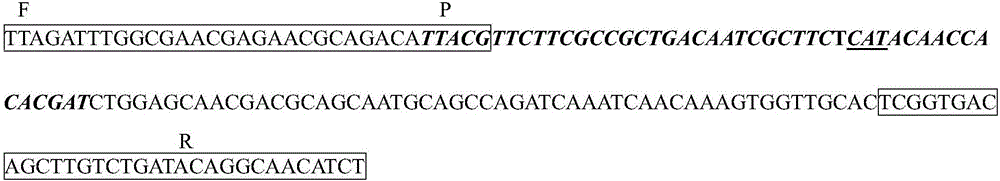Method for detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus
A technology of Vibrio hemolyticus and detection kit, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc. , strict technical requirements and other issues, to improve the food safety guarantee system, suppress the occurrence of epidemics, and show obvious results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
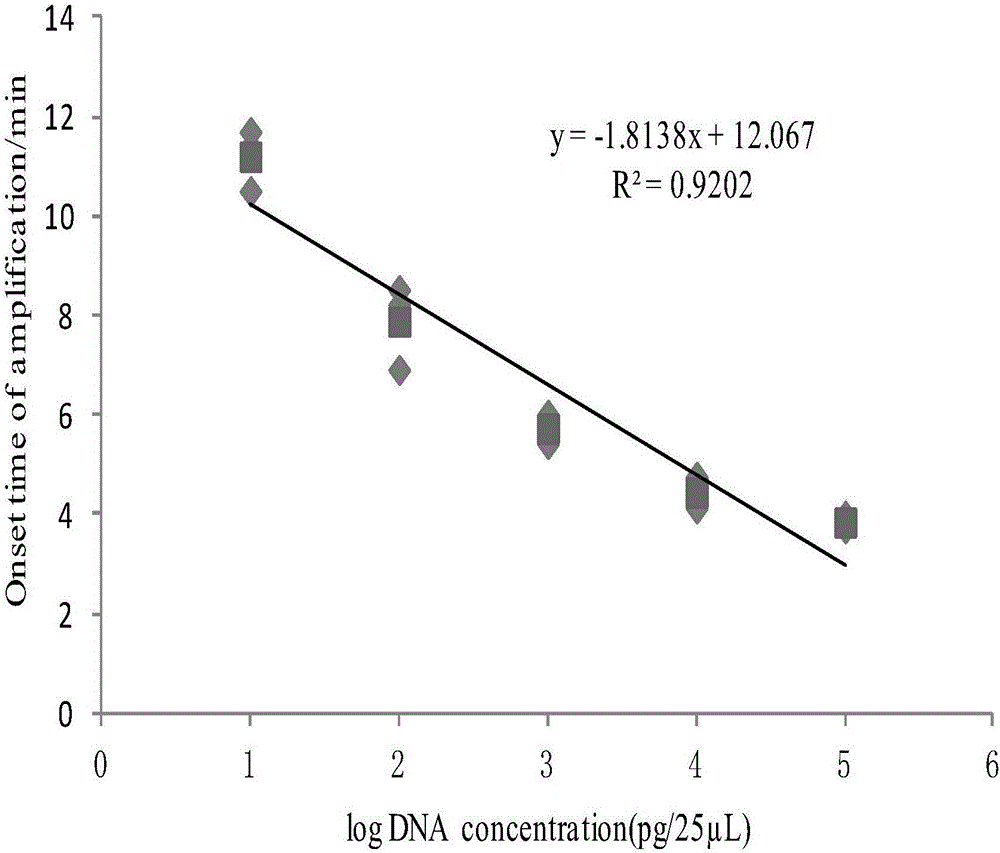
[0032] Embodiment 1: Screening of primers and probes and establishment of methods
[0033] The present invention designs primers and probes according to the thermolabile hemolysin (thermolabile hemolysin, TLH) coding gene tlh of Vibrio parahaemolyticus:
[0034] The published tlh gene sequence was found through NCBI, and the designed primers were compared by Primer-BLAST, which had good specificity. The gene located at positions 440-608 of the tlh gene sequence was used as the target fragment for real-time RPA primers and probes. design.
[0035] Design 4 sets of primer pairs and 1 probe for optimal primer screening. The primer sequences are fine-tuned sequences, and the sequences that bind to the probes are located in the middle of the amplification regions of the 4 pairs of primers. The primer sets and probe sequences are as follows:
[0036] Forward primer F1-RPA: 5′-CAACATTAGATTTGGCGAACGAGAACGCAGAC-3′(32bp)
[0037] Reverse primer R1-RPA: 5′-TTAAAGATGTTGCCTGTATCAGACAAGCT...
Embodiment 2
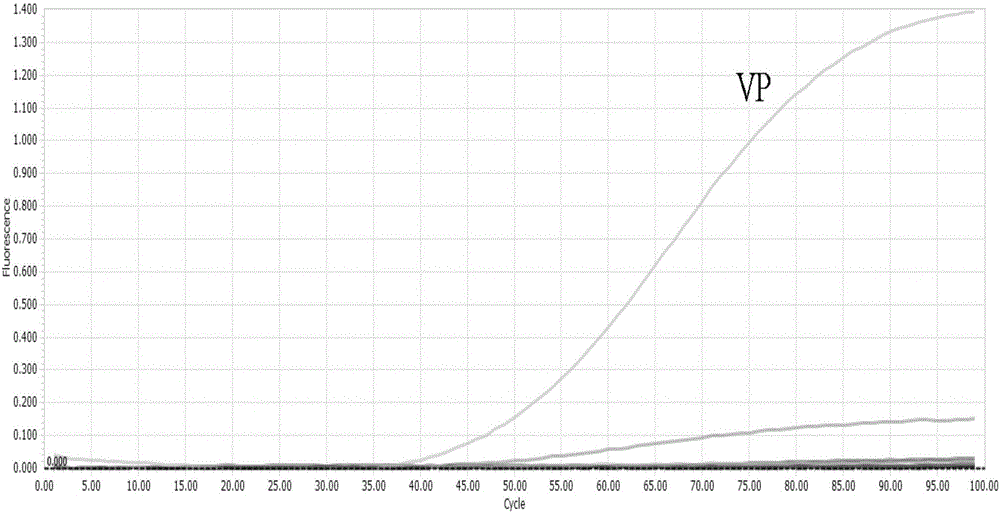
[0076] Embodiment 2 is applied to the detection of actual samples
[0077] 1 material
[0078] 9 parts of aquatic products come from the aquatic product circulation market, including 2 parts of sea melon seeds, 2 parts of white sea melon seeds, 2 parts of flower clams, and 3 parts of razor clams (10g net content per part).
[0079] 2 reagents
[0080] 3% sodium chloride alkaline peptone water (3% APW, selective enrichment culture of Vibrio parahaemolyticus), sterile water (nuclease-free)
[0081] 3 sample processing
[0082] The sample processing steps are slightly modified on the basis of "GB 4789.7-2013 Food Safety National Standard for Food Microbiological Examination of Vibrio parahaemolyticus".
[0083] 3.1 Immediately after collection of non-frozen samples, store them in a low-temperature freezer at 7°C to 10°C, and test them as early as possible.
[0084] 3.2 Shellfish take all the contents, including shellfish meat and body fluids. For shellfish, first wash the sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com