Novel macromolecule transduction domains and methods for identification and uses thereof
A large molecule, transduction domain technology, applied in the field of new macromolecule transduction domain peptides, can solve the problems of limited ability to cross the cell membrane and nuclear membrane, toxicity, and poorly understood pathways of cellular uptake
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
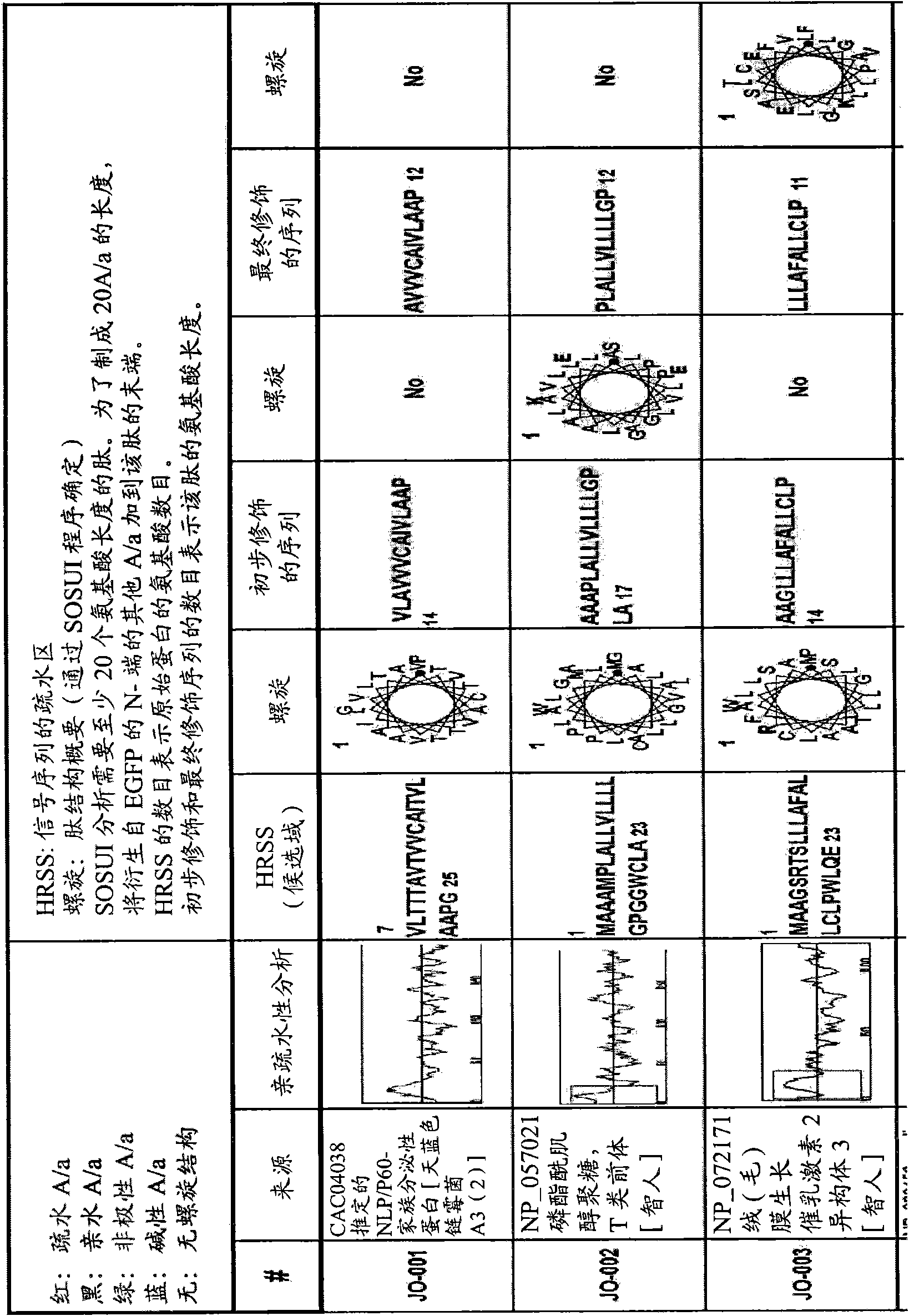
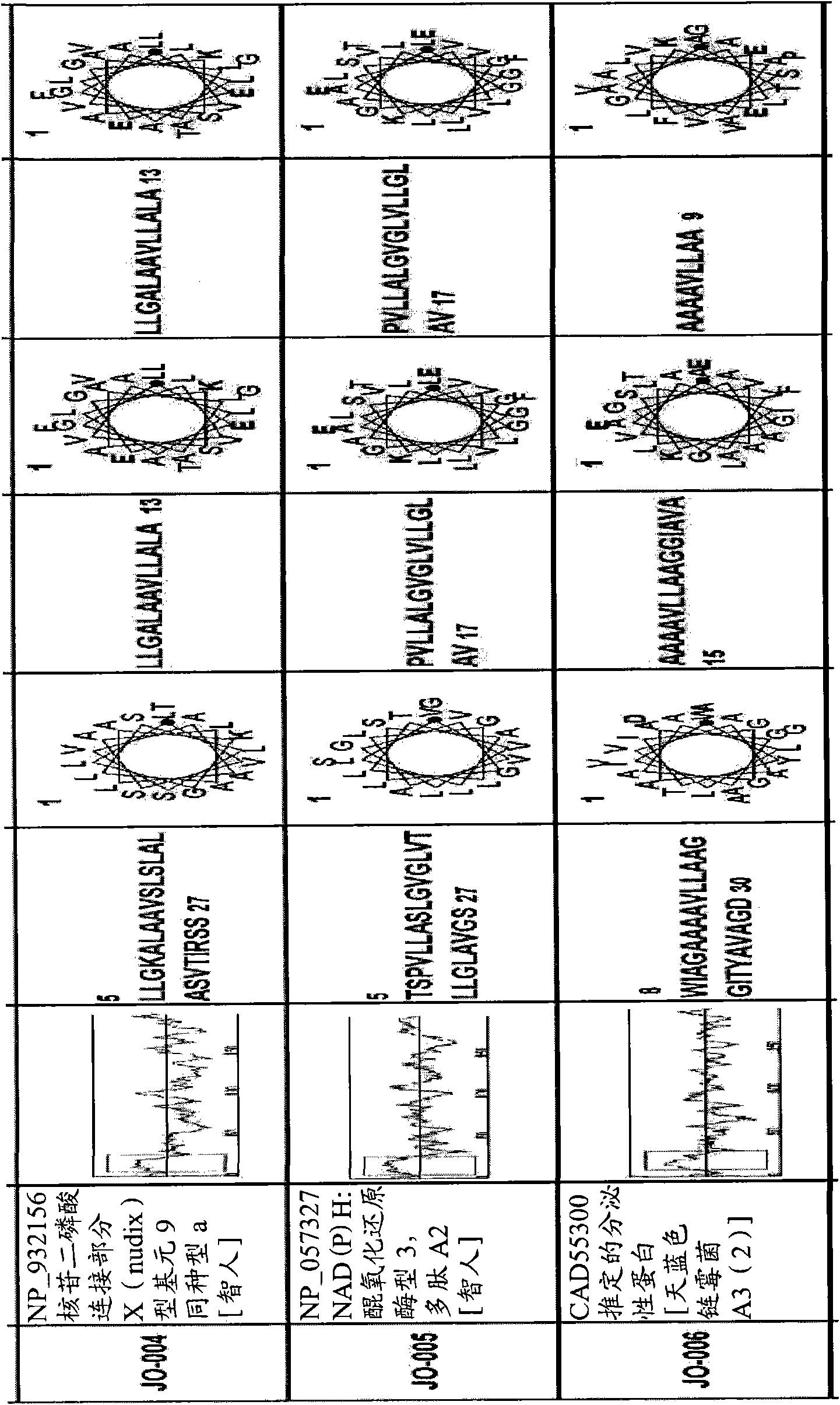
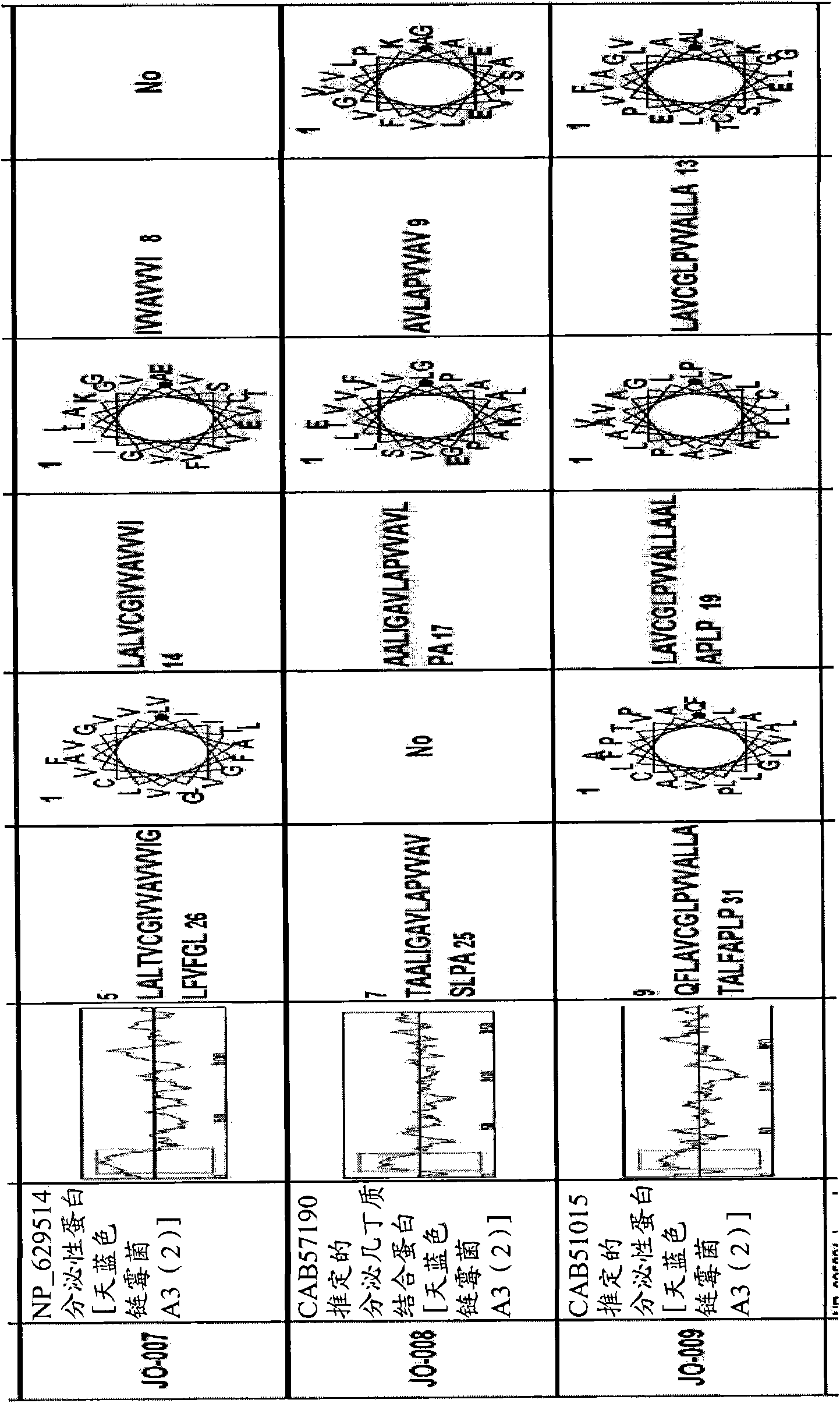
[0128] Example 1 -Recognition of new macromolecule transduction domain peptides
[0129] In order to identify new macromolecular transduction domain (MTD) candidate peptides that can potentially penetrate through the plasma membrane of living cells, several keywords are used, including "hydrophobic region of signal sequence", "hydrophobic region of signal sequence", and "secreted protein". "Signal sequence", "Hydrophobic signal sequence" and "Hydrophobic region of secreted protein" selected secreted proteins with signal sequence-like domains from the PubMed Entrez protein database. As a result, more than 1,500 secreted proteins with signal sequence-like domains were selected.
[0130] All selected secreted proteins with signal sequence-like domains were subjected to hydrophobicity analysis to determine whether they contained a single hydrophobic region at their N-terminus. Subsequently, computer-assisted analysis of chromosome and proteome information, namely the SOSUI system (a...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2 -Expression of recombinant protein fused to MTD
[0135] After confirming the feasibility of the MTD identified in Example 1 above entering cells, enhanced (type) green fluorescent protein (EGFP) was used as the full-length protein carrier molecule. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein cloned from jellyfish (Aquorea Victoria). GFP is one of the most widely used reporter proteins and produces green light when irradiated with blue or UV light (Inouye et al., FEBS Letters 351(2): 211-14 (1994)). In one embodiment of the present invention, the commercially available GFP expression vector pEGFP-C1 (Clontech) is used. The EGFP protein encoded by pEGFP-C1 is a mutant of wild-type GFP, which has been modified to produce stronger green light. In addition, when a foreign gene is inserted into multiple cloning sites of the pEGFP-C1 vector, the inserted foreign gene is expressed in the form of a recombinant protein together with EGFP.
[0136] In order to construct ...
Embodiment 3
[0153] Example 3 -Inducible expression and purification of recombinant protein fused to MTD
[0154] In order to express the cell-permeable recombinant protein fused to MTD prepared as described in Example 2 above, in BL21(DE3), BL21-Gold(DE3), BL21-CodonPlus(DE3) and BL21-GoldpLysS(DE3) strains, respectively Transfection of an expression vector containing His-MTD-EGFP recombinant protein. The EGFP expression vector containing kFGF4-derived MTD (SEQ ID NO: 387) was used as a positive control, and the EGFP expression vector fused to a non-functional missense peptide (SEQ ID NO: 389) was used as a negative control.
[0155] After transfection, the cells were grown in LB medium containing kanamycin (30μg / mL) at 37°C with vigorous shaking until the optical density was 600 (OD 600 ) Reaches between 0.4 and 0.6. Then, IPTG (isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside) was added to the final concentration of 0.6 mM to induce the expression of His-MTD-EGFP recombinant protein. Protein induction lasted...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com