Method and system for selecting customized drug using genomic nucleotide sequence variation information and survival information of cancer patient
A base sequence and genome technology, applied in the field of customized anti-cancer treatment drug selection methods and systems, can solve problems such as not easy and new drug development, and achieve highly reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Example 1. Detection of Synthetic Cancer Survival Gene Pairs by Cancer Type and Custom Drug Selection Using Them
[0091] 1-1. Selection of target data
[0092] Data for analysis were downloaded from the Tumor Genome Atlas Data Portal on March 4, 2015. The above data include 5,618 secondary (level2) somatic mutation data and 6,838 secondary clinical data. The above-mentioned secondary somatic mutation data are stored in the form of mutation annotation format (maf). For analysis the mutation position and mutation classification were applied. Multiple mutations are divided into "missense mutation", "nonsense mutation", "frameshift indel", "in frame indel", "splice site mutation" ; no phenotypic mutation (Silent mutation)", "intron (Intron)", 'non-coding region (UTR)" and "intergenic (Intergenic)", etc. The above-mentioned secondary clinical data include a variety of clinical data based on cancer The variables, actually used in the COX regression model, have been explo...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2. Distribution and Prognosis Prediction of Synthetic Cancer Survival Gene Pairs by Cancer Type
[0113] As shown in the above-mentioned Example 1, the results of synthetic cancer survival gene analysis were carried out, and 436 synthetic cancer survival gene pairs were selected in five kinds of cancers, and the results are shown in Table 1 (p1) . The screening criteria for the synthetic cancer survival gene pairs used in this example were strictly applied. Clearly, multiple combinations of conditions for detection of synthetic cancer survival gene pairs are possible, however, as shown in Example 1, there were also statistically significant differences in comparing double-lesioned and non-lesioned groups, and in comparing There was also a statistically significant difference in the two injury-only groups, in contrast to the three comparisons between the non-injury group and the two injury-only groups, where the strict criterion of no statistically significant d...
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3. Cancer Survival and Prognosis Prediction Using Synthetic Cancer Survival Burden by Cancer Type
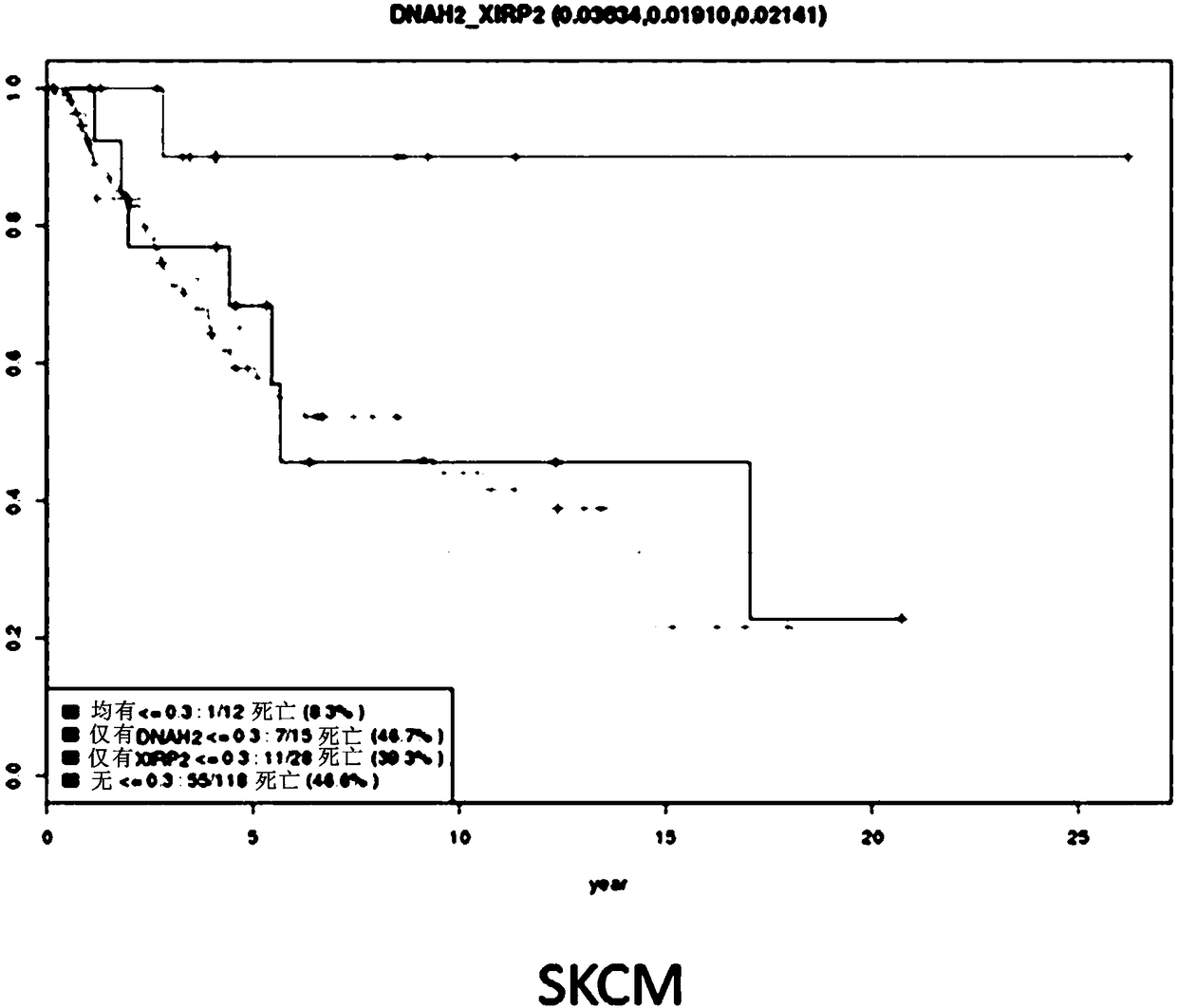
[0138] The effect of the number of synthetic cancer survival gene pairs in cancer patients on the prognosis and survival rate of cancer patients was analyzed. As an example, the results of 341 patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and 181 patients with skin melanoma are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7 middle.
[0139] First, 341 patients with lung adenocarcinoma were divided into three groups: 149 without any synthetic cancer survival gene pairs, 122 with more than one to less than ten, and 70 with more than ten. Survival analysis using COX regression models. The result is as Figure 6 As shown, the survival rate of 70 persons confirmed to have the most synthetic cancer survival gene pairs (having more than 10) was the highest, and the survival rate of 122 persons having more than one to less than ten was found to be the median value, without any synthetic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com