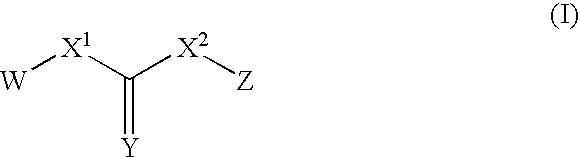Patents
Literature
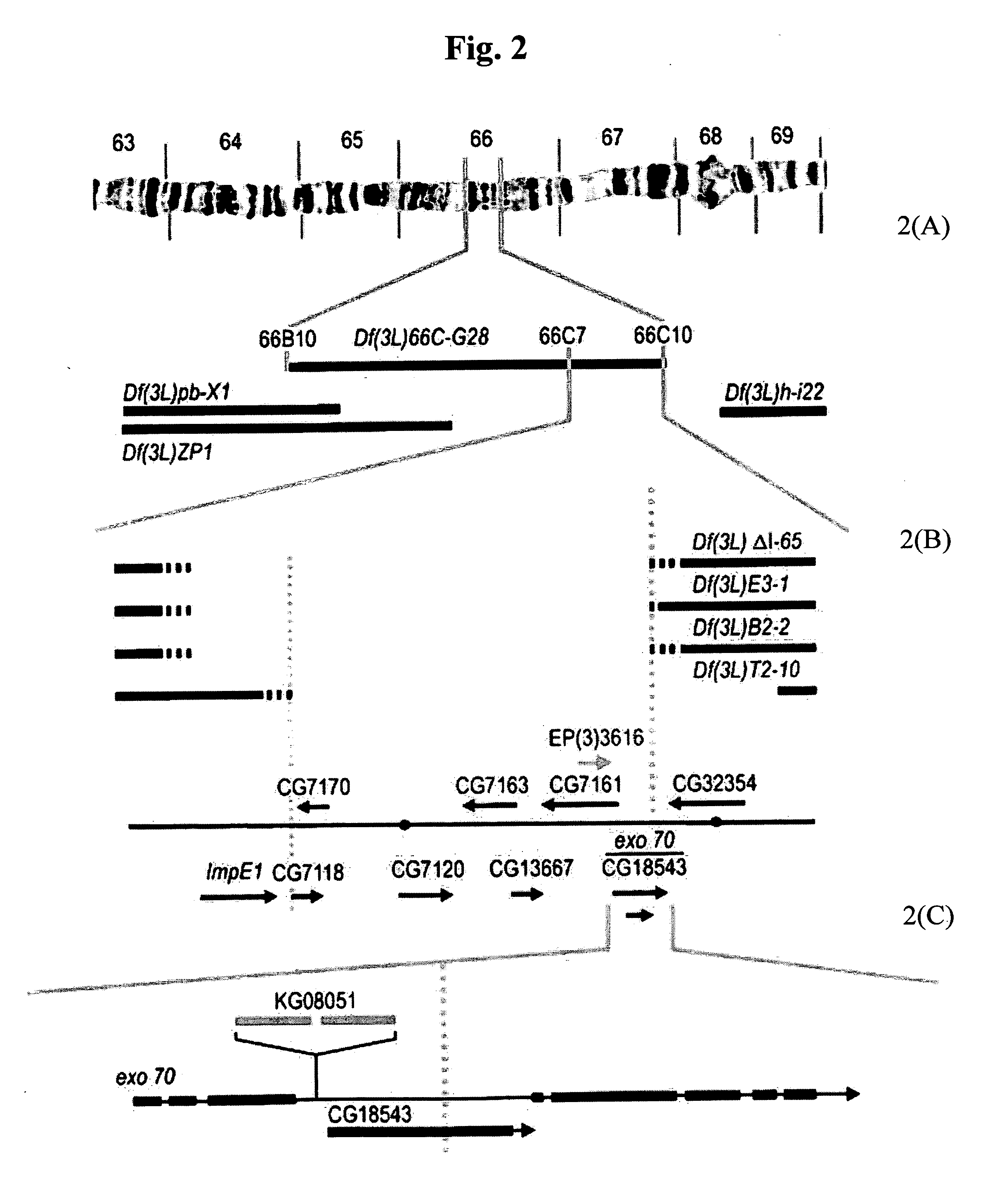
36 results about "Chromosome segregation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chromosome segregation is the process in eukaryotes by which two sister chromatids formed as a consequence of DNA replication, or paired homologous chromosomes, separate from each other and migrate to opposite poles of the nucleus. This segregation process occurs during both mitosis and meiosis. Chromosome segregation also occurs in prokaryotes. However, in contrast to eukaryotic chromosome segregation, replication and segregation are not temporally separated. Instead segregation occurs progressively following replication.
Compounds useful for inhibiting Chk1
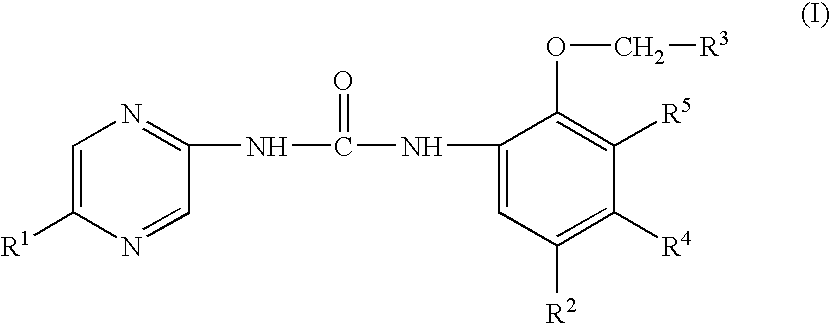
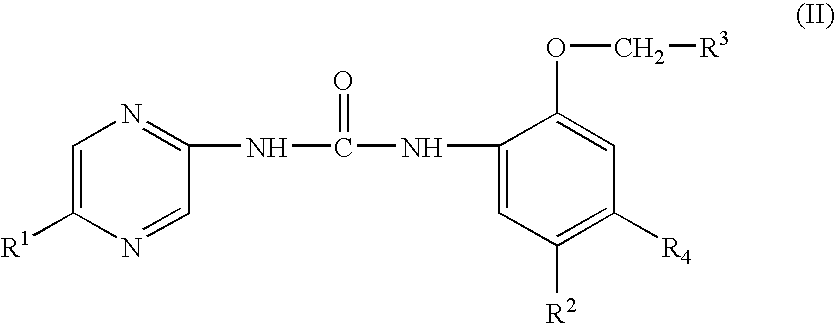
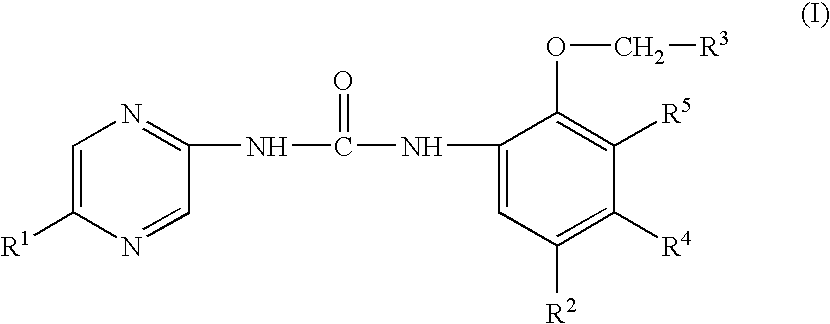
Aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Heteroaryl urea derivatives useful for inhibiting CHK1
Substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division, also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Compounds useful for inhibiting CHK1
InactiveUS20050245525A1Little or no activityUseful in treatmentBiocideOrganic chemistryArylCell division
Aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Determining cancer agressiveness, prognosis and responsiveness to treatment
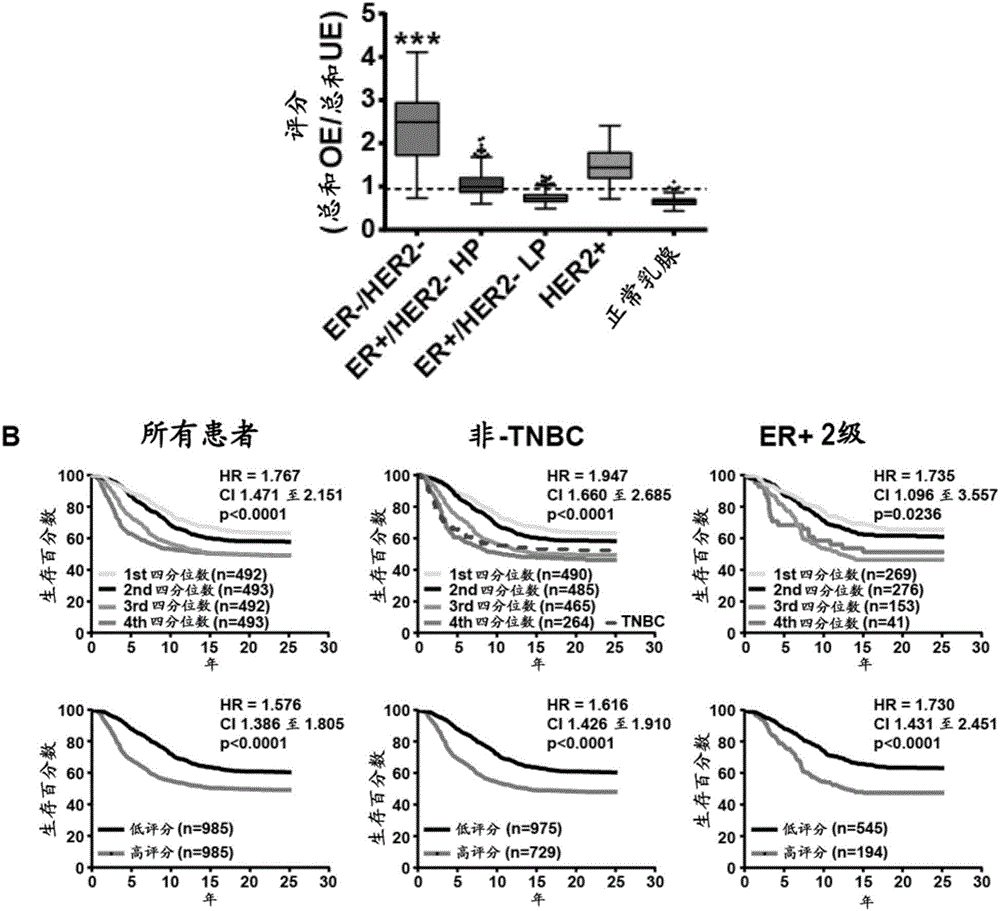
The invention provides methods of determining the aggressiveness, prognosis and response to therapy for particular cancers, which include comparing the expression levels of one or a plurality of differentially expressed genes from one or more 5 functional metagenes, including a carbohydrate / lipid metabolism metagene, a cell signalling metagene, a cellular development metagene, a cellular growth metagene, a chromosome segregation metagene, a DNA replication / recombination metagene, an immune system metagene, a metabolic disease metagene, a nucleic acid metabolism metagene, a post-translational modification metagene, a protein 10 synthesis / modification metagene and a multiple networks metagene. The method disclosed herein may be particularly suitable as a companion diagnostic for cancer therapies.
Owner:COUNCIL OF THE QUEENSLAND INST OF MEDICAL RES
Compounds useful for inhibiting CHK1
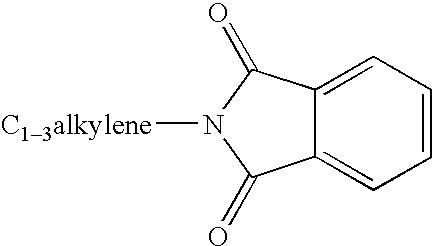
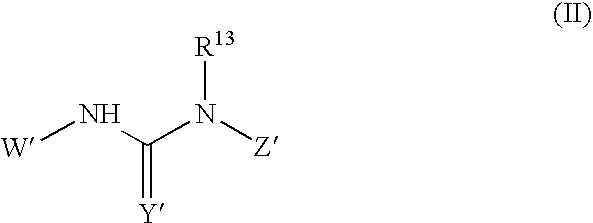
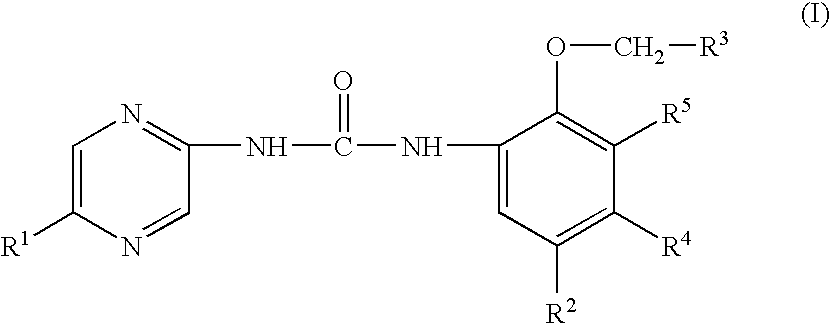
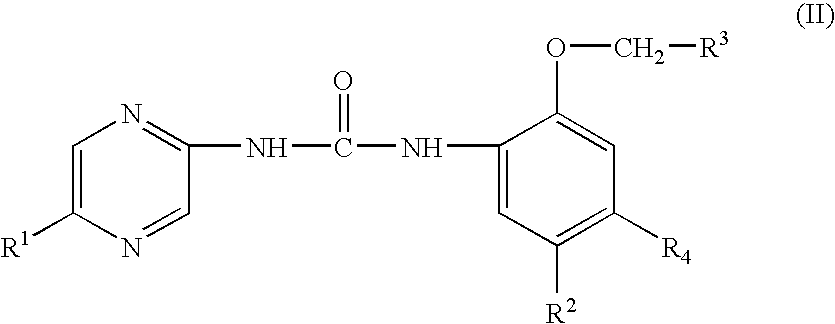
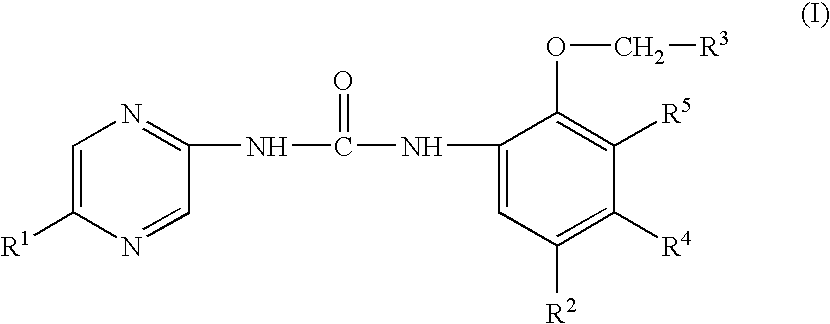
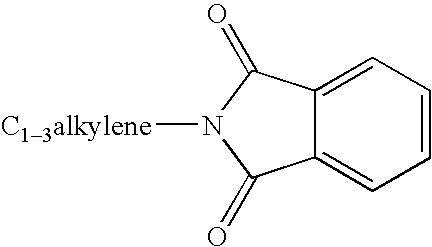
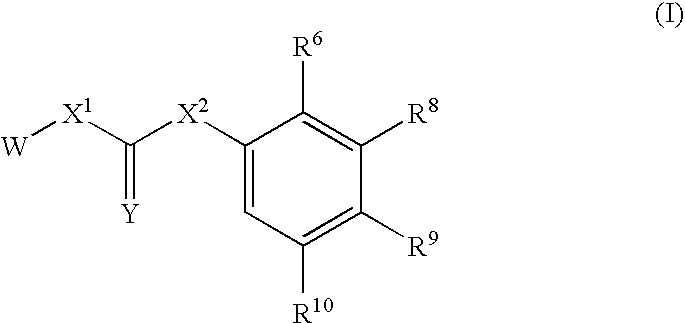
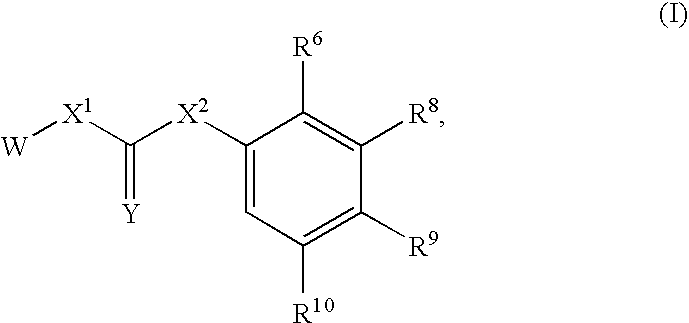
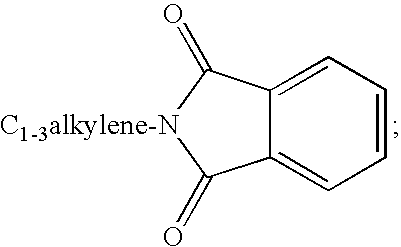
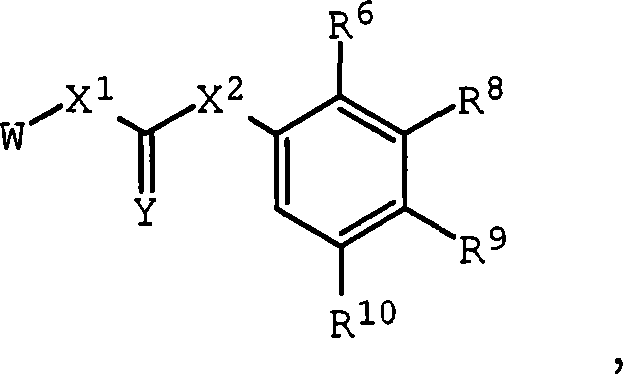
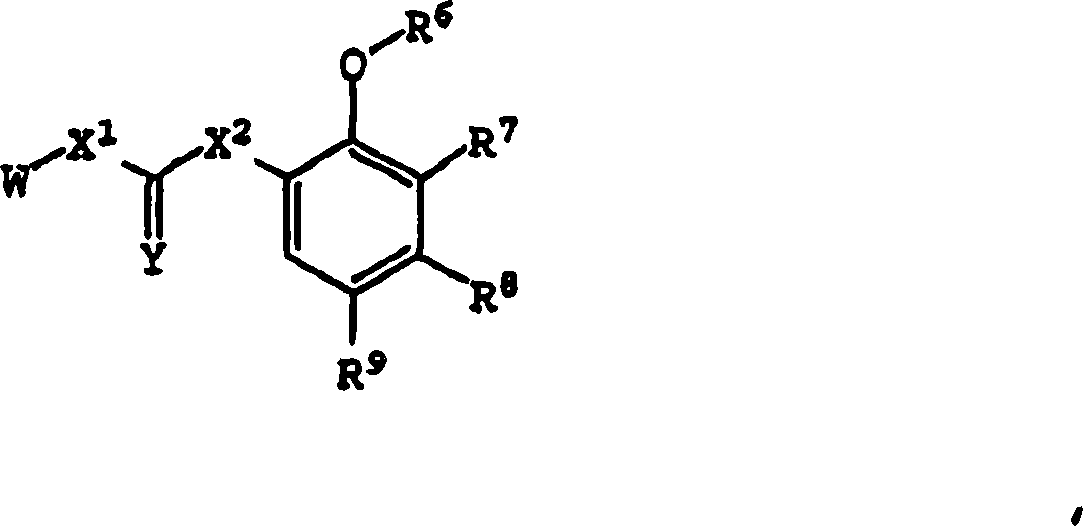
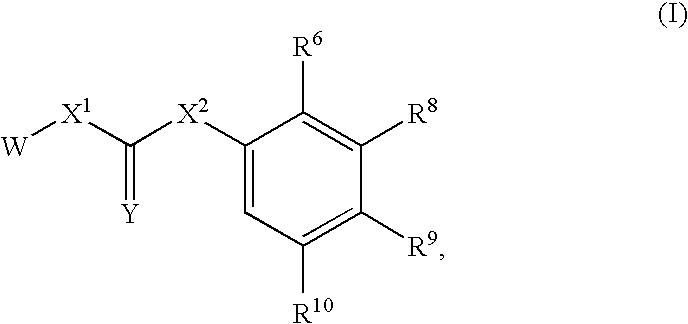
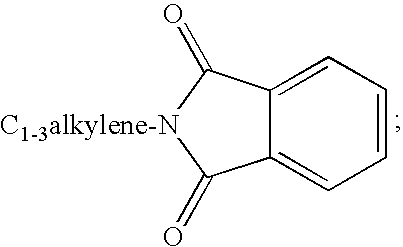
Substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and C1-3alkyleneOR3 conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed formula (I), wherein X1 is null, —O—, —S—, —CH2—, or —N(R1)—; X2 is —O—, . -£>. -, or —N(R1)—,—. . Y xs 0 or S; or =y represents two hydrogen atoms attached to a common carbon atom, —W is selected from the group consisting of heteroaryl, aryl, heterocycloalkyl, cycloalkyl, and C1-6alkyl substituted with a heteroaryl. or aryl group; R6 is —C≡C—R7 or heteroaryl; R8, R9, and R10, independently, are selected from the group consisting of halo, optionally substituted C1-6alkyl, C2-6alkenyl, C2-6alkynyl, OCP3, CF3, NO2, CN, NC, N(R3)2, OR3, CO2R3, C(O)N (R3)2, C(O)R3, N(R1)COR3, N(R1)C(O)OR3, N(R8)C(O)OR3, N(R1)C(O)C1-3alkyleneC(O)R3, N(R1)C(O)C1 -3alkyleneC(O)OR3, N(R1)C(O)C1-3alkyleneOR3, N(R1)C(O)C1-3alkyleneNHC(O)OR3, N(R1)C(O)C1-3alkyleneSO2.NR3, C1-3alkyleneOR3, and SR3; Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Heteroaryl urea derivatives useful for inhibiting chk1
Substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division, also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
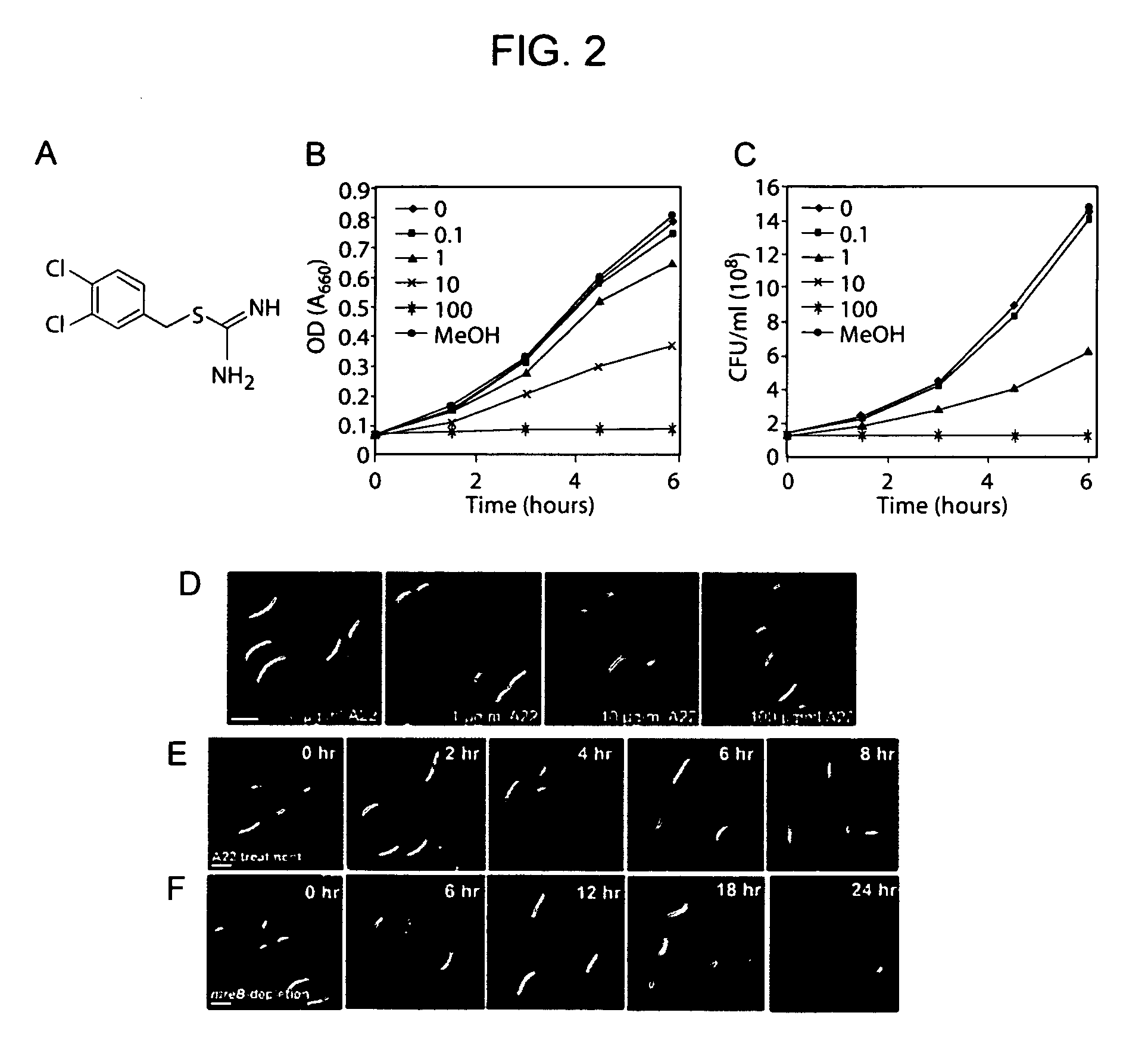
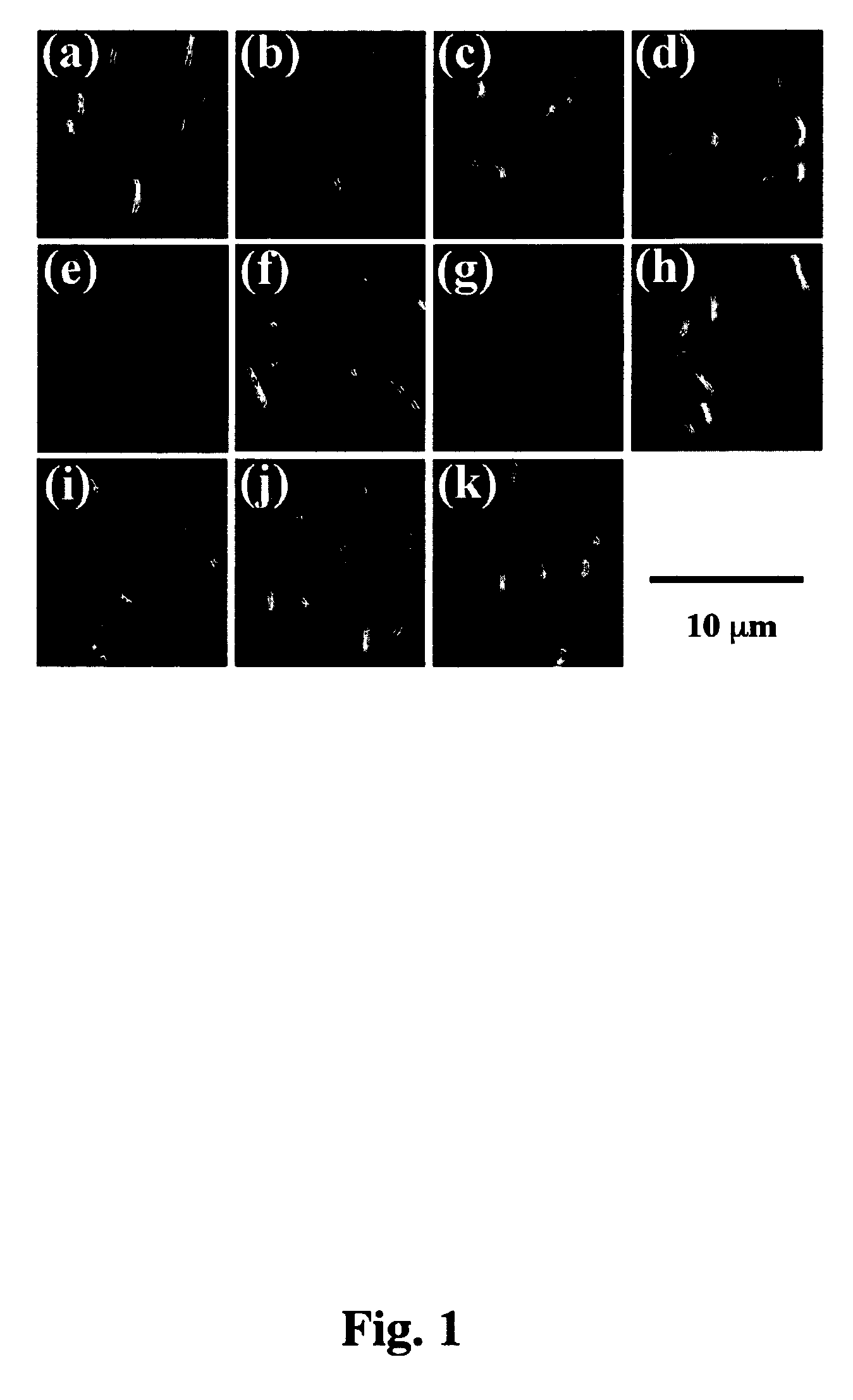
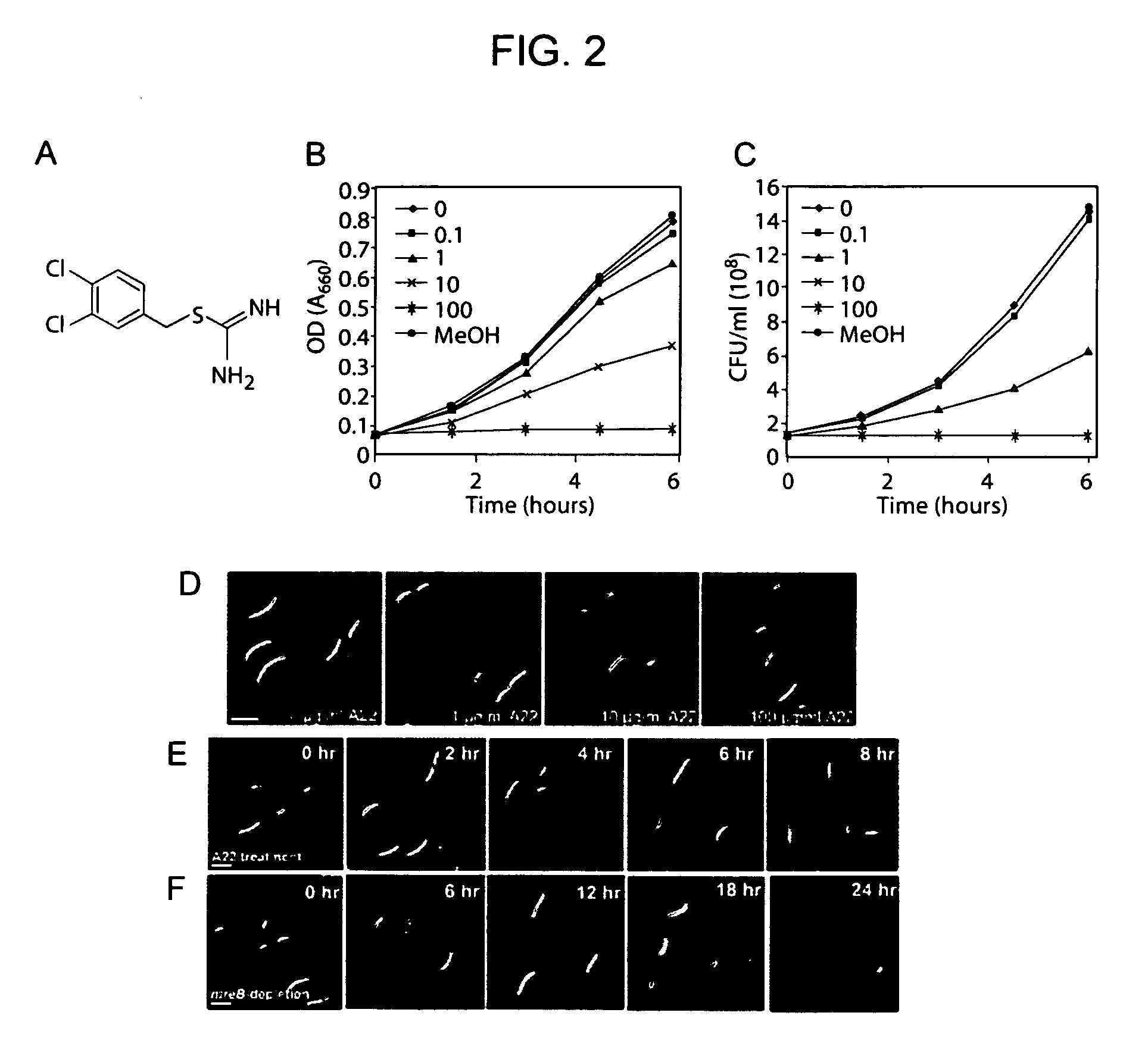
Antibiotics targeting MreB
InactiveUS20060241185A1Useful for developmentModel is usedBiocideOrganic chemistryActive agentChromosome segregation
The identification of MreB as essential for bacterial chromosome segregation provides a new target for antibiotic action. The MreB function is useful in the development of screening assays for new antibiotics, which may use, for example, genetic mutants in MreB, tests of MreB mediated chromosome segregation, and the like. In one embodiment of the invention, the antibiotic is an isothiourea compound, which may comprise a polyhalogenated benzyl group, e.g. at the 4 position, the 2,4 position, etc. A pharmaceutical composition comprising an MreB targeted antibiotic as an active agent is administered to a patient suffering from a microbial infection, particularly bacterial infections.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Compounds useful for inhibiting chk1
The present invention discloses aryl and heteroaryl substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and disorders associated with DNA damage or impaired DNA replication. The invention also discloses methods of making the compounds, and the use of the compounds as therapeutic agents for the treatment of, for example, cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation or cell division.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
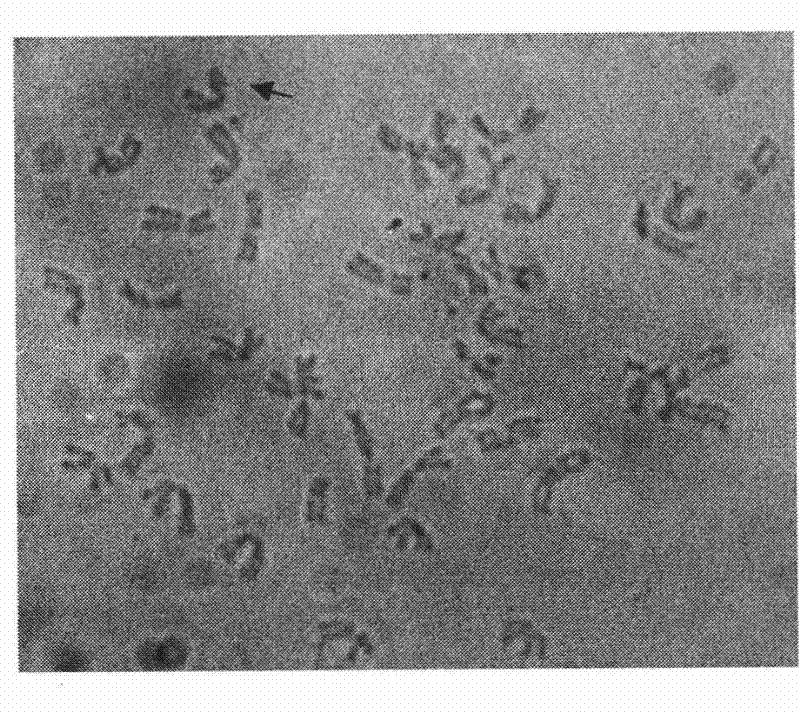
Method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN101580832AIntegrity guaranteedBroaden the range of separationLibrary creationDNA preparationChemical treatmentFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization. The method for separating the chromosomes in the plant cells comprises the following steps of: the fluorescence in-situ hybridization is carried out on the plant cells, the single chromosome of which is picked; by comparing with the corresponding fluorescence in-situ hybridization map of the normal plant cells, the picked single chromosome is defined to be which chromosome, thus separating a purpose chromosome. The method has the advantages of being capable of separating the chromosomes with similar types and specific bands, widening the separating range of the chromosomes, avoiding the unnecessary chemical processing in the manufacture process of the chromosome specimens, preventing the DNA of the chromosomes from being damaged, guaranteeing the completeness of the separated DNA. A microclone library of the whole chromosomes of the wheat can be obtained by applying the invention.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antibiotics targeting MreB
The identification of MreB as essential for bacterial chromosome segregation provides a new target for antibiotic action. The MreB function is useful in the development of screening assays for new antibiotics, which may use, for example, genetic mutants in MreB, tests of MreB mediated chromosome segregation, and the like. In one embodiment of the invention, the antibiotic is an isothiourea compound, which may comprise a polyhalogenated benzyl group, e.g. at the 4 position, the 2,4 position, etc. A pharmaceutical composition comprising an MreB targeted antibiotic as an active agent is administered to a patient suffering from a microbial infection, particularly bacterial infections.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Single chromosome segregation method, single chromosome high-throughput sequencing library construction method and application
InactiveCN105087484AOptimal dilution parameterSimple technical solutionMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood/immune system cellsChromosome segregationHomologous chromosome
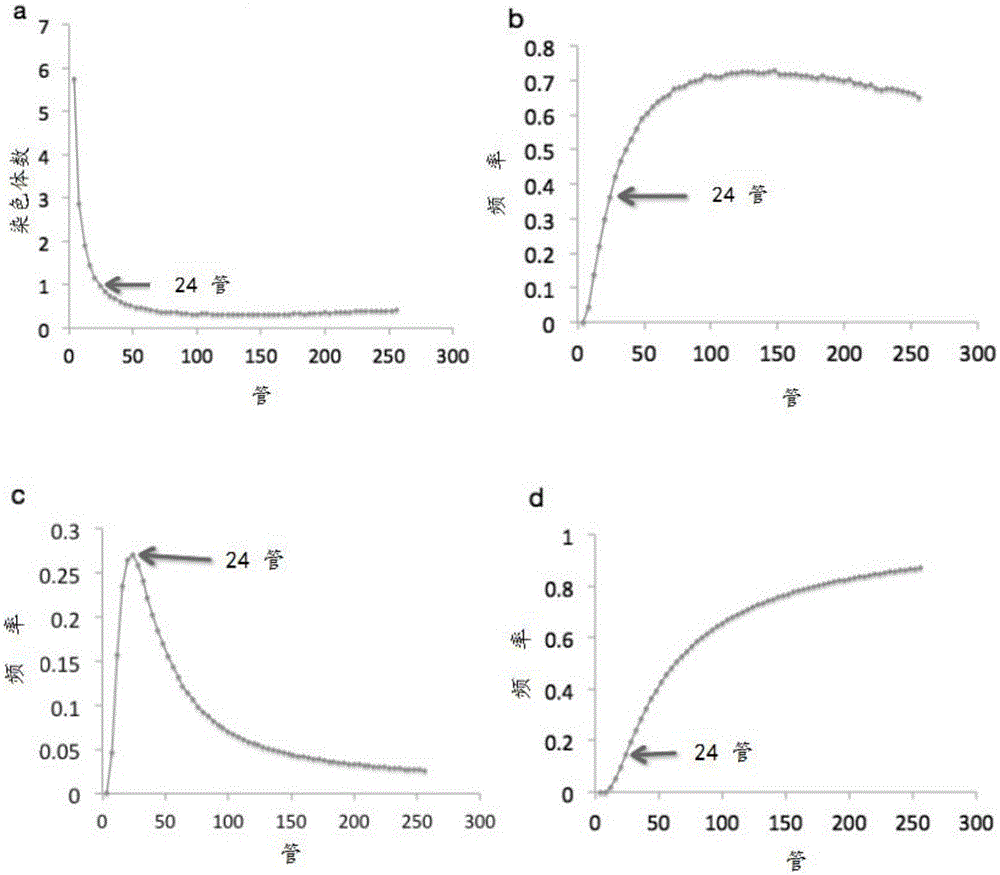
The invention provides a single chromosome segregation method, a single chromosome high-throughput sequencing library construction method and application. According to the technical scheme, optimal dilution parameters are obtained through computer simulation experiments, chromosomes in single cell are segregated by a dilution method to obtain single chromosomes, and high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis are conducted so as to judge out that mutant genes derive from the father or the mother in homologous chromosomes. Compared with that the homologous chromosomes serve as a mixed sample for sequencing, the single chromosome segregation method has the advantages that the single chromosomes are segregated by the dilution method, and the single chromosome segregation method can be used for haplotype sequencing and has important application value in scientific research and clinical application.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Bisarylurea derivatives useful for inhibiting CHK1
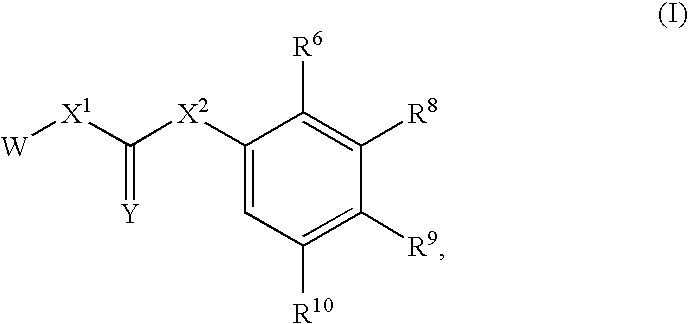
Aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed. Formula (I).
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
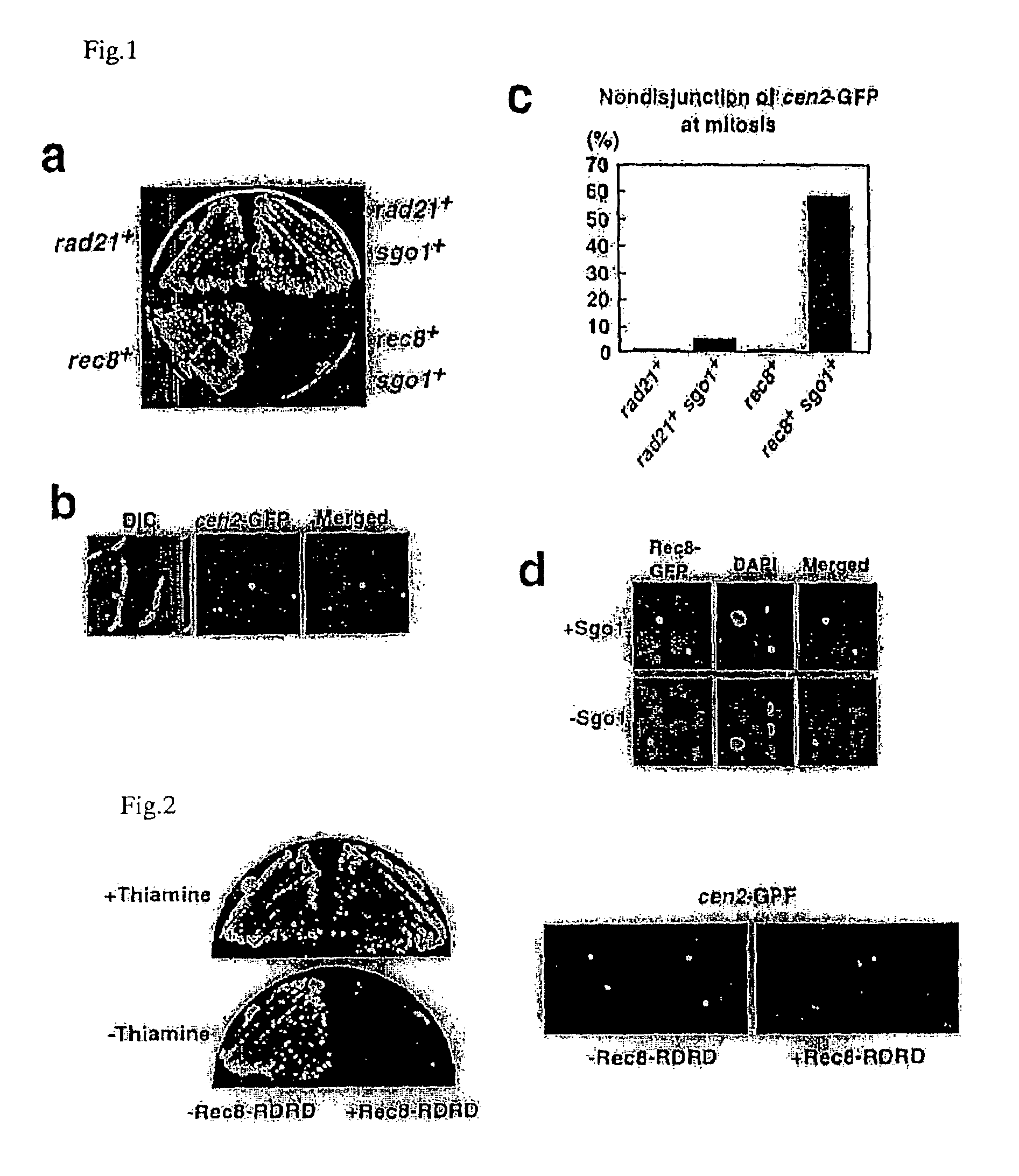
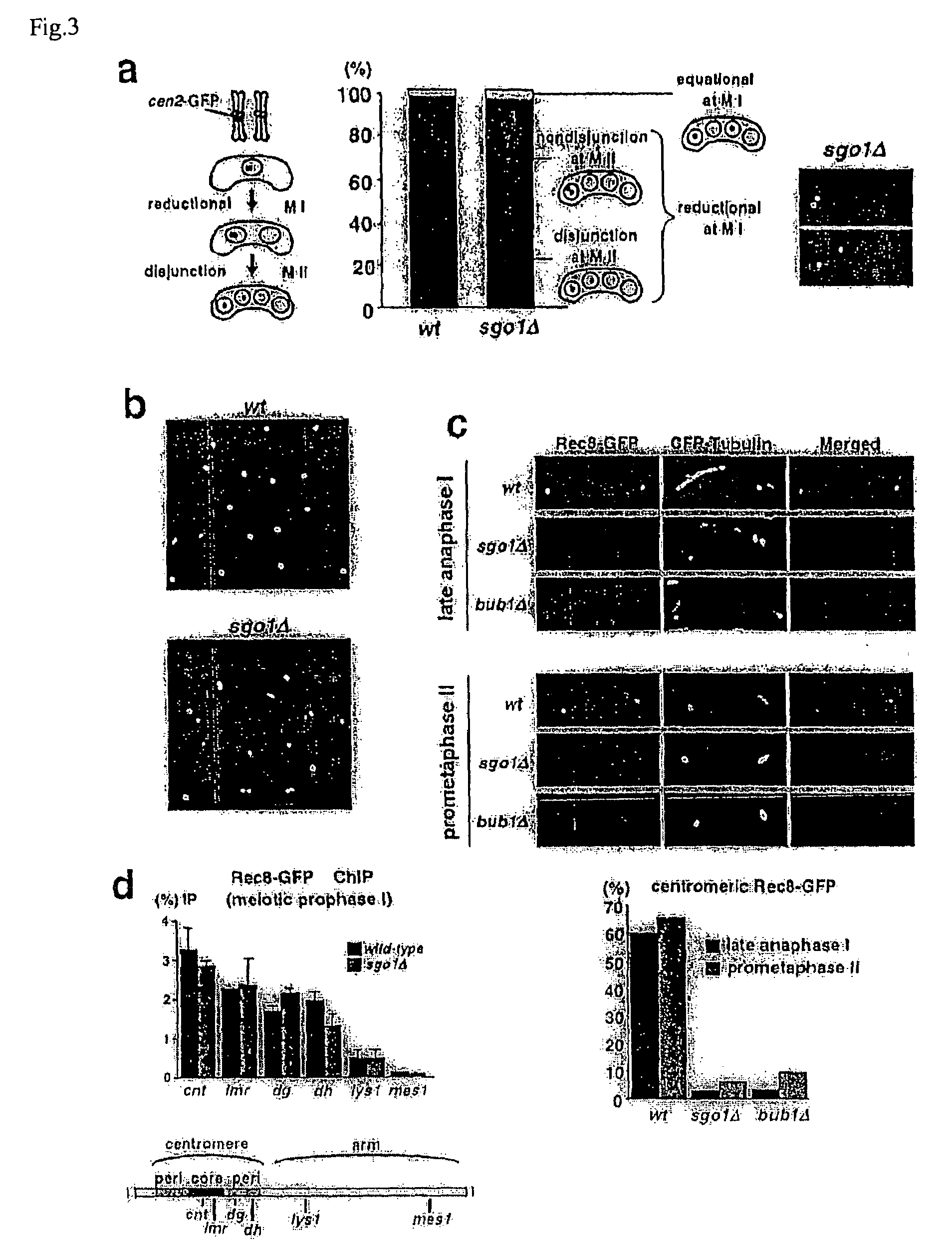
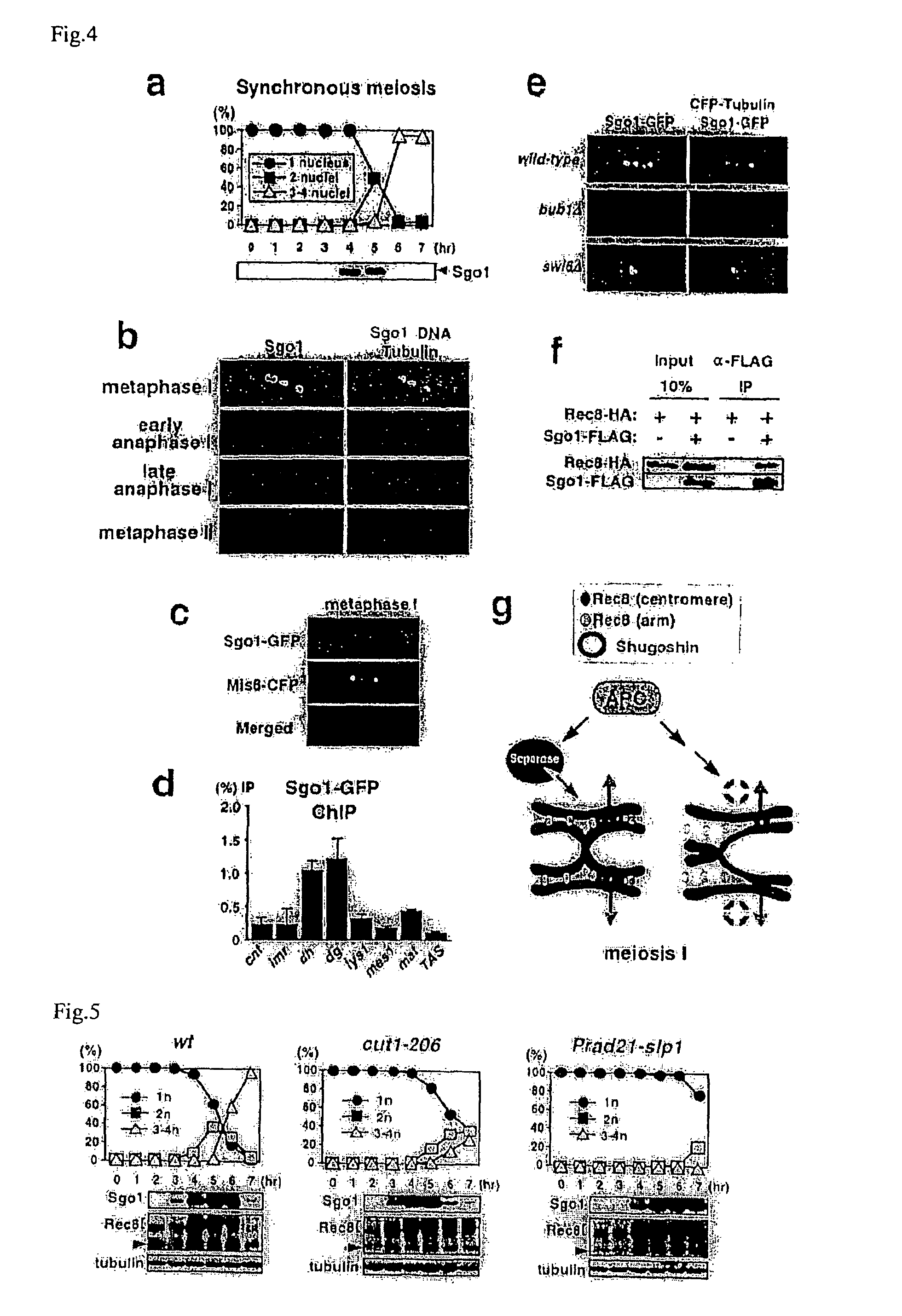
Novel centromeric protein shugoshin
InactiveUS20070160993A1Reduce in quantityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsChromosome segregationSchizosaccharomyces pombe
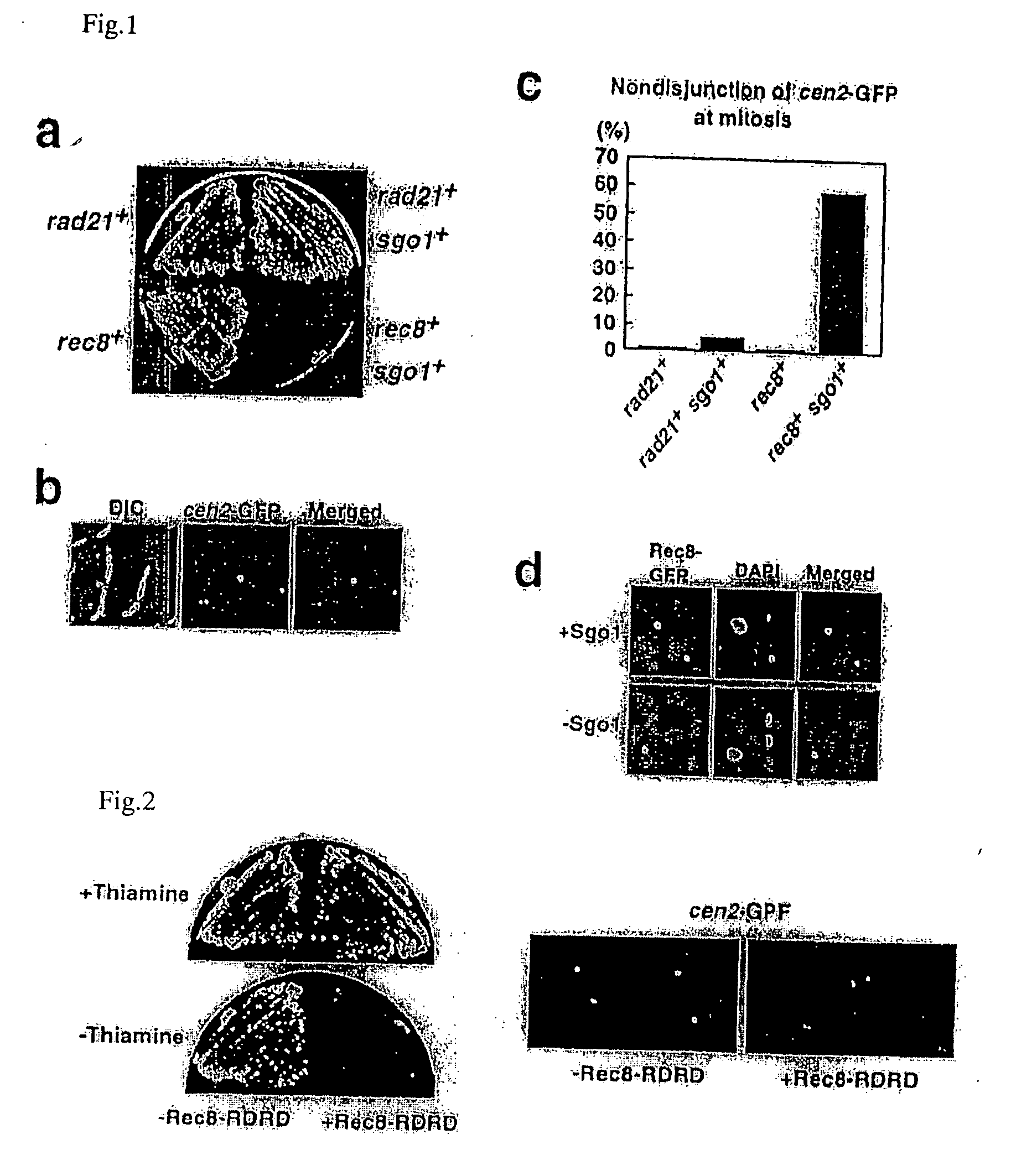
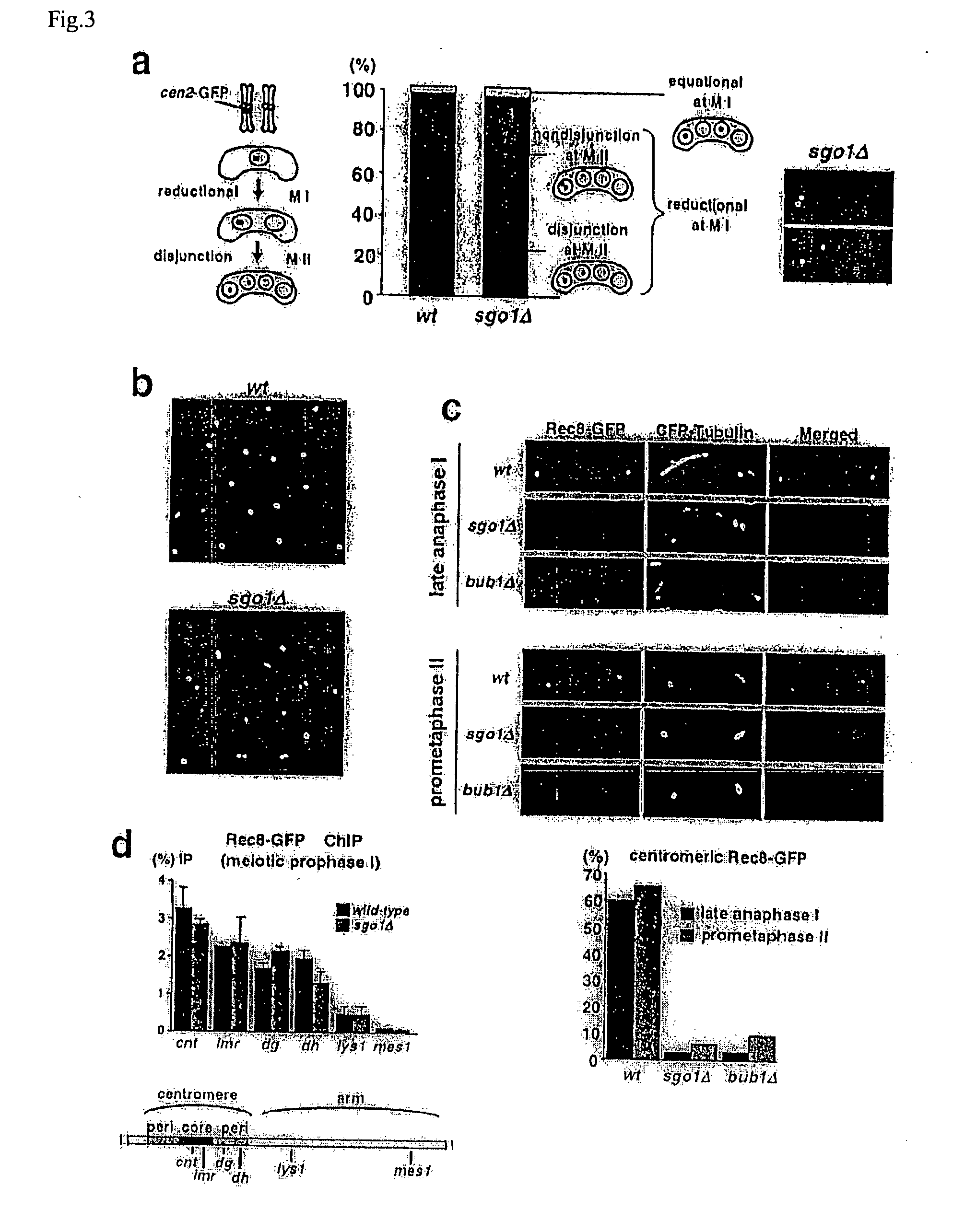
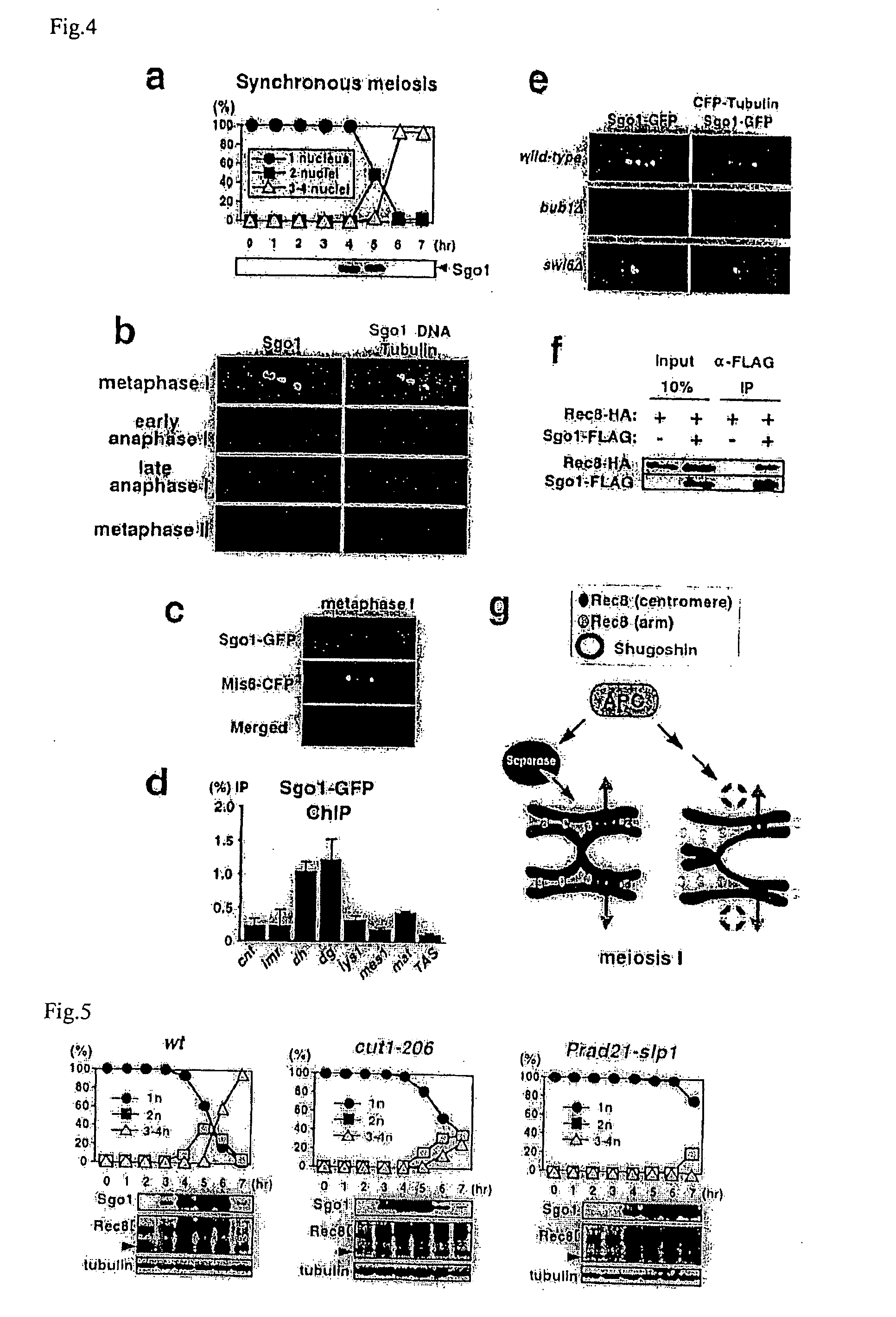
The present invention is to provide meiosis-specific novel kinetochore protein Sgo1 (shugoshin) derived from fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and a homologue or paralogue thereof having a regulatory activity of chromosome segregation; and DNAs encoding them; as a factor ensuring the retention of unidirection and cohesion in sister centromere at meiosis I in cooperation with cohesin. To elucidate the proteins protecting Rec8 during anaphase, the present inventor screened in fission yeast genes for a gene that inhibits mitotic growth and prevents sister chromatid from the separation at anaphase, when co-expressed with Rec8. In this approach, meiosis-specific protein Sgo1 that protects (Shugo) centromeric Rec8 from the degradation at anaphase I was indentified. Further, a budding yeast Sgo1 homologue and a fission yeast mitotic paralogue Sgo2 were identified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Non-toxic extract composition GPR.1 capable of efficiently extracting plant genome DNA and extraction method
ActiveCN108841820AHealth damageReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationChromosome segregationPlant cell
The invention relates to a non-toxic extract composition GPR.1 capable of efficiently extracting plant genome DNA and an extraction method based on the extract. The method specifically comprises the following steps: lysing plant cells with an SDS extraction buffer containing PEG8000, PVPP (Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone) and protease K, performing chromosome segregation and protein denaturation, and releasing nucleic acids; adding potassium acetate to remove most of the proteins and polysaccharides, and continuously precipitating the DNA twice by adopting a PEG8000 / high-salt solution and an ethanol / high-salt solution so as to remove the polysaccharides, polyphenol, RNA, NTP and other impurities, thereby finally obtaining lots of high-purity DNA. According to the method disclosed by the invention, lots of high-purity genome DNA can be extracted from leaves (young leaves or mature leaves) of multiple plants, and the method is non-toxic to the operator, small in environmental pollution, low incost and short in time.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Matrimony gene and protein
InactiveUS20060074232A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingNondisjunction
The present invention is generally directed to Matrimony (Mtrm) nucleotide sequences, polypeptides expressed from the nucleotide sequences and methods employing the Mtrm nucleotide and polypeptide sequences. The Mtrm nucleotide sequences of the invention express a dosage dependent polypeptide that mediates achiasmate chromosome disjunction. In particular, reduction in the amount of the Mtrm polypeptide will cause nondisjunction in the achiasmate chromosomes.
Owner:STOWERS INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Orychophragmus violaceus chromosome acetic acid orcein banding method
InactiveCN102329878AEasy to operateHas scientific research valueMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChromosome segregation
The invention discloses an orychophragmus violaceus chromosome acetic acid orcein banding method for solving the problems that the traditional chromosome separation banding method is not suitable for small chromosome plants such as orychophragmus violaceus, the procedure is complex, the operating conditions are not easily mastered and the banding success rate is low. Cell chromosomes can be easily separated by adopting acetic acid orcein for dyeing and combining a chromosome preparation method, the chromosomes have good shape after being lightly pressed and are clear in banding display, and identification of target chromosomes is facilitated. The plant chromosome banding method is very simple and convenient and easy in operation, is particularly suitable for banding pattern analysis of plants with small chromosomes, and is clear in displayed banding patterns, high in success rate and convenient for genetic analysis of plants.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
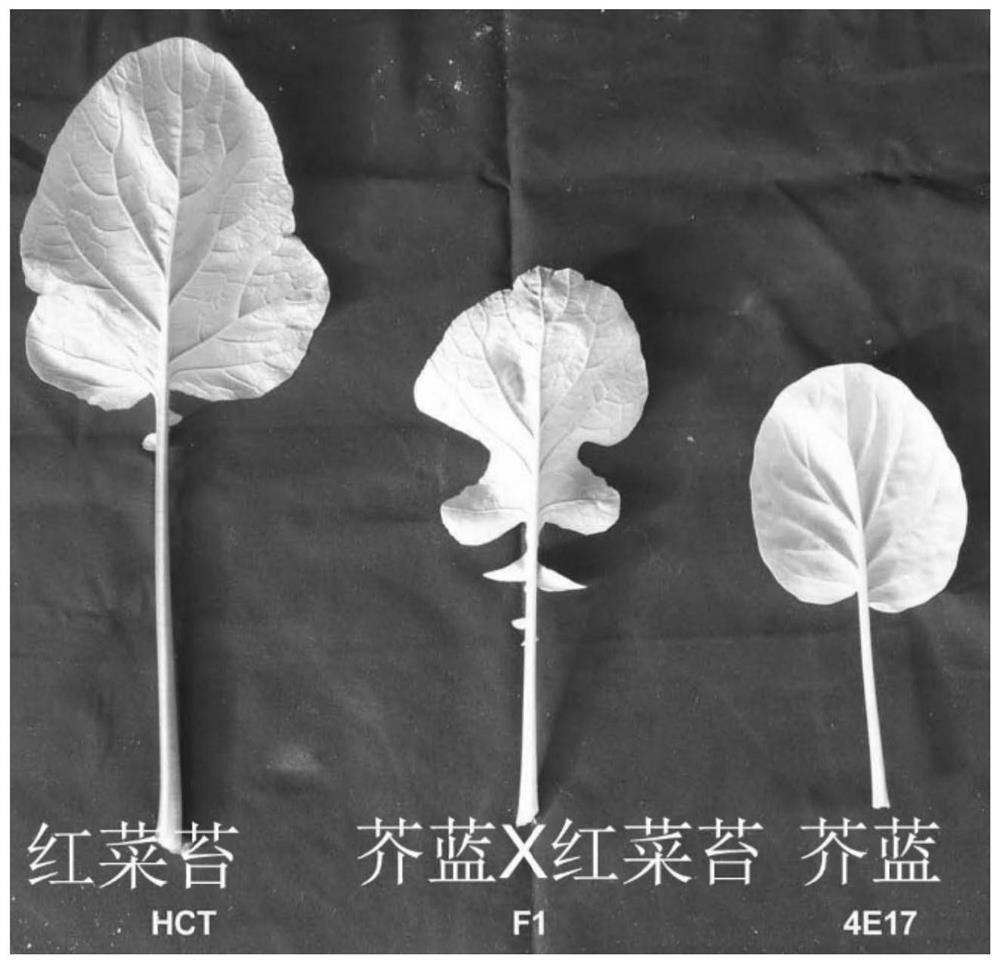
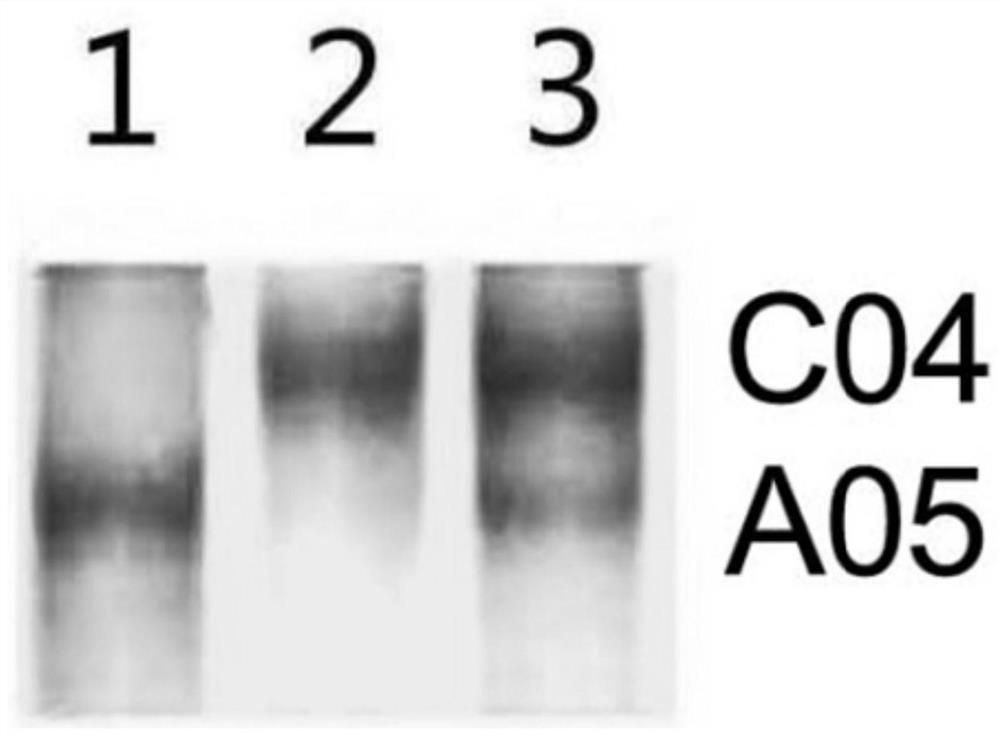
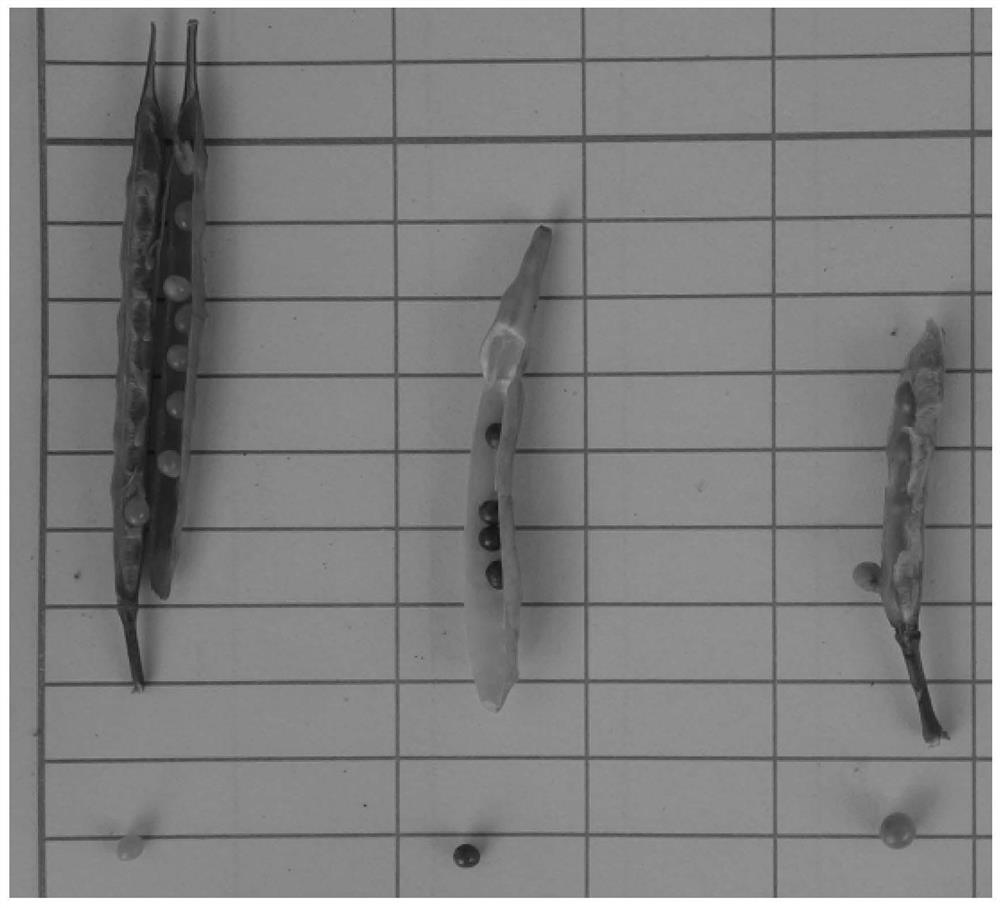
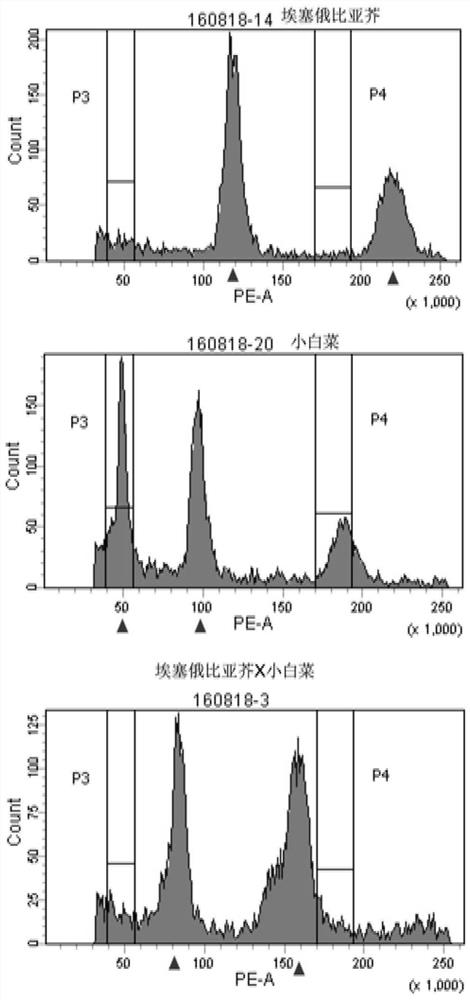
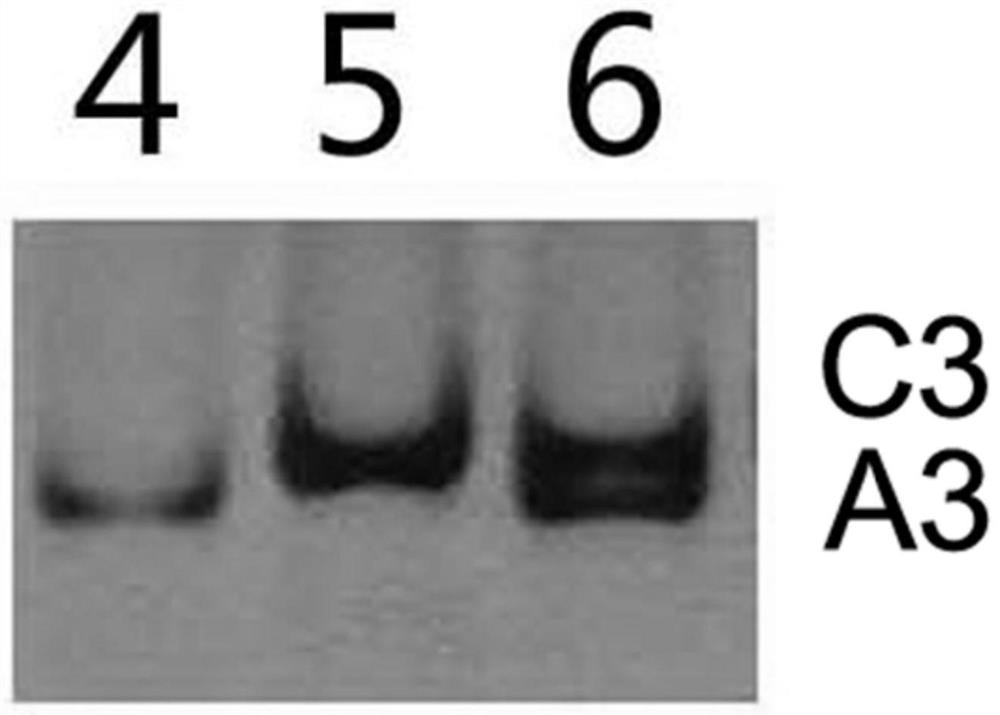
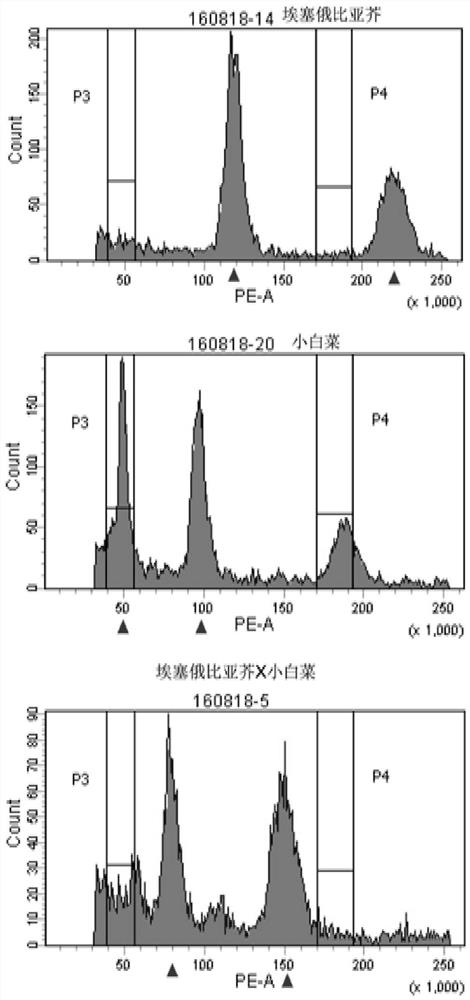
Molecular markers for identification of interspecific hybrids of kale and red cabbage and tracking chromosome segregation of a05 and c04 in their progeny
ActiveCN110423842BExpand genetic resourcesLow technical requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention provides a molecular marker and an identification method for identifying the chromosome segregation status of A05 and C04 of kale and beetroot interspecific hybrids and their progeny materials, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. The invention provides a molecular marker and an identification method for identifying the chromosome segregation of A05 and C04 of kale and beetroot interspecific hybrids and their progeny materials. The marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers, and the marker is used to identify kale and red The true hybrids of vegetable moss interspecific hybrids can also be used to identify the self-progeny, backcross progeny, chromosome appendage lines, and recombination segregated populations and plants of distant hybrids.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
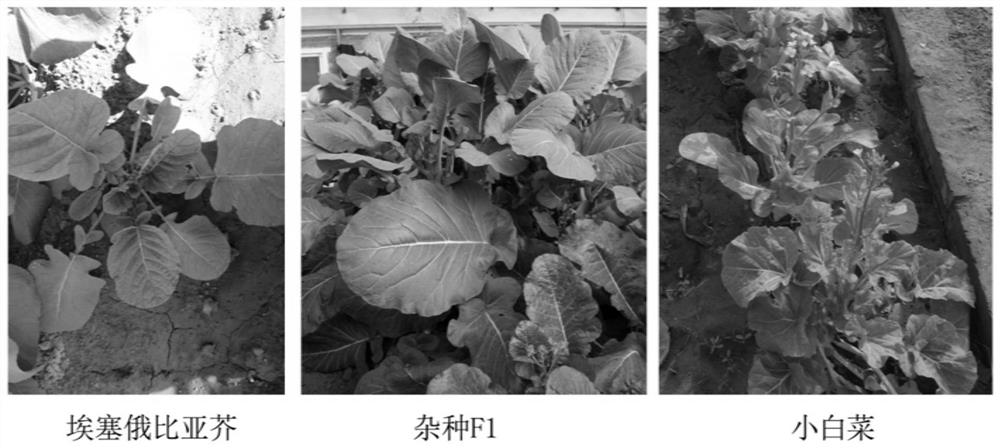
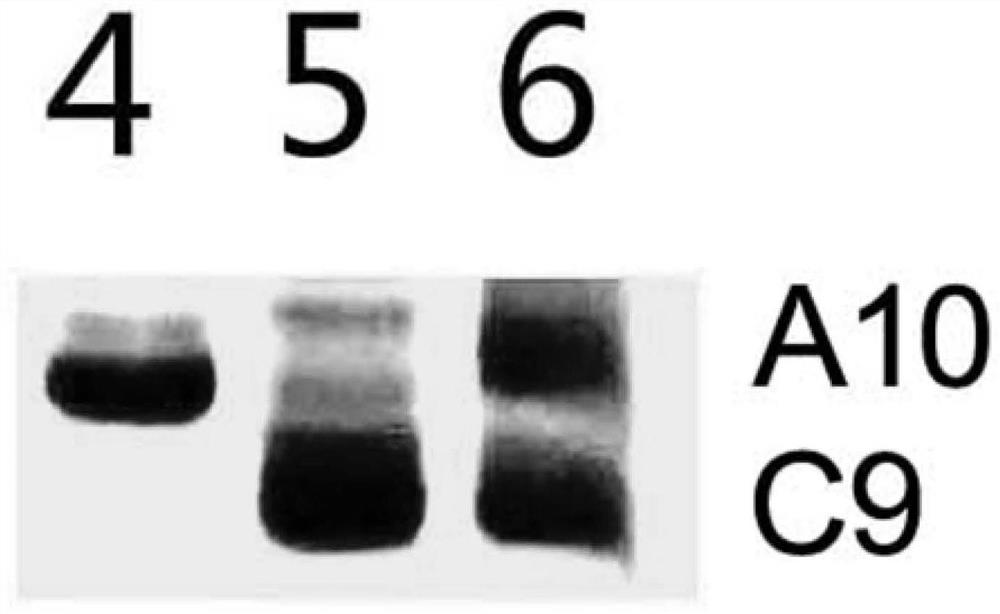
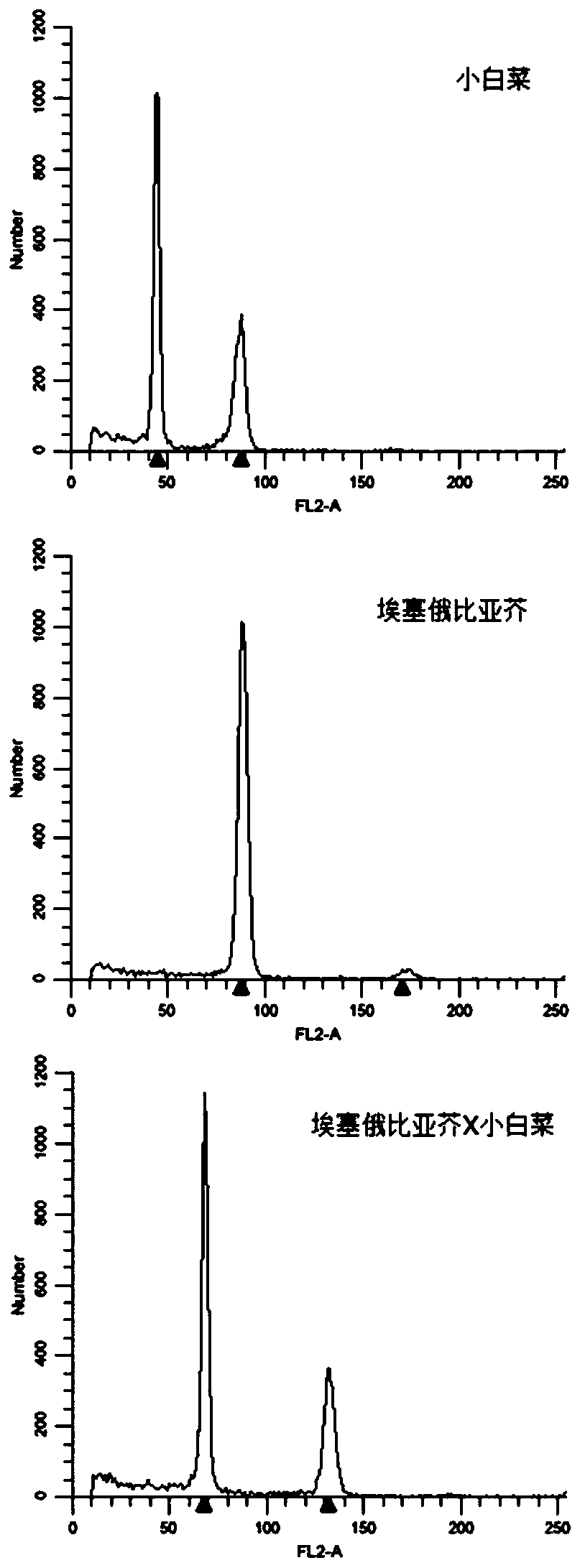
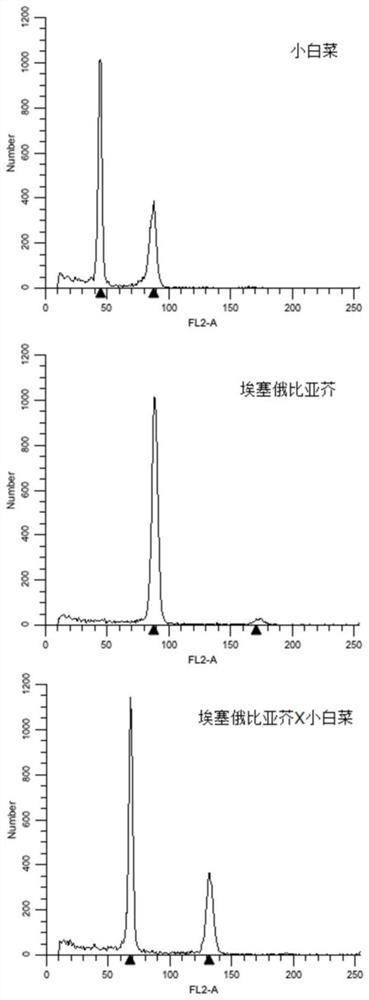
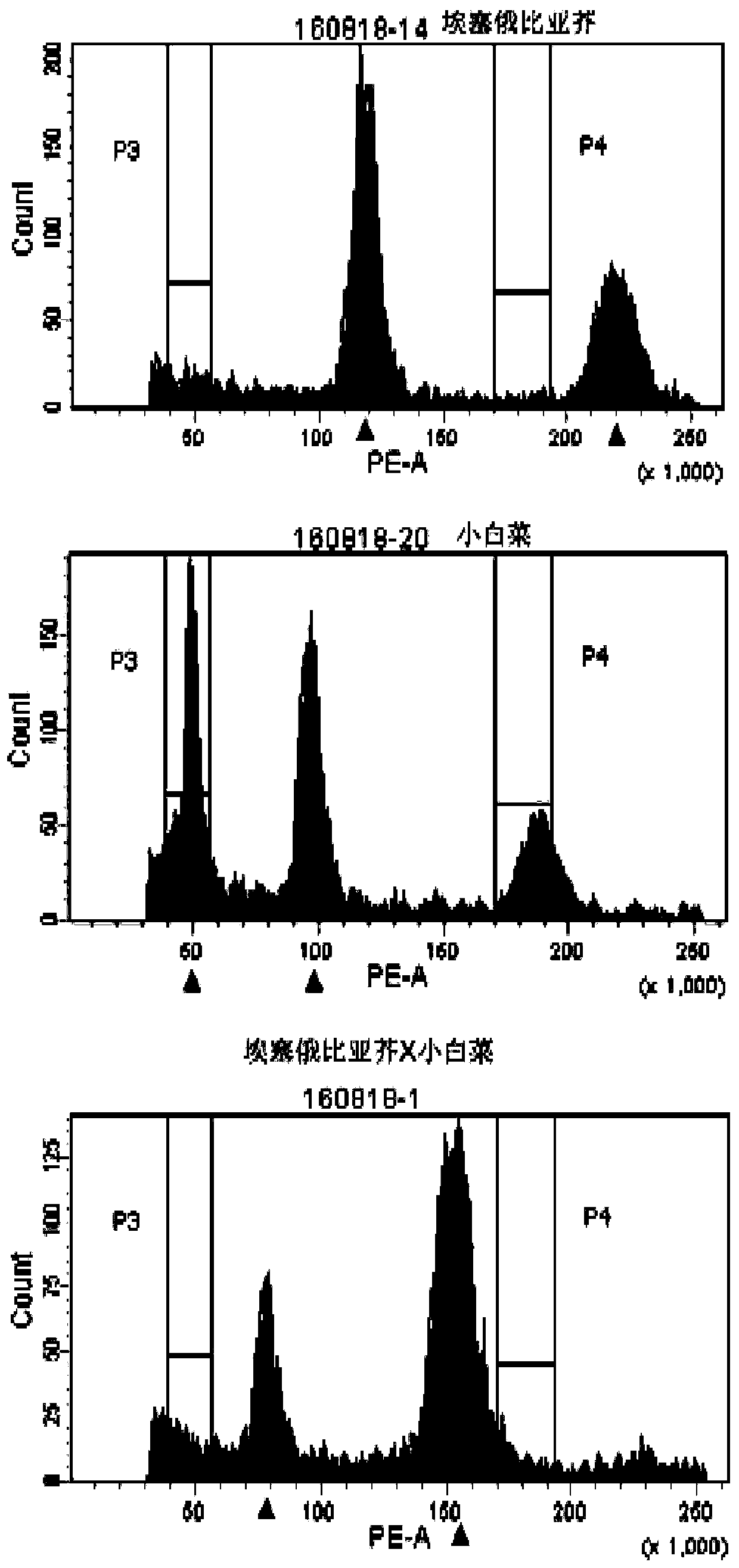
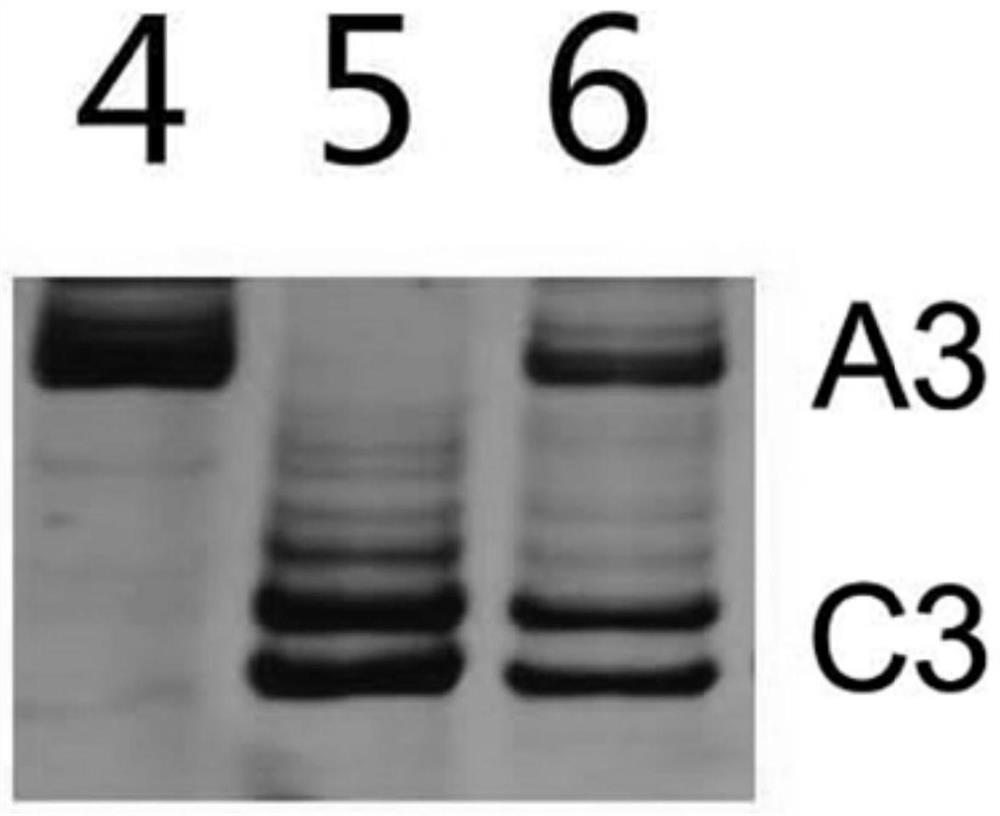
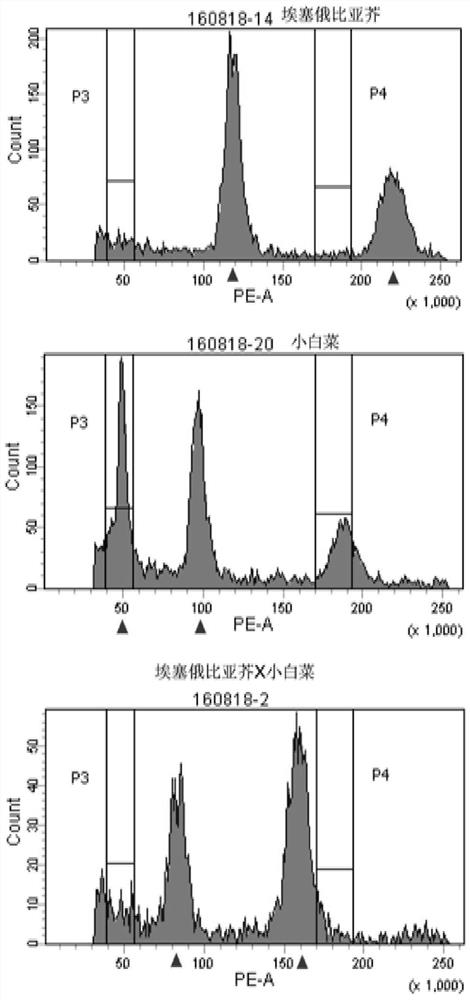
Molecular markers for identification of a10 and c09 chromosome segregation in hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and their progeny
ActiveCN110423841BExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular markers for identification of a03 and c03 chromosome segregation in hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and their progeny
ActiveCN110387432BExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a method for identifying hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and tracking the chromosomal separation of A03 and C03 offspring materials, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. This marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers, which can be used to identify the authenticity of hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard, and can also be used to identify and track self-crossed offspring, backcrossed offspring, chromosome addition lines, and recombination of distant hybrids Chromosomal segregation of A03 and C03 in segregating populations and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compounds Useful for Inhibiting Chk1
InactiveUS20080318974A1Inhibiting and preventing aberrant cell proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiseaseAryl
Aryl- and heteroaryl-substituted urea compounds useful in the treatment of diseases and conditions related to DNA damage or lesions in DNA replication are disclosed. Methods of making the compounds, and their use as therapeutic agents, for example, in treating cancer and other diseases characterized by defects in DNA replication, chromosome segregation, or cell division also are disclosed.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN101580832BIntegrity guaranteedBroaden the range of separationLibrary creationDNA preparationBiotechnologyIn situ hybridisation
The invention discloses a method for separating chromosomes in plant cells by using fluorescence in-situ hybridization. The method for separating the chromosomes in the plant cells comprises the following steps of: the fluorescence in-situ hybridization is carried out on the plant cells, the single chromosome of which is picked; by comparing with the corresponding fluorescence in-situ hybridization map of the normal plant cells, the picked single chromosome is defined to be which chromosome, thus separating a purpose chromosome. The method has the advantages of being capable of separating thechromosomes with similar types and specific bands, widening the separating range of the chromosomes, avoiding the unnecessary chemical processing in the manufacture process of the chromosome specimens, preventing the DNA of the chromosomes from being damaged, guaranteeing the completeness of the separated DNA. A microclone library of the whole chromosomes of the wheat can be obtained by applying the invention.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular marker for identifying interspecific hybrid between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and for tracking chromosome separation of progeny materials A03 and C03
ActiveCN110387433AExpand genetic resourcesEnrich daily dietary nutritionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCO-DOMINANTBirdsrape Mustard
The invention discloses a molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrid between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and for tracking the chromosome separation of progeny materialsA03 and C03, and belongs to the field of plant heredity and breeding. The marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers which can be used for identifying the true and false of the interspecific hybrid between the Chinese cabbage and the Ethiopian mustard, and can also be used for identifying and tracking self cross progeny, backcross progeny, and chromosome addition lines of distant hybrid, and the A03 and C03 chromosomal segregation of recombinant isolated population and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
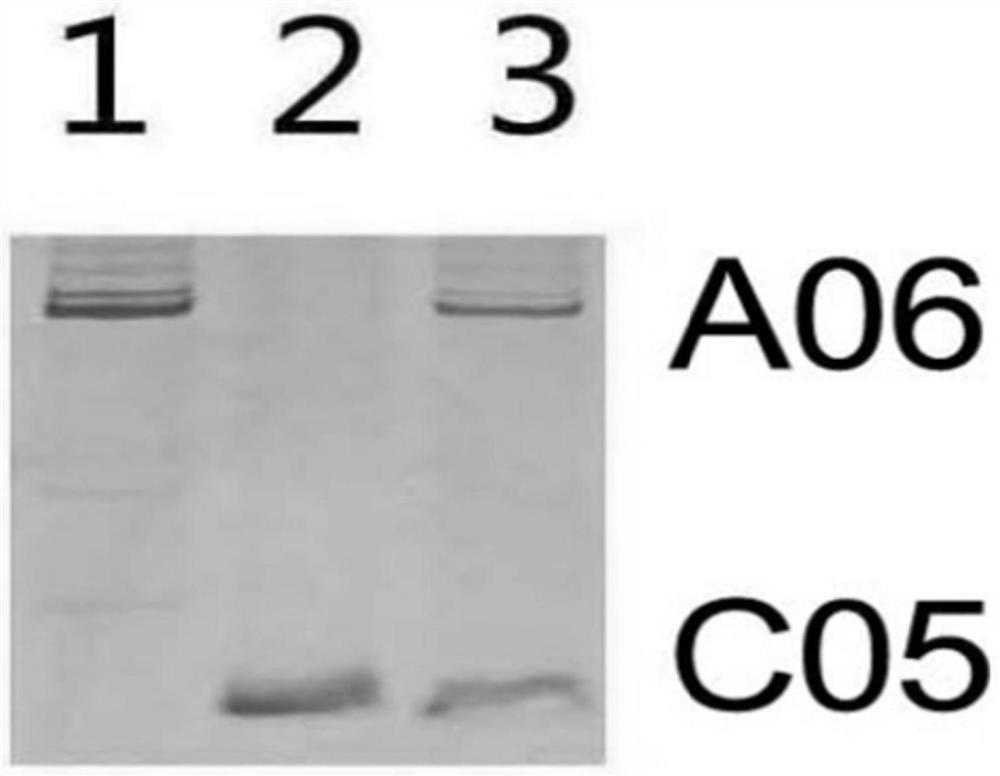
Molecular markers and methods for identifying a06 and c05 chromosome segregation in Brassica vegetable interspecific hybrids and progeny materials
ActiveCN110512022BRapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a method for identifying the segregation of A06 and C05 chromosomes of brassica vegetable interspecific hybrids and offspring materials, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. The molecular marker can quickly and accurately identify the interspecific hybrids of Brassica A genome (such as Chinese cabbage, red cabbage, etc.) . The method can identify distant hybrids of Brassica A genome and C genome plants and their backcross offspring, which can expand the genetic resources of Brassica vegetables, transfer new traits, enrich vegetable types, and enrich people's daily dietary nutrition.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata and tracking segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in offspring materials of interspecific hybrids
ActiveCN110499383AExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBirdsrape MustardBiology
The invention discloses a molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata and tracking segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in offspring materials of the interspecific hybrids, and belongs to the field of plant genetic breeding. The marker comprises a pair of codominant molecular marker bodies, and can be used for identifying the authenticity of the interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata, and can also be used for identifying and tracking selfing offsprings, backcross offsprings, chromosome addition lines and recombined segregation populations of distant hybrids and segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Centromeric protein shugoshin
InactiveUS7538191B2DepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsChromosome segregationSchizosaccharomyces pombe
The present invention is to provide meiosis-specific novel kinetochore protein Sgo1 (shugoshin) derived from fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and a homologue or paralogue thereof having a regulatory activity of chromosome segregation; and DNAs encoding them; as a factor ensuring the retention of unidirection and cohesion in sister centromere at meiosis I in cooperation with cohesin. To elucidate the proteins protecting Rec8 during anaphase, the present inventor screened in fission yeast genes for a gene that inhibits mitotic growth and prevents sister chromatid from the separation at anaphase, when co-expressed with Rec8. In this approach, meiosis-specific protein Sgo1 that protects (Shugo) centromeric Rec8 from the degradation at anaphase I was indentified. Further, a budding yeast Sgo1 homologue and a fission yeast mitotic paralogue Sgo2 were identified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
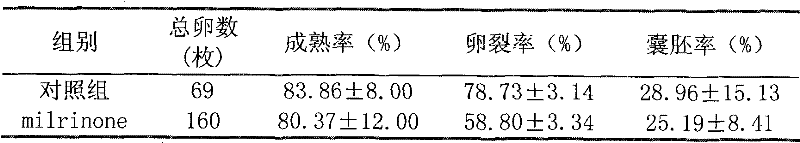
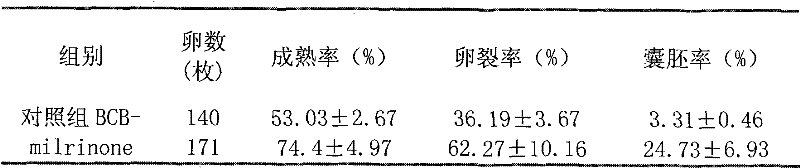
Method for improving in-vitro utilization rate of sheep oocyte
The invention provides a method for improving the in-vitro utilization rate of sheep oocyte, which comprises the following steps of: washing poor quality BCB-oocyte obtained by chromosome segregation for 2 to 3 times by using mature culture solution which contains 50 to 100mu Mol / L PDE3 inhibitor milrinone and culturing for 6 to 9 hours, and washing the BCB-oocyte for 2 to 3 times by using matureculture solution which does not contain the milrinone and culturing for 24 hours; removing granular cells around the oocyte, transferring the oocyte to cleaning solution, picking the oocyte and removing a first polar body, and counting the removal rate of the polar body, namely maturation rate; and activating the oocyte from which the first polar body is removed for 4 to 5 minutes by using 5mu Mol / L ionomycin and washing the oocyte for 1 to 3 times by using the cleaning solution, activating the oocyte for 2 to 3 hours by using 2mMol / L 6-methyl aminopurine which is balanced in a CO2 box 2 to 3 hours ago, washing the oocyte for 3 or 4 times by using the culture solution which is balanced in the CO2 box 2 hours ago, culturing the oocyte in the culture solution for 48 hours, counting cleavage rate, and counting blastocyst rate after 168 hours. In addition, the BCB-oocyte obtained by the chromosome segregation is washed by the mature culture solution for 2 to 3 times and cultured for 24 hours to be directly utilized. The method has great practical value for the in-vitro utilization of the sheep oocyte.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Isolated genomic polynucleotide fragments from chromosome 7
The invention is directed to isolated genomic polynucleotide fragments that encode human SNARE YKT6, human glucokinase, human adipocyte enhancer binding protein (AEBP1) and DNA directed 50 kD regulatory subunit (POLD2), vectors and hosts containing these fragments and fragments hybridizing to noncoding regions as well as antisense oligonucleotides to these fragments. The invention is further directed to methods of using these fragments to obtain SNARE YKT6, human glucokinase, AEBP1 protein and POLD2 and to diagnose, treat, prevent and / or ameliorate a pathological disorder.
Owner:RYOGEN
Molecular markers for identification of a02 and c02 chromosome segregation in hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and their progeny
ActiveCN110499383BExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a method for identifying hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and tracking the chromosomal separation of A02 and C02 offspring materials, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. This marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers, which can be used to identify the authenticity of hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard, and can also be used to identify and track self-crossed offspring, backcrossed offspring, chromosome addition lines, and recombination of distant hybrids Chromosomal segregation of A02 and C02 in segregating populations and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker for identifying A10 and C07 chromosome segregation conditions of interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbages and brassica carinata, and progeny materials of interspecific hybrids
ActiveCN110468228AExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The present invention discloses a molecular marker and a method for identifying interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbages and brassica carinata and tracking A10 and C07 chromosome segregation conditions of progeny materials of the interspecific hybrids, and belongs to the field of plant genetic breeding. The marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers, used for identifying authenticity of the interspecific hybrids of the Chinese cabbages and brassica carinata, and also can be used for identifying and tracking the A10 and C07 chromosome segregation conditions of self-bred progeny, backcross progeny, chromosome additional lines of distant hybrids , recombinant segregation populations and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular markers for identification of chromosome segregation of a03 and c03 in hybrids and progeny materials of Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard
ActiveCN110387433BExpand genetic resourcesEnrich daily dietary nutritionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com