System for detecting microbial interface adhesion based on surface plasmon imaging and method
A surface plasmon, detection system technology, applied in measurement devices, material analysis by optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of signal interference, inability to truly reflect the bacterial adhesion process, and lack of spatial resolution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. A system for detecting microbial interface adhesion based on surface plasmon imaging
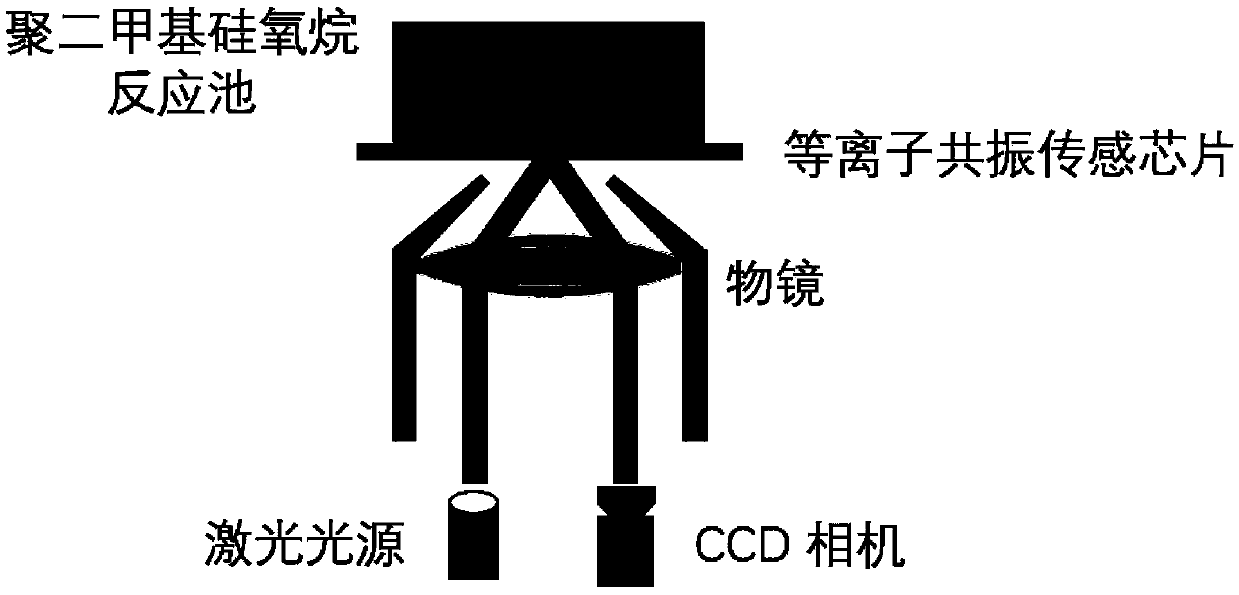
[0036] Such as figure 1As shown, the detection system includes a surface plasmon resonance microscopic imaging system provided with a plasmon resonance sensor chip and a self-assembled monolayer, a polydimethylsiloxane reaction chip set on the plasmon resonance sensor chip pool.
[0037] Wherein the surface plasmon resonance microscopic imaging system includes a laser generator, an incident angle adjustment component, an optical microscopic magnifying objective lens, a plasmon resonance sensor chip, and an image sensor arranged sequentially along the optical path.
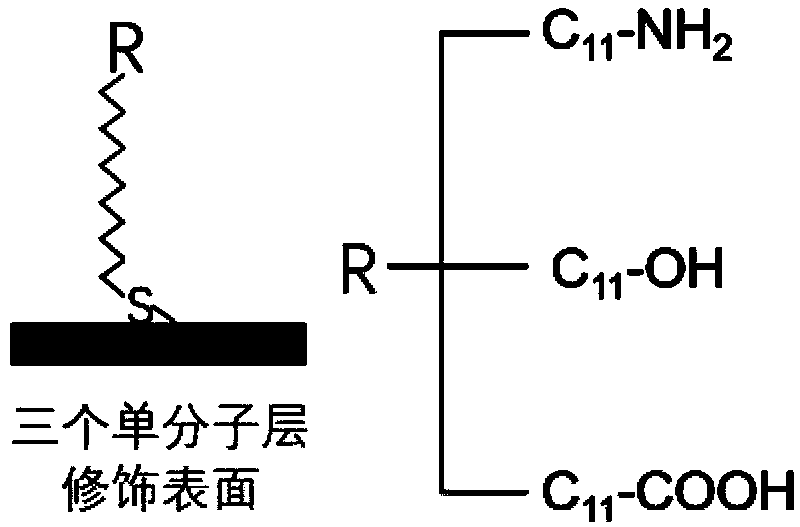
[0038] The plasmon resonance sensor chip is composed of a base material, a chromium layer, and a gold layer arranged in sequence. The specific preparation method is to first coat the upper surface of the glass substrate with a 2nm chromium layer, and then coat the upper surface of the chromium layer with a 48nm...
Embodiment 2
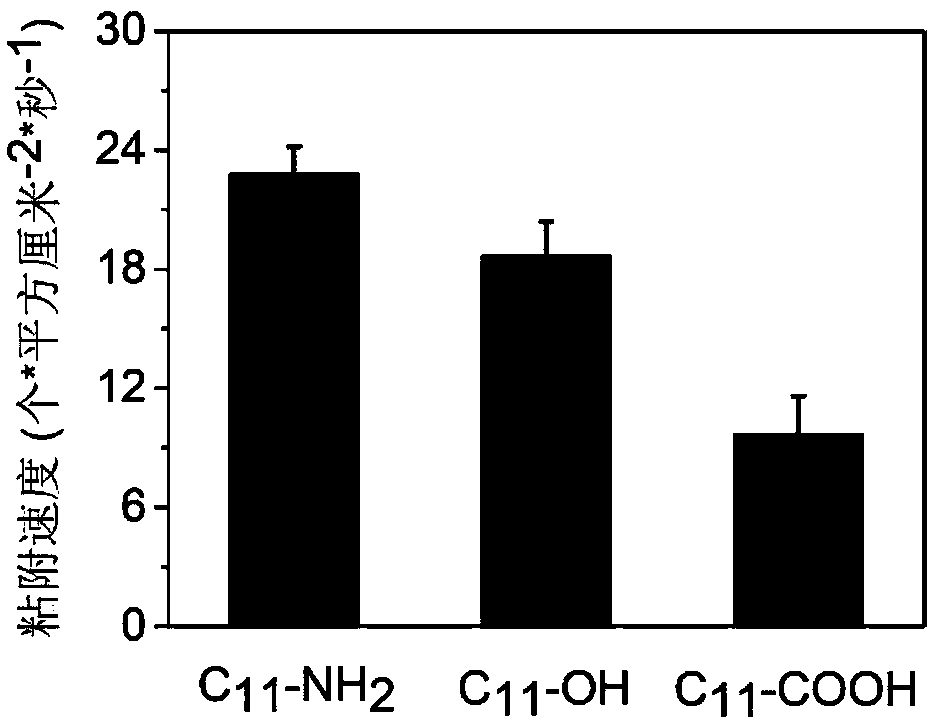
[0043] Embodiment 2, the detection of the adhesion kinetics of escherichia coli
[0044] Step 1, inoculate a single colony of Escherichia coli on the solid medium into 50 mL of LB medium, and cultivate for 12 hours to reach the plateau stage. Then the LB bacterial liquid was centrifuged at 6000 g for 5 min, and the supernatant was filtered off. Then add 5.7mM potassium chloride solution to the centrifuge tube to resuspend the bacteria, centrifuge the bacteria solution at the same speed and time, filter the supernatant again, repeat the above operation two to three times to wash away the LB medium. Finally, continue to add 5.7mM potassium chloride solution until the bacterial solution OD600=0.2, and set aside.
[0045] Step 2: Add 500 μL of the 5.7mM potassium chloride bacterial solution described in step 1 to the PDMS reaction cell on the plasmon resonance sensor chip, turn on the laser generator, SPR microscope, and image sensor respectively, adjust the laser intensity to 11...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com