Method for determining optimal SNP quantity as well as performing genome selective breeding on production performance of large yellow croakers through selection markers
A technology for genome selection and production performance, applied in the fields of genomics, biochemical equipment and methods, biological systems, etc., can solve the problem of inaccurate estimates of breeding values, and achieve the effect of saving breeding costs and reducing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
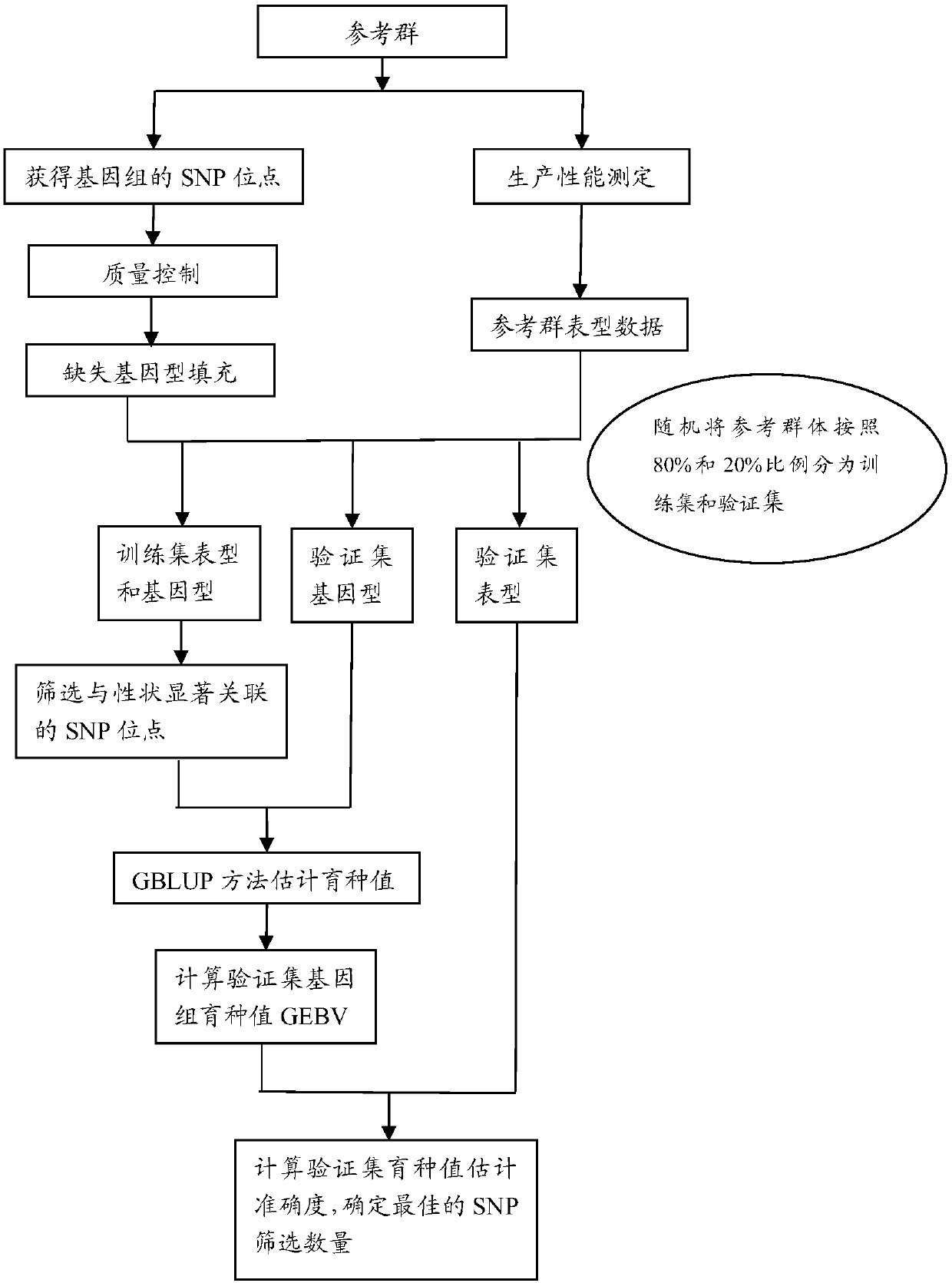
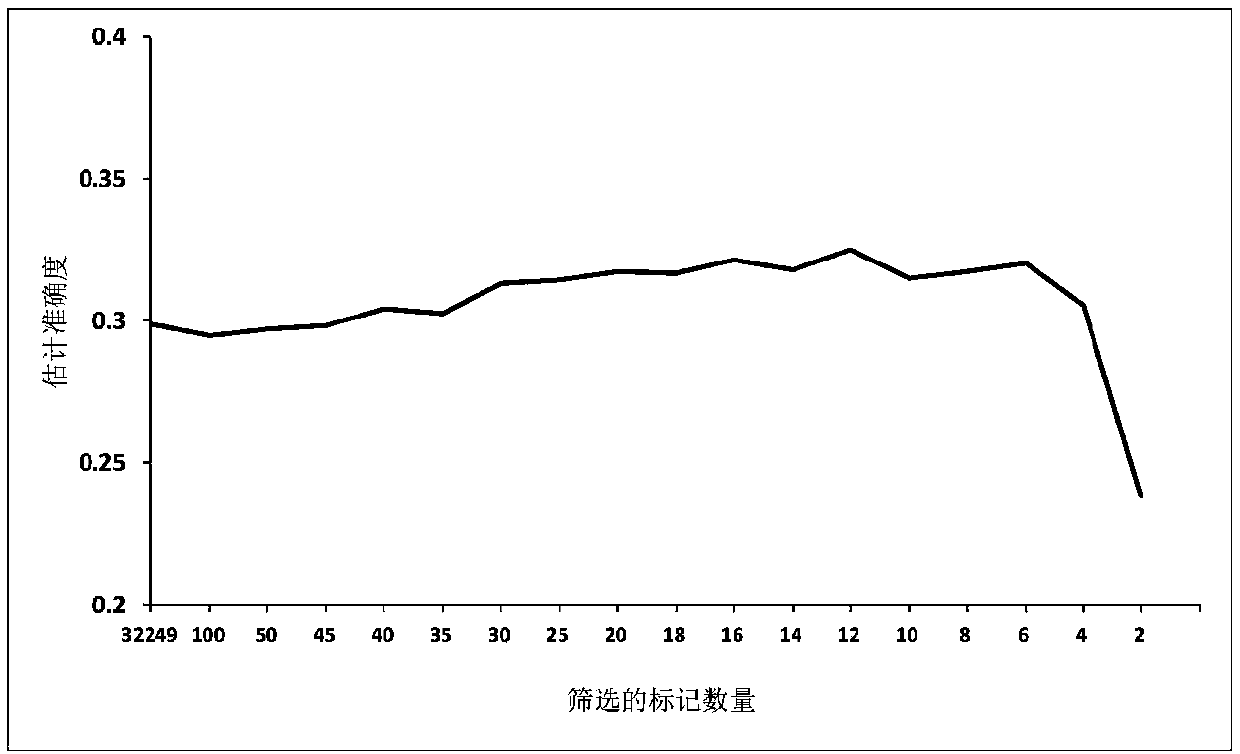
[0042] Example 1 Determination of SNP Screening Quantity
[0043] Experimental material: The experimental data is large yellow croaker, which was bred in Jinling Aquatic Technology Co., Ltd., Ningde City, Fujian Province. 30 male fishes and 30 female fishes were mixed in a tank. By injecting luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone A3 (LRH-A3), all parent fishes released sperm or eggs at almost the same time, so all offspring had the same age. When the offspring reached the age of 2, 176 individuals (including 61 males and 115 females) were randomly selected as the test material of this study, that is, the reference group, and the research trait was n-3 high unsaturated fatty acid content (n3-HUFA) .
[0044] Phenotype (n-3 high unsaturated fatty acid content) determination method: "The extraction of total lipids adopts the Folch method, and after total lipids are extracted, 50% KOH and ethanol are used for saponification and then heated with 7% BF3 and methanol (methanol) The ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Embodiment 2: The meat quality character screening experiment of 197 fish
[0075] Experimental material: The experimental data is large yellow croaker, which was bred in Jinling Aquatic Technology Co., Ltd., Ningde City, Fujian Province. 30 male fishes and 30 female fishes were mixed in a tank. By injecting luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone A3 (LRH-A3), all parent fishes released sperm or eggs at almost the same time, so all offspring had the same age. When the offspring reached the age of 2, 197 individuals (including 89 males and 108 females) were randomly selected.
[0076] The 12 SNP sites of these 197 fish were determined, and the genome breeding value GEBV was calculated by the GBLUP method (the solution equation set is shown in the R language package "EMMREML", version 3.1.). The 4 males and 5 females with the highest genome breeding value GEBV were selected as the breeding group, and 181 individuals (84 males and 97 females) were randomly selected from the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com