Method for improving aquatic animal whole-genome selective breeding efficiency
A whole-genome and aquatic animal technology, applied in genomics, proteomics, bioinformatics, etc., can solve the problems of low value, limited wide application, and limited application, so as to reduce typing costs, high prediction accuracy, The effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
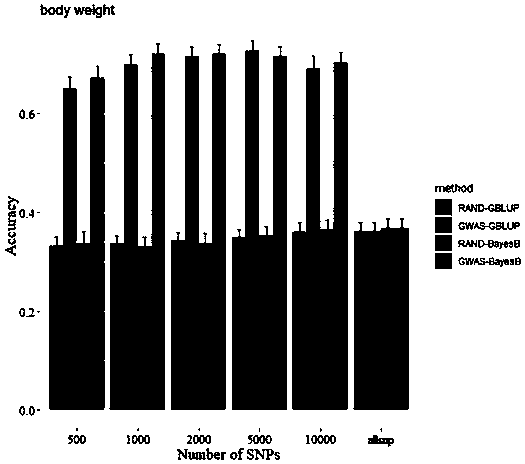
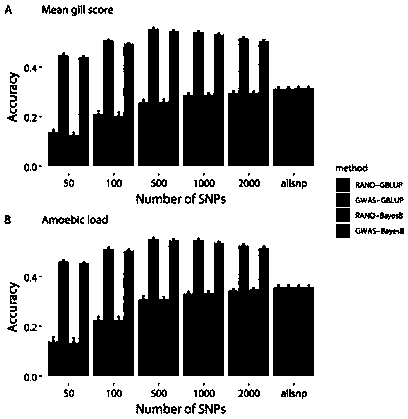
[0017] Example 1: A method for improving the efficiency of genome-wide selective breeding of aquatic animals
[0018] (1) Data source
[0019] 1. The data analyzed for prawns include SNP typing data and phenotype data of 200 individuals, and the SNP typing data are obtained by the 2b-RAD typing method (Wang Q., Yu Y., Zhang Q., Zhang X., Huang H.,Xiang J.&Li F.(2019)Evaluation on the genomic selection in Litopenaeus vannamei for theresistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus.Aquaculture 505,212-6), 2b-RAD sequencing data and the published reference genome of Litopenaeus vannamei (Xiaojun Zhang, Jianbo Yuan, Yamin Sun, Shihao Li, Yi Gao, Yang Yu, Chengzhang Liu, Quanchao Wang, Xinjia Lv, Xiaoxi Zhang, Ka Yan Ma, Xiaobo Wang, Wenchao Lin, Long Wang, Xueli Zhu, Chengsong Zhang, Jiquan Zhang, Songjun Jin, Kuijie Yu, Jie Kong, Peng Xu, Jack Chen, Hongbin Zhang, Patrick Sorgeloos, Amir Sagi, Acacia Alcivar-Warren, Zhanjiang Liu, Lei Wang, Jue Ruan, KaHou Chu*, Bin Liu*, Fuhua Li* ,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com