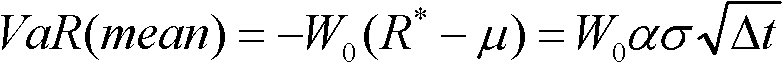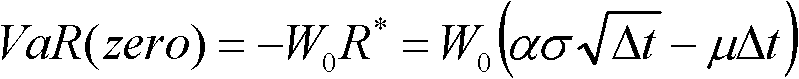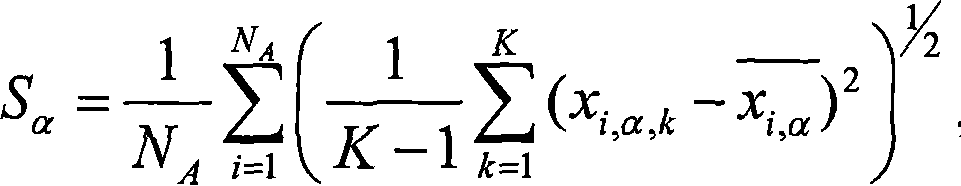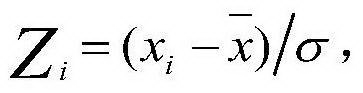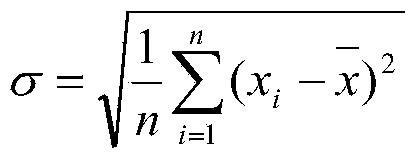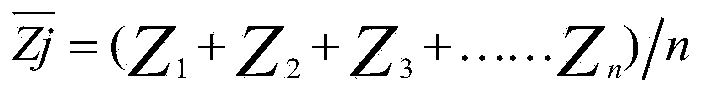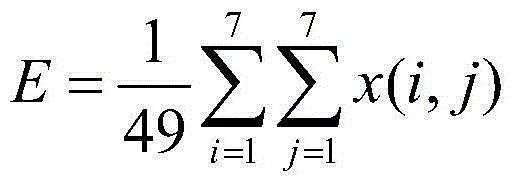Patents
Literature
60 results about "Geometric standard deviation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory and statistics, the geometric standard deviation (GSD) describes how spread out are a set of numbers whose preferred average is the geometric mean. For such data, it may be preferred to the more usual standard deviation. Note that unlike the usual arithmetic standard deviation, the geometric standard deviation is a multiplicative factor, and thus is dimensionless, rather than having the same dimension as the input values. Thus, the geometric standard deviation may be more appropriately called geometric SD factor . When using geometric SD factor in conjunction with geometric mean, it should be described as "the range from (the geometric mean divided by the geometric SD factor) to (the geometric mean multiplied by the geometric SD factor), and one cannot add/subtract "geometric SD factor" to/from geometric mean .
Processes for forming nanoparticles in a flame spray system
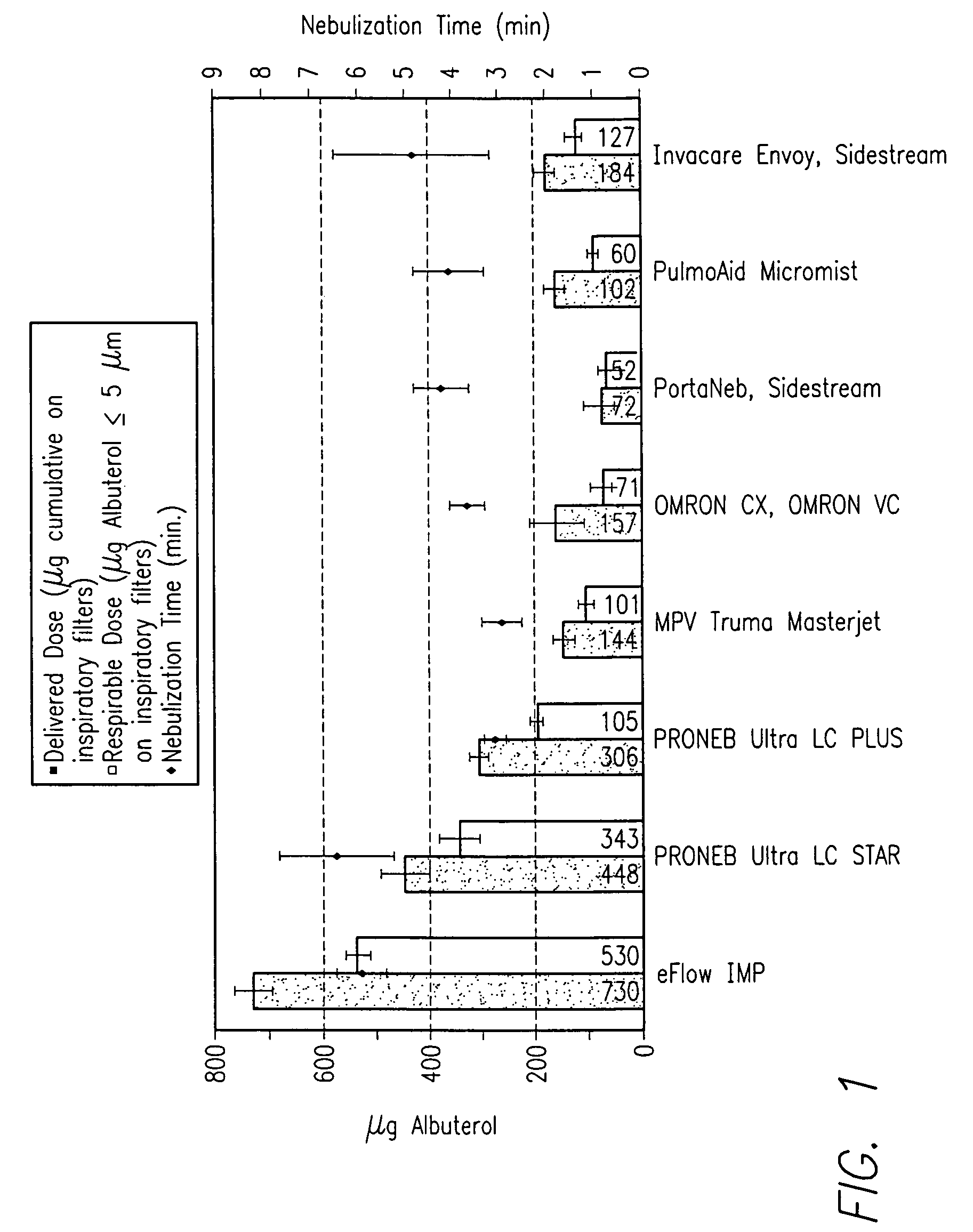
In one aspect, the process includes providing a precursor medium comprising a liquid vehicle and a precursor to a component, and flame spraying the precursor medium under conditions effective to form a population of nanoparticles, wherein the nanoparticles include the component. The population of nanoparticles, as formed, comprises less than about 5 percent by volume particles having a particle size greater than 1.0 μm. A size distribution of the population of nanoparticles may have a d50 value less than about 500 nm, and it may be unimodal. The size distribution may have a geometric standard deviation of less than about 2. The process may occur continuously for at least four hours or more. Greater than about 90 percent by weight of the precursor to the component in the precursor medium may be converted to the component in the nanoparticles. The process typically occurs in an enclosed flame spray reactor.
Owner:CABOT CORP
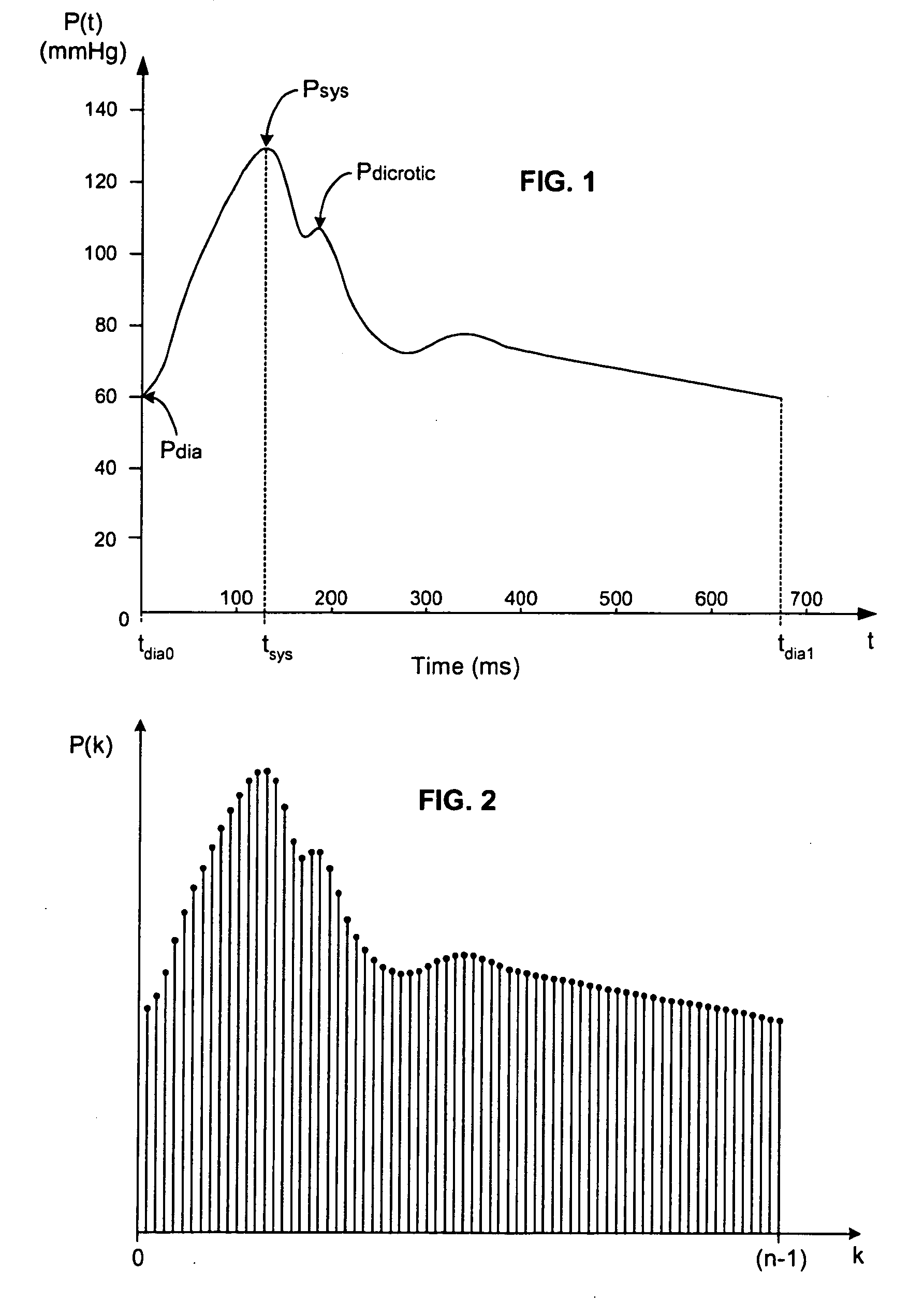
Real-time measurement of ventricular stroke volume variations by continuous arterial pulse contour analysis
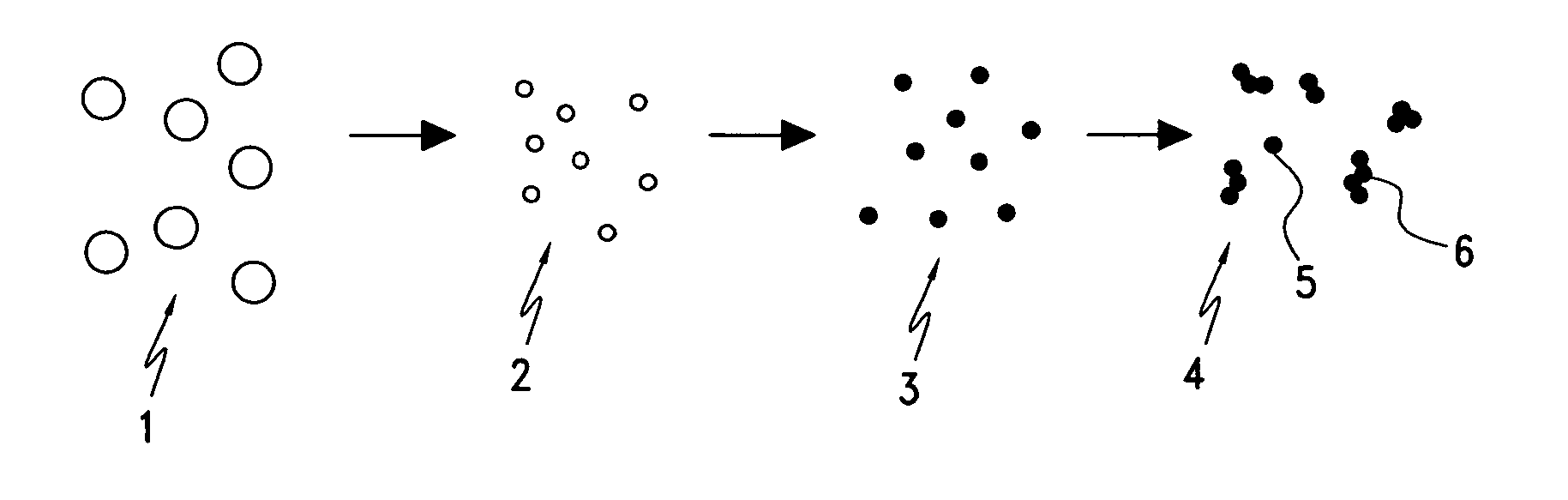
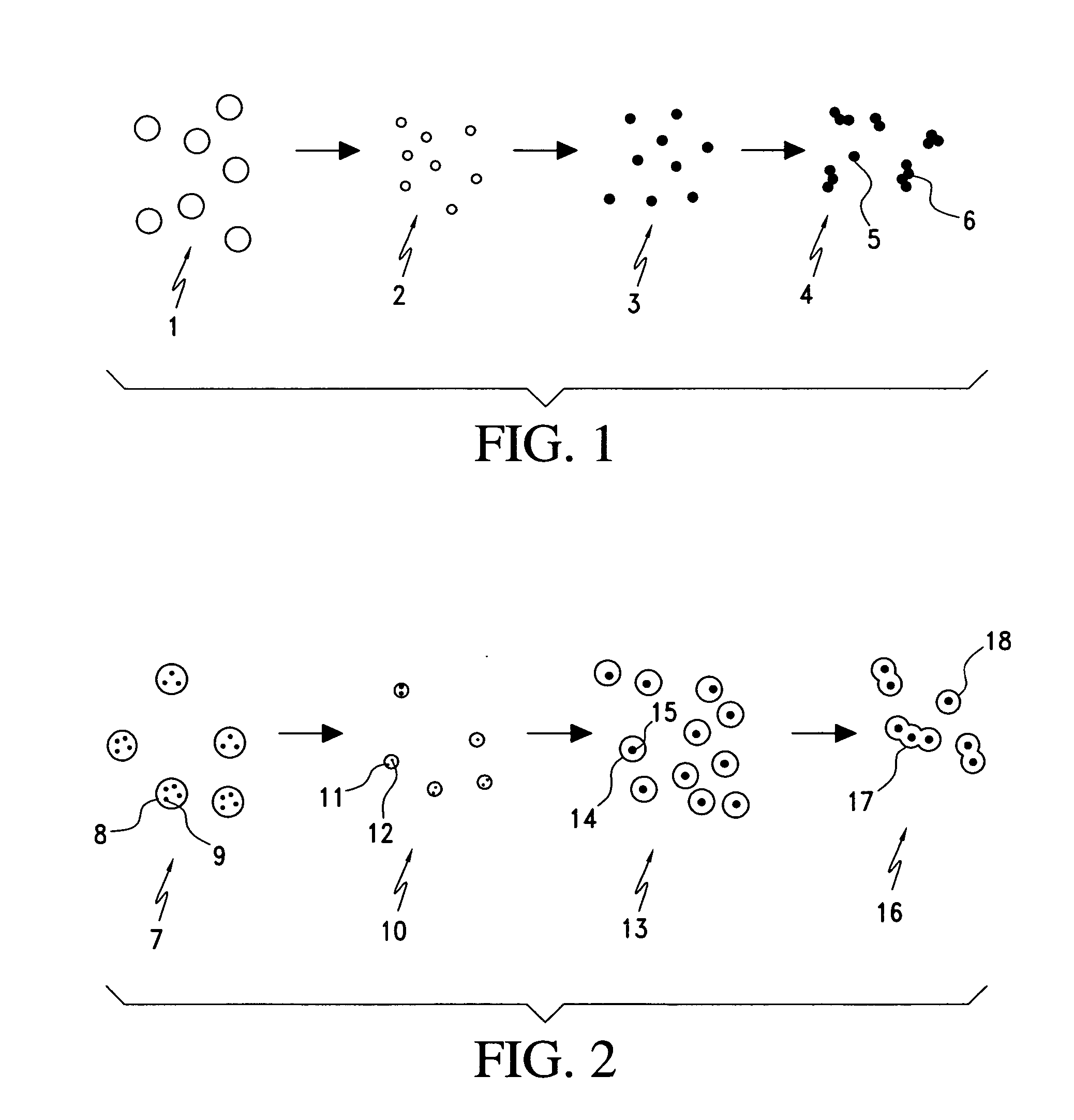
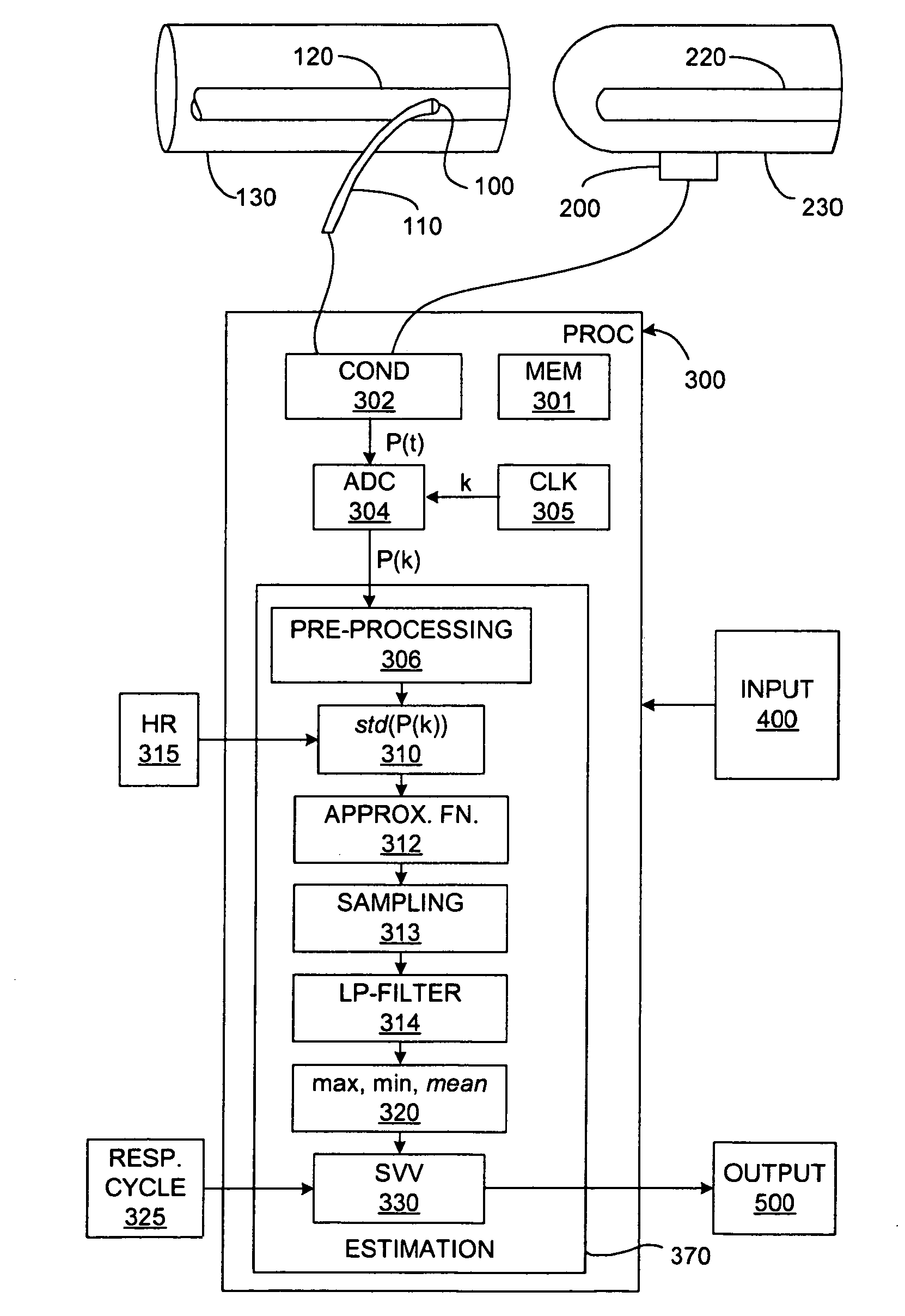
Ventricular stroke volume variation (SVV) is estimated as a function of the standard deviation of arterial blood pressure value measured over each of at least two cardiac cycles, preferably over each of the cardiac cycles in a computation interval covering a full respiratory cycle. In one embodiment, maximum and minimum standard deviation values are determined over the computation interval. SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the difference between the maximum and minimum standard deviation values and the mean of the standard deviation values. In another embodiment, SVV is then estimated proportional to the ratio of the standard deviation of the standard deviation values and the mean standard deviation over the entire computation interval. A pre-processing arrangement for improving reliability of estimates of more general cardiac or hemodynamic parameters is also disclosed and involves smoothing with an approximating function, and sampling and low-pass filtering at an adjustable rate.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
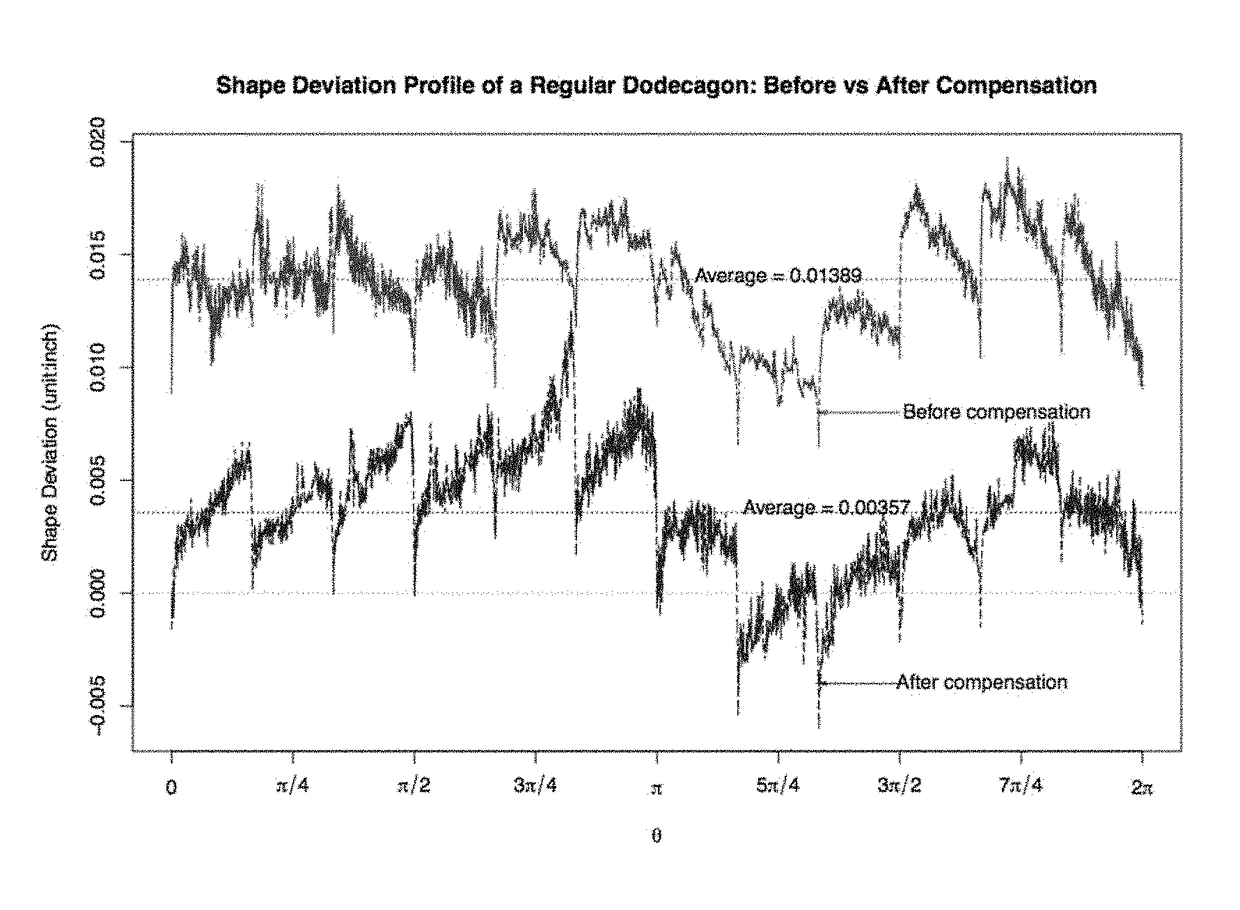
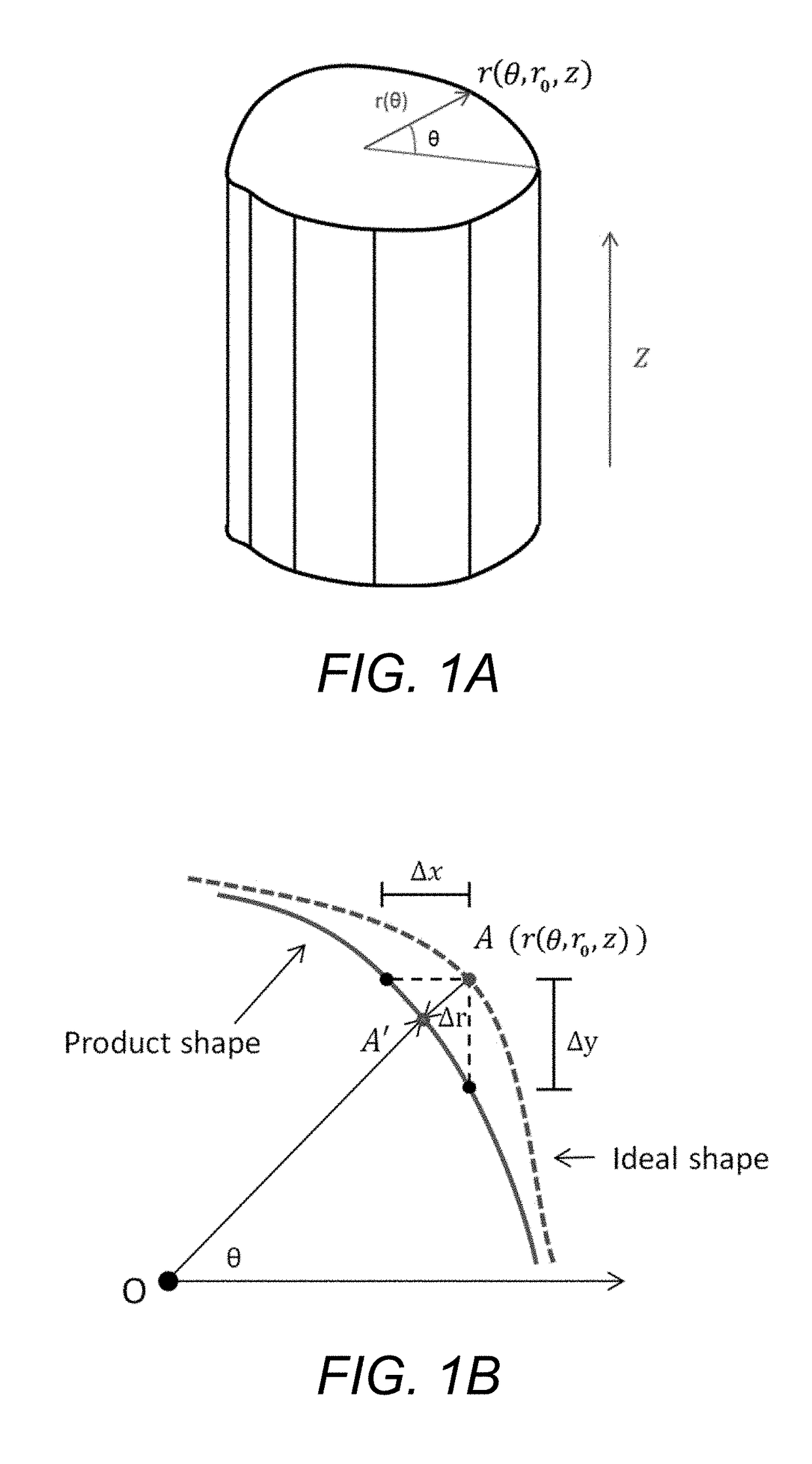
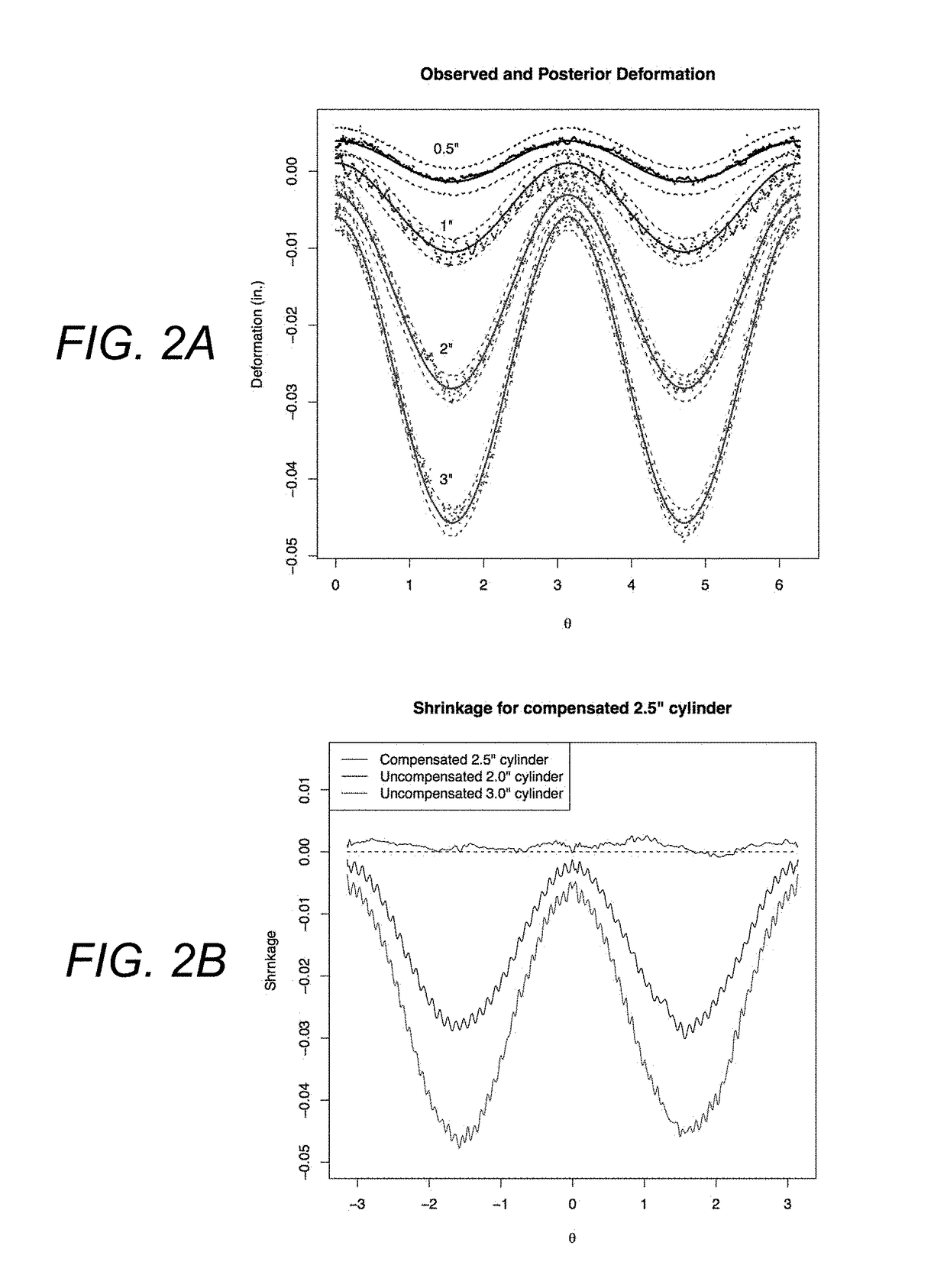
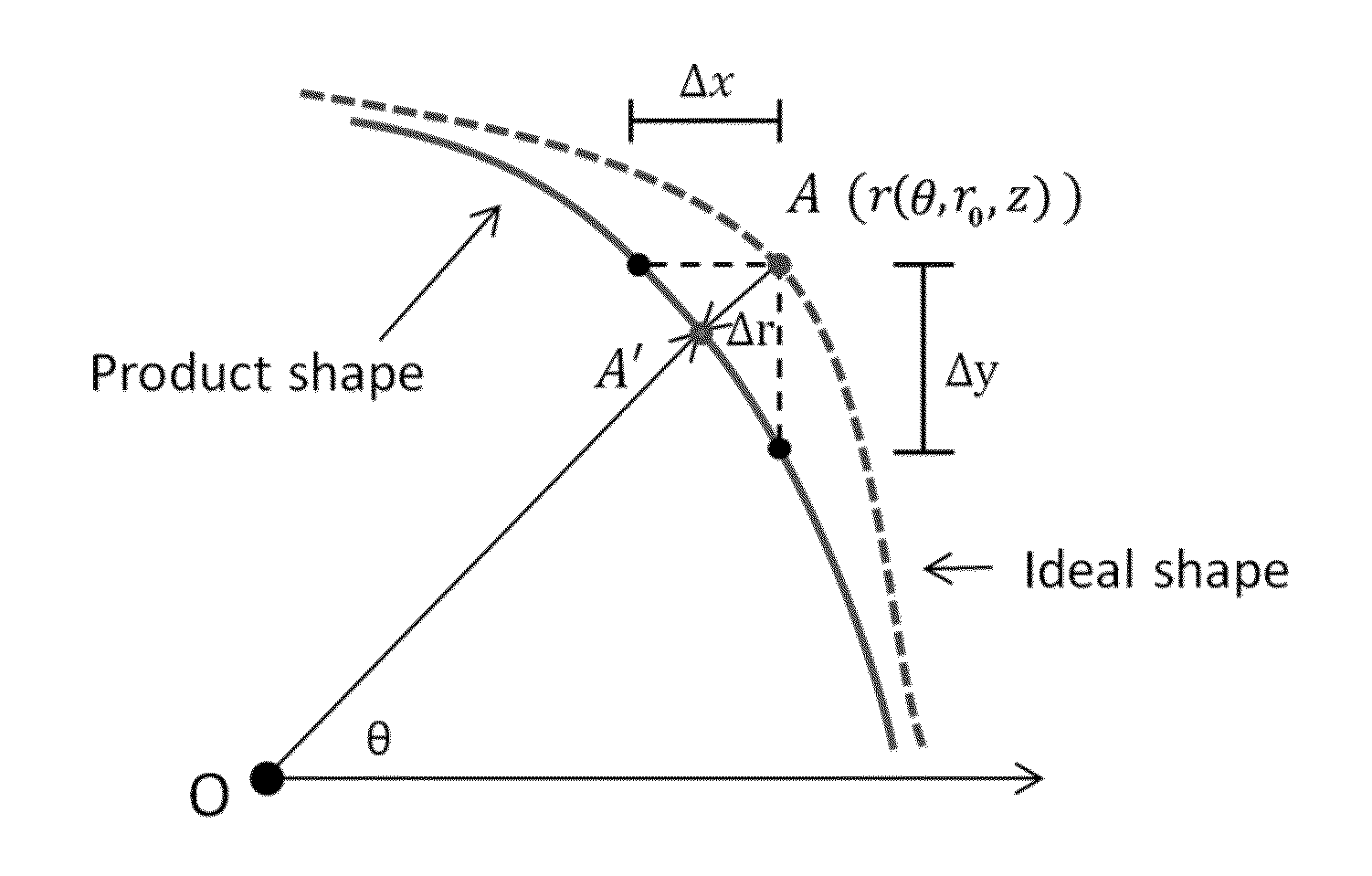
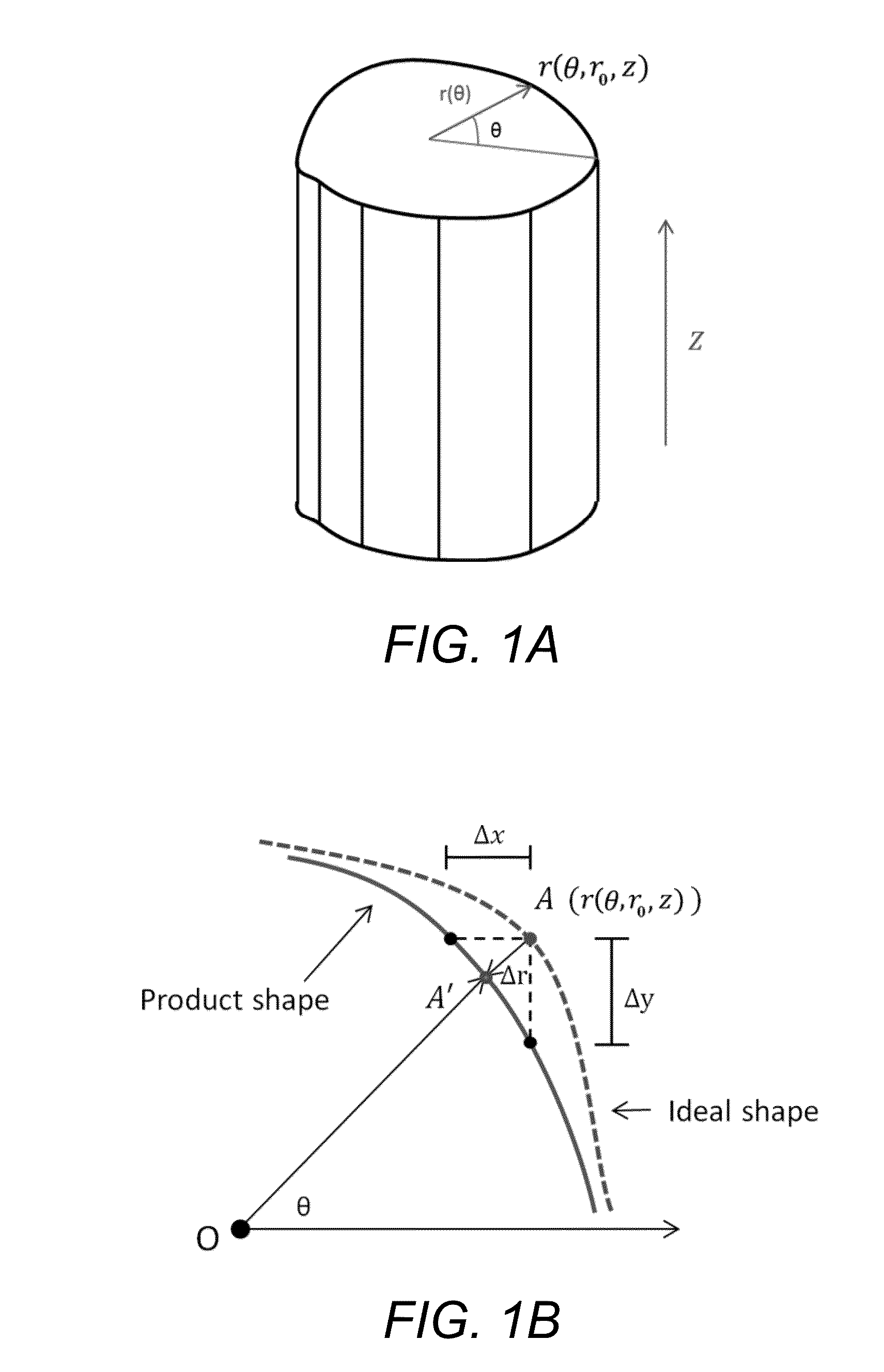
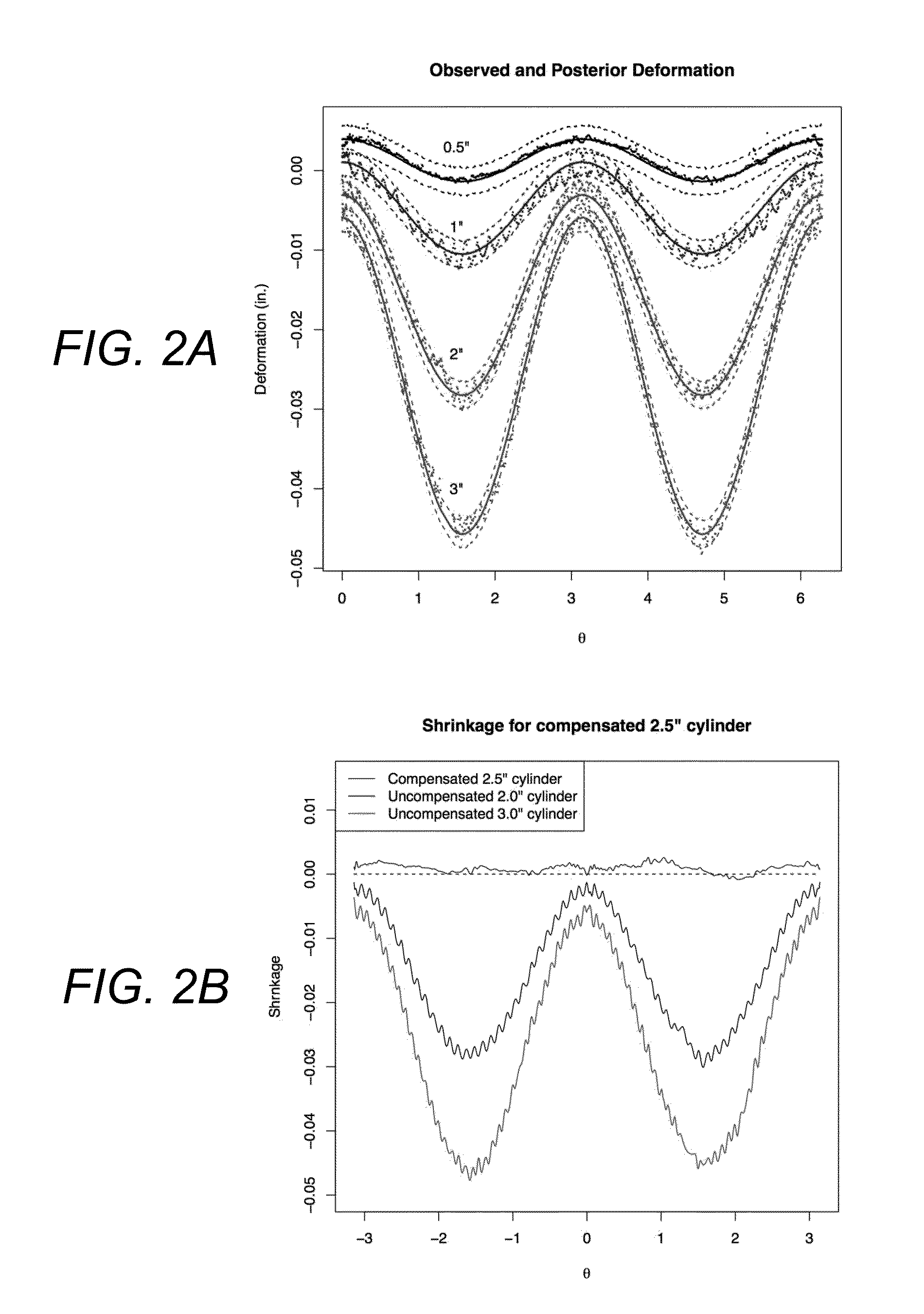
Statistical predictive modeling and compensation of geometric deviations of 3D printed products
ActiveUS9827717B2Accurate shapeEasy to adjust3D object support structuresManufacturing data aquisition/processingStatistical shape modelingPredictive modelling
A non-transitory, tangible, computer-readable storage media may contain a program of instructions that causes a computer system having a processor running the program of instructions to: receive design information indicative of the design of a three-dimensional object to be printed by a three-dimensional printer; receive test product deformation information indicative of deformation in the profiles of no more than five, three-dimensional test products that have a circular or polygonal cross section that were made by the three-dimensional printer; generate polygon product deformation information indicative of a predicted deformation of a polygon shape that the three-dimensional printer will print and that has a number of sides and a number of sizes that are both different from each of the number of sides and number of sizes that the no more than five, three-dimensional test products have; and generate adjustment information indicative of an adjustment needed to print a desired profile of the polygon shape that the three-dimensional printer will print to make the printed shape accurate.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
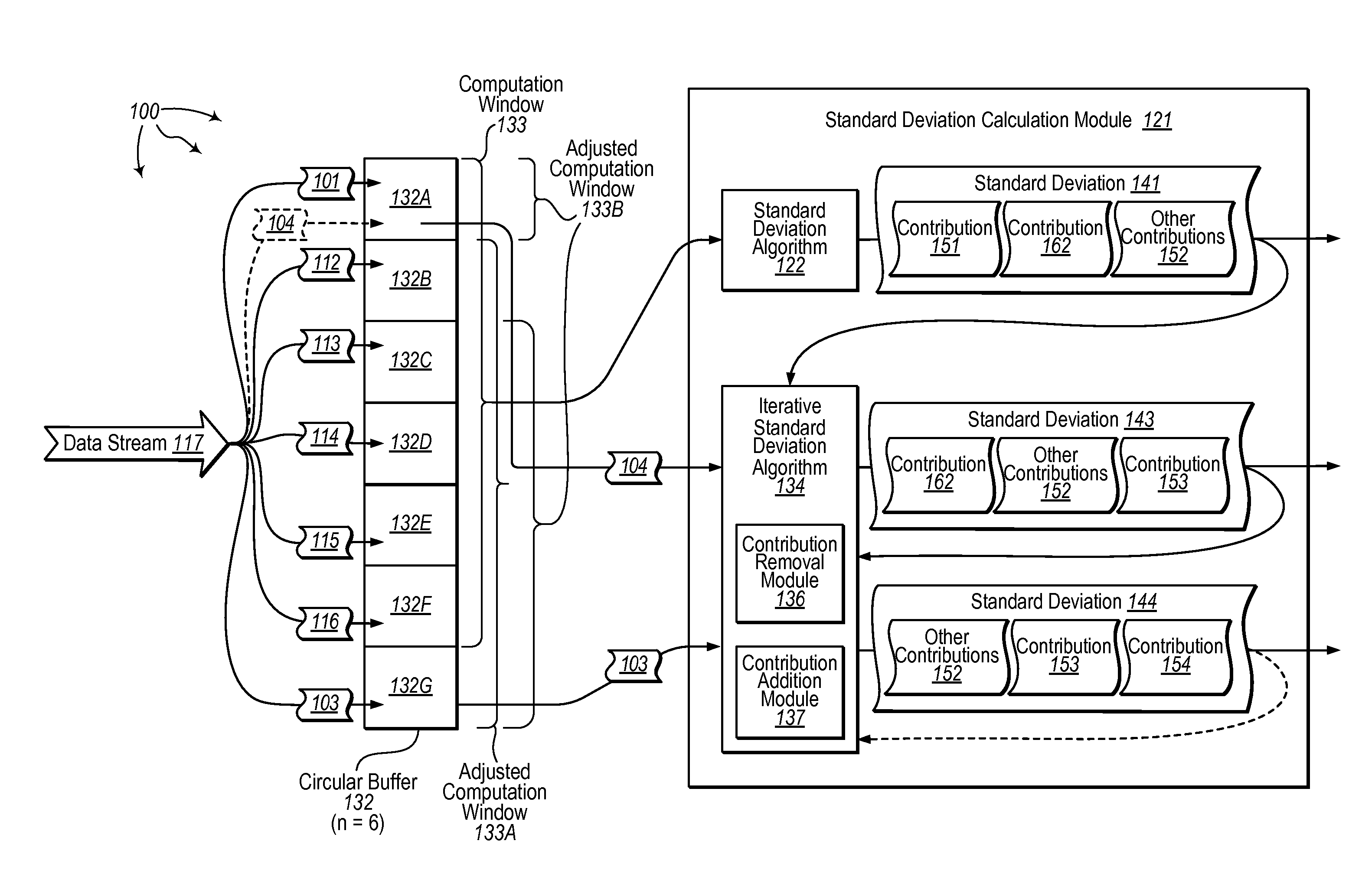
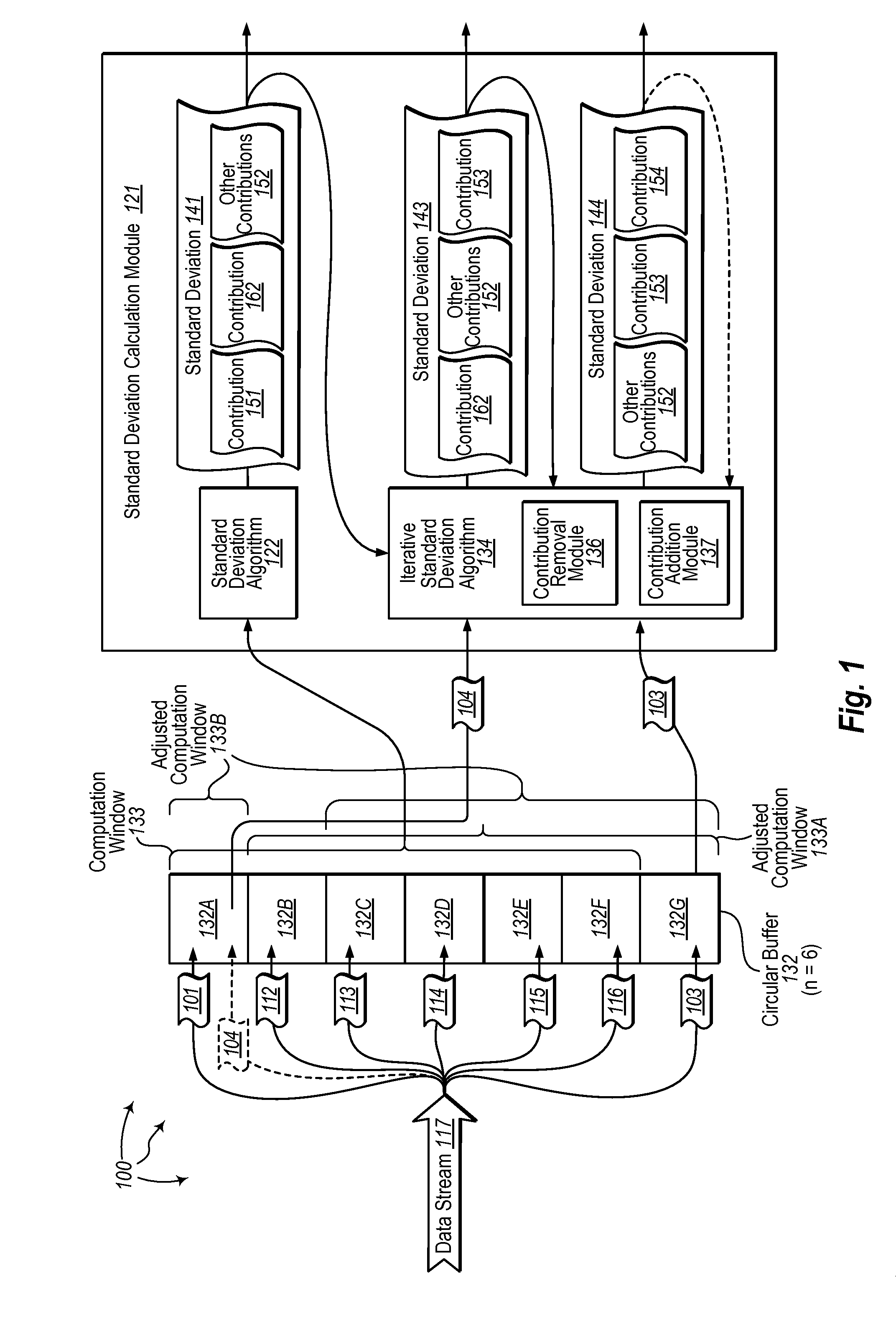
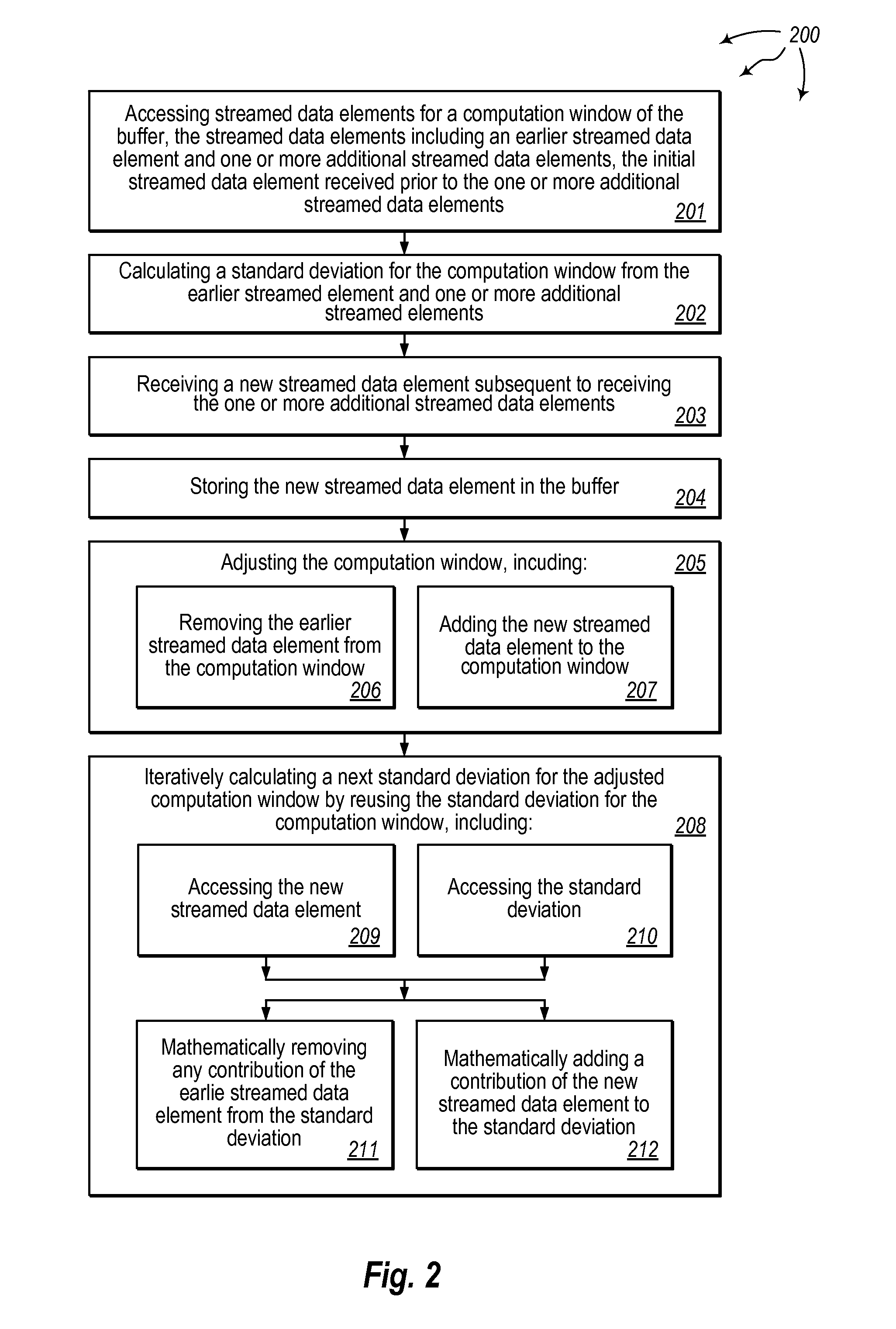
Iteratively calculating standard deviation for streamed data
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for iteratively calculating standard deviation for streamed data. Embodiments of the invention include iteratively calculating standard deviation in a current computation window based on the standard deviation calculation for a previous computation window. Iteratively calculating standard deviation avoids visiting all previous input and performing redundant computations thereby increasing calculation efficiency. In general, streaming data is added to a buffer of size n until the buffer is filled up. Once the buffer is filled, a sum and standard deviation are calculated for the first n data points. As new data elements are received, a new sum is calculated by reusing the prior sum and a new standard deviation is calculated by reusing the prior standard deviation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Statistical predictive modeling and compensation of geometric deviations of 3D printed products
ActiveUS20160046076A1Accurate shapeEasy to adjustProgramme controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusPredictive modellingComputer graphics (images)
A non-transitory, tangible, computer-readable storage media may contain a program of instructions that causes a computer system having a processor running the program of instructions to: receive design information indicative of the design of a three-dimensional object to be printed by a three-dimensional printer; receive test product deformation information indicative of deformation in the profiles of no more than five, three-dimensional test products that have a circular or polygonal cross section that were made by the three-dimensional printer; generate polygon product deformation information indicative of a predicted deformation of a polygon shape that the three-dimensional printer will print and that has a number of sides and a number of sizes that are both different from each of the number of sides and number of sizes that the no more than five, three-dimensional test products have; and generate adjustment information indicative of an adjustment needed to print a desired profile of the polygon shape that the three-dimensional printer will print to make the printed shape accurate
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Quasi-monodispersed submicron aerosol generating device using vaporization condensation process
InactiveCN101284220AGood monodispersityMonodisperse and cheapColloidal chemistry detailsMaterial analysisSprayerEngineering
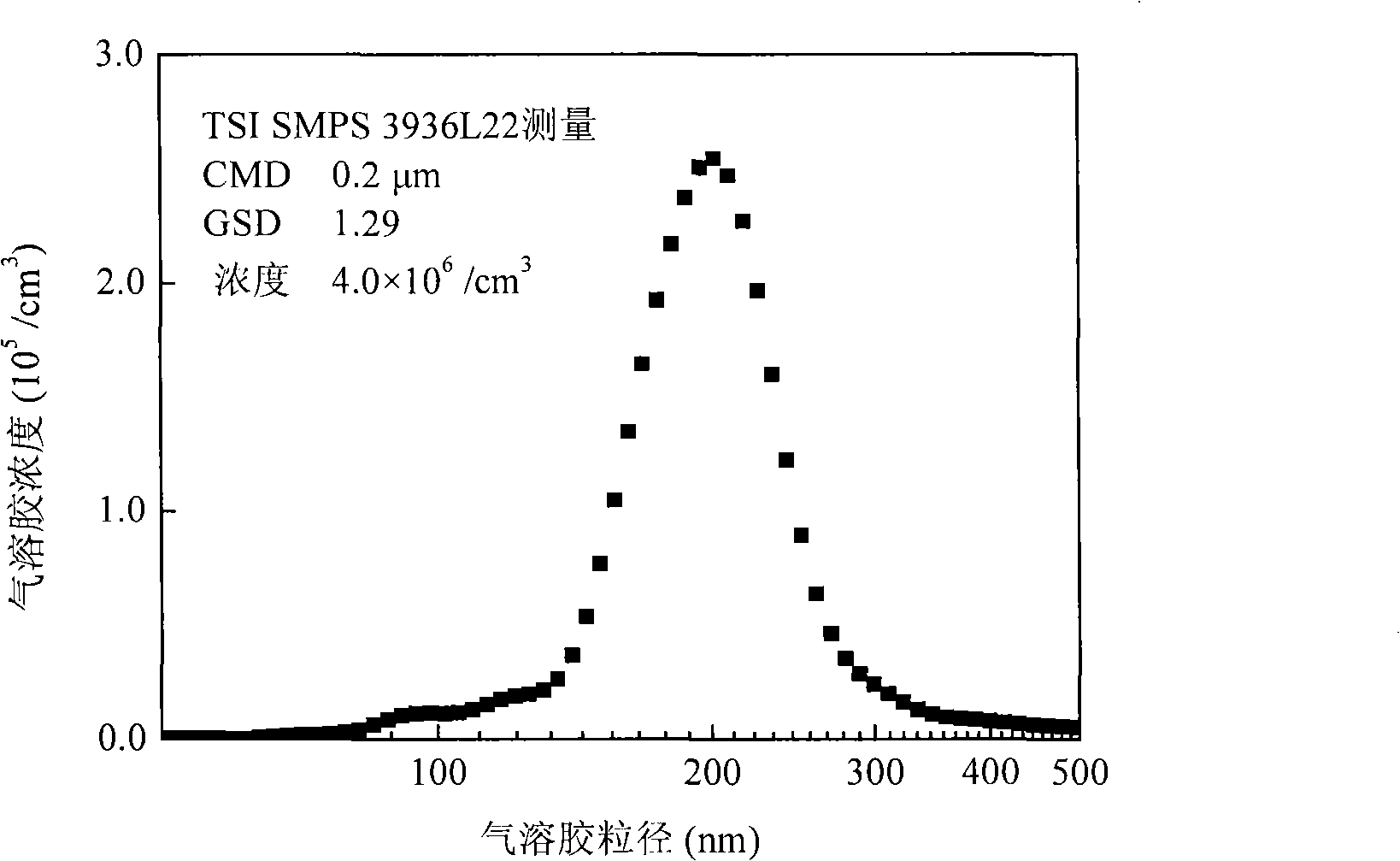
The invention relates to a generating device of quasi-monodispersed submicron aerosol by using an evaporation condensation method. The generating device comprises a high-pressure gas source, a first filter, a sprayer, a diffusion desiccator, a second filter, a saturator, a reheater, a condenser tube, and a first valve as well as a second valve, wherein, the first valve and the second valve are respectively used for adjusting the flow capacity of the second filter and the saturator; the high-pressure gas source adopts a high-pressure air source; the reheater and the condenser tube adopt metallic conduits; a baffle plate is arranged at a jet exit of the sprayer; a screen mesh or a closing ring is arranged at the inlet of the condenser tube. The generating device is convenient and durable, the running cost is low, the median diameter in aerosol generating counting ranges from 0.08 micrometres to 0.5 micrometres, the geometric standard deviation is less than 1.3, the counting concentration ranges from 1*10<4> to 1*10<8> / cm<3>, the stability and the repeatability are good when in generation, and the requirements of various equipment inspections and experimental researches can be satisfied.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
An image processing method and device
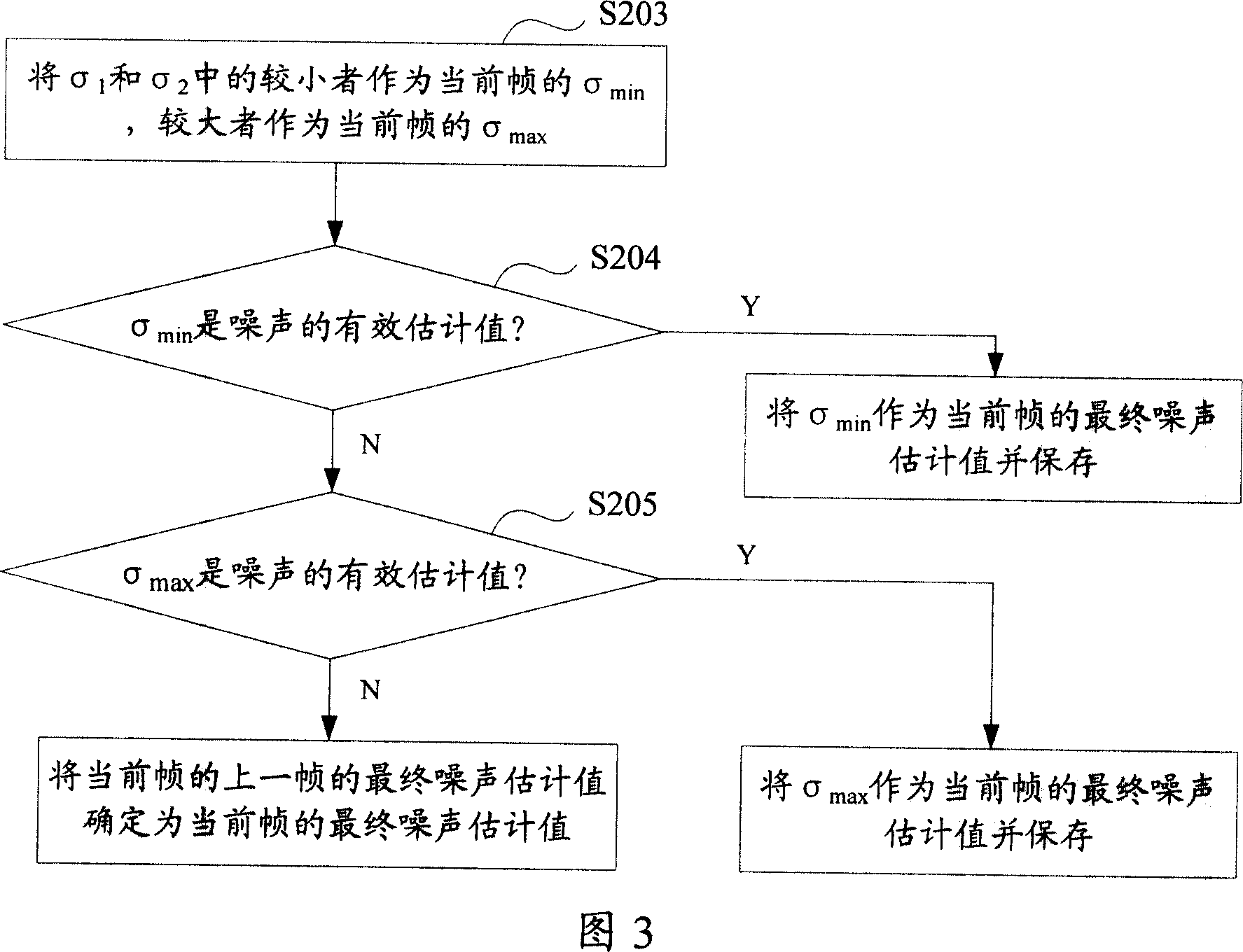
InactiveCN101018290AAccurate noiseImprove image processing capabilitiesTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionImaging processing
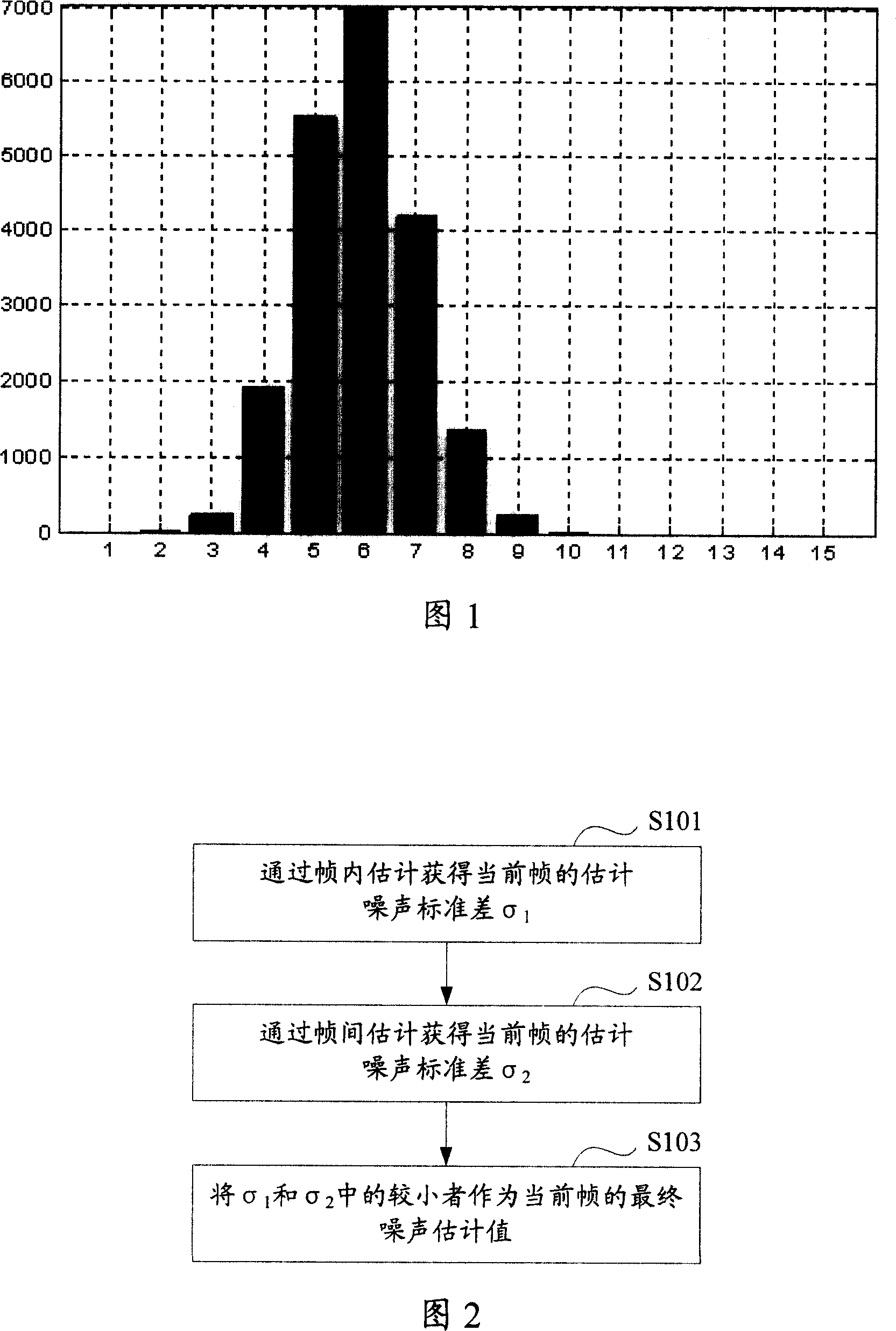
The disclosed image process method for obtaining more accurate noise standard deviation or variance comprises: blocking the image frame to obtain the standard deviation or variance of small block, or, blocking the frame with its neighbor reference frame to obtain standard deviation or variance of every difference block; counting number of the block with same standard deviation or variance, and determining the noise standard deviation or variance according to the standard deviation or variance of block with the greatest number.
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Quantitative trading method and system for financial derivatives
The invention mainly relates to the field of trading of financial derivatives, in particular to a quantitative trading method and system for financial derivatives, wherein the method and system can provide the trading auxiliary information to investors in real time for the investors to determine the trading strategy. The quantitative trading method for financial derivatives is based on a VAR (value at risk) model and calculates the VAR value VARm within the pre-determined probability range according to the risk standard deviation, confidence value and risk position time of the historical trades of the investors, wherein VARm=W0 alpha sigma kt, W0 is initial fund, alpha is normal distribution Z value corresponding to the confidence value, sigma is risk standard deviation, and kt is risk position time parameter; and the trading strategy is determined according to the trading VARm, the accuracy rate of the historical trade of investors, the risk rate of return and the maximum risk bearable to investors.
Owner:曾祥洪
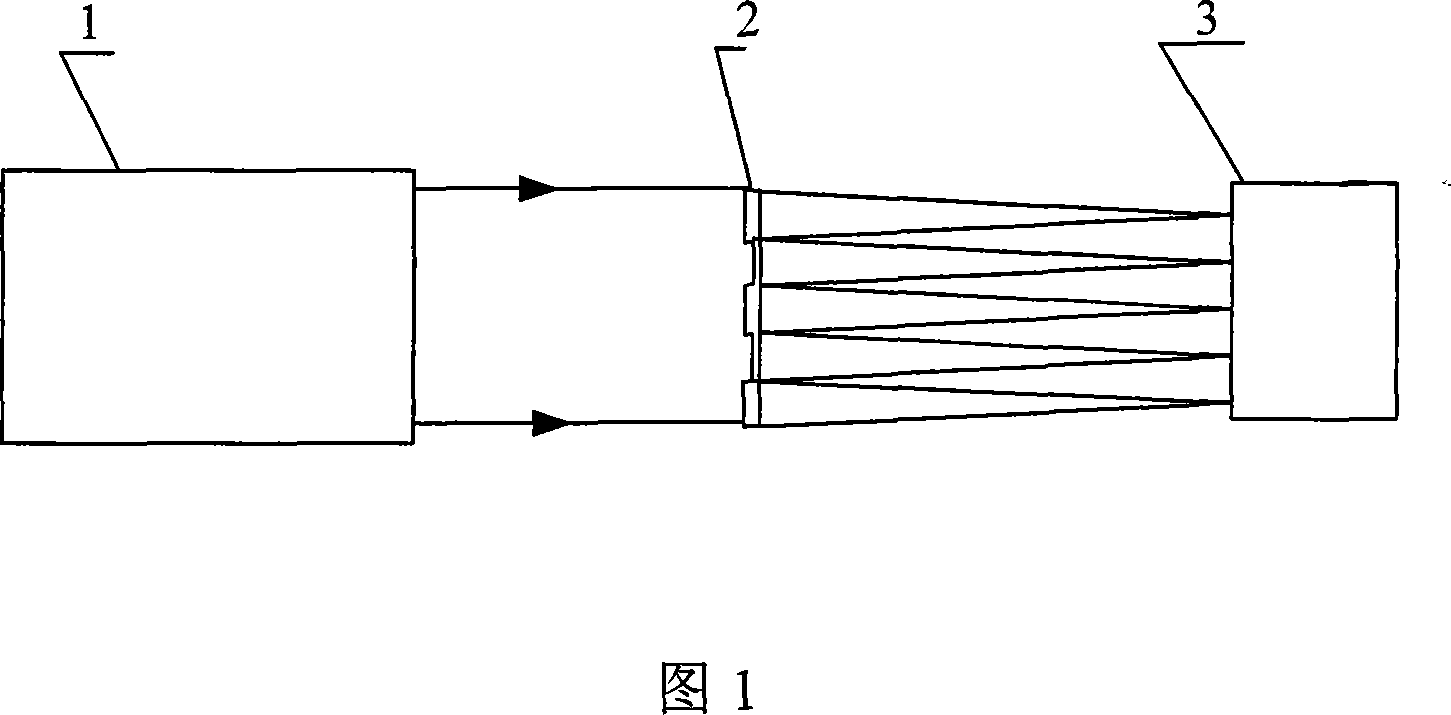
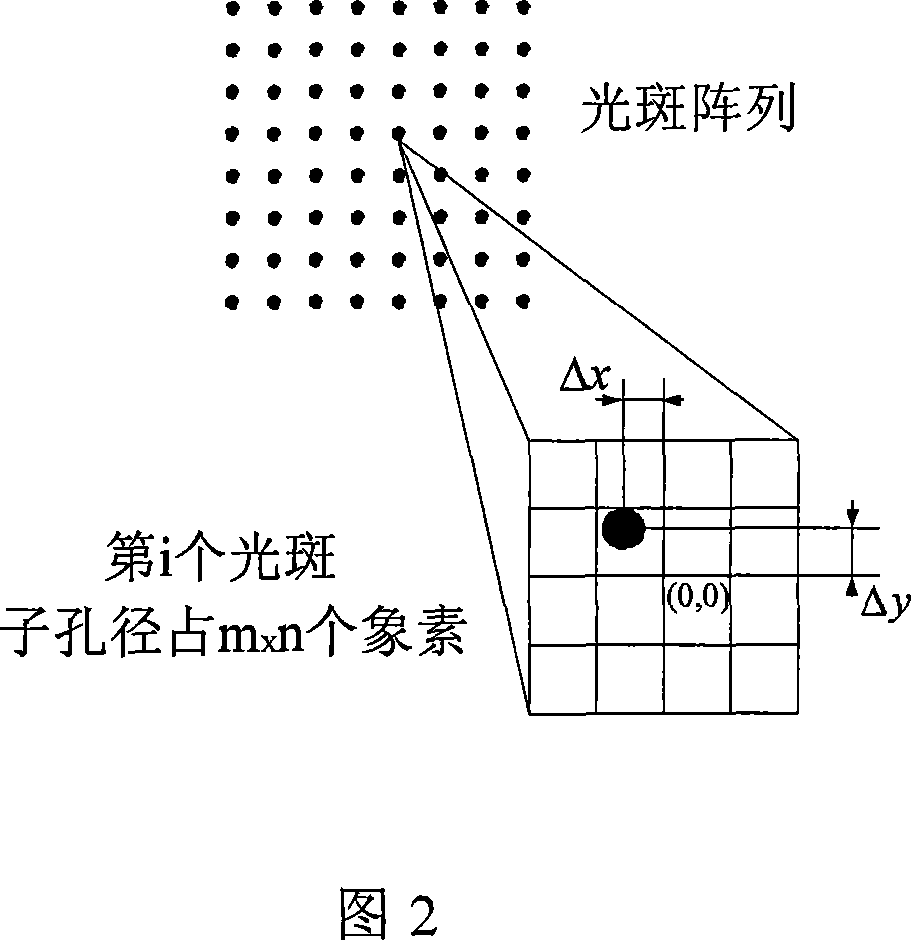
Hartman wavefront sensor mass center measurement precision optimization method
InactiveCN101055223AHigh repeatabilityInhibition effectOptical measurementsTesting optical propertiesWavefront sensorAlgorithm
A method for optimizing centroid measurement precision of Hartmann wavefront sensor includes the steps of: performing threshold processing to pixel data outputted by photoelectric detector; calculating order moment centroid of each subaperture spot using the pixel data of threshold processing, wherein alpha=1, 2, 3......L; calculating repeatedly the order moment centroid of each subaperture spot; calculating the mean value of order moment centroid standard deviation of each subaperture spot; finding out the corresponding minimum order, namely finishing the method for optimizing centroid measurement precision of Hartmann wavefront sensor. Repeatedly calculating alpha order moment centroid of each subaperture spot and obtaining corresponding centroid standard deviation, thereby obtaining the excellent corresponding order which the mean value of all subaperture centroid standard deviation is small, and the filtered high-order centroid algorithm is capable of suppressing more effectively the influence of noise to centroid computational accuracy with the most excellent repeatable accuracy of centroid measurement relative to other each order moment centroid algorithm, thereby improving wavefront reconstruction accuracy.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
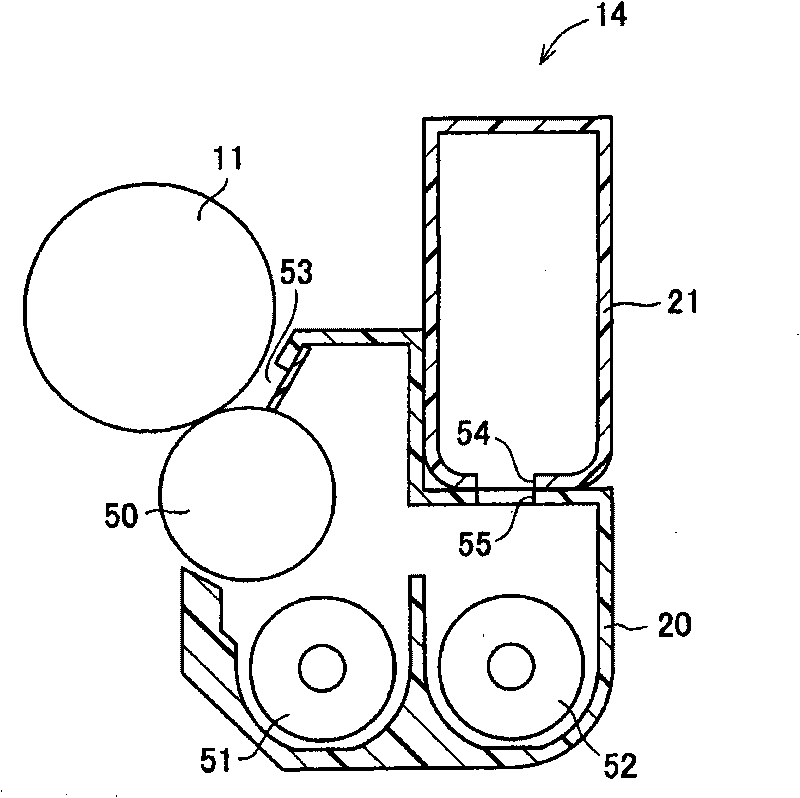
Toner, developer, developing device and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20100104323A1Improve cleanabilityGood fixabilityDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusGeometric standard deviationParticle-size distribution
A toner is provided. The toner includes toner particles, and silica particles and inorganic fine particles that are externally added to the toner particles, the inorganic fine particles having an average primary particle size smaller than that of the silica particles. The toner particles have a shape factor SF-1 of 130 or more and 140 or less, a shape factor SF-2 of 120 or more and 130 or less, and a volume average particle size of 5 μm or more and 8 μm or less. The silica particles have an average primary particle size of 80 nm or more and 150 nm or less, and an amount of water of 1.5% by weight or less. A particle size distribution of the silica particles is a logarithmic normal distribution, and a value of geometric standard deviation σg of the particle size of the silica particles is less than 1.30.
Owner:SHARP KK
Targeted delivery of lidocaine and other local anesthetics and a method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks
An anti-tussive nebulized solution for targeted delivery of lidocaine into conducting and central airways. A method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks or episodes using said lidocaine solution. A nebulized lidocaine solution administered in daily dose from about 10 mg to 80 mg of lidocaine dissolved in a saline and nebulized into an aerosol having a mass median aerodynamic diameter 3 μm to 10 μm and a geometric standard deviation less than 1.7 using an electronic nebulizer.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
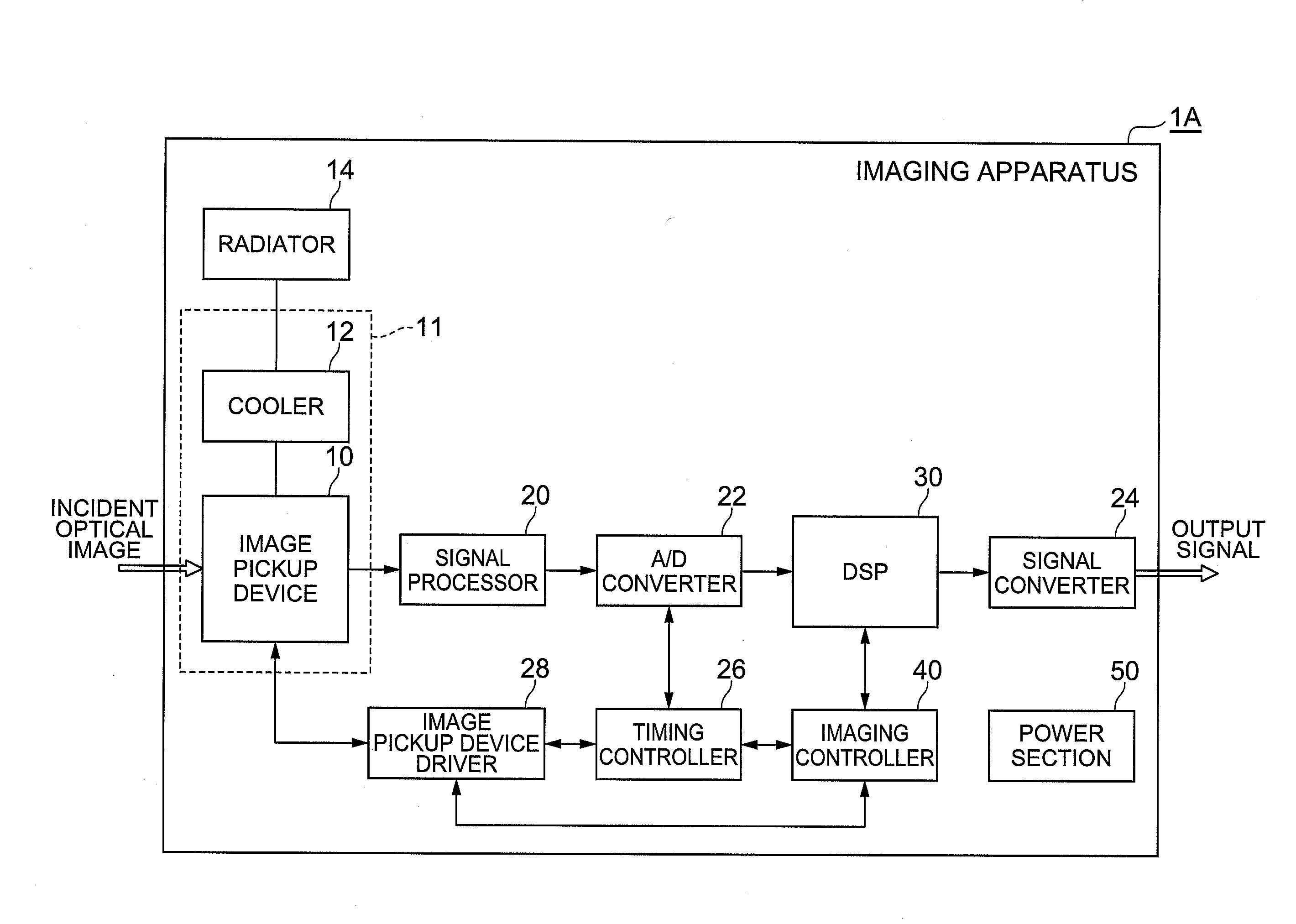
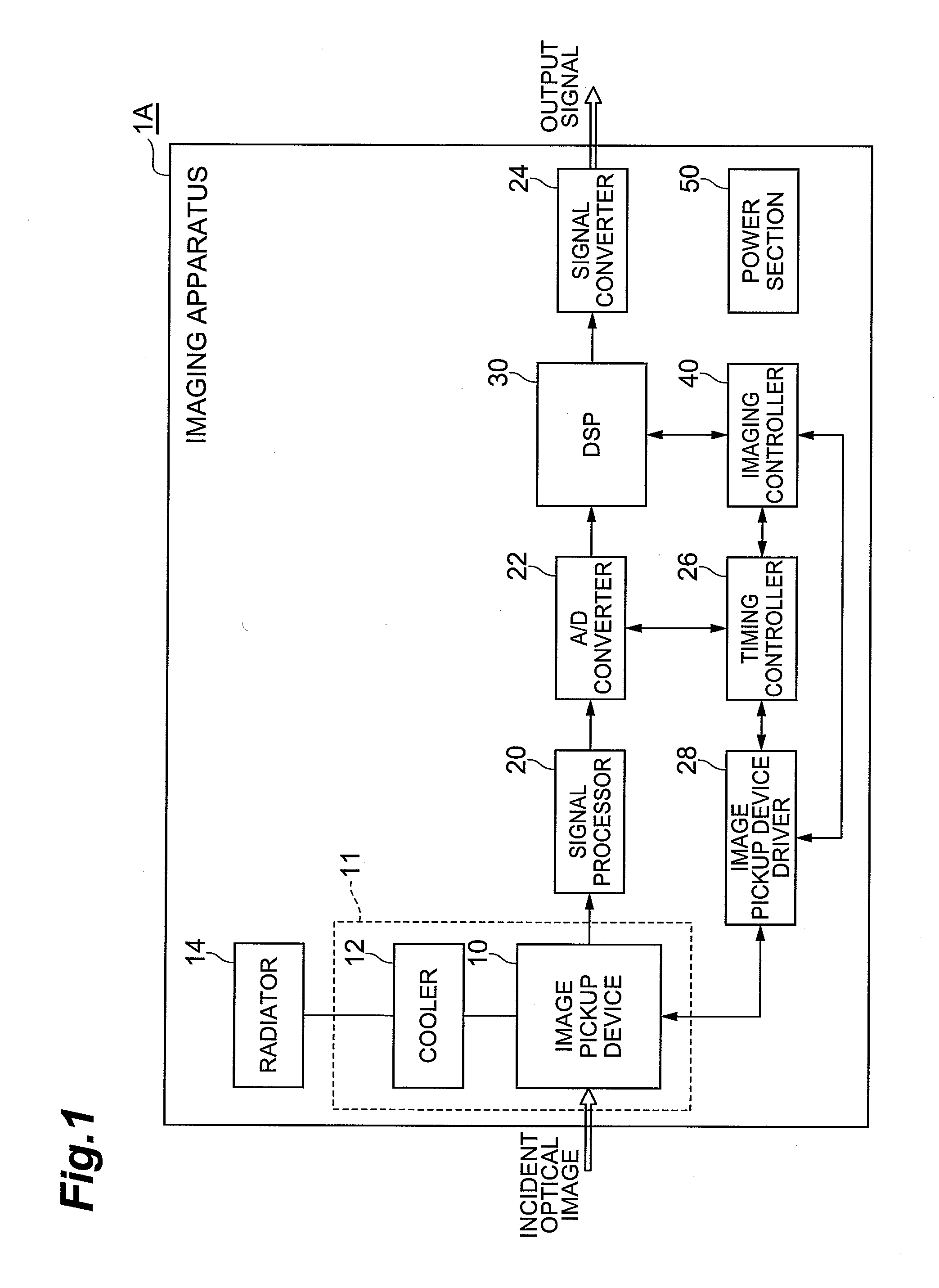
Imaging apparatus and gain adjusting method for the same
InactiveUS20080259197A1Accurately re-adjustedEasy gain adjustmentTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectron multiplierImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus 1A includes an electron multiplying solid-state image pickup device which has an electron multiplier section for multiplying charge signals generated in respective pixels; a multiplication gain setting part 41 for setting a multiplication gain in the electron multiplier section; a standard deviation calculator 34 for calculating a noise standard deviation of a noise image acquired under a predetermined condition by the image pickup device; a reference standard deviation storage 35 storing a reference standard deviation, and a standard deviation comparator 36 for comparing the noise standard deviation and the reference standard deviation and outputting an obtained comparison result. At the time of gain adjustment, the multiplication gain setting part 41 adjusts the multiplication gain based on the comparison result by the standard deviation comparator 36. Thereby, an imaging apparatus which enables the user's side to easily and accurately re-adjust the multiplication gain of charge signals in the electron multiplying solid-state image pickup device, and a gain adjusting method for the same are realized.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Quantitative evaluation method of aquatic plant species for repairing eutrophication water
InactiveCN103833139ASimple processShort cycleWater resource protectionSustainable biological treatmentEcological environmentEutrophication
The invention discloses a quantitative evaluation method of aquatic plant species for repairing eutrophication water. The quantitative evaluation method comprises the following steps: A, index screening, namely screening to-be-invested water physical and chemical indexes according to eutrophication water characteristics; B, field investigation, namely investing rivers or lakes by adopting a conventional method in a representative region range, recording names of all the aquatic plant species in a quadrat, collecting water samples, and determining physical index of water; C, standard non-dimension disposal calculation, namely classifying the aquatic plants into submerged plants, floating-leaved plants and emergent aquatic plants according to ecotypes, and calculating standard non-dimension disposal data of physical and chemical indexes of water to which each species corresponds according to ecotypes; D, weight giving and total standard deviation calculation, namely giving weight to the physical and chemical indexes, and calculating the general average and total standard deviation of the non-dimension disposal data of each species; E, sorting and quantitative evaluation. The quantitative evaluation method is simple and convenient to operate, fast and accurate, meets the wetland rejuvenation of the rivers, lakes and the like and can be used for promoting the high-efficiency restoration of wetland ecological environments and configuration of functional groups.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
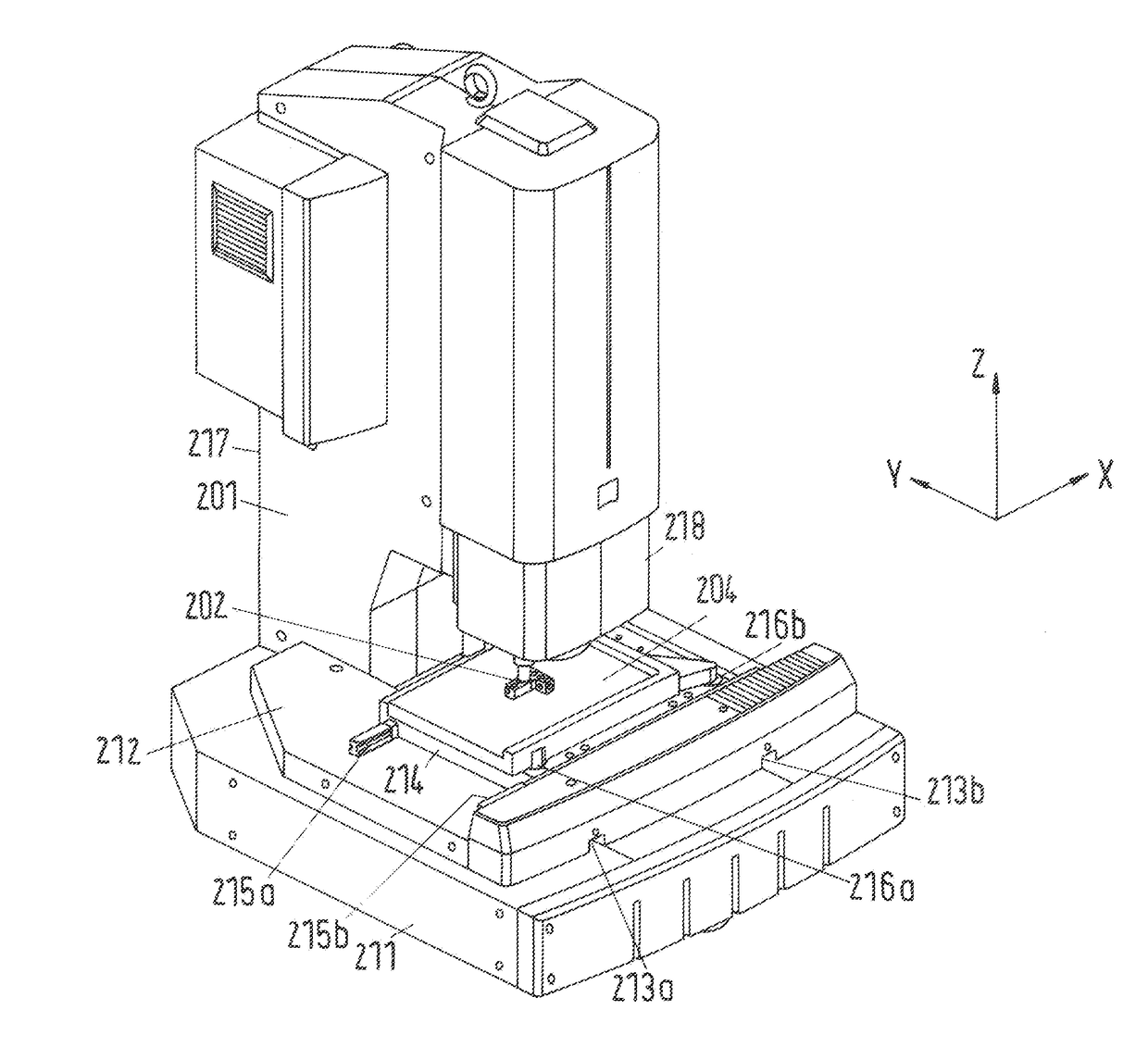
Identification of geometric deviations of a motion guide in a coordinate-measuring machine or in a machine tool
ActiveUS20170241759A1Little expenditure of timeImprove accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlCoordinate-measuring machineMachine tool
The invention relates to a method for identifying geometric deviations of a real motion guide from an ideal motion guide in a coordinate-measuring machine having a sensor for measuring a workpiece, or in a machine tool having a tool for processing a workpiece, wherein the coordinate-measuring machine or the machine tool has a movable part which is guided along the motion guide and by the motion guide.
Owner:CARL ZEISS IND MESSTECHN GMBH
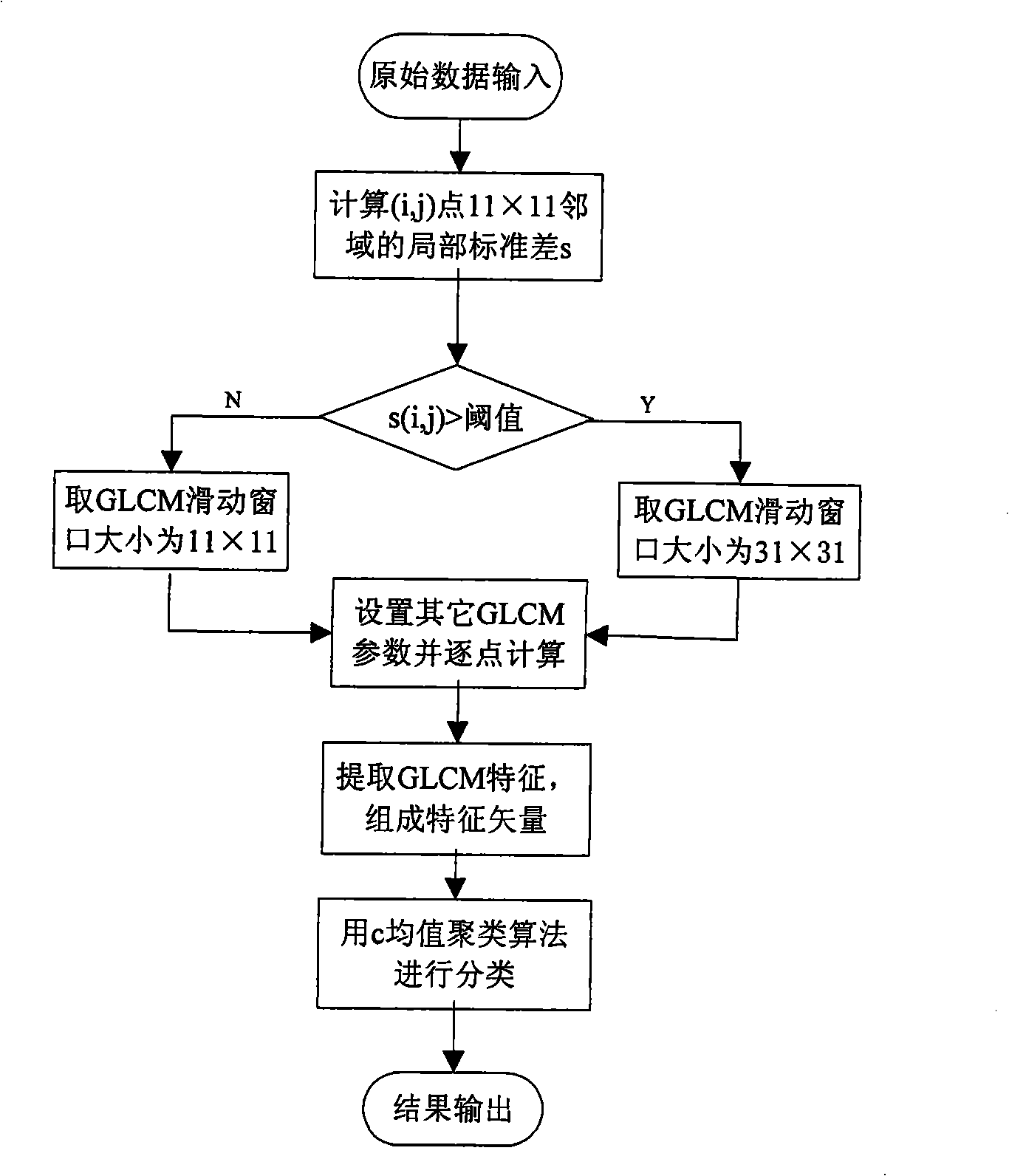
Self-adapting SAR image classification method based on local standard deviation
InactiveCN101320431ARemove the effect of object classificationReduce the impact of classification effectsScene recognitionCluster algorithmOriginal data
A self-adaptive SAR image categorization method based on local standard deviation is provide, which comprises: (1) according to an original data, calculating a local standard deviation s (i, j) for the neighborhood of certain point (i, j); (2) carrying out self-adaptive selection of a GLCM calculation window by the local standard deviation. The specific procedures are: setting the threshold value of s as sth; judging whether the certain point s (i, j) is larger than the threshold value sth; if the certain point s (i, j) is larger than the threshold value sth, selecting a large size window for the calculation of GLCM; if the certain point s (i, j) is smaller than the threshold value sth, selecting a small size window for the calculation of GLCM; (3) setting other parameters of GLCM and calculating the GLCM of the certain point according to the size of window; (4) extracting a characteristic quantity from GLCM to compose an eigenvector and categorize the characteristic vector by adopting a c mean value clustering algorithm. Therefore, the invention can enhance the categorization accuracy of larger military objects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
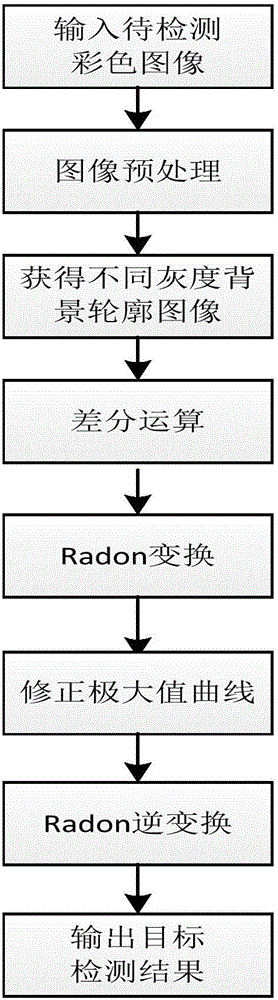
Target detection method based on local standard deviation and Radon transformation
ActiveCN105023013AOvercome the weakness of weak adaptabilityImprove applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageFalse alarm
The invention discloses a target detection method based on local standard deviation and Radon transformation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting a color image to be detected; (2) preprocessing the image; (3) acquiring different grayscale background profile images; (4) performing differential operation; (5) performing Radon transformation; (6) correcting a maximum value curve; (7) performing Radon inverse transformation; and (8) outputting a target detection result. According to the target detection method based on the local standard deviation and the Radon transformation, the defects that the complexity of the algorithm is too high, and false-alarm points are easily generated around the target when a point target is relatively weak in the prior art can be overcome well, and the efficiency and accuracy of image target detectioncan be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Targeted delivery of lidocaine and other local anesthetics and a method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks
An anti-tussive nebulized solution for targeted delivery of lidocaine into conducting and central airways. A method for treatment of cough and tussive attacks or episodes using said lidocaine solution. A nebulized lidocaine solution administered in daily dose from about 10 mg to 80 mg of lidocaine dissolved in a saline and nebulized into an aerosol having a mass median aerodynamic diameter 3 μm to 10 μm and a geometric standard deviation less than 1.7 using an electronic nebulizer.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
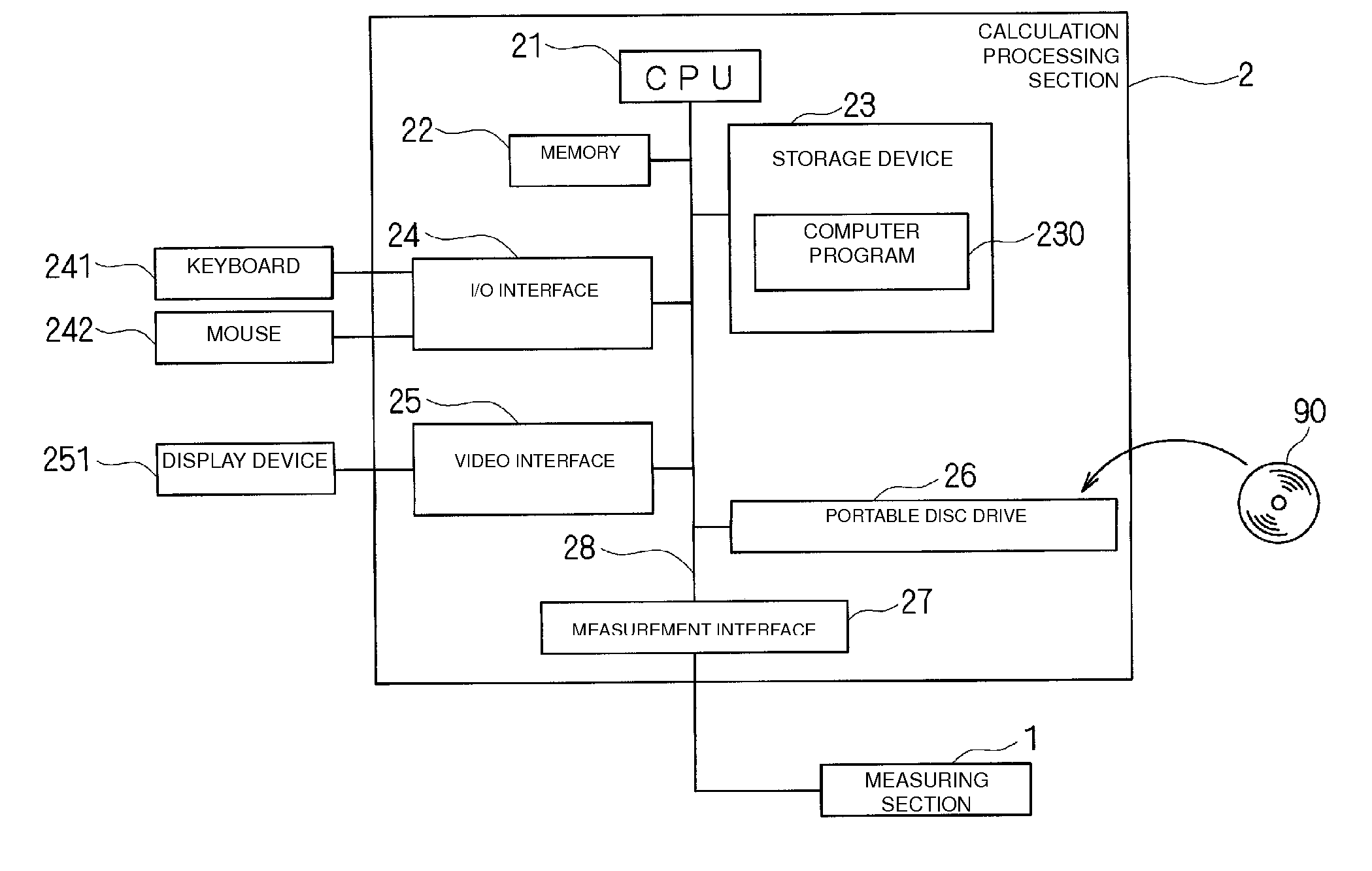
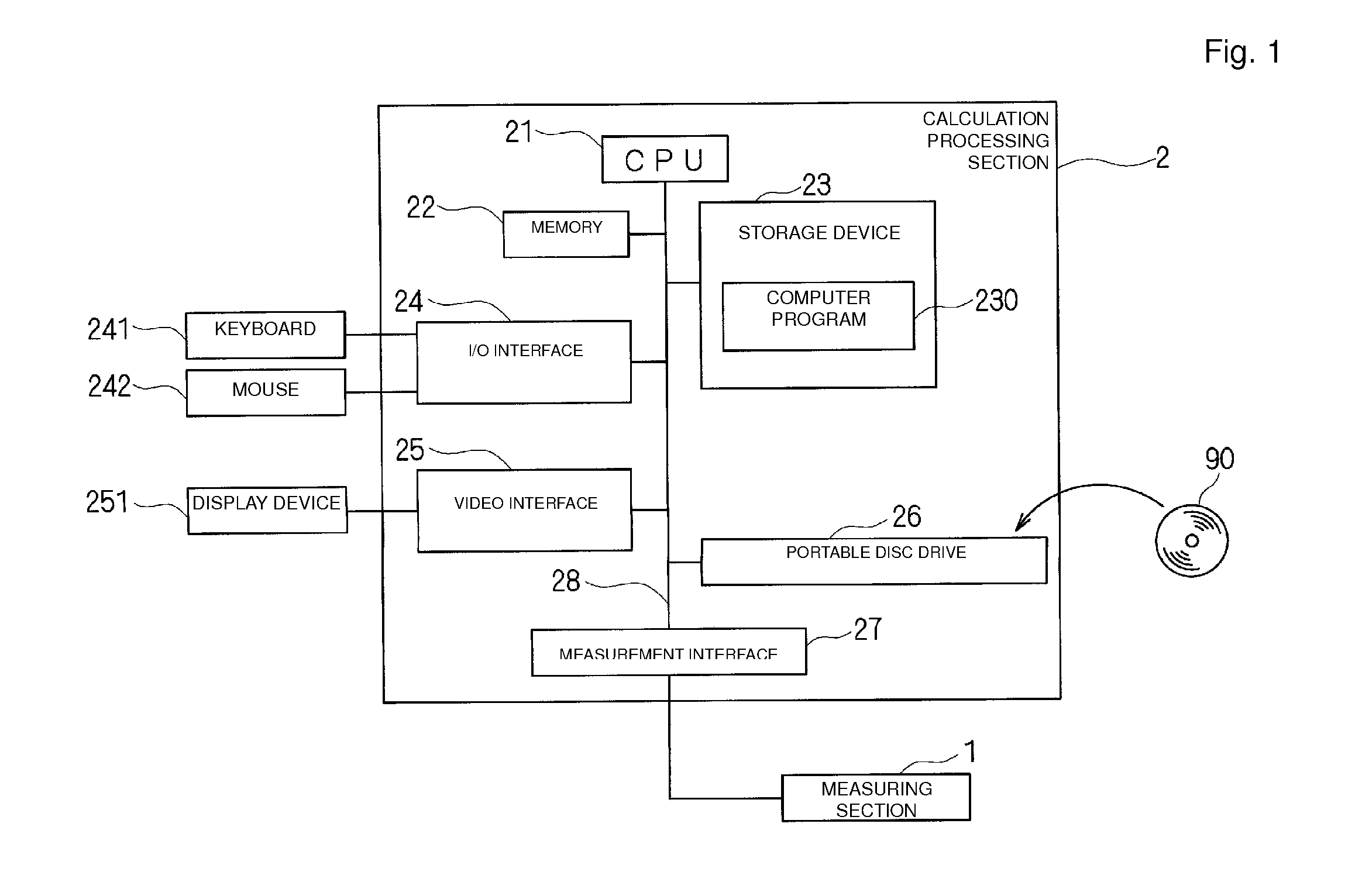
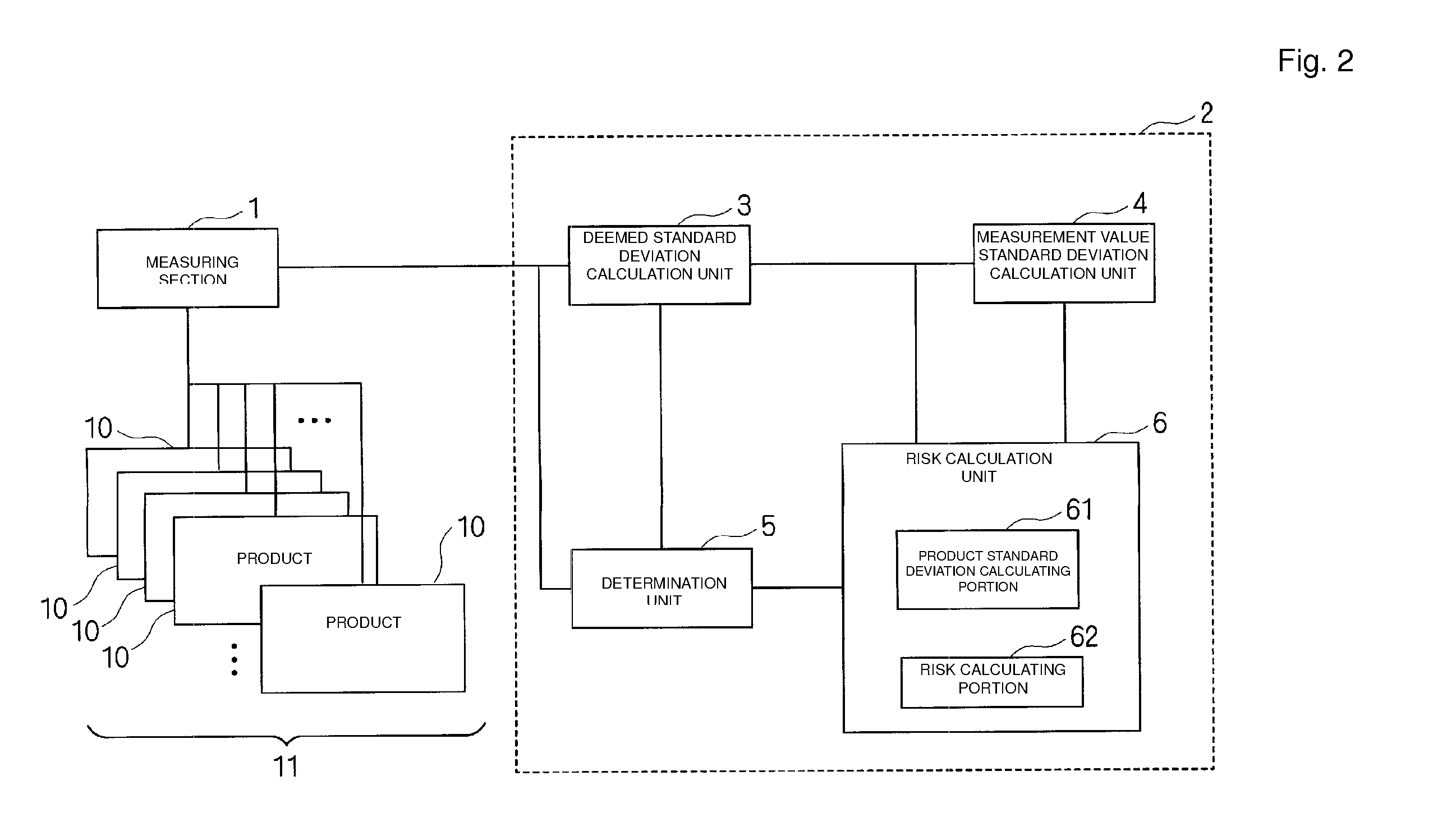
Product Inspection Device, Product Inspection Method, and Computer Program
ActiveUS20120095803A1Increased riskIncrease percentageFinanceStructural/machines measurementProduct inspectionReliability engineering
A product inspection device that includes a measuring section, a deemed standard deviation calculation unit, a measurement value standard deviation calculation unit, a determination unit, and a risk calculation unit. The measuring section measures characteristic values of products, the deemed standard deviation calculation unit calculates a deemed standard deviation, and the risk calculation unit calculates a consumer risk and a producer risk based on at least one of an average value of the measured characteristic values of some of the products contained in a measured product lot, the deemed standard deviation, or the measurement value standard deviation. The determination unit changes a inspection standard based on at least one of the calculated consumer risk or the calculated producer risk, and determines whether or not all the products contained in the product lot are non-defective articles with the changed inspection standard as a reference.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
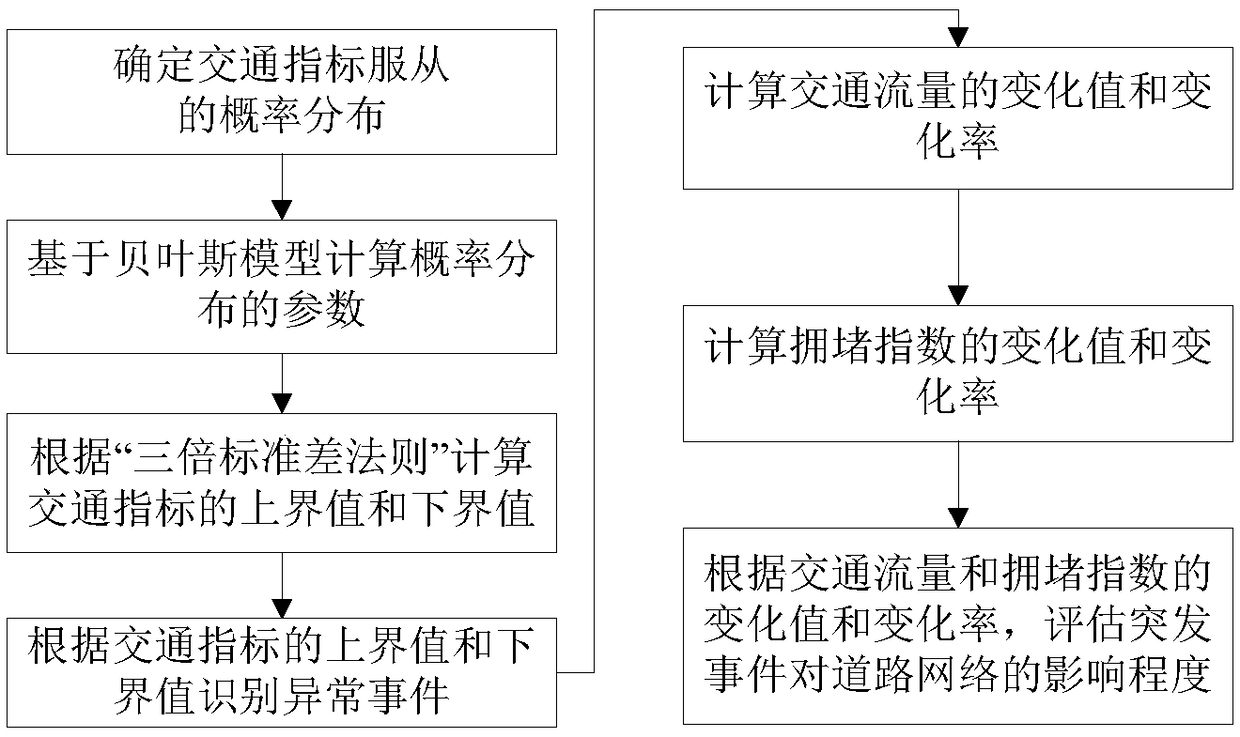
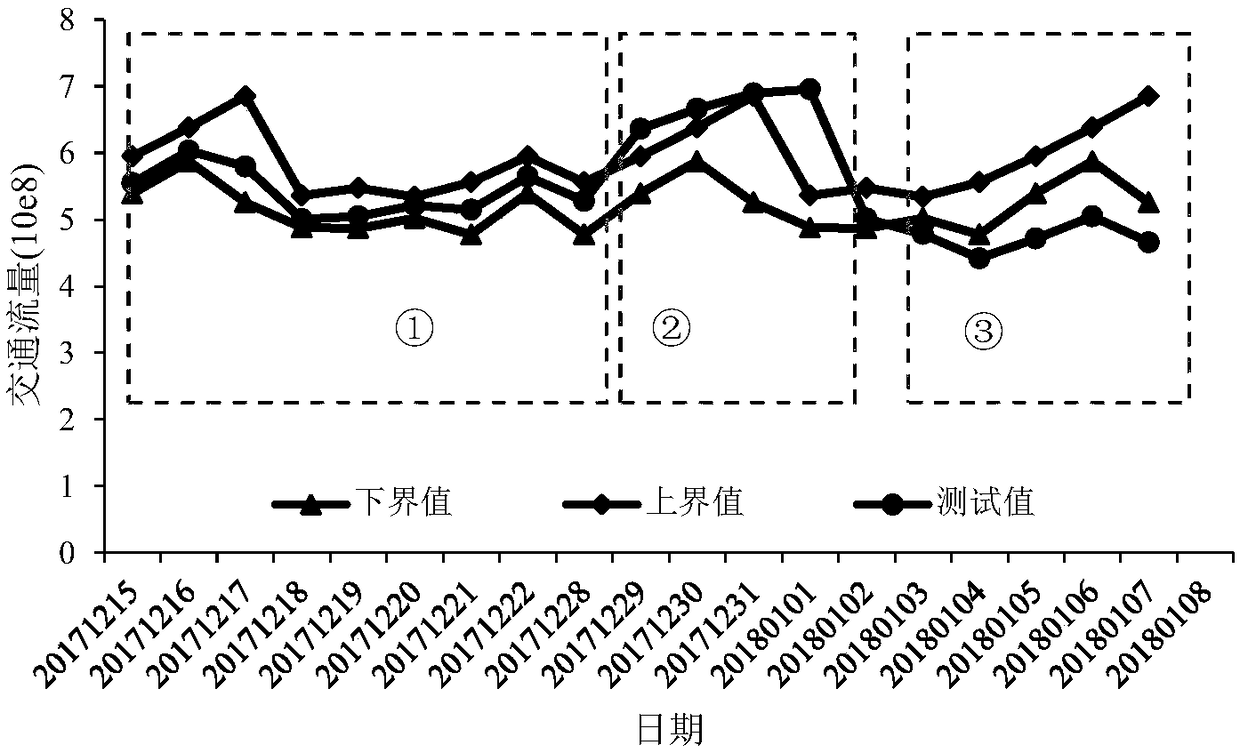
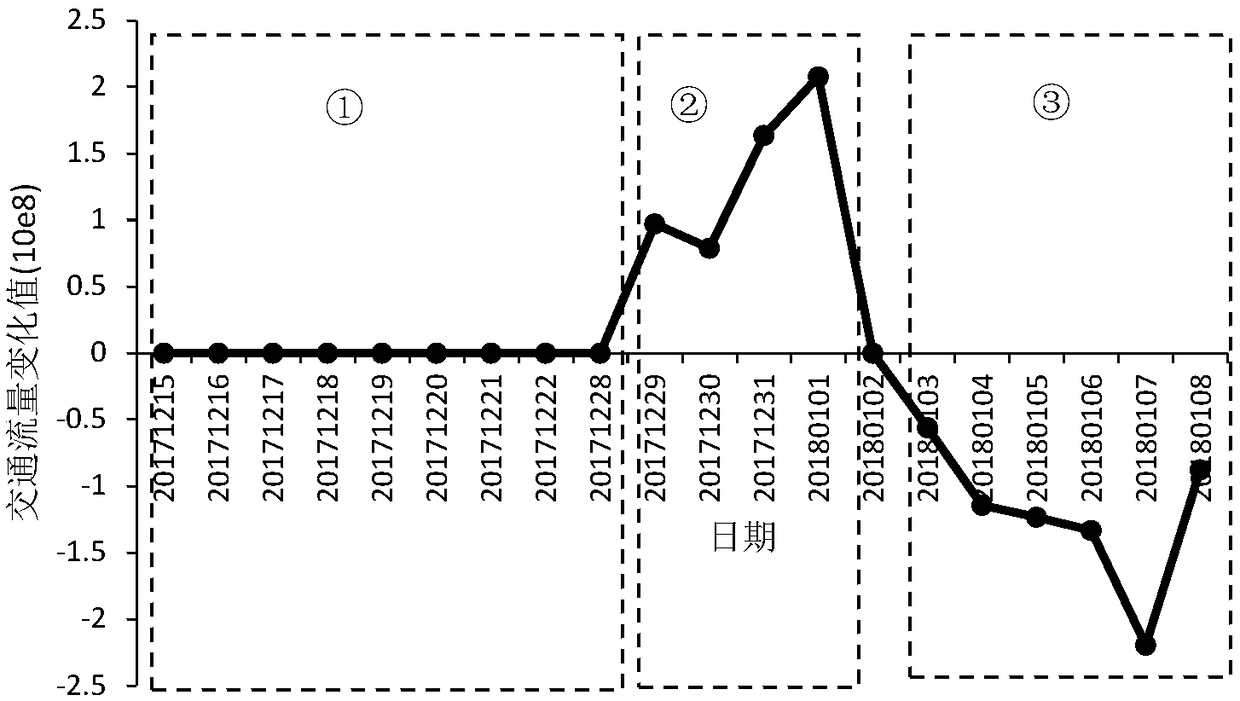
Road network evaluation method based on Bayesian model and triple standard deviation criterion
ActiveCN109409713AEffectively identify abnormal eventsMathematical modelsDetection of traffic movementTraffic congestionRoad networks
The invention provides a road network evaluation method based on a Bayesian model and a triple standard deviation criterion. The method comprises the following steps: the traffic indexes in the same period of time of a certain area are counted, and the probability distribution obeyed by the traffic indexes is determined according to the statistical result; calculating parameters of the probabilitydistribution by using a Bayesian model; according to the Bayesian model and the criterion of triple standard deviation, the range threshold of traffic index is calculated, and whether the road network is abnormal or not is judged by comparing the traffic index data with the range threshold of traffic index. If you determine that that road network is abnormal, according to the criterion of triplestandard deviation to calculate the change value and the change rate of network traffic flow, and the change value and the change rate of the traffic congestion index. As an index for evaluating the influence degree of the abnormal event on the road network, the invention can effectively identify the abnormal event of various road networks and the influence degree of the abnormal event on the traffic flow and the traffic congestion of the road network.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
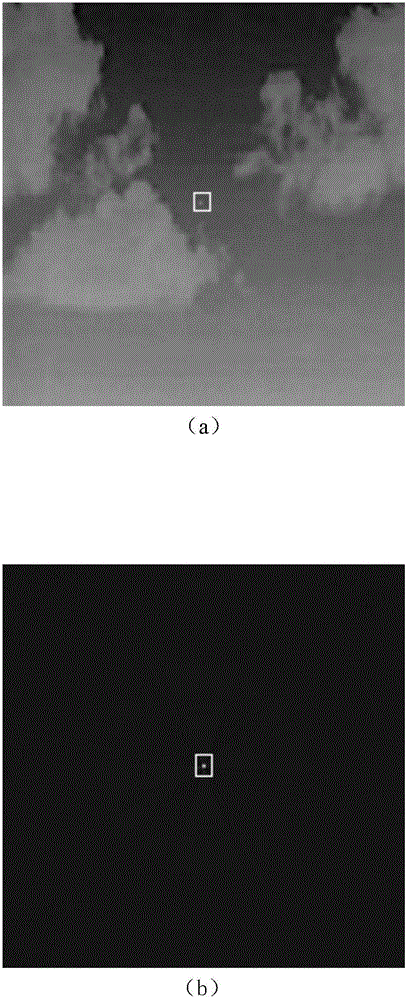
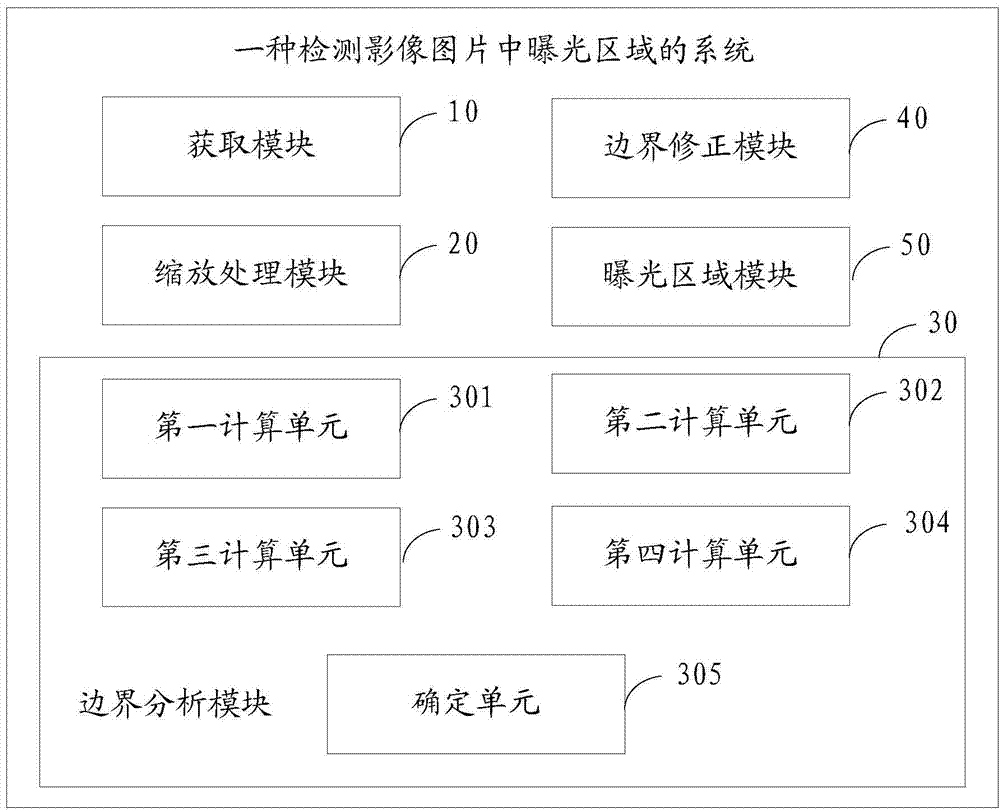
A method and system for detecting exposure area in image picture
The invention relates to the field of images, in particular to a method and system for detecting an exposure area in an image picture. Line standard deviation and row standard deviation of the image picture are obtained through calculating respectively, a line gradient corresponding to the line standard deviation and a row gradient corresponding to the row standard deviation are calculated, a weighted coefficient array of a line standard deviation gradient is calculated according to the line gradient, a weighted coefficient array of a row standard deviation gradient is calculated according to the row gradient, the line gradient multiplies the weighted coefficient array of the line standard deviation gradient to obtain a line standard deviation gradient weighting array, the row gradient multiplies the weighted coefficient array of the row standard deviation gradient to obtain a row standard deviation gradient weighting array, and an upper boundary, a lower boundary, a left boundary and a right boundary are determined through the line standard deviation gradient weighting array and the row standard deviation gradient weighting array at last, so that the final exposure area of the image picture is determined. According to the method and system for detecting the exposure area in the image picture, the exposure area in the image picture can be detected rapidly.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANGELL TECH
Image segmentation algorithm for local region characteristics through nonsubsampled contourlet transform
An image segmentation algorithm for local region characteristics through nonsubsampled contourlet transform comprises the following steps: firstly the nonsubsampled contourlet transform is carried out on an image; then the expression abilities of a local extreme value and local standard deviation on the edge of the image are utilized, and the local standard deviation and the local extreme value on each sub-band are extracted to be used as characteristic vectors; and the characteristic vectors are classified by using FCM, and accordingly the image is segmented. The method provided by the invention can be used for effectively segmenting texture images of multiple combinations, and has an excellent segmentation effect and superior segmentation performance. According to the algorithm, multiscale segmentation is taken into account, and image local region statistical characteristics are also taken into account, so the algorithm is a promising image segmentation technology.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Shockable rhythms recognition algorithm based on standard deviation of standard grid projection
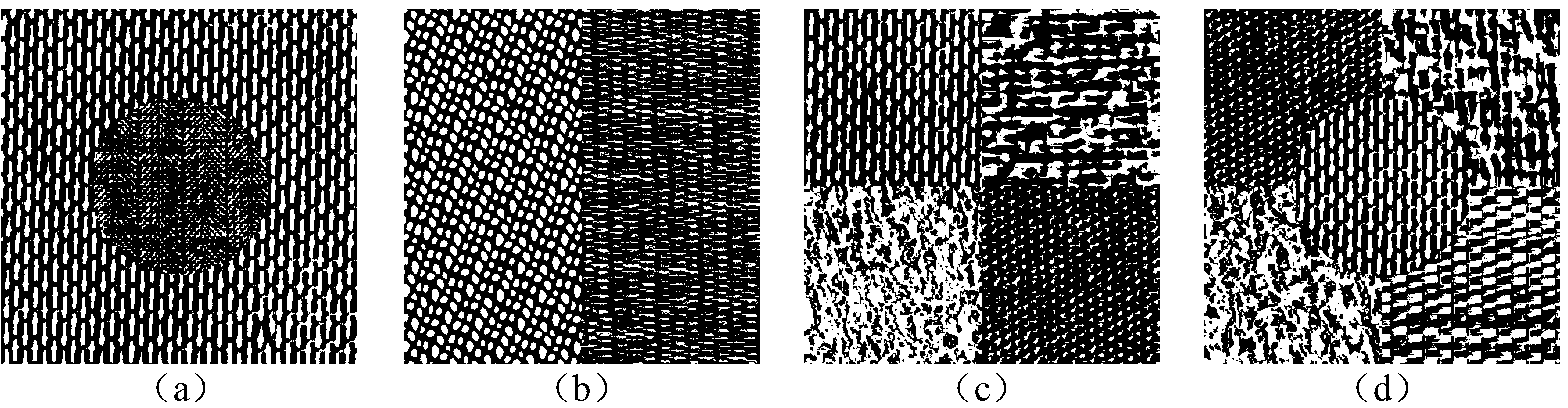
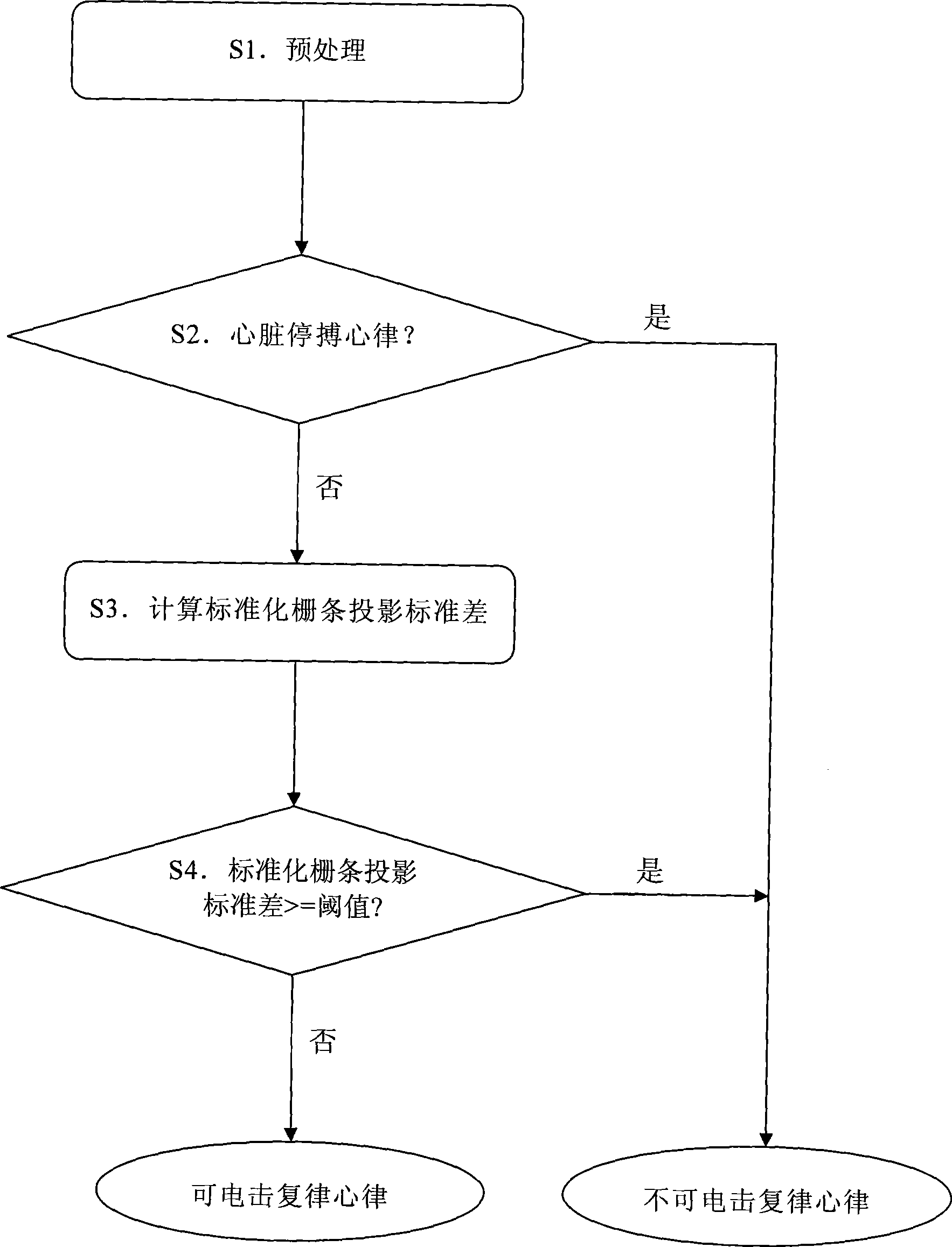
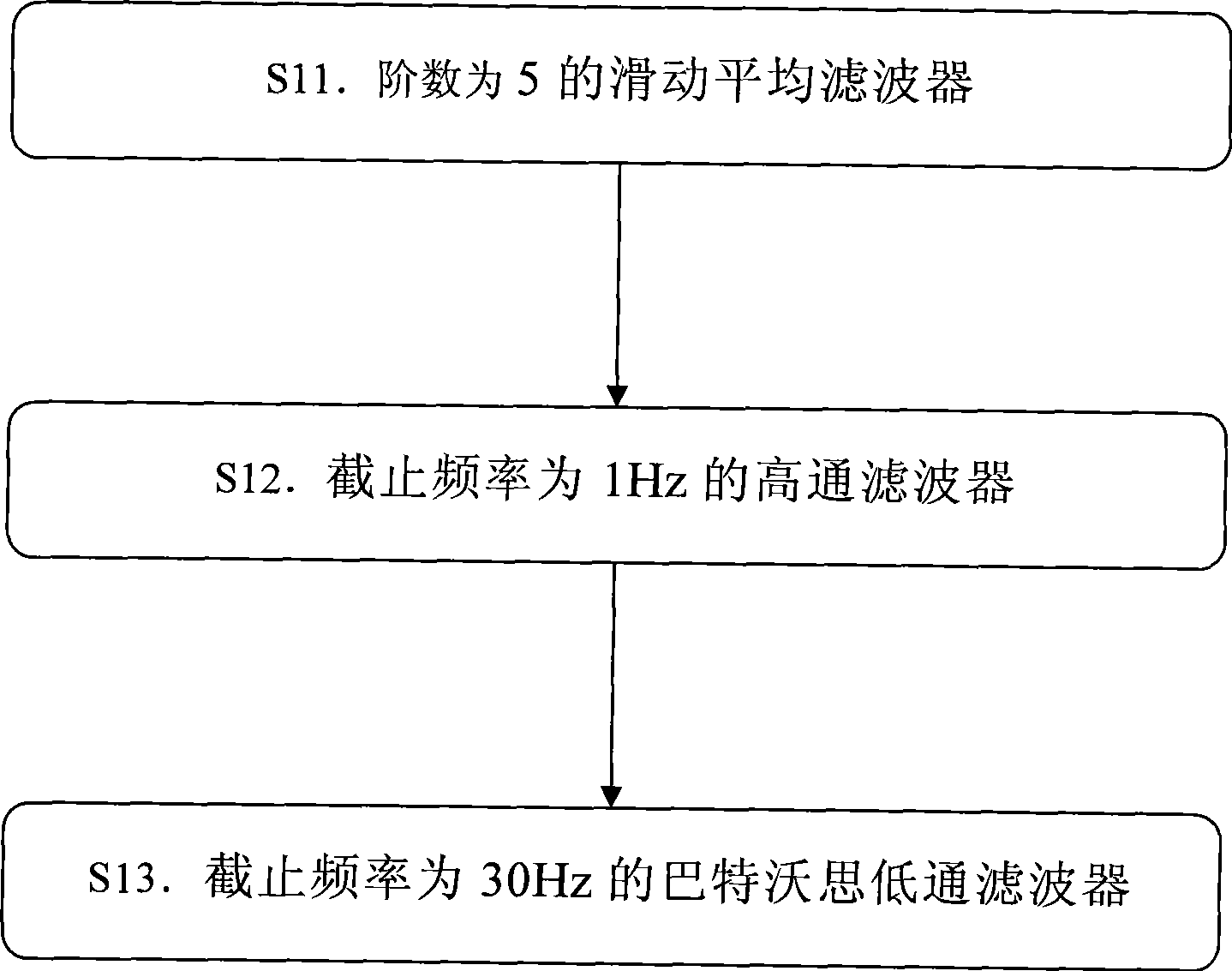
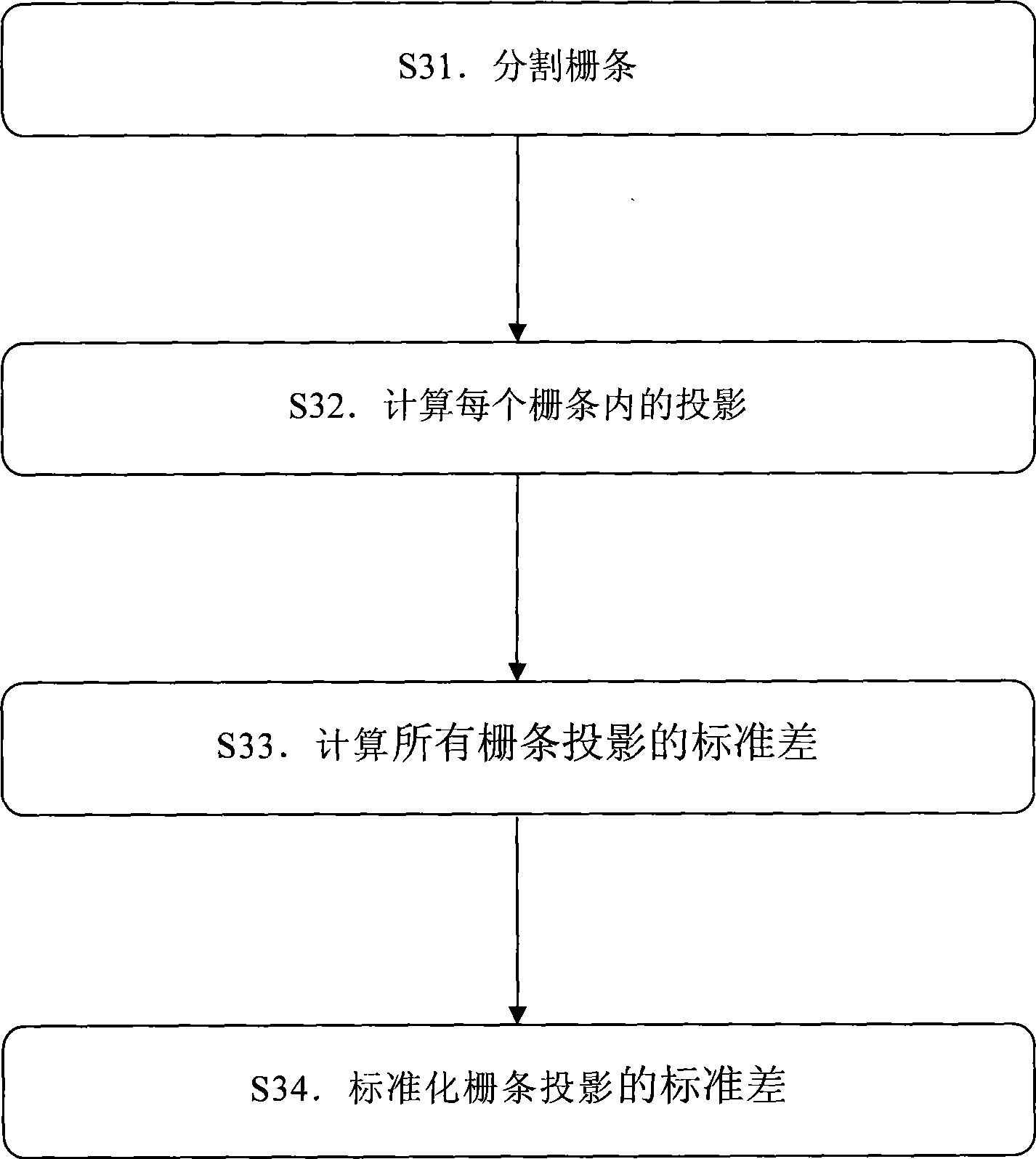
InactiveCN101474069AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalDisease
The invention relates to an electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart recognition algorithm based on the projection standard deviation of a standardization grizzly bar, which is applicable to an instrument or a device for diseases diagnosis. The recognition algorithm comprises steps as follows: S1. Electrical signals are pretreated; S2. The recognition of cardiac arrest rhythm of the heart is carried out on the electrical signals; if the electric signals are of cardiac arrest rhythm of the heart, non electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart is judged; if the electric signals are not of cardiac arrest rhythm of the heart, the following step S3 is carried out; S3. The projection standard deviation of the standardization grizzly bar is calculated; S4. The electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart and the non electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart are distinguished according to the projection standard deviation of the standardization grizzly bar. The recognition algorithm increases sensitivity and specificity of the electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart, simplifies the computational complexity of the recognition algorithm and can be applied to instruments and equipments such as existing ECG monitors and automatic external defibrillators and the like which recognize the electric shock conversion rhythm of the heart according to a body surface electrocardiogram.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Pretreatment method for rapid determination of persistent organic pollutants in atmospheric particulates
InactiveCN110231206AImplement extractionAchieve purification effectComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationParticulatesPretreatment method
The invention belongs to the field of environmental organic pollutant analysis method application and particularly relates to a pretreatment process of using a bimetallic composite oxide nanomaterialwith a special shape and a large specific surface as an accelerated solvent extraction filler for determination of multiple persistent organic pollutants in an atmospheric particulate sample. According to the pretreatment process, an isotope dilution mass spectrometry method is adopted for detection, the standard recovery rate of the multiple persistent organic pollutants in the particulate sampleis within the range of 80.0-120.0%, and relative standard deviations are all within the range of 0.5-7.0%. The pretreatment analysis method is rapid, accurate and effective, meets the requirement forgreen chemistry and can be applied to routine detection of multiple types of organic matter in atmospheric particulates.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
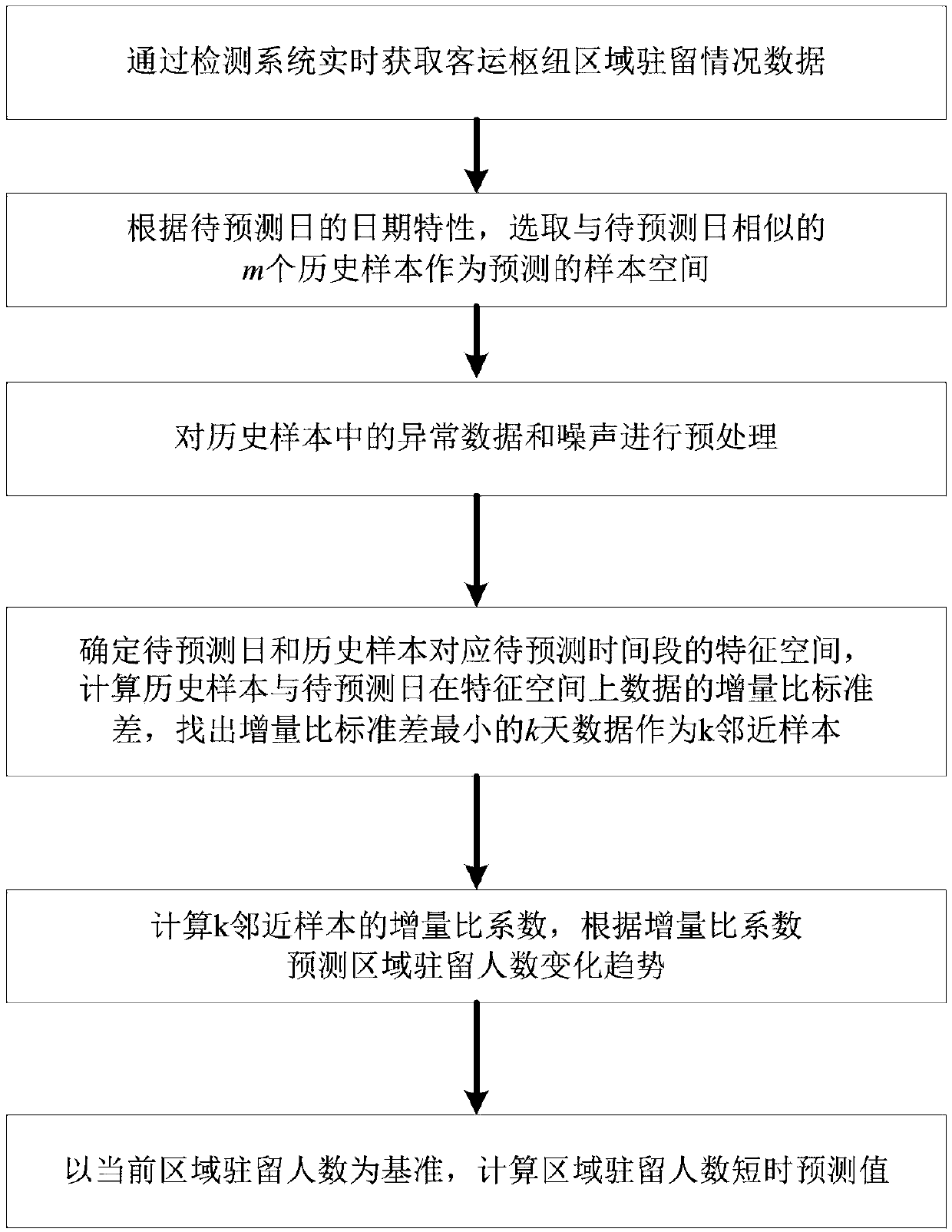
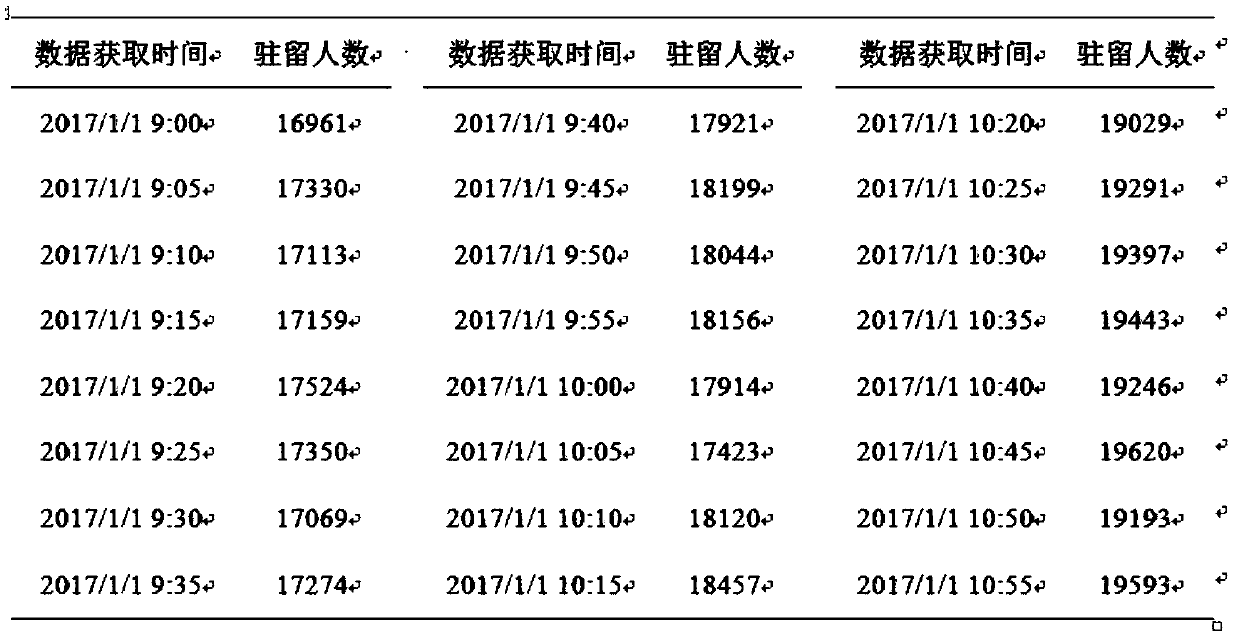
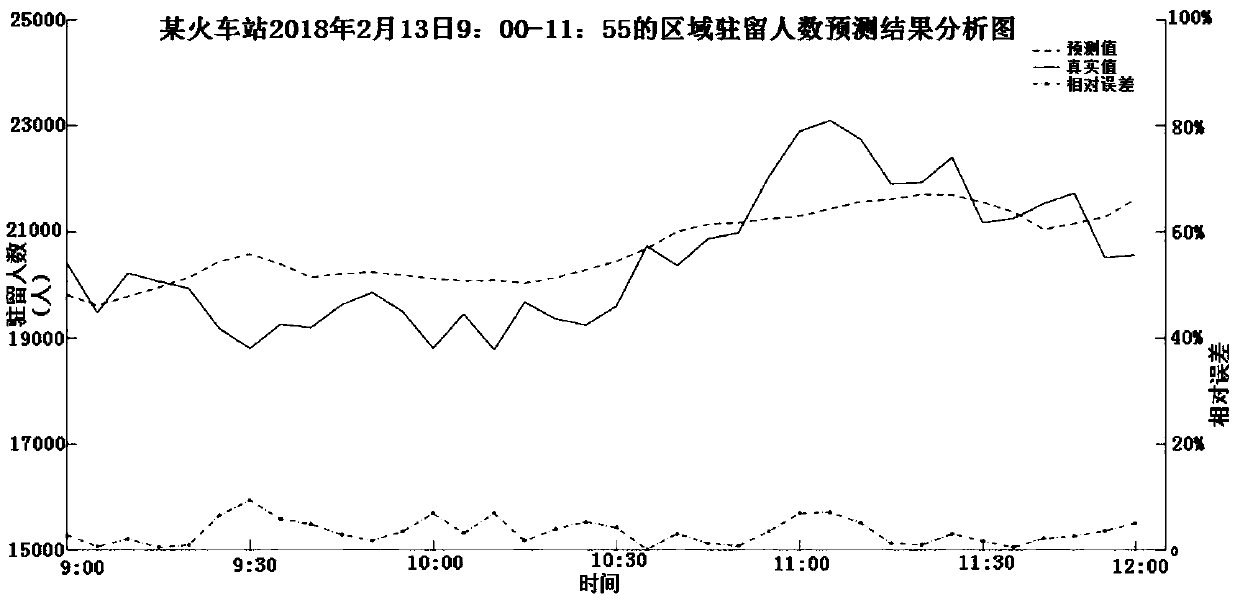
A passenger transport hub area resident number change trend short-time prediction method based on a kNN algorithm
ActiveCN109670540AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionCharacteristic spaceComputer science
The invention discloses a passenger transport hub area resident number change trend short-time prediction method based on a kNN algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining passenger transport hub area resident situation data in real time through a detection system; according to the date characteristics of the to-be-predicted day, selecting m historical samples similar to the to-be-predicted day as predicted sample spaces; preprocessing abnormal data and noise in the historical sample; determining a characteristic space of the to-be-predicted day and the historical sample corresponding to the to-be-predicted time period, calculating an increment ratio standard deviation of the data of the historical sample and the to-be-predicted day on the characteristic space, and finding out k-day data with the minimum increment ratio standard deviation as k adjacent samples; calculating an increment ratio coefficient of k adjacent samples, and predicting the change trend of thenumber of resident people in the region according to the increment ratio coefficient; and calculating a short-time prediction value of the number of resident people in the region by taking the currentnumber of resident people in the region as a reference. According to the method, the change trend of the number of resident people in the short-time area can be accurately predicted by using the historical data, so that a high-precision short-time area resident number prediction result is obtained based on the calculation of the number of resident people in the current area. The method is suitable for the intelligent traffic field.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
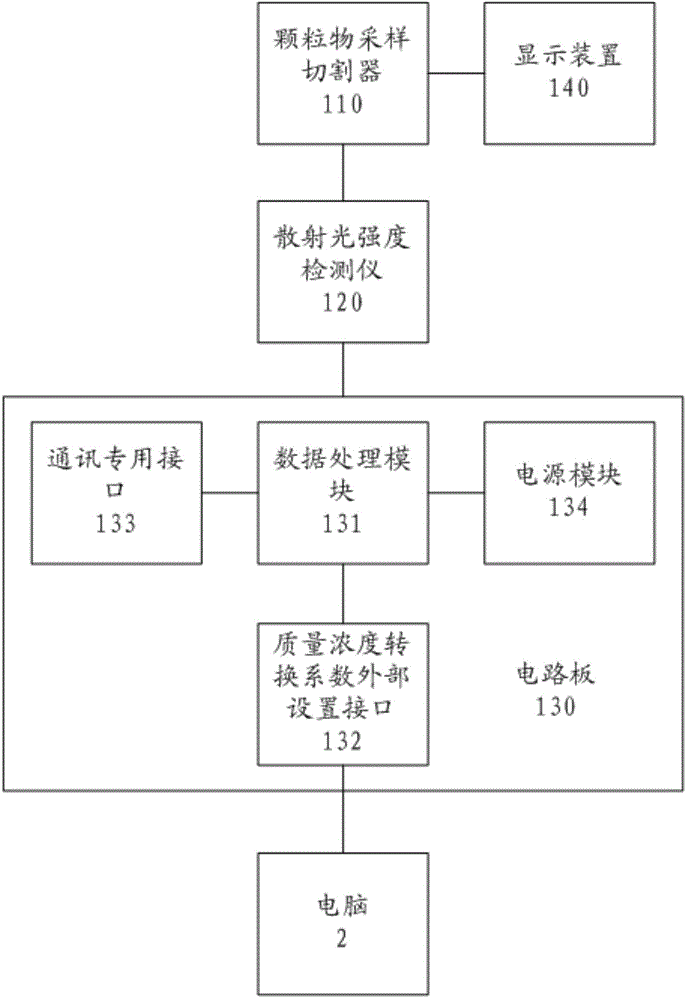
Light scattering-based particulate matter concentration detection device
InactiveCN104865173AReduce volumeReduce noiseScattering properties measurementsParticle suspension analysisDisplay deviceConversion coefficients
The invention discloses a light scattering-based particulate matter concentration detection device. The light scattering-based particulate matter concentration detection device comprises a particulate matter sampling and cutting device, a scattered light intensity detector, a circuit board, and a display device; the particulate matter sampling and cutting device is connected with the scattered light intensity detector; cut diameter of the particulate matter sampling and cutting device is 2.5+ / -0.2<mu>m, and collection efficiency geometric standard deviation is 1.2+ / -0.1<mu>m; the circuit board is provided with a data processing module, and a mass concentration conversion coefficient externally arranged interface; the data processing module is connected with the scattered light intensity detector; the mass concentration conversion coefficient externally arranged interface is connected with the data processing module; and the display device is connected with the data processing module. The light scattering-based particulate matter concentration detection device is convenient for people to obtain PM2.5 concentration at a certain time timely, and is capable of providing convenience for air quality PM2.5 index real-time monitoring, and air pollution degree evaluation of certain areas, and providing favorable conditions for active treatment of PM2.5 pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIBAO HIGH SCHOOL
Ferrite powder and formed body prepared by same
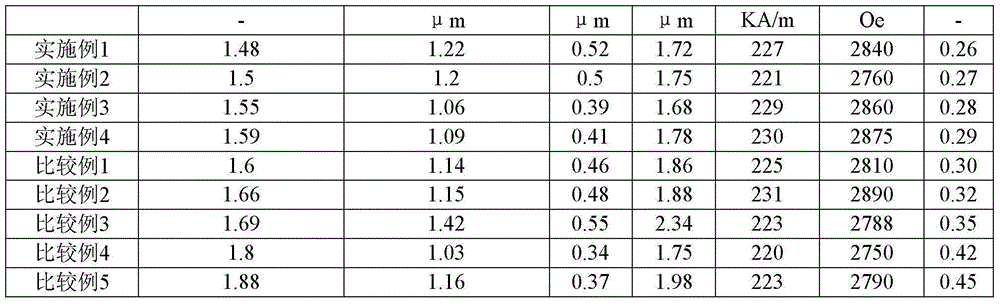
The invention discloses ferrite powder and a formed body prepared by same. In the granularity distribution determination of a laser diffraction granularity distribution instrument, the geometric standard deviation of the granularity distribution is 1.4 to 1.59, the average volumetric particle size is 0.9 to 1.5 micrometers, the particle size X10 of screen underflow with an accumulated ratio of 10 percent is 0.35 to 0.55 micrometers, and the particle size X90 of the screen underflow with accumulated ratio of 90 percent is 1.5 to 2.5 micrometers. By adopting the ferrite powder, the SFD can be effectively controlled to be less than or equal to 0.30, so that the homogenization degree of the coercivity is higher, the magnetic uniformity is better, the magnetic performance is higher, when a magnetic recording medium is formed, a transitional area between two recording sites is smaller, the recording density is higher, the signal sensitivity is better, the print-through effect of the magnetic recording medium is smaller, and the rewriting performance is better.
Owner:BGRIMM TECH CO LTD
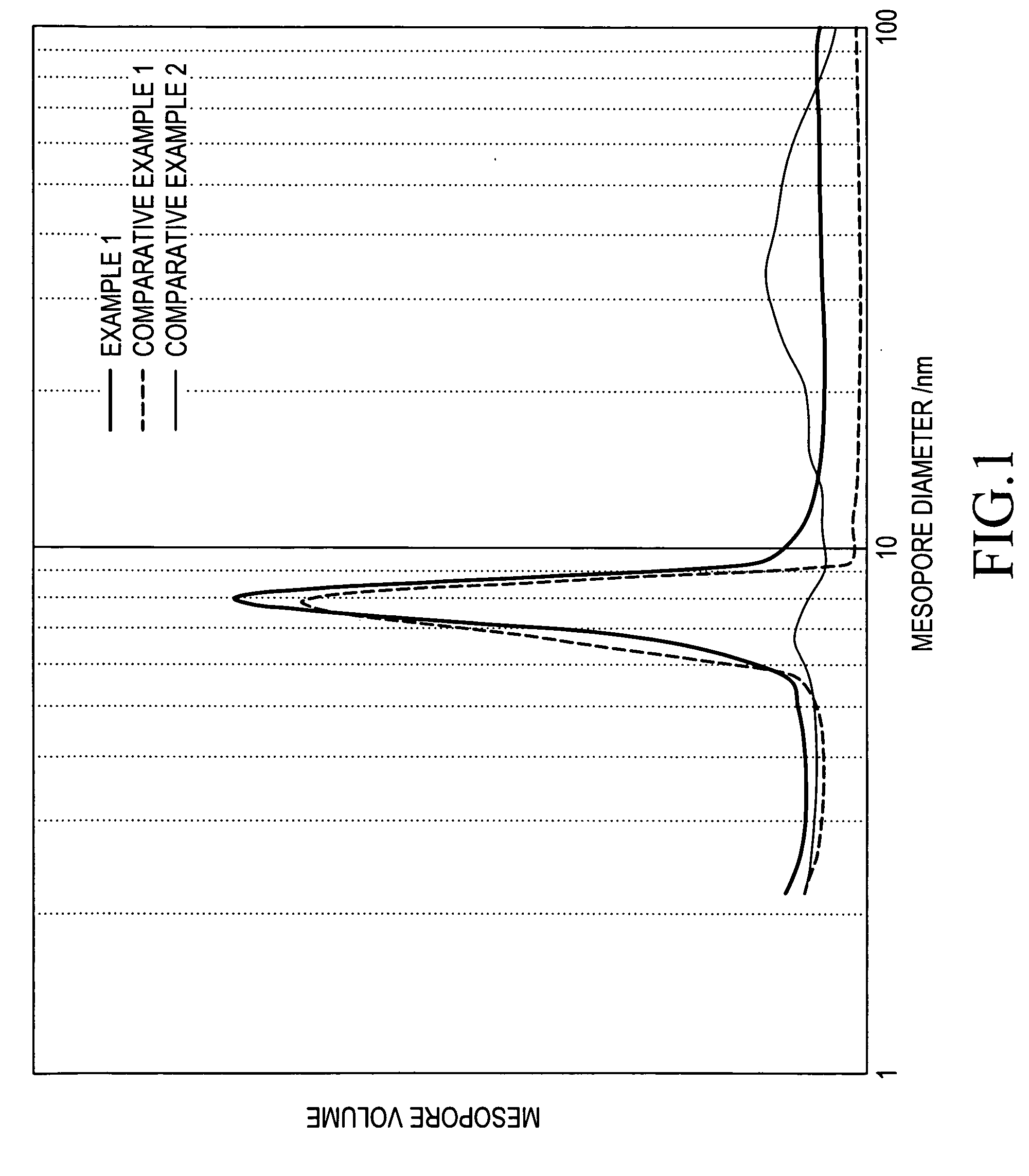
Mesoporous silica particles and production process thereof
InactiveUS20090060816A1High yieldEfficient productionSilicaDuplicating/marking methodsSilica particleMesoporous silica
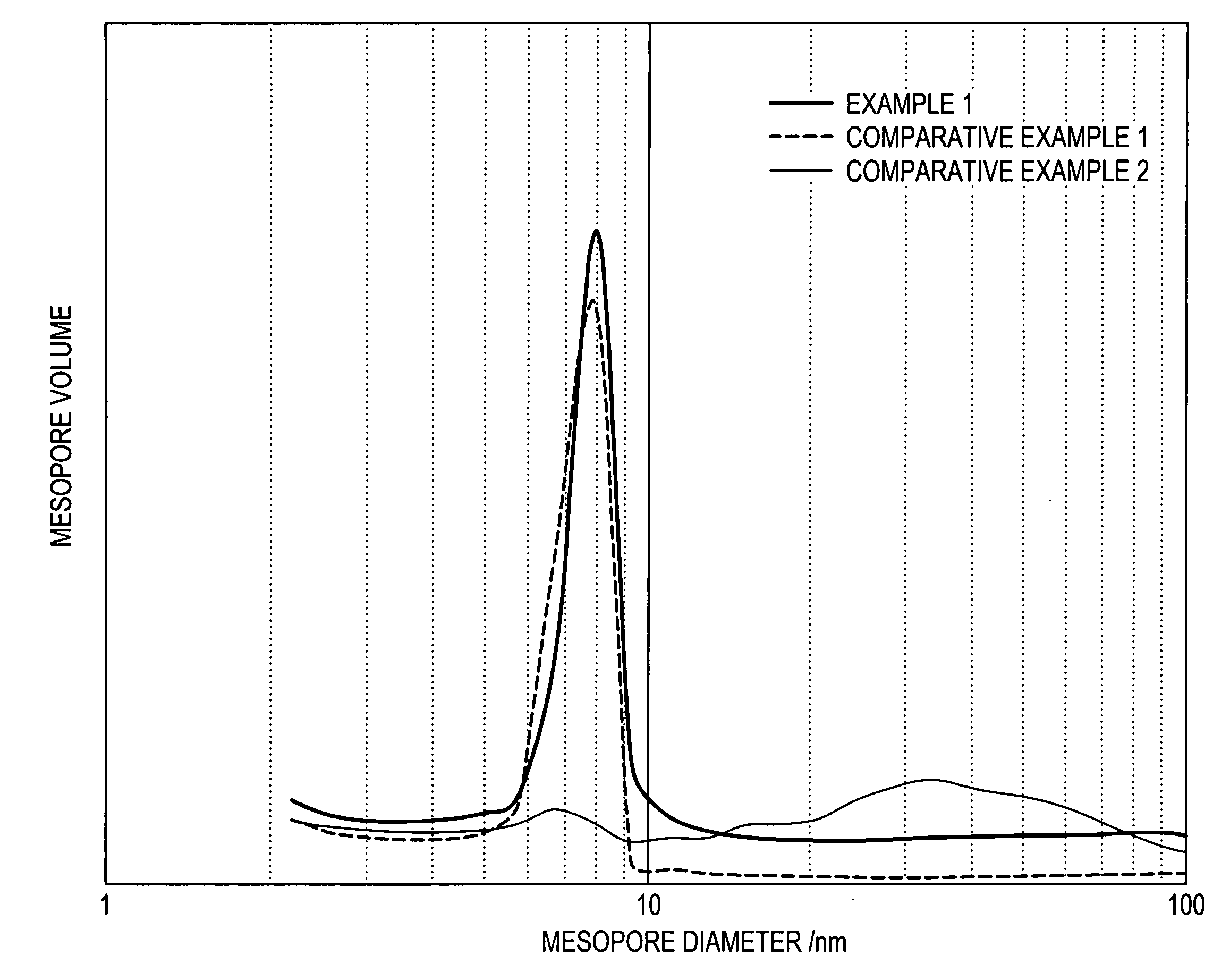
A process for wet pulverizing mesoporous silica particles while a surfactant exists in mesopores, and mesoporous silica particles having an average particle diameter of 1 μm or less, wherein the volume of mesopores having a diameter of 2 to 50 nm is 0.7 mL / g or more and the geometric standard deviation of a mesopore distribution is 2.0 or less. Mesoporous silica particles having a particle diameter in a submicron order can be obtained at a high yield without causing the marked collapse of mesopores and can be produced efficiently by using an ordinary pulverizer and safely by using an aqueous medium. The mesoporous silica particles having an average particle diameter of 1 μm or less are useful as an ink absorbent for ink jet recording paper, low-dielectric film, catalyst support, separating agent, adsorbent and medical carrier for medicines.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
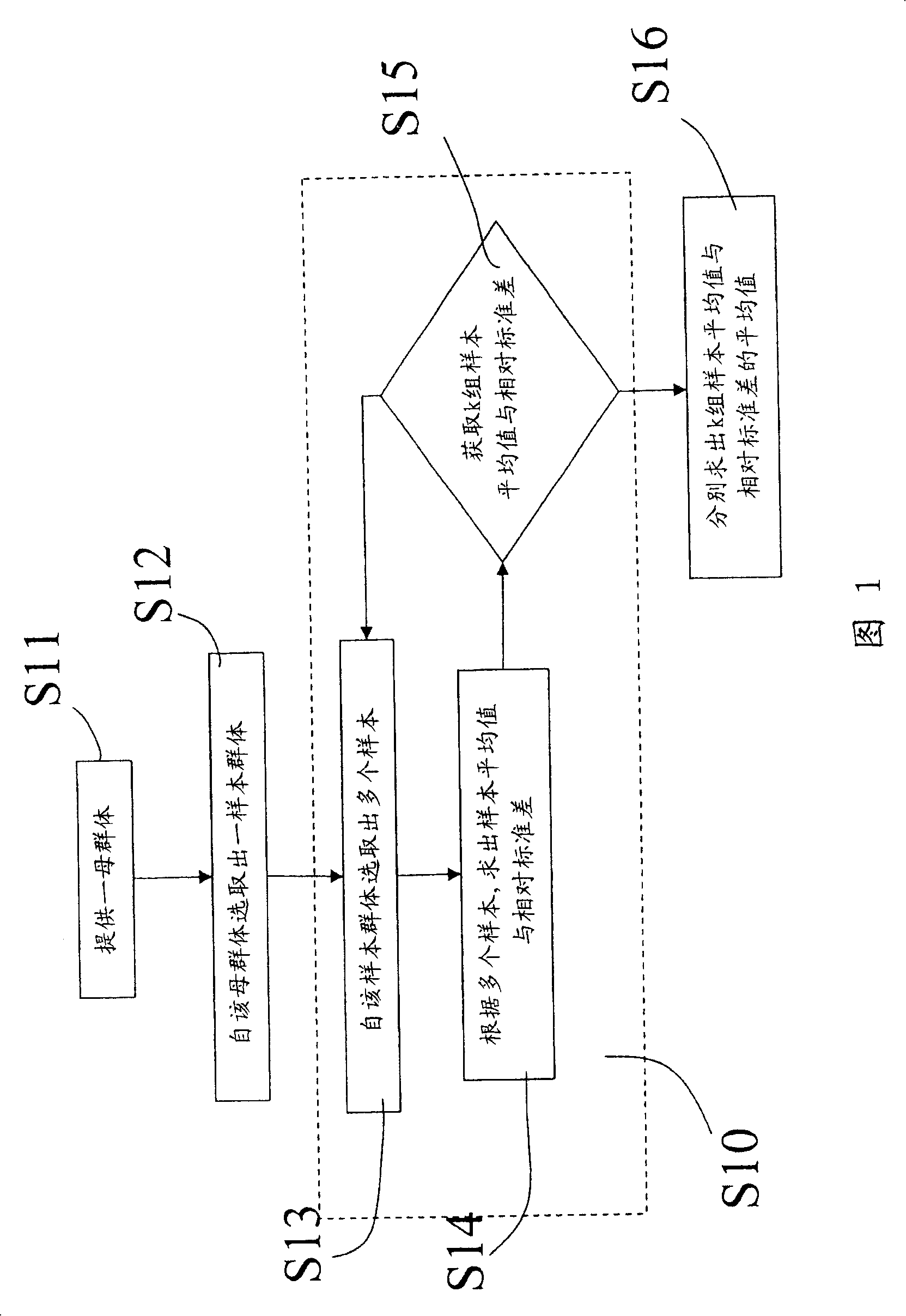
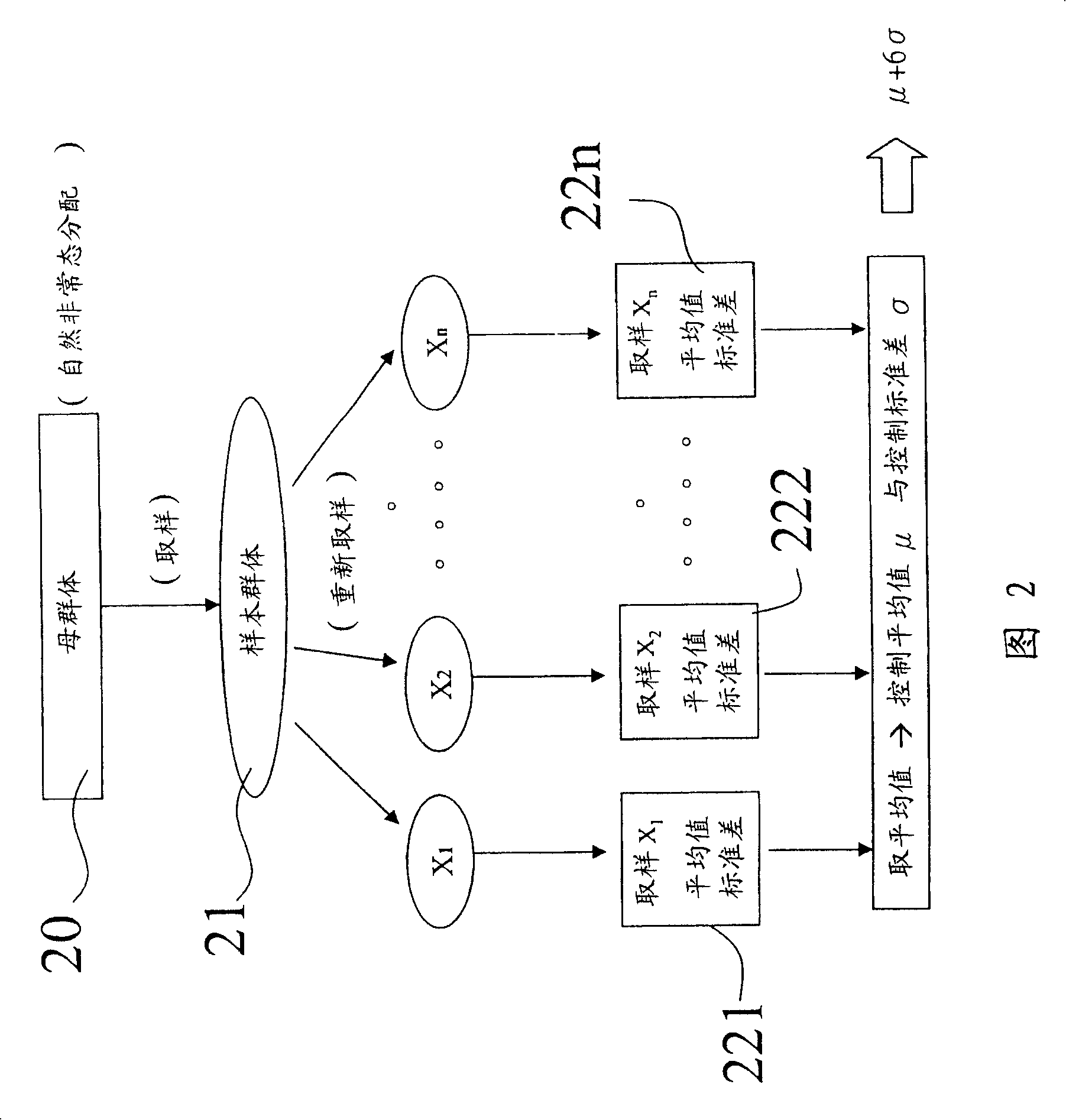
Establishment method of control specification limit
InactiveCN101174149ASampled-variable control systemsTotal factory controlRelative standard deviationComputer science
The invention provides a definition method specification of a control specification limit in a statistical process control (Statistical Process Control, SPC), which comprises the following steps: step a, a sample group is provided; step b, k groups of bootstrap samples groups are chosen from the sample group in a bootstrap resampling way; step c, the average value and the relative standard deviation of the k groups of bootstrap sample groups are calculated from the k groups of bootstrap resampling sample groups; and step d, a control average value and a control standard deviation are calculated from the k groups of sample average value and relative standard deviation, wherein the control specification limit is the function of the control average value and the control standard deviation.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
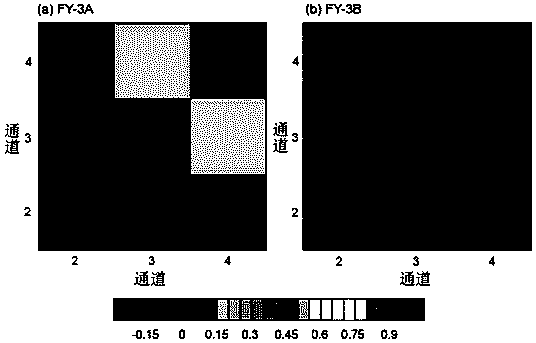
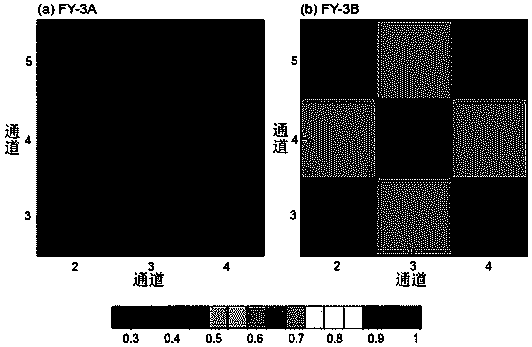
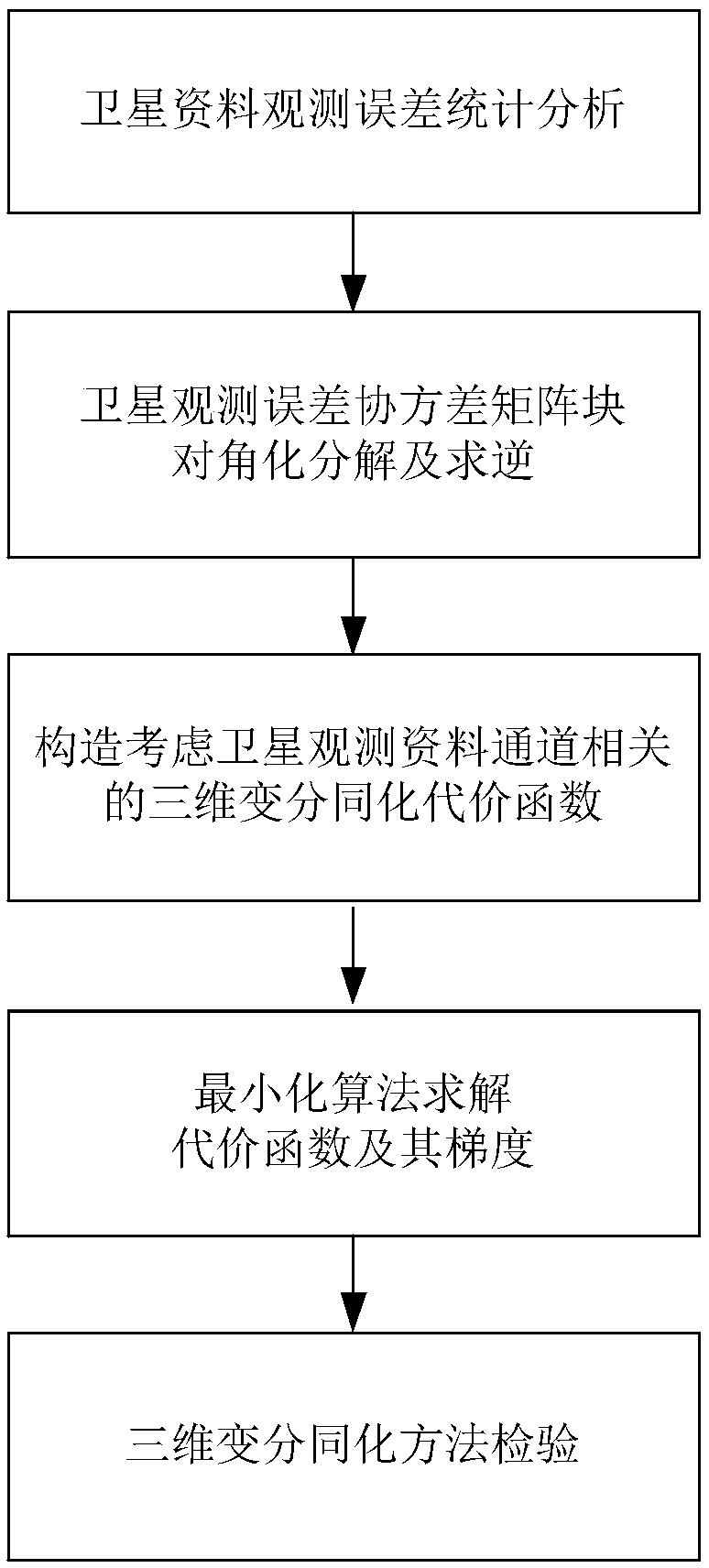
Three-dimensional variational assimilation method for satellite observation data considering channel correlation
ActiveCN109212631AExcellent analysis fieldSolve the problem that the correlation between channels of satellite observation data is not consideredWeather condition predictionPhase correlationMinimization algorithm
The invention provides a three-dimensional variational assimilation method for satellite observation data considering channel correlation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) diagnosing channel correlation and an error standard deviation of satellite observation errors by using posterior information; 2) performing diagonalization decomposition on satellite observation error covariance matrix block; 3) inversing the satellite observation error covariance matrix block; 4) constructing a three-dimensional variational assimilation cost function considering channel correlation of the satellite observation data; 5) solving the constructed cost function and a gradient thereof by using a conjugate gradient minimization algorithm, and obtaining an optimal analysis field; and 6) testing theconvergence of the constructed three-dimensional variational assimilation method. According to the method, the channel correlation and error standard deviation of the satellite observation data are diagnosed by using the posterior information, an observation error covariance matrix in three-dimensional variational assimilation is constructed, and a matrix inversion method is designed, thereby solving the problem that the correlation between satellite observation data channels is not considered in current three-dimensional variational assimilation.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Toner, developer, developing device and image forming apparatus
InactiveCN101727033AStable formationReduce qualityElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersSilica particleVolume average
A toner is provided. The toner includes toner particles, and silica particles and inorganic fine particles that are externally added to the toner particles, the inorganic fine particles having an average primary particle size smaller than that of the silica particles. The toner particles have a shape factor SF-1 of 130 or more and 140 or less, a shape factor SF-2 of 120 or more and 130 or less, and a volume average particle size of 5 [mu]m or more and 8 [mu]m or less. The silica particles have an average primary particle size of 80 nm or more and 150 nm or less, and an amount of water of 1.5% by weight or less. A particle size distribution of the silica particles is a logarithmic normal distribution, and a value of geometric standard deviation [sigma]g of the particle size of the silica particles is less than 1.30.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com