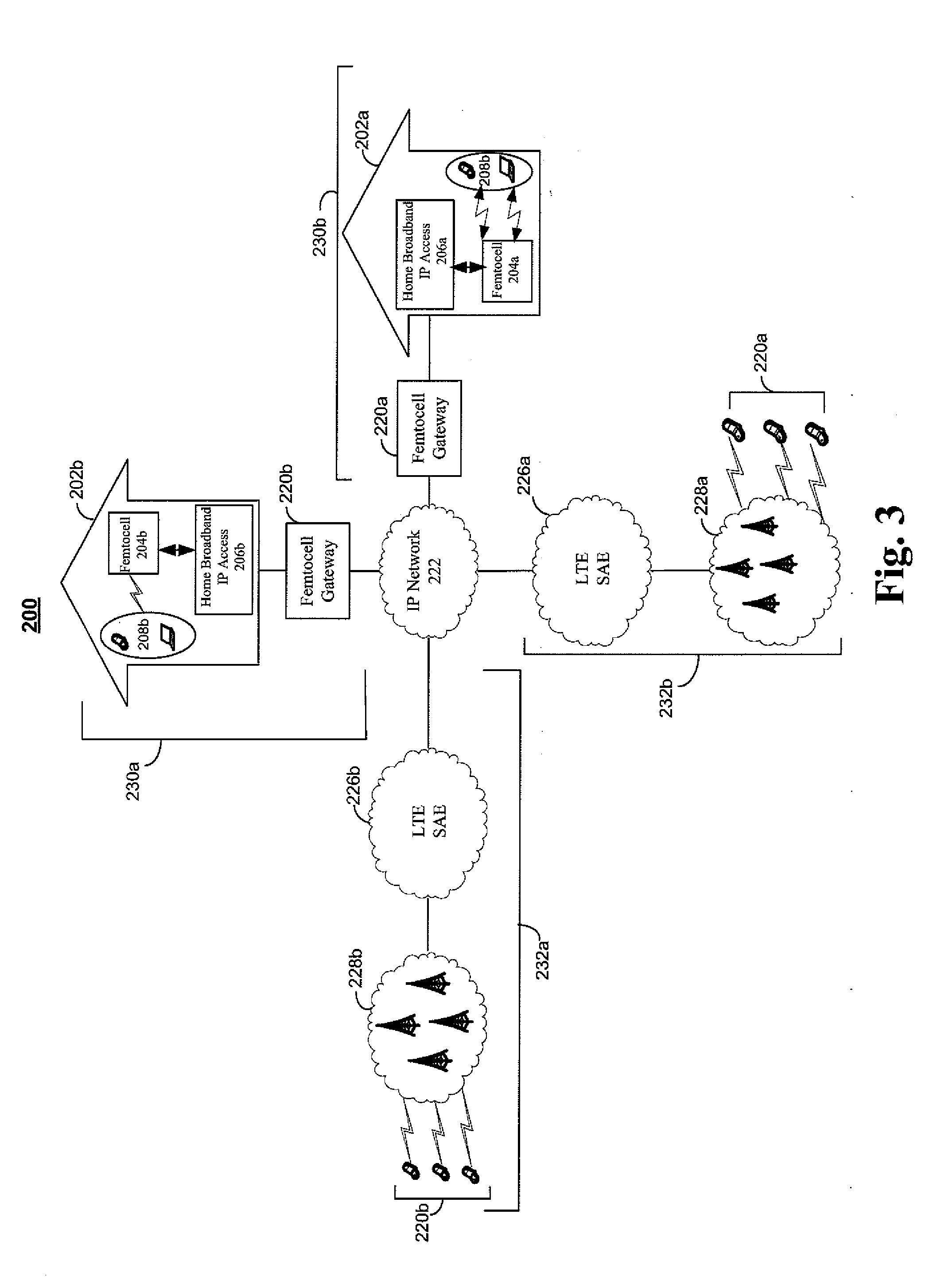
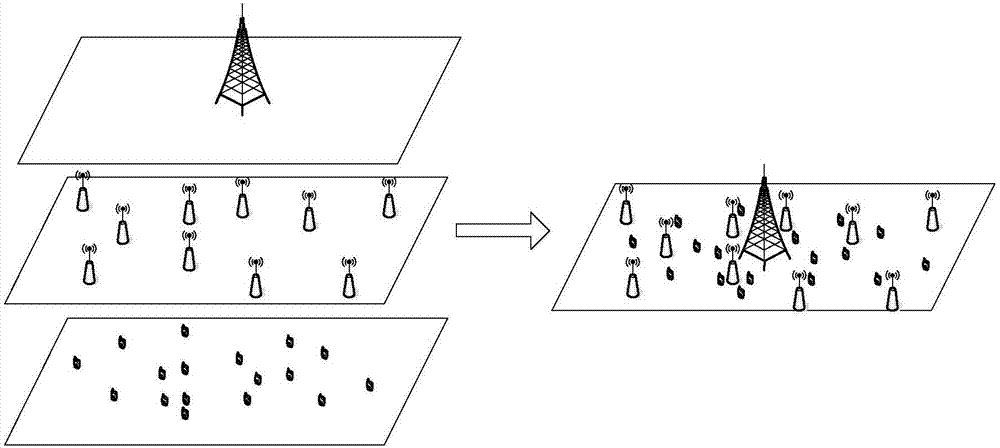
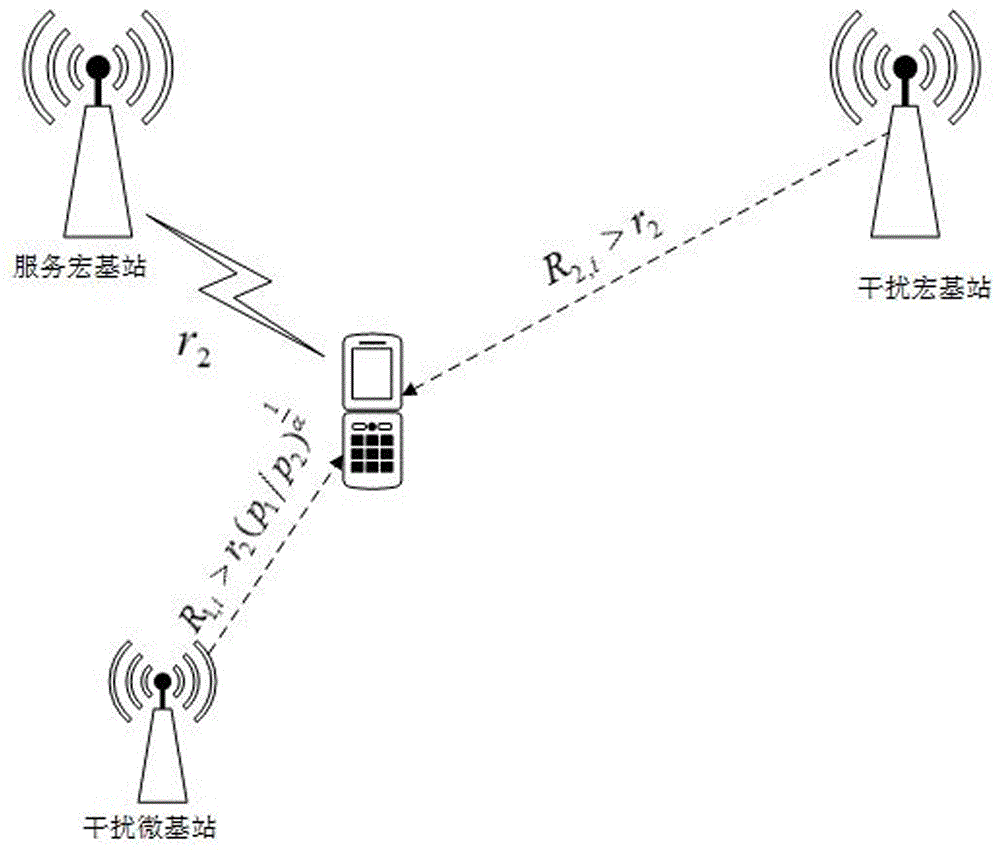
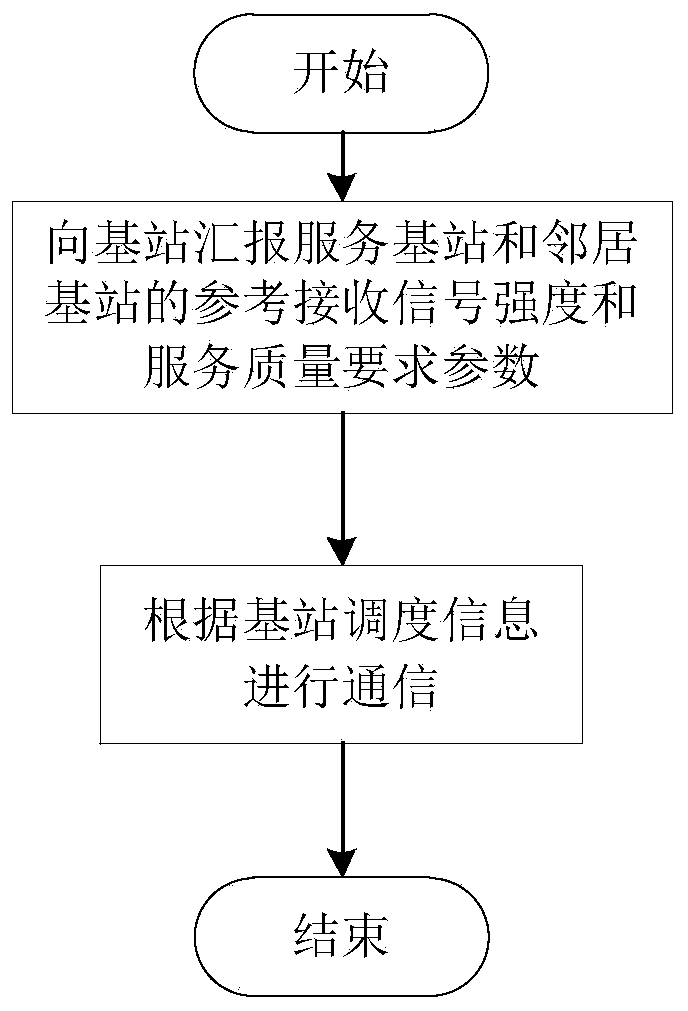
System and method for resource allocation of a LTE network integrated with femtocells
ActiveUS20110183678A1Maximize data rateNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesRadio networksExchange network
A resource scheduling and power allocation technique is provided for a LTE radio network integrated with femtocells. The technique utilizes a tri-phase approach that includes a stochastic geometric model of an exemplary radio network that generates a channel attenuation matrix for each channel at each PRB. A resource scheduling and power allocation procedure determines a near optimal assignment of mobile user to PRBs based on the channel attenuations, potential data rates, and transmit power subject to maximizing the data rates in accordance with a fairness objective. A discrete-event simulation procedure simulates the end-to-end transmission of the data packets in a packet-switch network in accordance with the assignments to analyze the behavior of the overall network.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
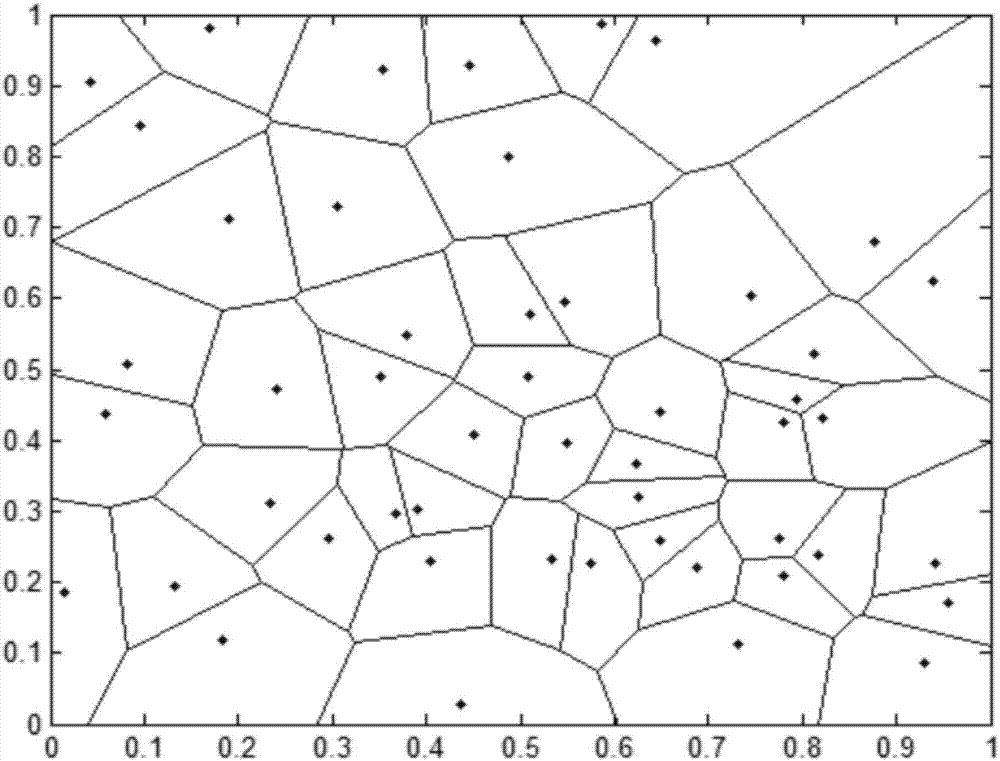
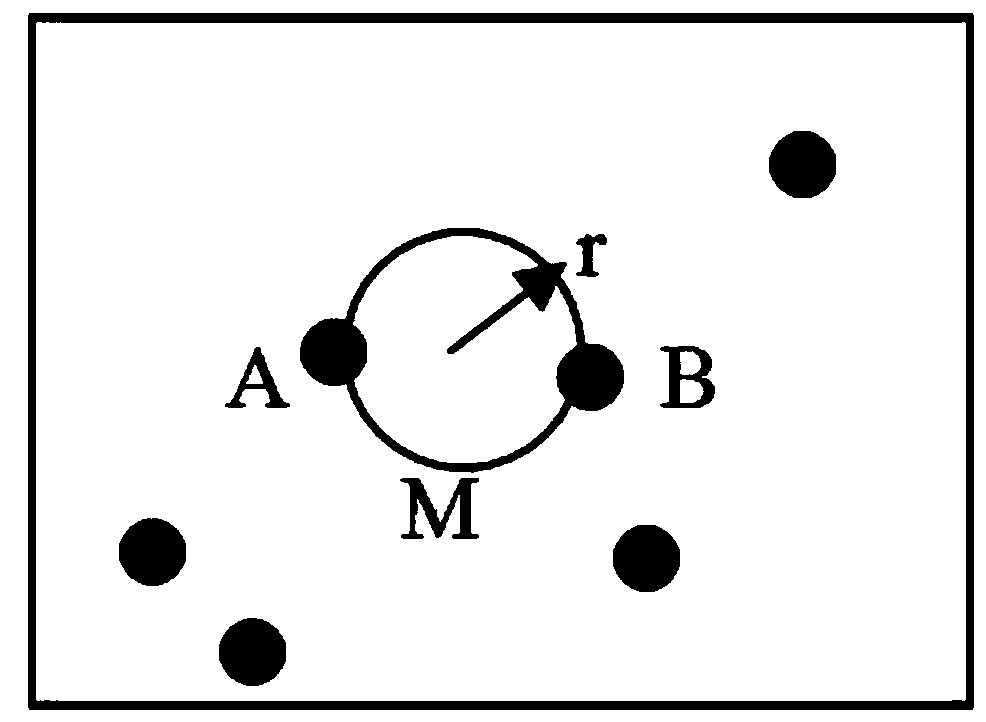
Heterogeneous cellular network base station deployment method based on Poisson cluster process
ActiveCN106454919AEasy to analyzeHigh probability of coverageWireless communicationProbit modelCoverage probability
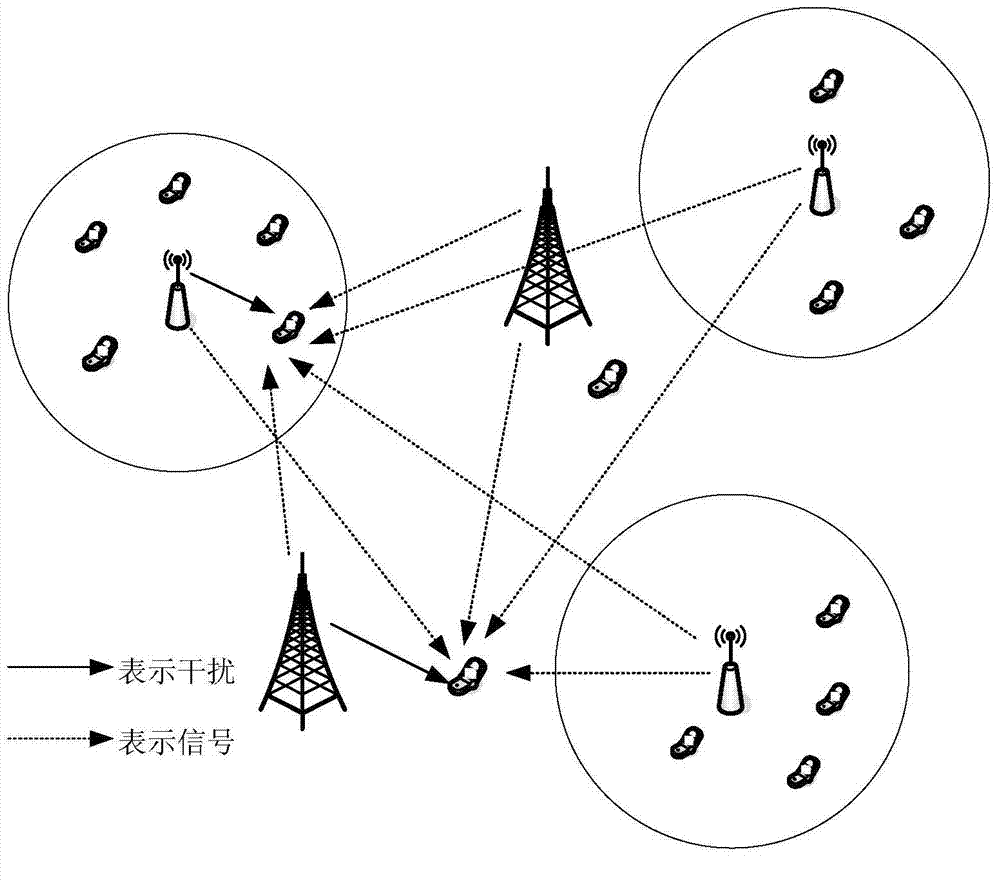
The invention provides a heterogeneous cellular network base station deployment method based on a Poisson cluster process. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of a random geometry theory, according to a hypothetical system model and adopting an instantaneous SINR cell selection mechanism as a cell selection mechanism of a user, deducing an SINR model based on the Poisson cluster process; carrying out analysis and inference on an interference model of a multi-layer heterogeneous cellular network by utilizing characteristics of the Poisson cluster process and a probability generation function thereof to obtain an interference distribution model; with the SINR model and the interference distribution model being combined, deducing a coverage probability model of the multi-layer heterogeneous cellular network; and carrying out simulated comparison and analysis on difference of coverage probabilities of the Poisson cluster process and a Poisson point process. The method is much closer to real communication scenes, is larger in coverage probability, can analyze coverage probability and throughput capacity better, and is of great importance in study of the heterogeneous cellular network in the future.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
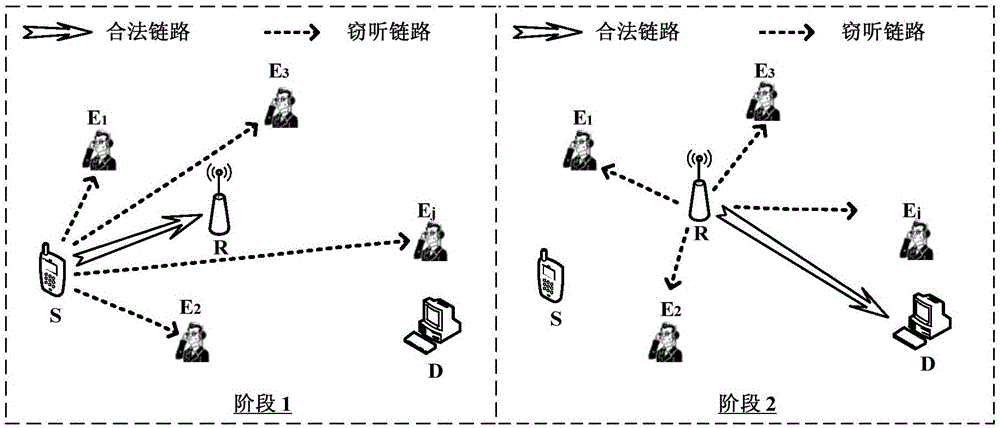
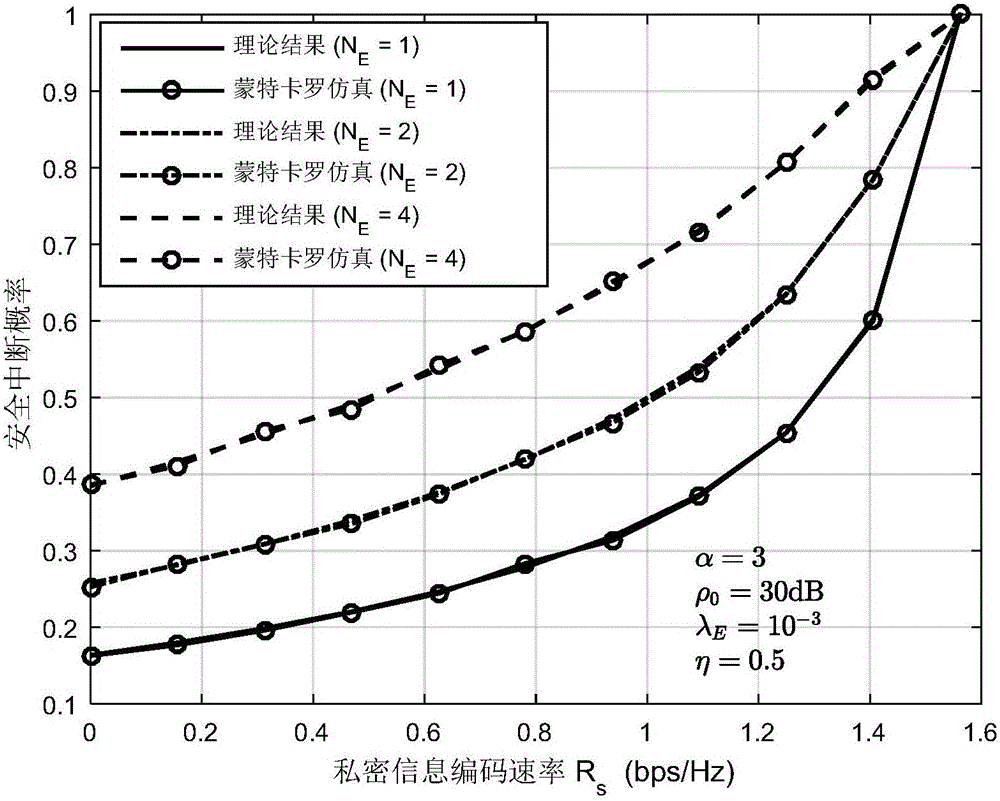
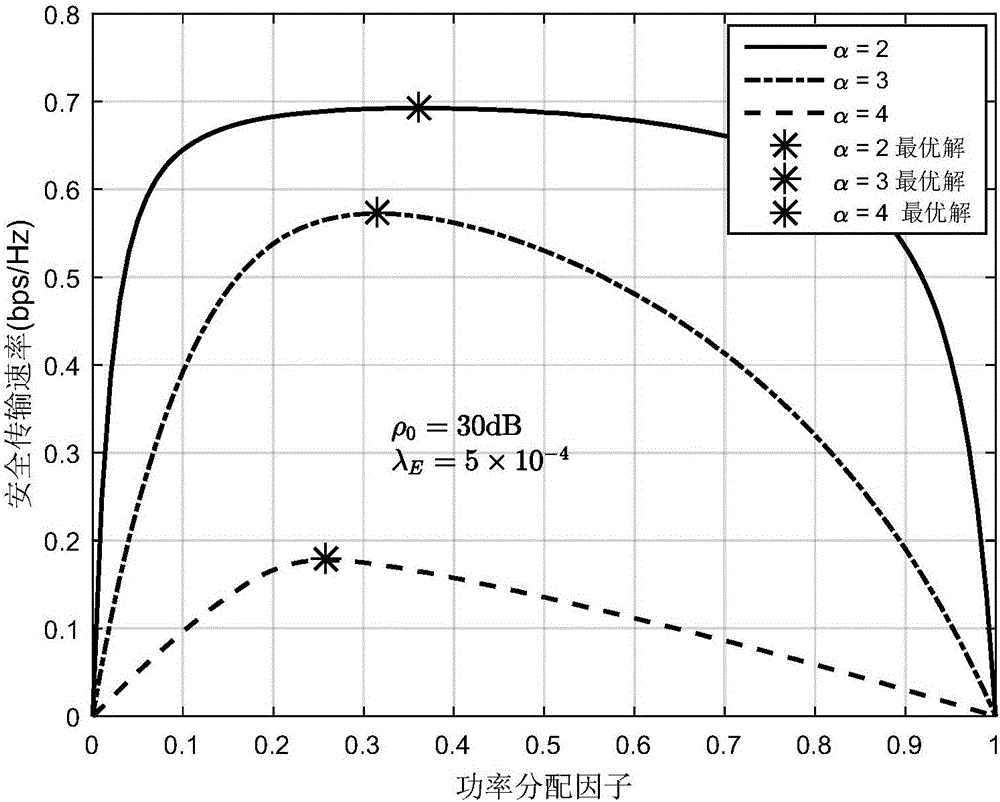
Relay transmission method based on physical layer safety in eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene
ActiveCN106131823AMaximize safe transfer rateEasy to implementTransmission monitoringSecurity arrangementTransmitted powerEavesdropping
The invention discloses a relay transmission method based on physical layer safety in an eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene. The method comprises the steps of 1), obtaining a safe interruption probability of two-hop relay transmission after two times of independent eavesdropping coding is carried out in the eavesdropping user randomly distributed scene based on a random geometric theory; 2), establishing an optimization problem of maximizing a safe transmission speed under the condition that the total transmitting power of a source node and a relay node is limited; and 3), obtaining a relay transmission method capable of maximizing the safe transmission speed through solution of the established optimization problem, wherein the method comprises two parts of power distribution and codebook rate design. According to the method, under the condition that the specific locations of the eavesdropping users are unknown, the communication reliability and safety are taken into comprehensive consideration, the safe interruption probability constraint is satisfied, and moreover, the safe transmission speed is maximized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
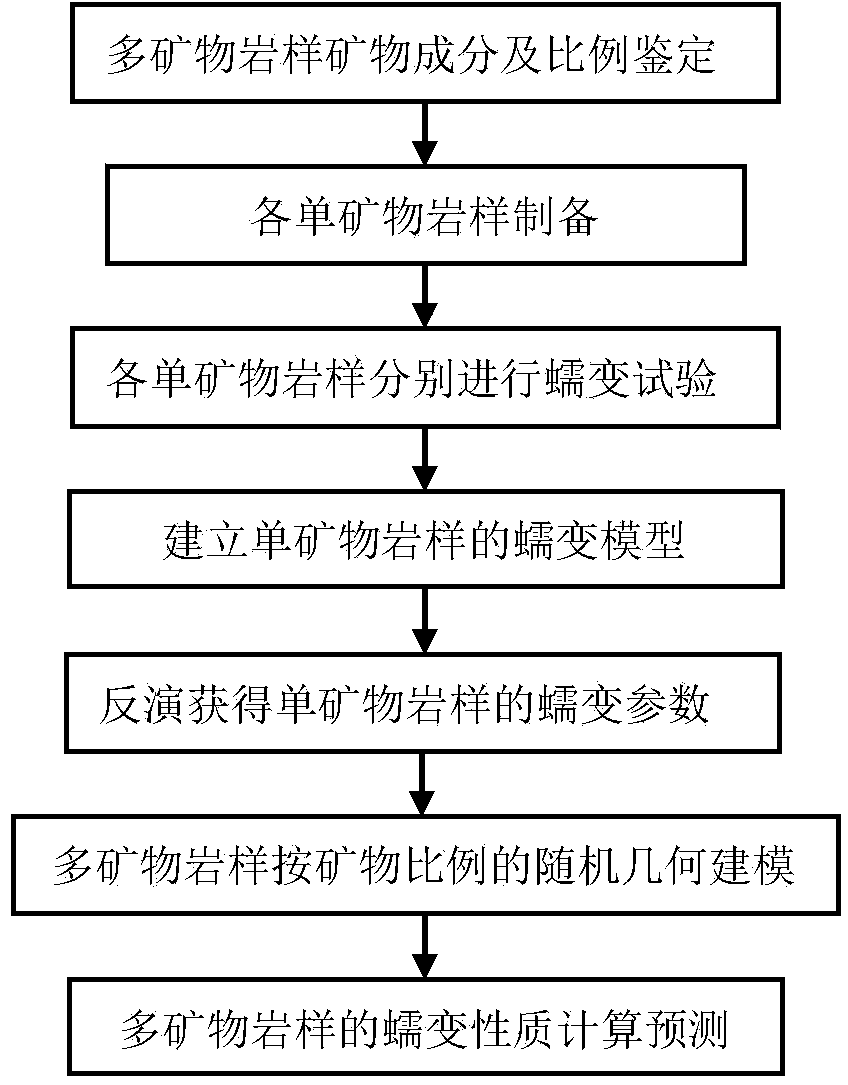
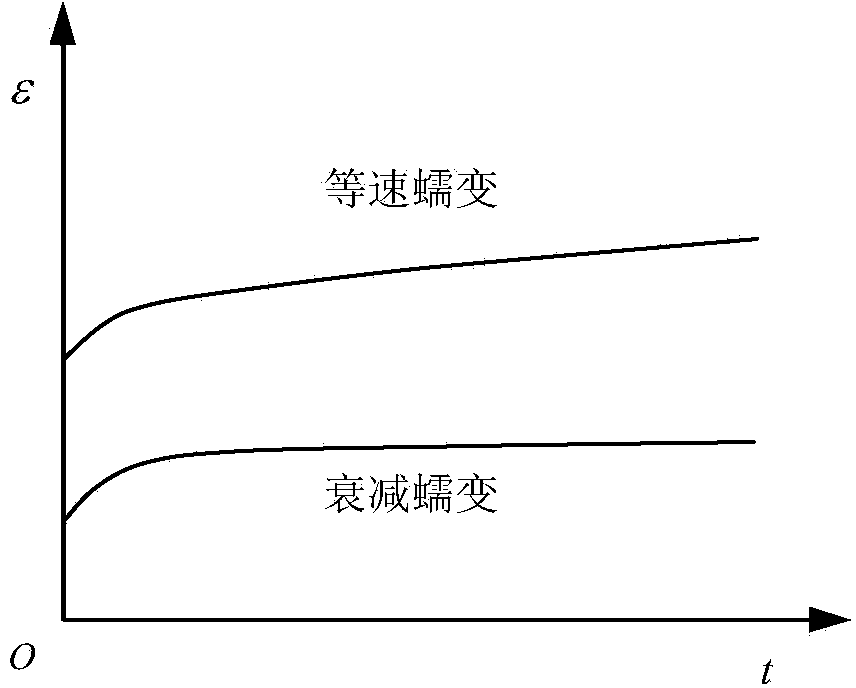
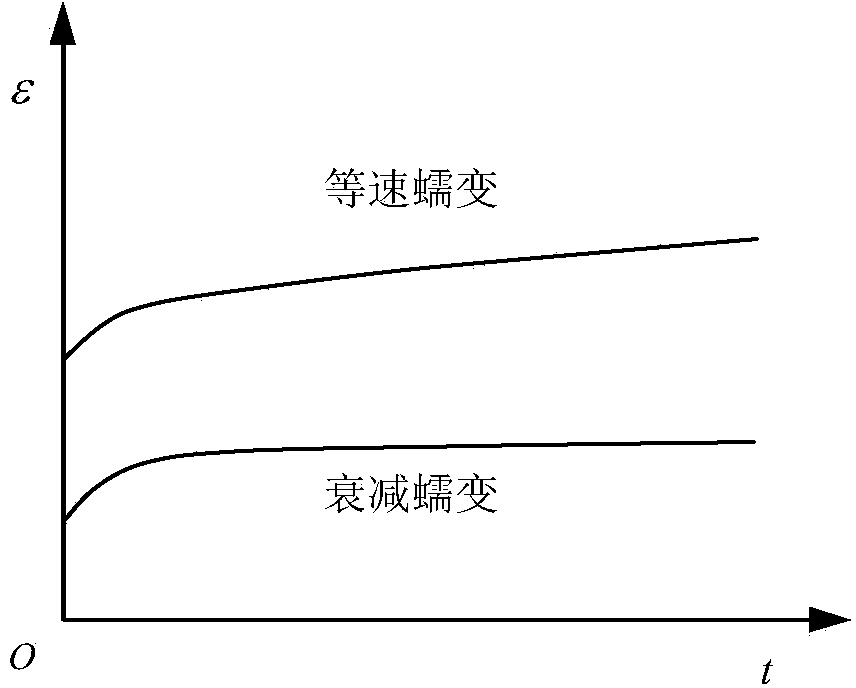
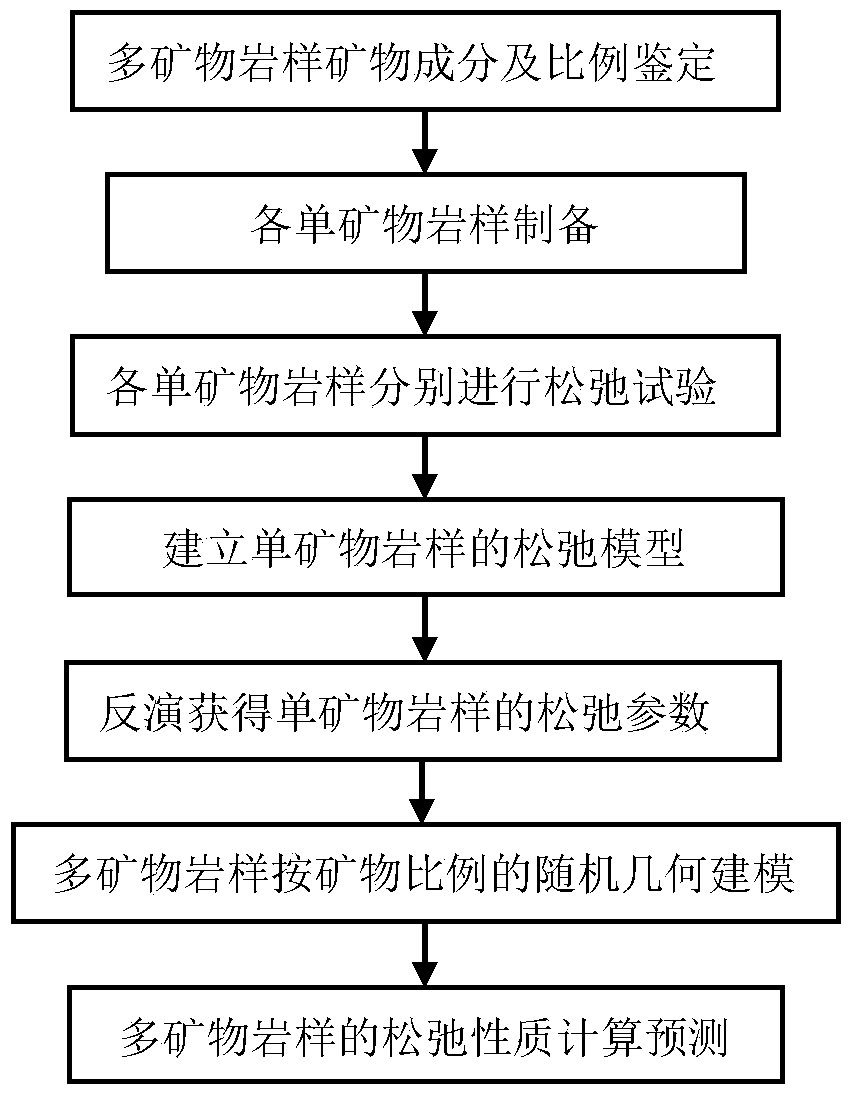
Mesoscopic structure simulation based rock creep property forecasting method
The invention belongs to the field of geotechnical engineering and particularly relates to a mesoscopic structure simulation based rock creep property forecasting method. The mesoscopic structure simulation based rock creep property forecasting method comprises the following steps of (1) identifying mineral components and proportions of multiple mineral rock samples; (2) preparing each single mineral rock sample; (3) respectively carrying out a creep experiment on each single mineral rock sample; (4) establishing a creep model of each single mineral rock sample; (5) inverting to obtain a creep parameter of each single mineral rock sample; (6) carrying out random geometric modeling on the multiple mineral rock samples according to the mineral components and the proportions; and (7) calculating and forecasting the creep properties of the multiple mineral rock samples. By using the structure simulation based rock creep property forecasting method, the practical mineral component condition of a practical engineering rock mass can be simulated in a laboratory or other places, so that the application range of the mesoscopic structure simulation based rock creep property forecasting method is wide.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
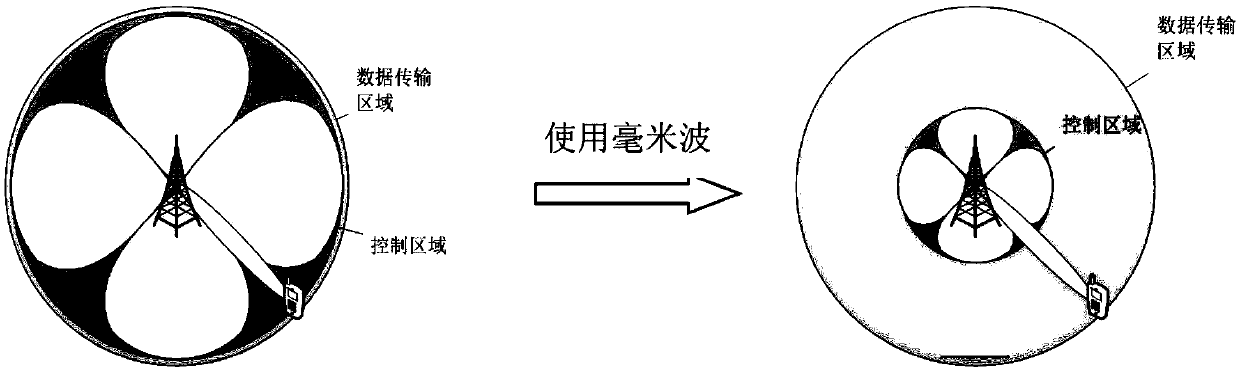
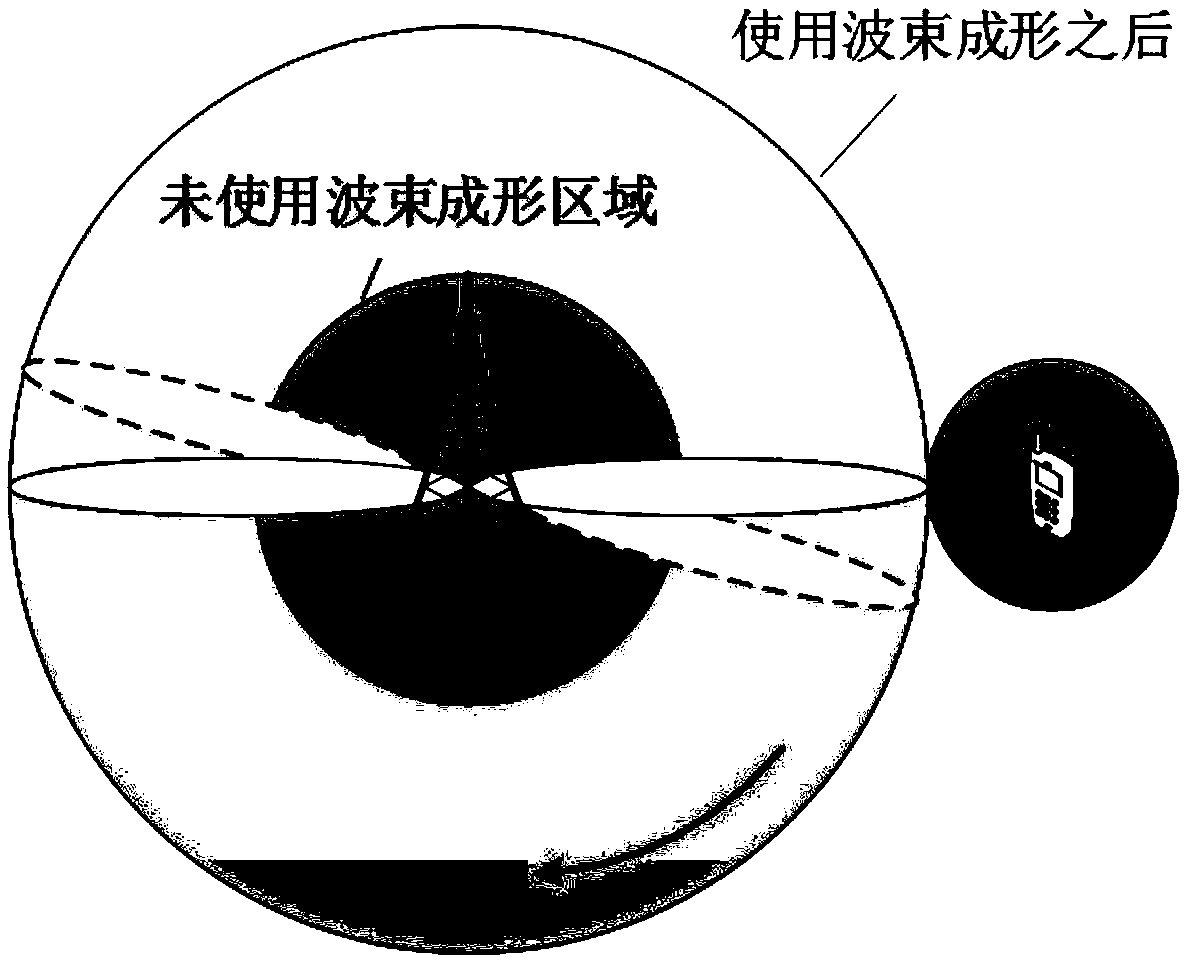
Beam optimization method based on user discovery stage in millimeter wave system
ActiveCN108964736AImprove performanceMaximum system capacitySpatial transmit diversityNetwork planningMillimeter wave communication systemsSystem capacity
The invention discloses a beam optimization method based on a user discovery stage in a millimeter wave system, comprising: modeling a millimeter wave communication system by adopting a random geometric method, and determining a path loss of the millimeter wave communication system and a beamforming gain model to obtain a receiving signal of the millimeter wave communication system; establishing coverage and capacity expressions of the millimeter wave communication system, comparing and analyzing the coverage performance of the system without considering interference and noise; determining therelationship between the capacity of the millimeter wave communication system and the search delay with the beam width as the intermediate quantity, optimizing the beam width to obtain the optimal system performance; using the beamforming technique in the user discovery phase of the millimeter wave to obtain the optimal beam width, and scanning the entire beam space for user search. By optimizingthe scanning beam width of the user discovery phase of the millimeter wave system, the invention solves the problem of the balance between the search delay and the system capacity, and obtains the optimal system performance, thereby saving the cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method to model vehicular communication networks as random geometric graphs
A method for generating mathematical analysis of a communication protocol in a vehicular communications network. The method defines features of a vehicular network, which may include a graph of a street map within a geographic area. A random geometric graph with a plurality of parameters is generated. A plurality of communications protocols on the vehicular network are defined. A communication protocol over the random geometric graph is redefined. A communication protocol's basic properties and associated features on the random geometric graph are analyzed. Results of the analysis are generated. The results of the analysis based on the random geometric graph's parameters are translated into results based on the vehicular network features. The random geometric graph with the parameters are displayed. The parameters may include: a number of graph nodes; and a probability that any two nodes are communicably connected being expressed as a function of the vehicular network features.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Energy-saving optimizing method for isomerous honeycomb wireless network
ActiveCN104735760AOptimal joint dormancy probabilityGuaranteed service qualityPower managementHigh level techniquesS distributionMacro base stations
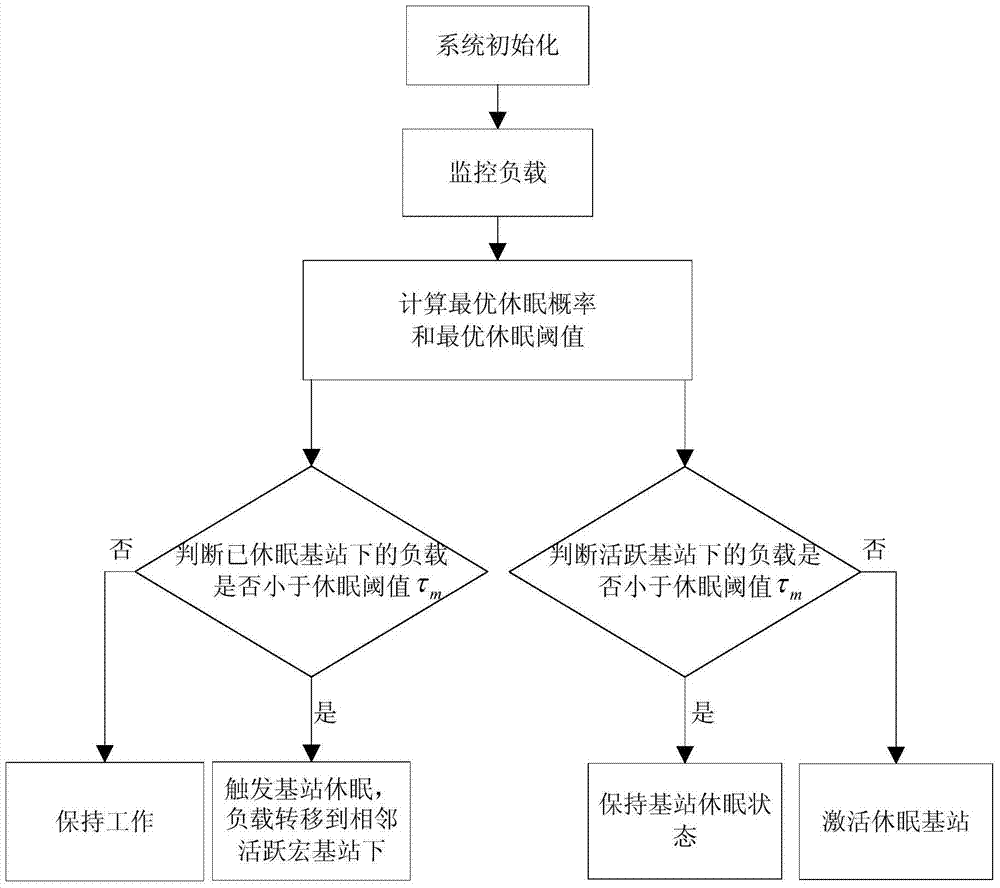
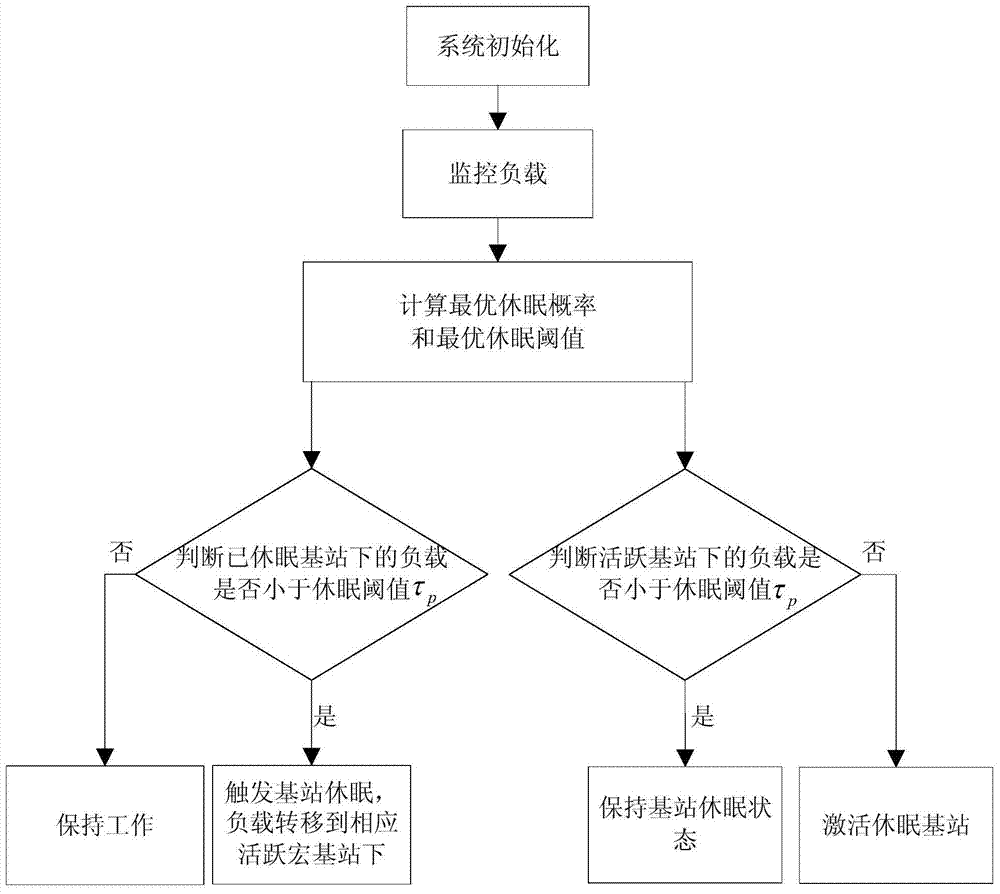
The invention relates to an energy-saving optimizing method for an isomerous honeycomb wireless network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The energy-saving optimizing method comprises the following steps of proposing an objective function with maximum energy efficiency through a poisson's distribution designed network model in a random geometry; optimizing the probability density of macro base stations and micro base stations by a method of solving an extreme value by using an advanced algebra multivariate function according to the objective function; calculating an optimal dormancy load threshold value of the macro base stations and an optimal dormancy load threshold value of the micro base stations according to the knowledge of a probability theory; and designing a dormancy strategy of the base stations according to the threshold values. By the energy-saving optimizing method, energy can be saved while the service quality of the network is guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
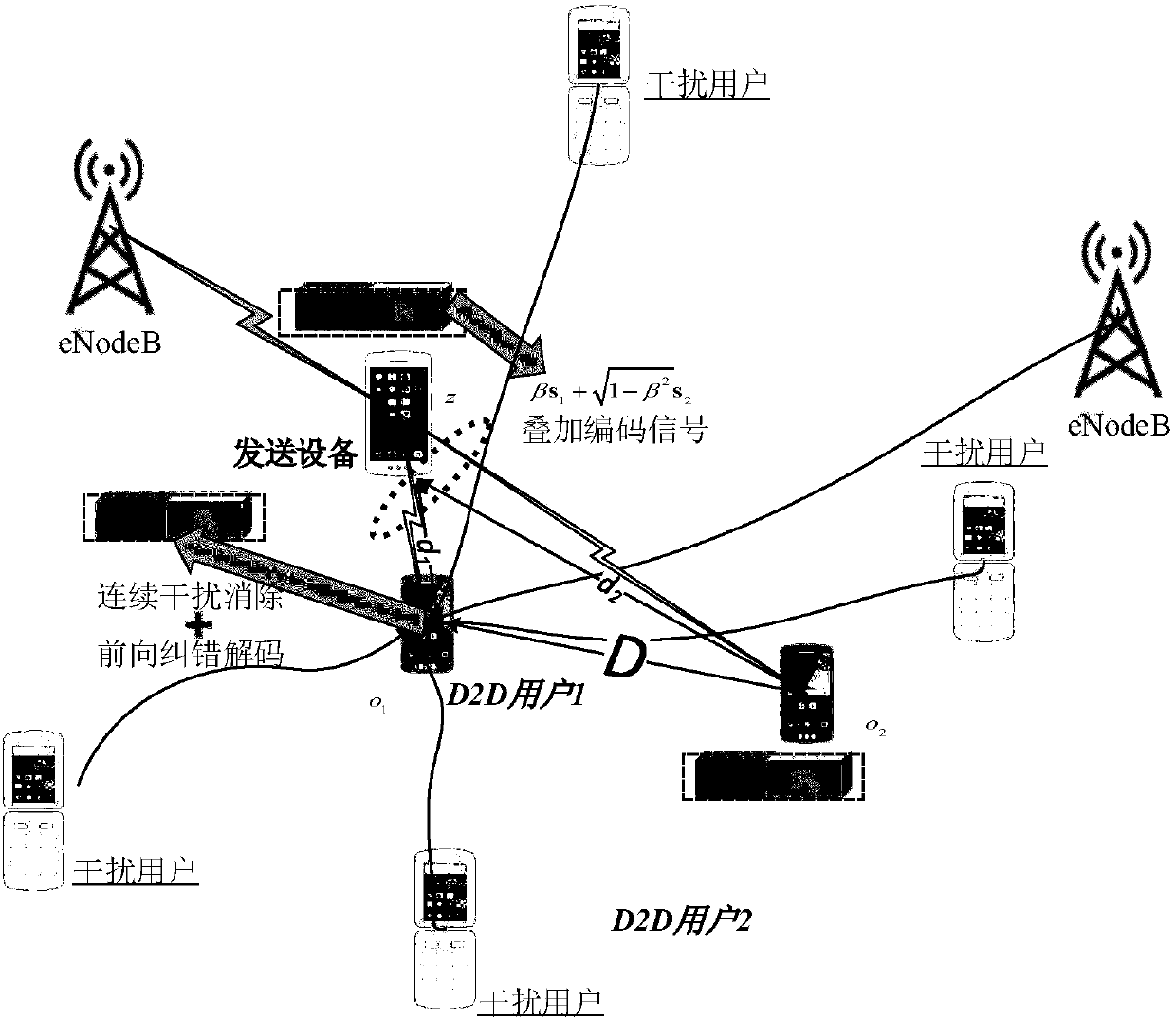
Large-scale D2D communication method based on HARQ assisted NOMA
ActiveCN108600997AImprove spectral efficiencyPower managementError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency spectrumNon orthogonal
The invention discloses a large-scale D2D communication method based on an HARQ assisted NOMA. The method comprises the steps of firstly using a random geometric method to analyze the influence of superimposed interference in a D2D network on an outage probability; then deducing a specific expression of spectrum efficiency by using a relation between the outage probability and the spectrum efficiency; and at last building a resource distribution optimization problem based on theoretical analysis results: by reasonably setting the information transmission rates of different D2D users, even occupying the distribution density of the D2D terminal having the same time frequency resources, the spectrum efficiency (throughput capacity or spatial spectrum utilization rate) is maximized and meanwhile the communication reliability is ensured. Simulation and numerical results show that the outage probability of the collaborative application scheme provided by the invention is reduced by 23% thanthat of the non-collaborative mode; in addition, the spectrum efficiency of the method using the non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) technology is improved by 17% than that using the orthogonal multiple access (OMA) technology.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
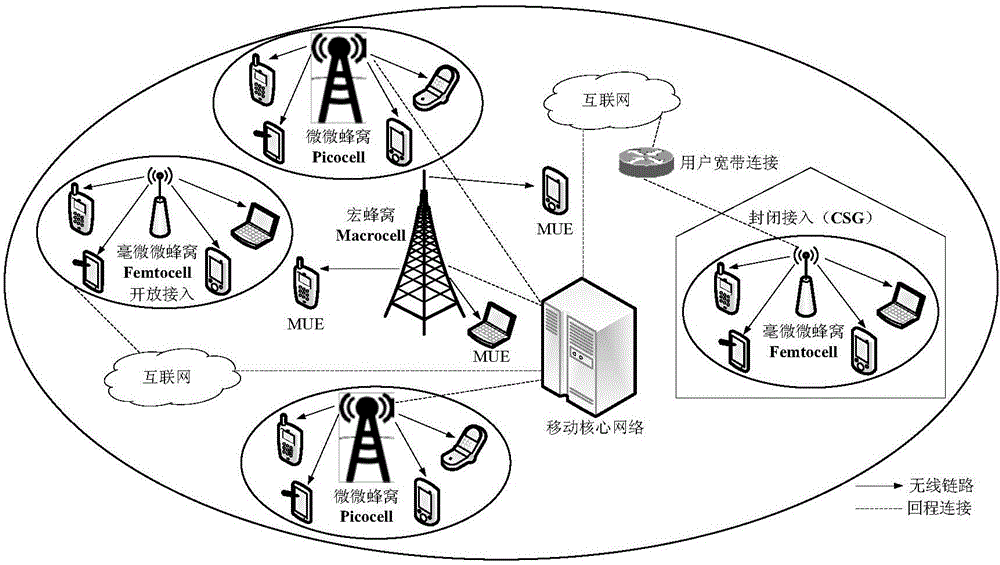
Method for acquiring Femtocell coverage probability
The invention discloses a method for acquiring Femtocell coverage probability. The method comprises that the position of a Femtocell station is modeled to be random and complies with Poisson point distribution, and the coverage probability is calculated according to the position of a macro cell where the Femtocell station is located on this basis. As a random geometry mathematical analysis tool is adopted in the calculating process and influences imposed on the coverage performance by environmental factors are considered, so that the method can acquire the Femtocell coverage probability more accurately, thereby providing an effective and accurate method for network coverage performance analysis and comparison.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Energy-saving base station dormant method for heterogeneous cellular network
ActiveCN104581904ATransmit power changeOutage Probability ChangePower managementHigh level techniquesTransmitted powerMicrocell
The invention provides an energy-saving base station dormant method for a heterogeneous cellular network. An optimal base station dormant scheme is adopted according to the outage probability of a system and uplink transmitting power of a user. Macrocells, microcells and picocells are deployed in the poisson point process in a three-layer heterogeneous cellular network scene, and the outrage probability of the system and the uplink transmitting power of the user are derived according to a random geometric theory; a system power consumption optimization problem is solved, a part of the macrocells start a dormant state, the microcells and the picocells are added, the transmitting power of the macrocells is adjusted, and accordingly, the maximum system power consumption gain is obtained.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Method for automatically detecting remote sensing ground object target based on stochastic geometry model
InactiveCN103218598AReduce the impact of universalityImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmRemote sensing
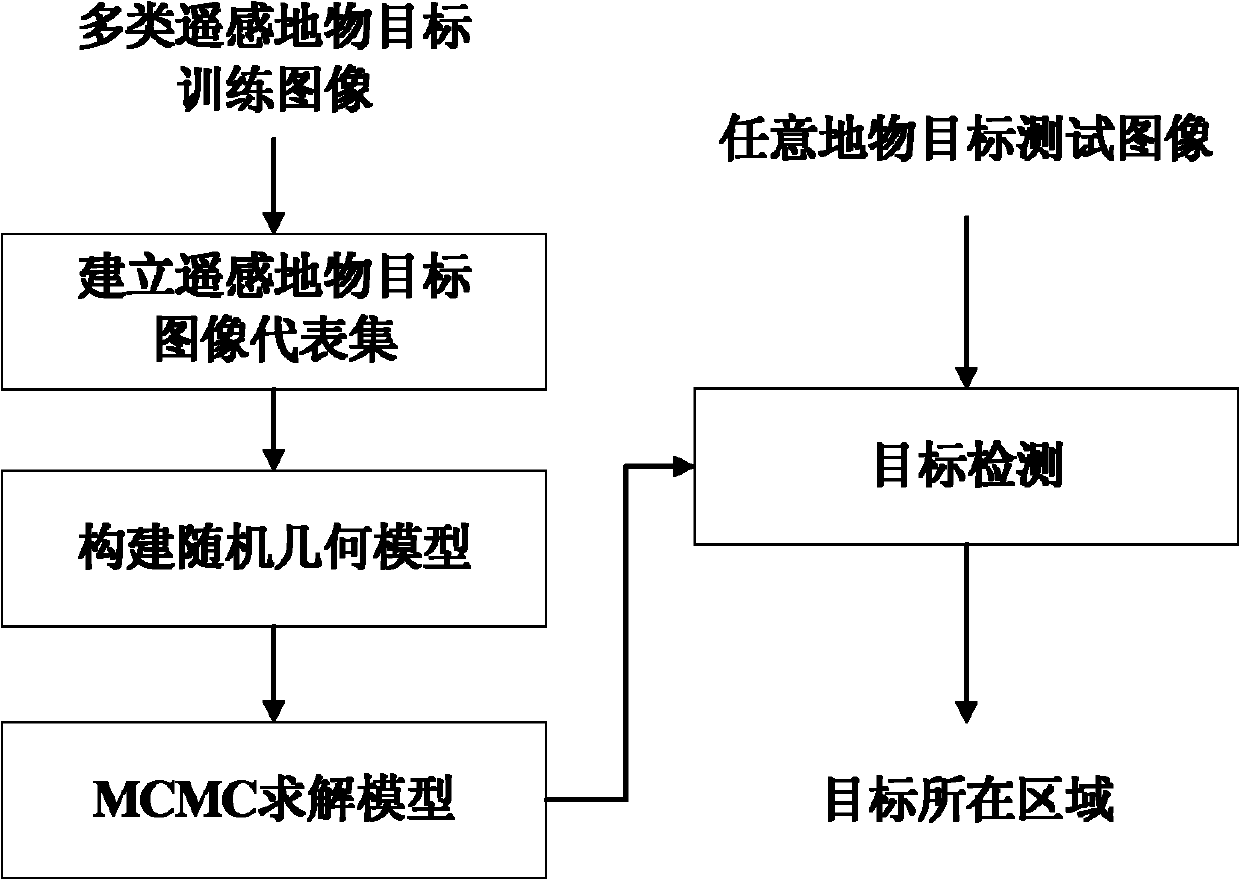
The invention provides a method for automatically detecting a remote sensing ground object target based on a stochastic geometry model. The method solves the automatic detection problem of a target with a relatively complex structure but relatively singular geometric component features in a remote sensing image. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a plurality of classes of image representative sets comprising the remote sensing ground object target; constructing the stochastic geometry model aiming at a target to be processed by taking geometric components for forming the target as processing units; after constructing the stochastic geometry model of the target components, converting the automatic detection problem of the target into an optimal configuration problem of a stochastic target seeking process; estimating the maximum value of the non-parameter probability density by using a Markov chain Monte Carlo method; and finally, detecting the target by using the stochastic geometry model, judging whether the target exists in the tested image or not, ending and outputting a result that no target exists if no target exists, and processing the image by using the stochastic geometry model to obtain the detection result corresponding to optimal configuration and outputting the final detection position of the target if the target exists.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
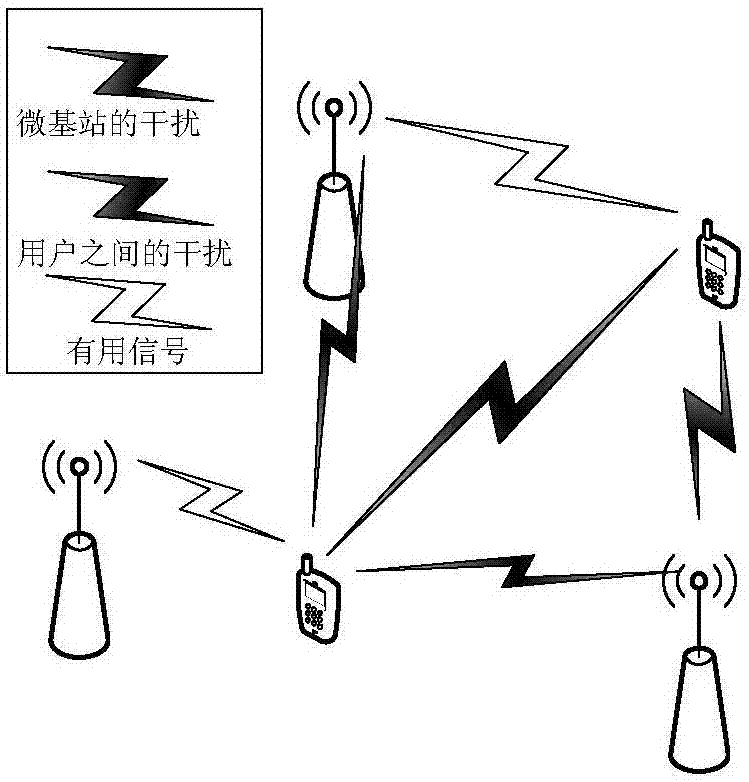
Cluster-based interference alignment method for two-layer network
ActiveCN106788812AEliminate cross-layer interferenceReduce cross-layer interferenceBaseband system detailsTransmission monitoringInterference eliminationCommunications system
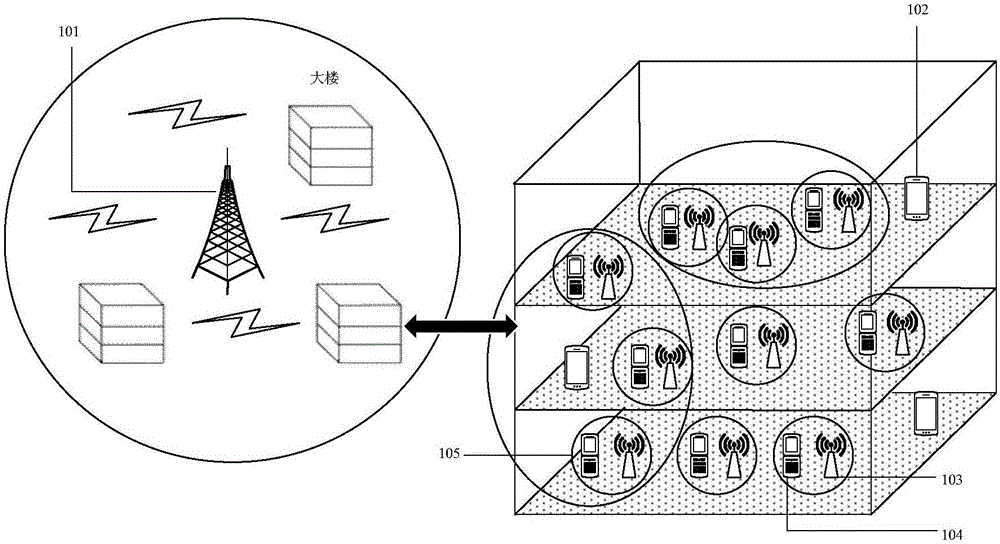
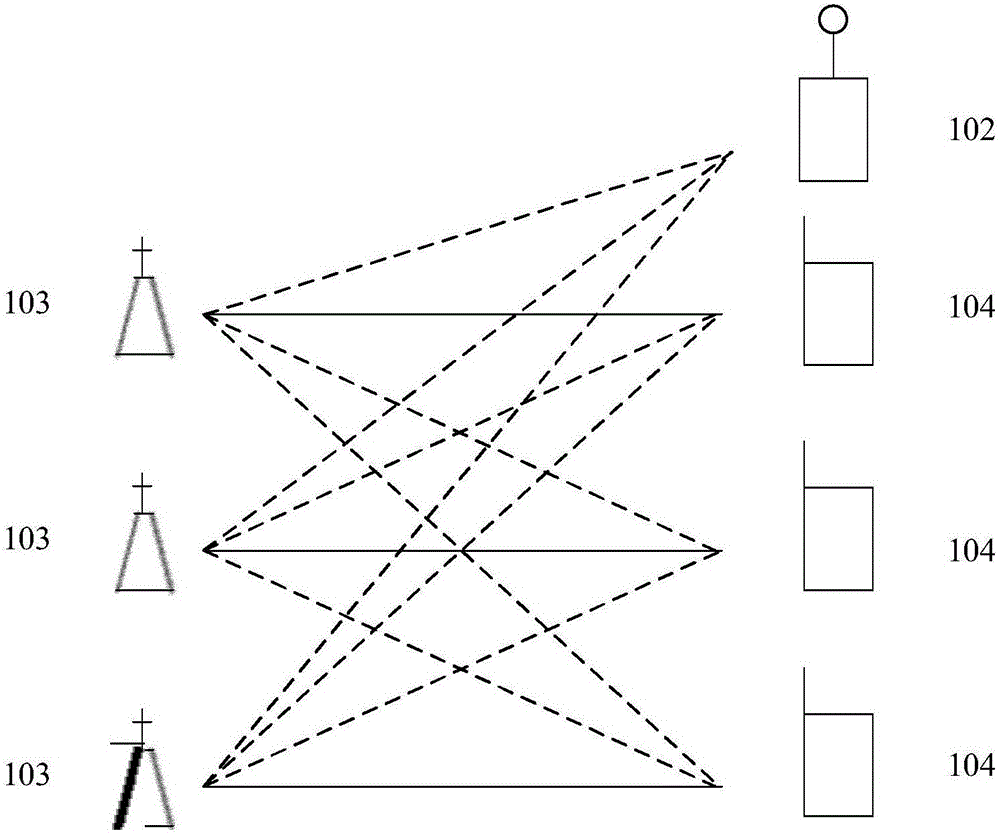
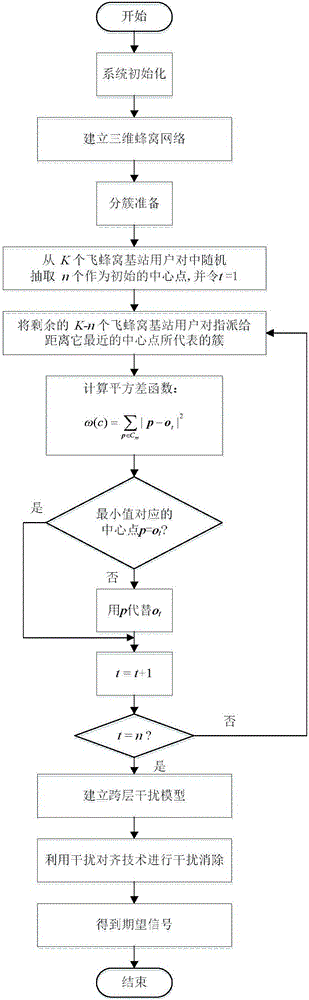
The invention discloses a cluster-based interference alignment method for a two-layer network. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, modeling the two-layer network based on stochastic geometry, then clustering femtocell base stations and users, and finally eliminating interference by using an interference alignment technology. A three-dimensional femtocell network structure model, particularly, a femtocell network model conforming to three-dimensional Poisson point process distribution, is close to the actual interference scene. Femtocell base stations and users are clustered according to the principle of square error function decrease, and cross-layer interference of macrocell users and each cluster and inter-cluster interference in a femtocell layer are finally eliminated by using the interference alignment technology, so that the complexity of interference management is reduced, and the method is applicable to actual communication systems.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Automatic detecting method of remote sensing ground object target based on random geometric model
InactiveCN103150566AReduce the impact of universalityImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingModel parameters
The invention discloses an automatic detecting method of a remote sensing ground object target based on a random geometric model and relates to the technique of image information processing. The method comprises the steps of establishing an image representation set of a multiclass remote sensing ground object target, choosing geometric parts of the ground object target as a processing unit, using prior knowledge that the characteristic of various geometric parts is single, relativity of parts of the same kind is big and the like, building the random geometric model for a combining way of the target and the parts, adopting the MCMC method to estimate a maximum of nonparametric probability density, obtaining a model parameter, and guiding the automatic detecting and positioning of the target from up down. The method can overcome the influence of part information loss of the target on the detecting result and reduce the universality influence of between-class difference among the target on the detecting method. The method has a good robustness and utility to the automatic detecting of the target with a relatively complex structure and the target (such as a plane and a ship) of a relatively single geometric part characteristic in a remote sensing image.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
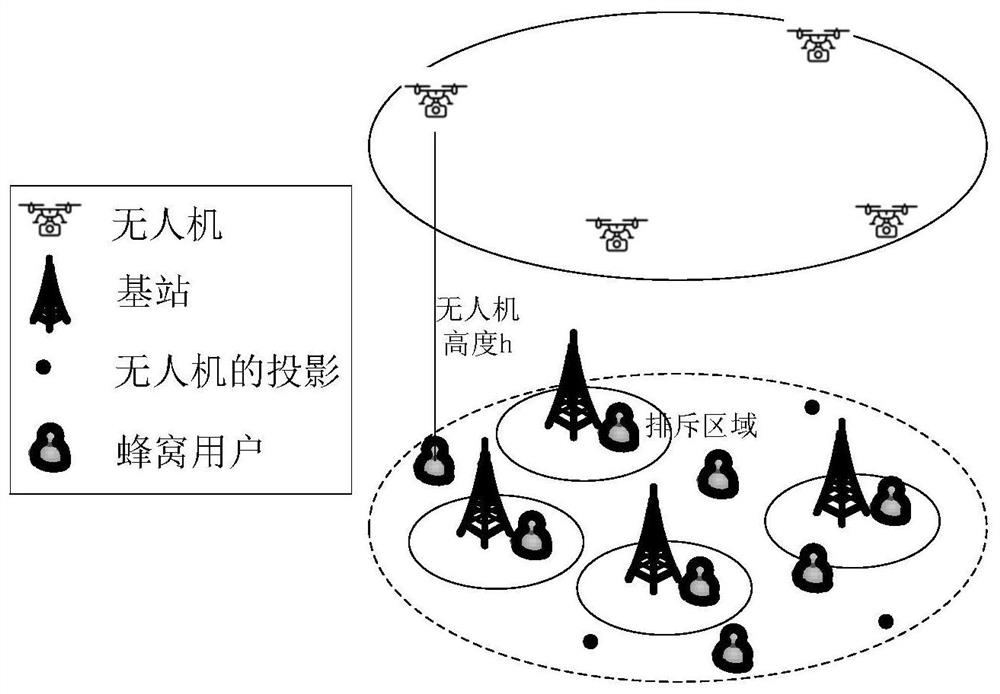
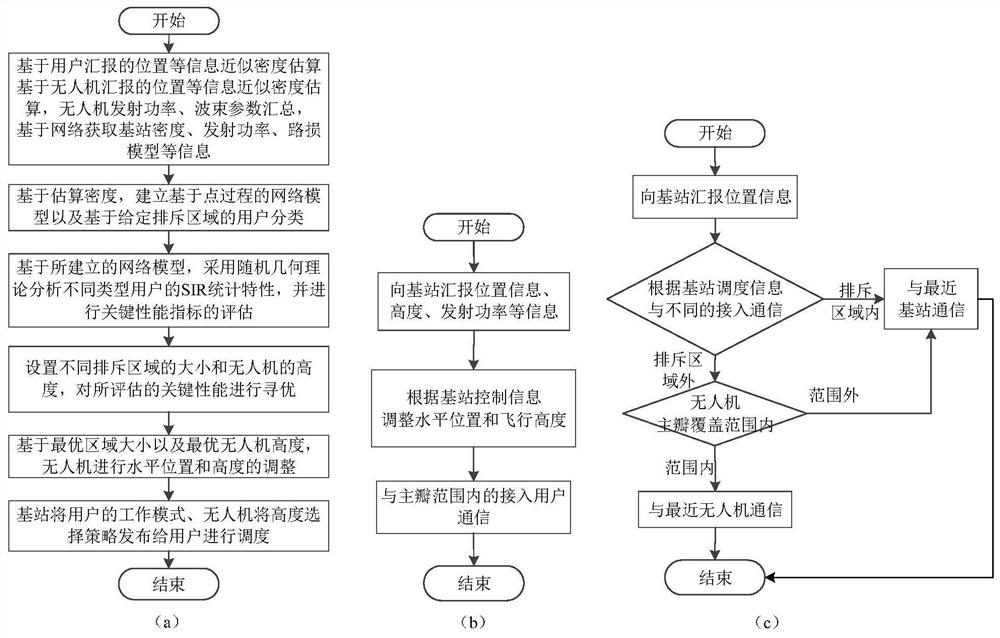
Unmanned aerial vehicle deployment method in unmanned aerial vehicle assisted cellular network
ActiveCN112672376AImprove communication performanceReduce the burden onNetwork planningHigh level techniquesInterference (communication)Simulation
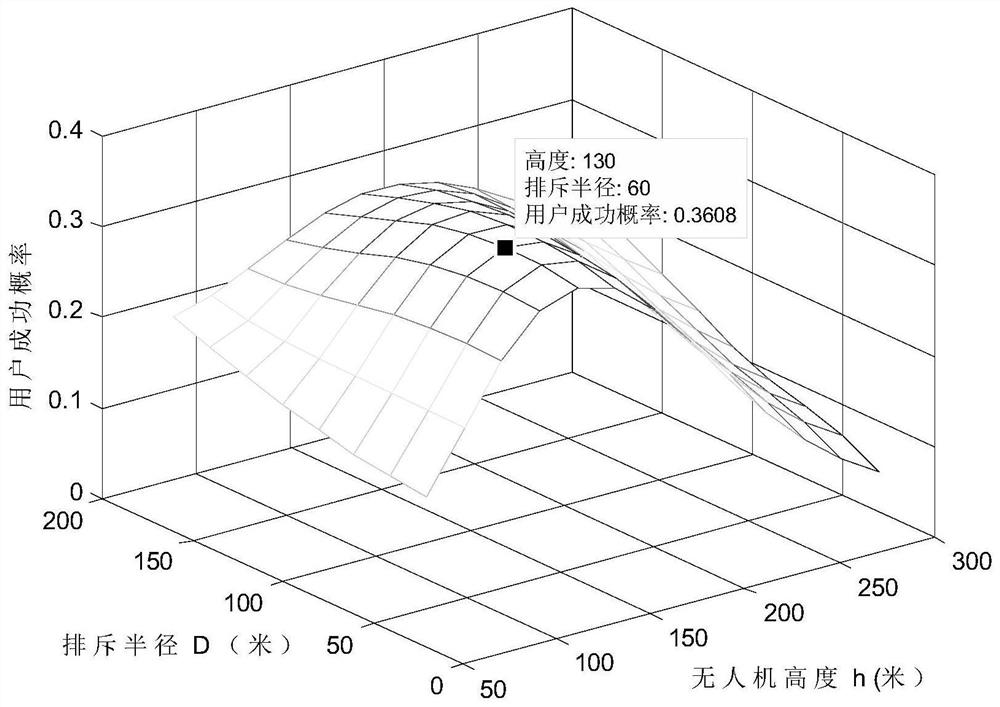
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle deployment method in an unmanned aerial vehicle assisted cellular network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the steps of: enabling a base station to collect information according to different information sources, and establishing a probabilistic sight distance transmission model according to the collected information; secondly, selecting unmanned aerial vehicle deployment scheme parameters and user classification; thirdly, based on the model and the proposed unmanned aerial vehicle deployment and user access method, selecting a key performance index according to a specific scene and demand; evaluating the selected key performance indexes of the three types of users by adopting an analysis method of a random geometry theory in a given group of parameter settings; after multiple sets of parameter settings are evaluated, searching the size of the optimal repulsion area and the optimal unmanned aerial vehicle height; and finally, implementing an unmanned aerial vehicle deployment scheme. The interference suppression and evaluation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and universality, can remarkably reduce signaling overhead and system complexity, is transparent for users, does not need the users to carry out additional measurement and report, and reduces the burden of the users.
Numerical method of calculating heat, mass, chemical and electric transport for three-dimensional porous solid
ActiveUS20120150510A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPetrographic thin sectionMorphometric analysis
This invention relates to a method of estimating fluxes for the processes of matter and field transport through fluid-saturated or gas-saturated porous solid. The method comprises obtaining three-dimensional porous solid images by, but not limited, X-ray microtomography, 3D NMR imaging, 3D reconstruction from petrographic thin-section analysis etc., digital processing and morphological analysis of the 3D core images by consecutive application of the image filtering, segmentation and multiple property recognition for obtaining digital 3D models of porous solid samples and performing a set of morphological and geometrical statistical property analysis. For the above mentioned 3D model (models) heat, mass, chemical and electric fluxes are modeled (separately or in combination) under given boundary conditions by means of numerical solver. The new models, which are statistically equivalent to the abovementioned model (models) are generated by means of random field and stochastic geometry theory; heat, mass, chemical and electric fluxes are simulated for new models. The obtained fluxes are averaged over realizations to be used in macroscopic calculations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
A power control method for heterogeneous network uplink
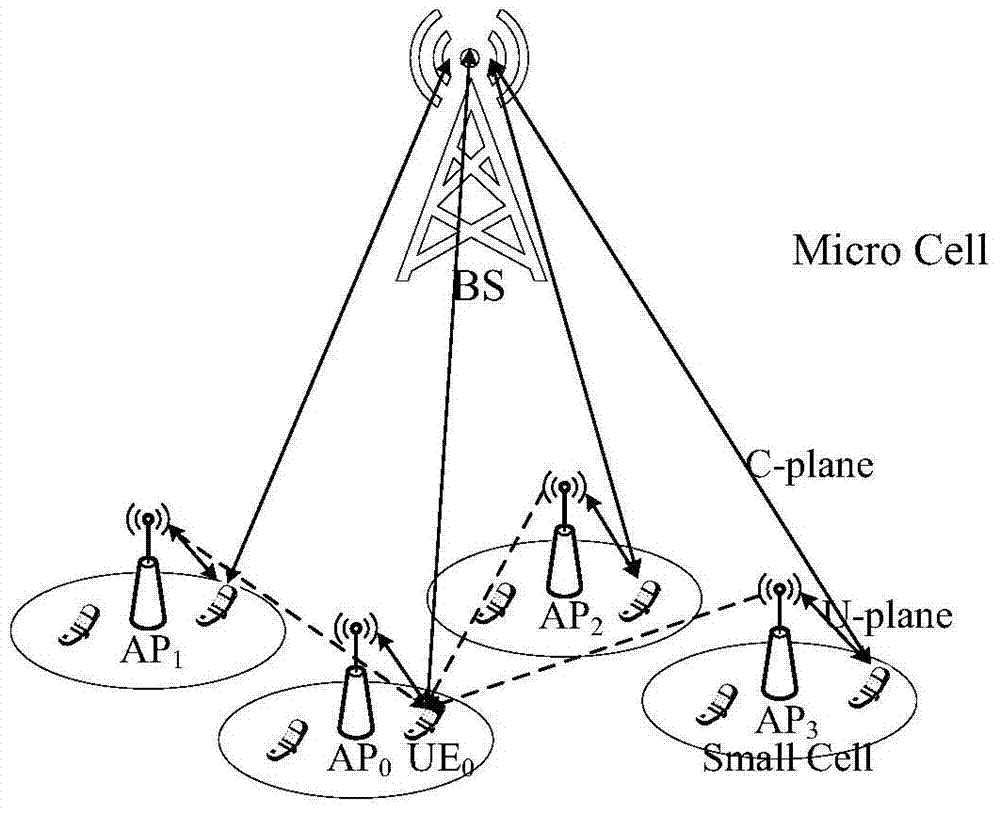
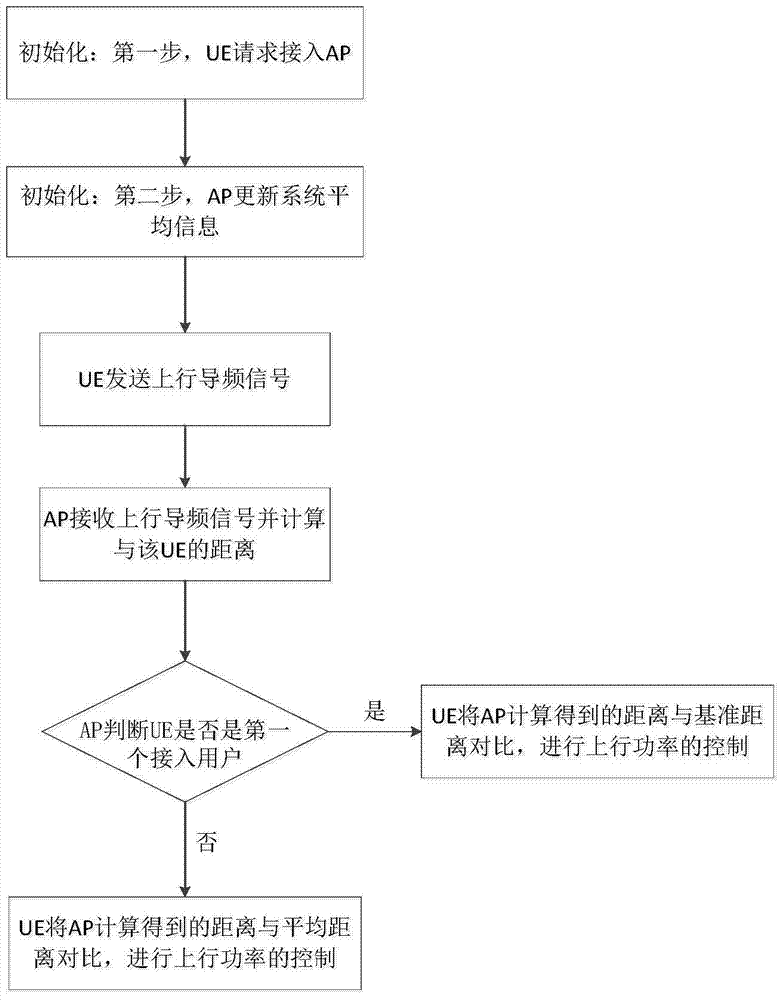
InactiveCN104853425AIncrease transfer rateAverage transfer rate optimizationPower managementHeterogeneous networkSmall cell
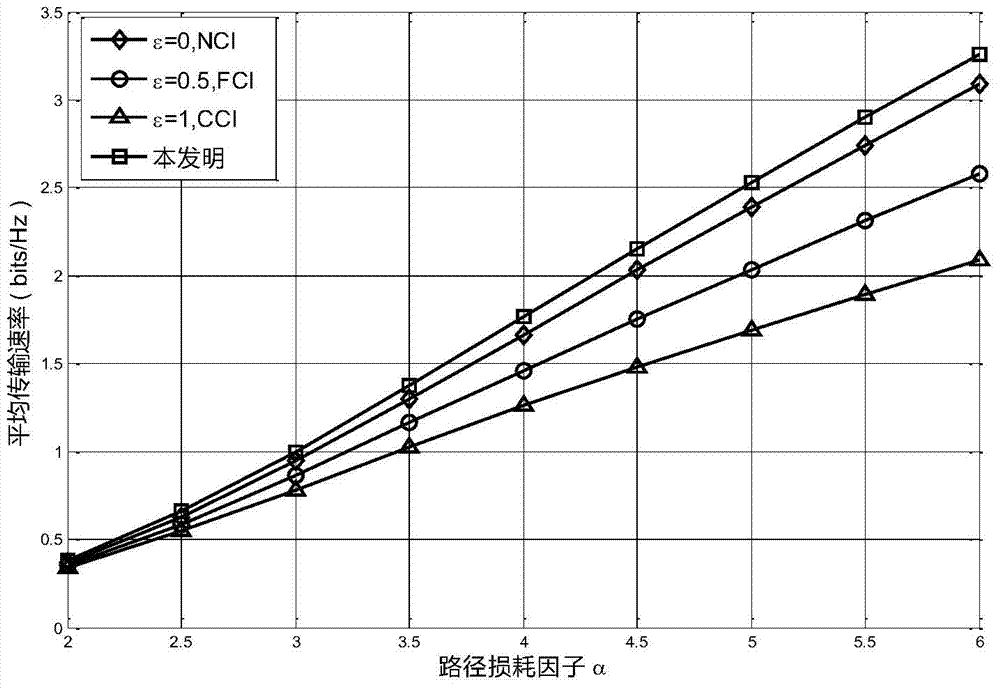
The present invention discloses a power control method for the heterogeneous network (HetNet) uplink. The method includes: firstly, a distance between user equipment (UE) and a corresponding access point (AP) is determined, i.e., the UE sends an uplink pilot signal to the corresponding AP, and the AP receives the uplink pilot signal and determines the distance between the UE and the corresponding AP according to the path loss of the pilot signal; and users at different distances from the AP are provided with different uplink powers in a same small cell, wherein the uplink power decreases with the increment of the distance according to a power function, i.e., the closer the user is to the AP, the greater the transmission uplink power is. The positions of the AP and UE in the present invention are separately modeled as two independent homogeneous Poisson's point distribution (PPP distribution), and the performance of the system is studied via random geometry. The analysis of the simulation result proves that, compared with the conventional power control strategy, the method of the present invention optimizes the energy efficiency to a certain degree while increasing the average transmission rate, thereby effectively improving the performance of the entire system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Meso-structure simulation based concrete creeping property prediction method
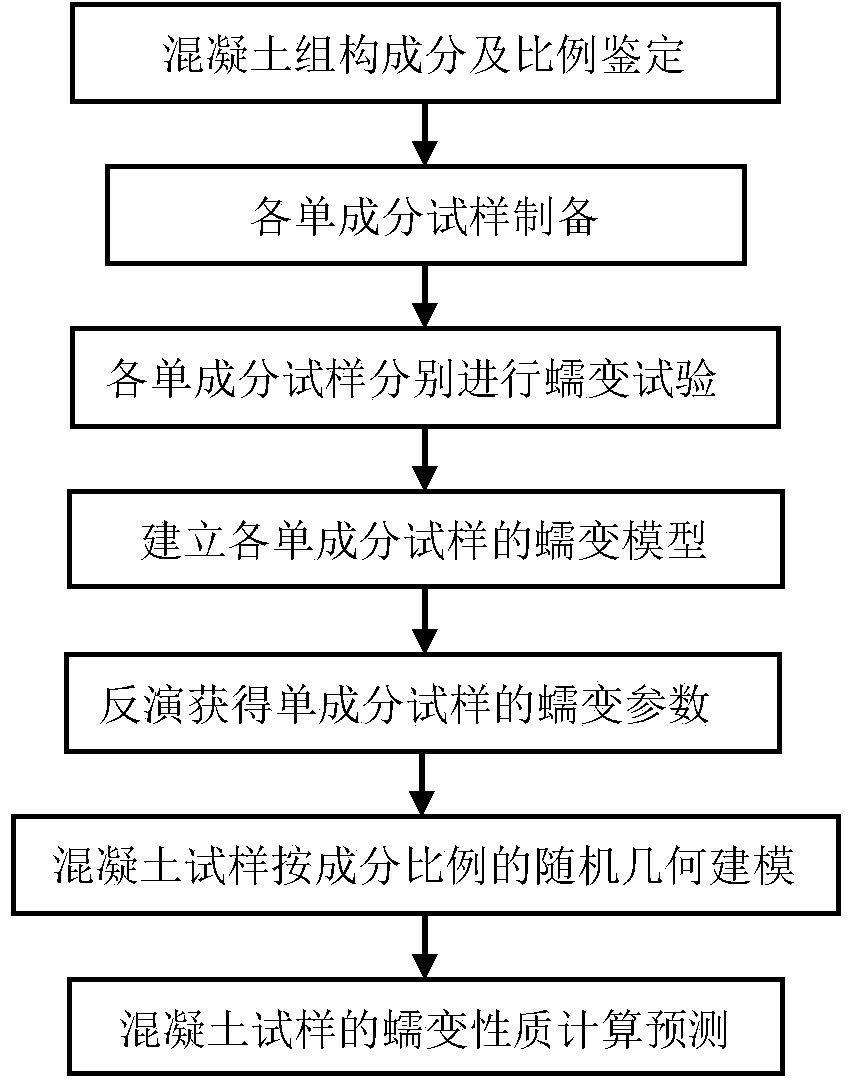
InactiveCN104298874APreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesGeometric modelingSimulation based
The invention belongs to the field of civil engineering and particularly relates to a meso-structure simulation based concrete creeping property prediction method. The meso-structure simulation based concrete creeping property prediction method comprises the following steps of 1 identifying concrete structure constituents and proportions; 2 preparing single-constituent samples; 3 respectively performing creep tests on the single-constituent samples; 4 establishing creep models on the single-constituent samples; 5 performing inversion to obtain creep parameters of the single-constituent samples; 6 conducting random geometric modeling on a concrete sample according to the constituents and proportions; 7 calculating and predicting the creeping property of the concrete sample. The meso-structure simulation based concrete creeping property prediction method can simulate the constitution situation of actual constituents of an actual concrete work, is not limited in laboratories and is wide in application range.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Wireless virtual mapping method in consideration of inter-cell interference under ultra-dense environment
ActiveCN107454601AReduce distractionsImprove throughputNetwork planningInterference ratioEngineering
The invention discloses a wireless virtual mapping method in consideration of inter-cell interference under an ultra-dense environment. The method comprises modeling a ultra-dense network by using a random geometric Poisson point process, determining a channel and interference model through a network model, then virtualizing a wireless frequency resources, and dividing the frequency of a spectrum resource by using a wireless network mapping method so that the receiving signal-to-interference ratio of a user is guaranteed, interference is reduced, the throughput of the entire system is improved. On one hand, the spectrum allocation method in the present invention has a good theoretical performance guarantee; on the other hand, the wireless virtual mapping method is beneficial to implementation and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for calculating lower bound of transmission capacity of mine laneway wireless sensor network
InactiveCN103546910AImprove transmission capacityGuarantee safety production monitoringNetwork topologiesAviationPotential accident
The invention discloses a method for calculating a lower bound of transmission capacity of a mine laneway wireless sensor network. Based on the stochastic theory, a two-dimensional cluster model and a lognormal channel model suitable for the mine laneway wireless sensor network are established, a Palm distribution mode in the stochastic geometry is further adopted, a signal interference model suitable for the mine laneway wireless sensor network is established, the Campbell theorem and the Markov inequation are adopted, and therefore the method for calculating the lower bound of the transmission capacity of the mine laneway wireless sensor network is obtained. By means of the method for calculating the lower bound of the transmission capacity of the mine laneway wireless sensor network, the mine laneway wireless sensor network can be optimized, the communication interruption rate of the mine laneway wireless sensor network can be lowered, the transmission capacity of the wireless sensor network is improved, and therefore safe production monitoring of a coal mine are guaranteed, and potential accidents are reduced. The calculation method can be popularized in other fields using the wireless sensor network, such as aviation, aerospace, environmental monitoring and modern agriculture.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Spectrum-energy efficiency balance method for double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network based on stochastic geometry
ActiveCN106792738AExpand coverageIncrease capacityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumHeterogeneous network
The invention provides a spectrum-energy efficiency balance method for a double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network based on stochastic geometry. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing the double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network by using a Poisson point process in the stochastic geometry; step 2, obtaining a total system throughput based on a probability density function and a probability generation function of the Poisson point process; step 3, obtaining a relation among spectrum efficiency, energy efficiency and network density of the overall system from the definitions of spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency; and step 4, obtaining a relation closed expression between the spectrum efficiency and the energy efficiency via the optimization theory. The method has the advantages: 1) the network coverage is enlarged, and the network capacity is improved; and 2) the density of the network can be effectively changed to realize spectrum-energy efficiency balance of the system. Therefore, the method has better mobile user experience, and provides an effective reference for 5G honeycomb deployment.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
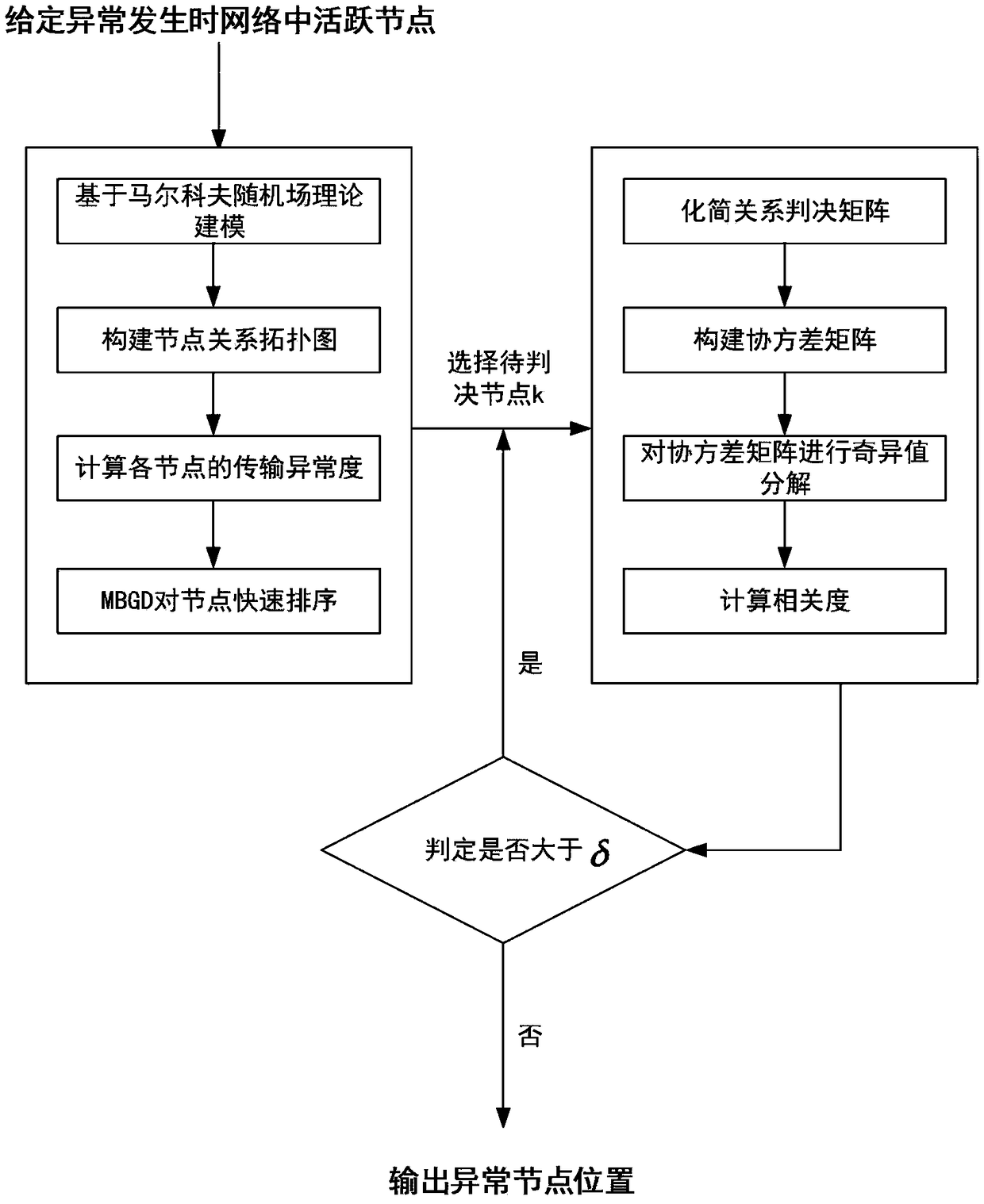
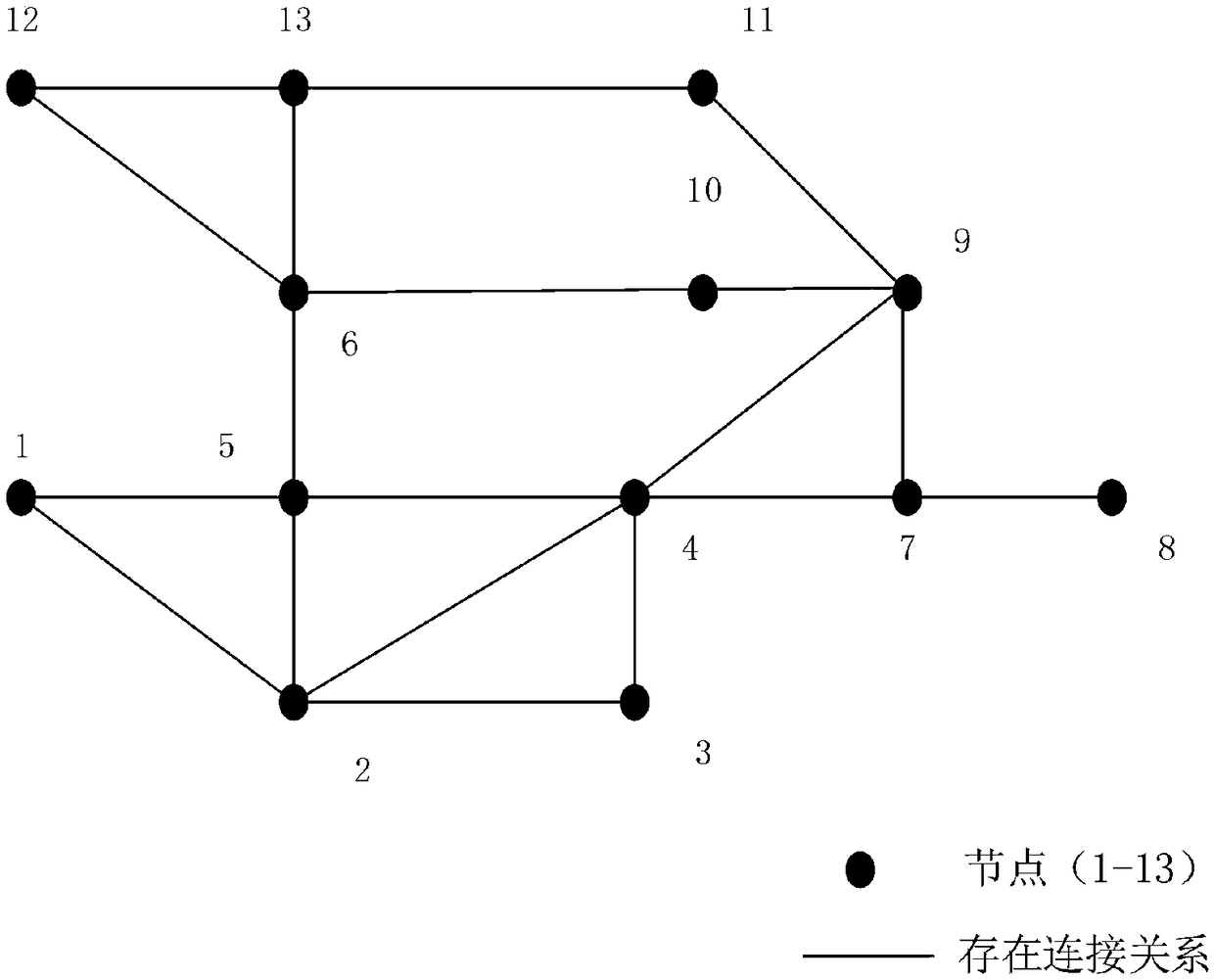
Random geometric data anomaly location method based on Markov random field theory
ActiveCN108768949ARapid positioningEliminate abnormal behavior in timeData processing applicationsData switching networksTopological graphAlgorithm
The invention relates to a random geometric data anomaly location method based on Markov random field theory. The random geometric data anomaly location method based on the Markov random field theorycomprises the following steps: establishing a power data network model based on the Markov random field theory, and constructing a corresponding node relationship topological graph; analyzing the topological difference degree of each node before and after the occurrence of the anomaly in the node relationship topological graph, and selecting anomaly nodes to be judged; and performing anomaly judgment on each suspected node to detect the anomaly node according to the correlation degree of a covariance matrix. By means of the random geometric data anomaly location method based on the Markov random field theory provided by the invention, the node location where the anomaly occurs in the power data network can be quickly located, and abnormal behaviors in the network can be eliminated in time;in addition, the random geometric data anomaly location method can effectively reduce the amount of computation required by the network anomaly location and reduce the additional load of the networkwhile ensuring the accuracy of location.
Owner:GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Geometric size probability statistics characteristic analysis method used in turbine disc probability reliability analysis
ActiveCN108920836AImprove computing efficiencyGuaranteed Stress ErrorGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputation processModel parameters
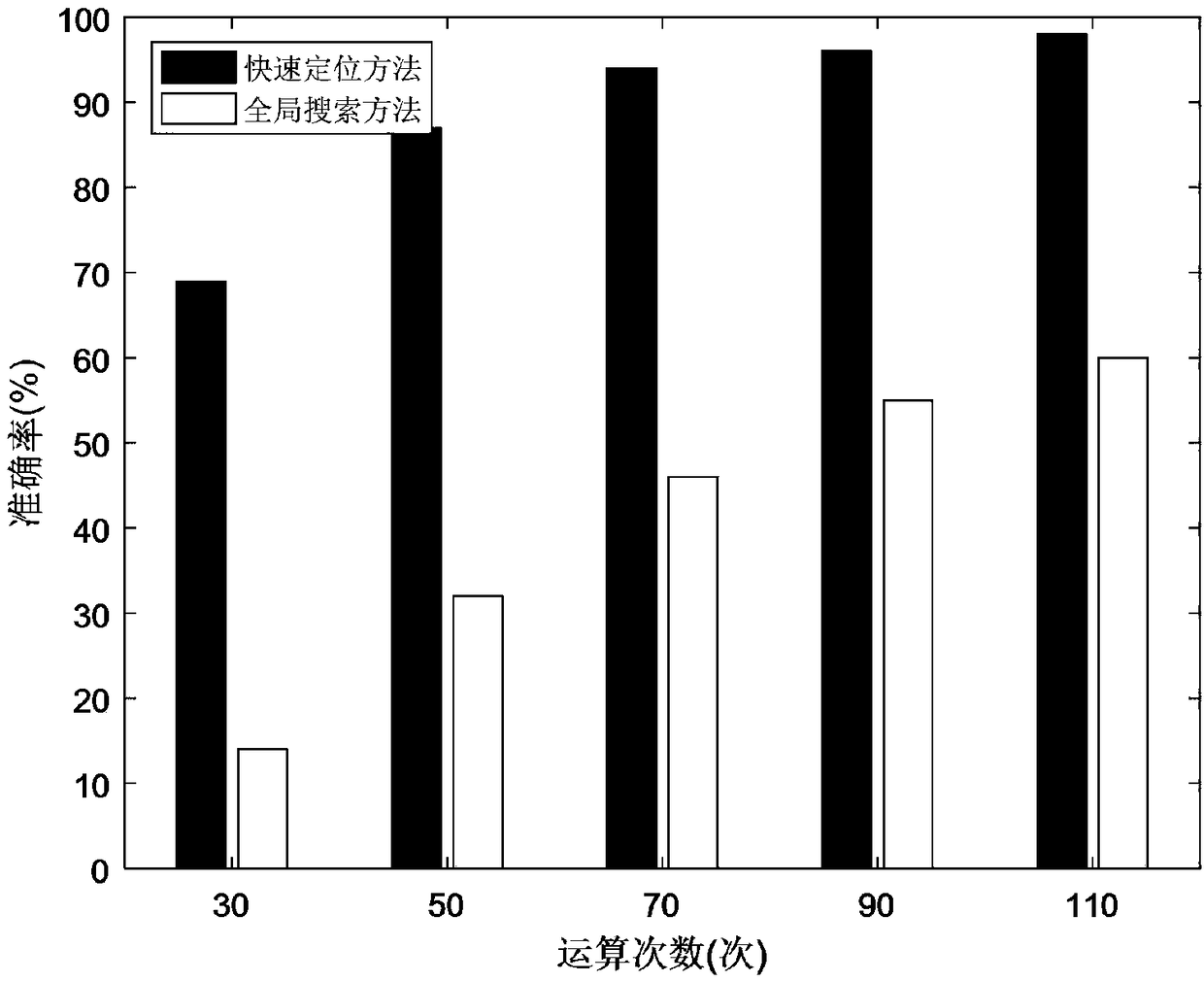
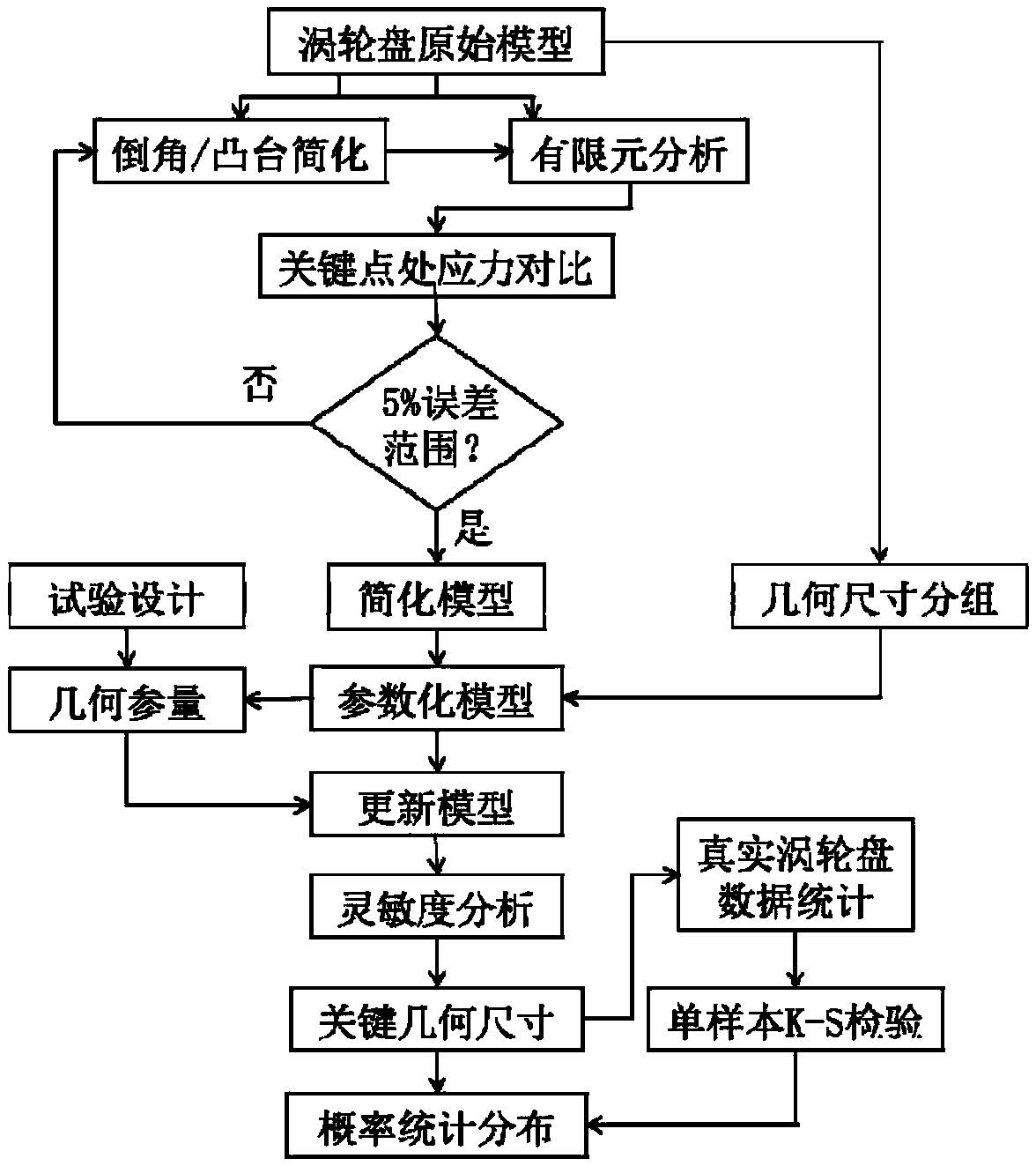
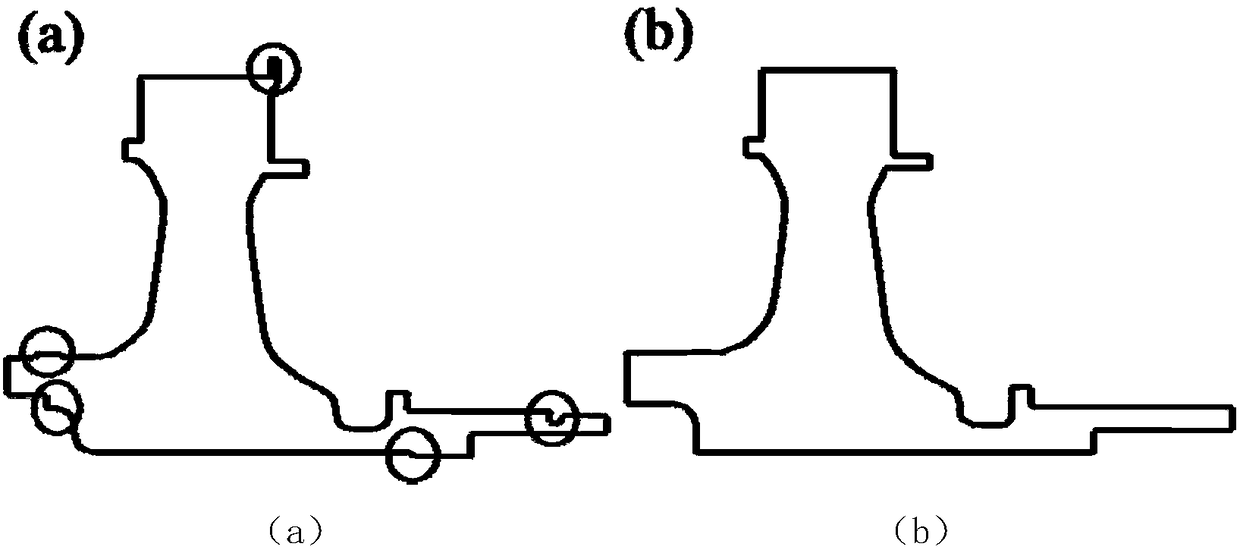
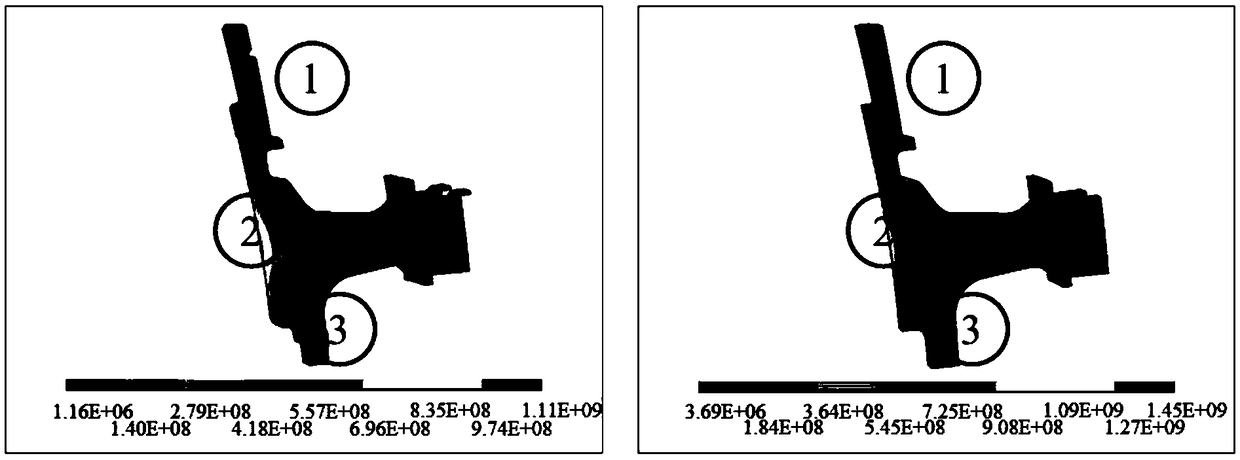
The invention relates to a geometric size probability statistics characteristic analysis method used in turbine disc probability reliability analysis. The geometric size probability statistics characteristic analysis method comprises the steps that a geometric model of a turbine disc is simplified, wherein a periodic sector is taken, and finite element calculation is performed according to periodic symmetric boundary conditions, and model simplification is performed in the calculation process; 2, parametric modeling of the model is performed, wherein geometrical fully-constrained parametric analysis is conducted on the simplified model to form a full-parametric model; 3, geometric dimensions are grouped, wherein parameters are divided into N groups during sensitivity calculation, and eachgroup includes about 10 parameters; 4, sensitivity analysis is performed, wherein an experiment design (DOE) method is adopted to conduct hypercube sampling on random geometric parameters, sensitivityanalysis is performed, and factors having the maximum counter stress influence are screened out; 5, dimension statistics and hypothesis testing are performed, wherein real turbine disc data is counted according to the screened key geometric dimensions, a single sample K-S checking method is utilized to check the distribution type of the key dimensions, and geometric size probability statistics distribution is obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Traffic load sharing method for delay-tolerant heterogeneous wireless mobile network
ActiveCN105072638AImprove forecast accuracyImprove load sharing efficiencyNetwork traffic/resource managementMobile WebTraffic load
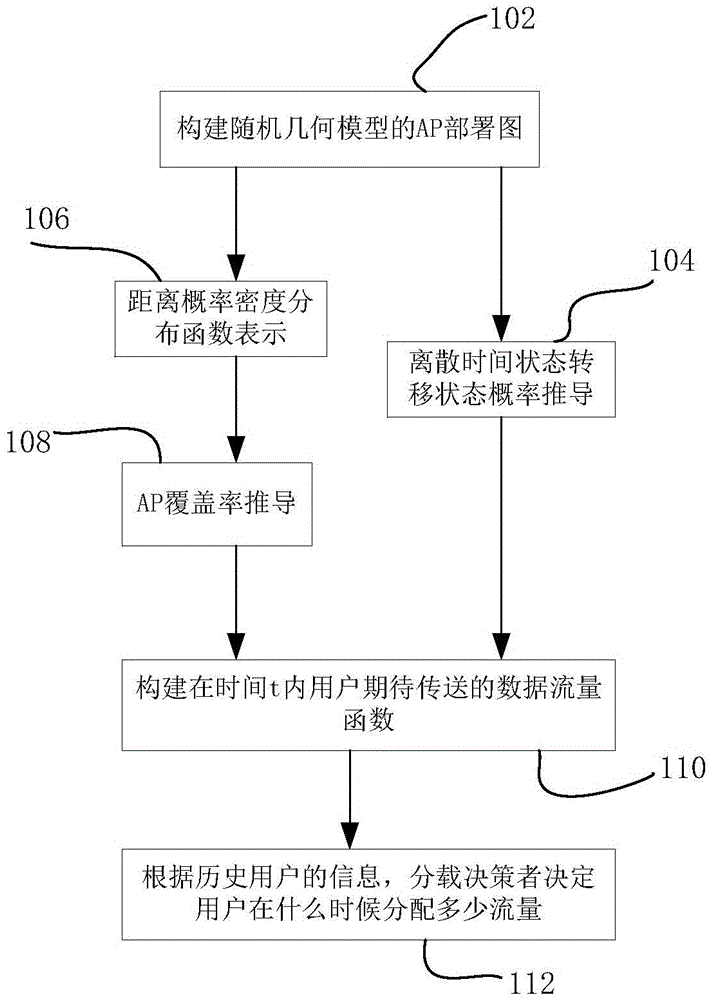
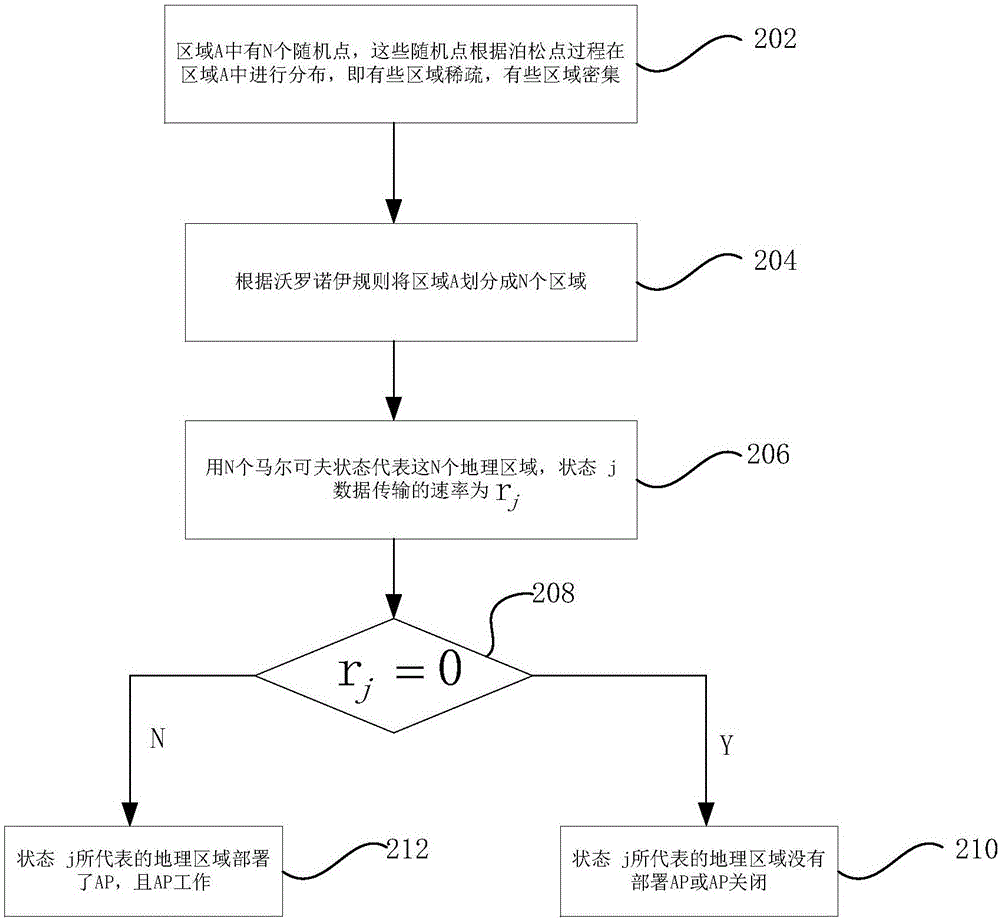
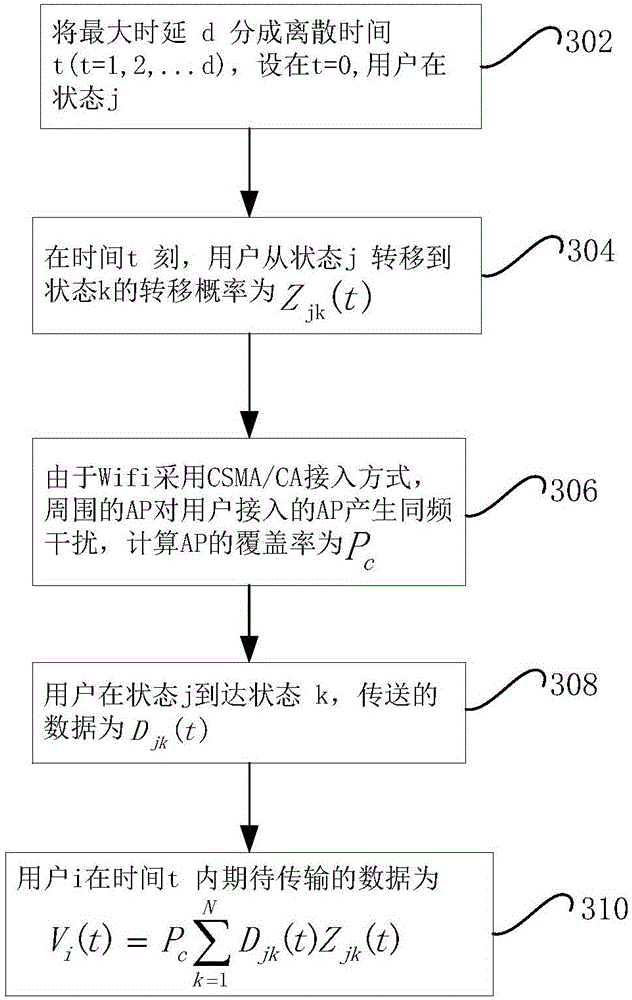
The invention discloses a traffic load sharing method for a delay-tolerant heterogeneous wireless mobile network, comprising the following steps: step 1, constructing an access point AP deployment diagram of a random geometry model in a specific area; step 2, determining the state transition probability of discrete time for a user in the specific area according to the AP deployment diagram constructed in step 1; step 3, determining a probability distribution function of the distance between the user and an AP communicating with the user; step 4, determining the coverage rate of the AP; and step 5, determining a data traffic function of shared load expected by the user in a certain period of time according to the results obtained in step 2, step 3 and step 4. By adopting the method of the invention, the prediction accuracy of load-shared traffic can be improved, and the traffic load sharing efficiency of WIFI can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Interference suppression method for underlay inter-device communication cellular network
ActiveCN110677914ACommunication performance deteriorationReduce the burden onNetwork planningMachine-to-machine/machine-type communication serviceInterference (communication)Engineering
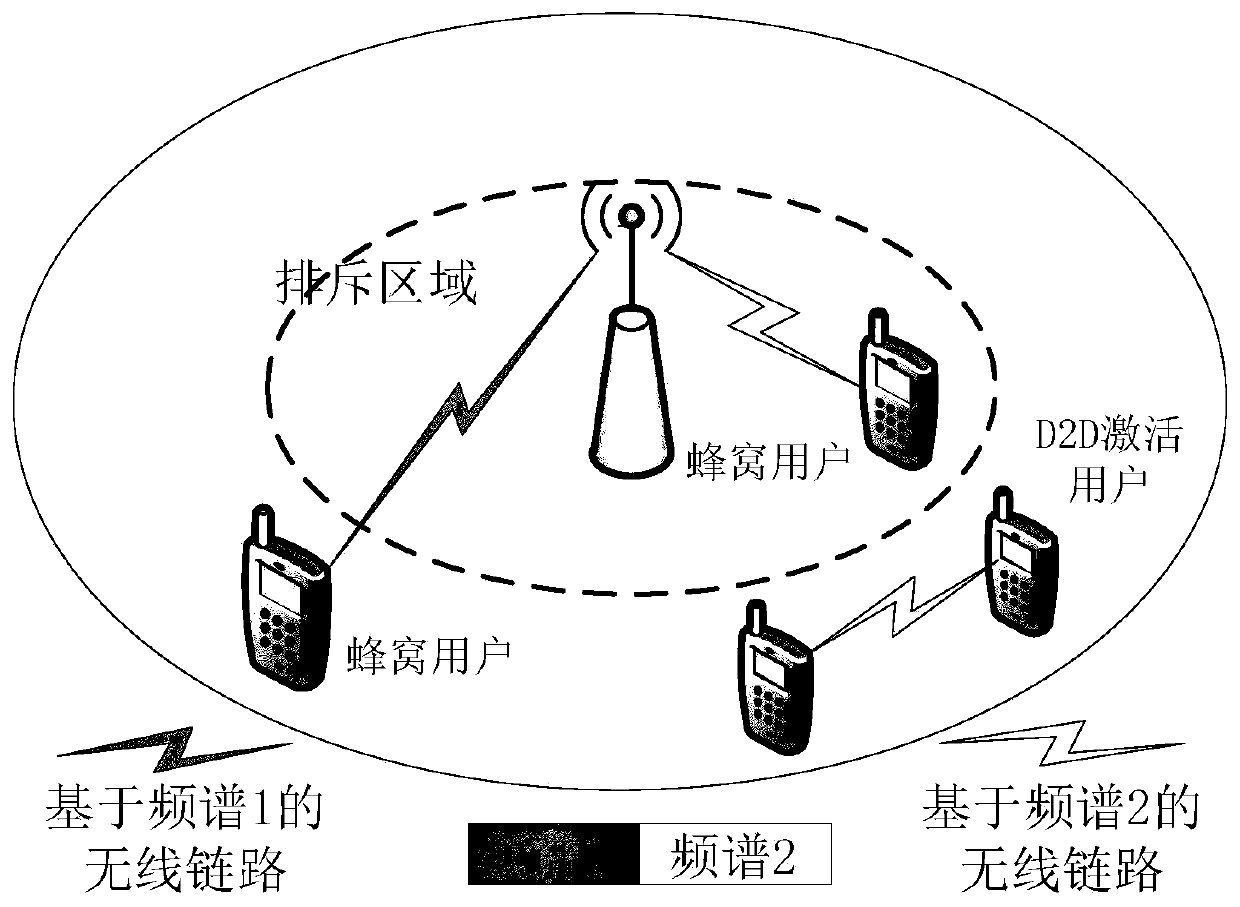
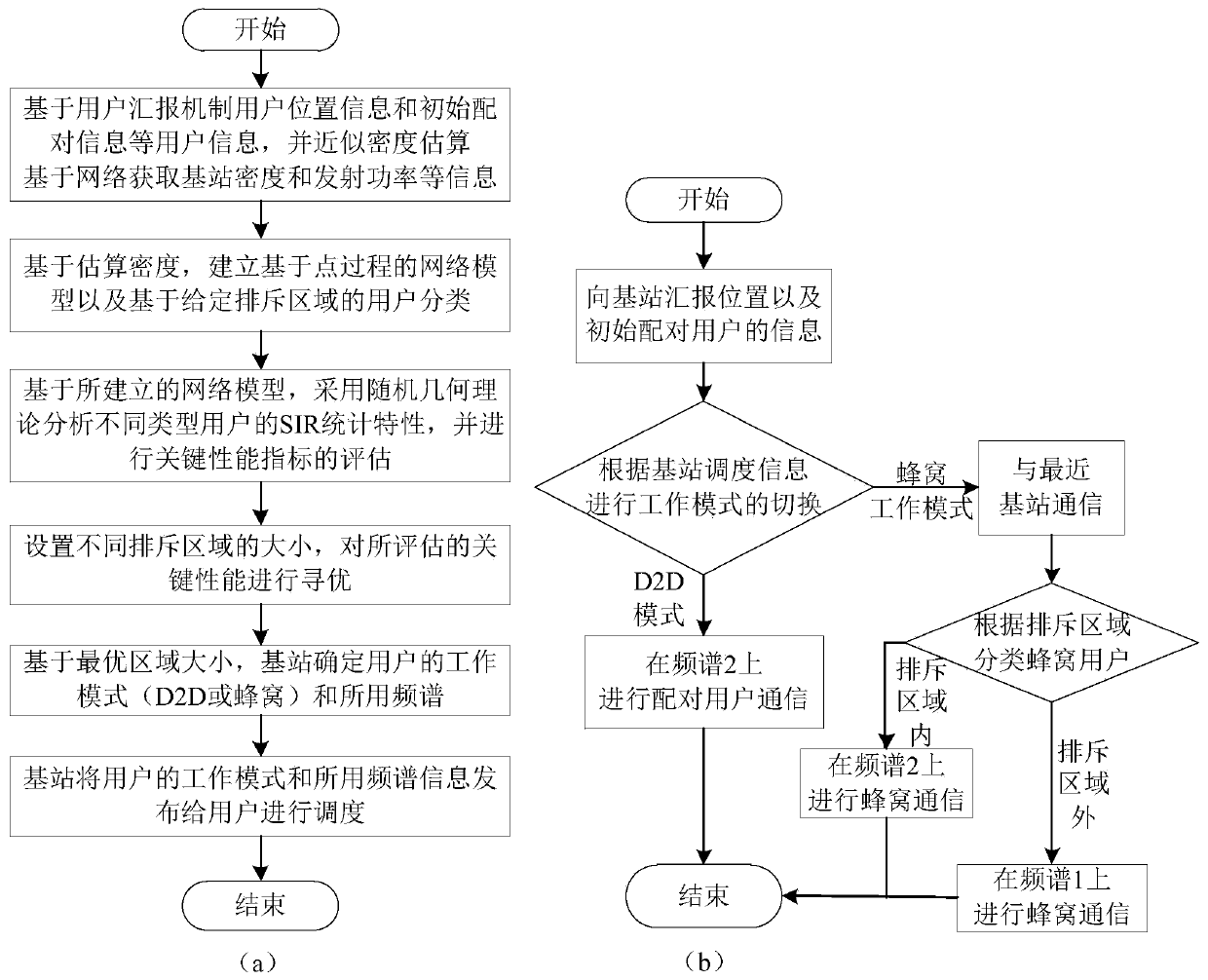
The invention discloses an interference suppression method for an underlay inter-device communication cellular network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: collecting information and establishing a model; and secondly, setting a rejection area, and adopting a hybrid spectrum allocation mode to reduce interference generated by activated D2D communication and received by cellular users outside the rejection area so as to realize interference suppression; thirdly, based on the established model and the interference suppression method, evaluating the key performance indexes of the cellular users and the D2D users by three analysis methods proposed based on a random geometry theory under the setting of a rejection region of a given base station, so as to find an optimal rejection region; finally, making a decision and publishing same. Decisions made by adopting the method can be effective in a long time range, a large amount of complex calculation and resource consumption caused by frequent decisions are avoided, the method has the advantages of being simple, rapid and universal, signaling overhead and system complexitycan be remarkably reduced, and user burden can be reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Inter-cell interference coordination method of millimeter wave cellular network
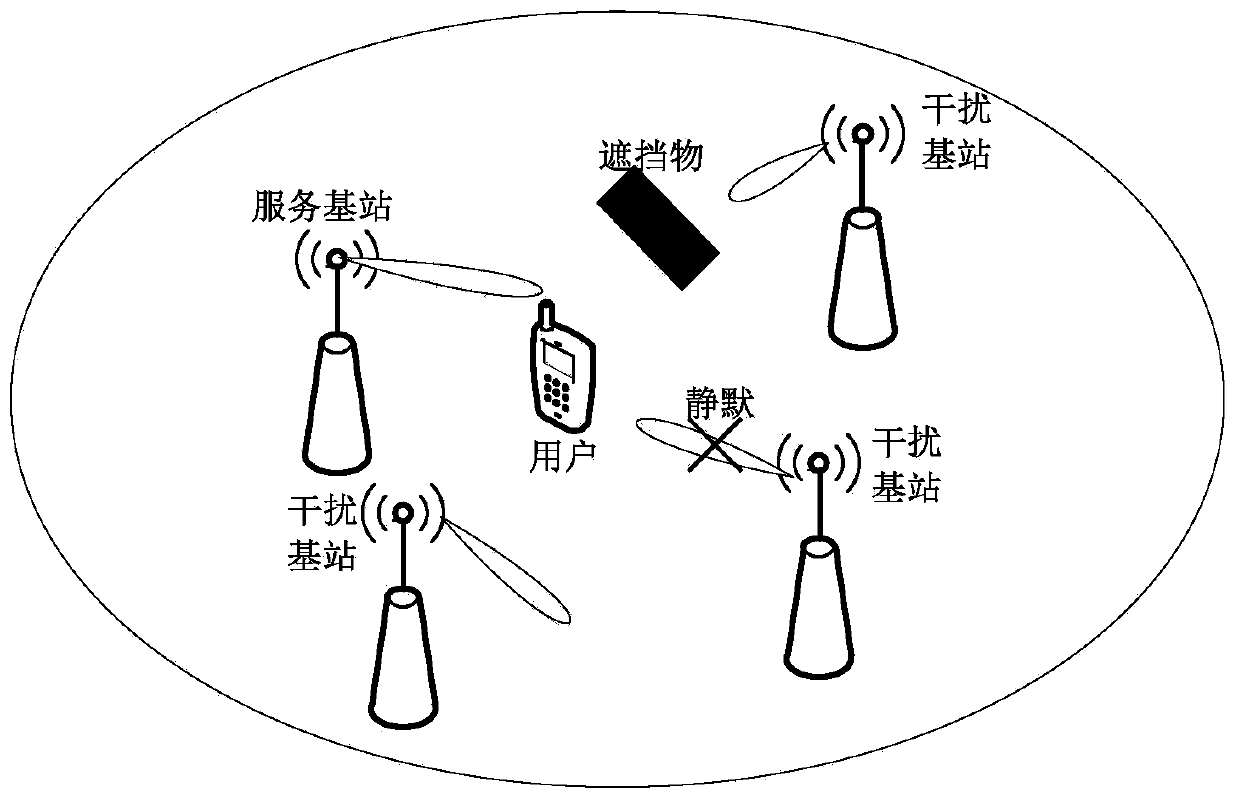
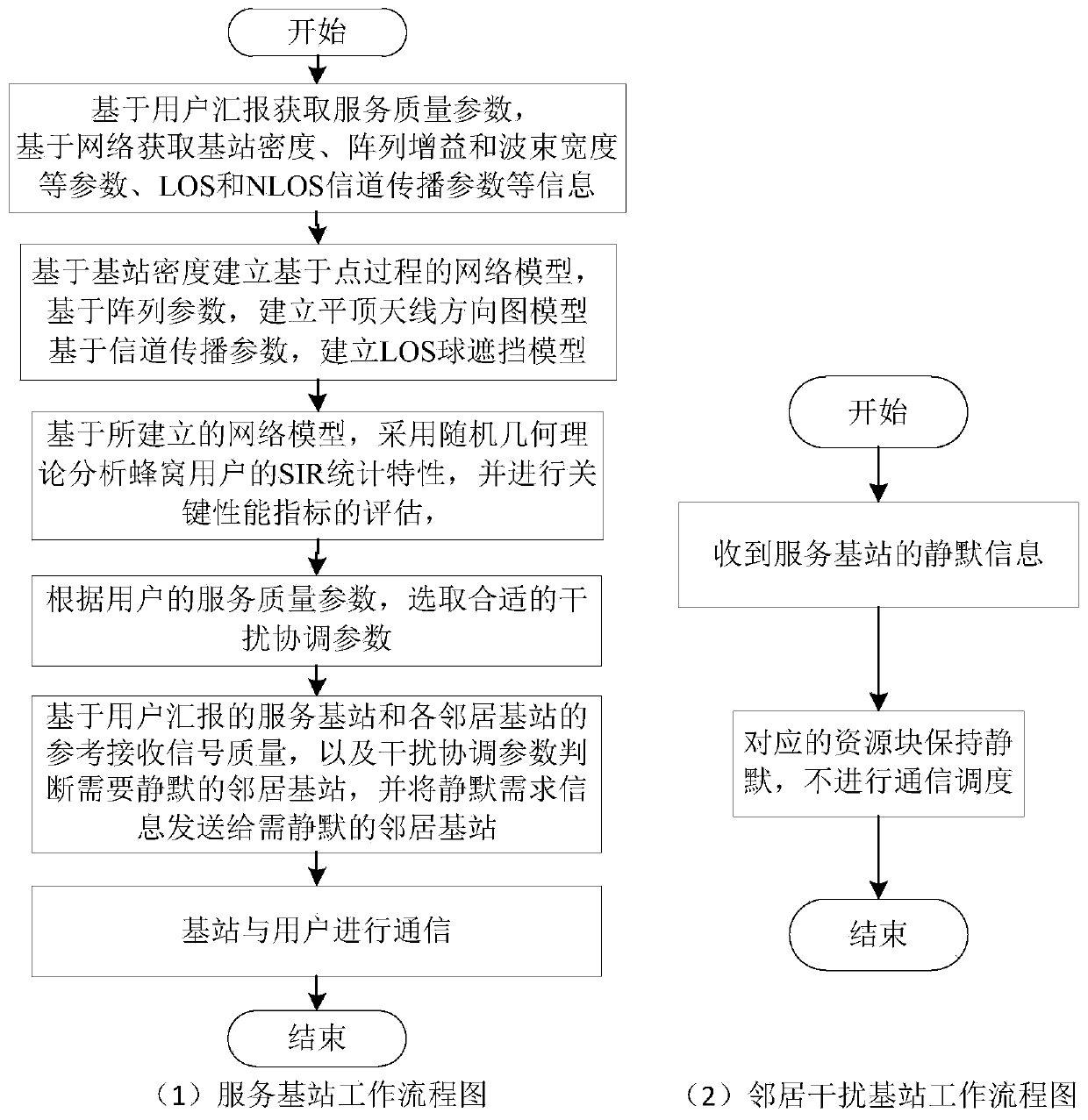
ActiveCN110972312AReduce the burden onReduce loadWireless communicationQuality of serviceInterference (communication)
The invention discloses an inter-cell interference coordination method of a millimeter wave cellular network, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. Firstly, information is collected and a model is established. Secondly, two interference coordination methods are provided, an interference coordination parameter rho is set to be greater than or equal to 1, and information transmission of a neighbor millimeter wave base station identified as a strong interference source on a specified time-frequency resource block is muted; thirdly, interference coordination parameters areselected. The method is based on the information collected in the step 1, the established model and the two interference coordination methods provided in the step 2. The key performance indexes of thecellular users are evaluated based on a random geometry theory, the target performance indexes meet the service quality requirements of the users by adjusting the interference coordination parameters, and the interference coordination parameters suitable for the current target network are determined as preconditions for executing the step 4. And finally, an interference coordination scheme is implemented. The inter-cell interference of the millimeter wave frequency band can be effectively suppressed, the communication service quality of millimeter wave cellular users is ensured, the user burden is reduced, and the load of a backbone network is remarkably reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for optimizing energy efficiency based on stochastic geometry in coexistence of wireless body area networks
InactiveCN107770750AImprove reliabilityImprove energy efficiencyPower managementParticular environment based servicesBody area networkBody area
The invention discloses a method for optimizing energy efficiency based on stochastic geometry in the coexistence of wireless body area networks. The method comprises the following steps: a) buildinga Poisson point process model by adopting a stochastic geometry method; b) calculating the probability density f(p) of transmission power of a node; c) calculating transmission success probability P<s>; and d) calculating energy efficiency etaEE of the node. A relationship between the transmission power and the energy efficiency in the coexistence of networks is analyzed, so that the energy efficiency of a system can be increased better in a wireless network coexistence design, and the aims of lowering interference and enhancing the network communication reliability are fulfilled.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
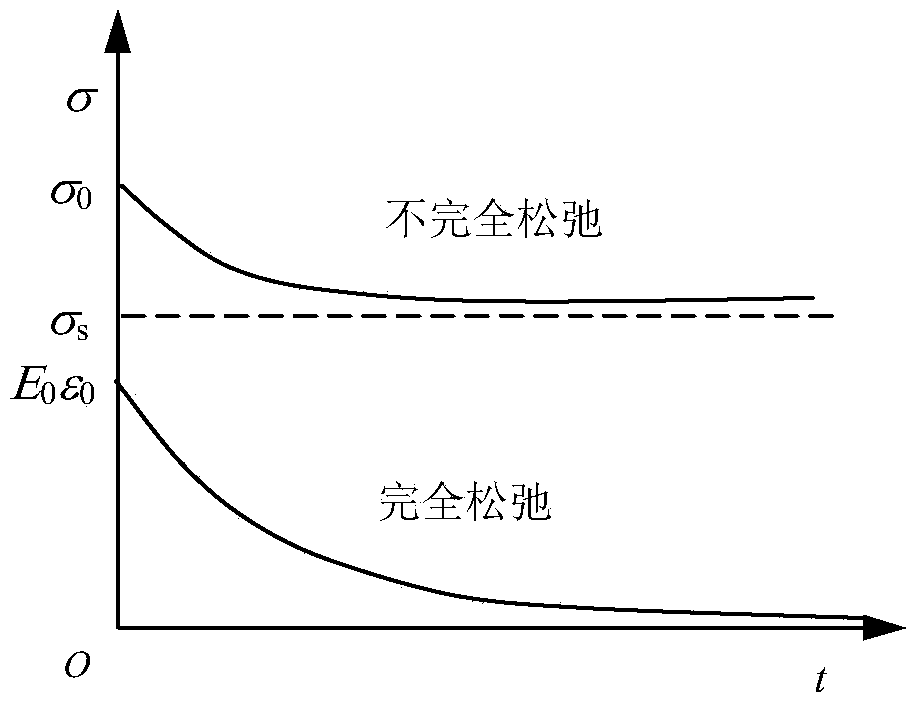
Mesoscopic structure simulation based rock stress relaxation property forecasting method
The invention belongs to the field of geotechnical engineering and particularly relates to a mesoscopic structure simulation based rock stress relaxation property forecasting method. The mesoscopic structure simulation based rock stress relaxation property forecasting method comprises the following steps of (1) identifying mineral components and proportions of multiple mineral rock samples; (2) preparing each single mineral rock sample; (3) respectively carrying out a stress relaxation experiment on each single mineral rock sample; (4) establishing a stress relaxation model of each single mineral rock sample; (5) inverting to obtain a stress relaxation parameter of each single mineral rock sample; (6) carrying out random geometric modeling on the multiple mineral rock samples according to the mineral components and the proportions; and (7) calculating and forecasting the stress relaxation properties of the multiple mineral rock samples. By using the structure simulation based rock stress relaxation property forecasting method, the practical mineral component condition of a practical engineering rock mass can be simulated in a laboratory or other places, so that the application range of the mesoscopic structure simulation based rock stress relaxation property forecasting method is wide.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
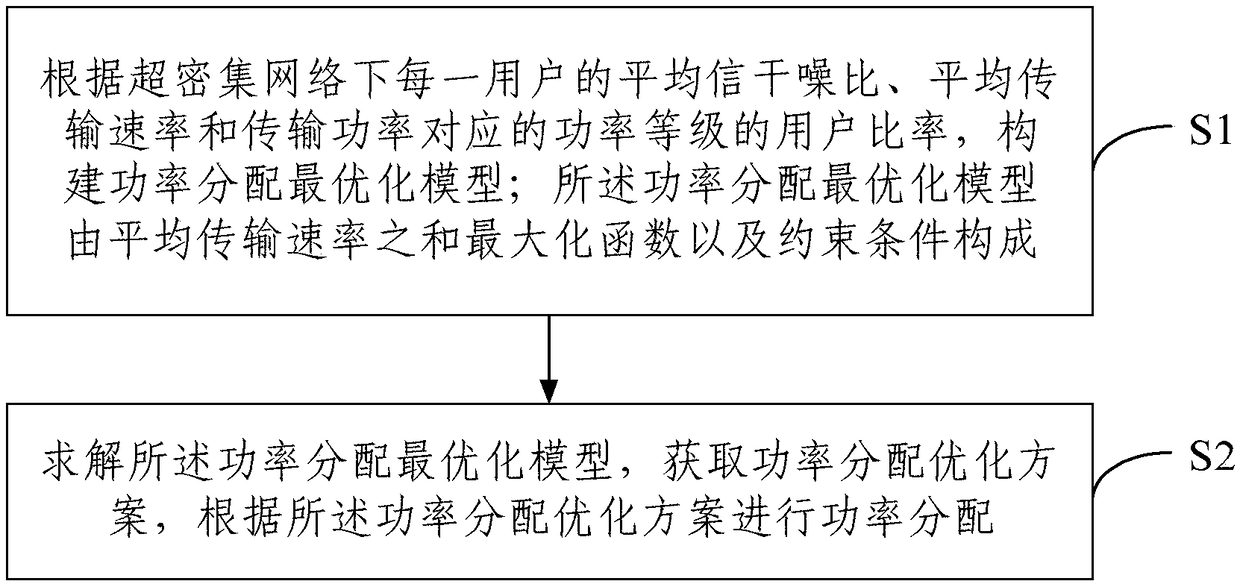
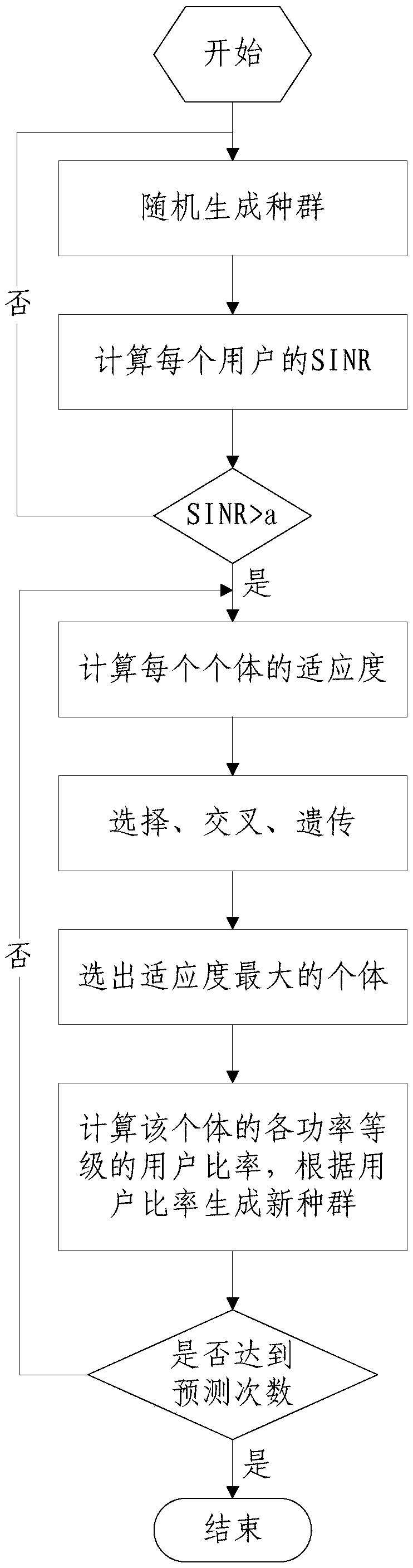
Power distribution method based on statistical property reference
ActiveCN109195222ASolve the problem of excessive calculation of resource allocationReduce measurementHigh level techniquesWireless communicationDistribution methodComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides a power distribution method based on statistical property reference. The method comprises the steps of: constructing a power distribution optimization model according to the average signal to interference plus noise power ratio, an average transmission rate and a power grade ratio corresponding to the transmission power used by a user of each used in a super intensive network, wherein the power distribution optimization model is formed by a maximization function of a sum of the average transmission rates and constraint conditions; and solving the powerdistribution optimization model to obtain a power distribution optimization scheme, and performing power distribution according to the power distribution optimization scheme. According to the embodiment of the invention, the method constructs the power distribution optimization model based on a random geometric theory to solve the problem that the resource distribution calculation amount is too large caused by sharp increasing network node quantity, reduce the system measurement and feedback cost, achieve efficient power distribution and improve the system performance and resource utilizationefficiency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Network flow prediction method and device and electronic equipment
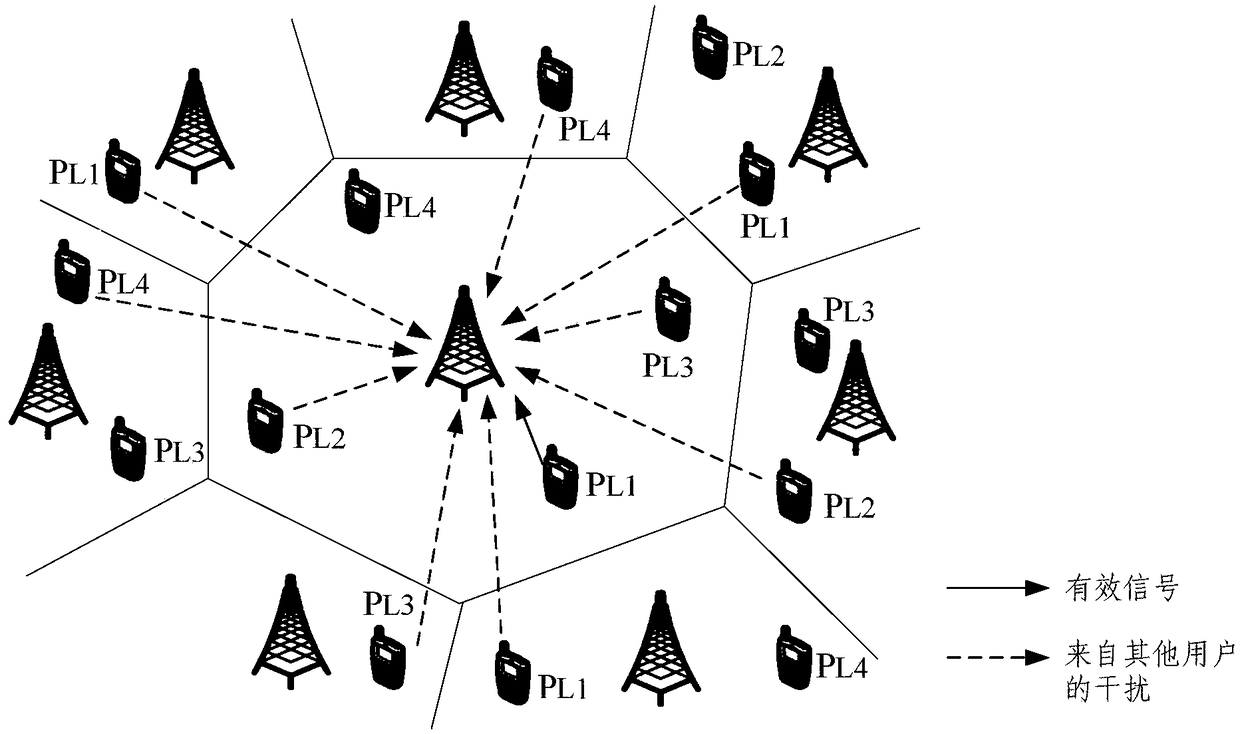
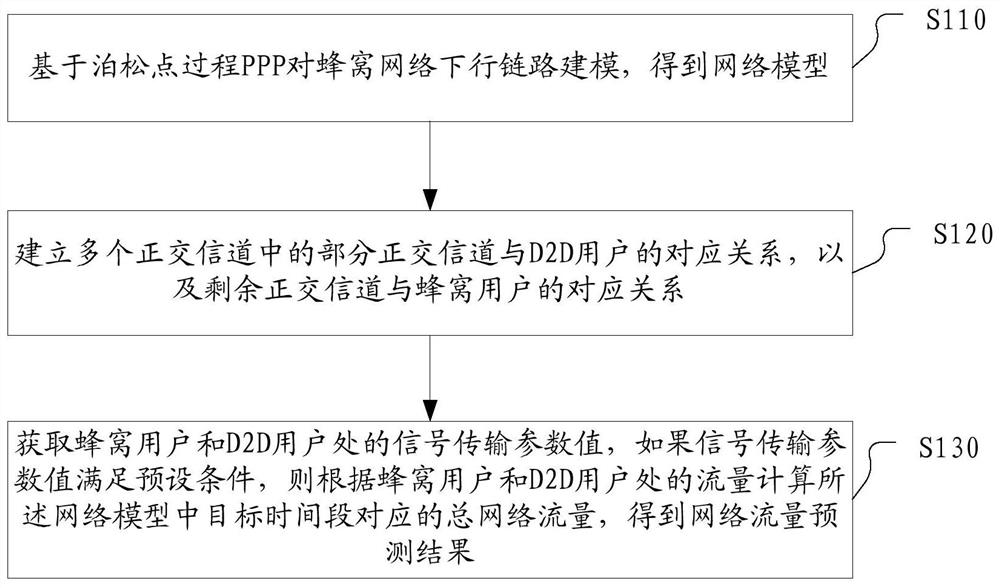
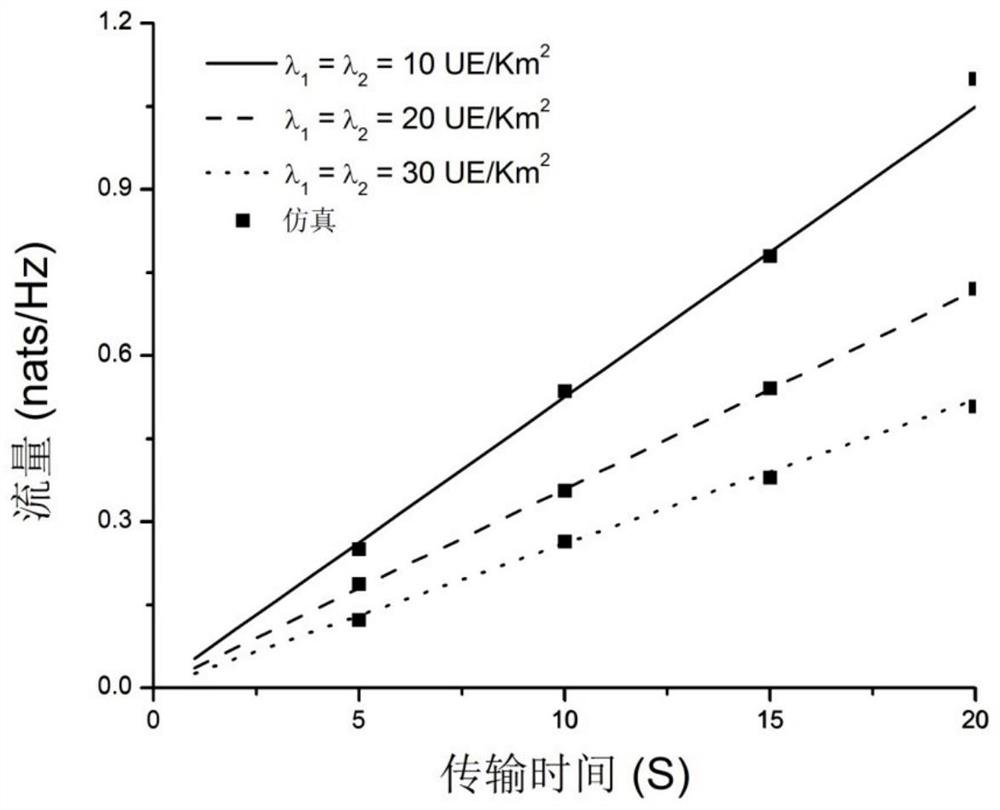
PendingCN111741450AAvoid uncertaintyEasy to analyzeData switching networksNetwork planningTraffic predictionResource assignment
The invention discloses a network flow prediction method and device, and electronic equipment. The network flow prediction method comprises the following steps: modeling a downlink of a cellular network based on a Poisson point process PPP to obtain a network model; establishing a corresponding relationship between a part of orthogonal channels in the plurality of orthogonal channels and the D2D users, and a corresponding relationship between the remaining orthogonal channels and the cellular users; and acquiring signal transmission parameter values at the cellular user and the D2D user, and if the signal transmission parameter values meet a preset condition, calculating the total network flow corresponding to the target time period in the network model according to the flow at the cellular user and the D2D user to obtain a network flow prediction result. According to the embodiment of the invention, the heterogeneous cellular network flow is analyzed and predicted based on the theoretical framework of random geometry, the prediction precision of the network flow is improved, and the maximization of the network flow is realized through spectrum resource allocation.
Owner:36TH RES INST OF CETC
5G authorization-free retransmission access technology outage probability assessment method
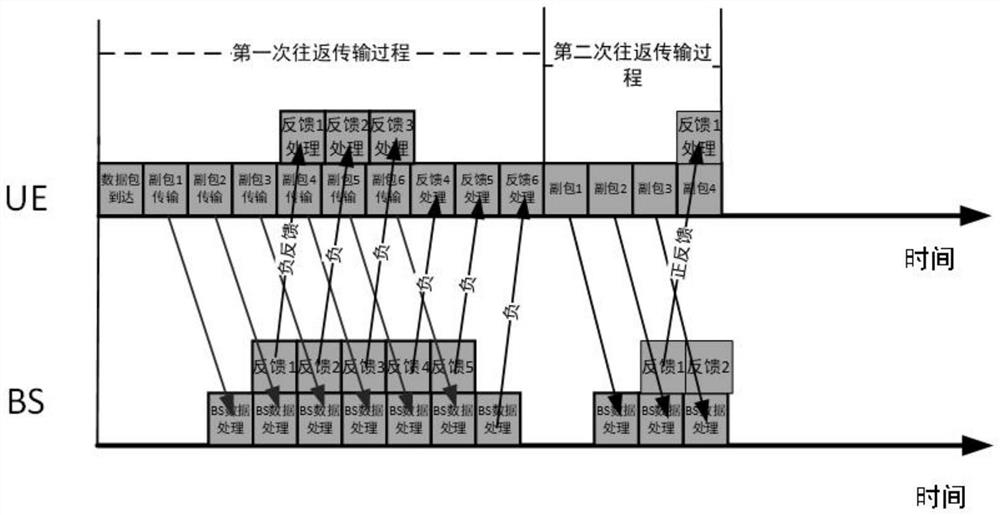
PendingCN114124311AAccurate descriptionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission monitoringFree accessSignal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio
The invention discloses a 5G authorization-free retransmission access technology outage probability evaluation method, which comprises the following steps that a real-time user transmits the same sub-packets on continuous time slots, the maximum value of the number of the sub-packets is K, and a base station side feeds back a decoding result to the user after receiving the sub-packets so as to decide whether to retransmit the sub-packets; system time delay analysis and outage probability modeling: analyzing and deducing transmission time delay of a one-time round-trip process of the system, and establishing an outage probability problem model in combination with time delay constraint: obtaining a signal to interference plus noise ratio of a receiving end according to a power threshold value and noise power, the outage probability is the probability smaller than a signal to interference plus noise ratio threshold value within the time delay constraint; and system transmission outage probability: utilizing a probability theory and stochastic geometry to solve an outage probability closed solution. According to the method, the system outage probability of combination of authorization-free access and auxiliary packet transmission can be accurately evaluated, and the influence of system parameters of a network on the information transmission outage probability can be revealed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com