Phage capable of splitting cattle streptococcus agalactiae and application thereof
A technology for Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of narrow lysis spectrum and unclear sequence type of Streptococcus agalactiae, and achieves the effects of good killing effect, no toxic side effects and high safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
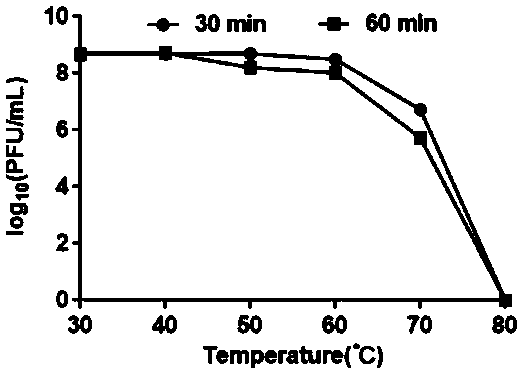
[0036] The isolation and preparation of embodiment 1 phage
[0037] The host bacterium of the phage used in the test of the present invention is the clinical isolate strain HZJG1201 of Streptococcus agalactiae.
[0038] The sample of the present invention is collected from a mastitis milk sample from an experimental farm in Yangzhou City, Jiangsu Province. The milk sample is centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 20 minutes, and then the supernatant is filtered with a 0.22 μm filter membrane. Take 10 mL of the filtered supernatant, add 0.5 mL of the overnight culture of the host bacteria, and then add sterile CaCl 2 Mix the mother liquor to a final concentration of 1.25mM, add 20mL of THB medium, place it in a 37°C incubator and incubate for 6-8h, take the above culture at 12000rpm, centrifuge for 30min, and take the supernatant; then take 10mL of the supernatant , add 0.5mL overnight culture of host bacteria, add sterile CaCl 2 Mix the mother liquor to a final concentration of 1.25m...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Amplification and purification of embodiment 2 phage
[0042] On the double-layer plate that forms phage plaques in Example 1, pick a single phage plaque with a larger diameter with the tip of a pipette, inoculate it in 3-5mL THB medium, add 0.1mL of phage host bacterial solution, Mix well, act at room temperature for 15 minutes, incubate at 37°C for 10-14h, centrifuge at 12000rpm at 4°C for 10min, take the supernatant, and add 0.3% chloroform. Repeatedly pick 4-5 single phage plaques in this way until the phages are purified into phage plaques of the same size.
[0043] Take 1 mL of freshly cultured host bacteria and add 0.3 mL of phage lysate (the ratio of a single phage culture to host bacteria is 1:1, 1:10 and 1:100, respectively). Incubate at 37°C for 20 minutes to make the phage particles adsorb to the host bacteria; add 100mL THB liquid medium, then add CaCl 2 The final concentration of the mother liquor was 1.25mM, cultured with shaking at 37°C for 12-16h, 120...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The transmission electron microscope detection of embodiment 3 bacteriophage
[0048] Take the purified phage particles (provided in Example 2) for electron microscope observation, add 10 μL of sample and drop it on the copper grid, wait for its precipitation for 15 minutes, absorb excess liquid with filter paper, and stain with 2% phosphotungstic acid (PTA) for 1-2 minutes , After drying, observe with a transmission electron microscope (Hitachi H-7650).
[0049] observe as figure 2 As shown, the head of the phage is a regular polyhedron, the diameter of the head is about 50nm, and the length of the tail is about 200nm. According to the "Classification of Viruses—The Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses" published by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) in 2011, vB_SagS_FSN1 belongs to the long-tailed bacteriophage family (Siphoviridae).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Head diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com