Whole-genome selective breeding method and apparatus
A whole-genome, selective breeding technology, applied in the direction of instruments, biological systems, evolutionary organisms, etc., can solve the problems of low accuracy of analysis results, and achieve the effect of promoting progress, improving effect, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
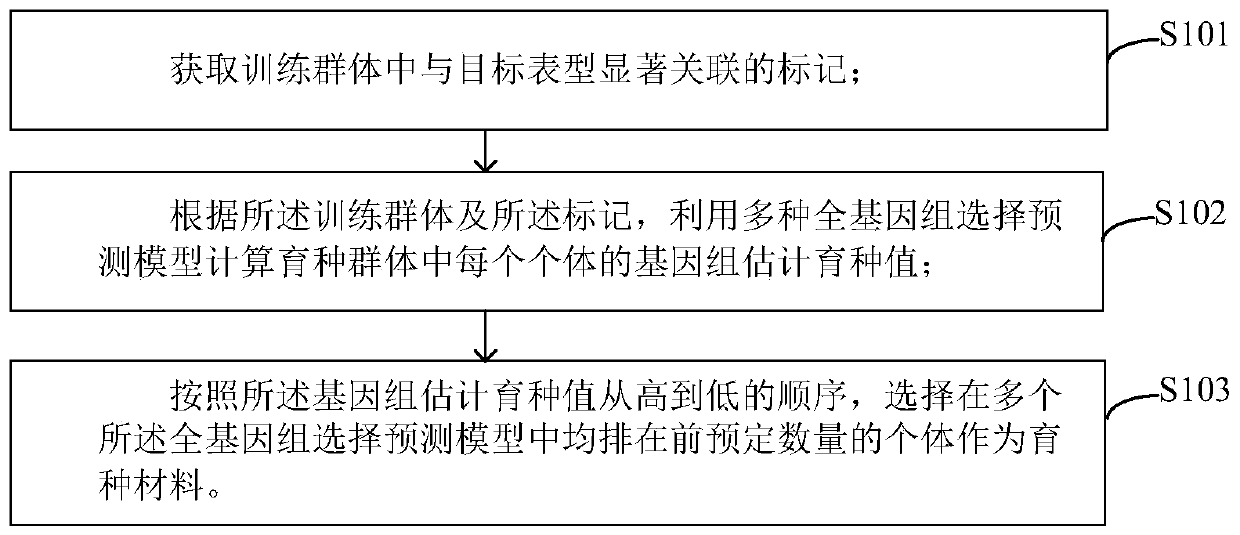
[0034] This embodiment provides a method for genome-wide selective breeding, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes:
[0035] Step S101, obtaining markers significantly associated with the target phenotype in the training population;
[0036] Step S102, according to the training population and markers, using multiple genome-wide selection prediction models to calculate the genome estimated breeding value of each individual in the breeding population;
[0037] Step S103 , according to the descending order of the estimated breeding value of the genome, select a predetermined number of individuals that rank first in multiple genome-wide selection prediction models as breeding materials.
[0038] The above-mentioned whole-genome selective breeding method calculates the genome-estimated breeding value of the breeding population by integrating multiple prediction models, and then uses the calculation results of multiple models to co-locate individual materials with high bre...
Embodiment 2
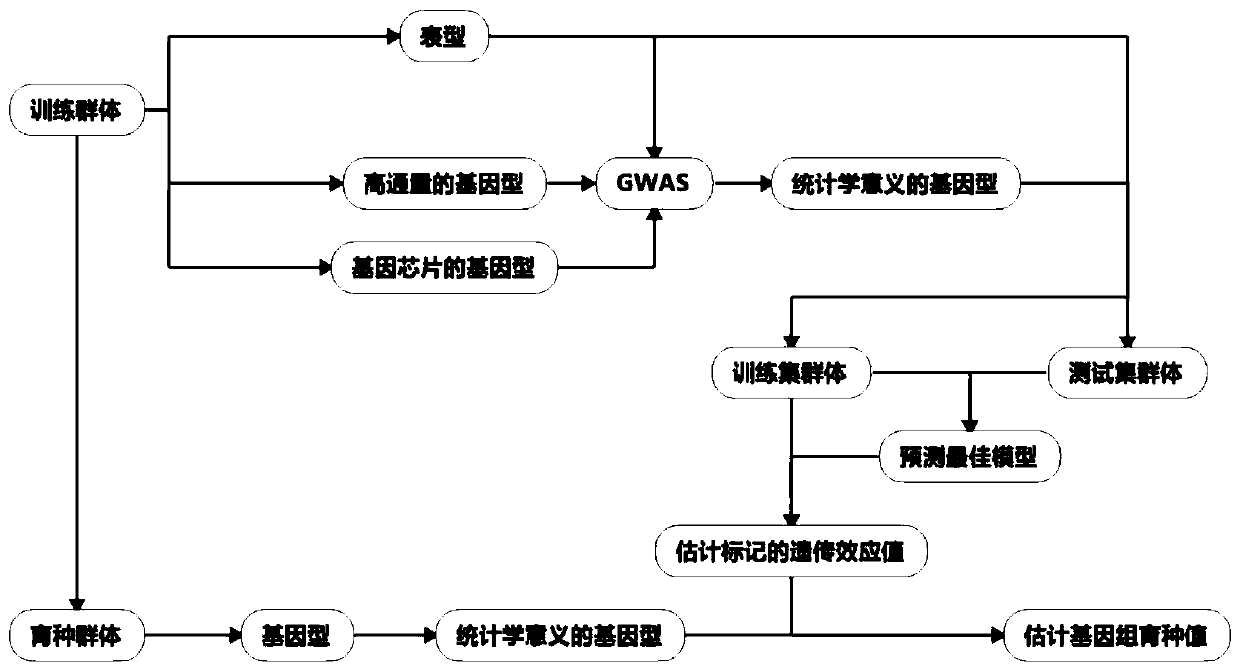
[0053] The present embodiment provides a genome-wide selective breeding method developed for the results of genome-wide association analysis (GWAS), and its detailed steps are as follows:
[0054] The data that needs to be prepared are the phenotype of the training population (TP), the genotype (ie, marker genotype) data of the TP, the GWAS result data of the TP, the genome selection (GS) prediction model, and the genes of the breeding population (BP) type data. Among them, the result file of the genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) only needs 3 lines, which are the chromosome number, the physical location of the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), and the P-value of the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). (i.e. p-values with a significant correlation with the target phenotype).
[0055] figure 2 The detailed flow of the genome selective breeding method of this embodiment is shown, in which two populations are required, a training population and a breeding population...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This embodiment discloses a method for genome selective breeding of a certain trait of sheep. Such as Figure 3A to Figure 3H6 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
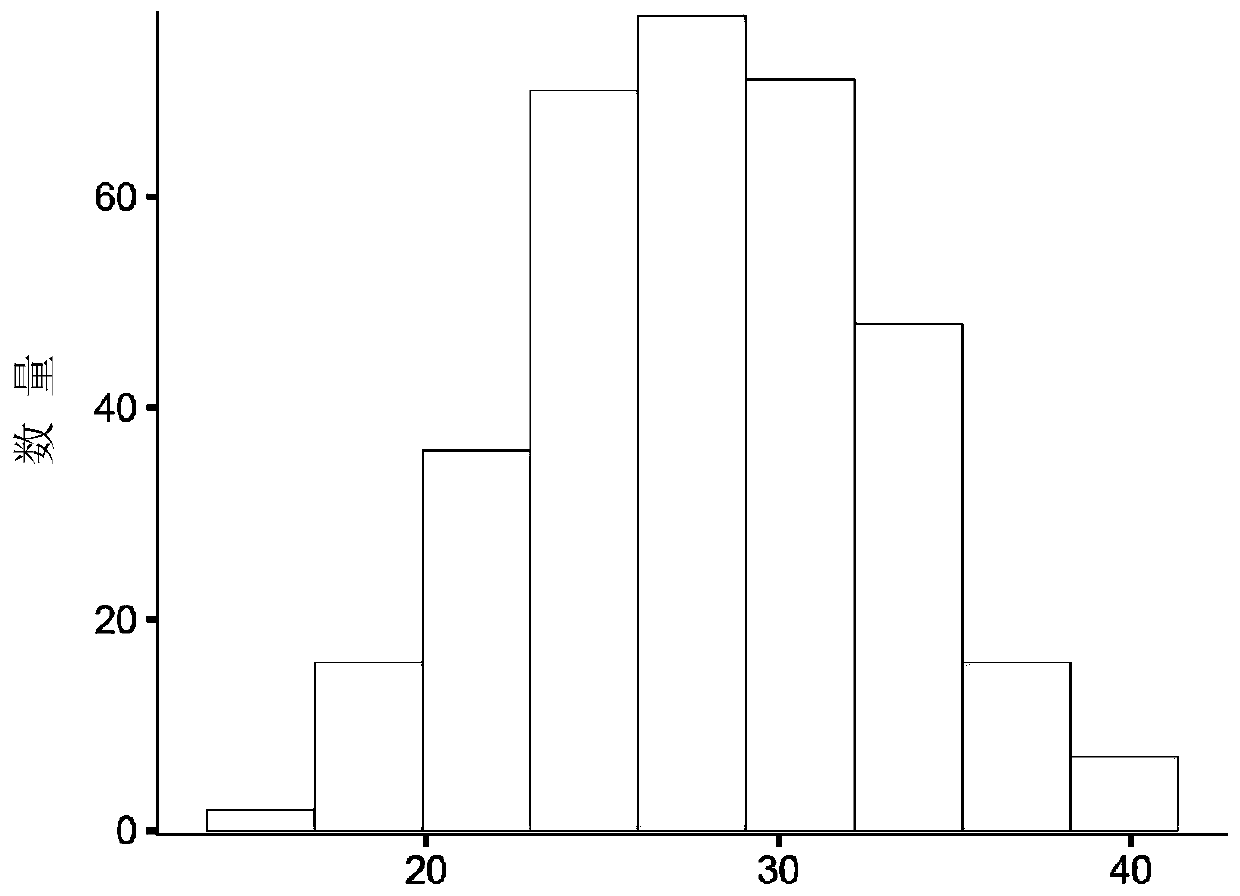
[0060] S1, analysis of phenotypic characteristics: Detect whether the phenotype of the quantitative trait conforms to the normal distribution or skewed distribution. If there is an extreme phenotype that deviates from the leverage value, it needs to be eliminated in time. The results are as follows Figure 3A shown;
[0061] S2, population stratification analysis: through principal component analysis (PCA) or population structure analysis (Structure), it is determined how many population structures the population has, and the calculated results are added to the genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) model as a fixed effect. The results are as follows Figure 3B shown;
[0062] S3, linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis: determine the attenuation distance of several groups and large groups, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com