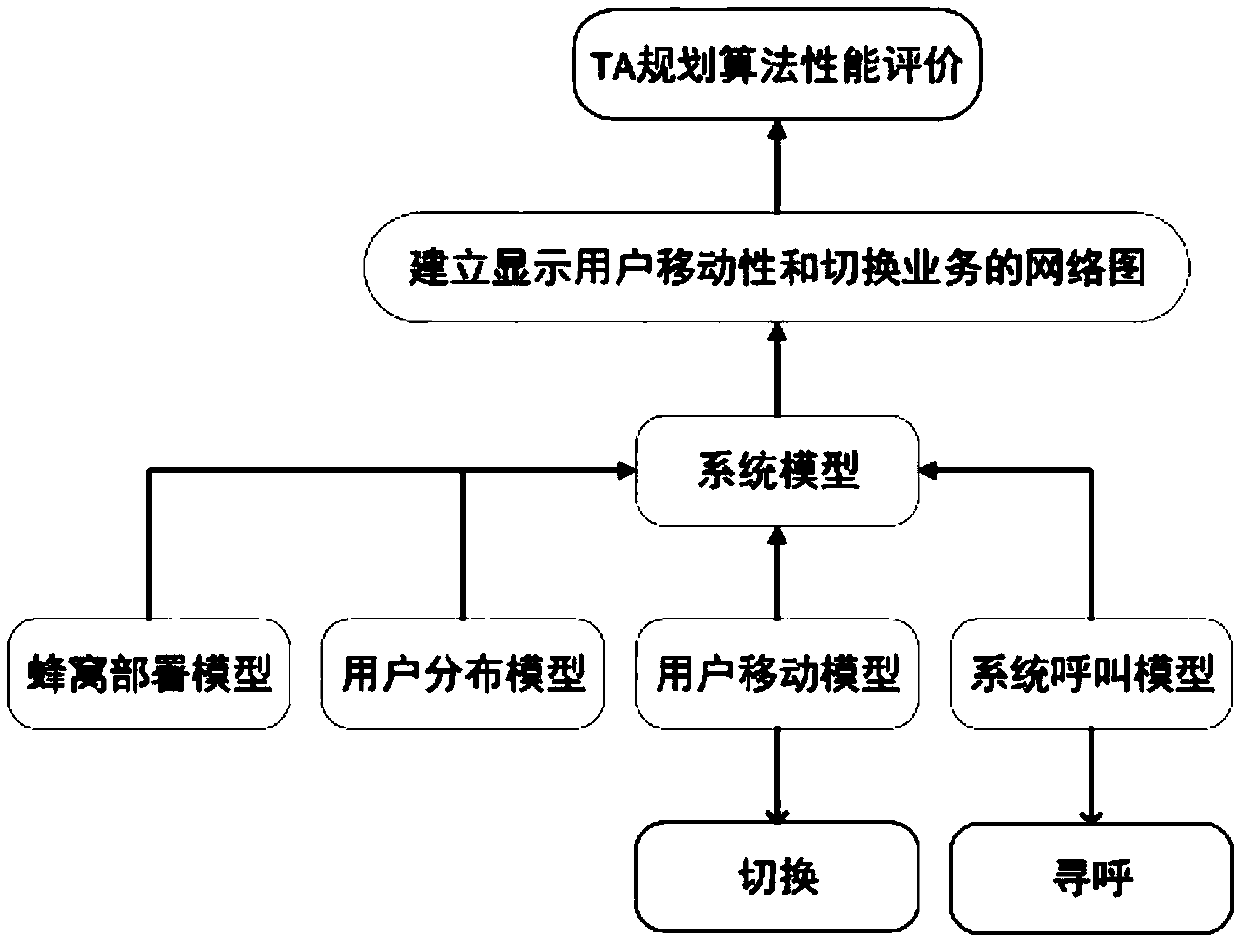
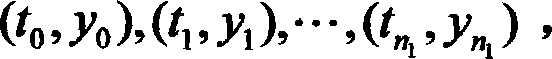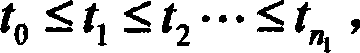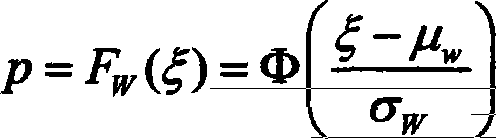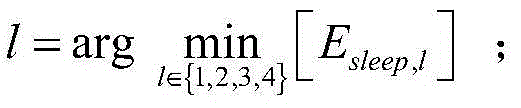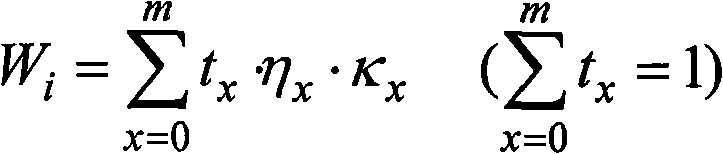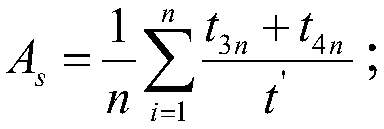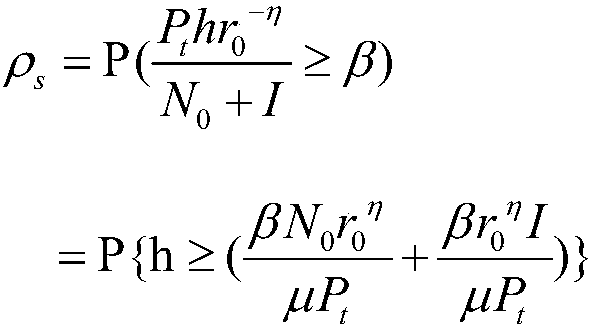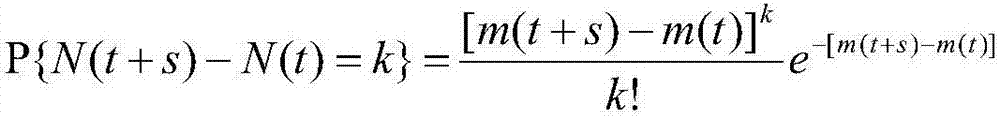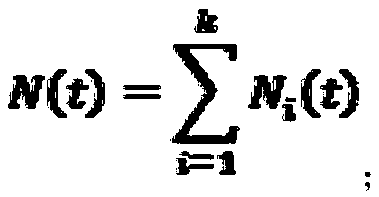Patents
Literature
68 results about "Poisson point process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability, statistics and related fields, a Poisson point process is a type of random mathematical object that consists of points randomly located on a mathematical space. The Poisson point process is often called simply the Poisson process, but it is also called a Poisson random measure, Poisson random point field or Poisson point field. This point process has convenient mathematical properties, which has led to it being frequently defined in Euclidean space and used as a mathematical model for seemingly random processes in numerous disciplines such as astronomy, biology, ecology, geology, seismology, physics, economics, image processing, and telecommunications.
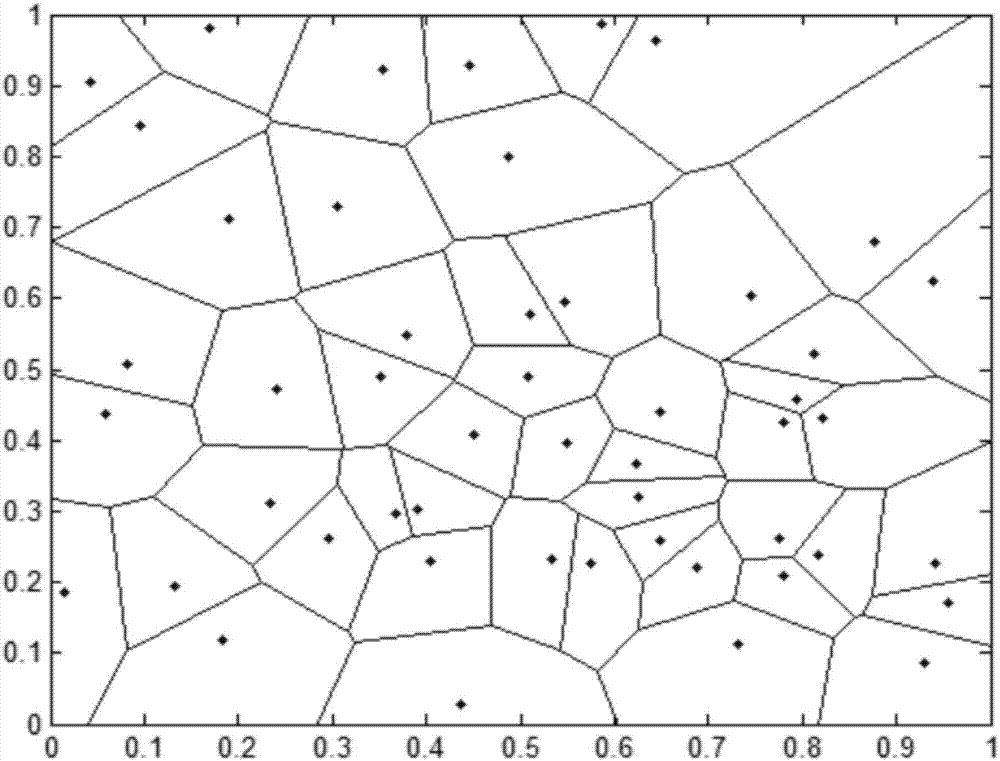
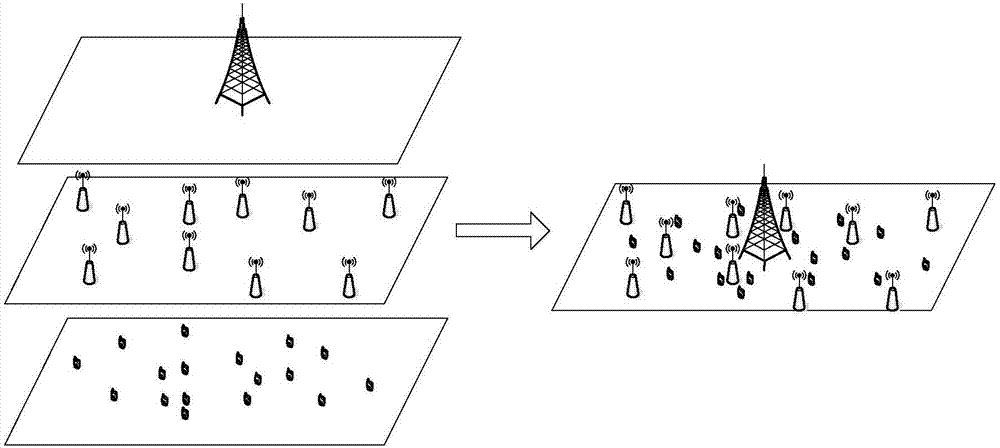
Heterogeneous cellular network base station deployment method based on Poisson cluster process
ActiveCN106454919AEasy to analyzeHigh probability of coverageWireless communicationProbit modelCoverage probability
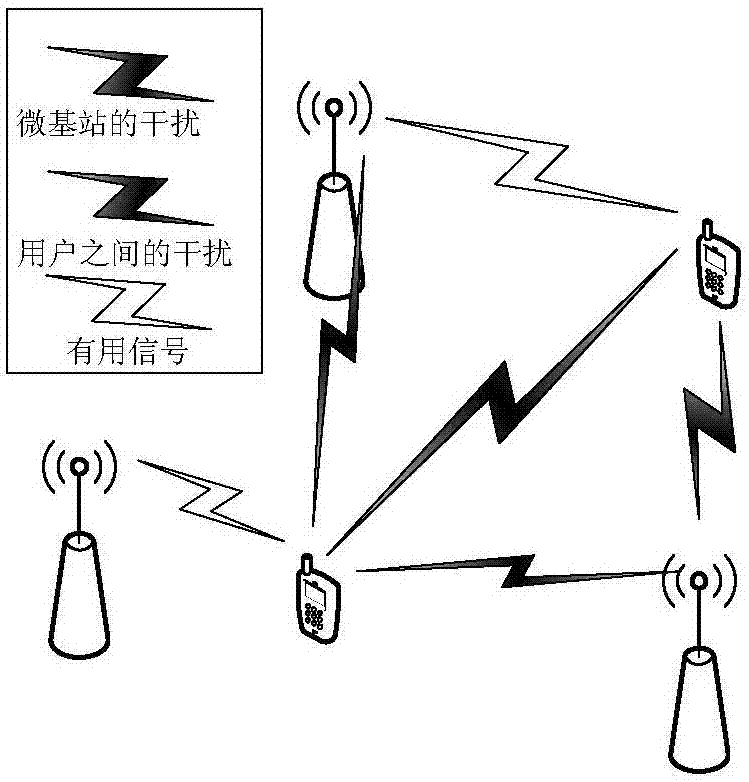
The invention provides a heterogeneous cellular network base station deployment method based on a Poisson cluster process. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of a random geometry theory, according to a hypothetical system model and adopting an instantaneous SINR cell selection mechanism as a cell selection mechanism of a user, deducing an SINR model based on the Poisson cluster process; carrying out analysis and inference on an interference model of a multi-layer heterogeneous cellular network by utilizing characteristics of the Poisson cluster process and a probability generation function thereof to obtain an interference distribution model; with the SINR model and the interference distribution model being combined, deducing a coverage probability model of the multi-layer heterogeneous cellular network; and carrying out simulated comparison and analysis on difference of coverage probabilities of the Poisson cluster process and a Poisson point process. The method is much closer to real communication scenes, is larger in coverage probability, can analyze coverage probability and throughput capacity better, and is of great importance in study of the heterogeneous cellular network in the future.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
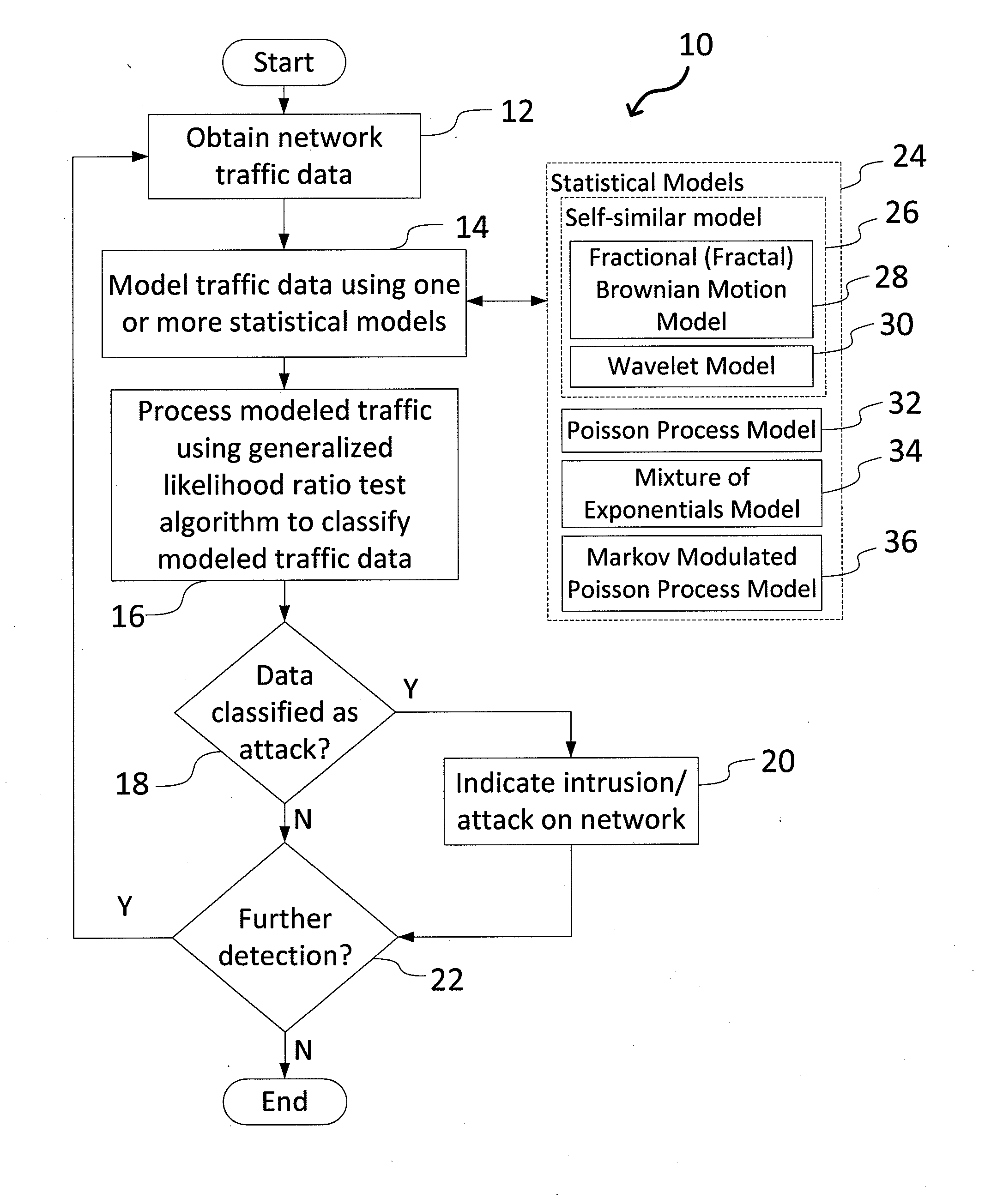
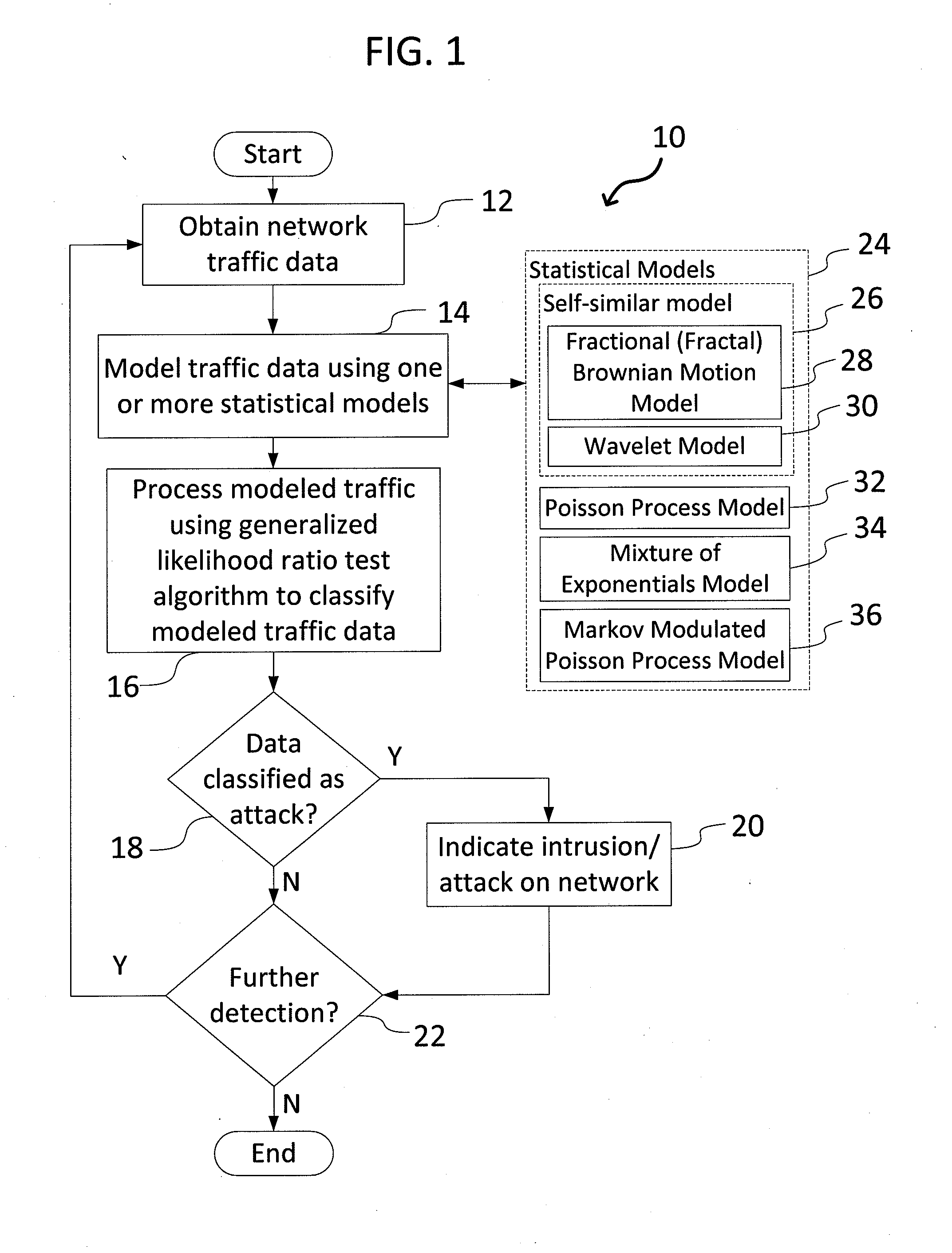
System and Method for Detecting Network Intrusions Using Statistical Models and a Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test
InactiveUS20140041032A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficTiered approach
A system and method for detecting network intrusions using one or more statistical models and a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) is provided. The system includes a computer system and a network intrusion detection engine executed by the computer system. To detect network intrusions, the system receives network traffic data, computes a likelihood using one or more statistical models, such as an Markov-modulated Poisson process, and processes the traffic data using a GLRT. The statistical models are used to assess the likelihood of seeing a particular pattern of network traffic. The GLRT is used to classify a particular pattern as either indicative of an attack or not indicative of an attack. The system could apply one or more types of statistical models, such as in a flexible multi-tiered approach.
Owner:OPERA SOLUTIONS
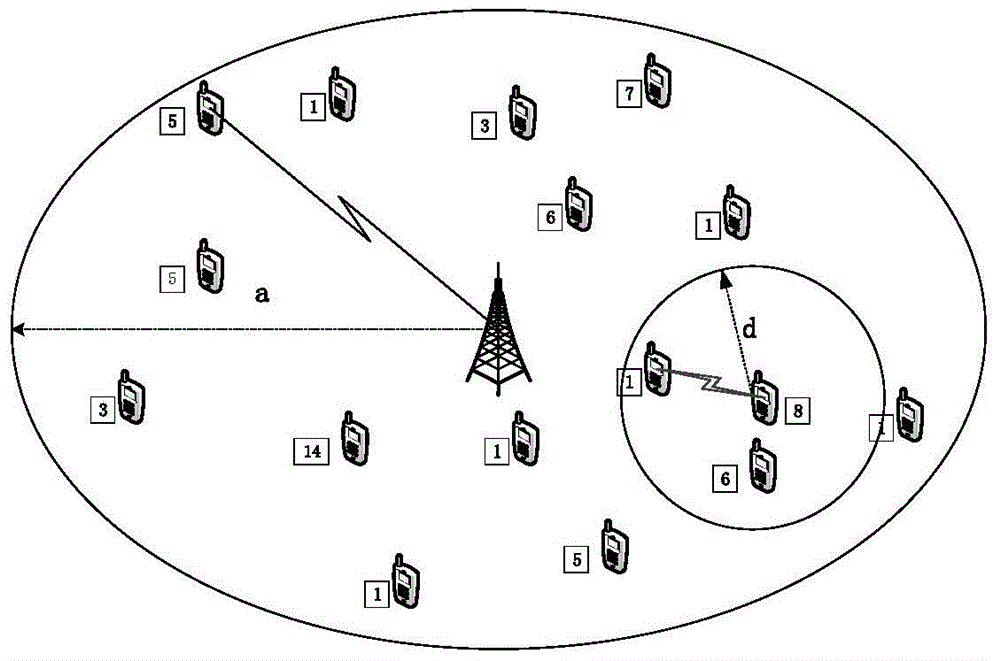
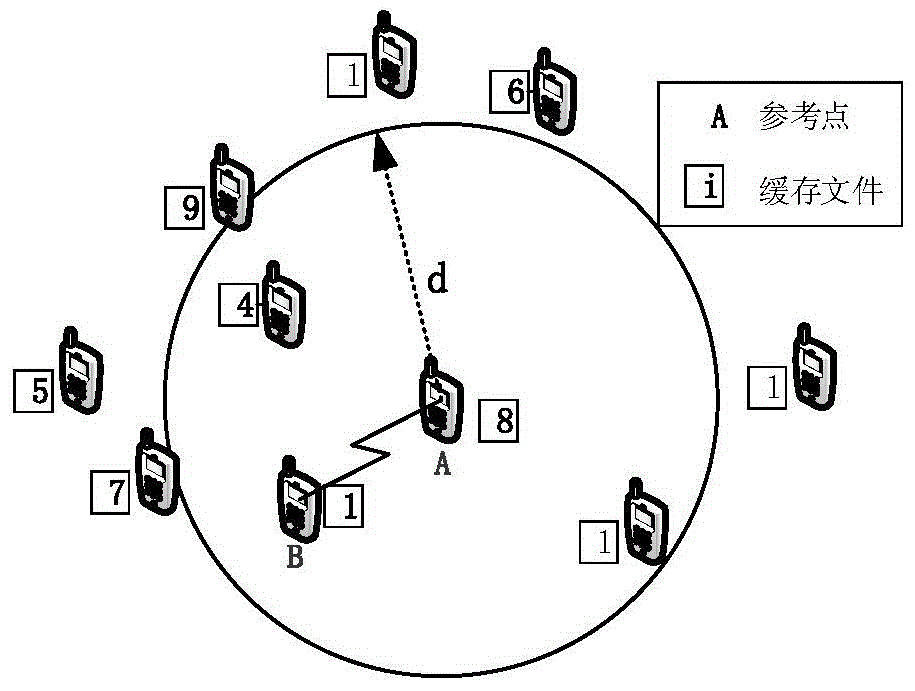
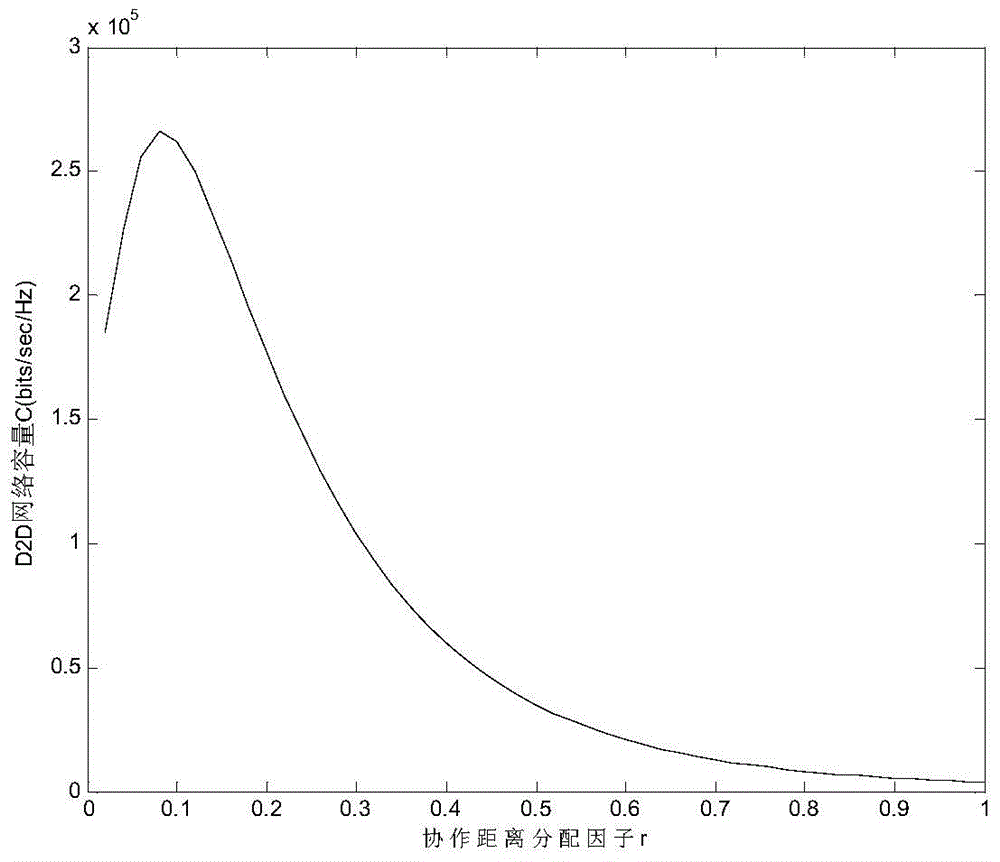
Method for calculating optimal cooperation distance of D2D fusion network based on file popularity
InactiveCN105791391AImprove performanceTransmissionHigh level techniquesComputer sciencePoisson point process
The invention discloses a method for calculating an optimal cooperation distance of a D2D fusion network based on file popularity. The method comprises the following steps: cell user movement is modeled as random distribution in a spatial Poisson point process, each user caches a video file, the user can obtain the video file by selecting a cellular mode or a D2D mode, the popularity of the video file is simulated by Zipf distribution, a user number ND2D activated by D2D and the user number NBS activated in the cellular mode in a single cell are obtained according to different features of D2D and cellular communication, then a single user obtains the network capacity of the fusion network by the average throughput in the D2D mode and the cellular mode, and a specific application scene and a service demand are obtained by an existing fast iterative algorithm, so the D2D fusion network obtains an optimal cooperation distance d* with the maximum throughput.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for predicting remaining life of equipment under competing failure conditions
InactiveCN103678858ASave moneyAvoid economic lossSpecial data processing applicationsModel parametersDependability
The invention relates to a method for predicting the remaining life of high-reliability equipment under competing failure conditions. The fault mode causing failure of the equipment is considered as a combination of two modes including the slow variation fault mode described with a Wiener model with drift and the abrupt fault mode described with the Poisson process. Supposing that the two fault modes are independent of each other, and the remaining life of the equipment can be acquired after the remaining lives of the equipment in the two fault modes are acquired respectively. The method specifically includes the steps of constructing a dynamic performance degradation database, establishing an equipment performance degradation model under the competing failure conditions, estimating model parameters and predicting the remaining life. With the method for predicting the remaining life of the equipment, the individual life characteristic quantities of the equipment can be predicted and analyzed, power theoretical bases and technological support are provided for the maintenance guarantee of the equipment, and the method has very good engineering application prospects.
Owner:PLA SECOND ARTILLERY ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY
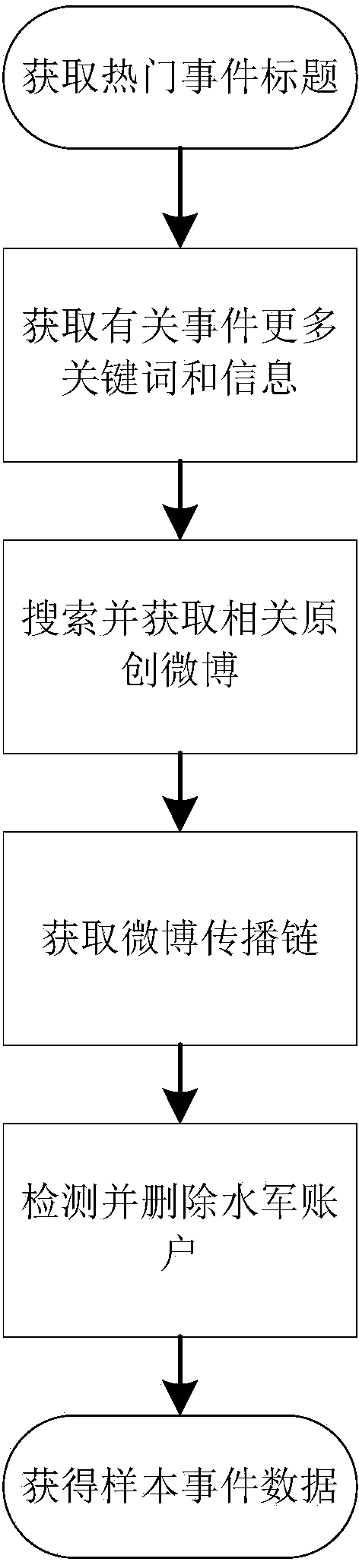
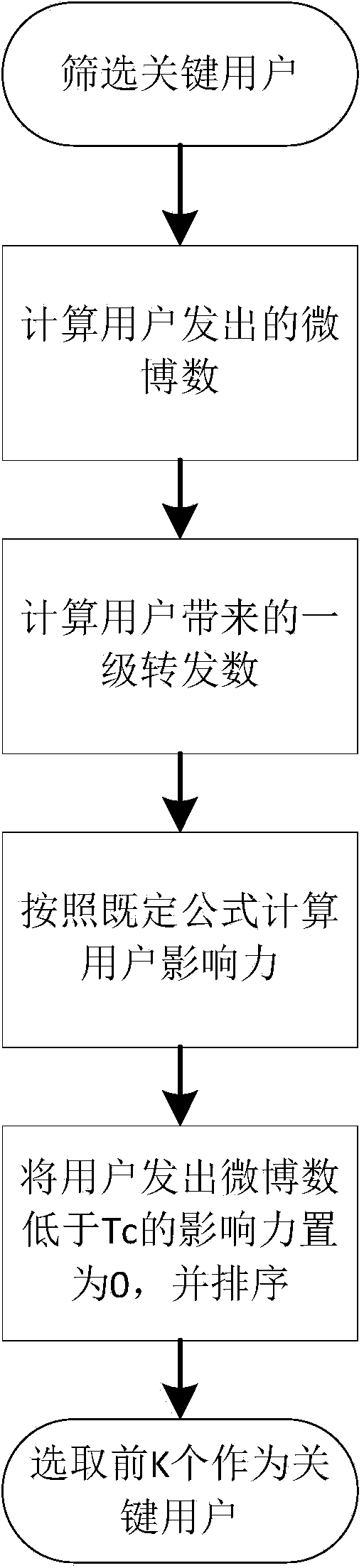
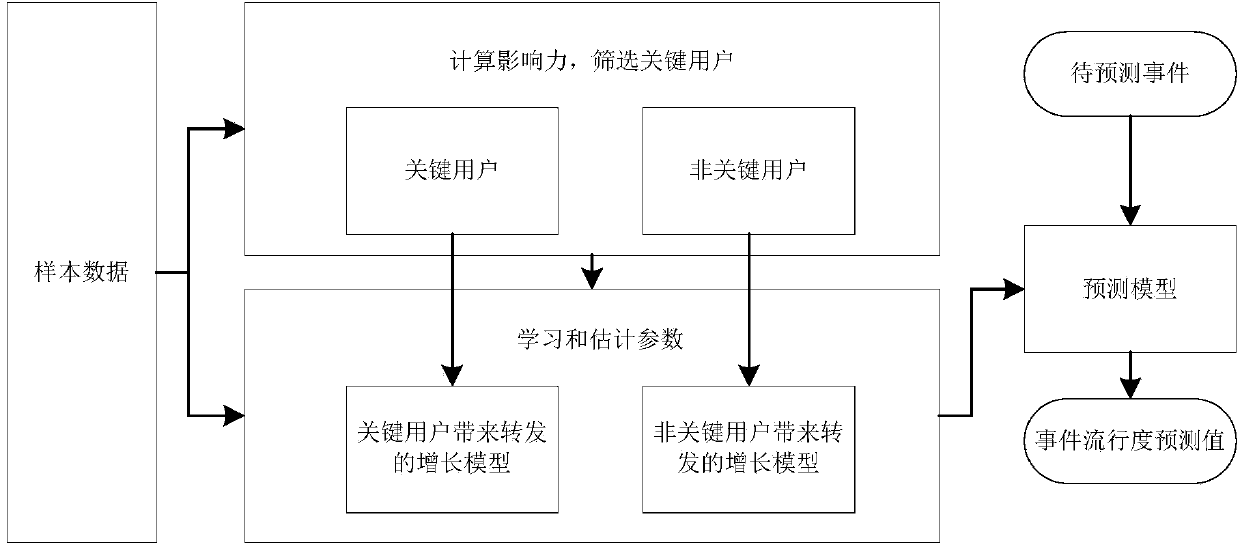
Poisson-process-model-based method for predicting event popularity in social network
The invention provides a Poisson-process-model-based method for predicting the event popularity in a social network. The method comprises the steps as follows: Step 1, selecting a sample event, and obtaining a micro-blog propagation chain of the sample event; Step 2, performing user influence calculation, screening users with the strong influence as critical users, and marking the rest users as non-critical users; Step 3, modeling micro-blog forwarding processes brought by the critical users as a Poisson process model, and simply processing micro-blog forwarding processes brought by the non-critical users; Step 4, learning and estimating parameters of the Poisson process model of the critical users and parameters of the non-critical users by the aid of information of the sample event; Step 5, giving a new event with evolution information in certain duration, and predicting the popularity of the new event at a certain moment in the future according to the model in Step 3. By the aid of the method, the better popularity prediction can be provided at the initial stage of a micro-blog event, and very effective help can be provided for reasonable guidance of development of the event.
Owner:上海深杳智能科技有限公司 +1
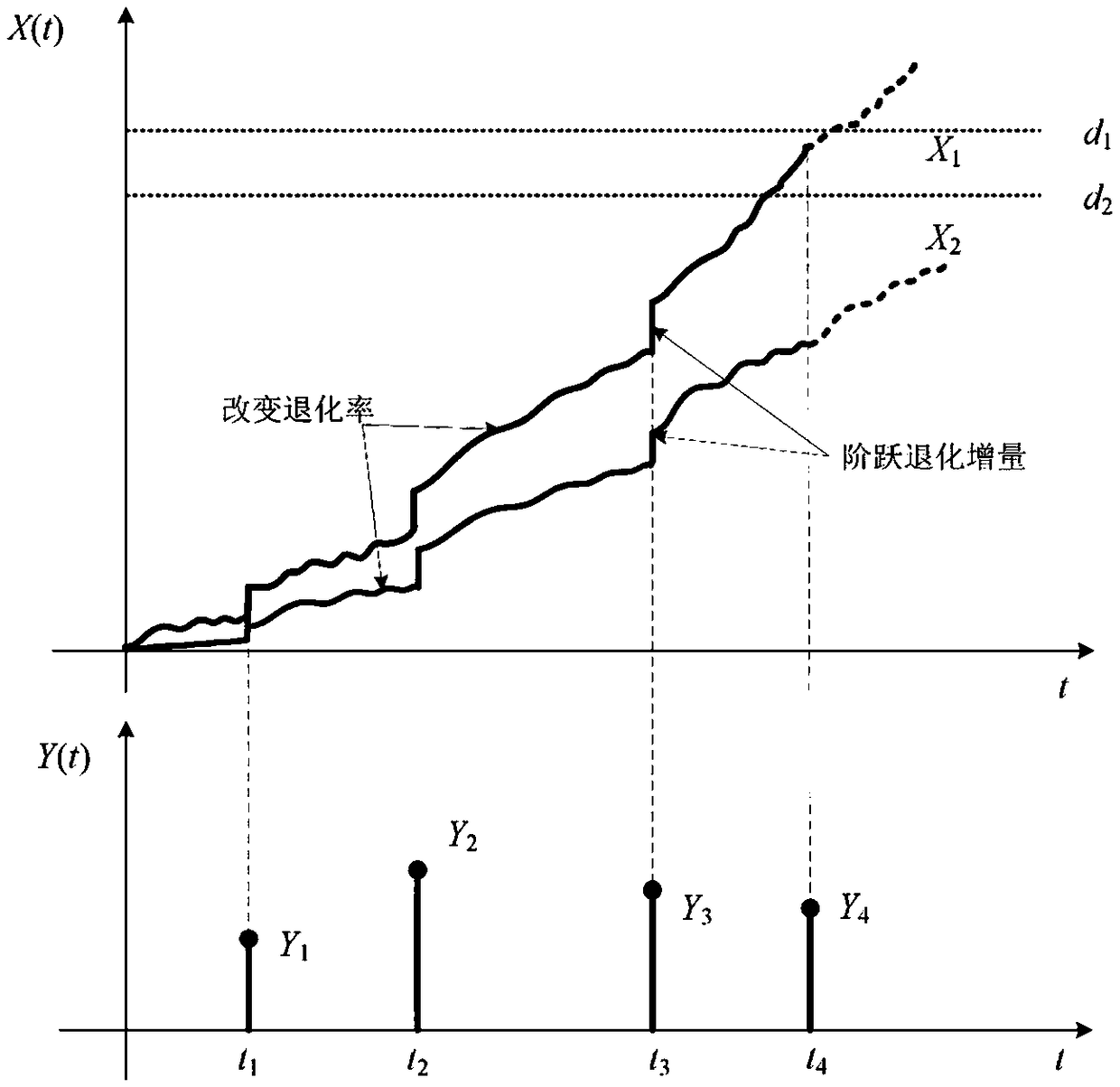
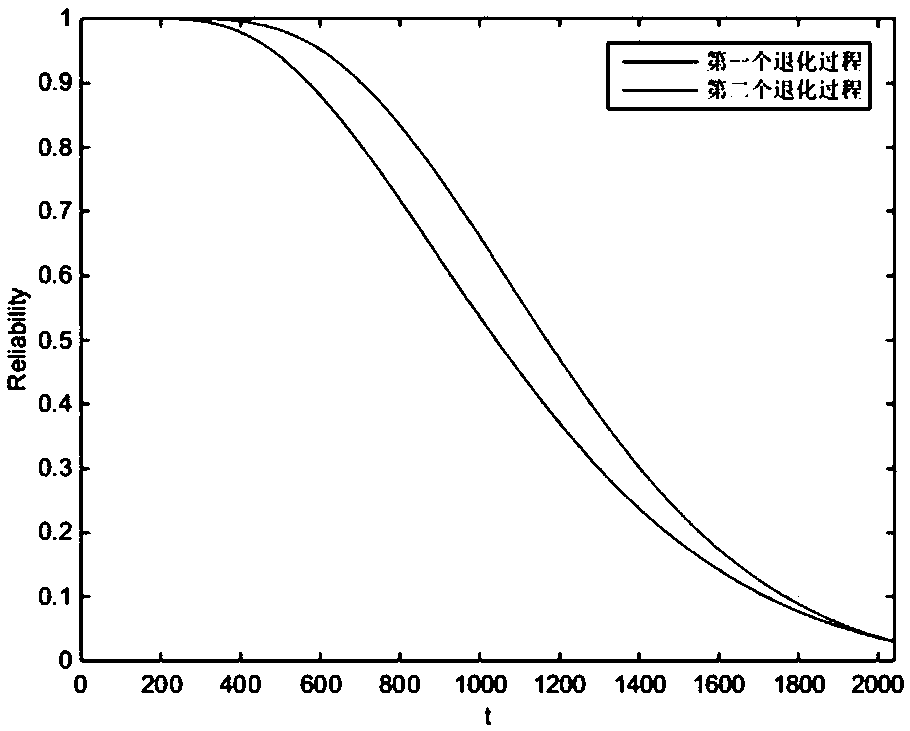
Reliability model of competitive failure systems with multiple degradation processes and stochastic shocks
ActiveCN109214094AAccurately describe nonlinearity and randomnessDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDegradation processPoisson point process
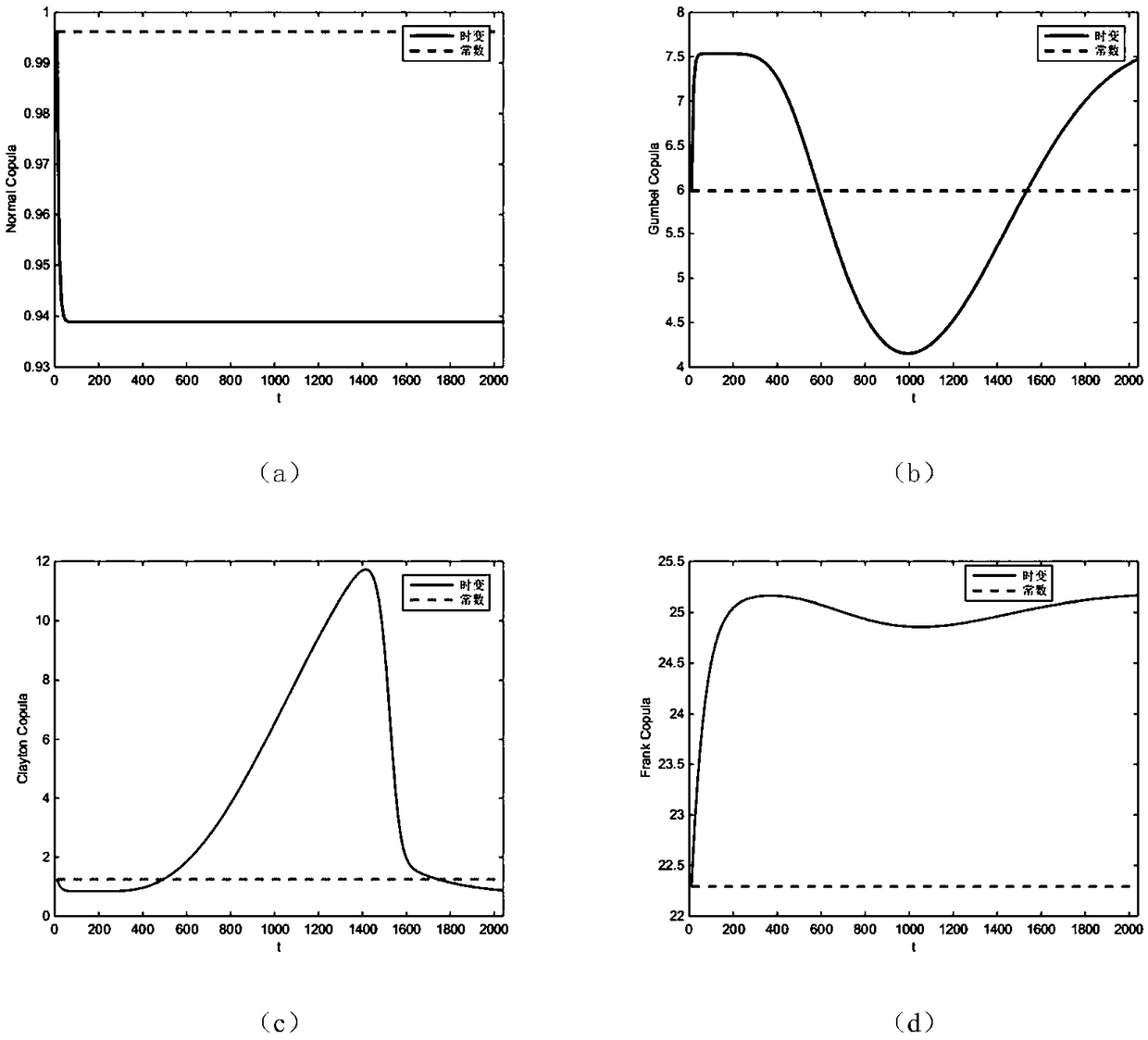
The invention discloses a new reliability model of a multi-degradation process and a stochastic impact competition failure system. It is assumed that random shocks obey homogeneous Poisson process, and the probability that the shocks are fatal and non-fatal is p (t) and q (t), respectively, where once the fatal shocks occur, the system will invalidate immediately; non-lethal shocks can have an impact on the degradation process, on the one hand,phase step degeneration increase will be increased, on the other hand, it will increase the degradation rate, and its effect is reflected by cumulativedamage. On this basis, by modifying the existing nonlinear Wiener process degradation model, the effect of non-lethal shock on degradation is considered, and the final system reliability function is established by time-varying Copula function. Finally, a numerical example is given to illustrate the mathematical model proposed in this paper.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Random traffic flow simulation method in road and bridge based on measured data
InactiveCN104933284AHigh precisionDetailed descriptionSpecial data processing applicationsTraffic flowParameter distribution
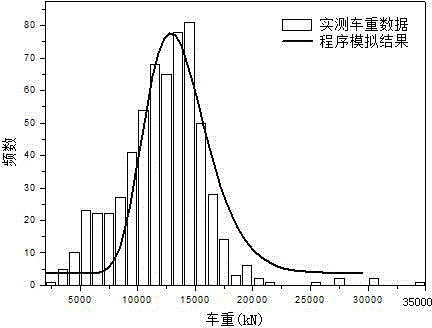
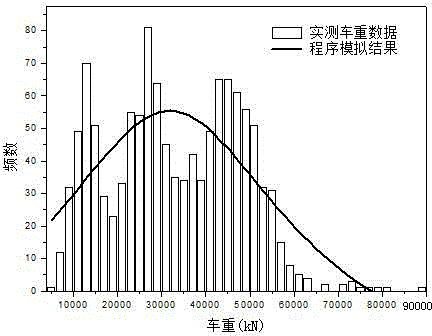
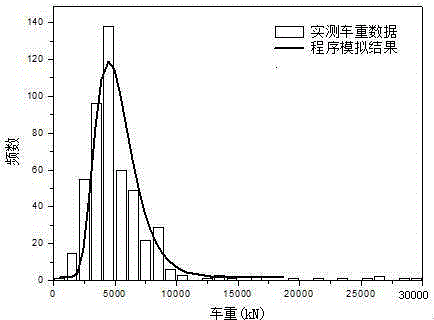
The present invention belongs to the technical field of architecture and transportation bridges, and more particularly relates to a random traffic flow simulation method in roads and bridges based on measured data. According to the method, an algorithm is compiled by using Monte-Carlo method and a time distance matrix for determining vehicle random head is calculated; by means of time series sequencing, when the time interval of the permutations is equal to the time distance of the traffic flow time matrix, a vehicle generation module is enabled to generate the vehicles that are running on the bridge at the time and attributes are assigned to the vehicles. When the interval of the permutations is less than the traffic flow time distance, the method according to the present invention is only applicable in executing a vehicle running module, and calculating horizontal and vertical locations of the vehicles that are running on the bridge at the time; according to the filtered Poisson process principle and in combination with the practically measured vehicle parameter distribution types, a random traffic flow simulation model is established, and the distribution regulations of randomness of vehicles is described.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Energy-saving base station dormant method for heterogeneous cellular network
ActiveCN104581904ATransmit power changeOutage Probability ChangePower managementHigh level techniquesTransmitted powerMicrocell
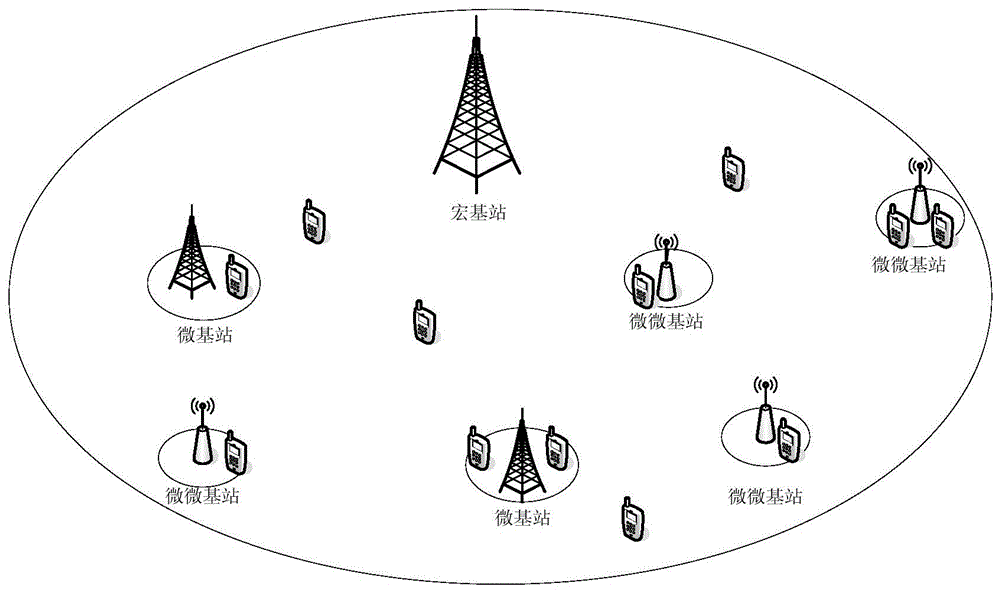
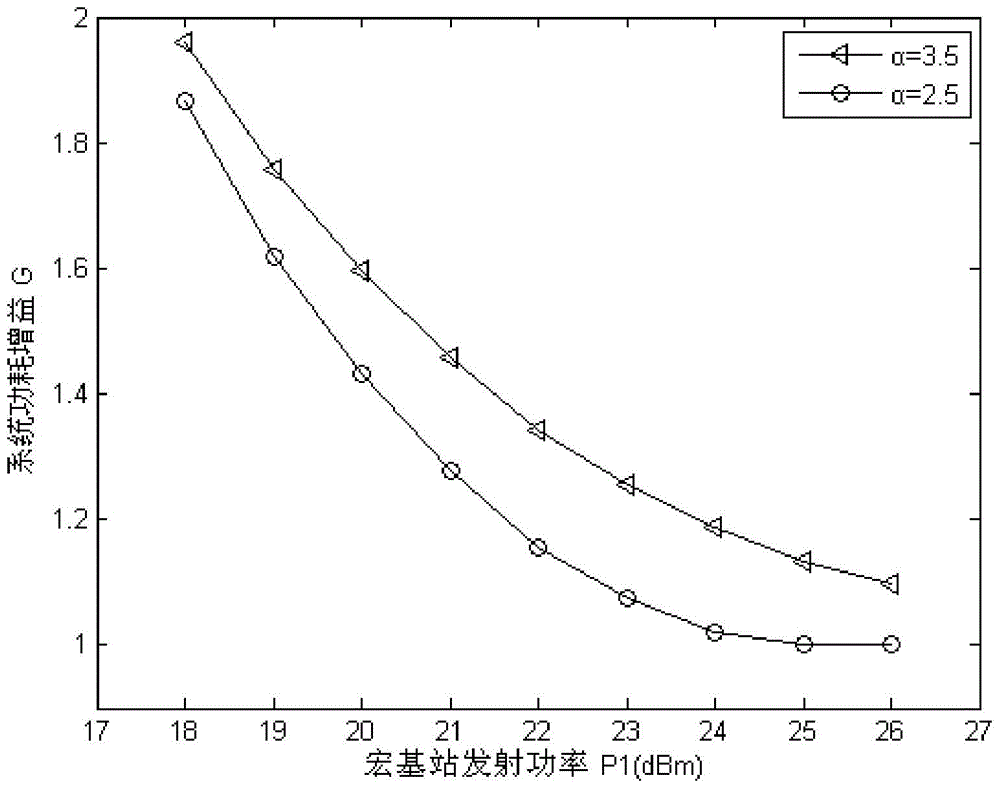
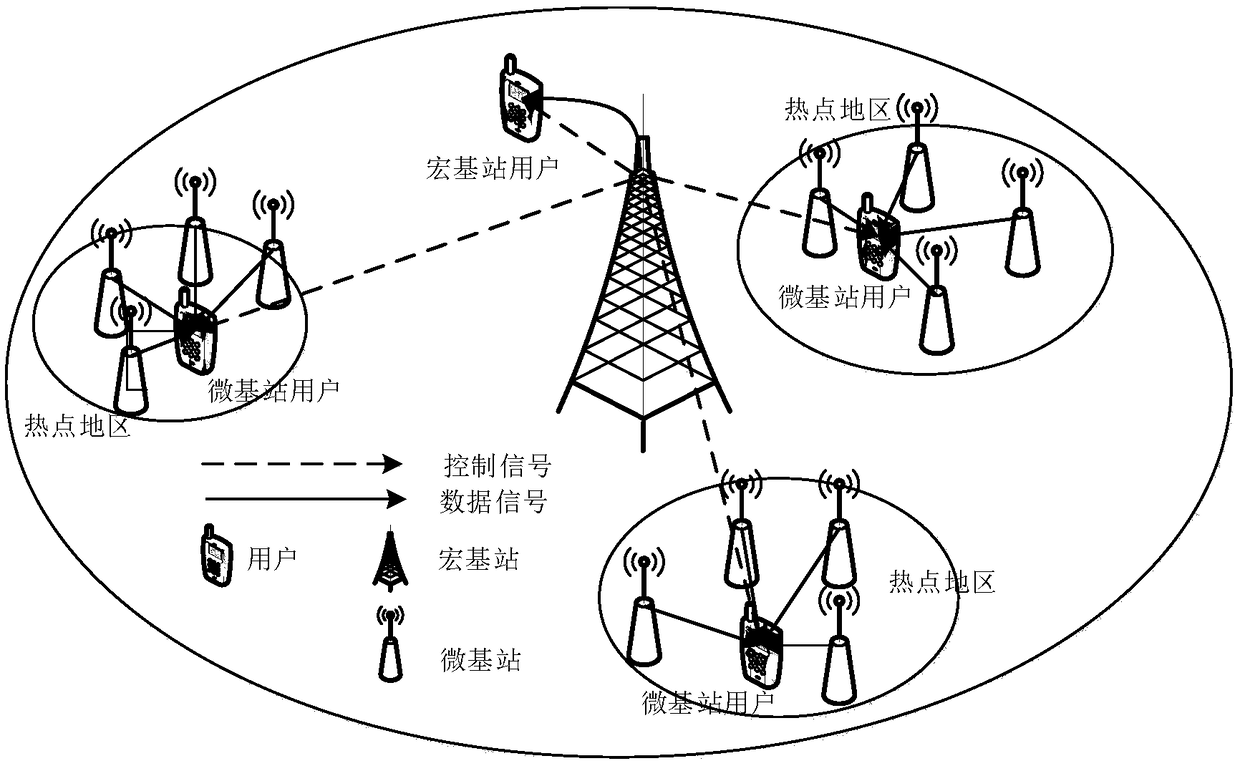
The invention provides an energy-saving base station dormant method for a heterogeneous cellular network. An optimal base station dormant scheme is adopted according to the outage probability of a system and uplink transmitting power of a user. Macrocells, microcells and picocells are deployed in the poisson point process in a three-layer heterogeneous cellular network scene, and the outrage probability of the system and the uplink transmitting power of the user are derived according to a random geometric theory; a system power consumption optimization problem is solved, a part of the macrocells start a dormant state, the microcells and the picocells are added, the transmitting power of the macrocells is adjusted, and accordingly, the maximum system power consumption gain is obtained.
Owner:CERTUS NETWORK TECHNANJING
Coverage and data plane separated super-dense heterogeneous cellular network user access method
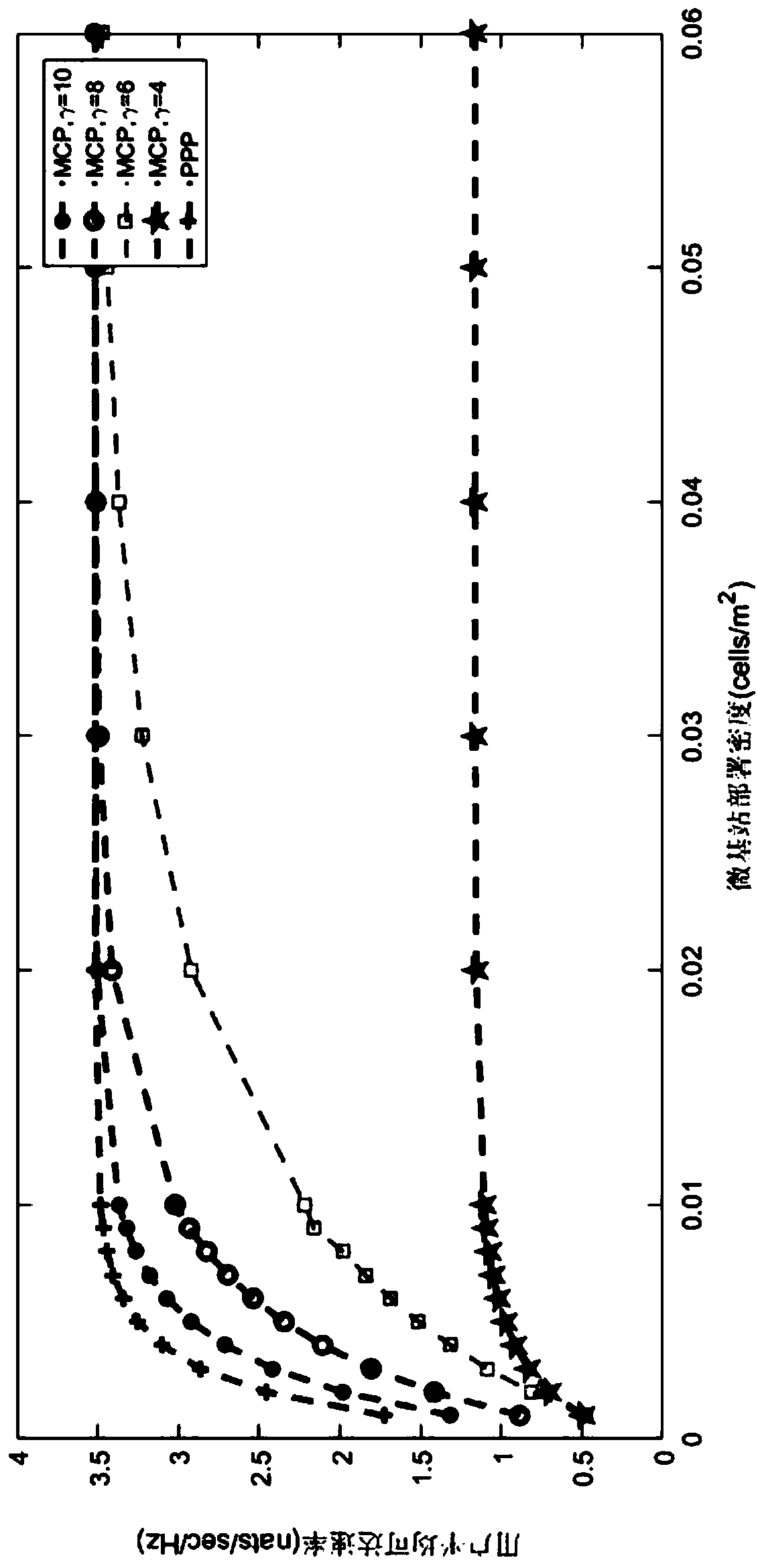
ActiveCN109327851AReduce switching timesIncreased achievable data rateAssess restrictionHigh rateData simulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of user accessing to a super-dense heterogeneous cellular network, and discloses a coverage and data plane separated super-dense heterogeneous cellular network user access method. The method comprises the following steps: building a microcellular base station system model based on a Poisson cluster process; assisting, by multiple micro base stations distributed around the same hotspot, a user in access service; building a macro base station system model based on a Poisson point process; on the premise that a macro base station is mainly used for completing a coverage function and the micro base stations are used for high-rate data transmission, respectively deducting an SINR (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio) distribution model and an interference distribution model which are received by a macro base station user and a micro base station user; deducting an average accessible rate when users in a network are served by different types of base stations by using the SINR distribution model and a known distance distribution model; and deducting a reliable closed upper bound and lower bound of Laplace transformation of the interferencedistribution model. A data simulation result shows that the coverage and data plane separated super-dense heterogeneous cellular network user access method provided by the invention can achieve a higher data rate.
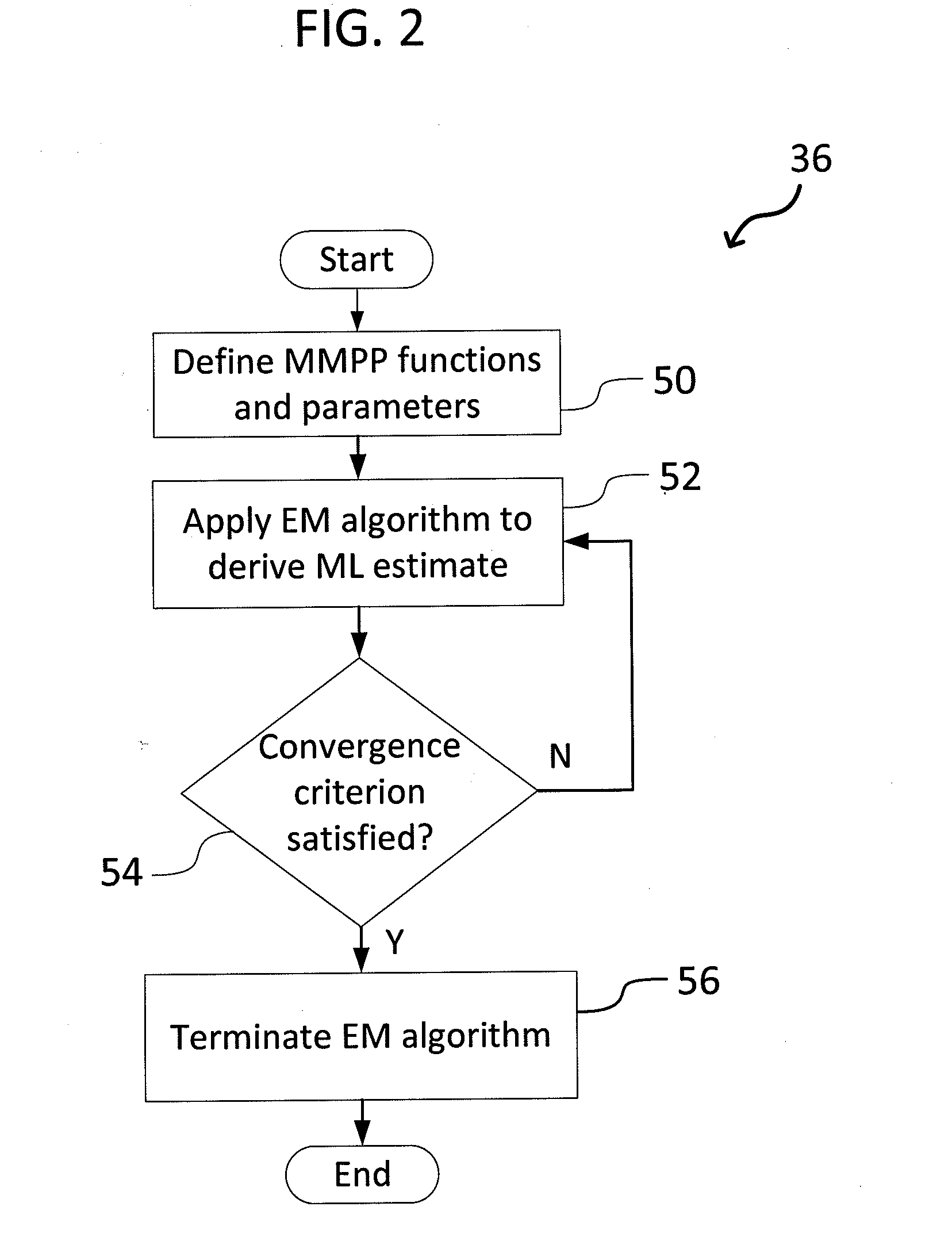
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cache optimization method of real-time vertical search engine objects
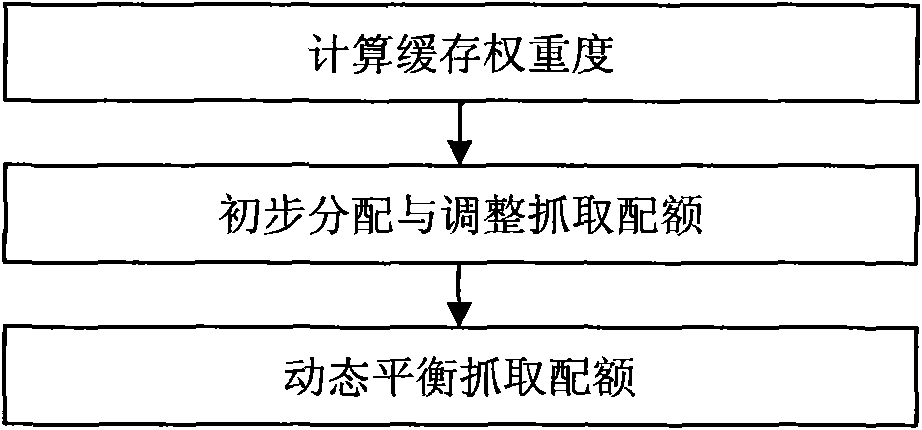
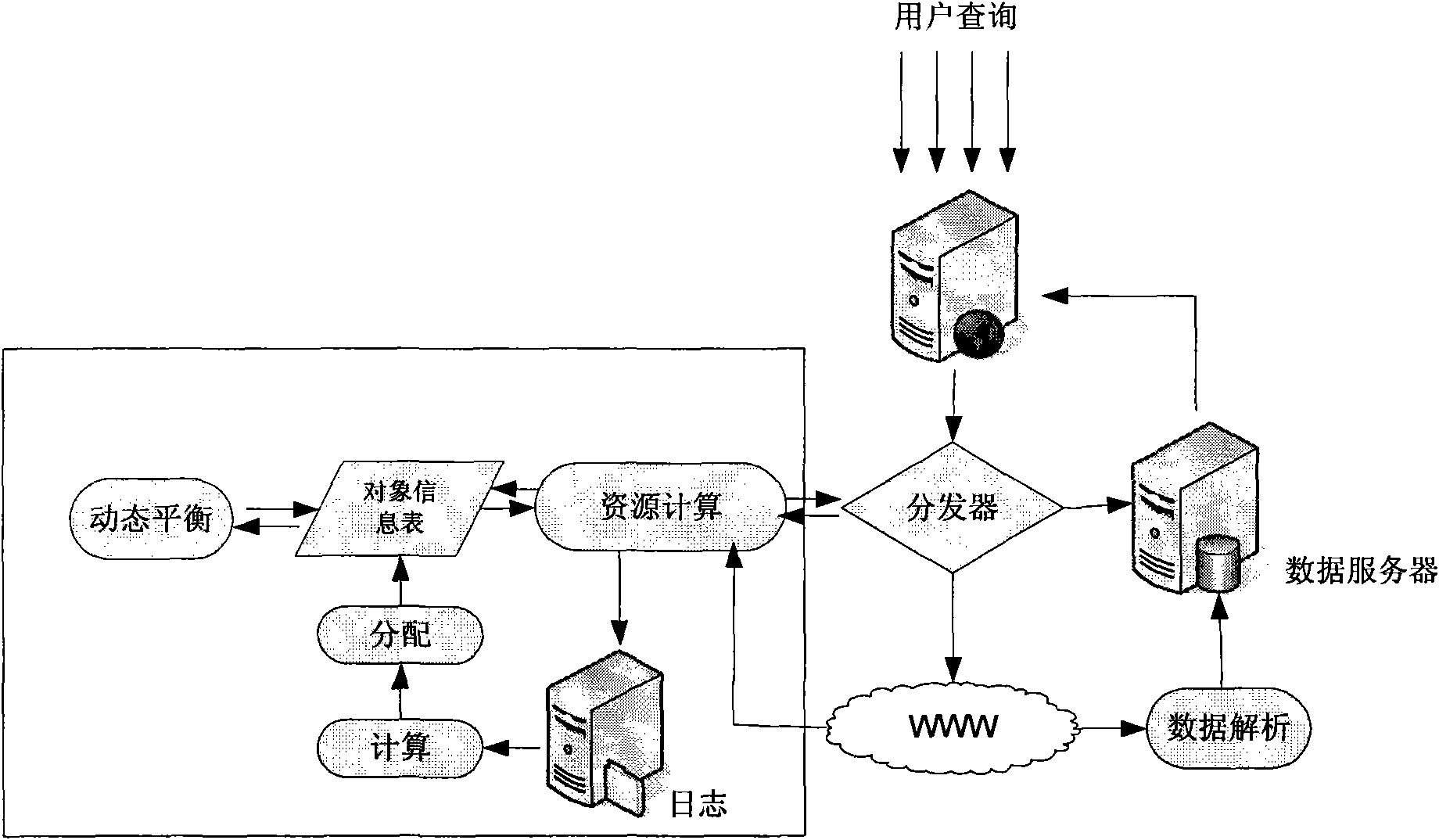
InactiveCN101667198AIncrease profitImprove experienceSpecial data processing applicationsCache optimizationDynamic balance
The invention discloses a cache optimization method of real-time vertical search engine objects, comprising the following steps: predicting the popularity trend of different objects and calculating the cache weights of different objects by utilizing the relation between the objects and the object properties; calculating the initial distribution and adjustment method of the grasping quota in each object by utilizing the characteristics the query to the same object by users conforms to a poisson process and the data grasping is used as query driving; and calculating the dynamic balance method ofthe grasping quota in each object by utilizing the characteristic that the true change frequency of data conforms to the poisson process. The invention increases the use ratio of the vertical searchengine on the grasping quota of a data site, increases user experience of real-time vertical search engine and realizes the adaptive configuration of the real-time vertical search engine to differentdata sites.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for gradually deforming an initial object distribution in a heterogeneous medium, generated by simulation of an object type stochastic model, to best adapt it to imposed physical constraints
InactiveUS7151845B2Control migrationCharacter and pattern recognitionGeological measurementsGraphicsPoint density
A geostatistical method for gradually deforming an initial distribution of objects, of geologic type for example, from measurements or observations, so as to best adapt it to imposed physical constraints of, for example, a hydrodynamic type having applications of geostatistical modelling of heterogeneous reservoirs of various objects: fracture, channels, vesicles, etc., for example. The objects are distributed in a zone of a heterogeneous medium according to a Poisson point process in form of figurative points with a point density λ(x) that varies according to their position (x) in the zone, a realization of a uniform random vector according to which the position of each object is defined while respecting density λ(x) is formed, and the uniform random vector is gradually modified according to a gradual deformation process so as to obtain gradual migration of each object until a final realization best adjusted to parameters relative to the structure of the medium, such as hydrodynamic parameters, is obtained.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Cluster-based interference alignment method for two-layer network
ActiveCN106788812AEliminate cross-layer interferenceReduce cross-layer interferenceBaseband system detailsTransmission monitoringInterference eliminationCommunications system
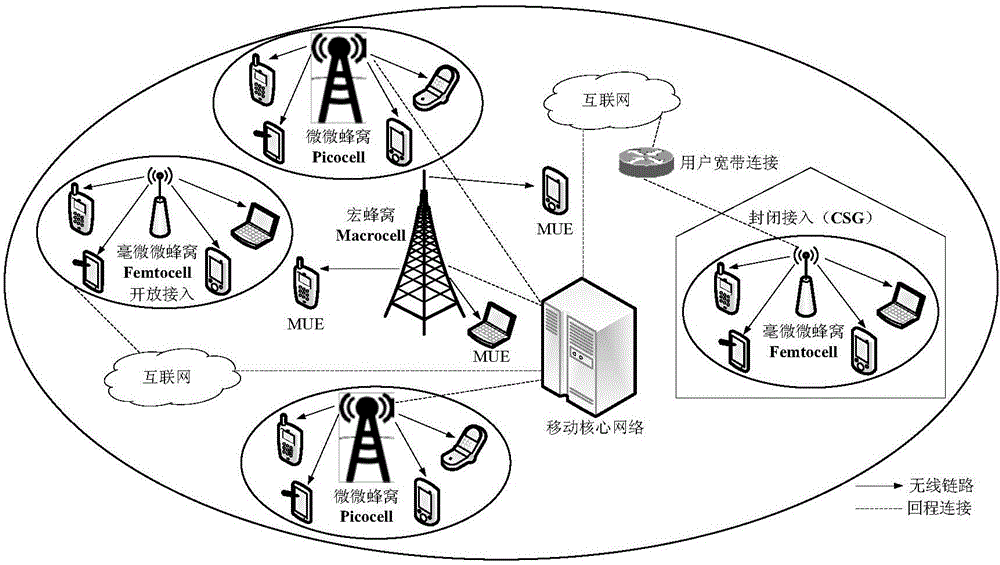
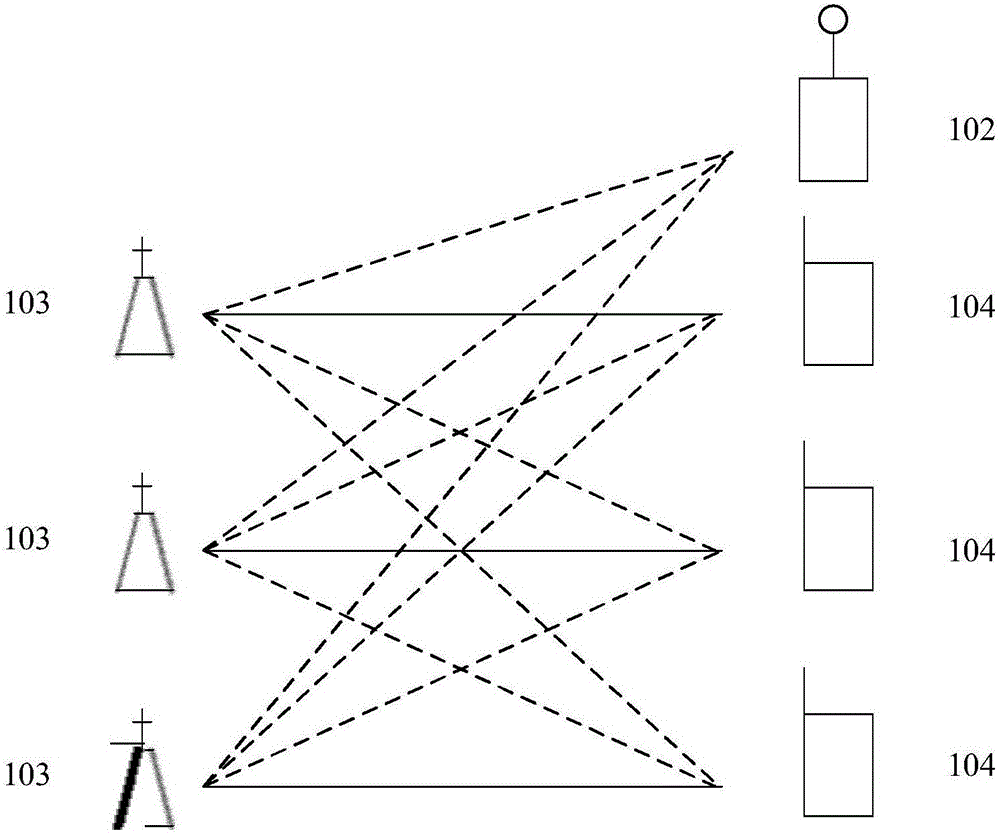
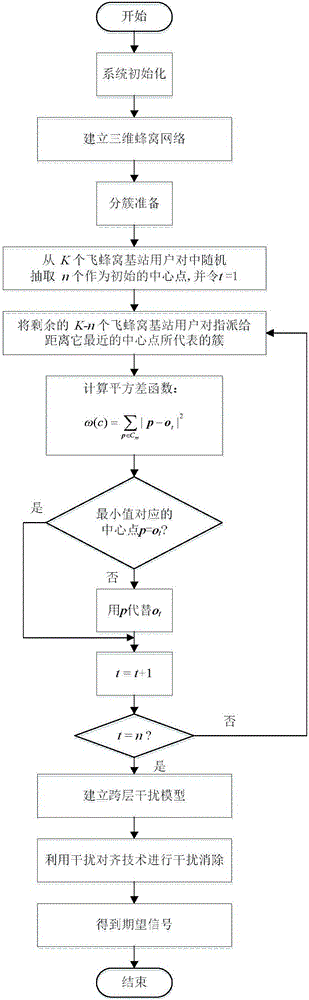
The invention discloses a cluster-based interference alignment method for a two-layer network. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, modeling the two-layer network based on stochastic geometry, then clustering femtocell base stations and users, and finally eliminating interference by using an interference alignment technology. A three-dimensional femtocell network structure model, particularly, a femtocell network model conforming to three-dimensional Poisson point process distribution, is close to the actual interference scene. Femtocell base stations and users are clustered according to the principle of square error function decrease, and cross-layer interference of macrocell users and each cluster and inter-cluster interference in a femtocell layer are finally eliminated by using the interference alignment technology, so that the complexity of interference management is reduced, and the method is applicable to actual communication systems.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
X-ray pulsar navigation TOA estimation method based on Bayes estimation
ActiveCN110186464AHigh precisionHigh real-time requirementsInstruments for comonautical navigationNested sampling algorithmProbit
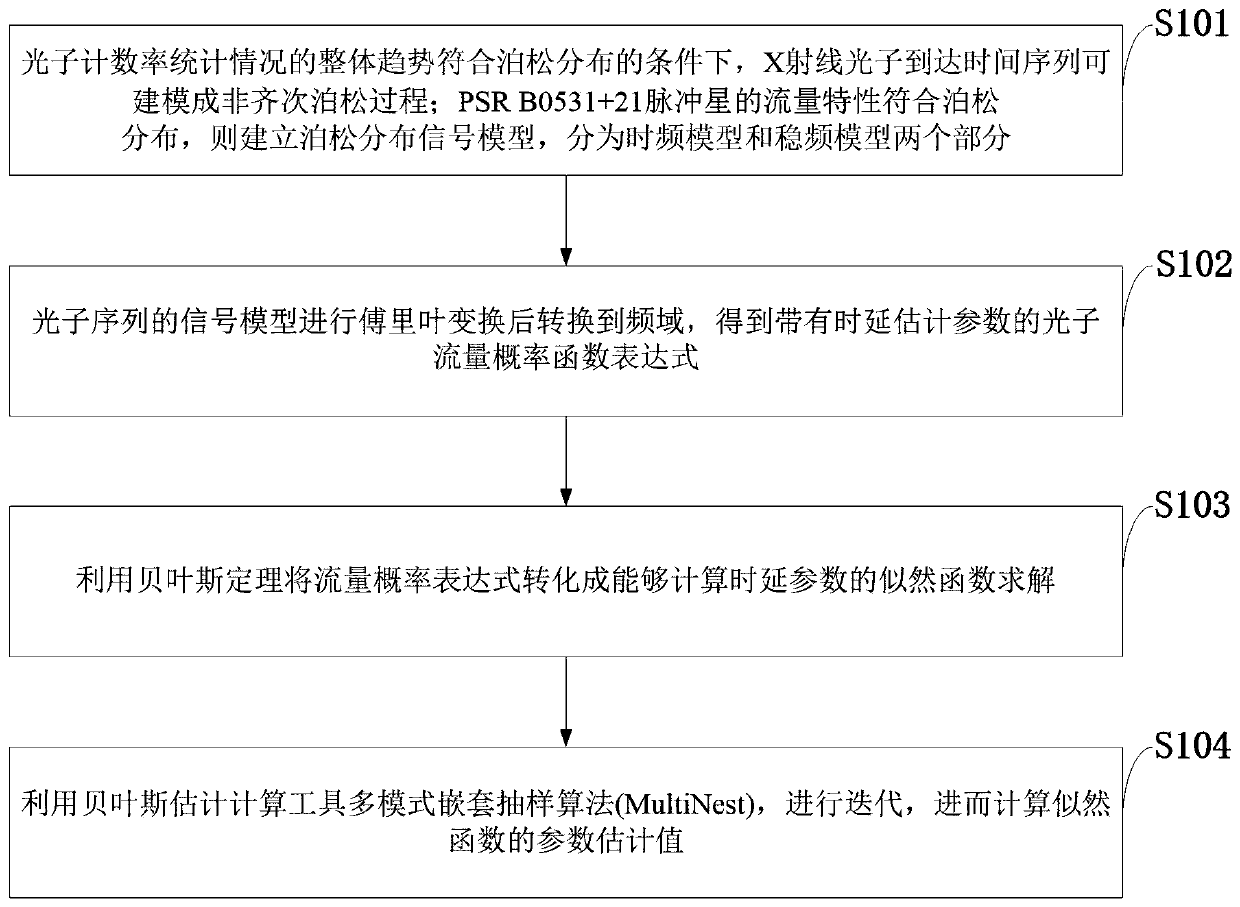
The invention belongs to the technical field of X-ray pulsar autonomous navigation and discloses an X-ray pulsar navigation TOA estimation method based on Bayes estimation. Under the condition that the overall trend of a photon counting rate accords with the Poisson distribution, an X-ray photon arrival time sequence can be modeled into a non-homogeneous Poisson process; the flow characteristics of PSR B0531 + 21 pulsars accord with the Poisson distribution, and a Poisson distribution signal model is established and divided into a time-frequency model and a frequency-stabilizing model; the frequency-stabilizing model of the photon sequence is selected to perform Fourier transform and then the frequency-stabilizing model is converted into a frequency domain to obtain a photon flow probability function expression with time delay estimation parameters; the photon flow probability function expression is converted into a likelihood function capable of calculating a time delay parameter by using a Bayes theorem for solving; and a Tool multi-mode nested sampling algorithm is calculated by Bayes estimation, iteration is carried out, and the parameter estimation value of the likelihood function is further calculated. The invention effectively improves the TOA estimation precision within the observation time and meets the future engineering development requirement of pulsar navigation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
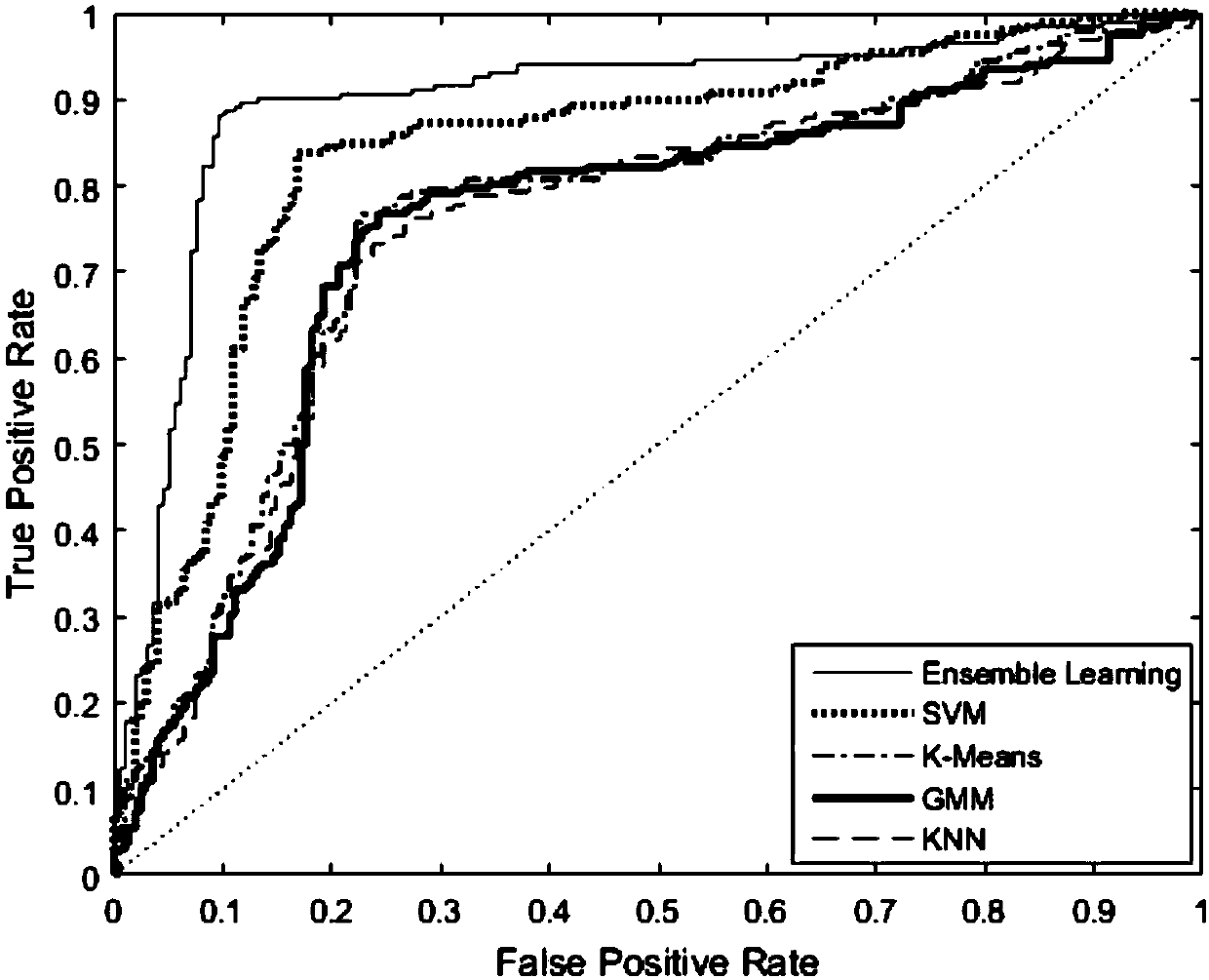
Full-duplex cognition radio network cooperation spectrum sensing method based on integrated learning
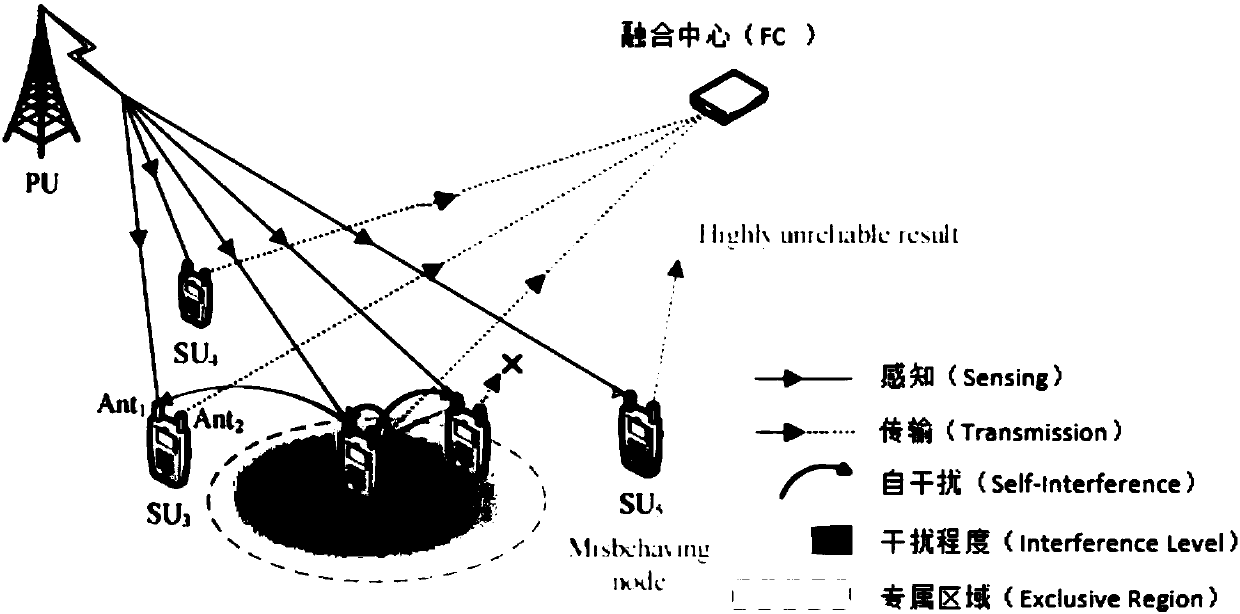
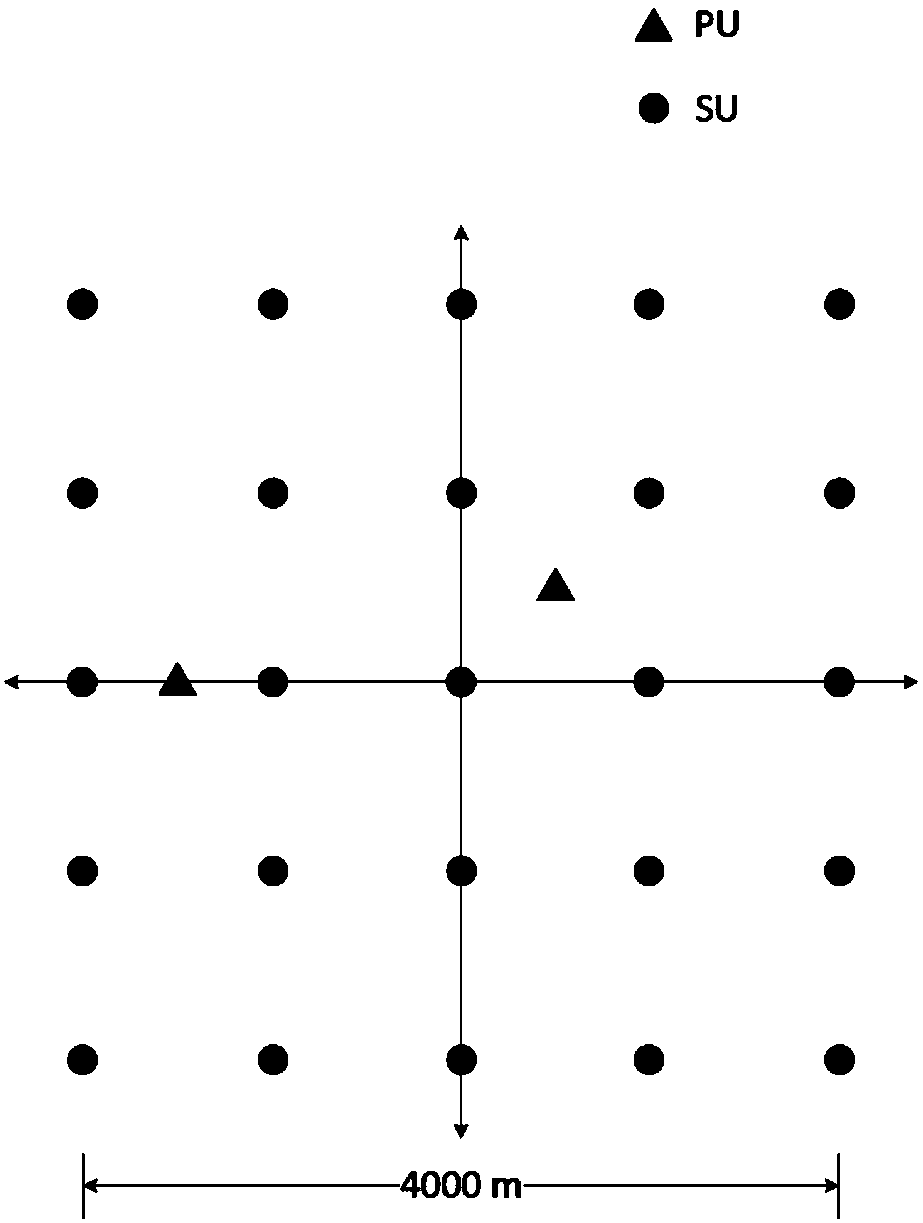
ActiveCN108242961AIncrease profitImprove throughputTransmission monitoringSelf interferenceRadio networks
The invention discloses a full-duplex cognition radio network cooperation spectrum sensing method based on integrated learning; the method is featured by comprising the following steps: 1, randomly forming positions of each secondary user in an area according to the Poisson point process distribution of the secondary users; 2, building a system framework according to work features sensed by the cooperation spectrum in the full-duplex cognition radio network; 3, building a secondary user energy detection model matched with a network model according to the self-interference and multi-signal source problems under the full-duplex mode; 4, analyzing and training statistic attributes of a concentration energy level vector; 5, selecting a single-layer decision tree as a weak classifier, and calculating each training data weighing coefficient and each weak classifier coefficient so as to build a strong classifier. The method can improve the system cooperation spectrum sensing performance, canincrease the radio frequency spectrum resource utilization rate, and can improve the cognition radio network throughput.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Minisatellite and its constellation availability evaluation method based on Monte Carlo simulation
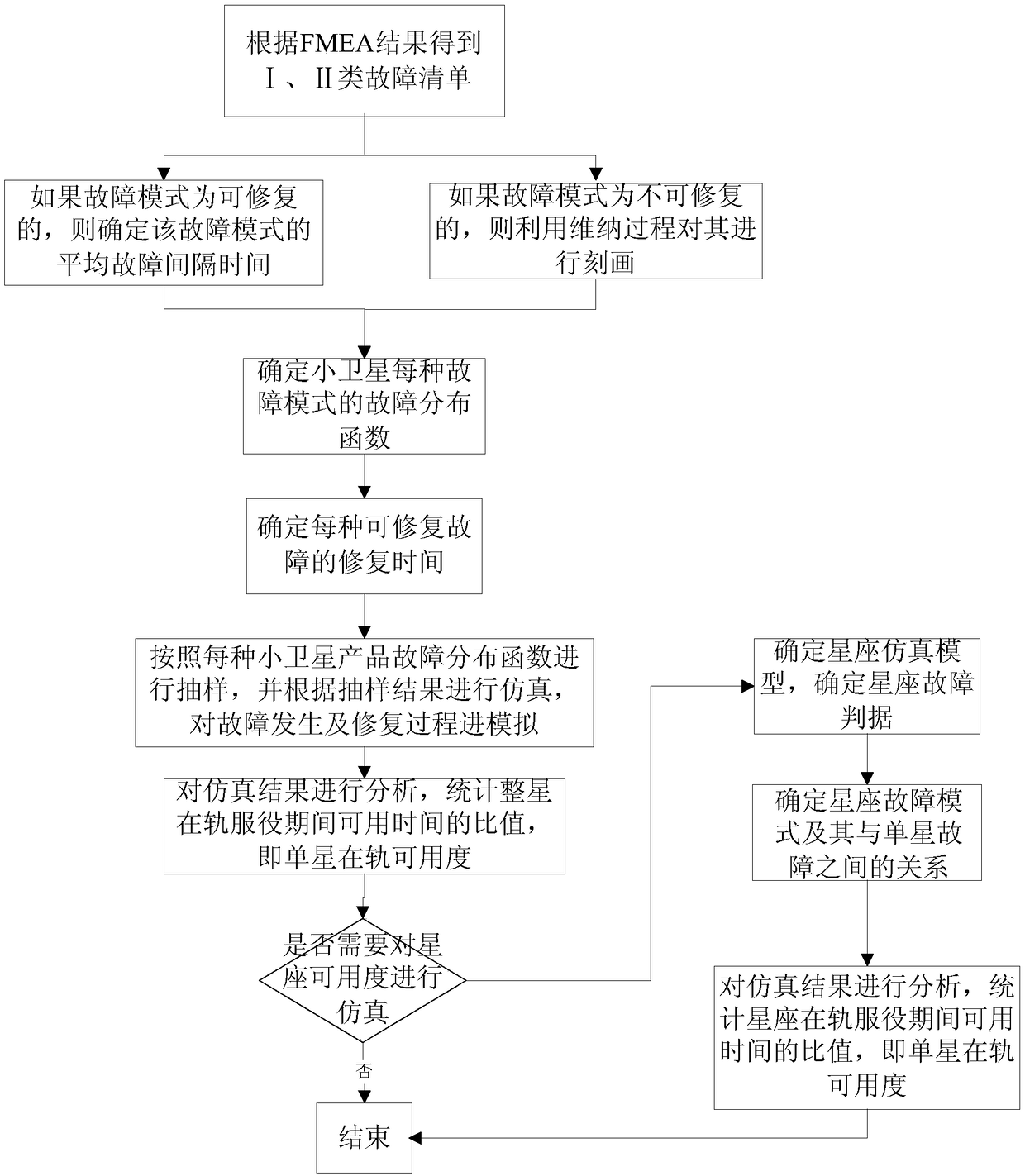
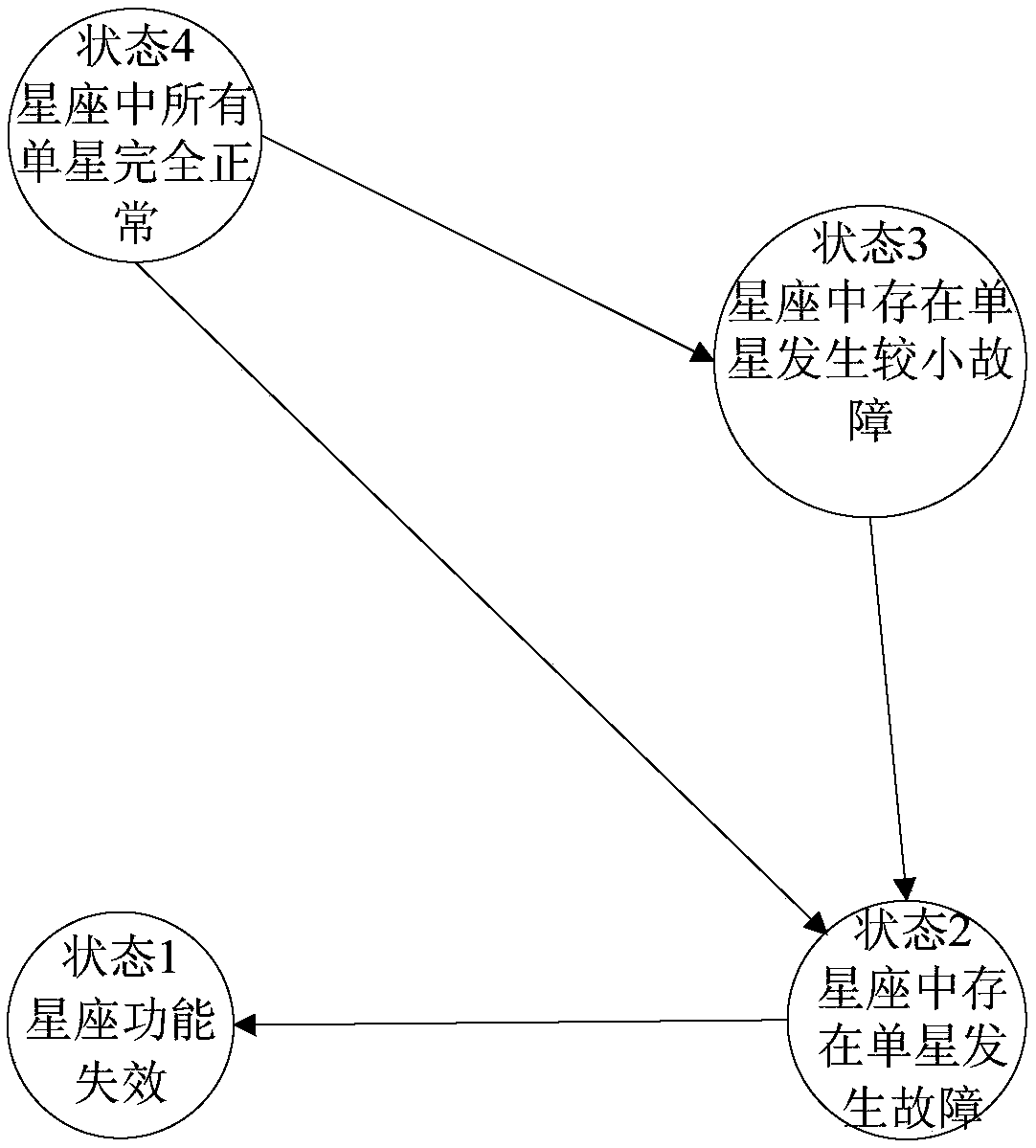
A minisatellite and its constellation availability evaluation method based on Monte Carlo simulation. The method includes following steps: 1, acquiring a fault list of faults of classes I and II in severity of classes I and II through FMEA analysis; dividing the faults in the list according to whether the faults are repairable or not; 2, for the repairable faults, utilizing the Poisson process tomodel fault laws, utilizing on-orbit data to calculate repairable fault failure rate, determining parameters of the Poisson process; for unrepairable faults, utilizing the Wiener process to model thefault laws, and utilizing ground test data or on-orbit failure data to determine parameters of the Wiener process; 3, determining minisatellite fault criteria and constellation fault criteria, and performing availability simulation on a minisatellite and its constellation; 4, through a simulation result, calculating a ratio of on-orbit normal working duration to service life of the minisatellite,and calculating on-orbit availability of the minisatellite and its constellation. By the method, complexity of availability evaluation can be effectively reduced while minisatellite availability evaluation result accuracy is ensured.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
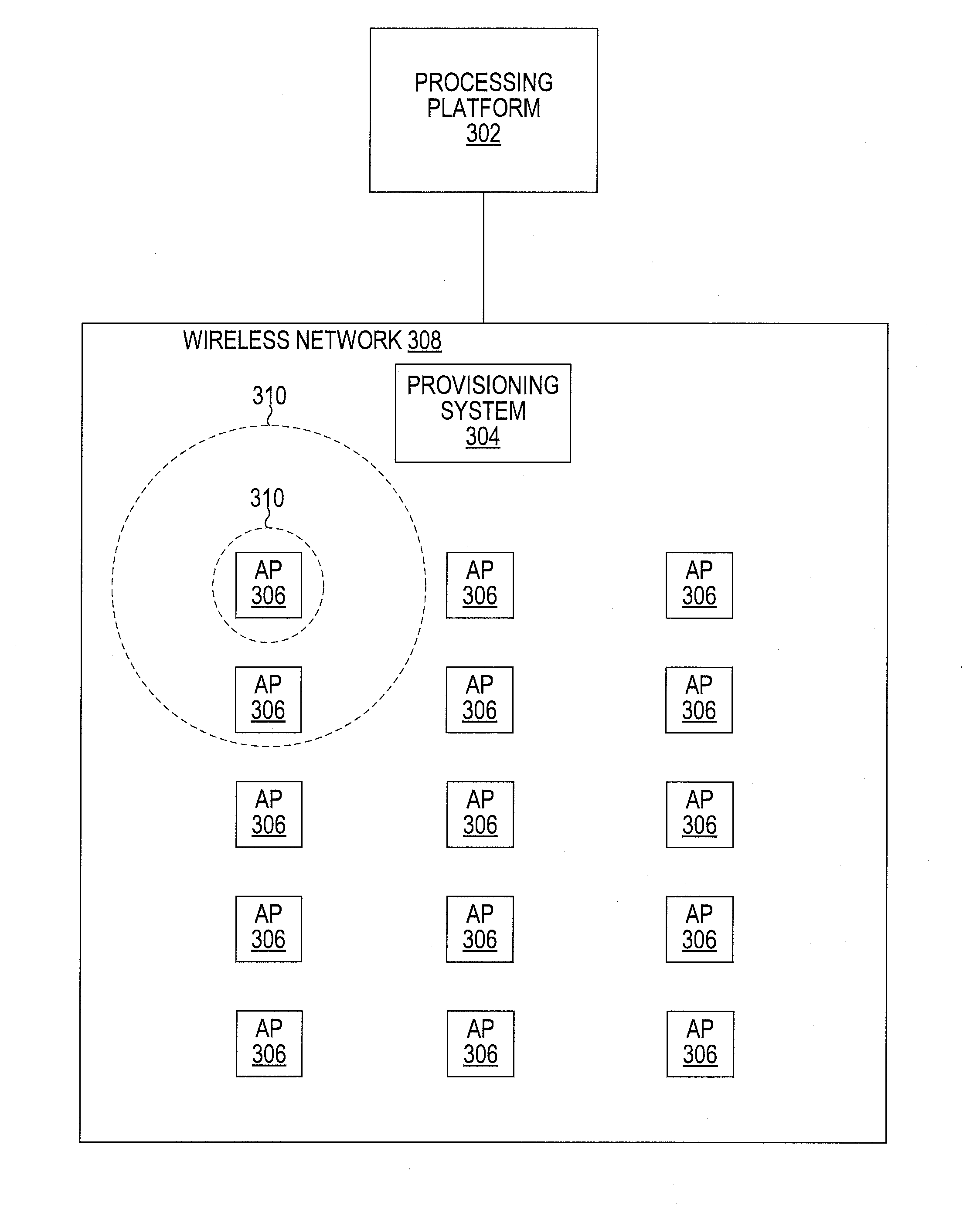
Method for provisioning a wireless network
A method that collects data and subjects it to statistical analysis to detect localized events, which assists in network provisioning. Illustratively, the data employed is hourly network traffic count that is collected at cell sites. By taking the advantage of additive property of Poisson process, the method integrates spatial neighbor information by aggregating temporal data in various areas, and iteratively estimating the event location and the radius of event impact by examining the posterior probability base on the aggregated data.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I LP
Wireless virtual mapping method in consideration of inter-cell interference under ultra-dense environment
ActiveCN107454601AReduce distractionsImprove throughputNetwork planningInterference ratioEngineering
The invention discloses a wireless virtual mapping method in consideration of inter-cell interference under an ultra-dense environment. The method comprises modeling a ultra-dense network by using a random geometric Poisson point process, determining a channel and interference model through a network model, then virtualizing a wireless frequency resources, and dividing the frequency of a spectrum resource by using a wireless network mapping method so that the receiving signal-to-interference ratio of a user is guaranteed, interference is reduced, the throughput of the entire system is improved. On one hand, the spectrum allocation method in the present invention has a good theoretical performance guarantee; on the other hand, the wireless virtual mapping method is beneficial to implementation and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Rolling bearing vibration performance reliability variation process detection method and rolling bearing vibration performance reliability variation process detection device
The invention relates to a rolling bearing vibration performance reliability variation process detection method and a rolling bearing vibration performance reliability variation process detection device. In the method provided by the invention, according to a time sequence counting process, extremely little variation intensity original information shown by bearing vibration is obtained at a short time interval; through the self-help re-sampling on the variation intensity original information, much variation intensity generating information is simulated; the generating information is processed by using a grey prediction model, and a variation intensity estimation value is obtained; a Poisson process is used for expressing a reliability function; and the variation process of the bearing vibration performance reliability is predicted in real time. The method and the device provided by the invention have the advantages that on the basis of the time sequence of the vibration information, the grey self-help principle is merged into the Poisson process, and a grey self-help Poisson method is provided for predicating the variation process of the rolling bearing performance reliability.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dynamic arrival spectrum sensing method based on absolute value accumulation
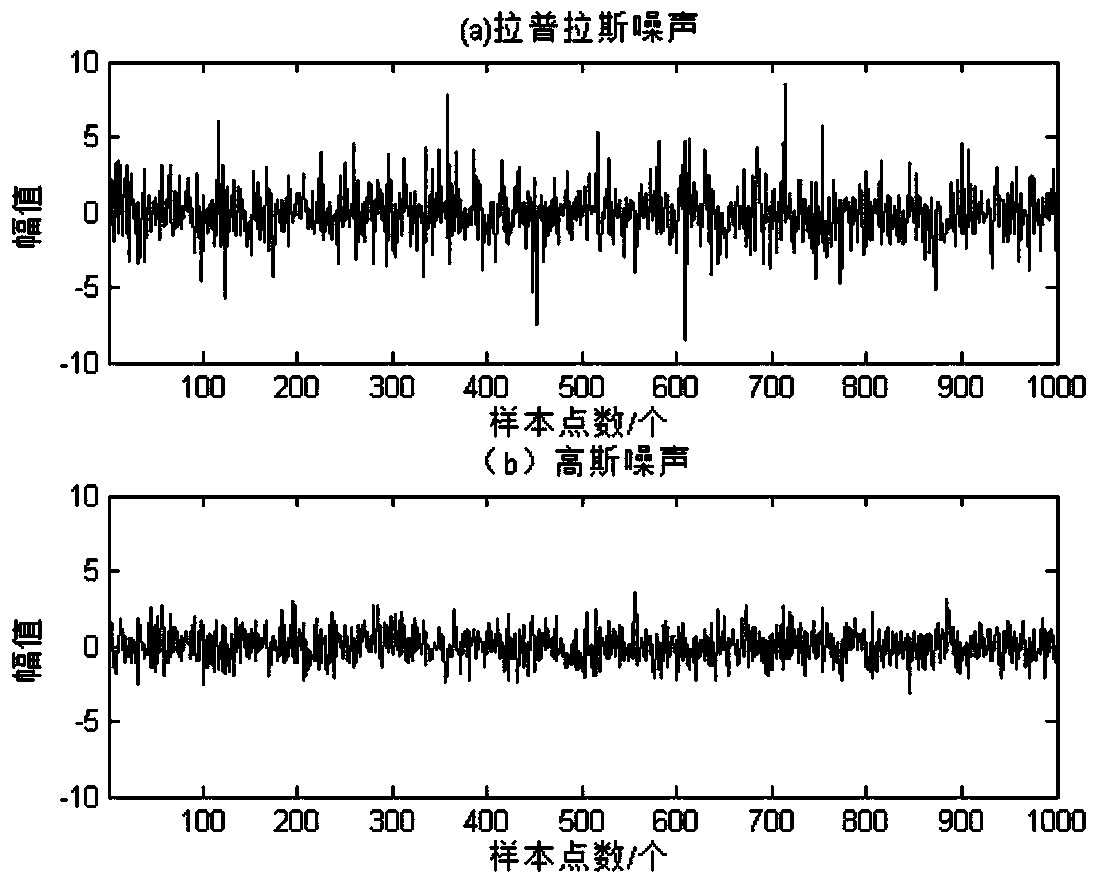
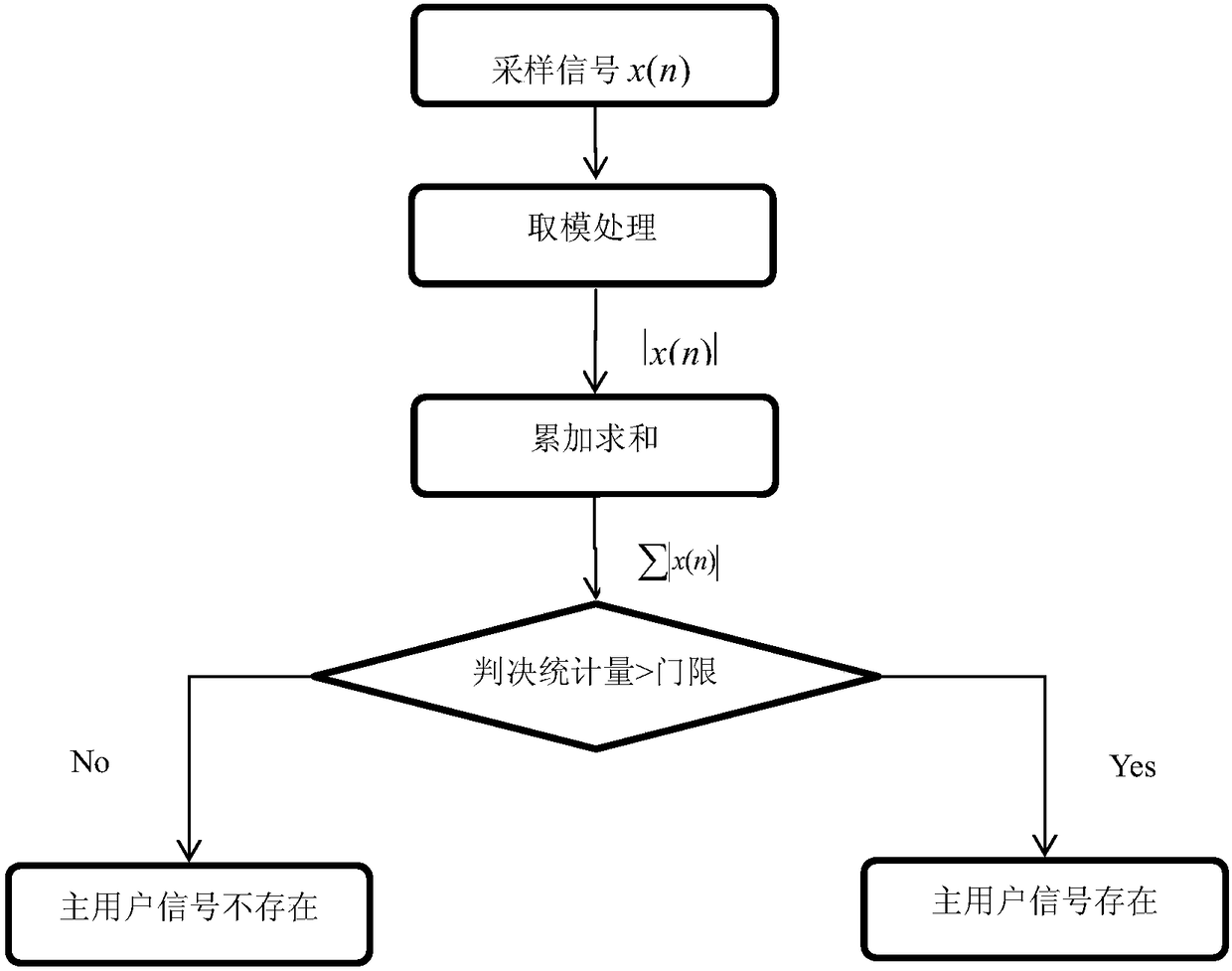
ActiveCN108494511AEasy to detectReduce the impact of spikesTransmission monitoringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Poisson point process
The invention provides a dynamic arrival spectrum sensing method based on absolute value accumulation. The method is mainly divided into two steps: a signal detection process and a signal decision process; and the method specifically includes the step that: a secondary user first takes a dynamic arrival signal of a Poisson process as a received signal, and then performs absolute value processing on the received signal, takes a cumulative summation result as the decision statistic, and further judges whether a primary user exists or not to achieve spectrum sensing. According to the scheme of the invention, in the case of low signal-to-noise ratios, the problem of 'spike' of Laplace noises can also be improved, the detection performance of an algorithm can be improved, and thus the effectiveutilization of spectrum can be achieved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for Provisioning a Wireless Network
ActiveUS20120147760A1Assist in provisioningError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic countWireless mesh network
A method that collects data and subjects it to statistical analysis to detect localized events, which assists in network provisioning. Illustratively, the data employed is hourly network traffic count that is collected at cell sites. By taking the advantage of additive property of Poisson process, the method integrates spatial neighbor information by aggregating temporal data in various areas, and iteratively estimating the event location and the radius of event impact by examining the posterior probability base on the aggregated data.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Spectrum-energy efficiency balance method for double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network based on stochastic geometry
ActiveCN106792738AExpand coverageIncrease capacityPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency spectrumHeterogeneous network
The invention provides a spectrum-energy efficiency balance method for a double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network based on stochastic geometry. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing the double-layer ultra dense heterogeneous network by using a Poisson point process in the stochastic geometry; step 2, obtaining a total system throughput based on a probability density function and a probability generation function of the Poisson point process; step 3, obtaining a relation among spectrum efficiency, energy efficiency and network density of the overall system from the definitions of spectrum efficiency and energy efficiency; and step 4, obtaining a relation closed expression between the spectrum efficiency and the energy efficiency via the optimization theory. The method has the advantages: 1) the network coverage is enlarged, and the network capacity is improved; and 2) the density of the network can be effectively changed to realize spectrum-energy efficiency balance of the system. Therefore, the method has better mobile user experience, and provides an effective reference for 5G honeycomb deployment.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Wireless energy supply multi-hop communication system node selection method
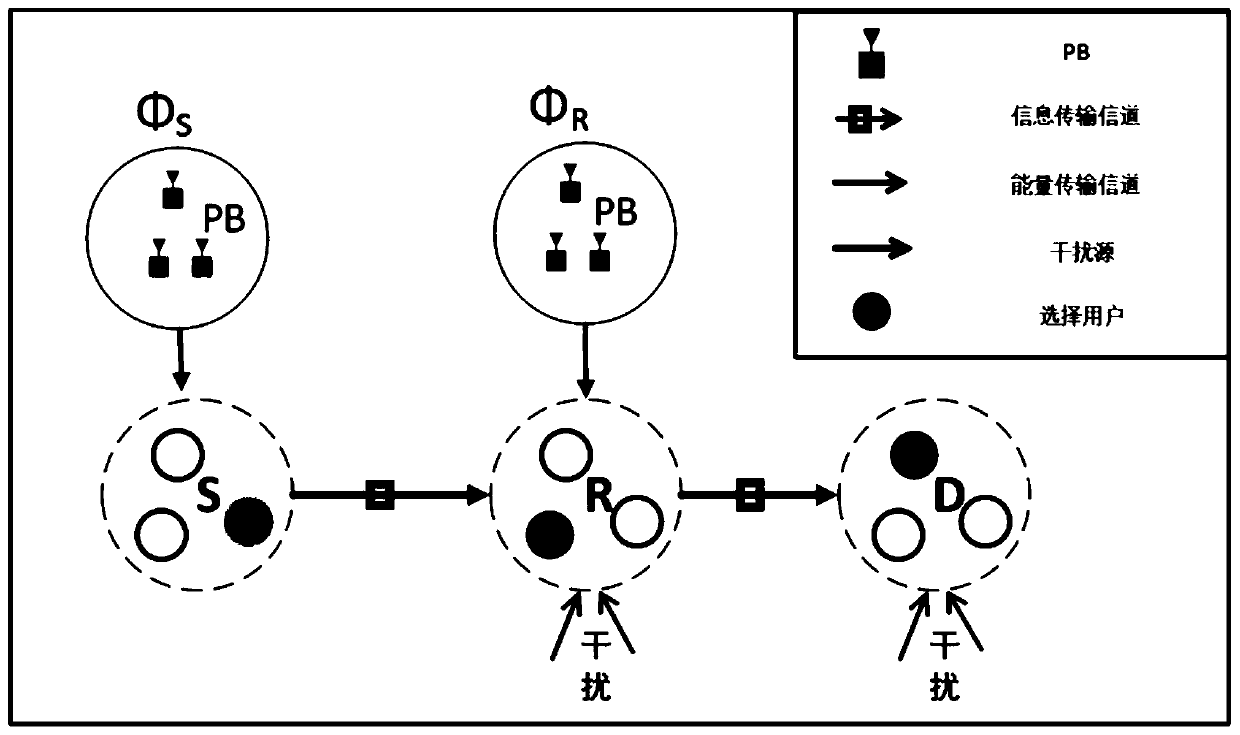
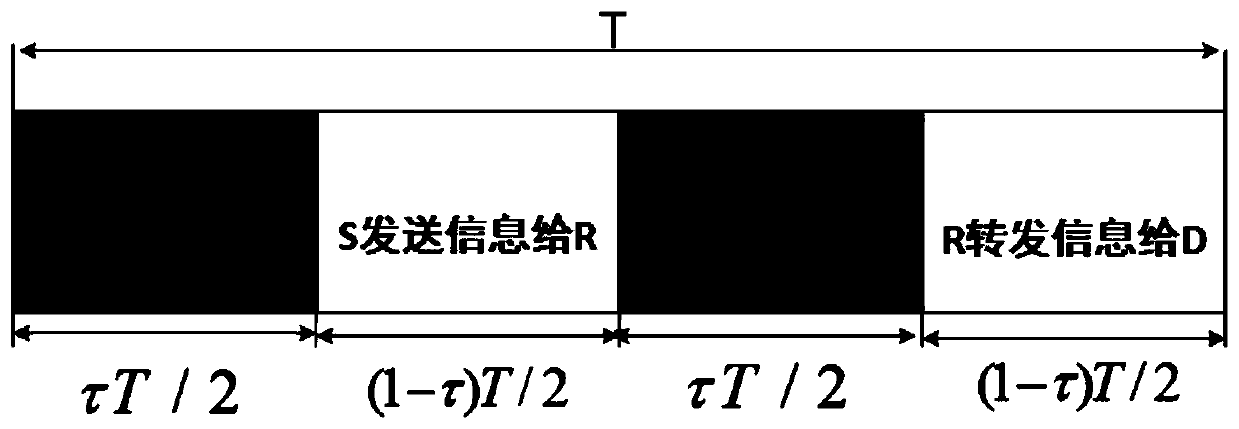
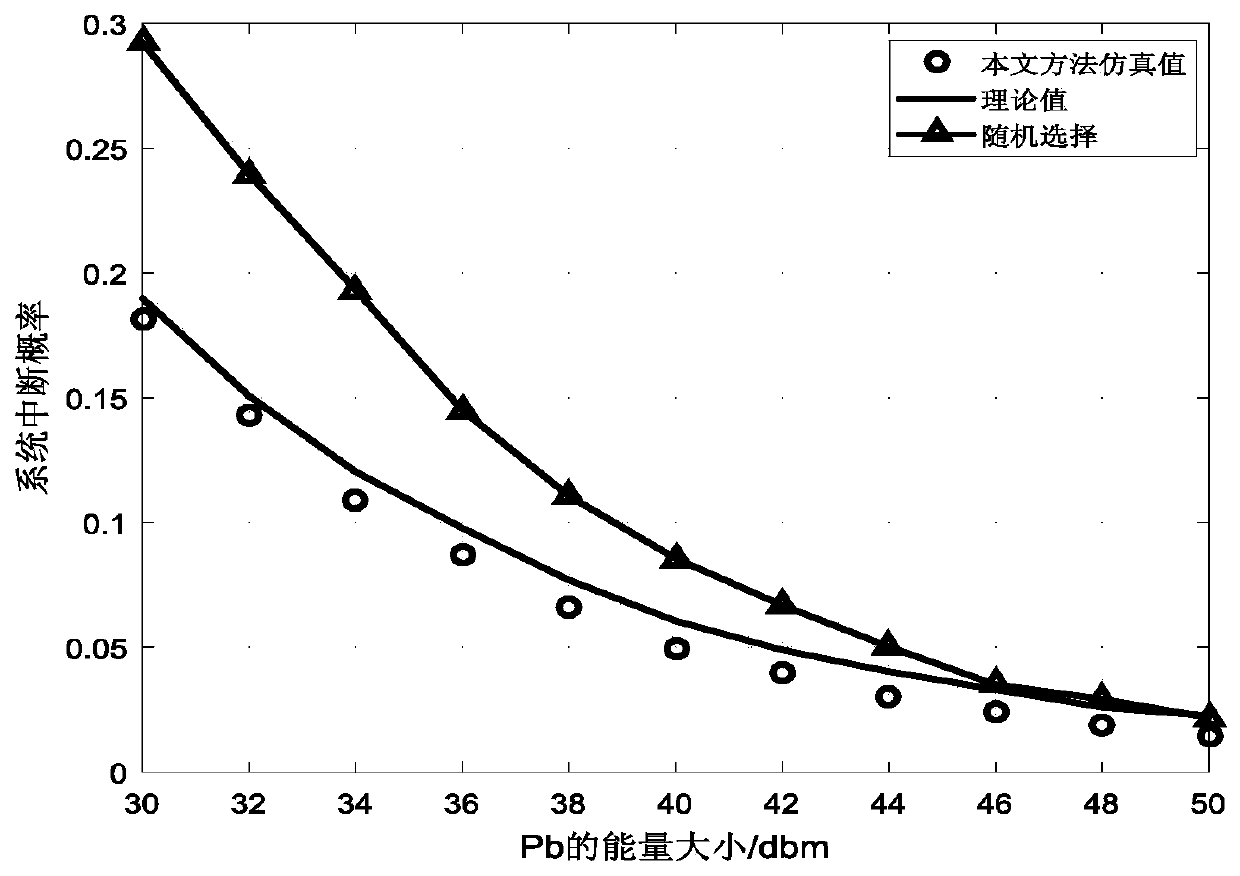
ActiveCN110366225AReduced probability of outageImprove stabilityWireless communicationInterference (communication)Communications system
The invention discloses a wireless energy supply multi-hop communication system node selection method, which comprises the following steps that: at a signal source S, all nodes collect energy firstly,then select the nodes and transmit information, and select a node SS with the maximum collected energy from the signal source S to send the information; at the relay R, if information needs to be forwarded, energy is collected from an environment radio frequency source for work, and then a node is selected as relay forwarding information, and the relay adopts a DF mode, and a node RS with the maximum collected energy is selected from all nodes with correct decoding in the relay R to forward the information to a receiving end; at a receiving end D, node receiving information with the maximum received signal to interference plus noise ratio is selected; and meanwhile, same-frequency interference signals existing in the system are considered, and the interference signals are modeled into a Poisson point process, and interference of nodes in the same cluster is used as a related event, and interference between different clusters is used as an independent event. A node selection scheme isprovided for the wireless energy supply multi-hop system, so that the system performance is improved, and the system outage probability is reduced.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for optimizing energy efficiency based on stochastic geometry in coexistence of wireless body area networks
InactiveCN107770750AImprove reliabilityImprove energy efficiencyPower managementParticular environment based servicesBody area networkBody area
The invention discloses a method for optimizing energy efficiency based on stochastic geometry in the coexistence of wireless body area networks. The method comprises the following steps: a) buildinga Poisson point process model by adopting a stochastic geometry method; b) calculating the probability density f(p) of transmission power of a node; c) calculating transmission success probability P<s>; and d) calculating energy efficiency etaEE of the node. A relationship between the transmission power and the energy efficiency in the coexistence of networks is analyzed, so that the energy efficiency of a system can be increased better in a wireless network coexistence design, and the aims of lowering interference and enhancing the network communication reliability are fulfilled.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
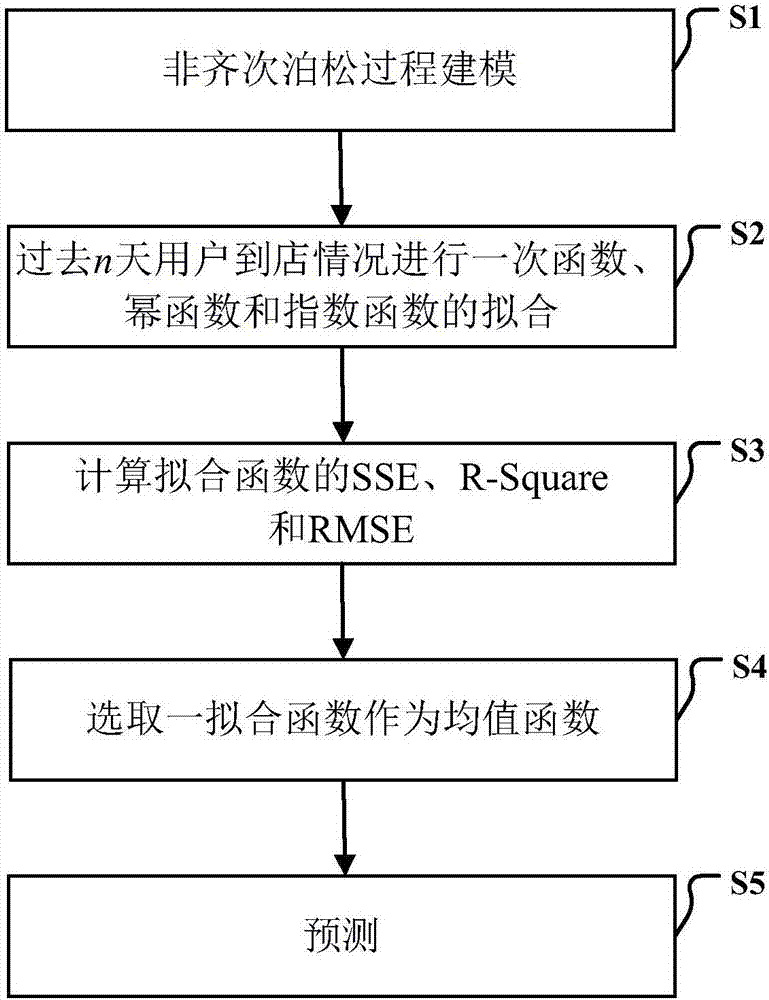
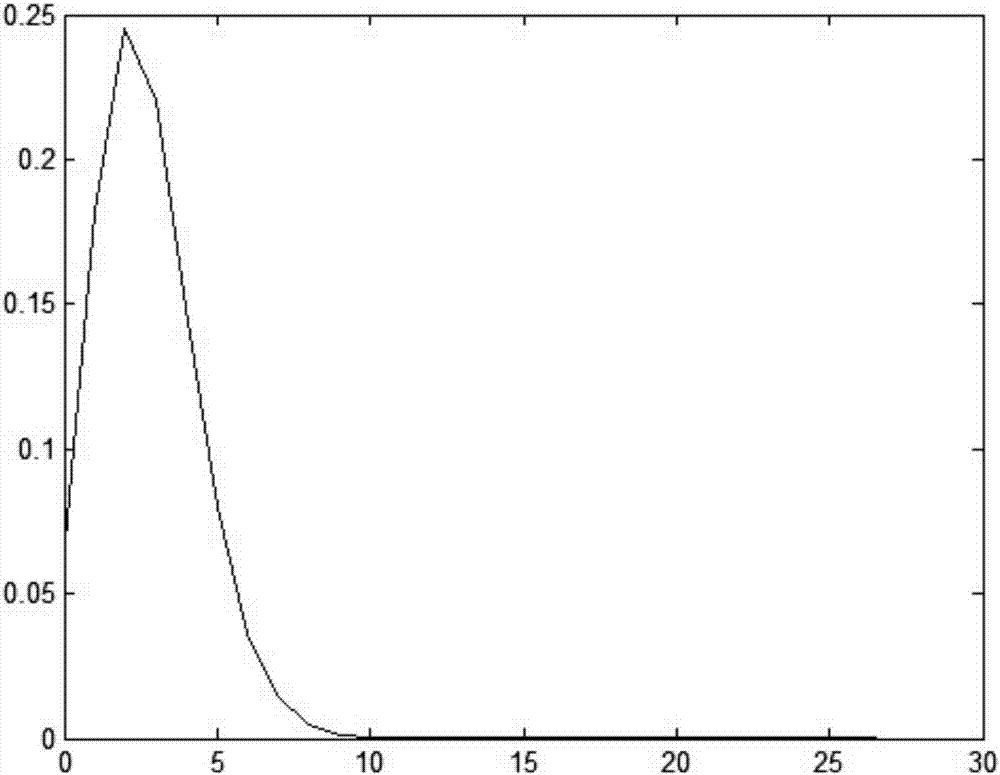
Poisson process user-to-shop behavior prediction based on automatic fitting mean function
InactiveCN107330726ASolve the number of shopsSolve needsMathematical modelsMarketingRational usePrediction algorithms
The invention discloses a Poisson process user-to-shop behavior prediction method based on an automatic fitting mean function, and in the prediction method, the Poisson process modeling prediction is performed by the means of an automatic fitting mean function in a case where a user-to-shop behavior of buying a commodity has a strong randomness, so as to fully analyze whether a user will go to the shop to buy a commodity in the future. According to the invention, the problems of the unknown supply and demand information relationship of the number of shops and commodity demanders in the unknown supply and demand information reflection is solved, and the problem that the customer loyalty cannot be evaluated in part is solved; meanwhile, a set of prediction algorithm suitable for the prediction of user-to-shop purchase and integrated with data acquisition, parameter training, training result analysis and modeling prediction is developed, the most appropriate prediction parameters for specified prediction indexes are set, and the purpose of accurate prediction is achieved; and finally, the invention solves the problem in the rational use of historical data and determination of the validity of prediction results by using the automatic fitting mean function.
Owner:四川银百迪科技有限公司
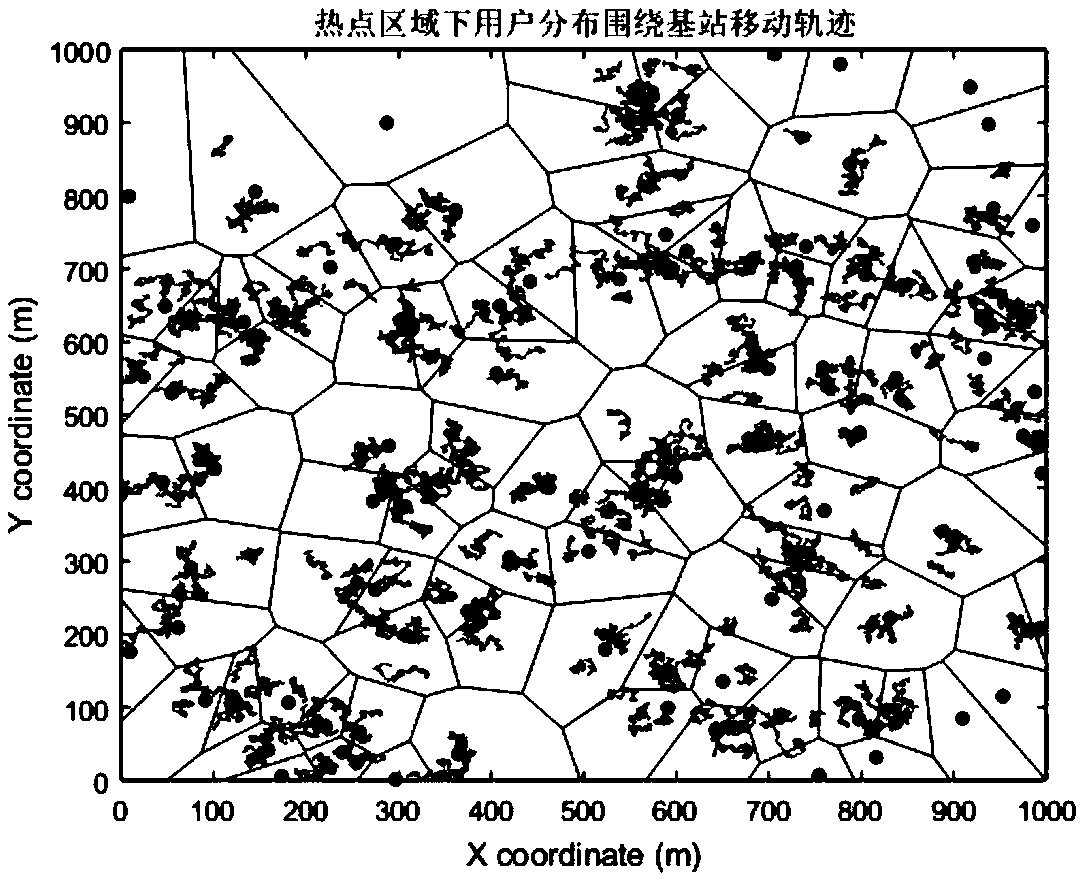
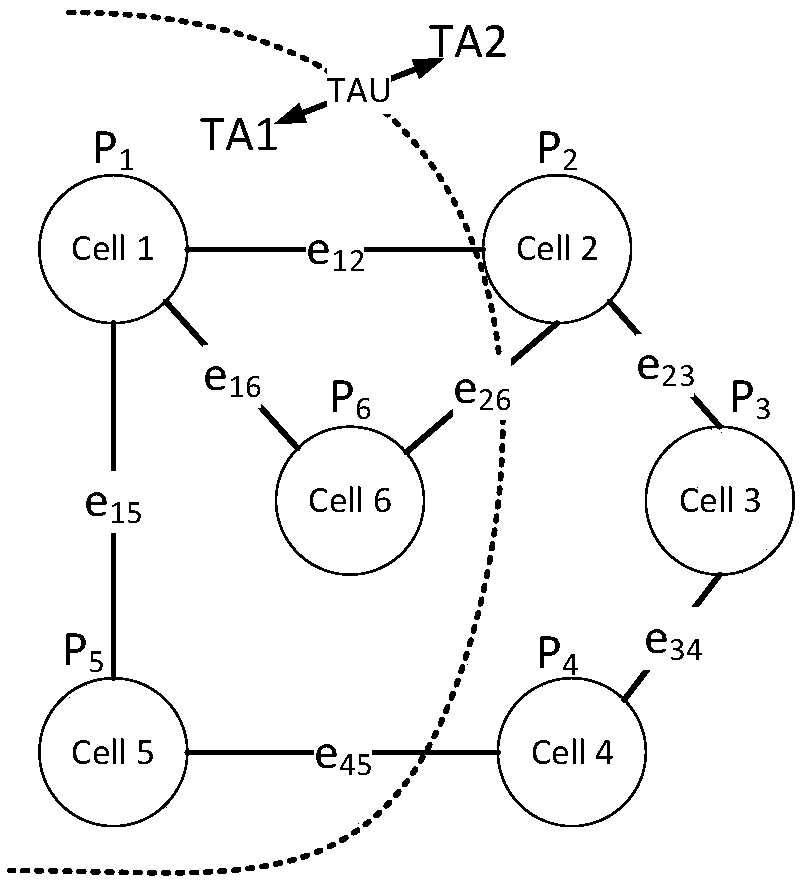
Tracking region planning method based on spectral clustering
ActiveCN109673015AReduce overheadNetwork planningCorrelation coefficientSpectral clustering algorithm
The invention provides a tracking region planning method based on spectral clustering. The method mainly is a user tracking region planning method under a small cellular network environment in a hotspot region. The entire though of the method provided by the invention is as follows: firstly constructing a system model based on small cellular deployment in the Poisson point process to produce a cellular network graph for displaying user mobility and paging characteristic; and then modeling a TA planning problem as a segmentation problem of a graph correlation coefficient; and then performing TAplanning on the produced network diaphragm by applying a spectral algorithm based on the graph theory
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
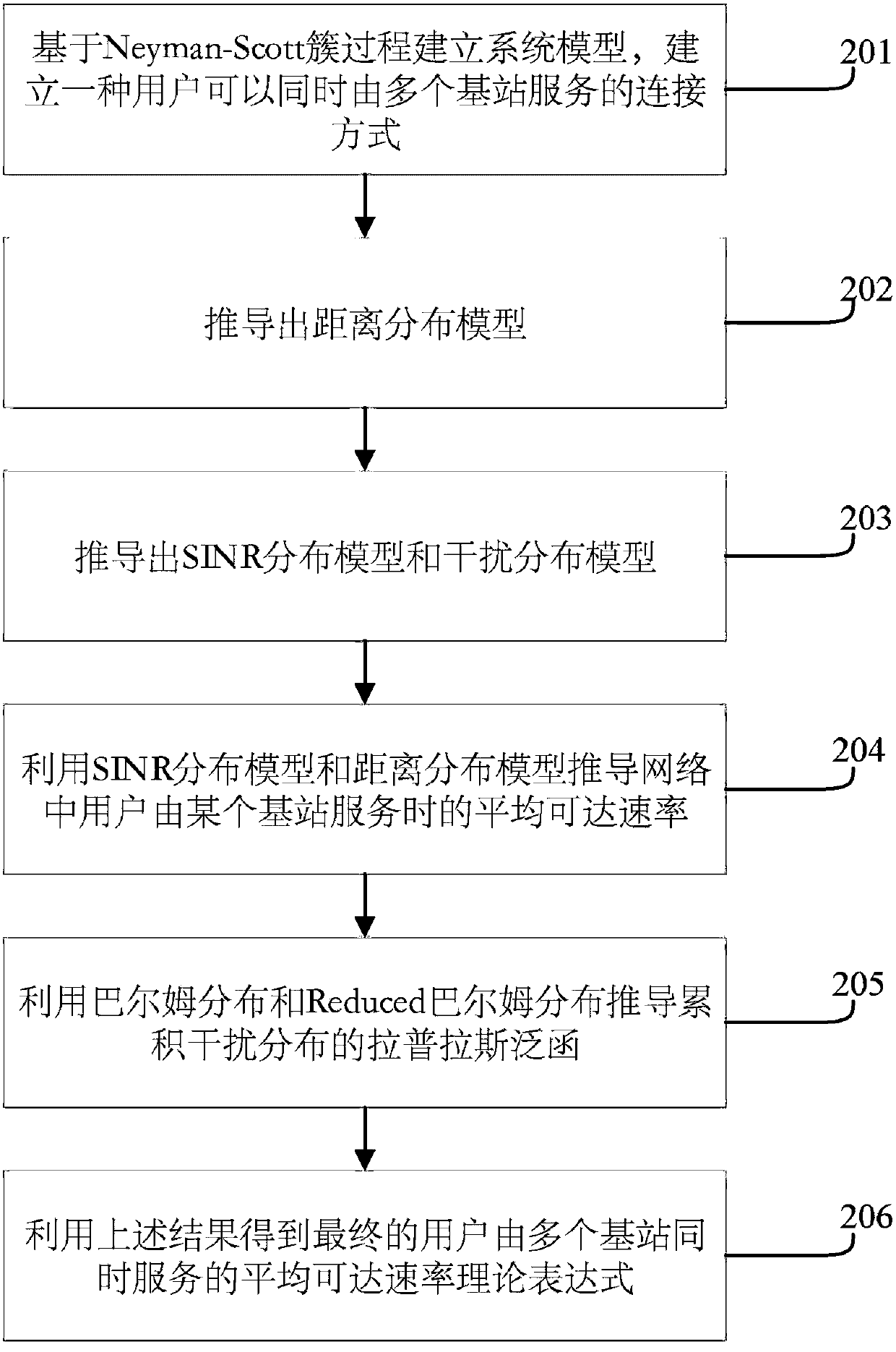
Network user access method based on Neyman-Scott cluster process
InactiveCN108566645AAvoid speed problemsTransmission monitoringNetwork planningAccess methodSimulation
The invention provides a network user access method based on a Neyman-Scott cluster process. The method comprises the following steps of 1), establishing a system model based on the Neyman-Scott cluster process; 2), deriving a distance distribution model between users and different base stations in clusters; 3), deriving an SINR distribution model and an interference distribution model; 4), deriving an average reachable rate when the users are served by certain base station, through utilization of the SINR distribution model and the interference distribution model; 5), analyzing the interference distribution model of an ultra dense network; 6), obtaining a final average reachable rate when the users are served by a plurality of base stations at the same time, through utilization of the result; and 7), showing that the average reachable rate of the users can be improved through utilization of the method, according to comparison. Compared with a Poisson point process, the method has theadvantages that the method is closer to a practical ultra dense network environment, a higher network average reachable rate is obtained, and the method is significant to the future practical deployment of the ultra dense network.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
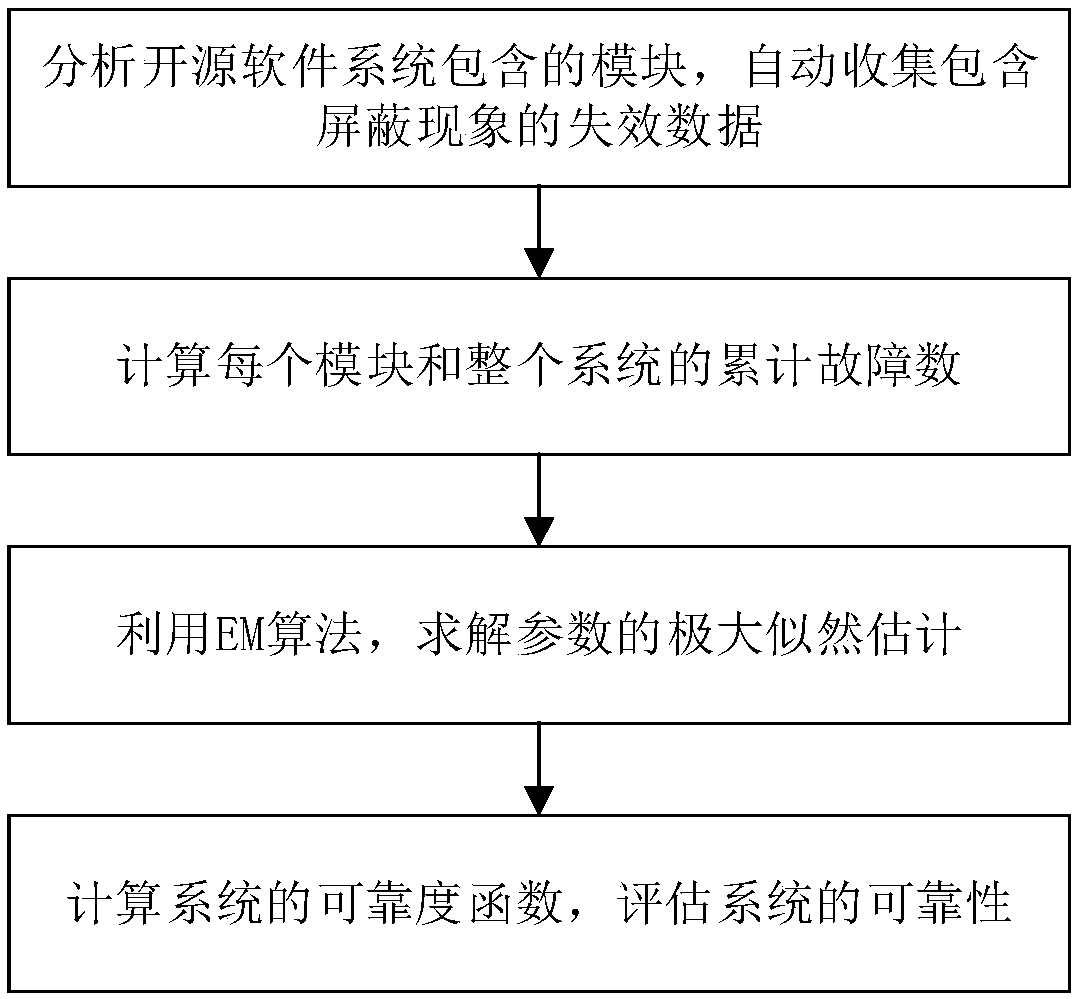
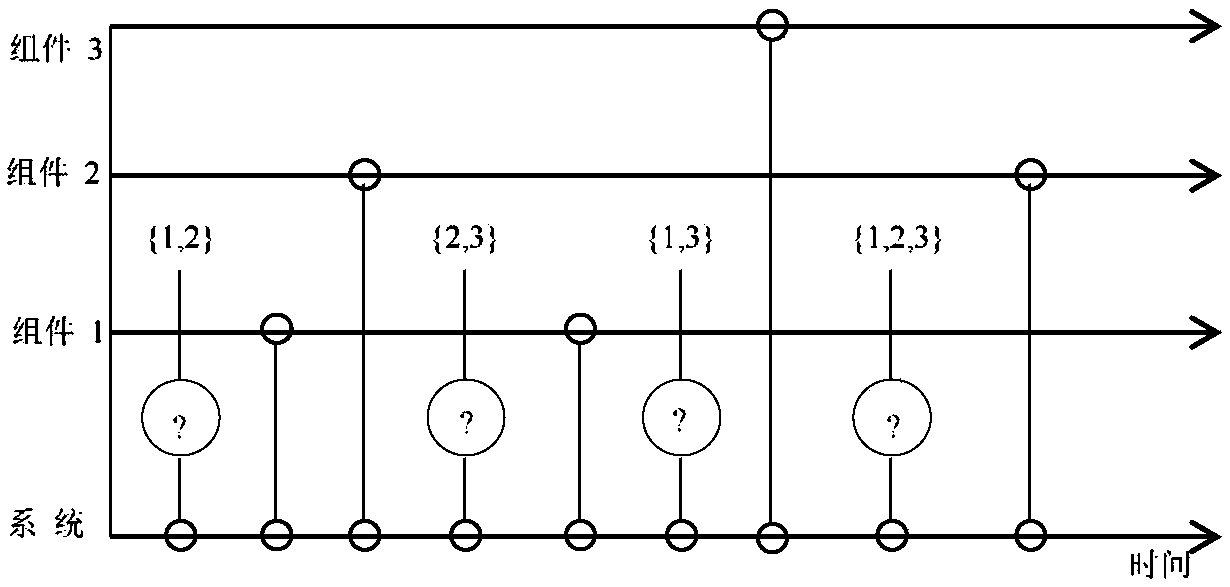
Shielding data-based open source software reliability evaluation method
InactiveCN108733407AMeet the needs of real-time rapid evaluation of software reliabilitySoftware metricsEvaluation resultFailure rate
The invention provides a shielding data-based open source software reliability evaluation method. According to characteristics of shielding data, and by utilizing a non-homogeneous Poisson process theory which can be superposed, a cumulative failure function and a failure rate of an open source software system are calculated, and the reliability of the open source software system is further evaluated. By using an EM (Expectation Maximization) algorithm, the problem that maximum likelihood estimation is difficult to implement in reliability evaluation of open source software under general shielding data can be solved, and a reliability evaluation result of the open source software can be timely given, so that the demand of rapidly evaluating the reliability of the software in real time is met.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF TECH
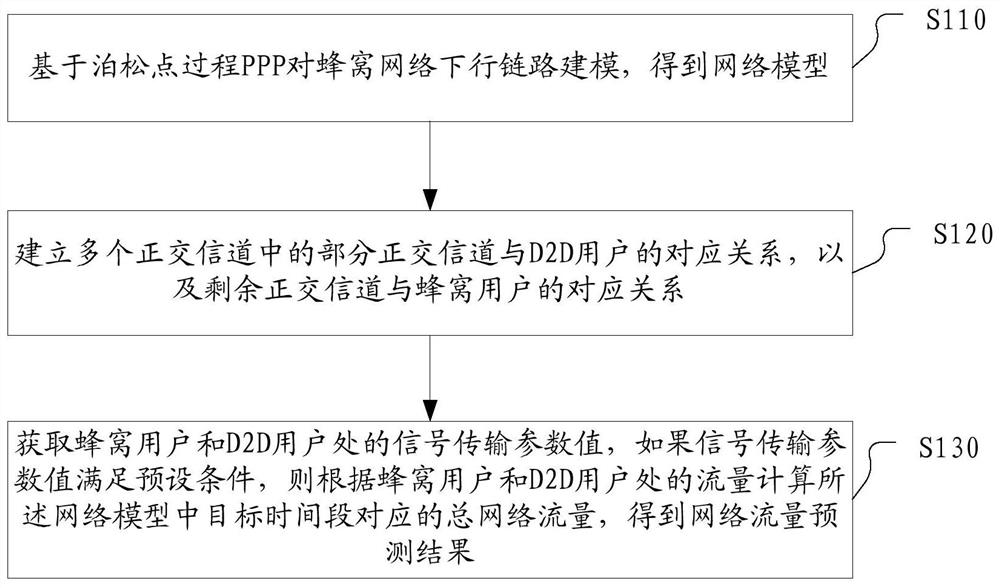
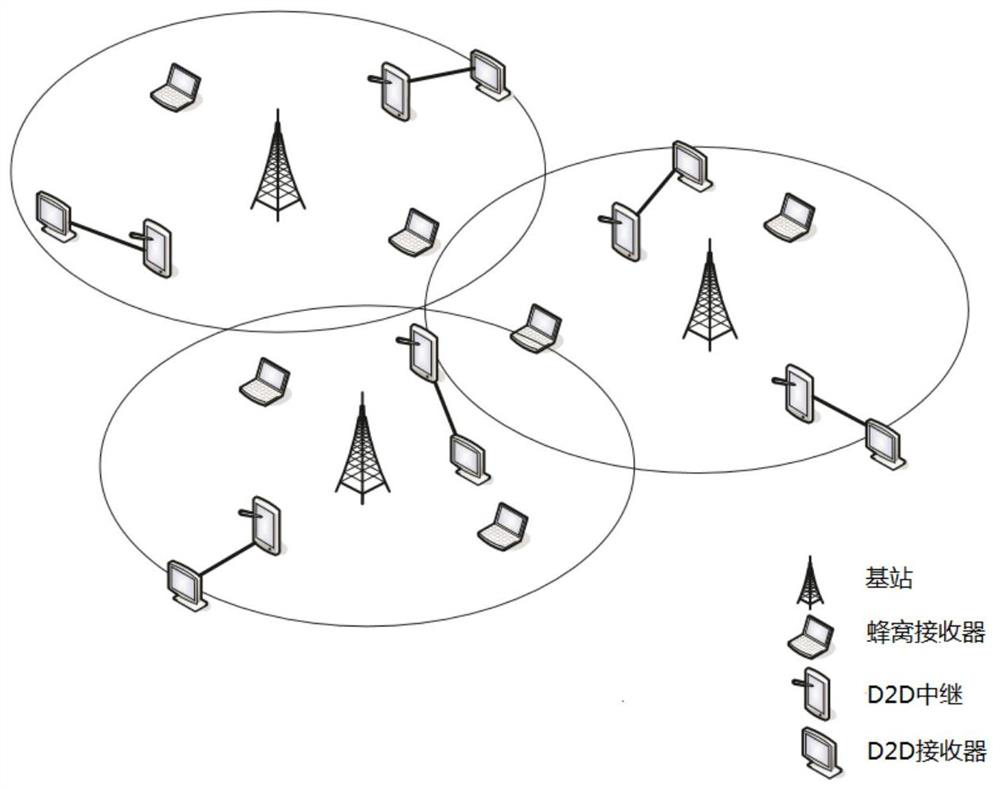
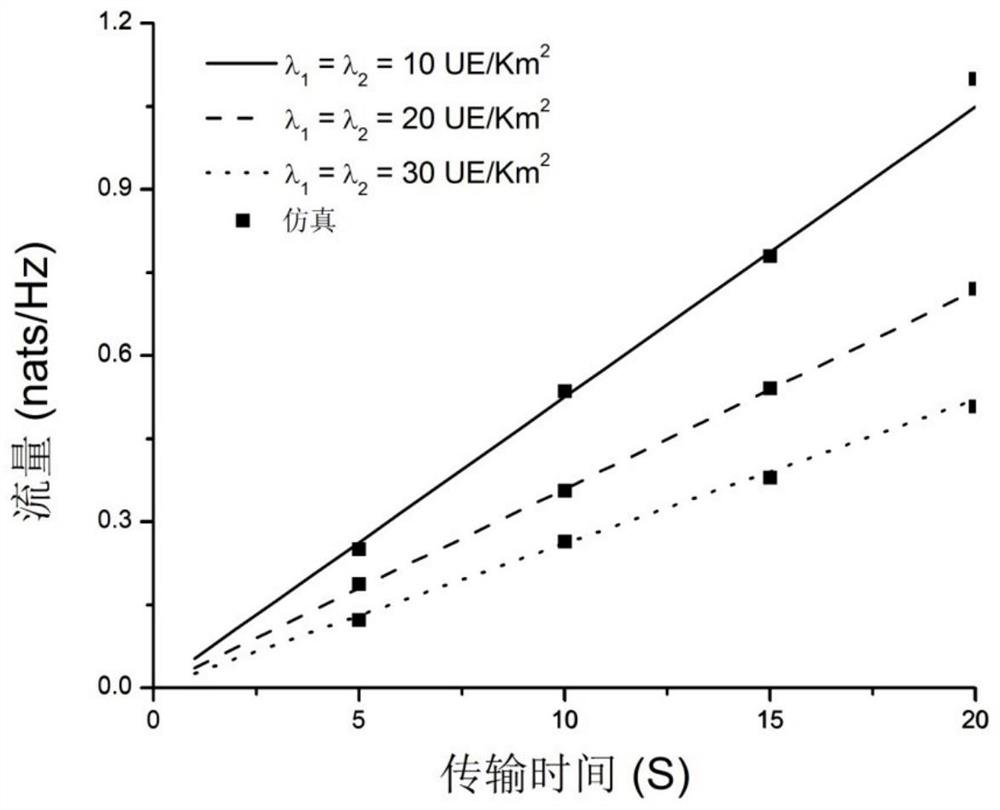
Network flow prediction method and device and electronic equipment
PendingCN111741450AAvoid uncertaintyEasy to analyzeData switching networksNetwork planningTraffic predictionResource assignment
The invention discloses a network flow prediction method and device, and electronic equipment. The network flow prediction method comprises the following steps: modeling a downlink of a cellular network based on a Poisson point process PPP to obtain a network model; establishing a corresponding relationship between a part of orthogonal channels in the plurality of orthogonal channels and the D2D users, and a corresponding relationship between the remaining orthogonal channels and the cellular users; and acquiring signal transmission parameter values at the cellular user and the D2D user, and if the signal transmission parameter values meet a preset condition, calculating the total network flow corresponding to the target time period in the network model according to the flow at the cellular user and the D2D user to obtain a network flow prediction result. According to the embodiment of the invention, the heterogeneous cellular network flow is analyzed and predicted based on the theoretical framework of random geometry, the prediction precision of the network flow is improved, and the maximization of the network flow is realized through spectrum resource allocation.
Owner:36TH RES INST OF CETC
Earthquake random event set simulation method considering large earthquake time correlation
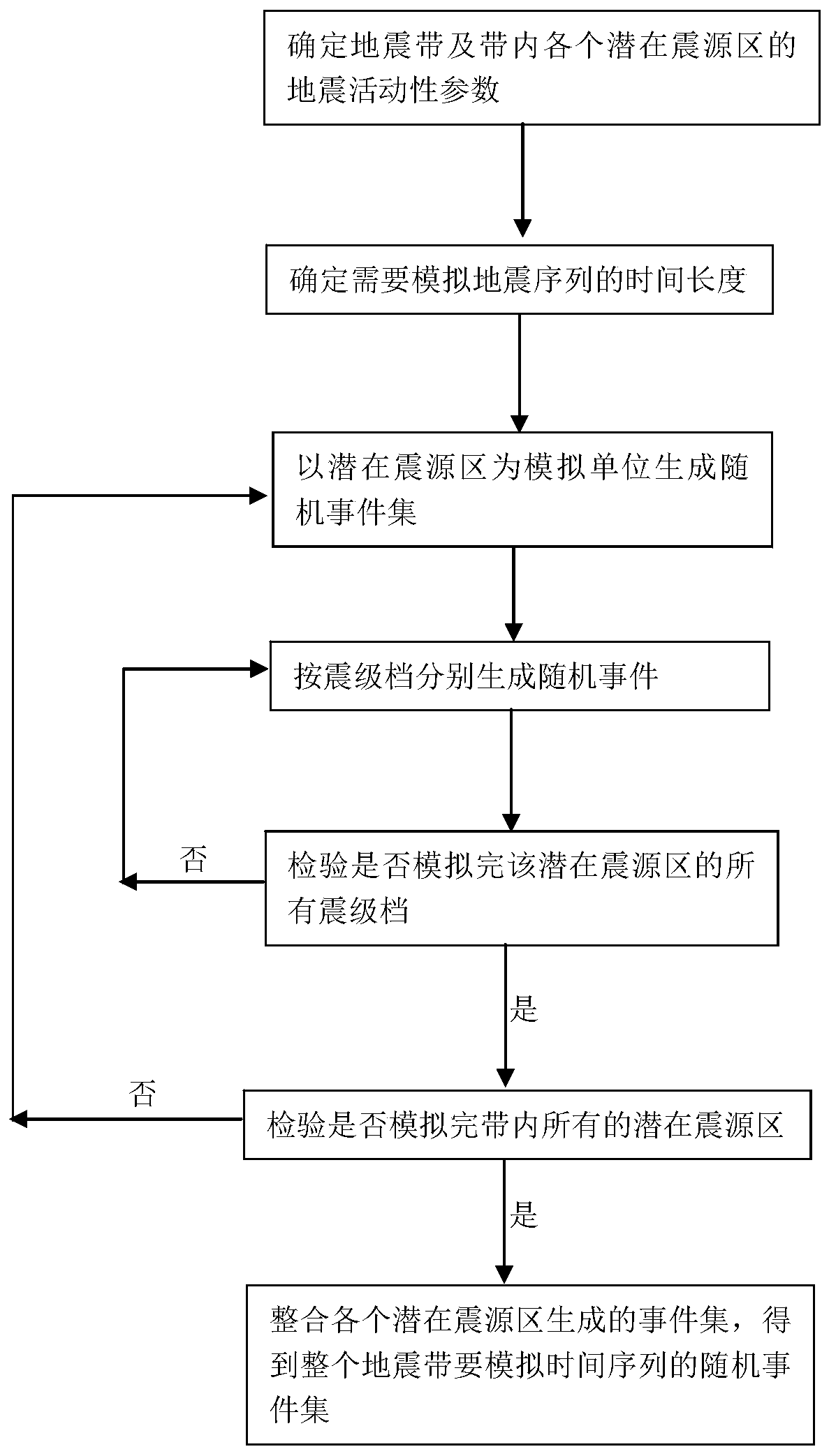
PendingCN111382908AEarthquake Hazard UnderestimationReflect spatiotemporal inhomogeneityForecastingResourcesTime correlationEarthquake engineering
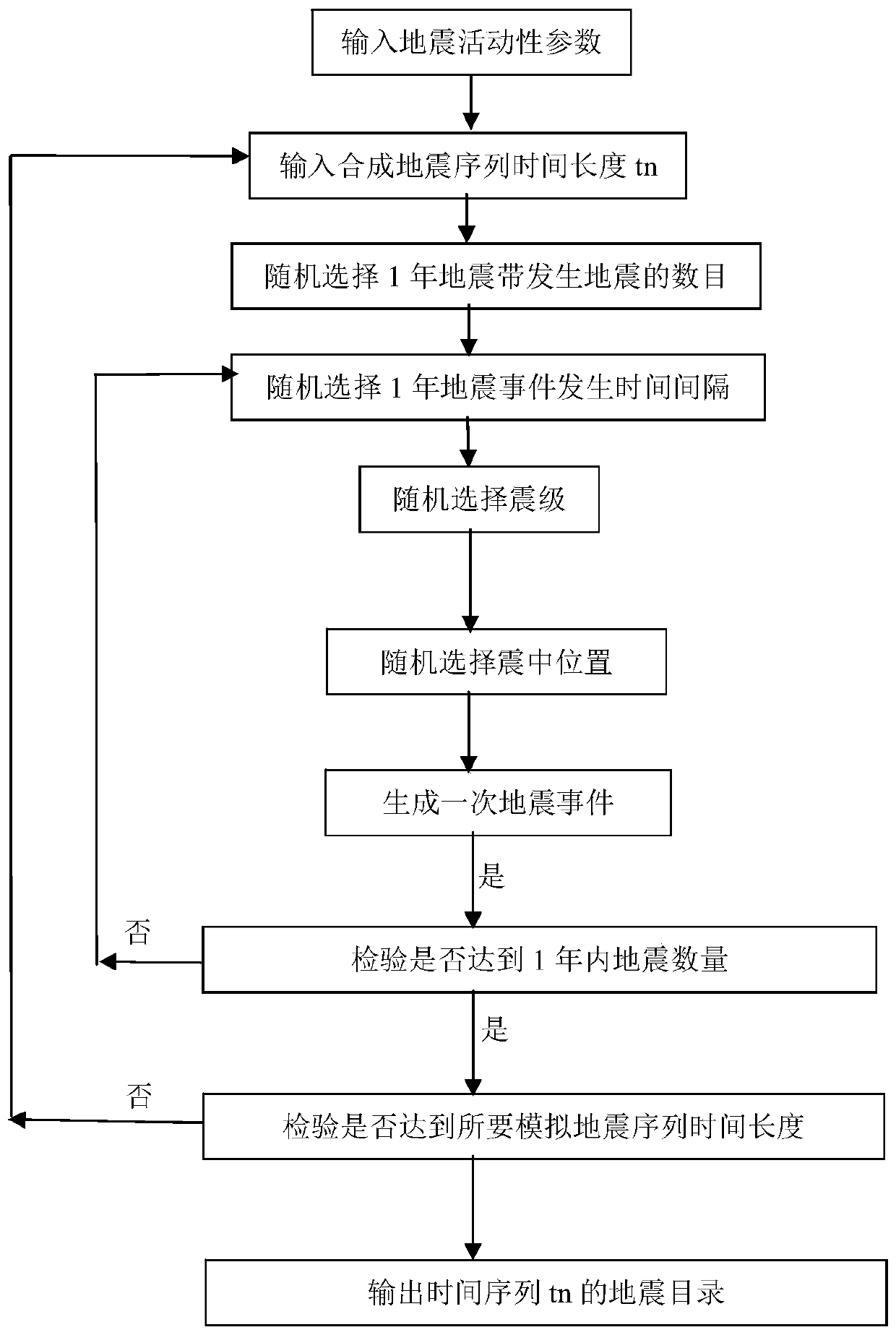
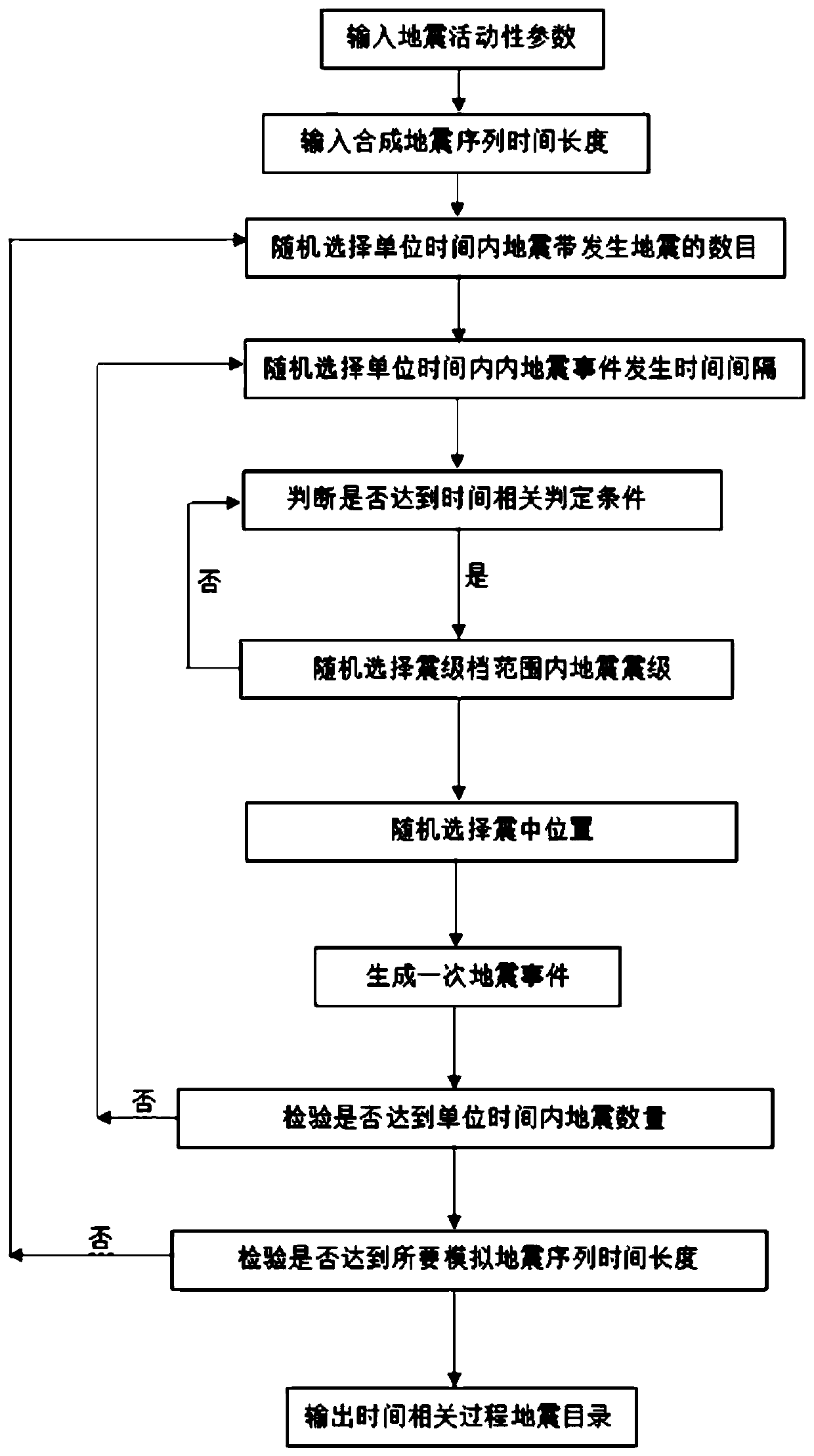
The invention relates to the field of seismic engineering and the field of giant disaster insurance services, and provides a seismic random event set simulation method considering large seismic time correlation, which comprises the following steps: determining seismic activity parameters on a seismic zone and a potential seismic source area; setting a random event set seismic sequence time length;for the potential seismic source area, generating a seismic random event set according to seismic magnitude grades; adopting a Poisson process model to obtain the magnitude, the size and the time ofthe earthquake for the low-magnitude gear; adopting a time correlation process model for a high-magnitude gear to obtain the magnitude, the size and the time of an earthquake; and integrating the seismic directories of the potential seismic source regions to obtain a seismic directory on the whole seismic zone. The invention creatively proposes that the seismic activity on the seismic zone integrally meets the Poisson distribution (time independent model) in statistical significance, and meanwhile, the potential seismic source region locally adopts a large seismic time correlation model, so that the whole and the local are organically combined, the accuracy and the practicability of seismic random event set simulation are greatly improved, and the method has a good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GEOPHYSICS CHINA EARTHQUAKE ADMINISTRATION
An optimal bread delivery method and system under random distribution
ActiveCN109299971AEasy to observeAccurate decisionMarket data gatheringComputer sciencePoisson point process
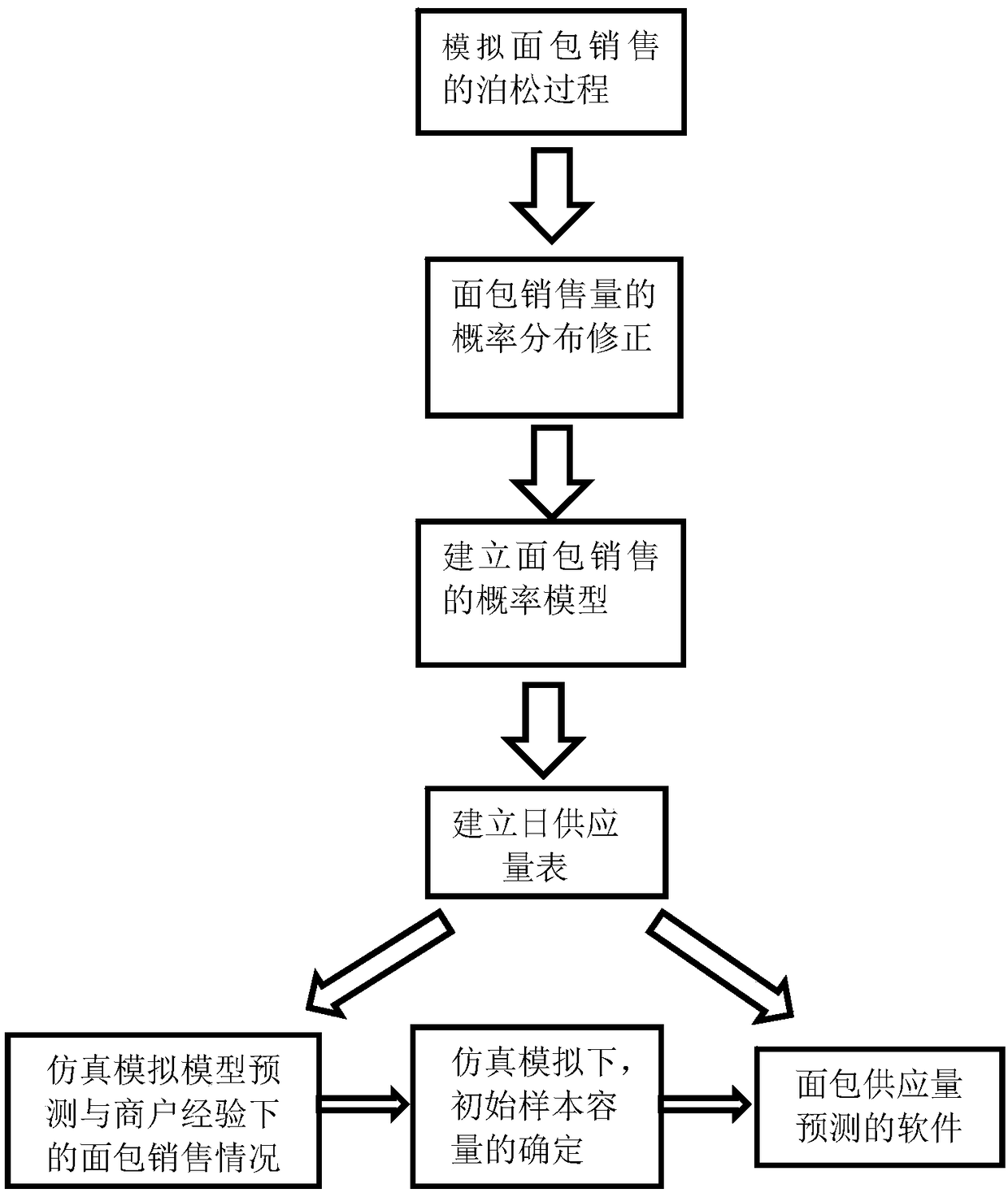
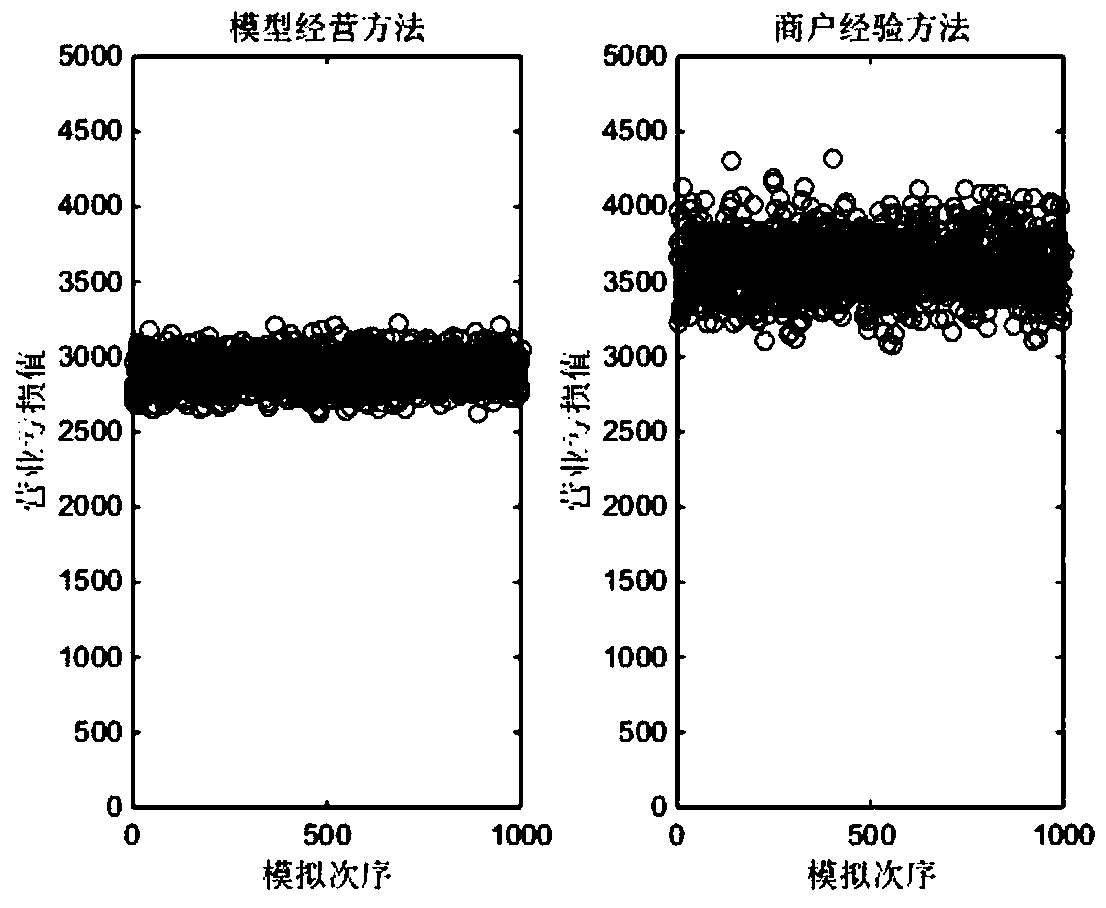
The invention relates to an optimal bread supply method and a system under random distribution. The method comprises the following steps: first, simulating a Poisson process of bread sales; 2, the probability distribution of bread sales is modified; 3, establish the probability model of bread sale; 4, establish a daily supply quantity table; the model in the invention studies the probability distribution of daily bread sales, can well explain the randomness of bread sales, and with the updating of sales data, the probability distribution of bread sales is modified in real time, so as to improve the generalization of the model. In the invention, the probability model is used to study the optimal supply quantity strategy of the next day's bread sales, which has little dependence on data anddoes not need a large amount of data to corroborate the sales law among the data. The invention focuses on the small and medium-sized bread retailers, helps them to effectively manage the sales and operation of bread products, effectively predicts the optimal supply quantity of the next day's products, and achieves the scientific decision of the bread sales strategy.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com