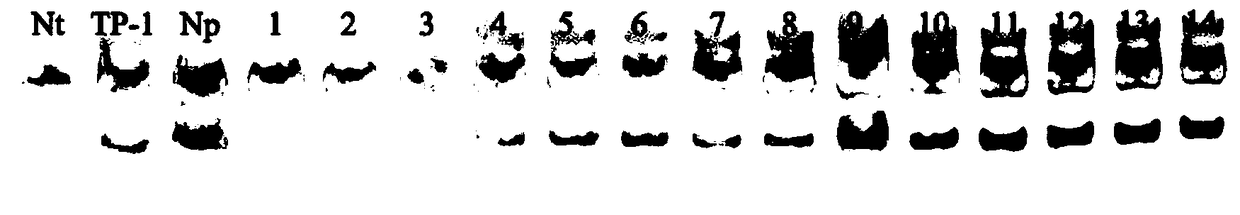Method for screening tobacco black shank resistance non-homologous chromosome plant by molecular marker
A technology of heterologous chromosomes and molecular markers, which is applied in the field of tobacco breeding and can solve problems such as inability to apply screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019]By screening 340 pairs of SSR primers from existing tobacco (N.tabacum), the screening process is as follows: extract plants (N.plumbaginifolia, anti-blackleg heterologous monomer addition lines TP-1 and Yunyan 87) by CTAB method The genomic DNA was detected by a nucleic acid concentration analyzer and agarose gel electrophoresis to detect no impurities and no degradation before PCR amplification; using the extracted genomic DNA as a template, PCR amplification was performed using 334 pairs of primers such as PT30061, PT30167, and PT54199. Amplification system: 15 μL of PCR amplification system was used, which contained 2 μL of 10× buffer (Takara Company), MgCl2 1.2 μL (25 mmol / L, Takara Company), dNTP 0.4 μL (10 mmol / L, Takara Company), rTaq 0.2 μL (5 U / μL, Takara Company), 1.5 μL of DNA template, 1.5 μl each of forward and reverse primers (10 μmol / L), and make up the rest with water. Amplification program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5min, denaturation at 94°C for 40s...
Embodiment 2
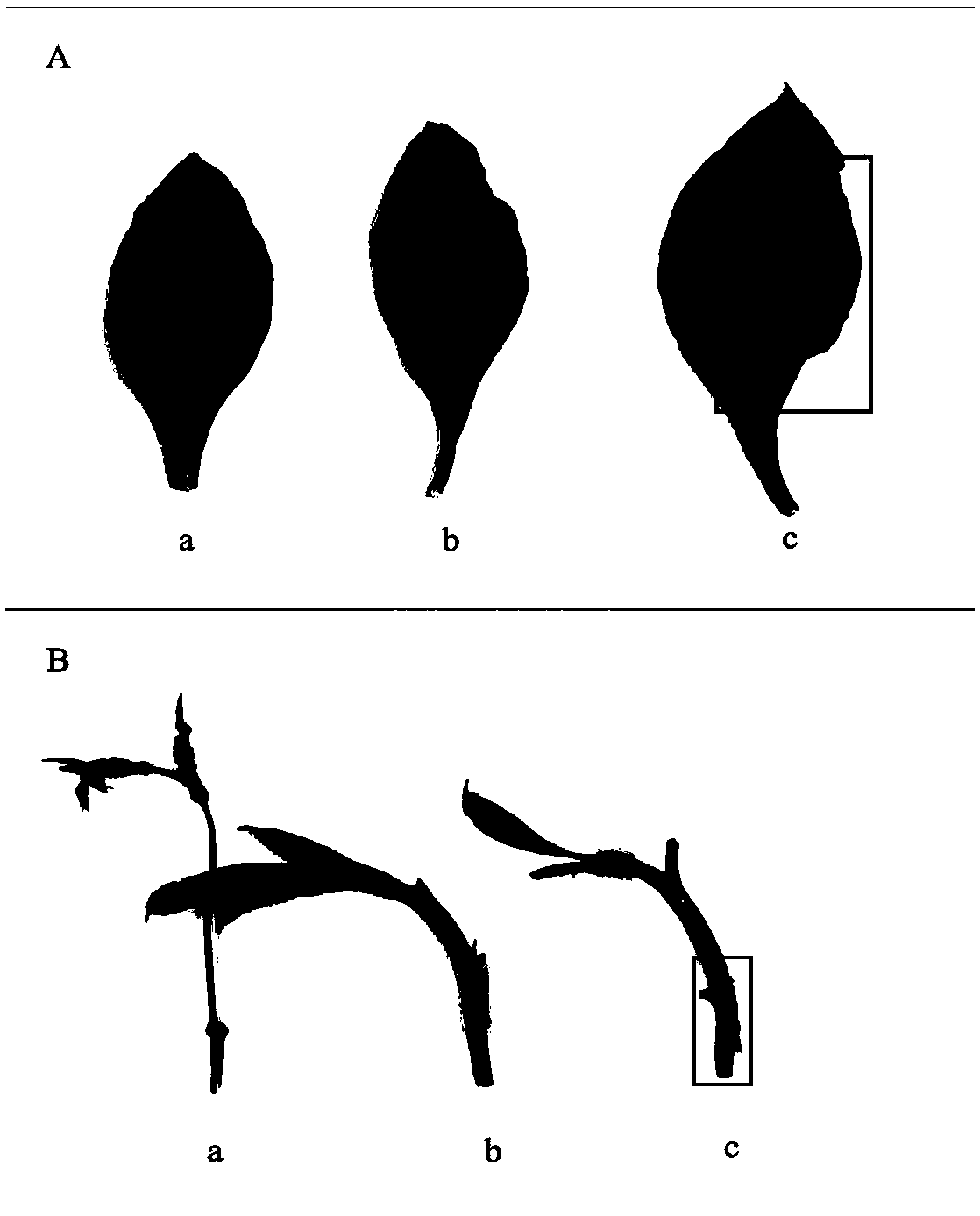
[0021] 1. Genomic DNA extraction: The DNA of the plant (black shank resistance tobacco-blue jasmine leaf tobacco heterologous monomer addition line self-bred progeny) was extracted by CTAB method, and no impurities and no impurities were detected by nucleic acid concentration analyzer and agarose gel electrophoresis. Perform PCR amplification after degradation;
[0022] 2. PCR amplification and electrophoresis: use the extracted genomic DNA as a template and primer PT54199 (PF: GCACTTCGTAGATGCGTTGA, PR: TCTCATGAGCAGGCTTCAAA) for PCR amplification, amplification system: use 15 μL of PCR amplification system, which contains 2 μL of 10 ×buffer (Takara Company), MgCl2 1.2μL (25mmol / L, Takara Company), dNTP 0.4μL (10mmol / L, Takara Company), rTaq 0.2μL (5U / μL, Takara Company), 1.5μL DNA template, positive 1.5 μl of each reverse primer (10 μmol / L), and make up the rest with water. Amplification program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5min, denaturation at 94°C for 40s, annealing at 56...
Embodiment 3
[0026] 1. Genomic DNA extraction: The DNA of the plant (the offspring of the allopentaploid backcross Yunyan 87 resistant to black shank tobacco-blue jasmine leaf tobacco) was extracted by the CTAB method, and no impurities were detected by the nucleic acid concentration analyzer and agarose gel electrophoresis , PCR amplification without degradation;
[0027] 2. PCR amplification and electrophoresis: use the extracted genomic DNA as a template and primer PT54199 (PF: GCACTTCGTAGATGCGTTGA, PR: TCTCATGAGCAGGCTTCAAA) for PCR amplification, amplification system: use 15 μL of PCR amplification system, which contains 2 μL of 10 ×buffer (Takara Company), MgCl2 1.2μL (25mmol / L, Takara Company), dNTP 0.4μL (10mmol / L, Takara Company), rTaq 0.2μL (5U / μL, Takara Company), 1.5μL DNA template, positive 1.5 μl of each reverse primer (10 μmol / L), and make up the rest with water. Amplification program: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5min, denaturation at 94°C for 40s, annealing at 56°C for 30s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com