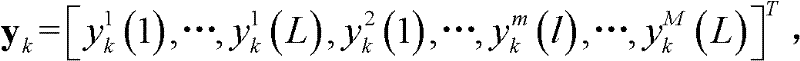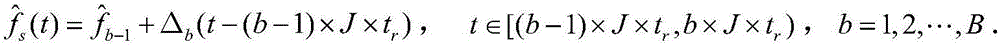Patents
Literature
117 results about "Likelihood-ratio test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
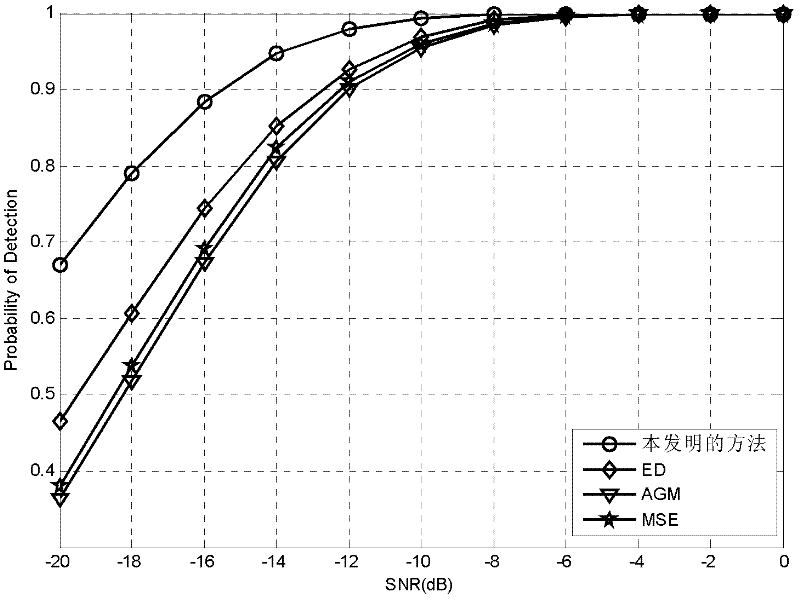
In statistics, the likelihood-ratio test assesses the goodness of fit of two competing statistical models based on the ratio of their likelihoods, specifically one found by maximization over the entire parameter space and another found after imposing some constraint. If the constraint (i.e., the null hypothesis) is supported by the observed data, the two likelihoods should not differ by more than sampling error. Thus the likelihood-ratio test tests whether this ratio is significantly different from one, or equivalently whether its natural logarithm is significantly different from zero.
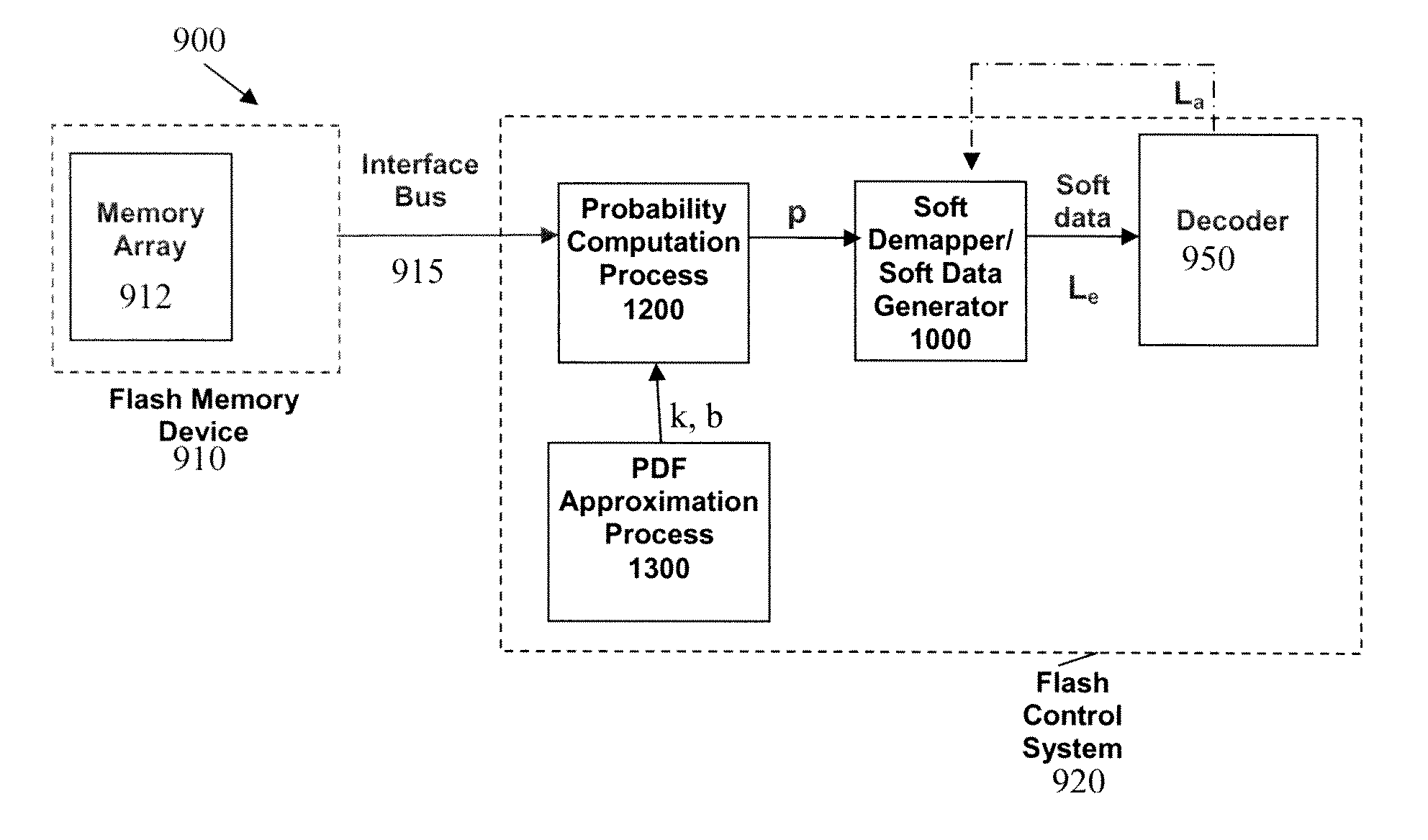
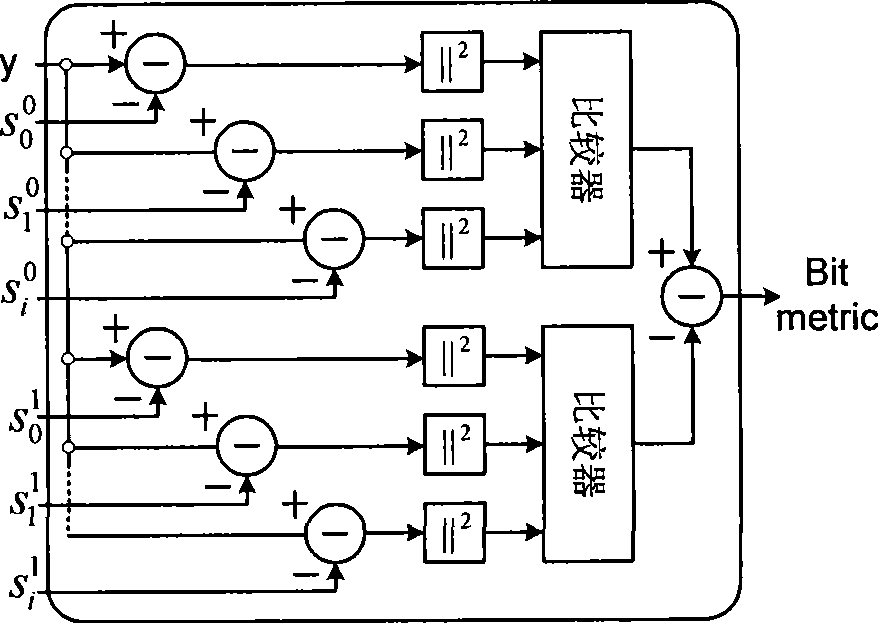
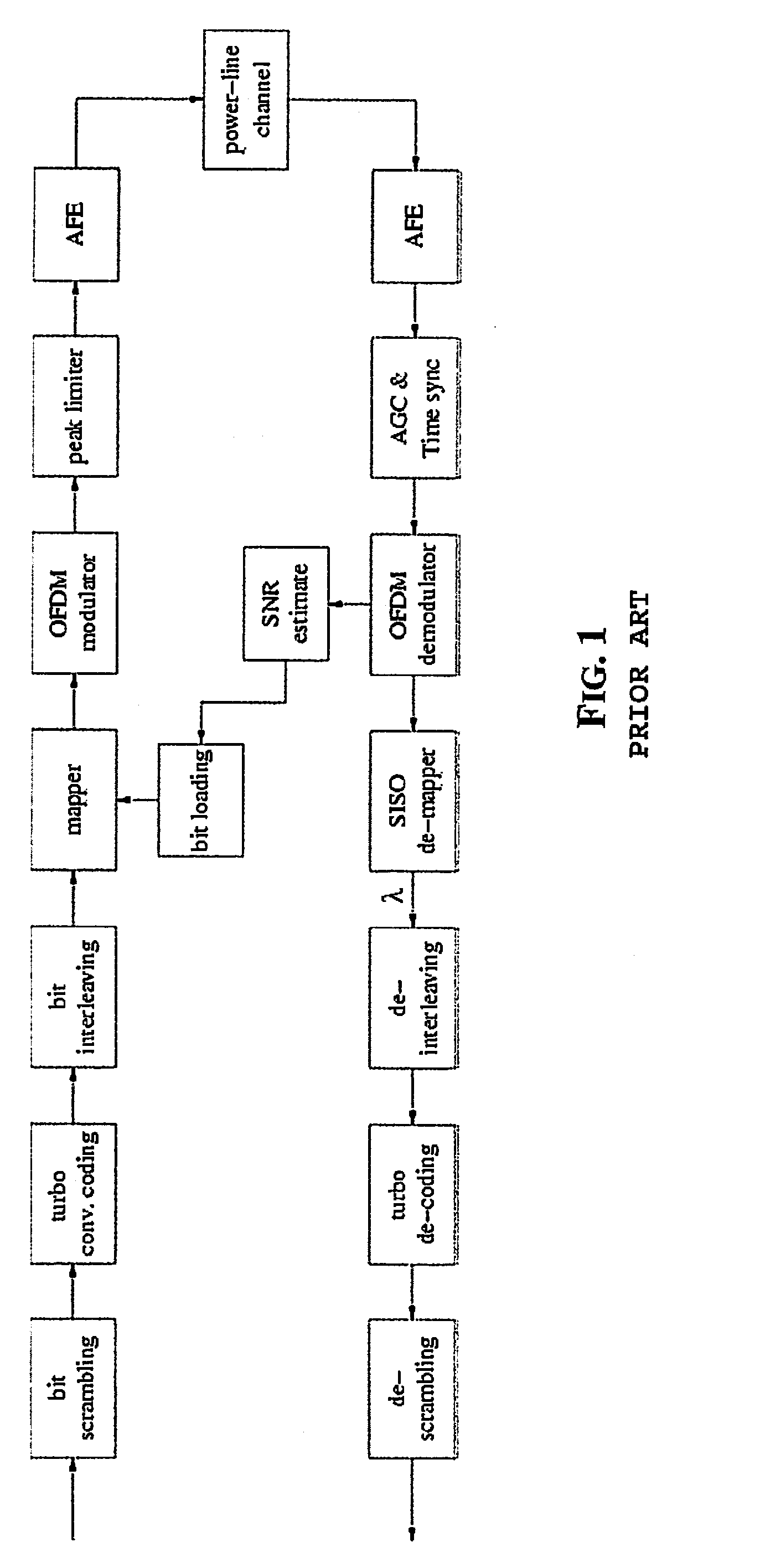
Methods and apparatus for computing soft data or log likelihood ratios for received values in communication or storage systems
ActiveUS20110246859A1Other decoding techniquesOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemSoft data
Methods and apparatus are provided for computing soft data or log likelihood ratios for received values in communication or storage systems. Soft data values or log likelihood ratios are computed for received values in a communication system or a memory device by obtaining at least one received value; identifying a segment of a function corresponding to the received value, wherein the function is defined over a plurality of segments, wherein each of the segments has an associated set of parameters; and calculating the soft data value or log likelihood ratio using the set of parameters associated with the identified segment. The computed soft data values or log likelihood ratios are optionally provided to a decoder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
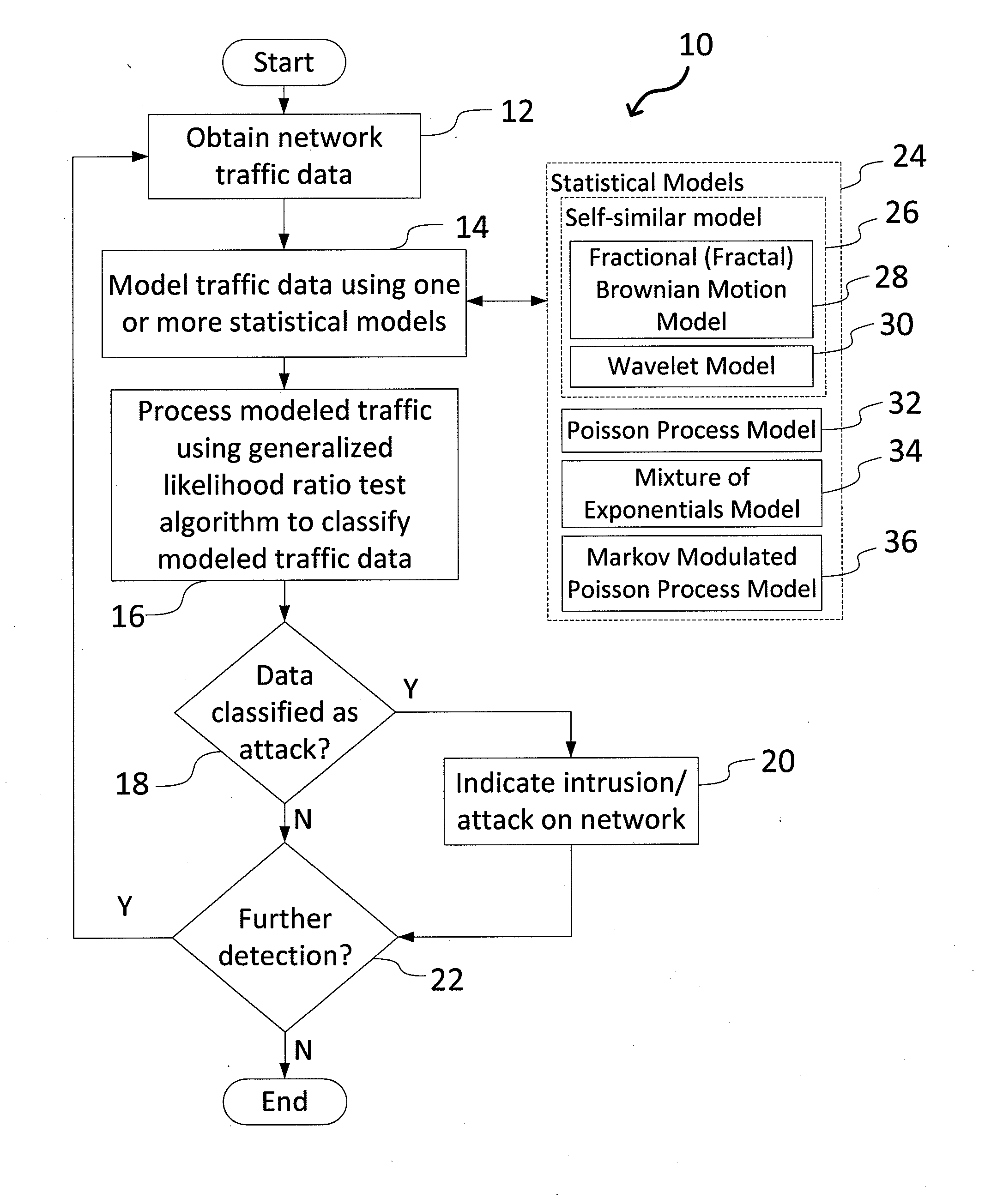
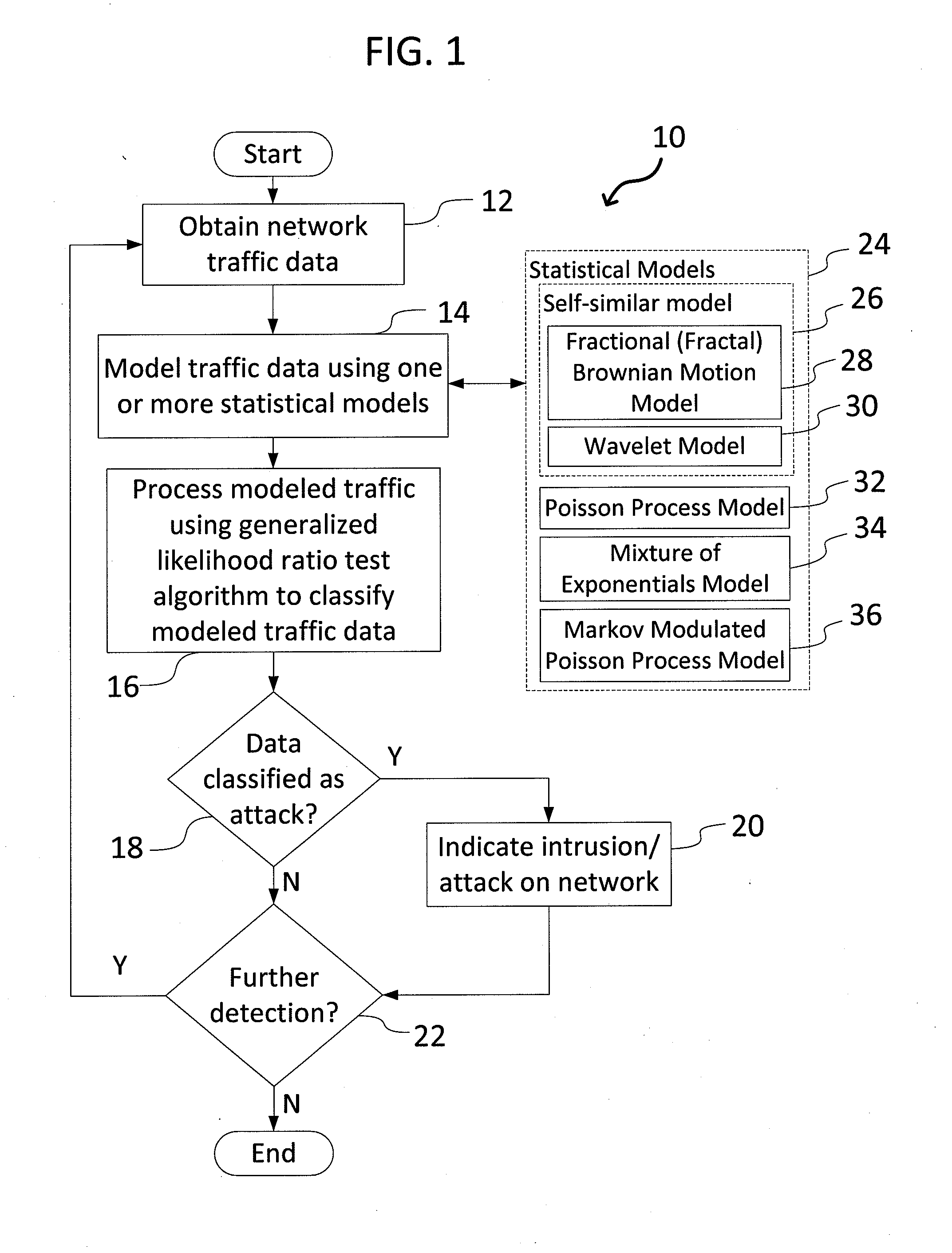
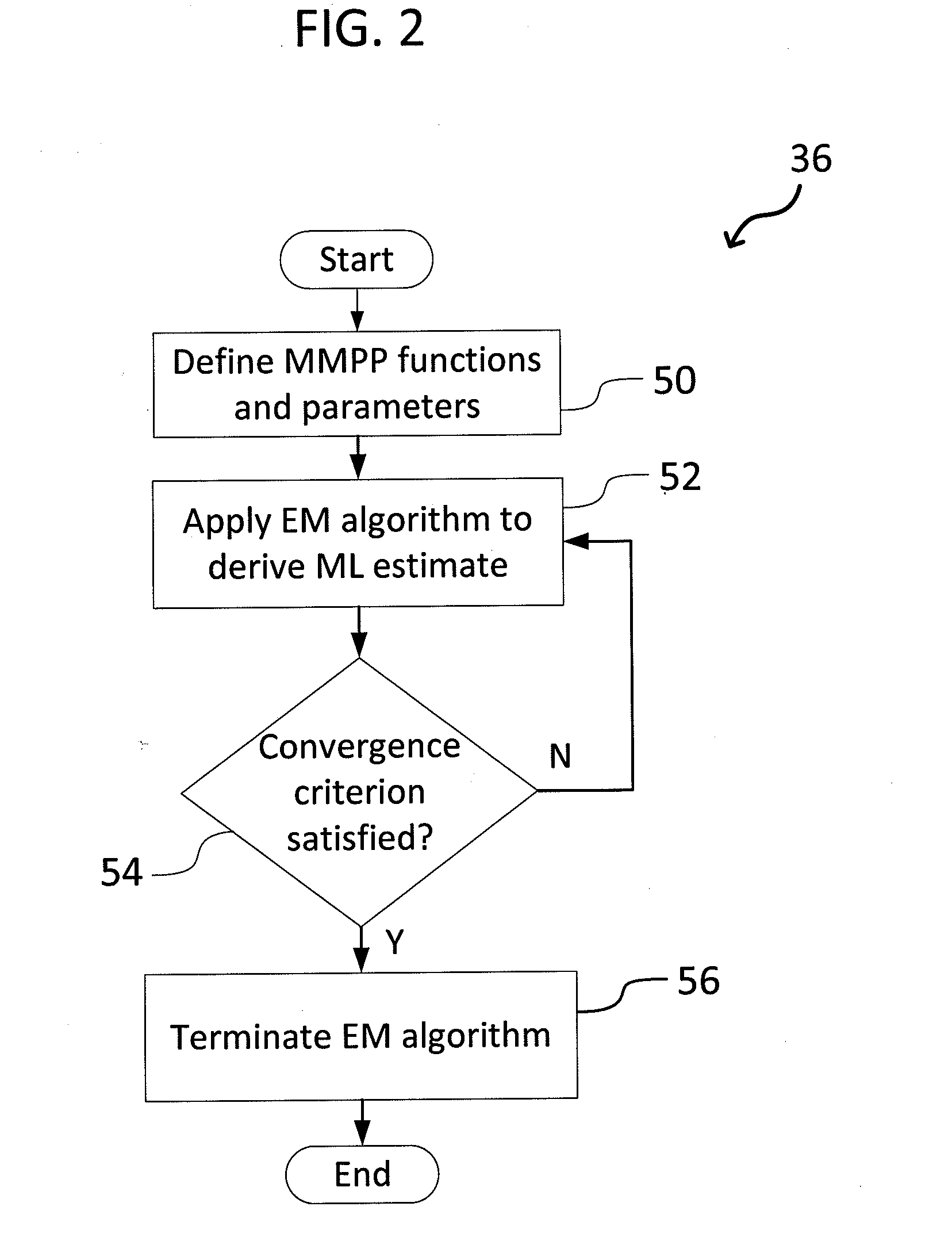
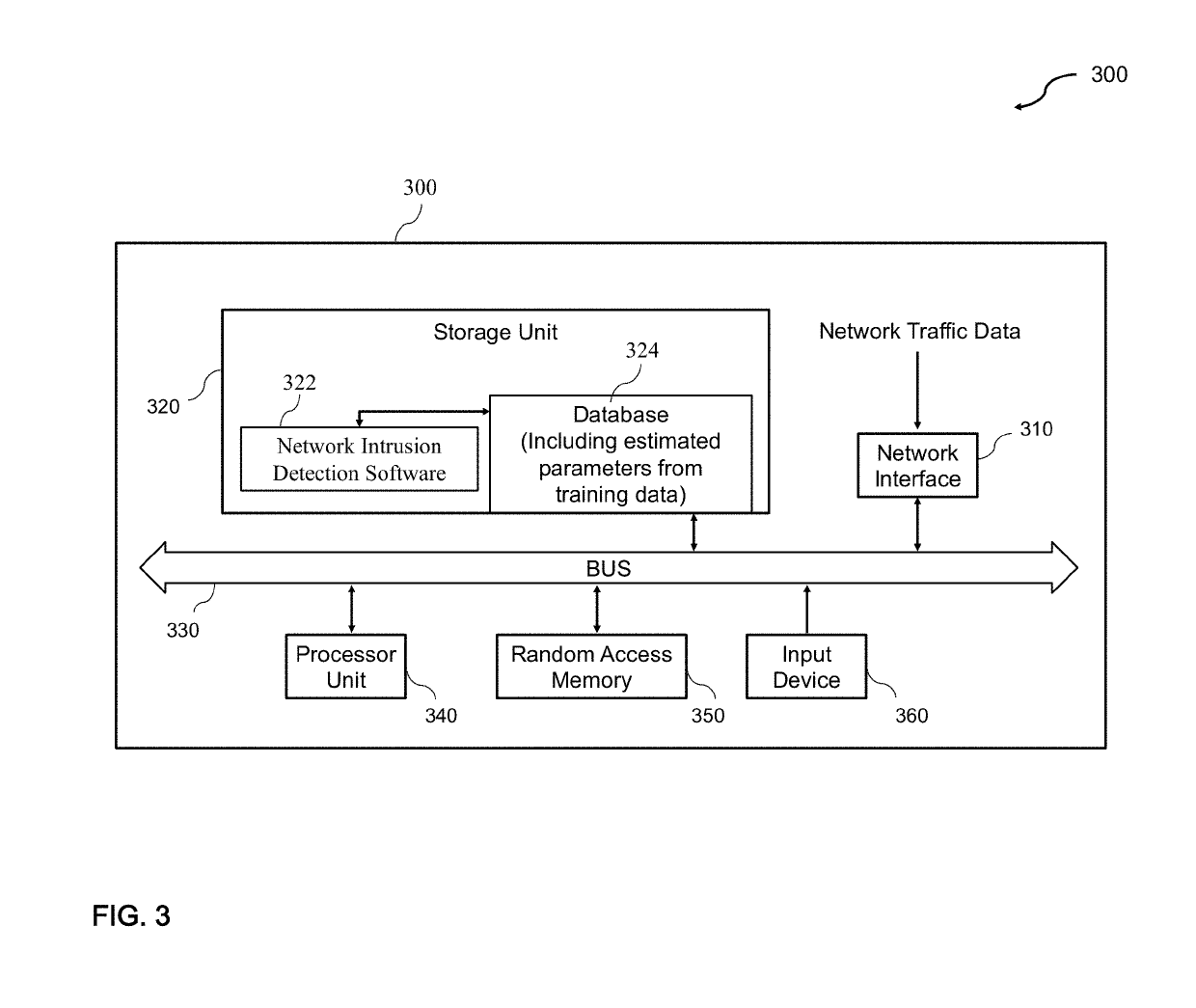
System and Method for Detecting Network Intrusions Using Statistical Models and a Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test
InactiveUS20140041032A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInternet trafficTiered approach
A system and method for detecting network intrusions using one or more statistical models and a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) is provided. The system includes a computer system and a network intrusion detection engine executed by the computer system. To detect network intrusions, the system receives network traffic data, computes a likelihood using one or more statistical models, such as an Markov-modulated Poisson process, and processes the traffic data using a GLRT. The statistical models are used to assess the likelihood of seeing a particular pattern of network traffic. The GLRT is used to classify a particular pattern as either indicative of an attack or not indicative of an attack. The system could apply one or more types of statistical models, such as in a flexible multi-tiered approach.
Owner:OPERA SOLUTIONS
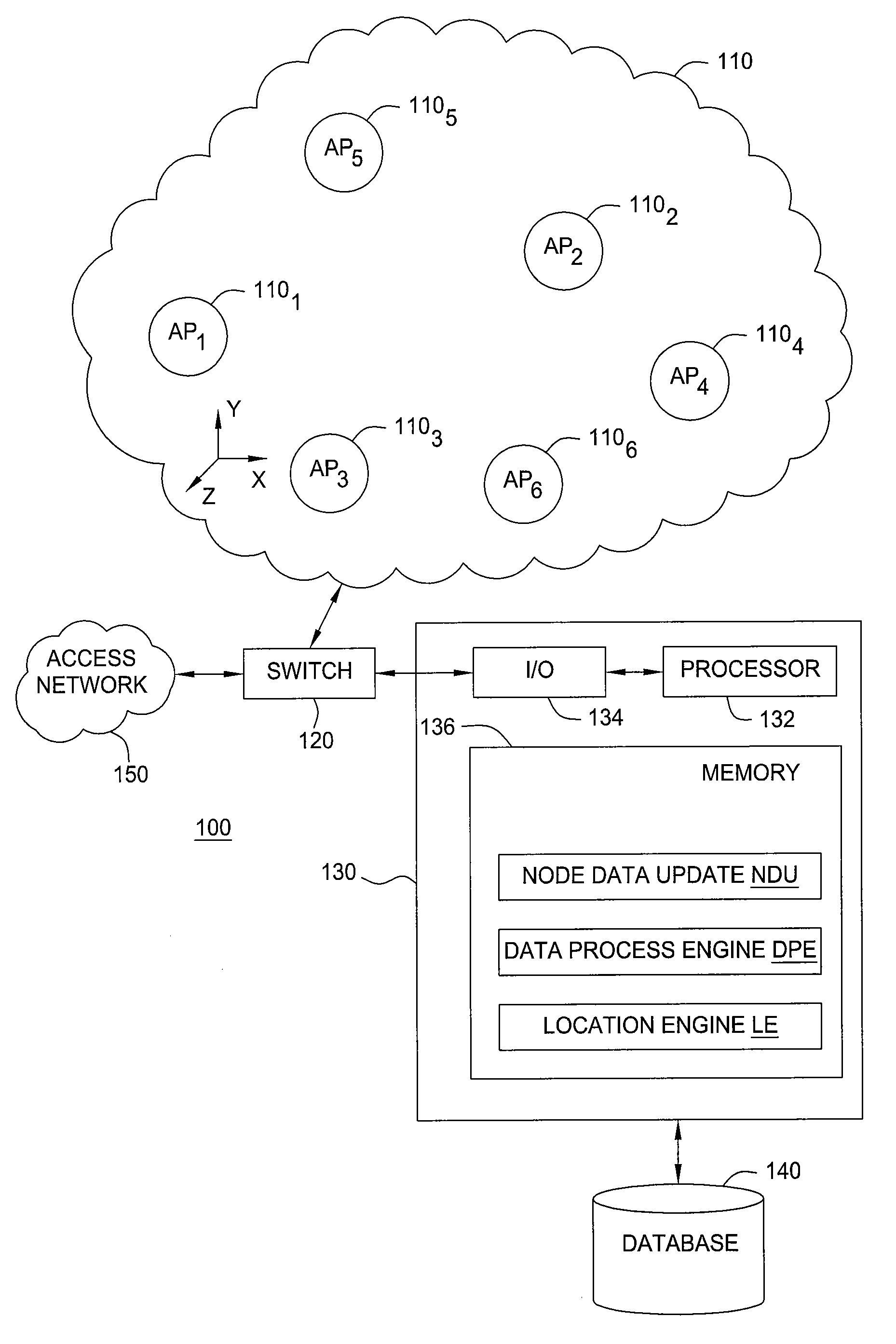
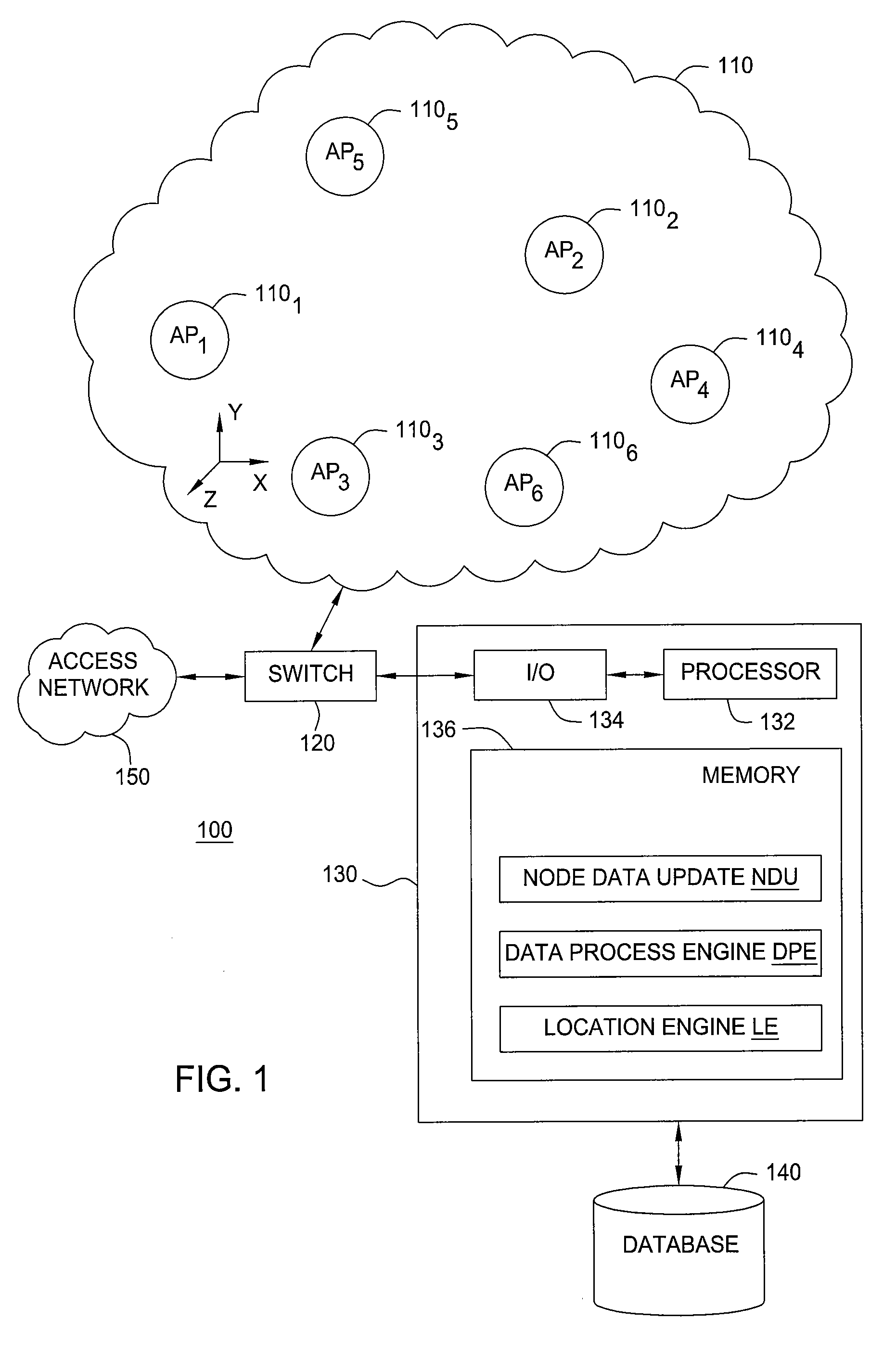
Detection of access point location errors in enterprise localization systems
ActiveUS20100329123A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLocalization systemLikelihood-ratio test
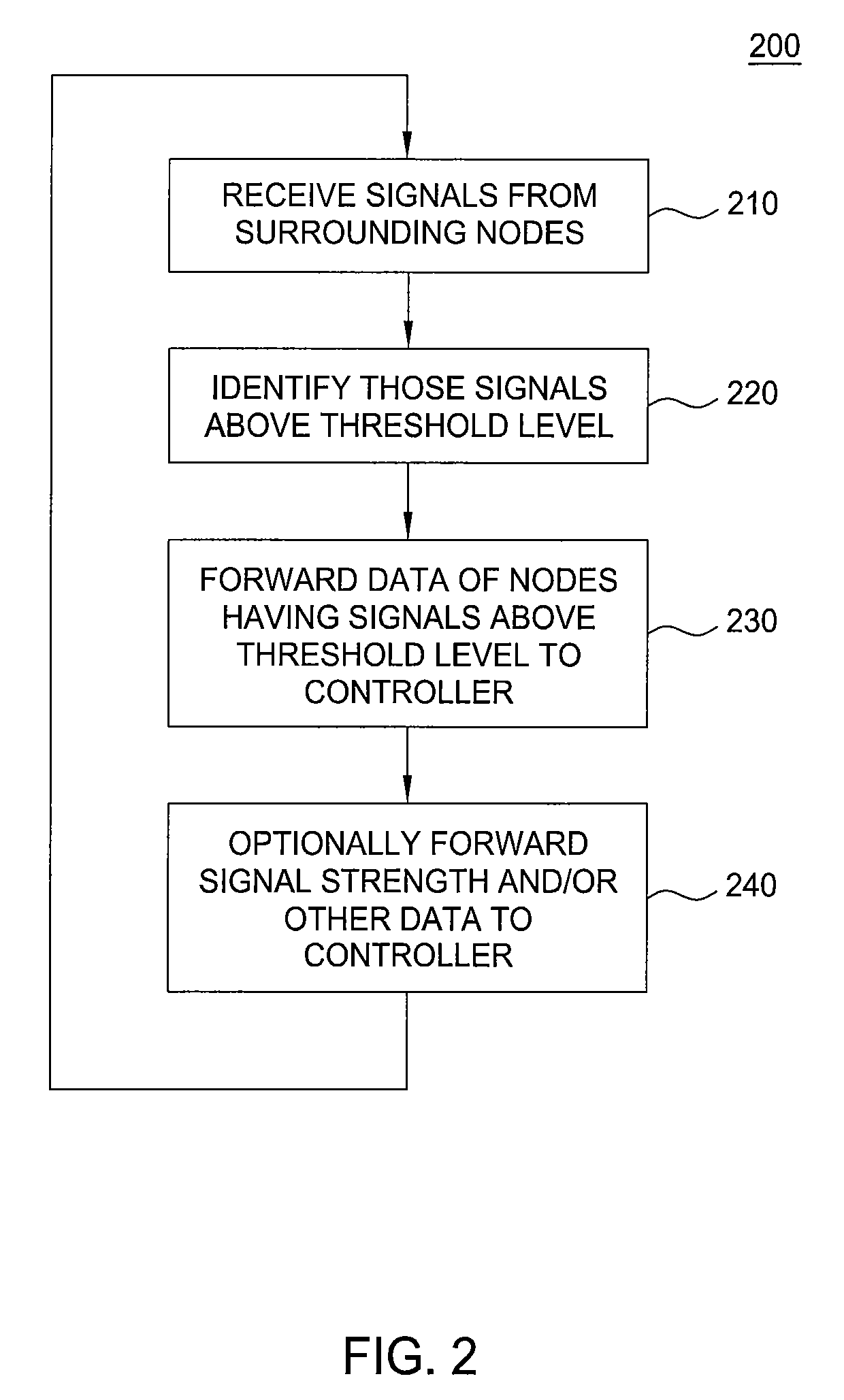
Method and apparatus for validating location information associated with an access point (AP) in a wireless local area network (WLAN) by subjecting neighborhood node proximity information retrieved from an AP and neighborhood node location information retrieved from a database to a likelihood ratio tests (LRT). The neighborhood node proximity information retrieved from an AP comprises a list of nodes exhibiting at the AP a signal strength above a threshold level T, or link quality information associated with those nodes having a signal received by the AP.
Owner:1BAR NET LTD
Identity authentication method and system
ActiveCN102238190AImprove accuracyUser identity/authority verificationSpeech analysisPasswordLikelihood-ratio test
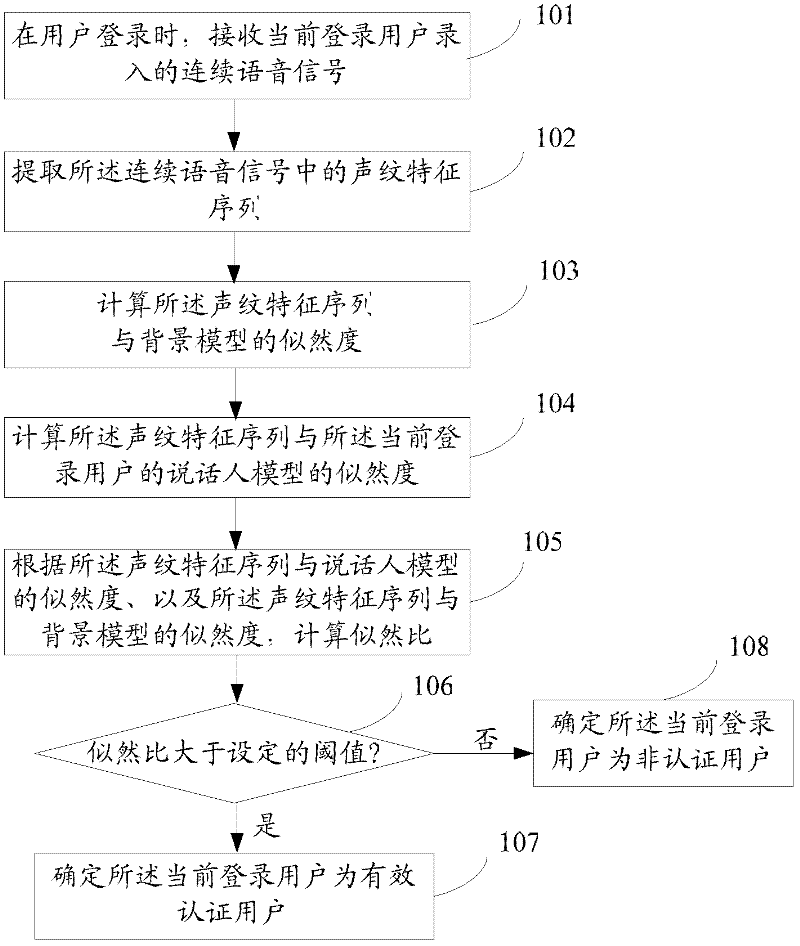
The invention discloses an identity authentication method and an identity authentication system. The method comprises the following steps of: in the login of a user, receiving a continuous voice signal recorded by the current login user; extracting a voiceprint characteristic sequence from the continuous voice signal; computing likelihood between the voiceprint characteristic sequence and a background model; computing the likelihood between the voiceprint characteristic sequence and a speaker model of the current login user, wherein the speaker model is a polyhybrid Gaussian model constructed according to the repetition times and frame number of the registration voice signals recorded in the login of the current login user; computing a likelihood ratio according to the likelihood between the voiceprint characteristic sequence and the speaker model and the likelihood between the voiceprint characteristic sequence and the background model; and if the likelihood ratio is greater than a preset threshold value, determining the current login user is an effectively authenticated user, otherwise determining the current login user is an unauthenticated user. By the method and the system, the voiceprint-password-based identity authentication accuracy can be improved.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
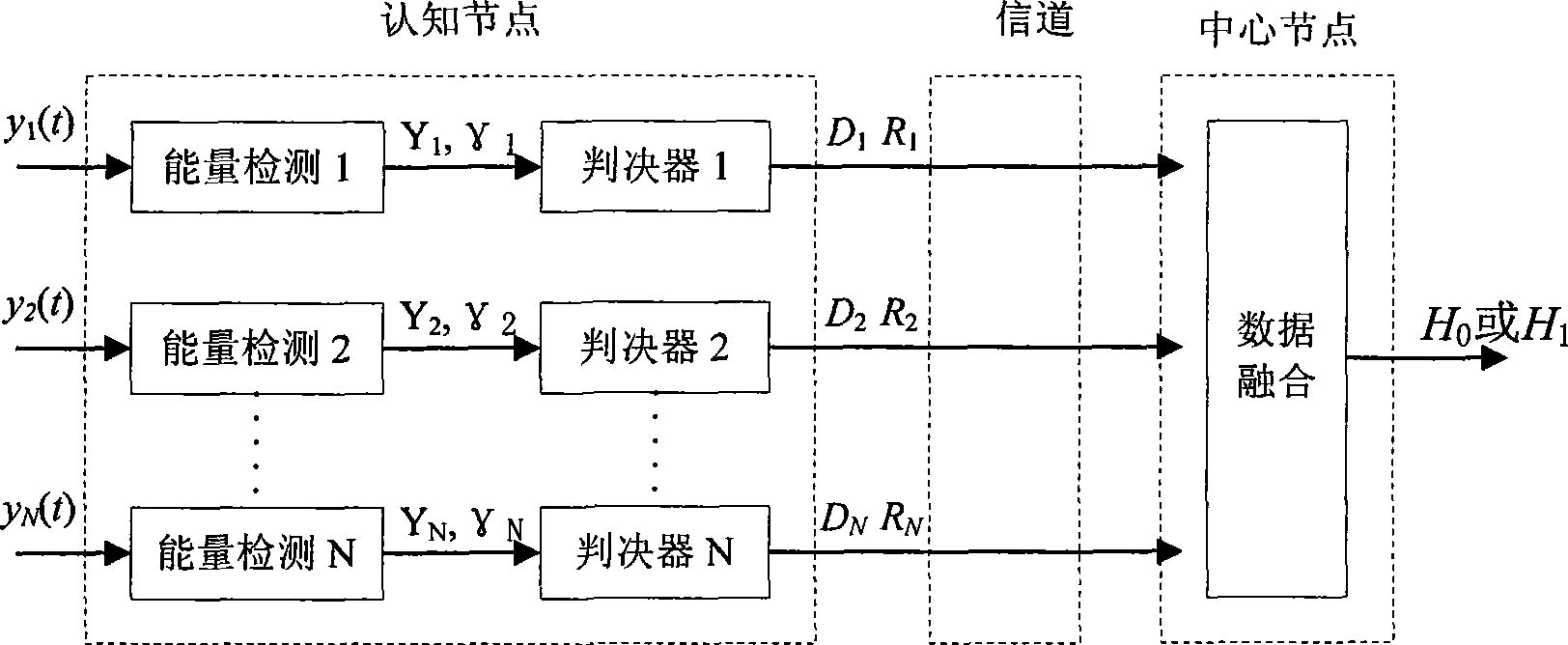
Cooperative spectrum sensing method based on likelihood ratio in cognitive radio
InactiveCN101521896AImprove reliabilityEasy to detectTransmission monitoringWireless communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Likelihood-ratio test
A cooperative spectrum sensing method based on likelihood ratio in cognitive radio provides that local judgment of cognitive nodes uses the maximum likelihood criterion, and the method effectively solves the reliability problem of the local judgment of the cognitive nodes in low signal to noise ratio. The method comprises two parts, namely local detection of the cognitive nodes and judgment of a central node, wherein the cognitive nodes use energy detection, and perform the local judgment based on the maximum likelihood criterion on an energy detection value so as to obtain local judgment results related to an authorization user, and the likelihood ratio is taken as a measure of the judgment reliability; and the various cognitive nodes send the local judgment results and a quantized local likelihood ratio to the central node, and the central node performs the cooperative judgment according to the results of the various cognitive nodes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
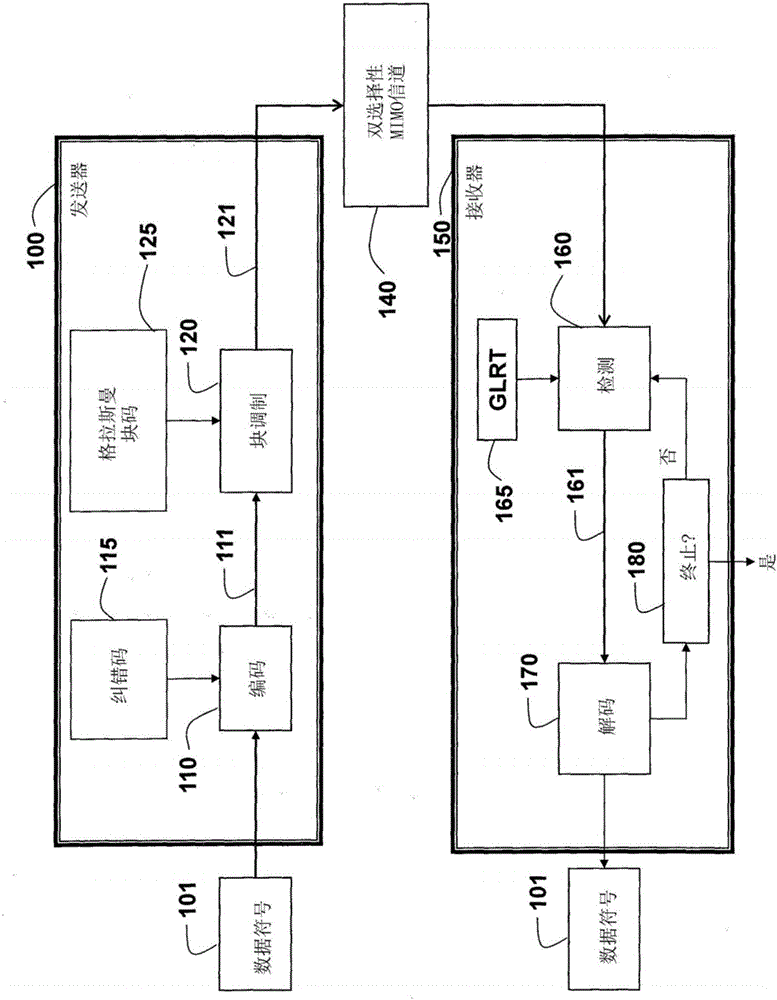
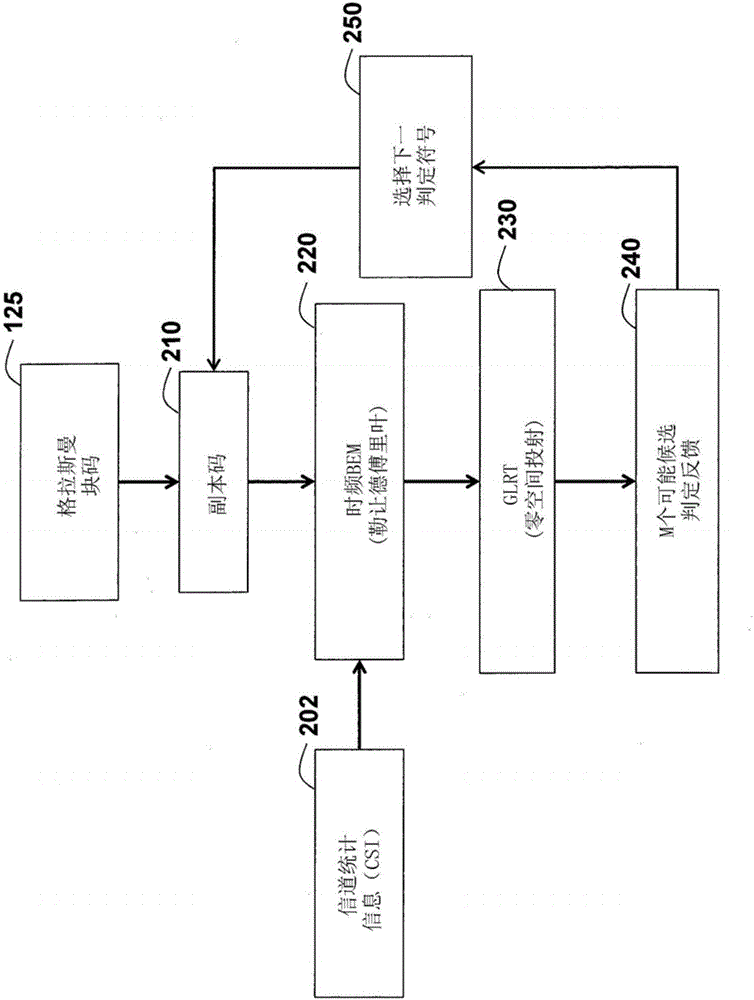
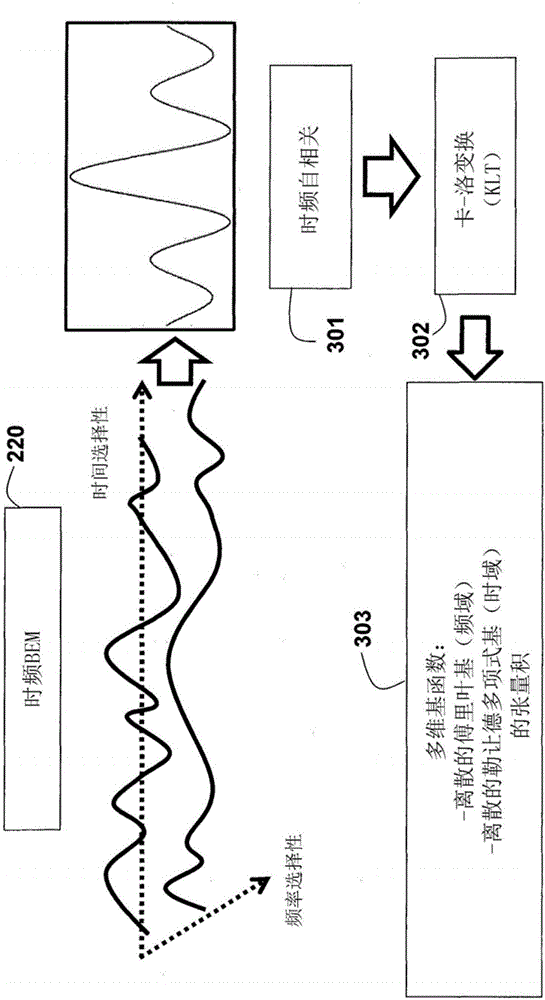
Method and system for communicating data symbols in a network
ActiveCN106105075AImprove performanceSuppress error propagationSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksChannel statisticsParallel computing
A method and system realize reliable wireless communications in non-coherent multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) doubly-selective channels. The method uses Grassmannian space-time-frequency block codes and an iterative generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) with a multi-dimensional basis expansion model (BEM), decision reordering, and a fixed number of surviving candidates. The computational complexity of a non-coherent MIMO equalizer becomes linear as a function of a code length and a size of a modulation alphabet. The codebook, the alphabet size, the bit labeling, and the block power are optimized using worst-case channel statistics or instantaneous channel states. The method can use soft-information feedback from error correction codes, such as low-density-parity-check codes to improve performance.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
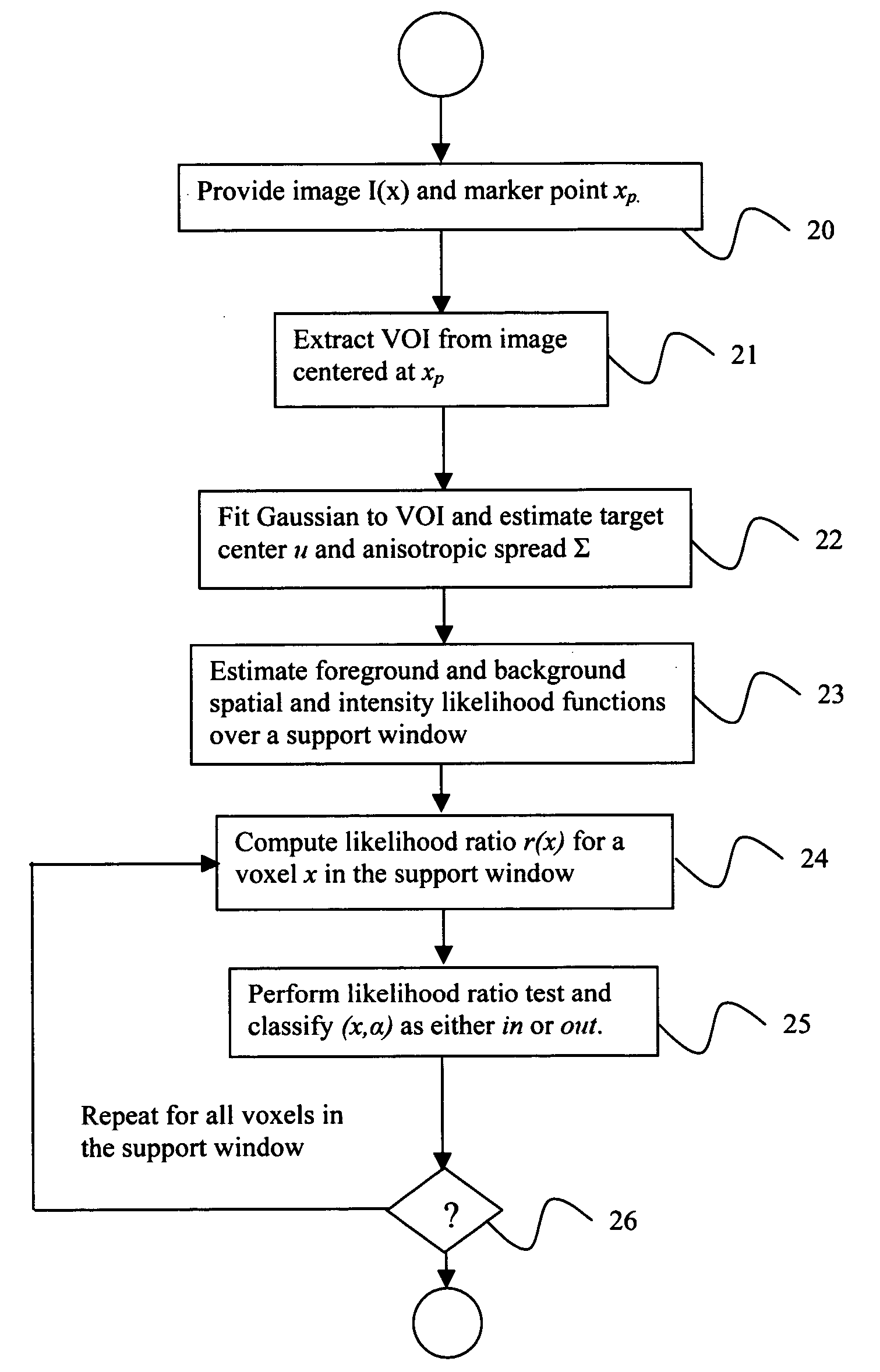
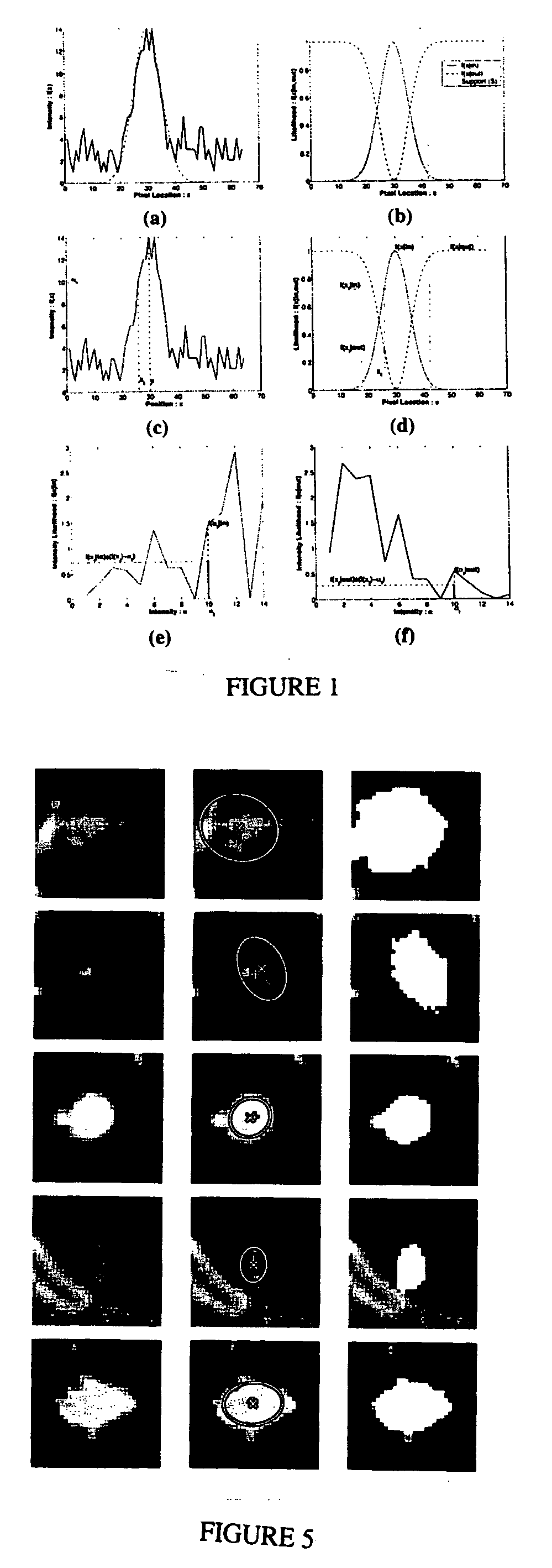
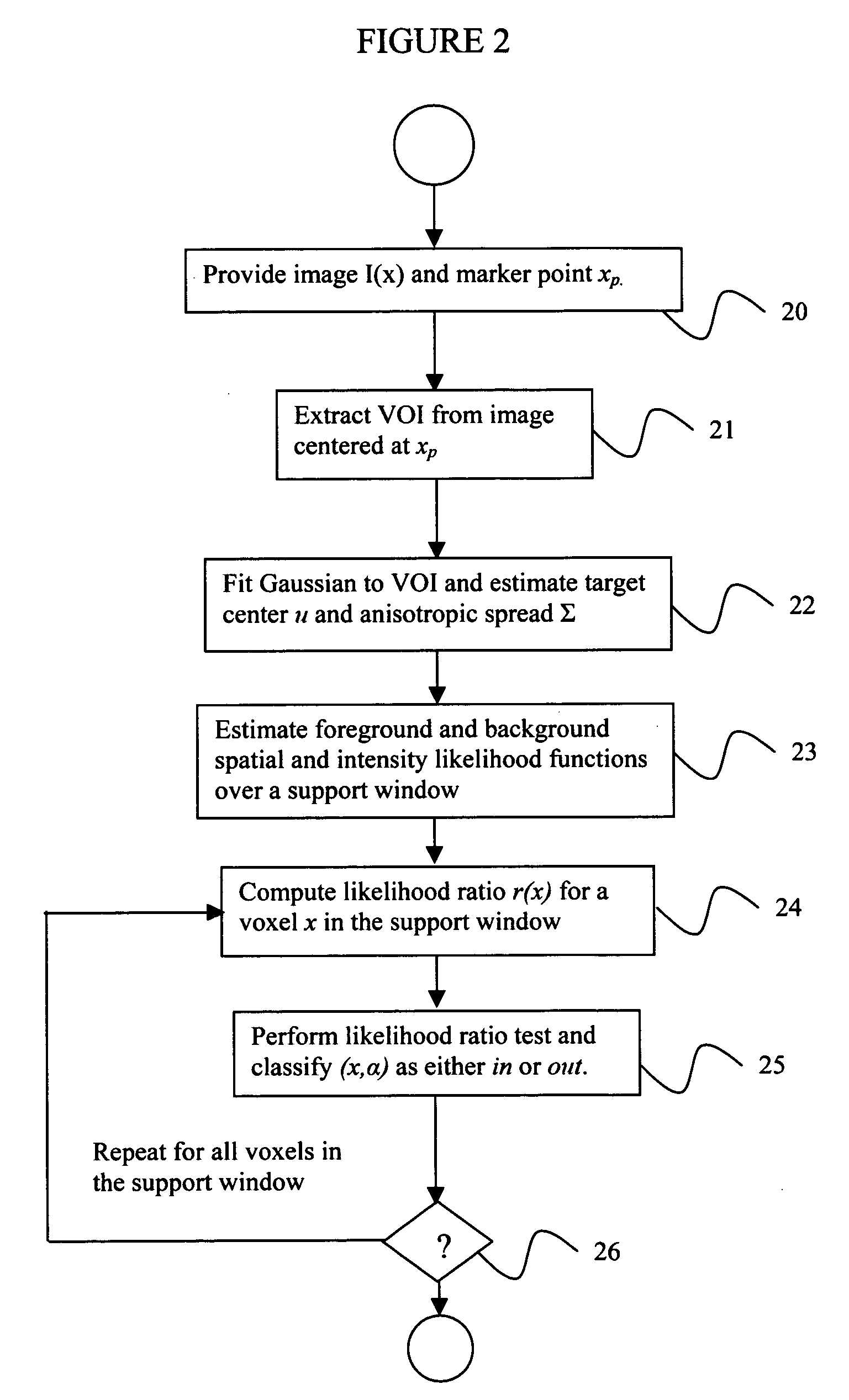
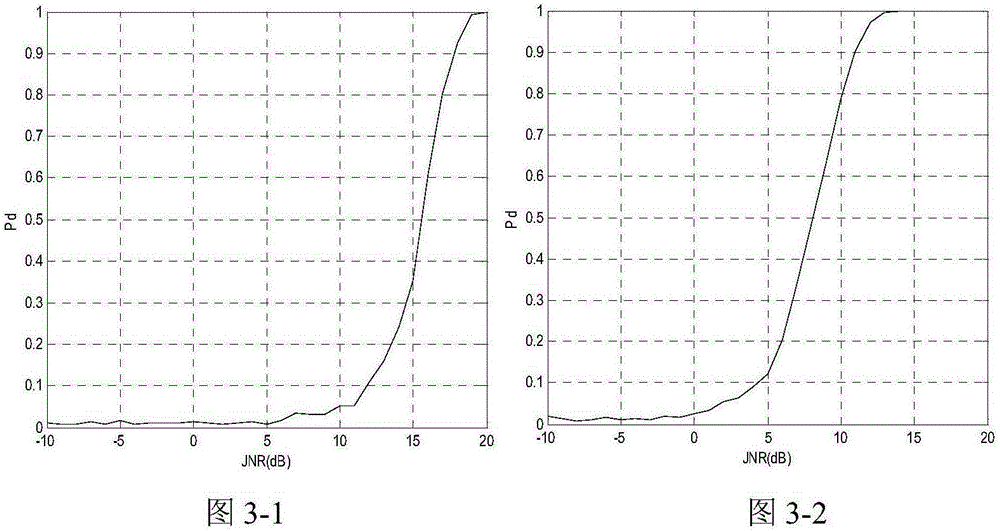
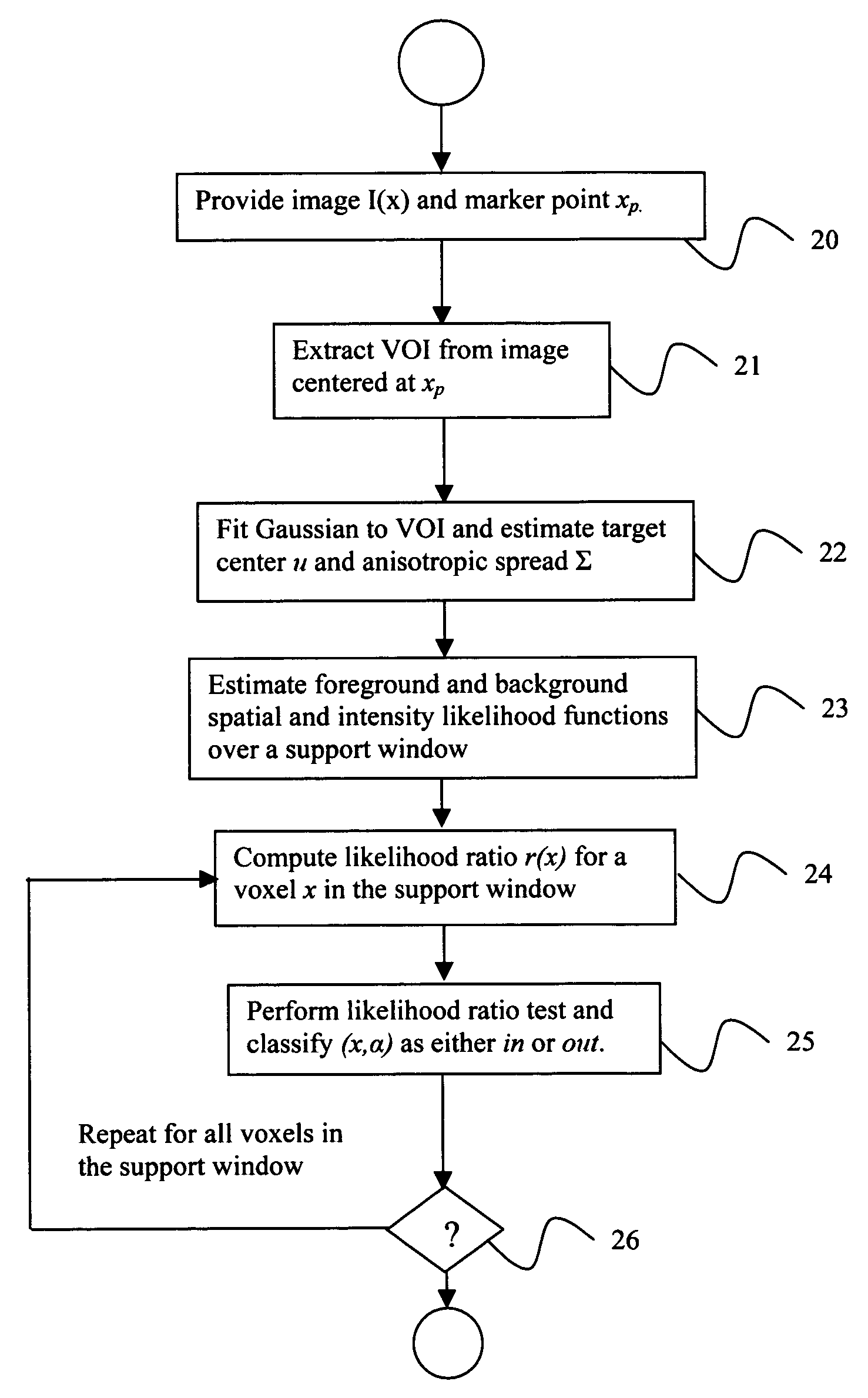
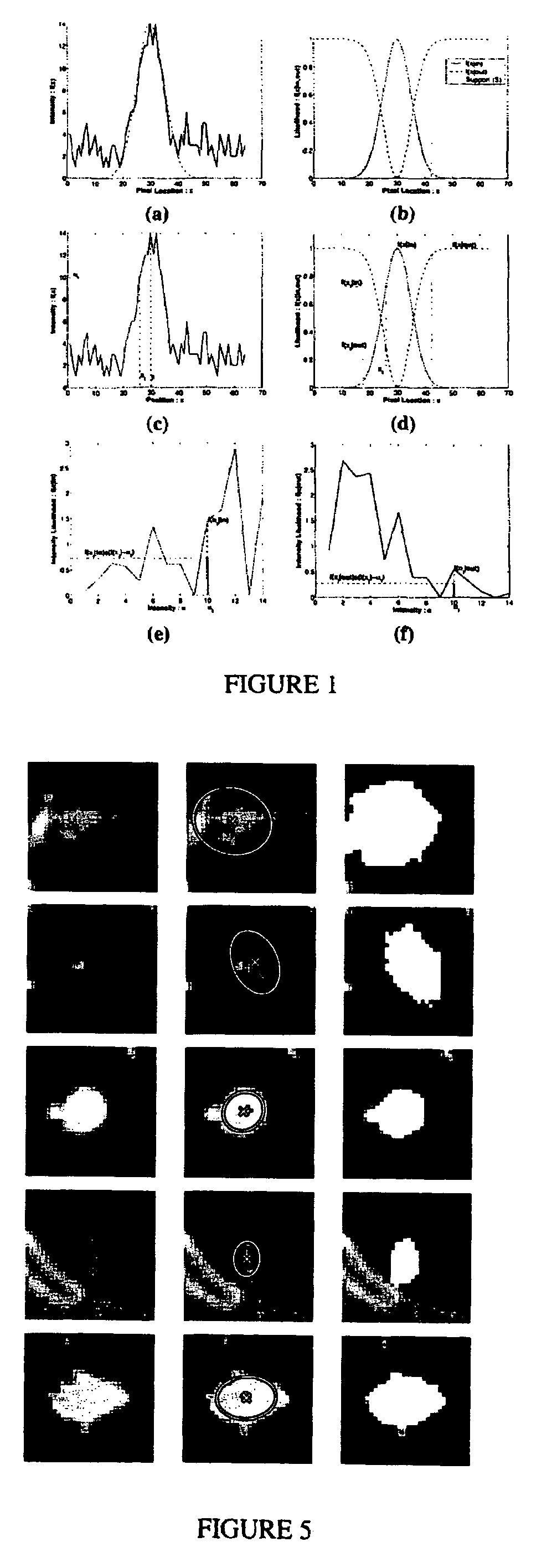
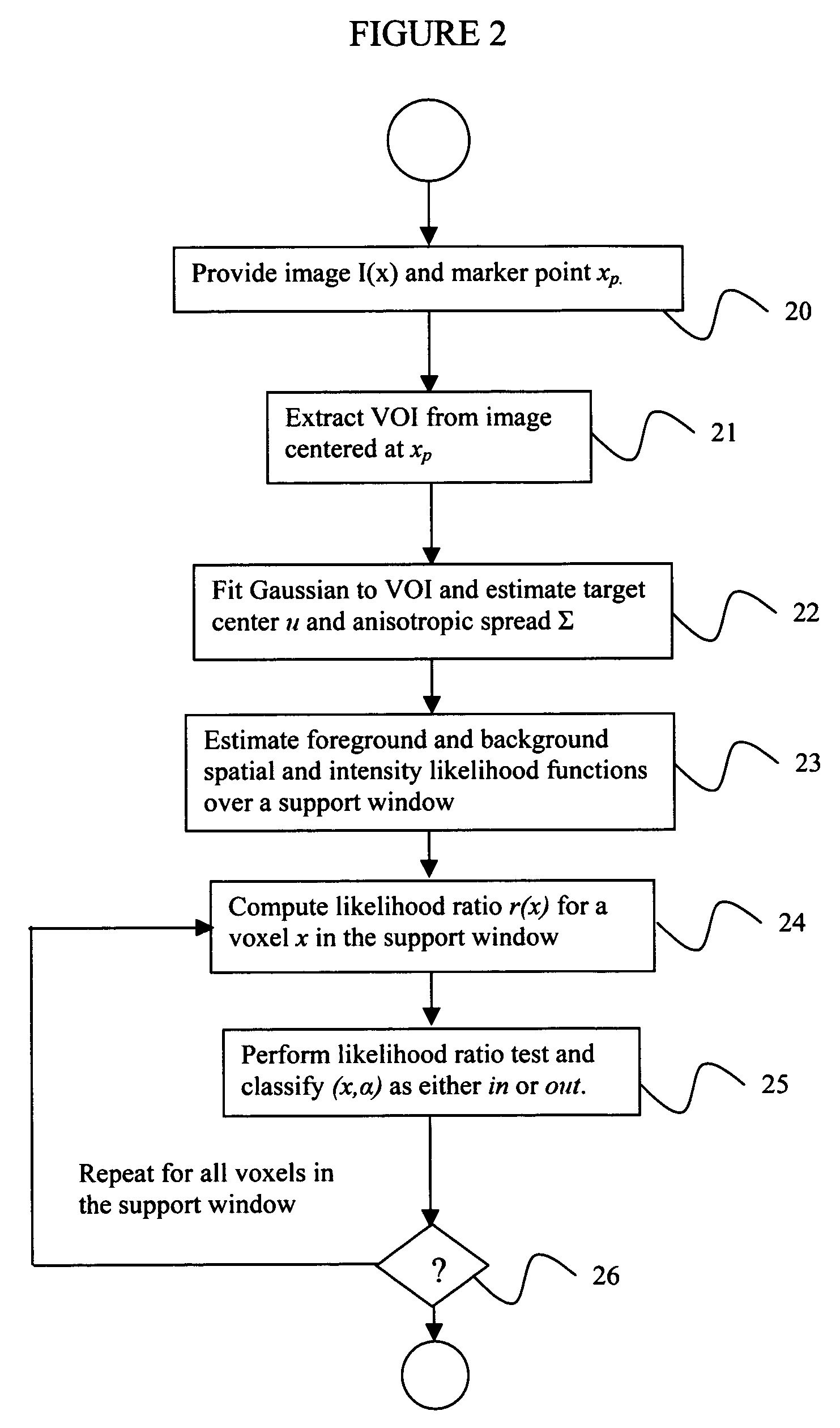
System and method for volumetric tumor segmentation using joint space-intensity likelihood ratio test
InactiveUS20060050958A1Segmentation difficultyEffective segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisAbnormal tissue growthA domain
A method for segmenting a digitized image includes providing a digitized volumetric image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points in an N-dimensional space, identifying a target structure in said image, forming a window about said target structure whose size is a function of the target scale, and performing a joint space-intensity-likelihood ratio test at each point within said window to determine whether each said point is within said target structure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Pattern change discovery between high dimensional data sets
ActiveUS20140122039A1Cancel noiseFacilitate underlying processComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationDirect computationMatrix decomposition
The general problem of pattern change discovery between high-dimensional data sets is addressed by considering the notion of the principal angles between the subspaces is introduced to measure the subspace difference between two high-dimensional data sets. Current methods either mainly focus on magnitude change detection of low-dimensional data sets or are under supervised frameworks. Principal angles bear a property to isolate subspace change from the magnitude change. To address the challenge of directly computing the principal angles, matrix factorization is used to serve as a statistical framework and develop the principle of the dominant subspace mapping to transfer the principal angle based detection to a matrix factorization problem. Matrix factorization can be naturally embedded into the likelihood ratio test based on the linear models. The method may be unsupervised and addresses the statistical significance of the pattern changes between high-dimensional data sets.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
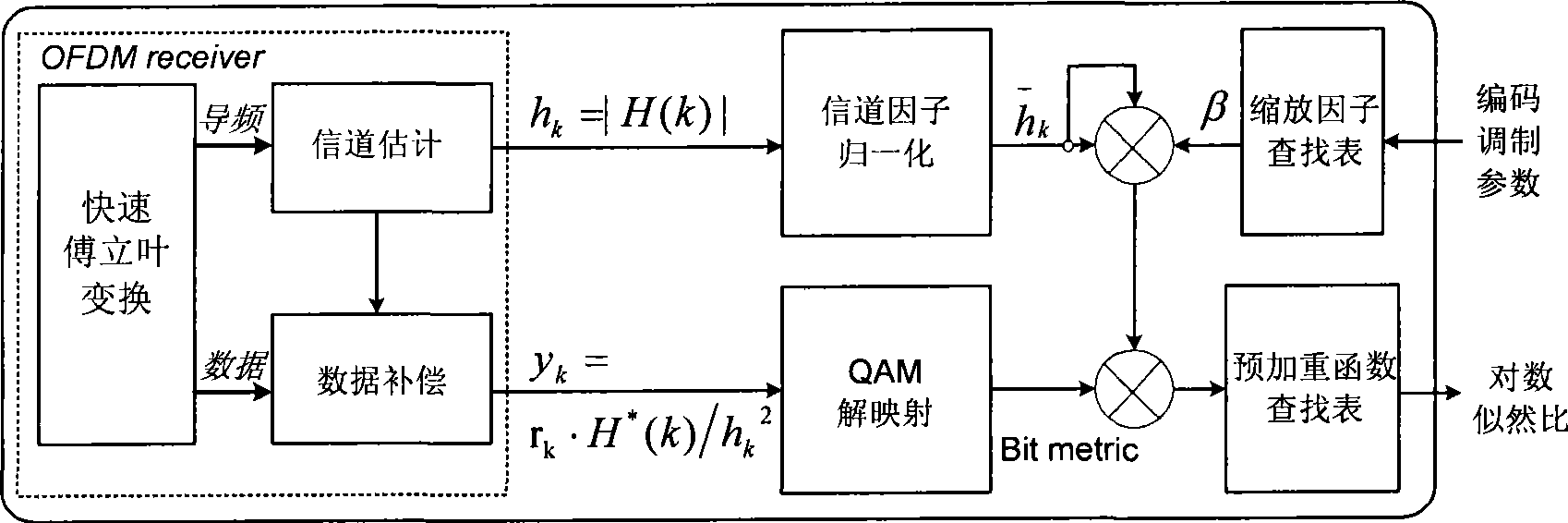
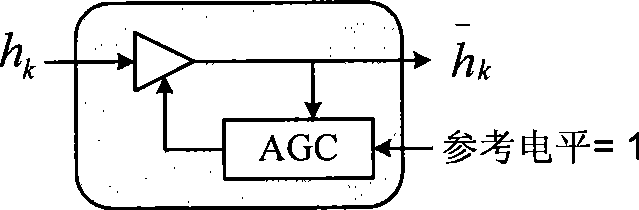
Method for generating log-likelihood ratio for QAM-OFDM modulating signal
InactiveCN101471749AEasy to implementImprove performanceError preventionBaseband system detailsEngineeringLikelihood-ratio test
The invention provides a method for producing log likelihood ratio of a quadrature amplitude modulation-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (QAM-OFDM) modulating signal. The method comprises the following steps: allowing an OFDM receiver to estimate the frequency domain channel factor of each QAM sub-carrier symbol; performing the channel compensation of each QAM sub-carrier symbol by utilizing the estimated frequency domain channel factor; normalizing the estimated frequency domain channel factor; multiplying the normalized frequency domain channel factor by a specified scaling factor that is selected from a look-up table; subjecting the compensated QAM symbol to the QAM de-mapping to obtain a basic bit measurement information; multiplying the basic bit measurement information by a scaling factor that is subjected to the normalization and the scaling treatment; and searching a pre-emphasis look-up table by utilizing the scaled soft information to obtain the final bit likelihood ratio and outputting the bit likelihood ratio. The method is universal, can obviously improve the system performance, and is applied to various modern broadband wireless multimedia communication systems. Additionally, the method is simple and free of complex calculation and is adaptive to the hardware implementation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
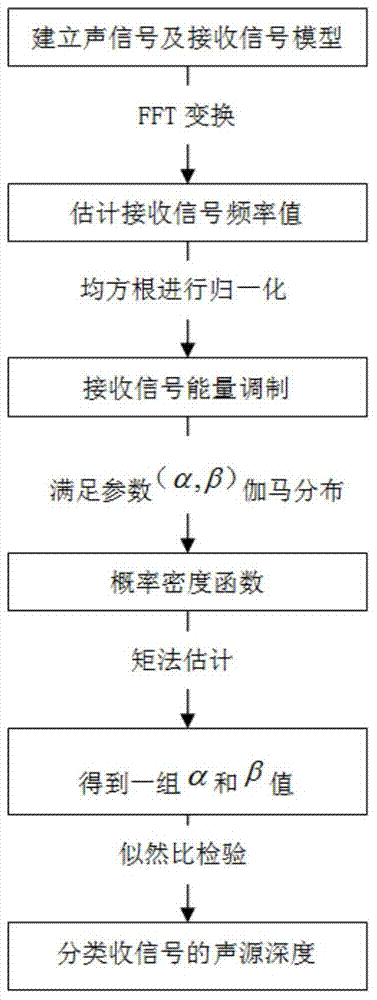
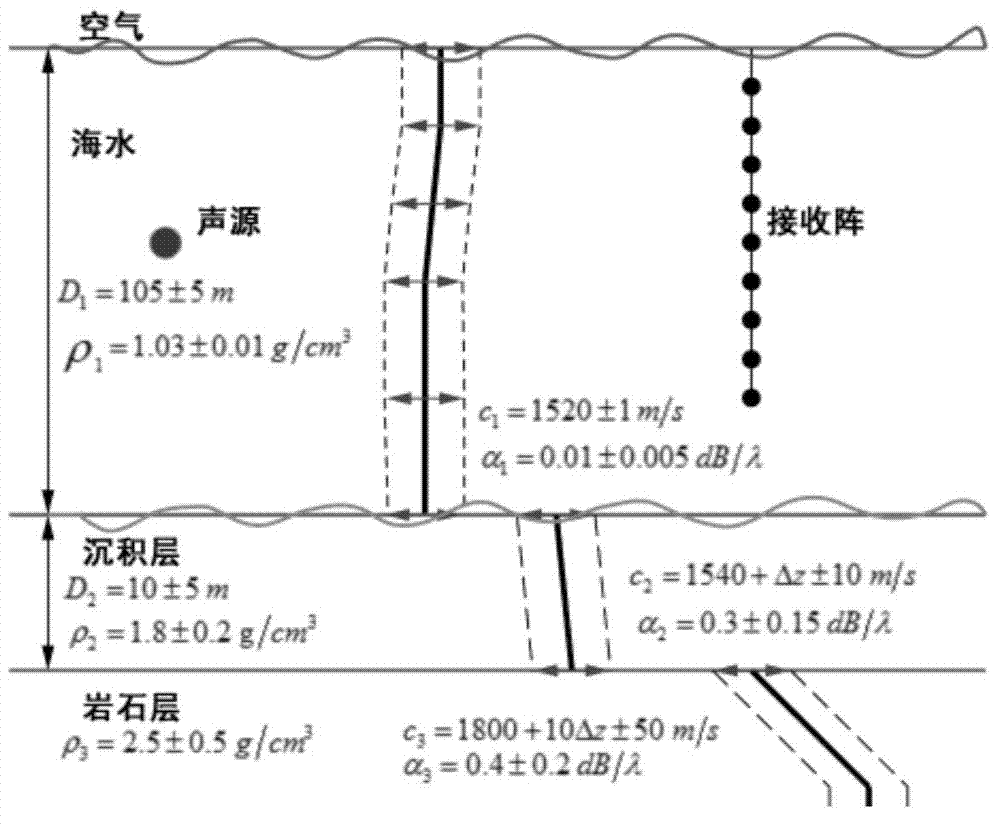
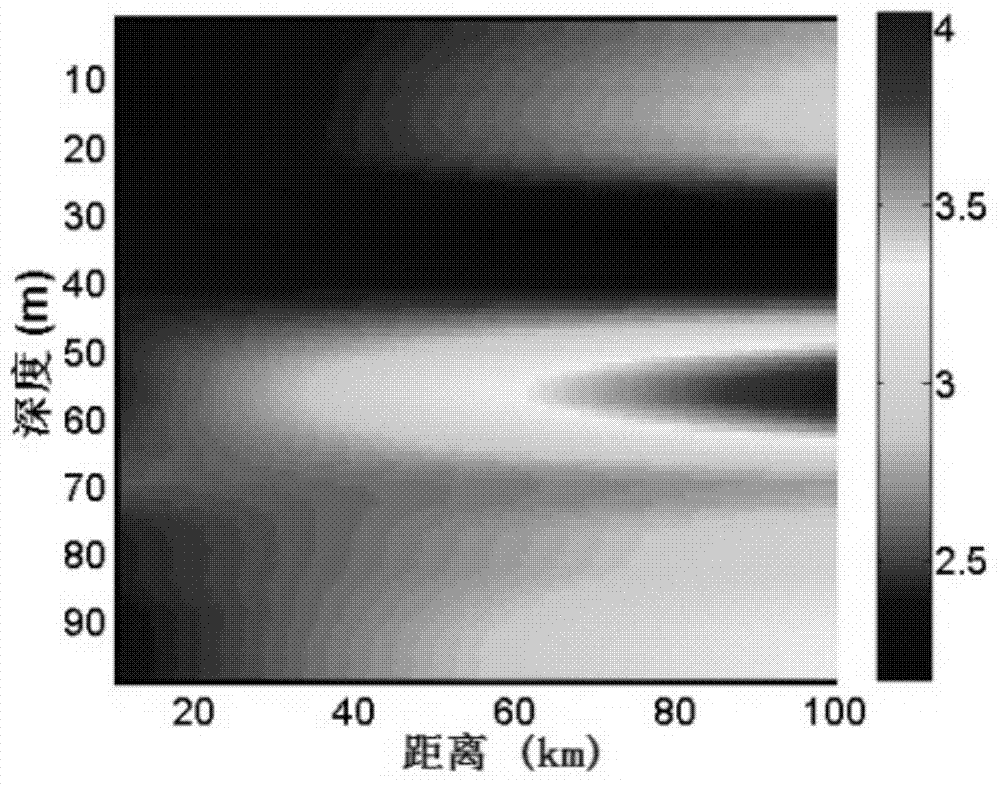
Shallow sea target depth classification method based on hydrophone array
ActiveCN104749568AImprove environmental adaptabilityWave based measurement systemsNormal densitySound sources
The invention provides a shallow sea target depth classification method based on a hydrophone array. Detection is performed by integrating information received by multiple hydrophones, a typical probability density function of energy field change produced by model-based deep and shallow sound sources is generated by acoustic propagation simulation, likelihood ratio test (LRT) is performed based on the probability density function to identify a received signal, prior knowledge is extracted according to the law of distribution of sound energy within the whole range of a sound field, and thus, depth classification is performed on the sound field target. The algorithm is easy to implement and high in environmental adaptability.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
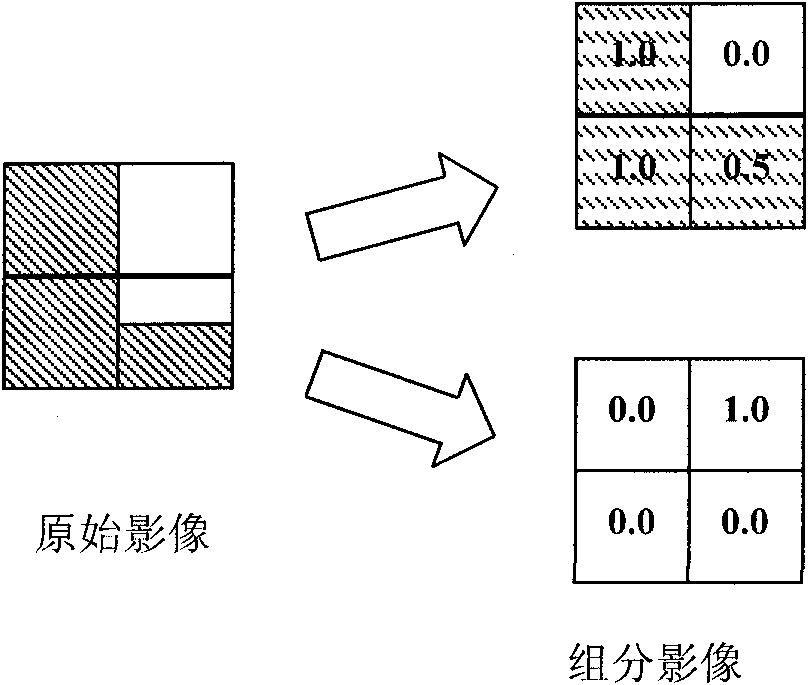
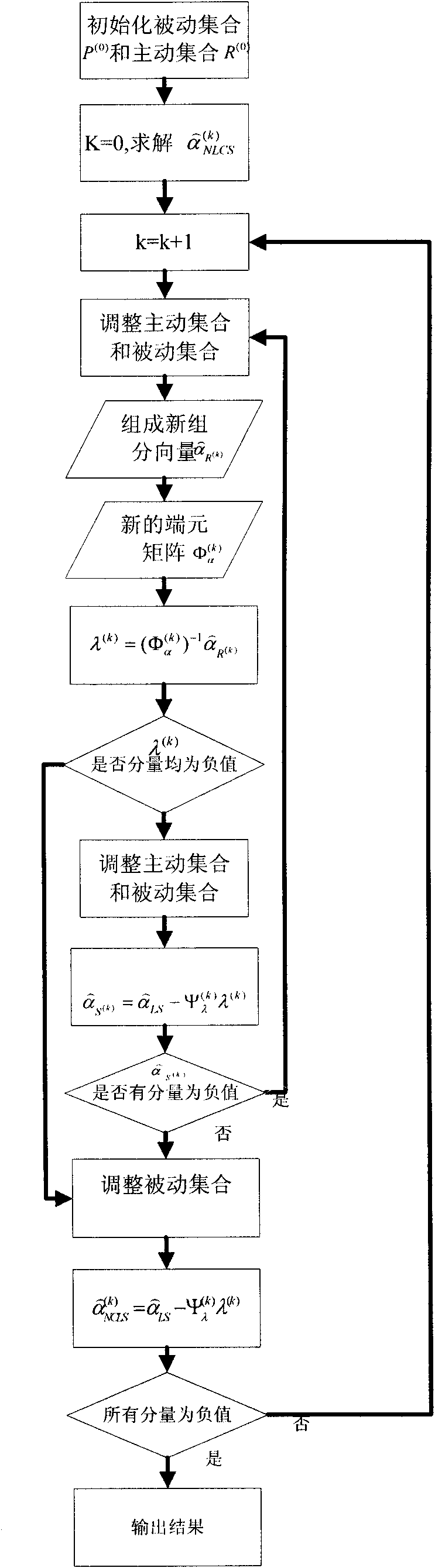
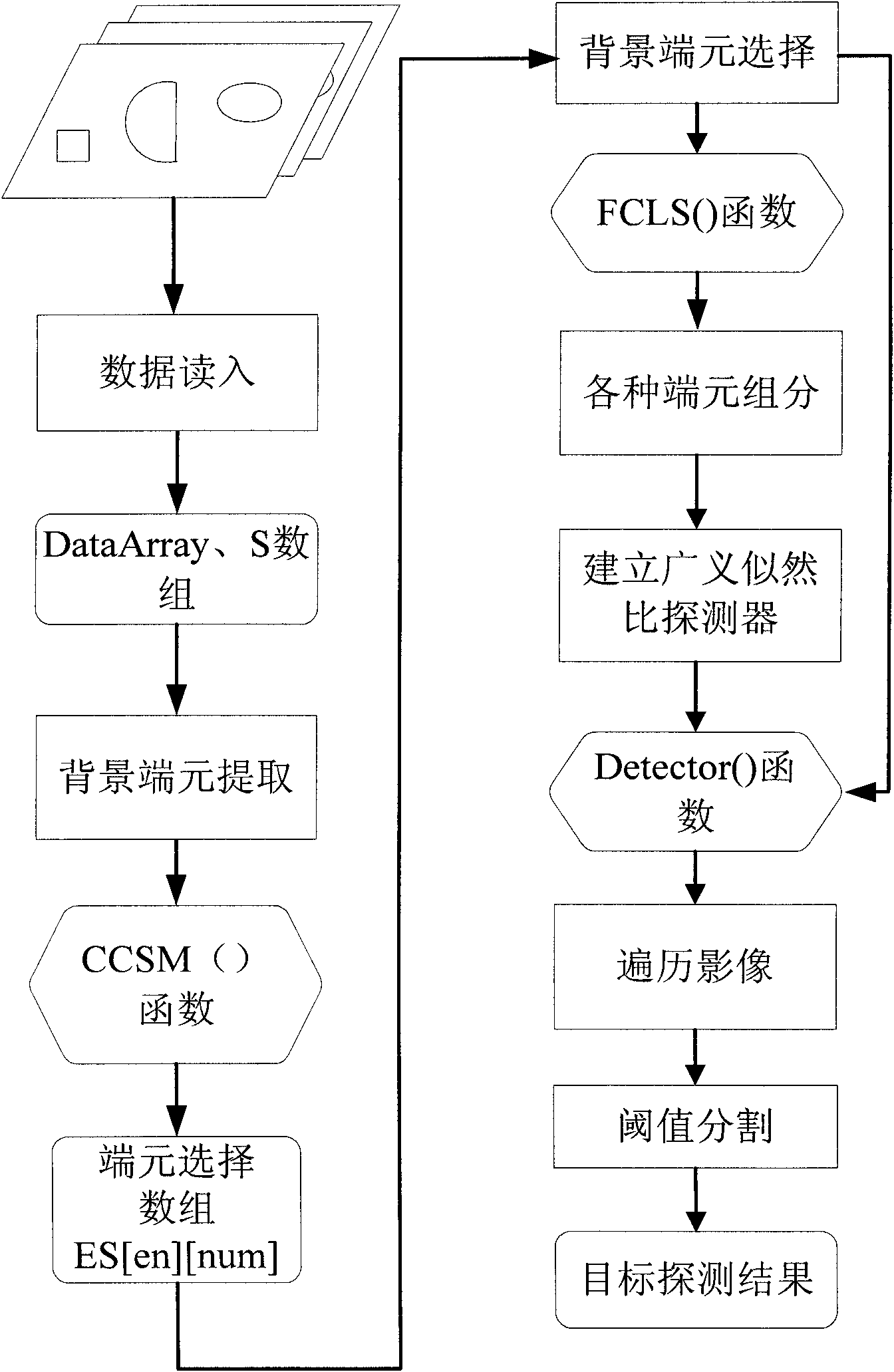
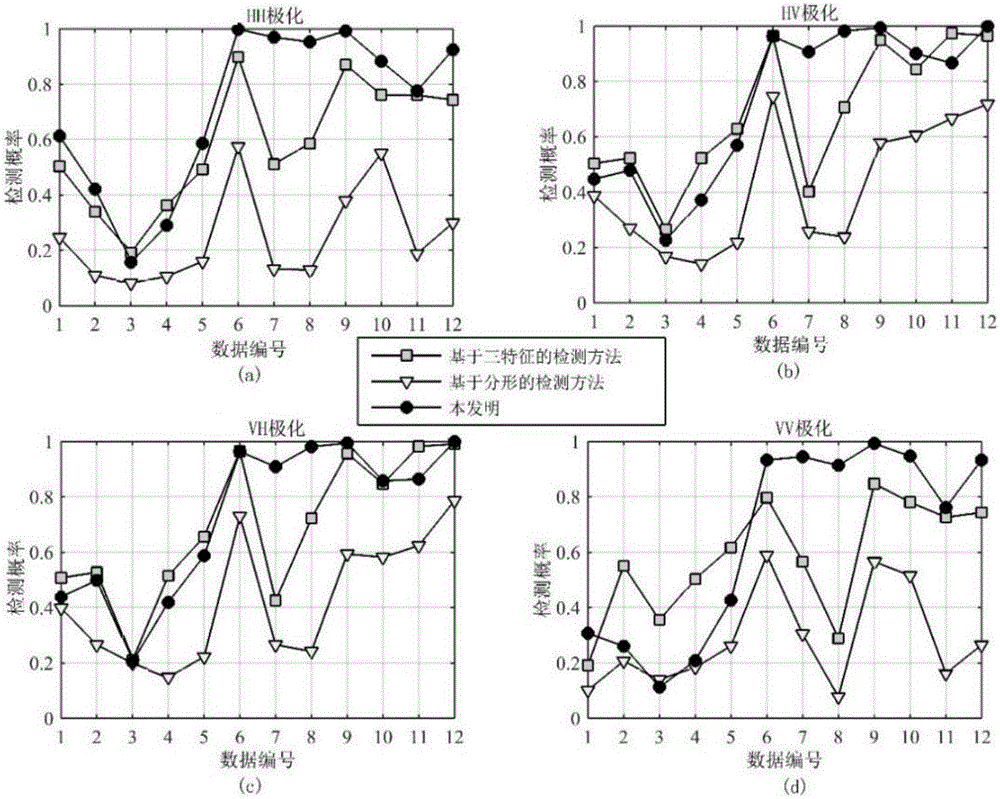
Hyperspectral remote sensing image target detecting method based on variable end members
InactiveCN101806898AReduce the impactImprove separabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationPrior informationDecomposition
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image target detecting method based on variable end members, comprising the following steps of: selecting a remote sensing image to be processed by target detection; acquiring prior information required for detection, wherein the prior information comprises spectral information of target end members and spectral information of background end members; traversing the remote sensing image to be detected by utilizing a cross correlation matching technique to determine the types of background end members in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected; carrying out spectral decomposition on the remote sensing image to be detected in a completely restricted least square way to acquire the component information of target end members and various background end members in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected; establishing a detector based on the GLRT (Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test); and traversing the remote sensing image to be detected by adopting the detector to acquire the detection function value of each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected, thereby judging whether targets exist in each pixel in the remote sensing image to be detected or not. The method of the invention has the characteristics of strong structuration, high adaptability, self-organization and self-learning.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
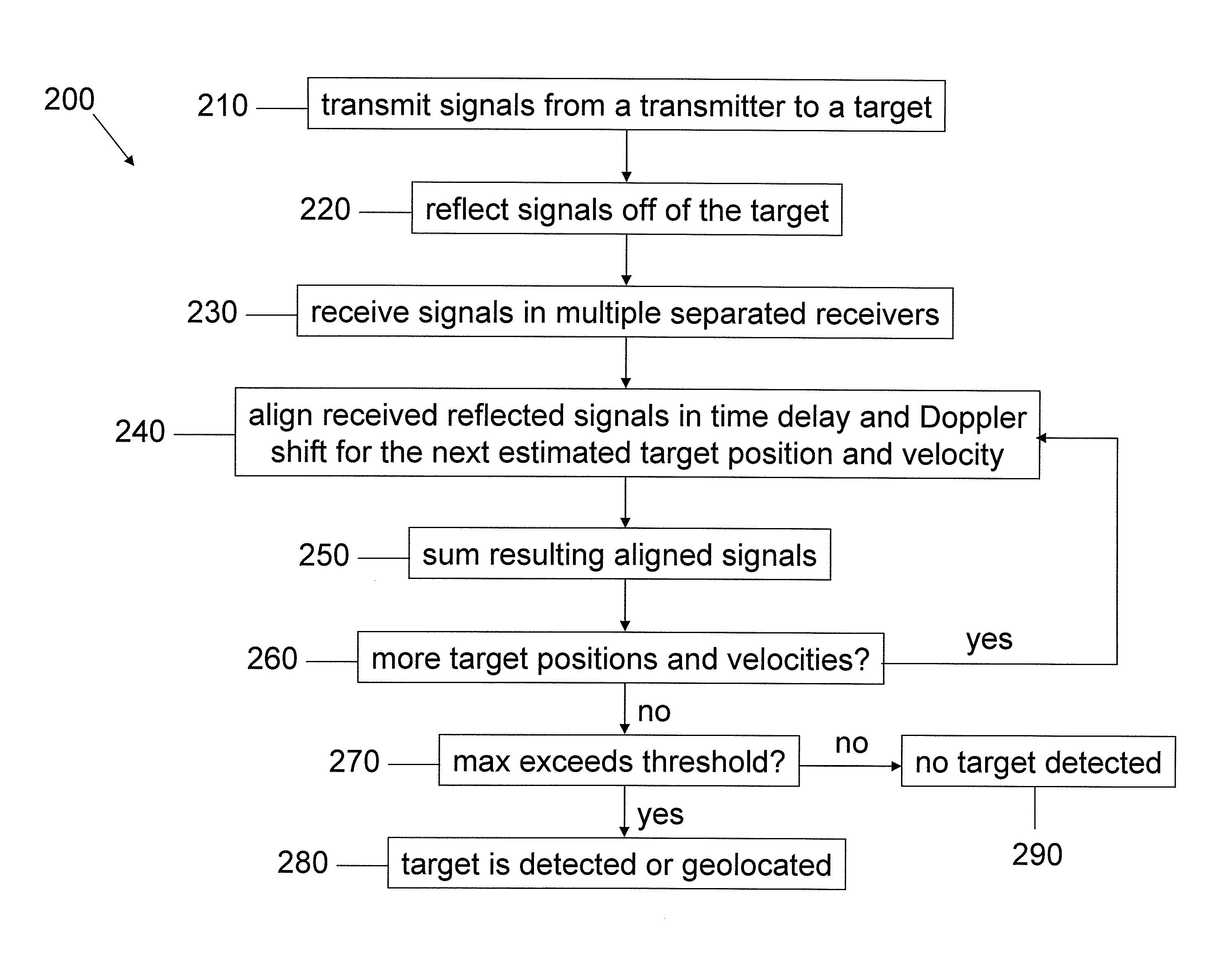
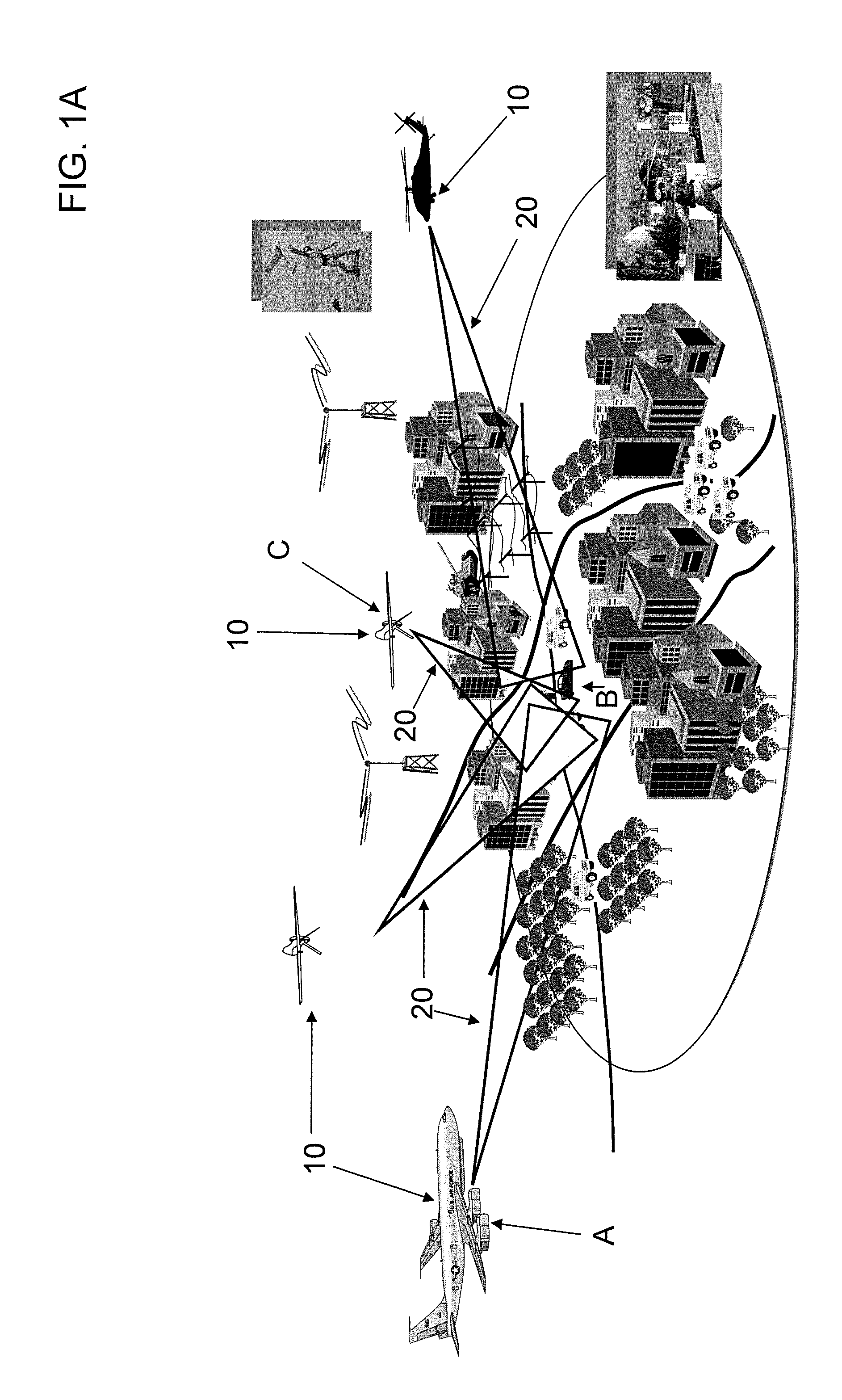
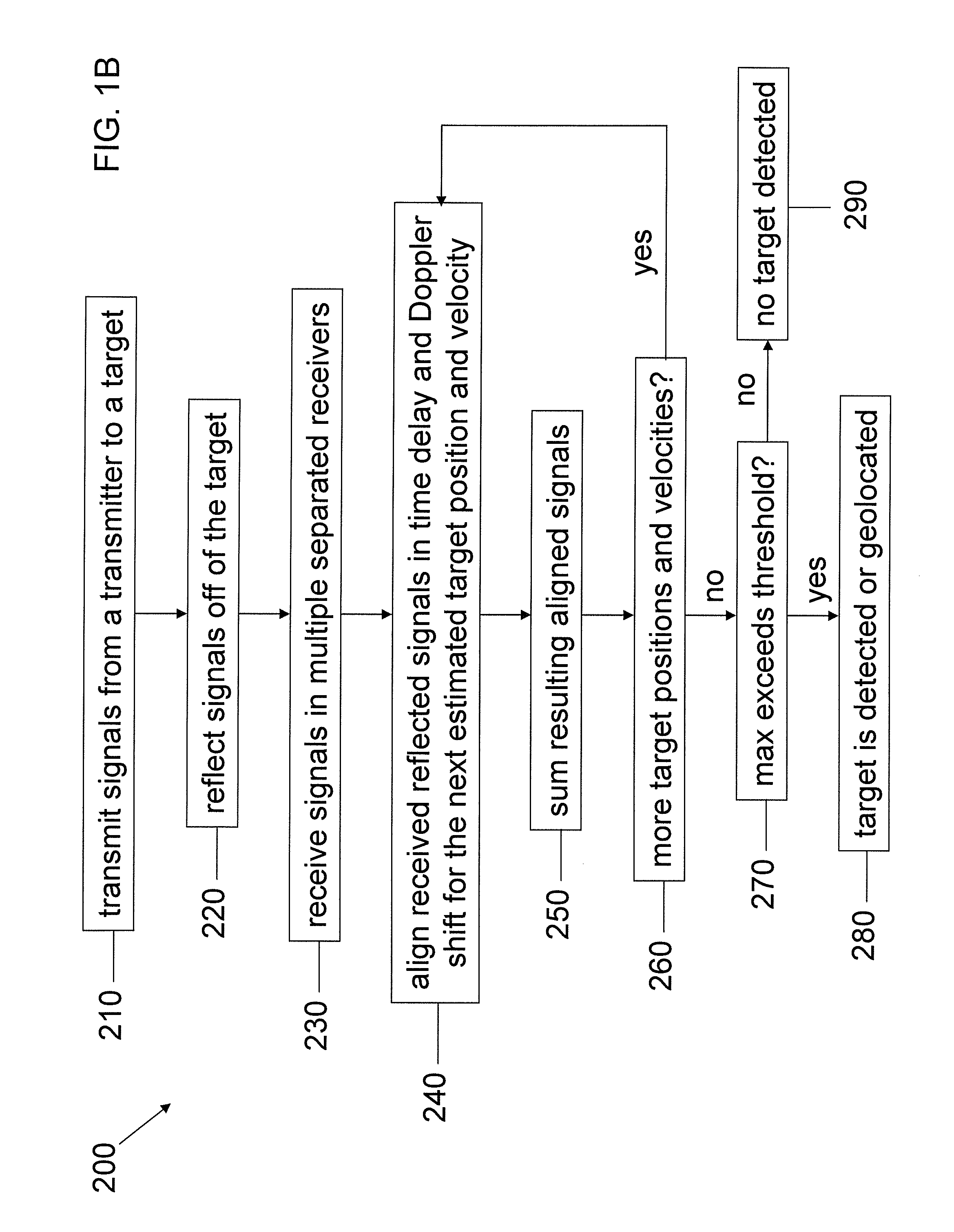
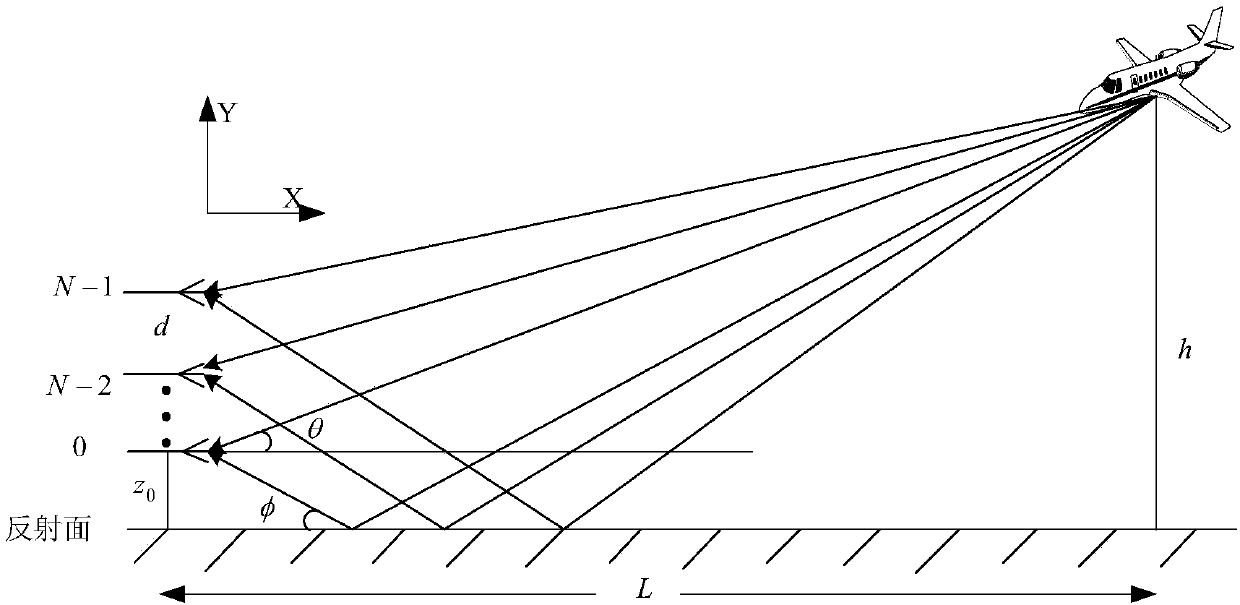
Multistatic target detection and geolocation
InactiveUS20120056772A1Improve detection accuracyImprove geolocation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime delaysRadar
Aspects of this invention are directed to the substantially improved detection and geolocation accuracy of targets (stationary or moving) by using the coherent data received at multiple airborne sensors. Further aspects are directed to aligning the (unknown) time-delayed and Doppler-shifted signals received at the multiple sensors relative to an arbitrary reference sensor, which depend on the unknown target position. This results in the target position and velocity vectors being simultaneously estimated and the detection peak enhanced by obtaining near coherent gain. Still further aspects are directed to the coherent generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) and the minimum variance distortionless response (MVDR) statistic for multistatic radar systems, conditioned on estimation of certain parameters that render the system coherent. Analytical and computer simulation results are presented to show substantially enhanced detection and geolocation of moving targets in clutter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
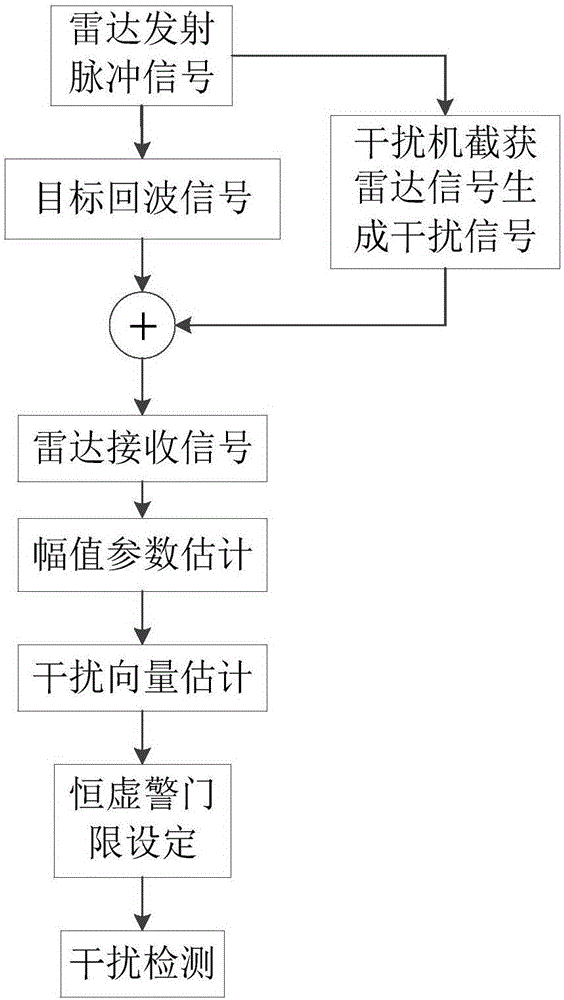
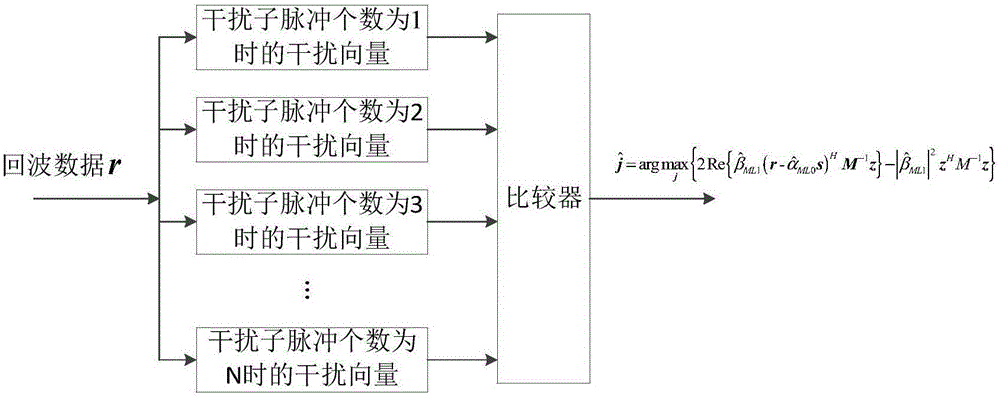
Detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference
ActiveCN105137396ASimple methodHigh accuracy of interference detectionWave based measurement systemsLikelihood-ratio testRadar signal detection
The invention discloses a detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference, belonging to the radar signal detection technology field and particularly relating to the radar interference signal detection technology. The detection method disclosed by the invention comprises steps of utilizing a generalized likelihood ratio method to perform estimation on unknown amplitude parameters in an echo signal and an interference vector, respectively obtaining maximum likelihood estimation value, and bringing the unknown amplitude parameter and the interference vector maximum likelihood value into the generalized likelihood ratio detector to detect interference. The detection method for SMSP interference and C&I interference improves interference detection accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for volumetric tumor segmentation using joint space-intensity likelihood ratio test
A method for segmenting a digitized image includes providing a digitized volumetric image comprising a plurality of intensities corresponding to a domain of points in an N-dimensional space, identifying a target structure in said image, forming a window about said target structure whose size is a function of the target scale, and performing a joint space-intensity-likelihood ratio test at each point within said window to determine whether each said point is within said target structure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
GLRT (General Likelihood Ratio Test) detection method based on oversampling
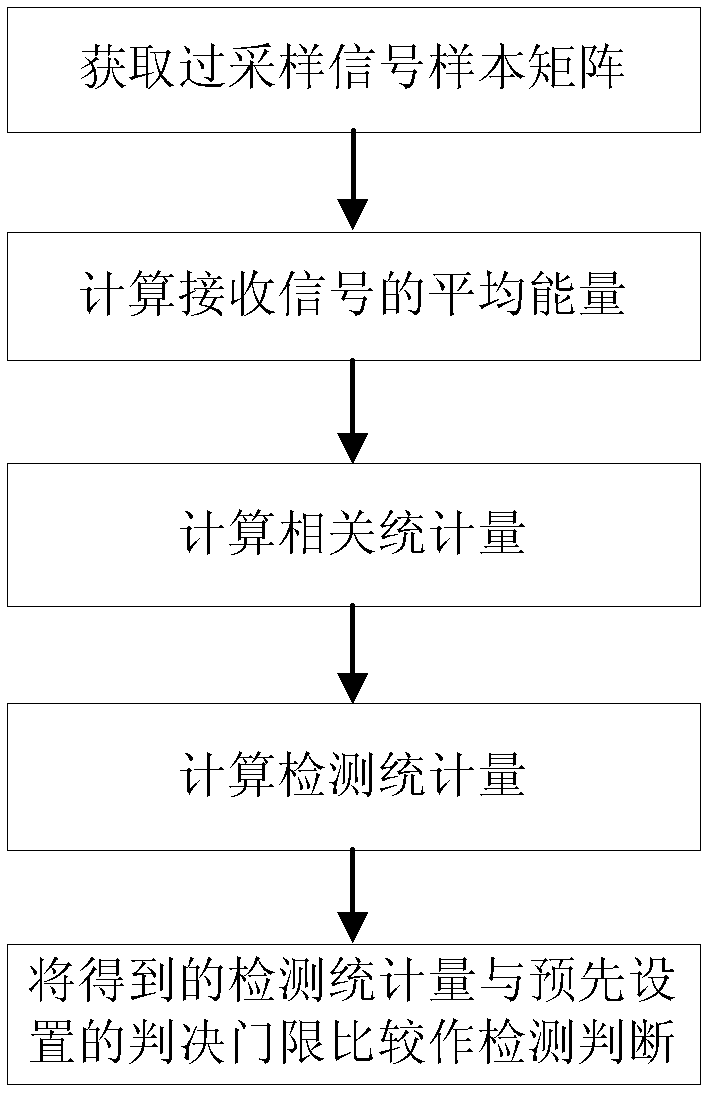
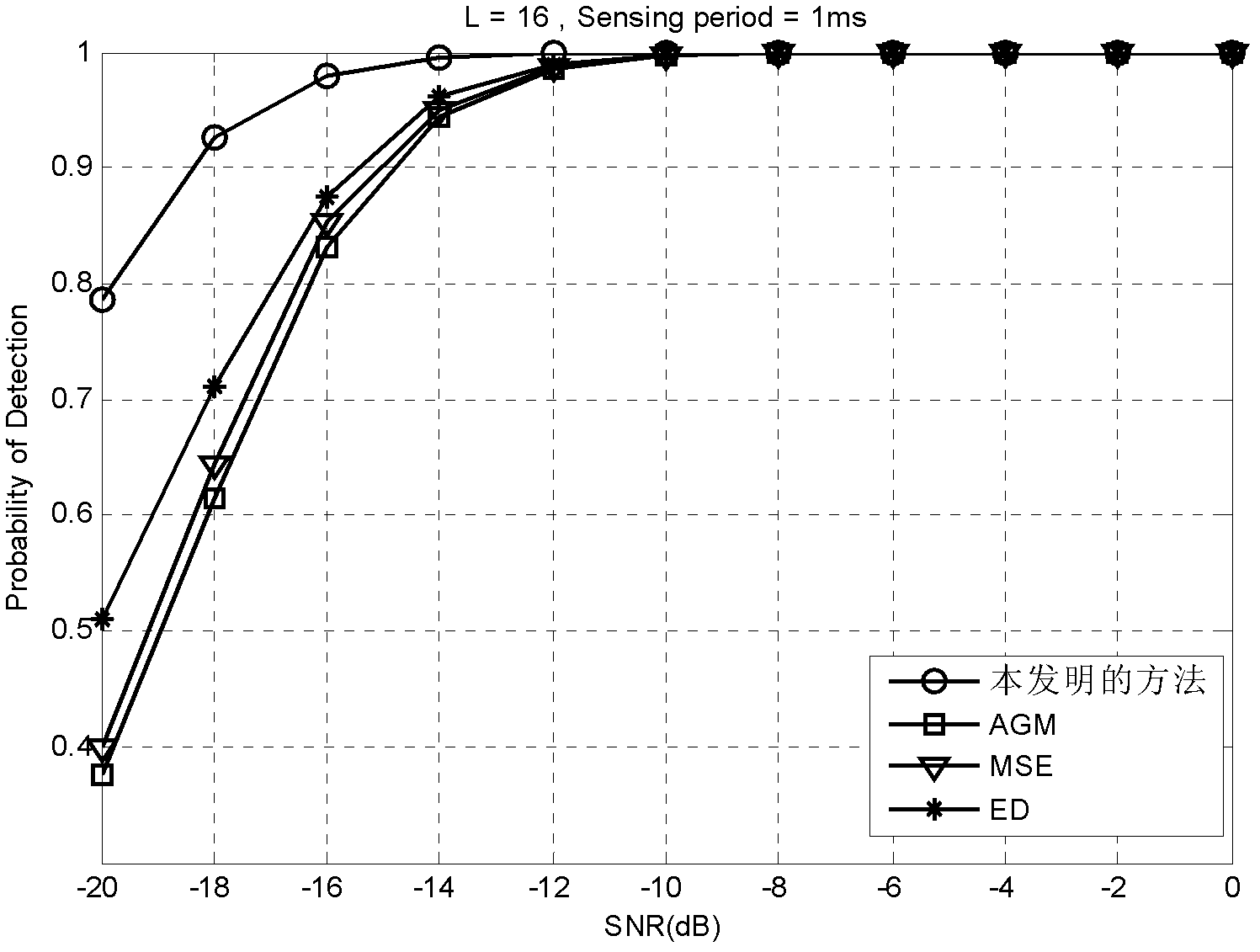
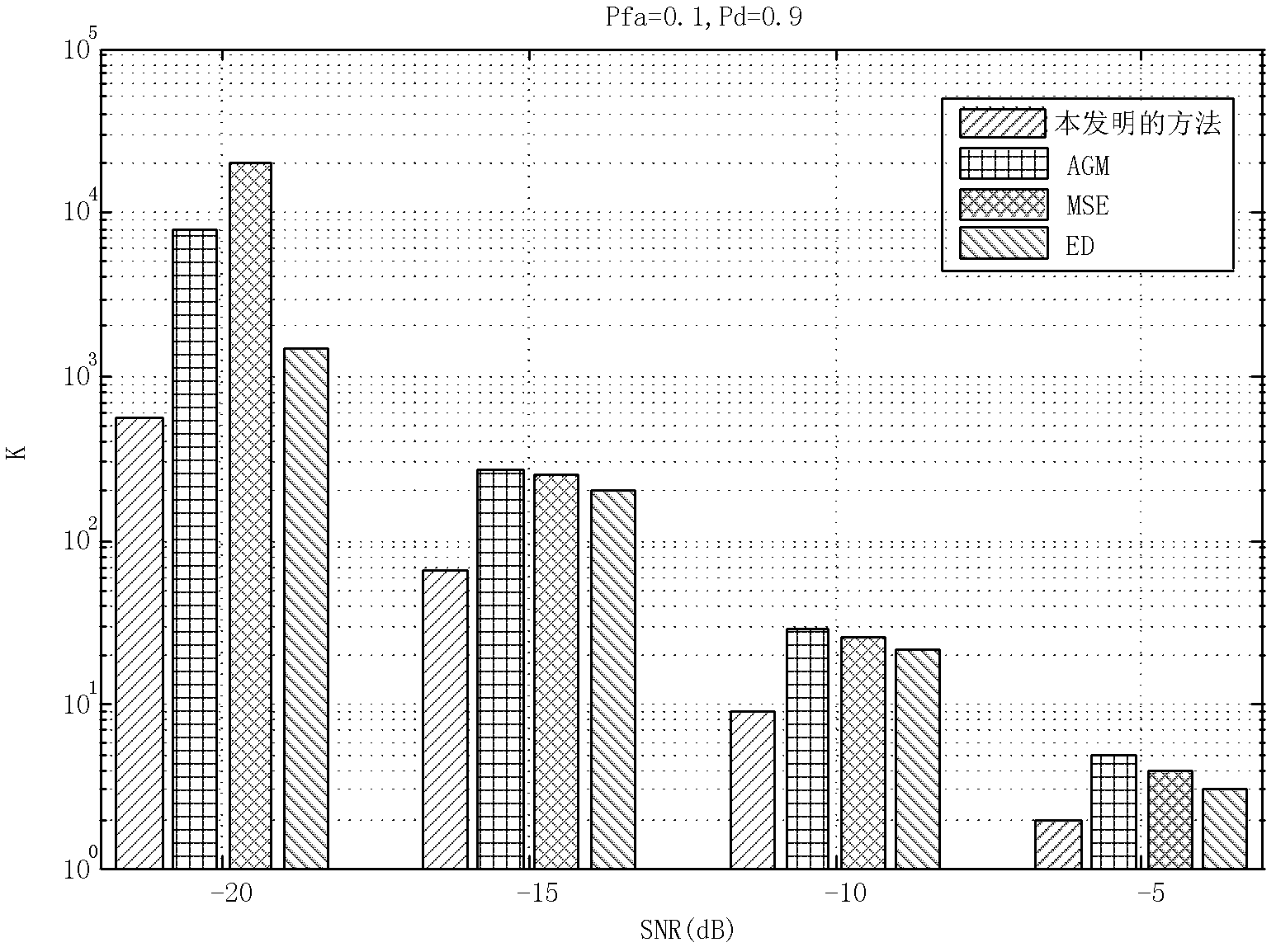
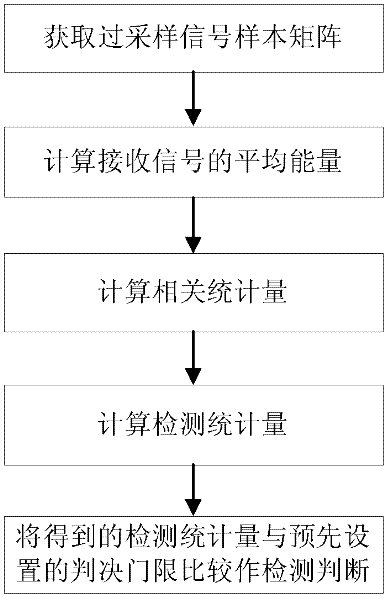
InactiveCN102404063AImprove robustnessHigh real-time requirementsTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumTime correlation
The invention discloses a GLRT (General Likelihood Ratio Test) detection method based on oversampling, which is proposed for the problem that the signal correlation cannot be utilized and large quantities of signal samples cannot be accumulated in a short time in the current GLRT detection algorithm. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: obtaining an oversampled signal sample matrix; calculating average energy of the received signals; calculating associate statistics; calculating detection statistical quantity; and comparing the obtained detection statistical quantity withthe predefined judgment threshold for detection and judgment. By the way of oversampling the received signals to obtain the average energy of the received signals and utilizing the time correlation of the MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) channel in calculation of the statistical quantity, the GLRT detection method based on oversampling disclosed by the invention has better detection performance, is not influenced by the noise variance estimation error and has strong robustness on the noise variance error, compared with the traditional frequency spectrum algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Space-time correlation GLRT (generalized likehood ratio test) method based on oversampling
InactiveCN102412918AImprove robustnessEasy to detectTransmission monitoringError prevention/detection by diversity receptionSpatial correlationFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a space-time correlation GLRT (generalized likehood ratio test) method based on oversampling. The method comprises the following specific steps: acquiring an oversampling signal sample matrix; calculating the average energy of receiving signals; calculating correlative statistic; calculating test statistic; and comparing the obtained test statistic with a preset judgment threshold to perform test judgment. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the average energy of the receiving signals is obtained through oversampling the receiving signals; and in the process of calculating the test statistic, the U calculation correlative statistic is obtained through utilizing the space-time correlation of an MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) channel, namely utilizing the space-time correlation matrix eigen value decomposition of a normalization channel, so that compared with the existing frequency spectrum detection algorithm, the method disclosed by the invention has better detection performance, cannot be affected by noise variance estimation error and has strong robustness to the noise variance estimation error.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
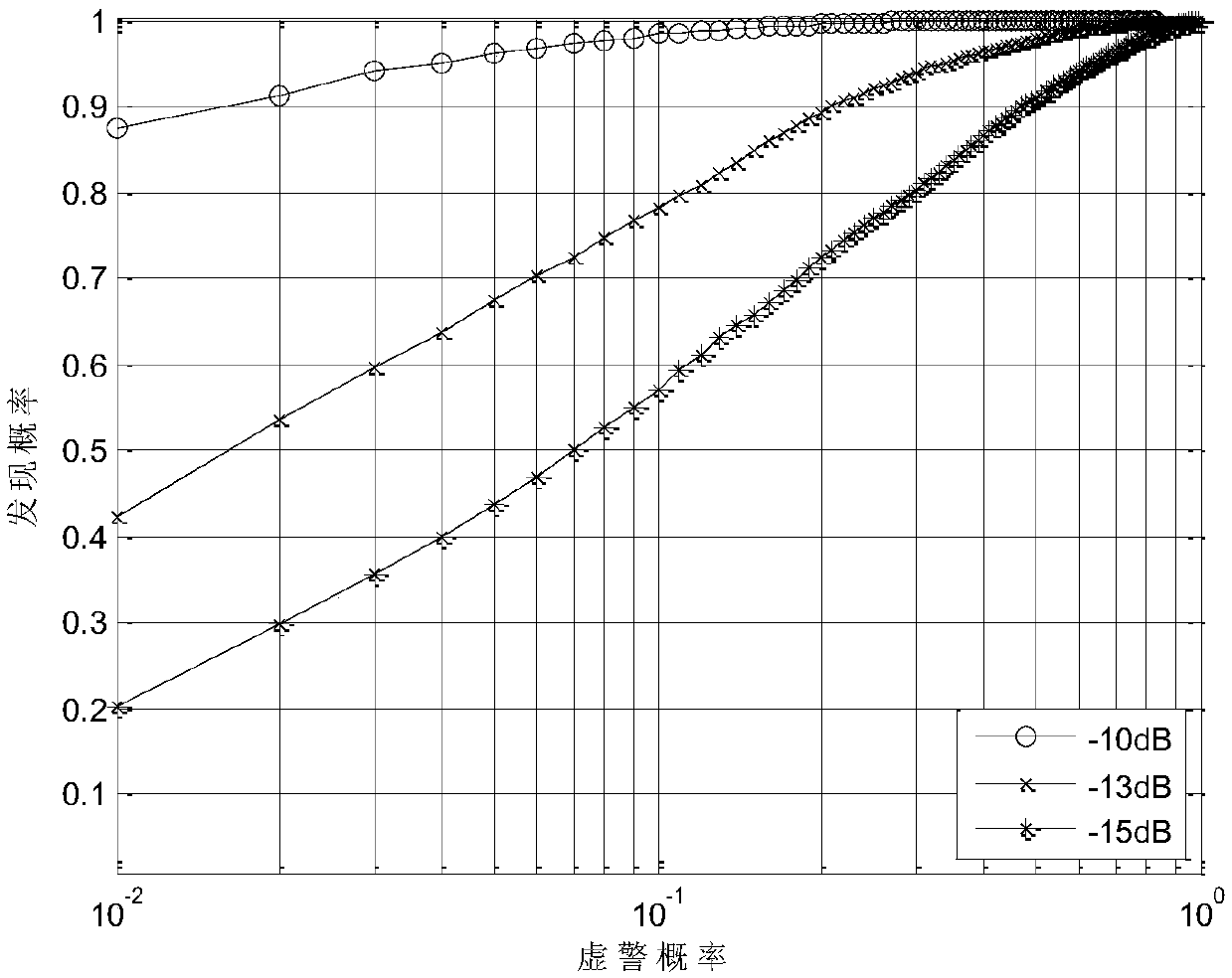
Noise robustness endpoint detection method based on likelihood ratio test
InactiveCN103730124AImprove robustnessExcellent multi-VAccSpeech analysisRobustificationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention discloses a noise robustness endpoint detection method based on a likelihood ratio test. The improvement is achieved from the three aspects of signal to noise ratio estimation, threshold value robustness setting and trailing distortion elimination respectively, so that the suggested algorithm has a better detection property under a low signal to noise ratio environment, in particular under a non-stationary noise environment compared with the prior art. The method and a multi-observation likelihood ratio test algorithm based on harmonic wave features have similar voice boundary detection accuracy, however, the method can have better voice detection precision than the multi-observation likelihood ratio test algorithm based on the harmonic wave features, and therefore it can be proved that the method is more excellent in performance than a traditional method. Meanwhile, the method has the similar performance under the 15dB and 25dB signal to noise ratio, and it shows that the method has good robustness to noise. The noise robustness endpoint detection method can be used as an important and effective method for front end preprocessing of a voice recognition system or a voiceprint recognition system in an actual environment, and thus good application value can be achieved.
Owner:上海交通大学无锡研究院
Low density odd-even check code iterative sequencing statistical decoding method
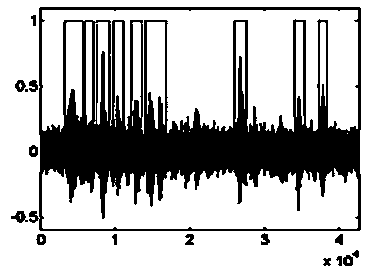
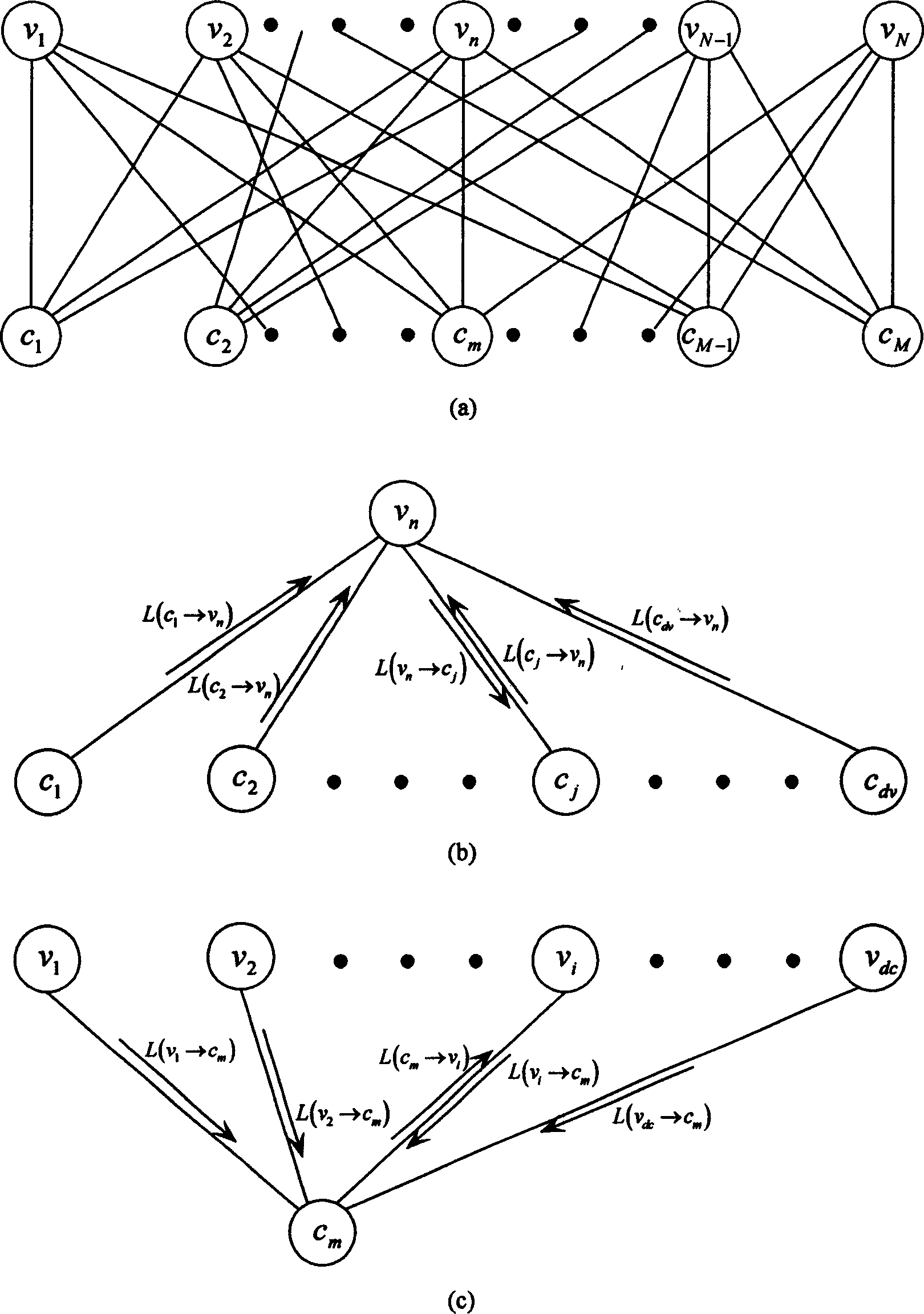
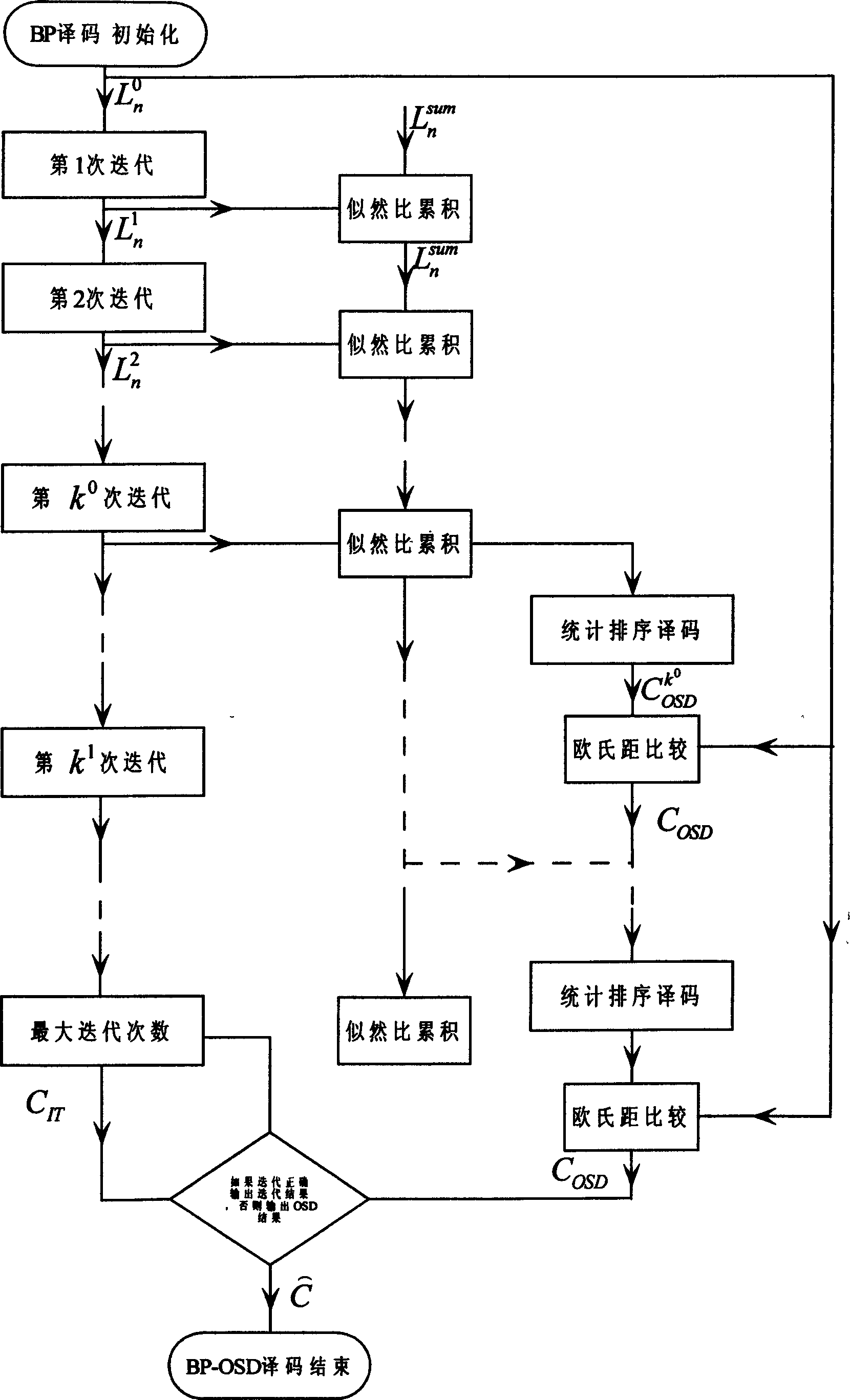
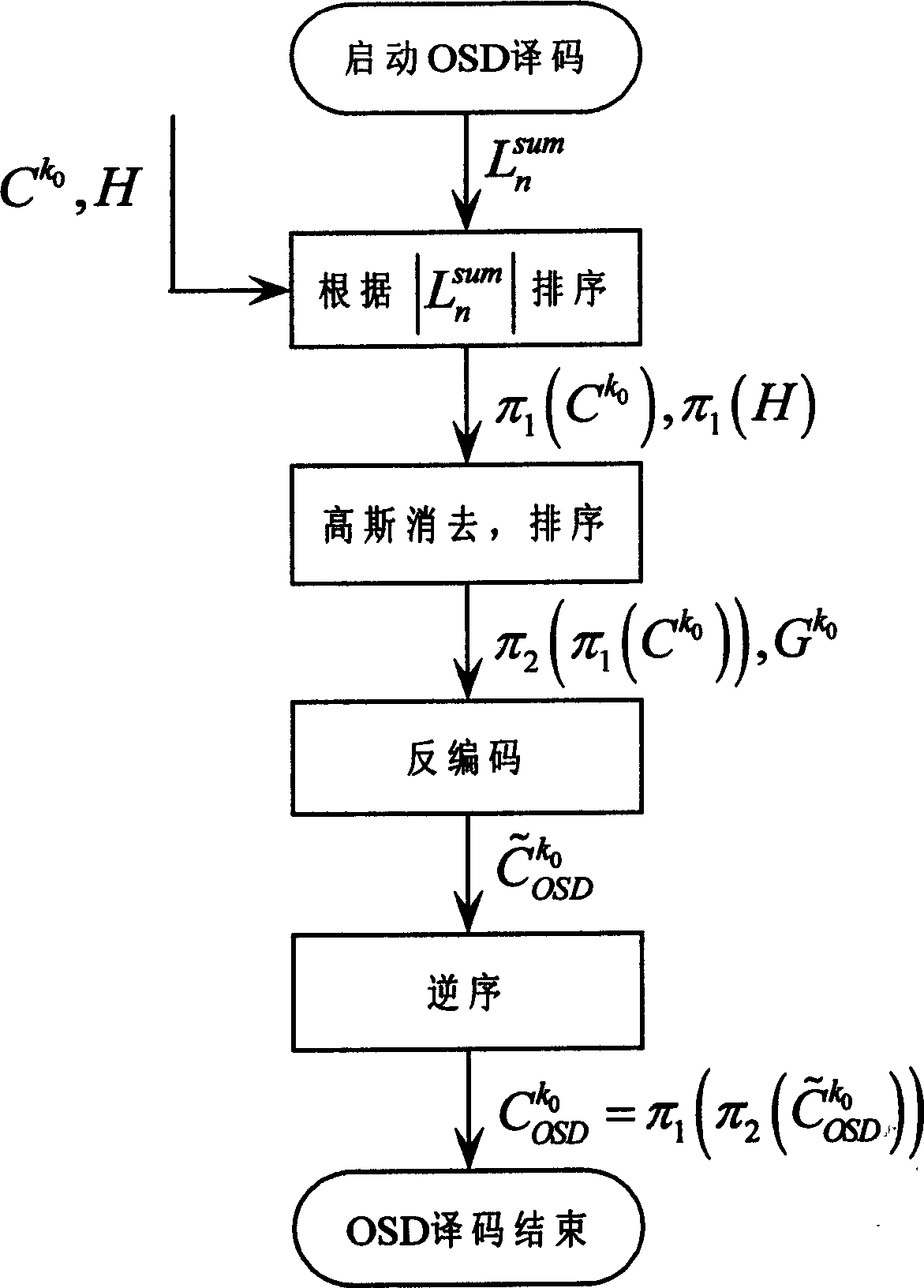
InactiveCN1859013ACorrectly decoded resultEliminate vibrationError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSingle error correctionLikelihood-ratio testLow density
This invention relates to an iteration sort statistic decode method for low density odd-even check codes (LDPC), in the process of decoding, a sort statistic decoding method is applied to assist the iteration decode based on the amplitude of the accumulation value of the likelihood ratio output in iteration each time by all variable nodes, namely, the variable nodes output and accumulate the likelihood ratios and the absolute value of the accumulated likelihood ratio is defined as the stability of the current iterated nodes then to sort the columns of the nodes and the check matrixes for ascending order based on the stability and carrying out gauss elimination to the sorted matrixes to generate a matrix combining the system after the gauss eliminatioin and code the sorted two stabilized node information sequences to get a set of code words for selection, if there is no final output for the iteration decode, then the code words for selection with the smallest Euclidean distance are selected and received as the decode output.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Simulation method of MIMO radar target detection under non-Gaussian clutter environment
InactiveCN102520400ADetection performance dropsEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsRadarLikelihood-ratio test
The invention discloses a simulation method of MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) radar target detection under non-Gaussian clutter environment. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a target detection model based on the auxiliary data which is close to a detected unit and does not contain the target; substituting a likelihood function with a detection signal to get the detection statistic; under a condition that a non-Gaussian clutter covariance matrix is known, obtaining a theoretical MIMO radar target detector by using a generalized likelihood ratio test theory. Under a condition that the non-Gaussian clutter covariance matrix is unknown, an appropriate clutter covariance matrix is estimated based on the auxiliary data, and the generalized likelihood ratio is substituted by the estimated clutter covariance matrix, thus, a MIMO radar adaptive detector is proposed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method of approximating log-likelihood ratios in qam digital transmissions and relative qam soft-output de-mapper
ActiveUS20080232499A1Improve approximationError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLikelihood-ratio testSymbol of a differential operator
Log-likelihood ratios are approximated for encoded bits modulated with a 2m-ary QAM constellation. Each symbol of the constellation is identified by a respective string of m bits. The log-likelihood ratio of each bit of the m bits is approximated with a product λ of a respective factor by a respective variable D that depends on a received signal and on communication channel characteristics. The approximating includes determining a value of at least one of the variables D using a parametric nonlinear function of an equalized replica ≈ of a respective received signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Low-altitude target detection method for frequency diversity array radar
ActiveCN107607938ASuppression of SNR lossImprove target detection probabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLikelihood-ratio testPhased array
The invention discloses a low-altitude target detection method for a frequency diversity array radar, belonging to the field of phased array radar low-altitude target detection. According to the method, due to the scanning characteristics of an FDA radar, the beam direction of the radar is related to a radial distance and a frequency difference, by introducing a frequency difference between different transmitting elements, a signal-to-noise ratio loss brought by a multipath effect in a low-altitude target environment can be effectively suppressed. Then, a generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) method is used to derive an FDA radar low-altitude target detector, and a target detection probability can be effectively improved under a certain false alarm rate. Finally, through the design of sub modules of matrix multiplication, matrix determinant calculation the like, an FDA radar low-altitude target detector is realized in an FPGA hardware platform, and the real-time detection of the FDAradar low-altitude target detection is effectively improved. In summary, according to the method, in a low-altitude target environment, the scanning characteristics of the FDA radar can be used to effectively complete the detection of a low-altitude target, and the method has high practicability in modern warfare.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
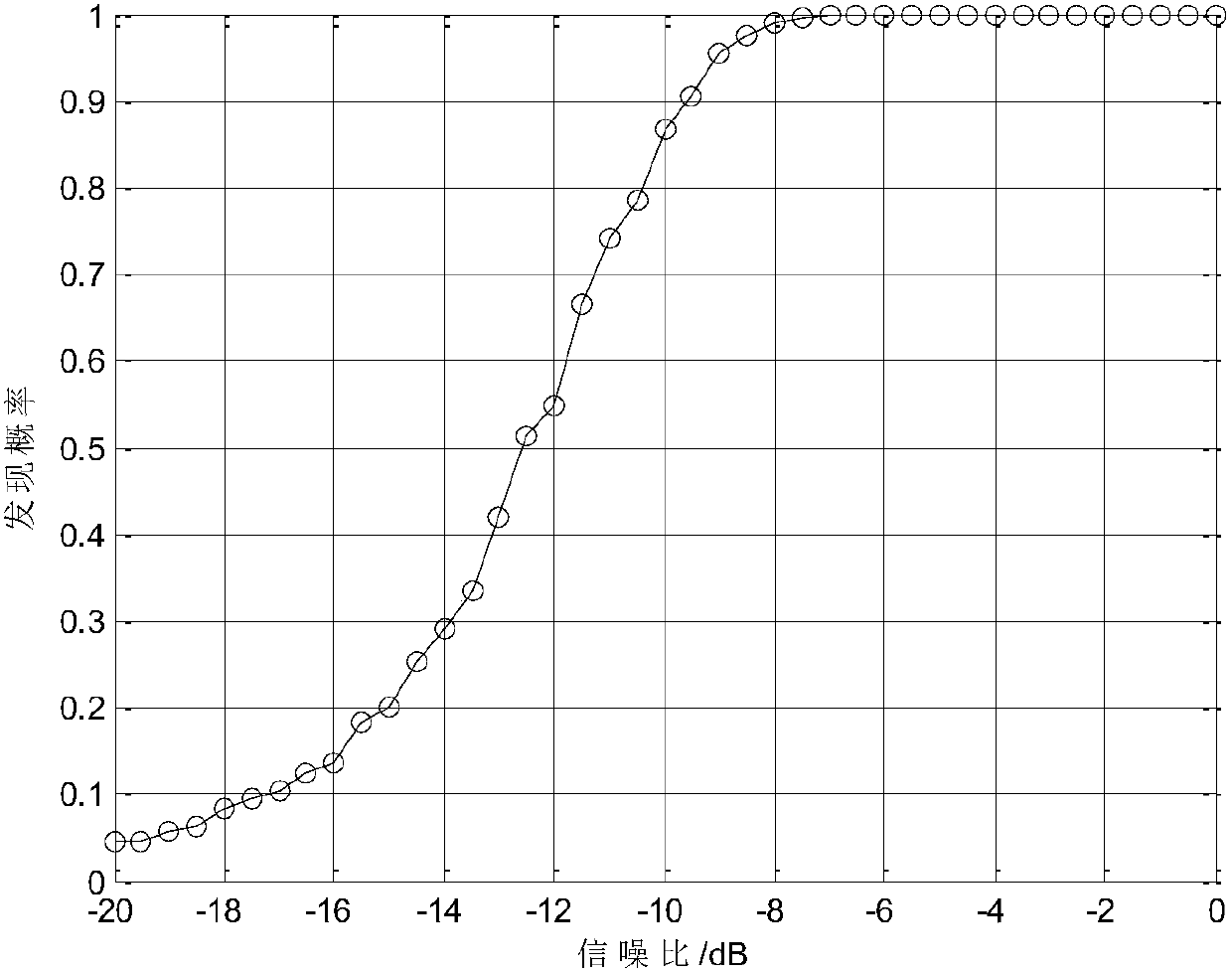
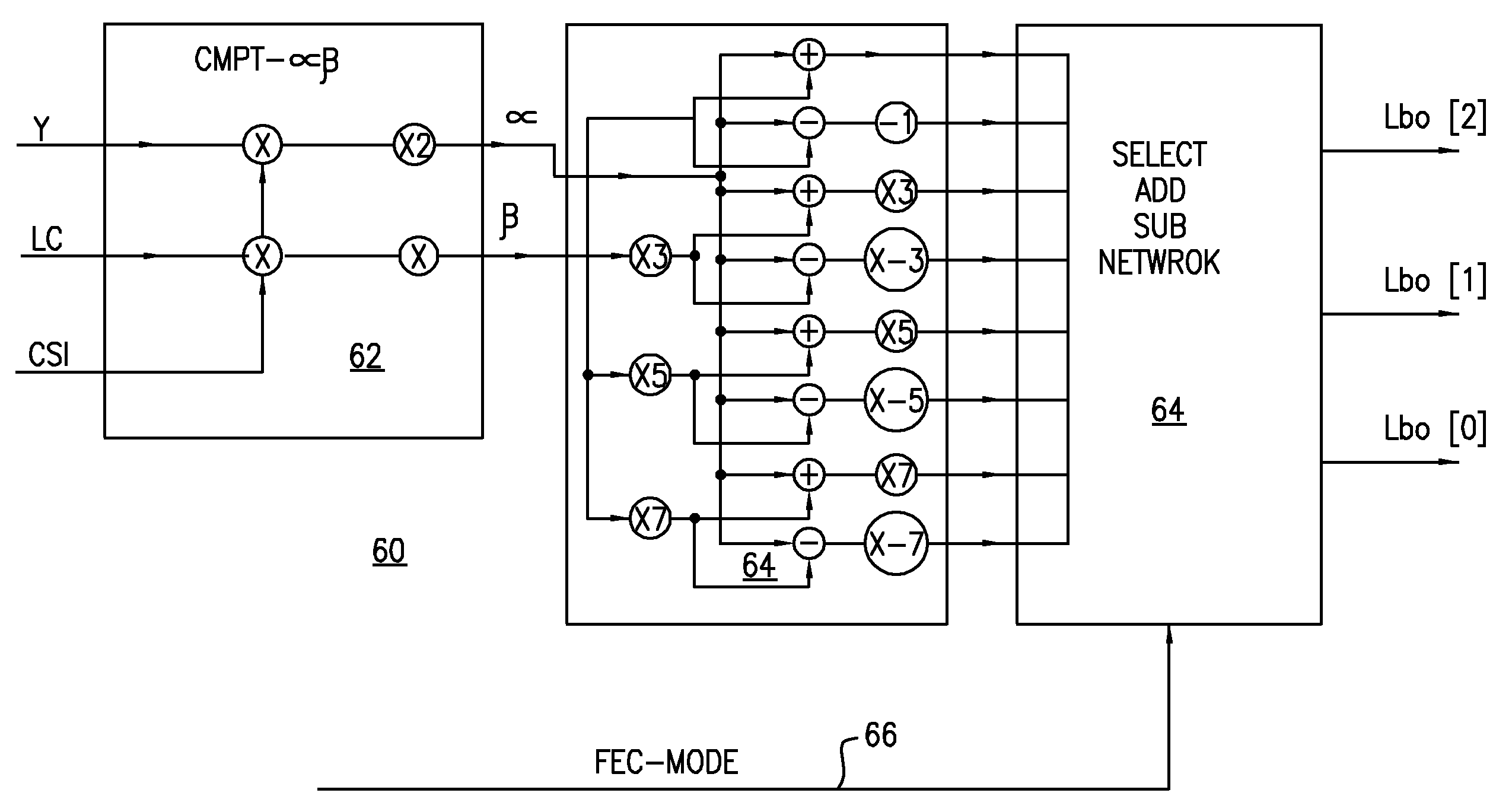
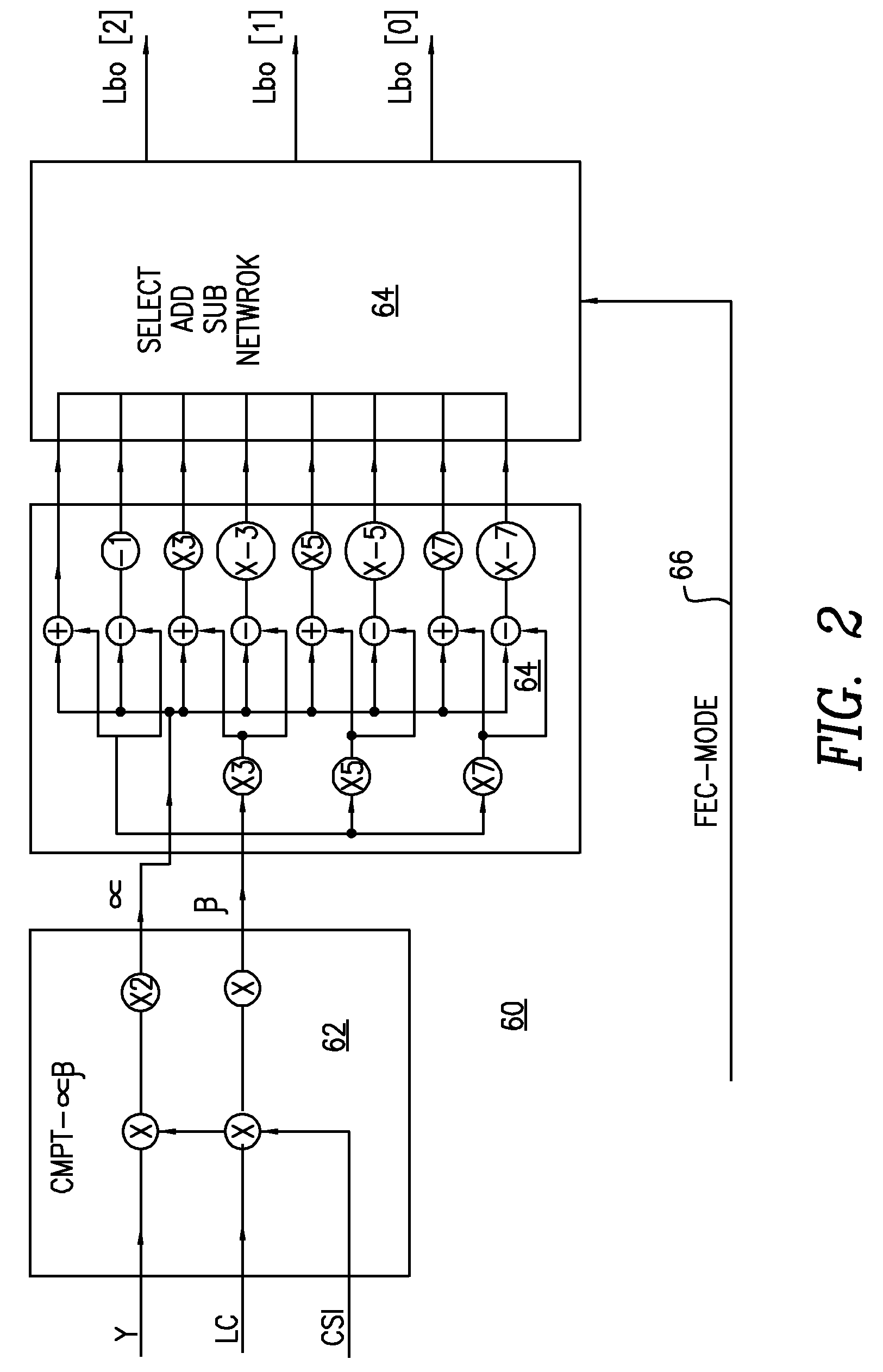
Method for forming a bit log-likelihood ratio from symbol log-likelihood ratio
InactiveUS20080107190A1Weight increaseIncrease probabilityError preventionSecret communicationCommunications systemForward error correction
In an OFDM (Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) communication system, a receiver comprising an inner forward error correction device, or an inner forward error correction device is provided. Either the inner forward error correction device, or the outer forward error correction device comprises an improved method for deriving a bit log-likelihood ratio derived from a symbol log-likelihood ratio. The method includes the steps of: providing two simplified parameters; and using the two simplified parameters in addition and subtraction only to derive the bit log-likelihood ratio derived from the symbol log-likelihood ratio.
Owner:LEGEND SILICON
Geographic space abnormal accumulation area scanning statistical method based on interaction force
ActiveCN106126918AImprove detection abilityEasy detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial Interaction ModelLikelihood-ratio test
The invention discloses a geographic space abnormal accumulation area scanning statistical method based on interaction force. The method comprises the following steps: based on a selected space adjacency type, establishing a spatial neighbor relation matrix; using a spatial interaction model to measure interaction strength between adjacent objects; based on a deep scan method or a breadth scan method, continuously selecting the adjacent objects whose interaction strength is maximum, and adding the adjacent objects into a candidate accumulation area, until the value of likelihood ratio LR / log-likelihood ratio LLR corresponding to high value anomaly accumulation no longer increases or the value of likelihood ratio LR / log-likelihood ratio LLR corresponding to low value anomaly accumulation no longer reduces or the candidate accumulation area reaches maximum specified dimensions, stopping to add the adding the adjacent objects into the candidate accumulation area; performing Monte Carlo simulation on the plurality of formed candidate accumulation areas, so as to detect an abnormal accumulation area which passes non-stochastic hypothesis testing. The method has stronger detection ability on abnormal accumulation areas which are in irregular shapes, and can easily detect the abnormal accumulation area which includes weak links, and non-abnormal geographic objects would not be included in the detected abnormal accumulation area.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Asymptotically optimal modulation classification method for software defined radios
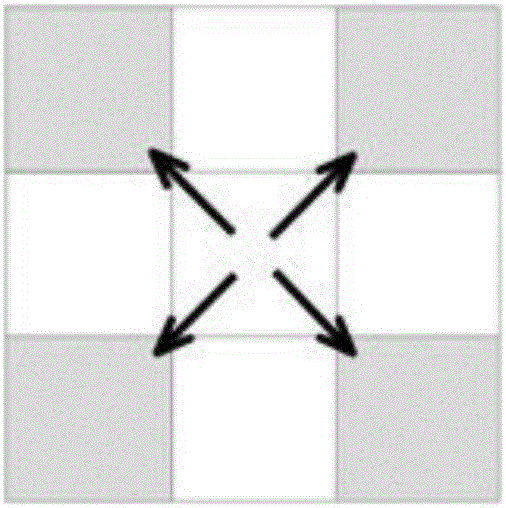
InactiveUS8223890B1Modulation type identificationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSoftware define radioClassification methods
A method for identifying the modulation scheme of a software defined radio in real-time without pilot symbols between transmitters and receivers, includes providing a predetermined look-up table (LUT) in the software-defined radio wherein the LUT is prepared by pre-calculating discrete likelihood ratio test (DLRT) function values; storing the pre-calculated DLRT values in said LUT; and indexing the pre-calculated DLRT values by addresses.
Owner:UNITED STATES REPRESENTED BY SEC OF THE ARMY
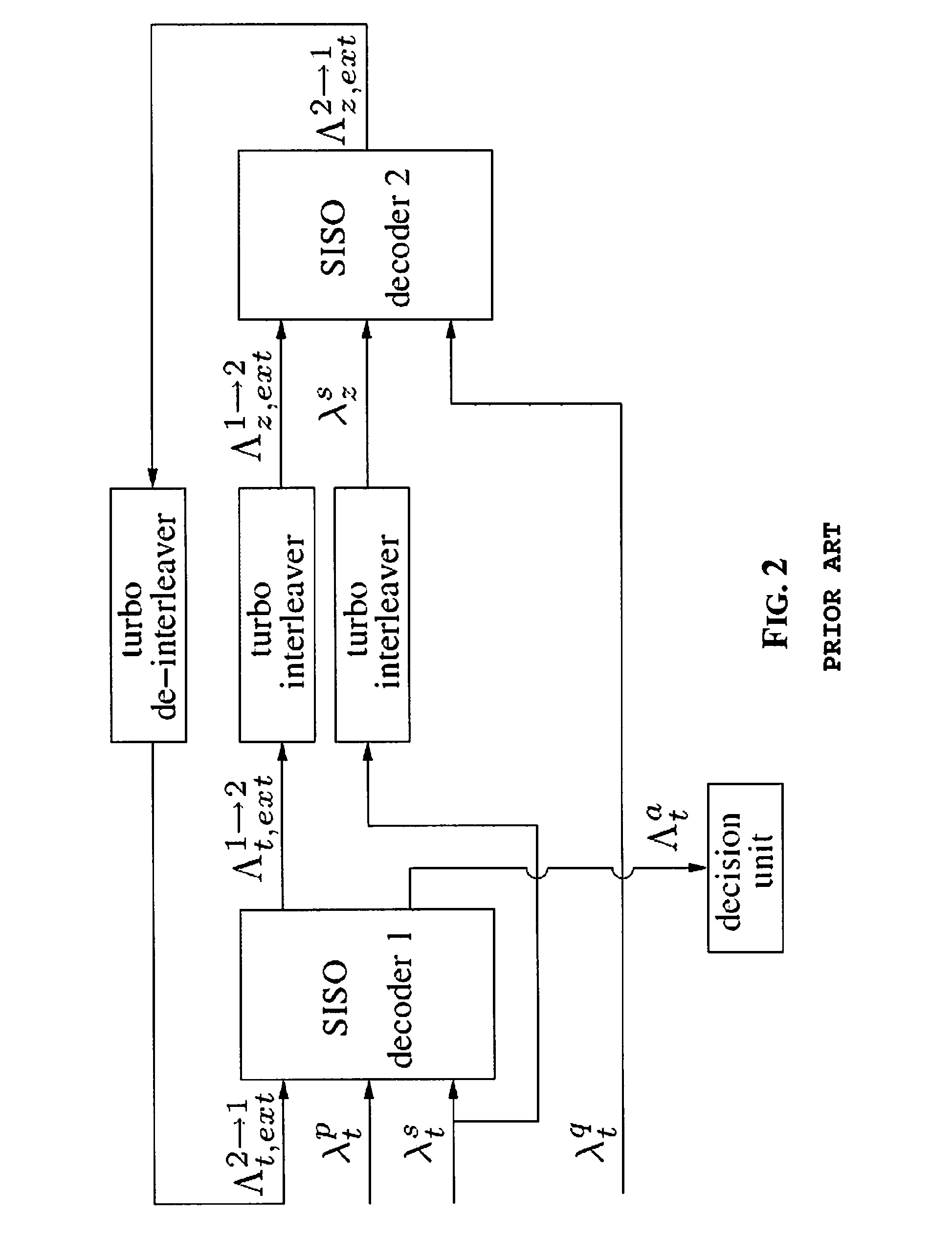
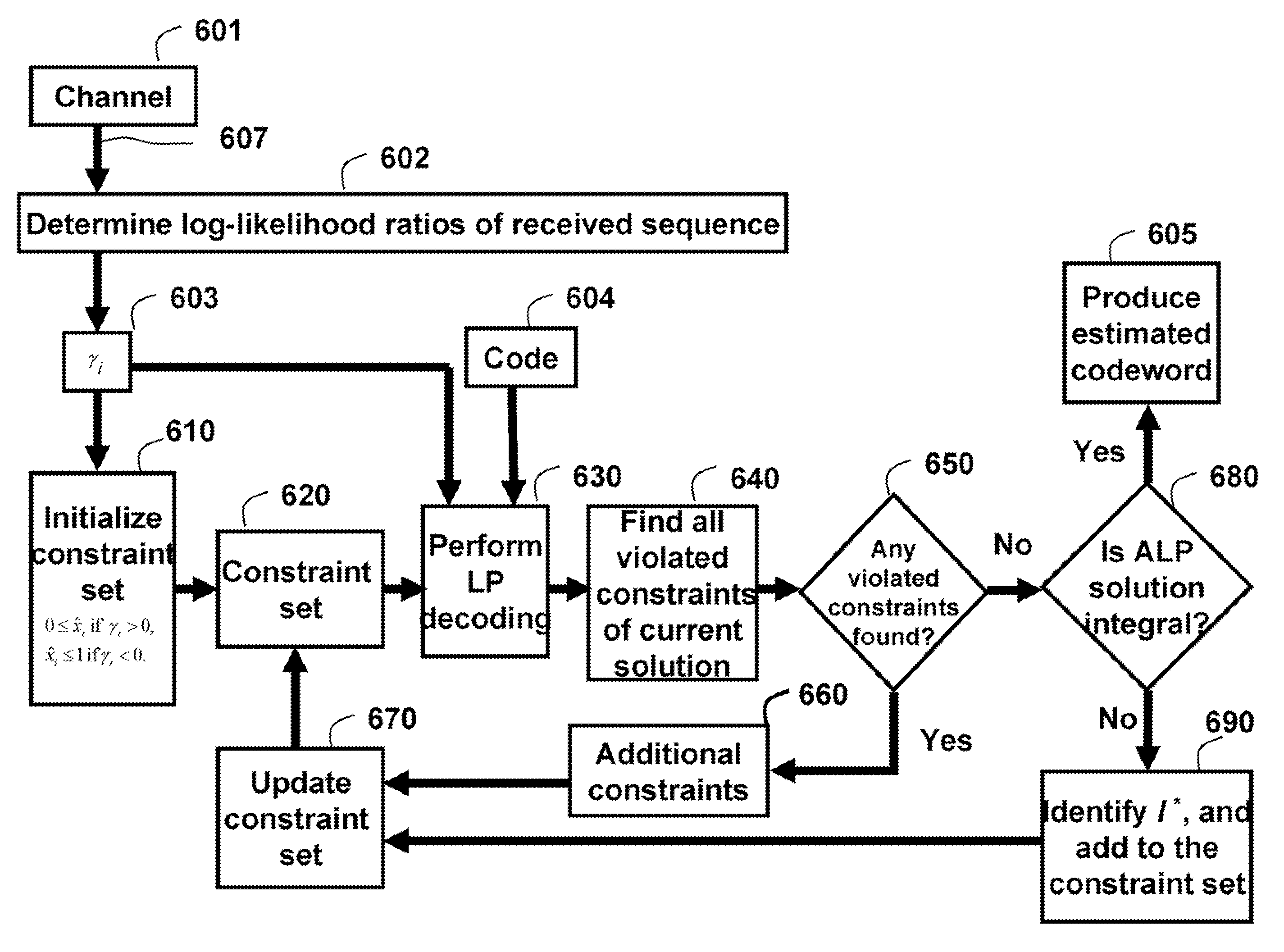
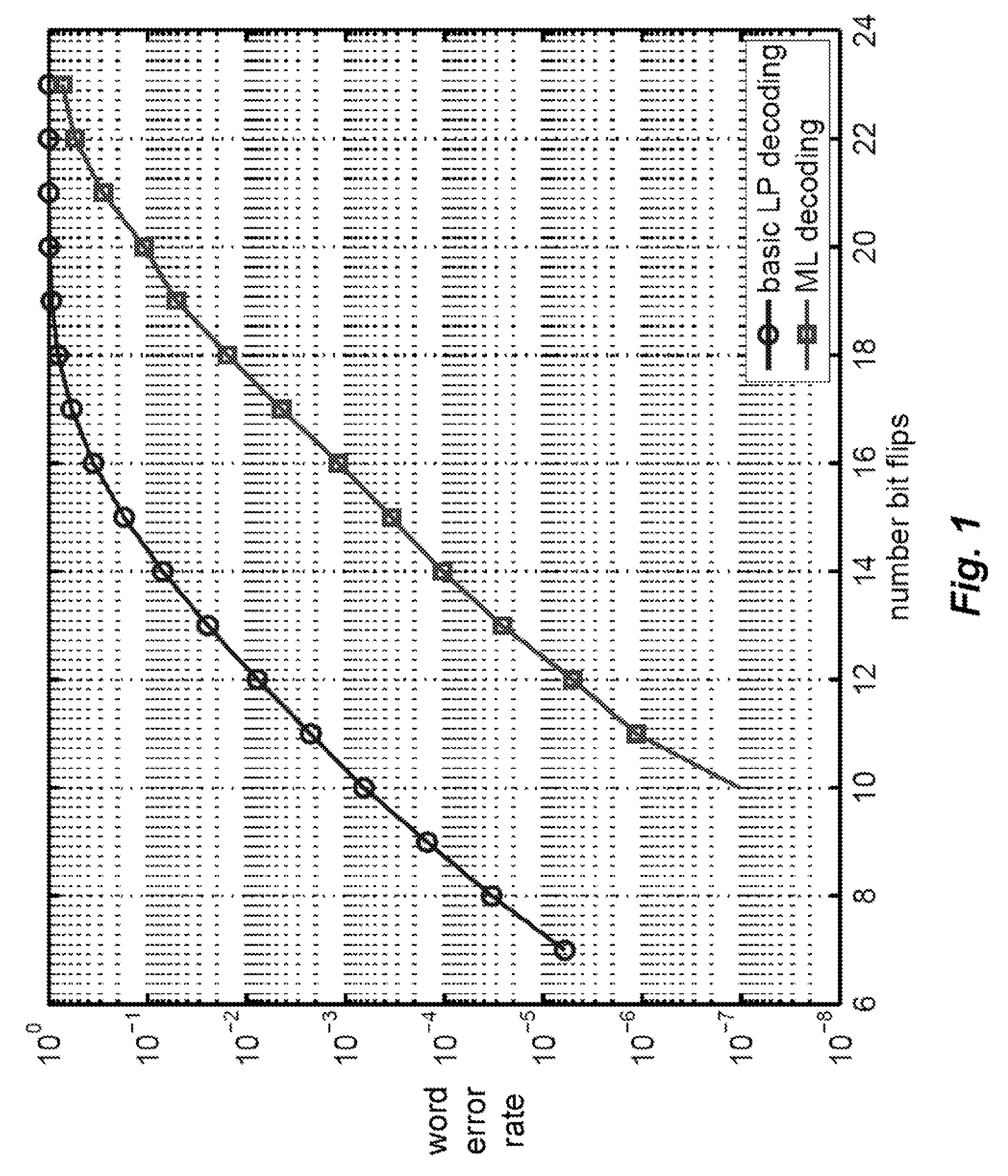
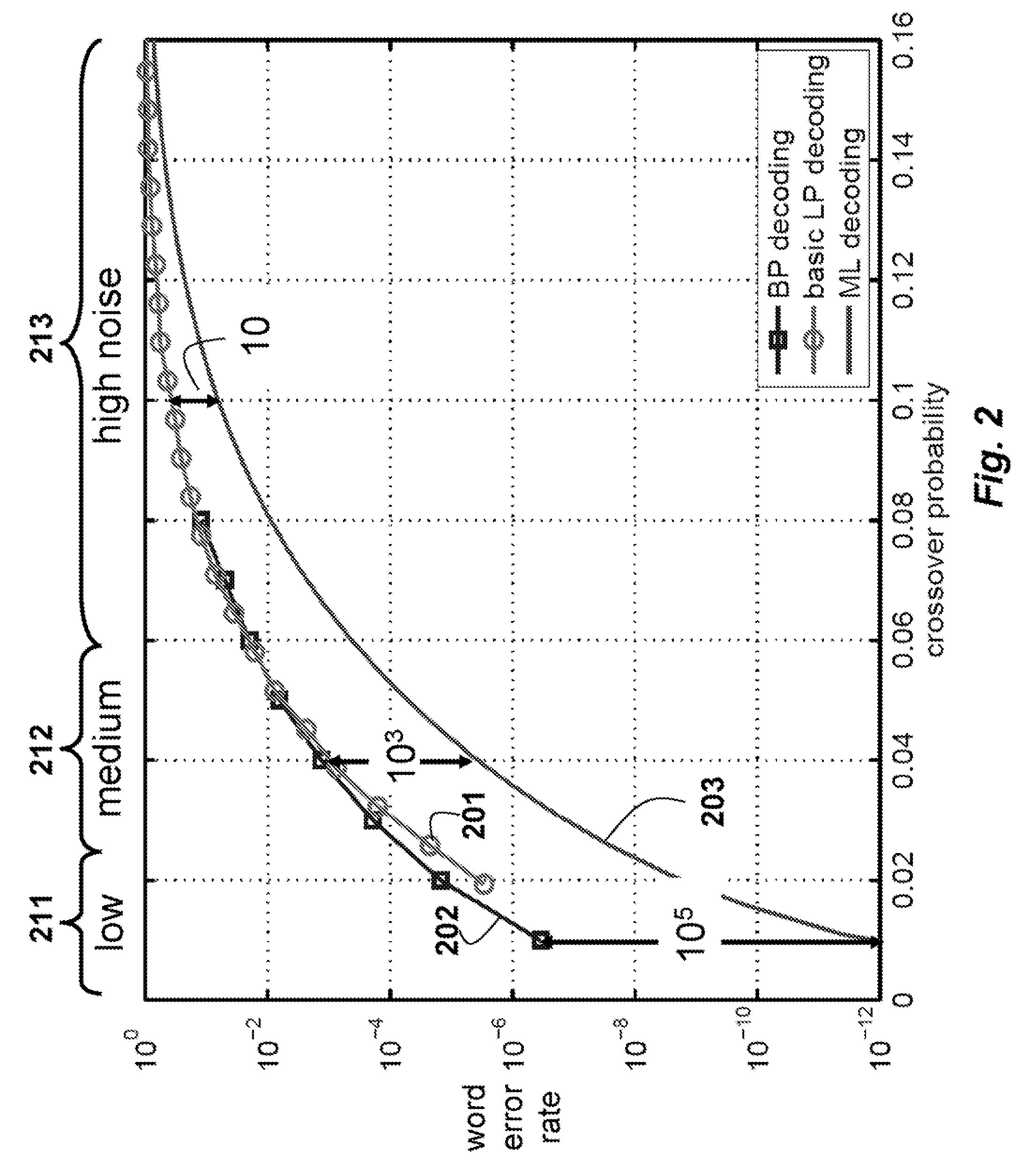
Maximum Likelihood Decoding via Mixed-Integer Adaptive Linear Programming
InactiveUS20080316069A1Extension of timeReduce error rateData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesLikelihood-ratio testLog likelihood
A method and system decodes a sequence of symbols received via a channel to a codeword of an error-correcting code. Log-likelihood ratios are determined from a sequence of symbols received via a channel. A set of constraints is initialized according to the log-likelihood ratios. An adaptive linear programming decoder is applied to the set of constraints and the log-likelihood ratios according to an error-correcting code to produce an estimate of the codeword and an updated set of constraints. If the estimate of the codeword is a non-integer pseudo codeword, further update the set of updated constraints with a set of integer constraints if the estimate of the codeword is the non-integer pseudo codeword, and proceeding with the applying step, and otherwise producing the estimate of the codeword as the final codeword.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Coherent detection method under complex Gaussian model based on inverse gamma texture
ActiveCN105093196AEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsLikelihood-ratio testDetection threshold
The invention belongs to the radar target detection technology field and discloses a coherent detection method under a complex Gaussian model based on an inverse gamma texture. By using the method, adaptive detection of a target under an uniform sea clutter background can be realized and detection performance is increased. The method comprises the following steps that a radar emits a pulse signal through a radar transmitter and receives an echo signal through a radar receiver; according to echo data, an observation vector of a detection unit and an observation vector of a reference unit are constructed; according to the observation vector of the detection unit and the observation vector of the reference unit in the echo data, a generalized likelihood ratio detector is constructed; a parameter in the generalized likelihood ratio detector is estimated so as to obtain an optimal coherent detector; according to a preset false alarm probability, a detection threshold is calculated; according to the detection threshold, the optimal coherent detector is used to detect a target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
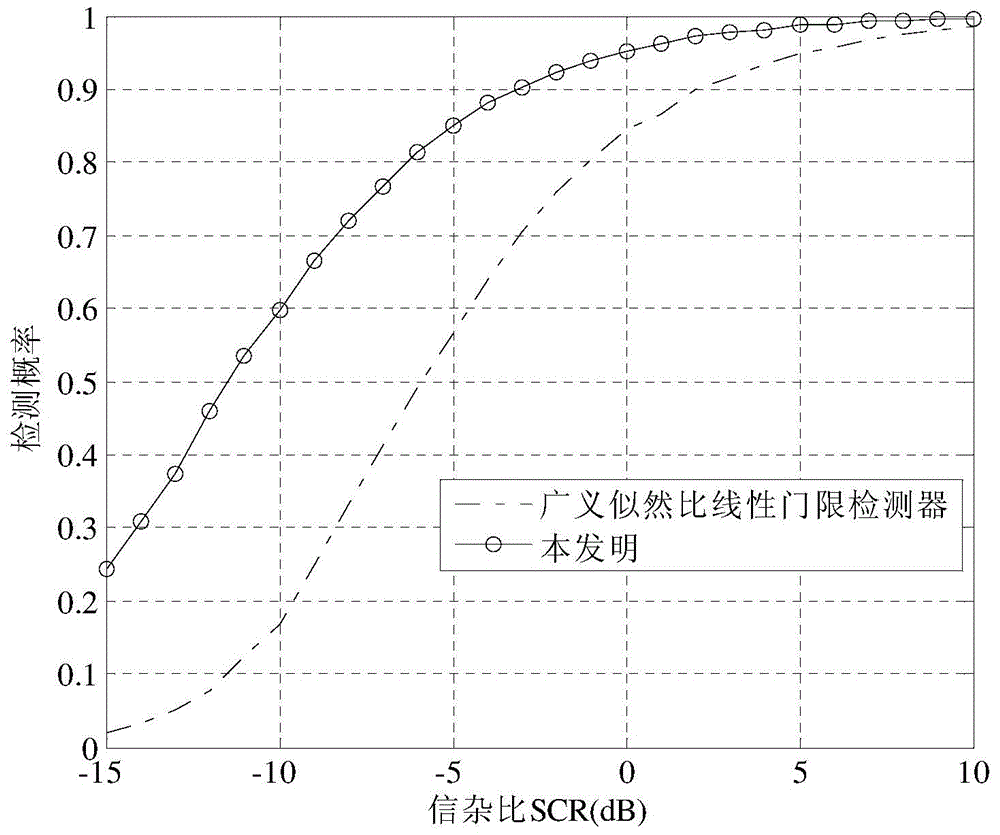
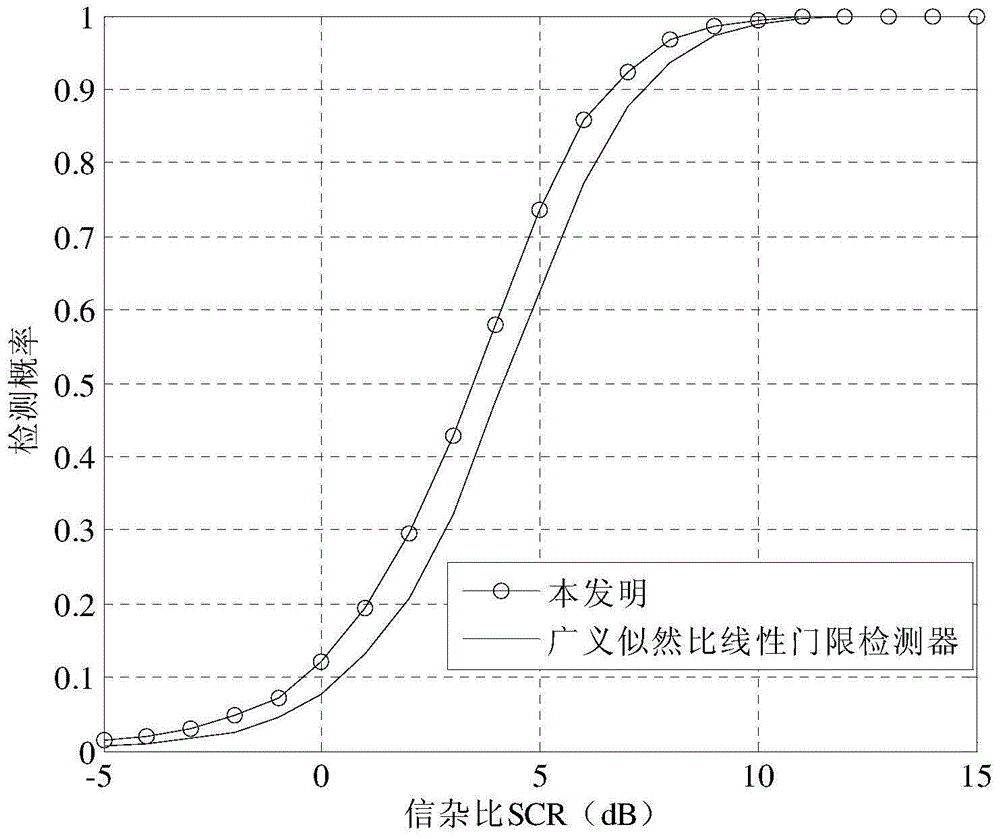
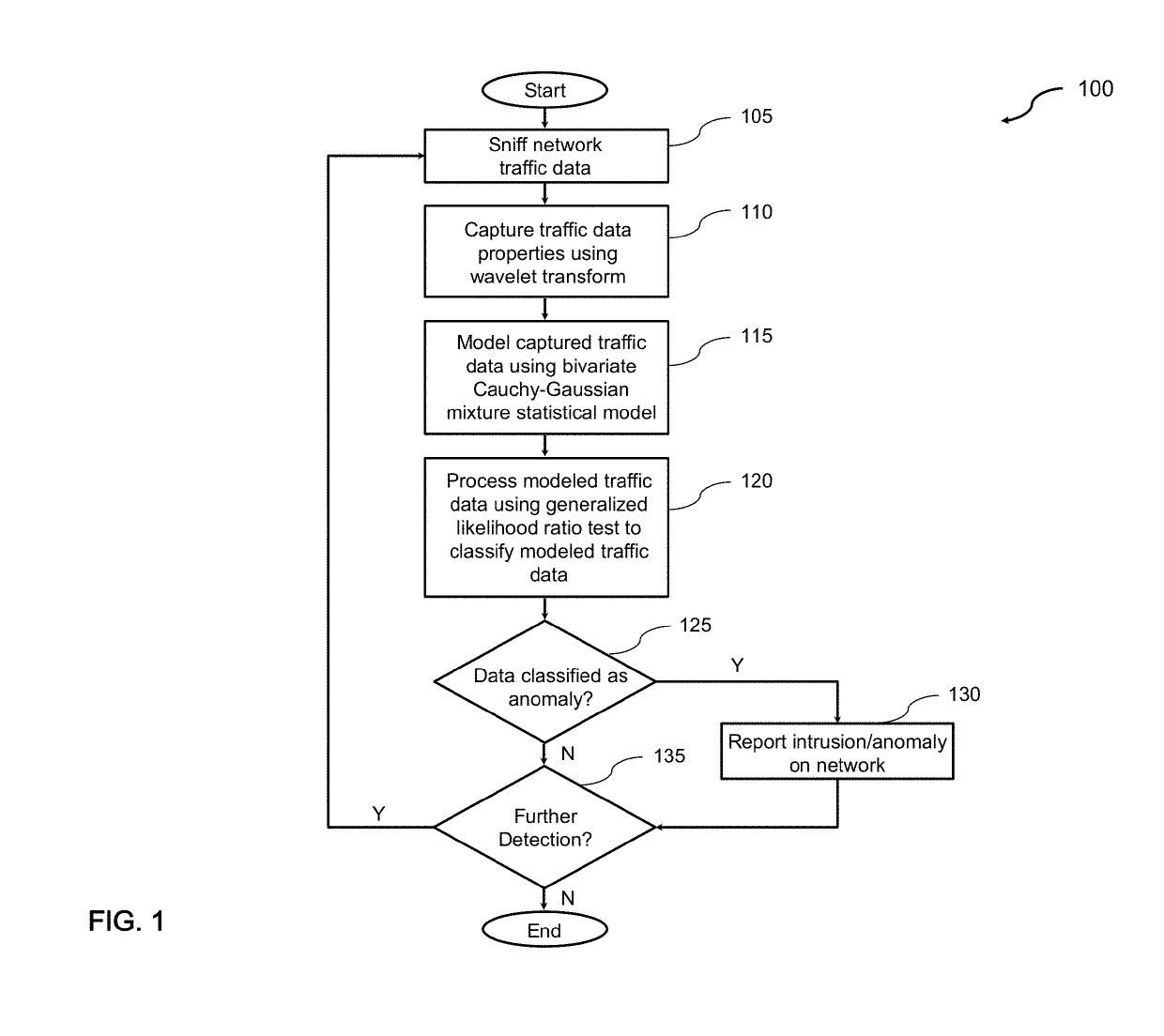
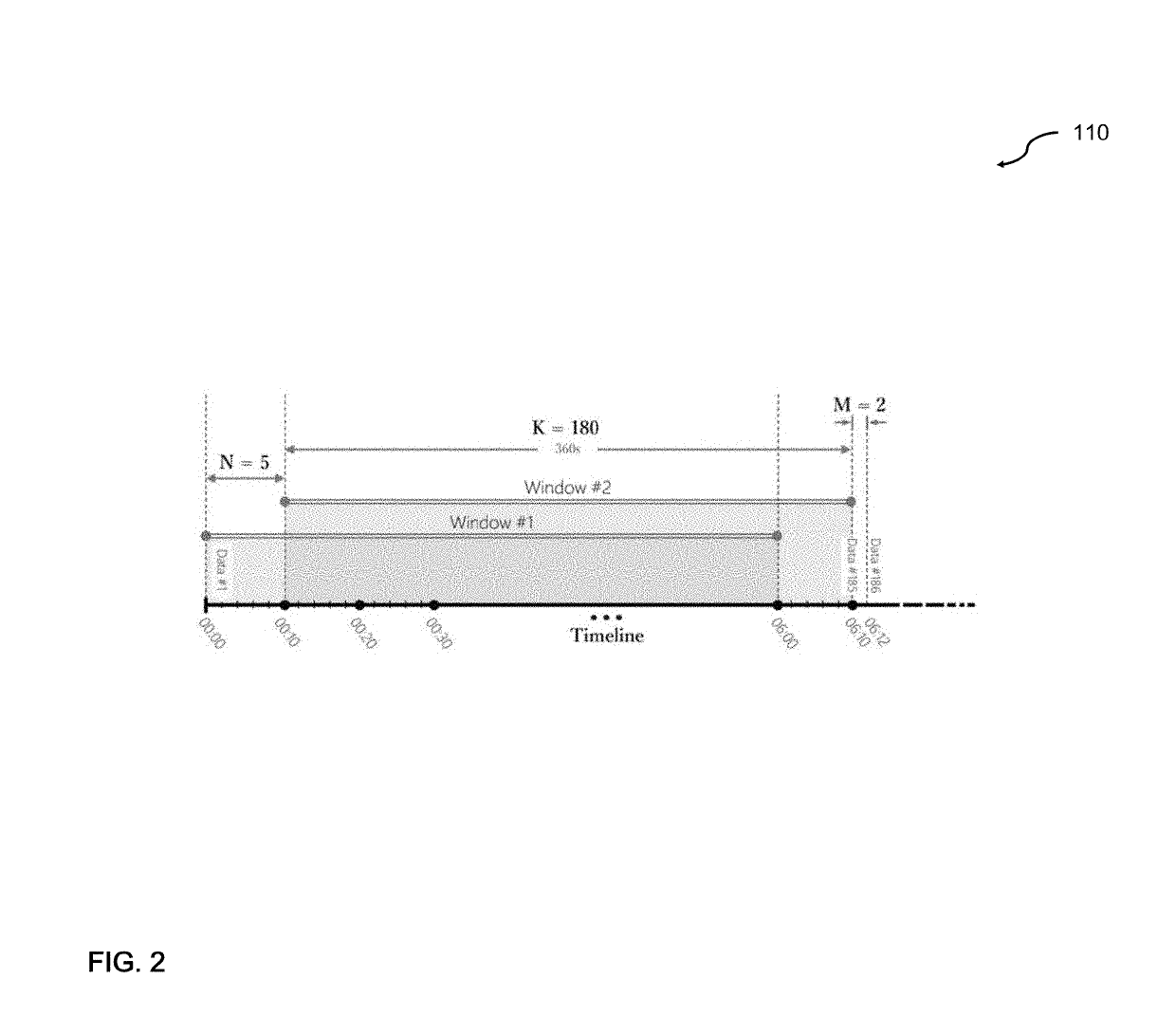
Generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT) based network intrusion detection system in wavelet domain
ActiveUS20190158522A1Improve accuracyIncrease analytical tractabilityMathematical modelsComputer security arrangementsFast algorithmLikelihood-ratio test
An improved system and method for detecting network anomalies comprises, in one implementation, a computer device and a network anomaly detector module executed by the computer device arranged to electronically sniff network traffic data in an aggregate level using a windowing approach. The windowing approach is configured to view the network traffic data through a plurality of time windows each of which represents a sequence of a feature including packet per second or flow per second. The network anomaly detector module is configured to execute a wavelet transform for capturing properties of the network traffic data, such as long-range dependence and self-similarity. The wavelet transform is a multiresolution transform, and can be configured to decompose and simplify statistics of the network traffic data into a simplified and fast algorithm. The network anomaly detector module is also configured to execute a bivariate Cauchy-Gaussian mixture (BCGM) statistical model for processing and modeling the network traffic data in the wavelet domain. The BCGM statistical model is an approximation of α-stable model, and offers a closed-form expression for probability density function to increase accuracy and analytical tractability, and to facilitate parameter estimations when compared to the α-stable model. Finally, the network anomaly detector module is further configured to execute a generalized likelihood ratio test for detecting the network anomalies.
Owner:AMIRMAZLAGHANI MARYAM +2
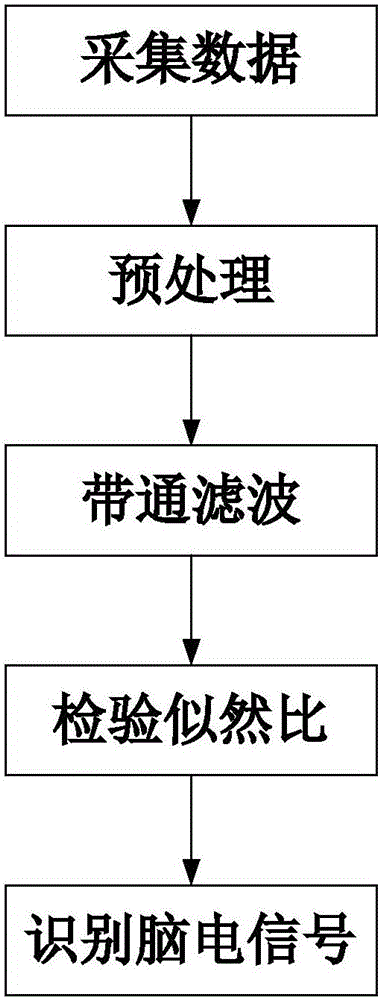
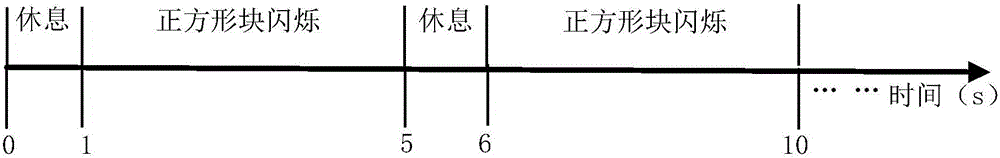
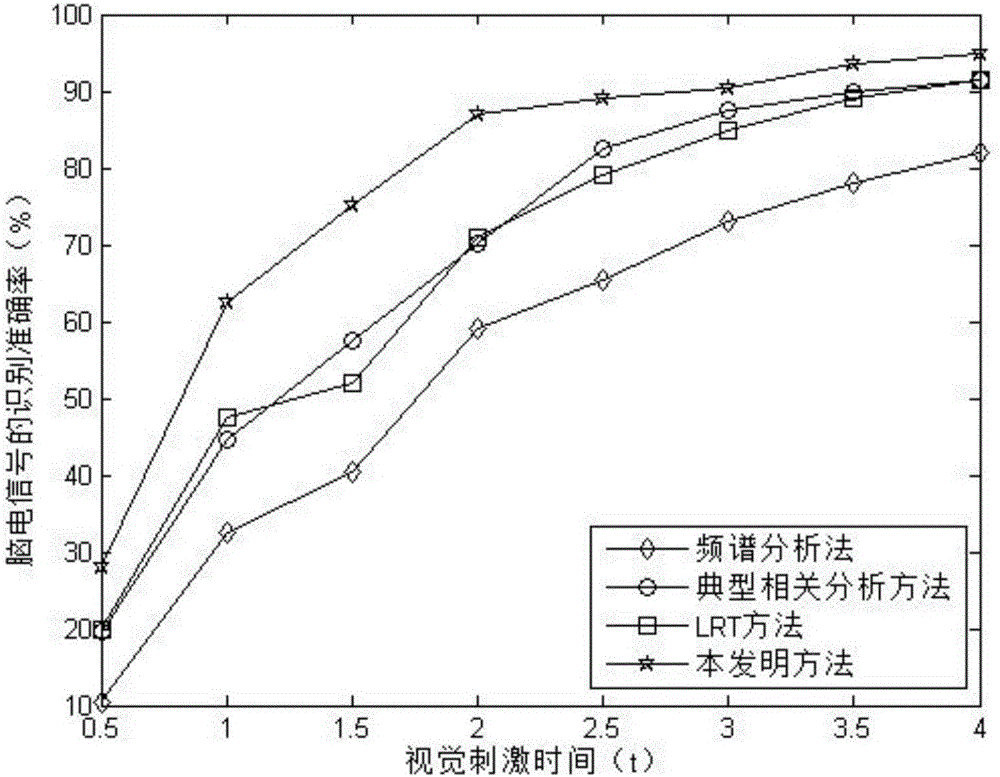
Stable state visual sense induced EEG signal processing method
ActiveCN105942975ARealize real-time detectionOvercome the shortcoming that the stimulation time is relatively long and not suitable for real-time detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStable statePattern recognition
The invention discloses a stable state visual sense induced EEG signal processing method comprising the following steps: 1, using an acquisition system to collect EEG signals of a subject under different visual sense frequency stimulation; 2, processing the EEG signals; 3, using a filter bank to filter the pre-processed EEG signals; 4, using a likelihood ratio calculating method to calculate the likelihood ratio between the filtered EEG signals and different visual sense stimulation frequencies, thus obtaining a likelihood ratio group; 5, finding the visual sense stimulation frequency corresponding to the biggest likelihood ratio from the likelihood ratio group, and finishing EEG signal identification. The stable state visual sense induced EEG signal processing method simultaneously uses the filter bank and the likelihood ratio calculation method so as to solve the problems that existing technology is less in identification object number, thus increasing identification object numbers, and improving EEG signal identification accuracy.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
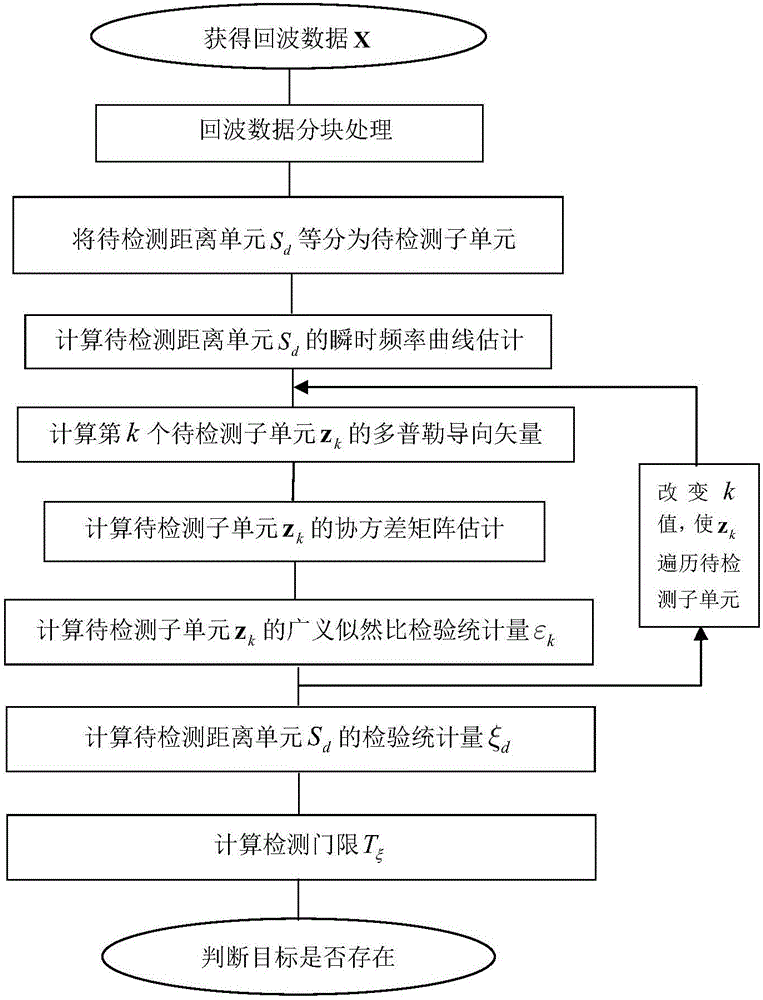
Sea-surface small target detection method based on front-back revenue reference particle filter
ActiveCN106569193AEasy to detectTroubleshooting Doppler MismatchWave based measurement systemsLow speedRadar detection
The present invention discloses a sea-surface small target detection method based on front-back revenue reference particle filter which mainly solves the problem that a conventional technology is not suitable for detecting the sea-surface low-speed floating small targets. The method comprises the realization steps of 1) obtaining and partitioning the echo data; 2) selecting a to-be-detected distance unit Sd in an echo data block and dividing the to-be-detected distance unit Sd into the to-be-detected sub-units; 3) calculating the instantaneous frequency curve function estimation of the to-be-detected distance unit Sd; 4) calculating a Doppler steering vector h and the covariance matrix estimation of the k-th to-be-detected sub-unit zk; 5) utilizing the h and the covariance matrix estimation to calculate the generalized likelihood ratio test statistic amount of the sub-unit zk; 6) accumulating the generalized likelihood ratio test statistic amount of all to-be-detected sub-units to obtain the test statistic amount xi k of the to-be-detected distance unit Sd; 7) calculating a detection threshold T xi; 8) comparing the xi k and the T xi to determine the existence of the targets. The sea-surface small target detection method of the present invention enables the radar detection performance to be improved, and can be used to detect the sea-surface floating small targets.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Log-likelihood ratio (LLR) dampening in low-density parity-check (LDPC) decoders
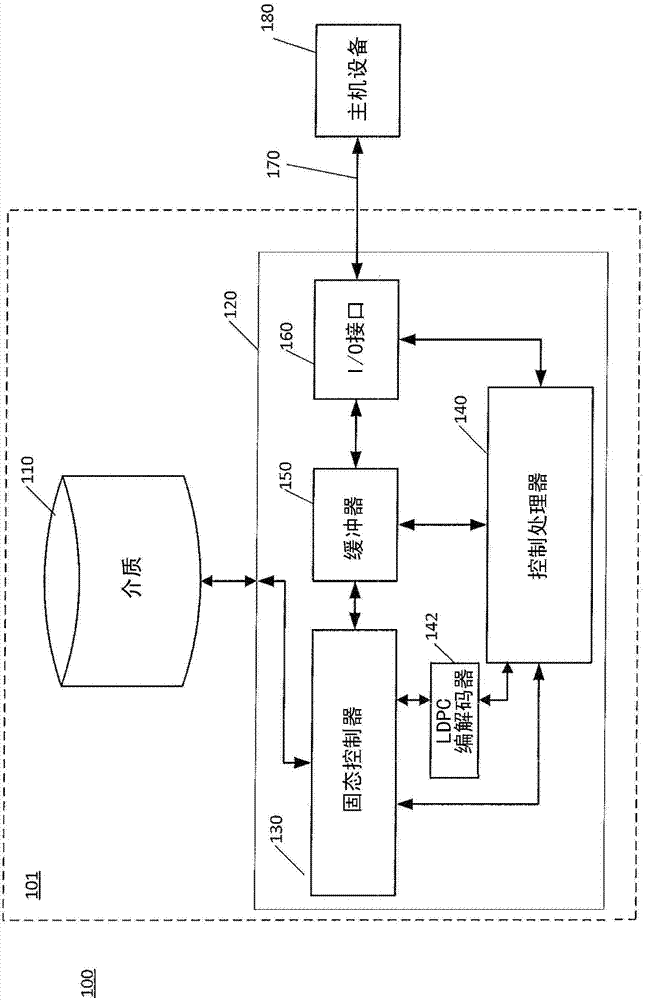
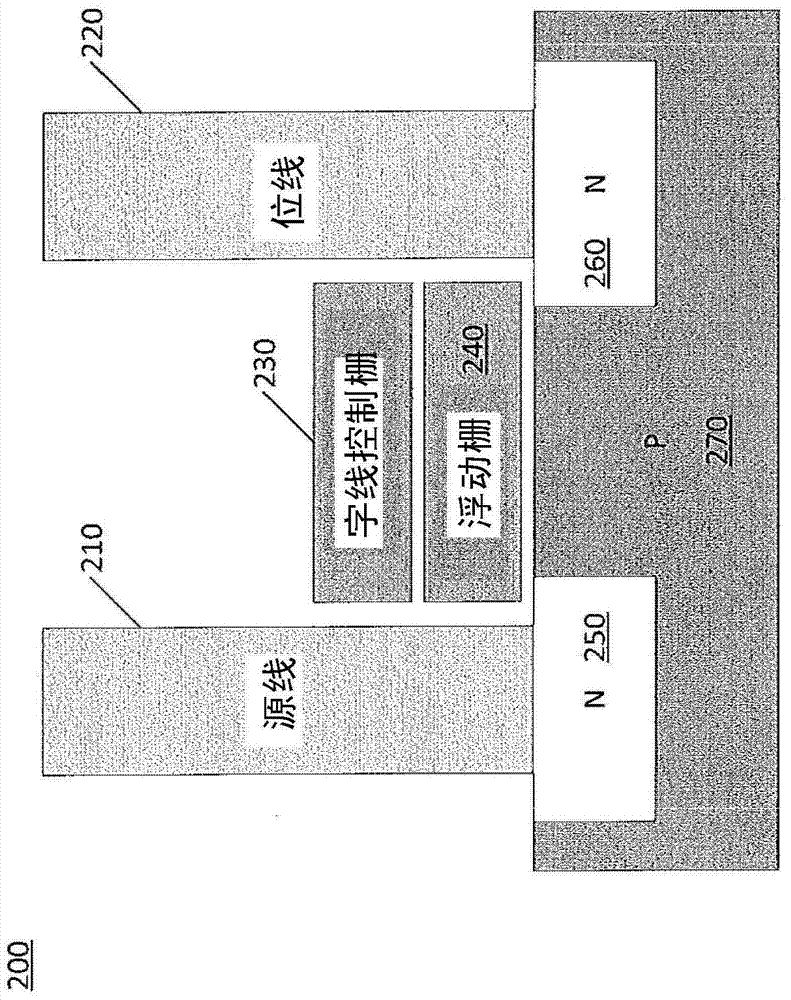
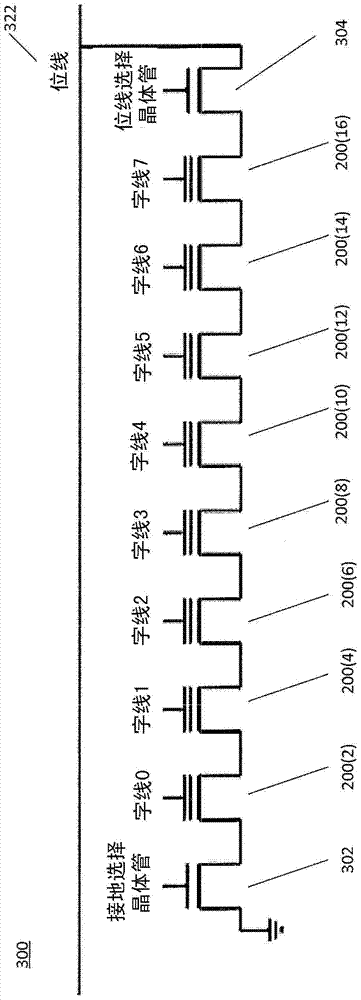
ActiveCN104283570AError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow densityLikelihood-ratio test
Described embodiments provide a media controller to read data stored in a media. The media controller determines a value for each bit of a shortened codeword from the media. The shortened LDPC codeword includes a plurality of non-shortened bits of a full codeword, where the full codeword includes the plurality of non-shortened bits and one or more shortened bits. Shortened bits correspond to bits unused in the shortened codeword. The media controller converts the determined values for each bit of the shortened codeword into a first set of log-likelihood ratio (LLR) values. The full codeword is decoded using the first set of LLR values for the shortened codeword. If the LDPC decoding fails, the media controller dampens one or more LLR values corresponding to non-shortened bits of the codeword to produce a second set of LLR values and starts a second LDPC decoding trial using the second set of LLR values. The dampening of LLR values includes scaling by a predetermined scaling factor and decreasing their magnitude by a predetermined amount.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com