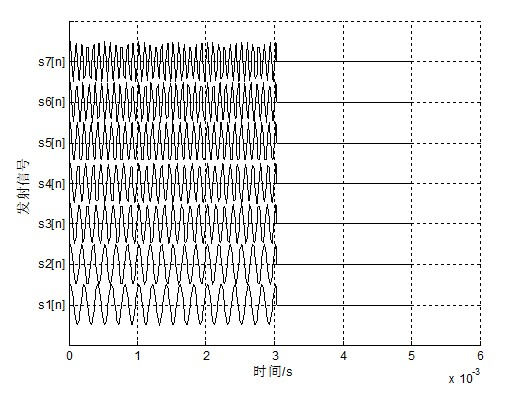
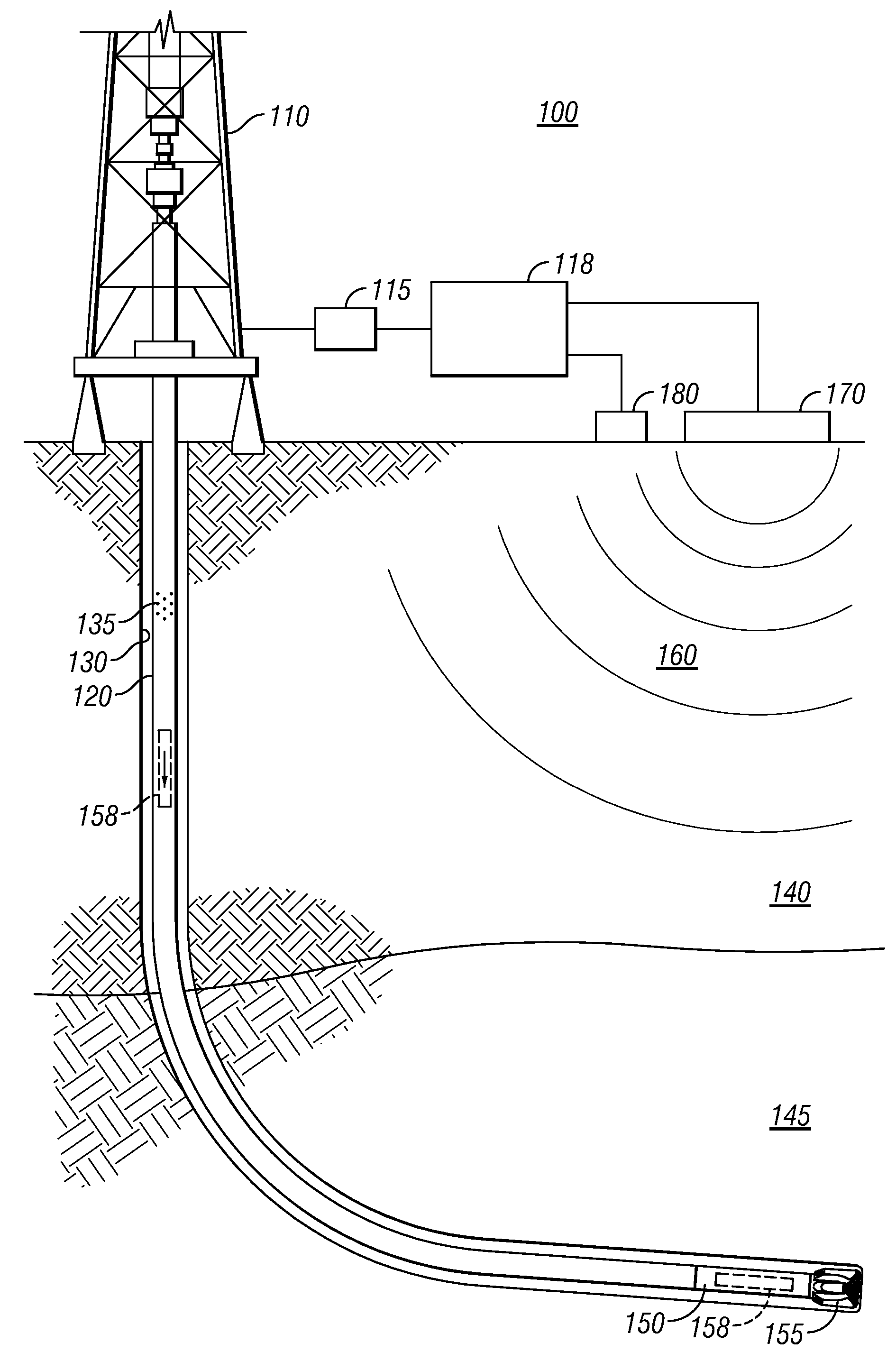
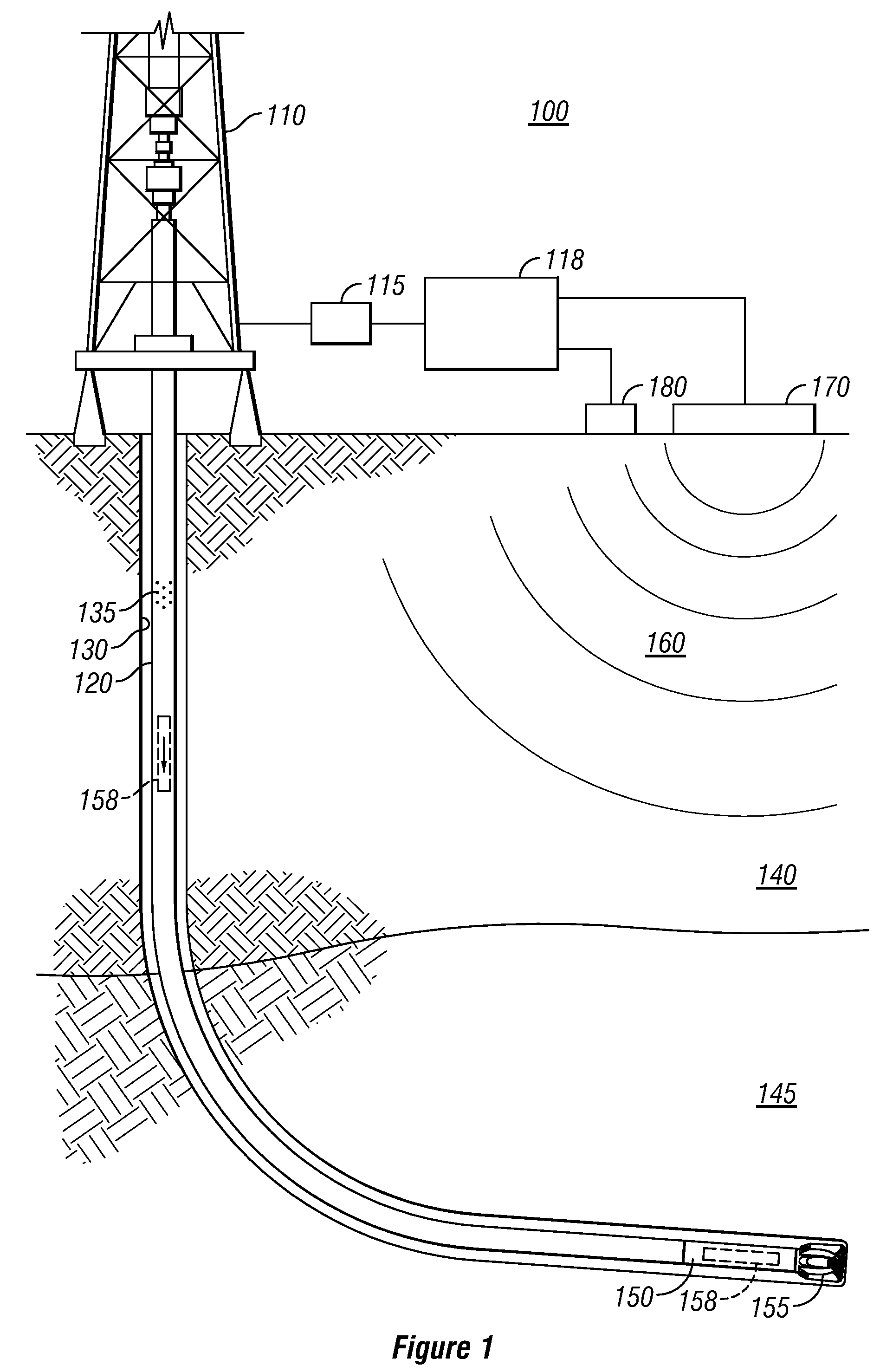
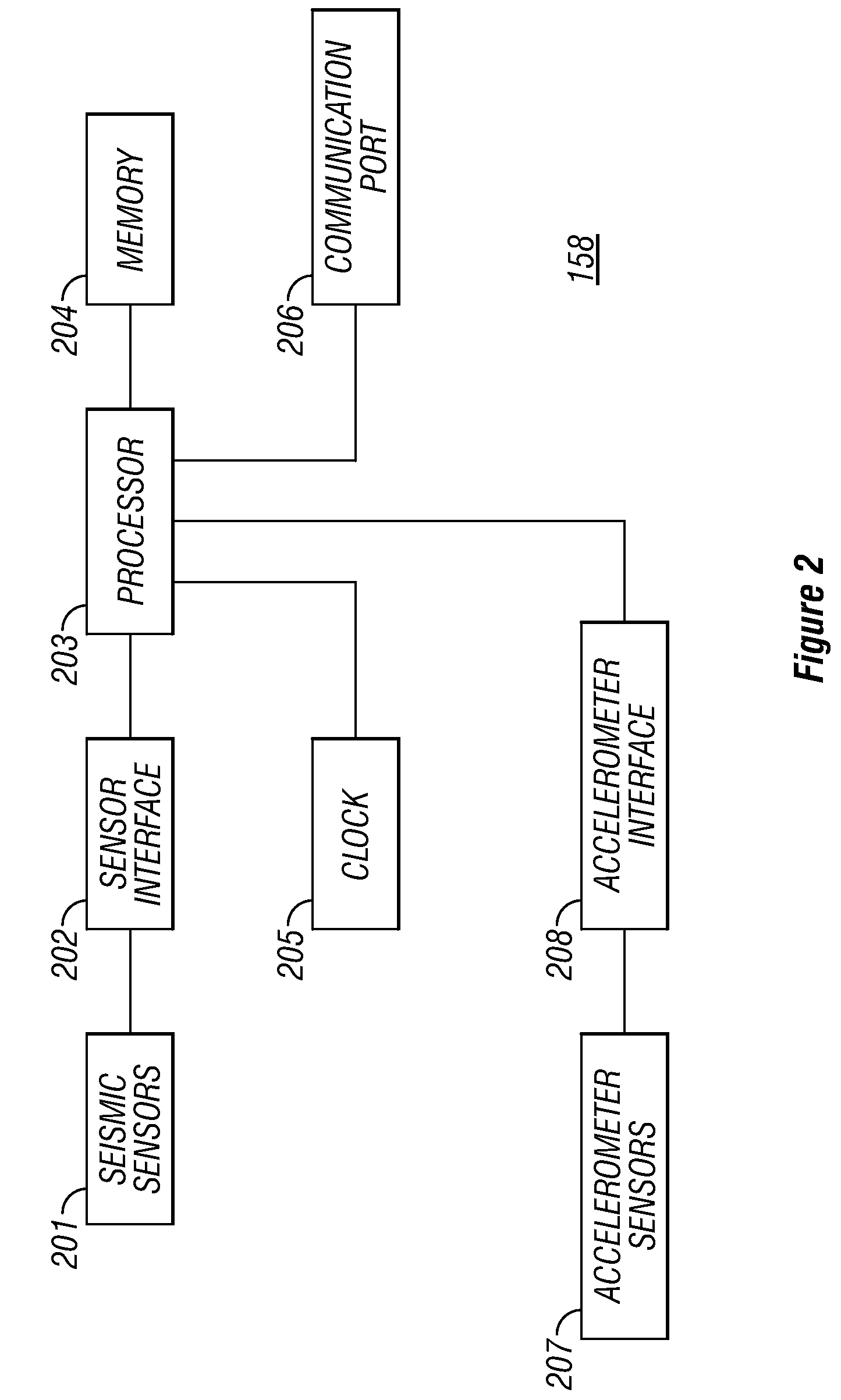
Patents
Literature
296 results about "Hydrophone array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
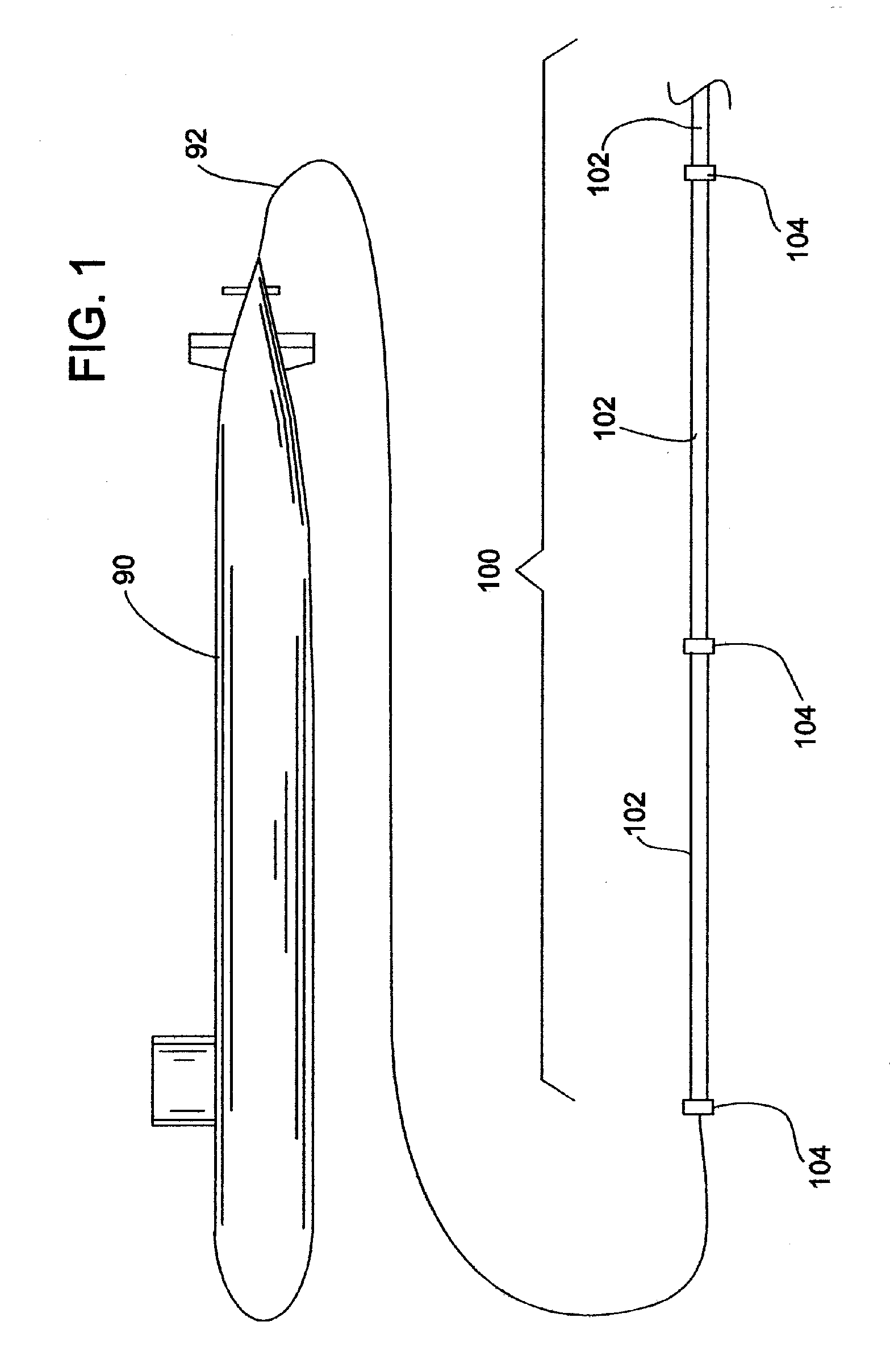
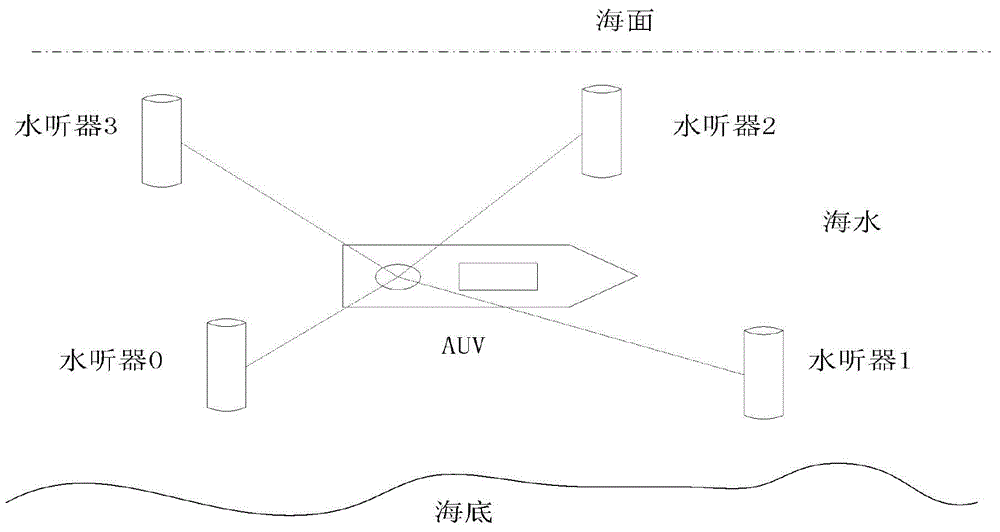
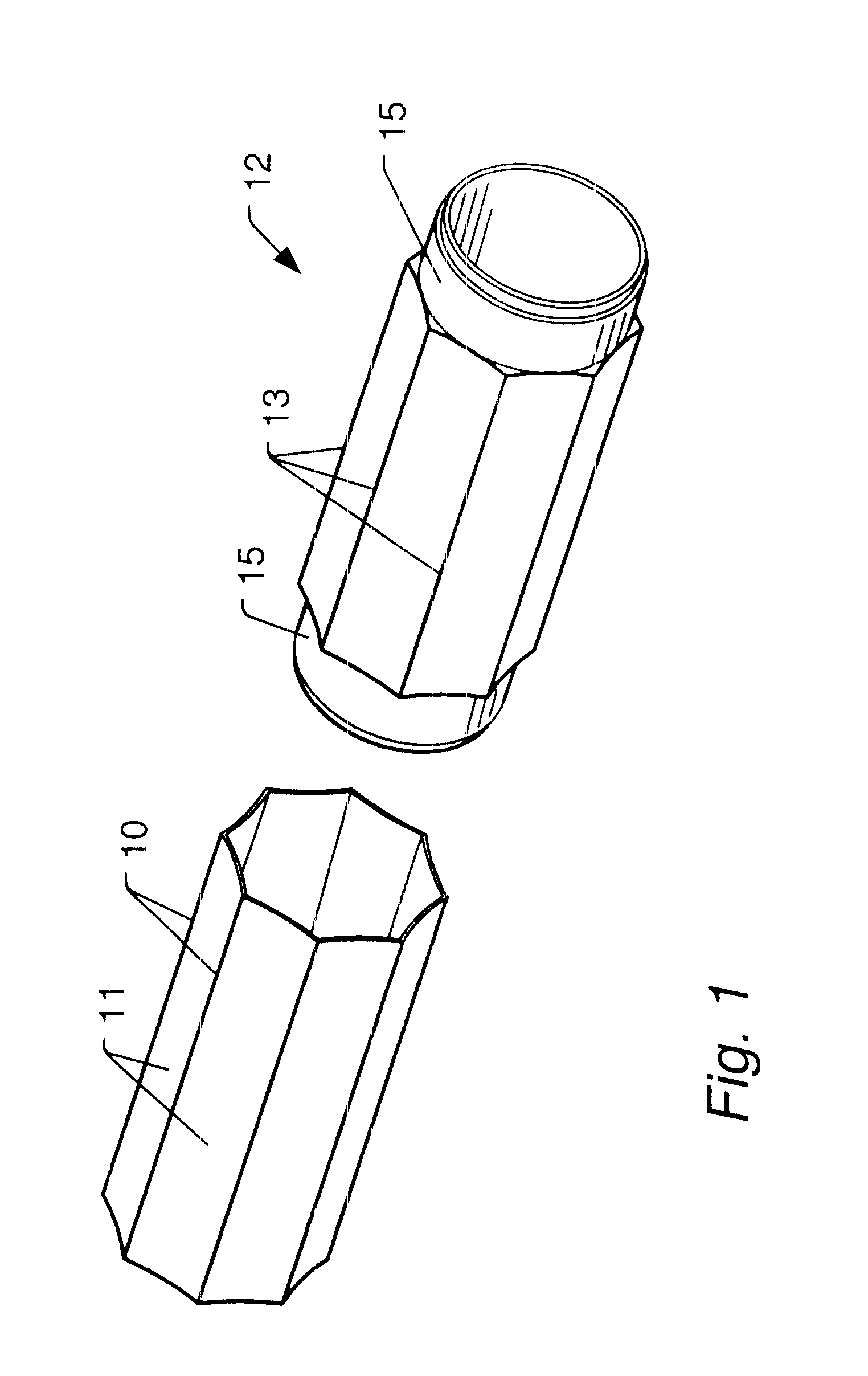
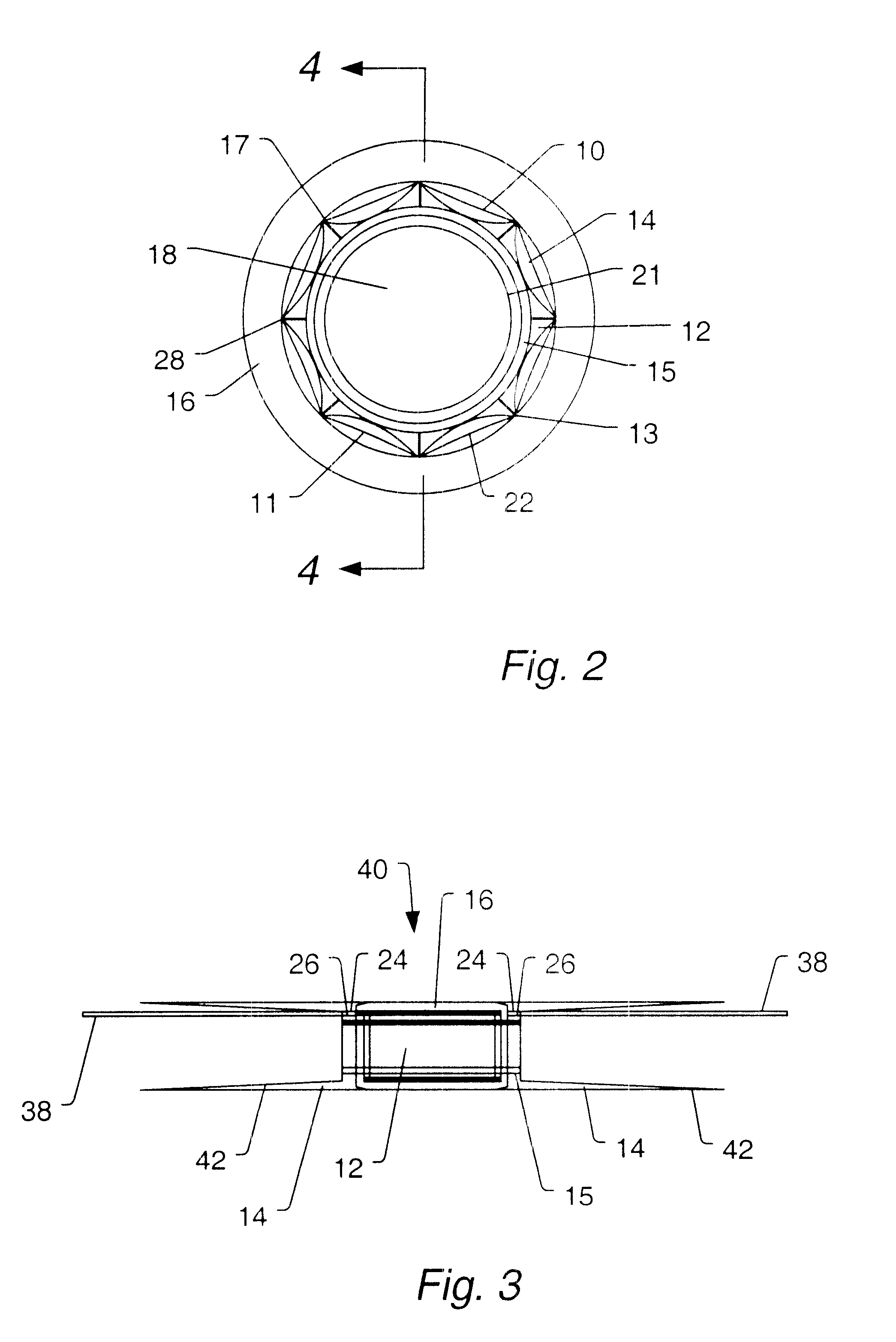
Hydrophone Arrays. A hydrophone array is made up of a number of hydrophones placed in known locations. These hydrophones maybe placed in a line on the seafloor, moored in a vertical line in the water column, or towed in a horizontal line behind a boat or ship, for example.
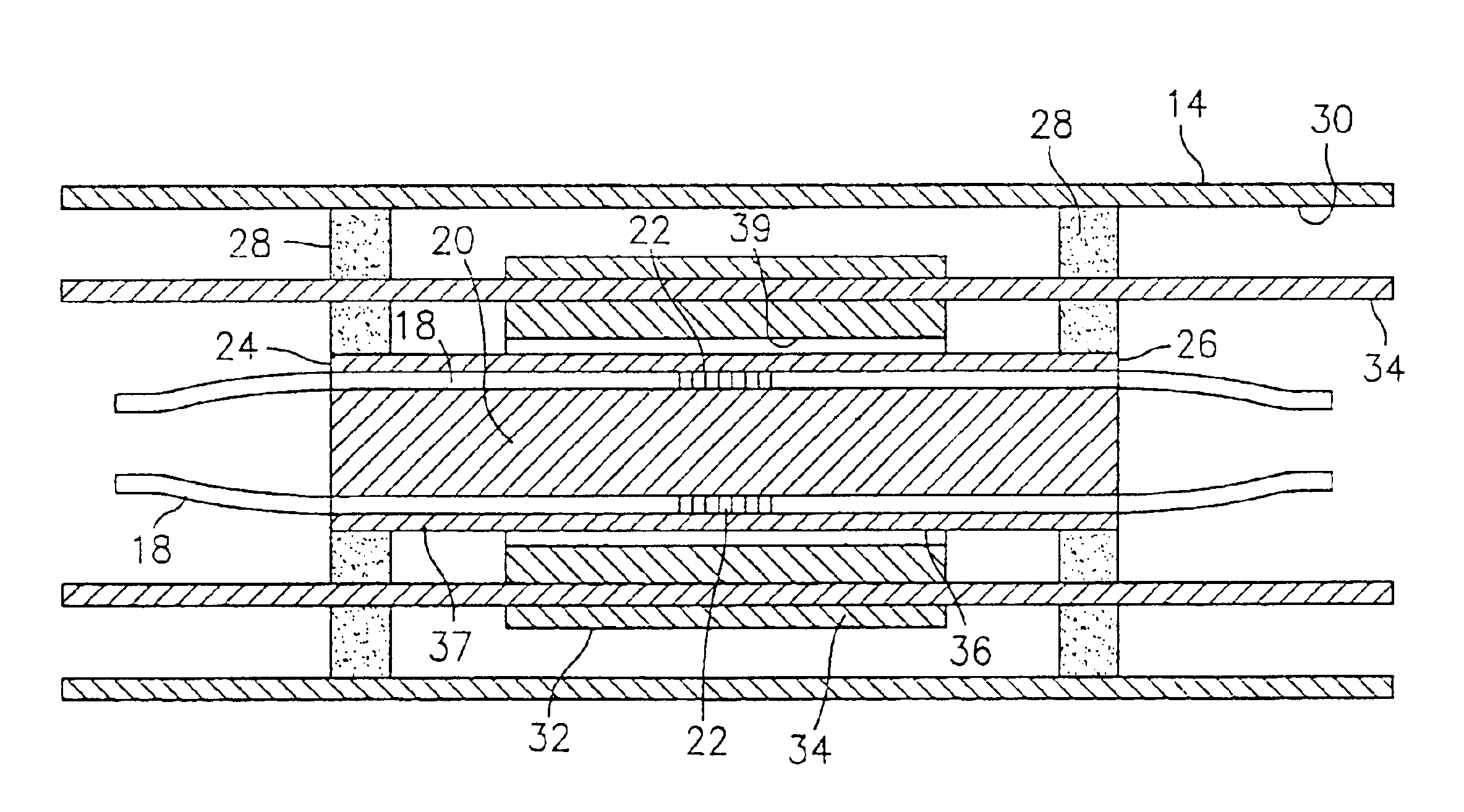
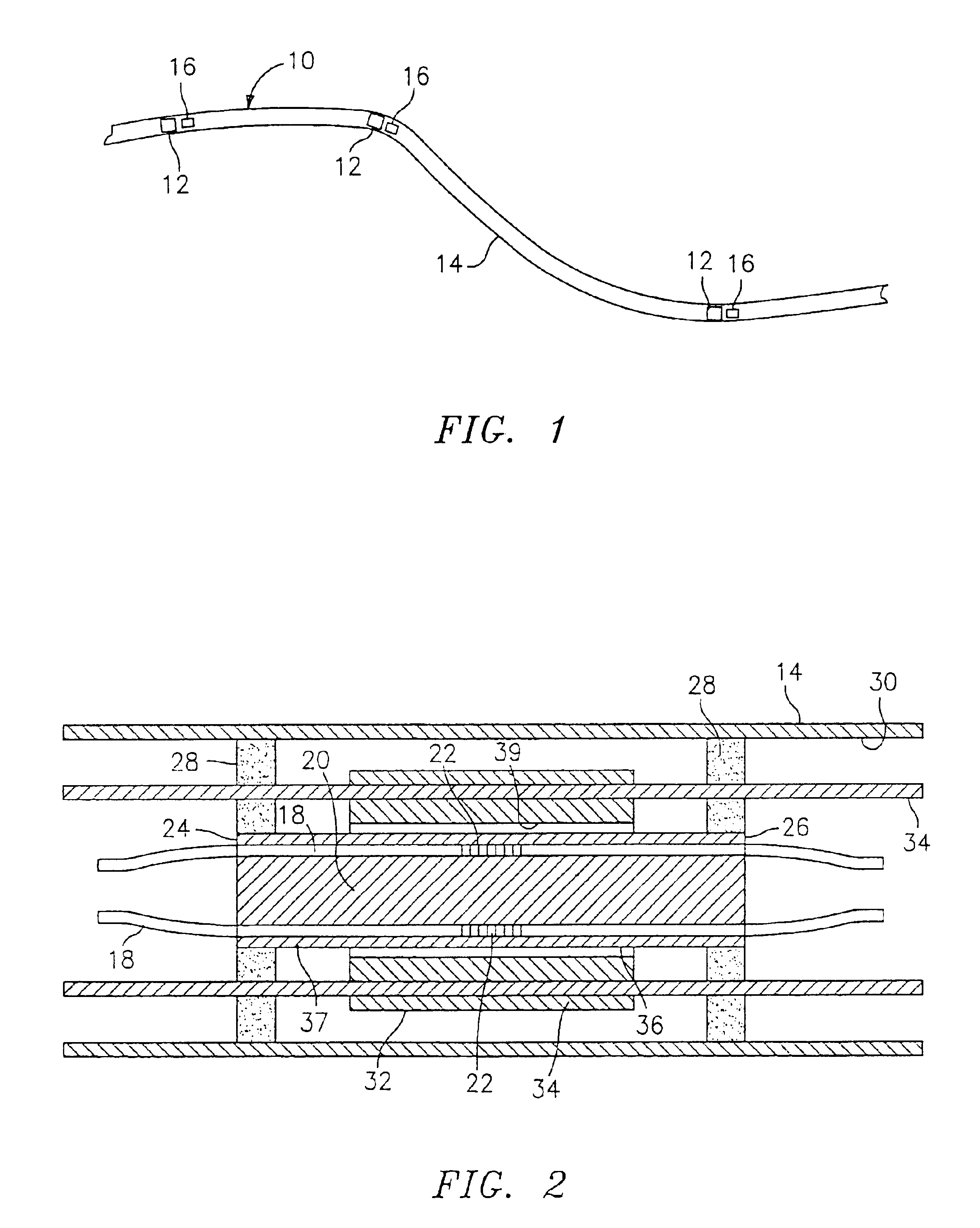
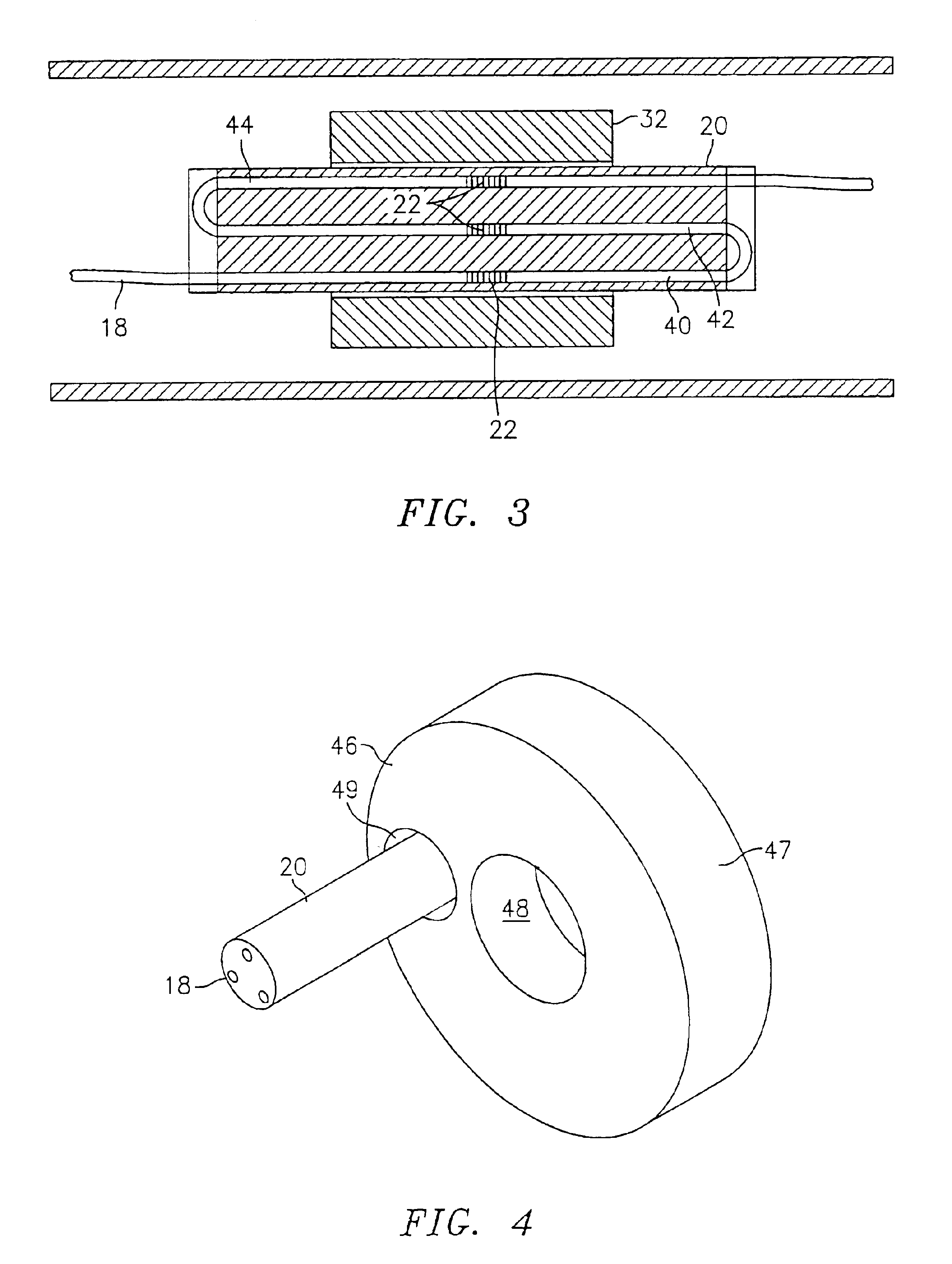
Mount for use in optical fiber hydrophone array
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Fiber splice tray for use in optical fiber hydrophone array
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
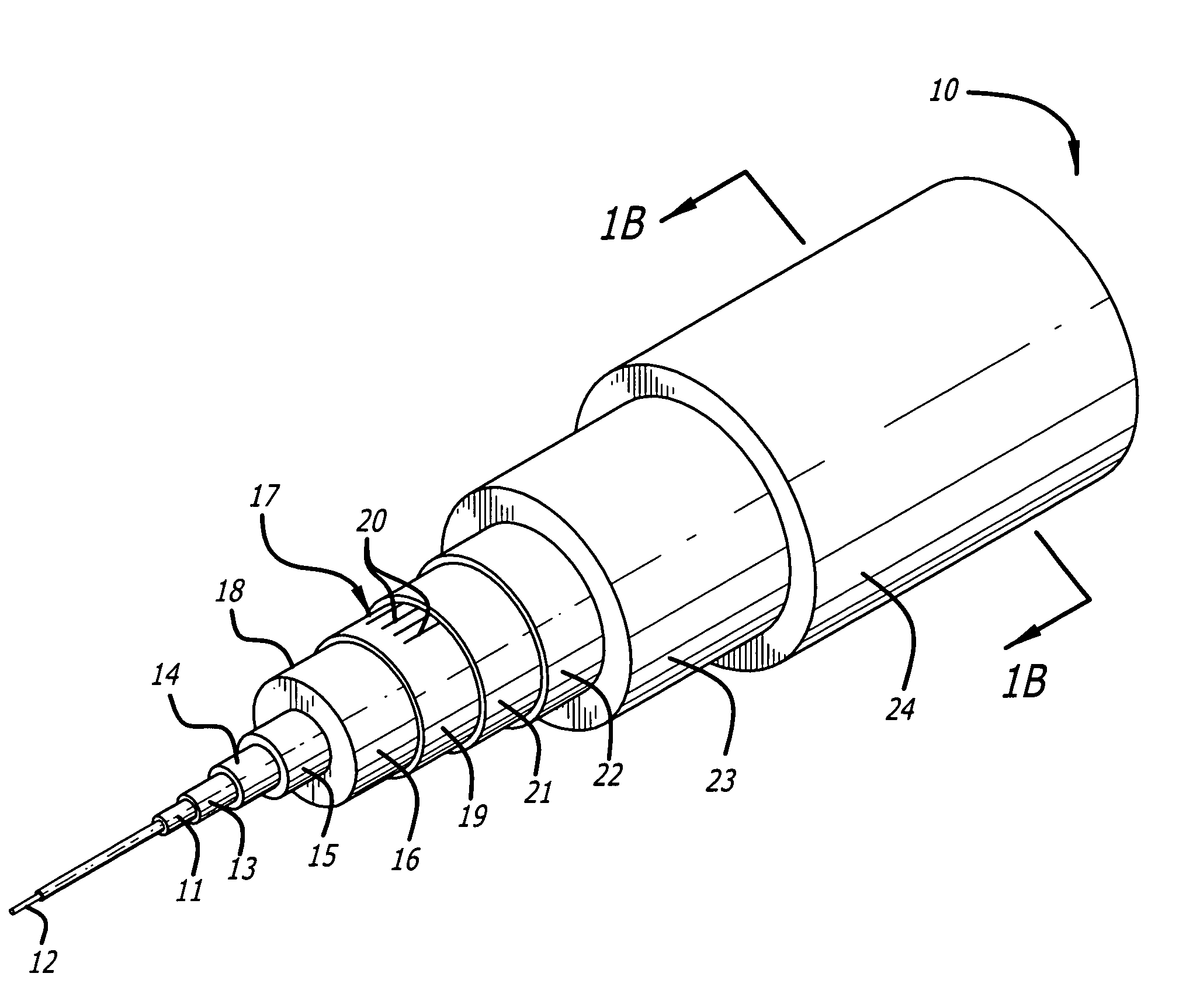
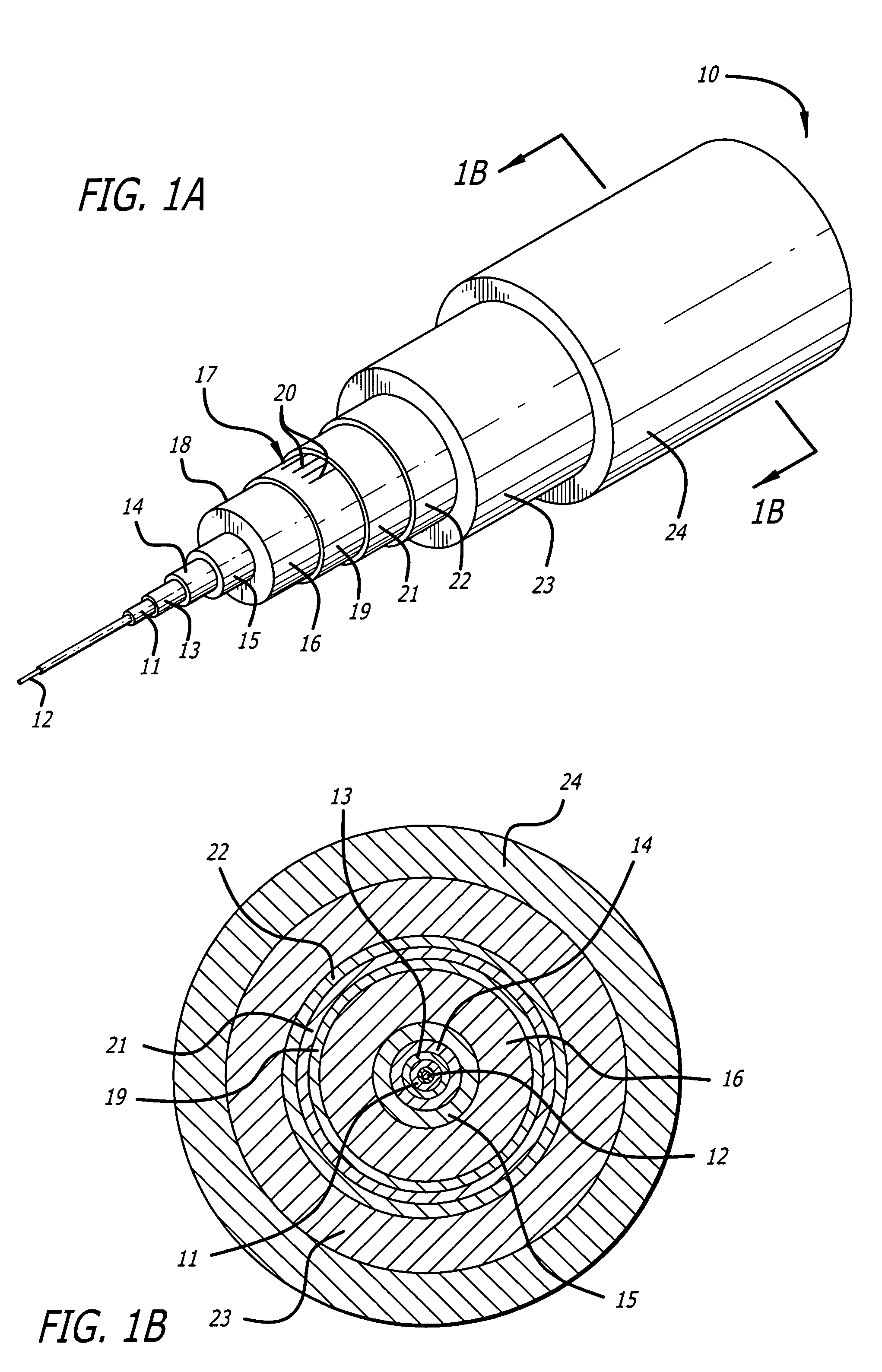
Fiber transition segment for use in optical fiber hydrophone array
InactiveUS7027695B2Reliable and protectedSmooth transitionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSeismic signal receiversFiberComputer module
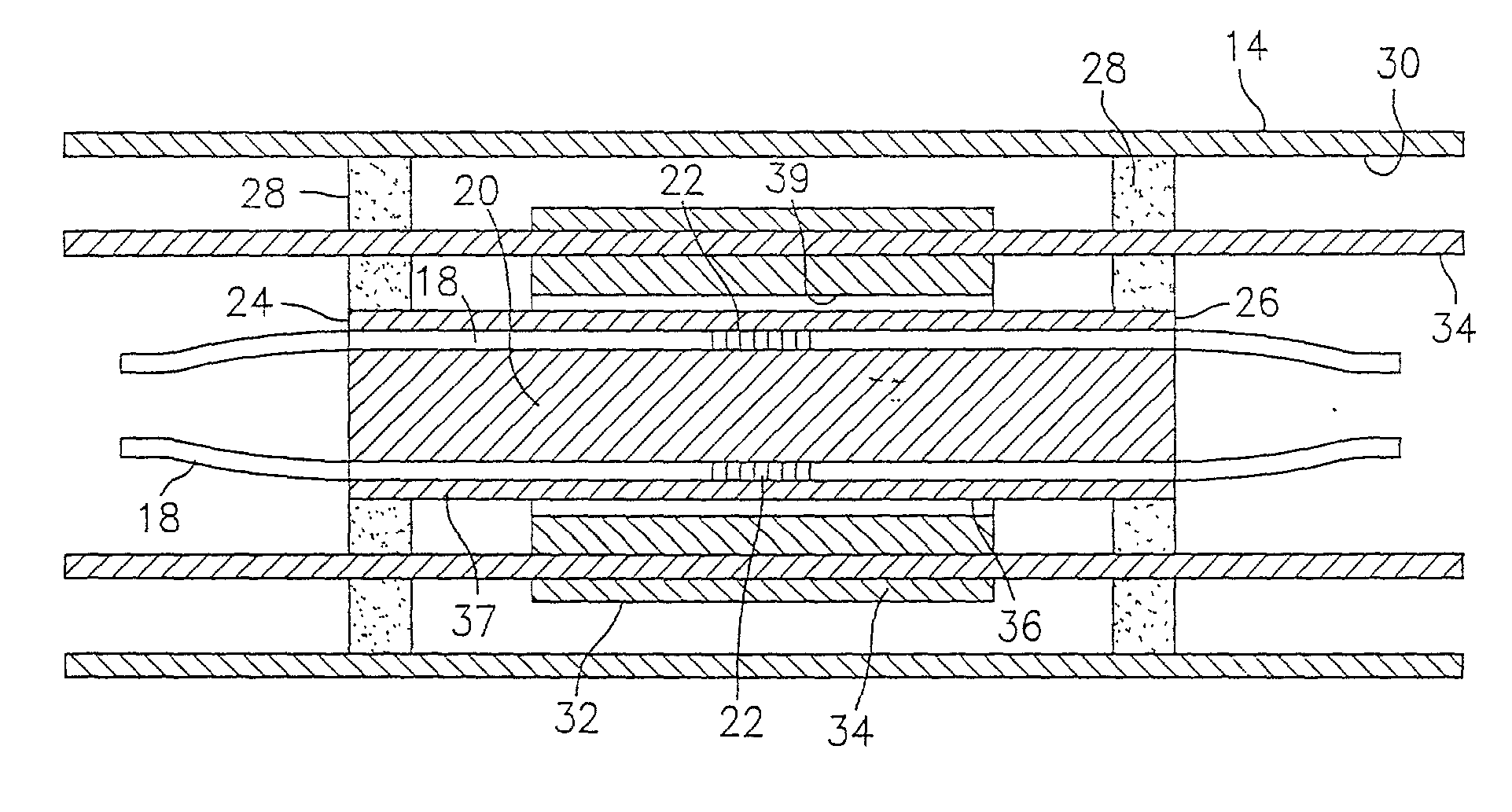
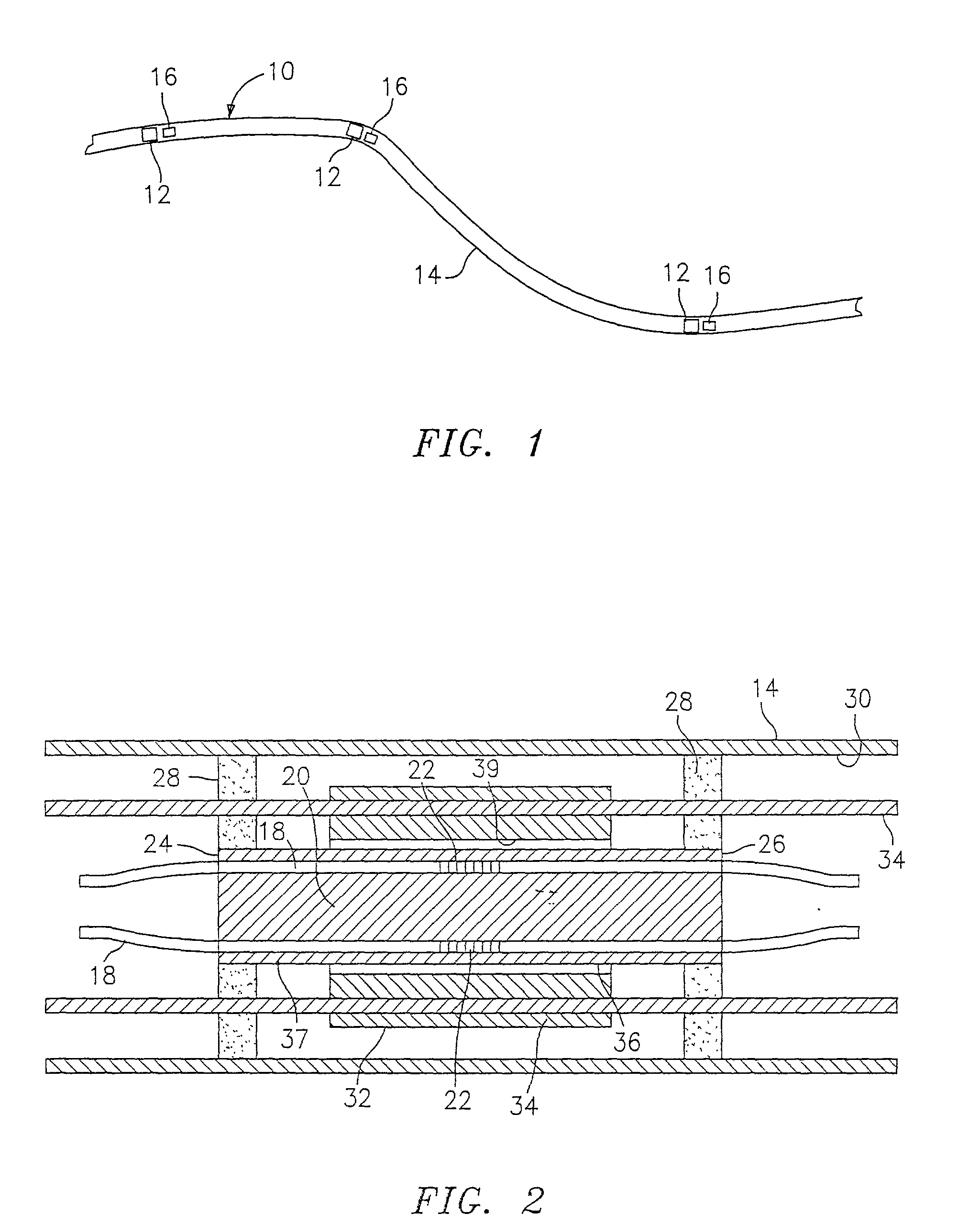
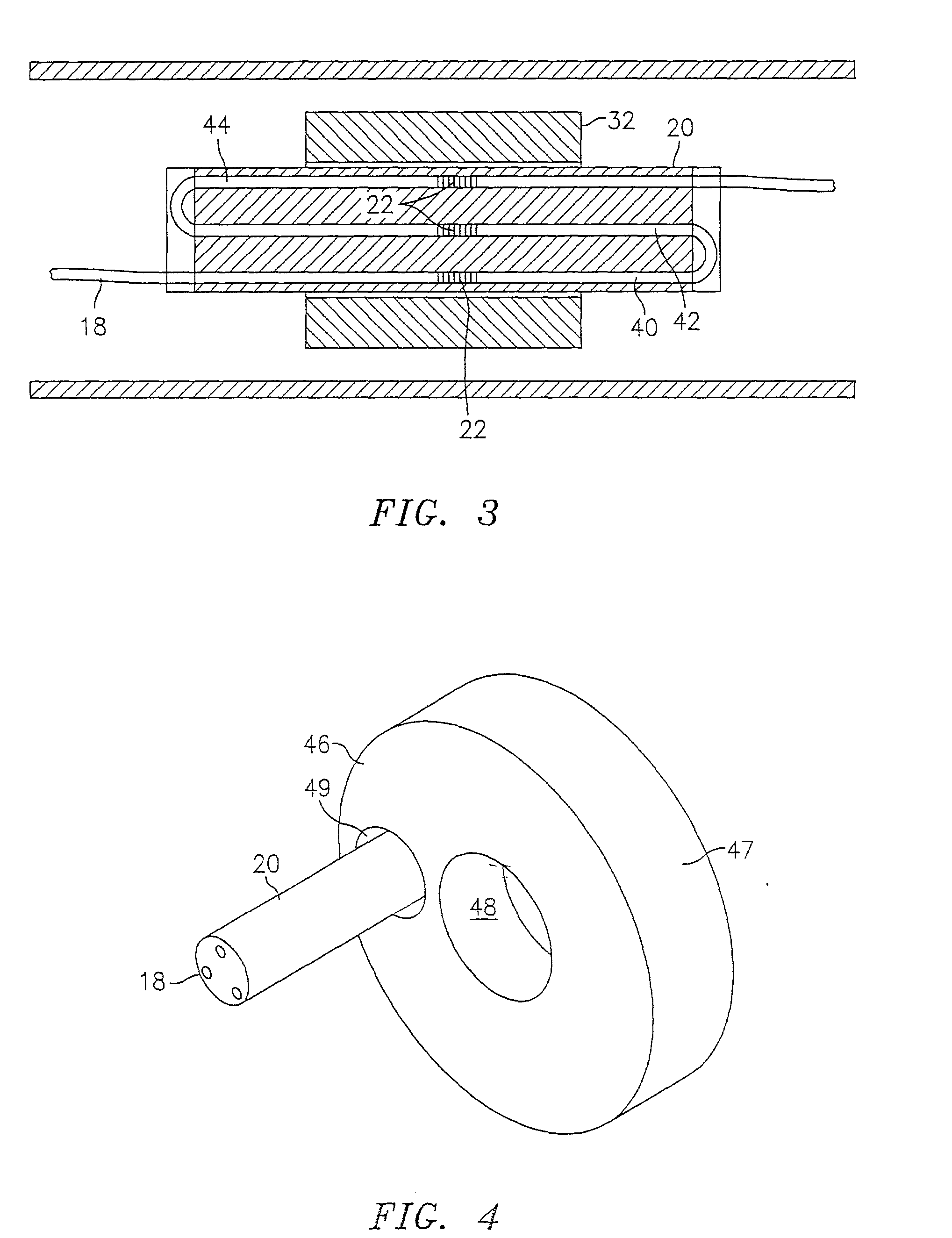
A fiber transition segment for transitioning an optical fiber from a hydrophone module to the central axis of the module. The segment comprises a conical, elongated element and a cylindrical portion of reduced diameter that protrudes longitudinally from the wide end of the conical element. The cylindrical portion is reciprocally mounted within an interconnect spring at the end of the hydrophone assembly. The fiber transition segment has a helical internal groove for receiving the optical fiber from the interconnect spring. The groove is aligned with and approximately matches the pitch of the groove in the interconnect spring to provide a smooth transition to the fiber transition segment and then to the central axis of the module.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ADVANCED INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Termination assembly for use in optical fiber hydrophone array
InactiveUS6865334B2Maintain integritySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFibre mechanical structuresFiberCoupling
A termination assembly for use in an optical hydrophone module, comprising a module oil seal and an optical fiber seal. The termination assembly is used at the ends of modules and provides a means for filling individual modules with fill fluid. A module oil seal comprises a cylindrical wall defining a cavity, with one end substantially closed and the other end open. An annular face plate on the open end makes a seal dividing a coupling and a clevis. A check valve is mounted to an orifice that passes through the substantially closed end of the module oil seal. Optical fibers pass through the substantially closed end and the optical fiber seal is provided around the optical fiber that passes therethrough. The fiber seal fits snugly in a module oil seal opening. Both components serve to provide a seal that can withstand high pressures and maintain optical fiber integrity.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
Woven fiber protection cable assembly for use in optical fiber hydrophone array
InactiveUS6879545B2Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFibre mechanical structuresFiberEngineering
A woven fiber protection cable assembly for use in an optical fiber hydrophone module. The assembly comprises an elastic woven fiber strap with at least one tube attached to one or more sides of the strap in a sinusoidal pattern. The strap at a first end and longitudinal middle portion is substantially aligned with the central axis of the hydrophone module. Two layers of the strap are fastened together in the longitudinal middle portion, and the first end of the strap comprises a loop. The two layers at the second end of the strap are spatially separated and on opposite sides overlap a fiber transition segment, around which one end of the tube is coiled. The elongation of the strap causes the period of the sinusoidal pattern to increase without imparting damaging stress to the optical fiber.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS MISSION SYST INC
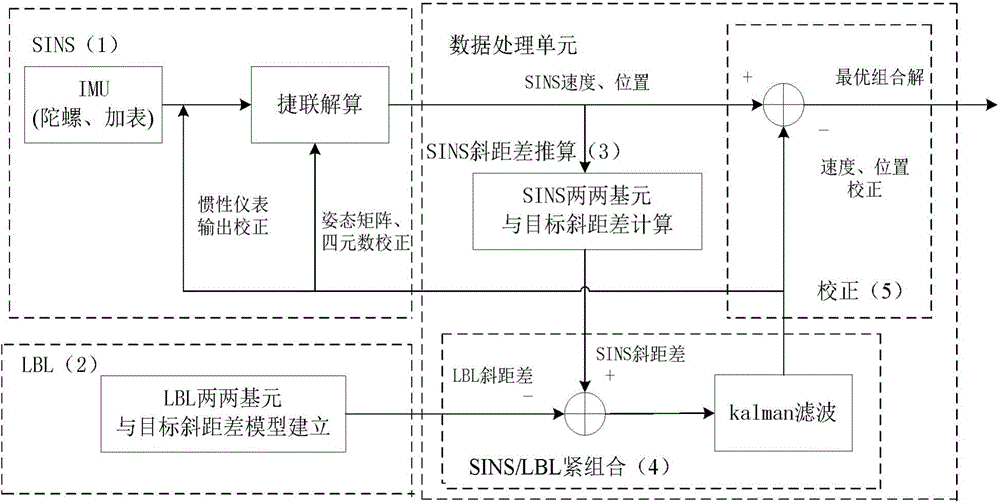
SINS/LBL (strapdown inertial navigation systems/long base line) tight combination based AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) underwater navigation positioning method
ActiveCN104457754ASolve the problem of error accumulation over timeReduce usageNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomRectangular coordinates
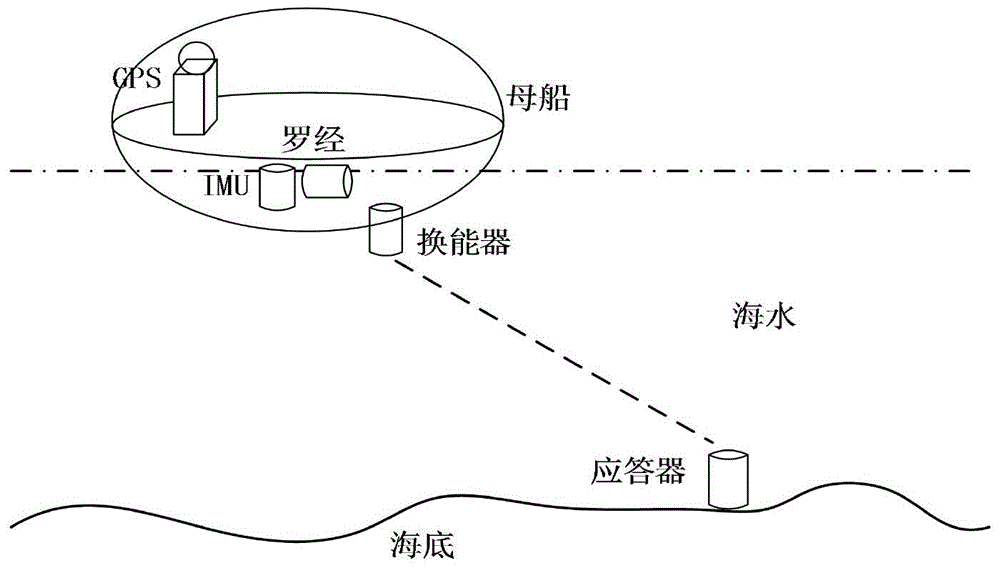
The invention provides an SINS / LBL (strapdown inertial navigation systems / long base line) tight combination based AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) underwater navigation positioning method. The SINS / LBL tight combination based AUV underwater navigation positioning method is characterized by comprising three major parts, namely an SINS mounted on an AUV, an LBL underwater sound positioning system laid on the seabed, and a data processing unit. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly performing a strapdown algorithm on IMU (inertial measurement unit) data to obtain AUV position information, and representing the position information by using earth rectangular coordinates; secondly reckoning an SINS slant-range difference according to the AUV position information provided by the SINS and hydrophone array position coordinates; and thirdly establishing an LBL slant-range difference model according to LBL positioning characteristics, and correcting SINS navigation positioning information according to filter estimation compensation by taking the difference value between the SINS slant-distance difference and the LBL slant-distance difference as an observed quantity of a kalman filter. According to the SINS / LBL tight combination based AUV underwater navigation positioning method, the use of GPS and other radio positioning systems is avoided at the same, and the AUV underwater operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
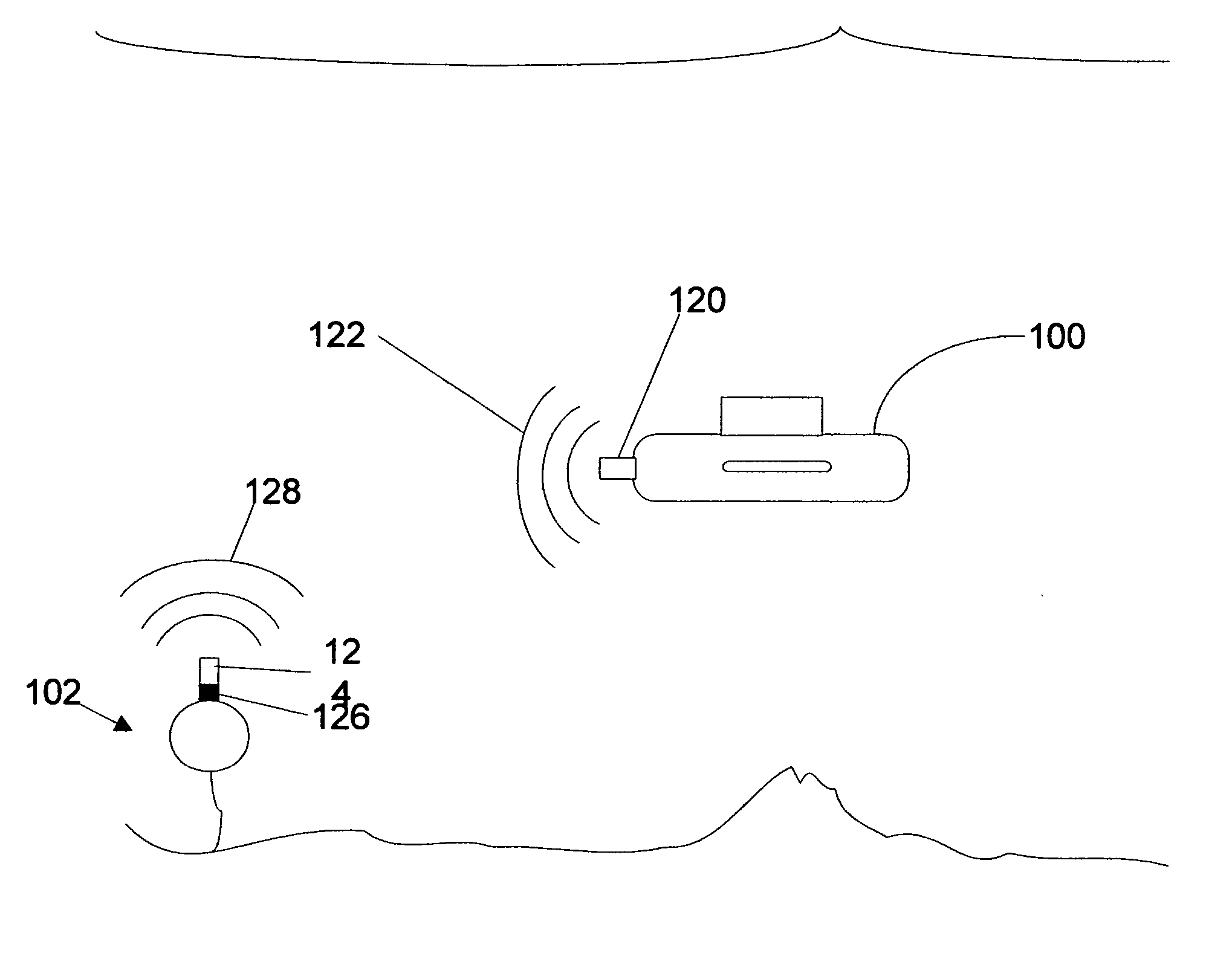
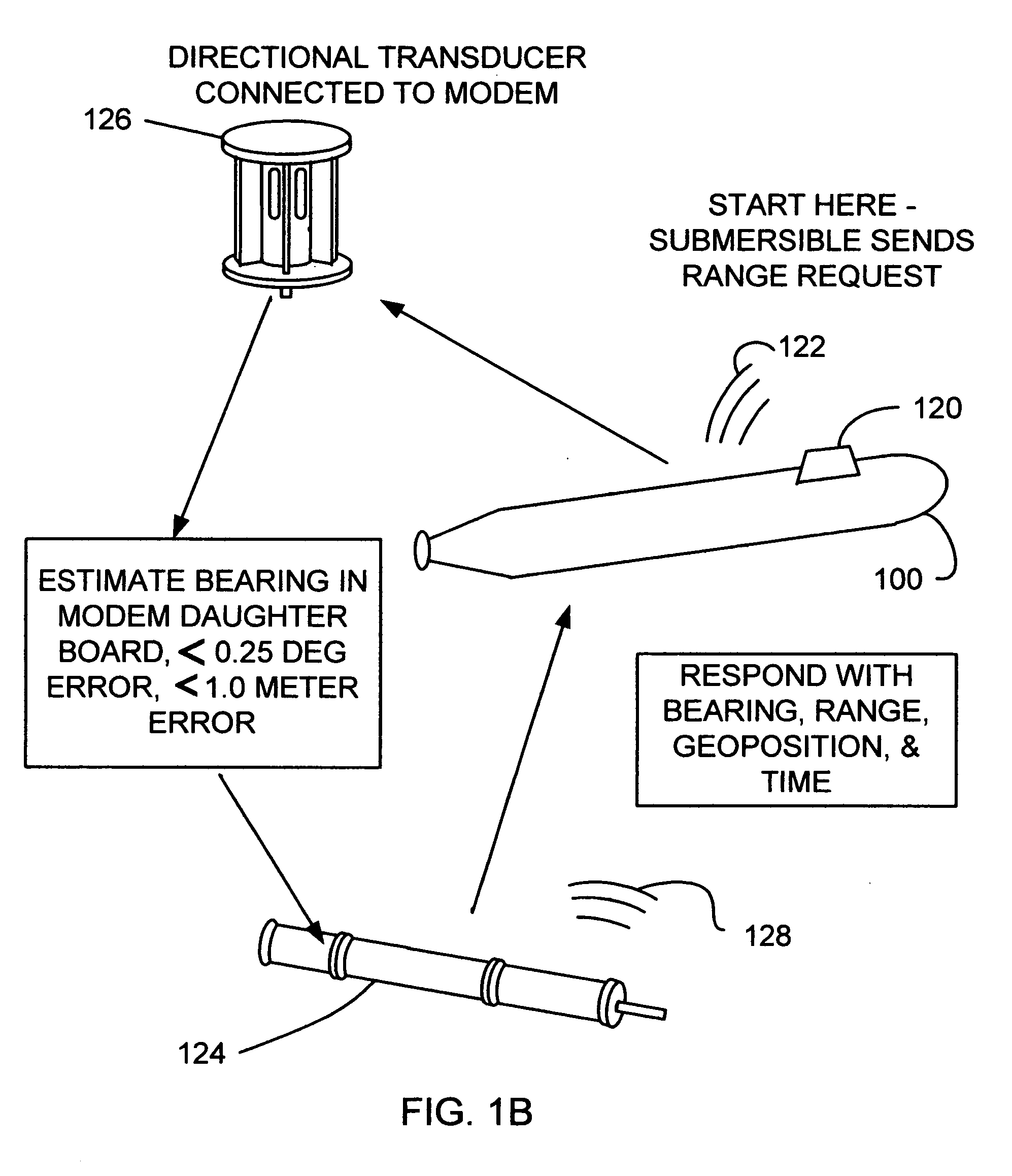
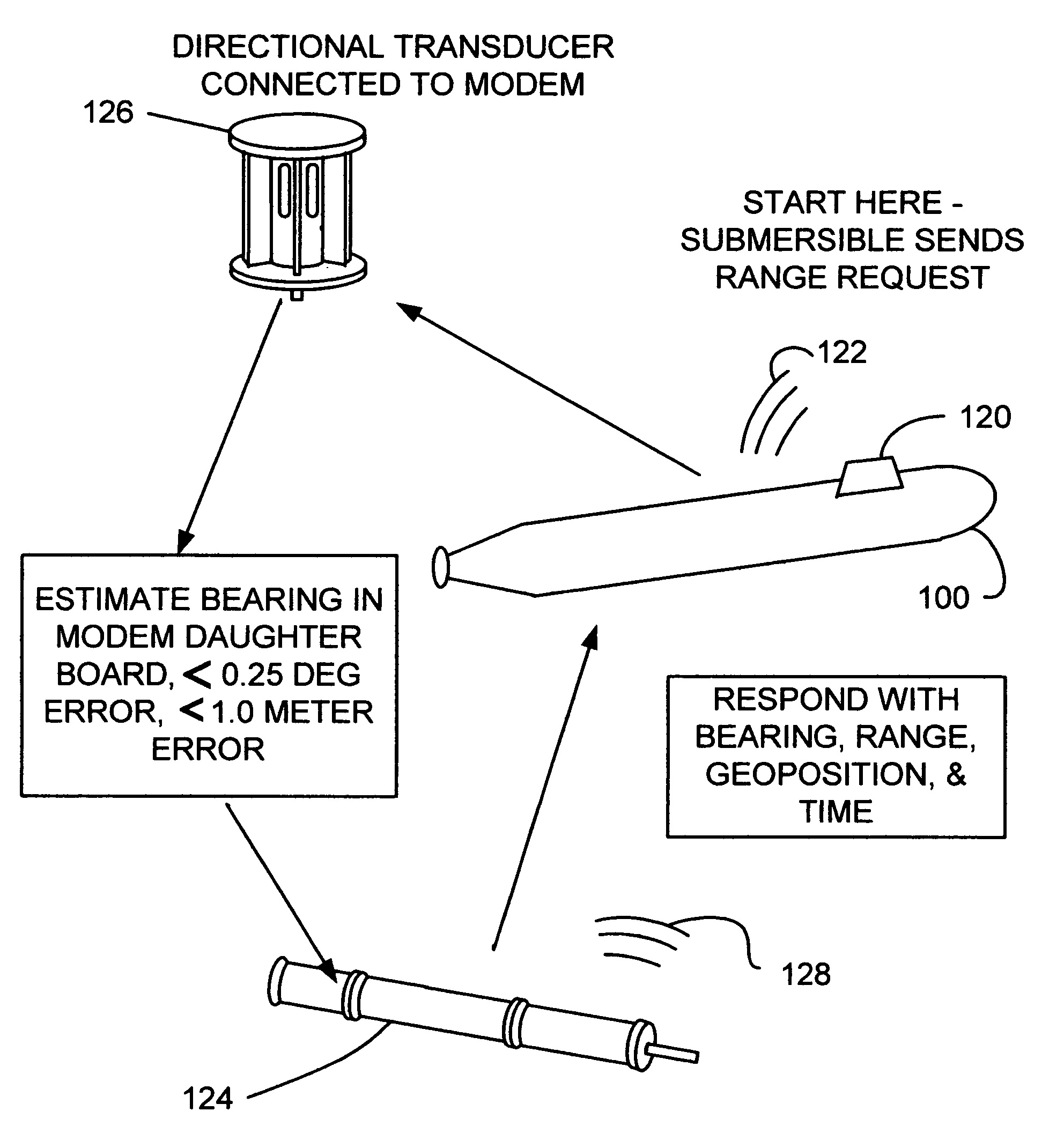
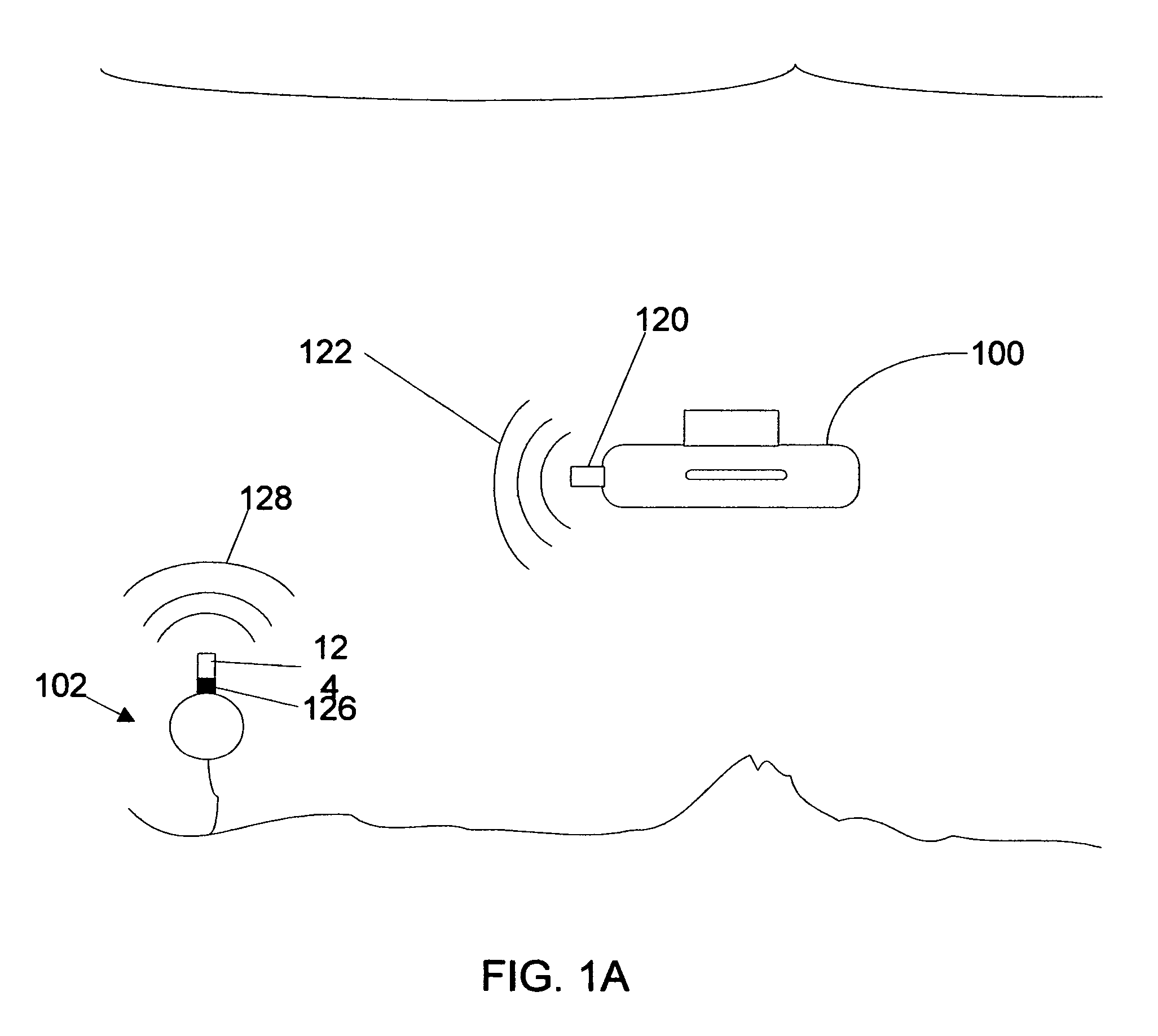
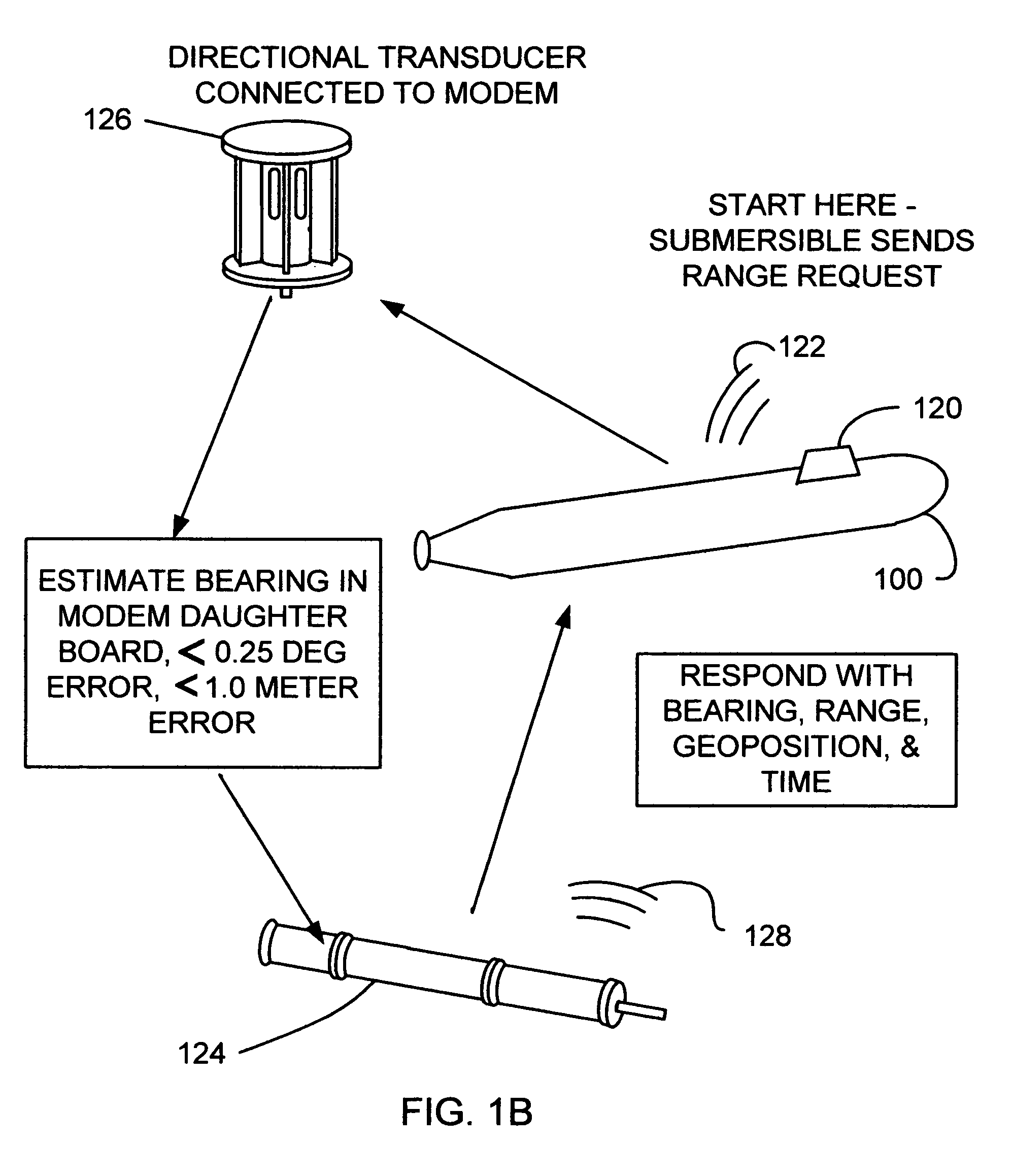
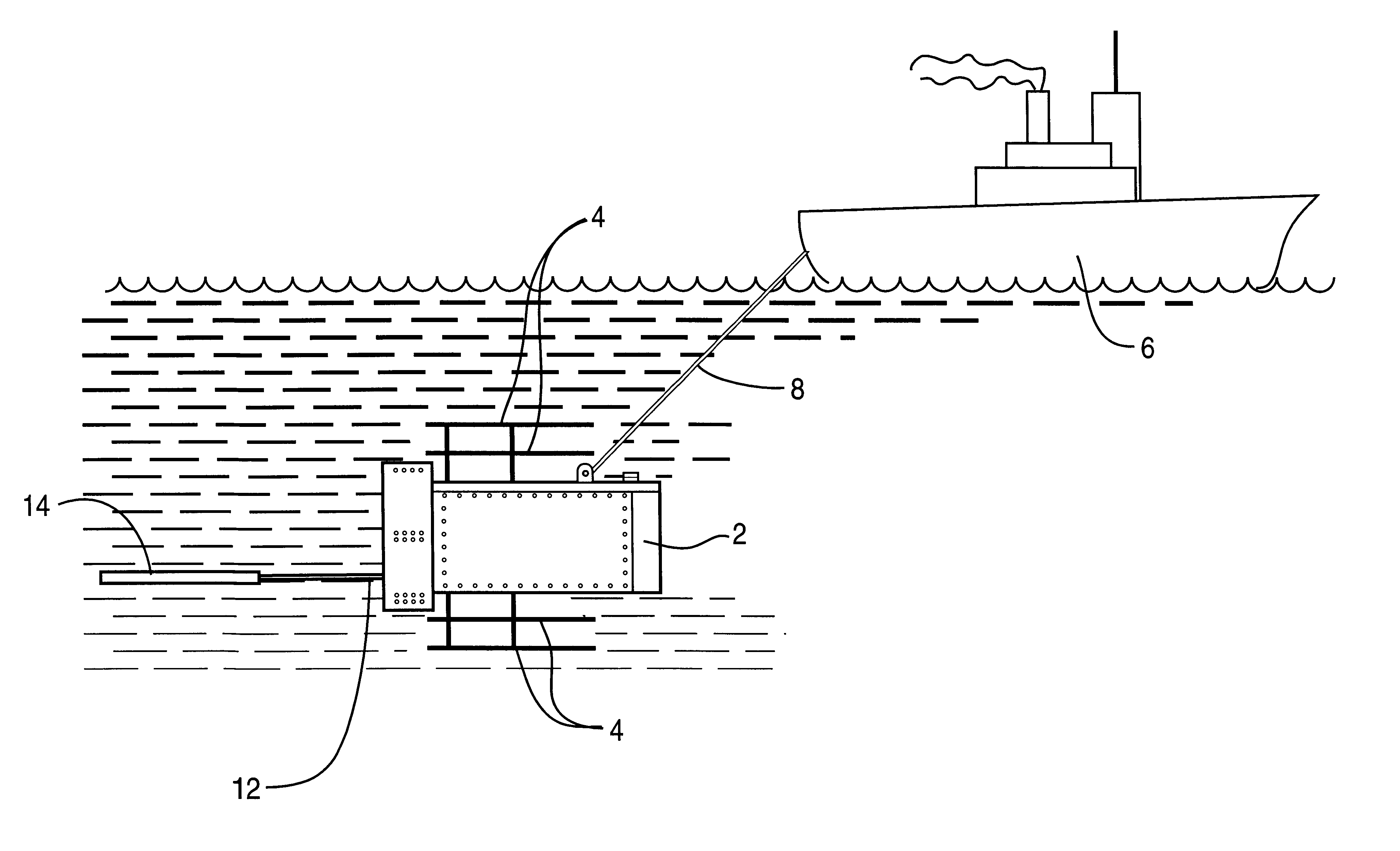
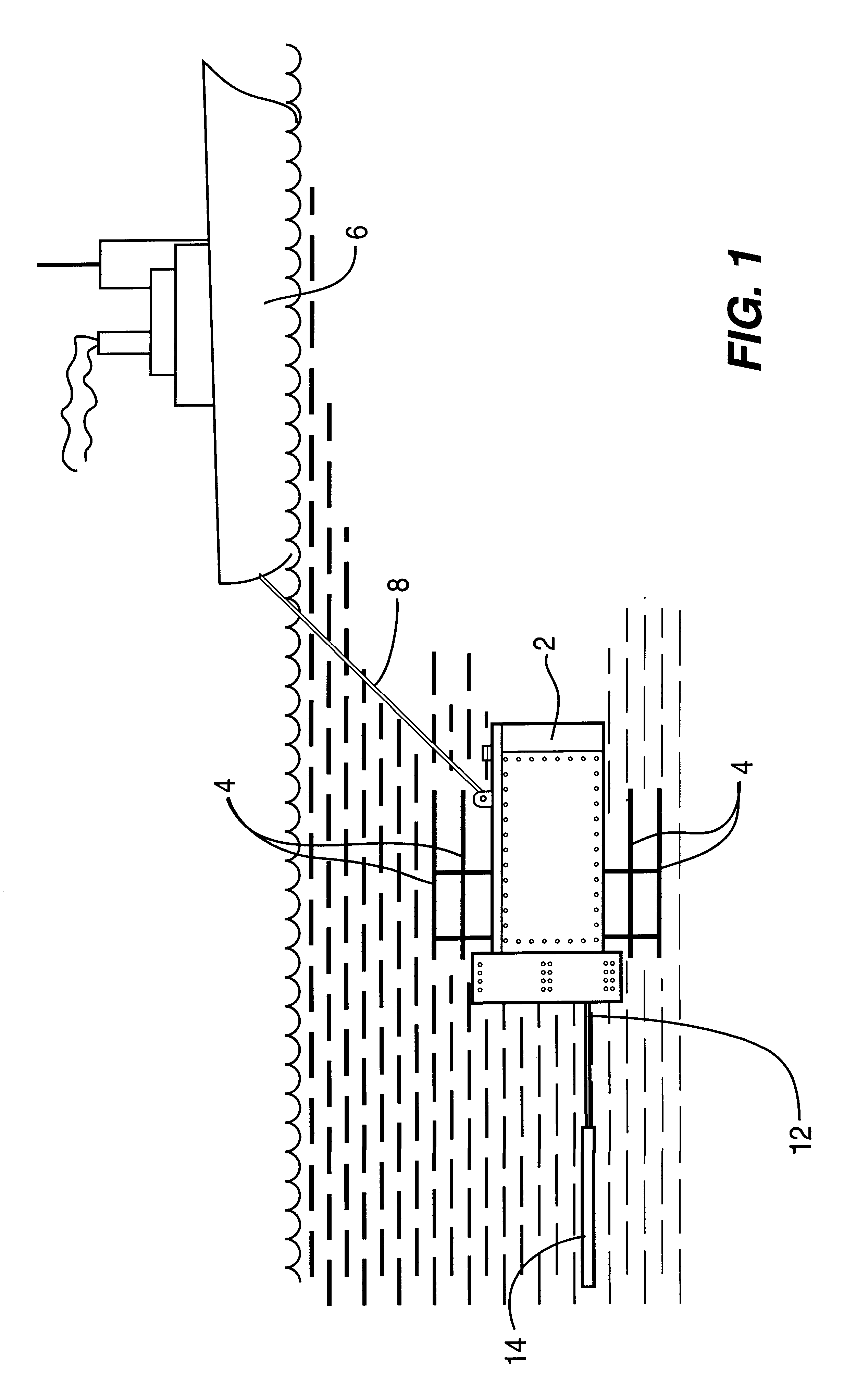
Underwater geopositioning methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20070025185A1Eliminate above-water visibilityAuxillariesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAcoustic transmissionModem device
A method and apparatus for determining the geophysical position of an autonomous underwater system utilizing underwater acoustic modems that exchange broadband underwater acoustic signals. The method of the invention includes the steps of initiating an exchange of broadband acoustic signals between the autonomous system of unknown geophysical position and a base system of known geophysical position wherein the depths of both systems is known. A bearing calculation is made on one of the signals transmitted between the systems, preferably through the use of an array of hydrophones placed closely together at predetermined locations on either the autonomous or base system. Also, the range between the two systems is determined by measuring the time of travel of at least one signal. By the acoustic transmission and sharing of information, as needed, about the known depths of the systems, the known geophysical position of the base system, and the range between the systems, sufficient data is gathered at one or both systems and used to determine the geophysical position of the autonomous system.
Owner:TELEDYNE INSTR INC
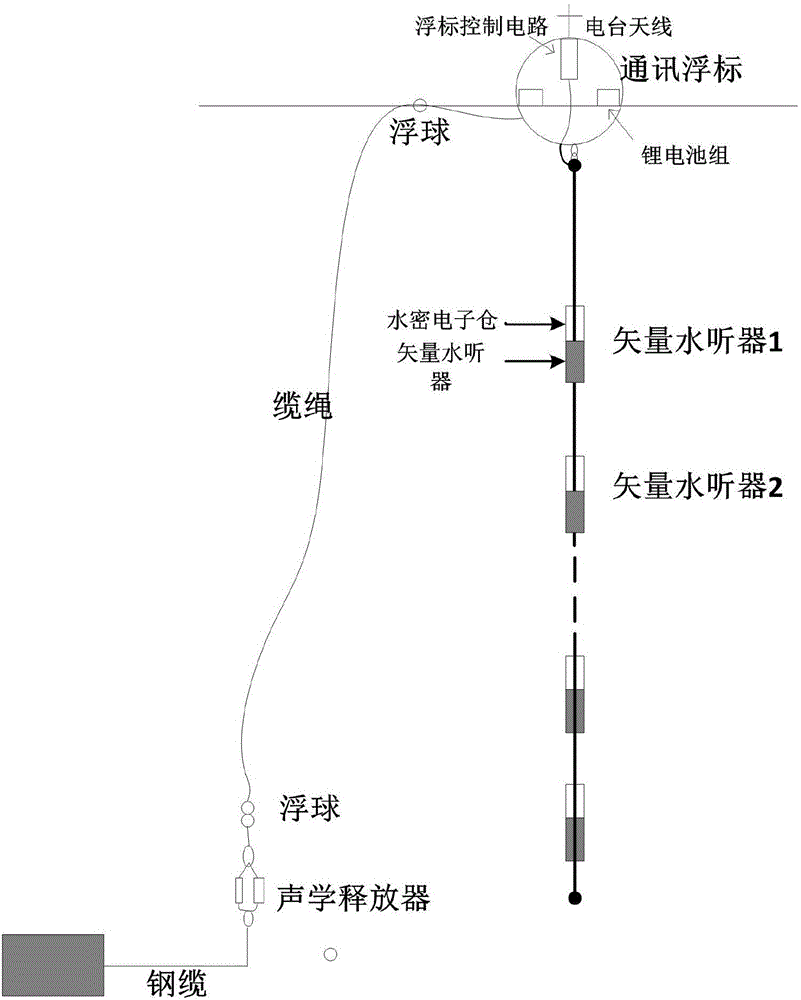
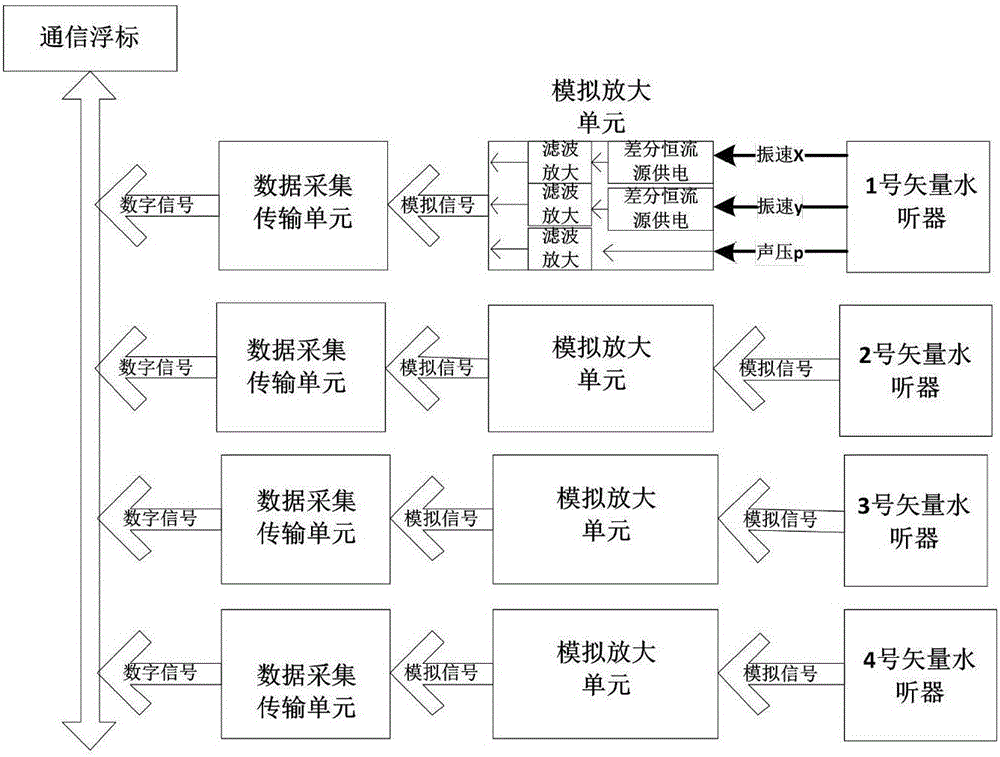
Real-time transmission multivariate vector hydrophone array subsurface buoy system
InactiveCN106568496AReduce vibrationQuality improvementVibration measurement in fluidTransmission systemsFree stateArray element
The invention belongs to the field of marine environment detection equipment, and particularly relates to a real-time transmission multivariate vector hydrophone array subsurface buoy system which acquires and stores marine environment noise of different depths. The real-time transmission multivariate vector hydrophone array subsurface buoy system comprises a vector hydrophone array, a watertight electronic storehouse, a communication cable, a buoy, an acoustic releaser and an anchor block. The vector hydrophone array is vertically arranged, the tail part is in the free state and the number of the array elements is freely adjusted according to the depth. The vector hydrophone array can simultaneously measure the marine environment information of different depths. As for the real-time performance, the acquired data can be uploaded to a shore station in real time to be processed with no requirement for waiting for recycling equipment to perform data recycling processing.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
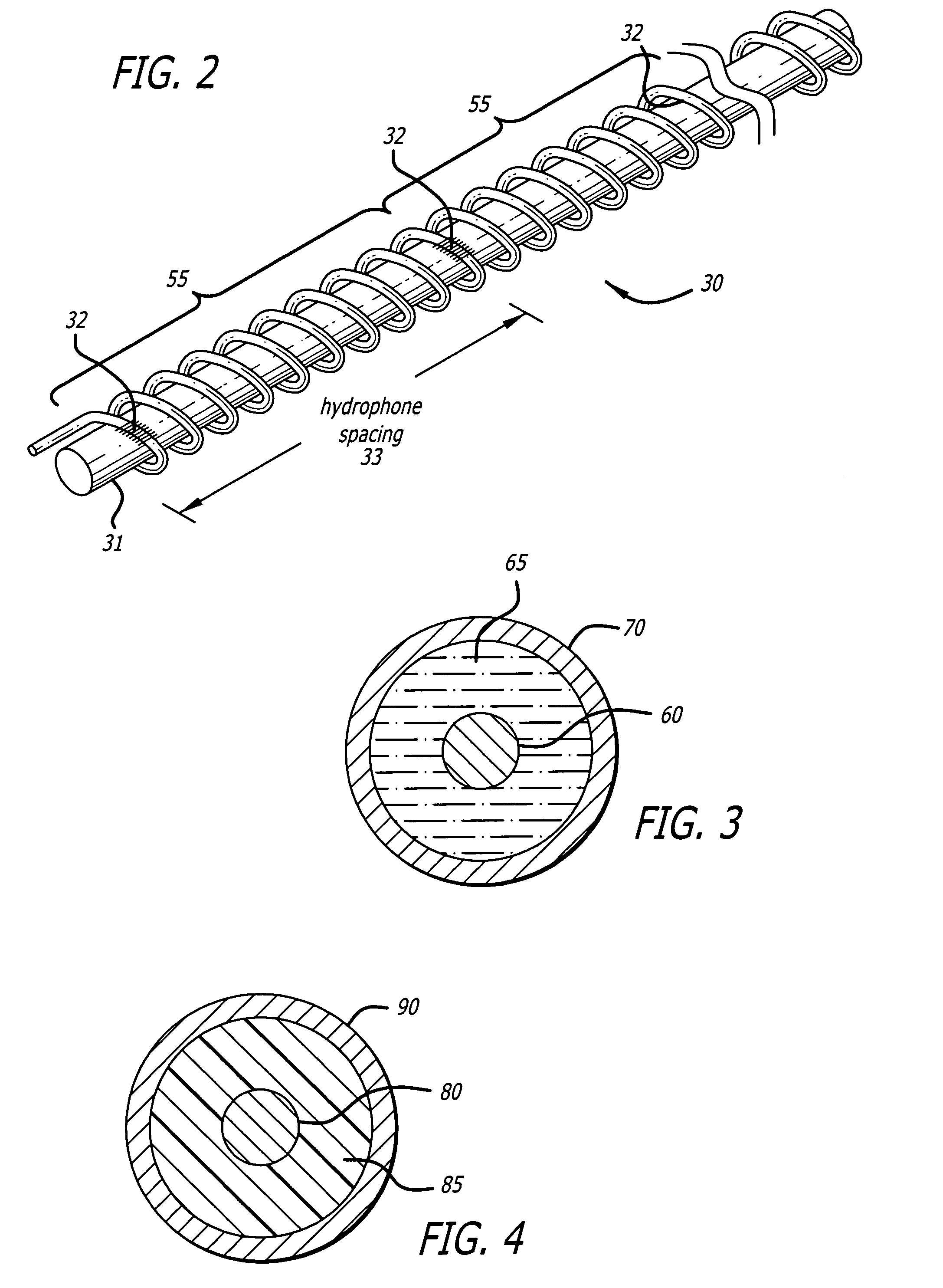
Rugged fiber optic array
InactiveUS7224872B2Reduce demandLimited bandwidthSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSeismic signal receiversElastomerMicrosphere
An array of fiber optic hydrophones or geophones is formed by winding of optical fiber around a continuous, yet flexible cylindrical core. The cylindrical core contains an elastomer filled with a specified percentage of voided plastic microspheres. The elastomer provides the necessary radial support of the optical fiber, and with the included voided microspheres, provides sufficient radial compliance under acoustic pressure for proper operation of the hydrophone. The cylindrical core can be made in very long sections allowing a plurality of fiber optic hydrophones to be wound onto it using a single optical fiber, with individual hydrophone elements separated by integral reflectors such as Fiber Bragg Gratings (FBSs). The center of the core may include a strength member and a central hollow tube for the passing of additional optical fibers. The aforementioned hydrophone array is then packaged within a protective outer coating or coatings as required for the specified application.
Owner:SABEUS PHOTONICS
Phase modulation and demodulation device based on fiber grating hydrophone array
ActiveCN107655561ASimplify complexitySimple structureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberPhase noise
The invention discloses a phase modulation and demodulation device based on a fiber grating hydrophone array. A fiber grating is used as a component of a hydrophone, and a reflection phase modulator with a Faraday rotating mirror is adopted, which makes the structure simpler and reduces the cost. Meanwhile, a PI / 2 phase modulation method is adopted, two orthogonal signals can be directly separatedby sampling, and there is no need for general reference signal mixing and filtering. Thus, the complexity of the algorithm is simplified, the phase noise is reduced, and the system is more applicable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Acoustic monitoring system and method based on ambient sea noise
ActiveCN106441553ASimple structureLow costSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMonitoring systemBuoy
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Non-kinking oil-filled acoustic sensor stave
InactiveUS7180828B1Easy to storePliable qualitySeismic signal receiversSound producing devicesCouplingEngineering
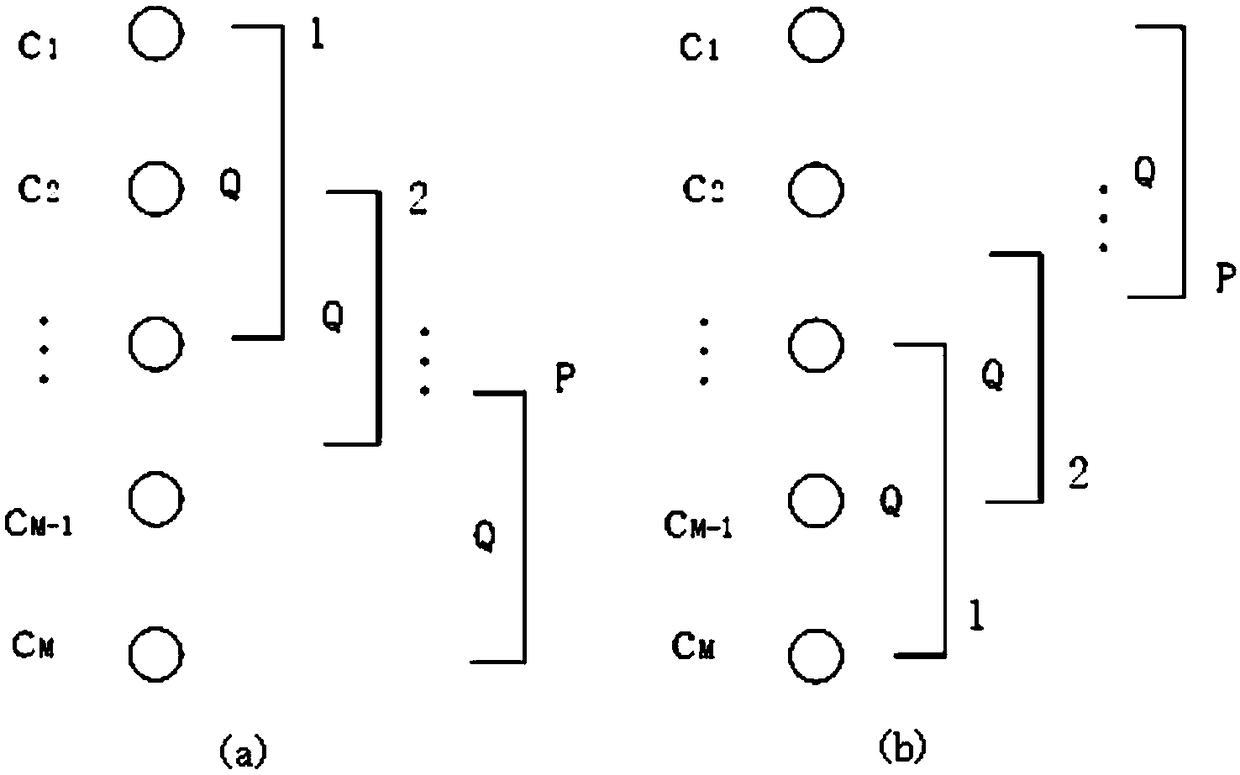
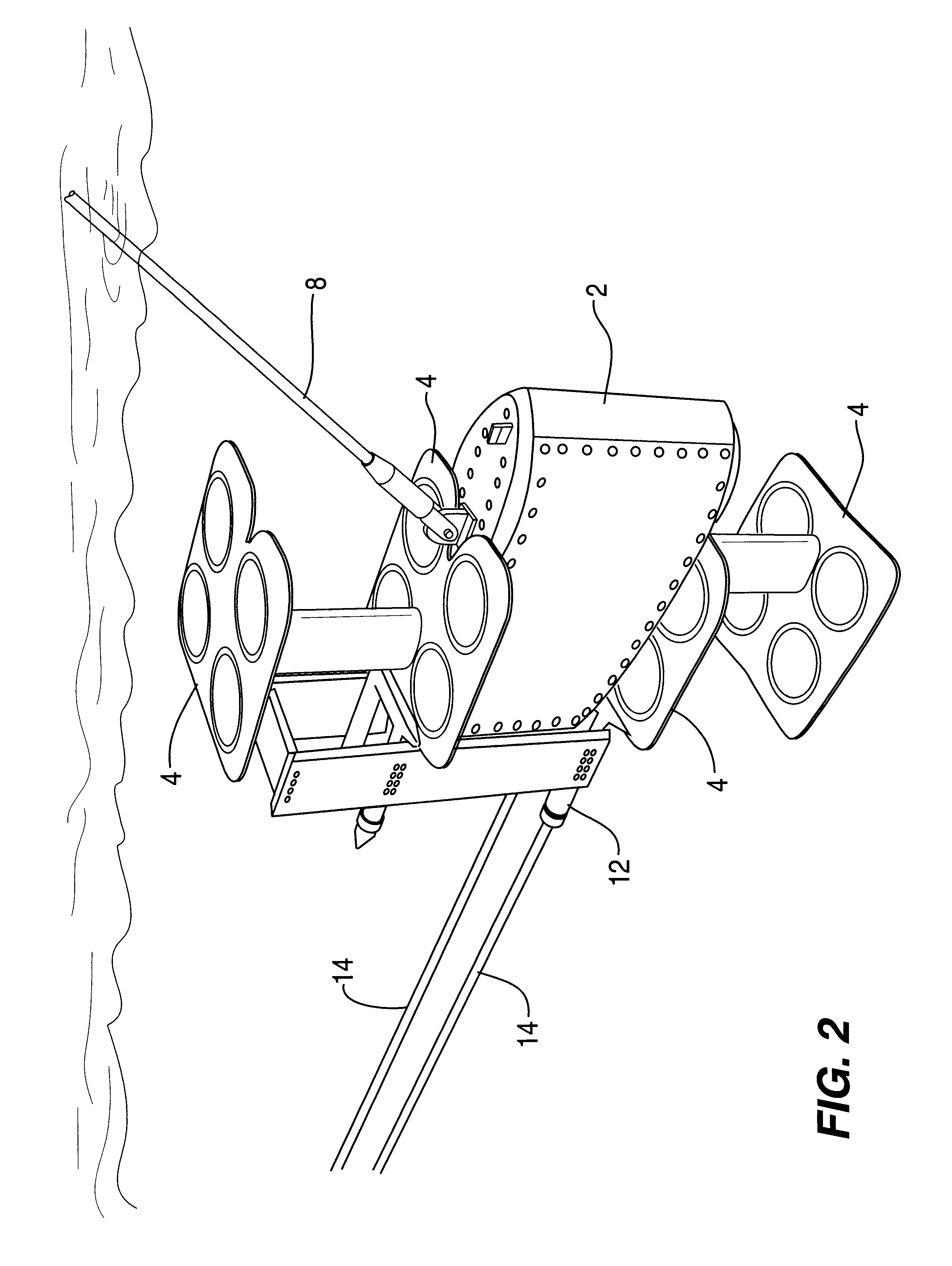
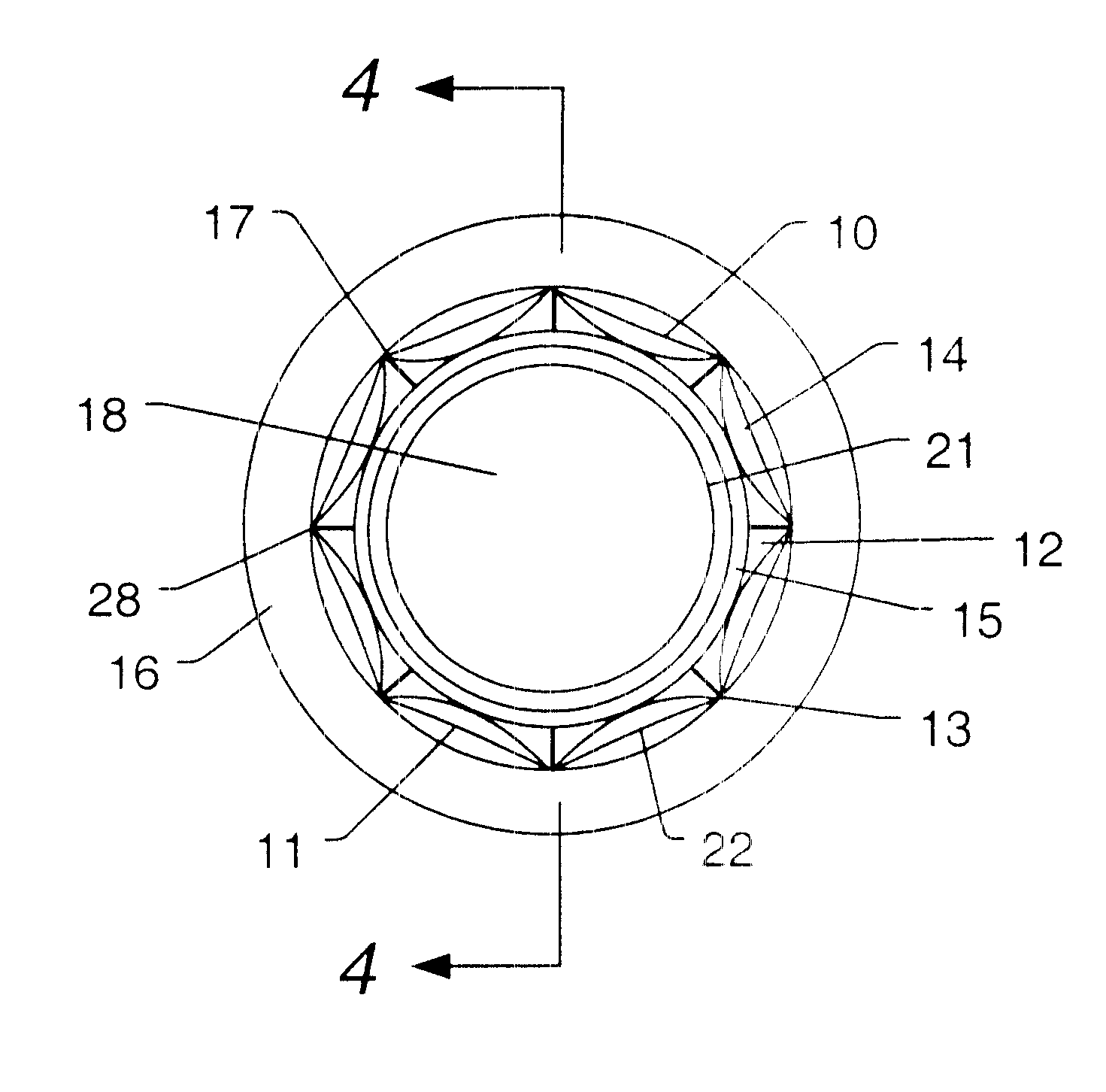
A hydrophone stave comprises a tubular member, a braided cord (or similar flexible structure), cylindrical hydrophones, pins, two plugs and two couplings. The hose (made of a thermoplastic material) is corrugated or convoluted, and is cuffed at both ends to permit a plug to engage at each end. Each coupling includes a wire rope (or similar flexible structure). Each hydrophone has a longitudinal through-aperture (through which the braided cord passes) and a perpendicularly transverse through-aperture (through which a pin passes while also passing through a void created between strands of the braided cord). The stave is suitable for incorporation into a hydrophone array assembly providing for a selected arrayal of hydrophones, e.g., an assembly including two opposite frames united therebetween by numerous congruous parallel staves, each stave including equally spaced hydrophones, each coupling linking a plug with a frame so that the staves are selectively arranged.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Underwater geopositioning methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7362653B2AuxillariesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionAcoustic transmissionInformation sharing
A method and apparatus for determining the geophysical position of an autonomous underwater system utilizing underwater acoustic modems that exchange broadband underwater acoustic signals. The method of the invention includes the steps of initiating an exchange of broadband acoustic signals between the autonomous system of unknown geophysical position and a base system of known geophysical position wherein the depths of both systems is known. A bearing calculation is made on one of the signals transmitted between the systems, preferably through the use of an array of hydrophones placed closely together at predetermined locations on either the autonomous or base system. Also, the range between the two systems is determined by measuring the time of travel of at least one signal. By the acoustic transmission and sharing of information, as needed, about the known depths of the systems, the known geophysical position of the base system, and the range between the systems, sufficient data is gathered at one or both systems and used to determine the geophysical position of the autonomous system.
Owner:TELEDYNE INSTR INC
Multi-target DOA estimation method and underwater sound vertical vector array system
ActiveCN109283492ARealize a full range of estimatesImprove position estimation accuracyPosition fixationWeighted spaceFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a multi-target DOA estimation method and an underwater sound vertical vector array system; the method comprises the following steps: receiving a multi-target signal based on the vertical vector hydrophone array; converting the received multi-target signal to obtain a frequency spectrum and a power spectrum, and extracting a line spectrum; using a vector regular correlationalgorithm to estimate a target sound source number; using a vector weighted space smooth algorithm to obtain a MUSIC space spectrum according to the extracted line spectrum; carrying out two dimensional searching decision for a space spectrum peak corresponding to the multi-target according to the estimation result of the target sound source number and the MUSIC space spectrum, and respectively obtaining a multi-target horizontal angle and a pitching angle; step6, integrating the horizontal angles and pitching angles calculated for each line spectrum, thus obtaining the multi-target DOA estimation result. The method uses the three-dimensional vertical vector hydrophone array to realize all-dimensional estimation of the target signal horizontal angle and pitching angle, thus improving theDOA estimation accuracy of the coherent multi-target signal.
Owner:THE THIRD RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Place calibration of sonar receive array
The invention pertains to sonar receive arrays. More particularly, the invention pertains to a process for calibrating the amplitude, position and phase angle of an array of underwater receive hydrophones with respect to one another. The process requires projecting an acoustic test signal at a known frequency from a towed underwater acoustic projector toward an array of towed, underwater, interconnected, receive hydrophones; detecting and determining the response of the receive hydrophones to said test signal by signal processing means; and calibrating at least one parameter for the operation of the receive hydrophones resulting from the response. Calibrated parameters include the amplitude, position and phase angle of the receive hydrophones relative to one another.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
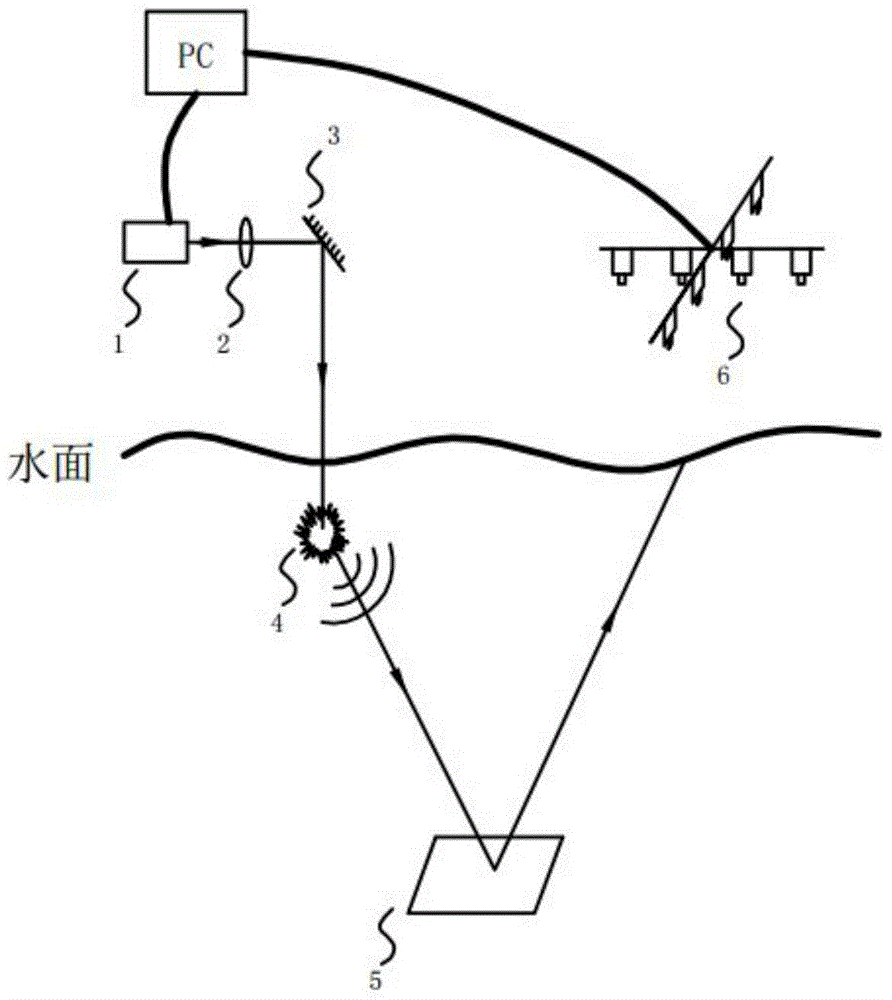
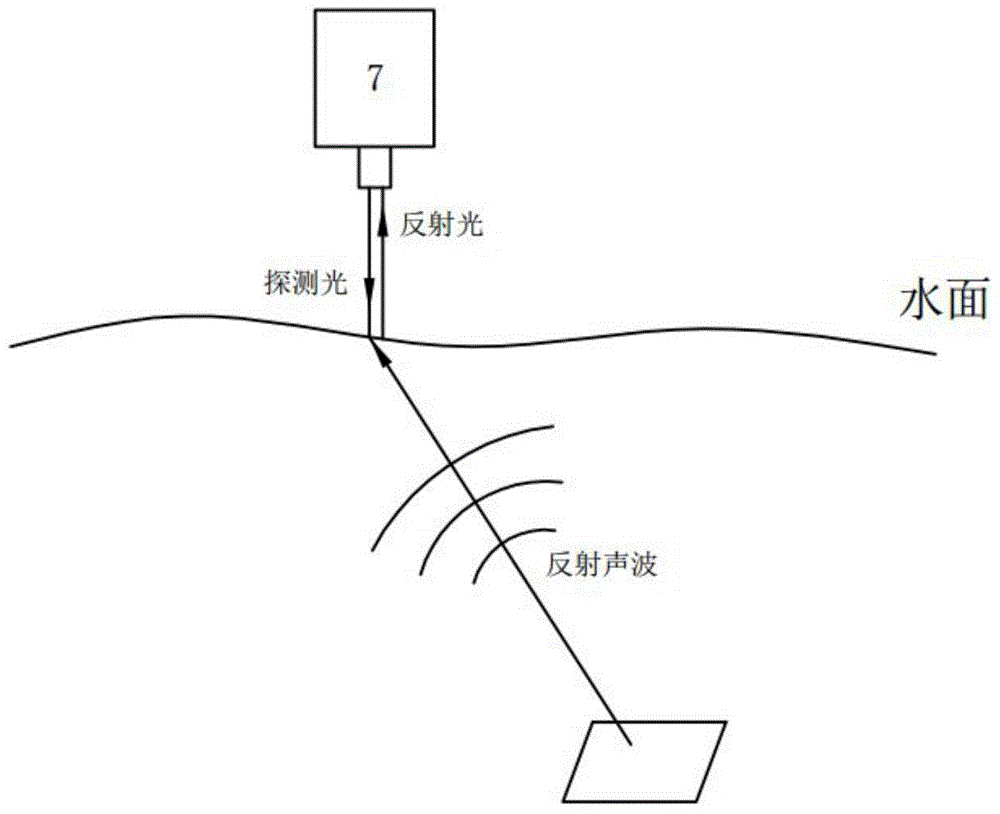
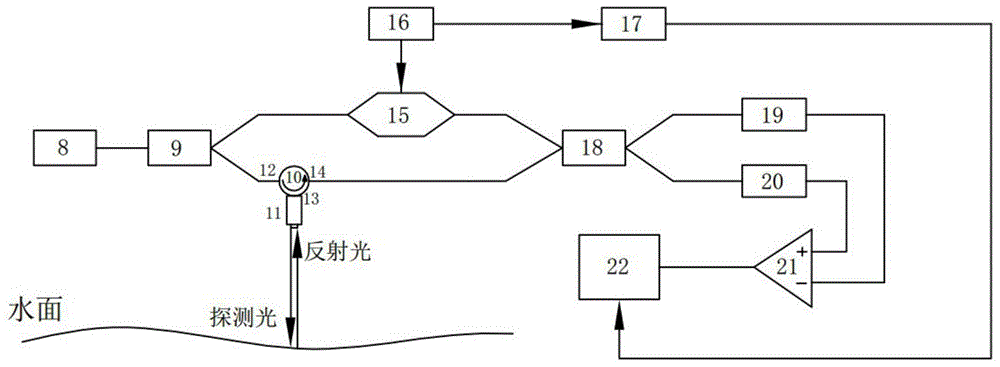
Measurement system and method for detecting orientation and size of underwater target on basis of laser sound source
ActiveCN104808208AAvoid disadvantagesAvoid attenuationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUsing optical meansSound sourcesFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a measurement system and method for detecting the orientation and the size of an underwater target on the basis of a laser sound source. According to the measurement system and method, the sound source is generated through lasers, laser energy is converted into sound wave energy, an acousto-optical coupling interference type optical fiber hydrophone array serves as a receiving sensor, the defects that in the optical measurement process, optical waves which are used are large in attenuation and the measuring distance is short are overcome, the defects of a sonar sensor in traditional acoustics detection are overcome, and the advantages that mobility and flexibility are high are achieved. Meanwhile, a sound source signal is generated through a laser-induced sound system, and generated sound signals have the advantages of being high in sound pressure level, wide in frequency spectrum, capable of conducting non-contact type control, and the like. An acousto-optical coupling interference type optical fiber hydrophone is used as the acoustic signal sensor, and the acoustic signal sensor has the advantages of being capable of detecting underwater acoustic signals in the non-contact mode, high in mobility, small in size, flexible in structural design, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
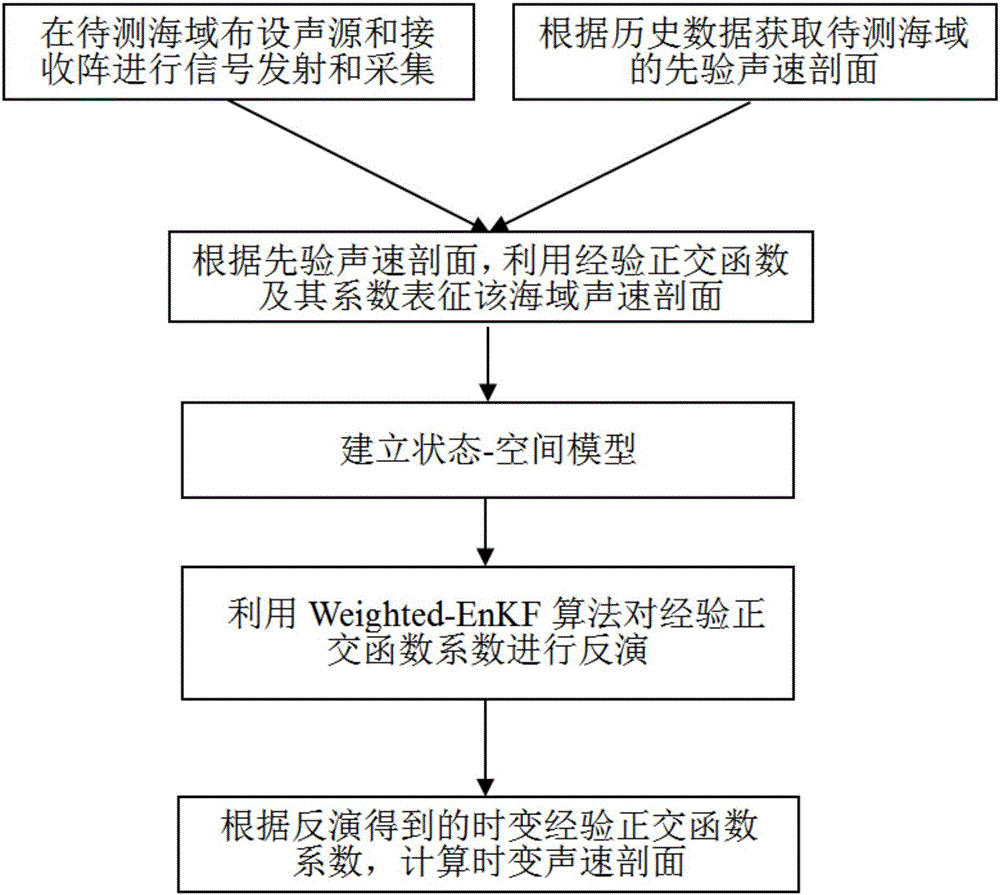
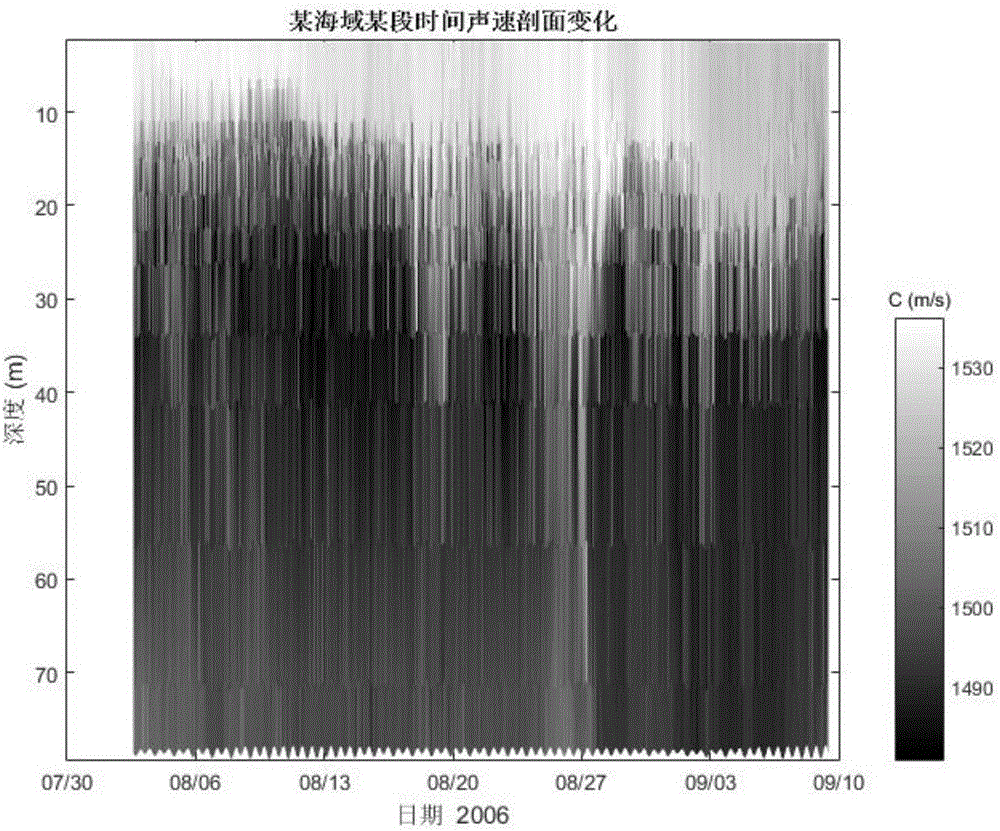
Acoustic velocity profile inversion method based on weighted-EnKF algorithm
InactiveCN105911551AImprove estimation performanceHigh precisionVelocity propogationAcoustic wave reradiationSound sourcesSignal on
Provided is an acoustic velocity profile inversion method based on a weighted-EnKF algorithm, comprising the steps of: 1) first, employing a sound source to emit sound signals on a sea area to be measured and employing a vertical hydrophone array to collect sound pressure signals; 2) obtaining a prior acoustic velocity profile according to historical data, and utilizing an empirical orthogonal function and a coefficient thereof to represent a sea area acoustic velocity profile; 3) utilizing an empirical orthogonal function coefficient evolution equation and a sound pressure observation equation to establish a state-space model; 4) employing a weighted-EnKF algorithm to perform inversion on the empirical orthogonal function coefficient; and 5) utilizing a time-varying inverse result and an acoustic velocity profile characterization formula to calculate the time-varying acoustic velocity field of the sea area. Through simulation examples, the feasibility of acoustic velocity profile inversion based on a weighted-EnKF algorithm is displayed, and the inversion precision is verified to be higher than the precision of a routine acoustic velocity profile inversion method based on EnKF.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
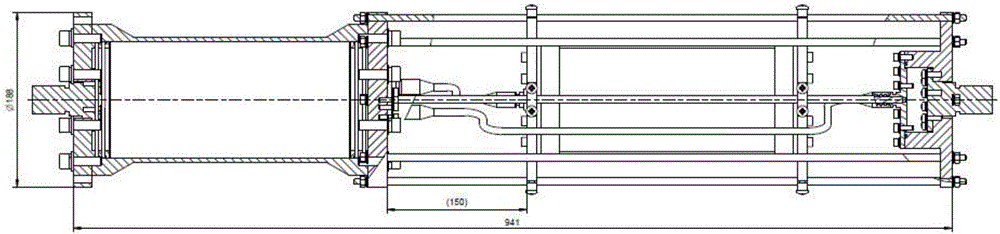
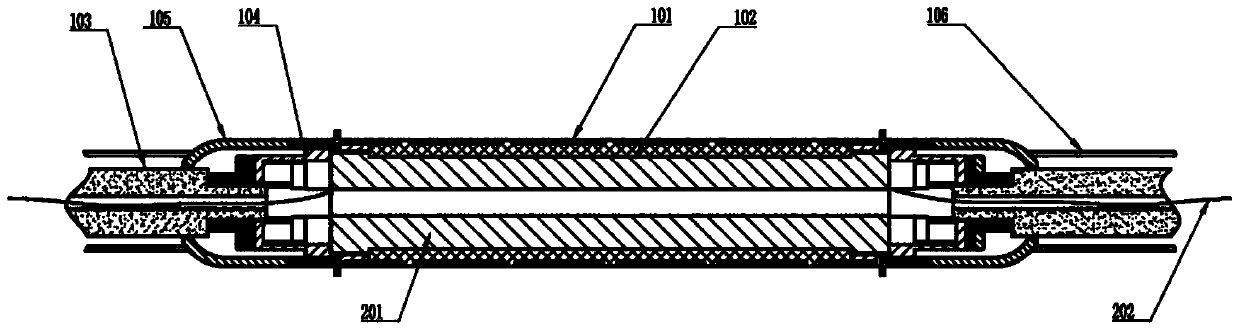
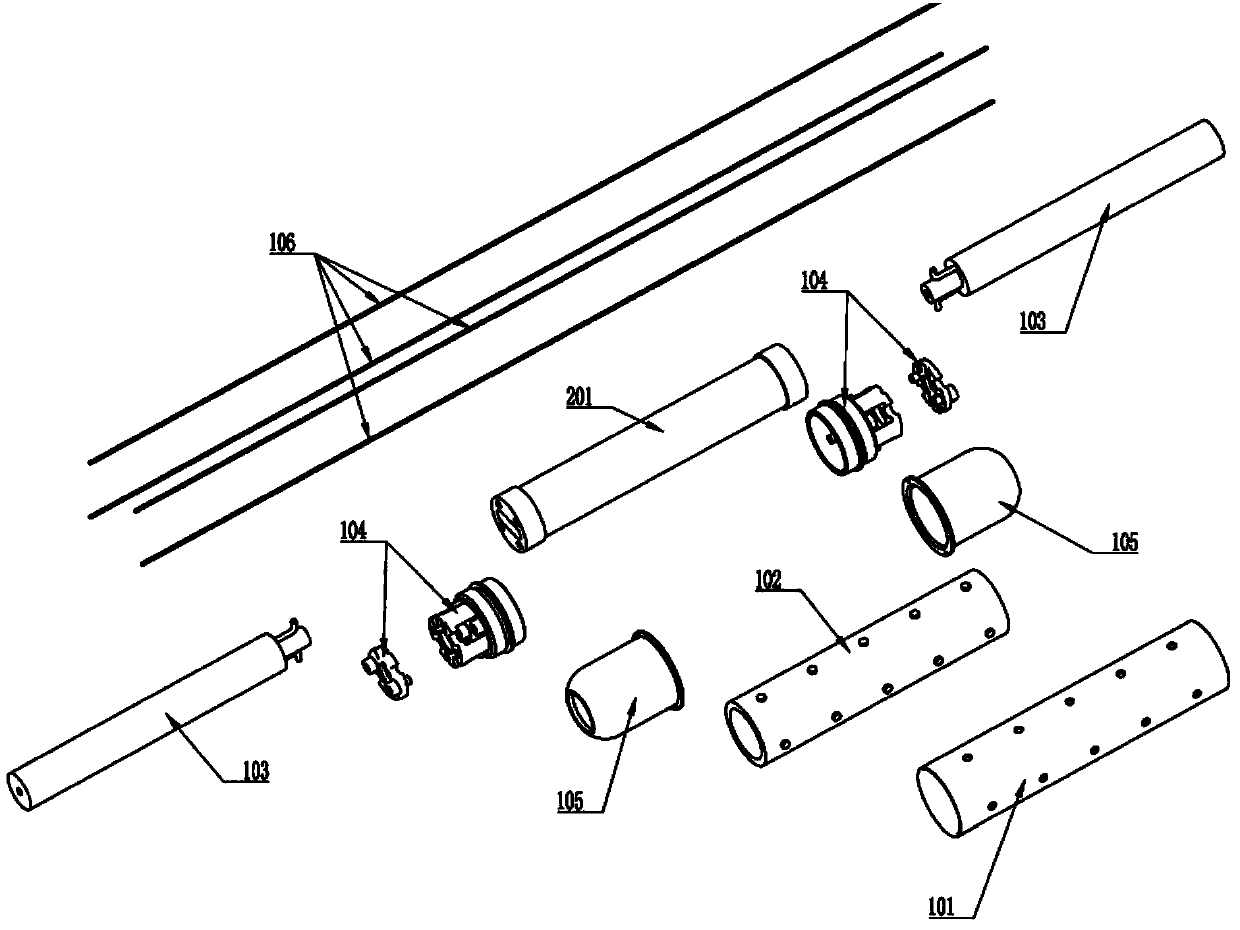
Novel packaging structure for fiber optic hydrophone probe and fiber optic hydrophone array
ActiveCN104215318ASolve problems in engineering applicationsAvoid destructionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansTransmission propertiesHydrophone array
A novel packaging structure for a fiber optic hydrophone probe and a fiber optic hydrophone array comprise an outer shell, polyurea composite material, an armored cable, a pressure plate connector, a transition connecting sleeve, a Kevlar rope, an acoustic sensor and the like. The outer shell is packaged under pressure through the acoustic sensor with pressure resistance and sound transmission of the probe considered; the polyurea composite material is watertight packaging material with excellent hydrophobic and sound transmission properties; the armored cable is used for connecting and packaging when a plurality of probes form an array and fibers among the probes are protected with good watertight and mechanical properties. Both ends of the acoustic sensor are connected with the armored cable through the pressure plate connector; an external sleeve of the pressure plate connector is sealed through a transition connected sleeve; a plurality of fixing holes are formed on the connected sleeve to fix the Kevlar rope and improve tensile strength of an arraying probe cable. Compared with the prior art, the packaging structure has high structural reliability, good water tightness and strong deepwater pressure capacity. Furthermore, engineering and mass assembly are easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
High-frequency closely-spaced piezoelectric film hydrophone array and production method thereof
ActiveCN103175601AImproved detection resolutionImprove electromagnetic compatibilityVibration measurement in fluidTransducerEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of underwater sound transducers, in particular to a high-frequency hydrophone array applicable to underwater phased array camera and a production method thereof, and solves the technical problems that a large cardinal number of high-frequency hydrophone array elements need to be accurately located and disposed in a limited array area and charge sensed by efficient coupling array elements is required to pick up and receive high-frequency weak underwater sound signals. A piezoelectric device PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) film, a rigid backing and PCBs (printed circuit board) are jointed; the high-frequency PVDF hydrophone backing is made of copper to increase sensitivity; multiple layers of PCBs are used as a substrate; a large number of array element backings are integrally pre-processed; the array element backing clusters are positioned and fitted to the PCB substrate; the backing units are separated by secondary processing; decoupling bars are added among the separated units; the piezoelectric film is adhered to form an array; finally, watertight sealing is performed to form the high-frequency piezoelectric film hydrophone array. The high-frequency hydrophone array is applicable to high-frequency sonar receiving arrays for imaging sonar, multi-beam sonar, side-scan sonar and the like.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Fiber optic curvature sensor for towed hydrophone arrays
InactiveUS20030072515A1Limiting maximum strainIncreased strain sensitivitySeismic signal receiversCoupling light guidesHydrophone arrayEngineering
The present invention relates to a system for sensing the curvature of a towed hydrophone array and a curvature sensor used in the system. The system has at least two curvature sensors positioned along the length of the array. Each of the curvature sensors comprises a bend member which bends as the array bends, at least one optical fiber within the bend member, and at least one detection device embedded within the at least one optical fiber to detect a change in the strain in the at least one optical fiber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
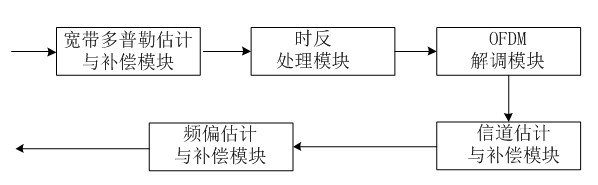
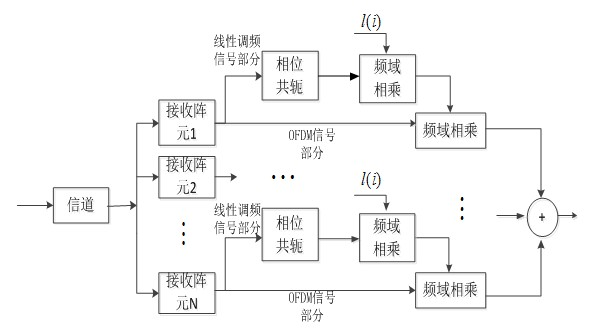
Underwater sound communication device and method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment
InactiveCN102546511AReduce multipath effectsEliminate delayMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringCombined treatment
The invention discloses an underwater sound communication device and a method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment. The underwater sound communication device comprises a signal transmitter, a power amplifier, a transmitting transducer, a receiving hydrophone array, a signal receiver and a signal processor, wherein the signal processor comprises a broadband Doppler estimation and compensation module, a time reversal processing module, an OFDM demodulation module, a channel estimation and compensation module and a frequency deviation estimation and compensation module. In the underwater sound communication device, the space time focusing characteristics of the time reversal are utilized to eliminate the multipath influence of the channel; a pulse channel response length can be shortened by the time reversal so as to reduce the length of an OFDM symbol guard interval and improve the communication efficiency; and because the guard interval is reduced, the length of the OFDM symbol can be shortened so as to enlarge a subcarrier frequency interval. With the method disclosed by the invention, interference among subcarriers can be reduced, and the available rate of the OFDM underwater sound communication is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
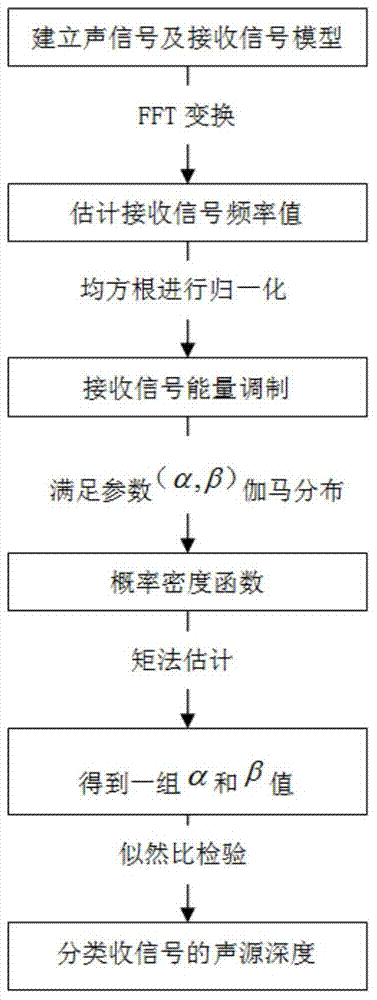
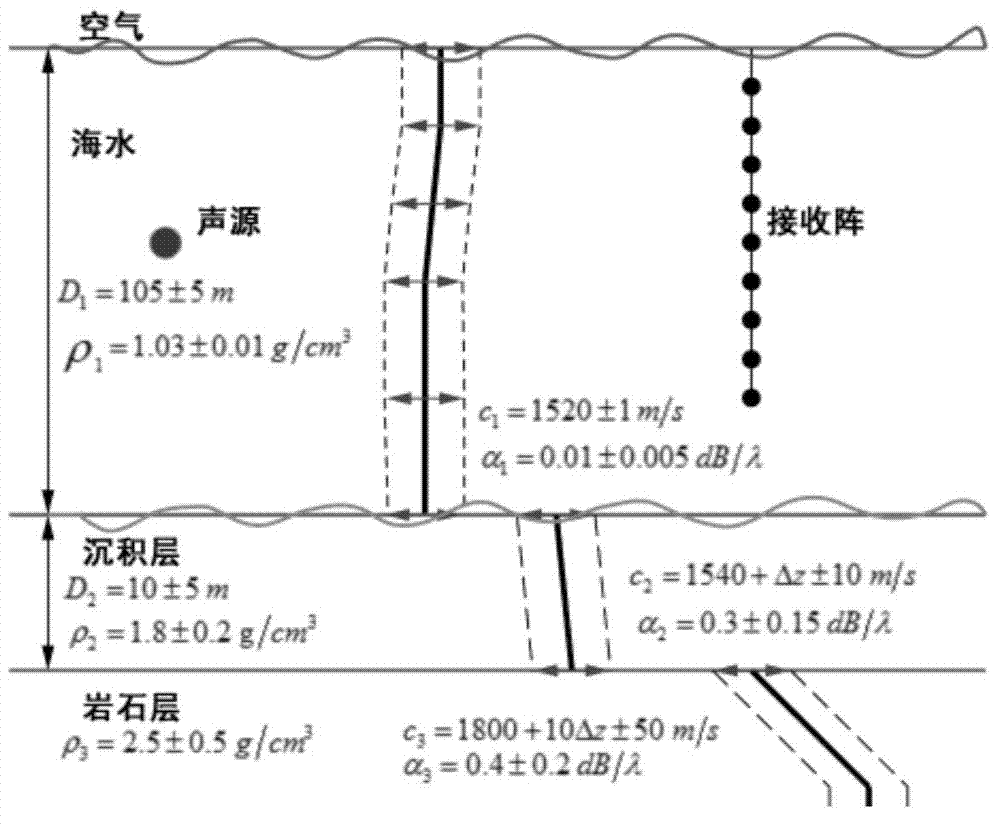
Shallow sea target depth classification method based on hydrophone array
ActiveCN104749568AImprove environmental adaptabilityWave based measurement systemsNormal densitySound sources
The invention provides a shallow sea target depth classification method based on a hydrophone array. Detection is performed by integrating information received by multiple hydrophones, a typical probability density function of energy field change produced by model-based deep and shallow sound sources is generated by acoustic propagation simulation, likelihood ratio test (LRT) is performed based on the probability density function to identify a received signal, prior knowledge is extracted according to the law of distribution of sound energy within the whole range of a sound field, and thus, depth classification is performed on the sound field target. The algorithm is easy to implement and high in environmental adaptability.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fiber optic curvature sensor for towed hydrophone arrays
InactiveUS6728431B2Limiting maximum strainIncreased strain sensitivitySeismic signal receiversCoupling light guidesFiberEngineering
The present invention relates to a system for sensing the curvature of a towed hydrophone array and a curvature sensor used in the system. The system has at least two curvature sensors positioned along the length of the array. Each of the curvature sensors comprises a bend member which bends as the array bends, at least one optical fiber within the bend member, and at least one detection device embedded within the at least one optical fiber to detect a change in the strain in the at least one optical fiber.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
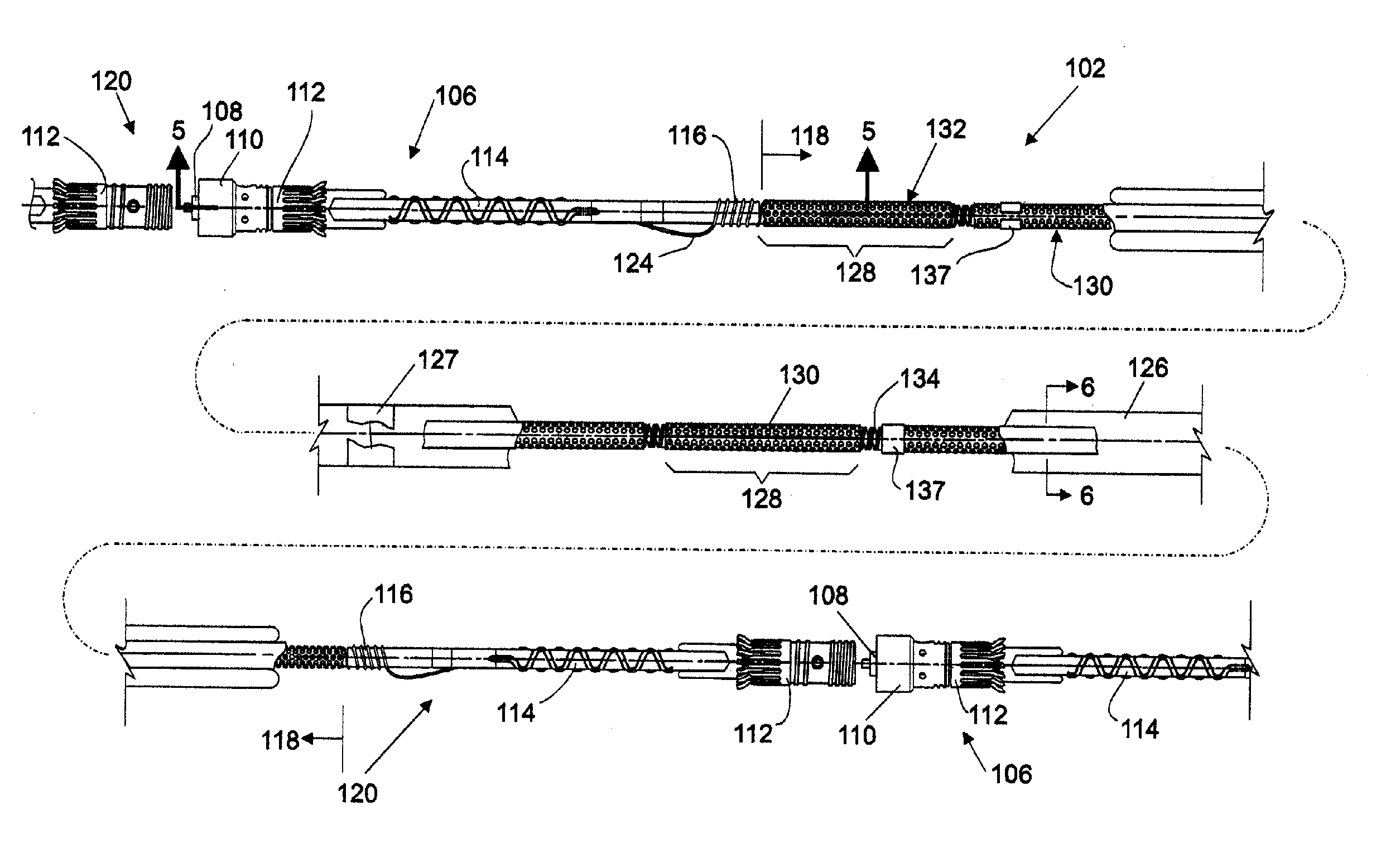
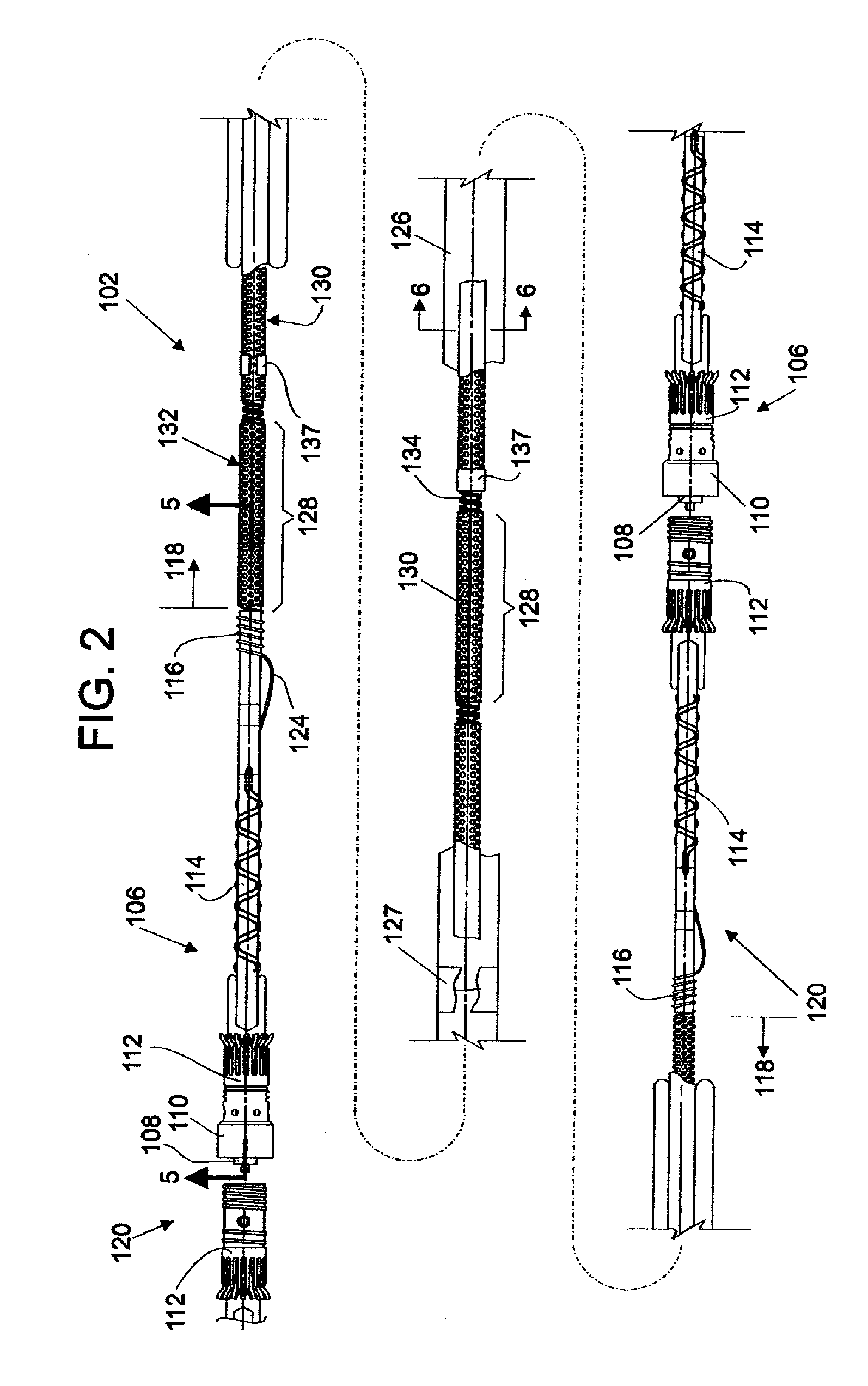
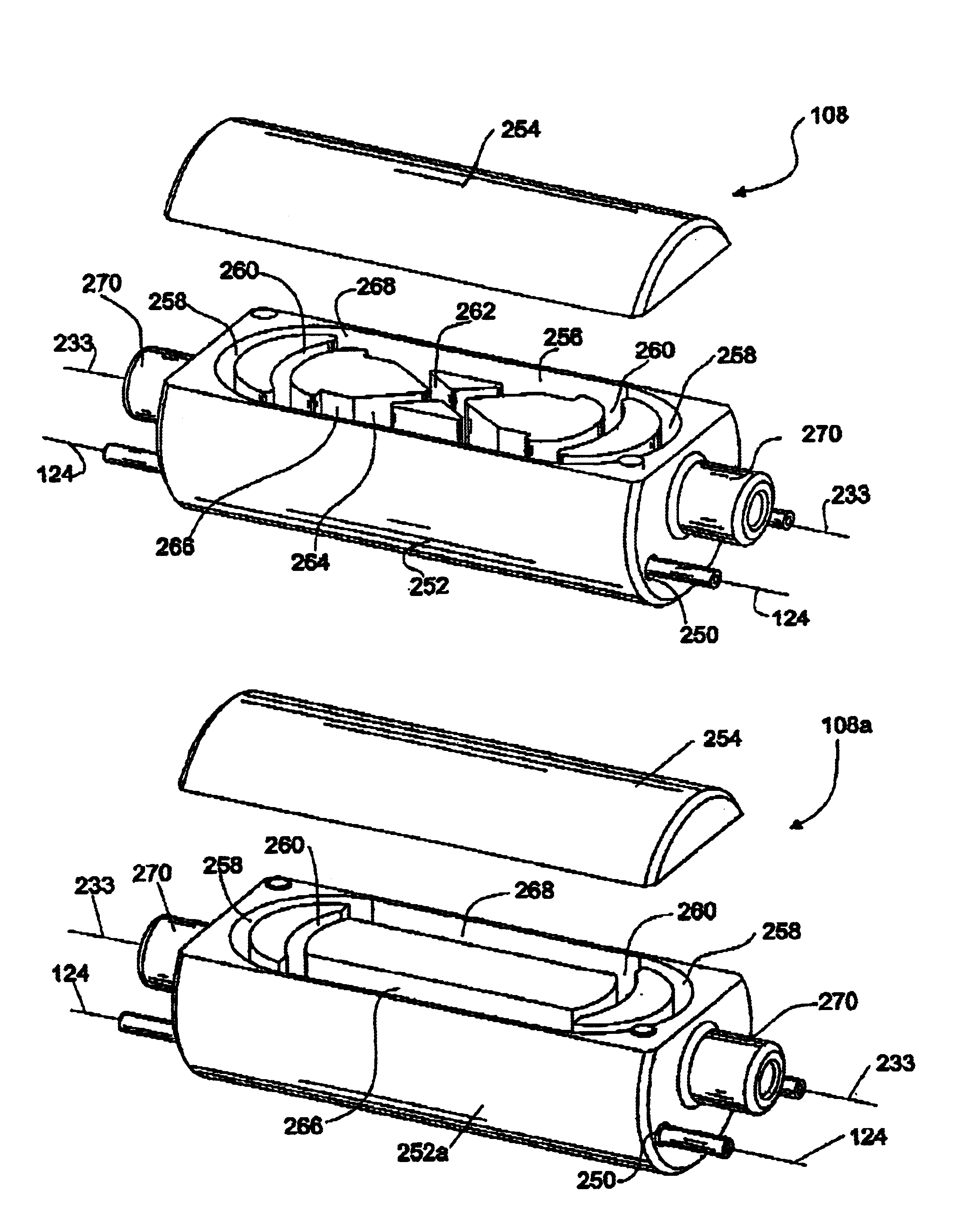
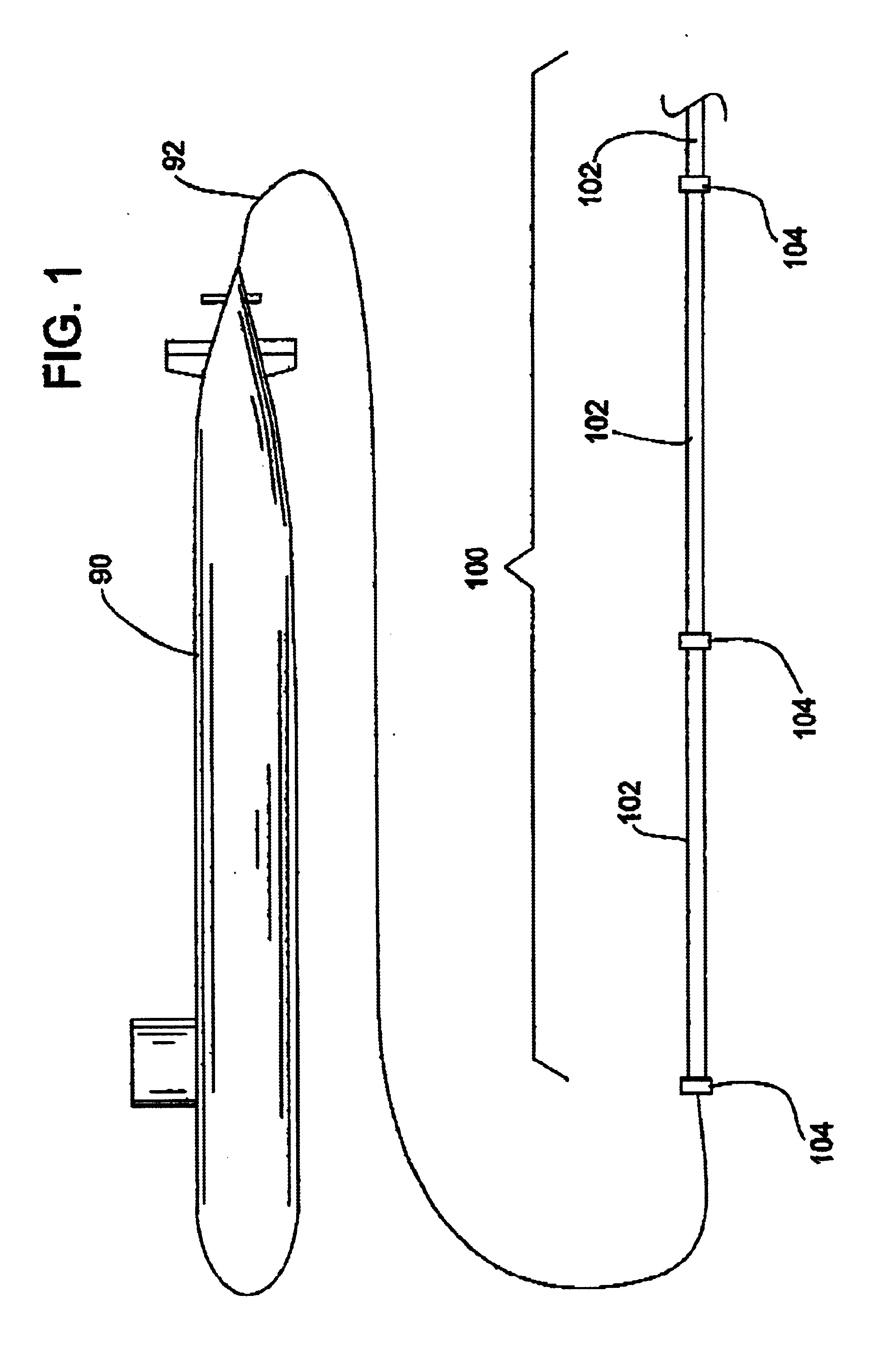
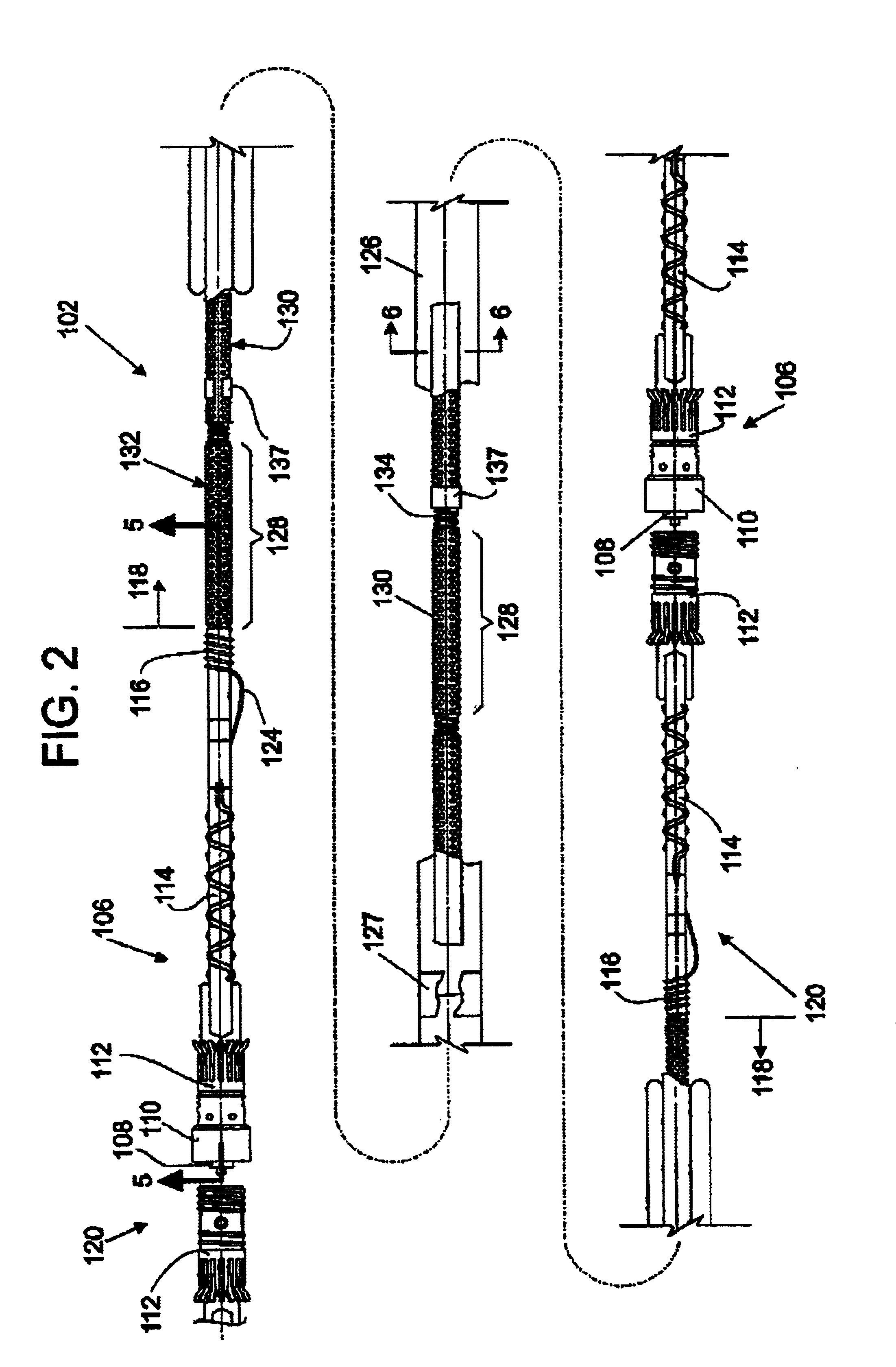
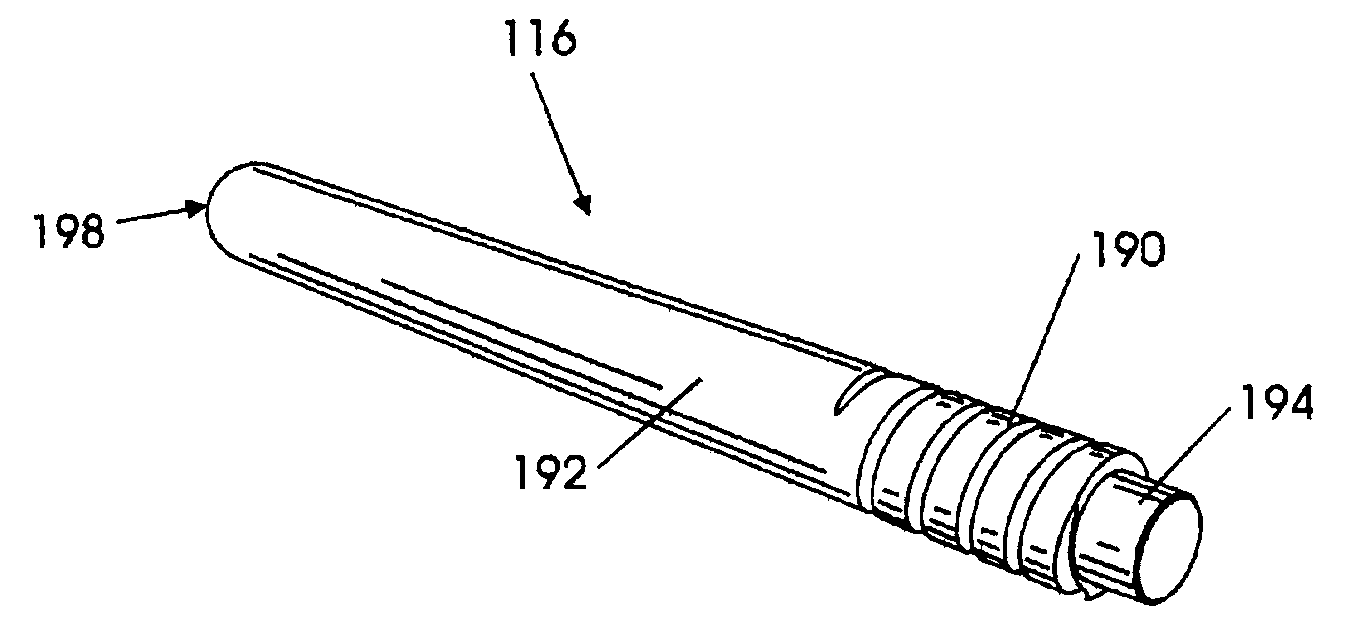
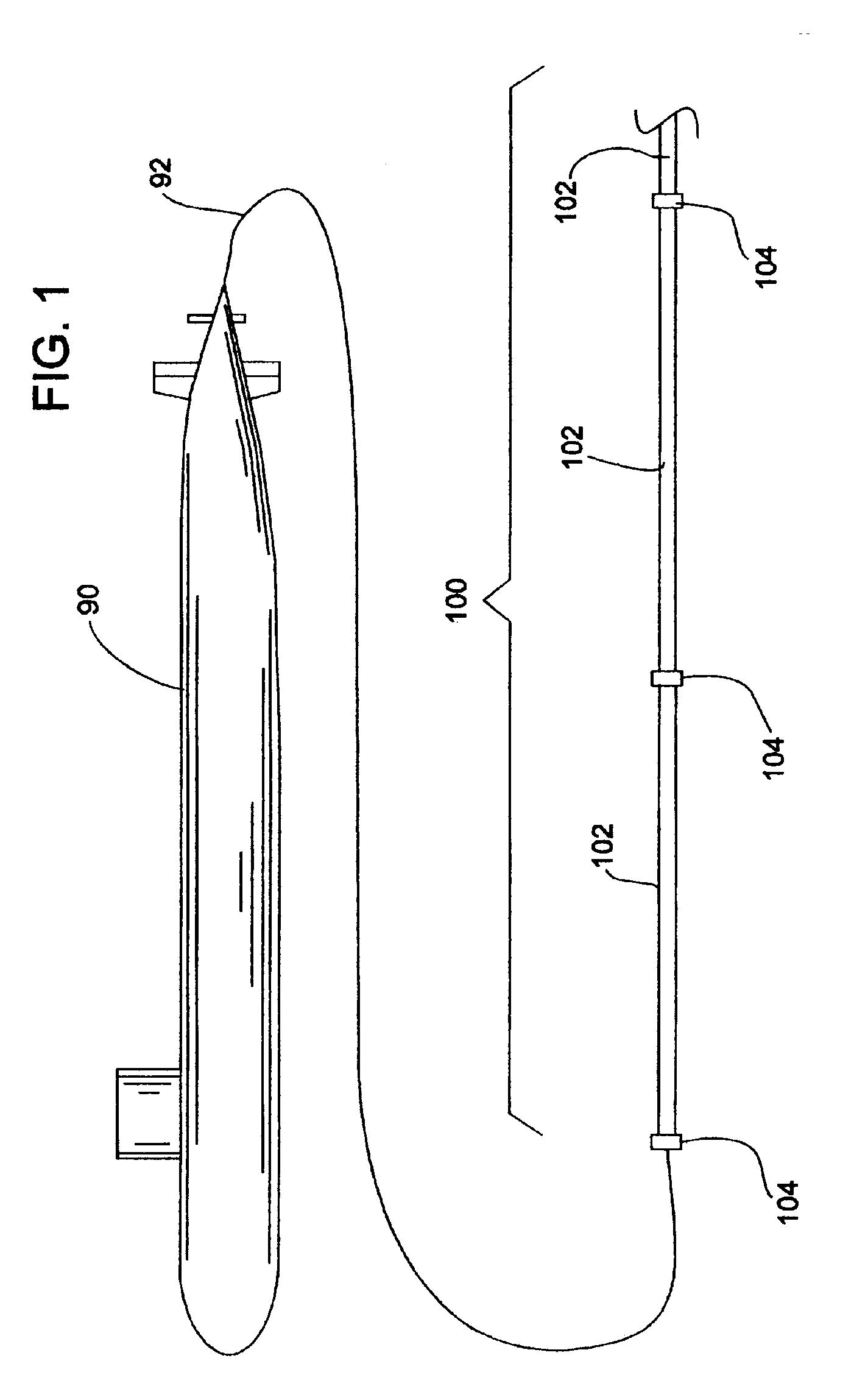
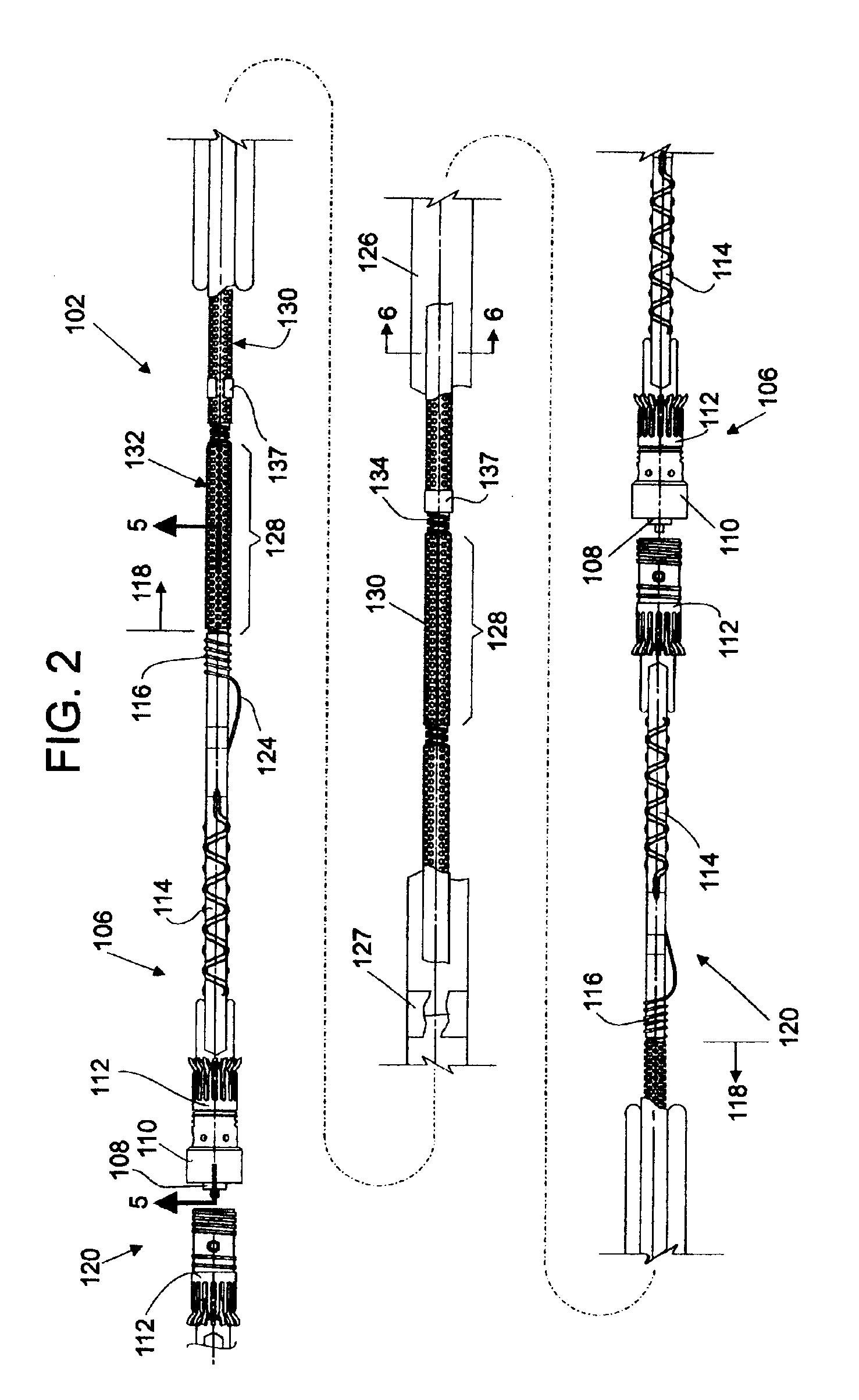
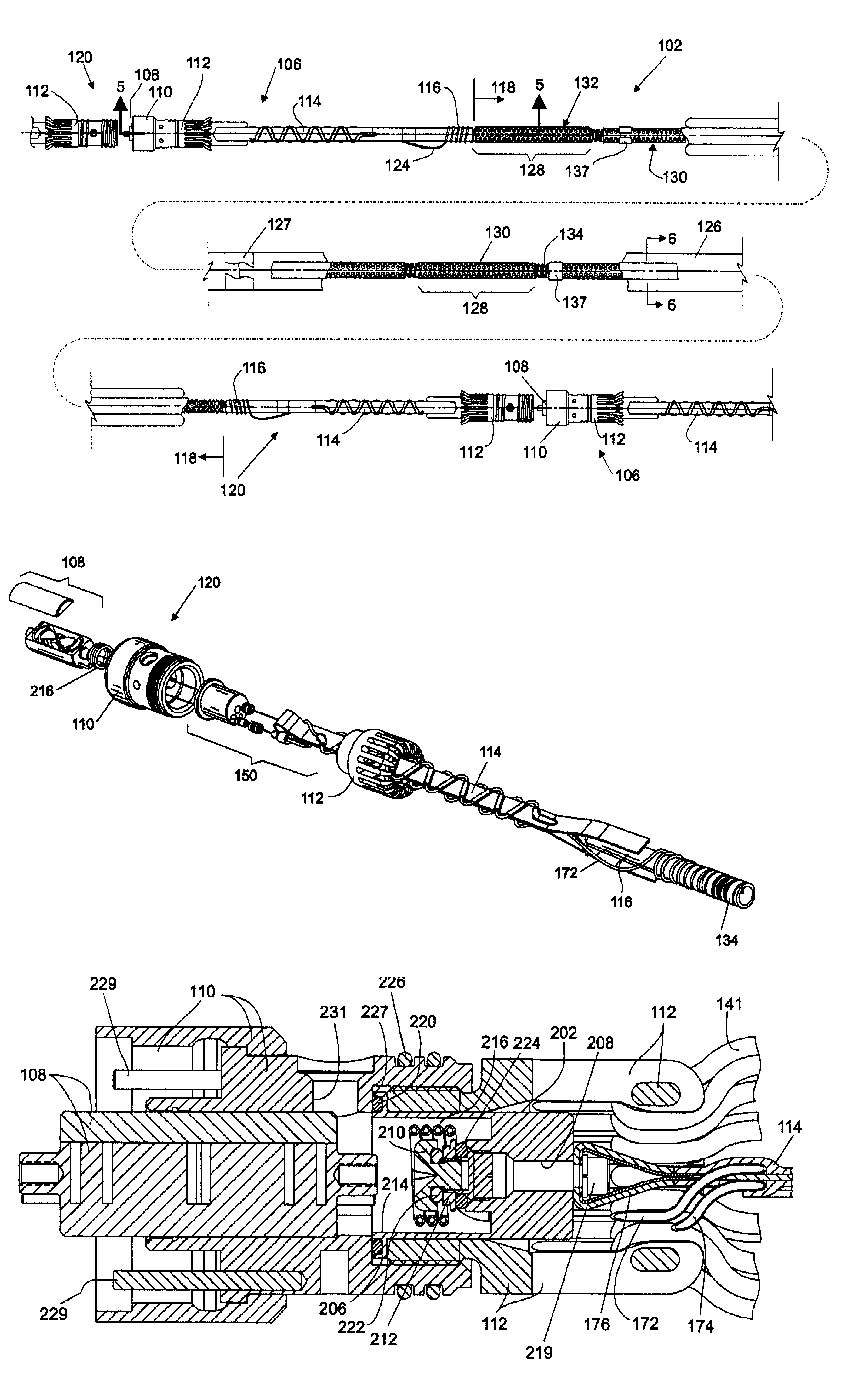
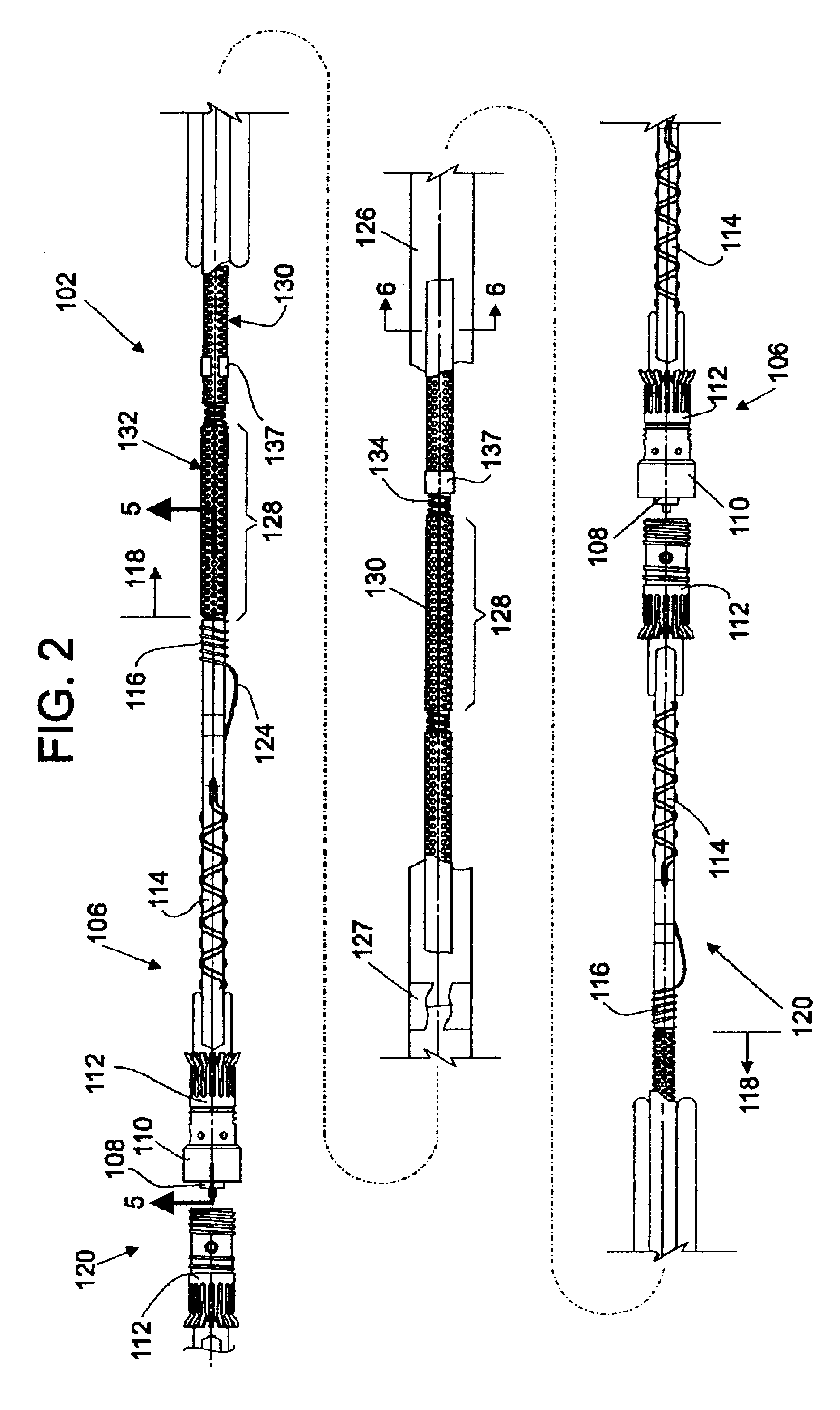
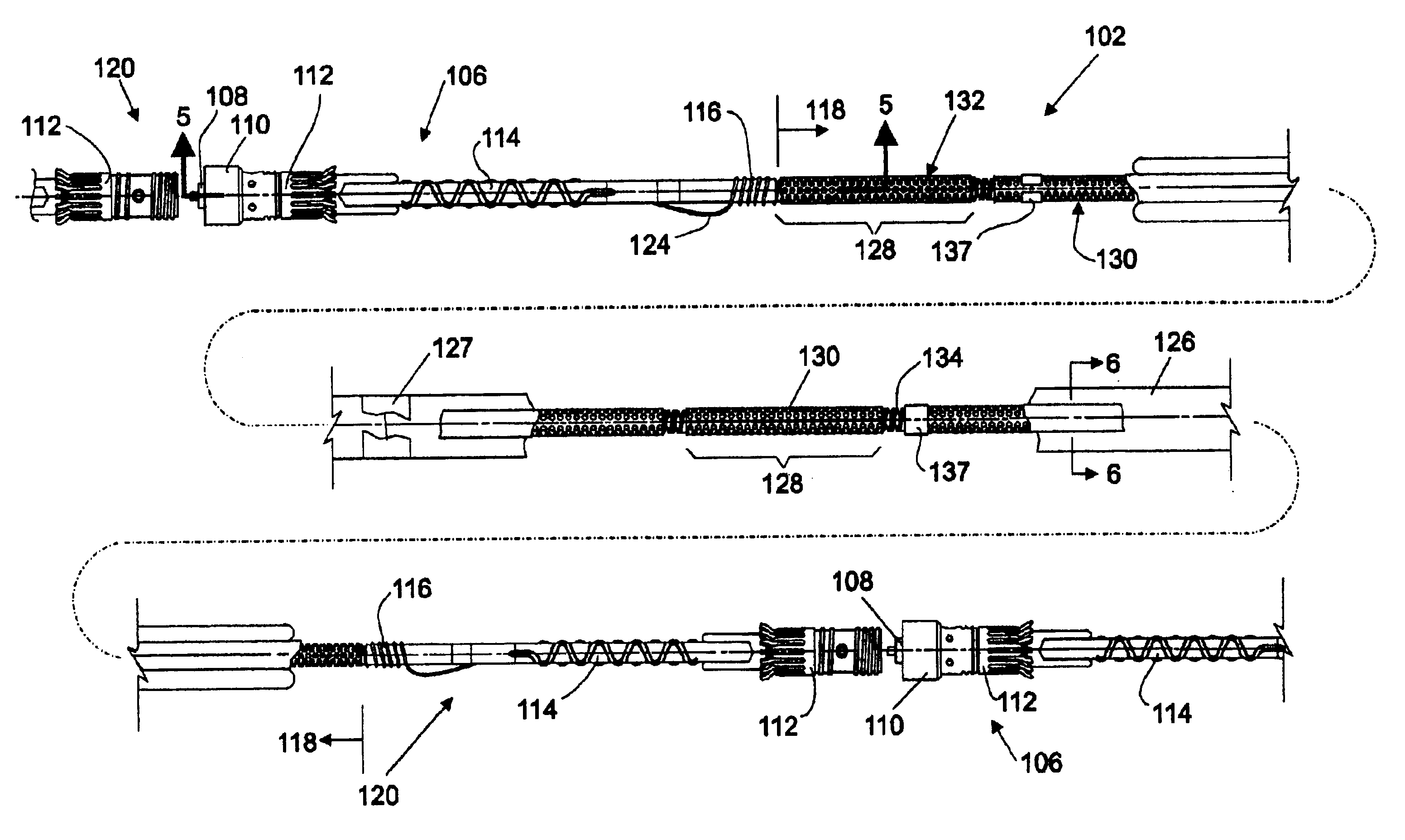
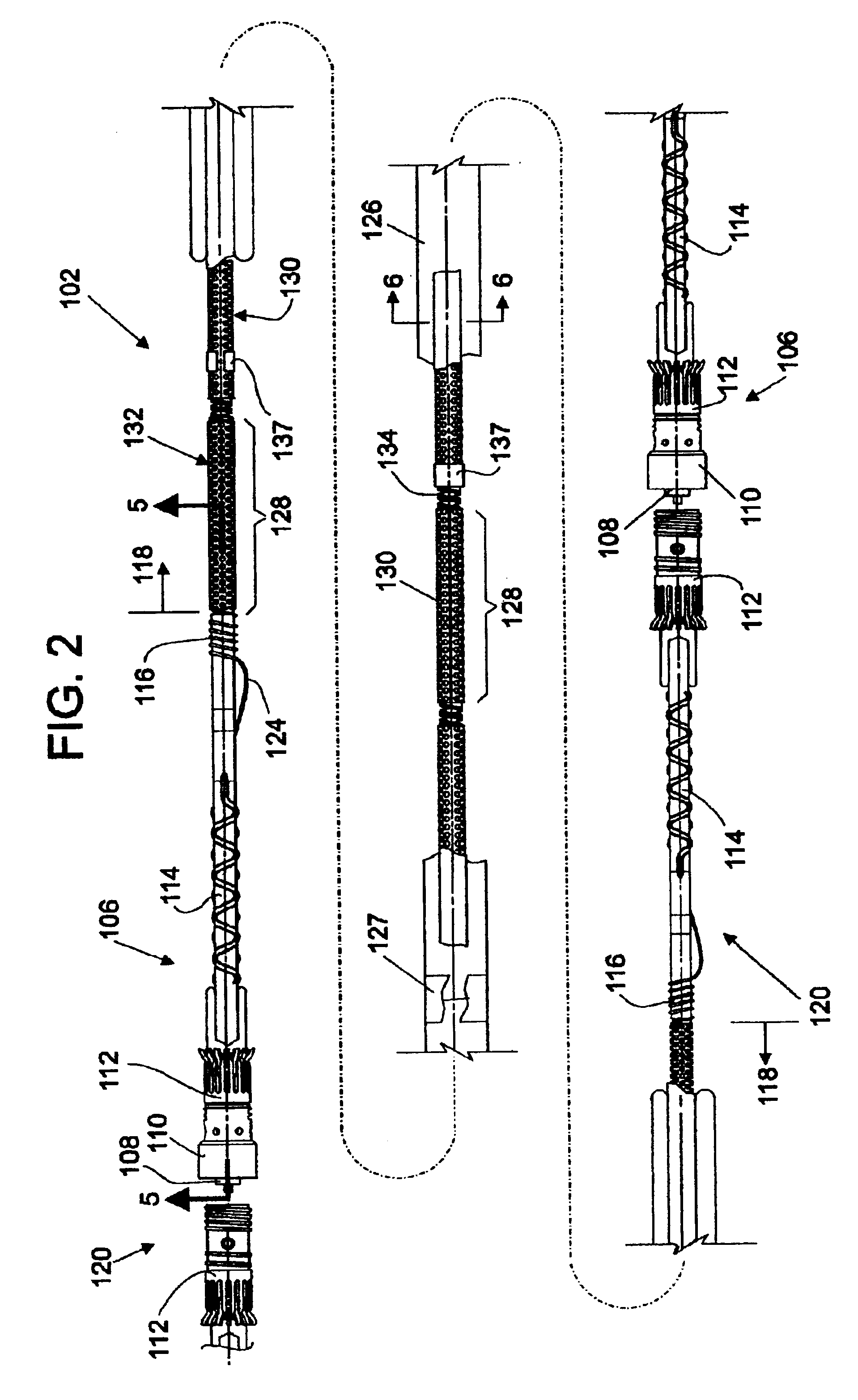
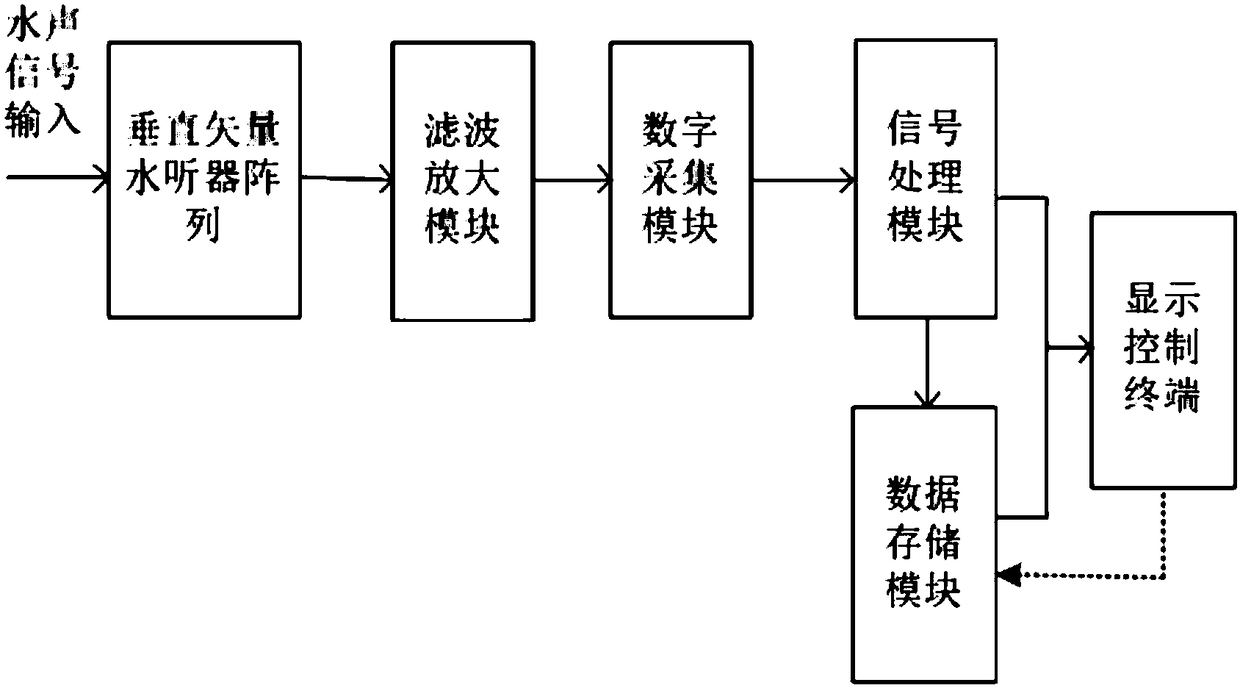
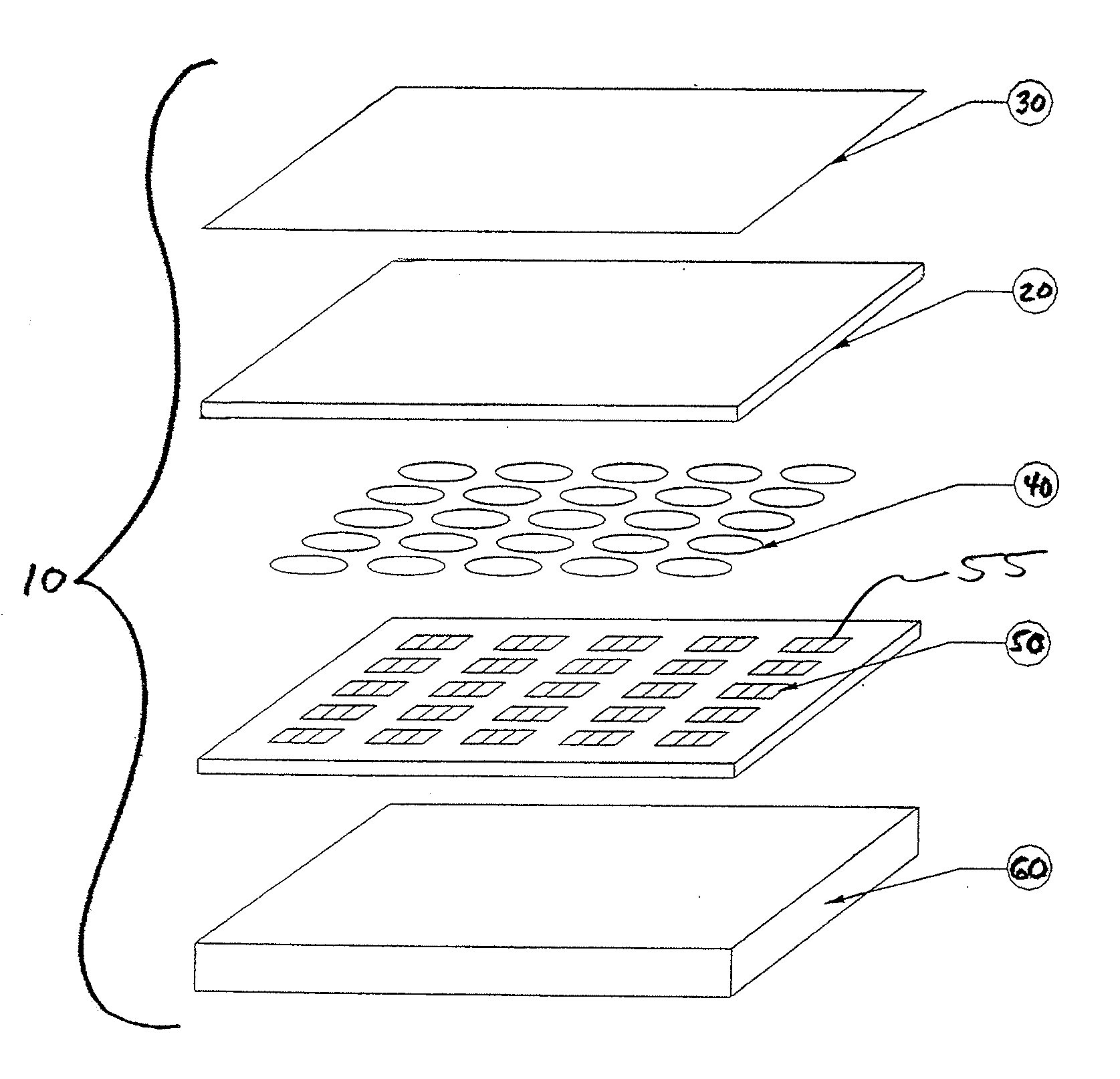
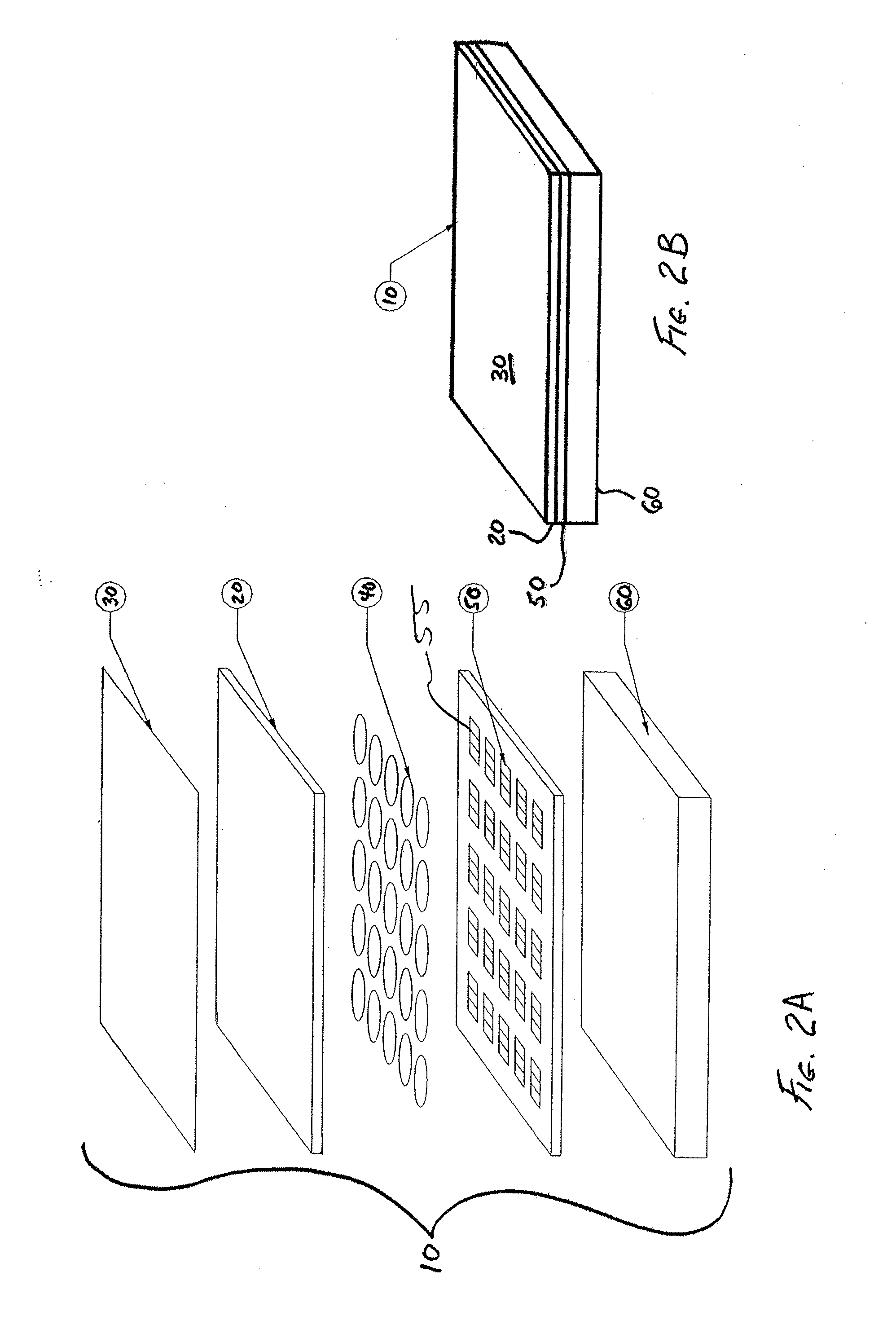
Hydrophone Array Module
ActiveUS20080037372A1Transducer detailsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSensor arraySignal on
A hydrophone array includes hydrophones having an electret means and may have TFT FETs to generate current in response to received longitudinal wave signals. The arrangement may also be used to transmit longitudinal wave signals. Storage capacitors may be coupled to each TFT FET output to act as sample and hold means. Digital switches may allow the sample and hold circuit to both reset and measure the output of the hydrophone element. Data lines may be used to indicate the location of the received signal on the longitudinal wave detector sensor array.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for a non-oil-filled towed array with a novel hydrophone design and uniform buoyancy technique
InactiveUS6498769B1Seismic signal receiversTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsEntry pointEngineering
A structure and method for constructing a non-oil-filled towed array providing a single cable entry point for each channel irregardless of the number of hydrophones used to make up a hydrophone group or array is described. The method and apparatus enables uniform buoyancy of the hydrophone array and the primary cable around which the hydrophone array is wound. Uniform buoyancy is achieved through the addition of hollow micro-spheres into a Reaction Injection Molded (RIM) polyurethane material used to mold the hydrophones. Additional buoyancy may be desired adjacent heavier cable sections where connectors and telemetry modules are located. An embodiment enables precise adjustment of hydrophone cable buoyancy by providing precise adjustment of the concentration of hollow glass micro-spheres in areas where more or less buoyancy is desired.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
MIMO (multiple input multiple output) based high-resolution underwater target detection device and method
InactiveCN102608609AIncrease the apertureIncrease spaceAcoustic wave reradiationImage resolutionTransducer
The invention discloses an MIMO (multiple input multiple output) based high-resolution underwater target detection device and method. According to the invention, a potential target is actively detected through a plurality of mutually-orthogonal detection waveforms transmitted by a transmitting transducer array in a hydroacoustic environment, and a hydrophone-array received target echo is received. Through MIMO processing, a method for carrying out detection and estimation on an MIMO frame is established, and the extension of waveform diversity gains and virtual array apertures is obtained. By using the MIMO based underwater target detection method disclosed by the invention, in the process of carrying out hydroacoustic target detection, compared with conventional phase control, a higher detection resolution and higher parameter identification performance can be obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Device and method for calibrating lineup of dragging linear array
InactiveCN104407340AEasy to implementSimple on-site operationWave based measurement systemsSound sourcesComputer module
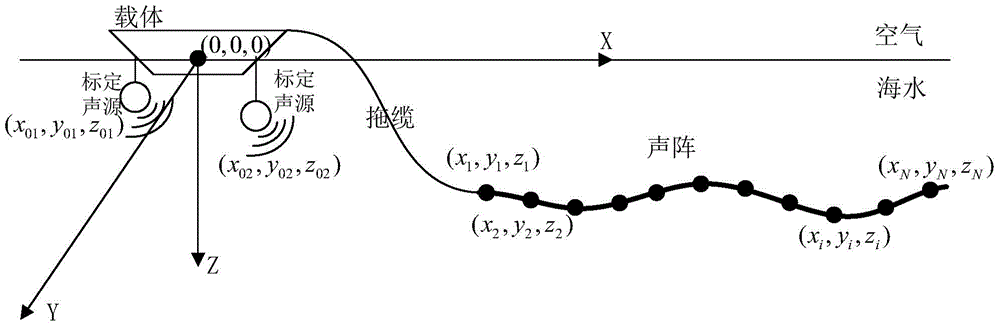
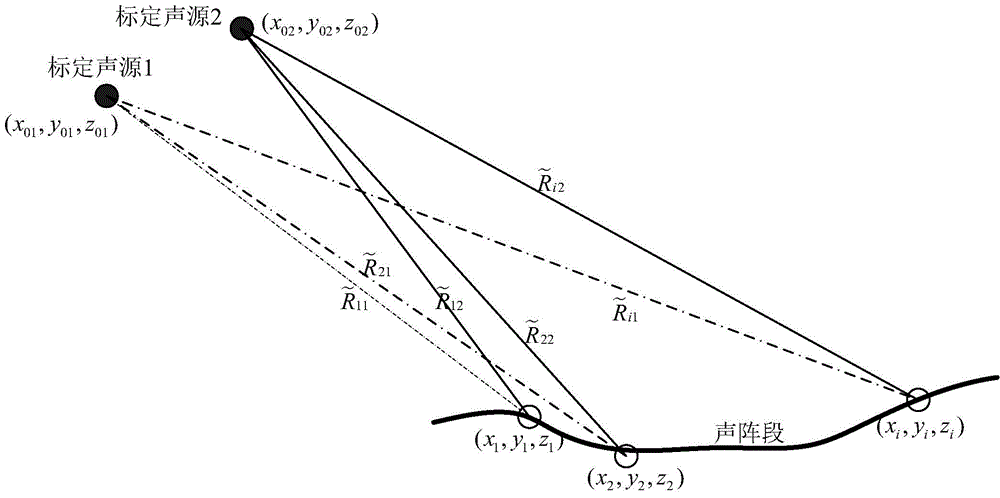
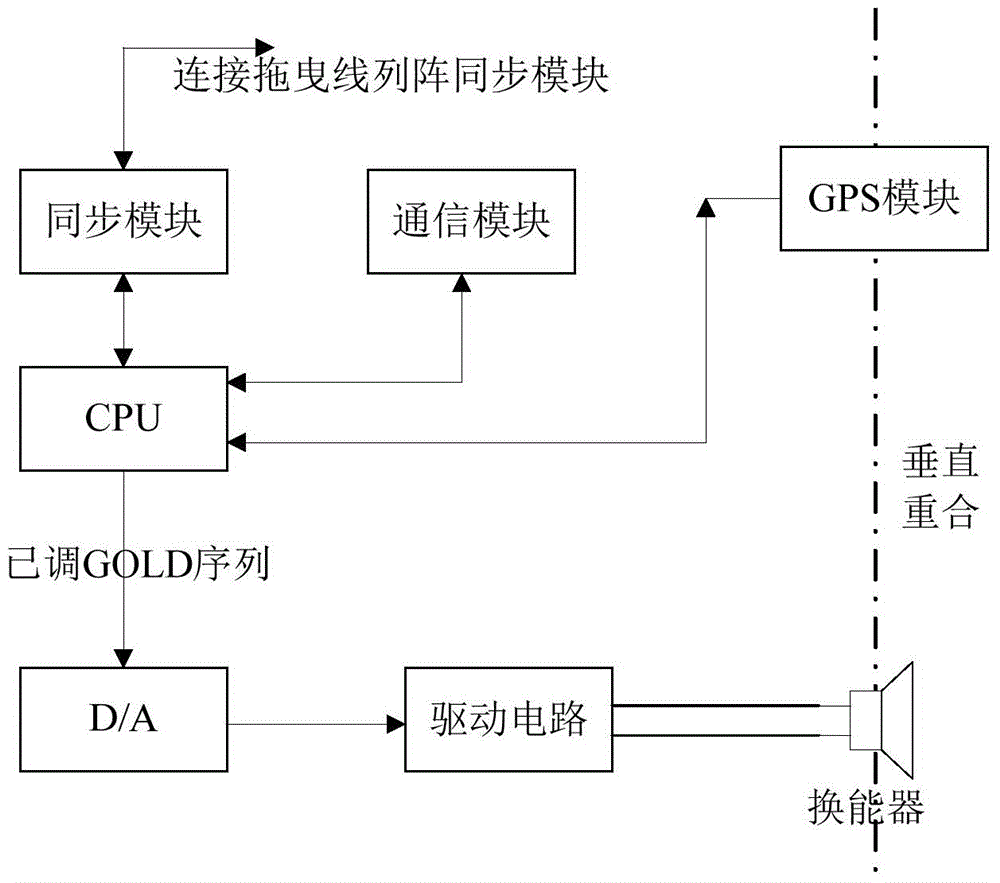
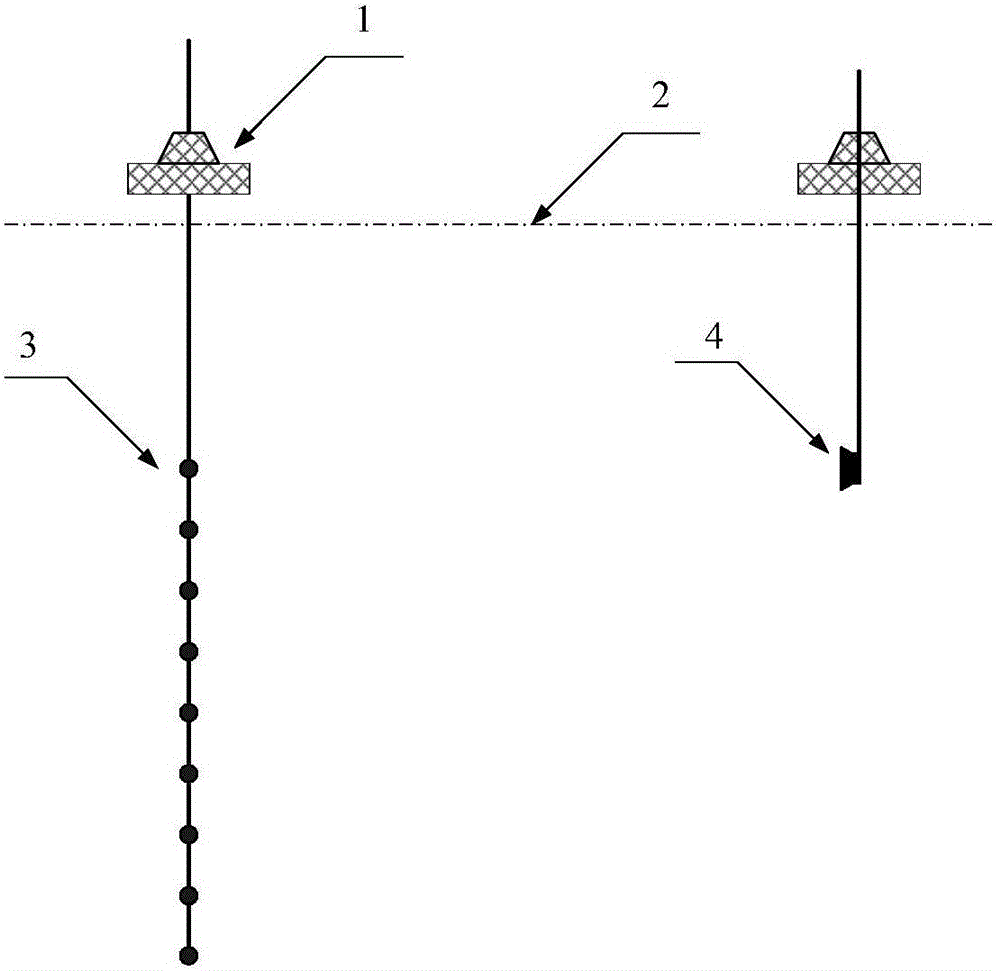
The invention discloses a device for calibrating the lineup of a dragging linear array. The hardware of the device mainly comprises a calibration sound source, a receiving hydrophone array, a signal acquisition transmission module array and a data processing module. The lineup calibration process mainly comprises the following steps: (1) calibrating a sound source to transmit a calibrated submarine sound signal in a system synchronous clock; (2) according to the system synchronous clock, enabling the signal acquisition transmission module array to start work while the sound signal is transmitted, that is, a timer starts timing and hydrophones acquires data; (3) recording the timing time of the timer while the signal acquisition transmission module array acquires the transmitted calibrated submarine sound signal, and transmitting the timing time to the data processing module; (4) estimating the distances between the hydrophones and the calibrated sound source according to the timing time; (5) estimating the coordinates of hydrophones through the data processing unit according to the estimation results in combination with depth sensor data, thereby realizing lineup calibration. By adopting the device and the method, position calibration of array elements of a dragging array can be conveniently achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Linear hydrophone array amplitude and phase consistency measuring method
InactiveCN105973447AAvoid phase errorImprove measurement efficiencyVibration measurement in fluidTransducerHydrophone array
The invention belongs to the field of underwater acoustic transducers, in particular to a method for measuring the amplitude and phase consistency of a linear hydrophone array. The invention includes mechanically fixing the hydrophone array on the lifting device, the lifting device lifts the hydrophone array up and down at a fixed interval, hangs the transmitting transducer at a certain distance from the hydrophone array, and the distance meets the requirements of the transducer. The far-field distance from the hydrophone, the hanging depth of the transmitting transducer is the same as the depth of the hydrophone at the top of the hydrophone array; the hydrophone array and the lifting device are mechanically fixedly connected, during the lifting process, the hydrophone array Always remain vertical with no horizontal wobble or movement. The invention adopts the method of moving the hydrophone in the vertical direction, which avoids the phase error caused by the distance error in the horizontal direction caused by moving the hydrophone in the horizontal direction or re-hanging the hydrophone during the consistency measurement of the traditional hydrophone.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
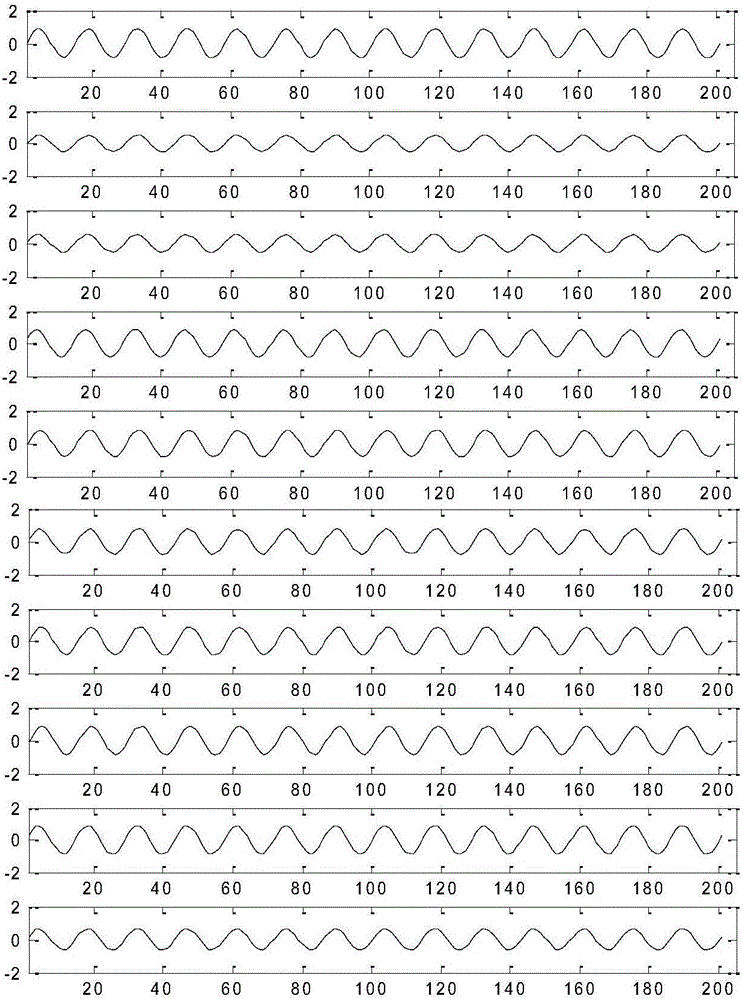
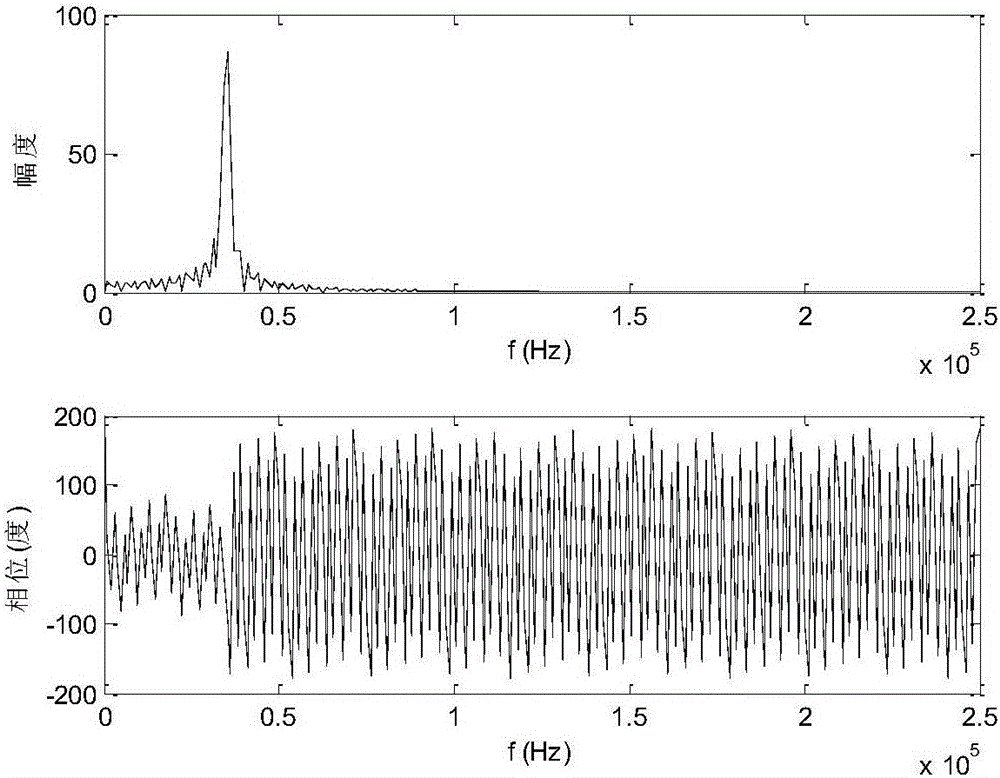
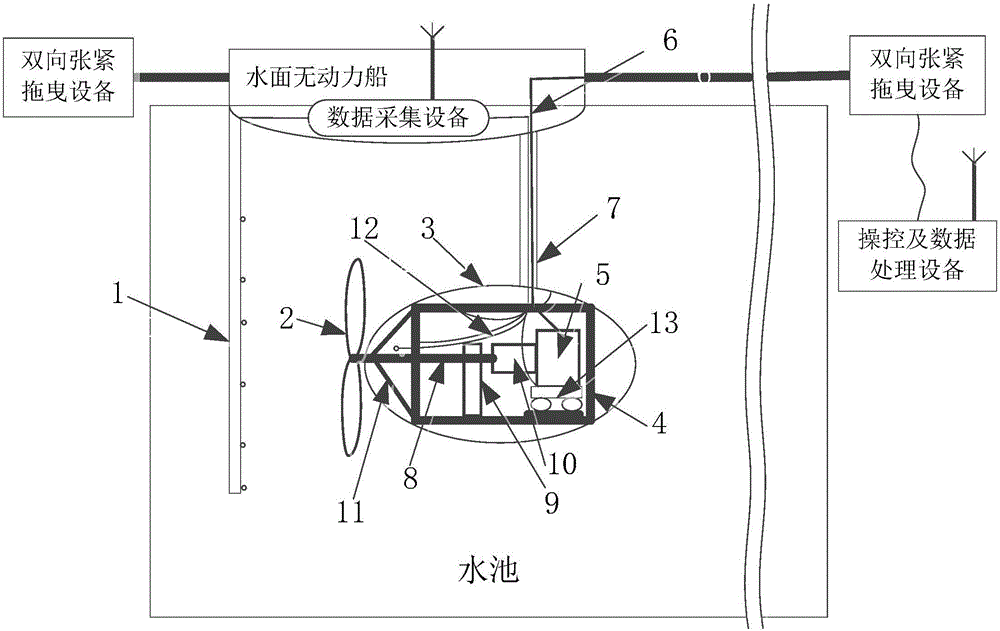
Direct sound production test device of large-proportion propeller model
The invention relates to a direct sound production test device of a large-proportion propeller model, and belongs to the technical field of underwater vehicle propeller noise control. The device comprises two-way tensioning drag equipment, a water-surface unpowered ship, data acquisition equipment, a power cable, control and data processing equipment, a hydrophone array, the propeller model, a main shaft system, a non-watertight shell, a watertight shell, a sensor, a supporting part, a rigid connecting part and a motor. Water-surface unpowered chip parameters, main shaft system parameters, motor parameters and two-way tensioning drag equipment parameters are determined according to the needed maximum thrust, dimension, weight, power and rotating speed of the propeller model; when the propeller model is not installed, the noise of a system is tested; a clutch is disconnected, and the no-load noise of the motor is tested; the test device is rectified according to the test result till test demands are met. The test device is good in test result repeatability, short in test period and low in cost.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com