Shallow sea target depth classification method based on hydrophone array
A classification method and target depth technology, which is applied in the field of hydrophone array signal sounding, can solve the problems of mismatching model parameters and real parameters, affecting the accuracy of sound source location, and not considering environmental parameters, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
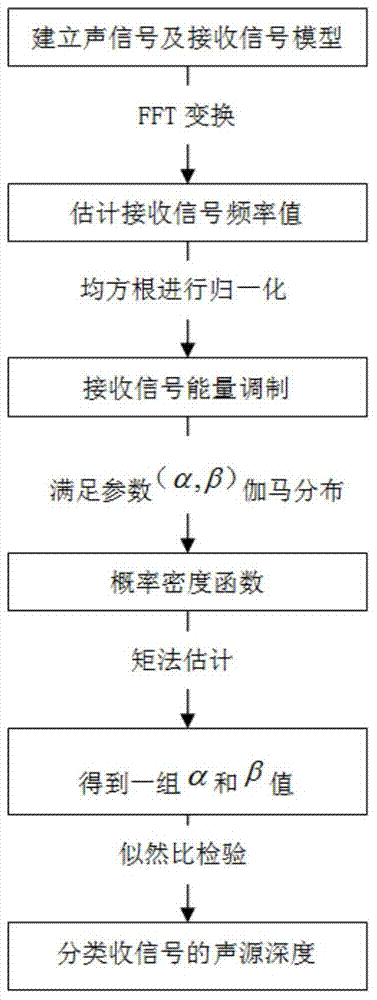
[0101] The first step is to establish a signal and environment model.
[0102] The first step of the depth recognition system is to preprocess the data and extract the energy value that changes with time from the received signal. A low-pass finite impulse response (FIR) filter with a 2Hz passband and 2048 samples was used to extract complex energy values.
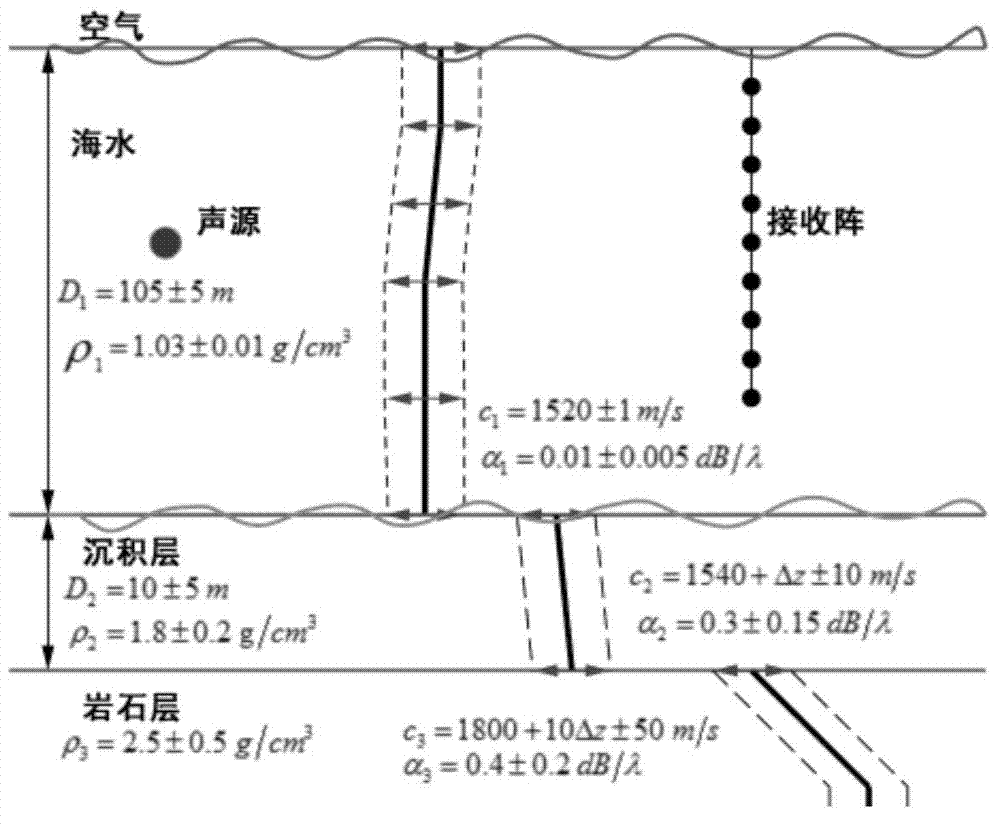
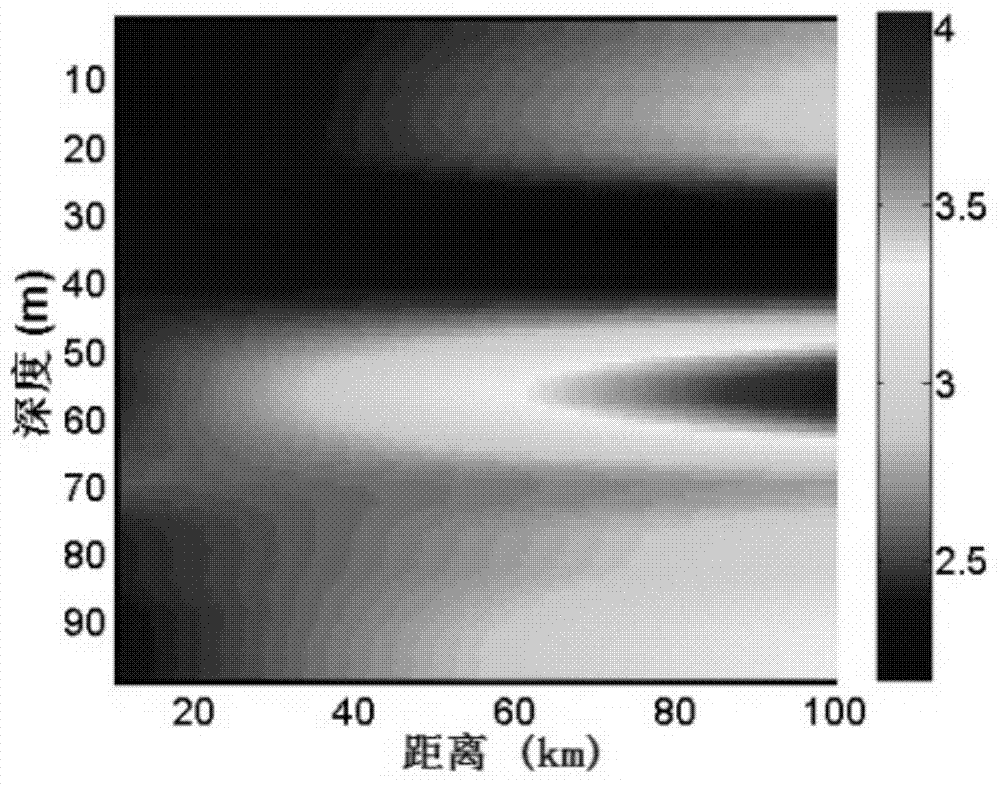
[0103] The environmental model adopts the arrangement of sound sources at a water depth of 30m in a shallow sea environment, and the frequency of the transmitted signal is 300Hz. A 90-element vertical array is used to receive signals, and the distance between array elements is 1m. The sound velocity profile in the experimental sea area is measured by XBT, and the XBT measurement error is about 0.2m / s. The sound velocity profile during the experiment is approximately 1520m / s constant sound velocity profile, with an average sound velocity disturbance of 0.8m / s. The wave height is measured by radar, and the average wave heig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com