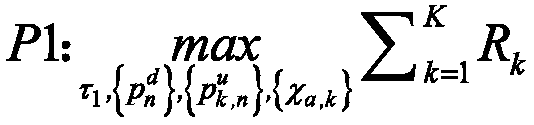Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Maximize data rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
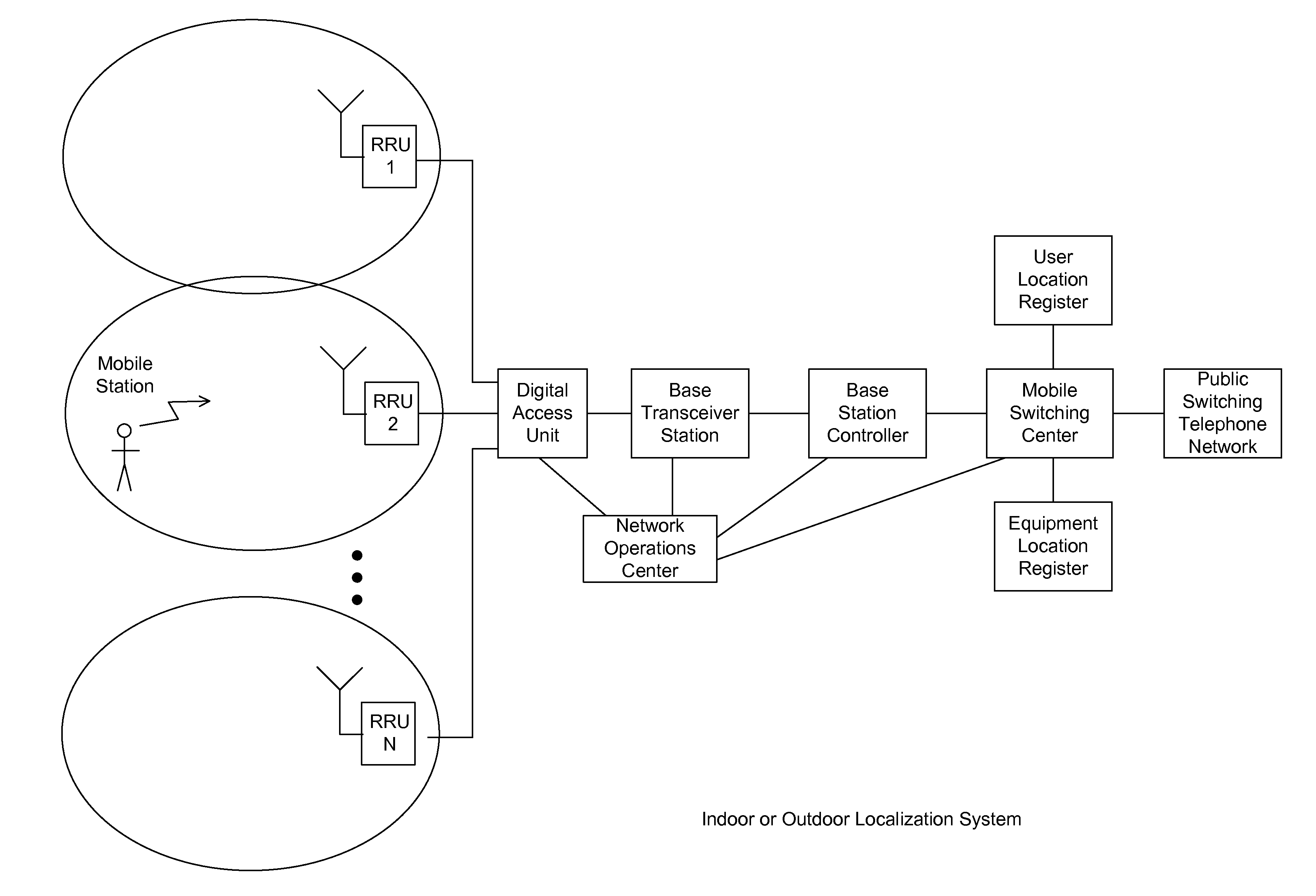
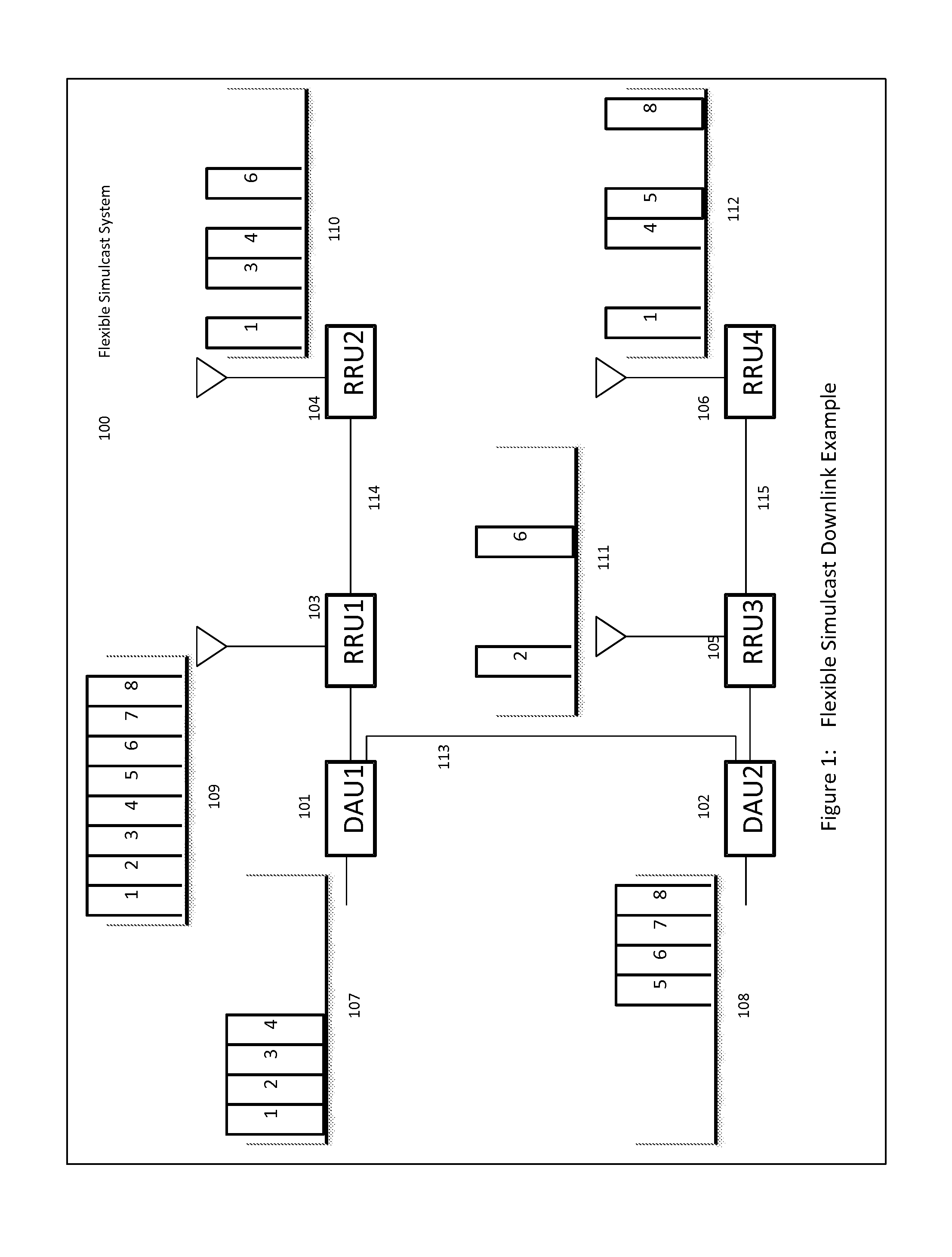
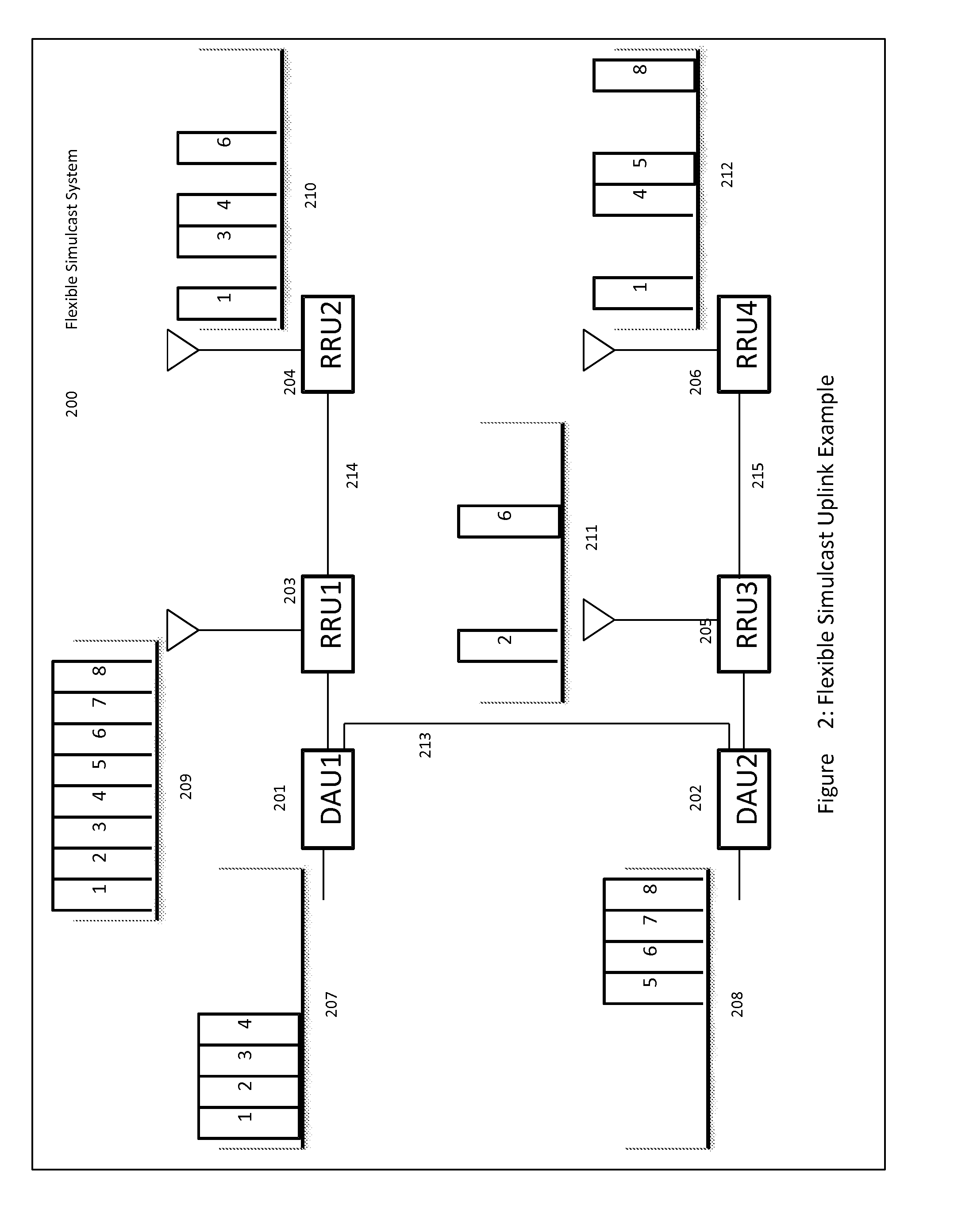
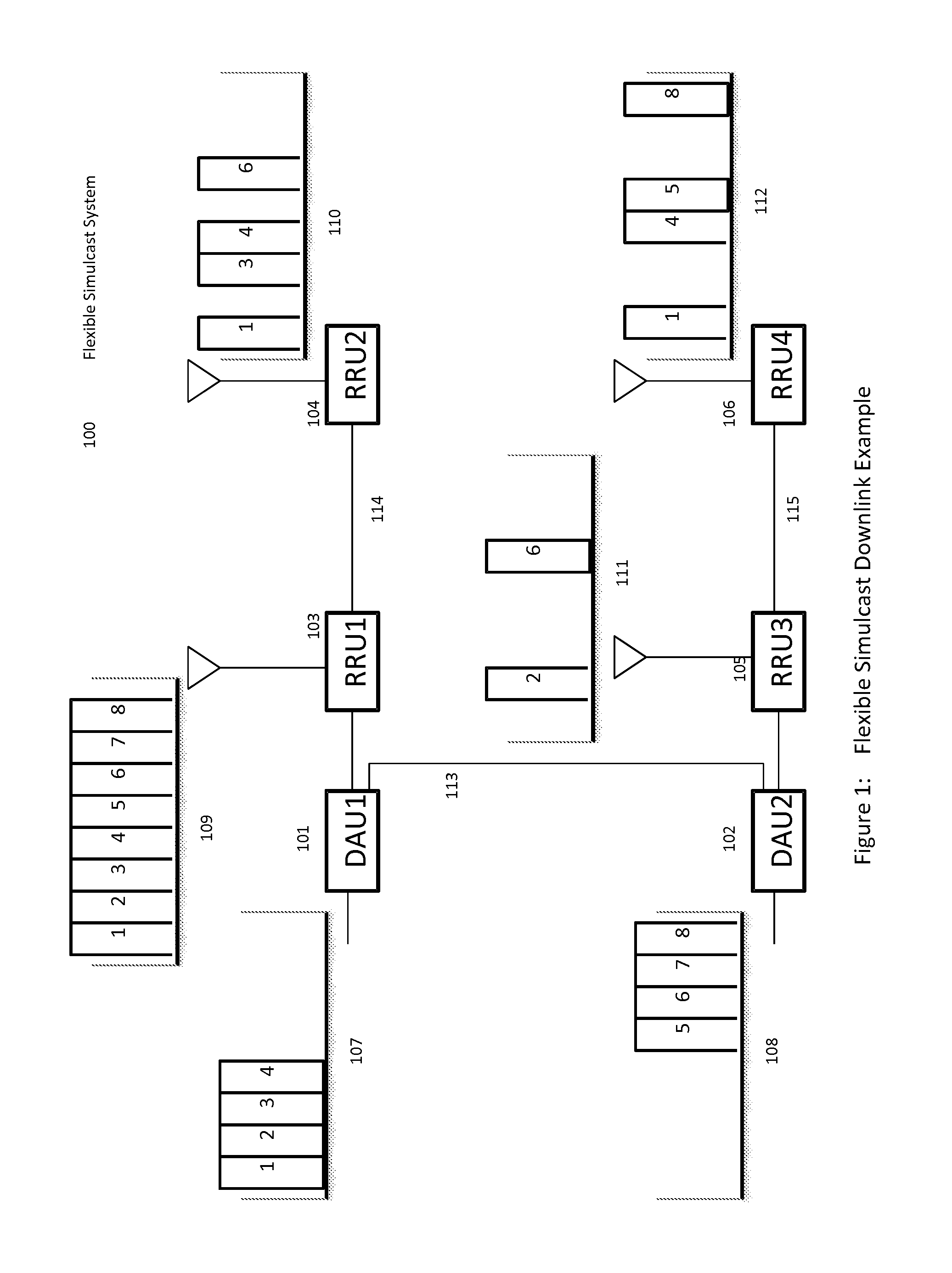
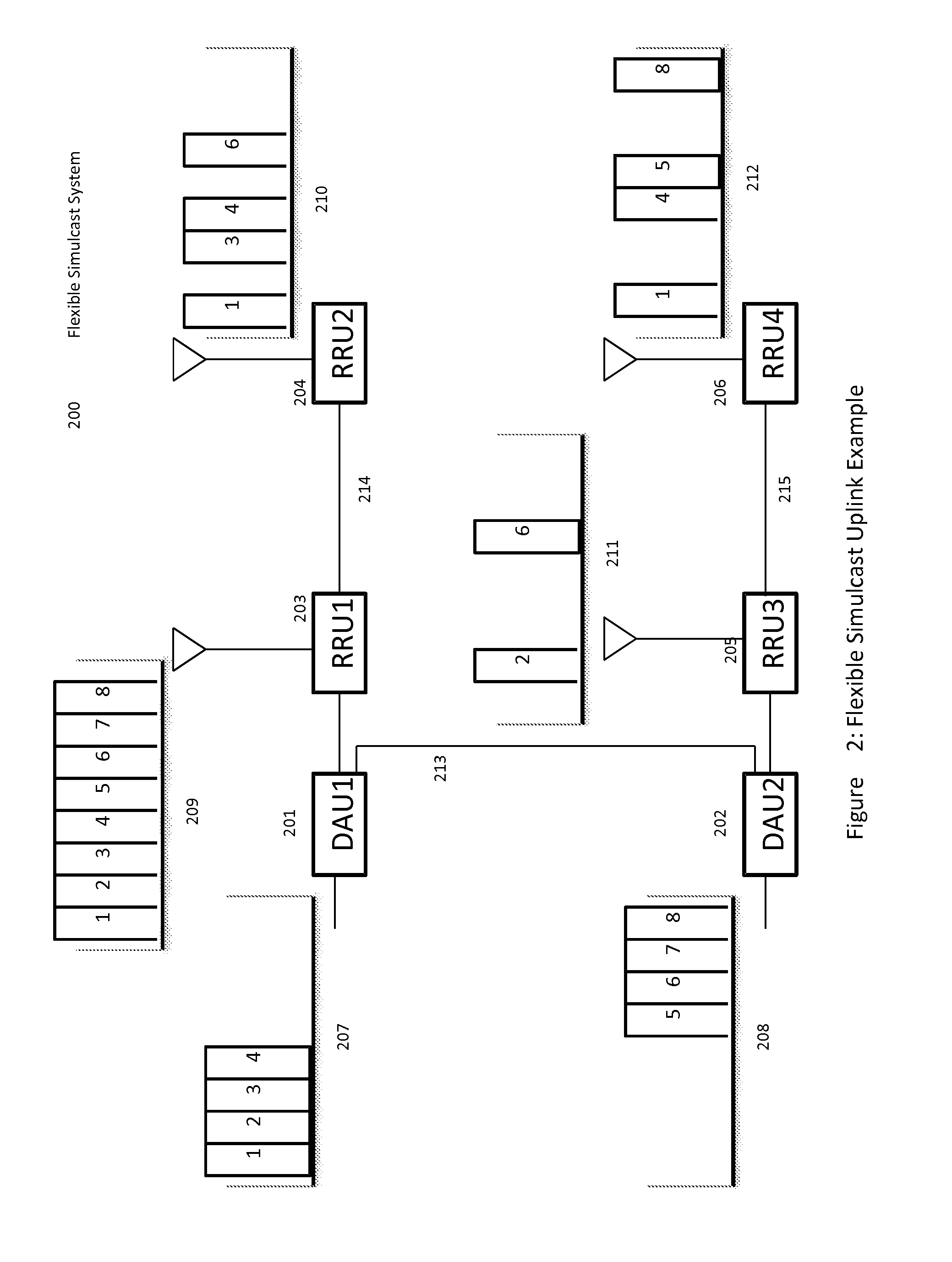
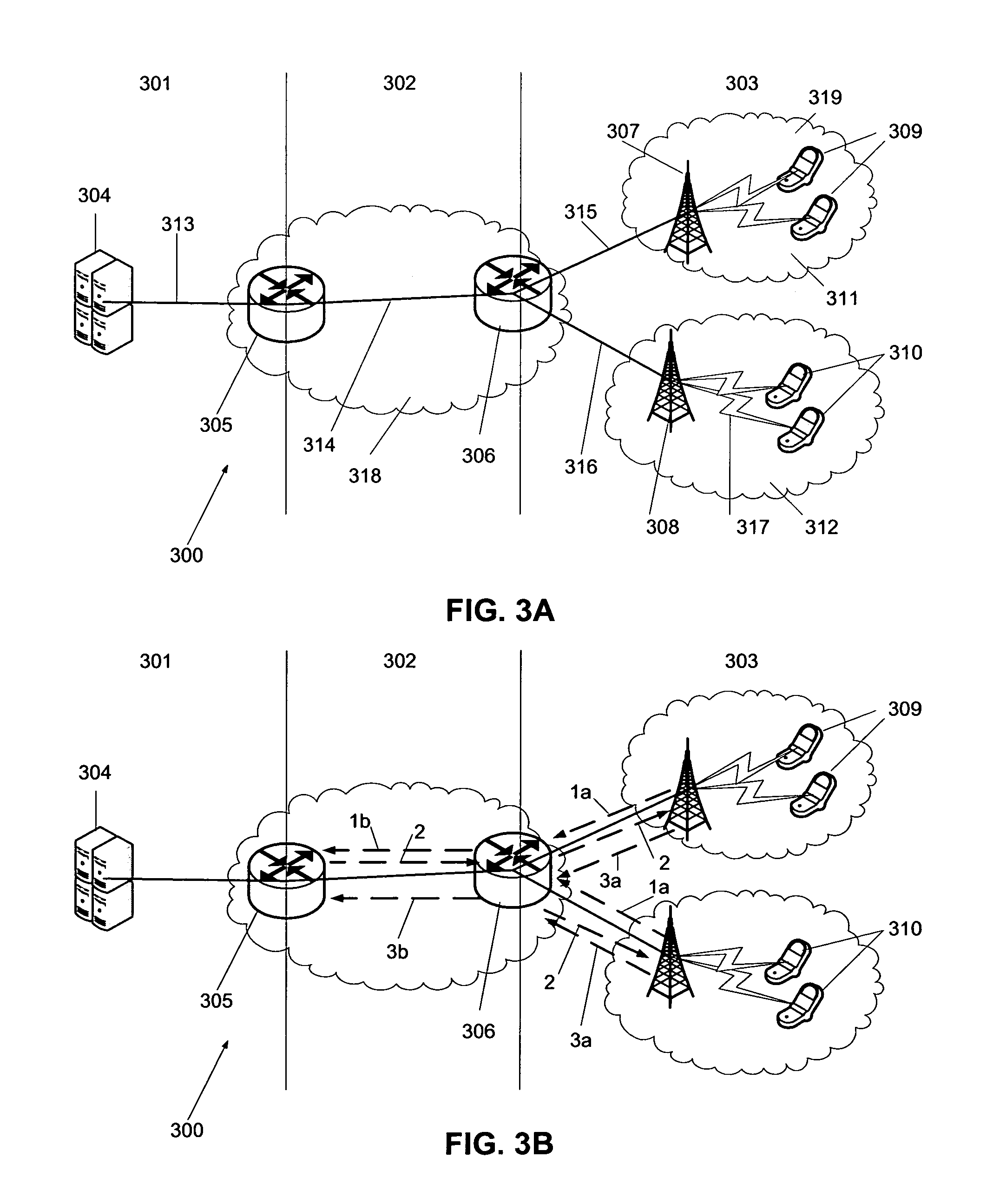
Remotely Reconfigurable Distributed Antenna System and Methods
ActiveUS20120039320A1Improve efficiencyImprove traffic capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
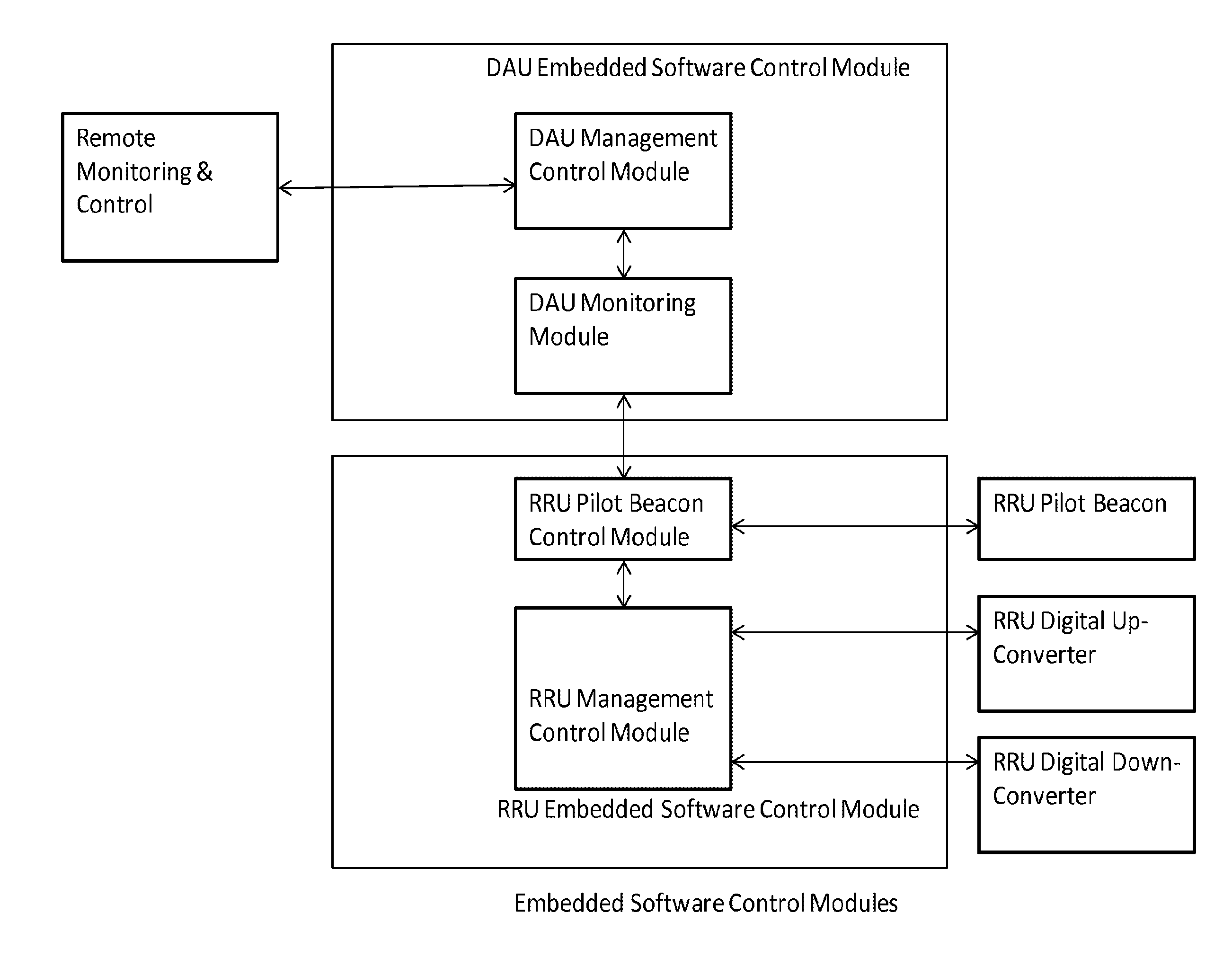
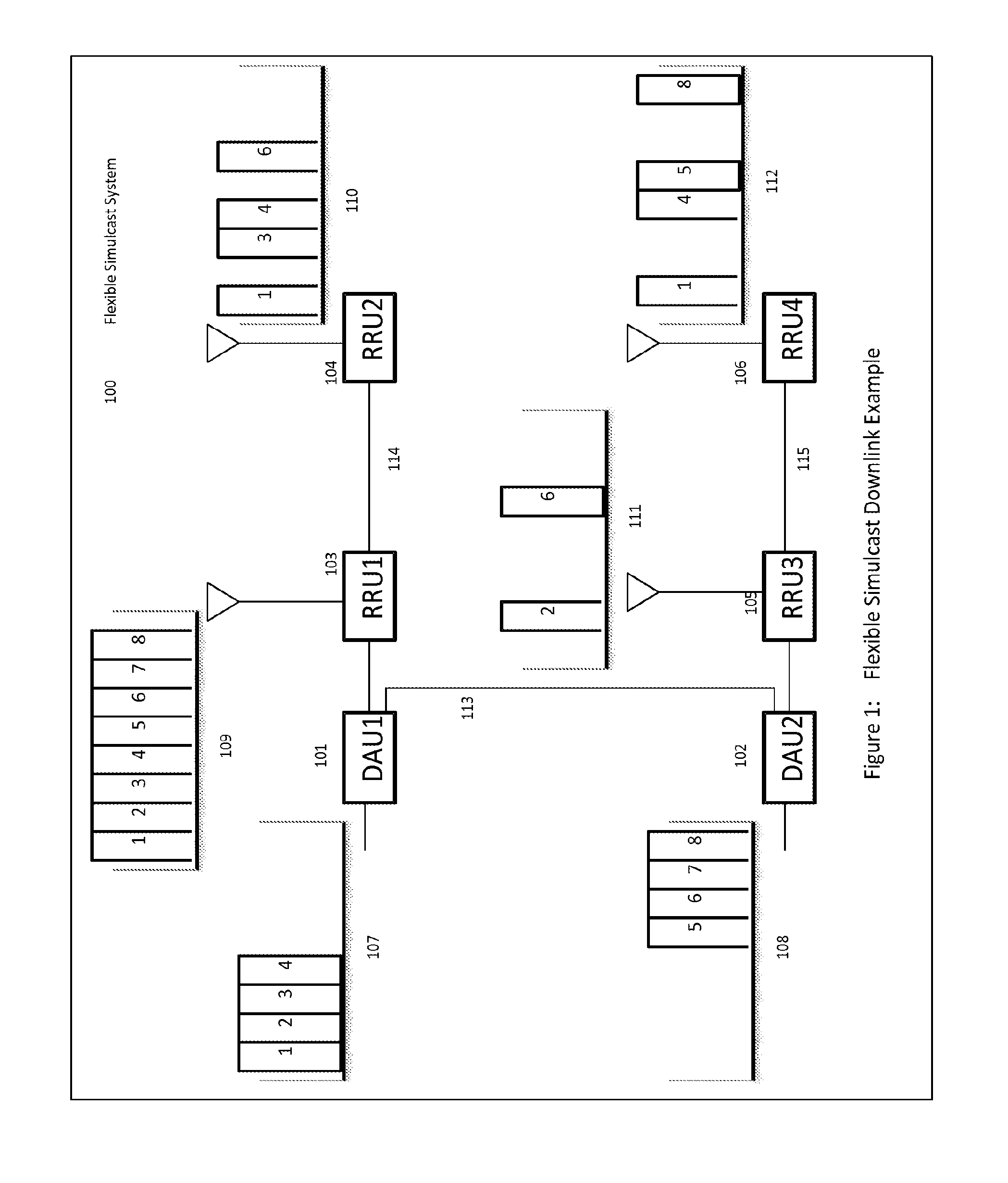
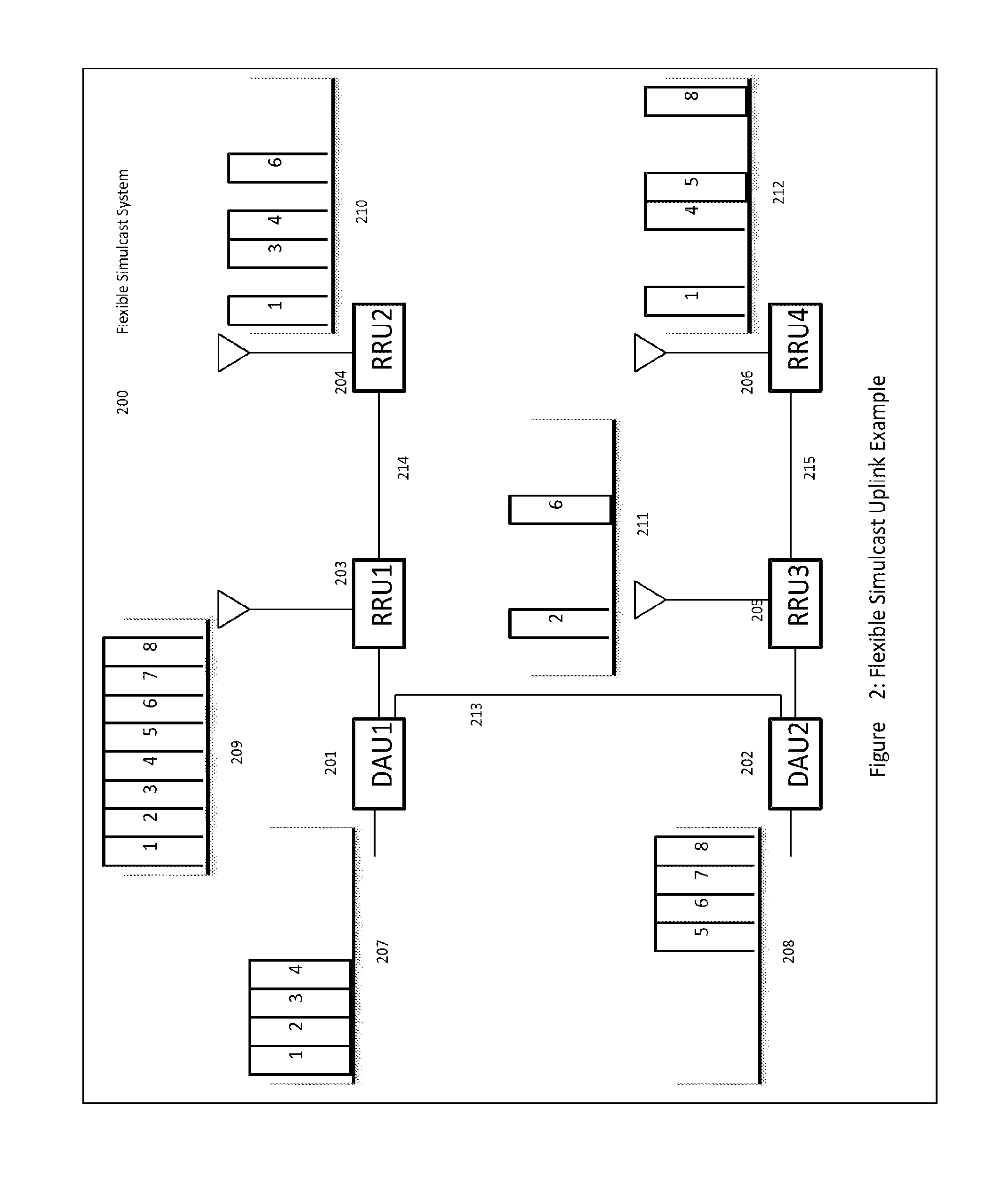
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, the SDR DAS can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
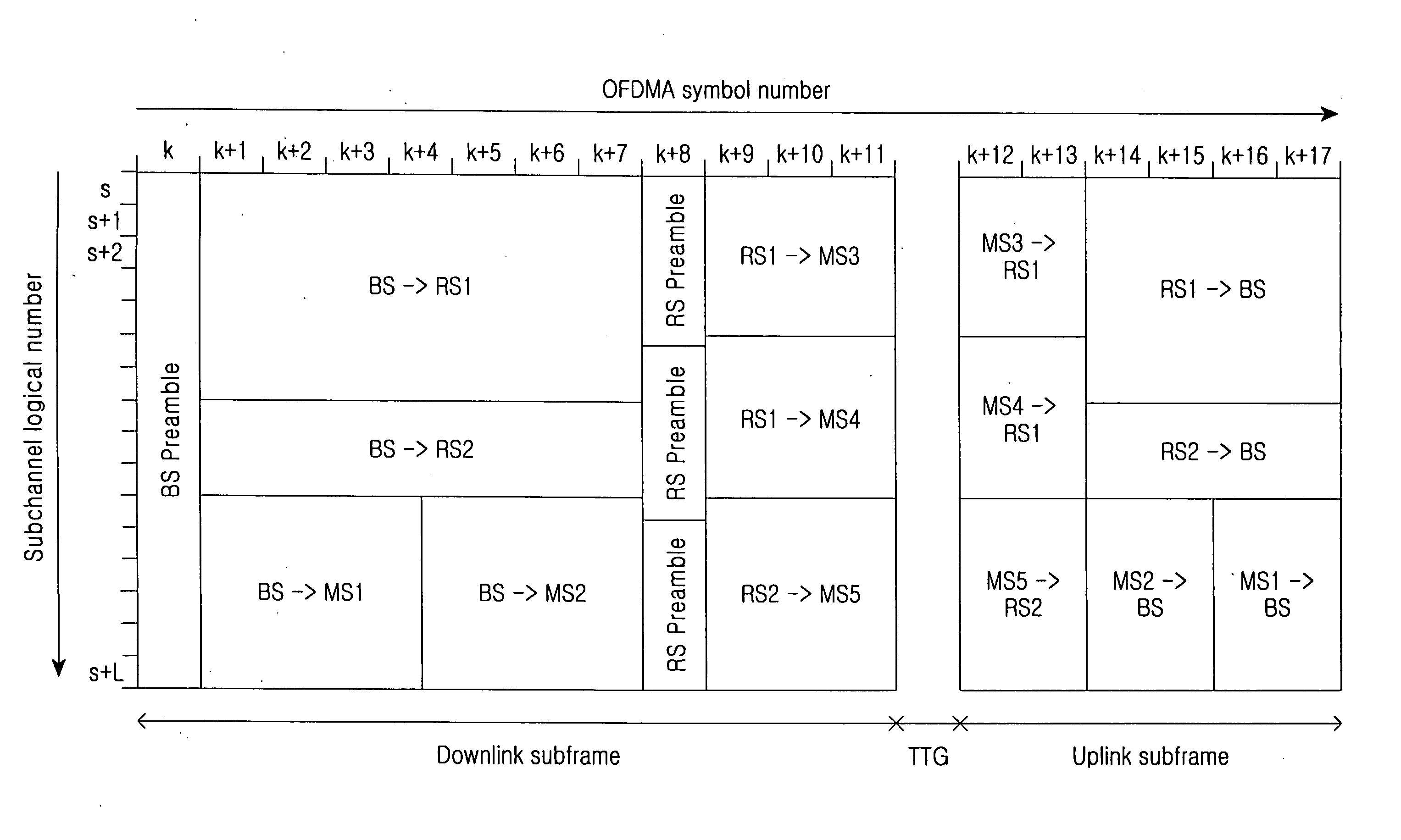
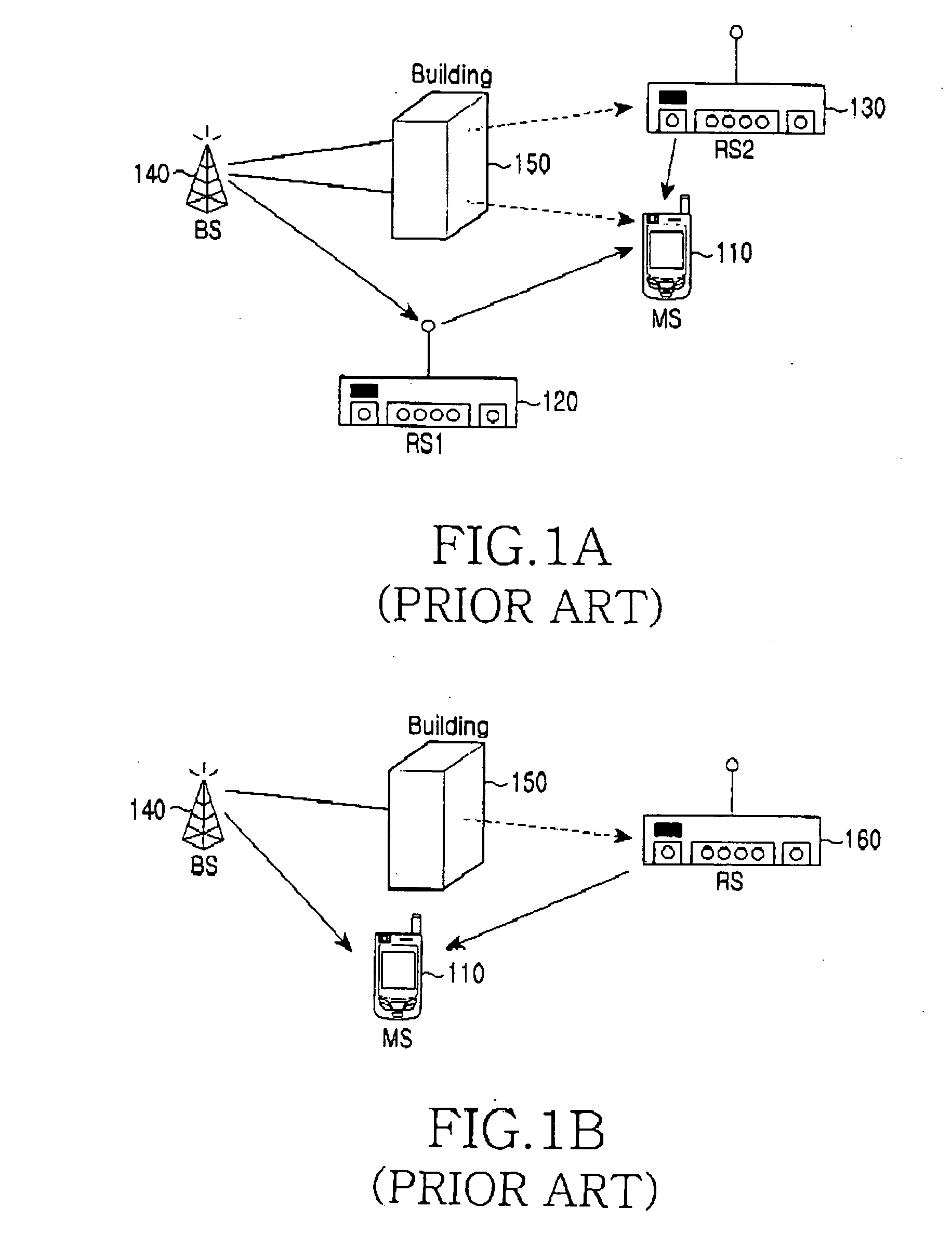
Routing apparatus and method in a multi-hop relay cellular network
InactiveUS20060285505A1Minimize message loadLoad minimizationNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationCellular networkRSS
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Remotely reconfigurable distributed antenna system and methods
ActiveUS8682338B2Increase capacityImprove efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersDistributed antenna systemCarrier signal
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc. As a result, the SDR DAS can increase the efficiency and traffic capacity of the operators' wireless network.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Method and apparatus for assigning data rate in a multichannel communication system
InactiveUS7046966B2High data rateEasy to usePower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemPower capability
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
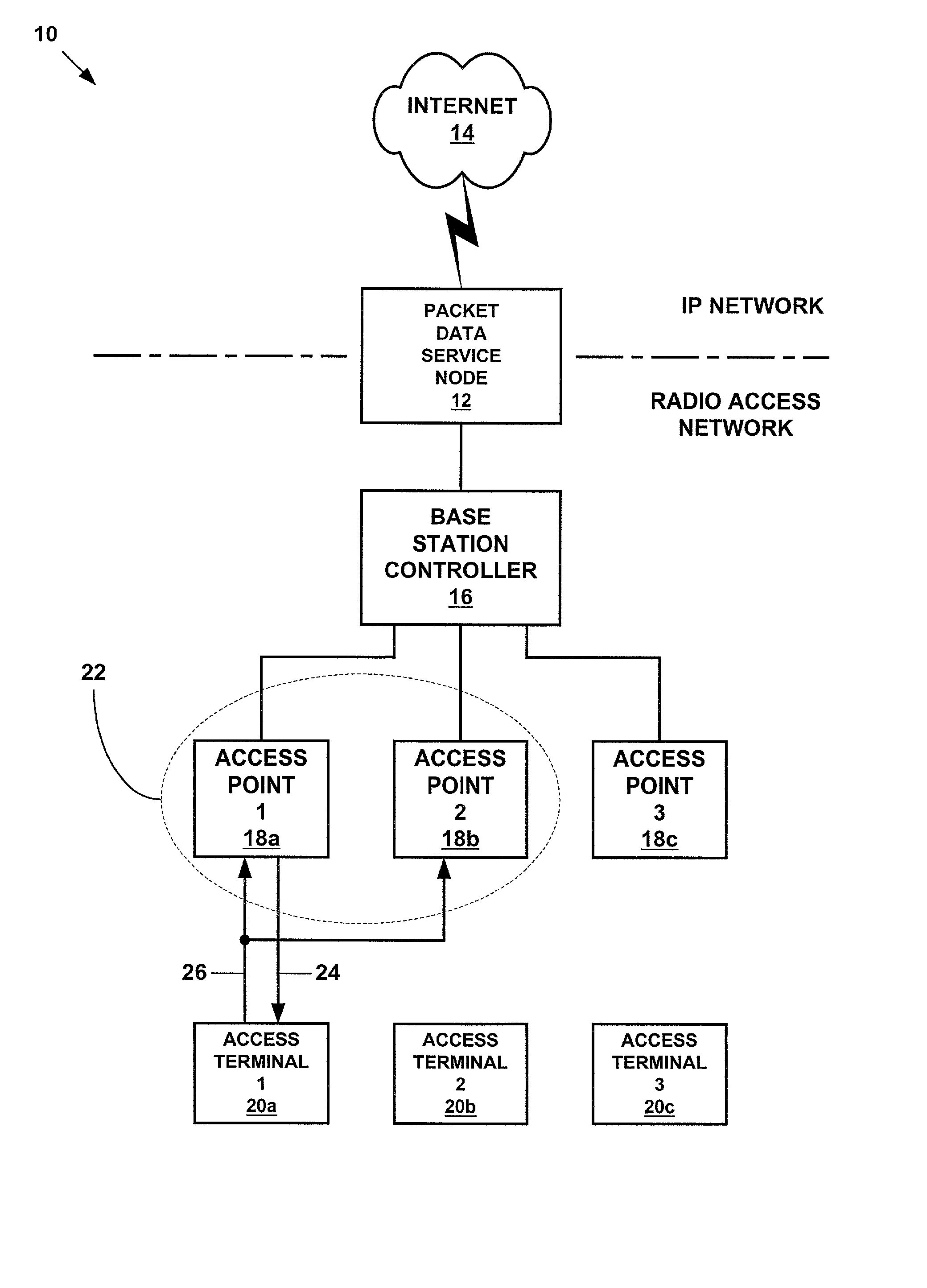
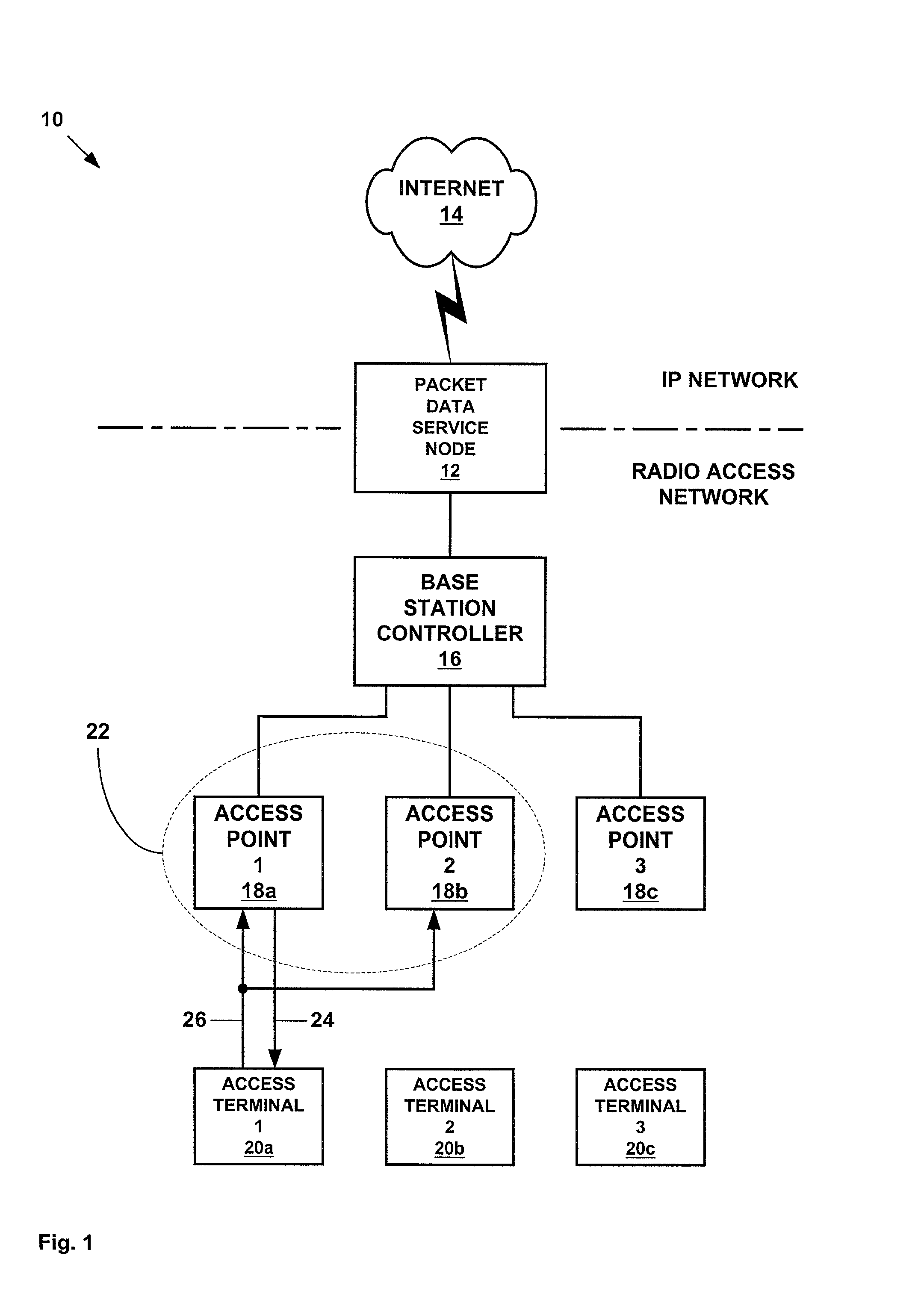
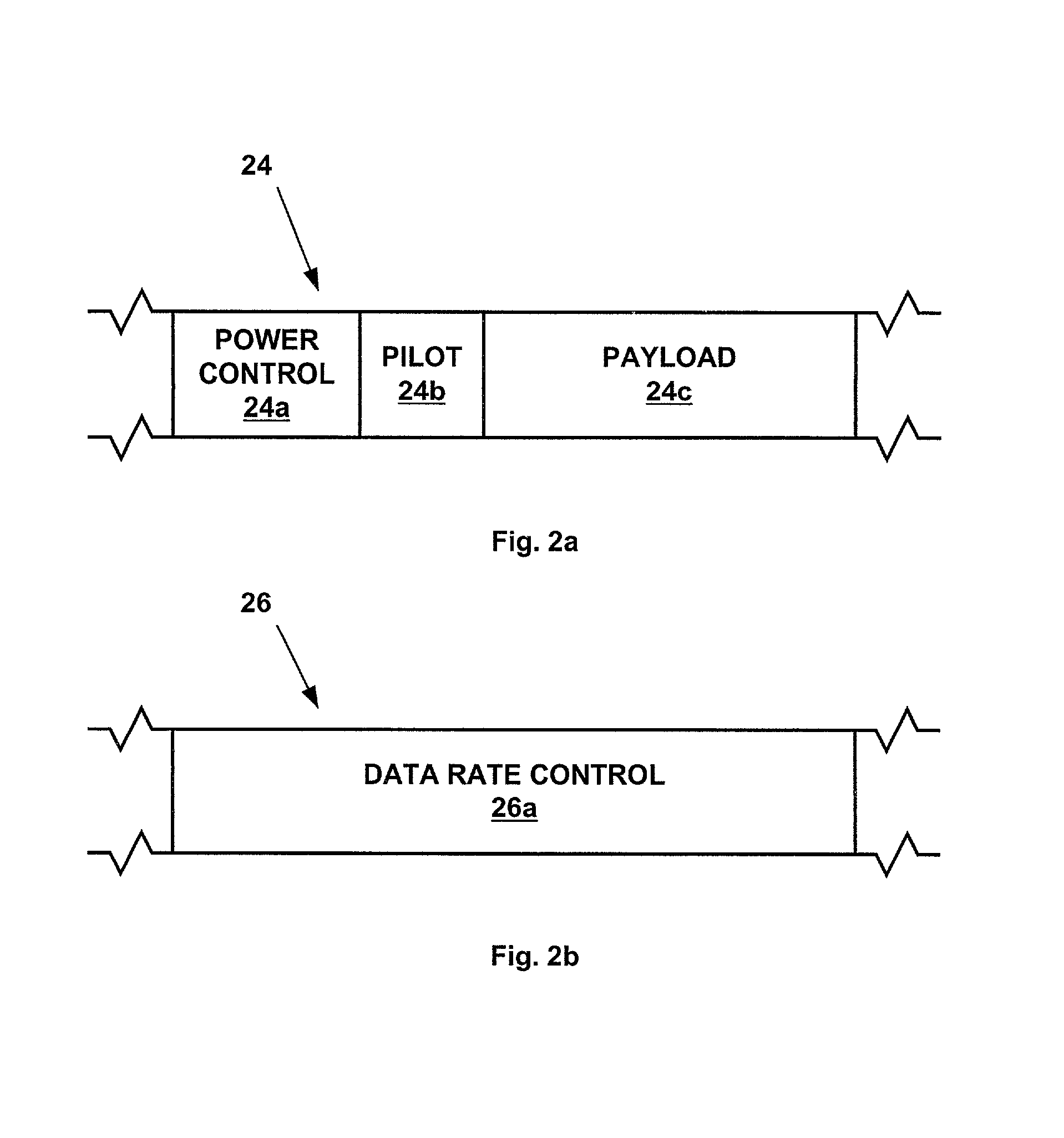
Method and apparatus for the transmission of short data bursts in CDMA/HDR networks
ActiveUS20020071445A1Effective resourcesMaximize data rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsTraffic channel
A method and apparatus for the transmission of short data bursts in CDMA / HDR networks. Dormant access terminals are assigned to a common traffic channel and rate group by an access point. The access point then informs the access terminals of the assigned common traffic channels and rate groups. The access point then transmits short data bursts to the dormant access terminals using the assigned common traffic channels and rate groups. If an access terminal fails to acknowledge receipt of a short data burst, then the access terminal is re-assigned to a new common traffic channel and rate group and transmission of the short data bursts is re-attempted. If an access terminal fails to acknowledge receipt of a short data burst more than a predetermined number of times, then the access terminal is placed in an active mode of operation. The transmission of short data bursts may be further assigned to time slots within the common traffic channels and rate groups in order to conserve the resources of the access terminals.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
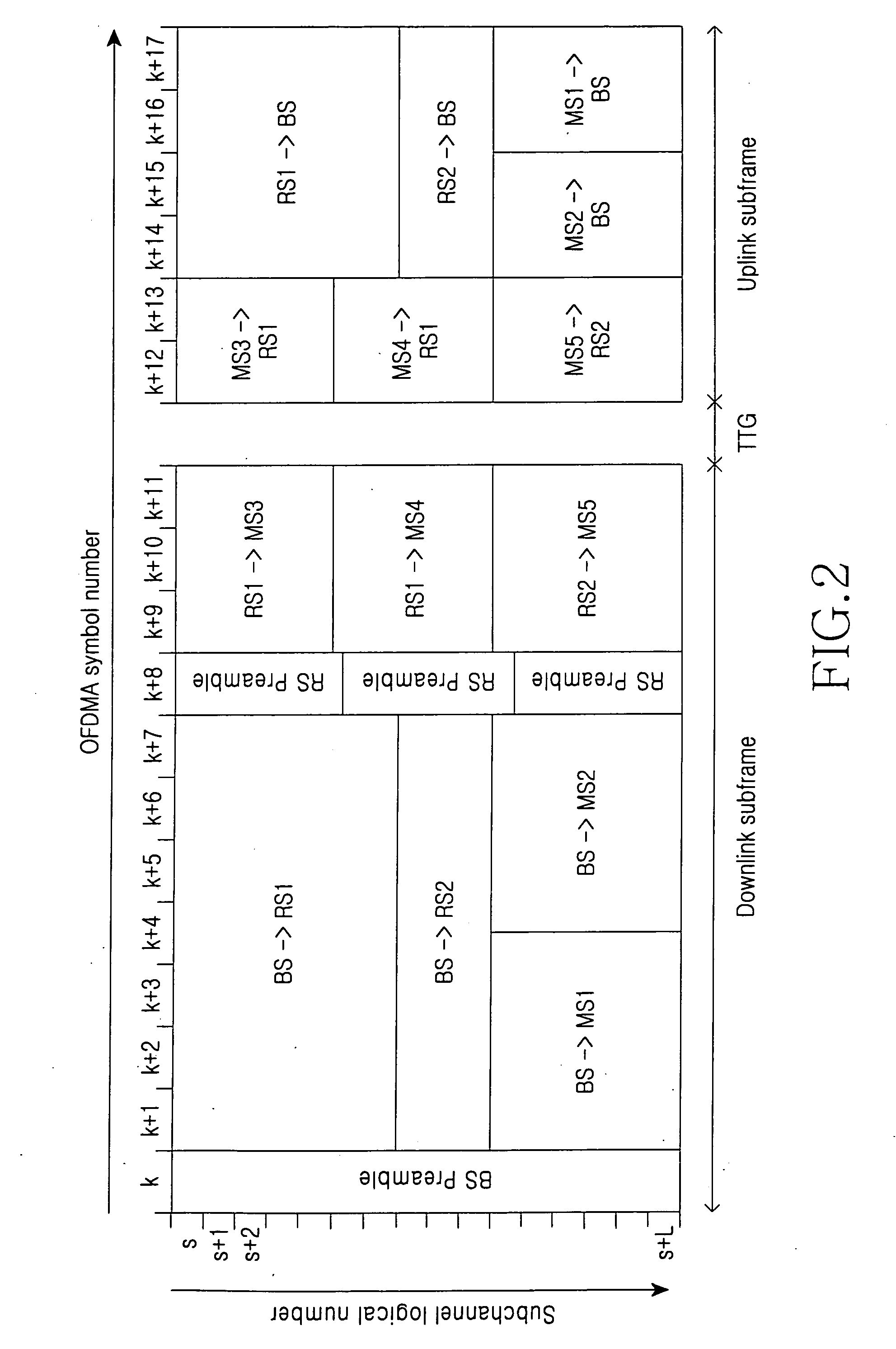
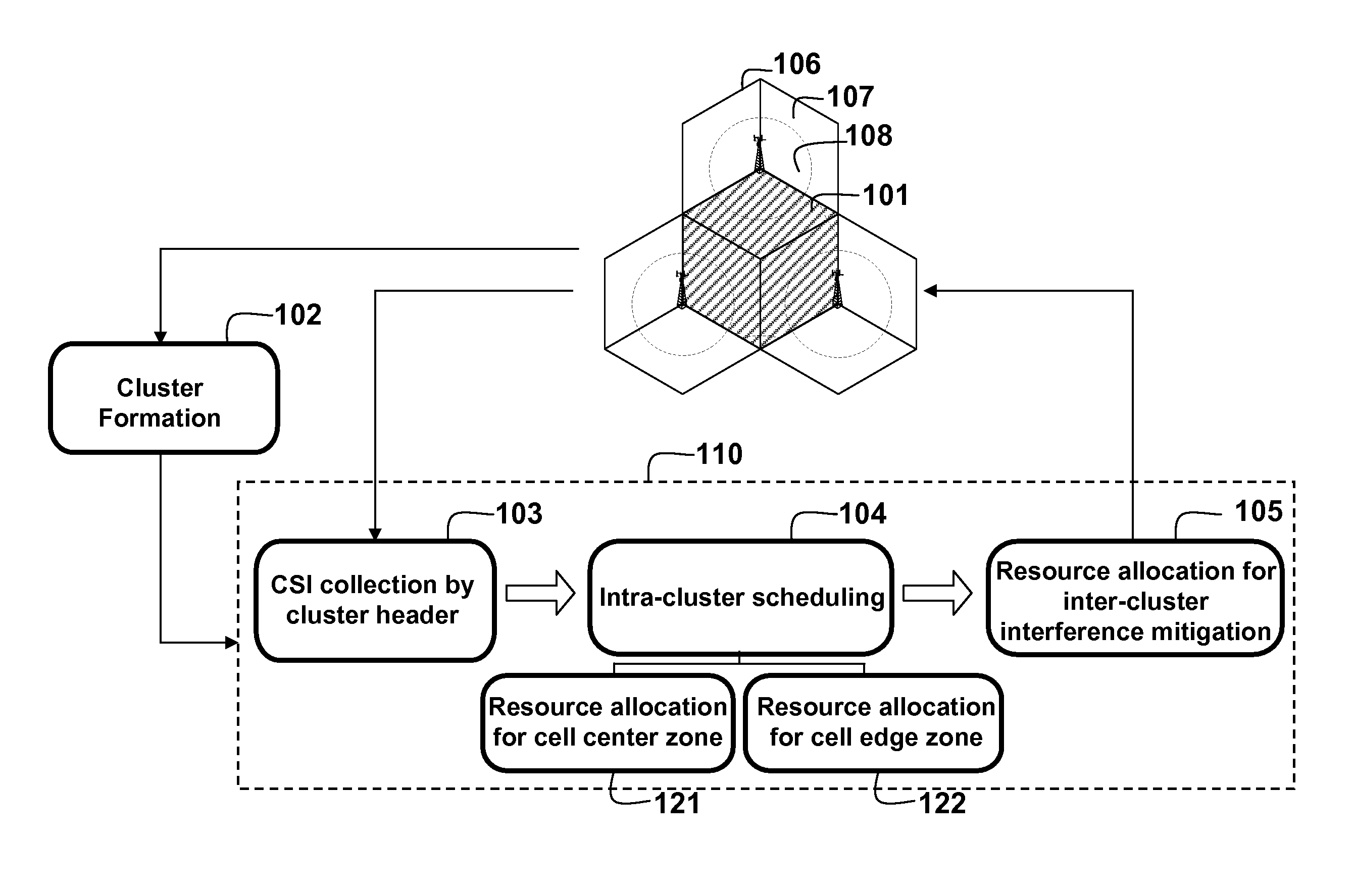
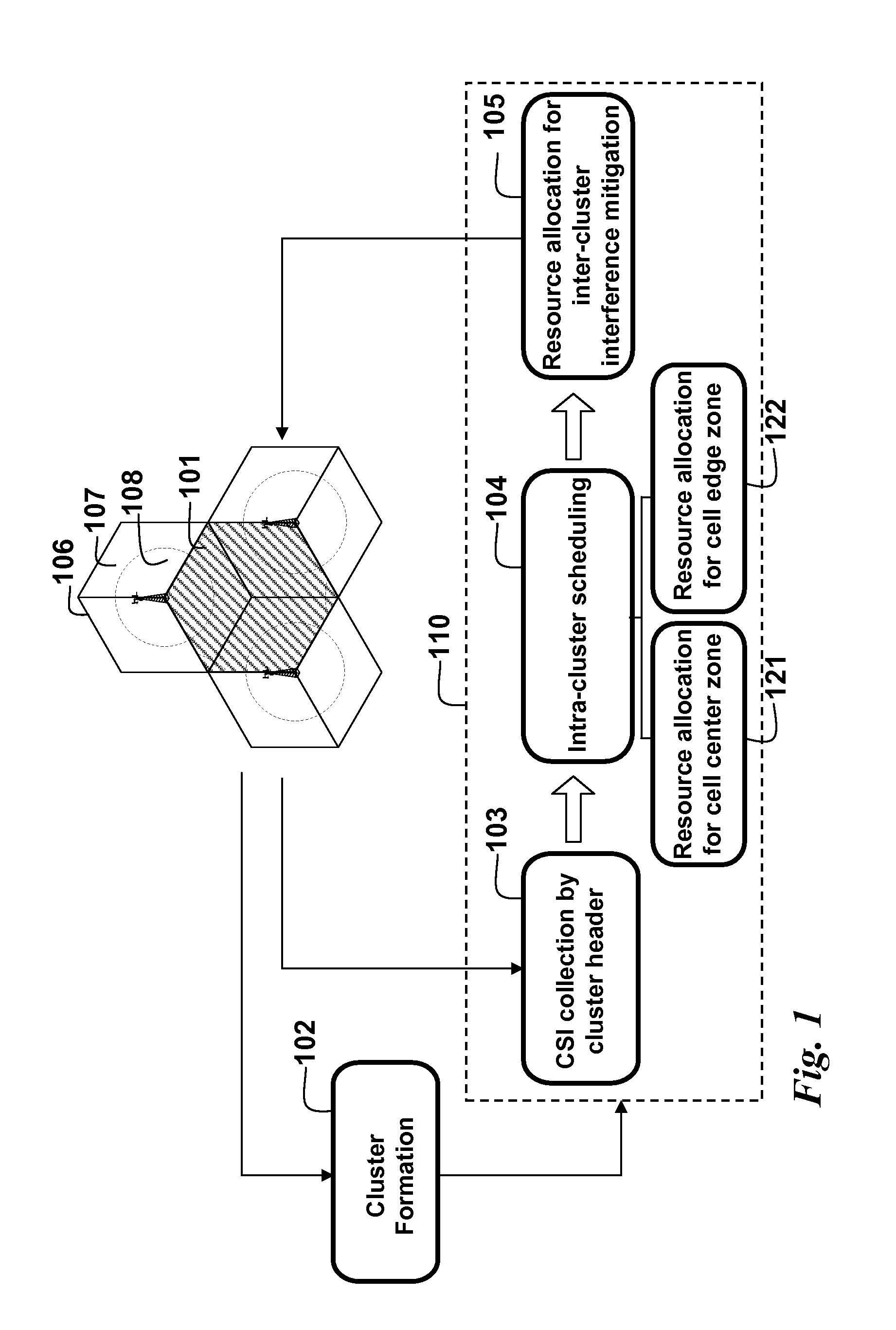
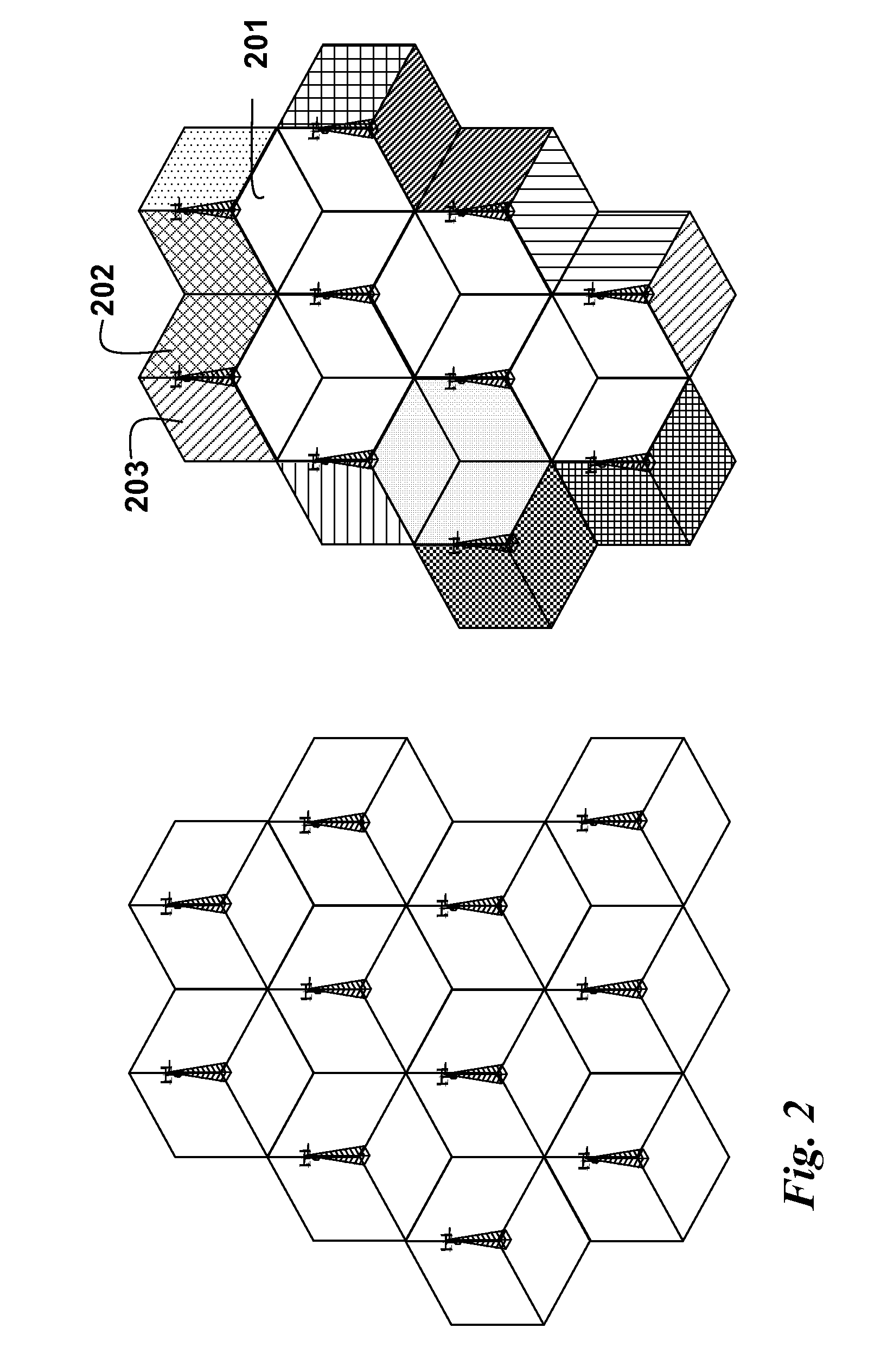
Clustering Based Resource Allocation in Multi-Cell OFDMA Networks
InactiveUS20100214997A1Interference can be avoided and reducedImprove performanceWireless commuication servicesNetwork planningOverlap zoneResource block
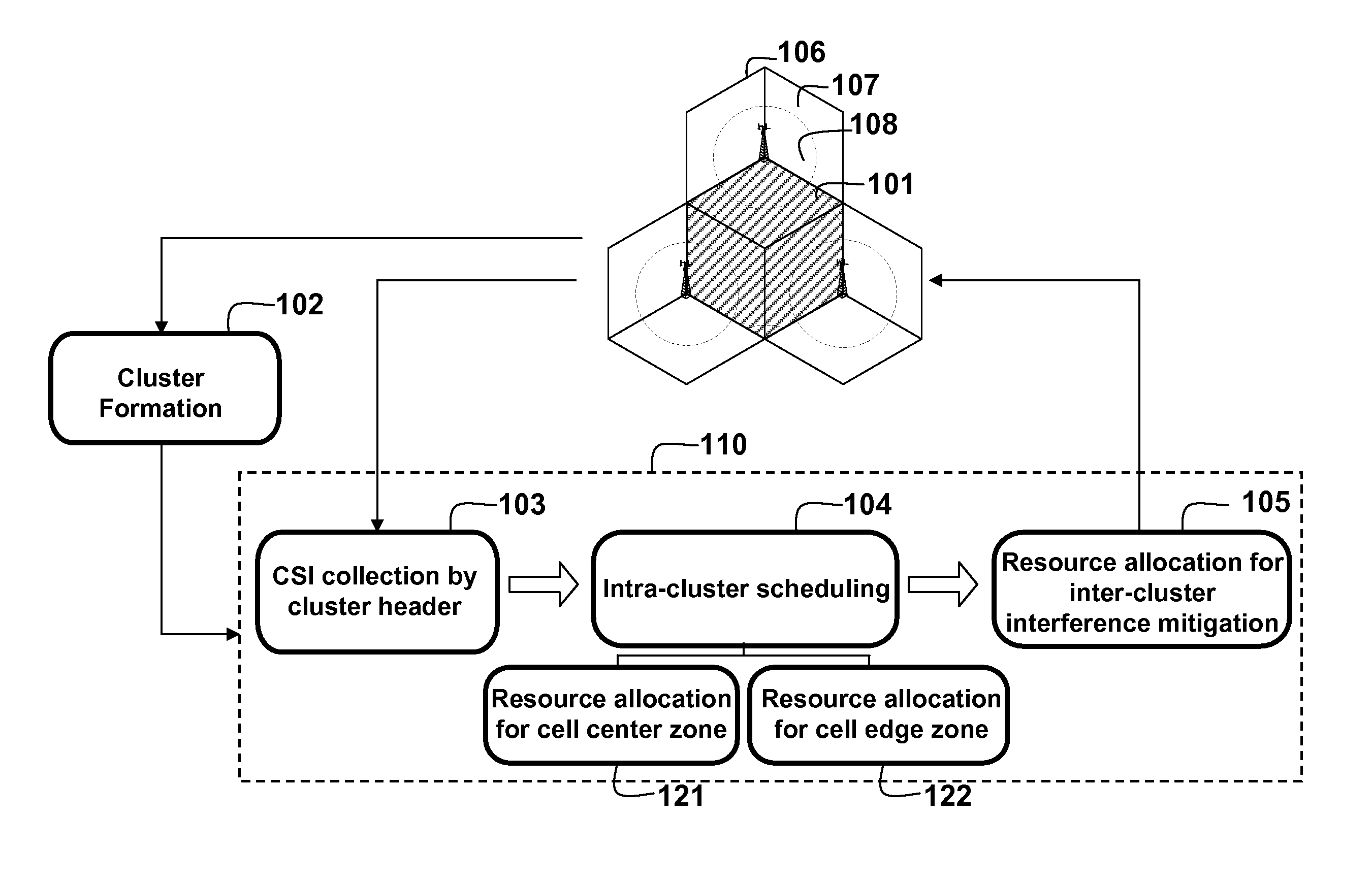
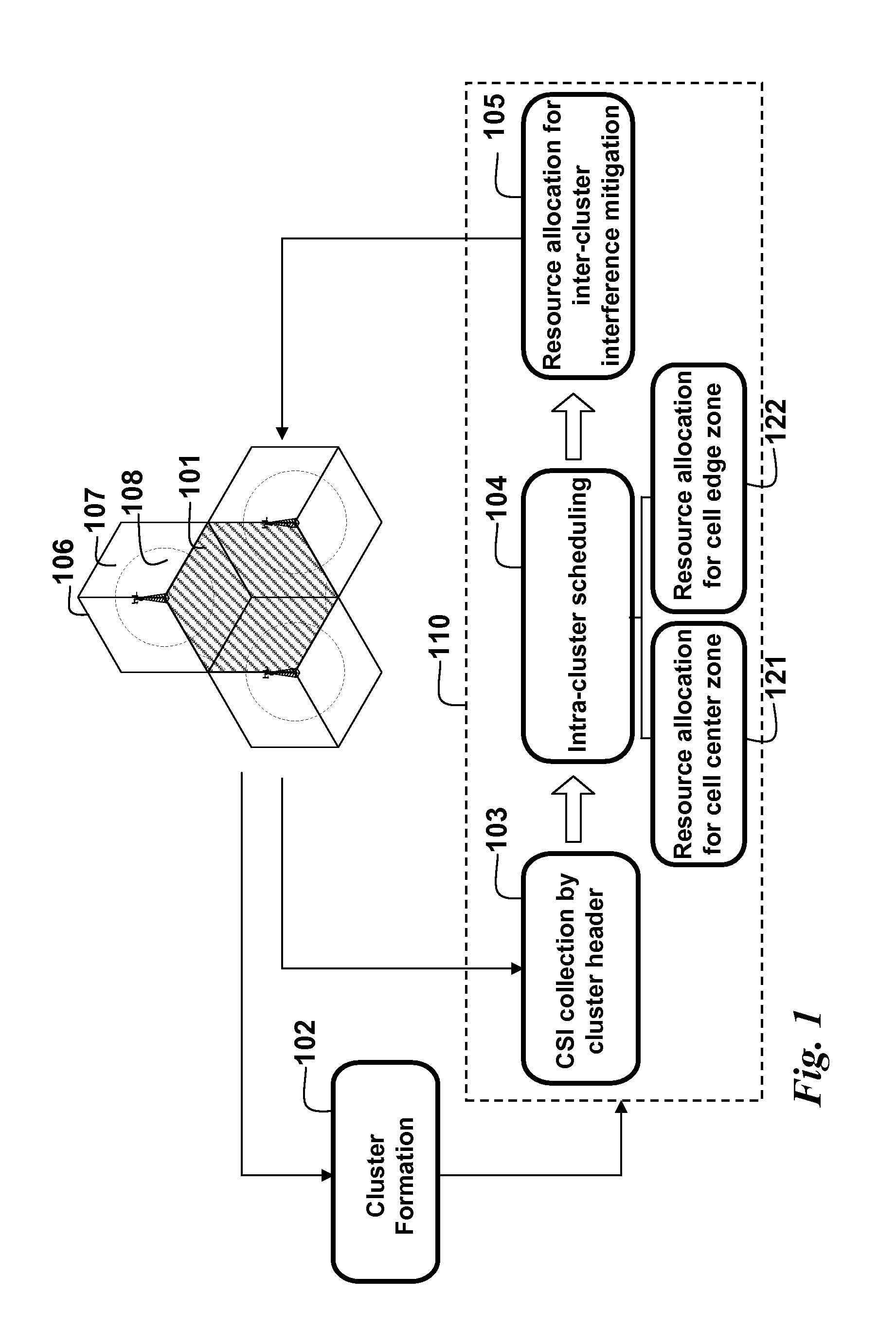
A method allocates resource in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) network, including a set of Base Stations (BSs) and a set of Mobile Stations (MSs) for each BS. OFDMA frame are constructed as multiple resource blocks, and each resource block contains symbols transmitted on different subcarriers. A cluster is formed from adjacent sectors of different neighboring cells to jointly optimize the resource allocation in multiple frames, and three non-overlap zones are sequentially identified in cluster: cell center zone, cell edge zone, and cluster corner zone. Resource allocation includes intra-cluster proportional fair scheduling and inter-cluster interference mitigation. Intra-cluster scheduling further includes resource allocation for cell center zone and resource allocation for cell edge zone.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
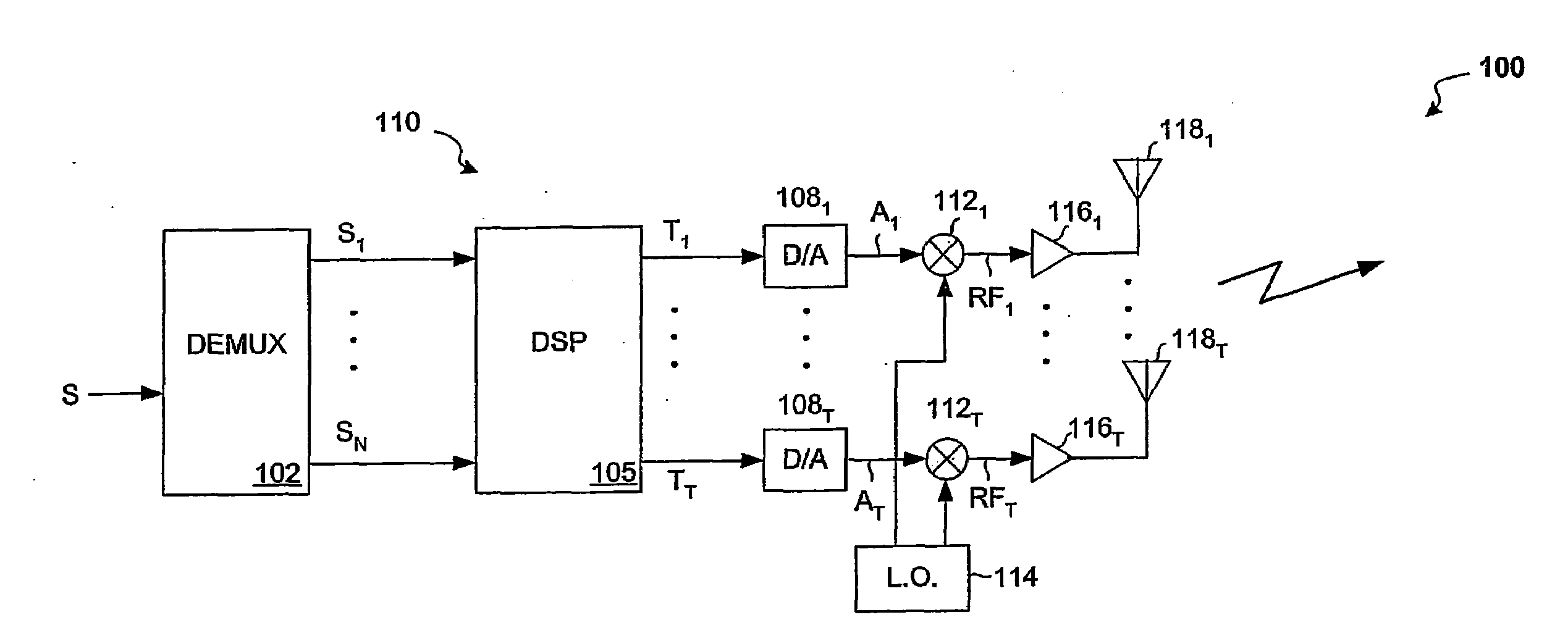
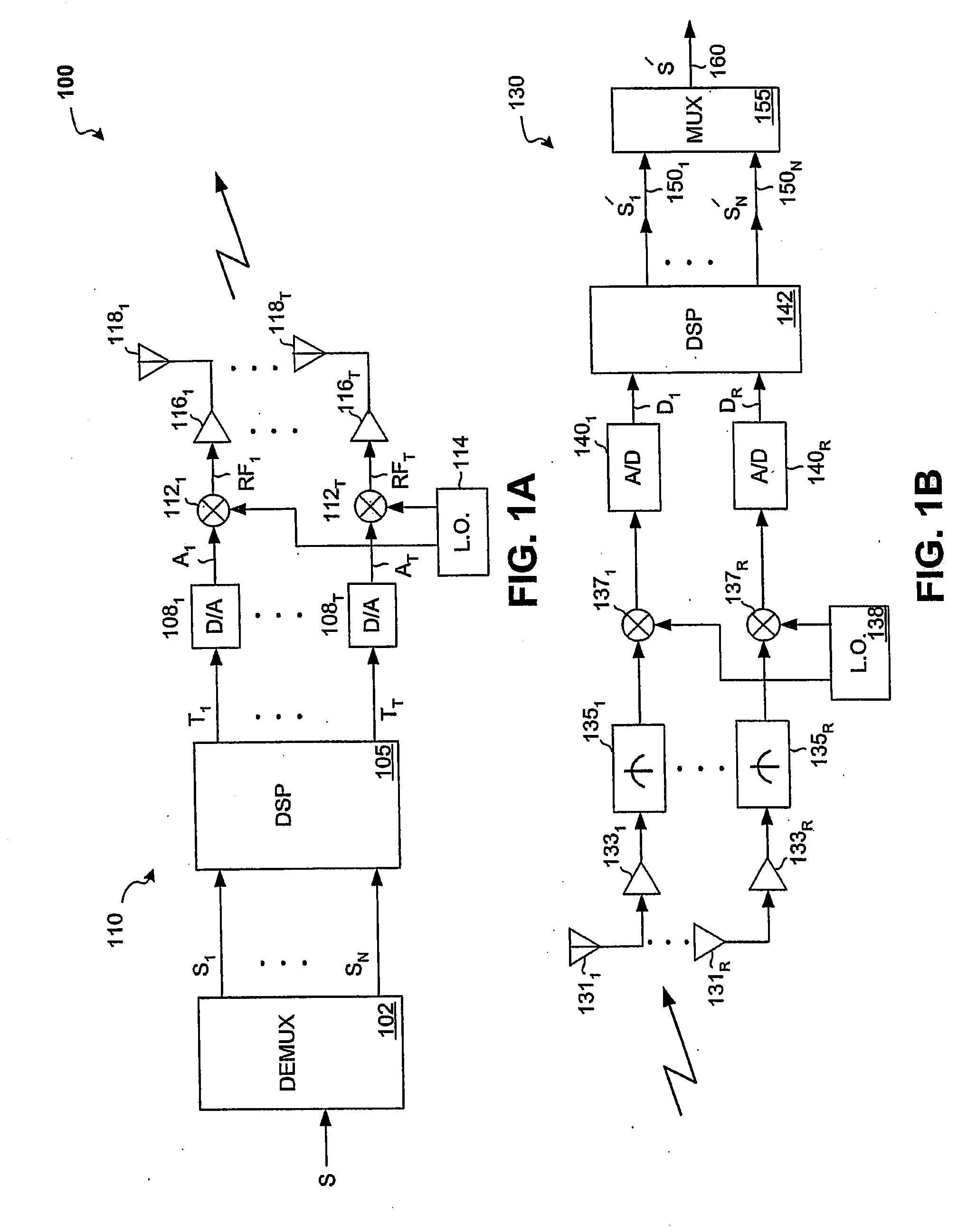
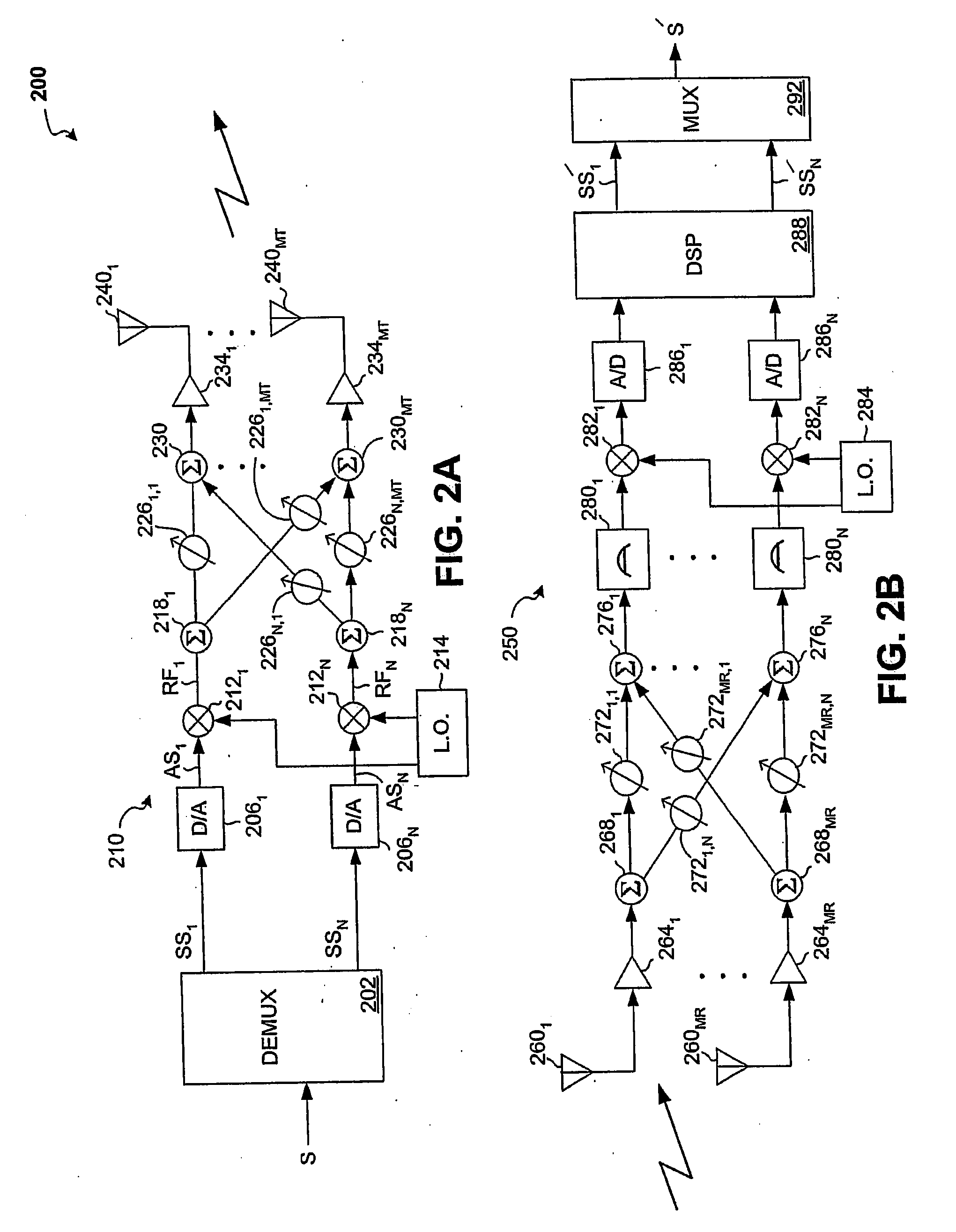
System and method for channel bonding in multiple antenna communication systems
ActiveUS20080261551A1Maximize data ratePower managementRadio transmissionCommunications systemChannel bonding
Systems and methods that provide channel bonding in multiple antenna communication systems are provided. In one embodiment, a method for signal transmission over a plurality of antennas of a transmitter may include, for example, one or more of the following: demultiplexing an input signal into a plurality of signal components; assigning each of the signal components to one of a plurality of logical channels; weighting each of the signal components with transmit baseband weight values; combining ones of the resultant weighted signal components to form a plurality of transmit weighted signals, each of the plurality of transmit weighted signals being assigned to one of the plurality of logical channels; and combining groups of the plurality of transmit weighted signals to form a plurality of output signals capable of being used to generate a plurality RF output signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple data stream transmission method and apparatus in relay system
InactiveUS20120020279A1InterferenceMaximize data rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareData stream
The present invention relates to a data transmission / receiving method and apparatus for overcoming interference between multiple data streams, by relaying only part of multiple data streams that are received from a source node during collaborative data transmission employing relay nodes. The multiple data stream transmission method of the present invention comprises: receiving a plurality of data streams from a source node; decoding the plurality of data streams received; selecting a portion of the successful decoded data streams; encoding the selected portion of the data streams; and sending the encoded data stream portion to a destination node.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC +1
Remotely reconfigureable distributed antenna system and methods
ActiveUS20140286247A1Increase capacityImprove efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower amplifiersSoftware define radioDistributed antenna system
The present disclosure is a novel utility of a software defined radio (SDR) based Distributed Antenna System (DAS) that is field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation-independent), multi-carriers, multi-frequency bands and multi-channels. The present disclosure enables a high degree of flexibility to manage, control, enhance, facilitate the usage and performance of a distributed wireless network such as flexible simulcast, automatic traffic load-balancing, network and radio resource optimization, network calibration, autonomous / assisted commissioning, carrier pooling, automatic frequency selection, frequency carrier placement, traffic monitoring, traffic tagging, pilot beacon, etc.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
Method, apparatus and system for progressive refinementof channel estimation to increase network data throughput and reliability
InactiveUS20080298382A1Improved channel estimationIncrease data rateModulated-carrier systemsColor television with bandwidth reductionTone mappingCarrier signal
A communication method and device operates in a network in which a multiplicity of communication devices communicate over a shared communication channel. The communication device includes a transmitter that transmits to a second communication device over the shared communication channel a first packet P1, employing a starting tone map TMS that includes a starting transmission scheme for a set of carriers of said channel, a receiver that receives over the shared channel a partial tone map PTM1 from the second communication device, and a tone map generator that generates an updated tone map TM1 based on the starting tone map TMS modified in accordance with the partial tone map PTM1. The transmitter transmits over the shared channel a second packet P2 to the second communication device, employing the updated tone map TM1. The partial tone map may be received as part of an acknowledgment packet from the second communication device.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and systems for decentralized interference management in a multi-antenna wireless communication system
InactiveUS20150078186A1Reduce distractionsMaximize data rateSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemTransmitted power
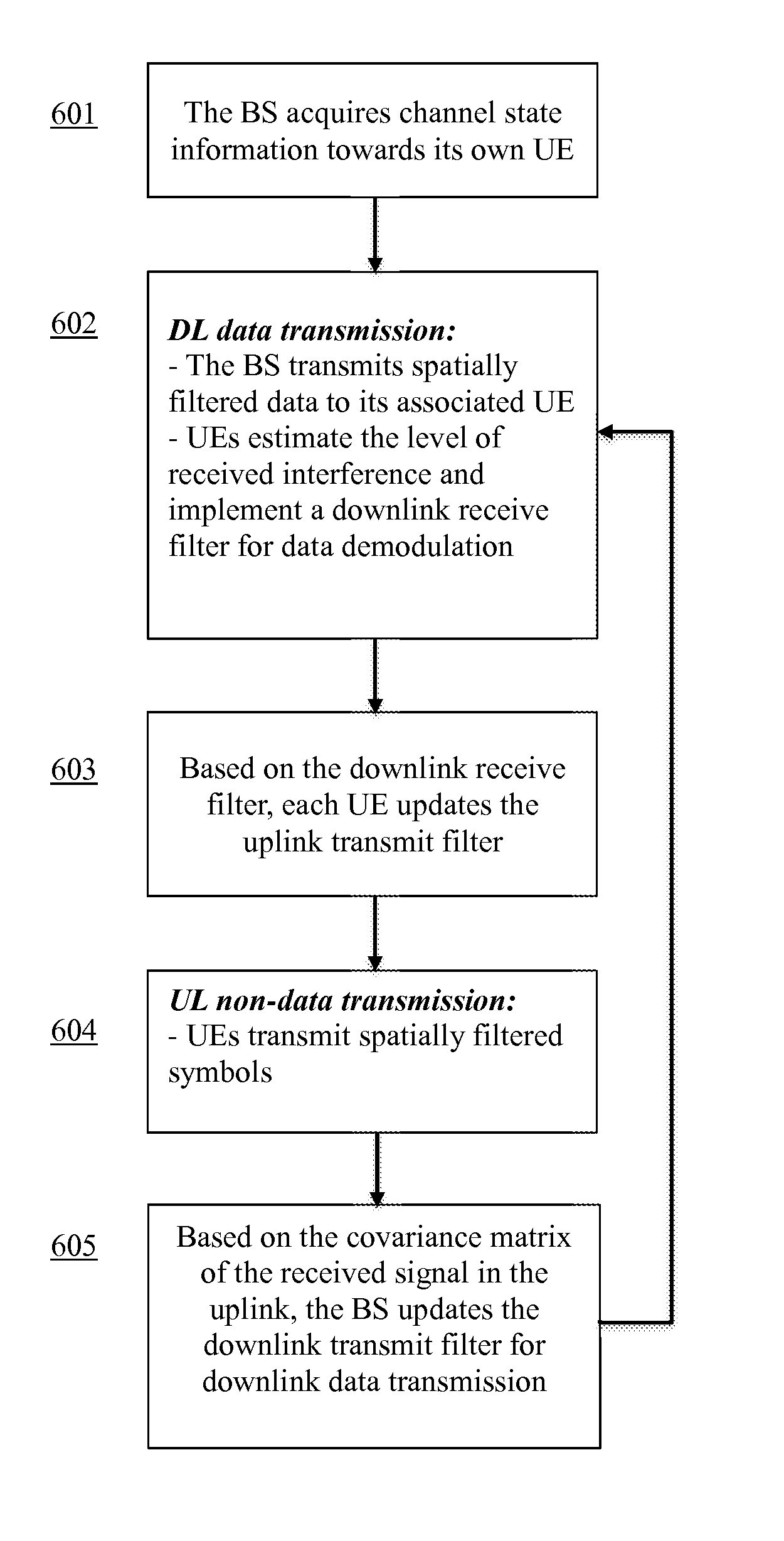
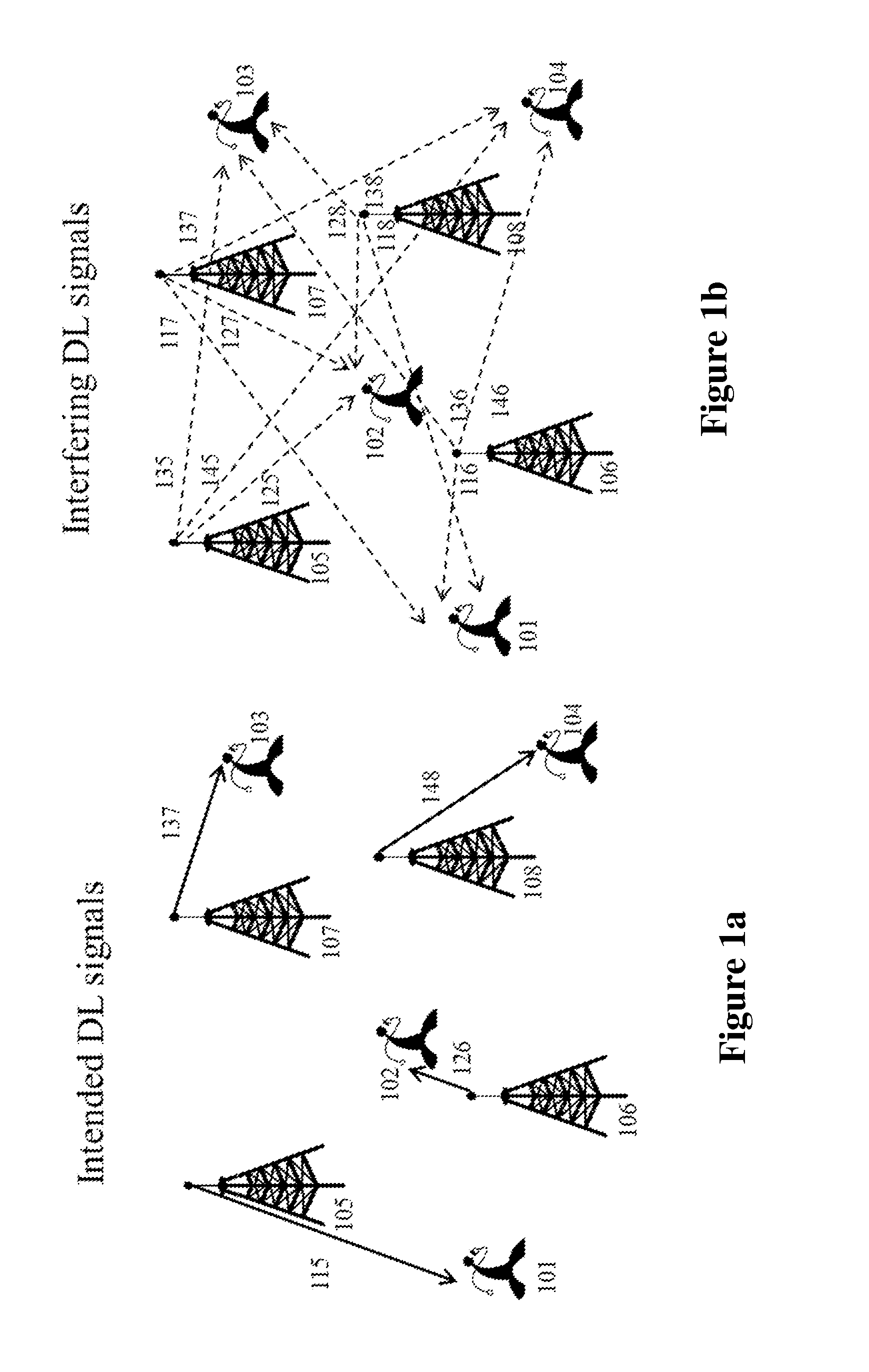
A method that includes interference control at transmitters and interference mitigation at receivers in a wireless communication system is disclosed. Embodiments of the present invention exploit the interference sensitivity at neighboring terminals by taking into account the reciprocity of propagation radio channels in Time Division Duplexing systems (TDD). It can be applied to design the resource allocation for downlink (DL) and uplink (UL) transmissions in a wireless communication system. The methods include the self-configuration of the transmit power, the transmit precoder and the receive filter, at each transmitter and receiver in a multi-cell network. Systems are also provided and configured for implementing the methods of the invention.
Owner:UNIV POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA
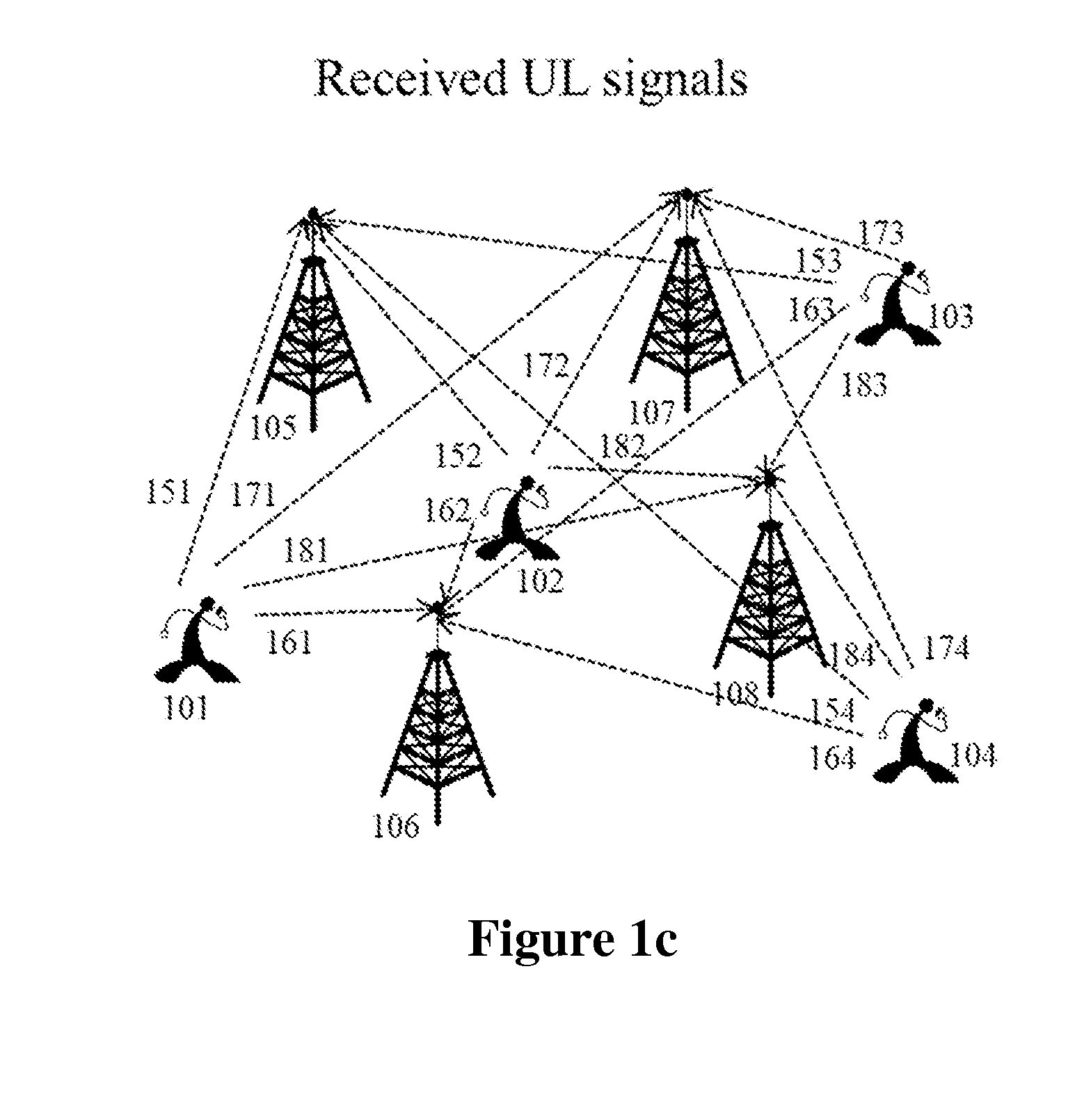
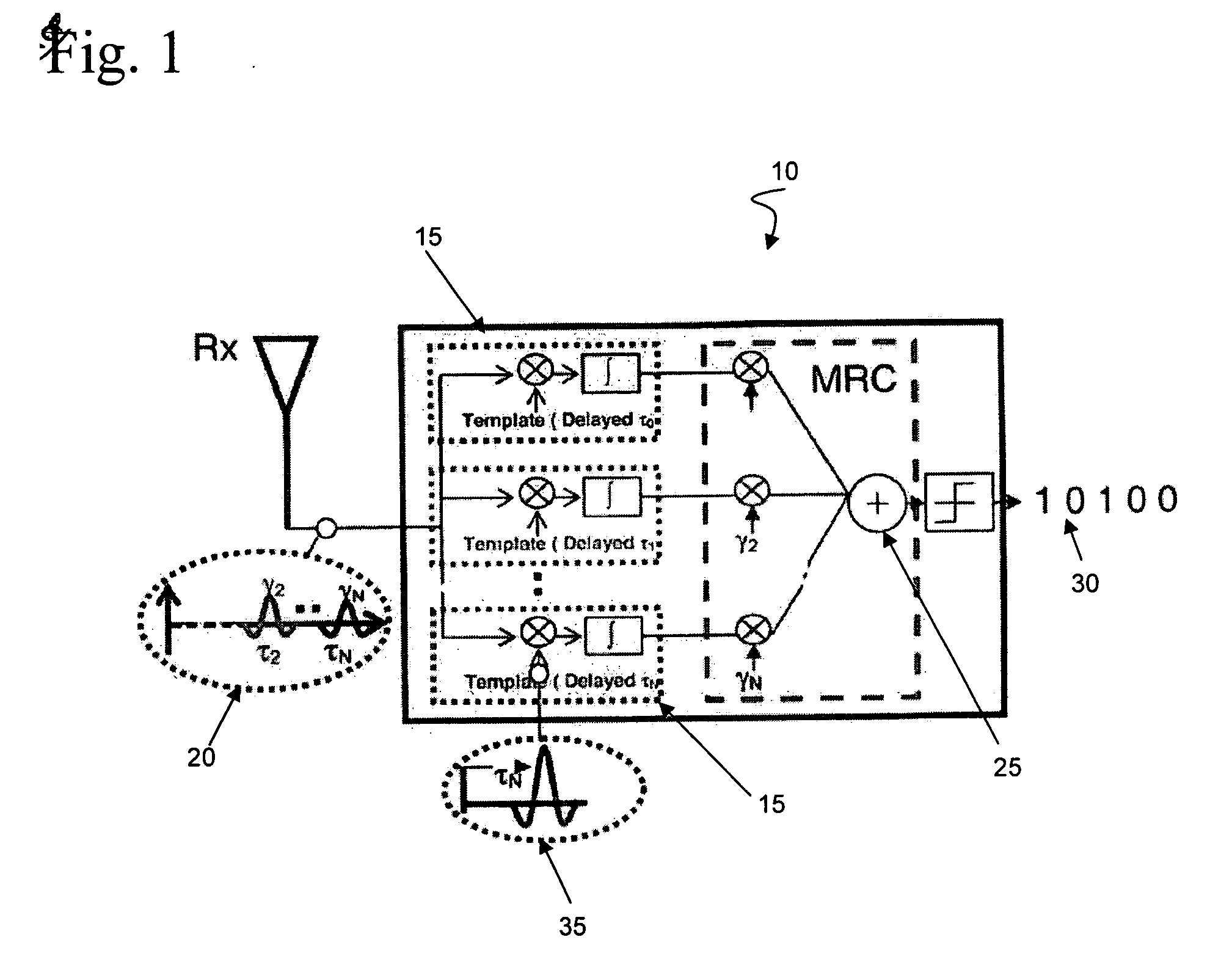
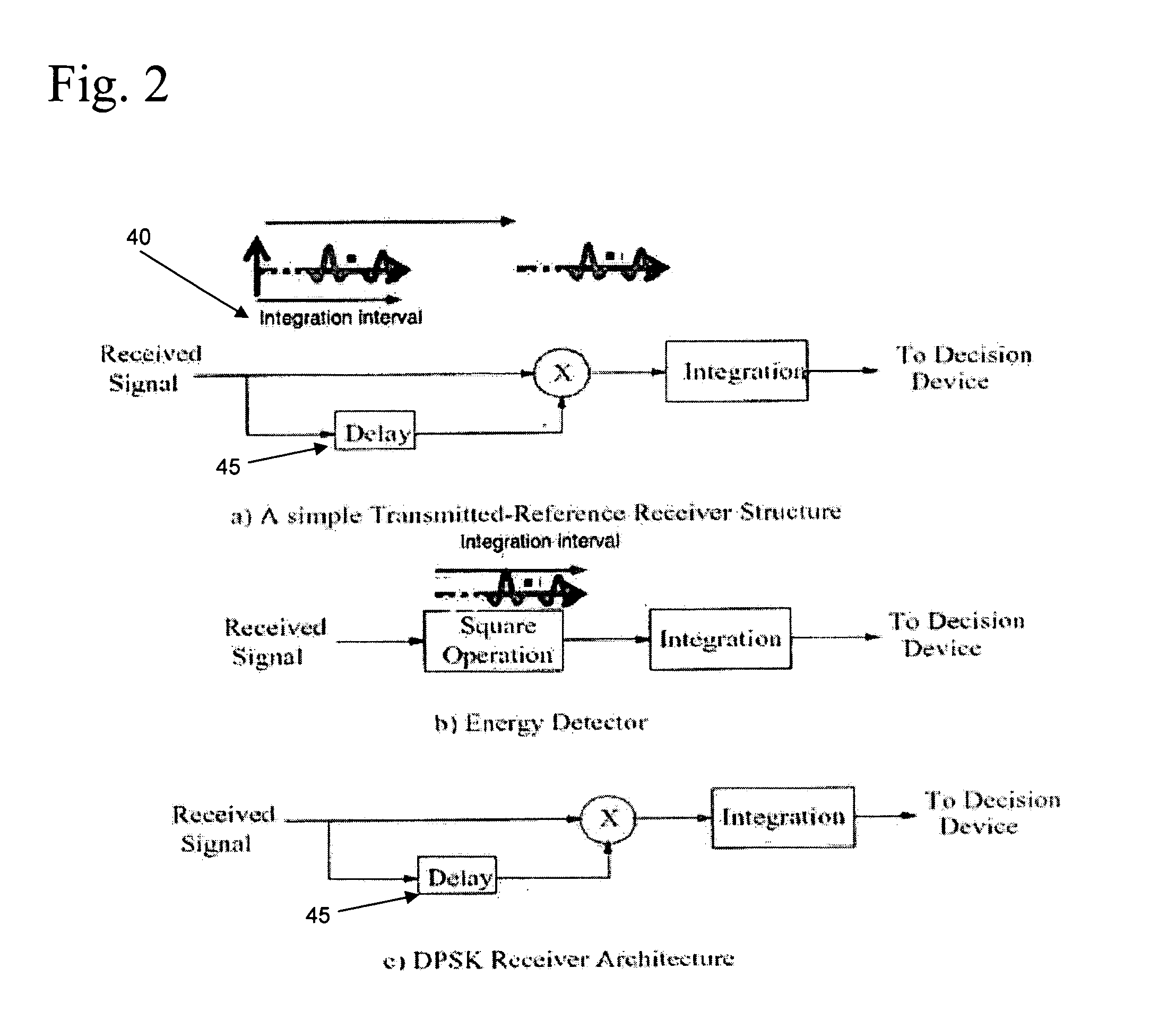
Adaptive Ultrawideband Receiver and Method of Use
ActiveUS20070153881A1Improve accuracyImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringBroadband
In accordance with the present invention, novel methods for adaptive receiver design and related parameter estimation techniques for efficient and non-coherent reception of ultrawideband signals are presented. Efficient estimation of maximum excess delay of the channel for enabling many useful adaptation techniques is additionally provided. Also, noise power estimation which significantly improves the performance of the receivers is presented.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
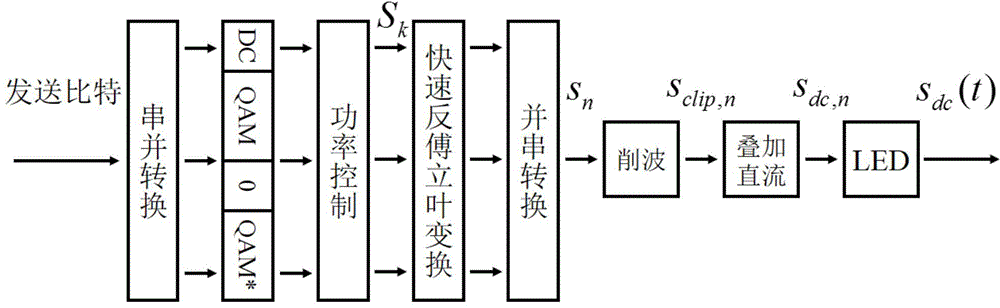
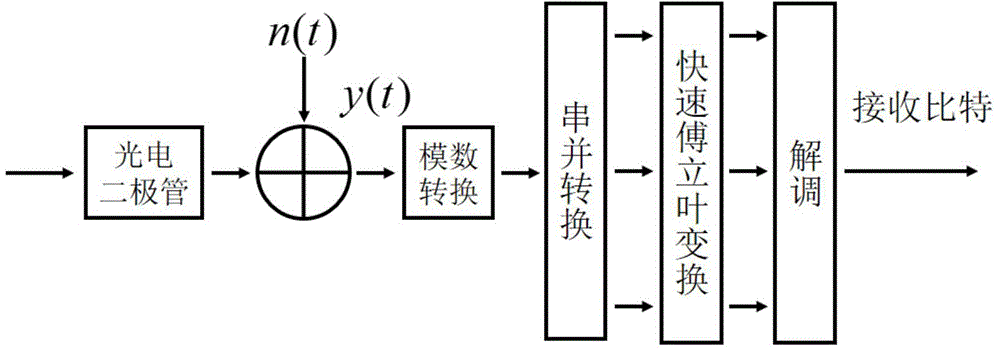
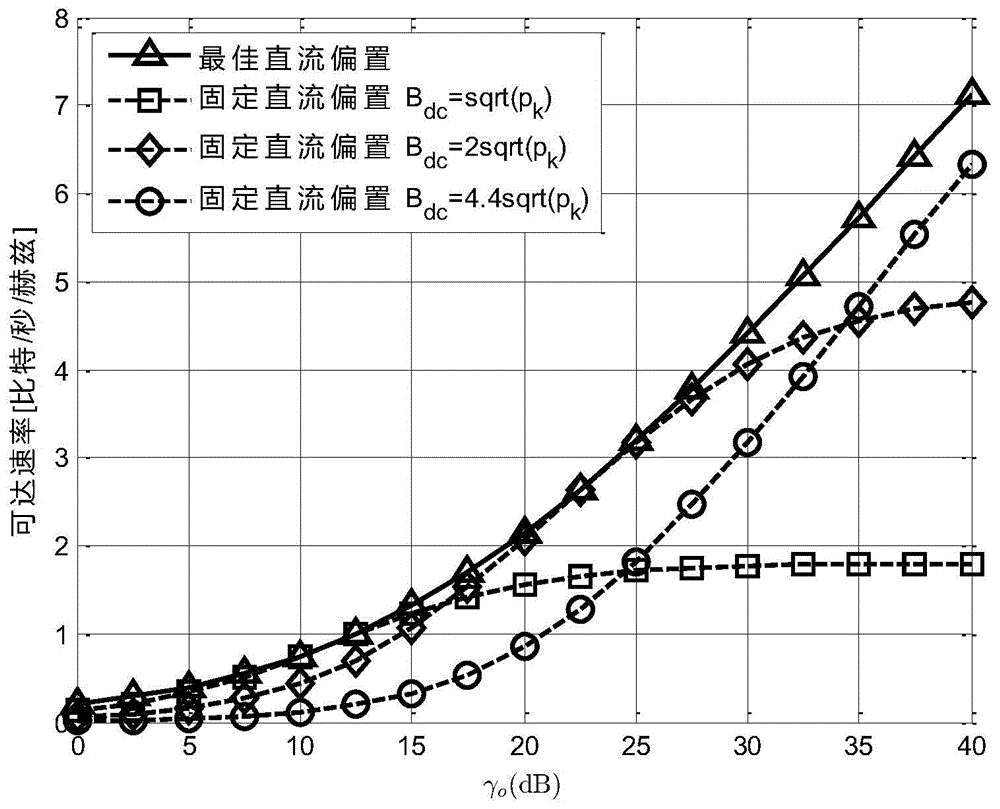
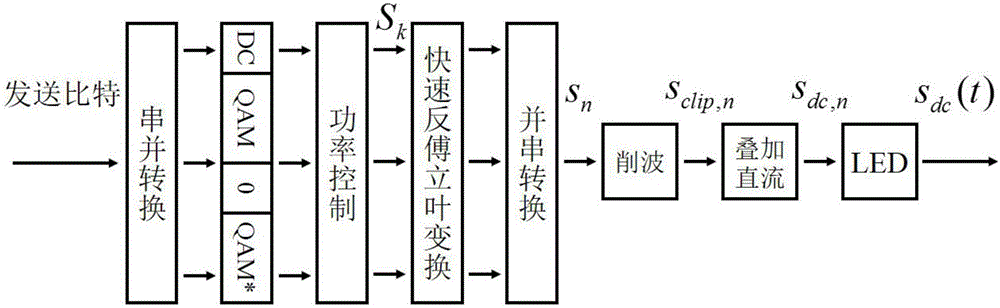
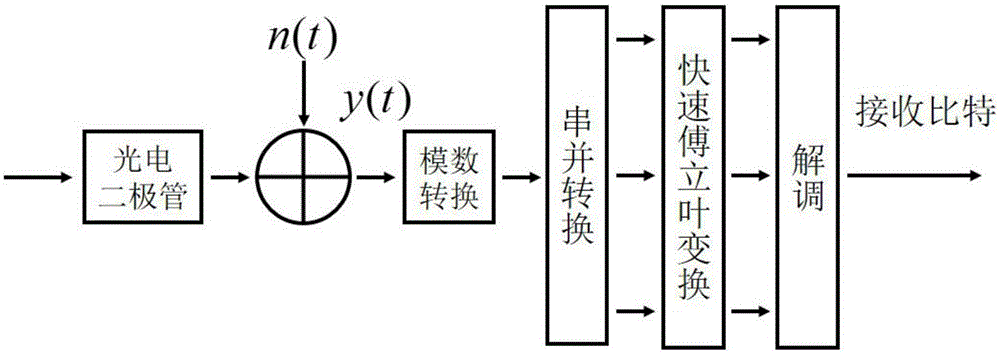
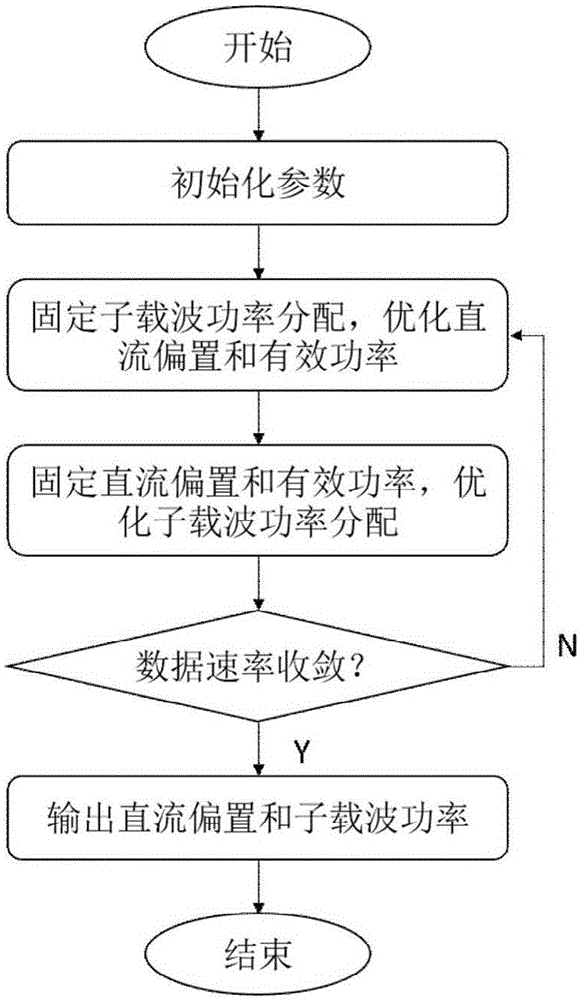
DCO-OFDM DC bias and rapid power optimizing method under double restrictions
ActiveCN104618300AStrong practical valueImprove performanceClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsFast optimizationEngineering
The invention discloses a DCO-OFDM (Direct-Current-Biased Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) DC bias and rapid power optimizing method under double restrictions aiming at visible light communication. DCO-OFDM DC bias and subcarrier power optimizing is a complex non-convex and non-linear optimizing problem. The DCO-OFDM DC bias and rapid power optimizing method can quickly seek the optimum DC bias Bdc and subcarrier power pk distribution scheme on the conditions of optical power limitation or electric power limitation or both optical power limitation and electric power limitation. The DC bias Bdc and subcarrier power pk obtained through the DCO-OFDM DC bias and rapid power optimizing method can maximize the data rate of the system or minimize the bit error rate in the fixed modulation scheme. The DCO-OFDM DC bias and rapid power optimizing method has the advantages of fast rate of convergence, small calculation amount, easiness in achievement, high result accuracy, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
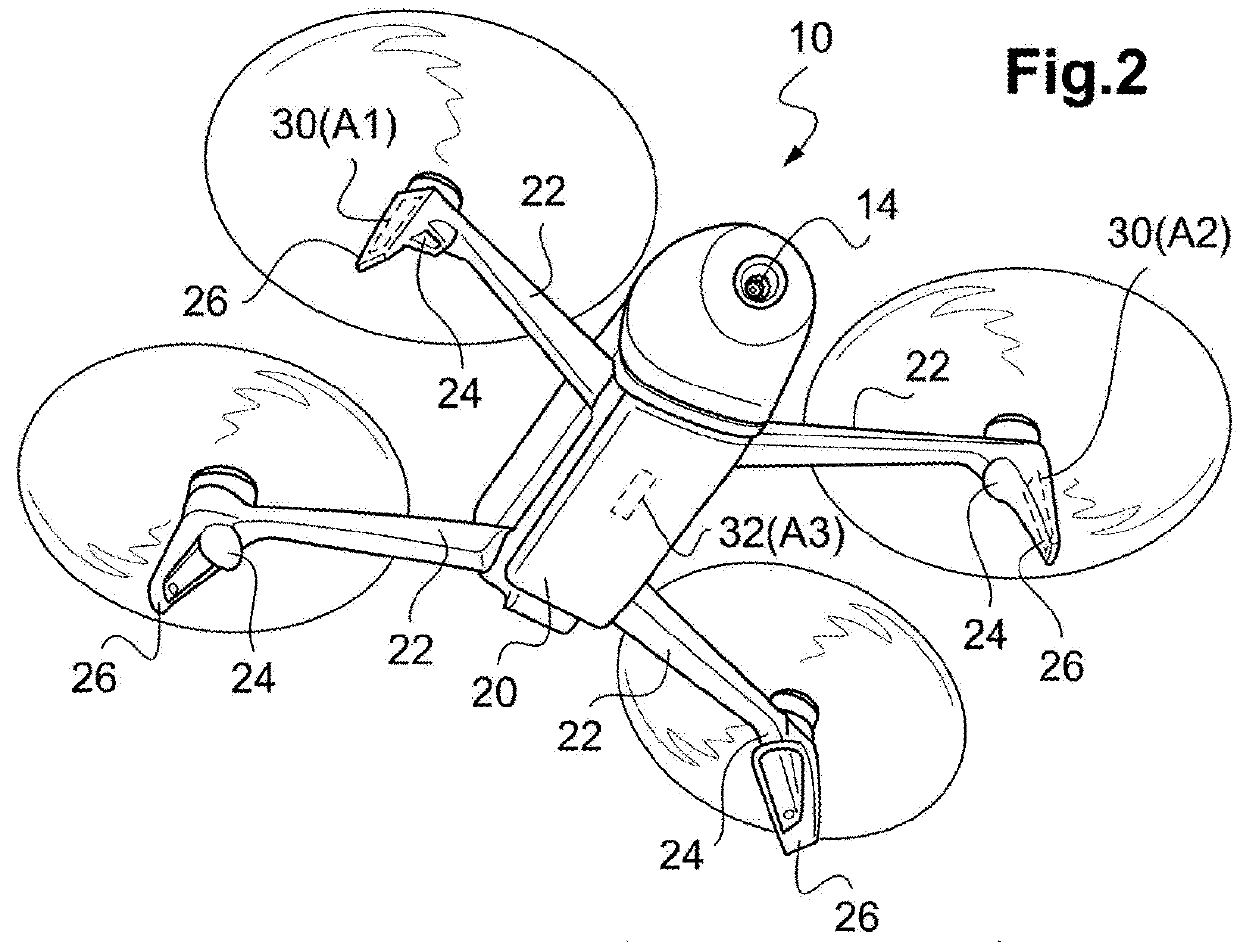
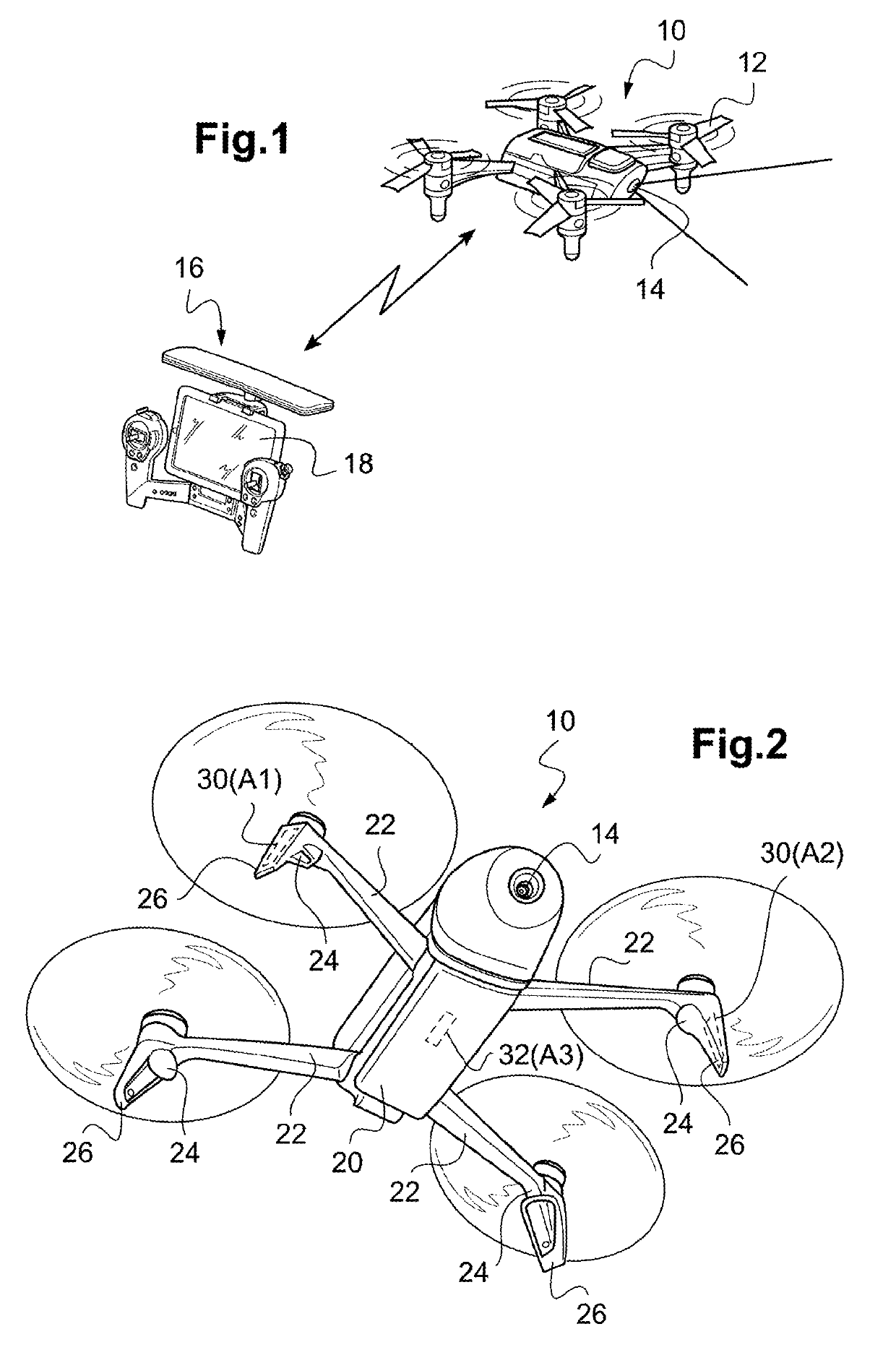
Drone with dynamic antenna diversity
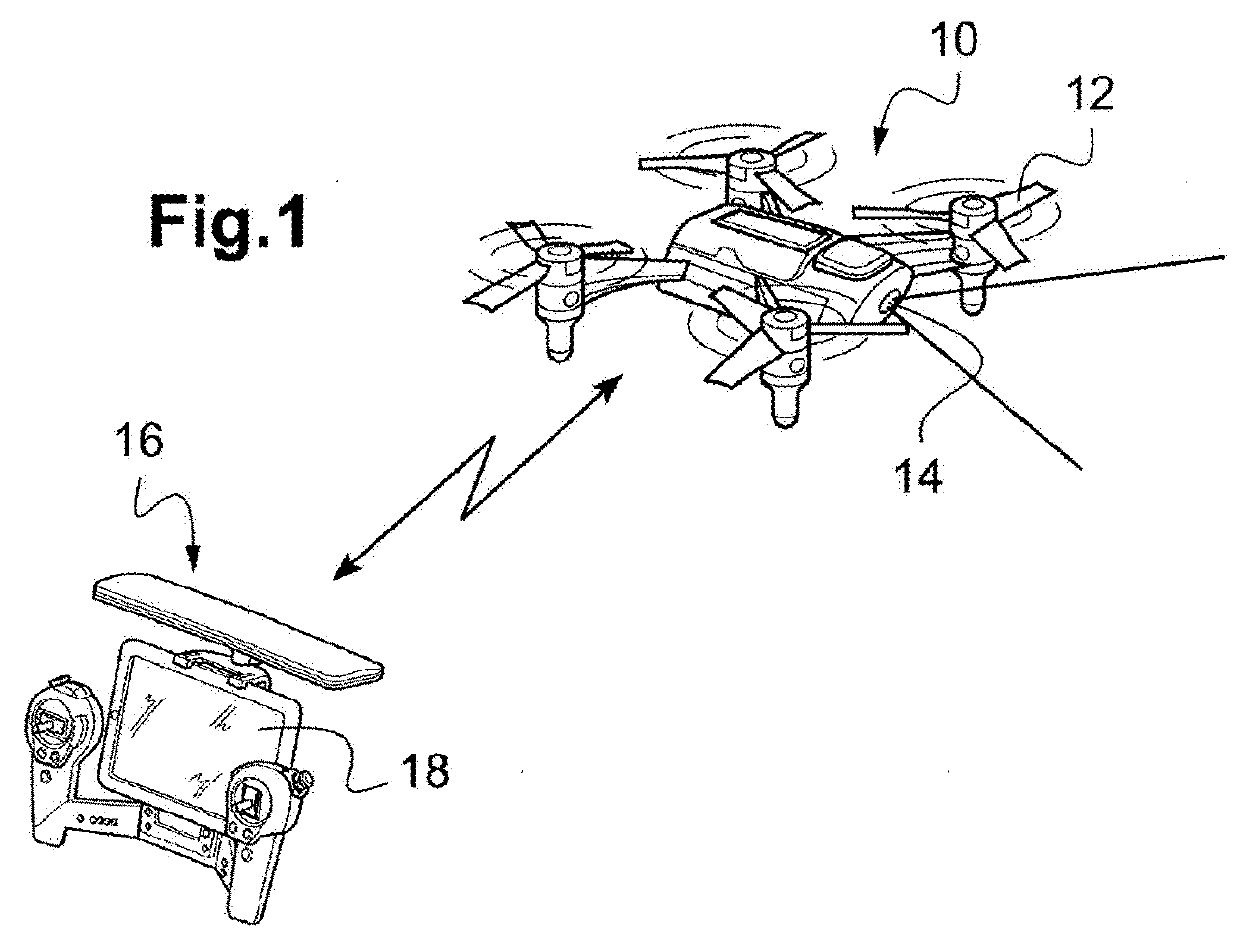
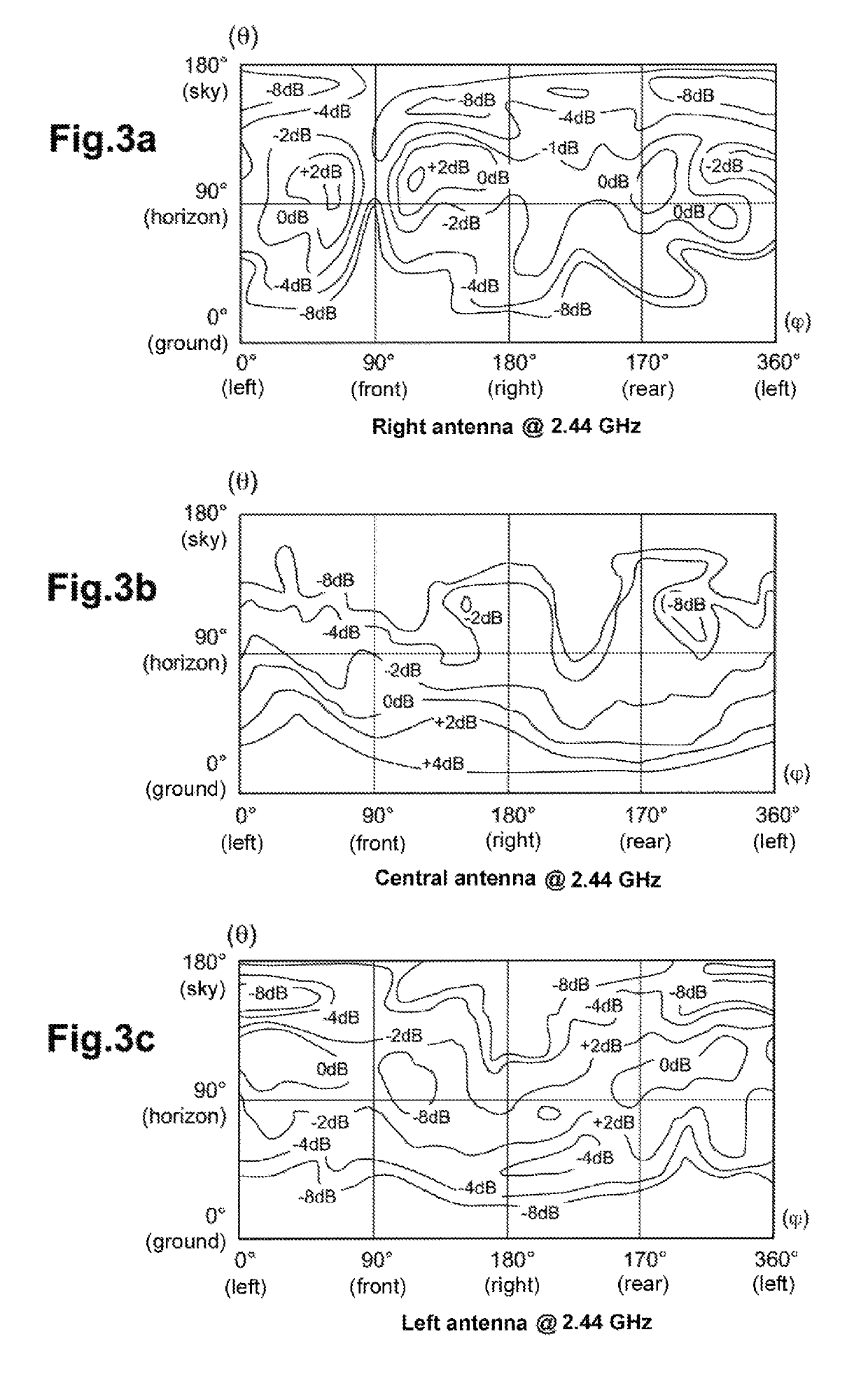
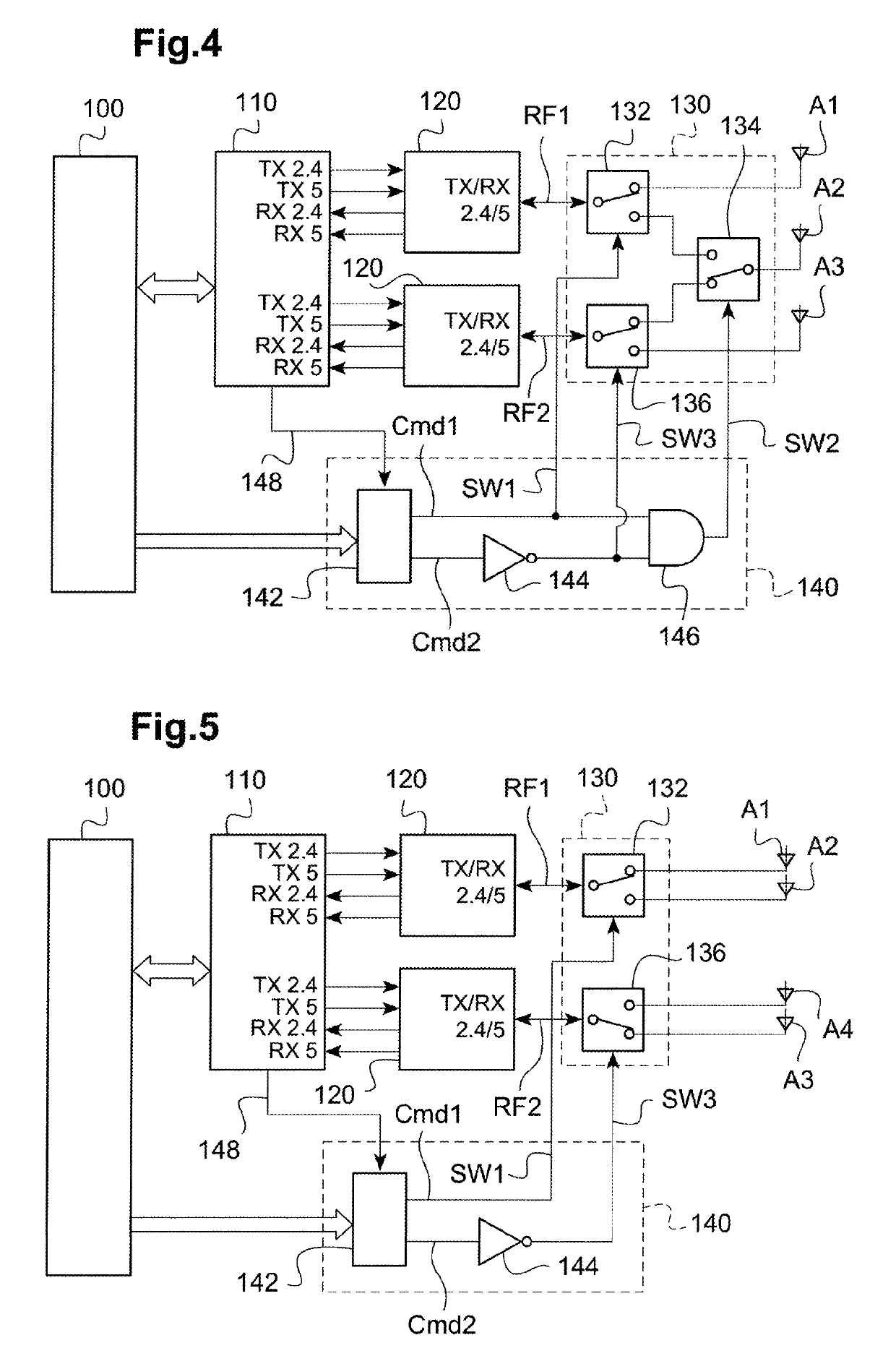
ActiveUS20180183496A1Maximize data rateMinimizing signal to noise ratioAircraft componentsSpatial transmit diversityDiversity schemeAntenna diversity
The drone comprises M antennas, with in particular two offset antennas located symmetrically at the ends of two arms for the connection to the propulsion units (24), and a ventral antenna under the drone body. The radio transmission is operated simultaneously on N similar RF channels, with 2≤N<M. An antenna switching circuit couples selectively each of the N RF channels to N antennas out of the M antennas according to a plurality of different coupling schemes, dynamically through a piloting logic selecting one of the coupling schemes. The selection is operated as a function of a signal delivered by the drone-borne microprocessor, as a function of the flight and signal transmission conditions, determined at a given instant.
Owner:PARROT
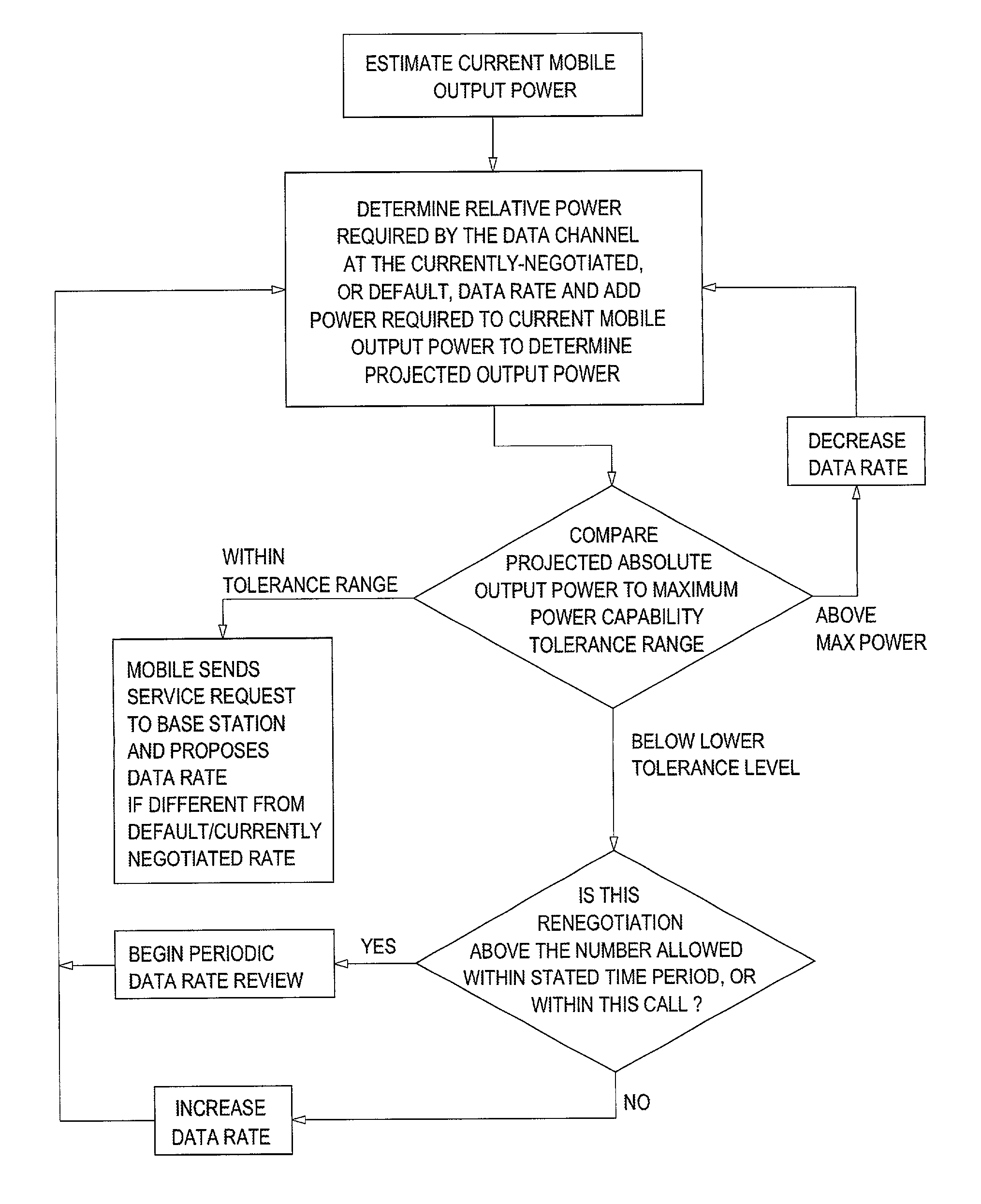
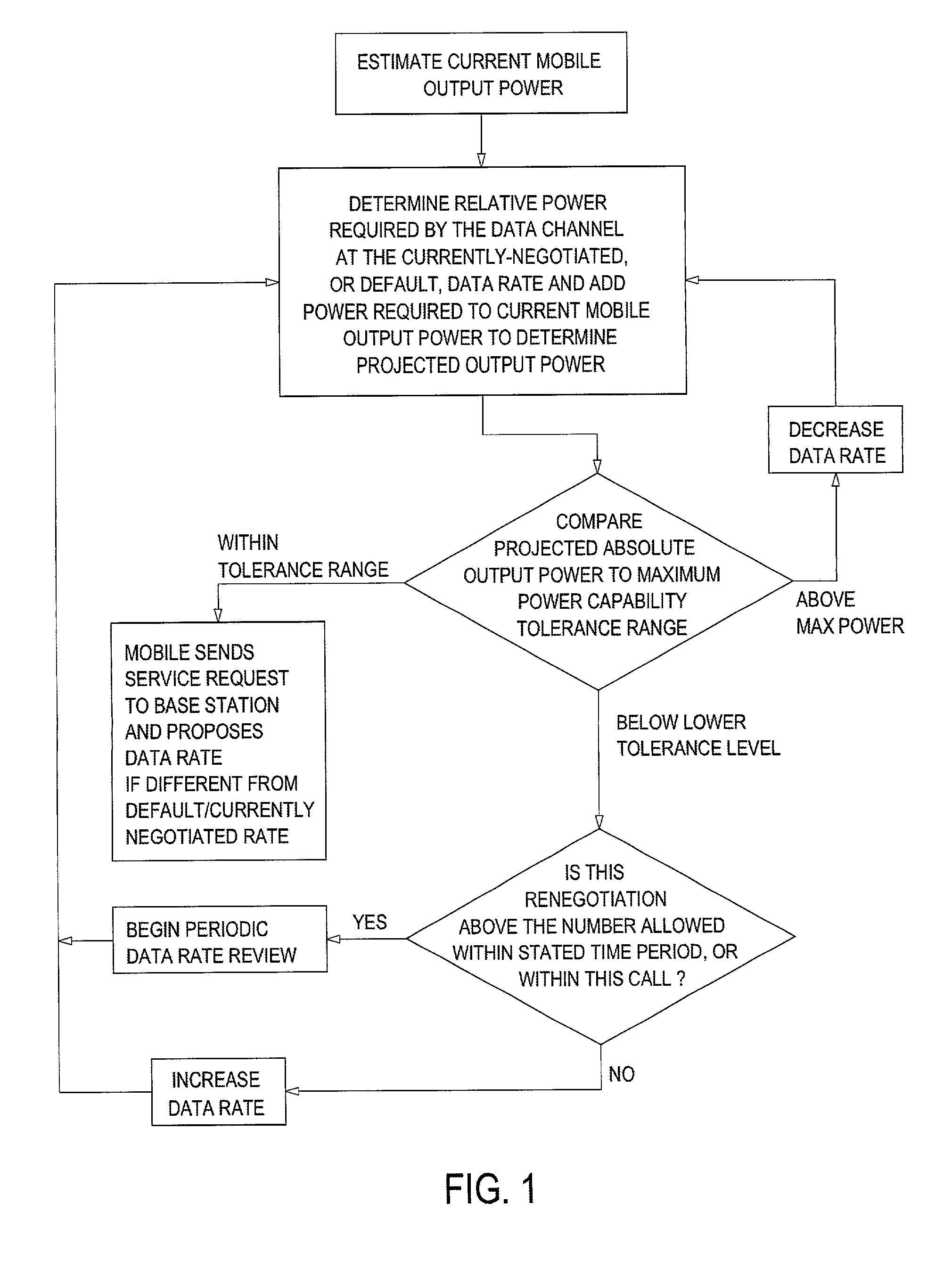
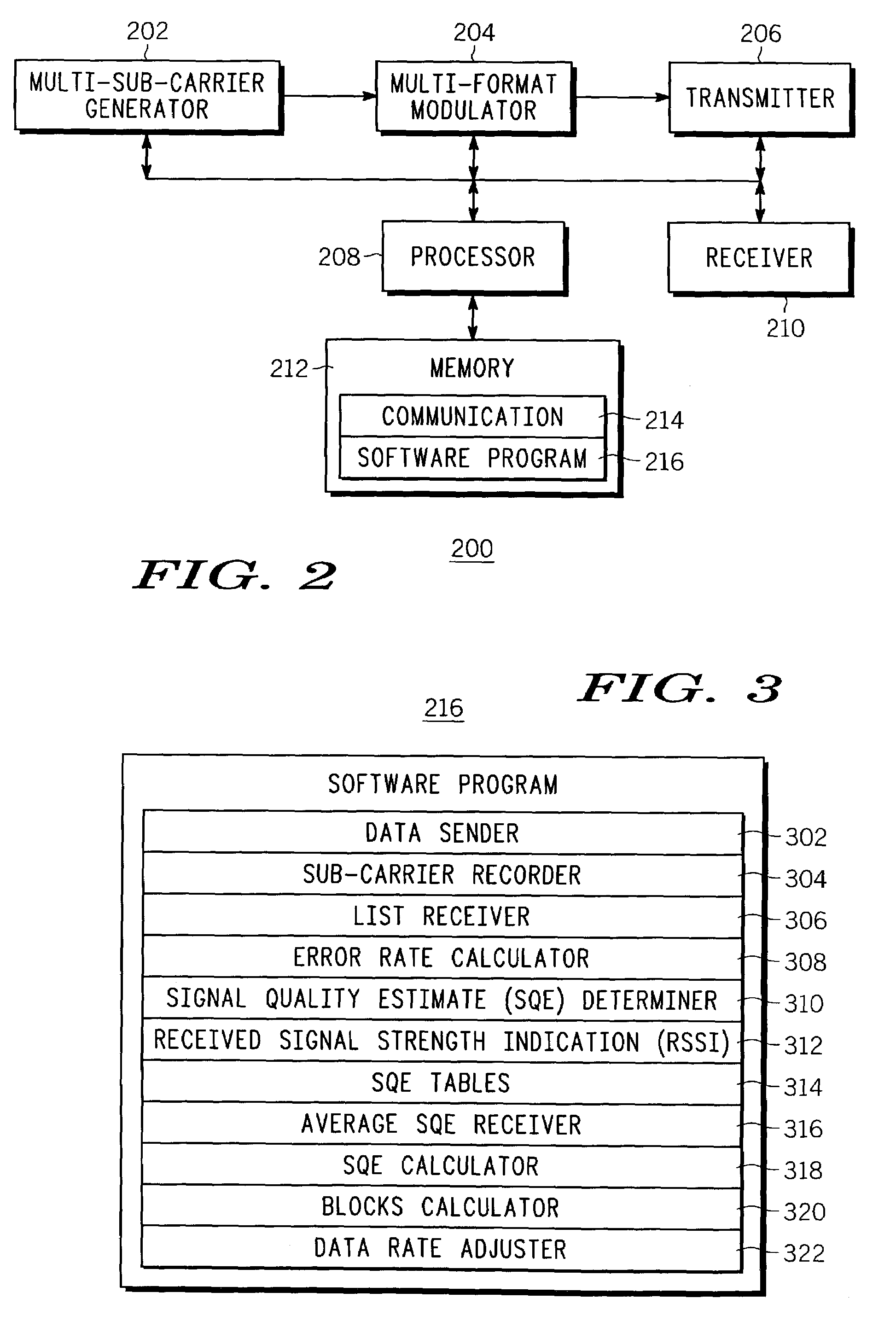
Method and apparatus for maximizing a data rate of a wireless data communication system
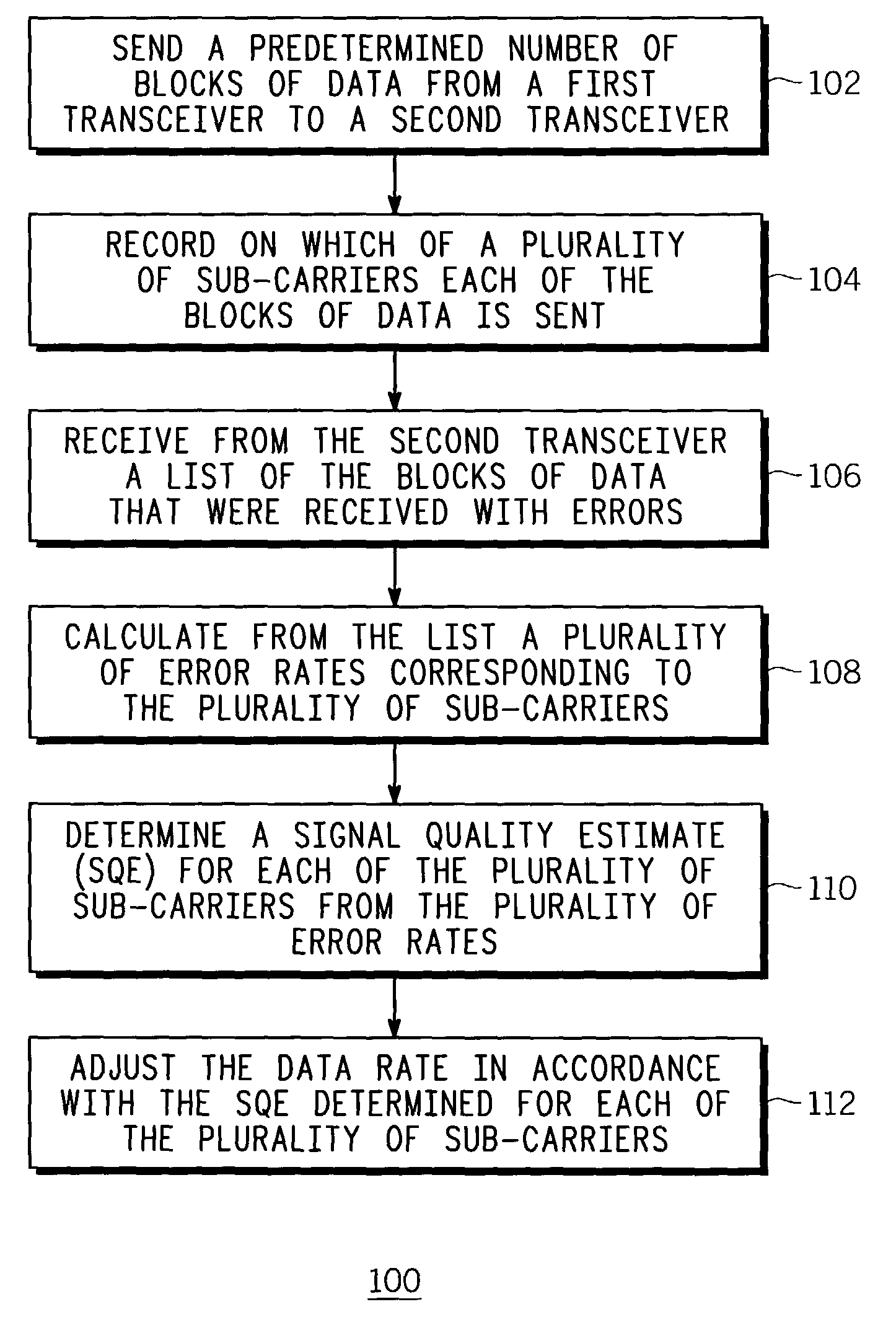
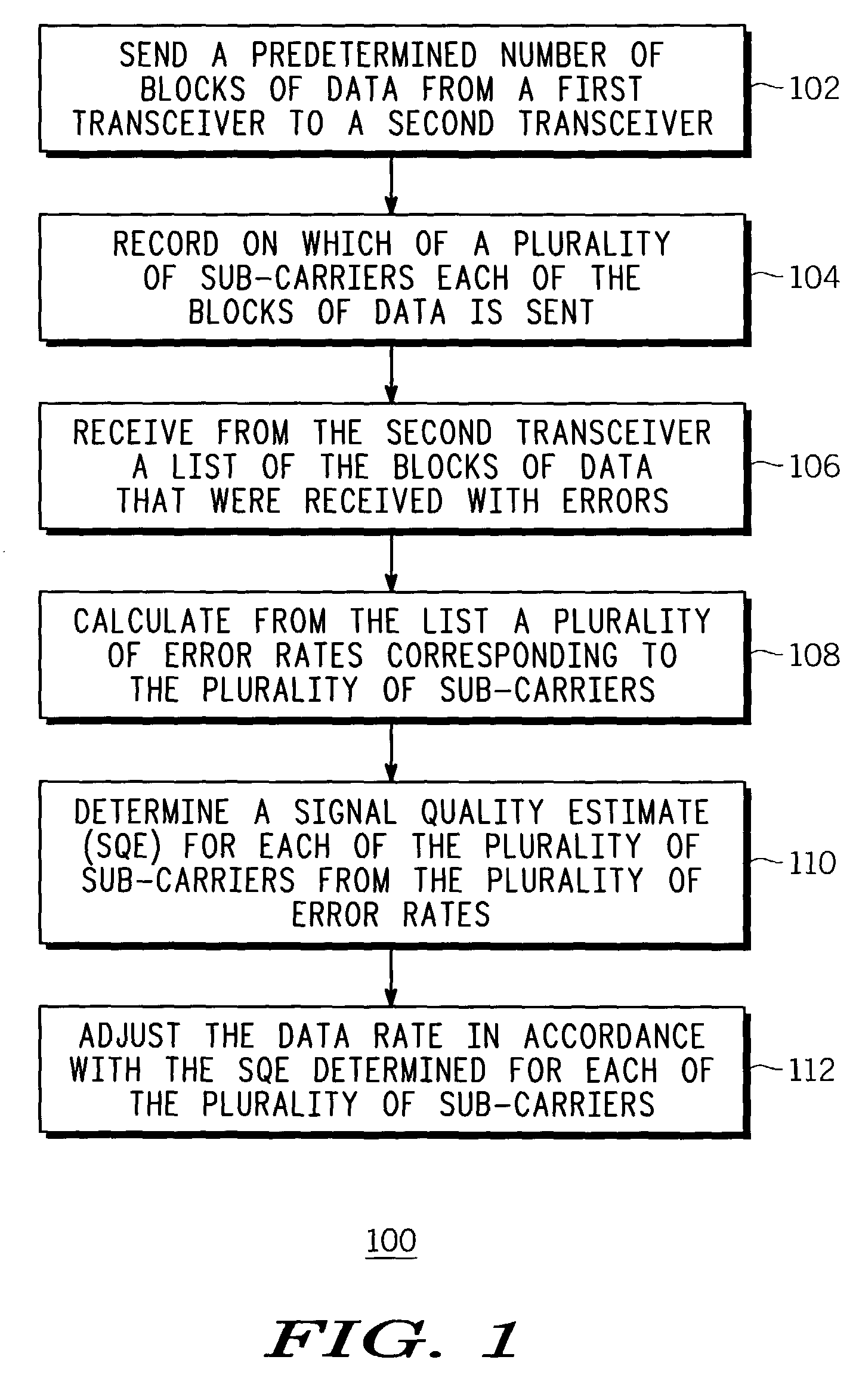
ActiveUS7212542B2Maximize data rateError prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCarrier signalSubcarrier
A first transceiver (200) sends (102) a predetermined number of blocks of data to a second transceiver, and records (104) on which of a plurality of sub-carriers each of the blocks of data is sent. The first transceiver receives (106) from the second transceiver a list of the blocks of data that were received with errors, and calculates (108) from the list a plurality of error rates corresponding to the plurality of sub-carriers. The first transceiver then determines (110) the SQE for each of the plurality of sub-carriers from the plurality of error rates, and adjusts (112) the data rate in accordance with the SQE determined for each of the plurality of sub-carriers. These processes can be implemented as a method that is facilitated by a software program.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
DCO-OFMD direct current bias and power joint optimization method under non-flat channel
ActiveCN105119698AStrong practical valueThe optimal solution is accurateCriteria allocationMulti-frequency code systemsChannel parameterCarrier signal
The invention discloses a direct current bias and sub-carrier power joint optimization method of a visible light communication DCO-OFMD system under a non-flat channel. The object of the optimal design is to maximize system data rate by adjusting the direct current bias and the sub-carrier power under certain luminous power limitation or electric power limitation. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) initializing relative parameters such as a channel parameter, a limitation condition, an initial sub-carrier power distribution, and so on; (2) fixing the sub-carrier power distribution, and optimizing direct current bias size and effective power; (3) fixing the direct current bias size and the effective power, and optimizing the sub-carrier power; (4) repeatedly executing the steps (2) and (3) until there is a convergence, and outputting the final direct current bias size and the sub-carrier power. The method of the invention could accurately obtain the optimal direct current bias size and a sub-carrier power distribution solution under a plurality of conditions such as luminous power limitation, electric power limitation, and so on, and the optimization method is fast in rate of convergence, easy to realize and high in result precision.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Programmable optical vector modulator and method for use in coherent optical communications
ActiveUS7085500B2Maximize transmissionMaximize data rateElectromagnetic transmittersFiberOptical communication
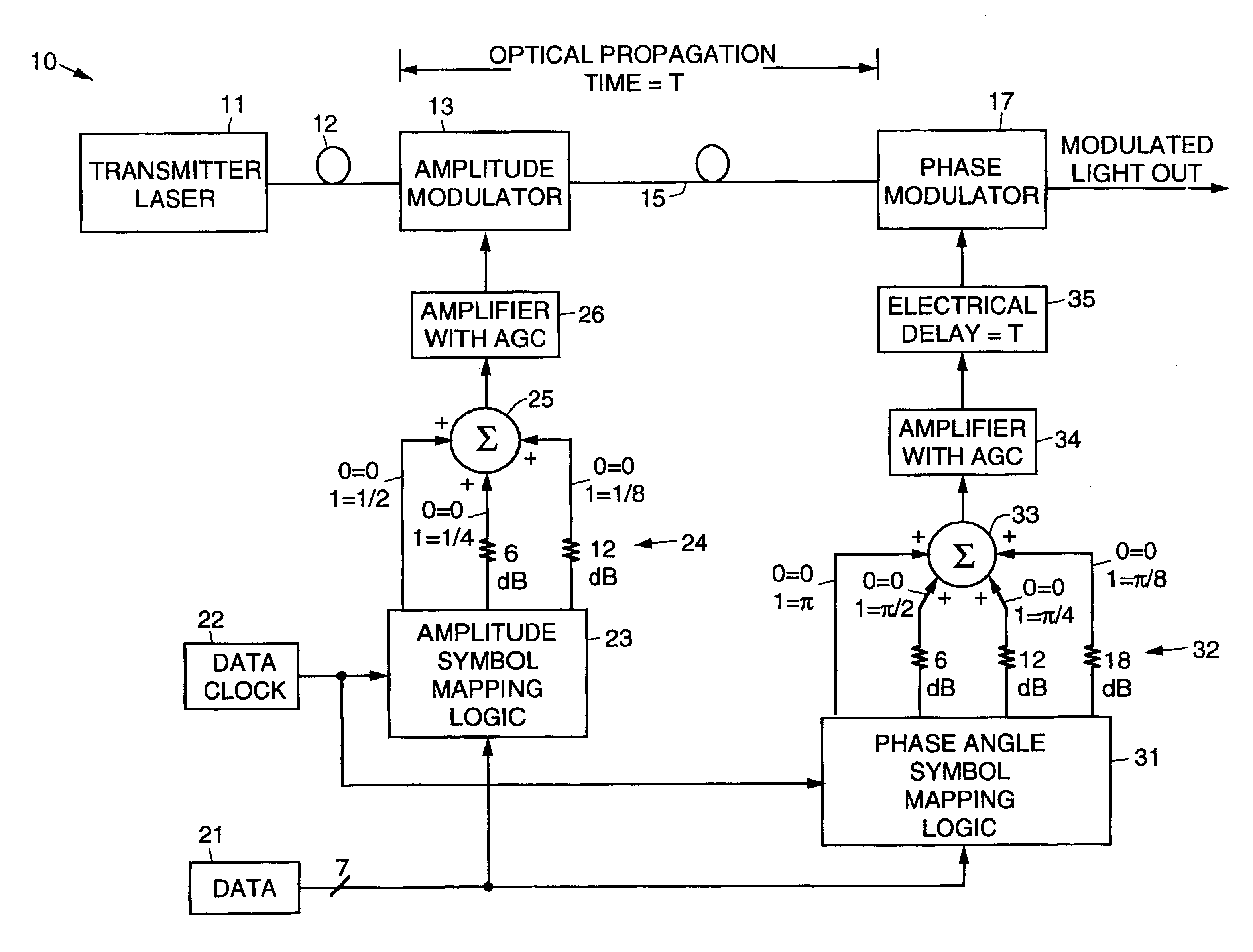
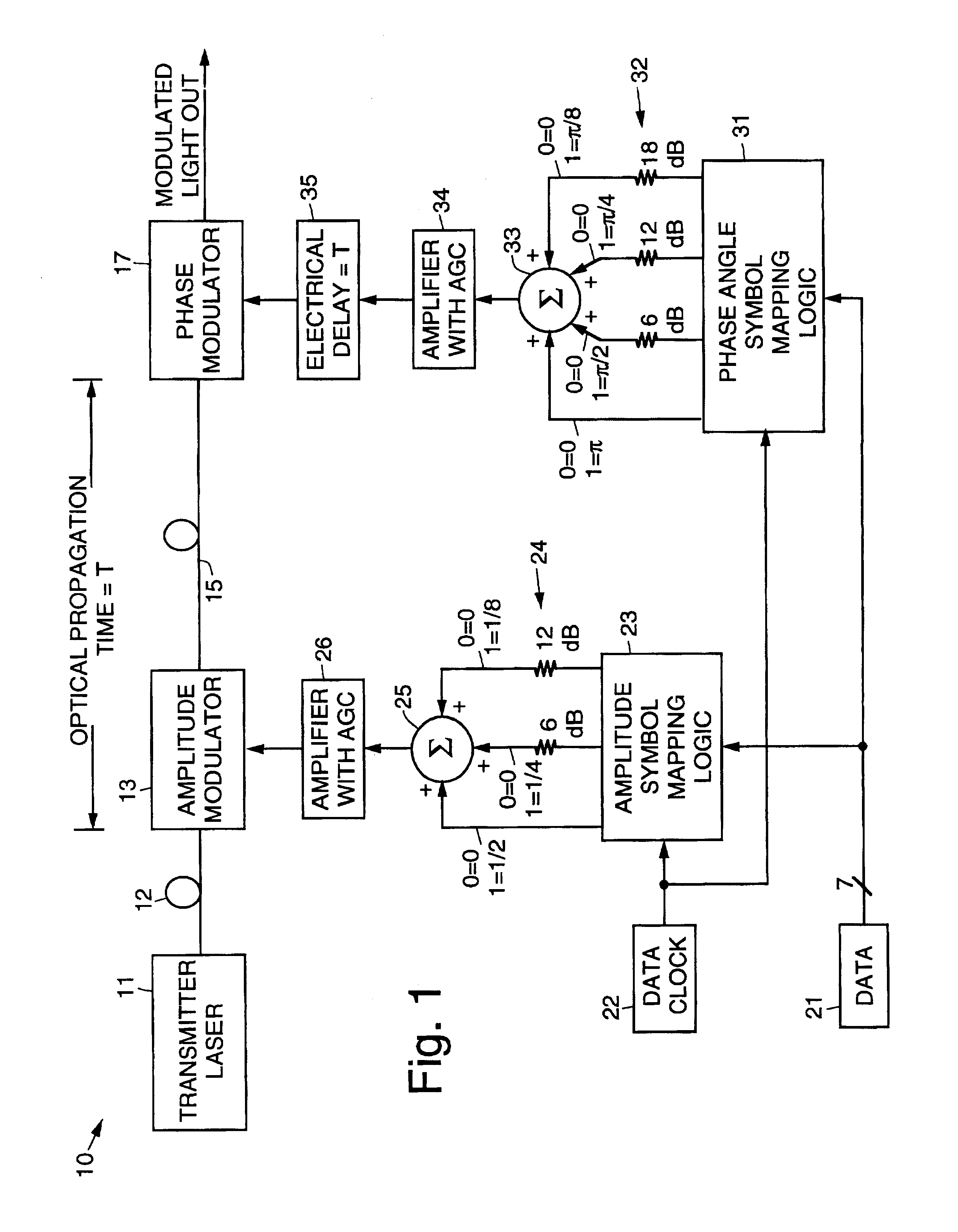
A transmitter comprising a programmable optical vector modulator and method for coherent optical signal communication. The transmitter includes a transmitter laser whose output is coupled by way of an optical fiber to an amplitude modulator. The output of the amplitude modulator is coupled by way of a length of optical fiber to a phase modulator. The phase modulator generates a modulated light output from the transmitter. Amplitude modulation is achieved by inputting data and a data clock signal to amplitude symbol mapping logic whose outputs are selectively weighted, summed, amplified and input to the amplitude modulator to amplitude modulate the output of the transmitter laser. Phase modulation is achieved by inputting the modulating data and the data clock signal to phase angle symbol mapping logic whose outputs are selectively weighted, summed, amplified, delayed to synchronize with the arrival of the light from the amplitude modulator, and input to the phase modulator to phase modulate the amplitude modulated output of the transmitter laser. The programmability of the vector modulator allows the transmission of an M-ary modulation format that maximizes the data transmission for a given optical dynamic range and bit error rate target. Also, the programmability allows for rapid change in modulation format to maximize data transmission for changes in optical dynamic range and bit error rate target. The M-ary constellation may be predistorted to compensate for equipment piece part variation and fiber nonlinear effects; in particular the effect commonly known as “self-phase modulation”.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
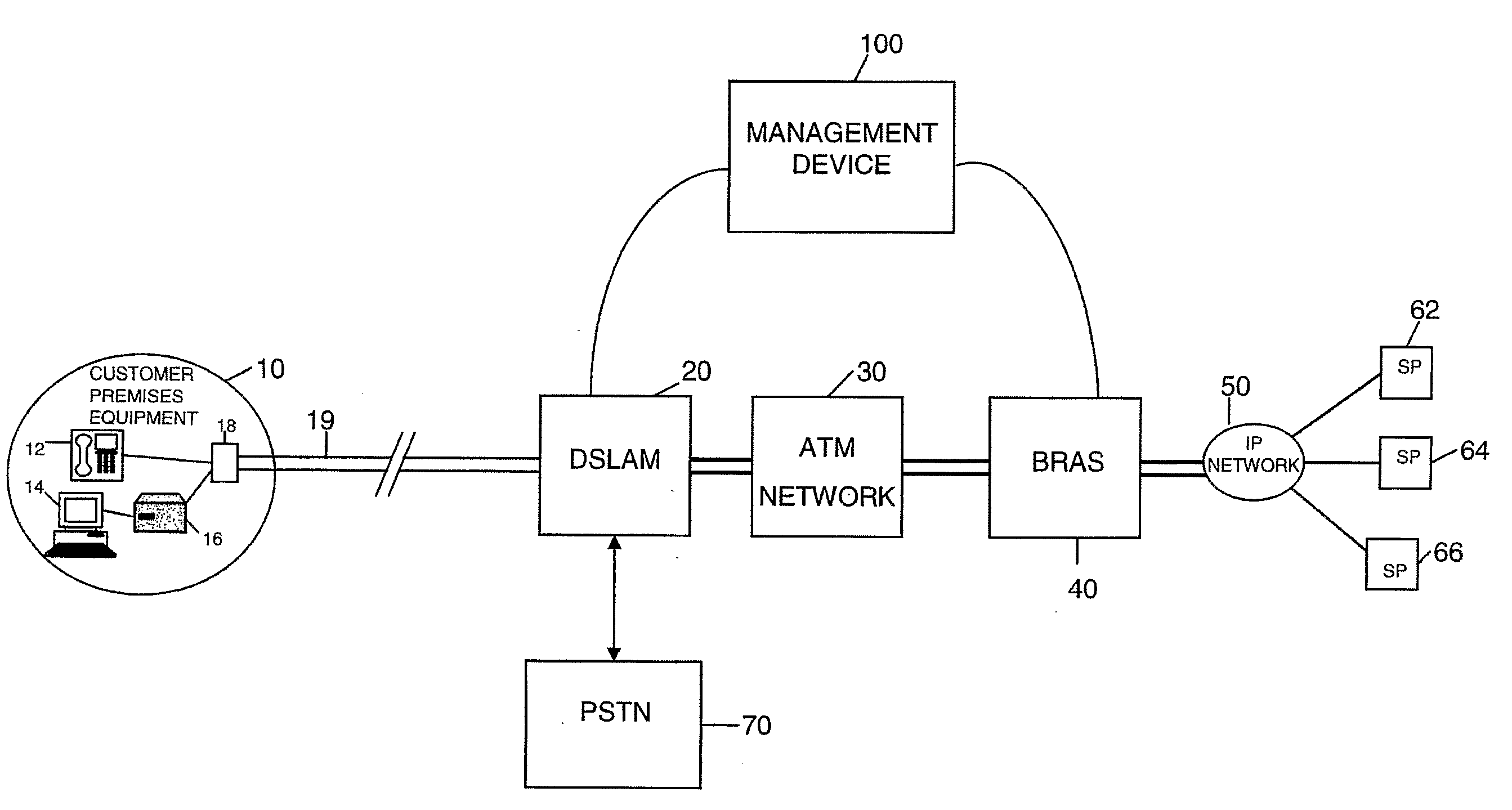
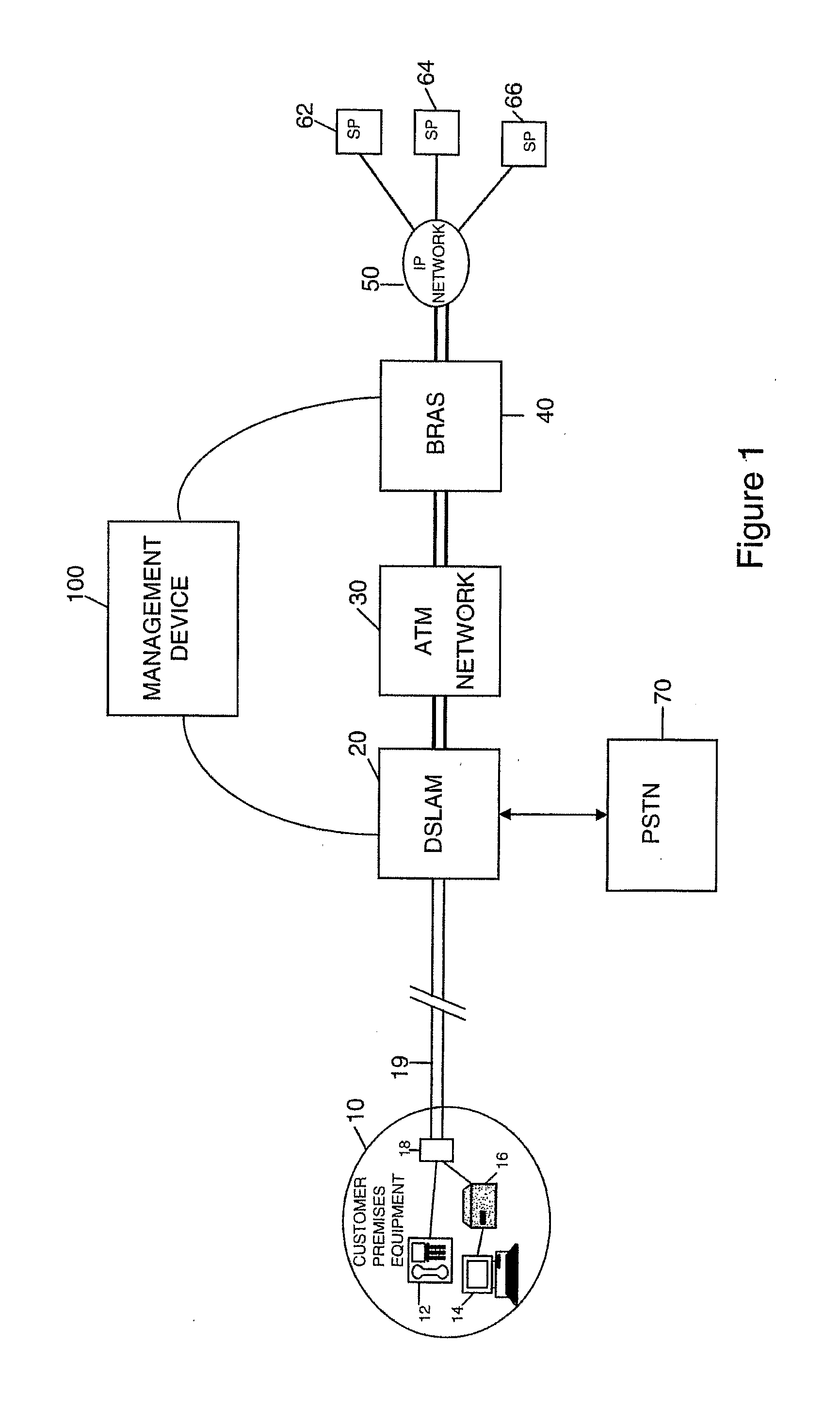
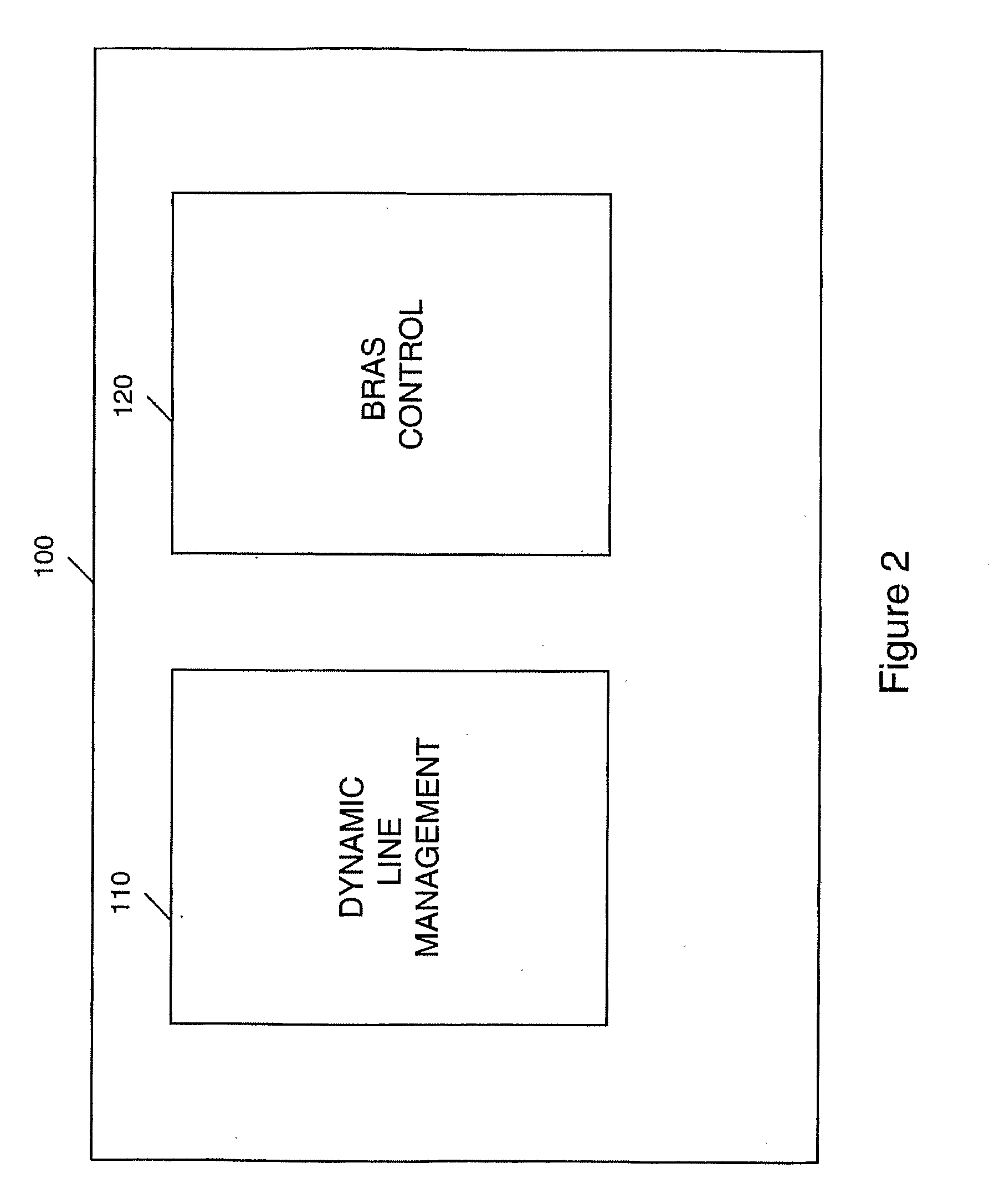
Data communications
ActiveUS20110019575A1Rate be controlReduce noiseEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Data transmission
In a method and system for operating an ADSL access network which has a plurality of data connections (19) between the access network and end user devices (10), and in which the access network controls the rate at which data is transferred between the user devices and an onward connection (50), the access network stores a plurality of capped profiles each of which specifies a respective upper data rate to which the connection is limited and which is below the maximum achievable rate for the connection. The access network operates using a Dynamic Line Management (DLM) algorithm which, for a given data connection, operates to enable data transfer at a variable data rate up to the maximum rate, monitors the error performance and signal to noise margin variation for different data rates and, in the event that one or both are outside respective limits for a predetermined period, selects and applies one of the capped profiles to limit the upper data rate, selection being determined by the highest data rate achieved for which the error performance was within acceptable limits.
Owner:BT NEWGATE
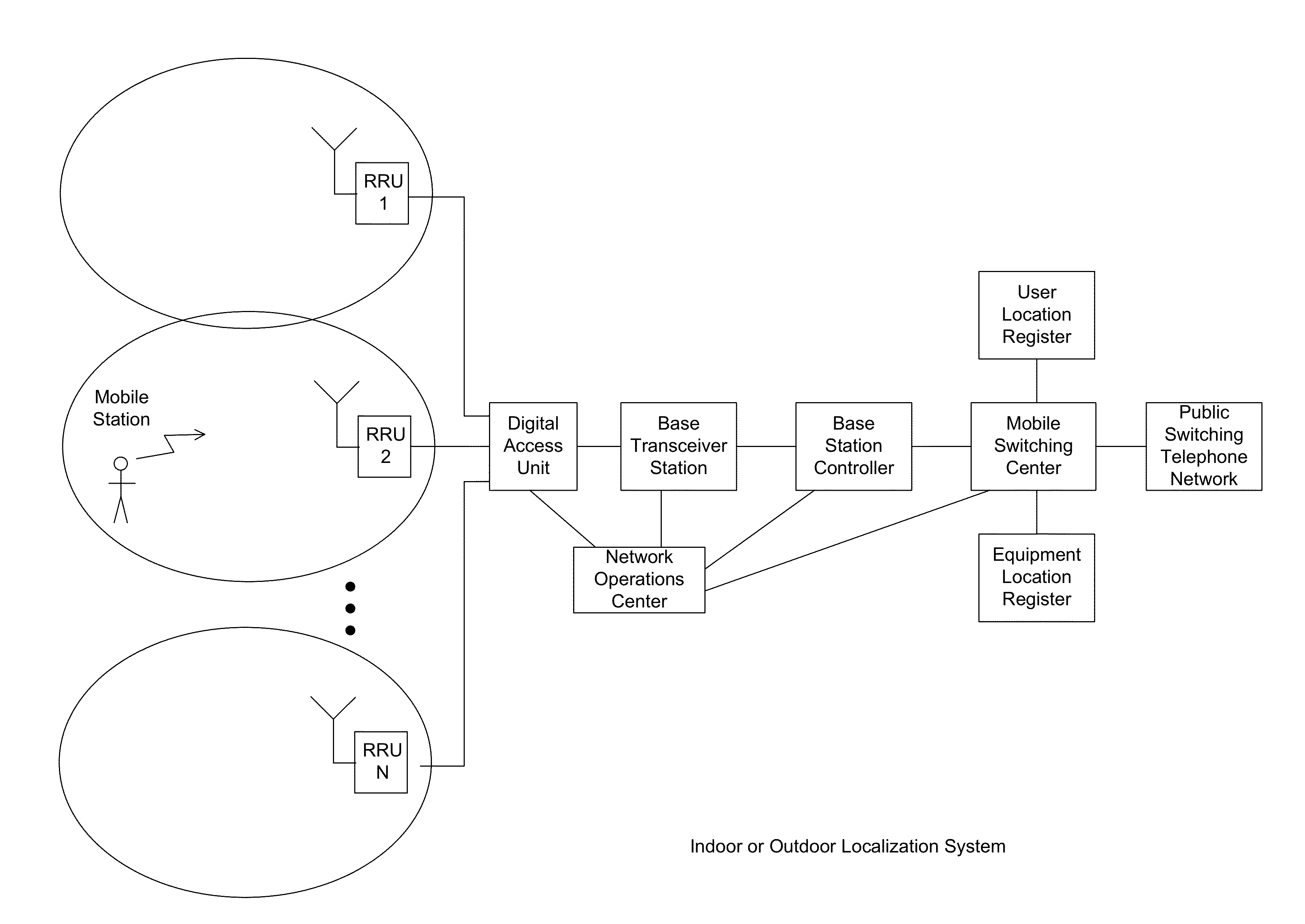
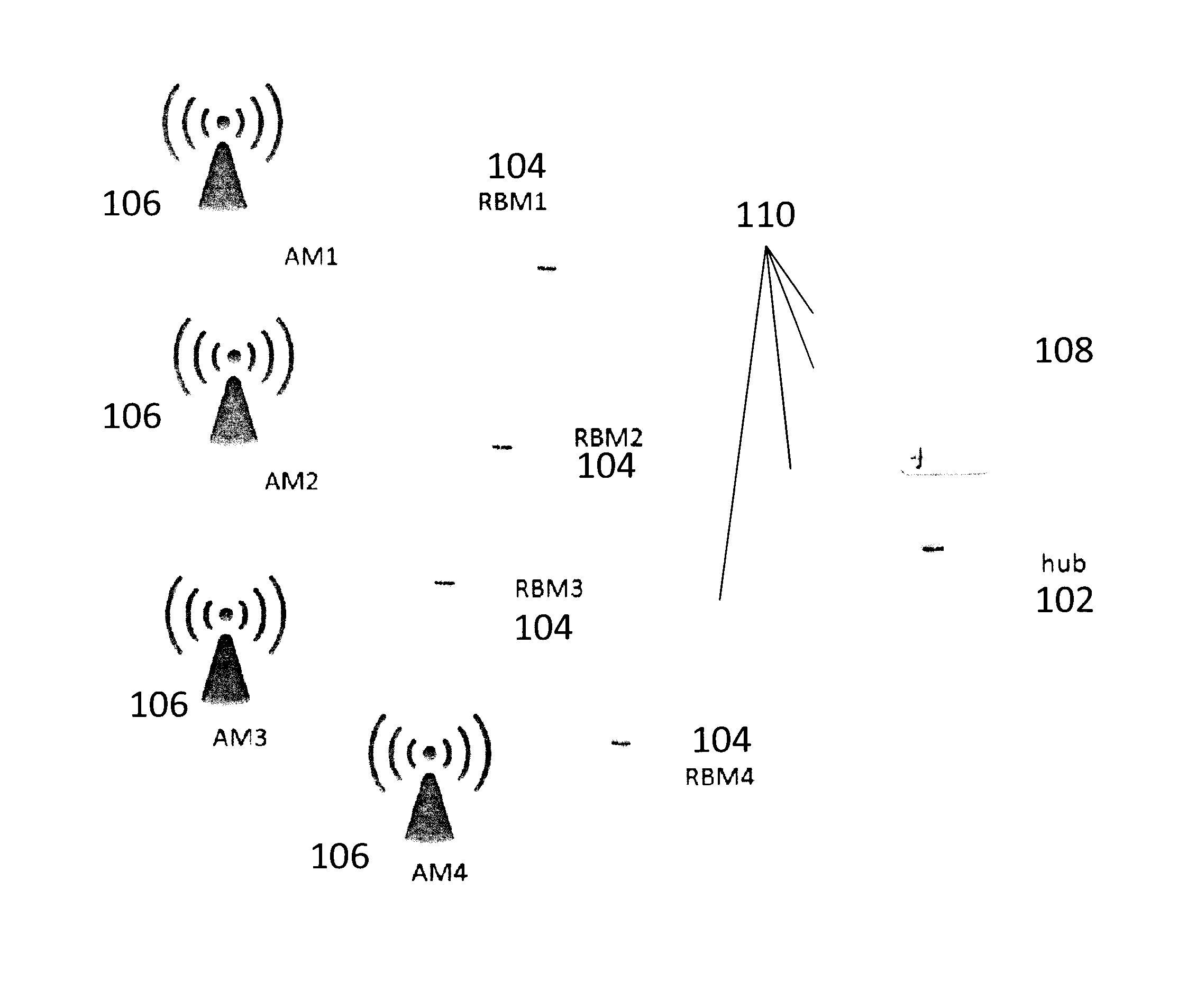
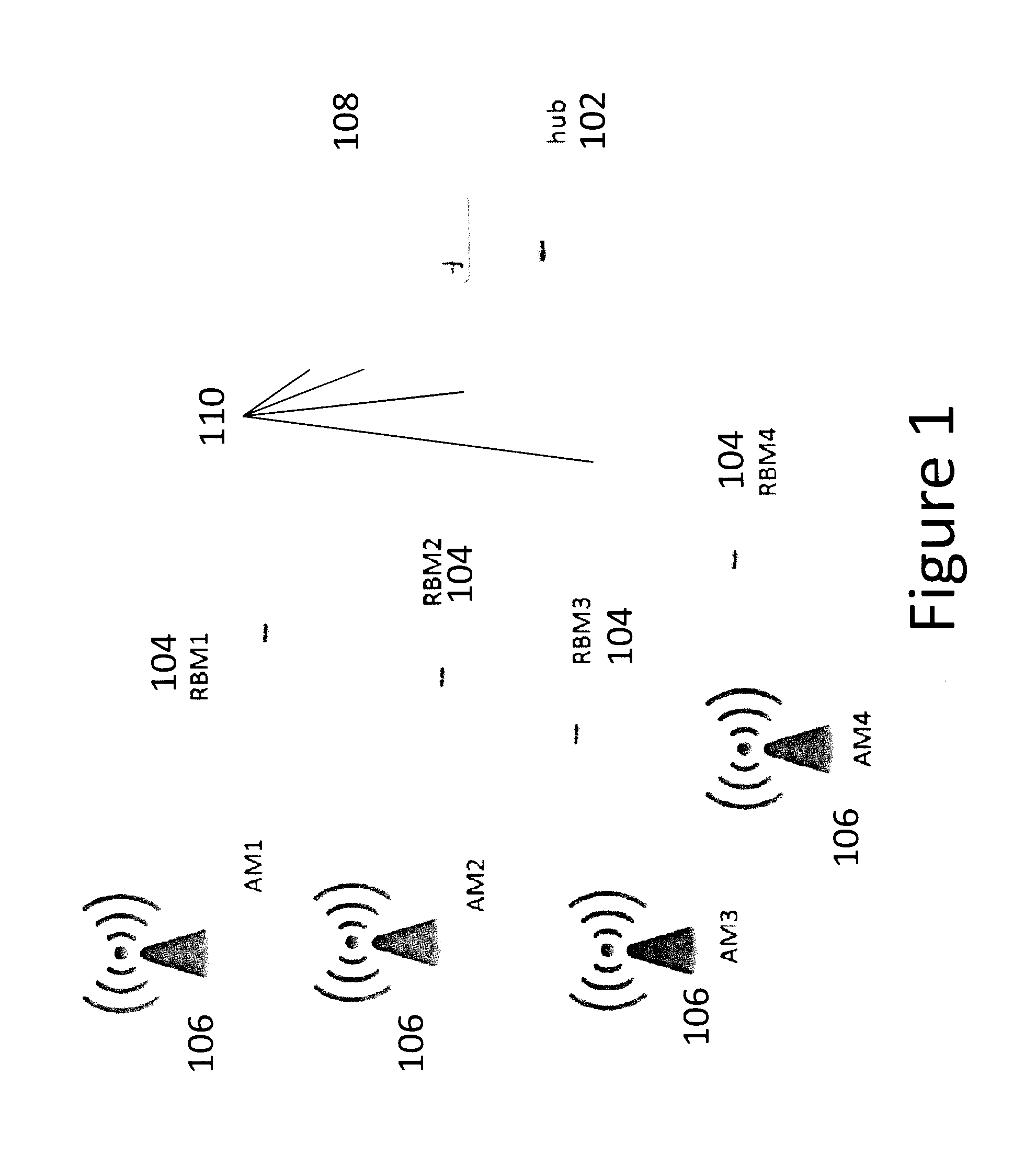
Method and apparatus for determining network clusters for wireless backhaul networks
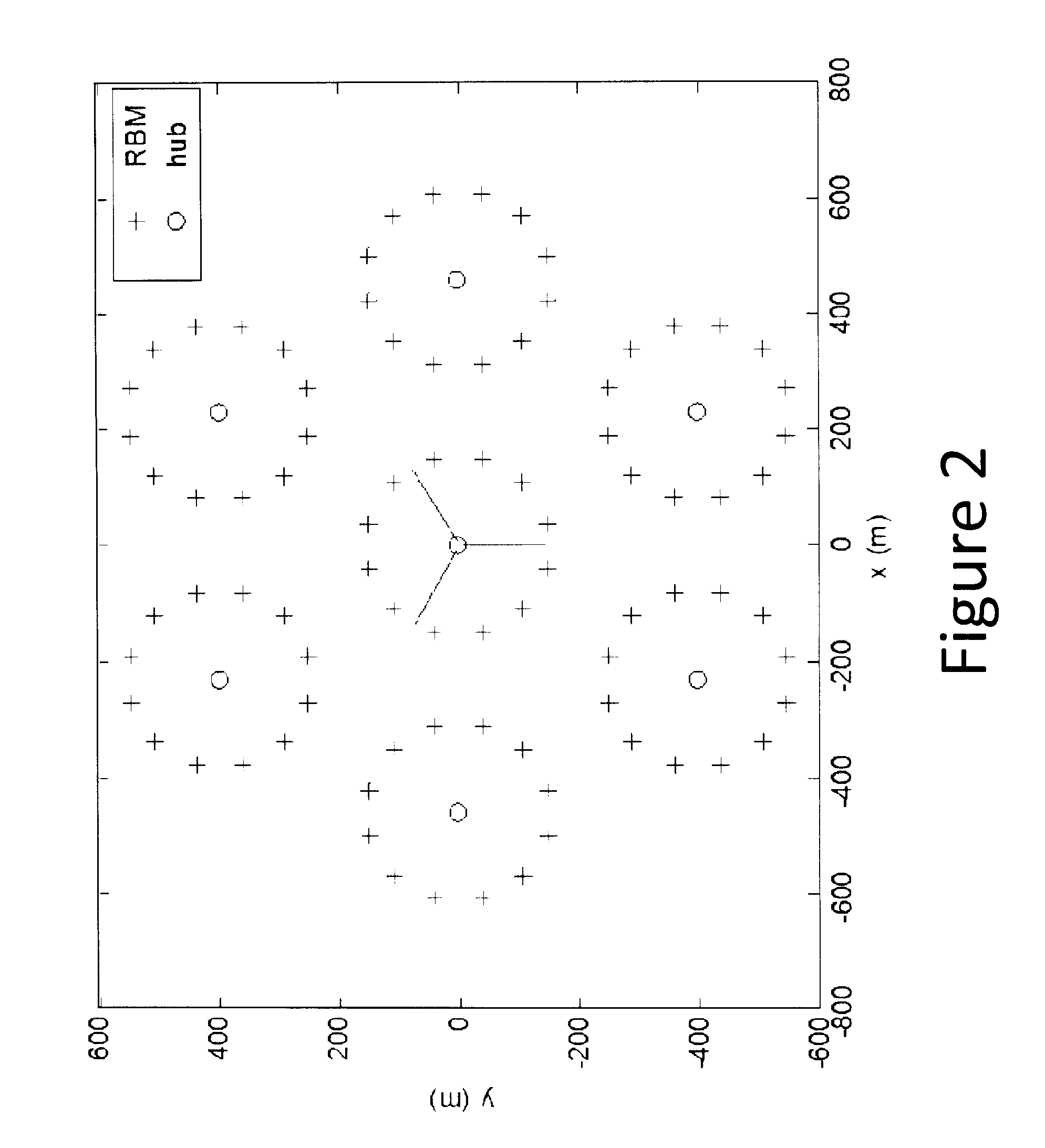
ActiveUS20140126514A1Eliminate, orReduce disadvantagesWireless commuication servicesRound complexityComputation complexity
Practical methods and apparatuses are provided for determining network clusters in wireless backhaul networks comprising a plurality of hubs and Remote Backhaul Modules (RBM) (104) based on link quality value (LQV) metrics. From an input LQV table of LQV values for each hub-RBM link (110), the link quality values are first ranked. Clusters are then identified from all the possible links based on the order of the highest link quality value to the lowest link quality value, any constraints on the number of RBMs per cluster, and clustering each RBM only once. Links with strong link quality values are chosen to optimize the LQV metric. LQV based clustering achieves a higher average LQV, e.g., average spectrum efficiency or weighted sum spectrum efficiency, for the entire backhaul network compared to the geographic location based clustering. The method is straightforward to implement and has low computational complexity.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
Clustering based resource allocation in multi-cell OFDMA networks
InactiveUS8144657B2Interference can be avoided and reducedImprove performanceWireless commuication servicesNetwork planningOverlap zoneResource block
A method allocates resource in an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) network, including a set of Base Stations (BSs) and a set of Mobile Stations (MSs) for each BS. OFDMA frame are constructed as multiple resource blocks, and each resource block contains symbols transmitted on different subcarriers. A cluster is formed from adjacent sectors of different neighboring cells to jointly optimize the resource allocation in multiple frames, and three non-overlap zones are sequentially identified in cluster: cell center zone, cell edge zone, and cluster corner zone. Resource allocation includes intra-cluster proportional fair scheduling and inter-cluster interference mitigation. Intra-cluster scheduling further includes resource allocation for cell center zone and resource allocation for cell edge zone.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Antenna selection and resource allocation method in wireless energy supply communication network
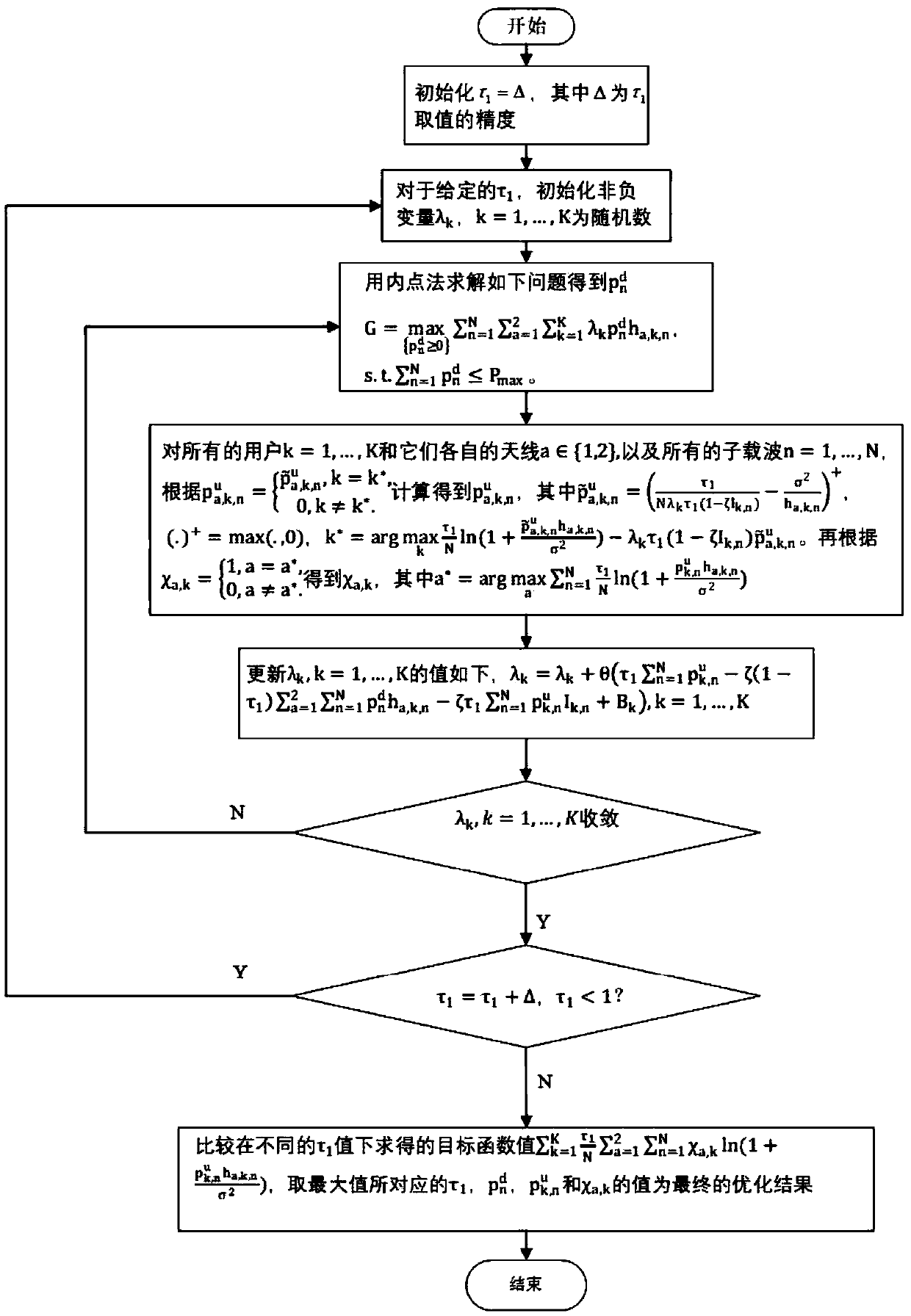
ActiveCN109661034AMaximize data rateReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationSelf recoveryNetwork architecture
The invention discloses an antenna selection and resource allocation method in a wireless energy supply communication network. The wireless energy supply communication network constructed by the method is a multi-user network architecture based on an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing technology, and comprises a hybrid access point; the hybrid access point is connected with K users downwards; and each user has two antennas for transceiving radio frequency signals. The method is based on an energy self-recovery technology; by combining antenna selection and resource optimal allocation,under the energy causality constraint, a total data rate of the users is maximized, resource allocation efficiency in the wireless power supply communication network is promoted, and the total data rate of all the users is maximized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
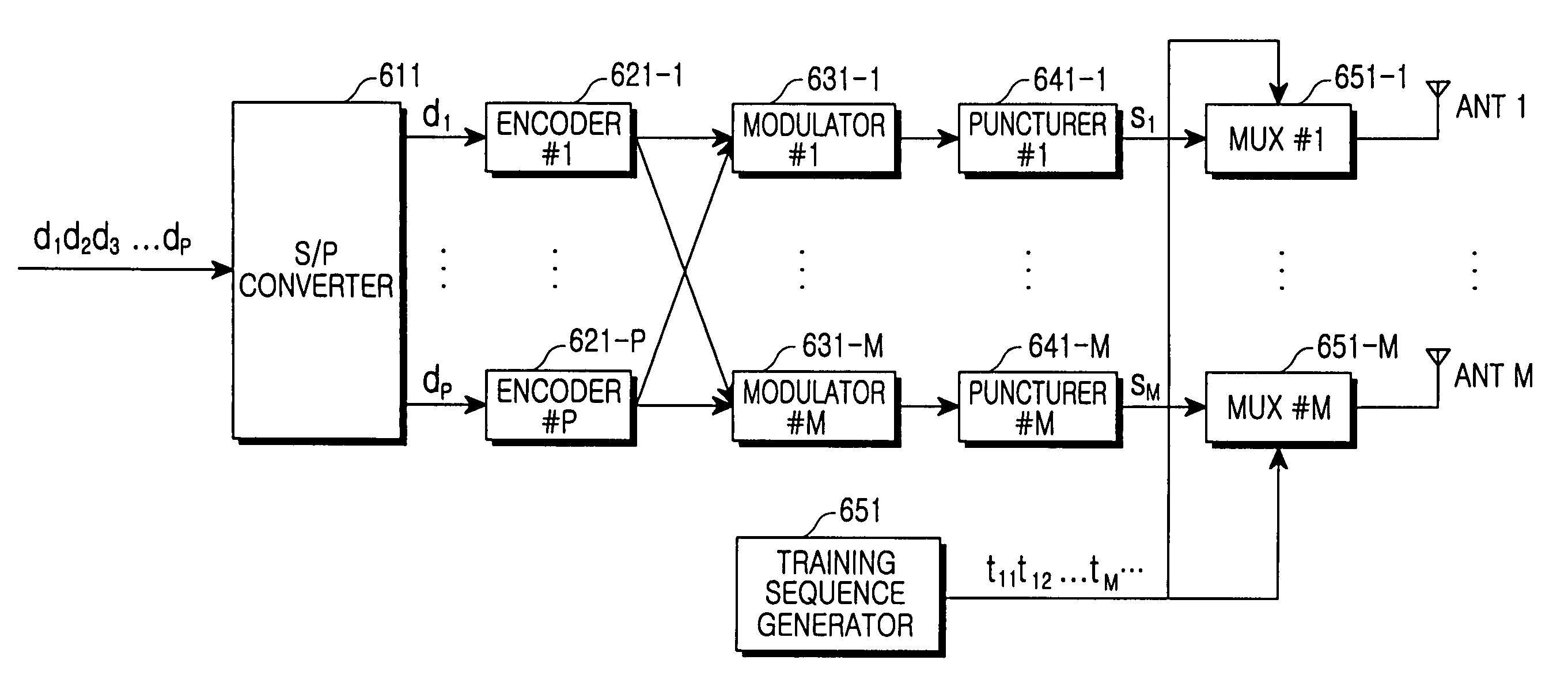
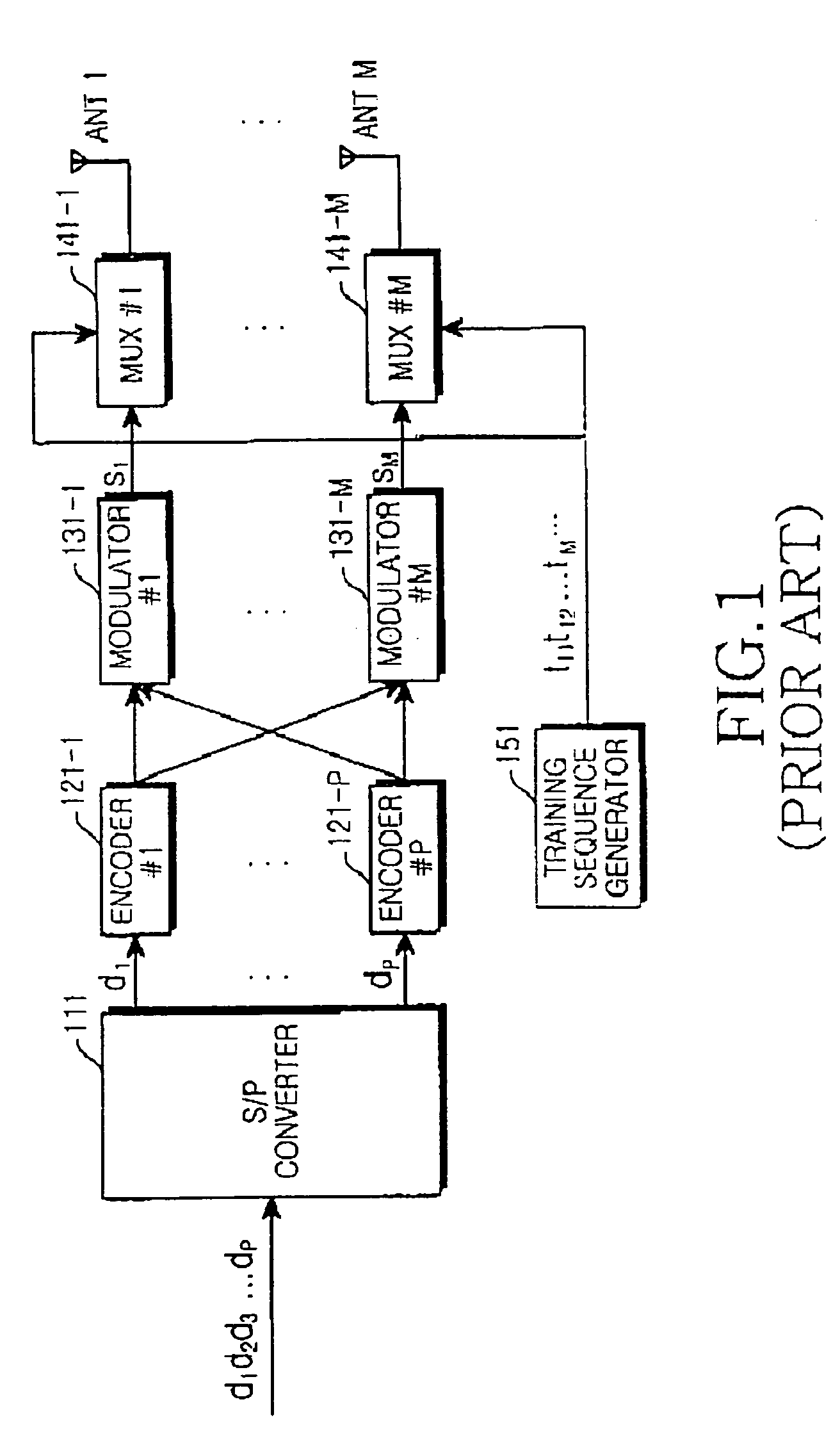
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving a pilot sequence in a mobile communication system using space-time trellis code
ActiveUS7480339B2Maximize data rateSpatial transmit diversityOther decoding techniquesMobile communication systemsComputer science
A mobile communication system includes M transmission antennas, P encoders for receiving P information bit streams and encoding the received information bit streams with a space-time trellis code (STTC), and M modulators for modulating information bit streams output from the P encoders in a predetermined modulation scheme and outputting modulation symbol streams. A sequence used for channel estimation is generated, and the sequence is transmitted in substitute for at least one modulation symbol in a predetermined position through the M transmission antennas, for each of the modulation symbol streams output from the M modulators.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless multicast for layered media
ActiveUS8125903B2Maximize perceived qualityReduce resource consumptionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunicationsData rate
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
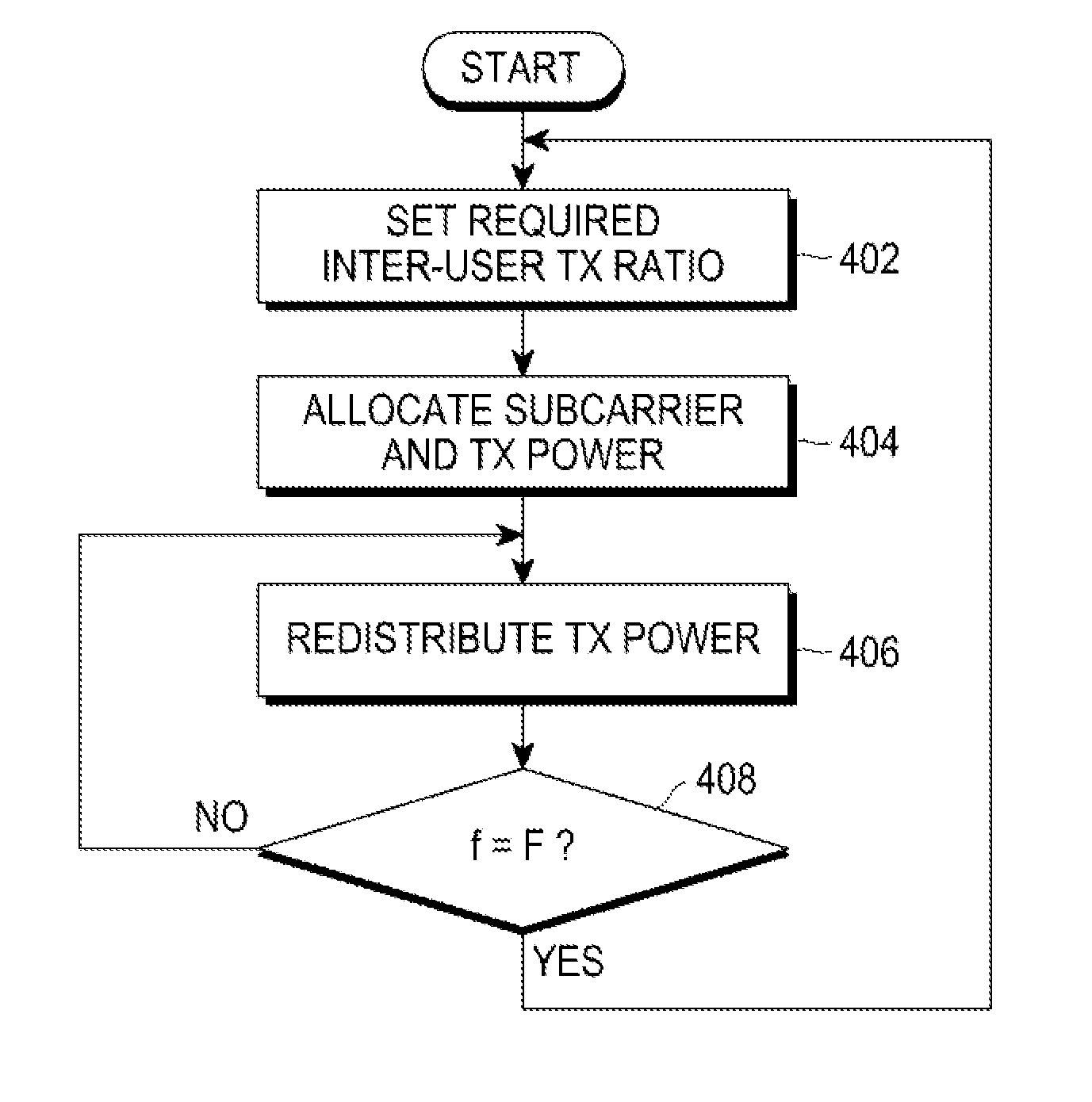
Method and apparatus for adaptively allocating resources in multi-user OFDM system
ActiveUS20110128927A1Maximize data ratePower managementTransmission path divisionCarrier signalSubcarrier
A method and apparatus for adaptively allocating resources by a Base Station (BS) apparatus in a multi-user OFDM system is provided. The method includes receiving users' required rates and channel state information from a plurality of user terminals, setting a required inter-user transmission ratio and a number of multi-frames based on information about the users' required rates, allocating a subcarrier and transmit power to each user terminal based on the channel state information and the required inter-user transmission ratio for a period corresponding to the set number of multi-frames, and redistributing the transmit power allocated to the subcarrier. The method and apparatus can maximize the total data rate of a system while satisfying required inter-user transmission ratios in a multi-user OFDM system based on a multi-frame environment.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for RF signal combining and adaptive bit loading for data rate maximization in multi-antenna communication systems
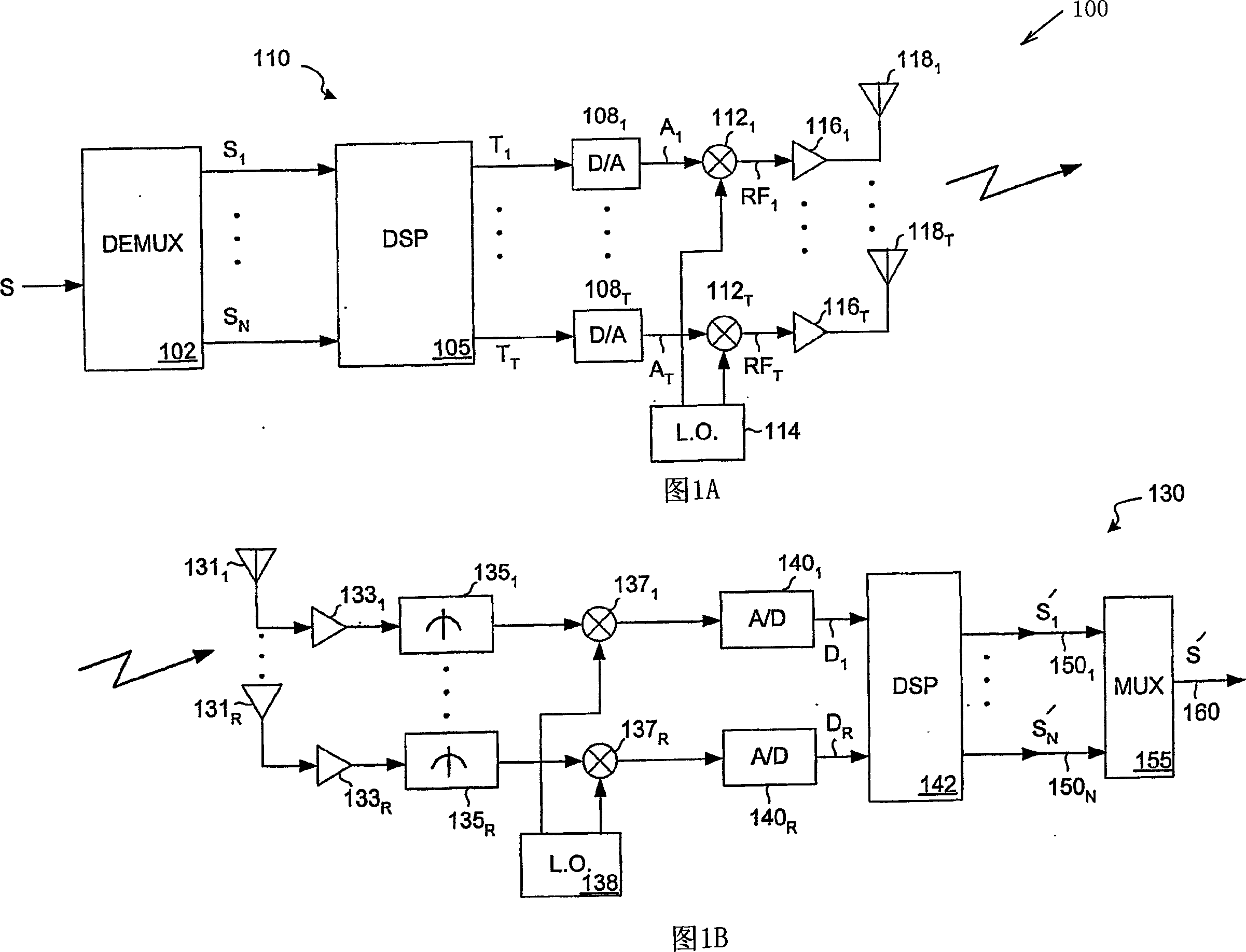
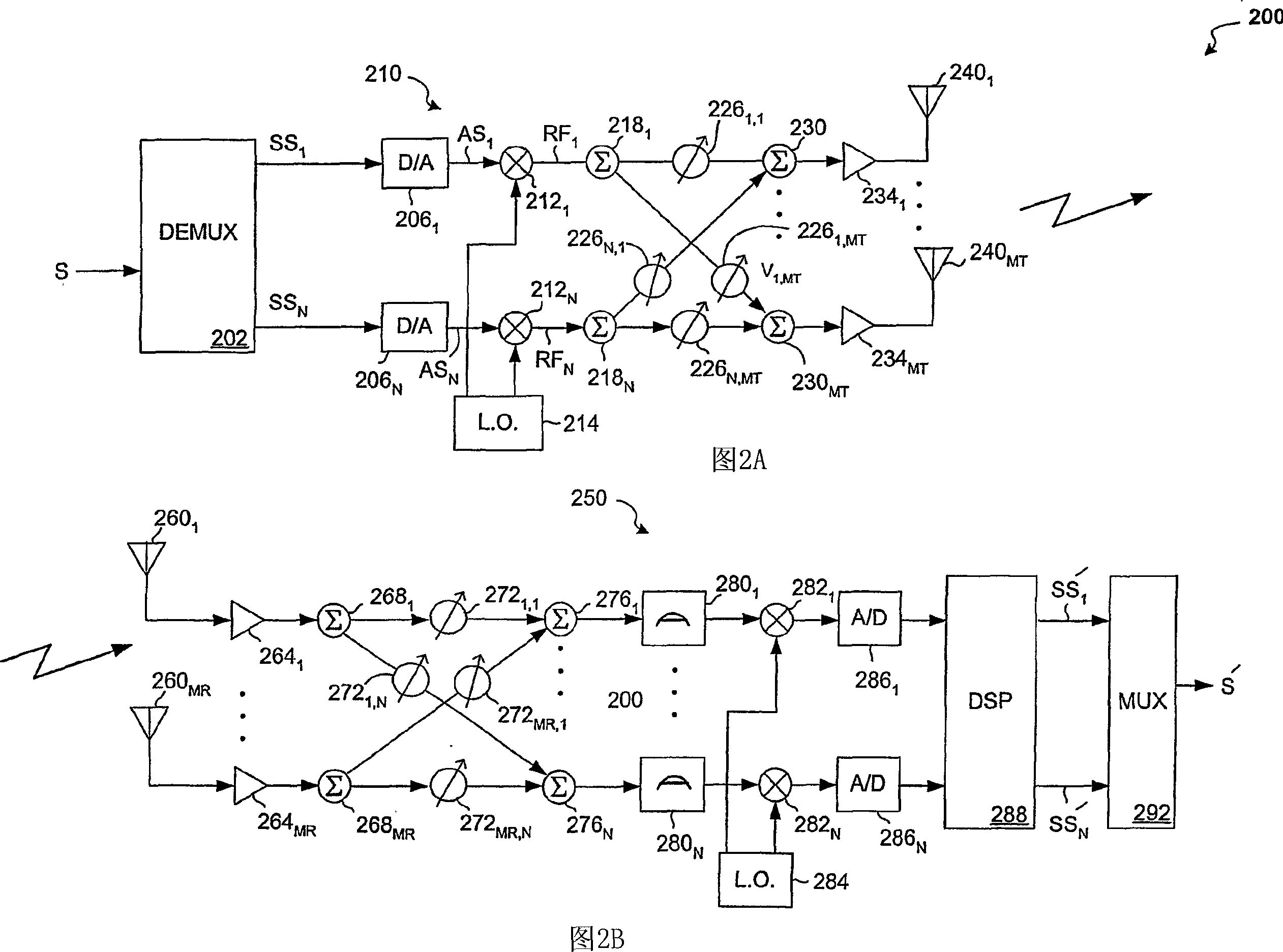
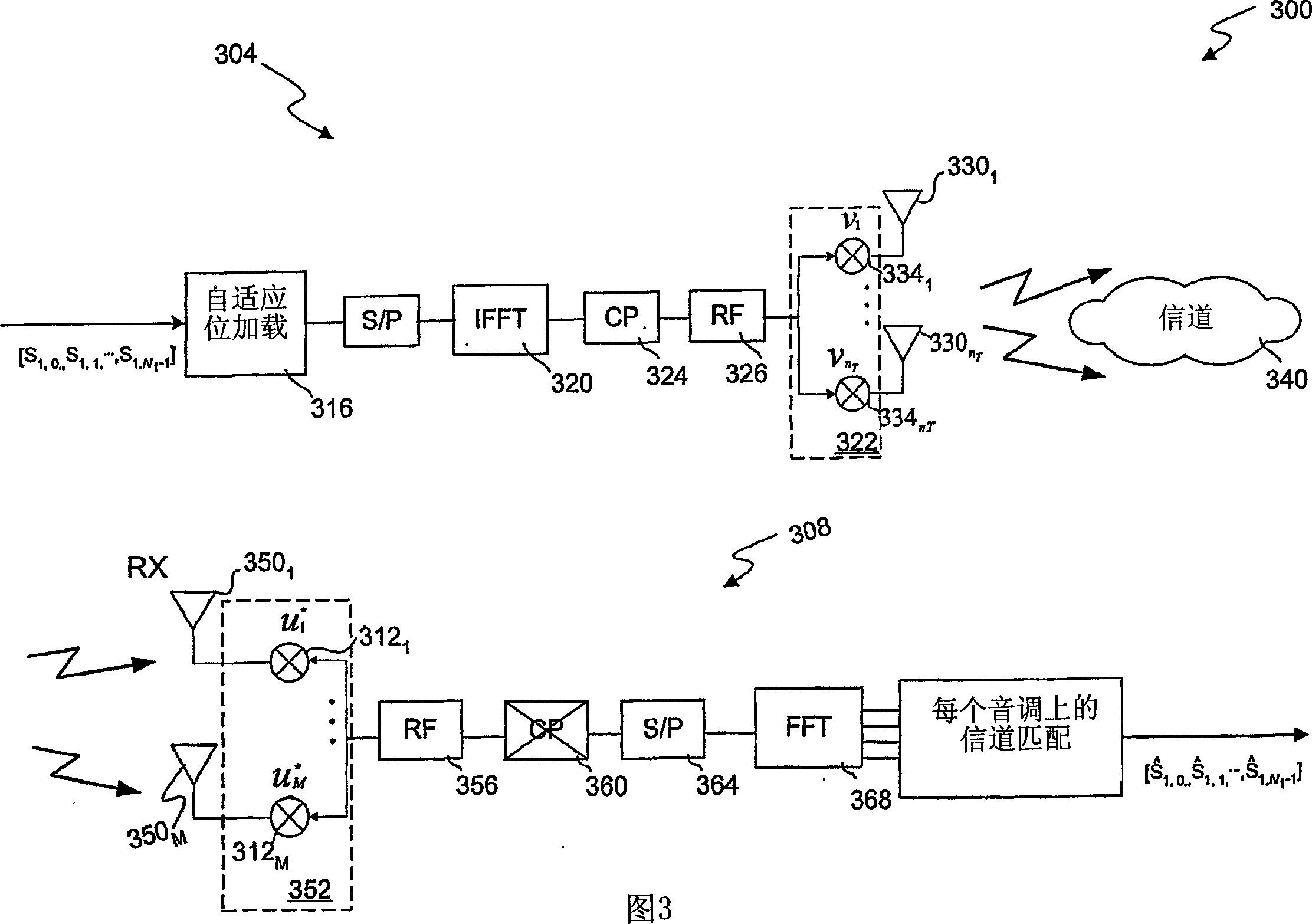
InactiveCN1820441AMaximize data rateMaximize weight combinationSpatial transmit diversityCriteria allocationSubcarrierWeight value
A system and method for generating weight values based on maximum data rate for weighting elements included within signal weighting and combining arrangements used in various multi-antenna transmitter and receiver structures is disclosed herein. Weighting values for a given signal combining arrangement are set so as to maximize an output data rate of the applicable multi-antenna system in the presence of adaptive bit loading of the subcarriers of a transmitted signal. The disclosed techniques may be employed to maximize a data rate of a multi-antenna communication system by using adaptive bitloading and RF and baseband weighting schemes. In this case a search is conducted over various combinations of RF and baseband weights in order to find the weight combination which, when adaptive bitloading is also employed, maximizes the data rate.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
High data rate inter-satellite communications links method
InactiveUS6873644B1Maximize data rateIncrease spectral efficiencyRadio transmissionTelecommunications linkTelecommunications
High data rate inter-satellite communications links method for a plurality of satellites comprising providing, for each satellite, an ultrafast time hopping wireless satellite communications link of an allowed bandwidth in which data is transmitted using individual packets or pulses in a sequence of such packets or pulses, causing the individual packets or pulses to be short in duration so that the individual packets are pulsed and signal energy is spread over the allowed bandwidth substantially simultaneously and instantaneously. A time hopping sequential code is used to position the packets or pulses precisely in sequence thereby providing optimum use of frequency space and also providing noninterfering transmission channels due to the orthogonality of the coding scheme used.
Owner:BARRETT TERENCE W
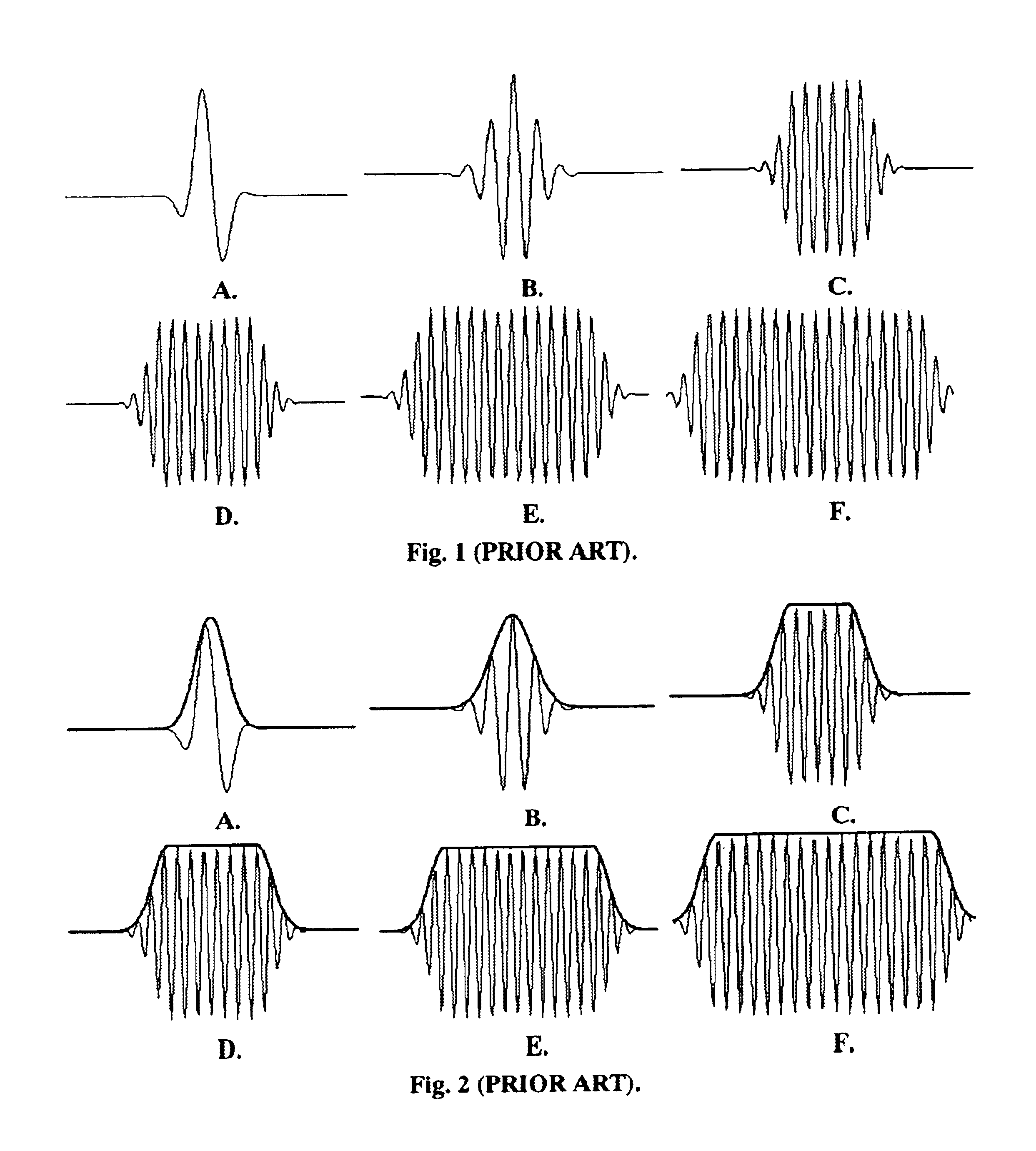
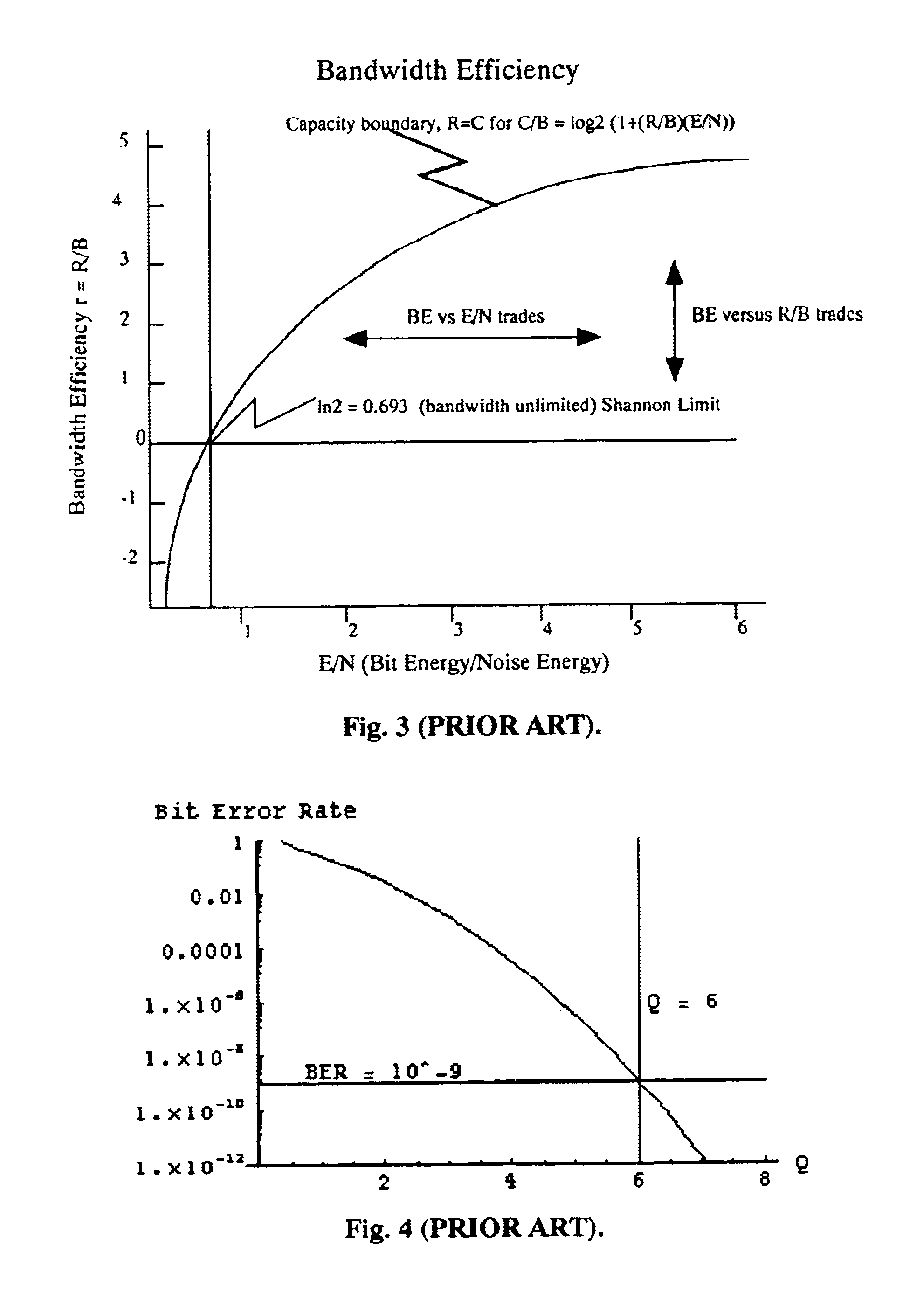
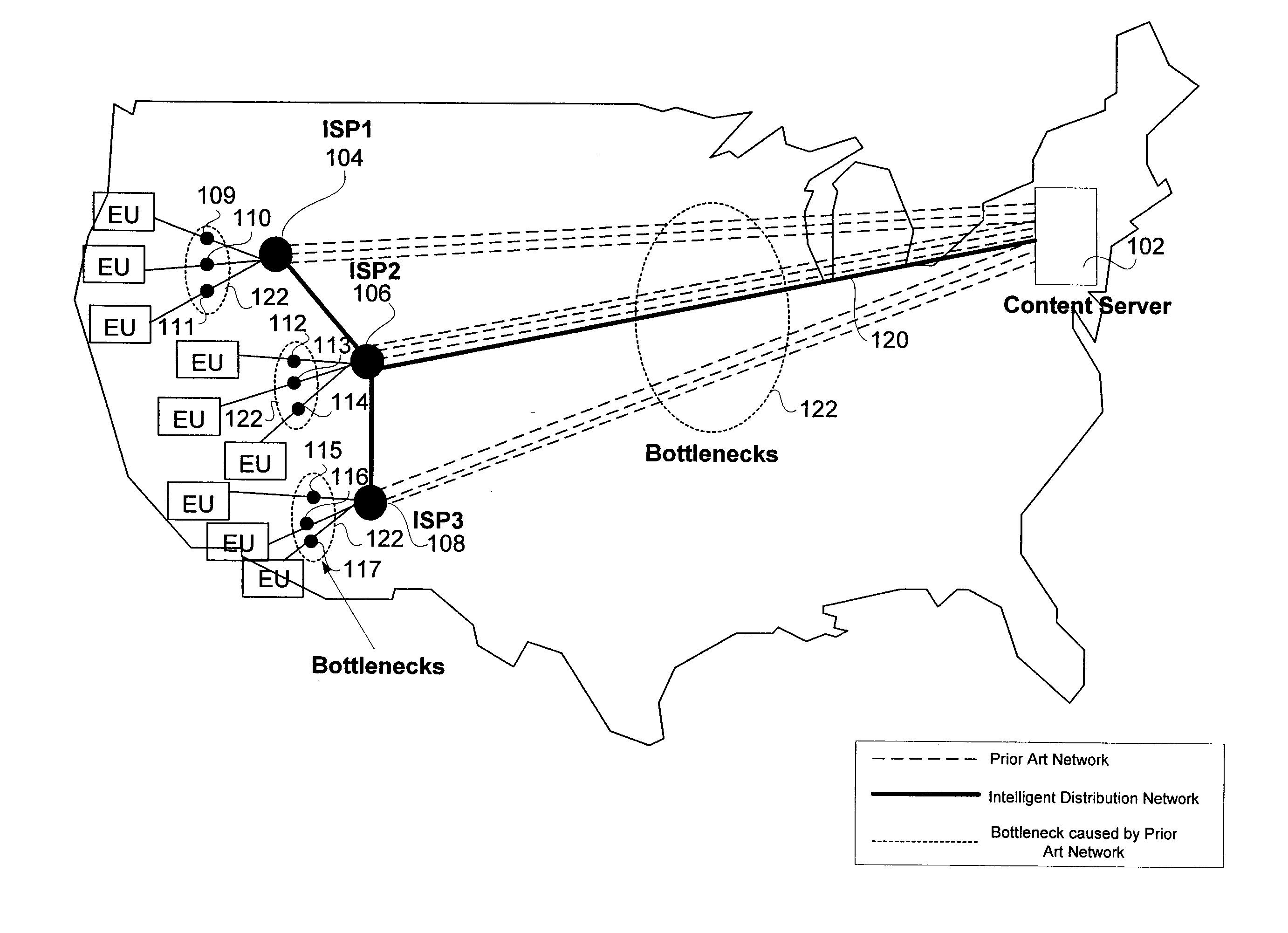
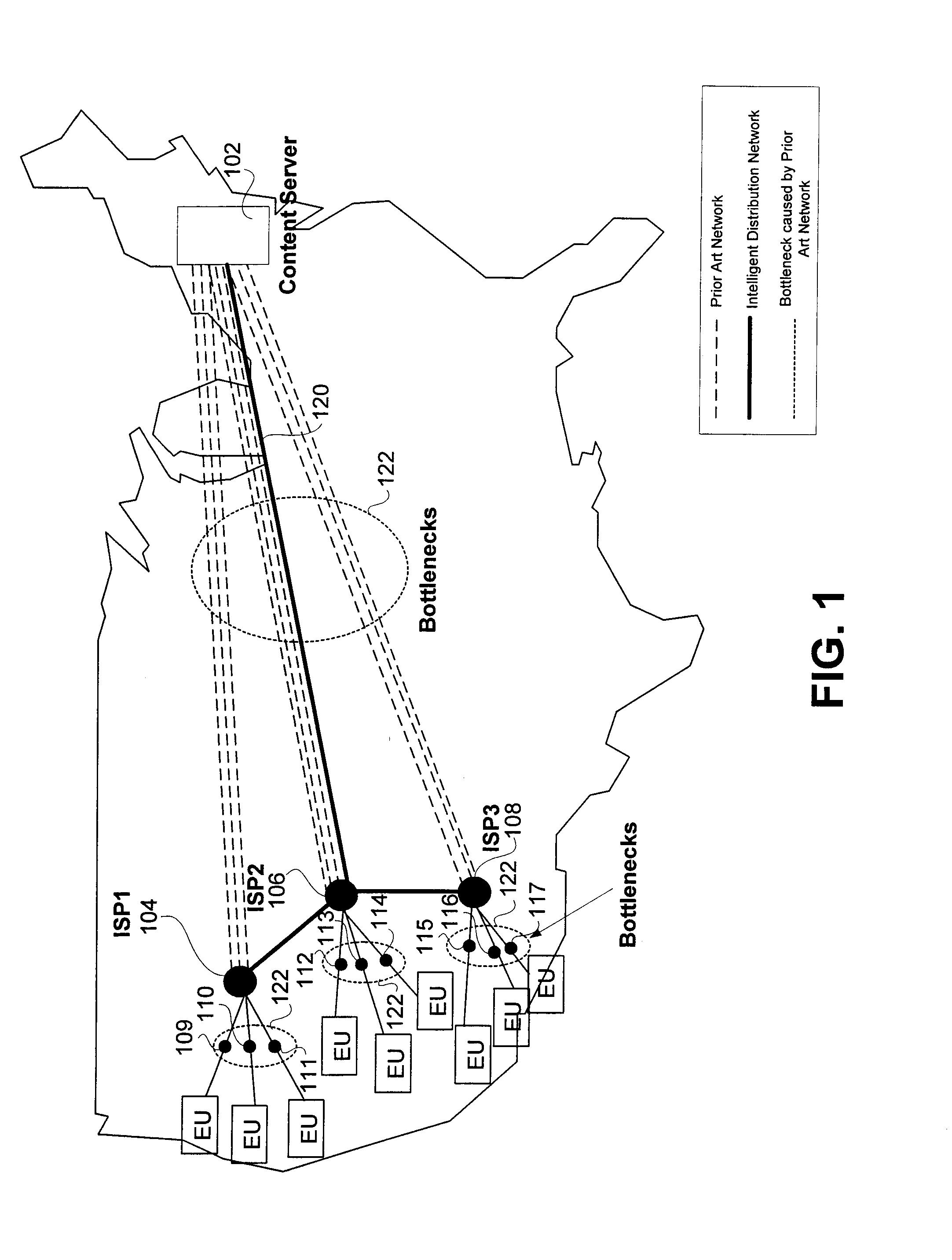
System and method for distribution of data packets utilizing an intelligent distribution network
InactiveUS20140173056A1Reduce deliveryMinimize impactMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork linkDistribution networks
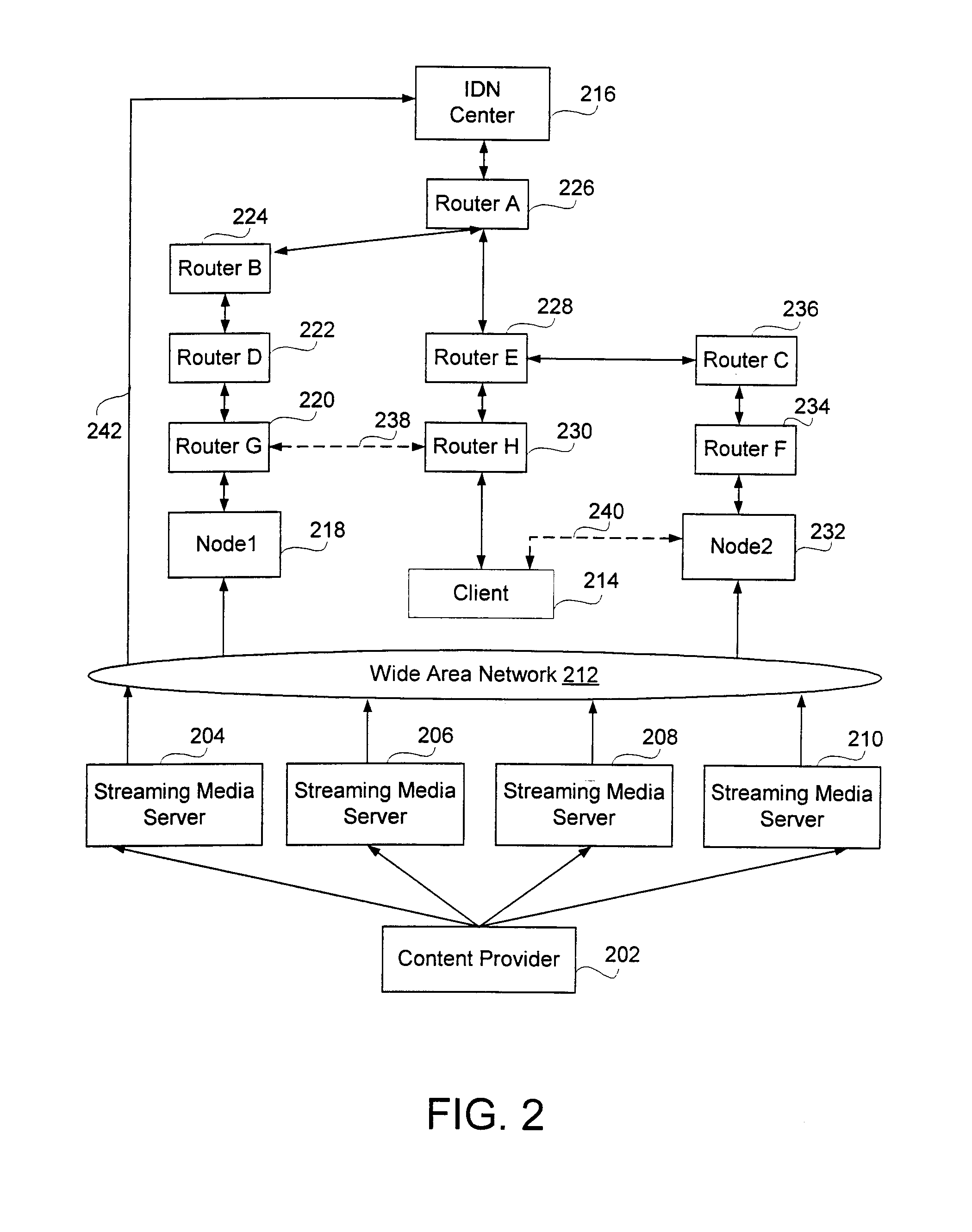
A system and method for efficient distribution of streamed media content to large and diversely located client locations is provided whereby an intelligent distribution network (IDN) center manages the delivery of the streamed media to a plurality of clients. The IDN center determines the most efficient delivery route to each client by utilizing trace routes between the IDN center, IDN nodes, various transmission devices and the client. Once a ‘best performing’ IDN node and network link is determined, the IDN center directs the client to the ‘best’ node and instructs deliver of a content stream along the ‘best’ link. Upon receiving the streamed media, the ‘best’ node replicates the stream and delivers the media to the client. Additional clients may ‘piggyback’ off the initial content stream by obtaining a replication of the media from their ‘best’ nodes which are, or connected to nodes, already transmitting / receiving the initial content stream.
Owner:MEDIA POINTE
Achieving high-rate multi-hop data delivery in vehicular networks
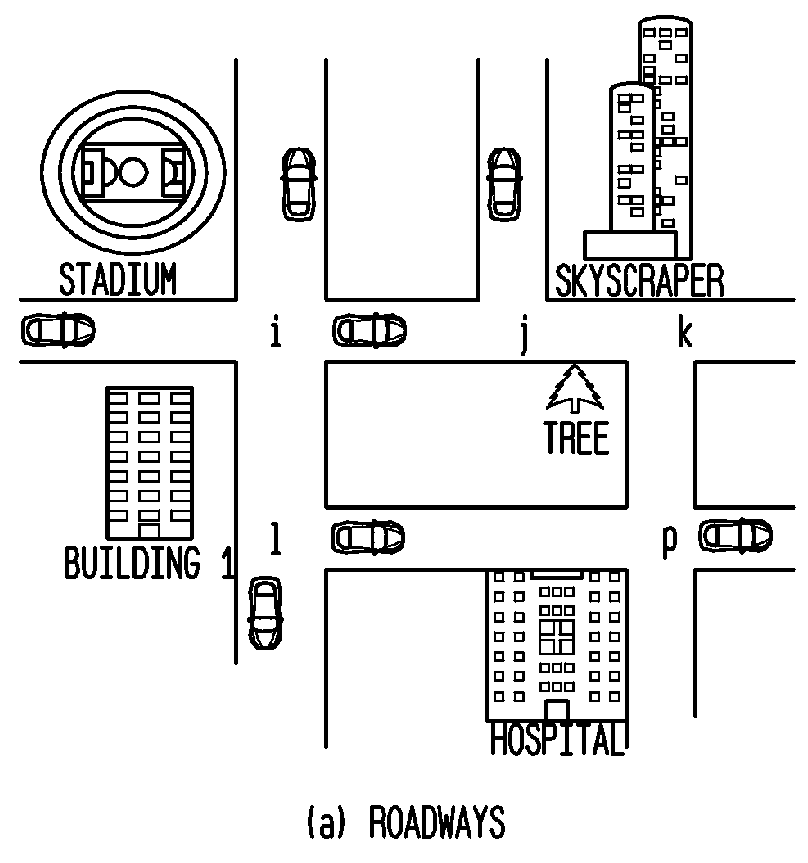
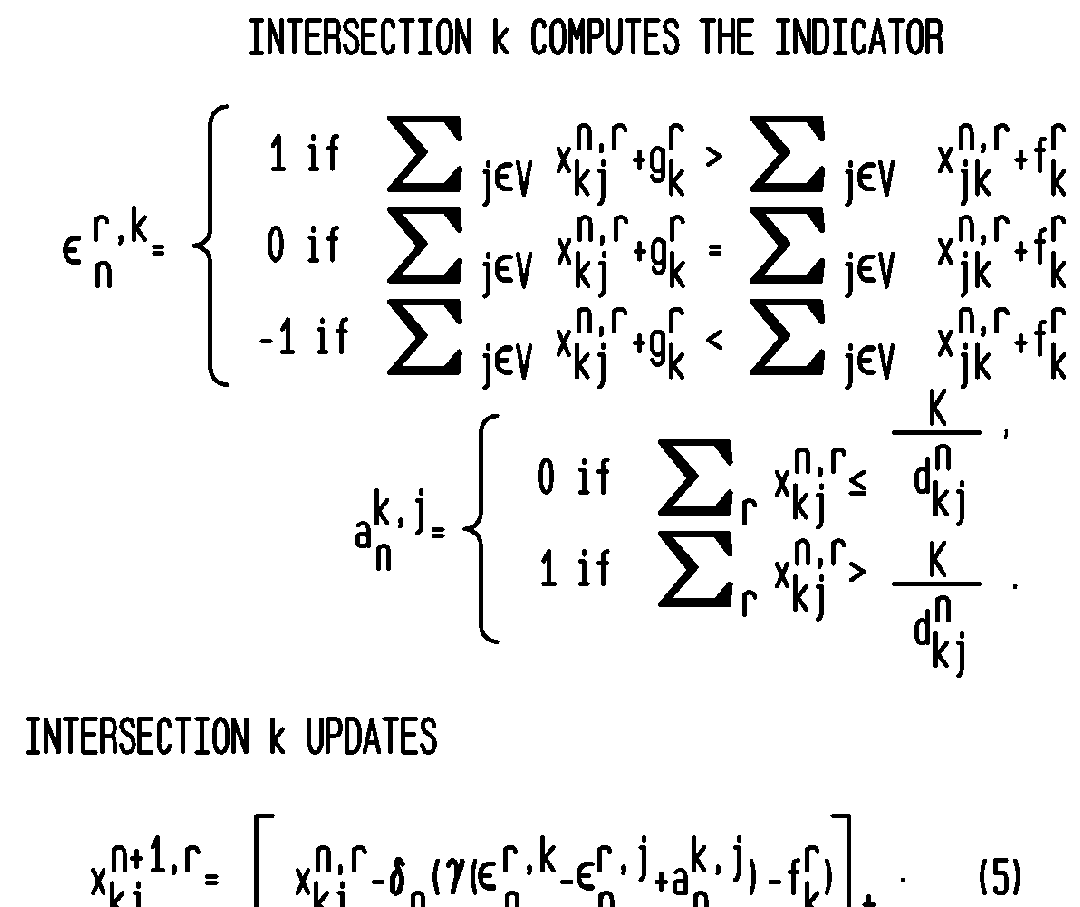
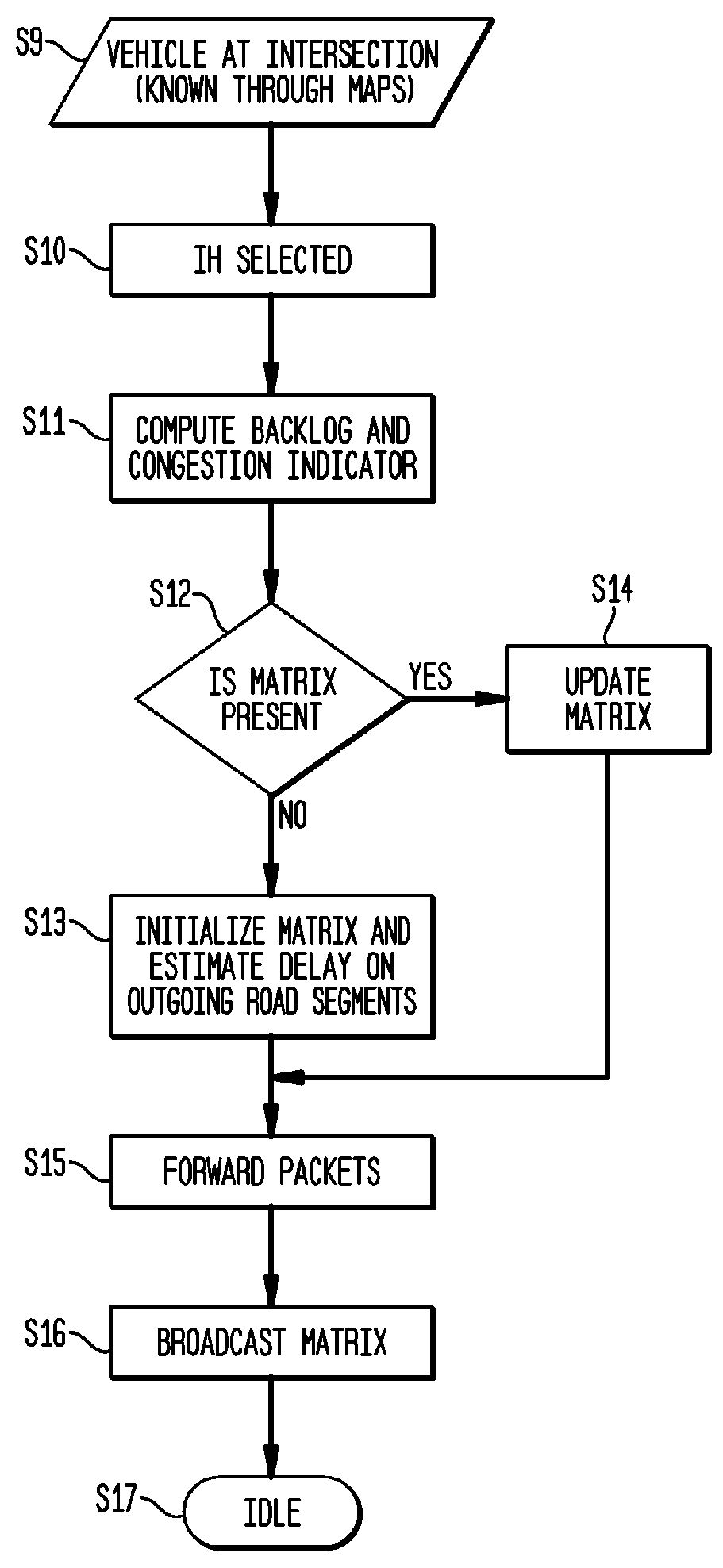
ActiveUS8169897B2Efficient forwardingMaximize data rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsHigh rateData transmission
A method for high rate data delivery in a multi-hop vehicular network comprises at each source vehicle, initiating a packet having a flow tag, assigning an identifier of the content and the current location to the flow tag, and forwarding the packet; at each destination vehicle, setting a flow request and broadcasting at the current intersection; further on movement, setting the flow request at the new intersection, and at each intersection, selecting a header vehicle at the intersection, computing backlog and congestion indicators and listening for broadcasts with a matrix and the flow requests at the header vehicle, determining if the matrix is present, updating the matrix in accordance with the backlog and congestion indicators if the matrix is present, initializing the matrix and estimating the delay on the outgoing road segments if the matrix is not present, forwarding the packet flow, and broadcasting the matrix from the header vehicle.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
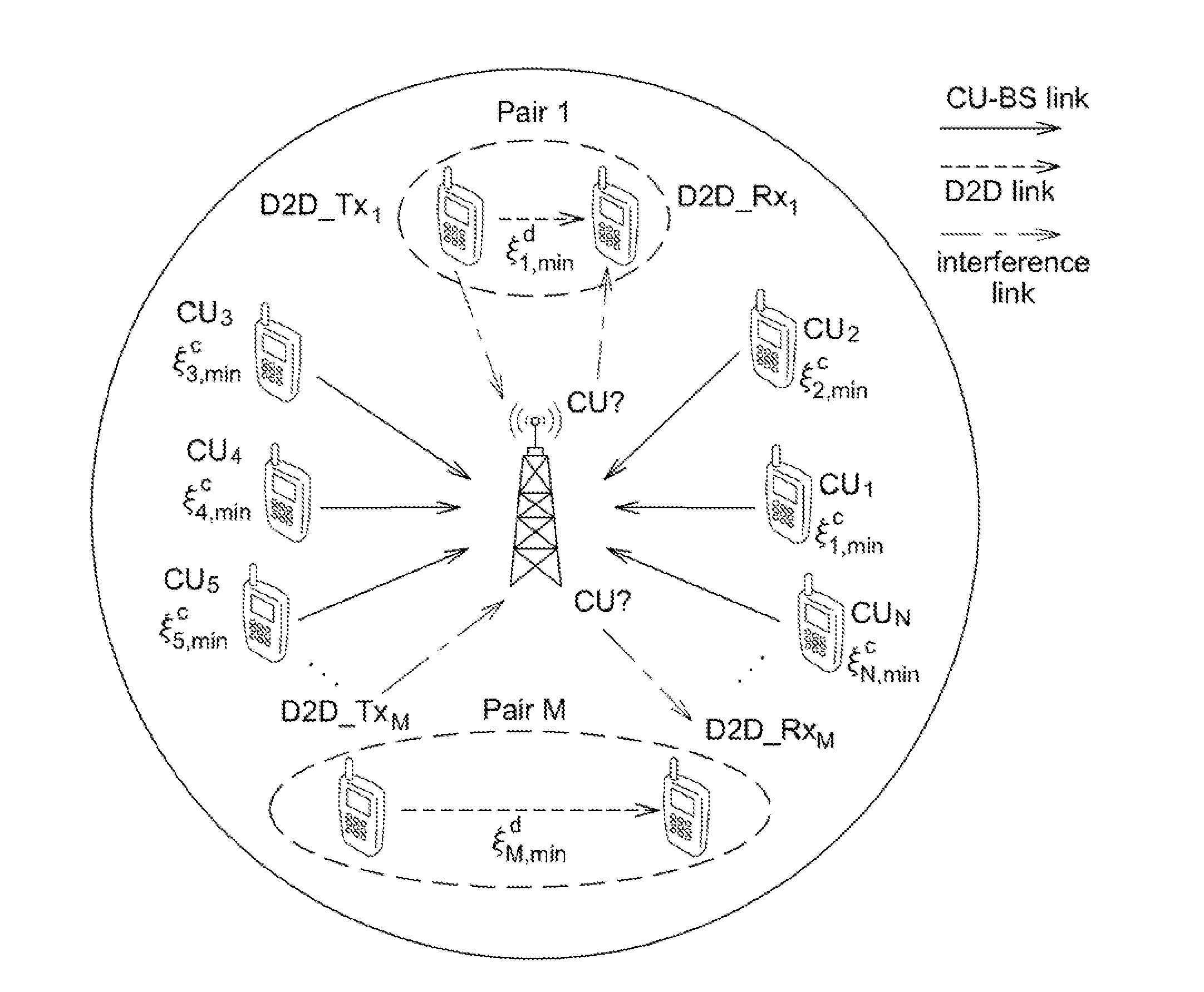
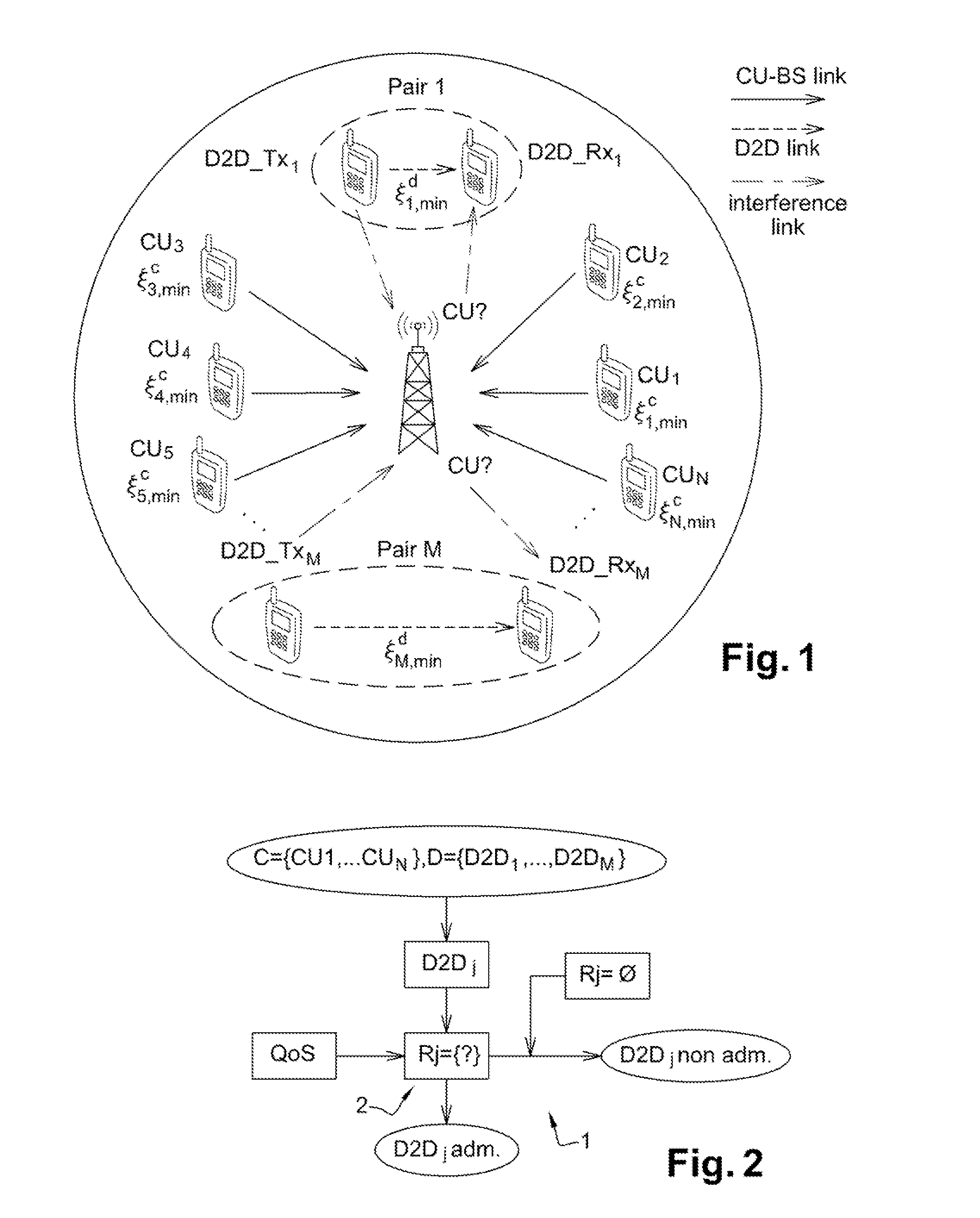
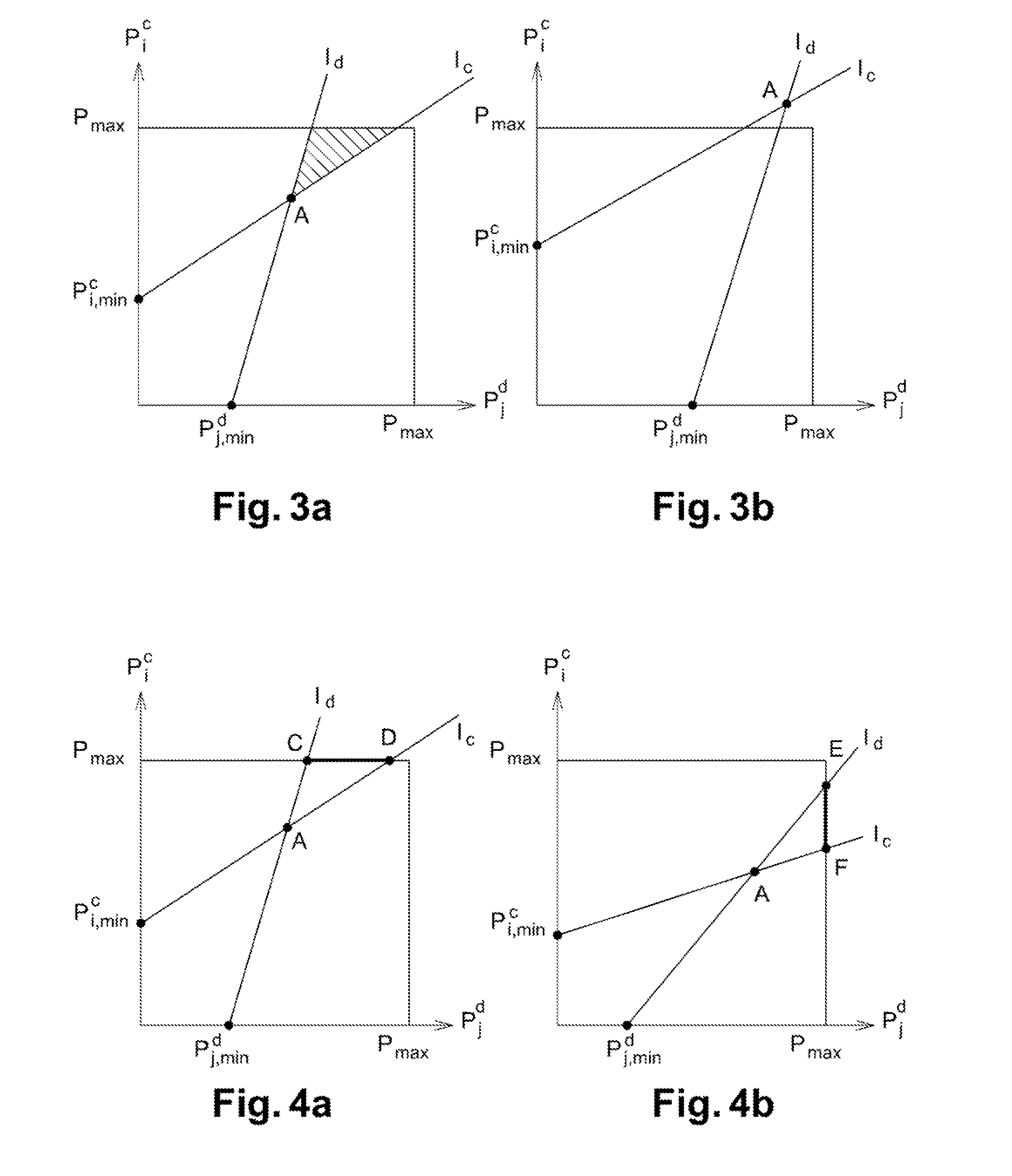
Method of communication in an access network with d2d communication, and a corresponding base station, computer program product, and data medium
ActiveUS20150257185A1Maximize data rateGuaranteed service qualityNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementAccess networkFrequency spectrum
A communication method is provided, which is implemented by a base station of an access network in order to allocate spectrum resources among terminals identified by the station, the station having already allocated all of its spectrum resources to identified terminals having communication set up via the base station. These terminals determine a group of terminals. The method includes: verifying admissibility of a pair of terminals that are candidates for direct communication by determining a set of served terminals that are candidates for sharing their respective spectrum resources with the pair under the sole constraint of the candidate terminal and the pair satisfying their respective QoS criteria.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
Drone with dynamic antenna diversity
ActiveUS10491272B2Maximize data rateMinimizing signal to noise ratioAircraft componentsSpatial transmit diversityCouplingDiversity scheme
The drone comprises M antennas, with in particular two offset antennas located symmetrically at the ends of two arms for the connection to the propulsion units (24), and a ventral antenna under the drone body. The radio transmission is operated simultaneously on N similar RF channels, with 2≤N<M. An antenna switching circuit couples selectively each of the N RF channels to N antennas out of the M antennas according to a plurality of different coupling schemes, dynamically through a piloting logic selecting one of the coupling schemes. The selection is operated as a function of a signal delivered by the drone-borne microprocessor, as a function of the flight and signal transmission conditions, determined at a given instant.
Owner:PARROT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com