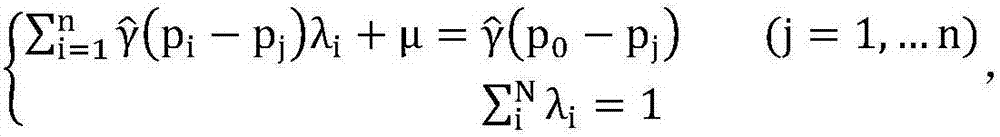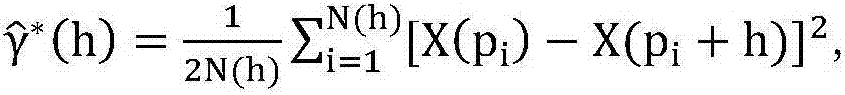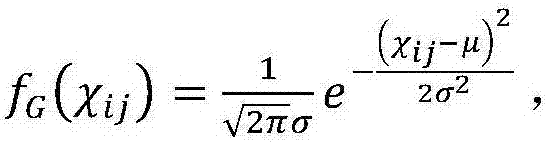Patents
Literature
96 results about "Soft data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Information that is susceptible to interpretation and opinion is known as Soft Data. As access to data continues to grow, businesses will need to incorporate both Hard and Soft Data into their solutions for improved, real-time decision support as a way to differentiate their service offerings. 1. Hard Data.
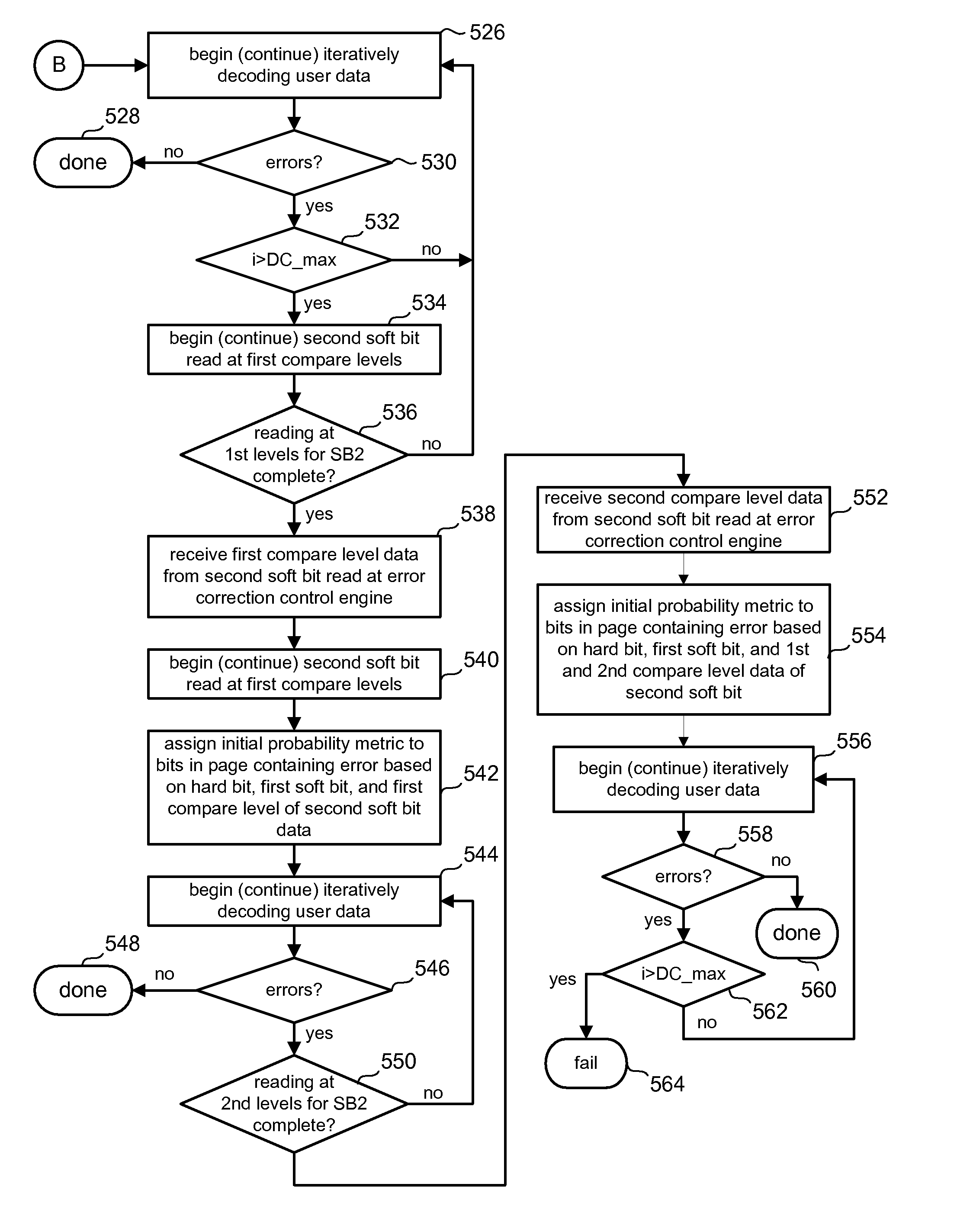
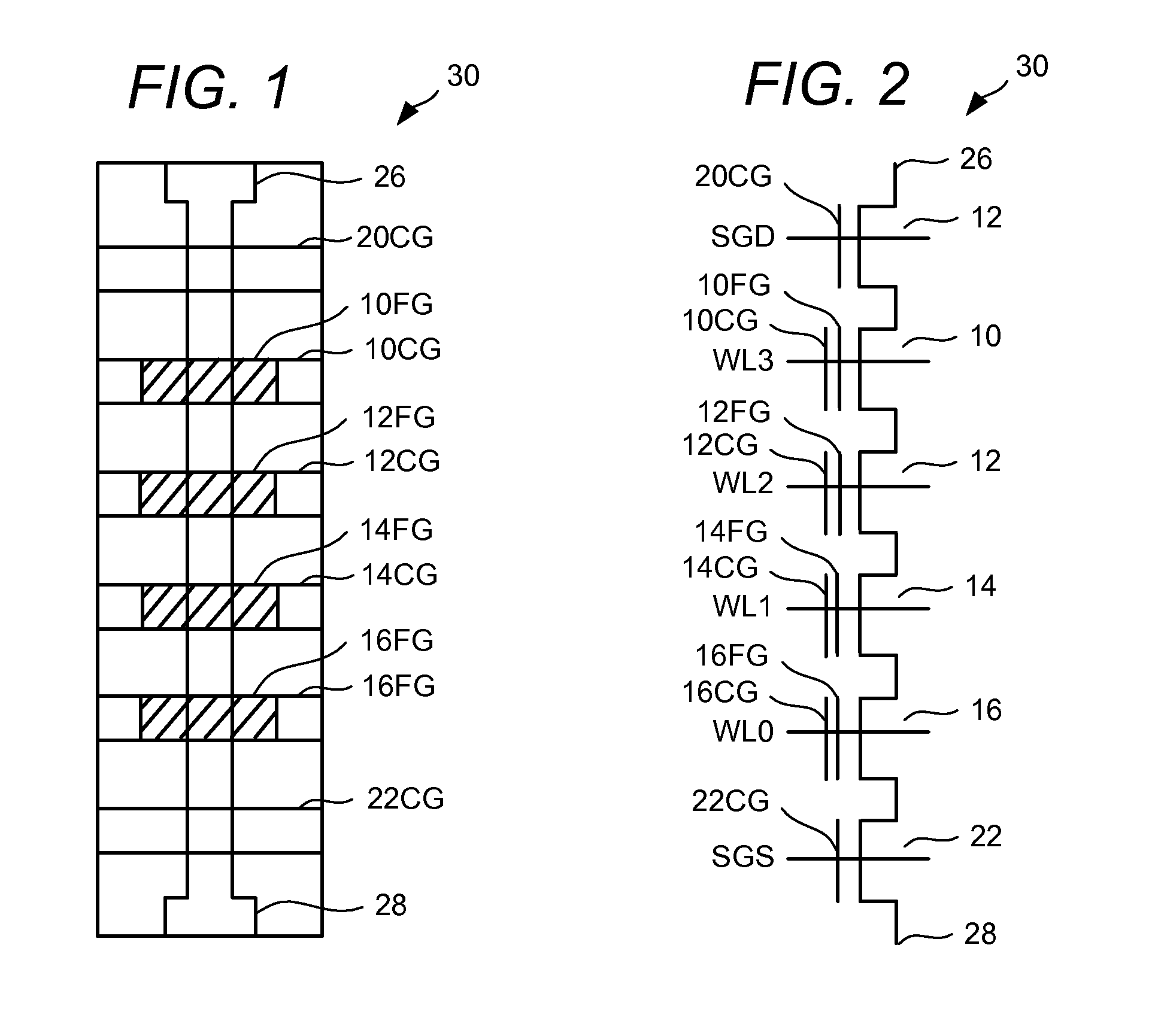
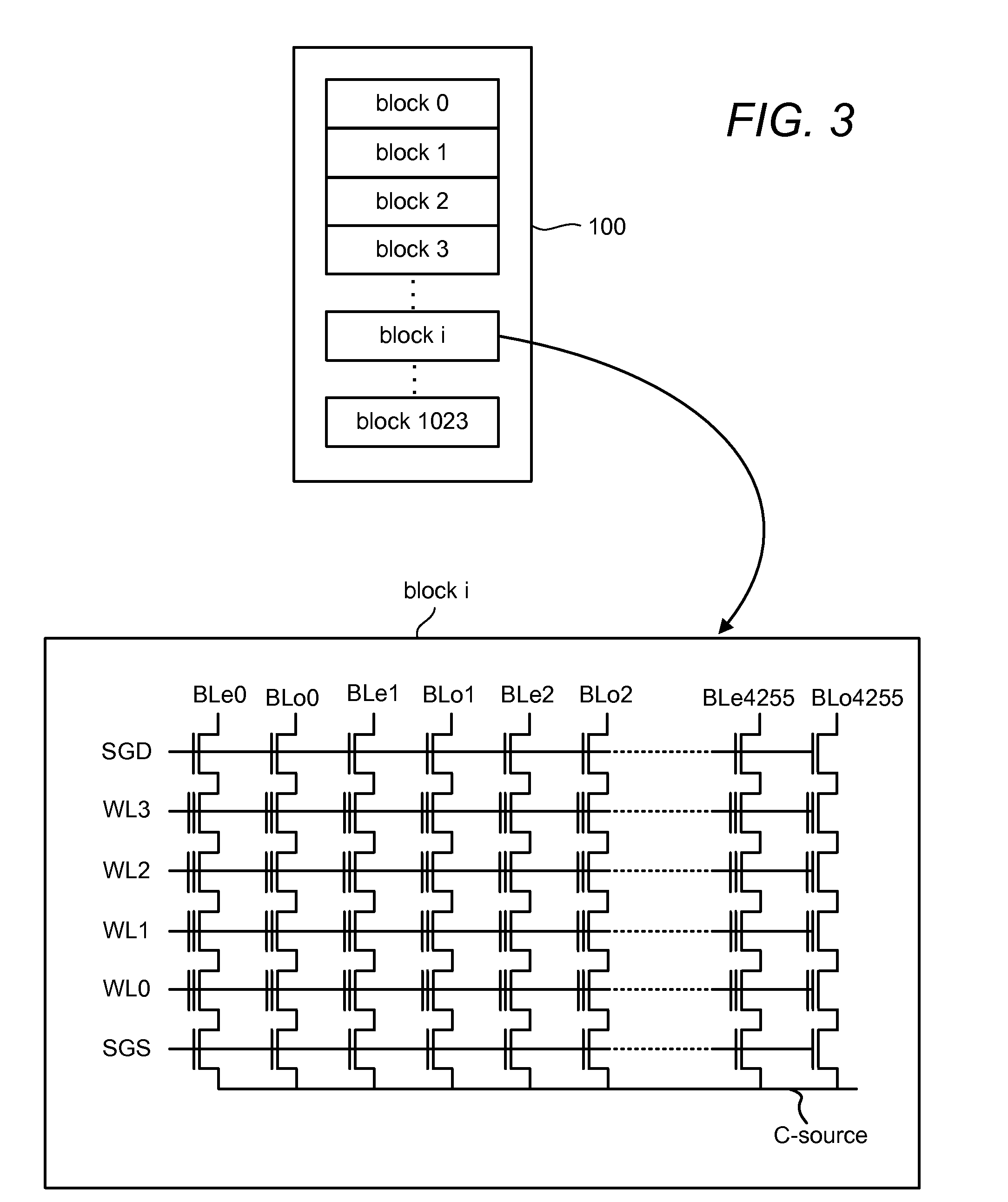
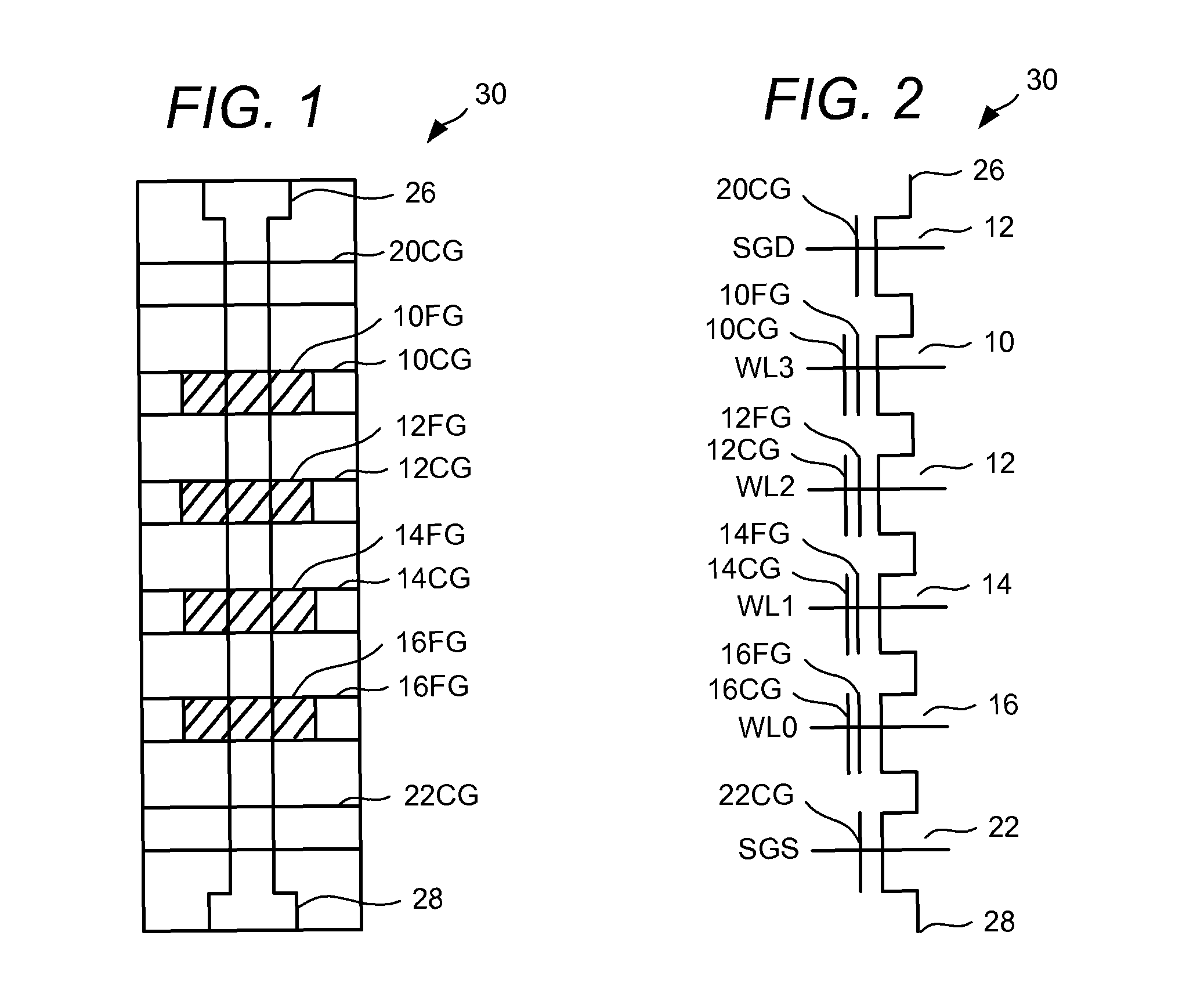
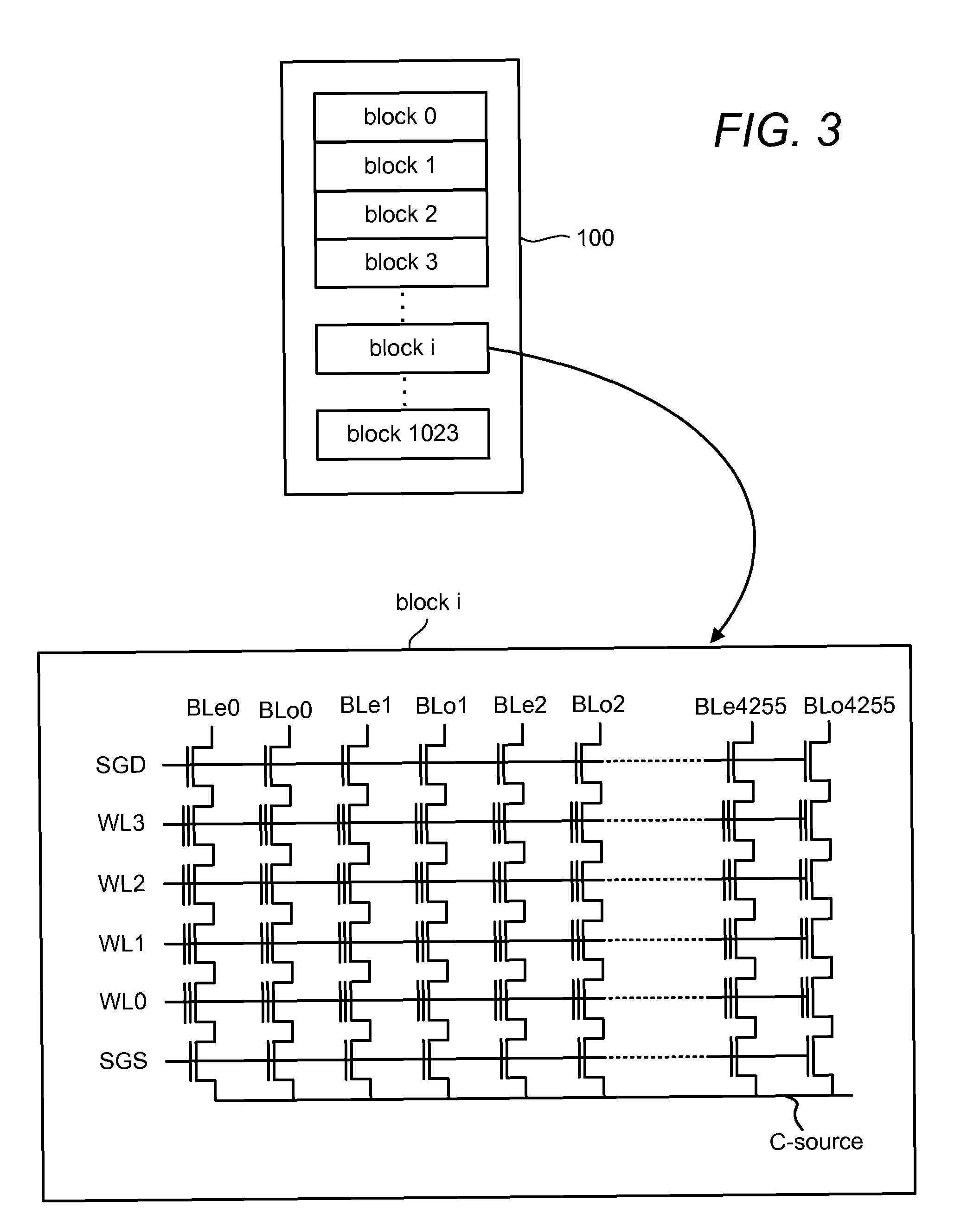
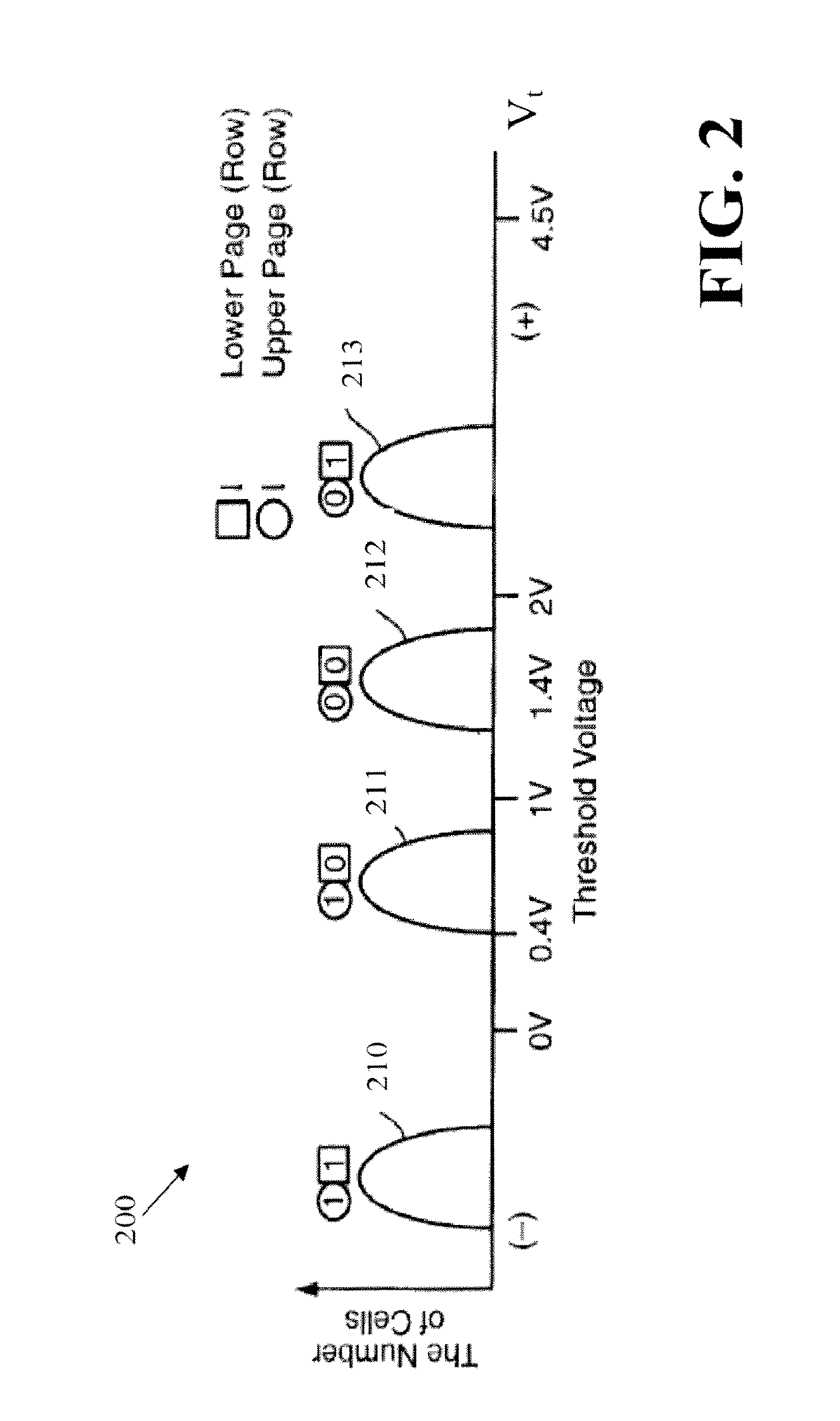
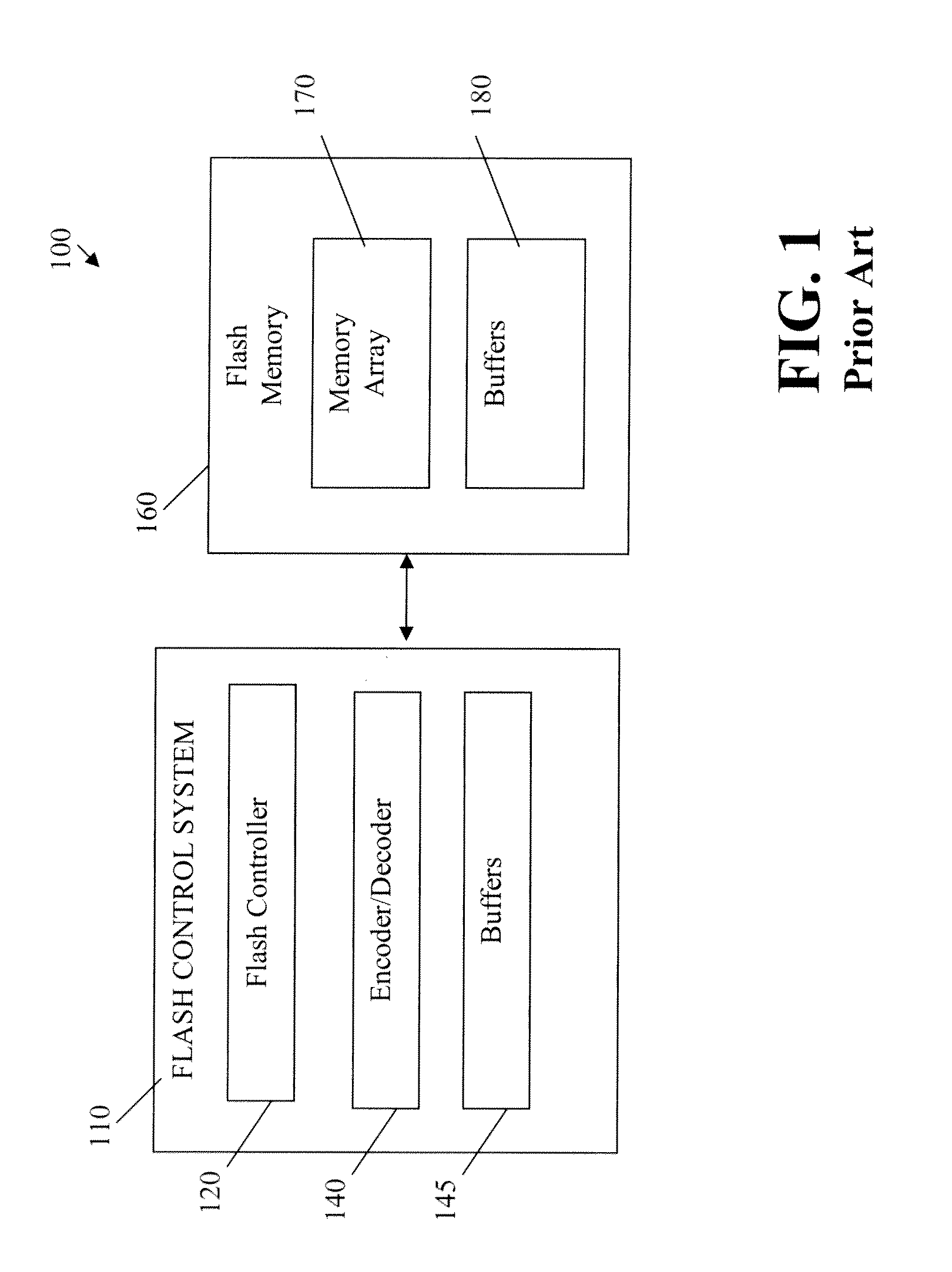
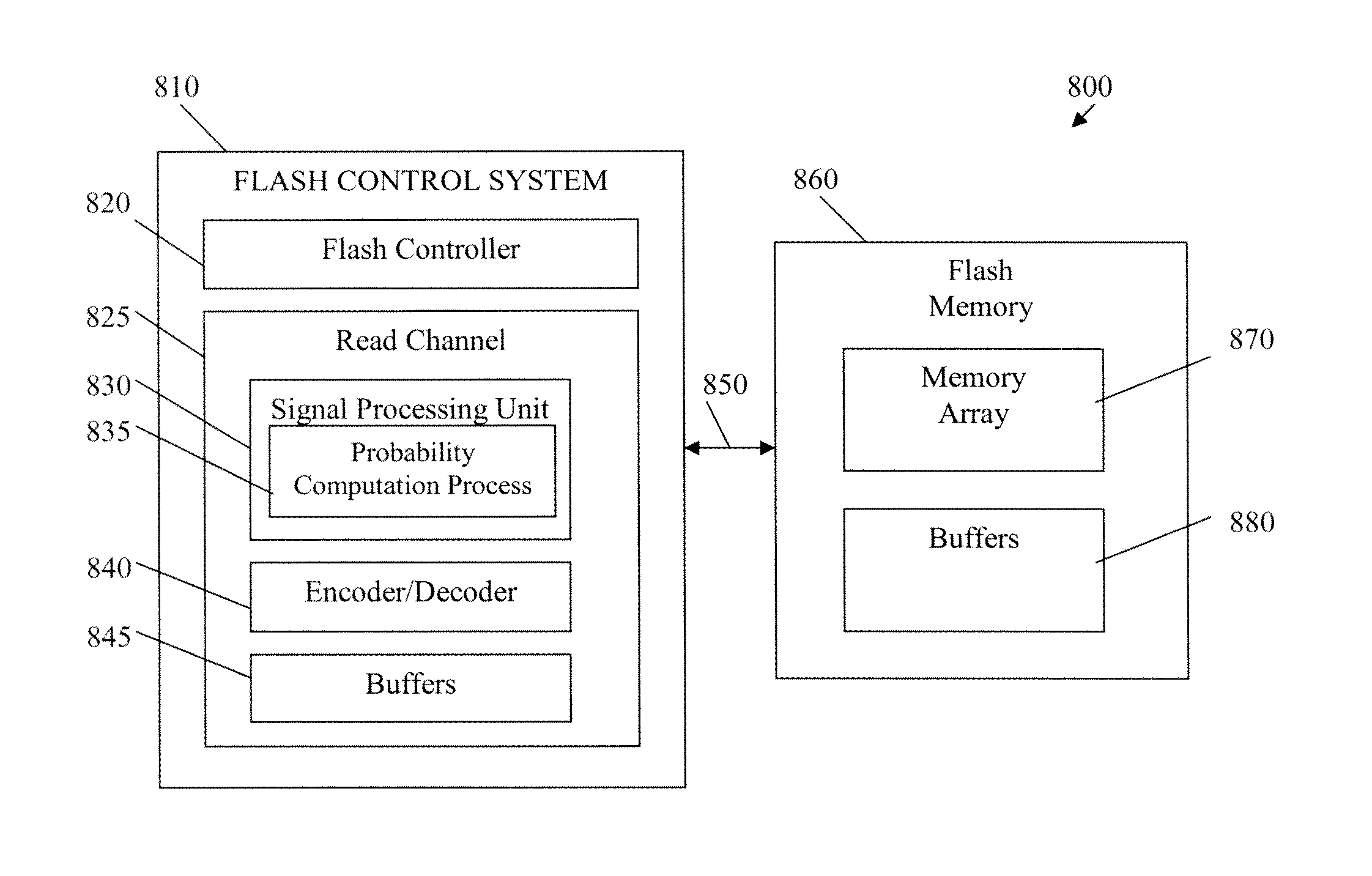
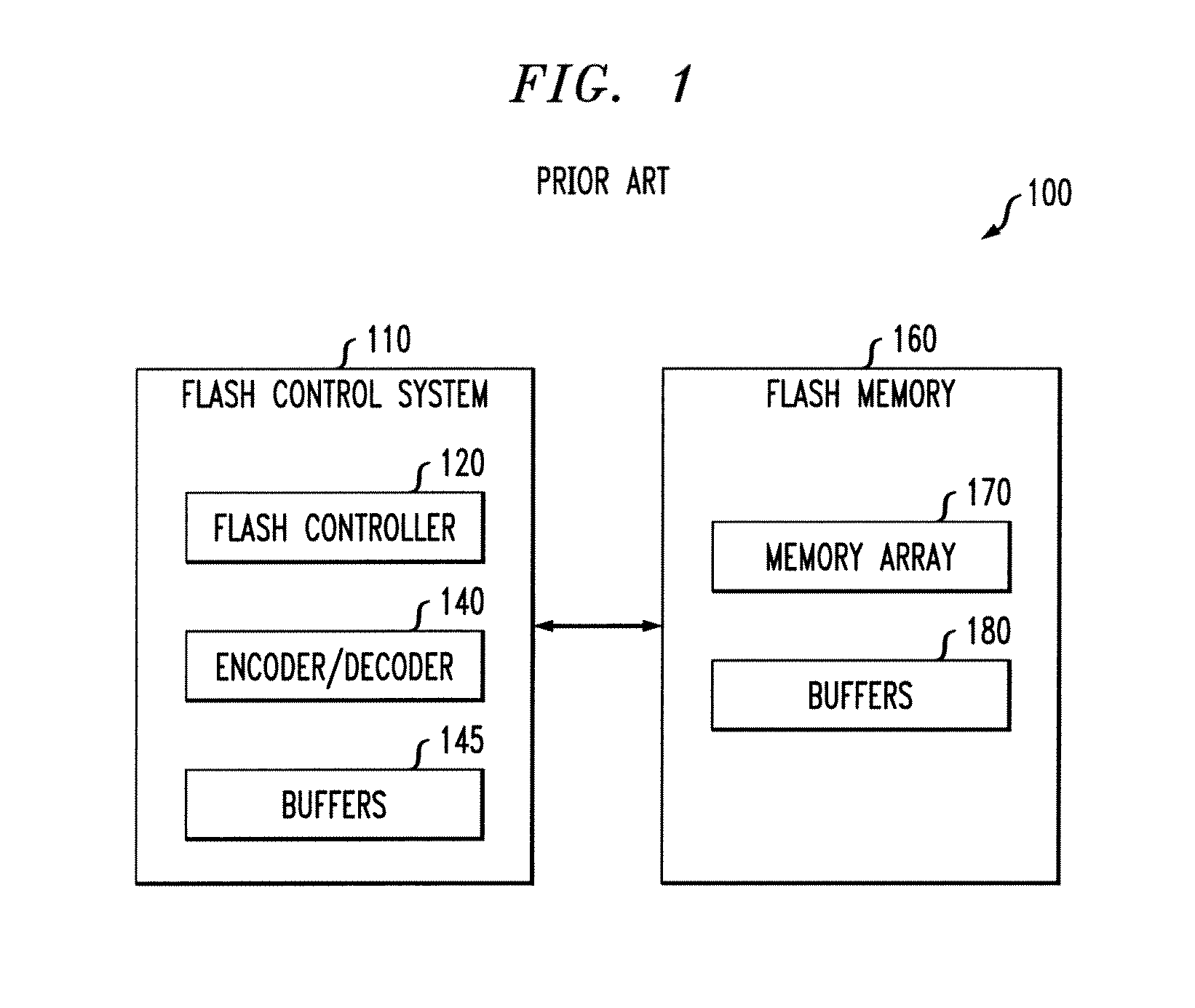
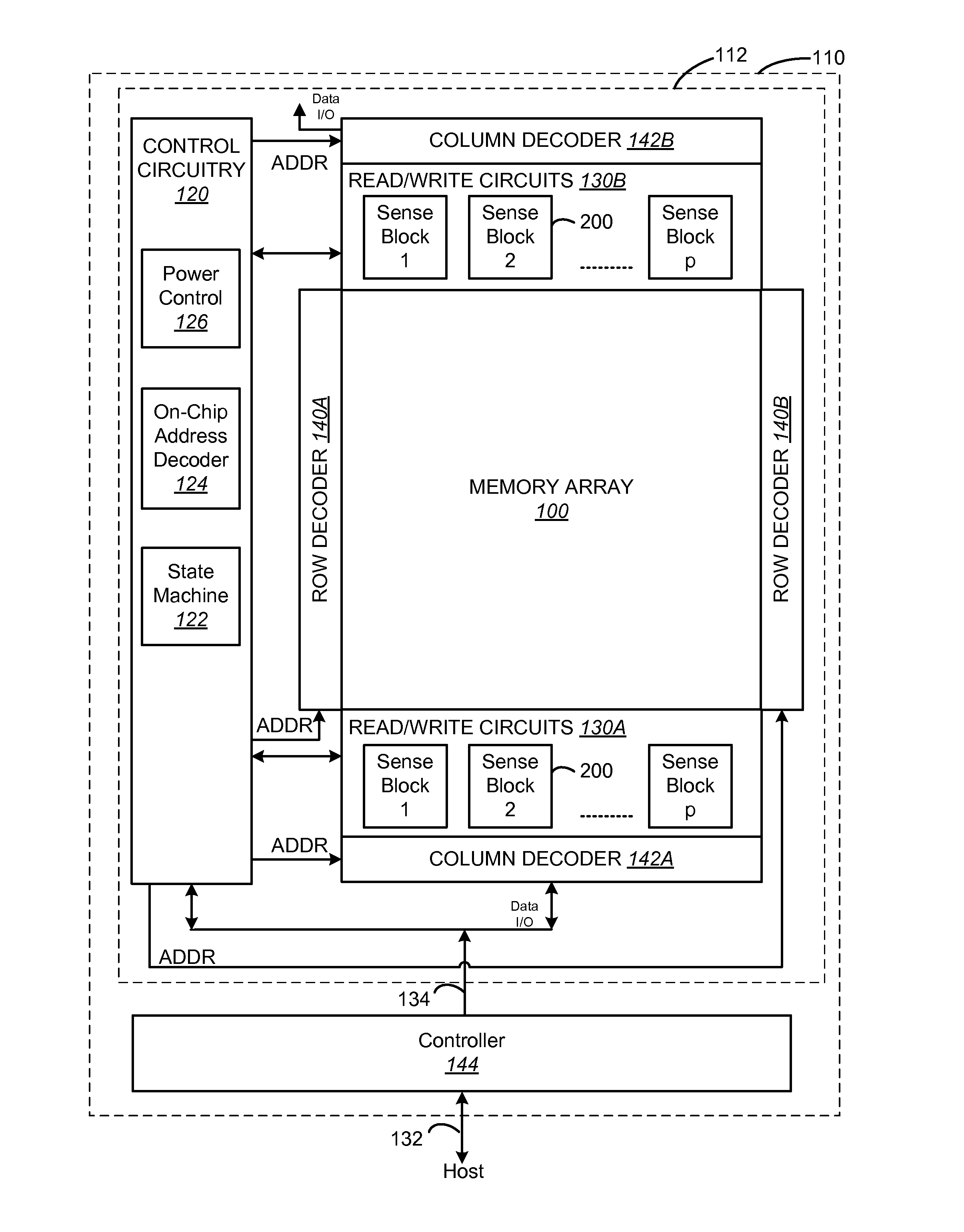
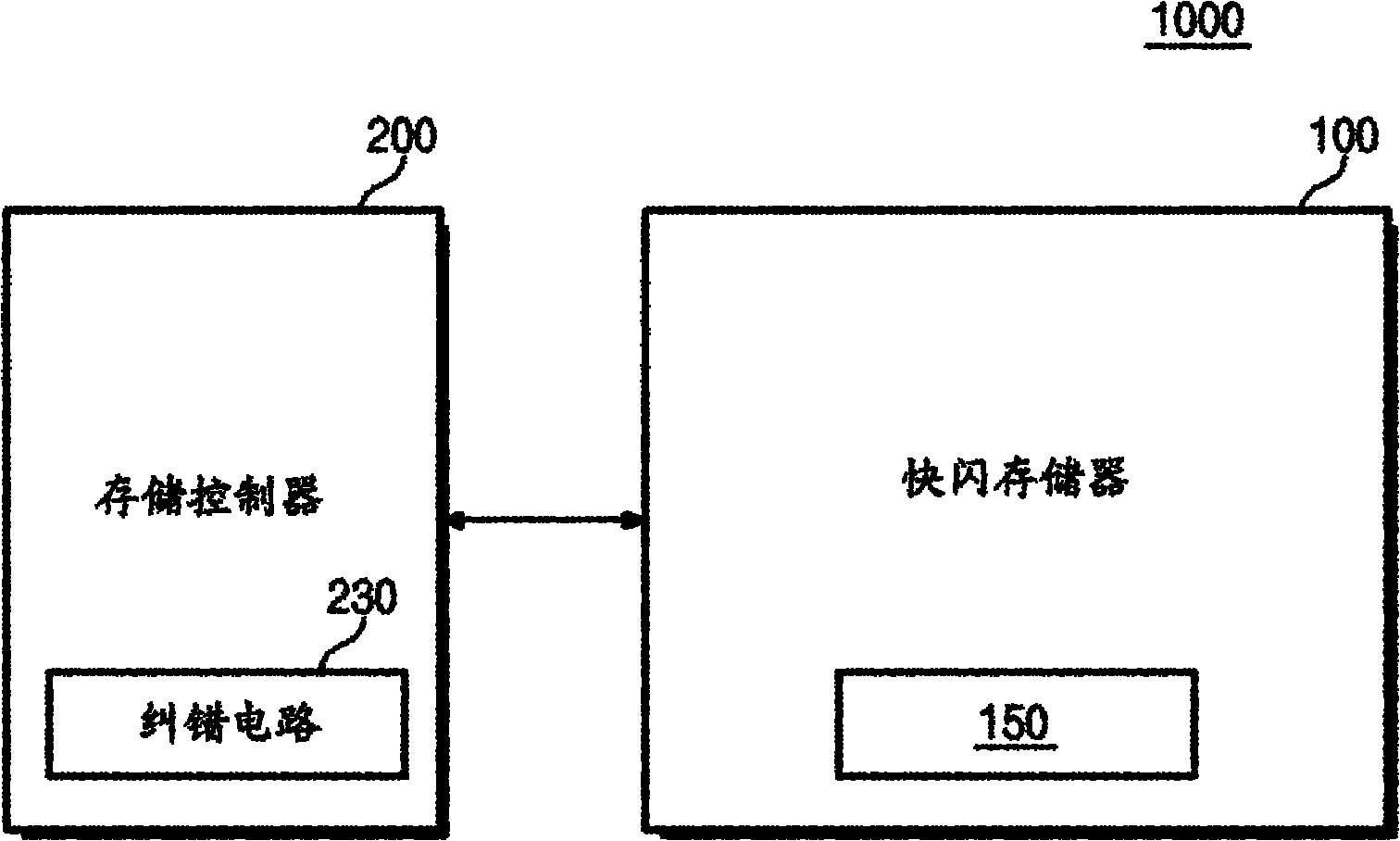
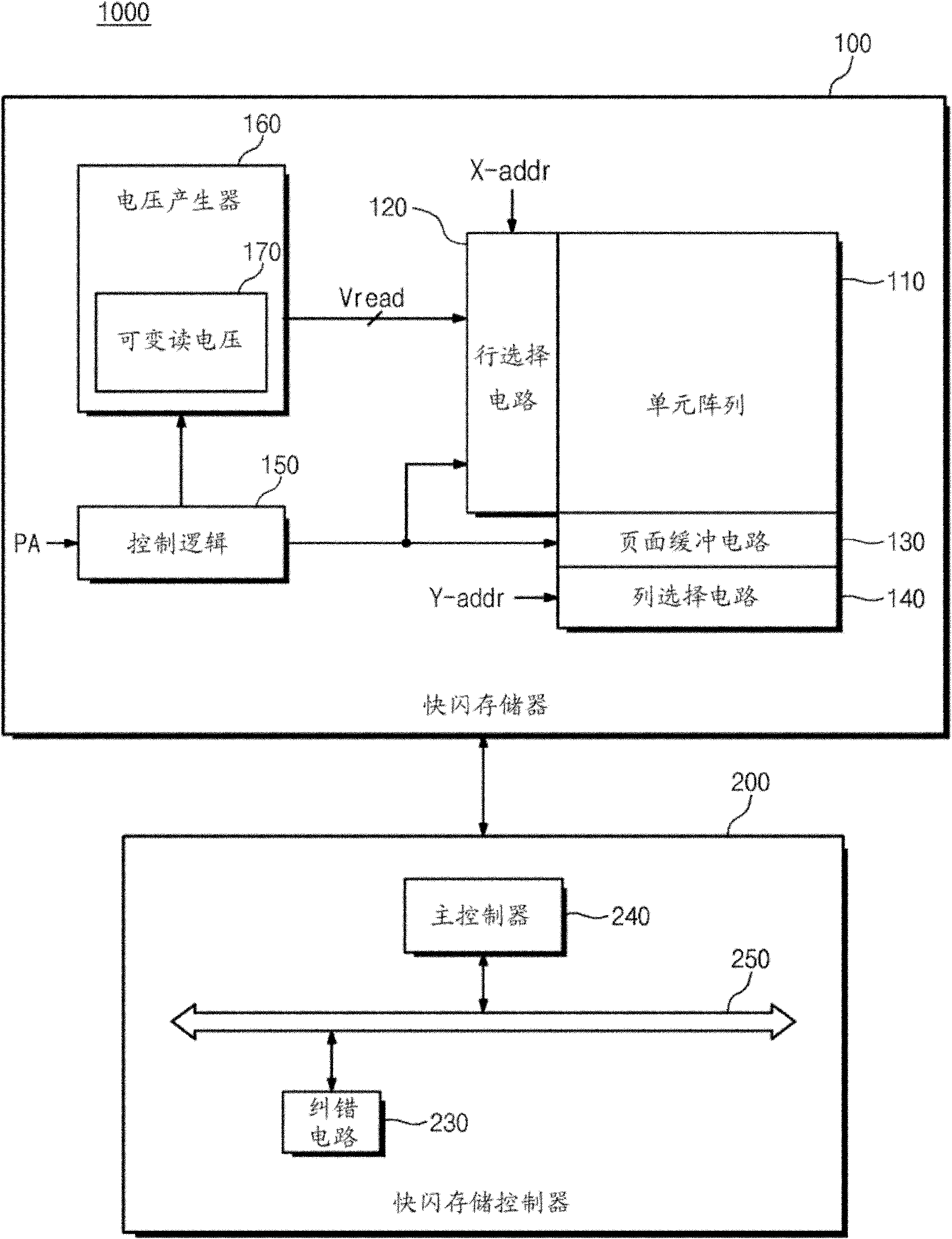
Soft bit data transmission for error correction control in non-volatile memory
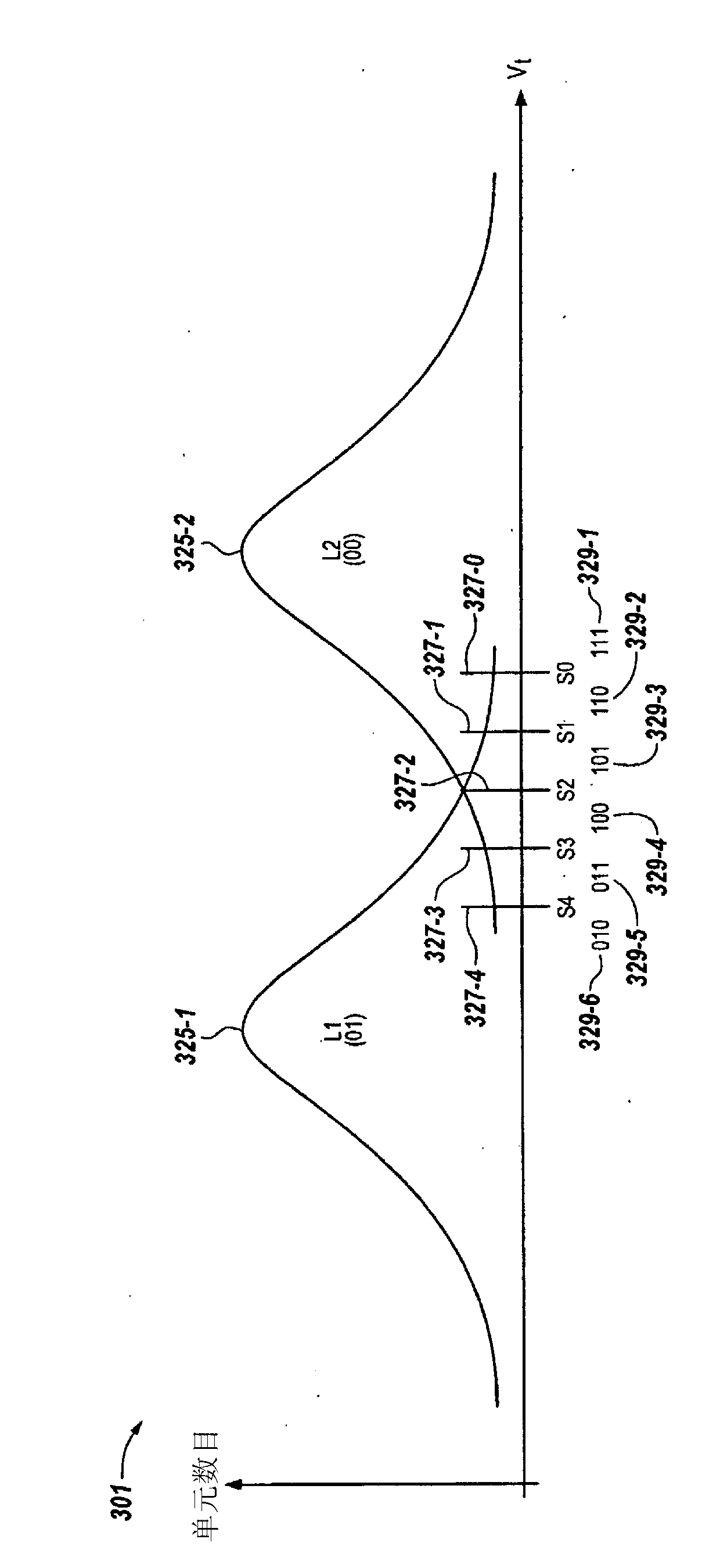
ActiveUS20080244338A1High resolutionError detection/correctionCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeSoft data
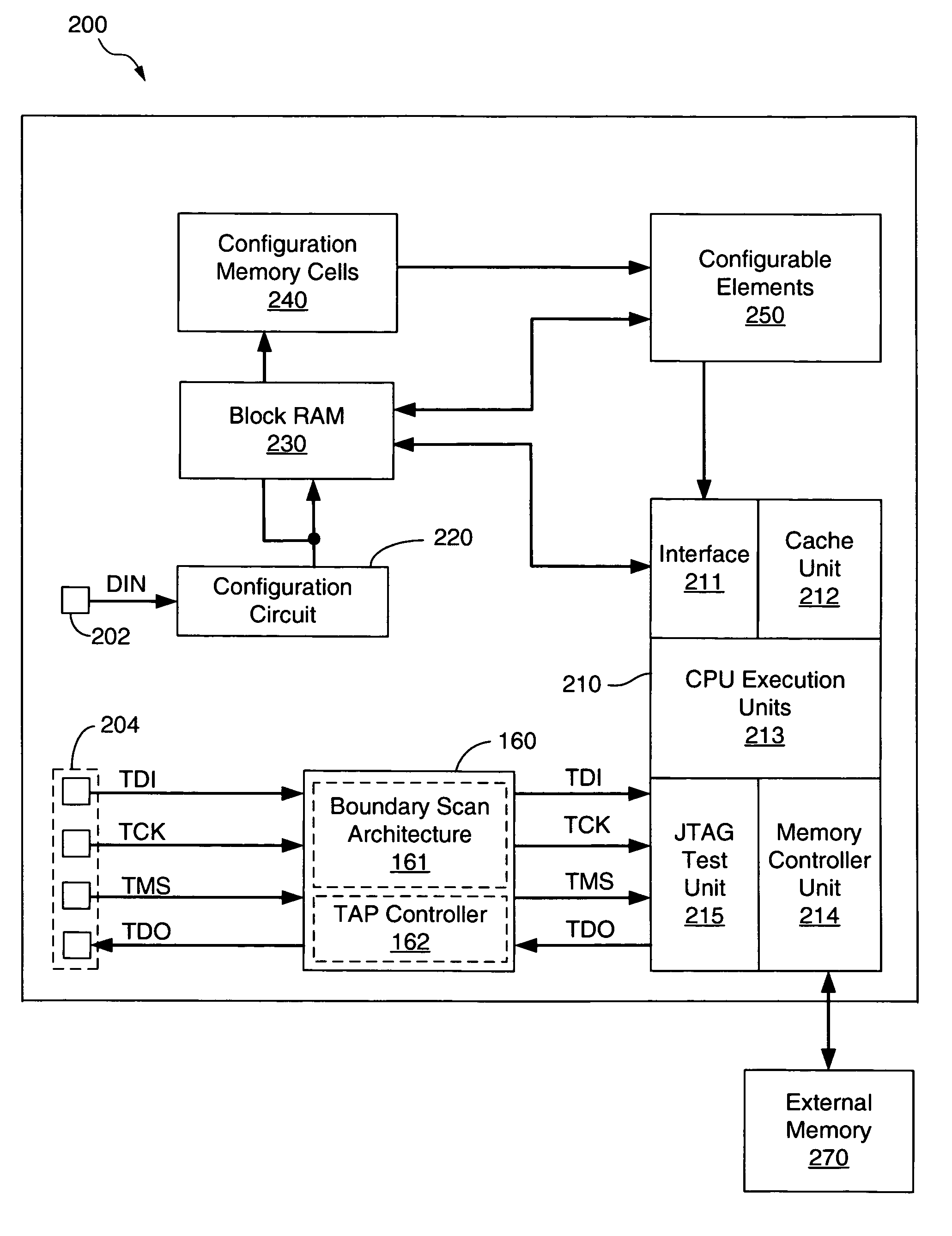
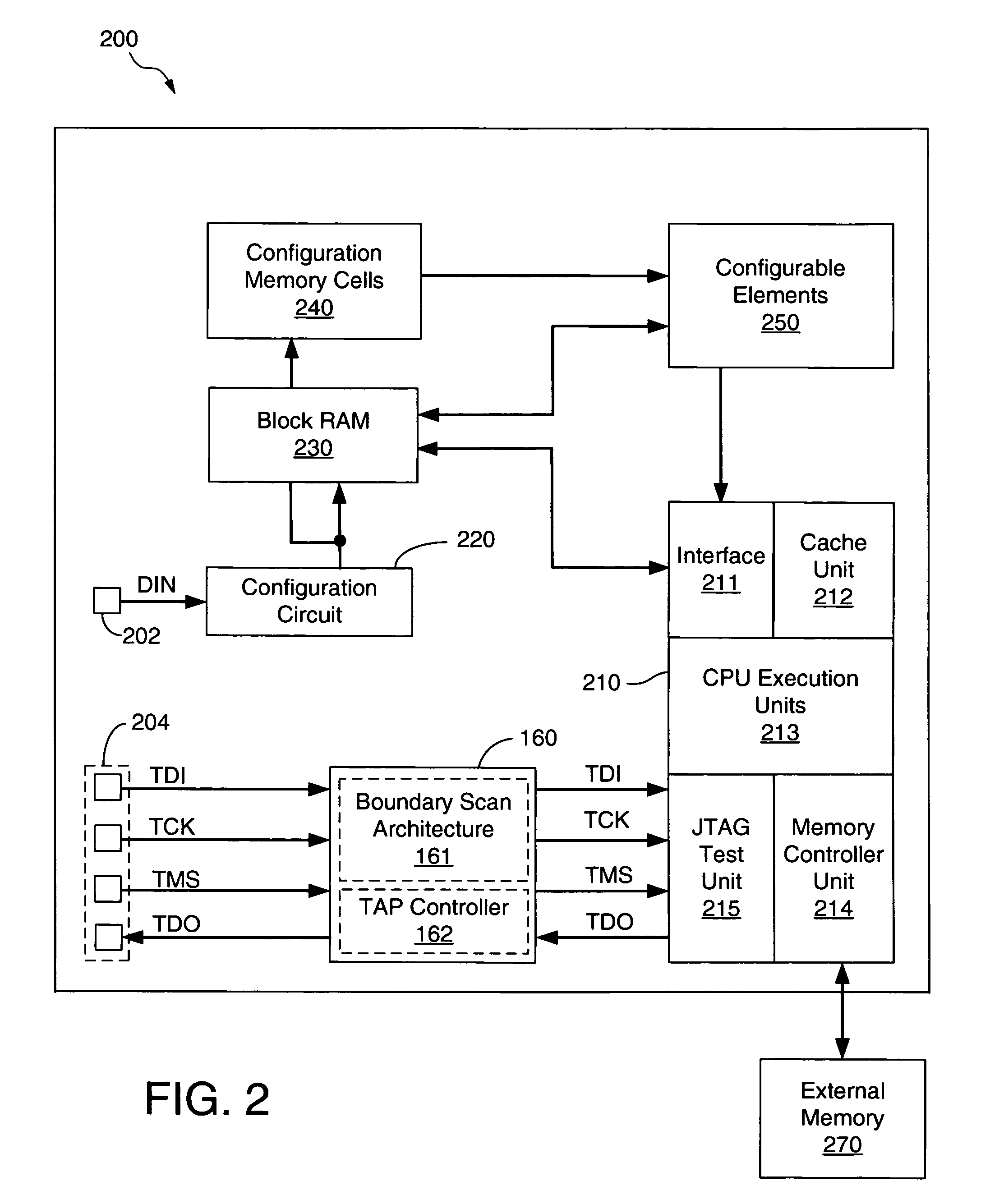
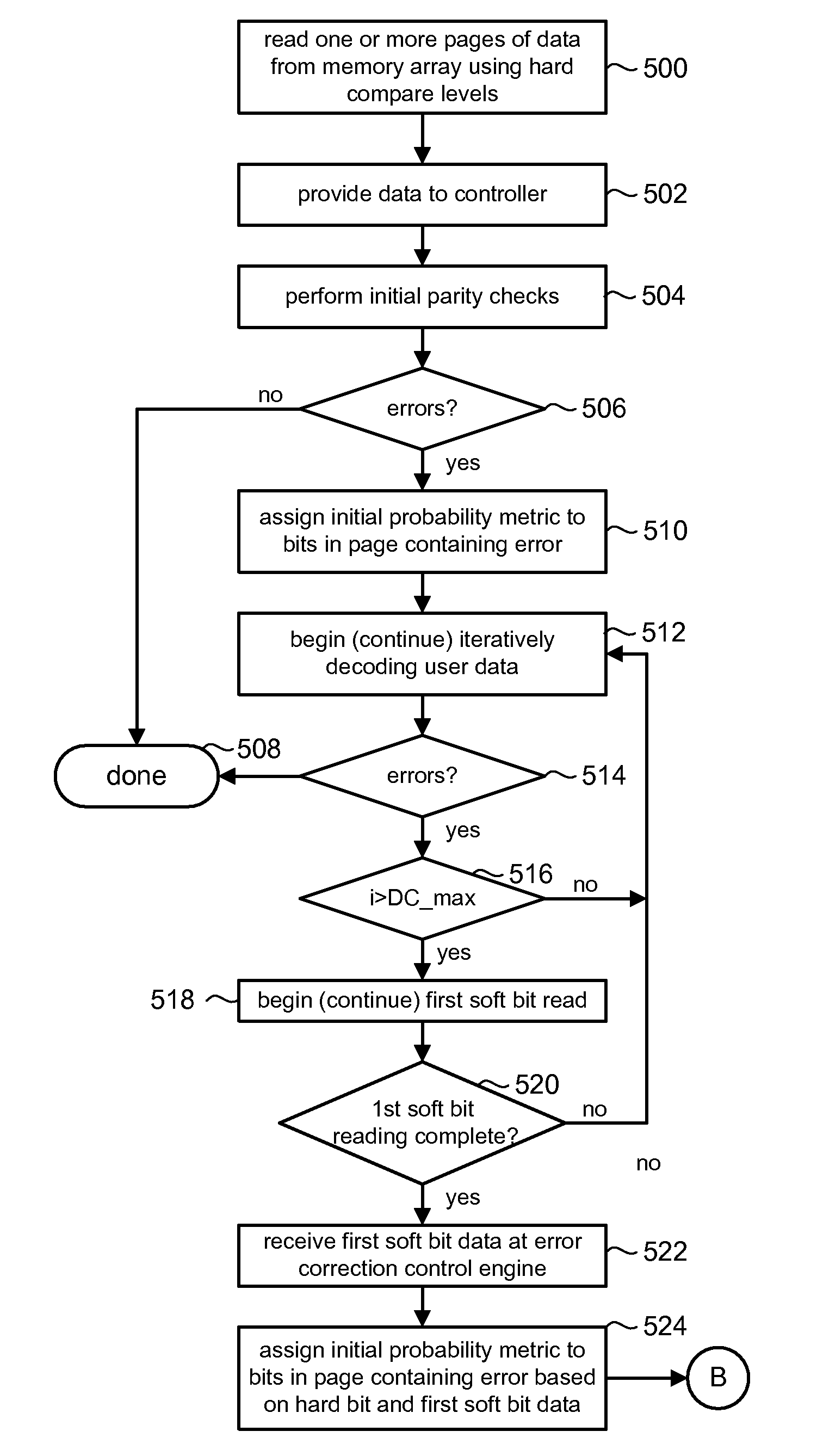
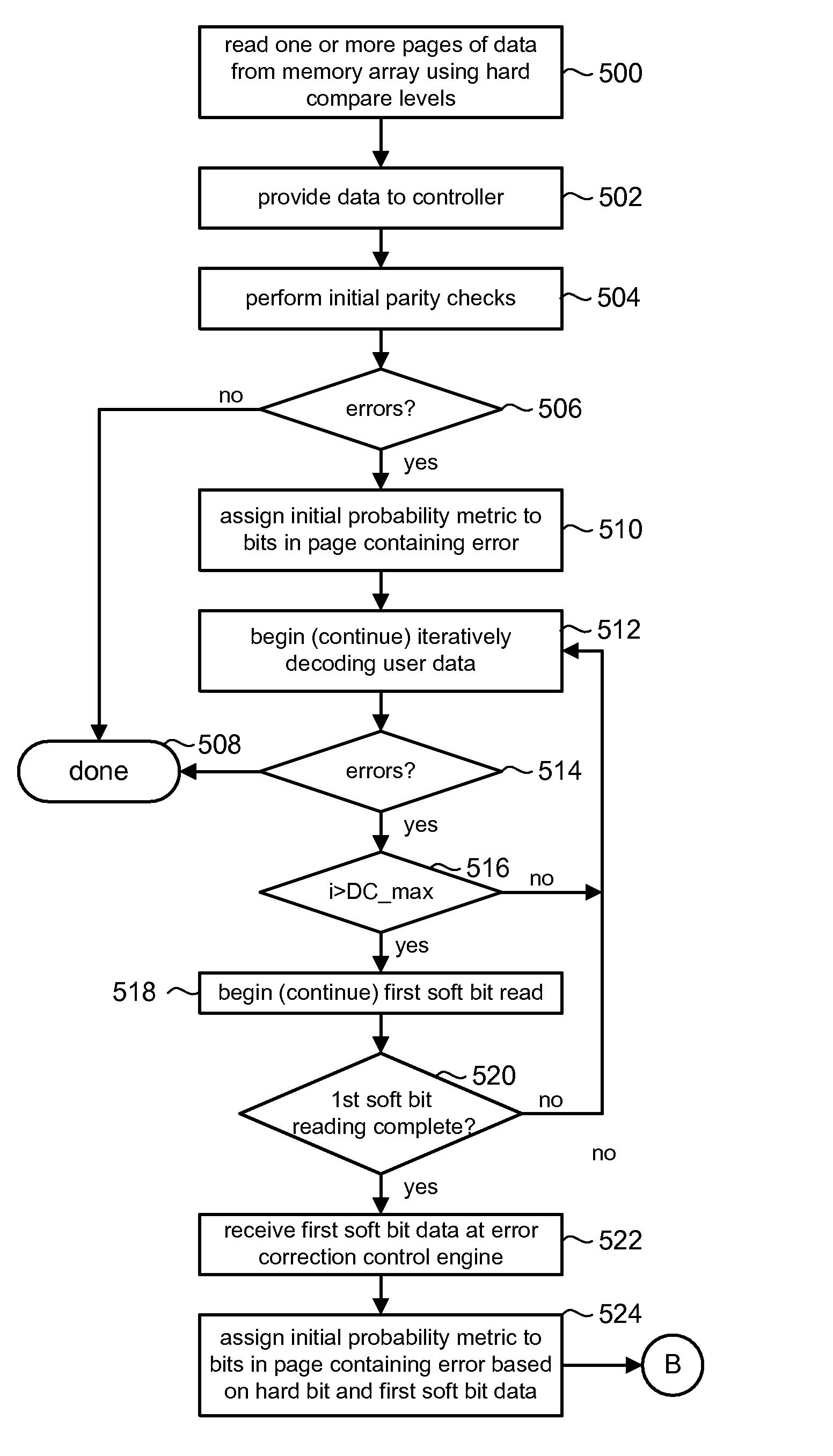
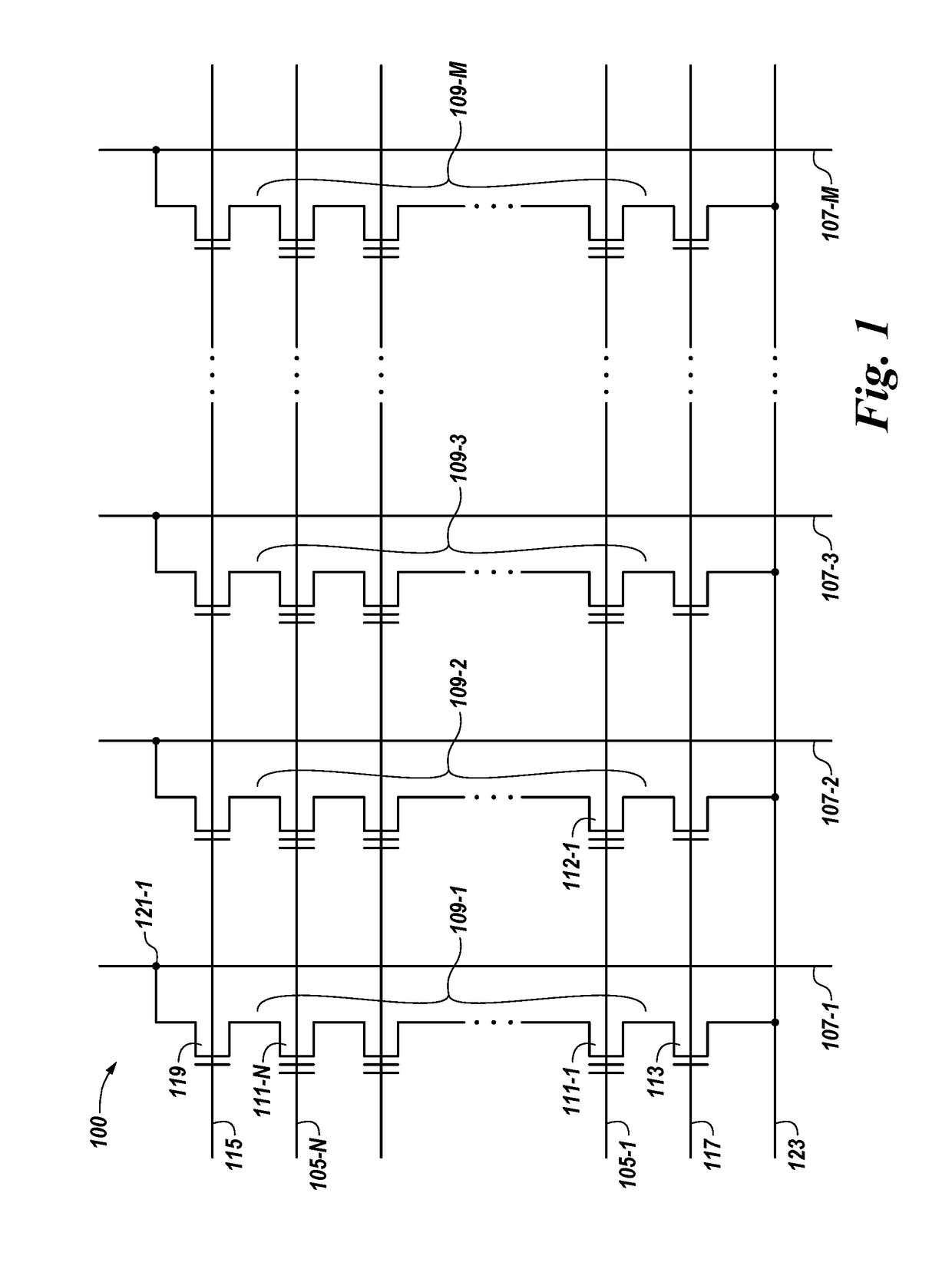
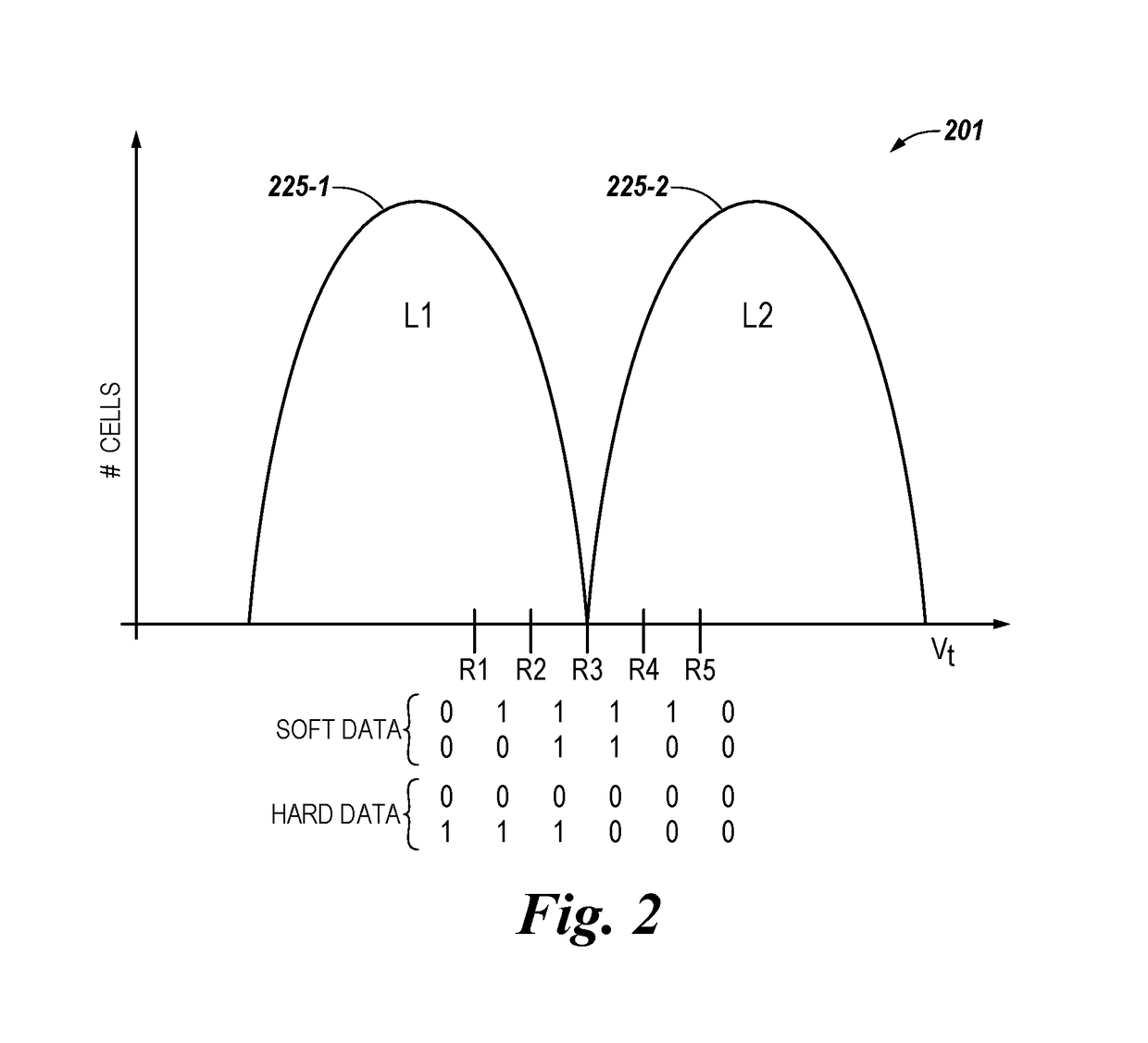
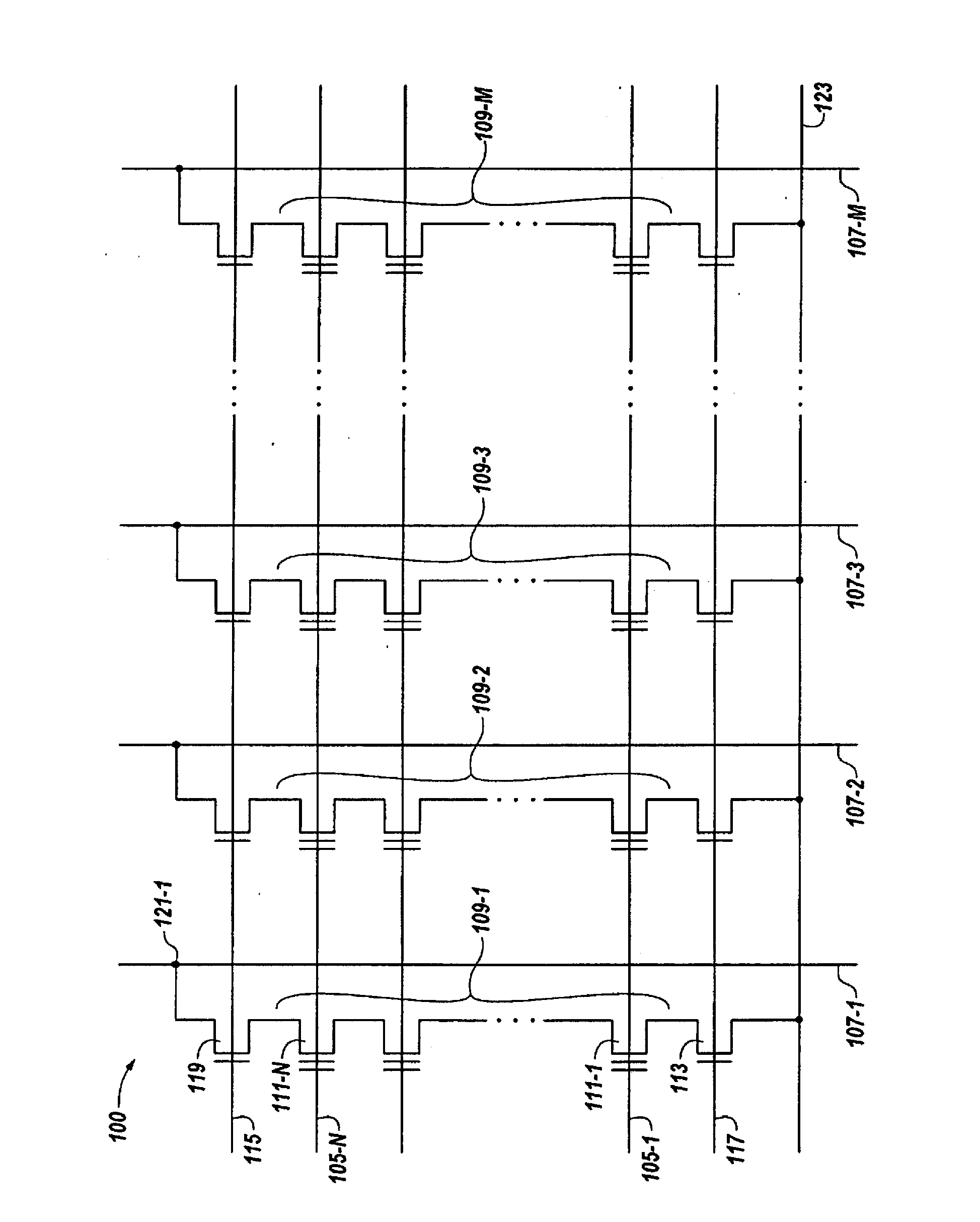
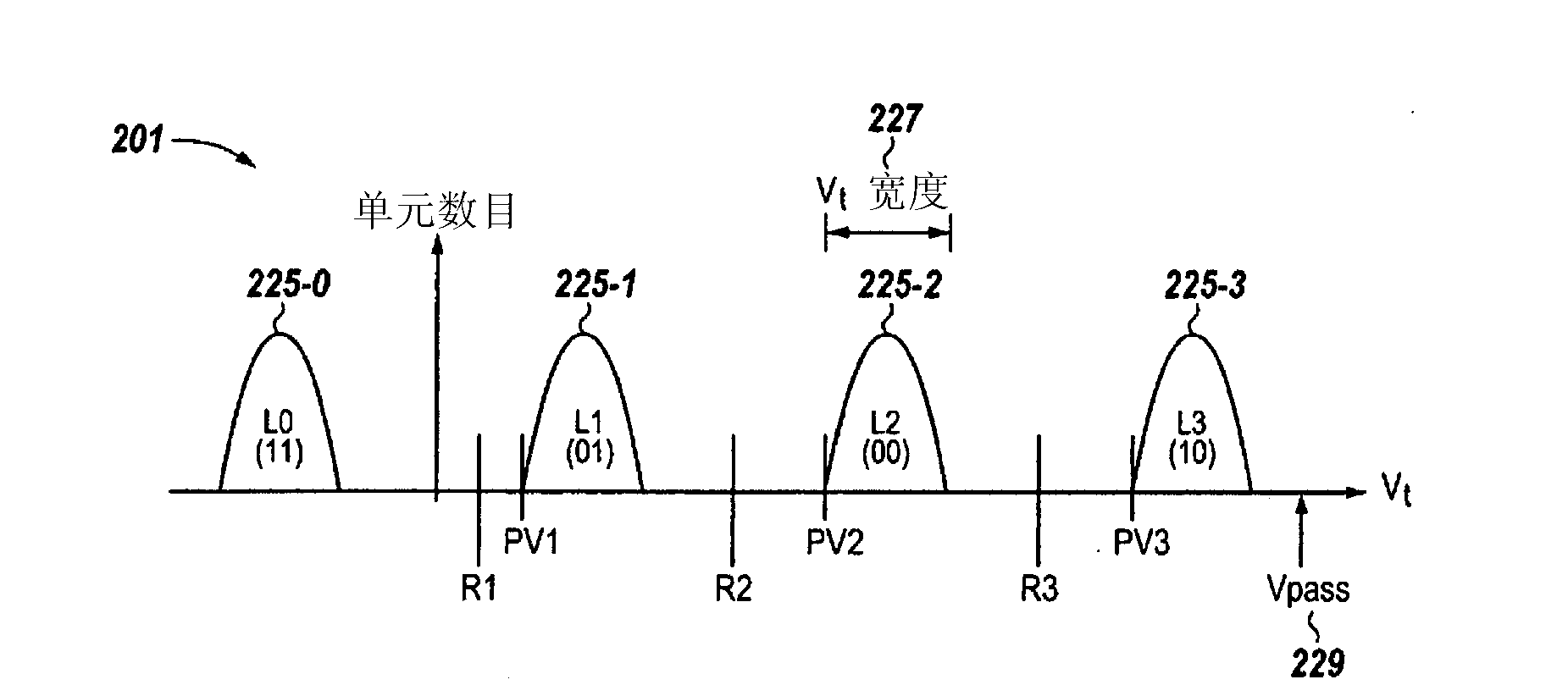
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Non-Volatile Memory with Soft Bit Data Transmission for Error Correction Control
ActiveUS20080244360A1High resolutionData representation error detection/correctionError detection/correctionLow-density parity-check codeSoft data
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +1
Hard/soft error detection
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Methods and Apparatus for Soft Data Generation for Memory Devices Based on Performance Factor Adjustment
InactiveUS20110167305A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionElectrical resistance and conductanceRetention time
Methods and apparatus are provided for soft data generation for memory devices based on a performance factor adjustment. At least one soft data value is generated for a memory device, by obtaining at least one read value; and generating the soft data value based on the obtained at least one read value and an adjustment based on one or more performance factors of the memory device. The read values may comprise, for example, data bits, voltage levels, current levels or resistance levels. The read values may be soft data or hard data. The possible performance factors include endurance, number of read cycles, retention time, temperature, process corner, inter-cell interference impact, location within the memory array and a pattern of aggressor cells. One or more pattern-dependent performance factors and / pr location-specific performance factors may also be considered. The generated soft data value may be a soft read value that is used to generate one or more log likelihood ratios, or may be the log likelihood ratios themselves.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Integrated data download
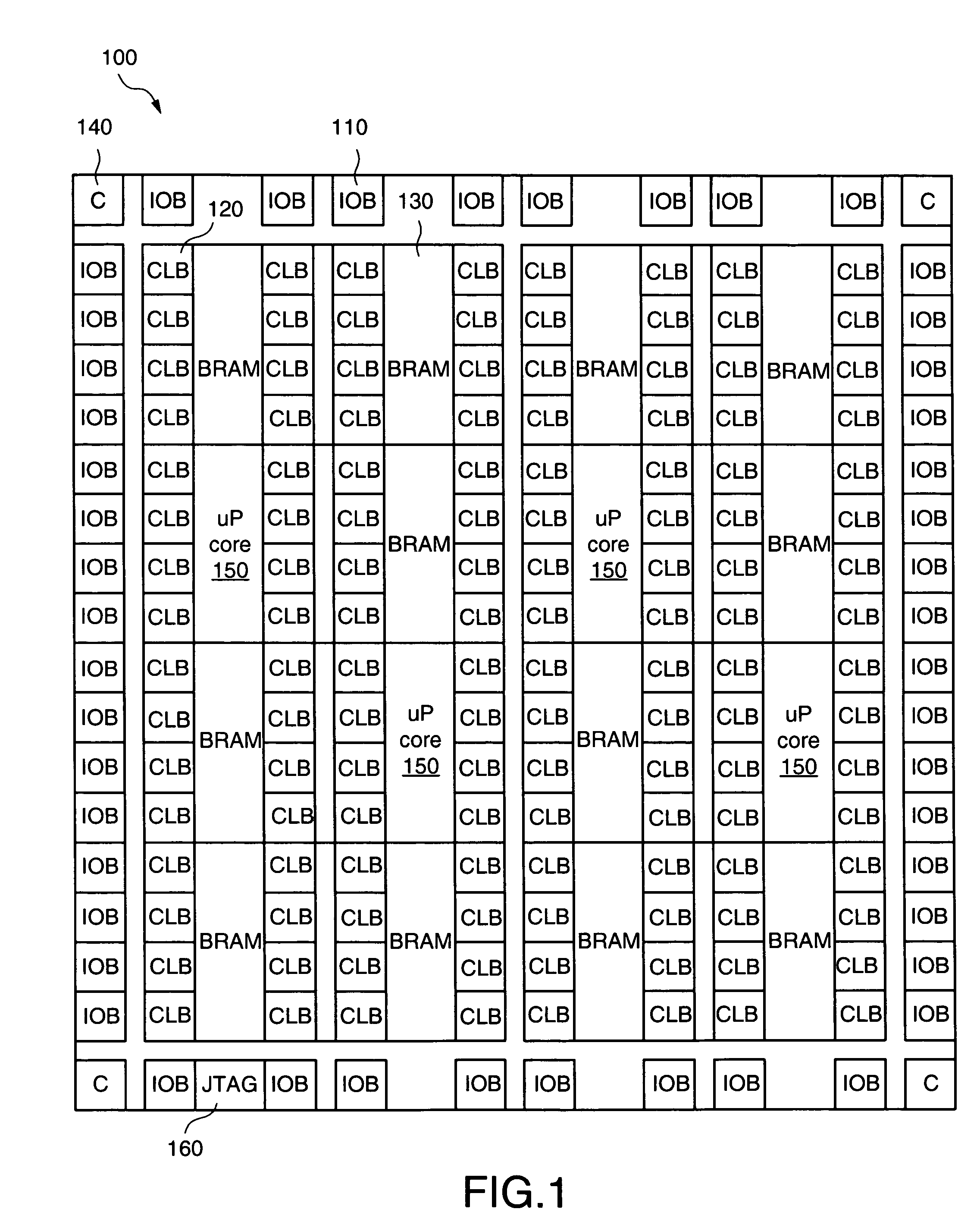
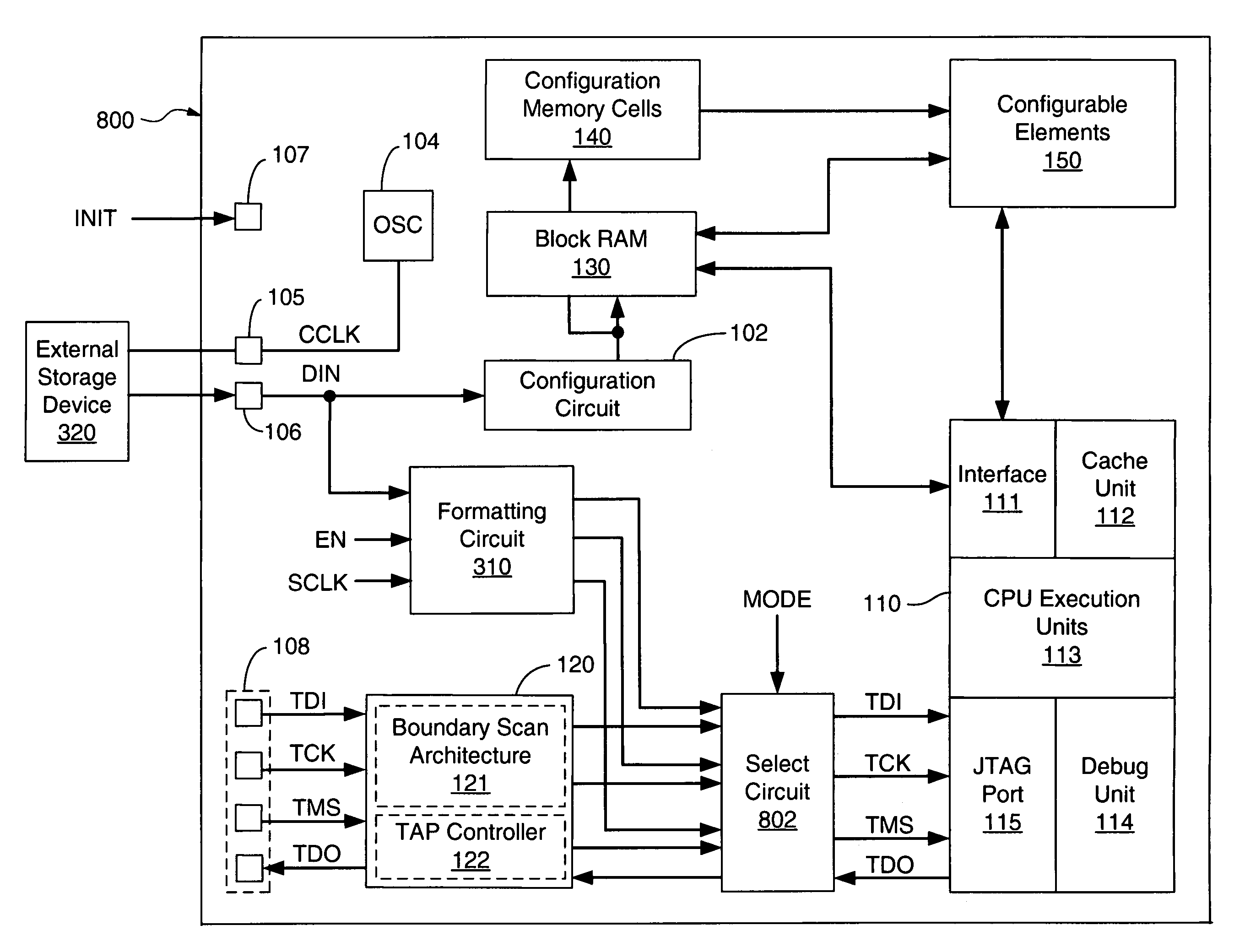
A bitstream having a plurality of data sets is provided to an integrated circuit device such as an FPGA having test circuitry capable of routing data to the device's internal resources, with each data set including configuration information and a trigger signal. Successive data sets of the bitstream are sequentially processed by the test circuitry in response to the trigger signals to sequentially initialize the device's resources to various states. For some embodiments, each data set includes configuration data to configure one or more configurable elements of the device to implement a desired design and includes soft data for use by a processor embedded within the device. For one embodiment, control logic is provided to selectively wait for a predetermined time period before processing a next data set.
Owner:XILINX INC
Soft bit data transmission for error correction control in non-volatile memory
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Methods and Apparatus for Soft Data Generation for Memory Devices Based Using Reference Cells
ActiveUS20110225350A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionSoft dataComputer science
Methods and apparatus are provided for soft data generation for memory devices using reference cells. At least one soft data value is generated in a memory device by writing a known data to one or more reference cells; reading one or more of the reference cells; obtaining a read statistic based on the read one or more reference cells; and obtaining the at least one soft data value based on the obtained read statistic. The read statistics can optionally be obtained for one or more desired locations of a memory array; or for a given pattern, PATT, in one or more aggressor cells. The read statistic can optionally comprise asymmetric statistics obtained for a plurality of possible values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE +1
Non-volatile memory with soft bit data transmission for error correction control
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC +1
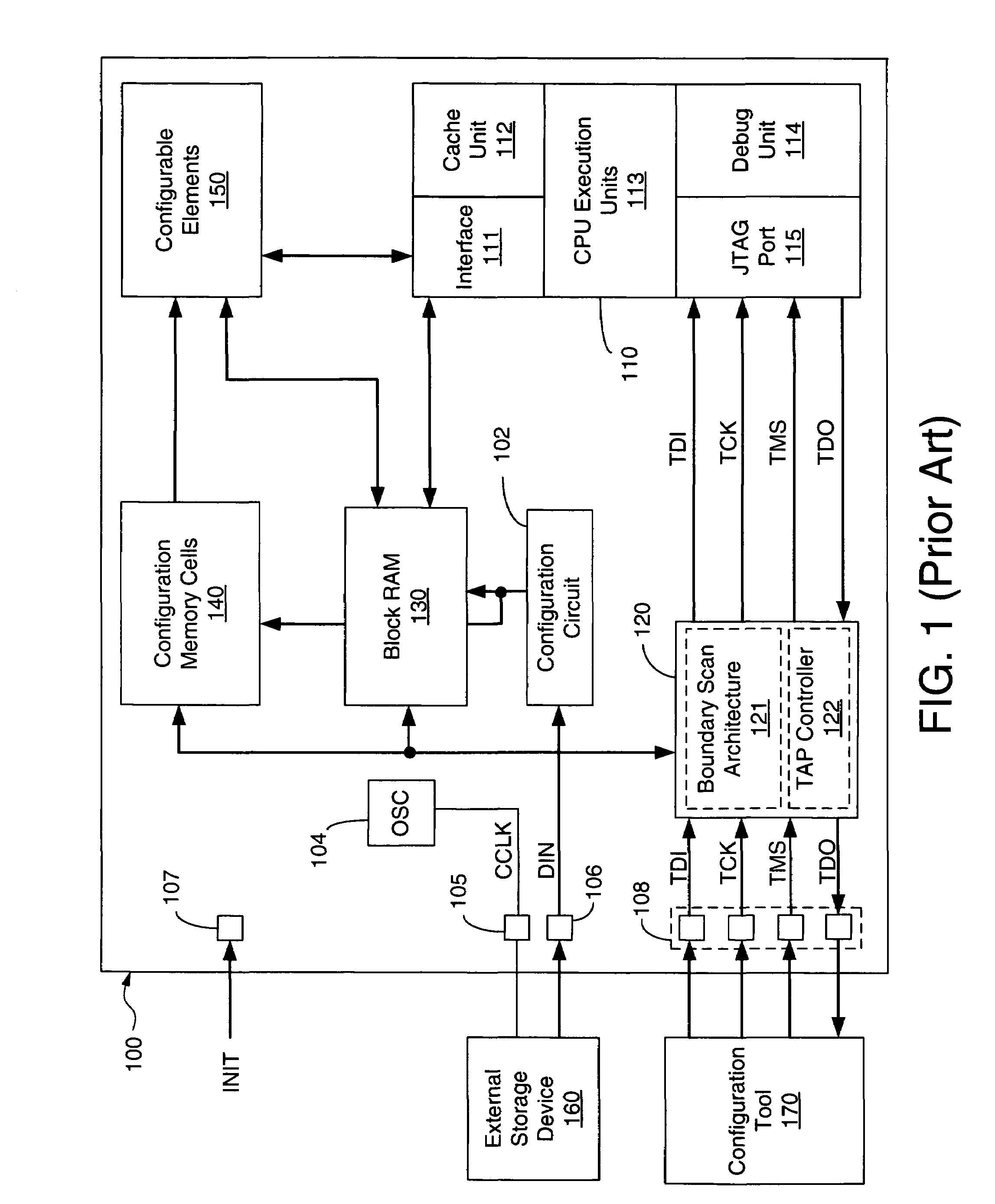
Configuration logic for embedded software
ActiveUS7313730B1Reduce configuration timeIncreased durabilityError detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsExternal storageEmbedded software
An integrated circuit such as an FPGA containing an embedded processor having test circuitry capable of controlling the processor's resources using JTAG commands includes a formatting circuit that formats soft data received from an external storage device into a JTAG-compatible bitstream that can be used by the processor's test circuitry to access and / or control the processor's resources at any time, thereby allowing the embedded processor's resources to be accessed and controlled during FPGA configuration operations before the processor has been initialized to an operational state without using an external configuration tool. For some embodiments, the formatting circuit is a state machine that formats soft data such as firmware code, software programs, processor commands, and the like received from the external storage device into a JTAG-compatible bitstream that can be loaded into and / or used to access the resources of the embedded processor via the processors' test circuitry.
Owner:XILINX INC +1
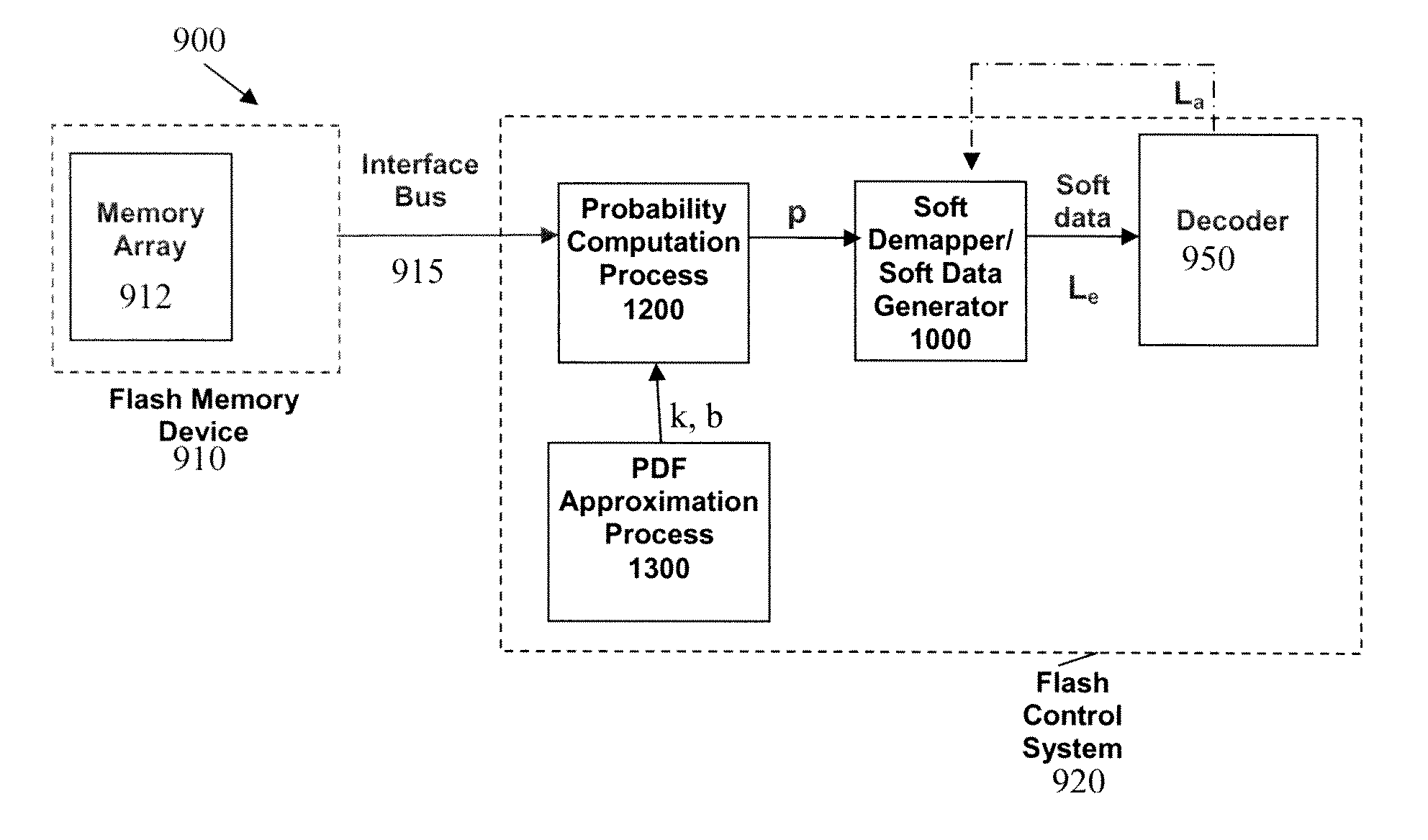
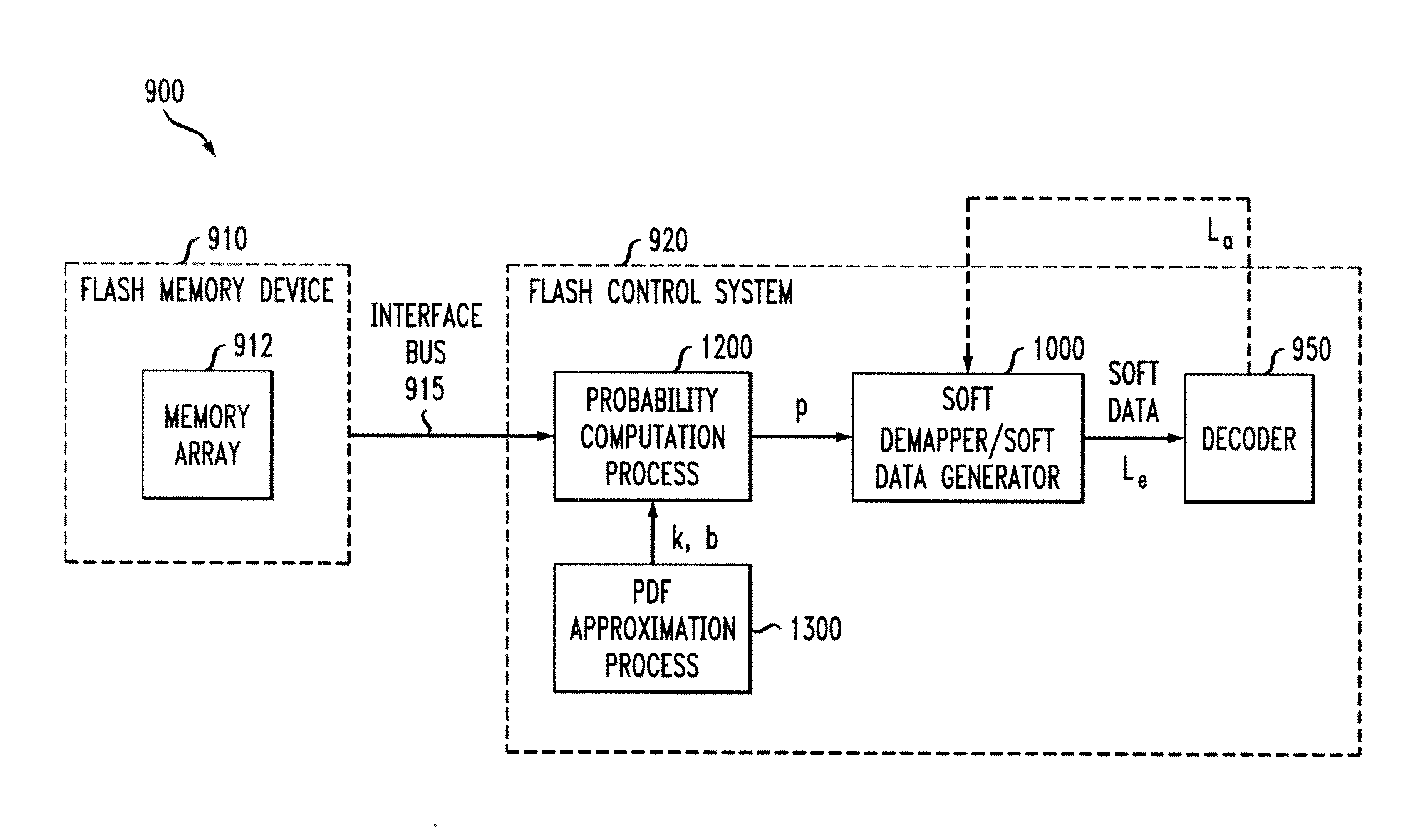
Methods and apparatus for computing soft data or log likelihood ratios for received values in communication or storage systems
ActiveUS20110246859A1Other decoding techniquesOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemSoft data
Methods and apparatus are provided for computing soft data or log likelihood ratios for received values in communication or storage systems. Soft data values or log likelihood ratios are computed for received values in a communication system or a memory device by obtaining at least one received value; identifying a segment of a function corresponding to the received value, wherein the function is defined over a plurality of segments, wherein each of the segments has an associated set of parameters; and calculating the soft data value or log likelihood ratio using the set of parameters associated with the identified segment. The computed soft data values or log likelihood ratios are optionally provided to a decoder.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
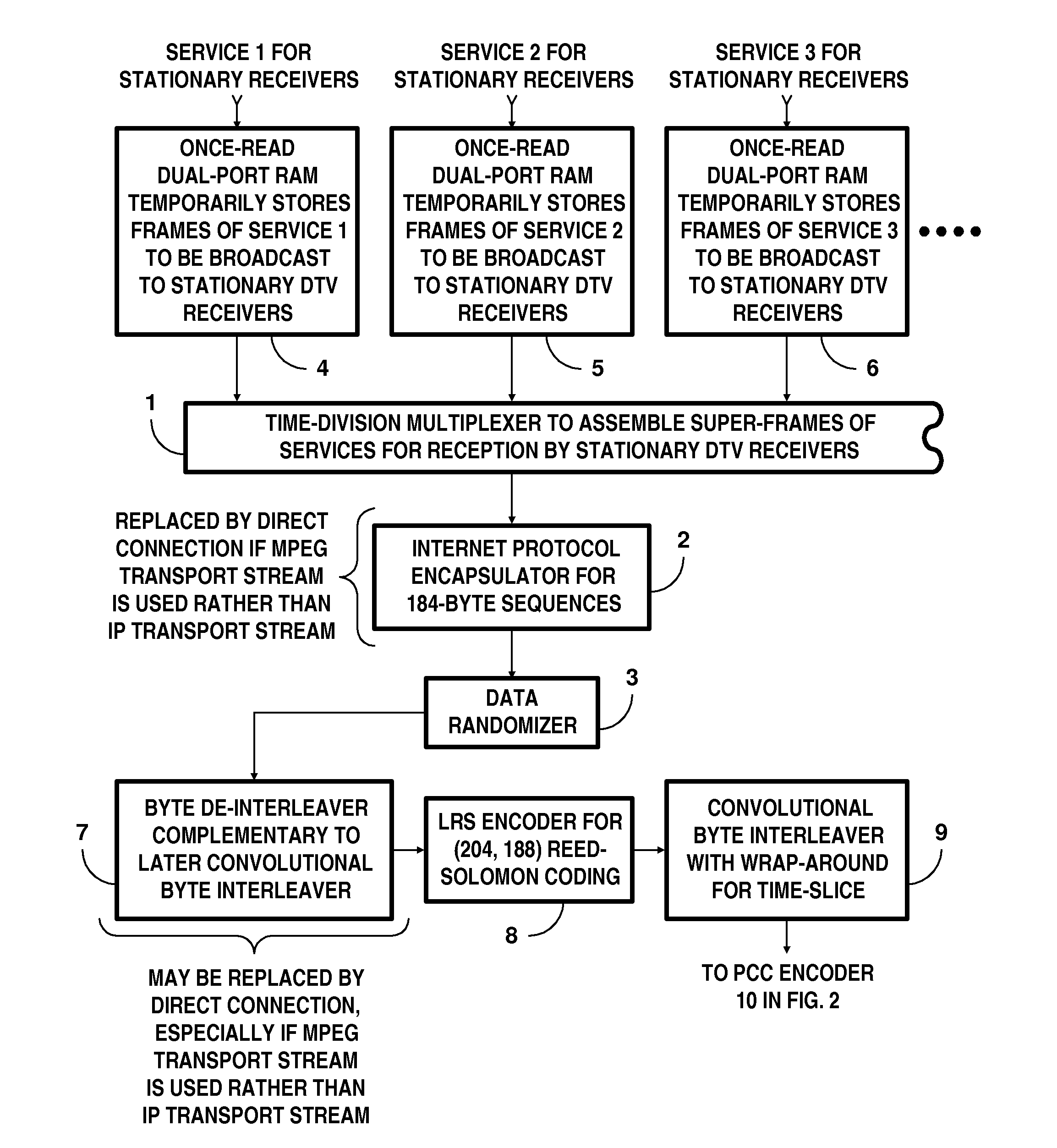
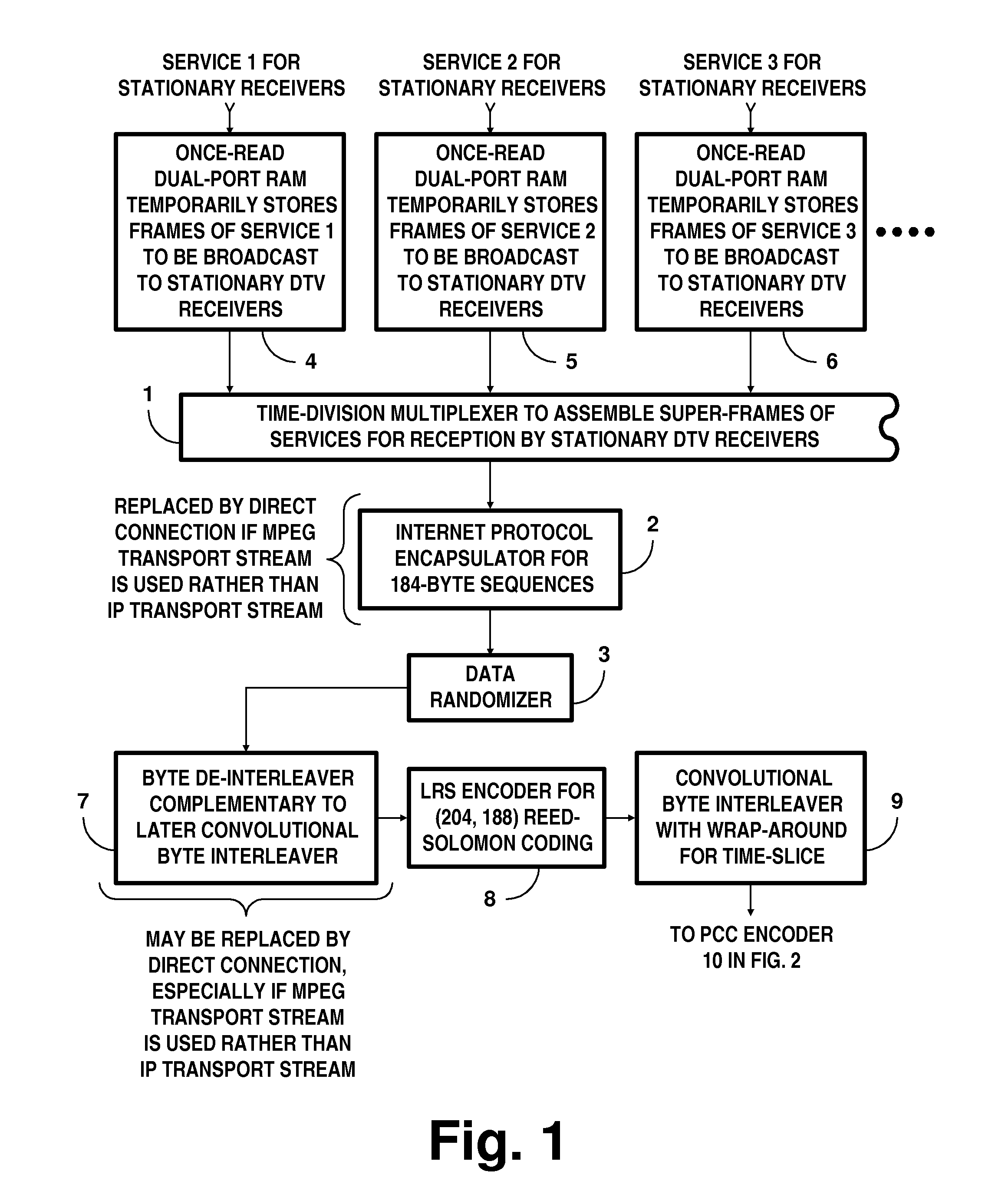
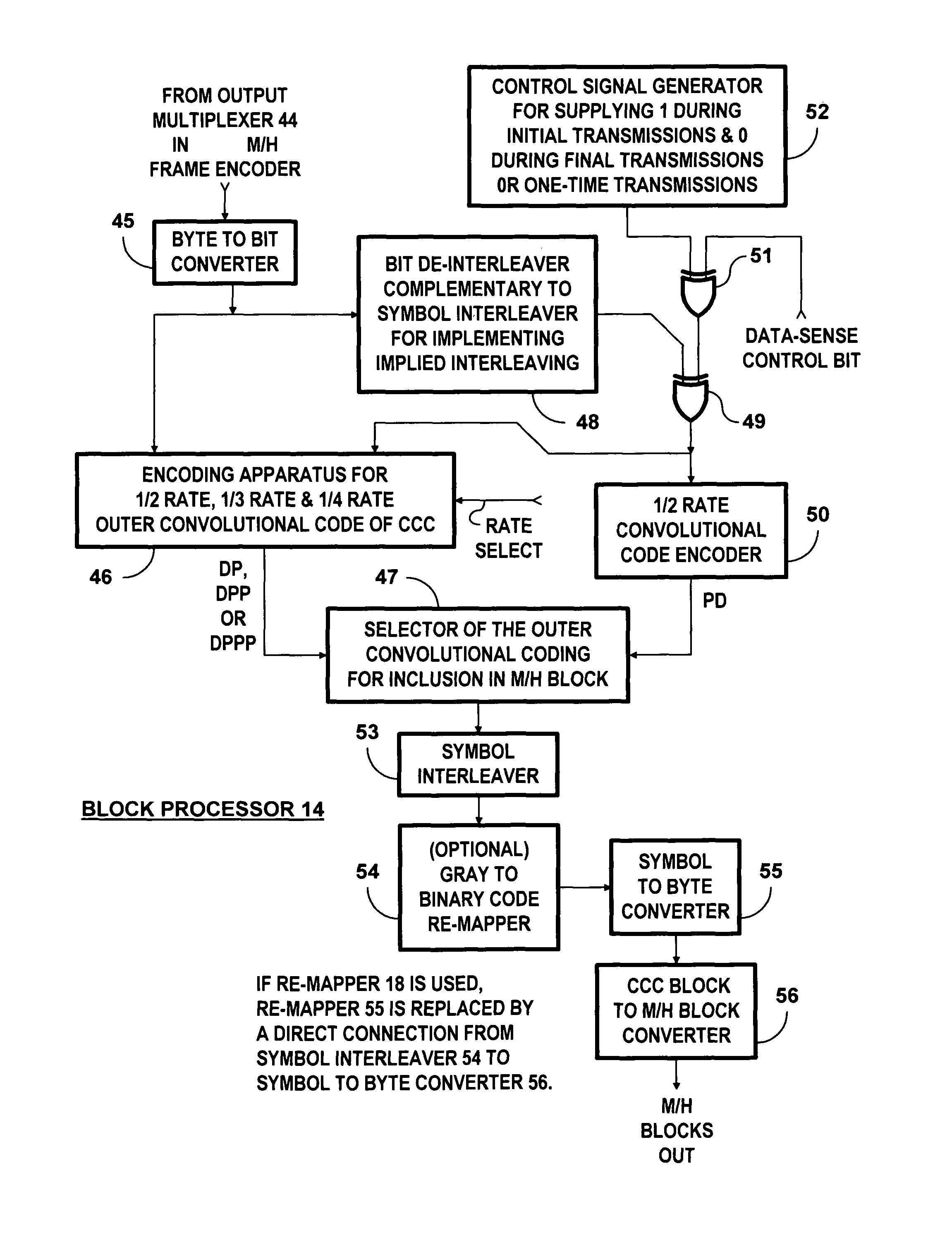
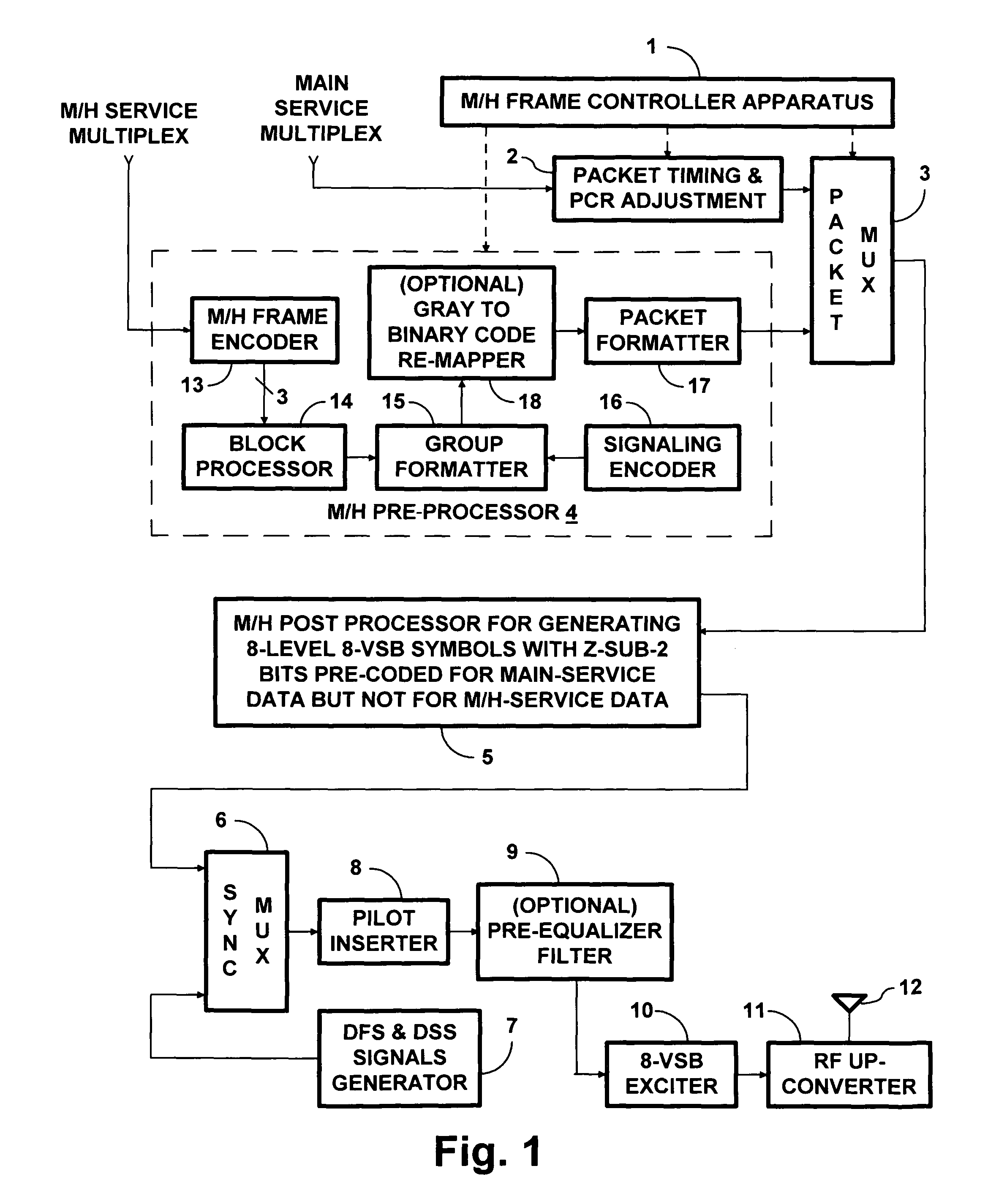
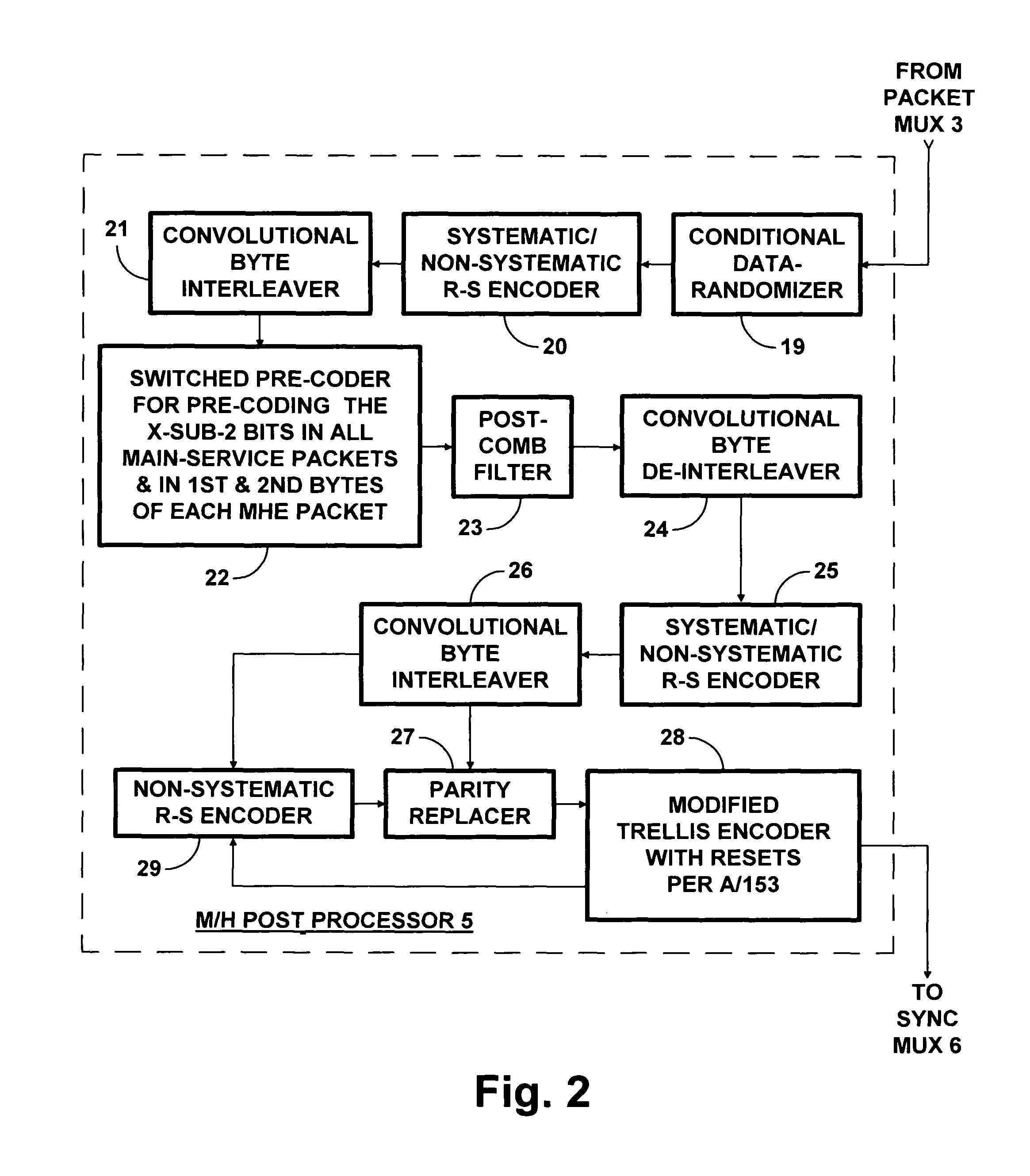
Receivers for COFDM digital television transmissions
InactiveUS20130028336A1Improve the level ofAvoid the needPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionSoft dataByte
A receiver of COFDM digital television signals includes an inner decoder for iterative soft-decision decoding of concatenated convolutional coding (CCC) and an outer decoder for Reed-Solomon (RS) coding. The receiver generates error flags for identifying code symbols to be erased before the output symbols from the inner decoder are byte de-interleaved and supplied to the outer decoder. Generation of those flags depends on soft decoding results from the inner decoder. The method of locating errors ascribes to each byte supplied to the outer decoder for RS coding the highest lack-of-confidence level specified by the soft data bits associated with that byte. The method is described as being extended to locate byte errors in plural-dimension cross-interleaved Reed-Solomon codes (CIRC) apt to be employed in DTV broadcasting to mobile and handheld receivers.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
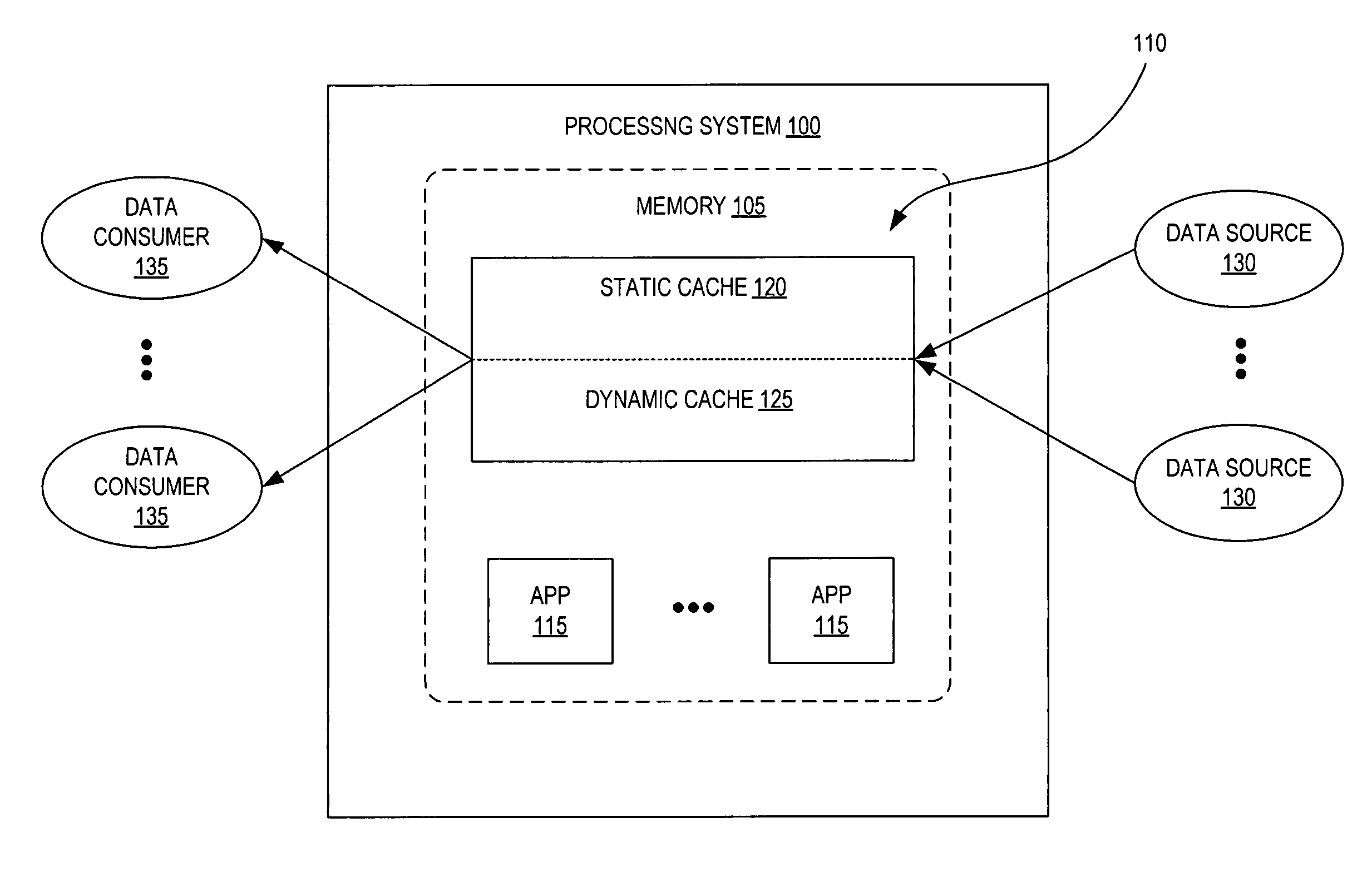
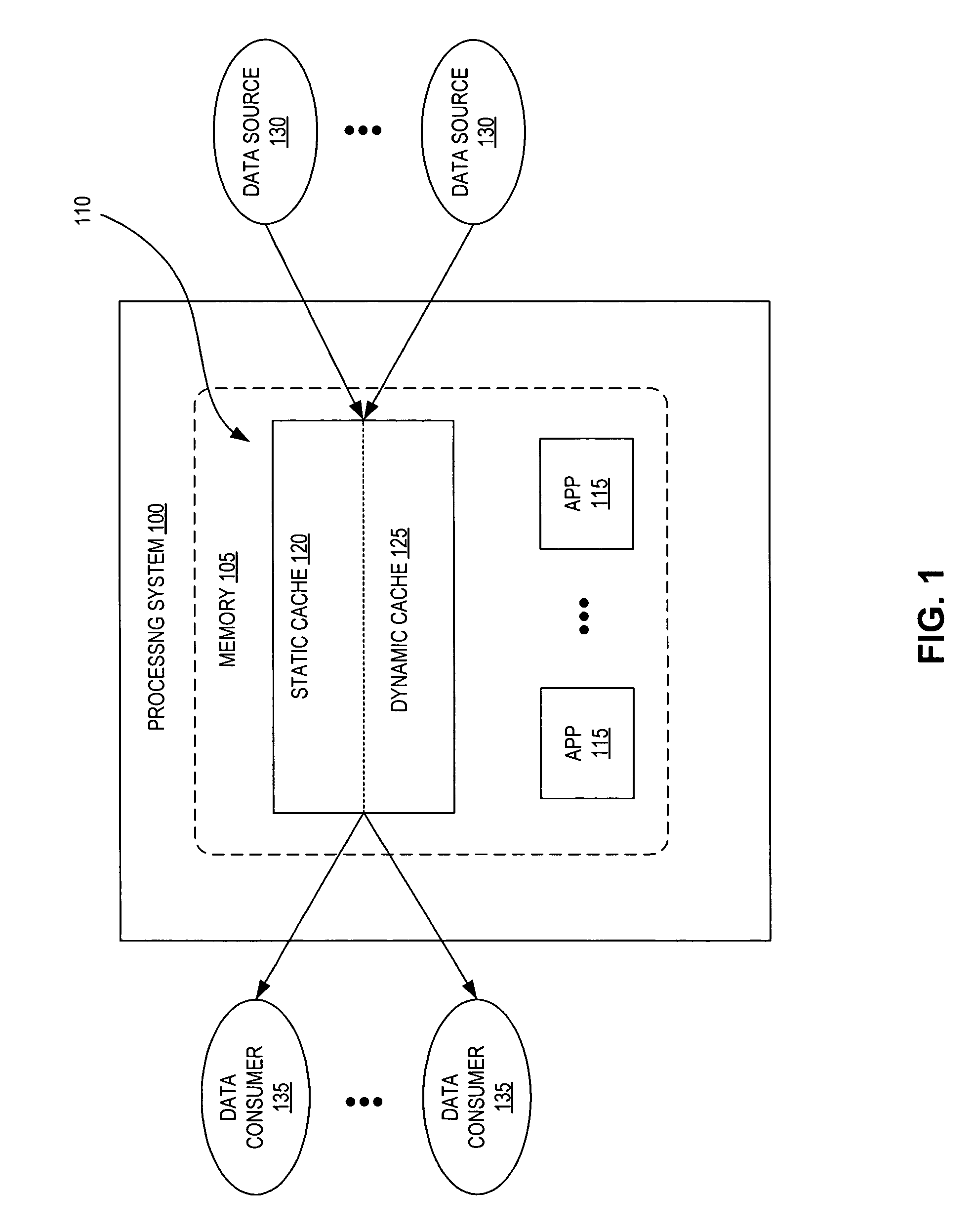
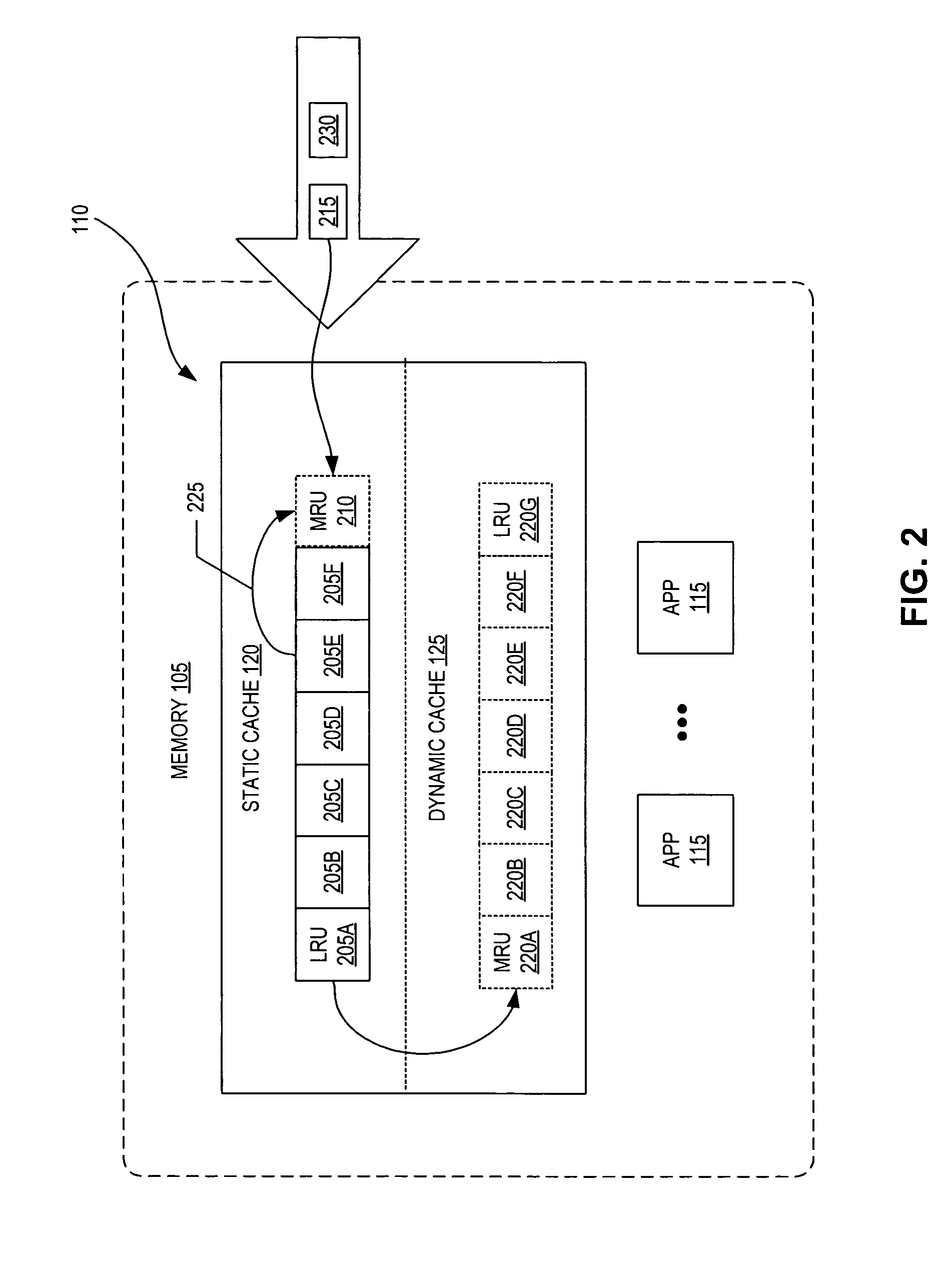
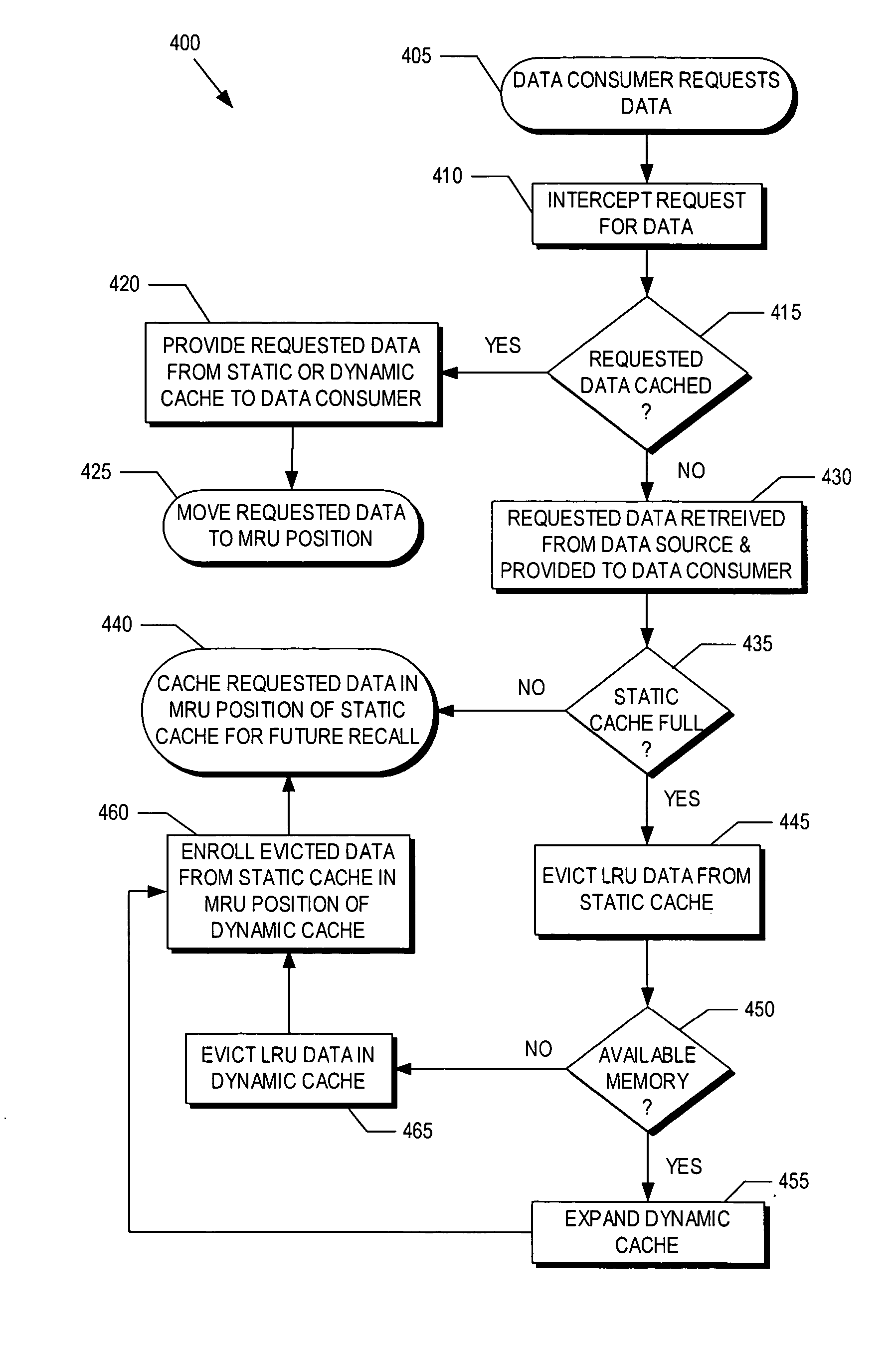
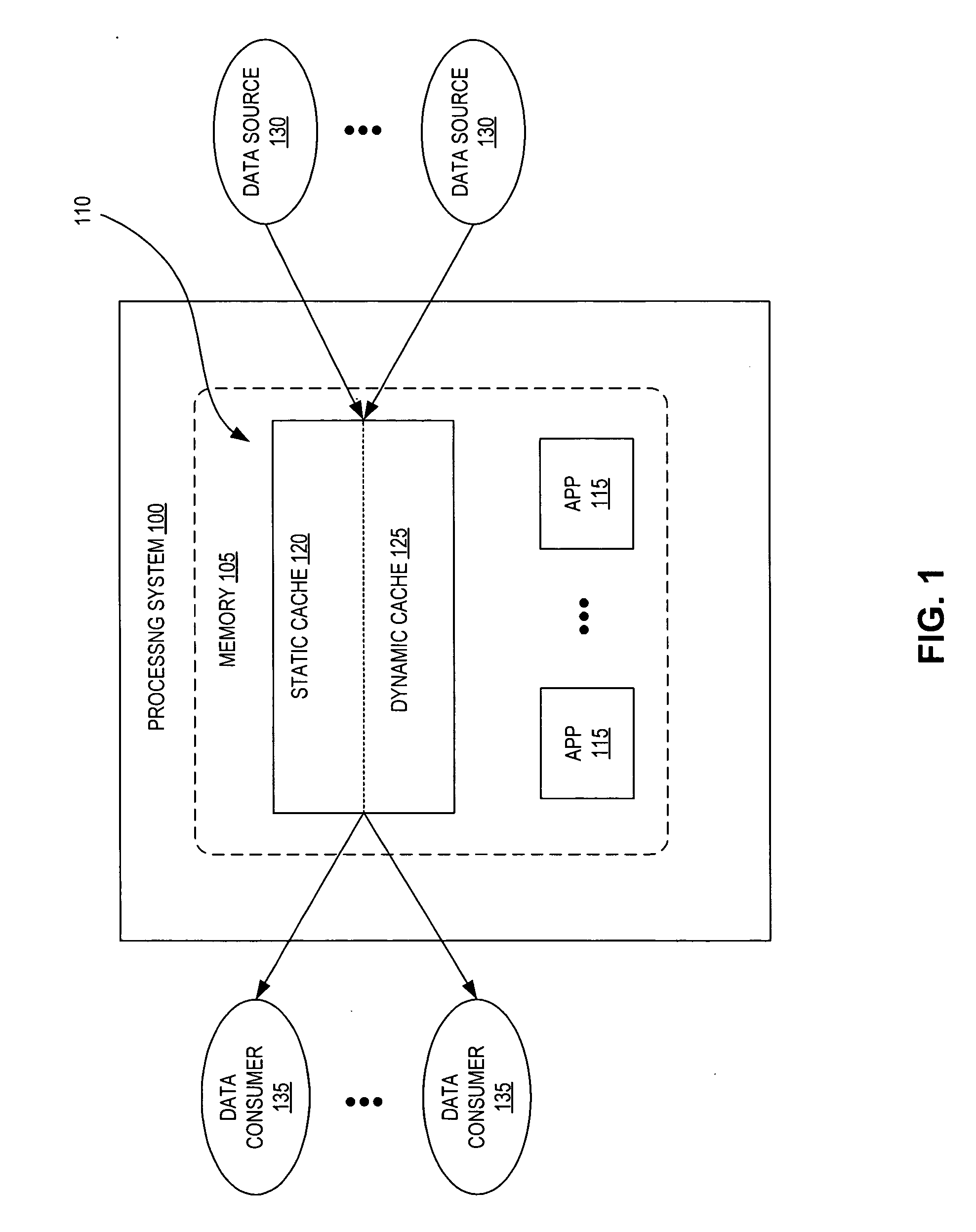
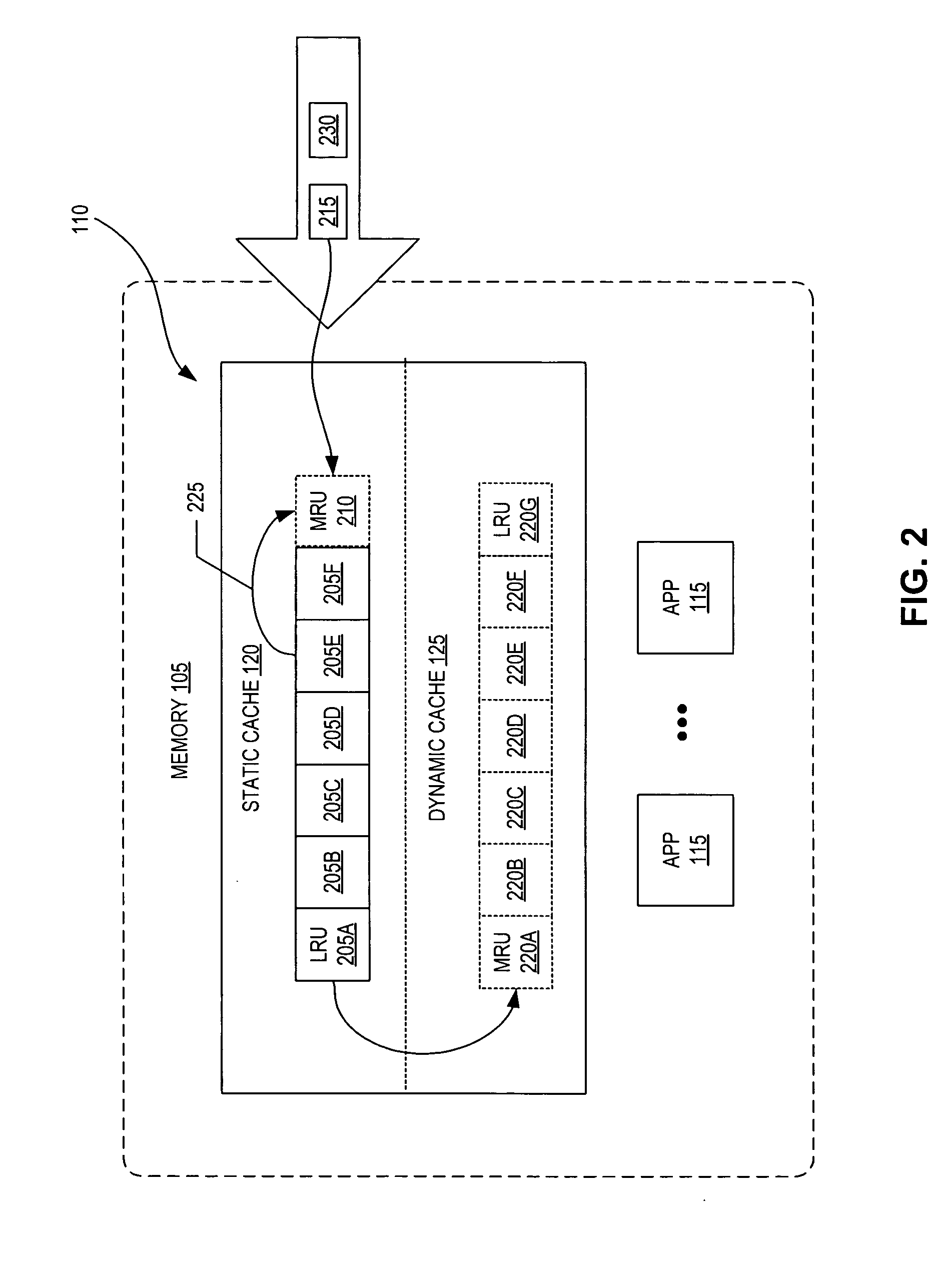
Hybrid-cache having static and dynamic portions
ActiveUS7330938B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData sourceParallel computing
System and method for a hybrid-cache. Data received from a data source is cached within a static cache as stable data. The static cache is a cache having a fixed size. Portions of the stable data within the static cache are evicted to a dynamic cache when the static cache becomes full. The dynamic cache is a cache having a dynamic size. The evicted portions of the stable cache are enrolled into the dynamic cache as soft data.
Owner:SAP AG
Methods and apparatus for approximating a probability density function or distribution for a received value in communication or storage systems
ActiveUS20110246842A1Error minimizationRead-only memoriesLogical operation testingCommunications systemNormal density
Methods and apparatus are provided for approximating a probability density function or distribution for a received value in communication or storage systems. A target distribution is approximated for a received value in one or more of a communication system and a memory device, by substantially minimizing a squared error between the target distribution of the received values and a second distribution obtained by mapping a predefined distribution, such as a Gaussian distribution, through a mapping function, wherein the second distribution has an associated set of parameters. The mapping function can be, for example, a piecewise linear function. The second distribution has a plurality of segments and each of the segments has an associated set of parameters. The associated set of parameters can be used to compute probability values, soft data values or log likelihood ratios.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
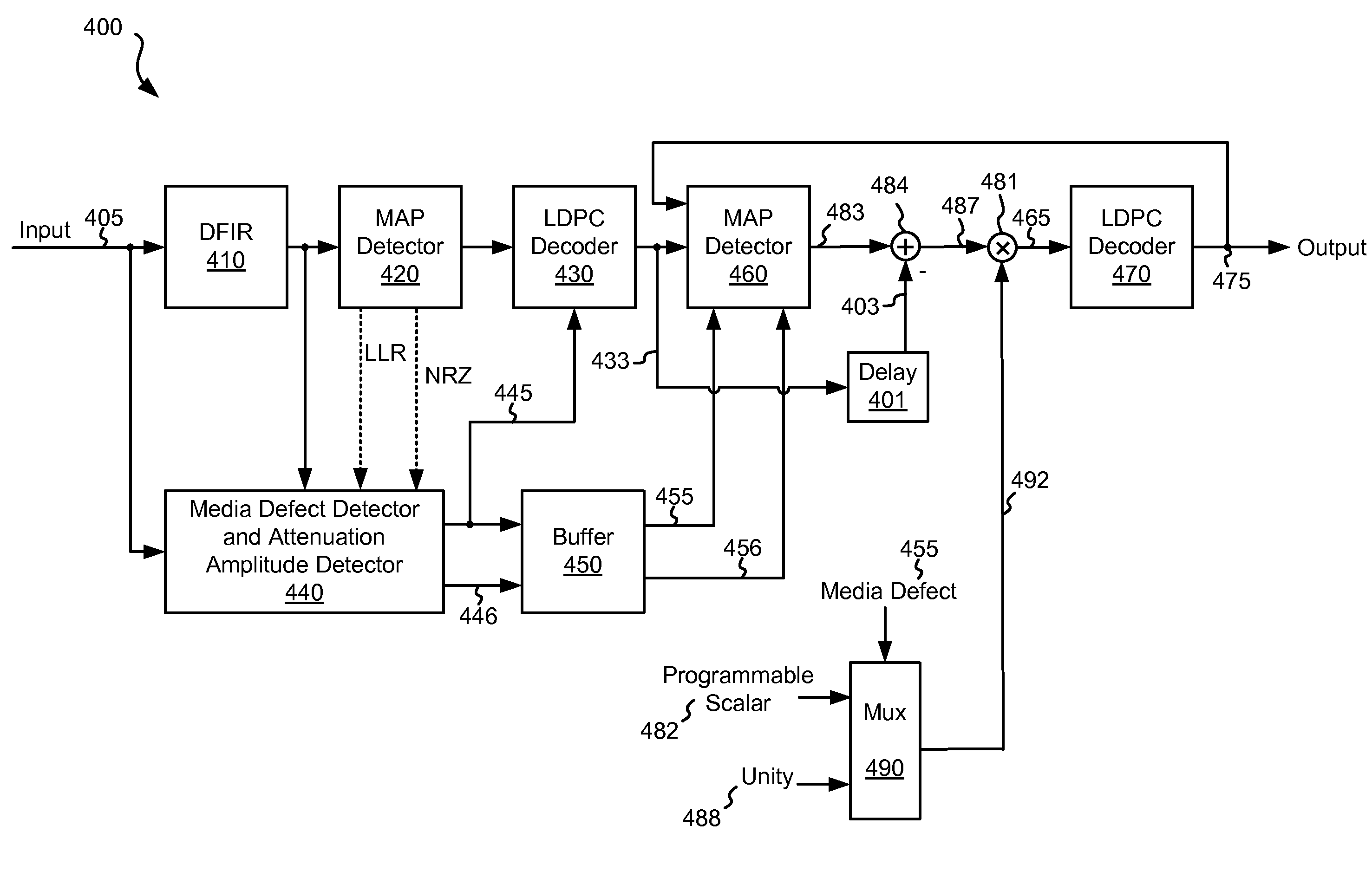
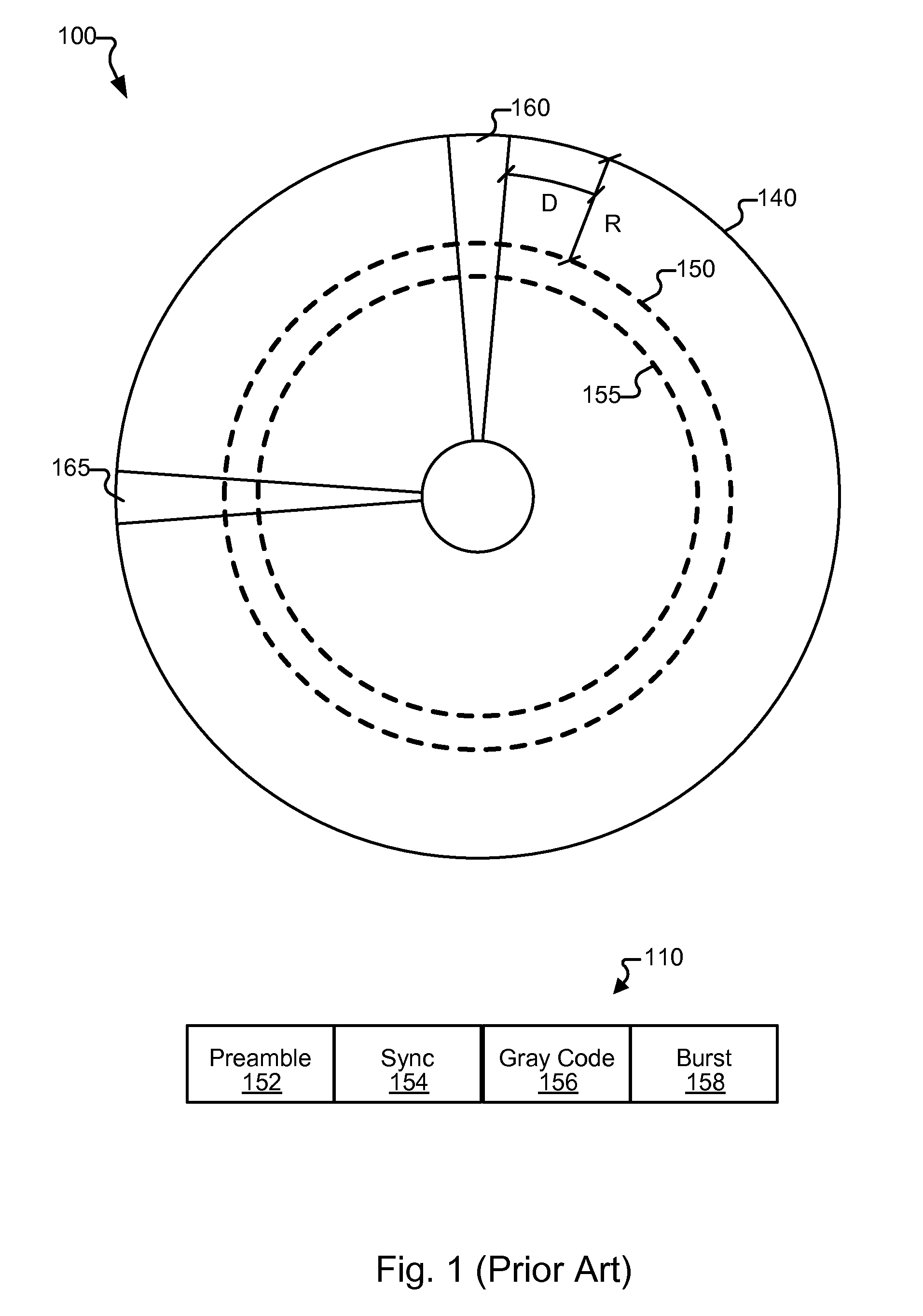
Systems and Methods for Multilevel Media Defect Detection
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for deriving data from a defective media region. As an example, a method for deriving data from a defective media region is disclosed that includes providing a storage medium and performing a media defect detection that indicates a defective region on the storage medium. A first data decode is performed on data corresponding to the defective region. The first data decode yields a first output. It is determined that the first output failed to converge and based at least in part on the failure of the first output to converge, a second data decode is performed on the data corresponding to the defective region. The second data decode includes zeroing out any soft data corresponding to the defective region and providing a second output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Hybrid-cache having static and dynamic portions
ActiveUS20050262306A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingData source
System and method for a hybrid-cache. Data received from a data source is cached within a static cache as stable data. The static cache is a cache having a fixed size. Portions of the stable data within the static cache are evicted to a dynamic cache when the static cache becomes full. The dynamic cache is a cache having a dynamic size. The evicted portions of the stable cache are enrolled into the dynamic cache as soft data.
Owner:SAP AG
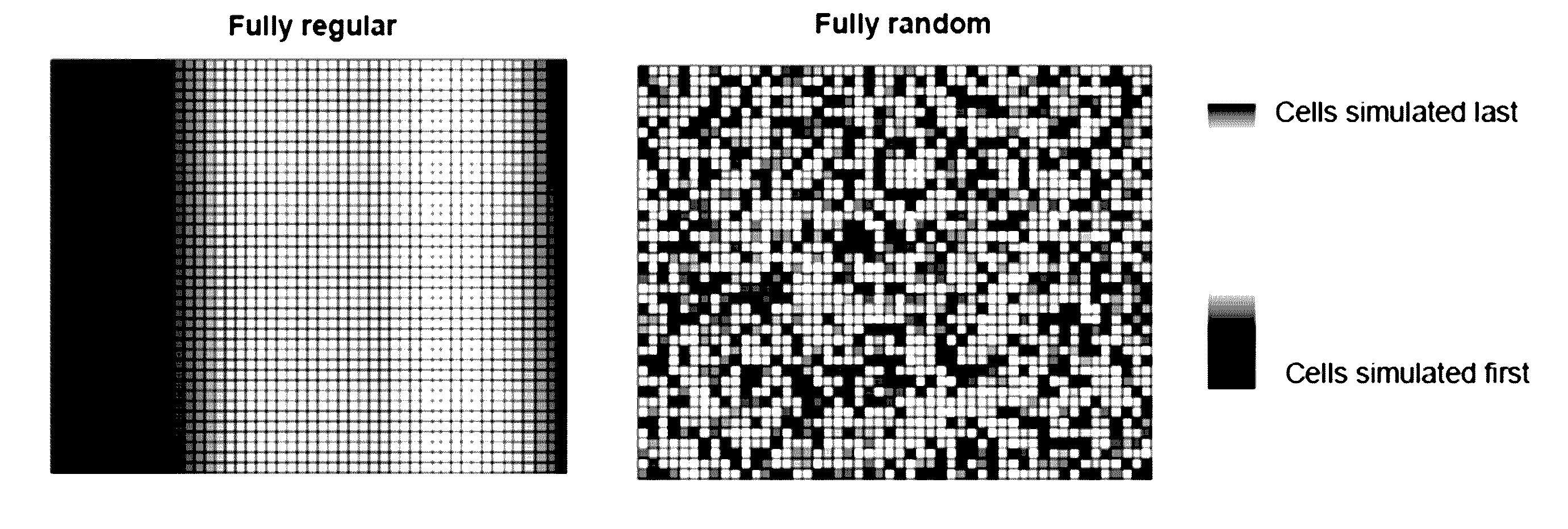
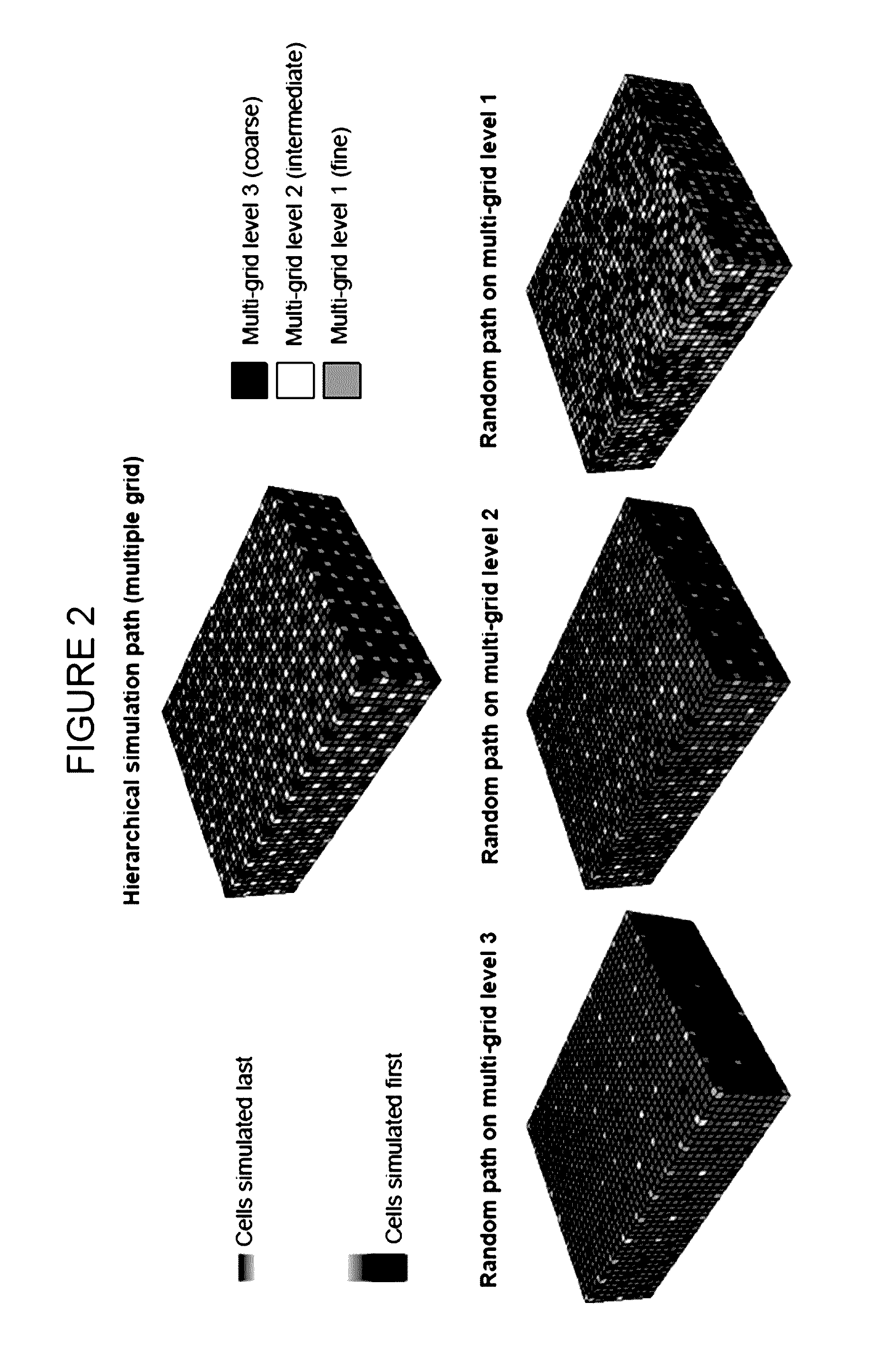
Geobody continuity in geological models based on multiple point statistics
ActiveUS20170011149A1Improve geobody continuityImprove hard data conditioningSeismologyGeomodellingSoft dataMultiple point
The present disclosure describes a method that improves the long-range geobody continuity in Multiple Point Statistical methods, wherein the coarsest multi-grid level cells are simulated in a regular path, and the subsequent level cells are simulated in a random path as usual. The method is general and is applicable to different cases: such as hard data conditioning, soft data conditioning, non-stationarity modeling, 2 or more than 2 types of facies modeling, and 2D and 3D modeling. The method is particularly useful in reservoir modeling, especially for the channelized systems, but can be generally applied to other geological environments.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Methods and apparatus for approximating a probability density function or distribution for a received value in communication or storage systems
ActiveUS8504885B2Error minimizationError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesCommunications systemNormal density
Methods and apparatus are provided for approximating a probability density function or distribution for a received value in communication or storage systems. A target distribution is approximated for a received value in one or more of a communication system and a memory device, by substantially minimizing a squared error between the target distribution of the received values and a second distribution obtained by mapping a predefined distribution, such as a Gaussian distribution, through a mapping function, wherein the second distribution has an associated set of parameters. The mapping function can be, for example, a piecewise linear function. The second distribution has a plurality of segments and each of the segments has an associated set of parameters. The associated set of parameters can be used to compute probability values, soft data values or log likelihood ratios.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
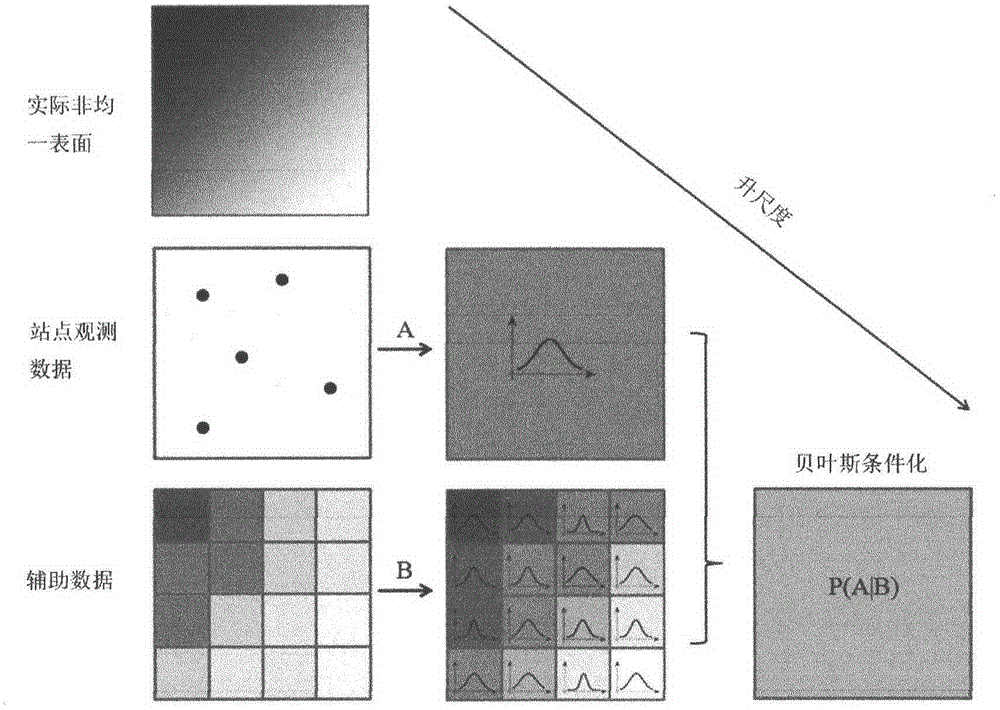
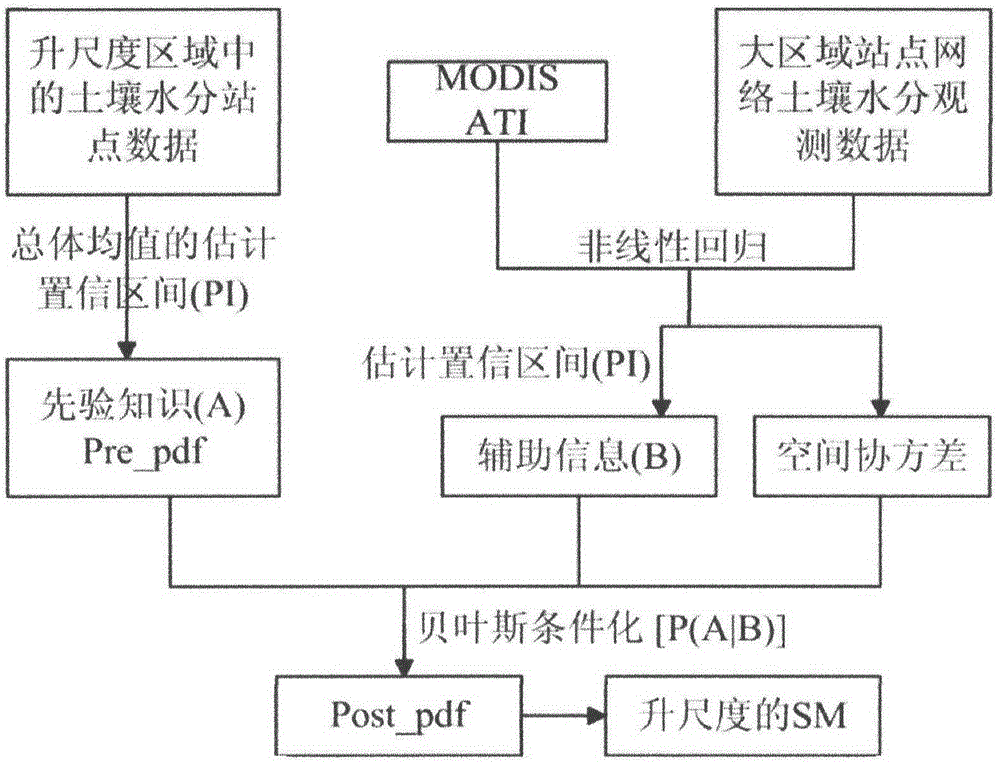
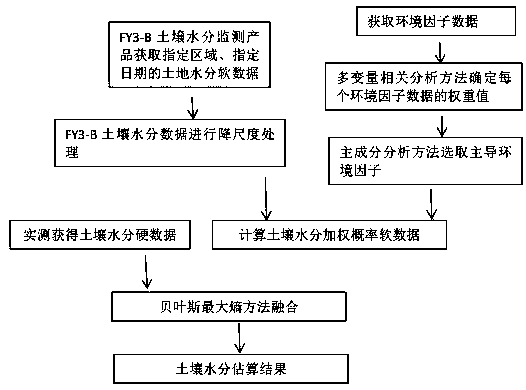
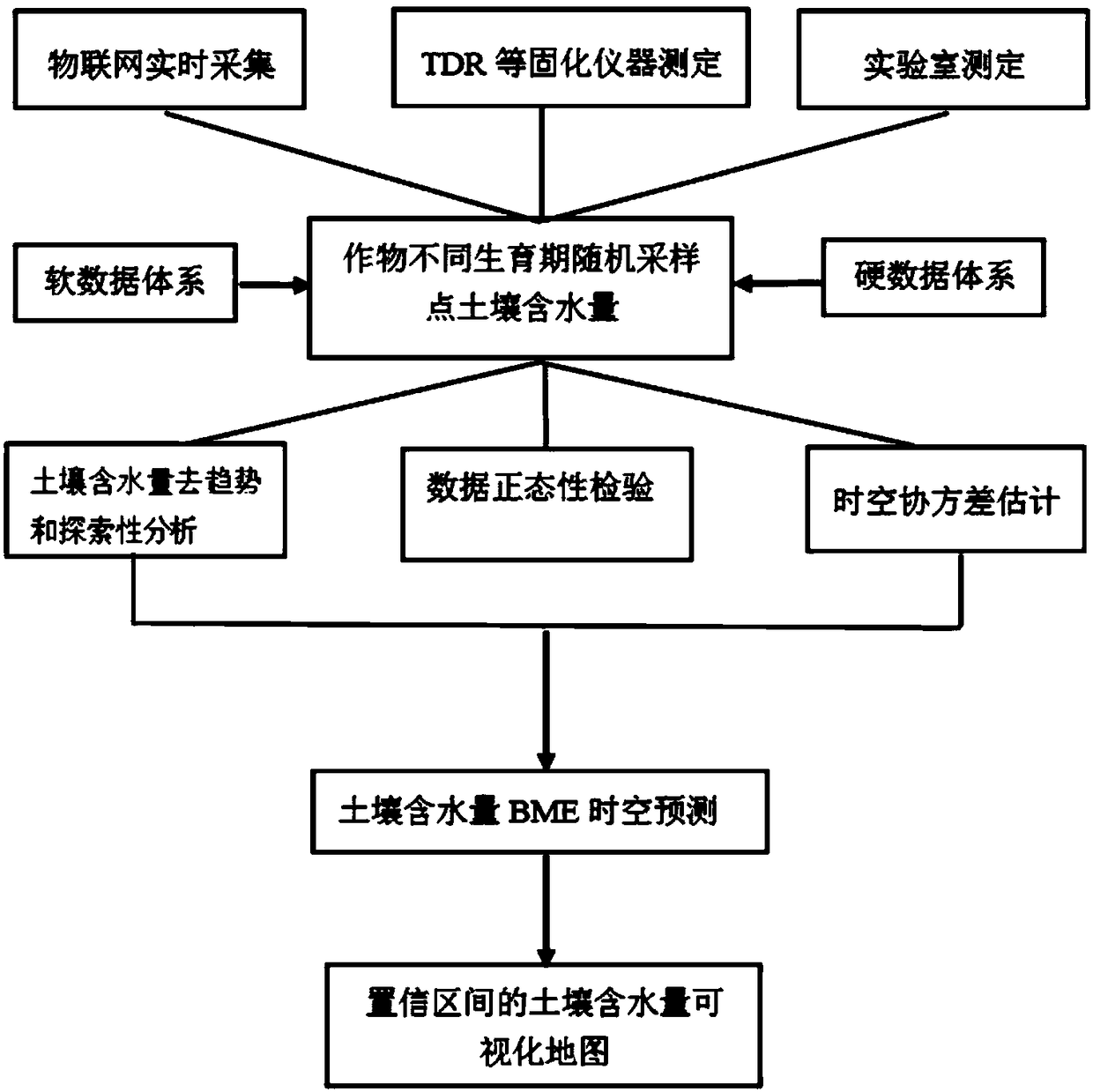
Soil moisture site data upscaling method based on Bayesian theory
InactiveCN104573393AReduce uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsConfidence intervalSoft data
The invention discloses a soil moisture site data upscaling method based on the Bayesian theory. The soil moisture site data upscaling method includes steps of estimating prior probability density distribution function pre_pdf of a target variable on the basis of sparse site observation data in an upscaling area; inversing MODIS ATI into SM by establishing nonlinear regression relation between the SM and the MODIS ATI, estimating an estimated confidence interval of the soil moisture nonlinear regression and probability distribution as soft data in a probability form; integrating the prior distribution of the target variable and auxiliary information of the probability form from the MODIS ATI through the Bayesian theory, and acquiring posterior probability density distribution function post_pdf of the target variable; calculating the value of the target variable in the maximum probability through maximization of the posterior probability distribution function. By the soil moisture site data upscaling method, uncertainties caused by scale difference between soil moisture remote sensing products and ground site authentication data are effectively reduced. The soil moisture site data upscaling method can be applied to upscaling application of other ground surface parameters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Image simulation method based on continuous multiple-point geostatistics method, soft data and hard data
The invention discloses an image simulation method based on a continuous multiple-point geostatistics method, soft data and hard data. For the prediction simulation of permeability images, soft data and hard data are comprehensively utilized to provide a method simulating permeability distribution by using the continuous multiple-point geostatistics method so as to obtain a simulation result similar to the structure characteristics of training images. Compared with the condition that only hard data is used and condition data is not provided, the invention has the highest simulation precision when using soft data and hard data and has minimum CPU time and memory consumption. Compared with the two-point geostatistics method, the continuous MPS method can simulate permeability images more accurately, so that the invention can be widely applied to the application development fields, such as geothermal energy, oil and natural gas fields, coal bed gas and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Soft Bit Data Transmission For Error Correction Control In Non-Volatile Memory
InactiveUS20110252283A1Logical operation testingCode conversionLow-density parity-check codeSoft data
Data stored in non-volatile storage is decoded using iterative probabilistic decoding. An error correcting code such as a low density parity check code may be used. In one approach, initial reliability metrics, such as logarithmic likelihood ratios, are used in decoding sensed states of a set of non-volatile storage element. The decoding attempts to converge by adjusting the reliability metrics for bits in code words which represent the sensed state. Soft data bits are read from the memory if the decoding fails to converge. Initial reliability metric values are provided after receiving the hard read results and at each phase of the soft bit operation(s). In one embodiment, a second soft bit is read from the memory using multiple subsets of soft bit compare levels. While reading at the second subset of compare levels, decoding can be performed based on the first subset data.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Monitoring error correction operations performed in memory
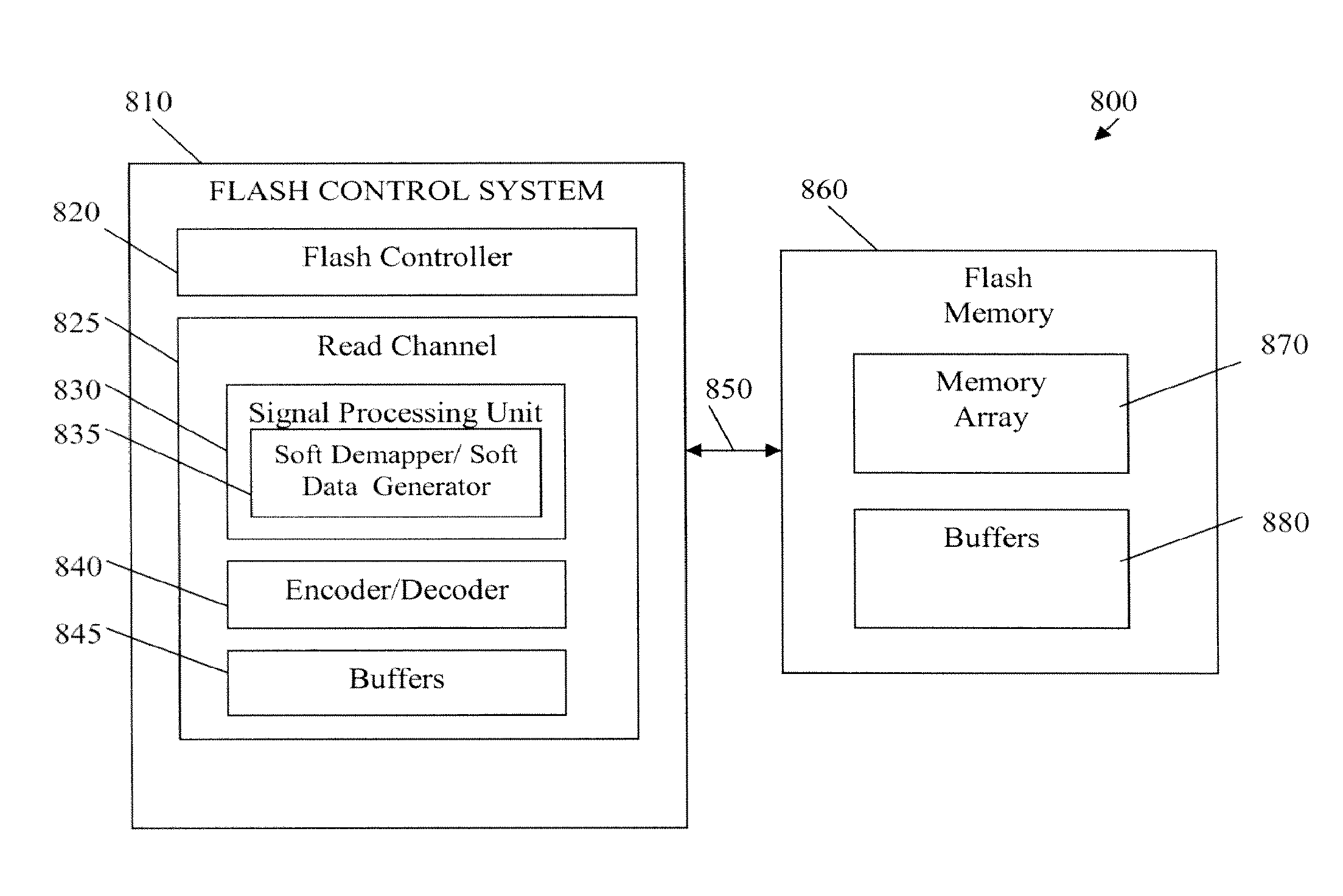
The present disclosure includes apparatuses and methods for monitoring error correction operations performed in memory. A number of embodiments include a memory and circuitry configured to determine a quantity of erroneous data corrected during an error correction operation performed on soft data associated with a sensed data state of a number of memory cells of the memory, determine a quality of soft information associated with the erroneous data corrected during the error correction operation performed on the soft data, and determine whether to take a corrective action on the sensed data based on the quantity of the erroneous data corrected during the error correction operation and the quality of the soft information associated with the erroneous data corrected during the error correction operation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Determining and using soft data in memory devices and systems
The present disclosure includes methods, devices, and systems for determining and using soft data in memory devices and systems. One or more embodiments include an array of memory cells and control circuitry coupled to the array. The control circuitry is configured to perform a number of sense operations on the memory cells using a number of sensing voltages to determine soft data associated with a target state of the memory cells, and adjust a sensing voltage used to determine the target state based, at least partially, on the determined soft data.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
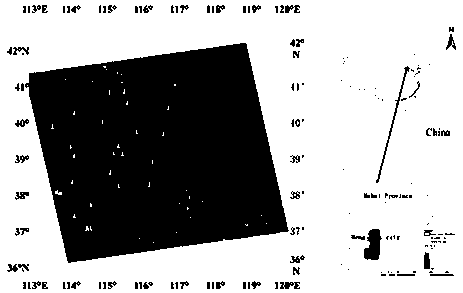
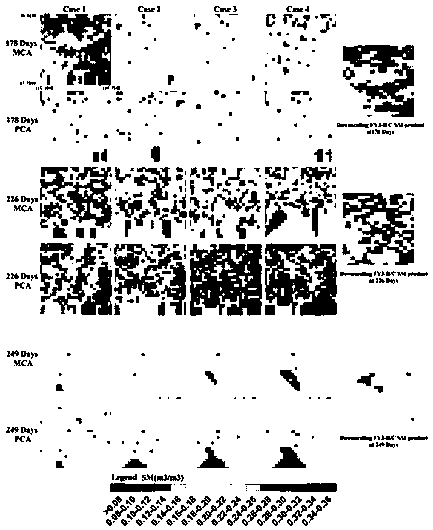
Bayesian soil moisture estimation method based on multi-source remote sensing data
PendingCN110427995AHigh precisionHigh resolutionEarth material testingCharacter and pattern recognitionPrincipal component analysisSoft data
The invention relates to a Bayesian soil moisture estimation method based on multi-source remote sensing data. According to the Bayesian soil moisture estimation method, aiming at how to obtain high-precision soil moisture weighting probability soft data, 12 kinds of multi-source data are fused for the first time to calculate the weighting probability soft data, including downscaling FY3-B soil moisture products, and obtaining albedo (A), vegetation index NDVI (V) and surface temperature LST (T) by using MODIS products; elevation data is acquired by using an ASTER product; gradient, slope direction, plane curvature, profile curvature, surface roughness, humidity index and fluctuation amplitude data are obtained through calculation according to the elevation data obtained by the ASTER product; and weighted probability soft data is obtained by adopting two weight determination methods of multivariable correlation analysis and principal component analysis. The Bayesian soil moisture estimation method also analyzes precision analysis of different soft data quantities, proposes to guarantee sufficient soft data quantities, and plays an important role in obtaining higher-precision soil moisture spatial distribution.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
Soil property interpolation estimation method
InactiveCN107423561AEasy to operateReasonable interpolation resultSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsSoil propertiesEstimation methods
The invention discloses a soil property interpolation estimation method. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, generating prior probability distribution of soil property to-be-measured variables by utilizing a Kriging method; S2, generating soft data by utilizing a correlational relationship between environment factors and prediction points; S3, updating the probability distribution of the soil property to-be-measured variables by utilizing a BME method; and S4, drawing a soil space property map by utilizing the probability distribution of soil the property to-be-measured variables. According to the method, the Kriging method which is simple to operate and mature and a Bayesian maximum entropy method which is accurate and reasonable are combined, so that the interpolation process is more simple and convenient and interpolation result is more reasonable.
Owner:YUNNAN HANZHE TECHN CO LTD
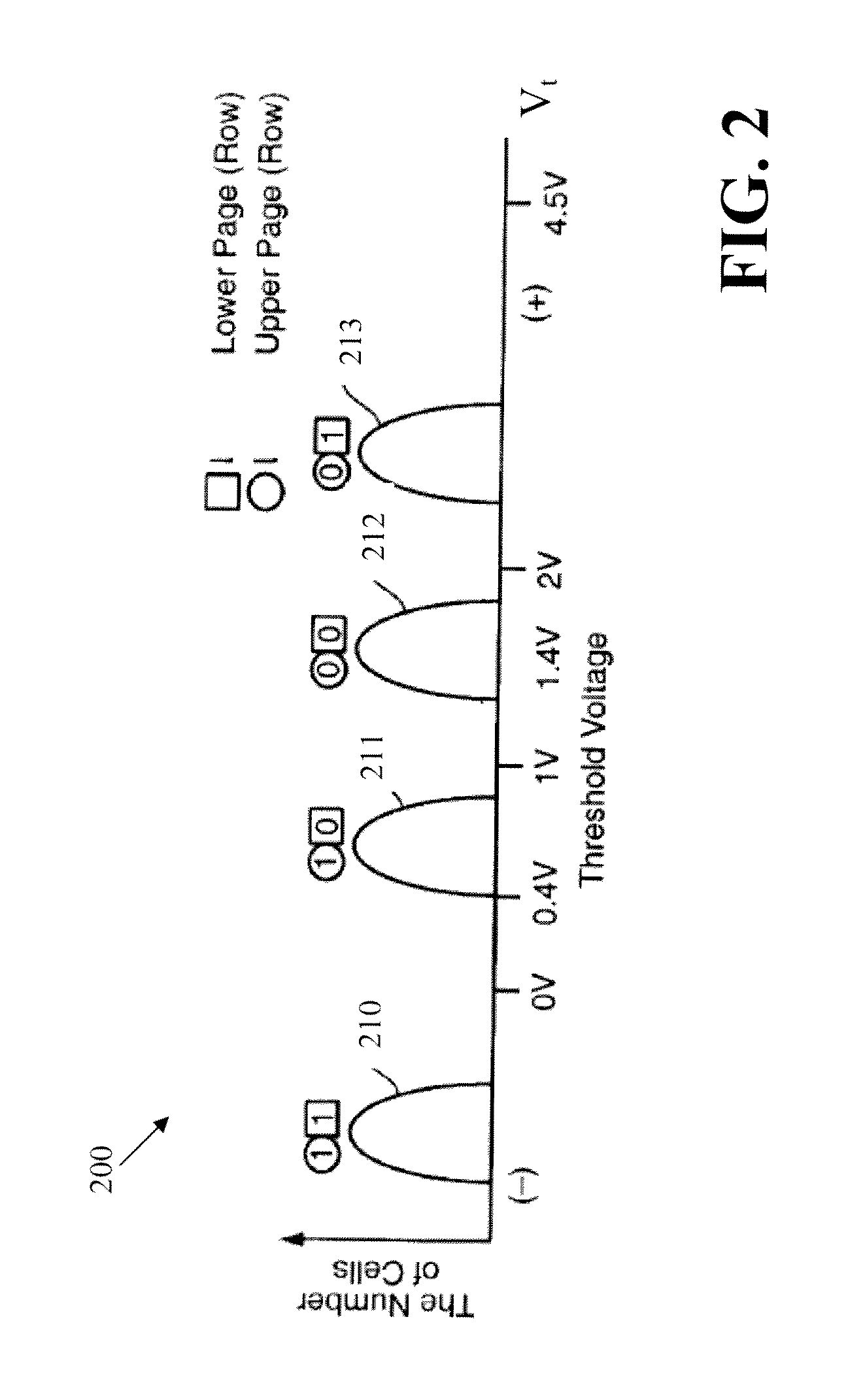
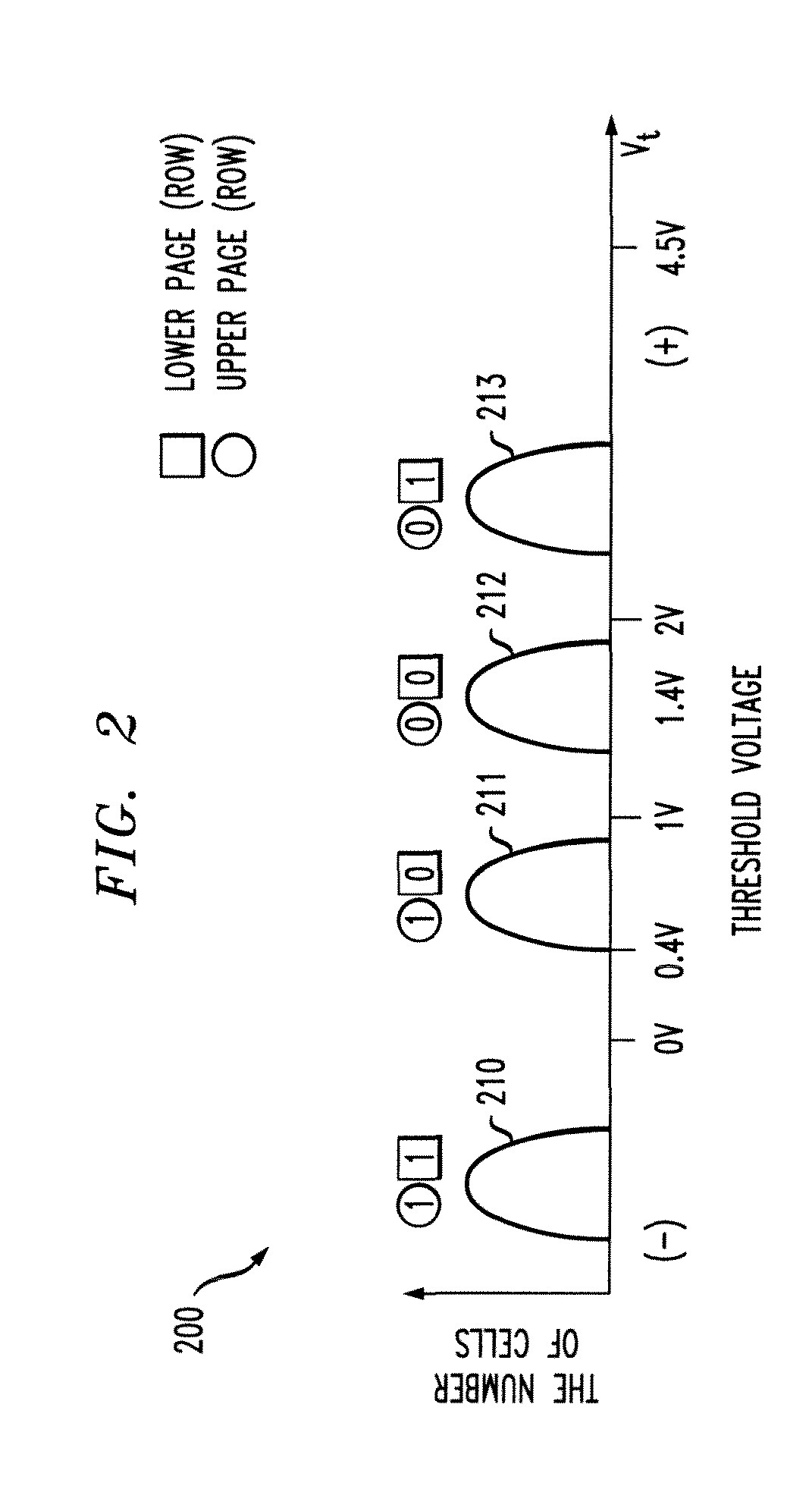
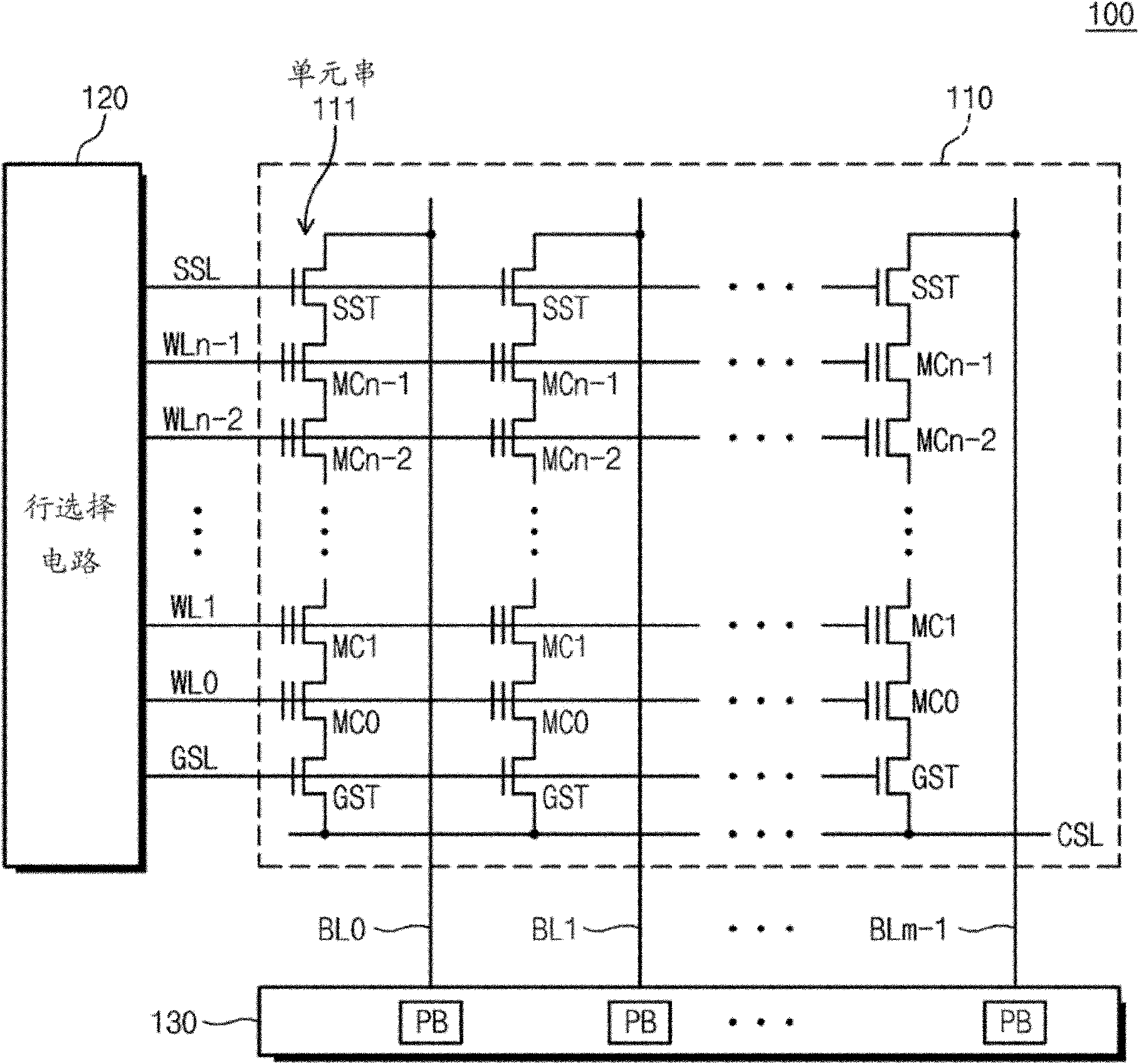
Flash memory devices having multi-bit memory cells therein with improved read reliability
ActiveCN102148058AImprove error correction efficiencySmall sizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsSoft data
Integrated circuit memory devices include an array of nonvolatile N-bit memory cells, where N is an integer greater than one. Control circuitry is also provided to reliably read data from the N-bit memory cells. This control circuitry, which is electrically coupled to the array, is configured to determine, among other things, a value of at least one bit of data stored in a selected N-bit memory cell in the array. This is done by decoding at least one hard data value and a plurality of soft data values (e.g., 6 data values) read from the selected N-bit memory cell using a corresponding plurality of unequal read voltages applied to the selected N-bit memory cell during a read operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A soil moisture prediction method based on Bayesian maximum entropy
ActiveCN109002604AConserve waterAvoid smoothing effectsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAfter treatmentCovariance
The invention discloses a soil moisture prediction method based on Bayesian maximum entropy, which comprises the following steps: selecting an exemplary soil plot and setting a plurality of random sampling points on the soil plot; constructing a hard database and soft database of soil moisture content; using the hard and soft databases to deal with soil water content of random sampling points, including de-trend and exploratory analysis of soil water content, data normality test and spatio-temporal covariance estimation. Bayesian maximum entropy method and the hard database and soft database are combined to predict the soil water content after treatment. The invention integrates the hard data and the soft data together, predicts and estimates the posterior condition probability of the soilmoisture content, and improves the prediction accuracy of the soil moisture content.
Owner:INST OF S&T INFORMATION SHANDONG ACADEMY OFAGRI SCI +1
Burst-error correction methods and apparatuses for wireless digital communications systems
Frames of data that have transverse Reed-Solomon (TRS) coding and subsequent cyclical-redundancy-check (CRC) coding are subjected to de-interleaving before concatenated convolutional coding (CCC). The de-interleaving is related to the symbol interleaving of the outer convolutional coding prior to the inner convolutional coding so as to result in implied interleaving of data bits in the CCC on which wireless digital transmissions are based. The CCC is turbo decoded in a receiver for the wireless digital transmissions and re-interleaved to reproduce soft data, hard data bits of which data are TRS coded. CRC coding is decoded during the turbo decoding procedures and used to influence the confidence levels of the soft data. The confidence levels of the soft data are used for locating byte errors when the TRS coded hard data bits of the soft data are decoded.
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
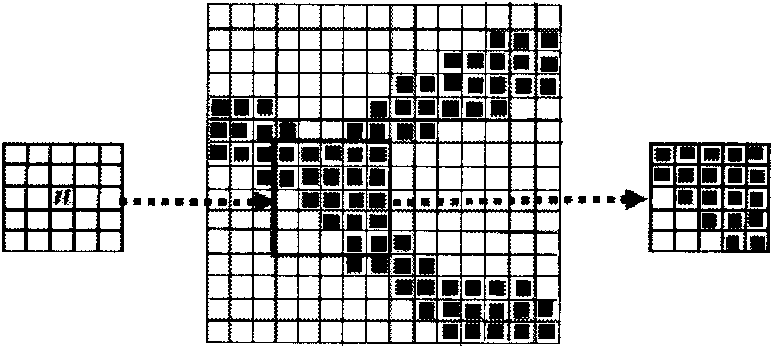
Information predicting method based on soft and hard data
The invention discloses a multipoint geology statistics method based on a filter. The method comprises the following steps: (1) scanning a training image by utilizing a data template to obtain a data event; (2) using the filter to carry out classification to patterns in the training image by using a continuous type MPS method, so as to realize dimension reduction; and (3) combining the use of soft and hard data to carry out simulated prediction. In order to correctly predict unknown information, the method takes soft data and hard data simultaneously as conditional data of the simulation image in the multipoint geology statistics method commonly, thus improving the precision of predictive result of unknown information. The method can be widely applied to a plurality of scientific fields such as medicine, geology, meteorology, mining and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Receiver for optical or electromagnetic signals with iterative equalization and error correction plus a method for improving the exactness in relating binary data to a digitalized -data transmitting, analog electromagnetic or optical-electrical signal
InactiveUS20050169406A1Reduced minimum optical-signal-to-noise ratio valueImproving system budgetDelay line applicationsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringAnalog signal
A receiver is described for optical or electromagnetic signals comprising a digital equalizer and a Forward Error Correction, said digital equalizer and FEC combined together to obtain an iterative equalization and error-correction loop, plus a method is described for improving the exactness in relating binary data to a digitalized-data transmitting, analog electromagnetic or optical-electrical signal arriving at a receiver, comprising the steps a) transforming the arriving analog signals into analog signals in the form of digital soft data representing interim values, which indicate the value of the amplitude of the analog signal, b) feeding the soft data to a digital equalizer, c) sequential determination of the interim value representing the boundary at which the decision would have to be made whether a ‘0’ or a ‘1’ had to be related to the soft data when transformed to binary data in the digital equalizer, d) feeding the soft-data signal further processed in the way described to a soft-in / soft-out FEC, e) error correction of the soft data by means of the check bits contained in the signal, f) removal of the check bits, g) output of the error-corrected signal in the form of soft data, h) preprocessing the signal for reinjection into a digital equalizer, i) feeding back the signal to the digital equalizer placed in the signal path, and k) repeating steps c) to j) until no further improvement of the data quality can be detected or until a predefined number of iteration loops have been executed, and l) hard decision and transformation of the soft data preprocessed in the way described into binary data.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method of channel estimation
InactiveUS20060062336A1Multiple-port networksError preventionChannel impulse responseSelf correlation
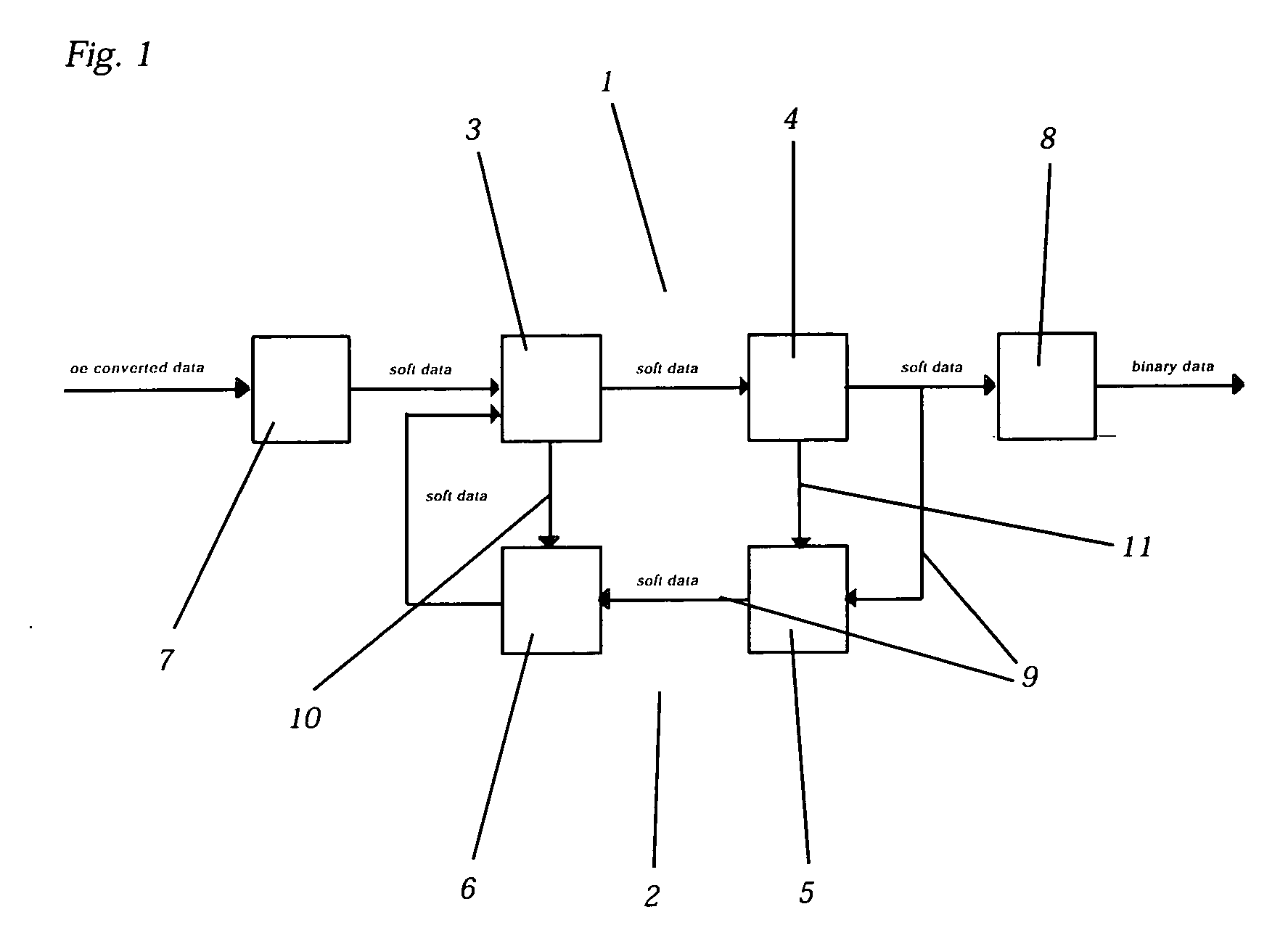
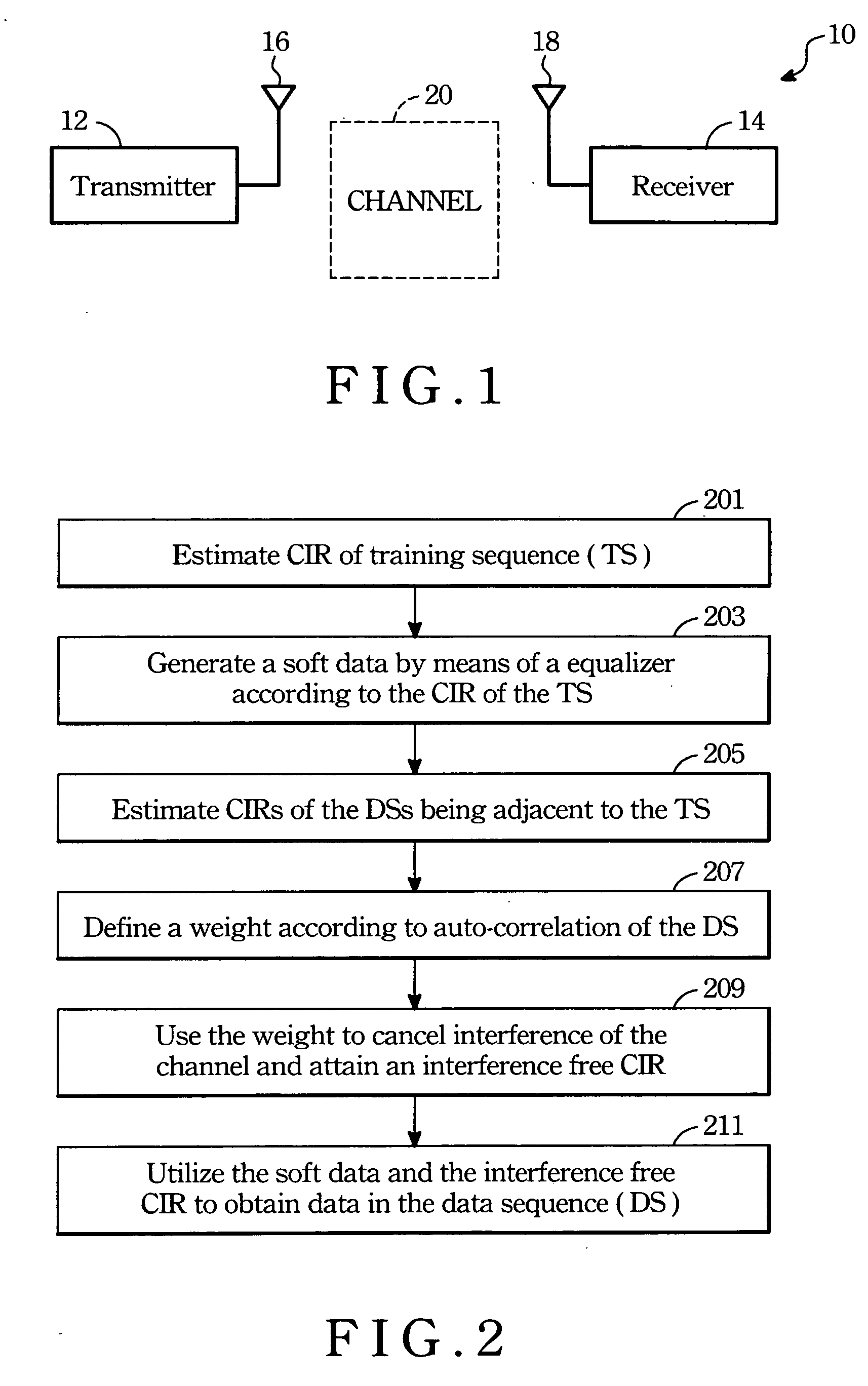
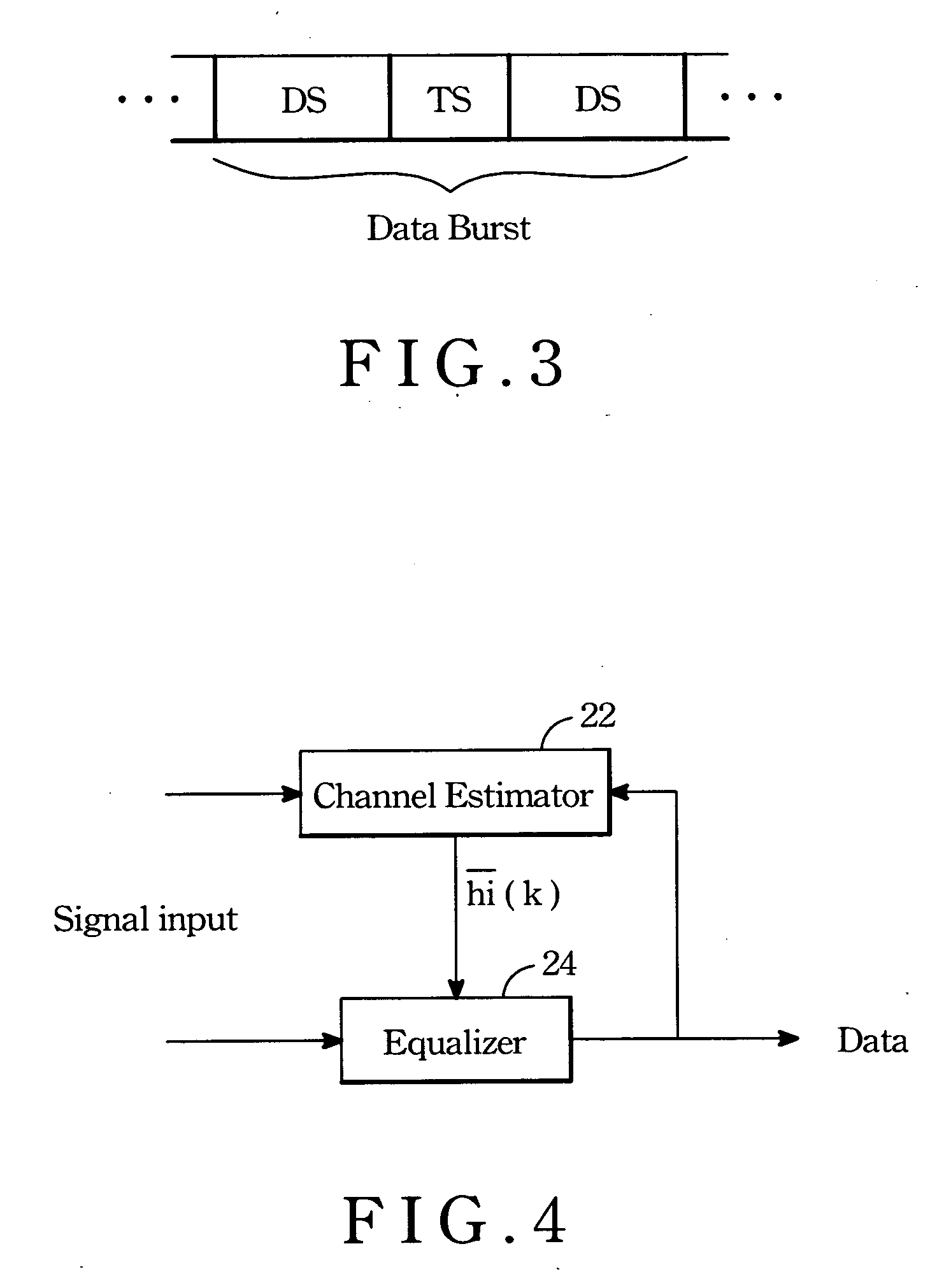
A method for channel estimation is provided. Firstly is to estimate channel impulse response (CIR) of training sequence. Next is to generate a soft data by means of an equalizer according to the CIR of the training sequence. Subsequently is to estimate CIRs of data sequences according to the interposed training sequence by correlation channel estimation. Next is to define a weight by means of auto-correlation of the estimated data sequence and then to cancel the interference of channel by the weight. Finally is to use the soft data and the non-interference CIR to find out the data stored in the data sequence.
Owner:BENQ CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com