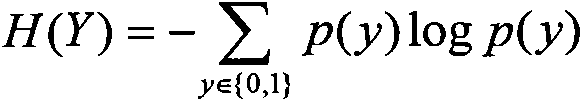Method for filtering SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) unrelated to complex diseases from whole-genome
A genome-wide and disease-based technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as missing high-order SNP interactions, complex calculations required in the filtering process, and large amounts of calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
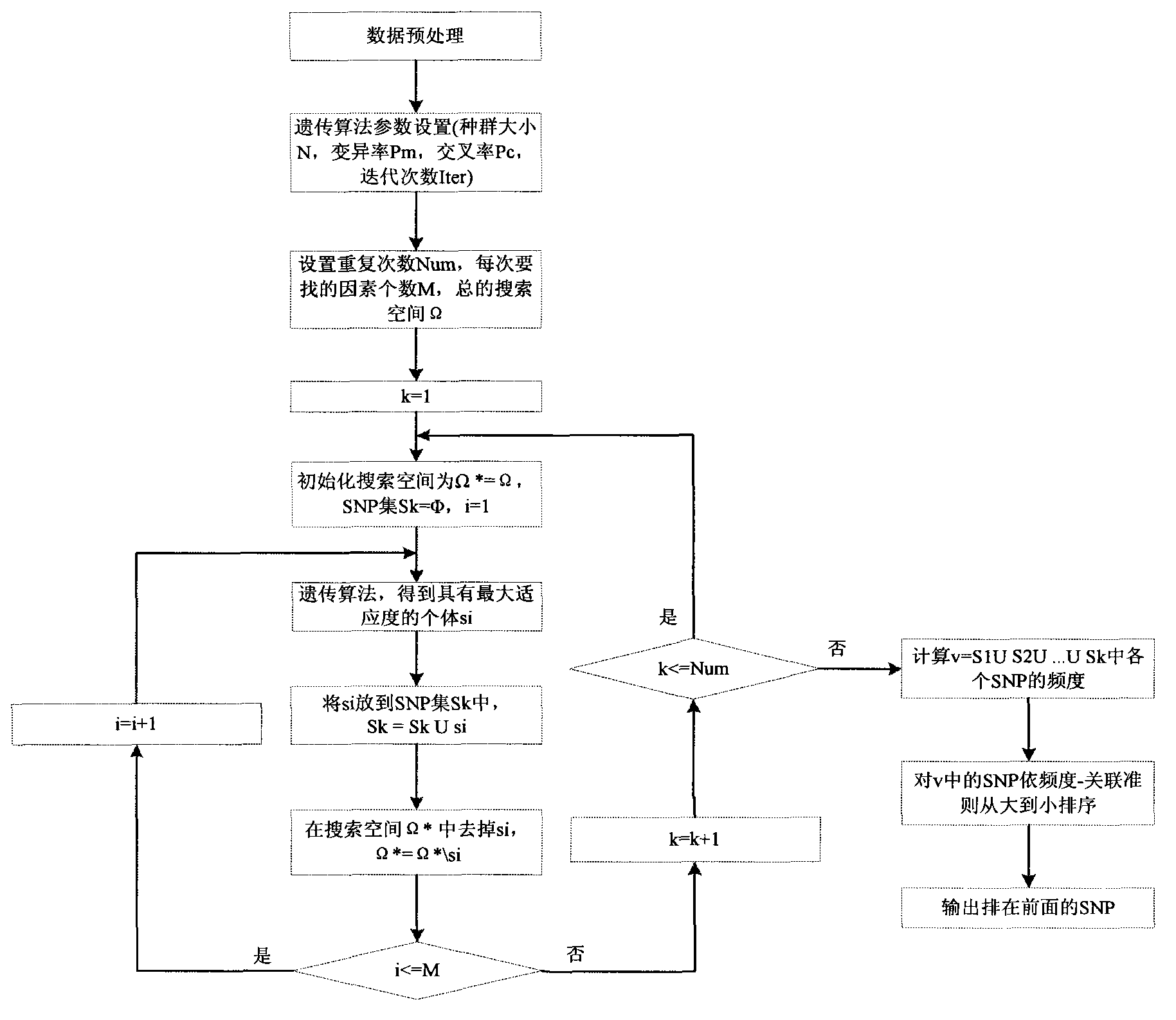
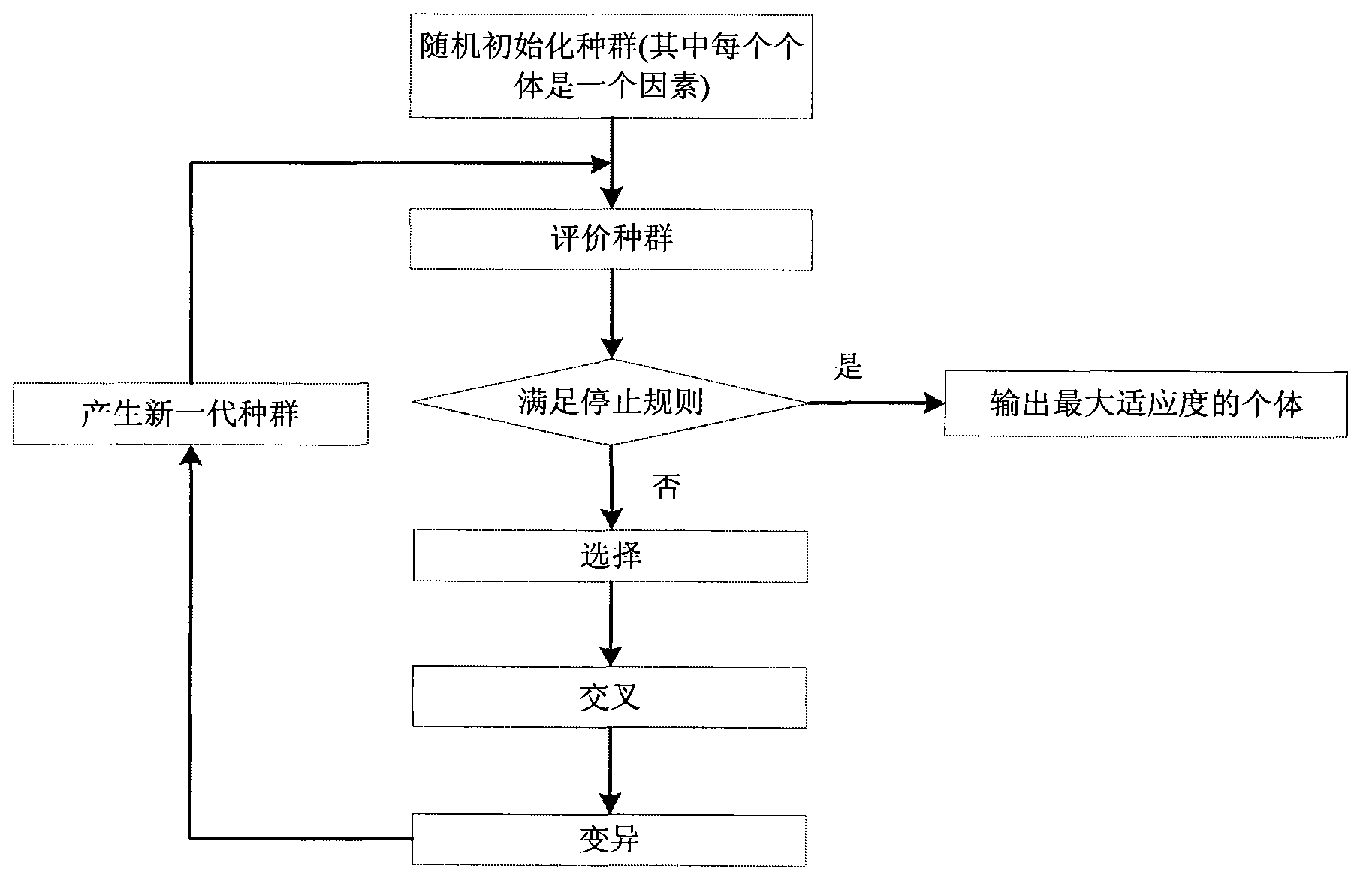
[0026] refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , the method of the present invention is called the FGSA method, and its specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0027] Step 1, preprocessing and initializing the SNP data.
[0028] (1.1) According to the principle that the variation of any gene in the homologous chromosome alleles can have the same impact on the disease, the SNP data is processed into where x i ∈ {0, 1, 2, 3} d is the value of the corresponding site of SNP i: when the two alleles at the corresponding site are homozygous for AA, take 1, for homozygous aa, take 2, for heterozygote Aa or aA, take 3, and when the corresponding site is Take 0 when the allele data of is missing; y i ∈ {1, 2} for sample x i 1 represents the disease group, 2 represents the control group, N represents the number of samples in the SNP data, d represents the number of SNPs in the data, only contains 0, 1, 2, 3 data, where 0 represents missing data , the set of SNPs involved is denot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com