DCO-OFDM DC bias and rapid power optimizing method under double restrictions
A technology of DC bias and optimization method, which is applied in the field of visible light communication, and can solve problems such as signal distortion and waste of energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] In order to better understand the technical content of the present invention, specific examples are given and described as follows in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
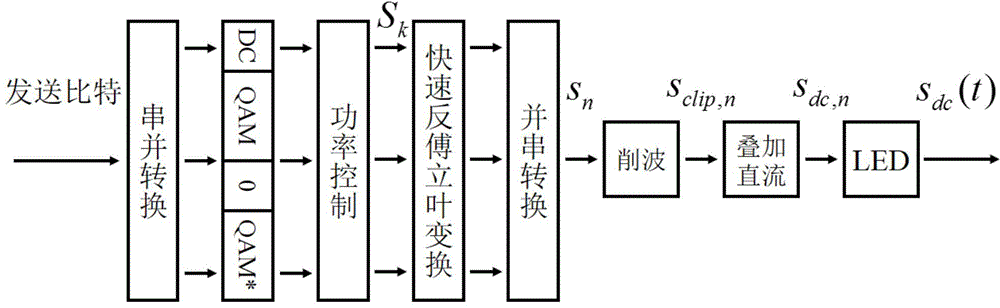
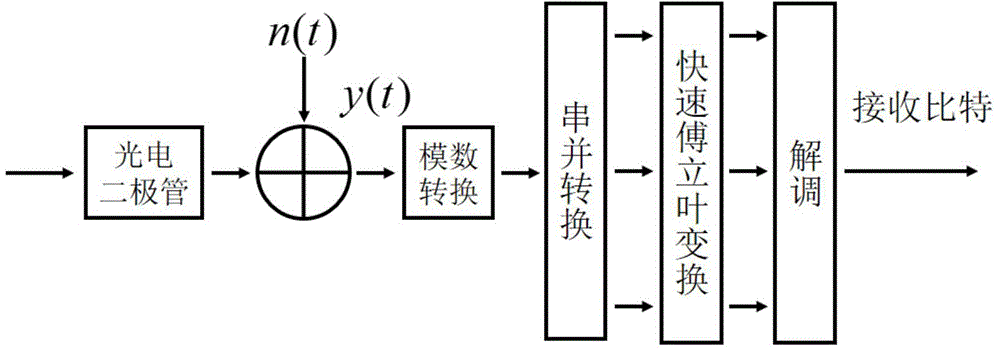
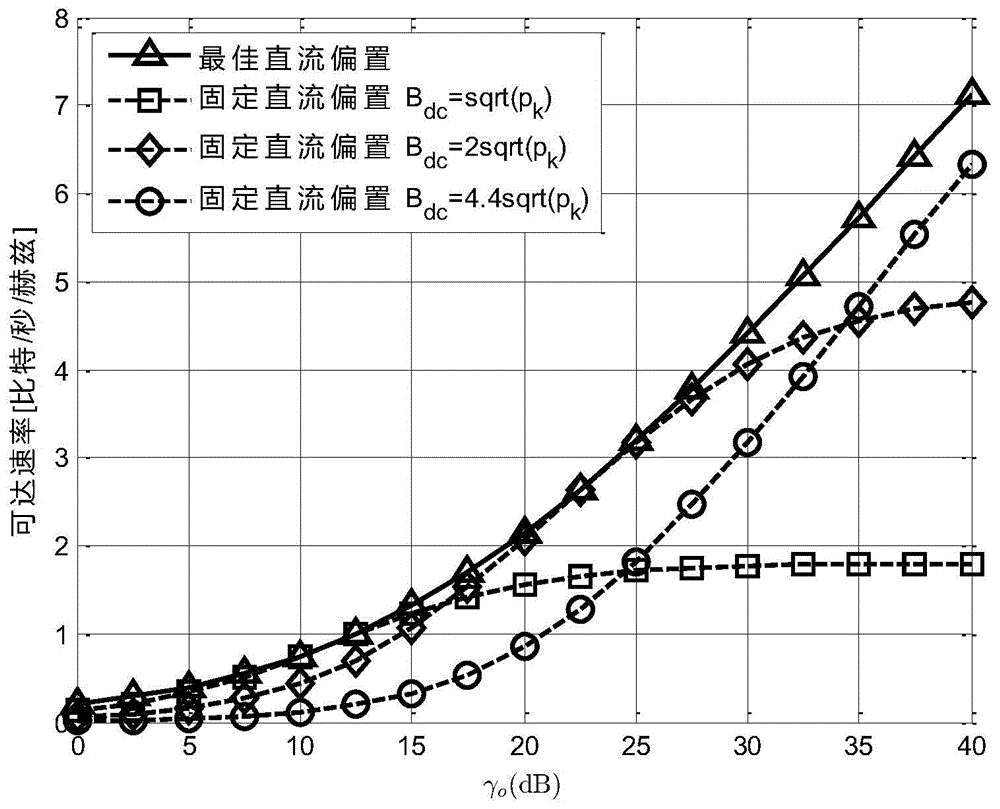
[0036] refer to figure 1 As shown, according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the working process of the DCO-OFDM transmitter is as follows: the DCO-OFDM system has a total of 2K subcarriers, and each subcarrier is modulated and power allocated to obtain the symbol S k , with power p on each subcarrier k =E[|S k | 2 ]. Since optical communication requires the output signal to be a real number, the signal needs to satisfy and S 0 = S K =0. because The resulting symmetry only considers the power of subcarriers k=1,...,K−1. The time-domain signal s is obtained by inverse fast discrete Fourier transform (IFFT). n . Then in the time domain signal s n Overlay size is B dc The DC component of s dc,n =s n +B dc , and cut off the part that is still less than zero afte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com