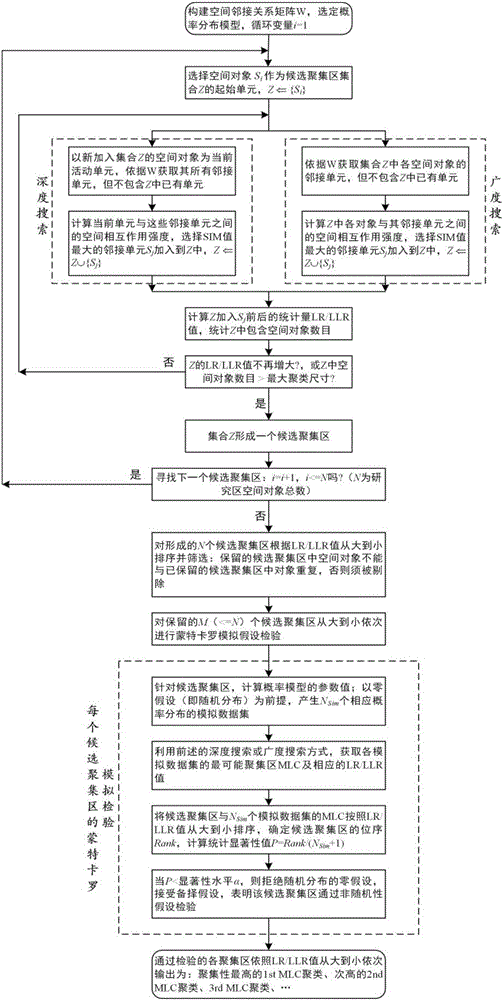
Geographic space abnormal accumulation area scanning statistical method based on interaction force
An interaction force and geospatial technology, applied in the field of scanning statistics of geospatial anomaly gathering areas based on interaction force, can solve the problem of not considering the interaction effect of geospatial objects, and achieve the effect of accurate detection and strong detection ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0129] Example 1: Simulation data set I
[0130] The simulated data set I includes 4 data sets, and each data set contains an MLC cluster of different shapes, such as band, S-shape, O-shape, and cross-shape, such as Figure 4(a) ~ 4(d) shown.
[0131] The total number of spatial units per data set N = 400, the overall attribute b of each unit i = 40, the instance attribute c of the unit in the cluster i = 20, the instance attribute c of the unit outside the cluster i = 10. The number of cluster space units in the four data sets are 40, 40, 80, 80 respectively, and the MLC cluster size ratio (referring to the ratio of the number of MLC cluster units to the total number of data set units N) is 0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2.
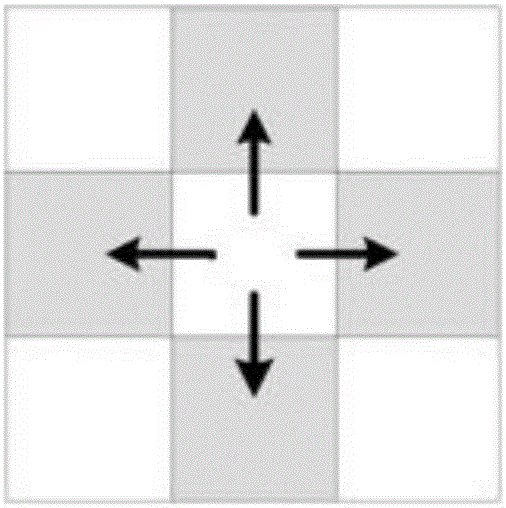
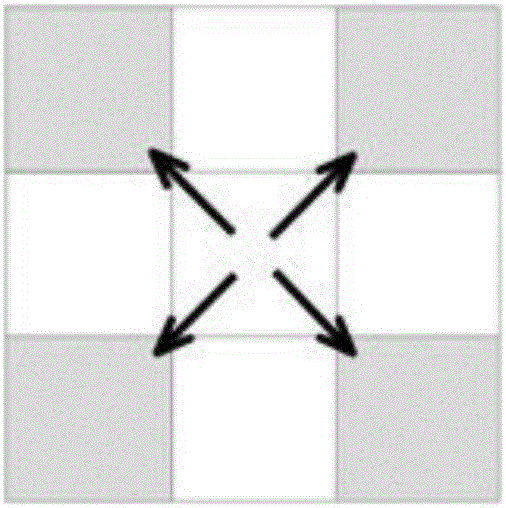
[0132] Spatial adjacency takes the form of queens whose common boundaries and vertices are directly adjacent. The parameters k and b of the spatial interaction SIM model take the value of 1, a takes the value of 2, and d adopts the ordinary Euclidean distance bet...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Example 2: Simulation Dataset II
[0147] The simulated data set II includes two data sets, each of which contains an MLC cluster with depressed units, and the shapes of the MLC clusters are bands and crosses, as shown in Figure 5(a) and Figure 6(a) , a depression unit refers to a cluster unit whose event rate is slightly higher than that of the units outside the cluster, but significantly lower than that of other units in the cluster. The existence of the depression unit increases the detection difficulty of the spatial scanning method , when the detection ability of the scanning method is weak, the clustering results may be interrupted here because the sunken units cannot be detected. The banded cluster contains 1 sunken unit, and the cross-shaped cluster contains 3 adjacent sunken units on the left and right sides. If no sunken unit is detected, a small number of cluster units isolated by the sunken unit (the banded cluster is isolated Open 1 unit, the left and righ...
Embodiment 3
[0154] Example 3: Simulation Dataset III
[0155] The simulated dataset III includes two datasets III(a) and III(b), each of which contains two MLC clusters of different shapes, such as Figure 7(a) , 7(b) shown. The total number of spatial units per data set N = 400, the overall attribute b of each unit i = 40, the instance attribute c of the unit in the cluster i =20, instance attribute c of the unit outside the cluster i =10.
[0156] Ⅲ(a) contains two clusters of O-shape and I-shape, the numbers of cluster space units are 80 and 40 respectively, the total number of cluster units is 120, and the ratio of the total size of clusters is 0.3. Ⅲ(b) contains two clusters of L-shape and S-shape, the numbers of cluster space units are 40 and 40 respectively, the total number of cluster units is 80, and the ratio of the total size of clusters is 0.2. These two data sets are used to compare and test the three methods of SIM depth scanning, SIM breadth scanning and Kulldorff cir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com