Rapid maize breeding and population improvement method
A corn breeding and population technology, applied in the field of breeding, can solve the problems of inaccurate character identification, difficult phenotype identification, long cycle, etc., and achieve the effects of controllable genetic diversity, improved breeding efficiency, and accurate phenotype.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1. According to the breeding objectives, breeding background, and heterosis group types, the basic comprehensive population can be constructed. It can be formed by mixed pollination of 2-5 corn parental inbred lines, or can be directly formed by self-separation of hybrids. This embodiment adopts the following Those, specifically the F of the hybrid Zhongdan 909 2 Generation separation population to build basic population (P 0 ).
[0024] 2. Use 55K high-density (more than 10,000 is better, 55K) SNP molecular markers are used for marker analysis on parental materials. The markers used come from 55K corn chips (Xu C., Ren Y., Jian Y., Guo Z. , Zhang Y., Xie C., Fu J., Wang H., Wang G., Xu Y., Li P., Zou C. Development of a maize 55K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding. Molecular Breeding, 2017 , 37:20).
[0025] 3. For the basic group P 0 Perform haploid induction and double to generate 150 DH lines (D 0 group).
[0026] 4. To D 0 The pop...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Carry out the test according to the same method of embodiment 1 step 1-5.
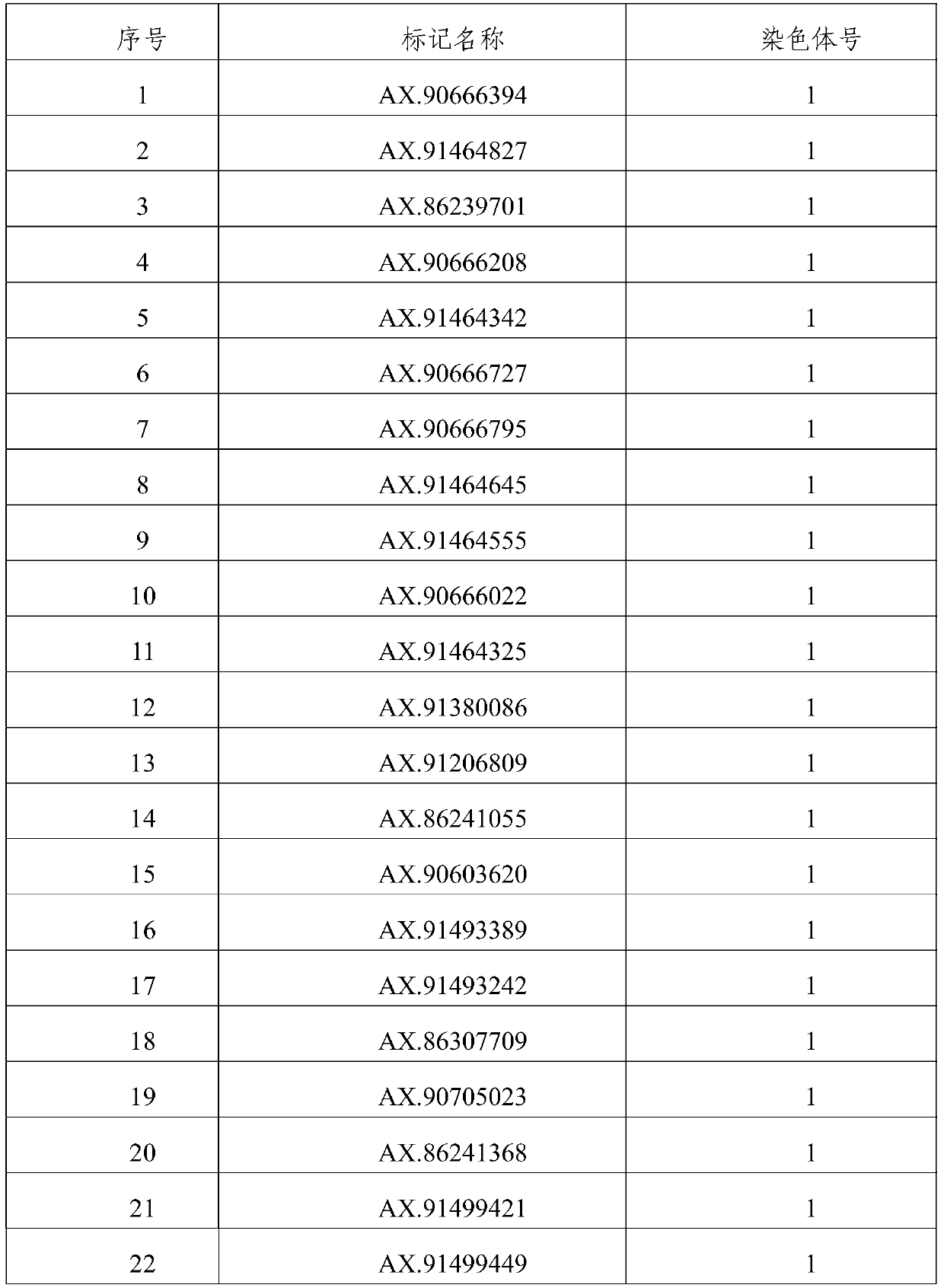
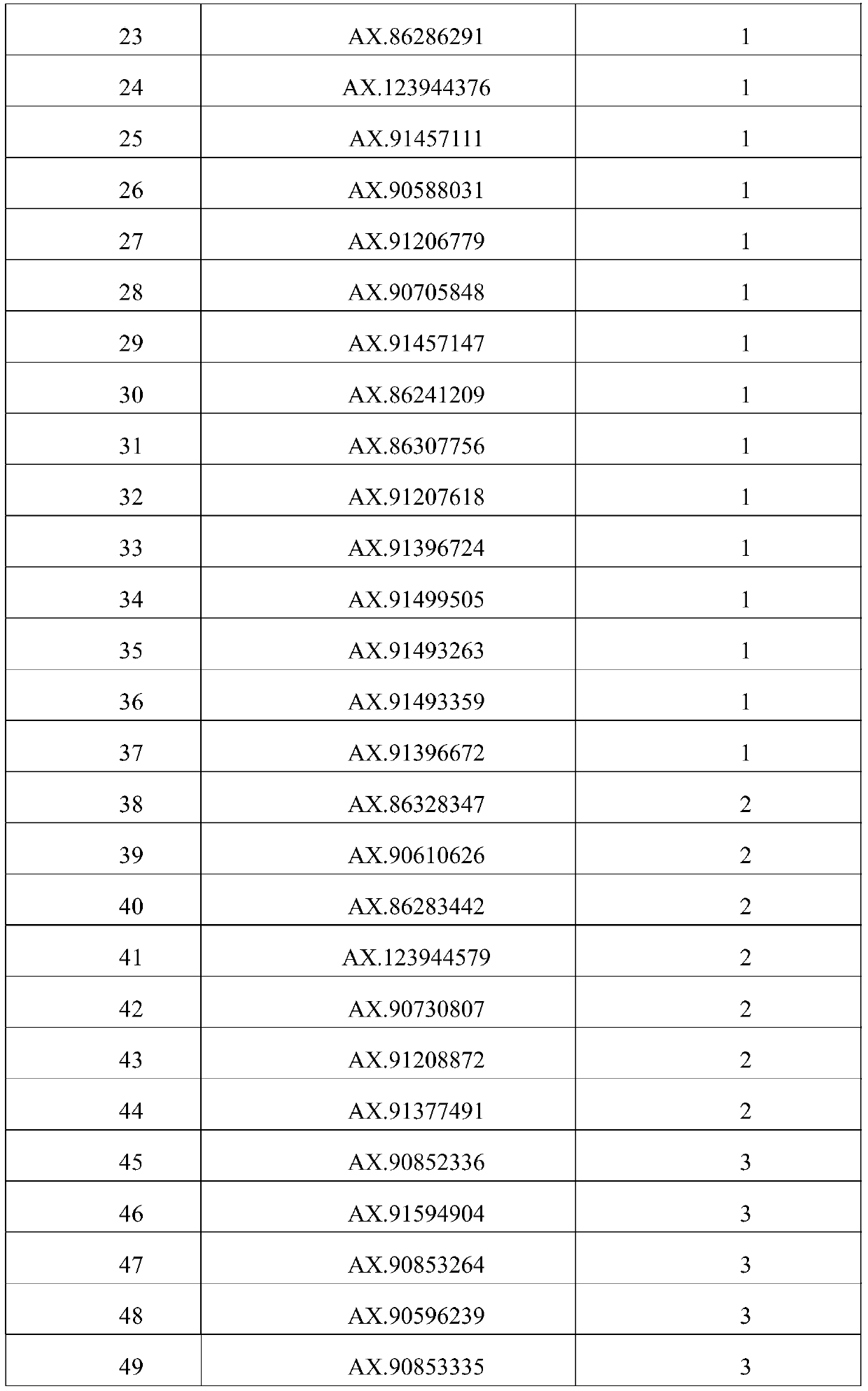
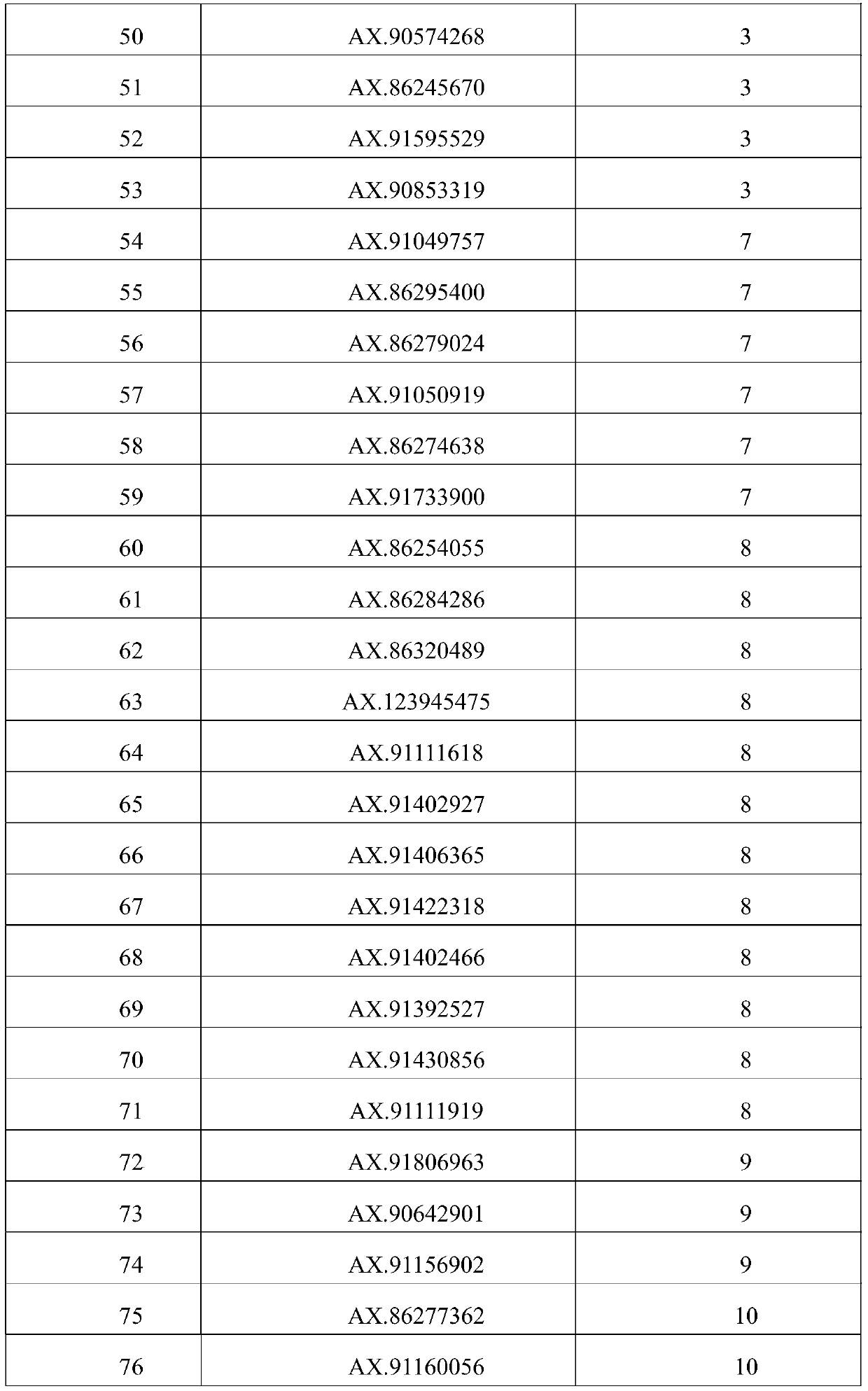
[0043] 6. Use the linkage analysis method to excavate 80 loci controlling grain weight markers, see Table 2 for details. The markers are derived from the corn 55K chip (Xu C., Ren Y., Jian Y., Guo Z., Zhang Y., Xie C ., Fu J., Wang H., Wang G., XuY., Li P., Zou C. Development of a maize 55K SNP array with improved genome coverage for molecular breeding. Molecular Breeding, 2017, 37:20).
[0044] Table 2 control grain weight marker sites
[0045]
[0046]
[0047]
[0048]
[0049] 7. Combining phenotype identification, trait linkage site information and high-density molecular detection data, a genome-wide selection model is established for phenotype prediction of offspring populations. In this example, the established genome-wide selection model was used to predict the grain weight phenotypes of 150 DH line populations derived from Zhongdan 909, and the prediction accuracy reached 7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com