Method for continuously refining L-lactide from crude L-lactide
A technology of lactide and refining tower, which is applied in the direction of organic chemistry and can solve problems such as difficult operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] The molecular weight of polylactic acid is controlled by the amount of hydroxyl impurities in lactide. Lactide containing different lactic acid impurities was polymerized into polylactic acid to illustrate the effect of lactic acid impurity content on the molecular weight of polylactic acid. Polymerization at 160°C using 0.1 wt% stannous octoate as catalyst in a dry inert atmosphere N 2 next.
[0045] Lactic acid impurity content (%wt)
Embodiment 2
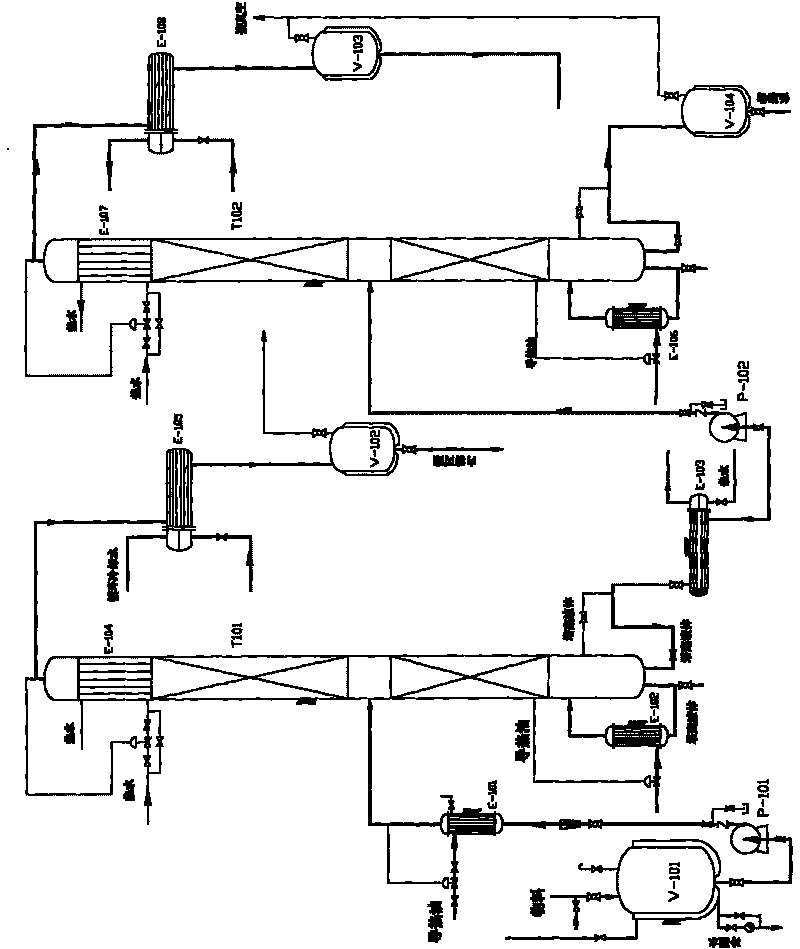
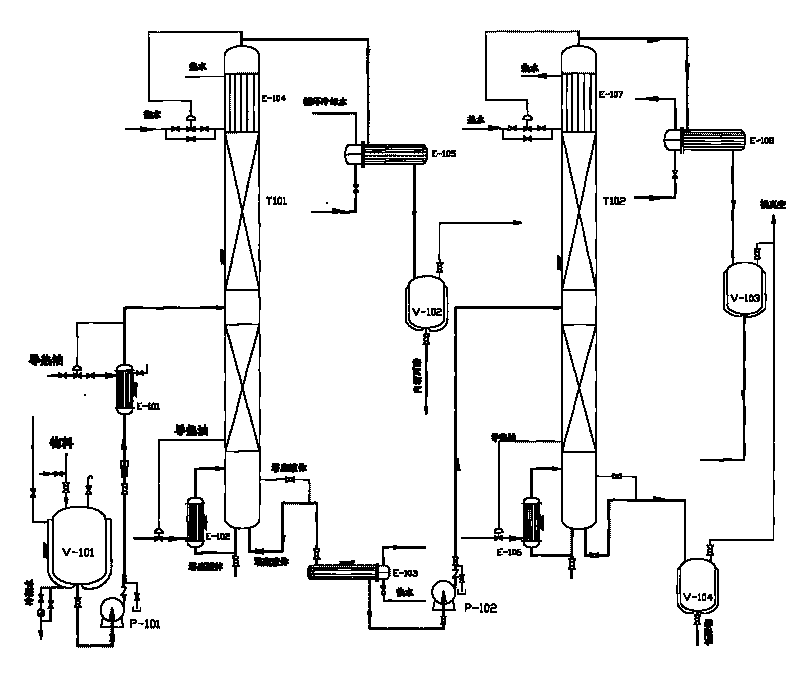
[0047]The 80kg / h rectified lactide was continuously refined in the light-removing tower containing top stream, liquid bottom stream and the refining tower containing top stream, liquid bottom stream and steam side stream. Water, lactic acid and meso-lactide are concentrated in the top stream of the light removal tower, and L-lactide and lactic acid oligomers are concentrated in the bottom stream of the light removal tower. Then, the bottom flow of the light removal tower is sent to the middle part of the refining tower through the feeding pump. The L-lactide is concentrated in the top stream of the refining tower, and the lactic acid oligomers are concentrated in the bottom stream of the refining tower, and the obtained L-lactide can be directly polymerized without further refining to obtain high molecular weight polylactic acid. In order to enhance the contact between vapor and liquid and minimize liquid column storage, structural packing materials are used to fill the light ...
Embodiment 3
[0053] The 80kg / h rectified lactide was continuously refined in the light-removing tower containing top stream, liquid bottom stream and the refining tower containing top stream, liquid bottom stream and steam side stream. Water, lactic acid and meso-lactide are concentrated in the top stream of the light removal tower, and L-lactide and lactic acid oligomers are concentrated in the bottom stream of the light removal tower. Then, the bottom flow of the light removal tower is sent to the middle part of the refining tower through the feeding pump. A small amount of by-products such as water, lactic acid and meso-lactide are concentrated in the top stream of the refining tower, lactic acid oligomers are concentrated in the bottom stream of the refining tower, and L-lactide is discharged through the steam side stream of the refining tower, containing L-lactide The vapor side stream of the refining tower of lactide has almost no lactic acid and lactic acid oligomers, and can be dir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com