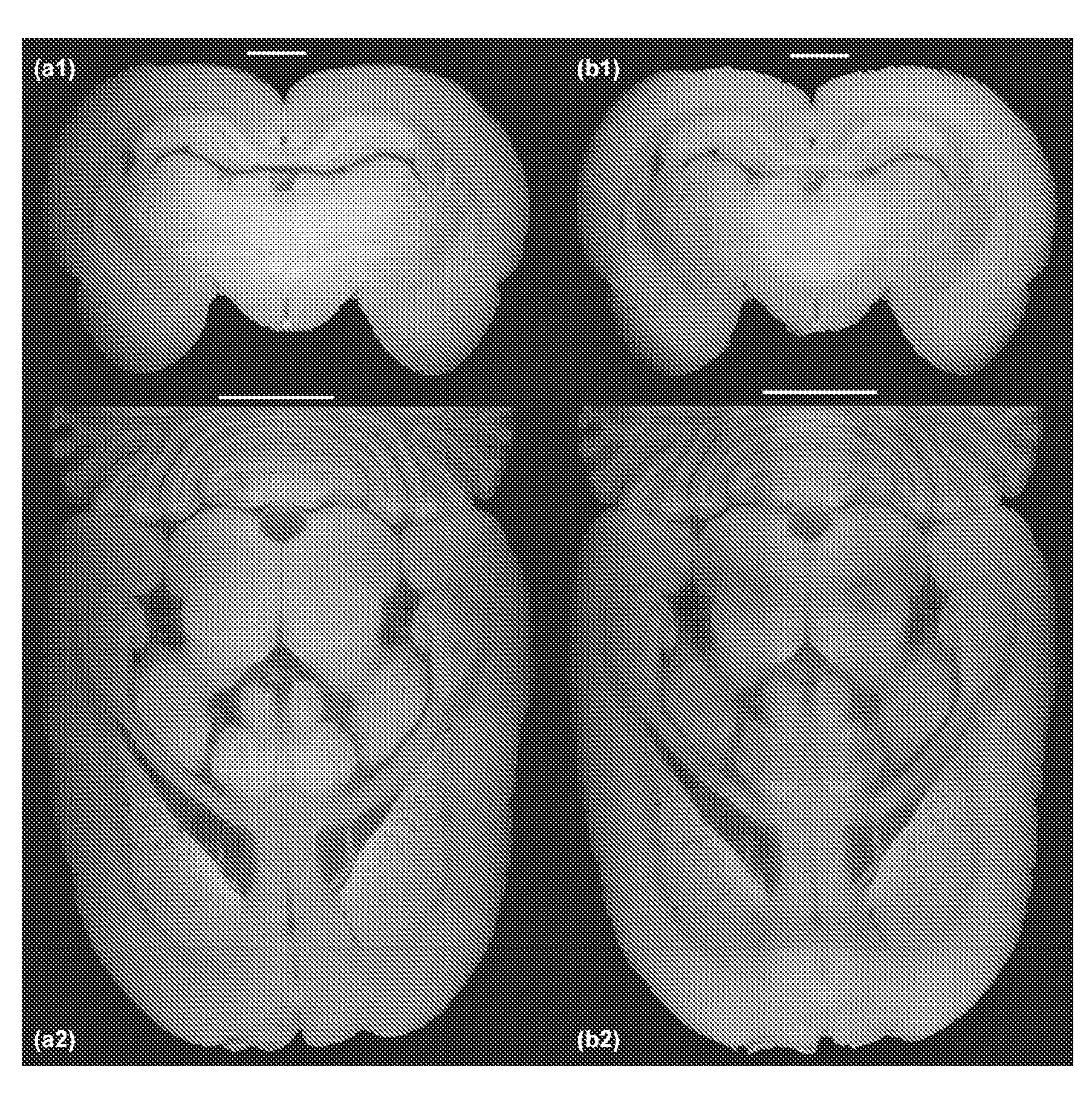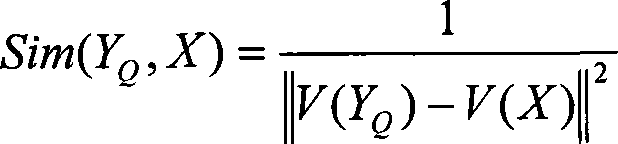Patents
Literature
263 results about "X ray radiography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
X-ray (Radiography) X-ray or radiography uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the body's internal structures. X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. They are often used to help diagnosed fractured bones, look for injury or infection and to locate foreign objects in soft tissue.
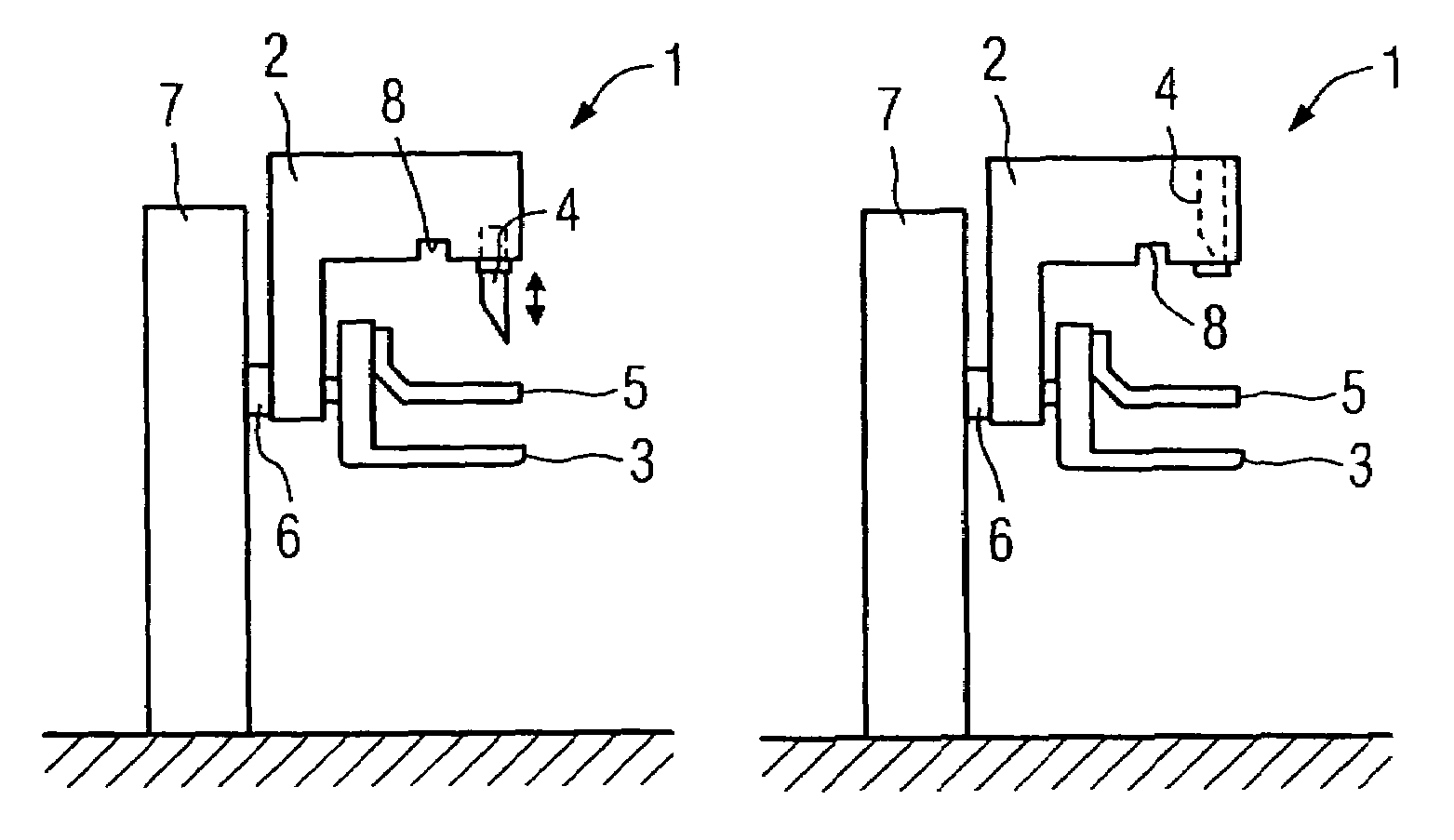
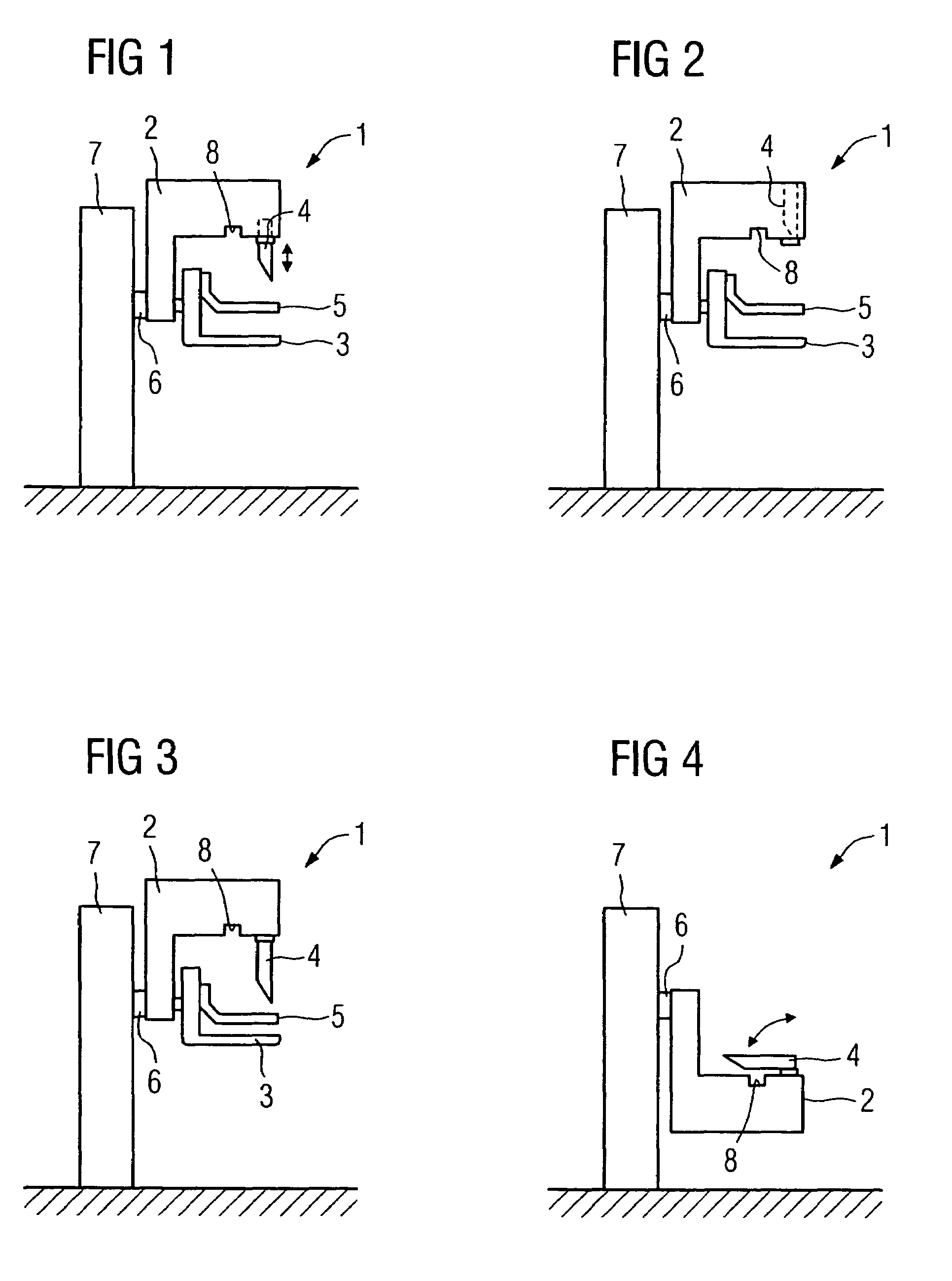
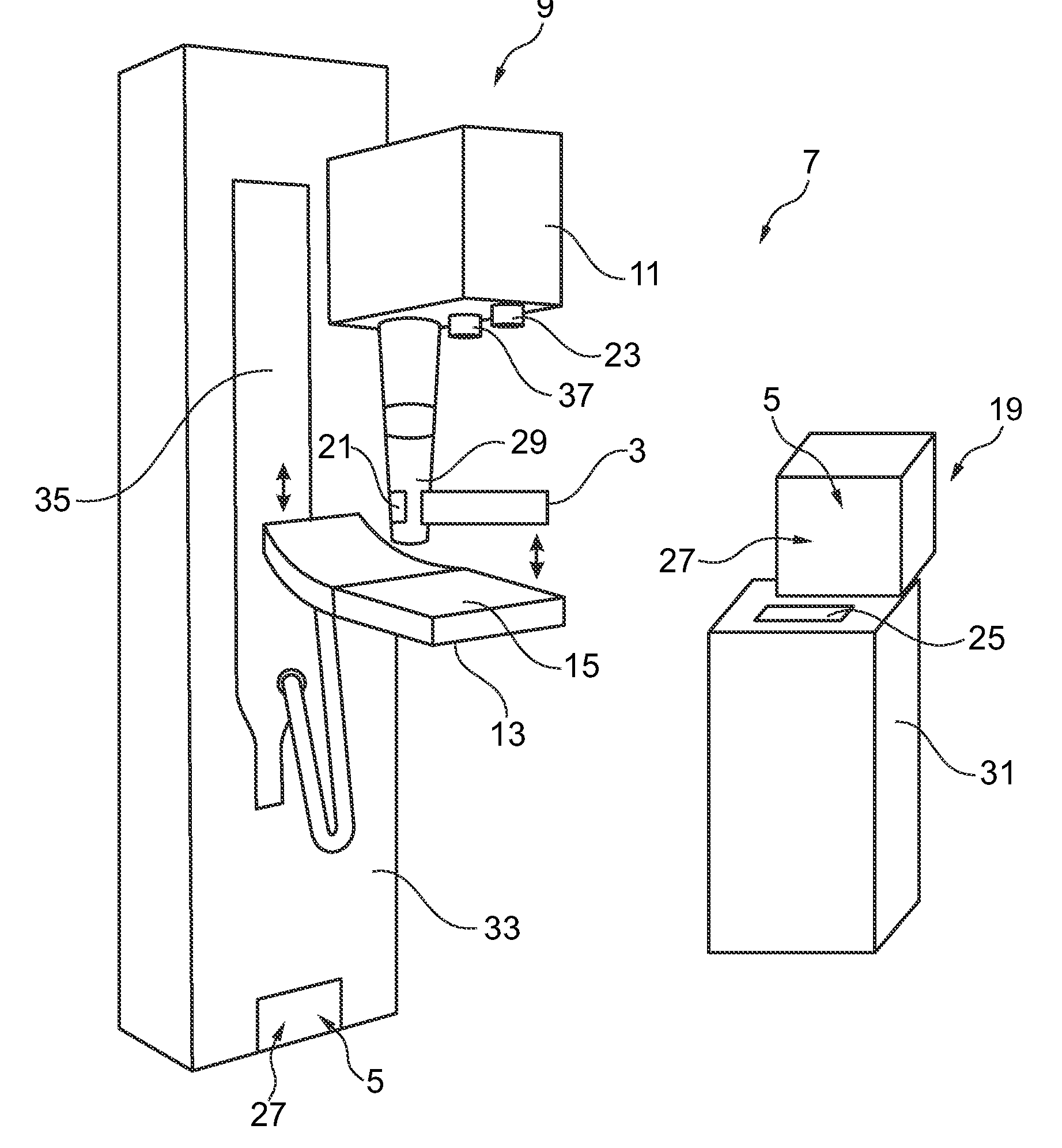
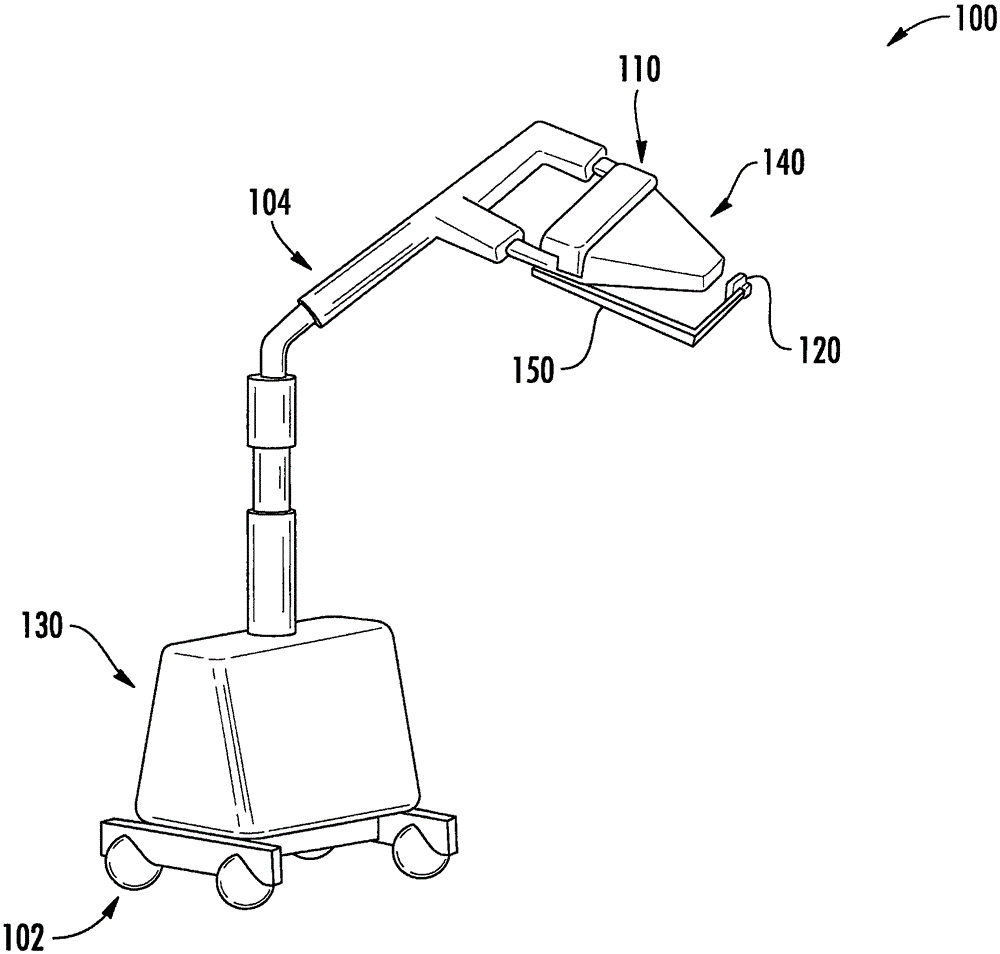
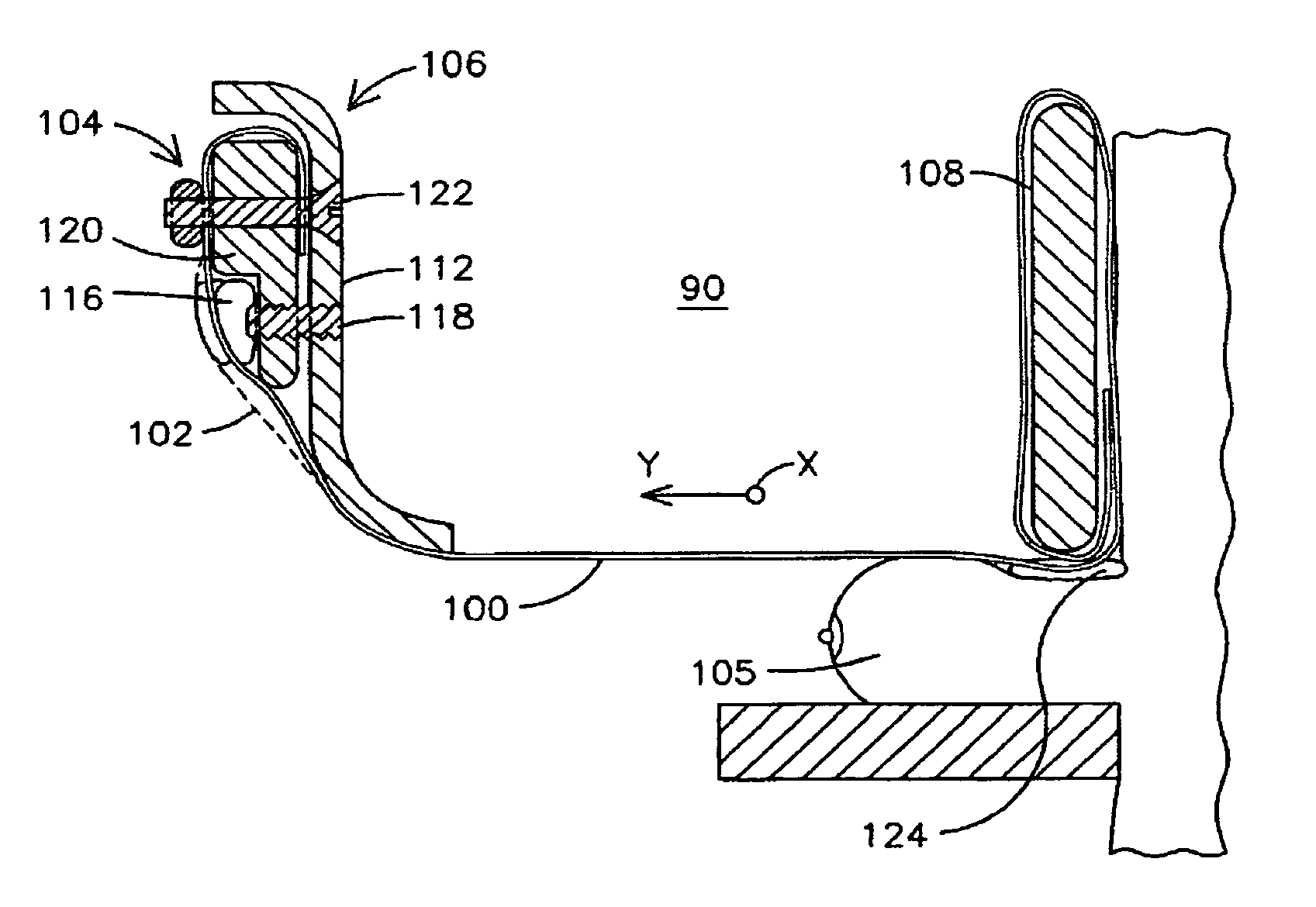
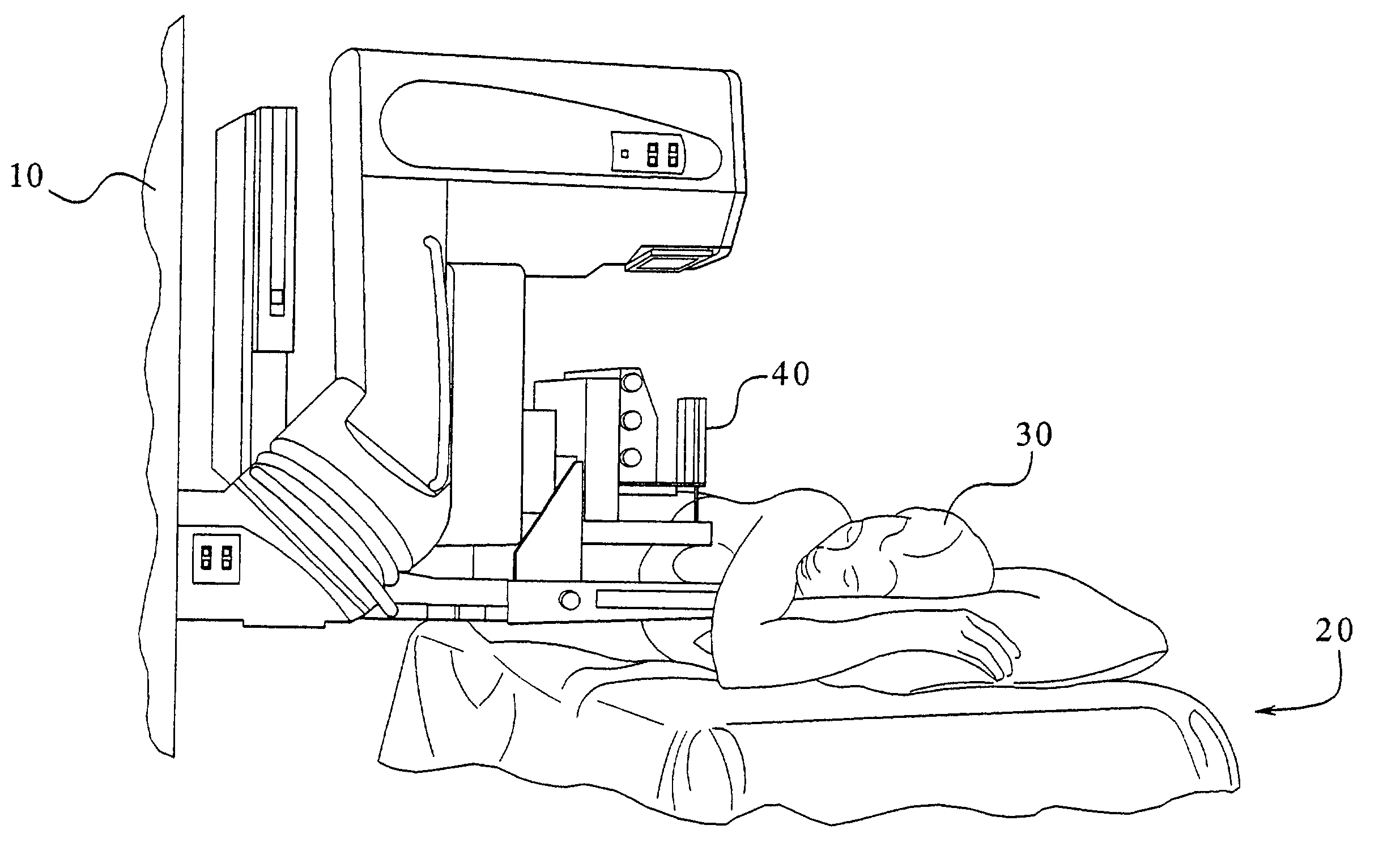
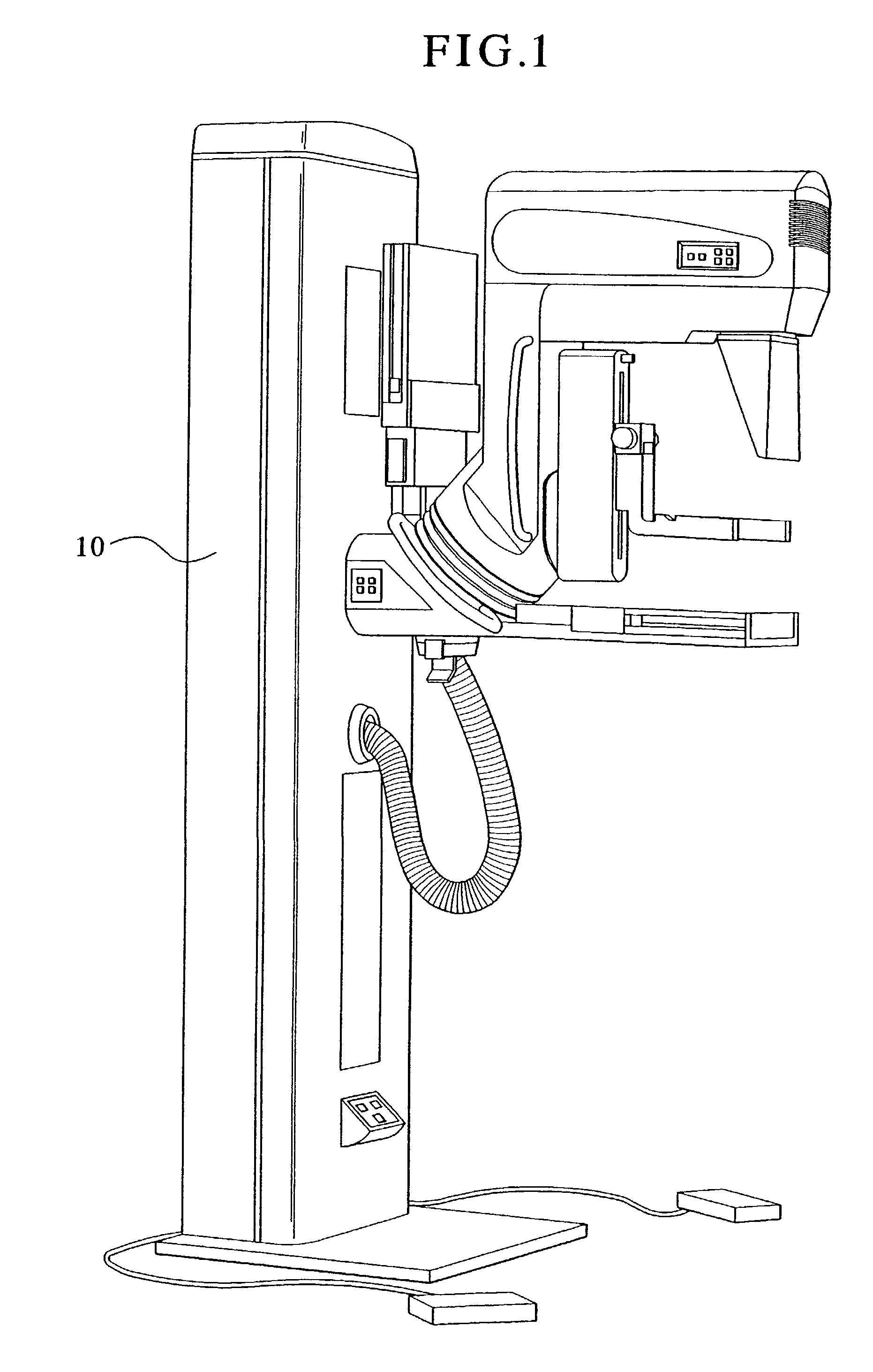
Mammograph system with a face shield
ActiveUS7315607B2Less damageLess fatiguePatient positioning for diagnosticsX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayEngineering
The present embodiments relate to a mammograph system with a face shield. The mammography system includes an X-ray emitter head; an object table; and a face shield. The face shield is movably supported by the X-ray emitter head and is movable into at least first and second positions. In the first position, the face shield is retracted into the X-ray emitter head. In the second position, at least a portion of the face shield protrudes out of the X-ray emitter head.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
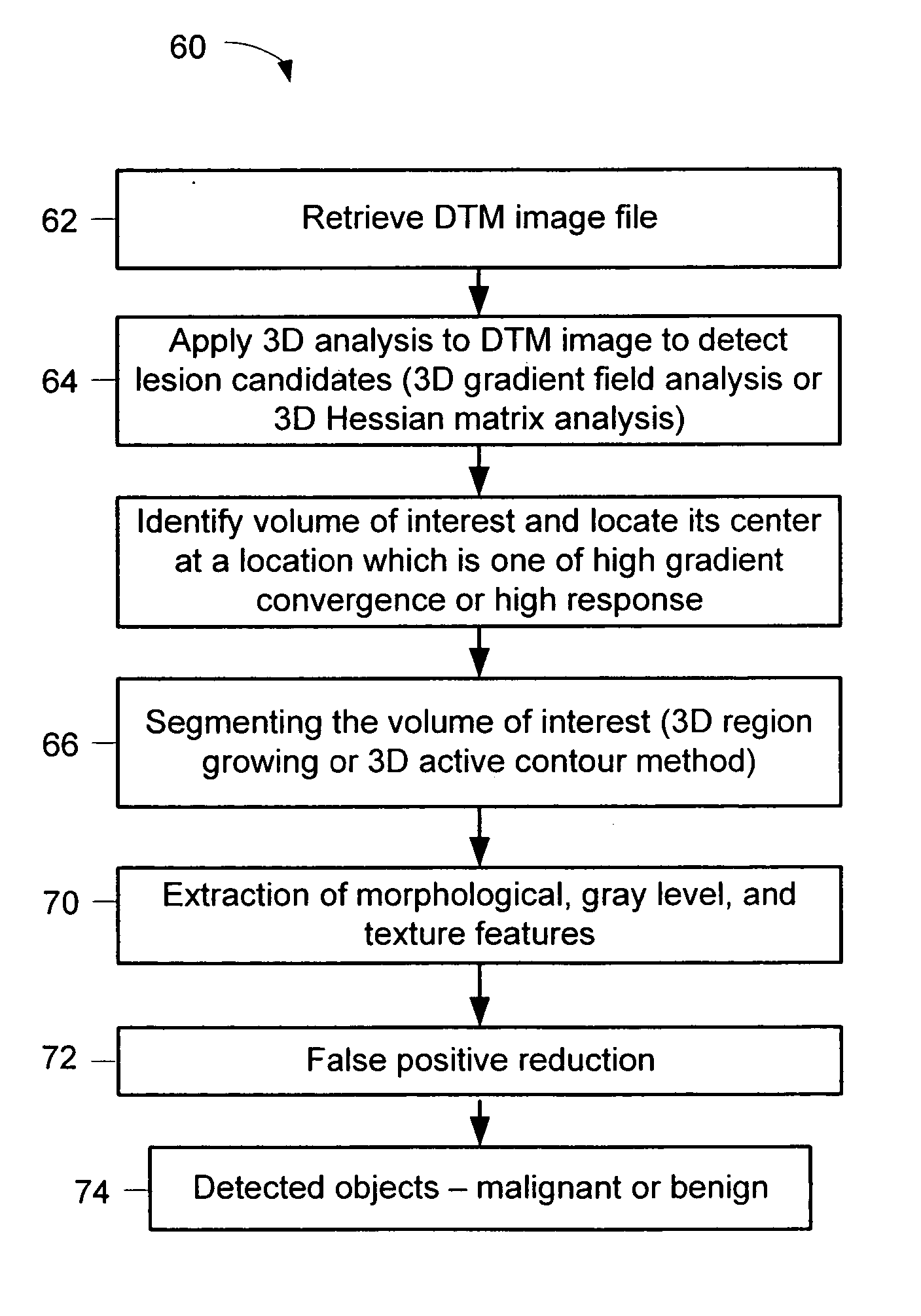
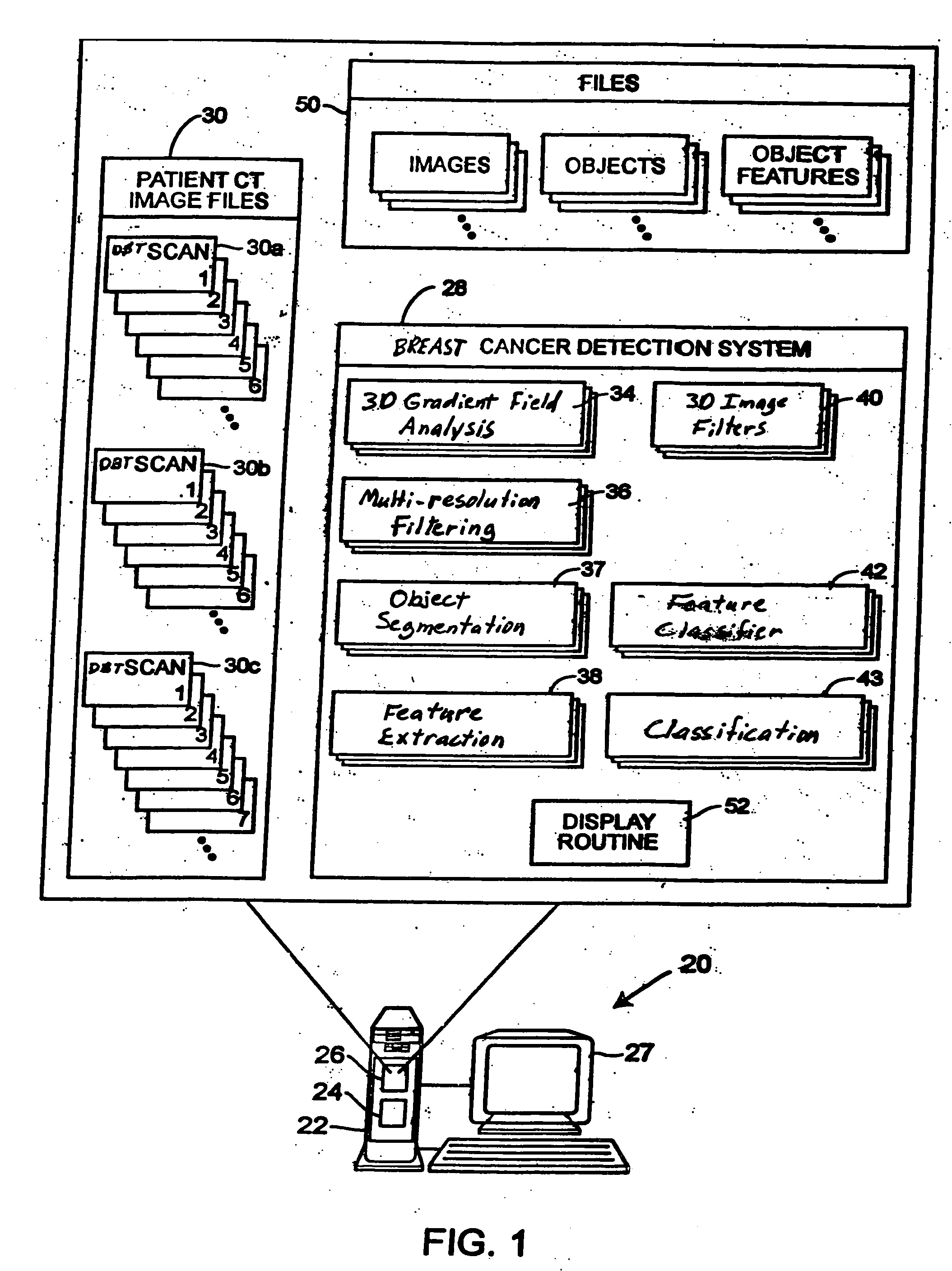
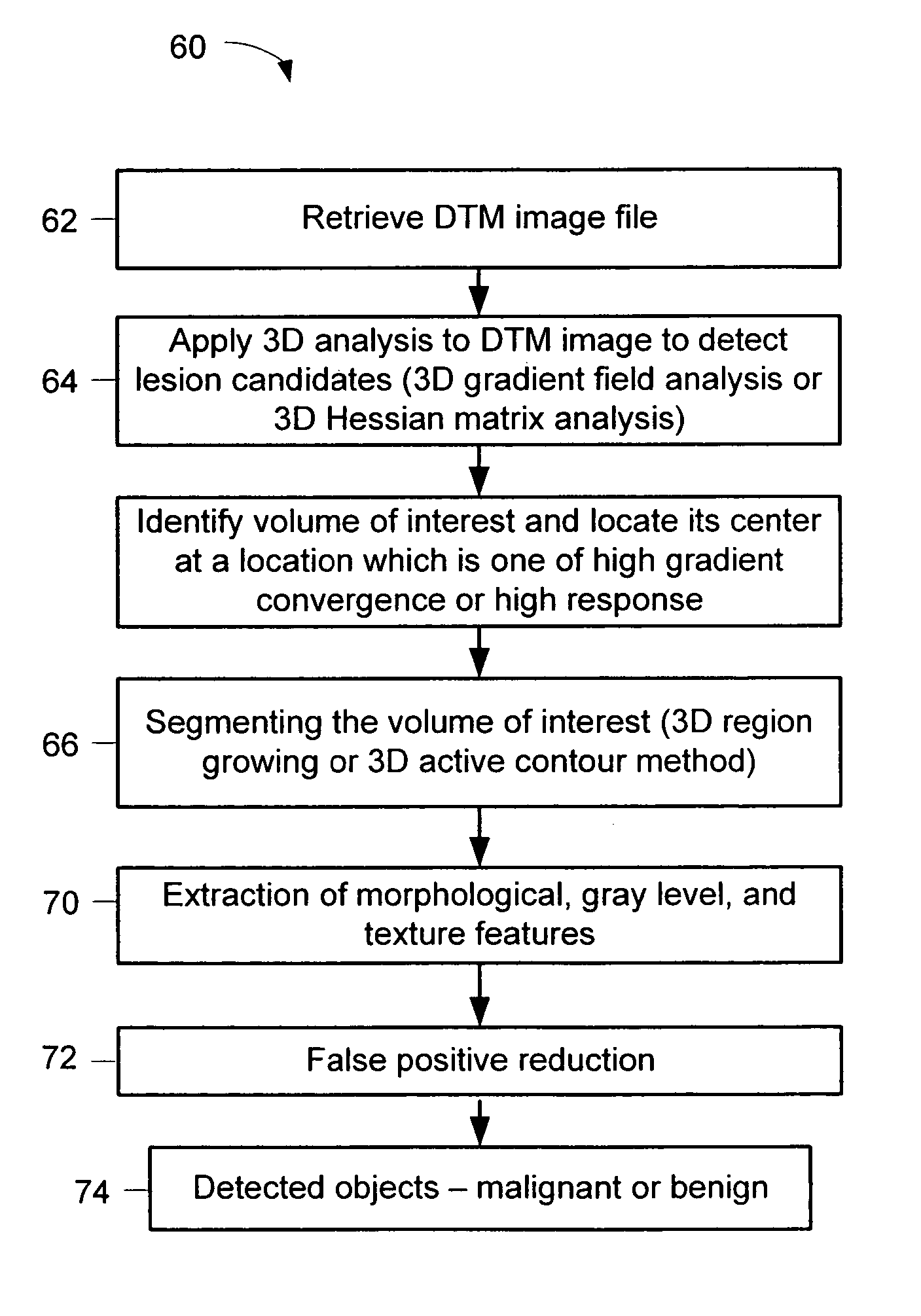
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS20060177125A1Improve breast cancer detectionExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS8855265B2Reduce impactImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
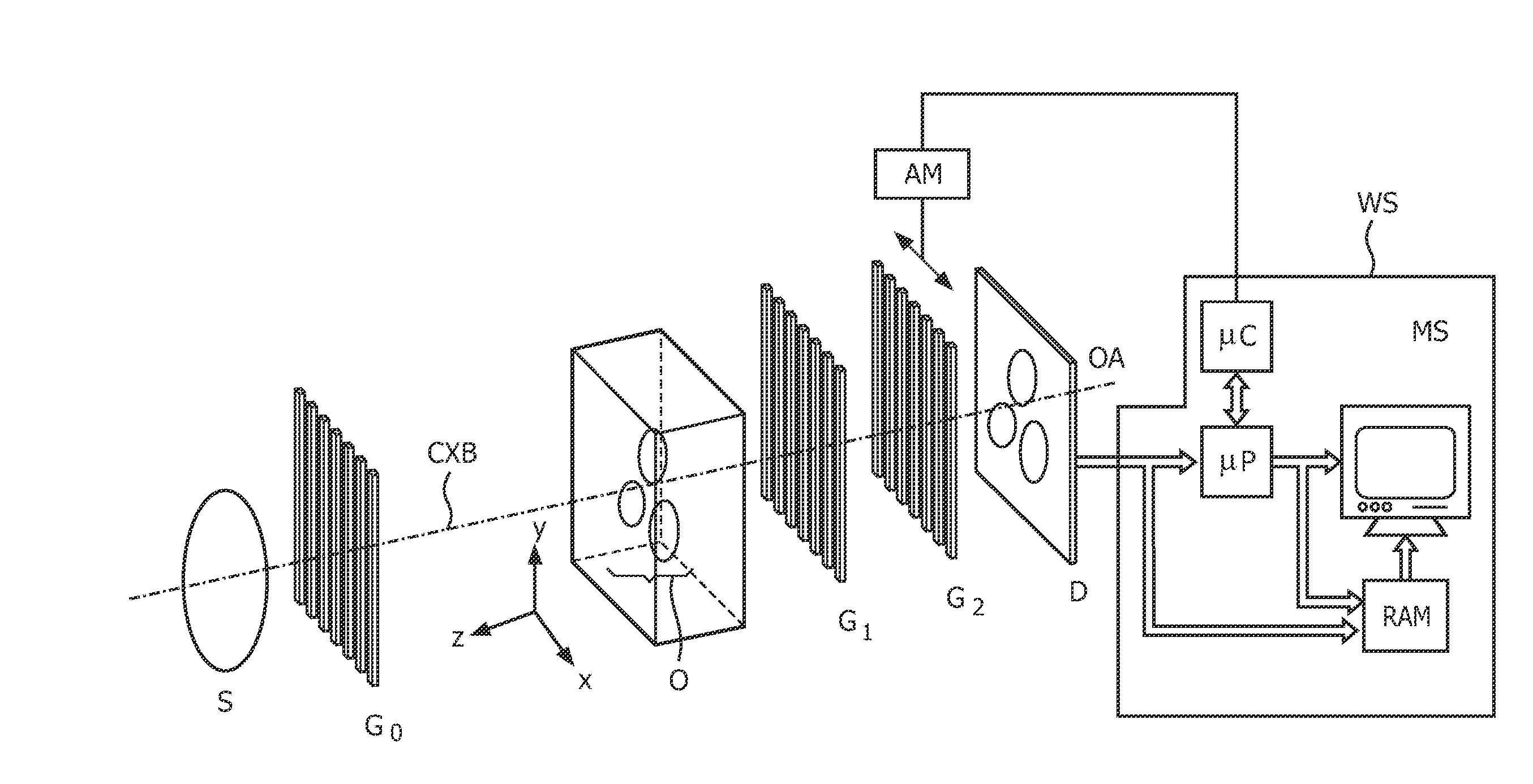
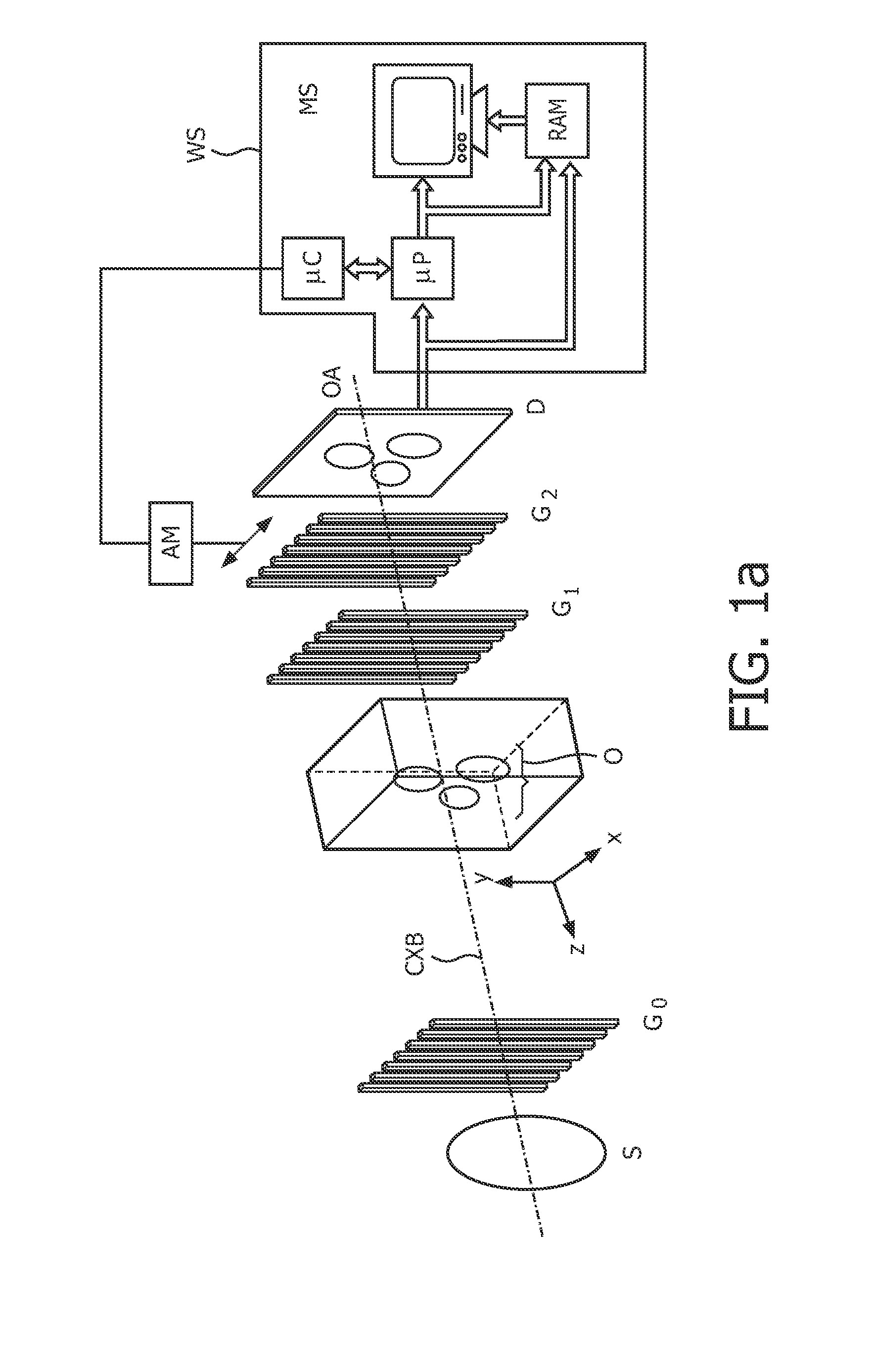
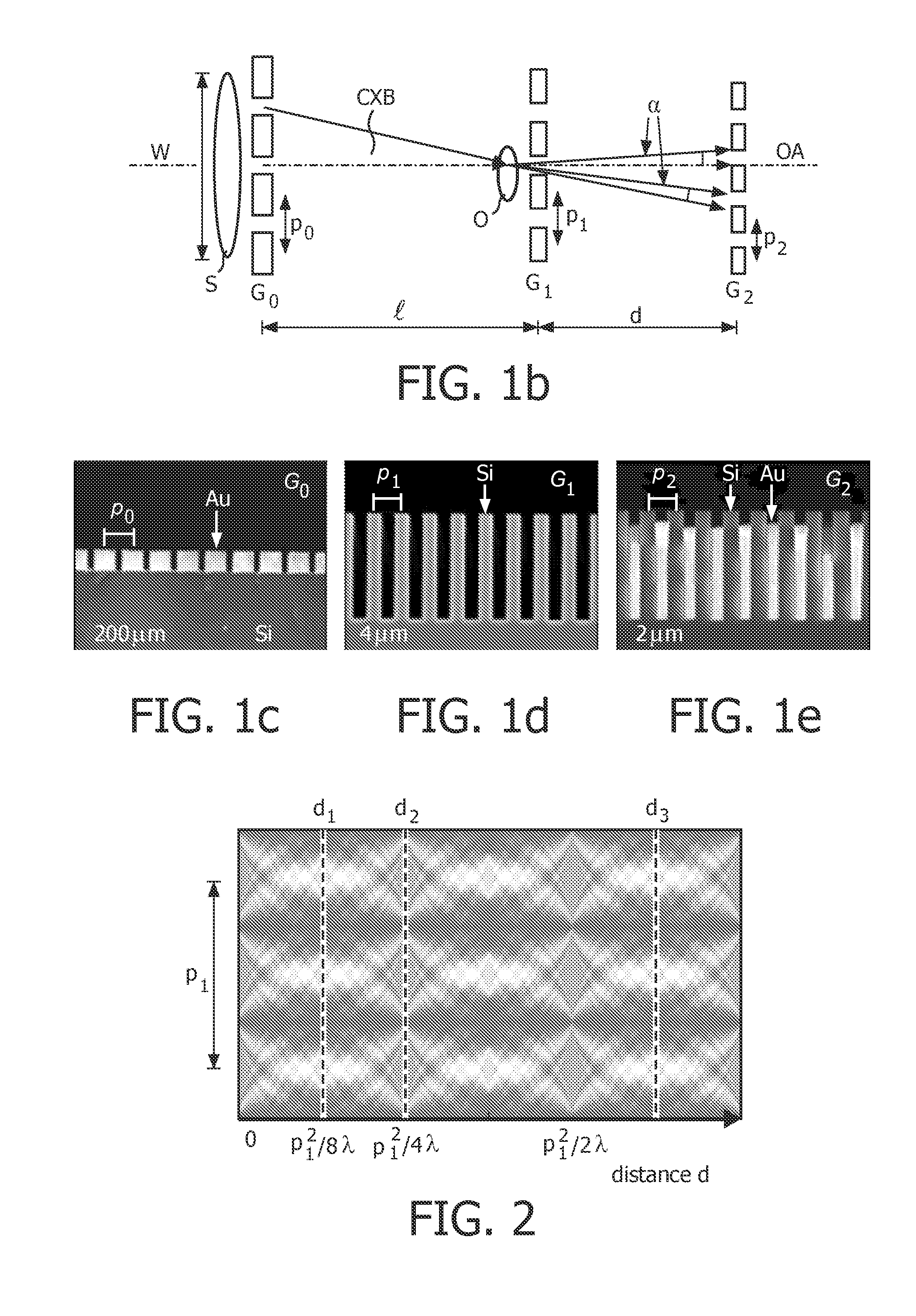
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Correction method for differential phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120099702A1Good estimateImprove image qualityImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionHard X-raysBeam splitter
The present invention generally refers to a correction method for grating-based X-ray differential phase contrast imaging (DPCI) as well as to an apparatus which can advantageously be applied in X-ray radiography and tomography for hard X-ray DPCI of a sample object or an anatomical region of interest to be scanned. More precisely, the proposed invention provides a suitable approach that helps to enhance the image quality of an acquired X-ray image which is affected by phase wrapping, e.g. in the resulting Moiré interference pattern of an emitted X-ray beam in the detector plane of a Talbot-Lau type interferometer after diffracting said X-ray beam at a phase-shifting beam splitter grating. This problem, which is further aggravated by noise in the obtained DPCI images, occurs if the phase between two adjacent pixels in the detected X-ray image varies by more than π radians and is effected by a line integration over the object's local phase gradient, which induces a phase offset error of π radians that leads to prominent line artifacts parallel to the direction of said line integration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Surgical targeting system
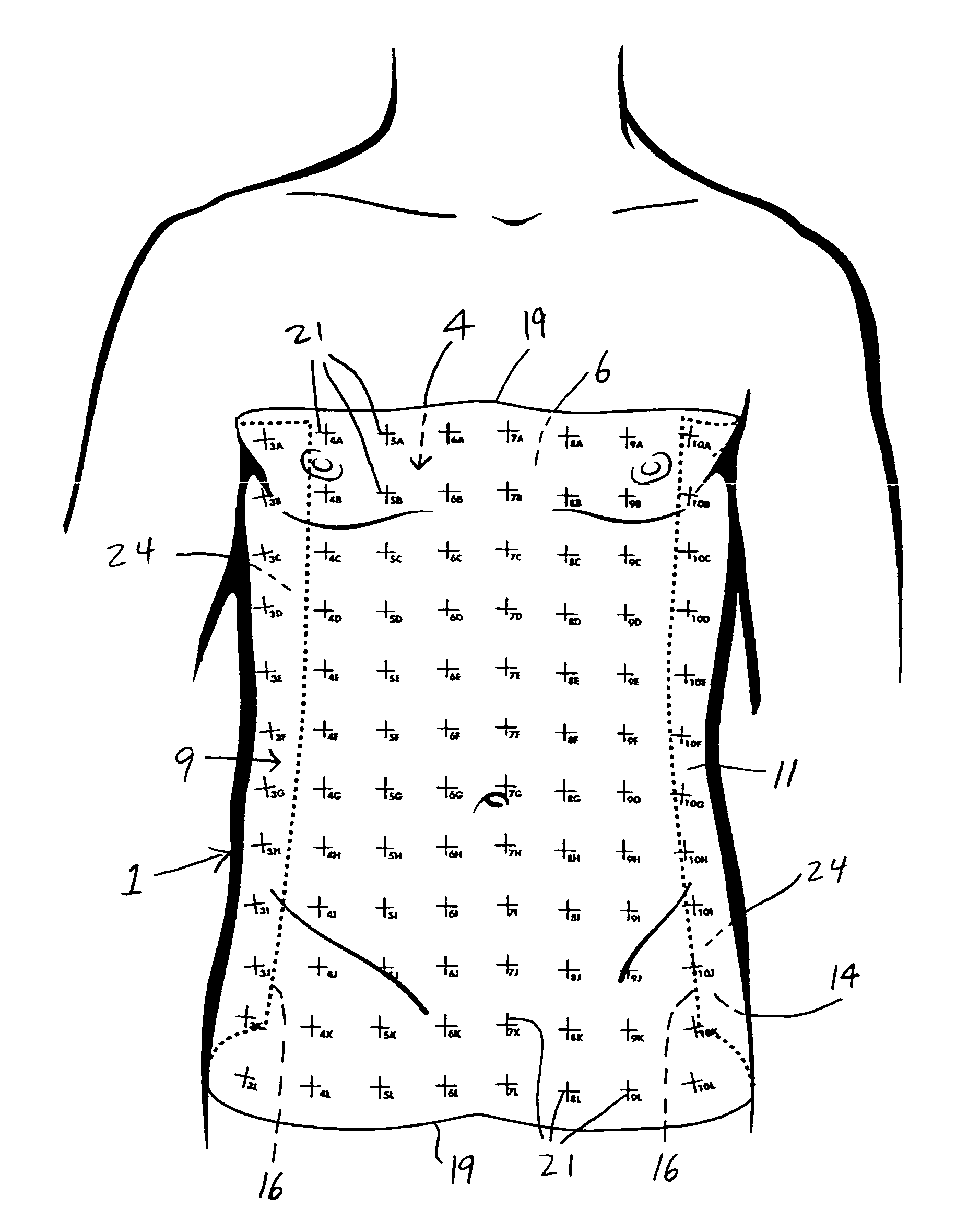
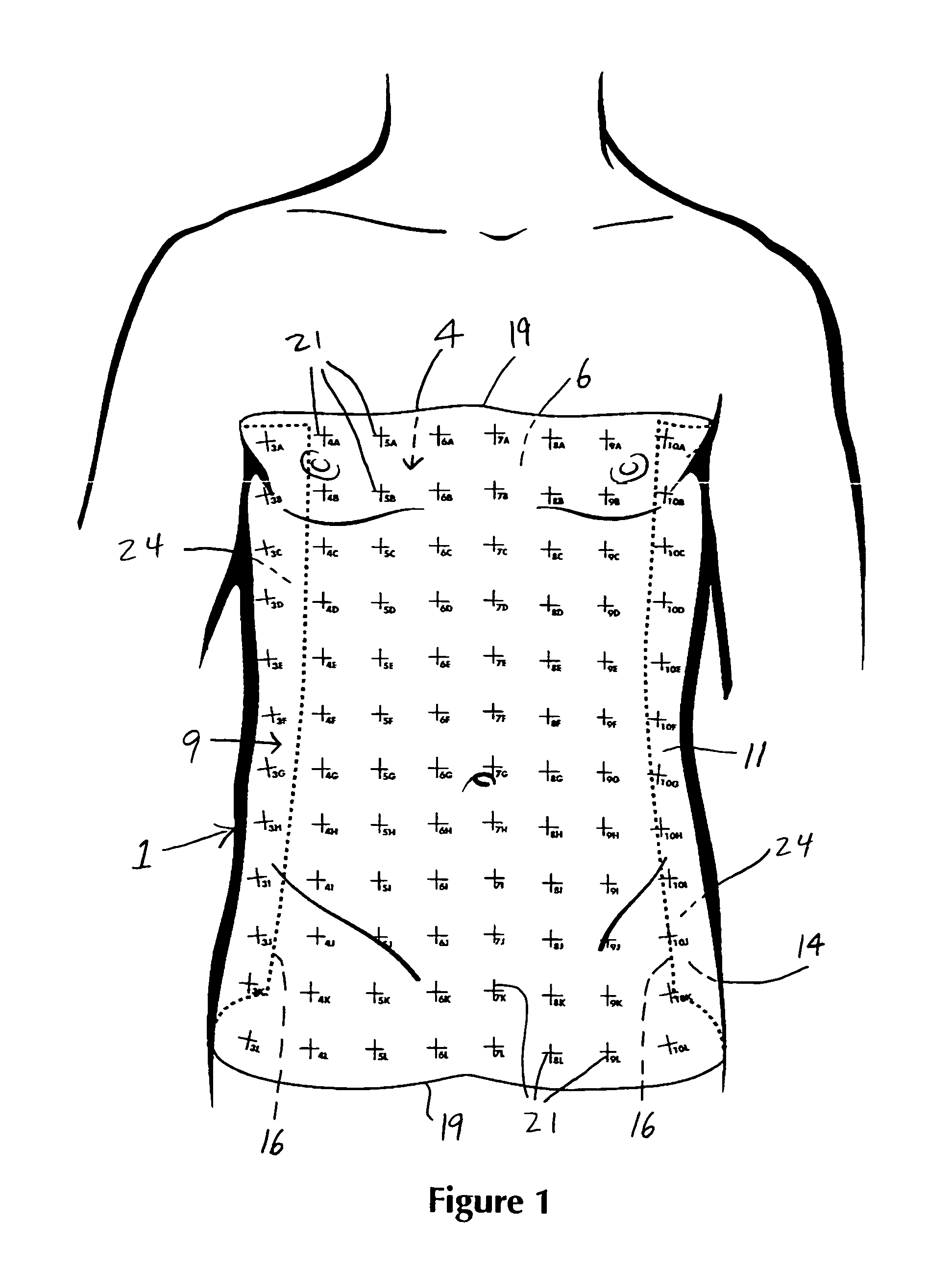
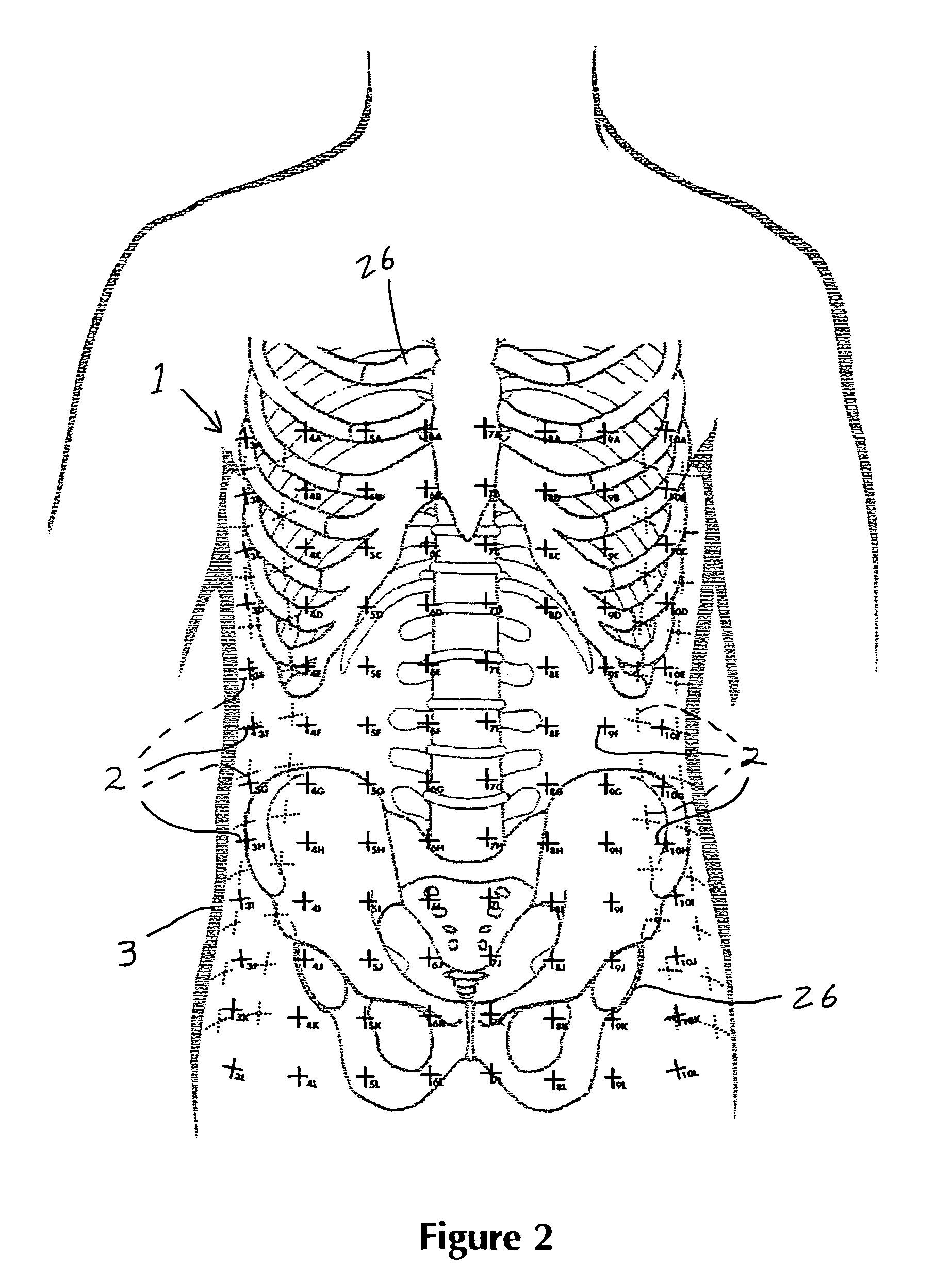
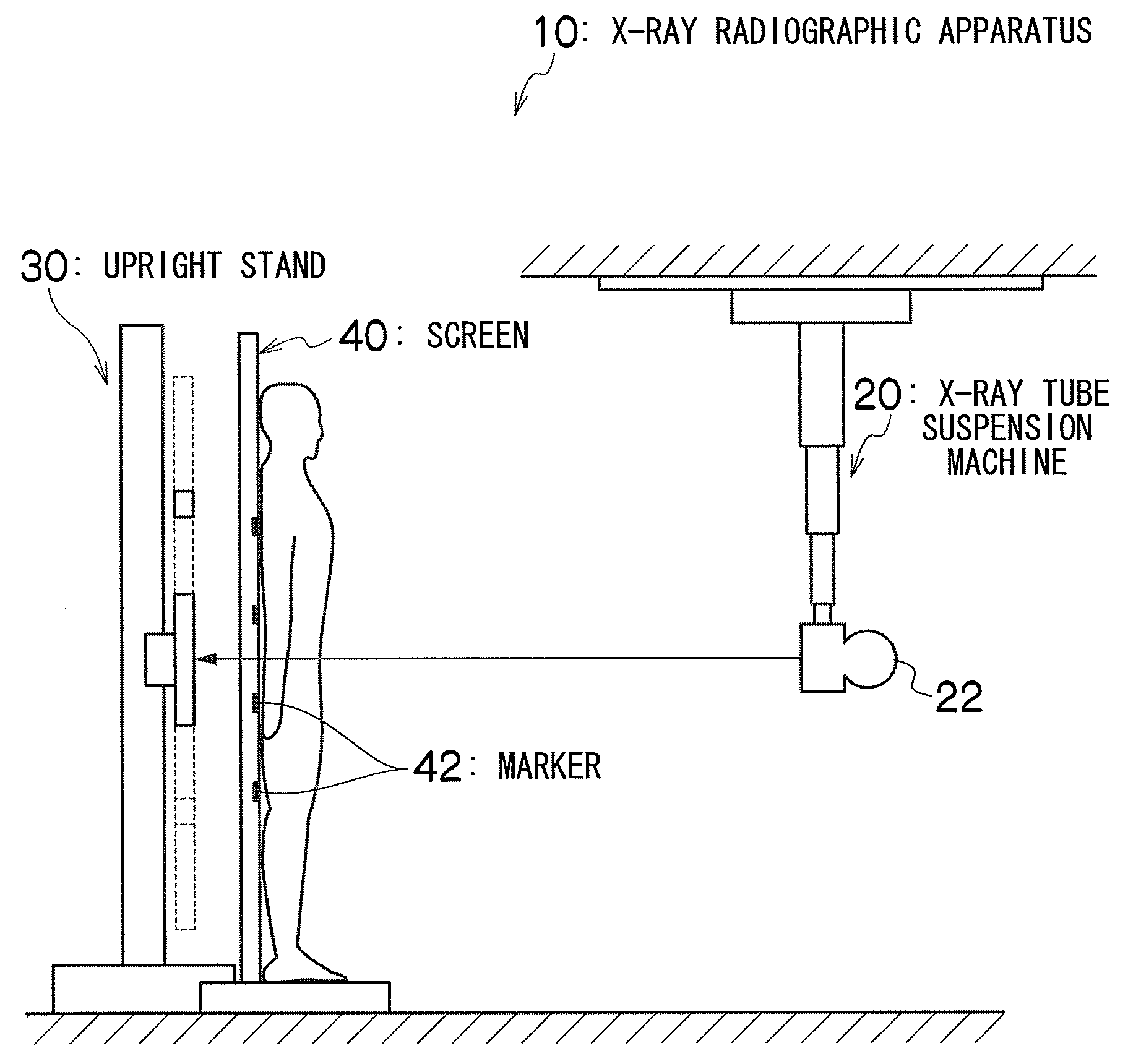
A targeting device for providing a series of coordinates / lines within a sheet of sterile, flexible material with an adherent surface which is applied to the skin (after suitable surgical preparation). The sheet is non-porous and may have a topical antiseptic on the side which is applied to the skin. A fluoroscope or roentgenographic image of the portion of the body to which the adherent film is applied will show the underlying skeletal and radiopaque elements as well as the overlying surgical grid. Once the targeting device is applied, the coordinates on the grid lines are clearly visible on the surface of the skin as well as on the fluoroscopic or radiographic image and by knowing the direction of the fluoroscopic or radiographic beam, the operator will be able to thereby correlate a specific locus on the skin with an underlying skeletal element or other underlying radiopaque structure. By applying the targeting device to the part of the body in a circumferential or nearly circumferential manner, and utilizing a radiolucent operating room table, and a radiograph or C-arm fluoroscope, targeting techniques using the targeting device can be utilized at surgery. Multiple targeting or percutaneous procedures can be performed at the same sitting with the application of a single device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method and apparatus for medical X-radiography
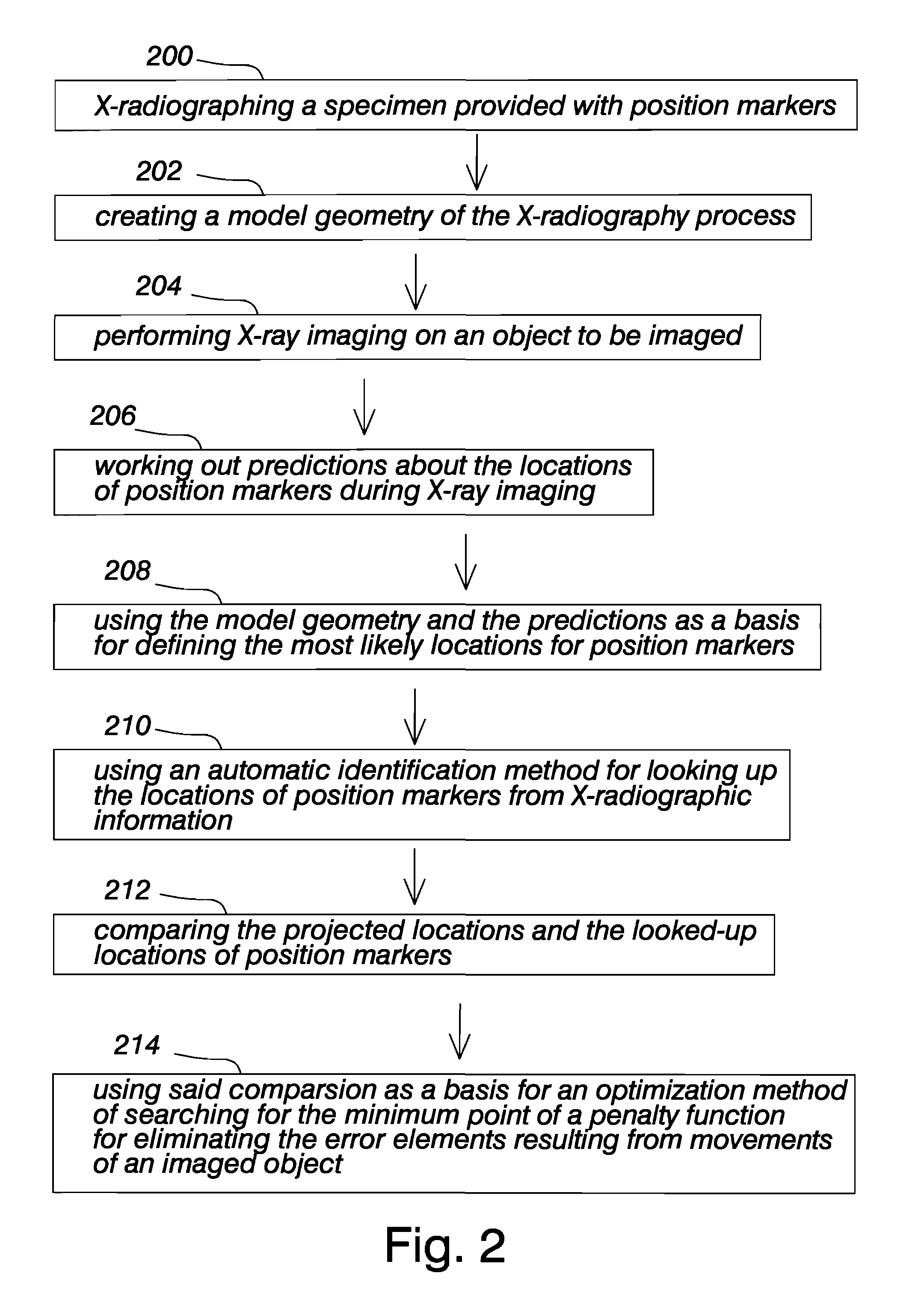
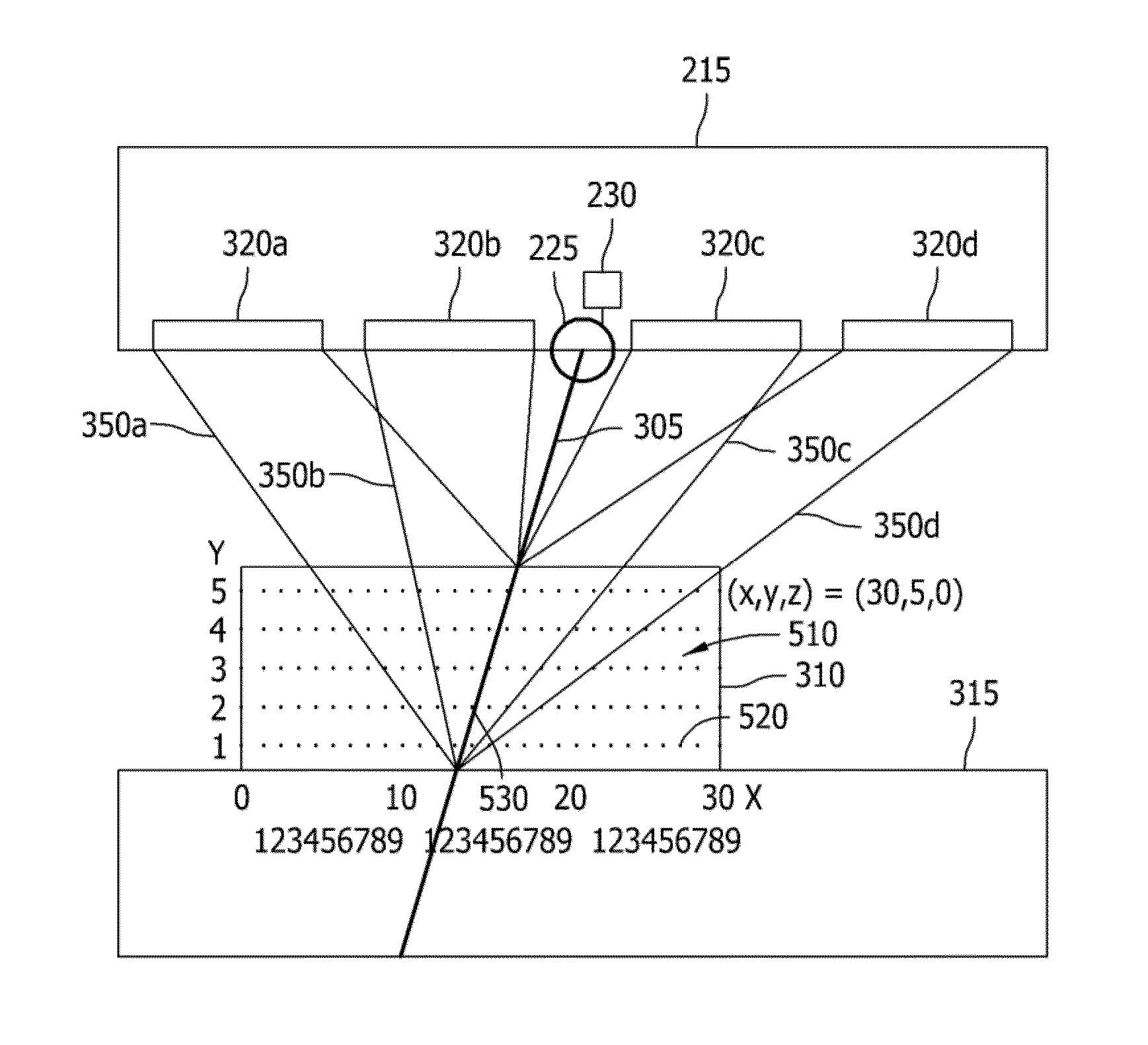
ActiveUS7494277B2Eliminate errorsEliminating error elementForeign body detectionRadiation beam directing meansSoft x rayX-ray
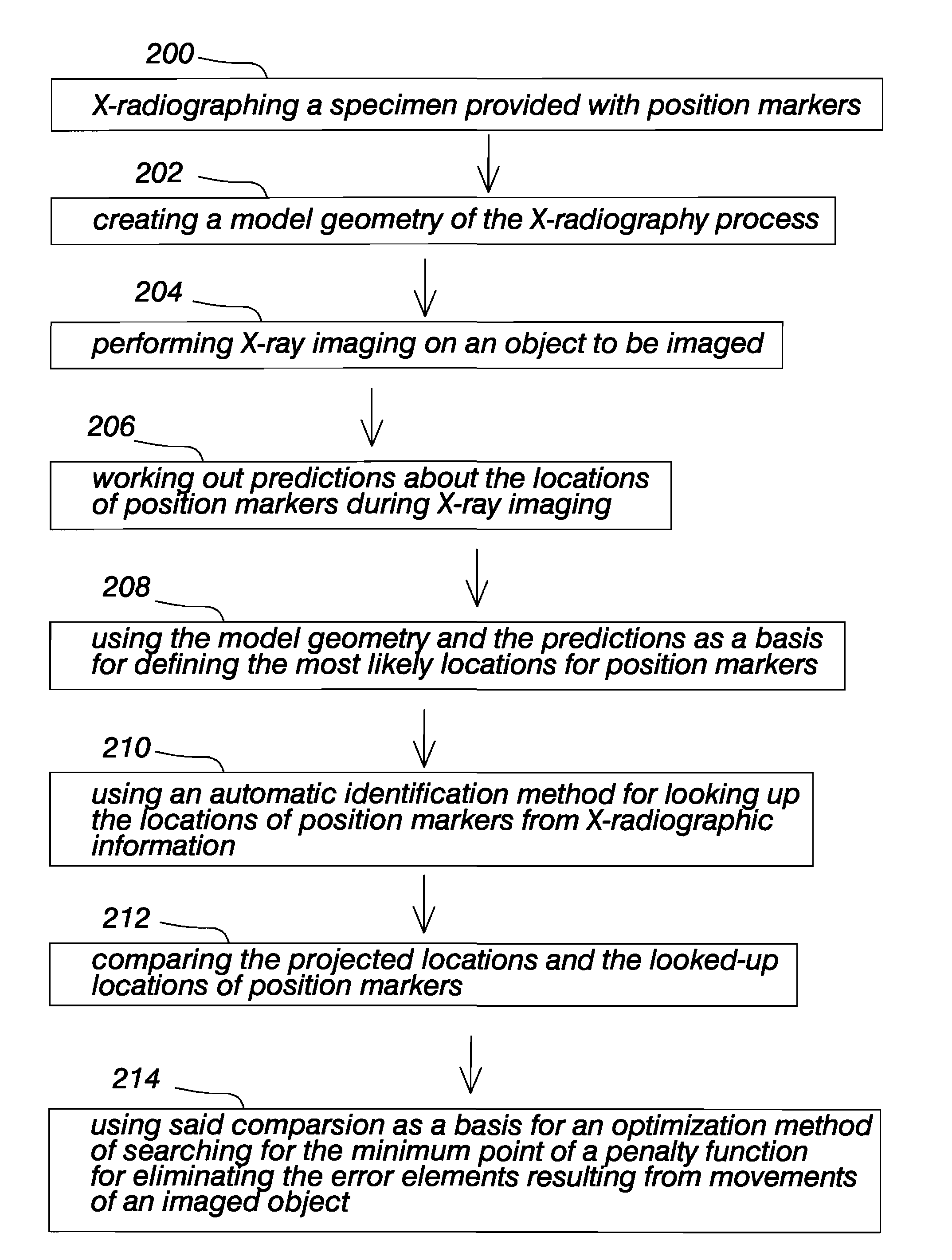
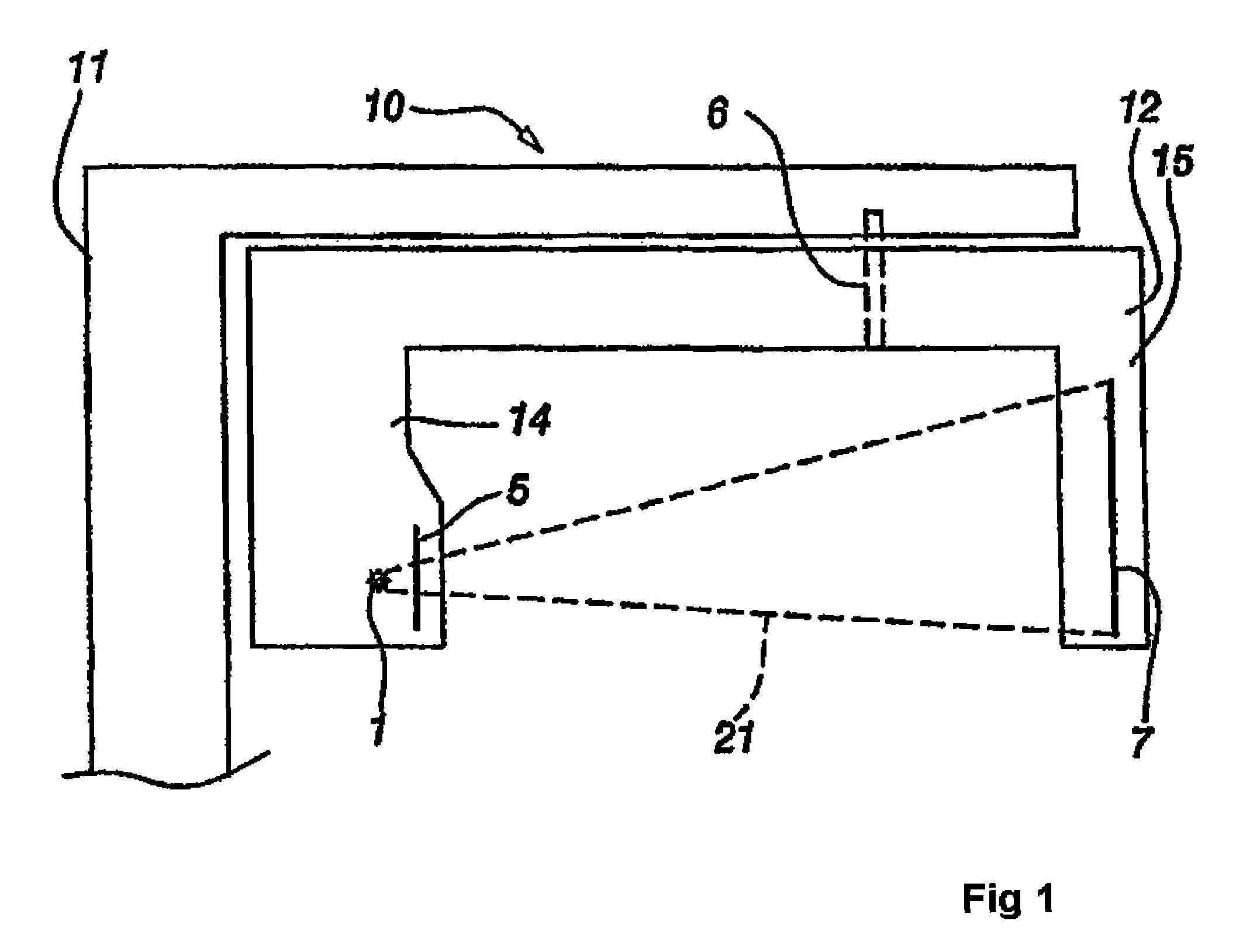
The invention relates to a method for eliminating error elements caused by movements of an imaged object in X-radiography, said method comprising performing X-radiography on an imaged object for compiling three-dimensional X-radiographic information. The method comprises creating a model geometry of an X-ray imaging process, said creation work comprising a determination of the location for two or more position markers in a set of coordinates graded for an X-ray imaging apparatus. When X-radiography of an imaged object is completed, predictions are worked out regarding the locations of position markers during the imaging session. The locations and predictions determined on the basis of the model geometry are used as a basis for defining projected or most likely locations for the position markers and an automatic position markers identification method is applied for finding the locations of position markers from within a search area in the X-radiographic information. When the locations of at least two position markers have been found with the automatic position markers identification method, a minimization of offsets between the projected locations of position markers and the locations of position markers looked up by the automatic identification method is performed by searching for a minimum point of the function for eliminating the error elements resulting from movements of an imaged object.
Owner:PALODEX GROUP
Methods and systems for volumetric reconstruction using radiography
ActiveUS8989342B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray radiography
Methods and systems for use in generating a volumetric reconstruction of an object using scattered X-ray radiography. An X-ray beam is directed towards a point within a target object. Scattered X-rays are measured by detectors and measurement data is stored. The X-ray beam is directed towards different points. Measurement data associated with each point is analyzed using a ray tracing methodology to assign contrast values to each point. A volumetric image is generated therefrom.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Low dose single step grating based X-ray phase contrast imaging
InactiveCN102325498ASmall doseImage quality is not degradedMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation diagnosticsHard X-raysGrating
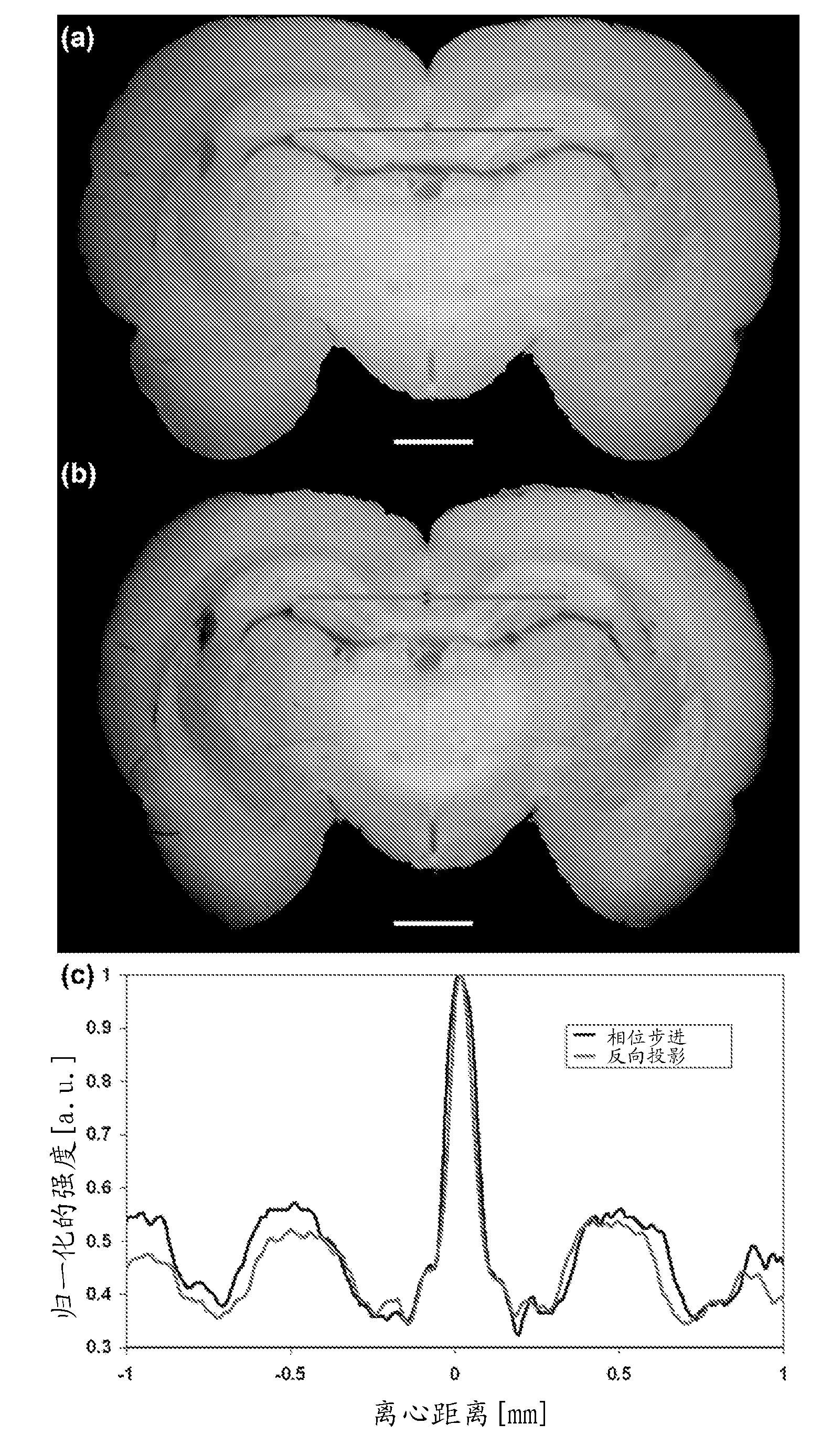
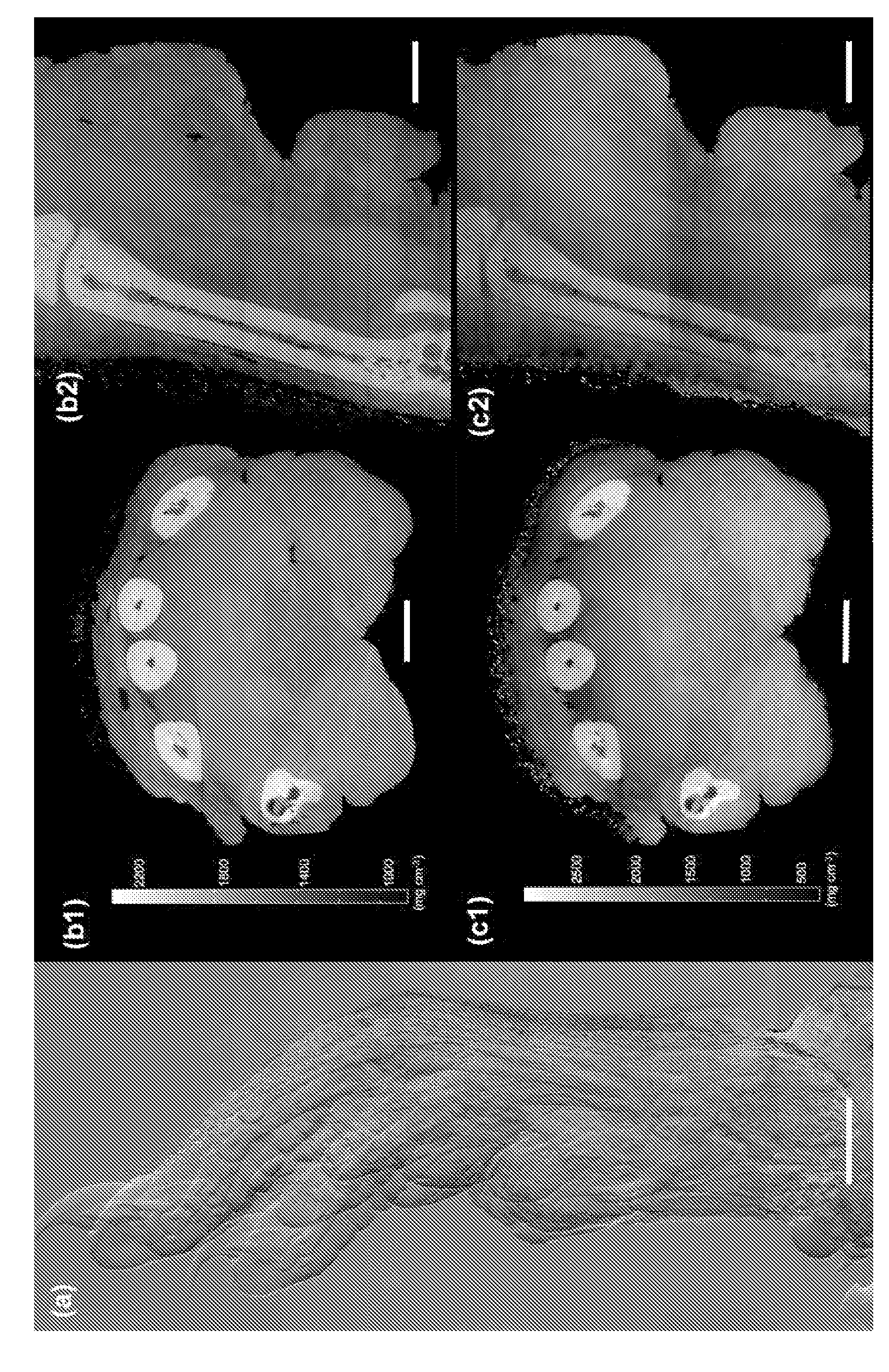
Phase sensitive X-ray imaging methods can provide substantially increased contrast over conventional absorption based imaging, and therefore new and otherwise inaccessible information. The use of gratings as optical elements in hard X-ray phase imaging overcomes some of the problems that have impaired the wider use of phase contrast in X-ray radiography and tomography. So far, to separate the phase information from other contributions detected with a grating interferometer, a phase-stepping approach has been considered, which implies the acquisition of multiple radiographic projections. Here,an innovative, highly sensitive X-ray tomographic phase contrast imaging approach is presented based on grating interferometry, which extracts the phase contrast signal without the need of phase stepping. Compared to the existing phase step approach, the main advantage of this new method dubbed 'reverse projection' is the significantly reduced delivered dose, without degradation of the image quality. The new technique sets the pre-requisites for future fast and low dose phase contrast imaging methods, fundamental for imaging biological specimens and in-vivo studies.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Radiation imaging apparatus, radiation imaging system, and program
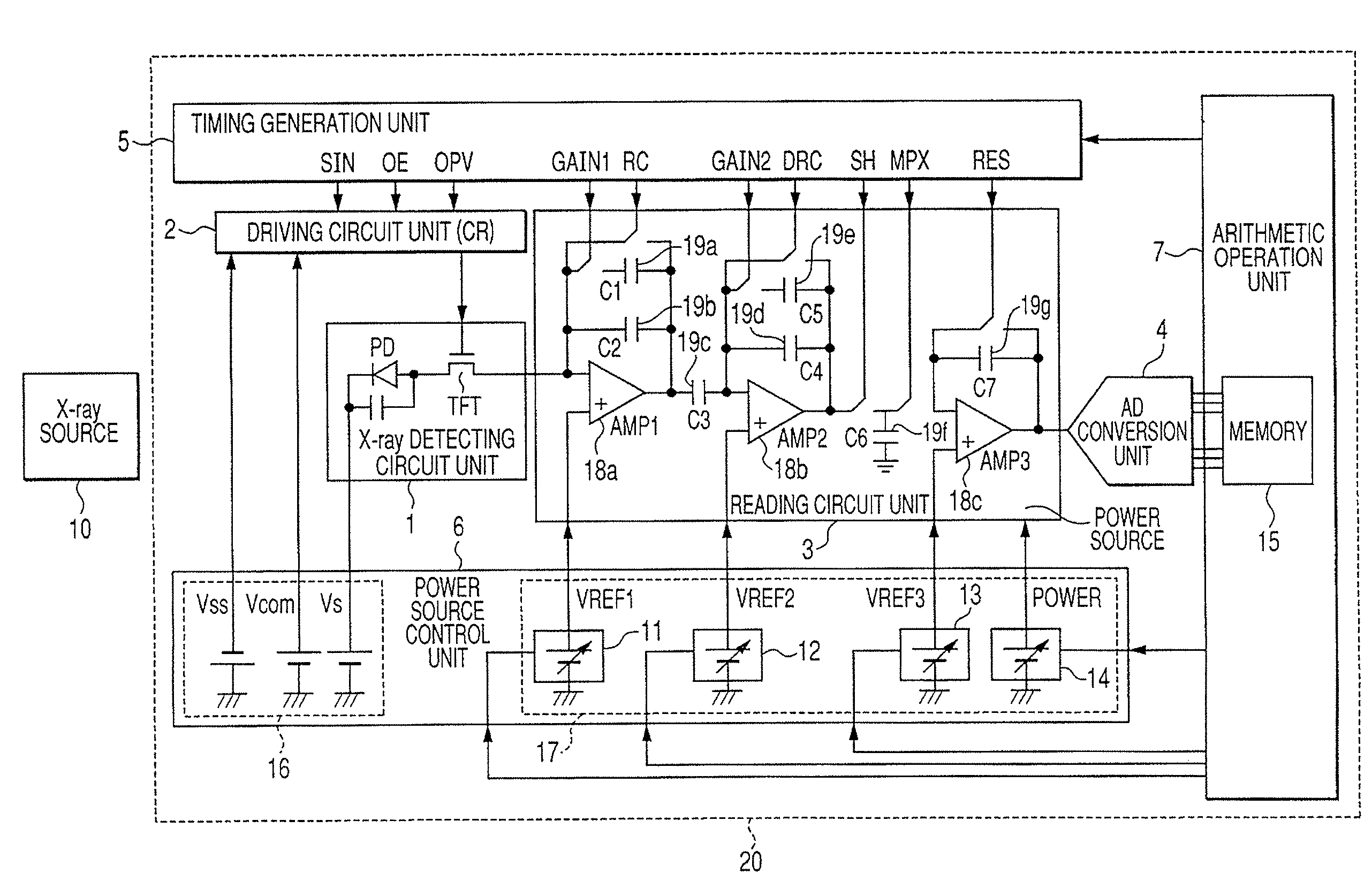
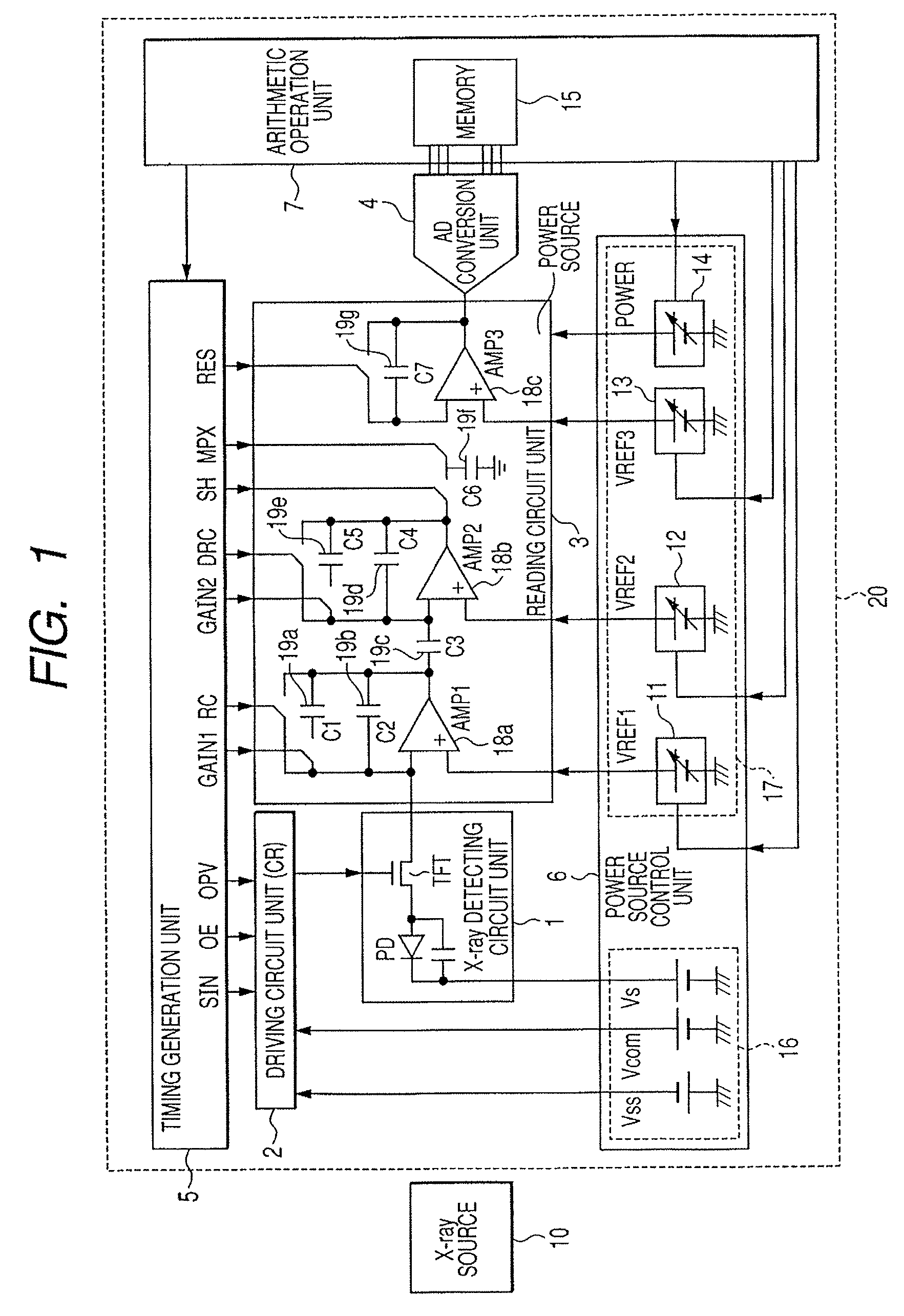
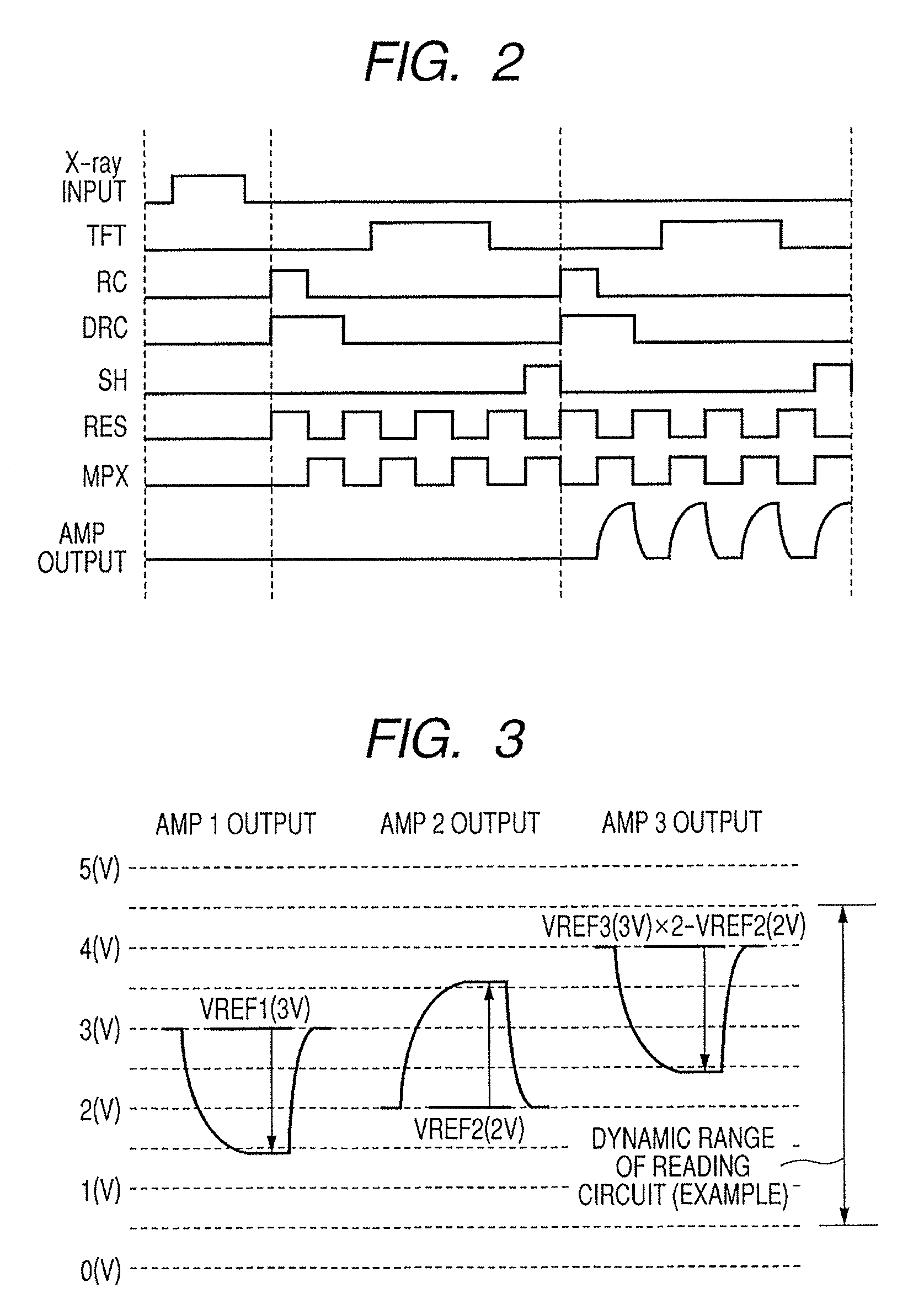
InactiveUS7381963B2Accurate imagingObtain goodTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesRadiation imagingX-ray
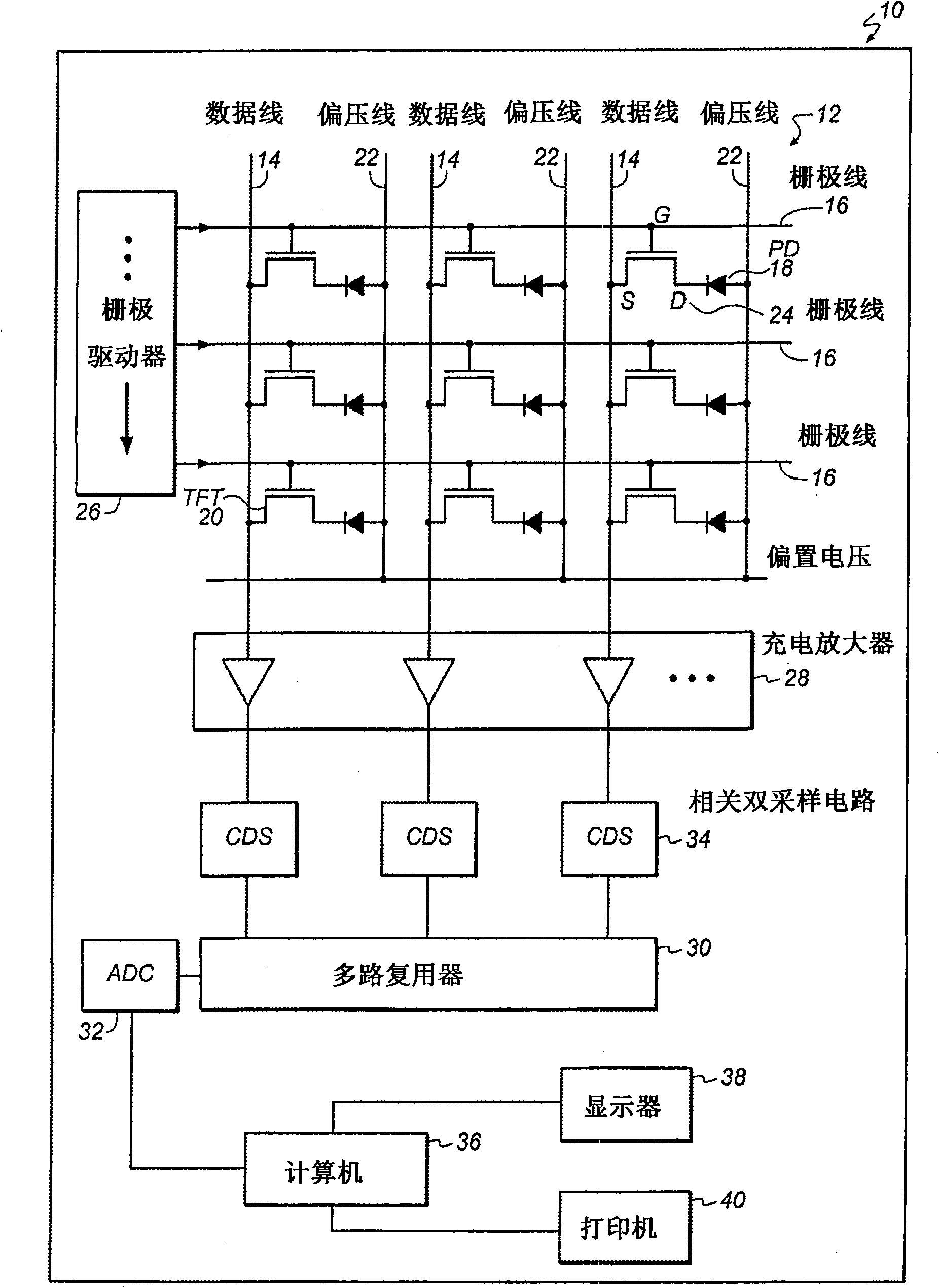
It is made possible that, in accordance with a plurality of radiographing modes such as the still image radiographing mode and the moving image radiographing mode, the outputs both in the irradiation period and in the non-irradiation period are made to fall within the dynamic range of the radiographing system, whereby an accurate, high-S / N-ratio X-ray radiographic image is obtained. For that purpose, in accordance with the plurality of radiographing modes, an arithmetic operation unit adjusts a power source to control voltage to be applied to a reading circuit unit or an Analogue-Digital conversion unit, such that, in each of the radiographing modes, both an electric signal in the X-ray irradiation period and an electric signal in the X-ray non-irradiation period fall within the dynamic ranges of the reading circuit unit and the Analogue-Digital conversion unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Computerized detection of breast cancer on digital tomosynthesis mammograms
InactiveUS7646902B2Breast enlargementExtension of timeImage enhancementImage analysisTomosynthesisGray level
A method for using computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) for digital tomosynthesis mammograms (DTM) including retrieving a DTM image file having a plurality of DTM image slices; applying a three-dimensional gradient field analysis to the DTM image file to detect lesion candidates; identifying a volume of interest and locating its center at a location of high gradient convergence; segmenting the volume of interest by a three dimensional region growing method; extracting one or more three dimensional object characteristics from the object corresponding to the volume of interest, the three dimensional object characteristics being one of a morphological feature, a gray level feature, or a texture feature; and invoking a classifier to determine if the object corresponding to the volume of interest is a breast cancer lesion or normal breast tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
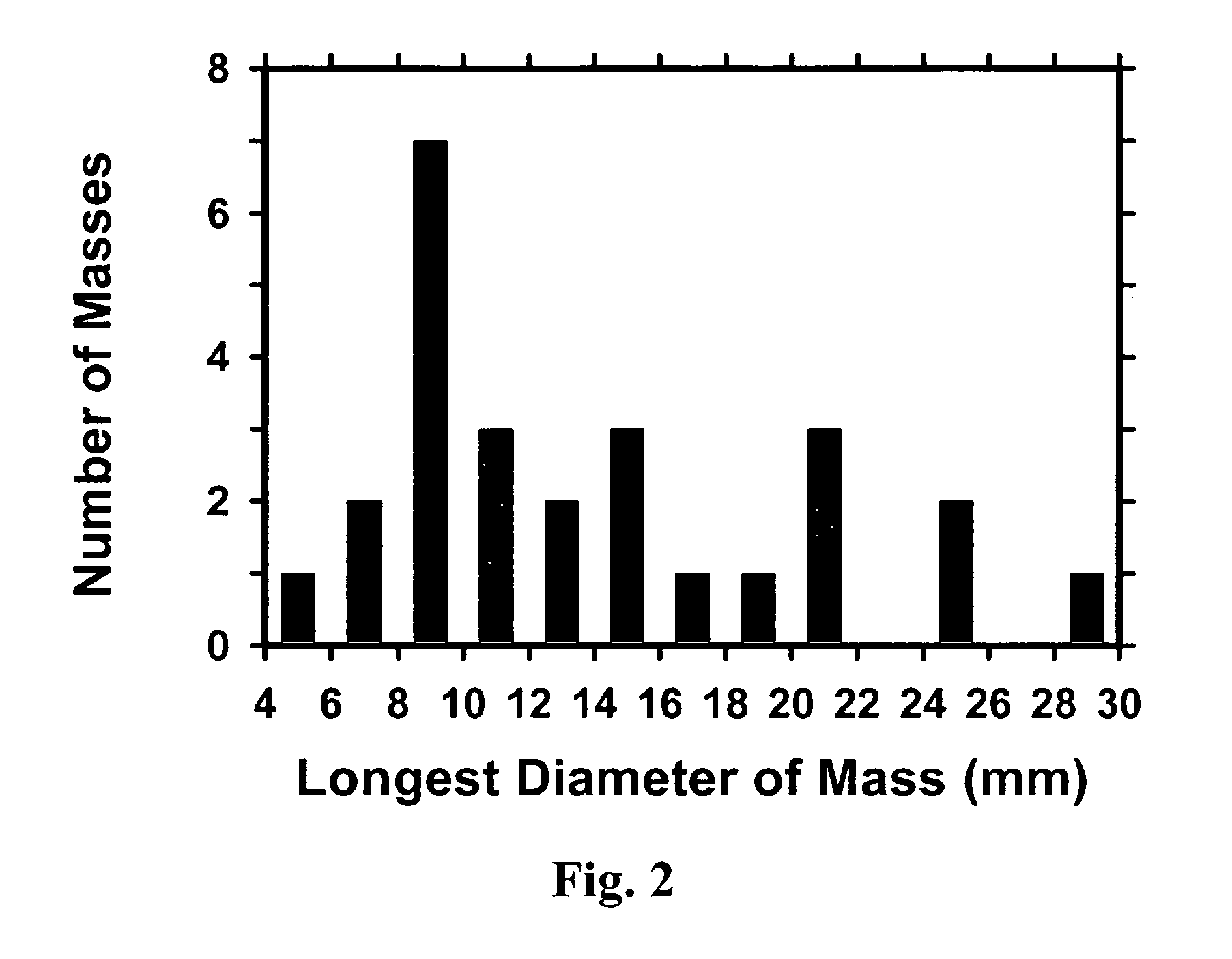
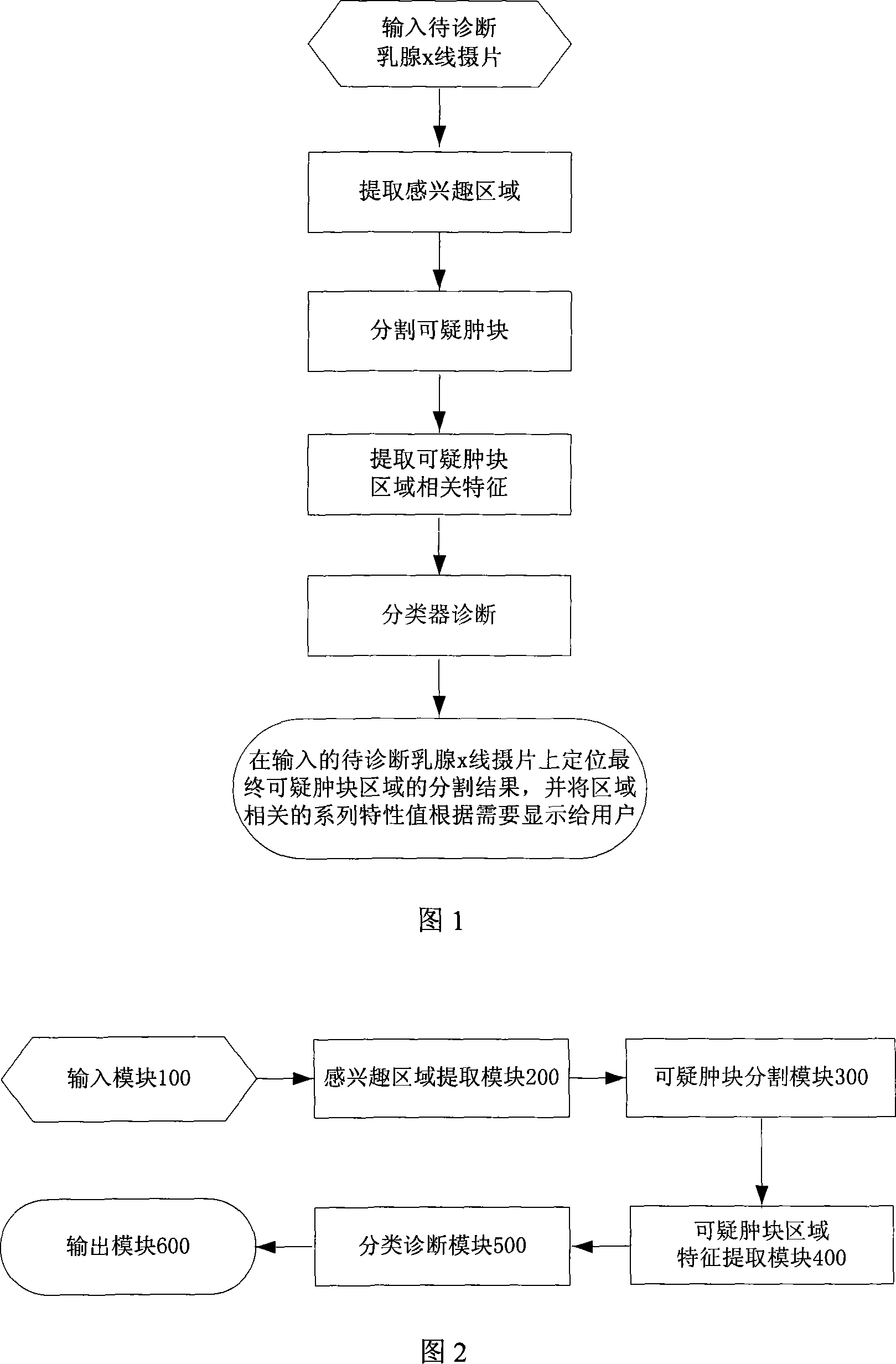
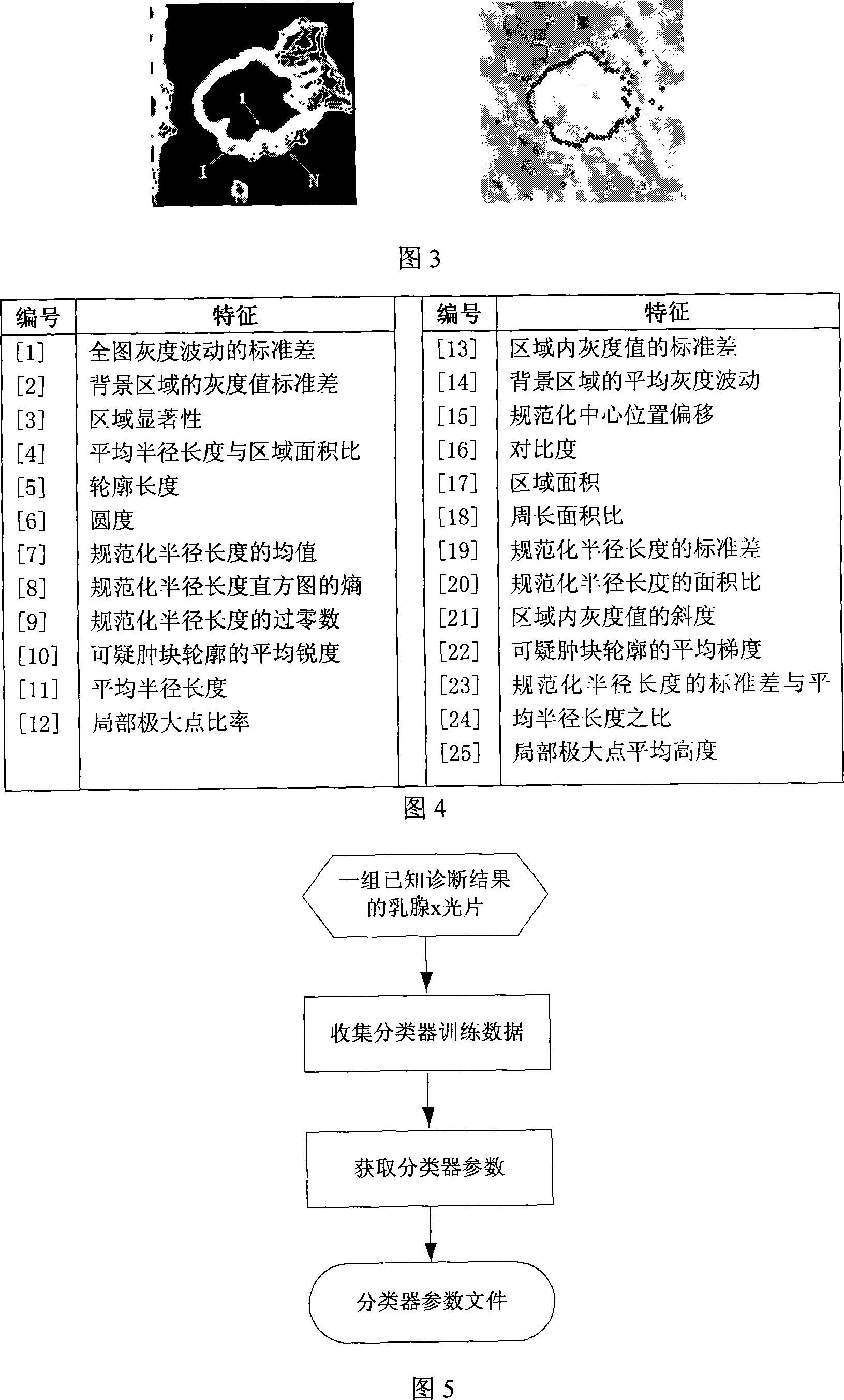
Galactophore cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method based on galactophore X-ray radiography and system thereof
InactiveCN101103924AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsRadiation diagnosticsFeature extractionDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a breast cancer computer auxiliary diagnosis method and system based on galactophore X-ray radiograph. A galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis is input into the system of the invention firstly, and is treated through an extracting module in a region of interest, a partitioning module and a feature extracting module in a region of doubtful lump, hereby a series of relative feature values about the doubtful lump region; then the feature values are input into a trained classifier which classifies and identifies the doubtful lump region and lastly the computer automatic examined final result of portioning the doubtful lump region is located on the input galactophore X-ray radiograph for diagnosis and the calculated relative feature values of the region are displayed to a roentgenologist according to requirements to indicate the roentgenologist about the region needing special attention and relative important parameters of the region. The invention can improve the accurateness and efficiency of the breast cancer diagnosis by the roentgenologist to some extent and help the roentgenologist to bring forward a diagnostic opinion and a therapeutic schedule more objectively and effectively.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
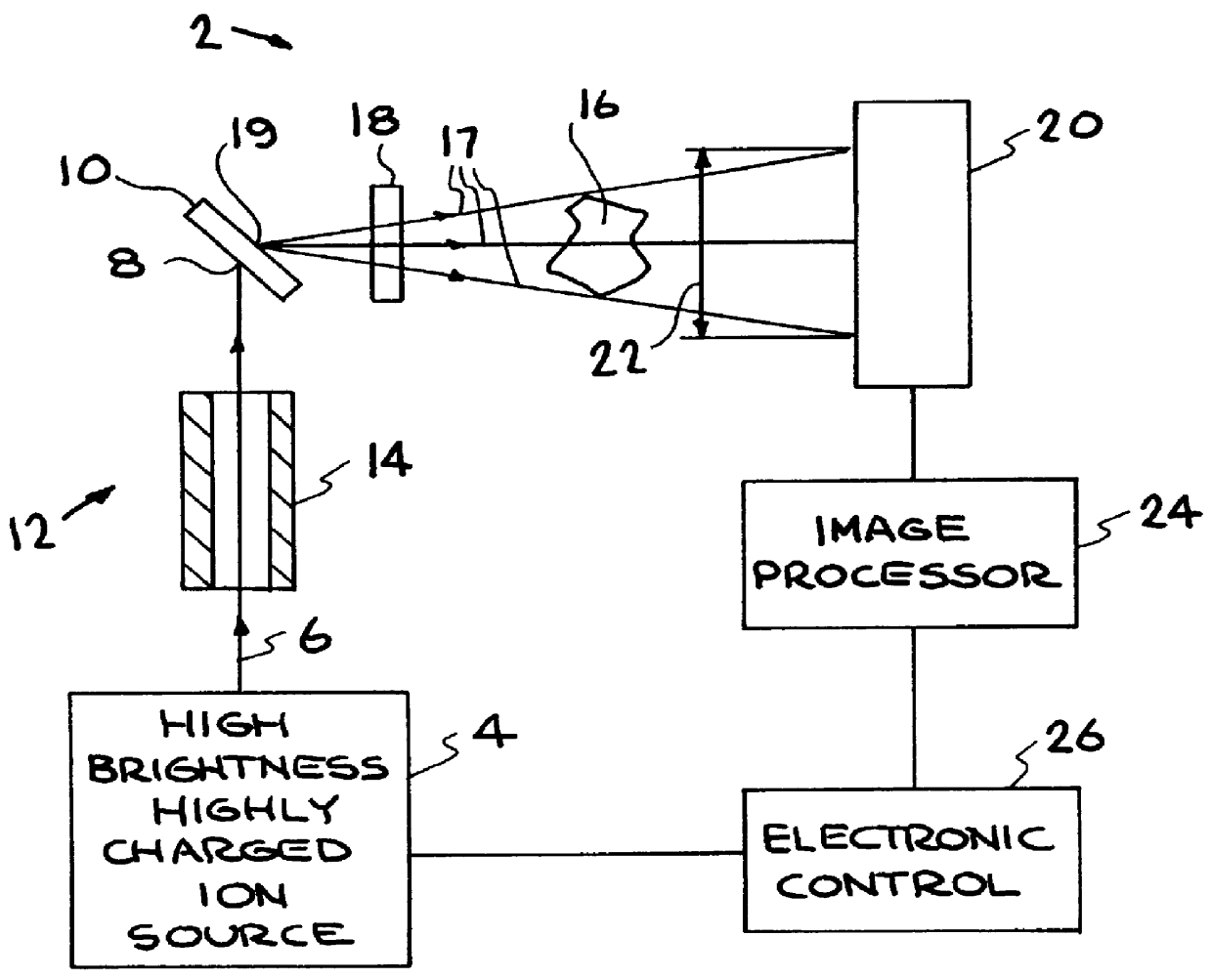
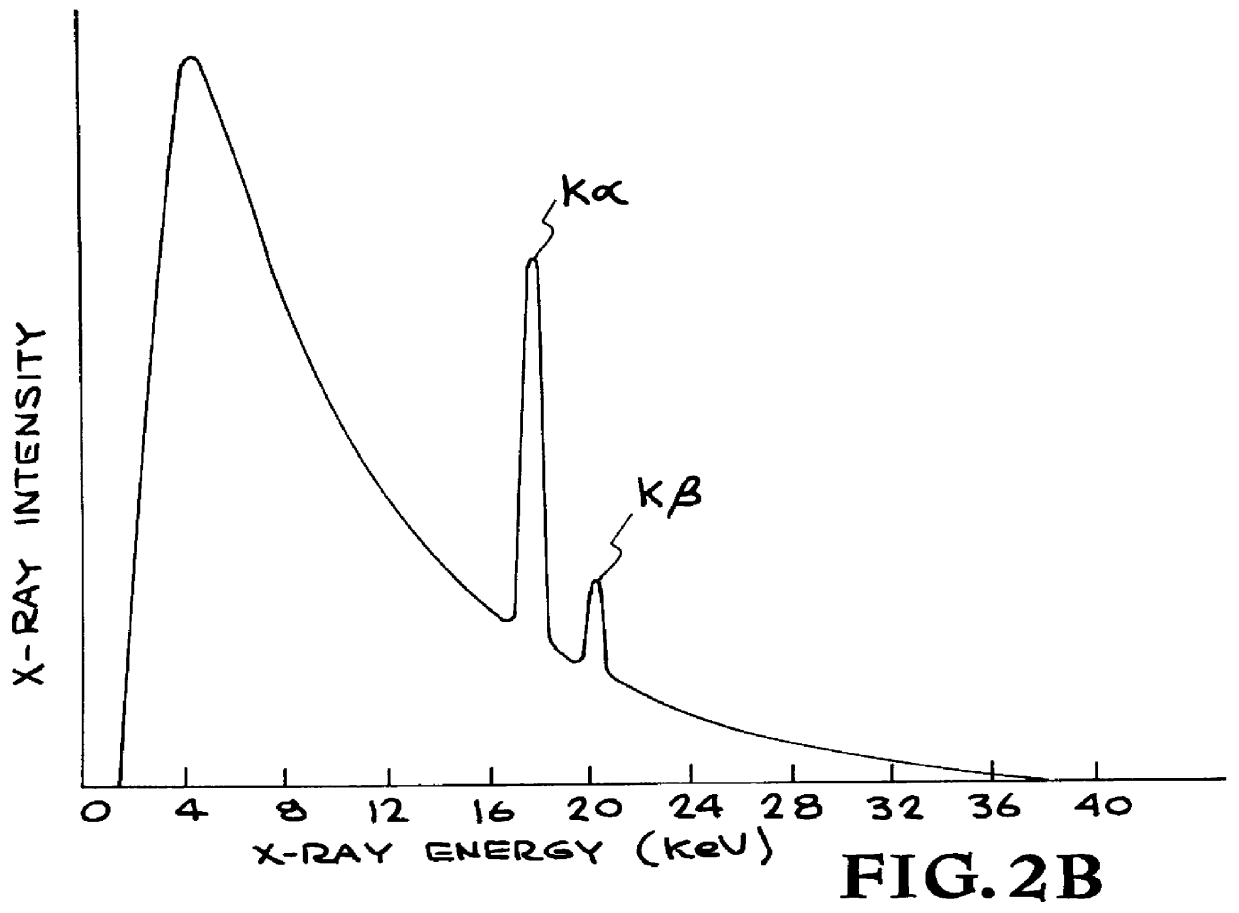
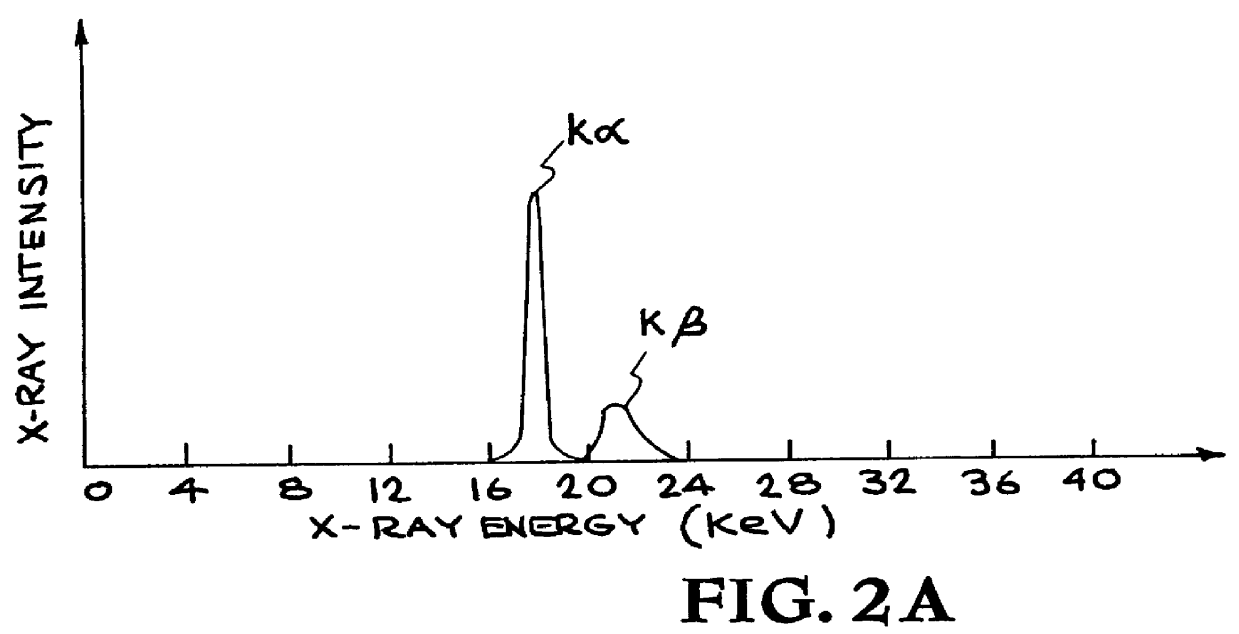
X-ray radiography with highly charged ions
An extremely small (1-250 micron FWHM) beam of slow highly charged ions deexciting on an x-ray production target generates x-ray monochromatic radiation that is passed through a specimen and detected for imaging. The resolution of the x-ray radiograms is improved and such detection is achieved with relatively low dosages of radiation passing through the specimen. An apparatus containing an electron beam ion trap (and modifications thereof) equipped with a focusing column serves as a source of ions that generate radiation projected onto an image detector. Electronic and other detectors are able to detect an increased amount of radiation per pixel than achieved by previous methods and apparati.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
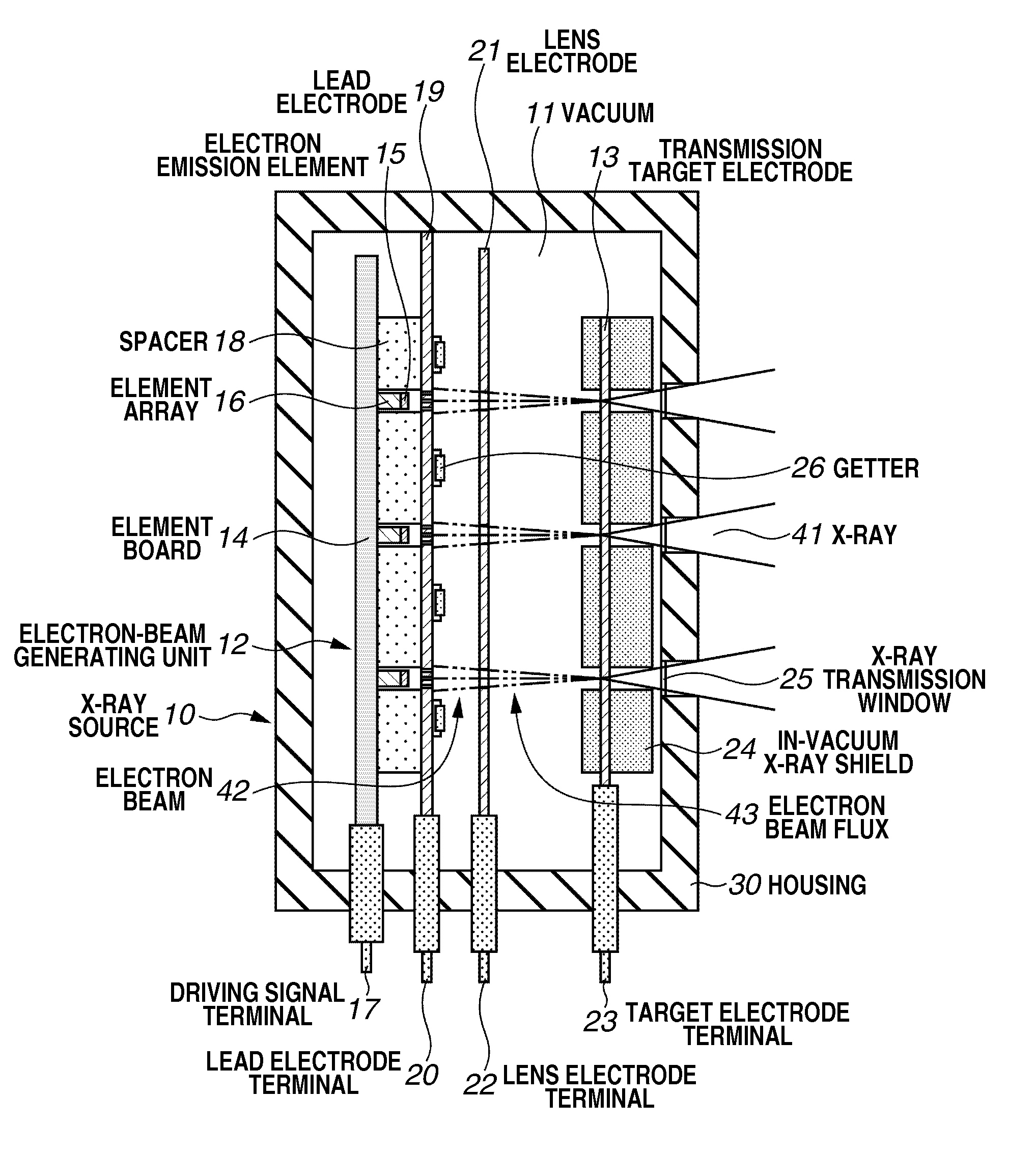
X-ray source and x-ray photographing apparatus including the source
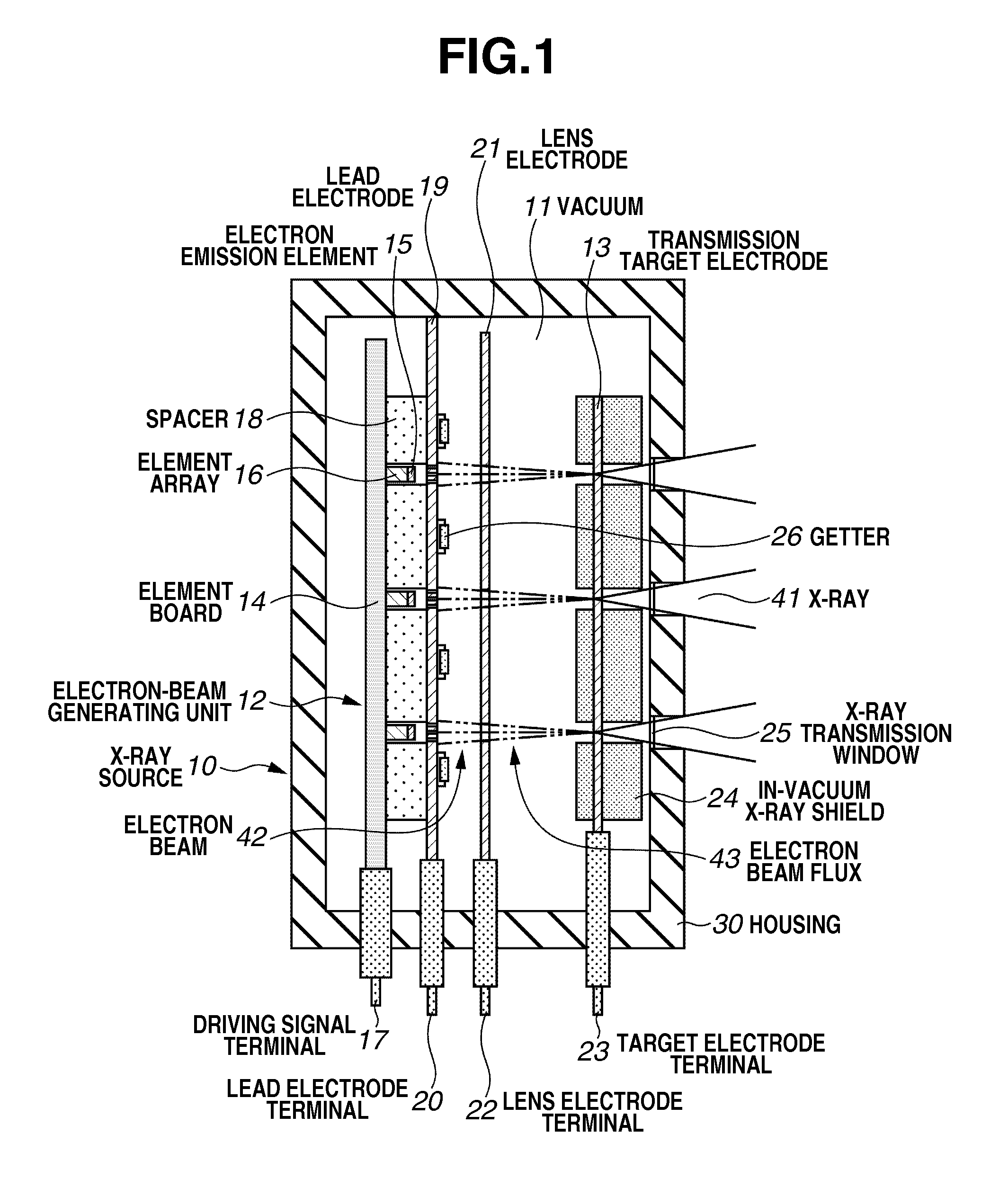
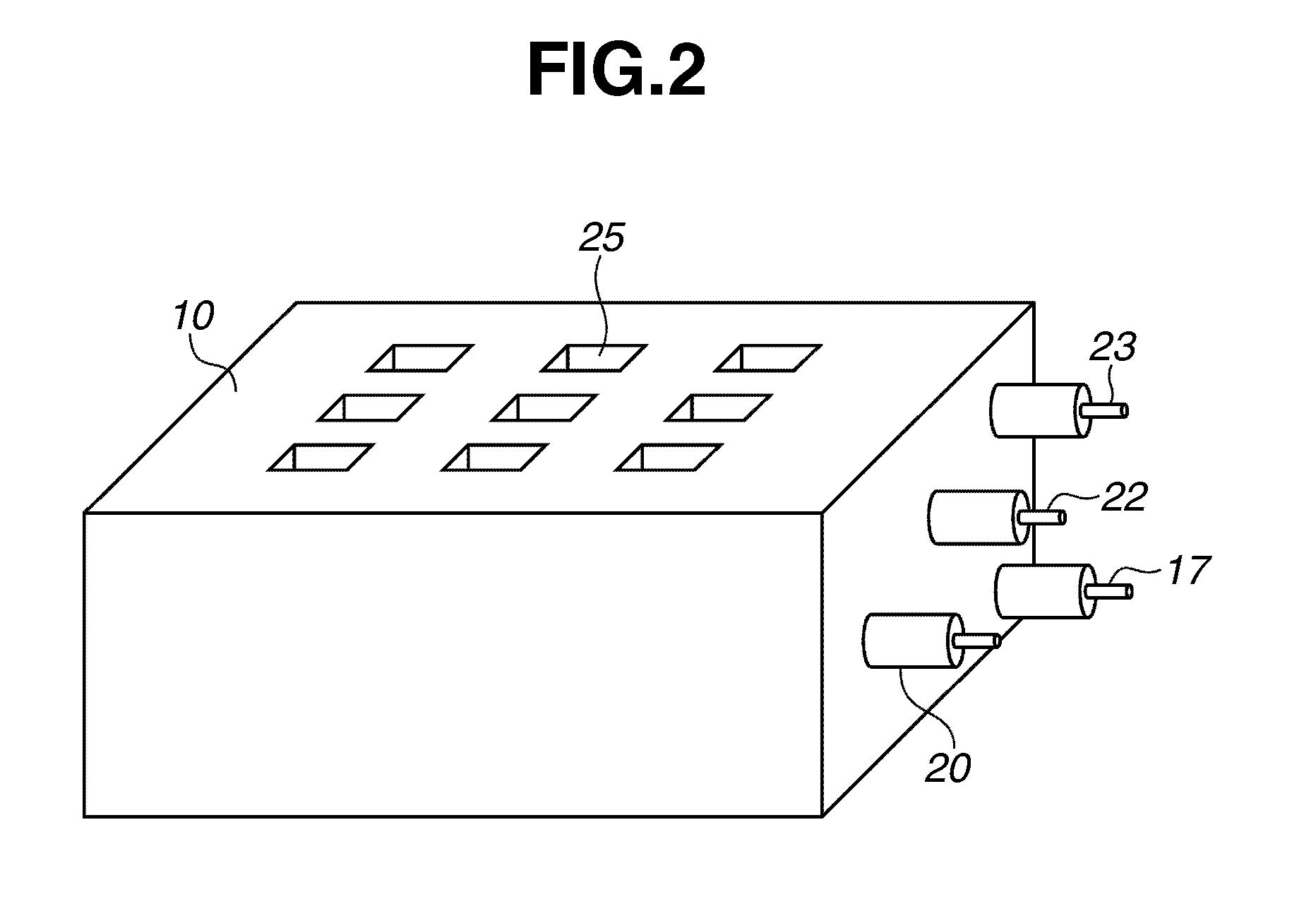
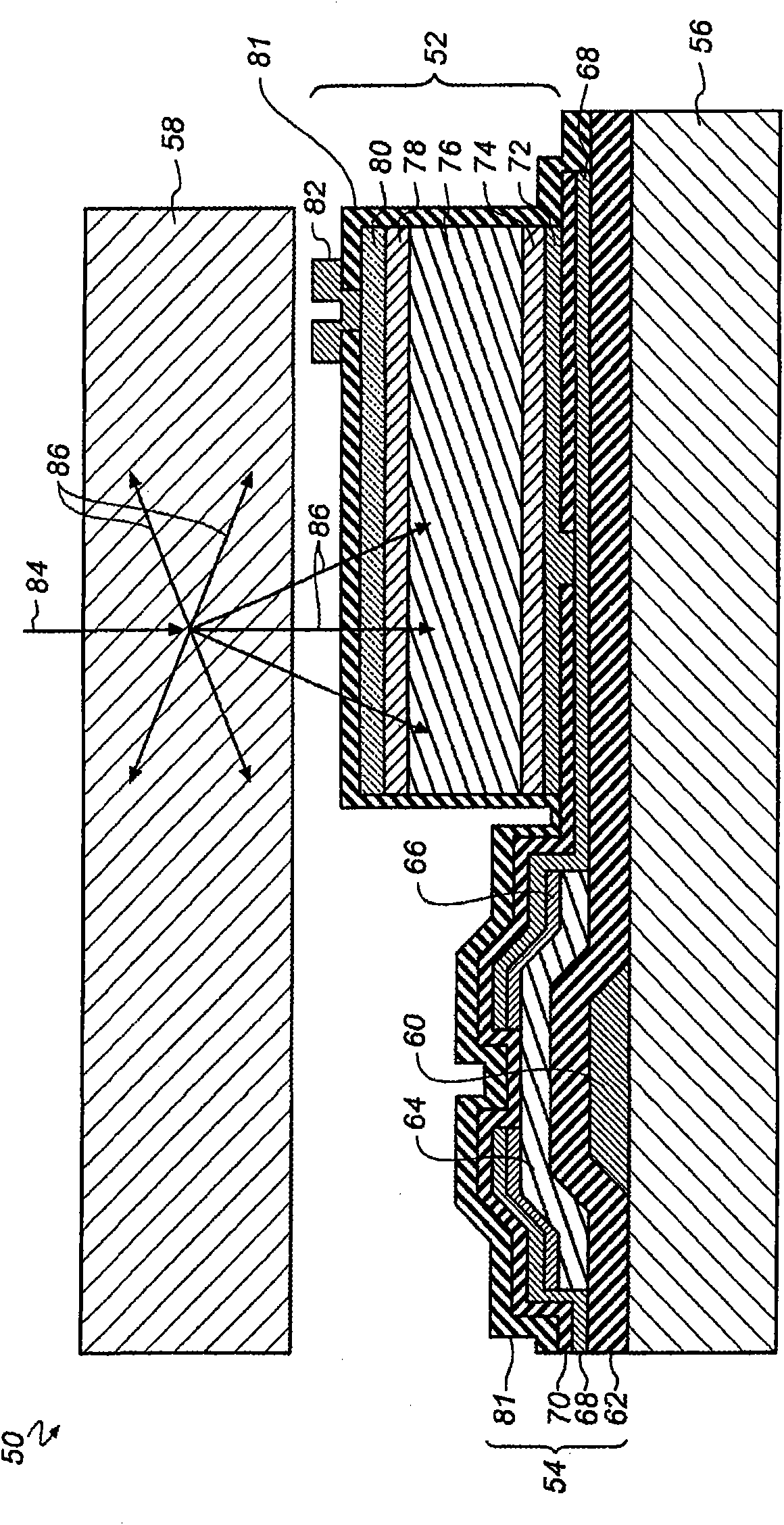
InactiveUS20110255664A1Avoid changeImprove efficiencyX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube vessels/containerX-rayX ray radiography
An X-ray source includes an electron-beam generating unit that generates an electron beam, and a transmission type target electrode to be irradiated with the electron beam to generate X-ray radiation. A plurality of convex portions each having an inclined surface with respect to an incident direction of the electron beam is formed on a surface of the transmission type target electrode.
Owner:CANON KK
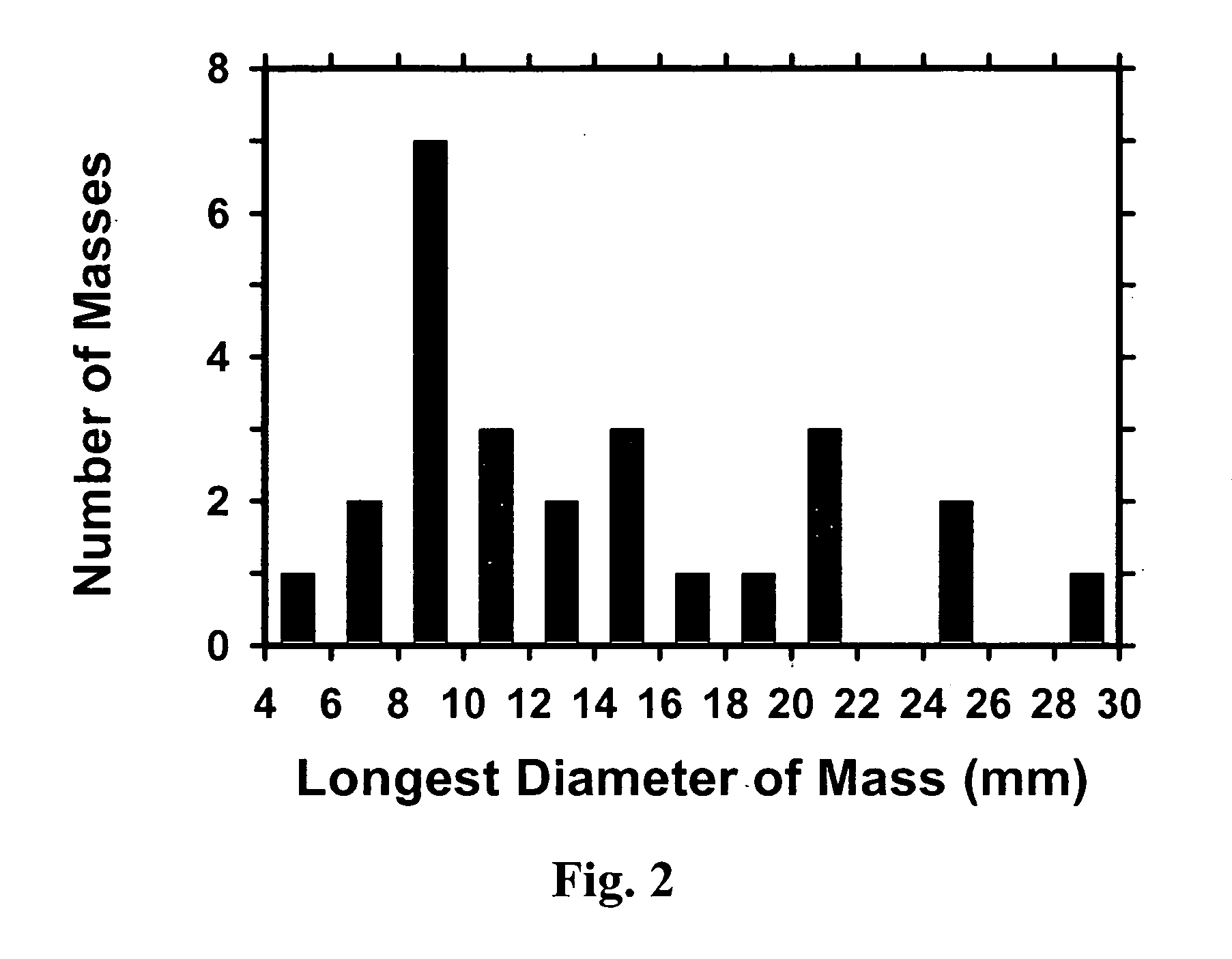
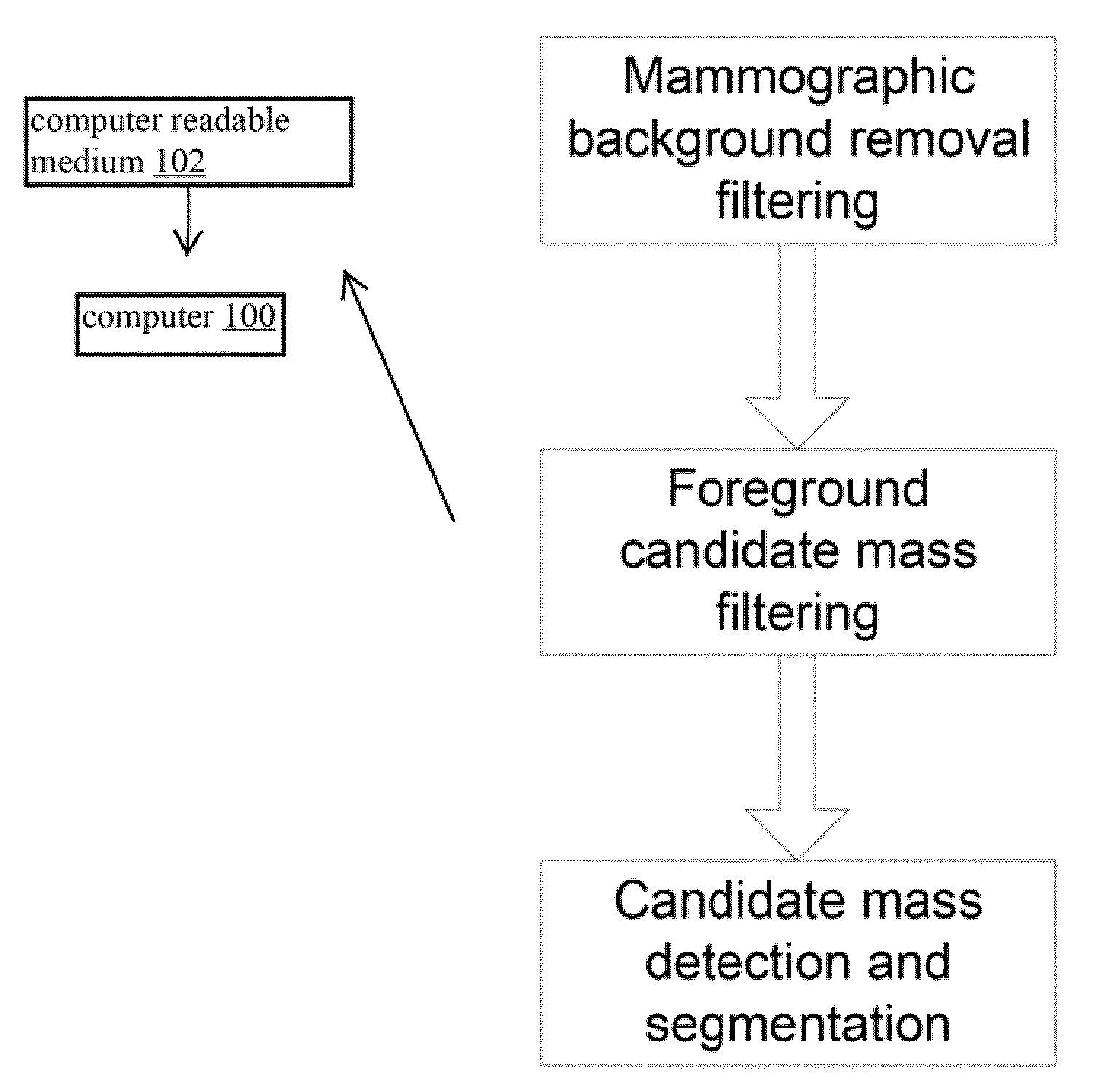
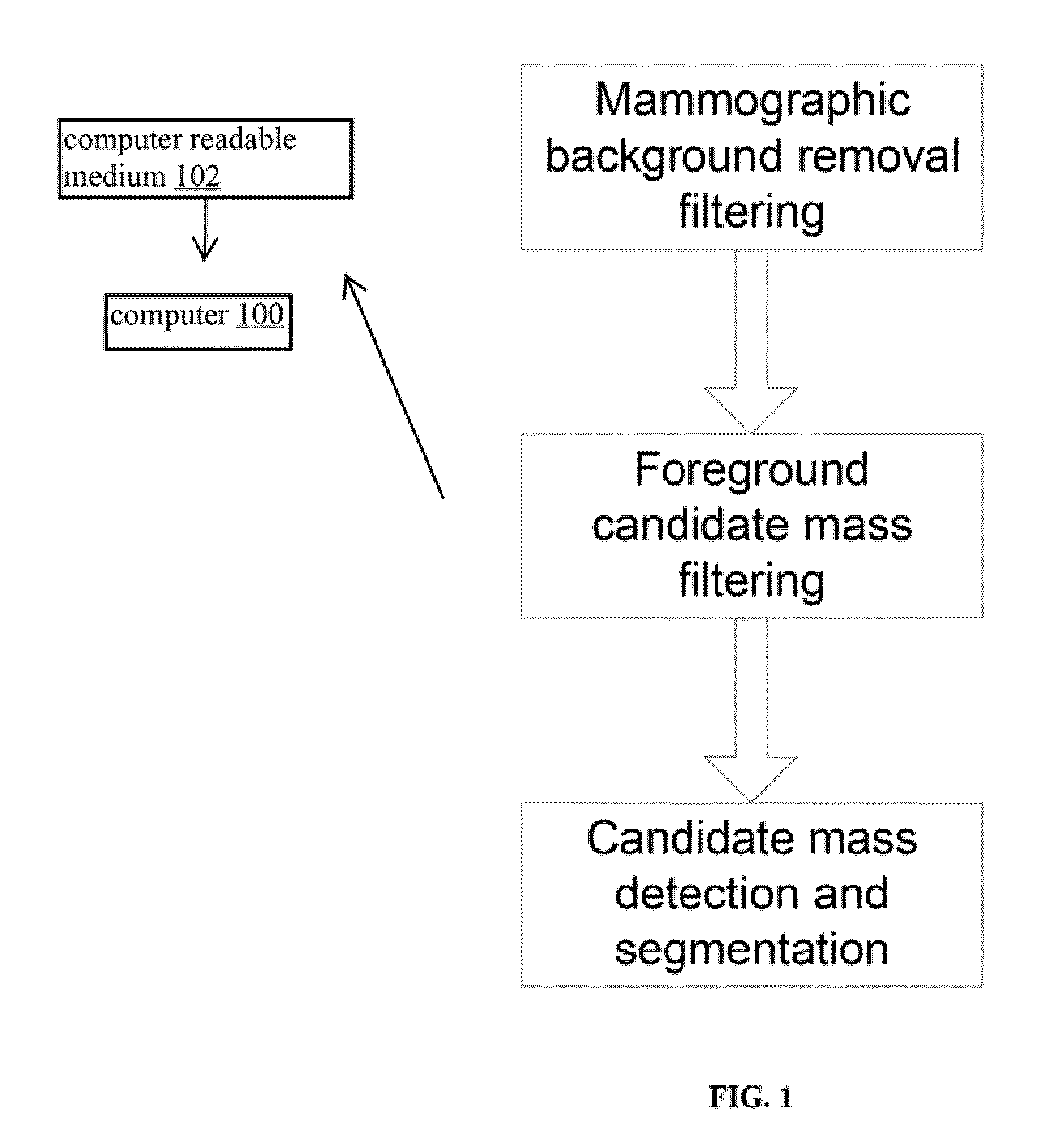
Method for Mass Candidate Detection and Segmentation in Digital Mammograms
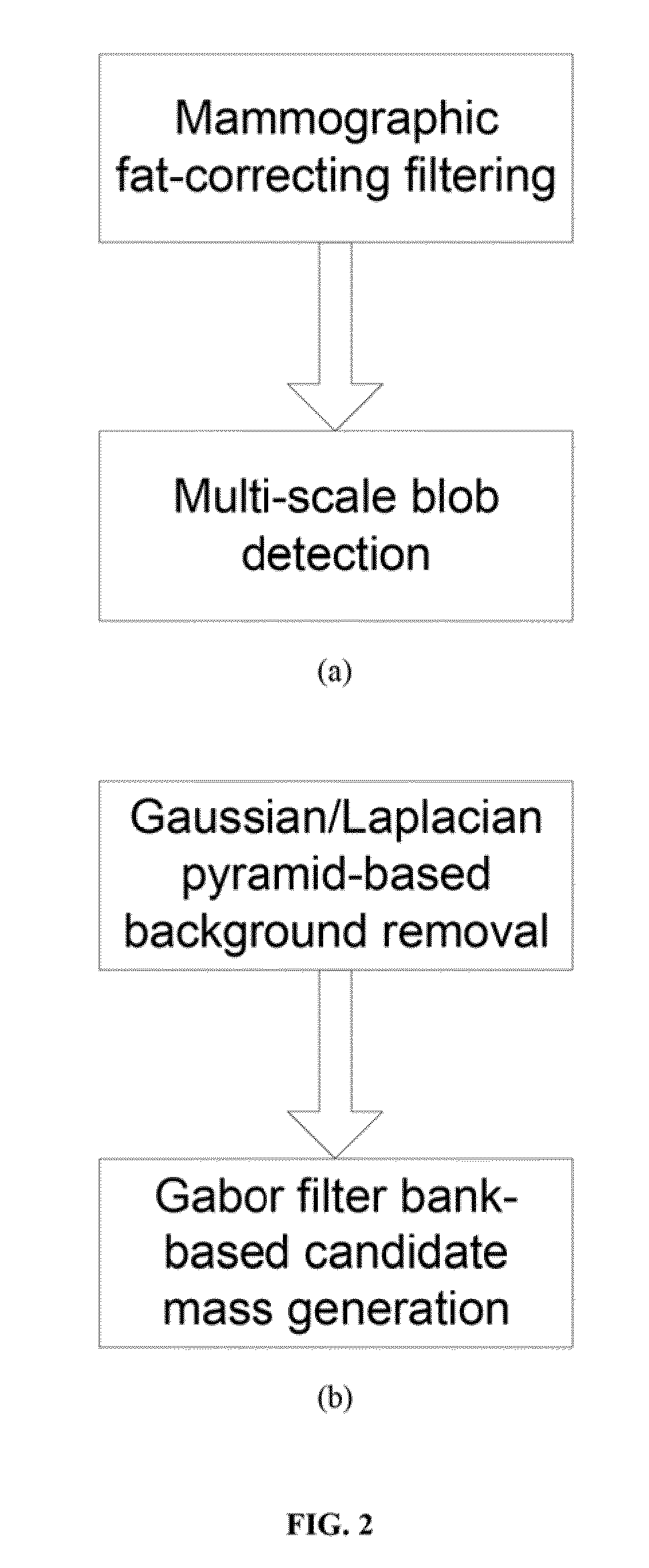
A basic component of Computer-Aided Detection systems for digital mammography comprises generating candidate mass locations suitable for further analysis. A component is described that relies on filtering either the background image or the complementary foreground mammographic detail by a purely signal processing method on the one hand or a processing method based on a physical model on the other hand. The different steps of the signal processing approach consist of band-pass filtering the image by one or more band pass filters, multidimensional clustering, iso-contouring of the distance to centroid of the one or more filtered values, and finally candidate generation and segmentation by contour processing. The physics-based approach also filters the image to retrieve a fat-corrected image to model the background of the breast, and the resulting image is subjected to a blob detection filter to model the intensity bumps on the foreground component of the breast that are associated with mass candidates.
Owner:AGFA NV
Image positioning method and system for tomosynthesis in a digital X-ray radiography system
InactiveUS6960020B2Improve image qualityRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisTomosynthesisImage resolution
The present invention provides a method and system for determining the position of the image of a target object or the position of the x-ray source in digital tomosynthesis, as the x-ray source is moved relative to the object so as to obtain multiple two-dimensional images of the object from multiple angles. At least one marker, characterized by a simple and known image pattern, is disposed between an x-ray source and a detector system. The shift in the image of the object, resulting from the movement of the x-ray source during tomosynthesis, is calculated to a desired resolution using the readily observable shift in the image of the marker. The x-ray source may be translated along a plane parallel to the plane of the detector system, or may be rotated about a fixed center.
Owner:ANLOGIC CORP (US)
Dual-screen digital radiographic imaging detector array
ActiveCN101561505ADetection speedHigh mechanical strengthTelevision system detailsX-ray/infra-red processesSoft x rayPhosphor
A radiographic imaging device has a first scintillating phosphor screen having a first thickness and a second scintillating phosphor screen having a second thickness. A transparent substrate is disposed between the first and second screens. An imaging array formed on a side of the substrate includes multiple photosensors and an array of readout elements.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
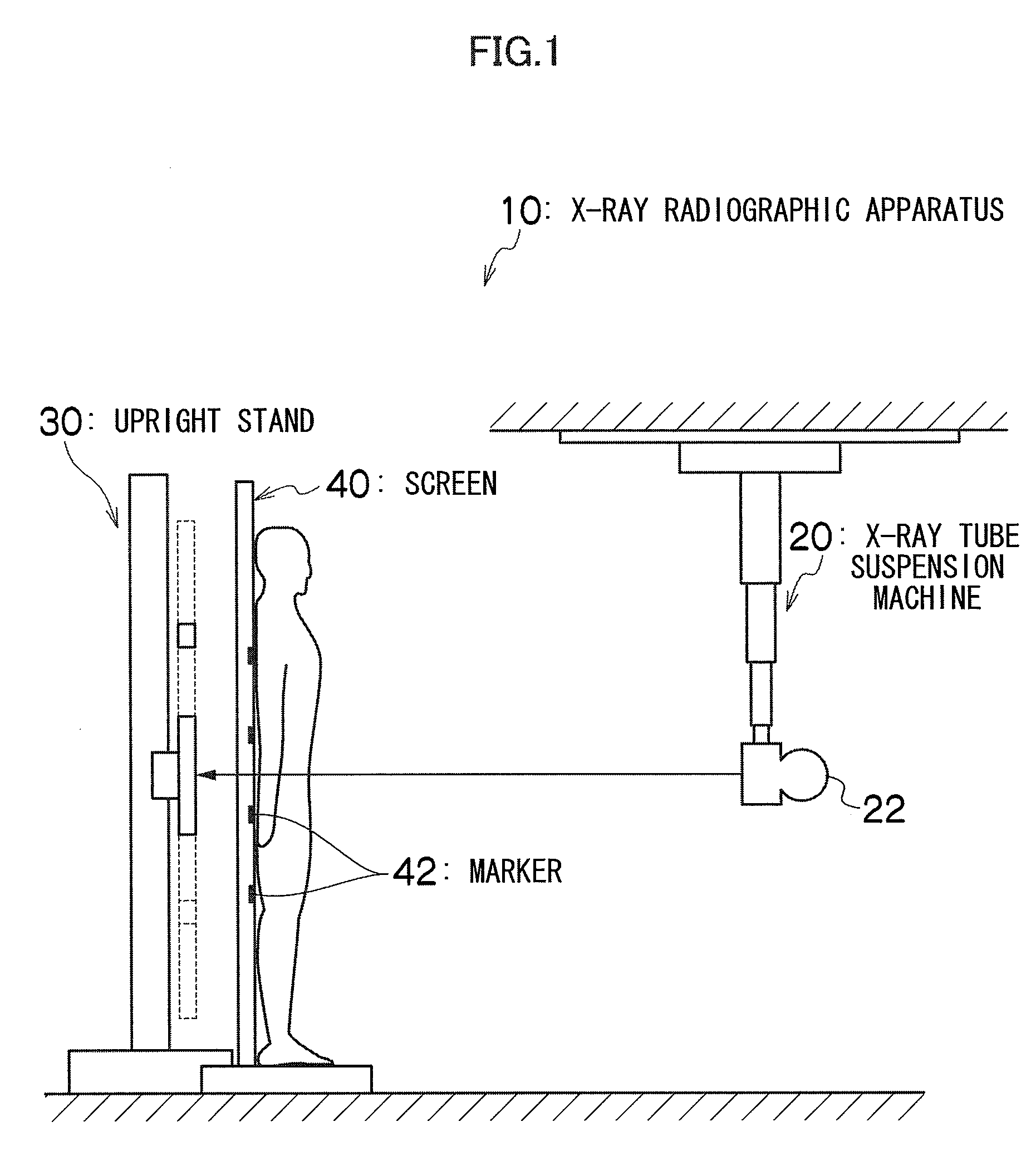
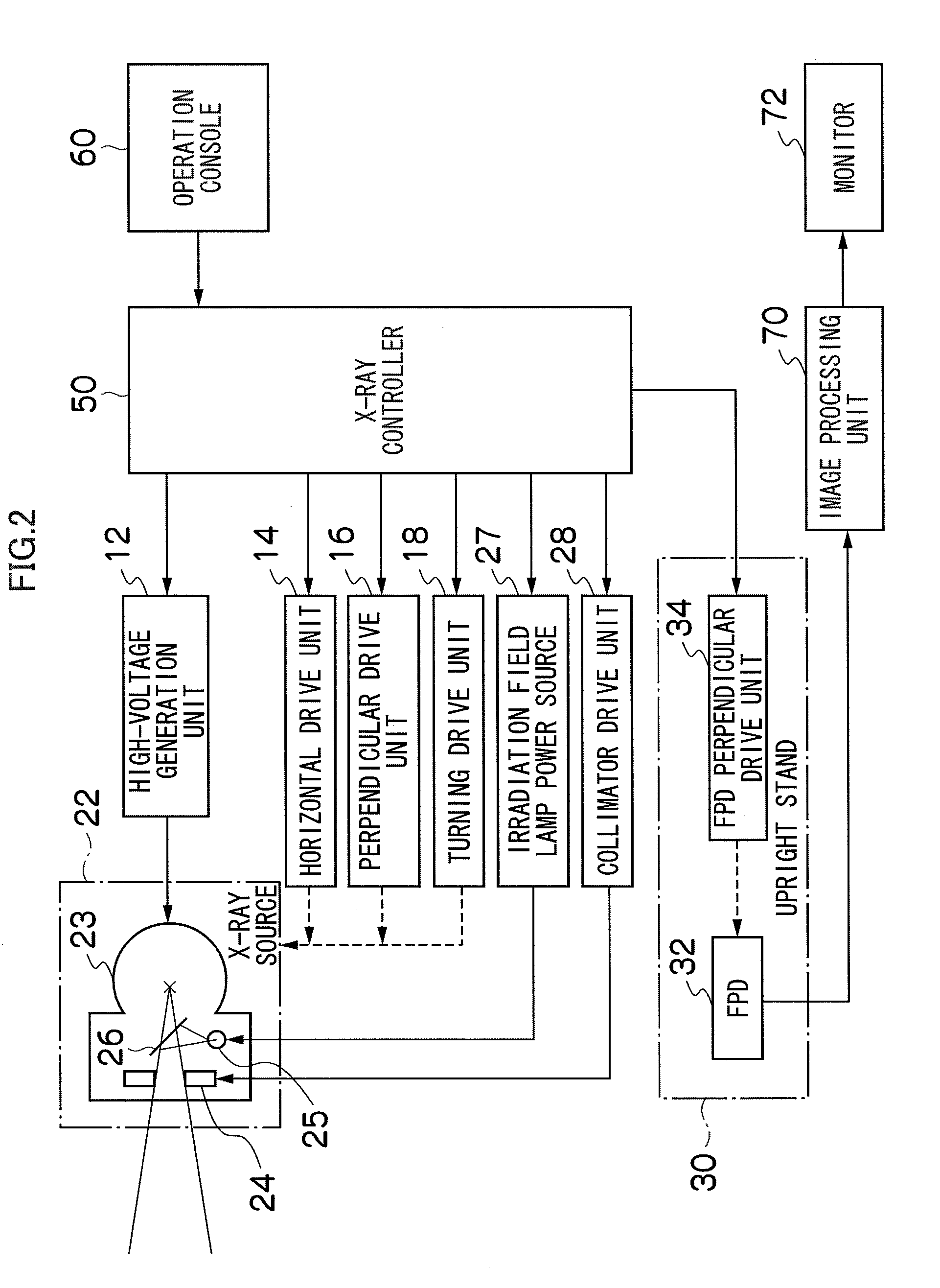
X-ray radiographic apparatus and method
InactiveUS20090245464A1Easy to implementImprove accuracyRadiation beam directing meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayAperture angle
An entire area of an FPD on which an alignment marker provided in a screen is projected is set in advance as a fixed overlapping area (Ctop to Cbottom) according to the long length imaging area and / or the X-ray source position. When determining a plurality of field-of-view area areas for dividing an imaging area for long length imaging into a plurality of areas and taking images, the field-of-view areas (FOVNT to FOVNB) and the FPD positions PN corresponding to the respective field-of-view areas are determined so that adjacent field-of-view areas overlap each other at the set fixed overlapping area. The X-ray source height, the X-ray irradiation direction, the collimator aperture angle and the FPD position are controlled so as to apply an X-ray only to each of the determined field-of-view areas.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
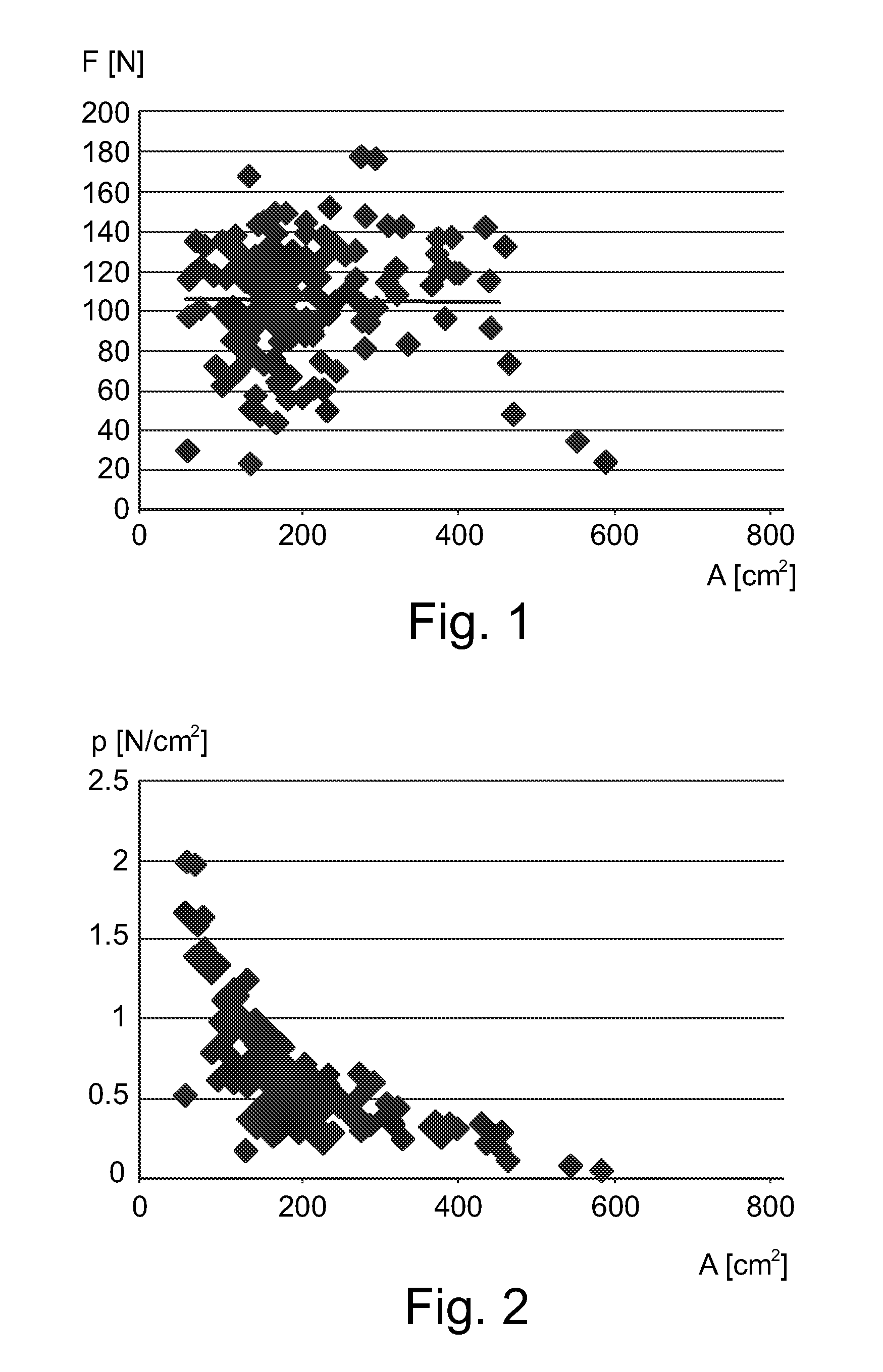
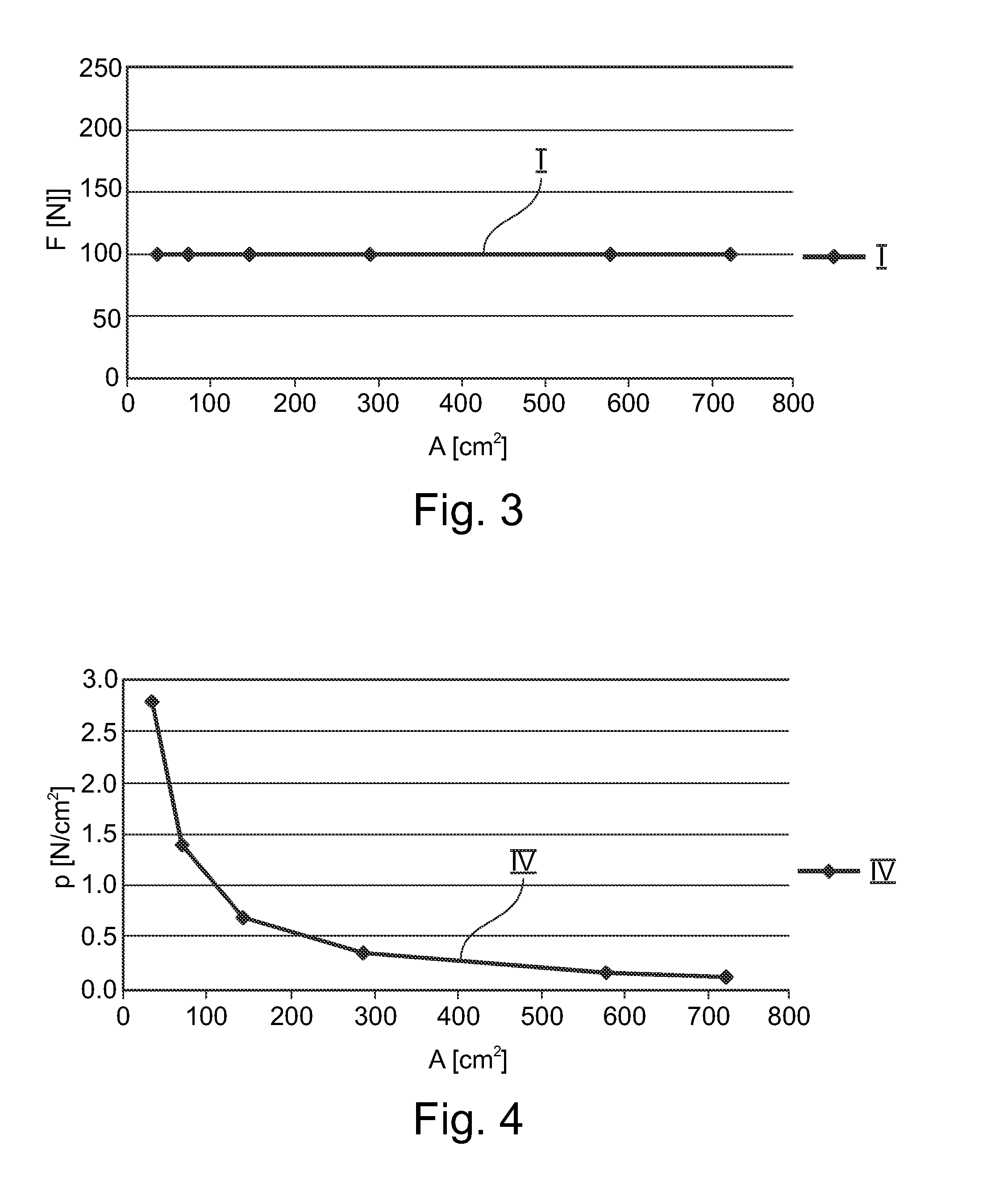
Individual monitoring of compression for mammographic examinations
ActiveUS20140328458A1Force measurementPatient positioning for diagnosticsPersonalizationX ray radiography
The present invention relates to mammography. In particular, the present invention relates to a method and a corresponding system for individually monitoring a compression force in an apparatus for mammographic examination for personalized compression guidance. In order to provide a personalized guidance for the compression of the breast in a first step (S1a, S1b, S1c) a breast contact area (A) between a breast under examination and a compression plate (3) or a support plate (15) is determined. In a next step (S5) a compression force limit is determined based on the breast contact area (A). Then, in a further step (S9a, S9b, S9c) an output signal (5) representative of the relation between the breast contact area (A) and the compression force limit is provided to a user such that the user may decide whether to complete or to continue the application of compression force.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
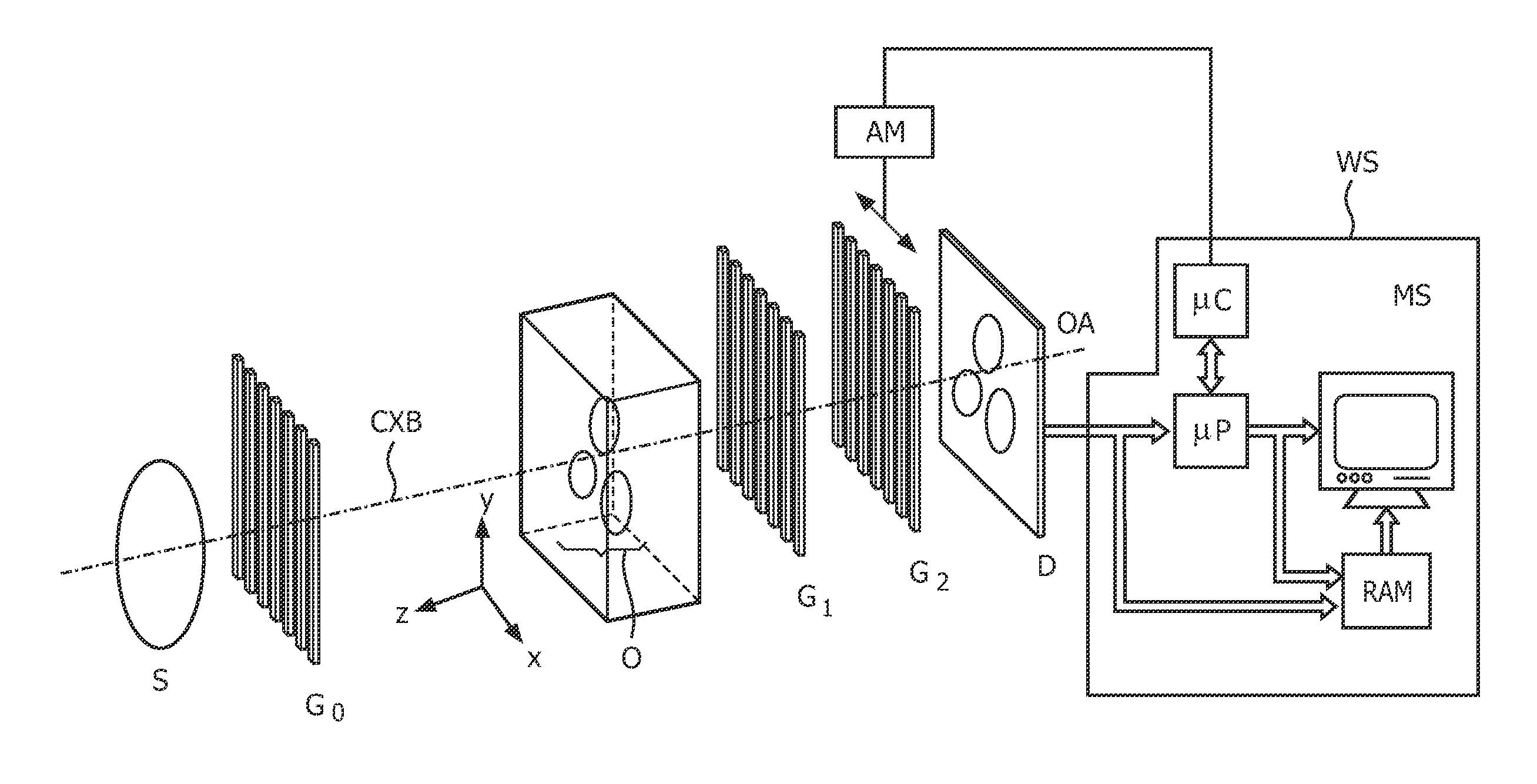
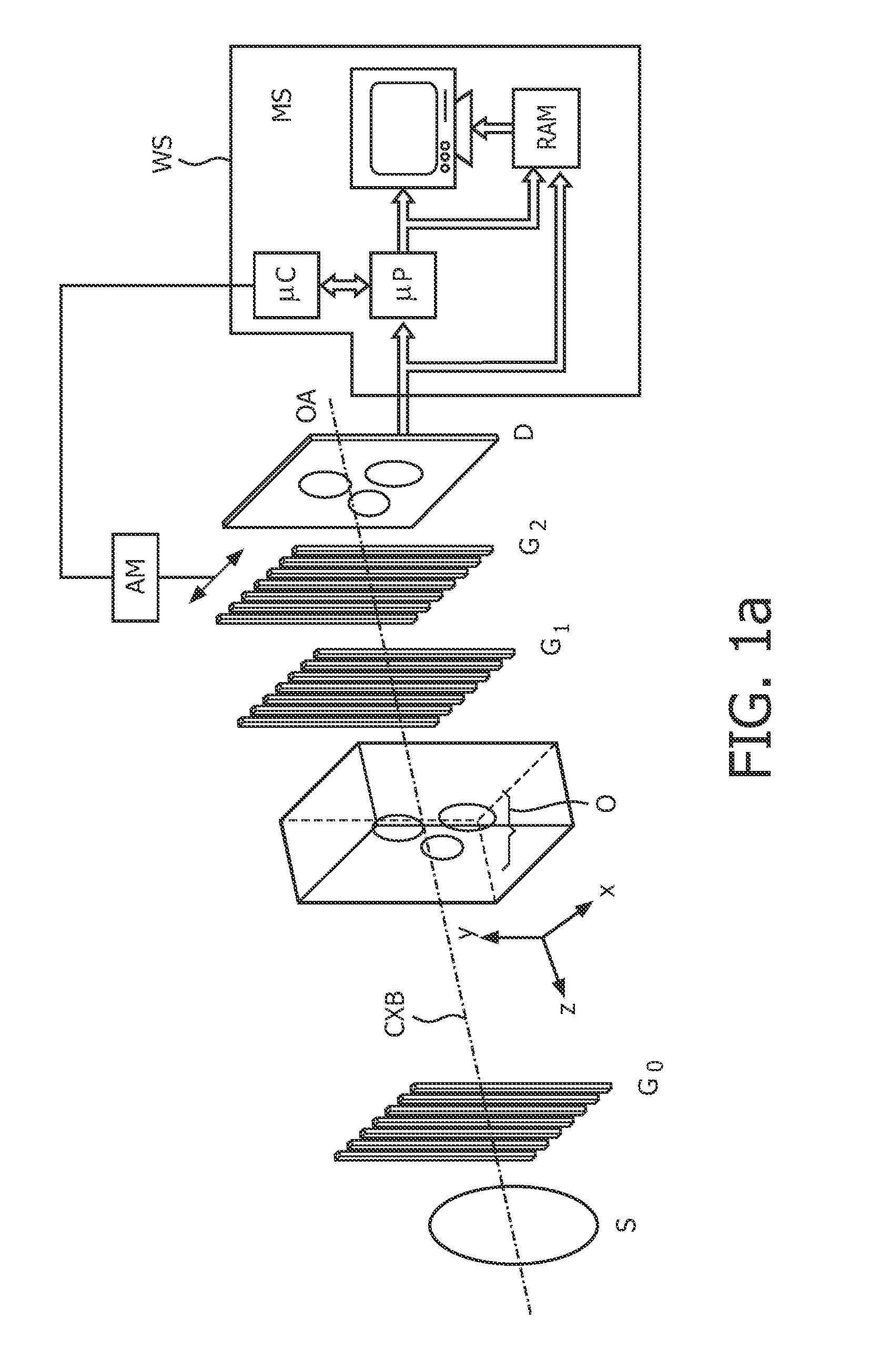
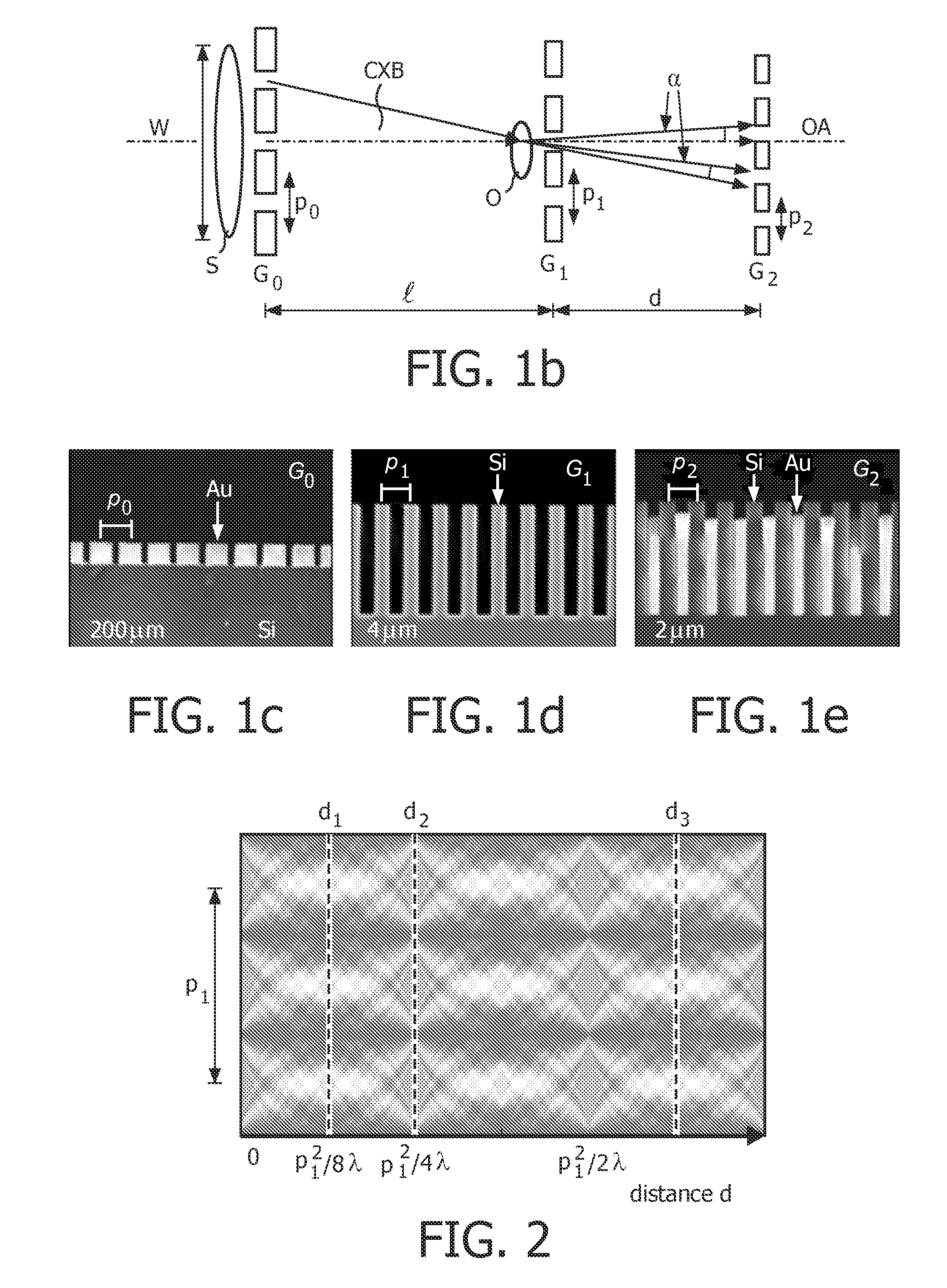
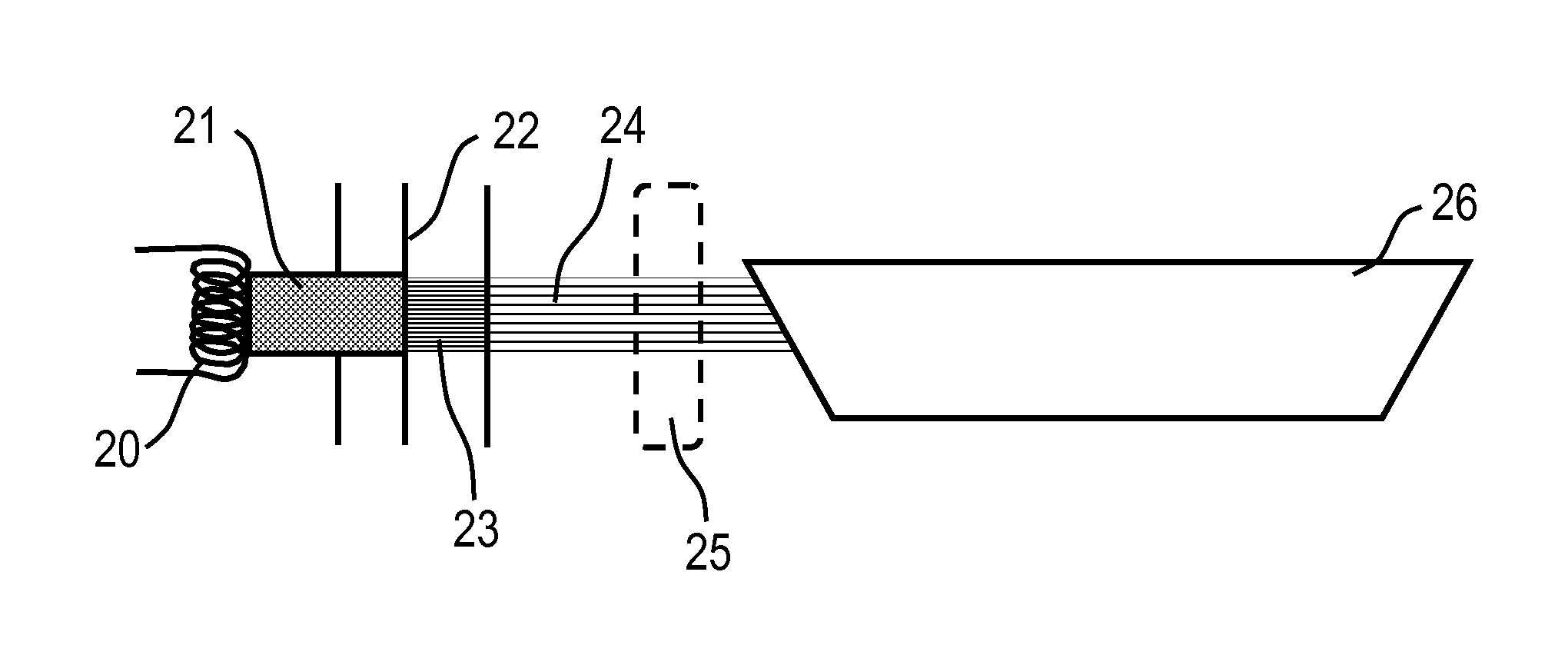
X-ray radiography system for differential phase contrast imaging of an object under investigation using phase-stepping
InactiveUS20150030126A1Simple phase contrastHigh resolutionImaging devicesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingPhase gratingLight beam
An X-ray radiography system for differential phase contrast imaging of an object under investigation by phase-stepping is provided. The X-ray radiography has an X-ray emitter for generating a beam path of quasi-coherent X-ray radiation, an X-ray image detector with pixels arranged in a matrix, and a diffraction or phase grating, in which the X-ray emitter has an X-ray tube with a cathode and an anode. The X-ray tube is constructed in such a way that an electron ray beam originating from the cathode is associated with focusing electronics which produce, from electrons which are incident on an anode, at least one linear-shaped electron fan beam.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
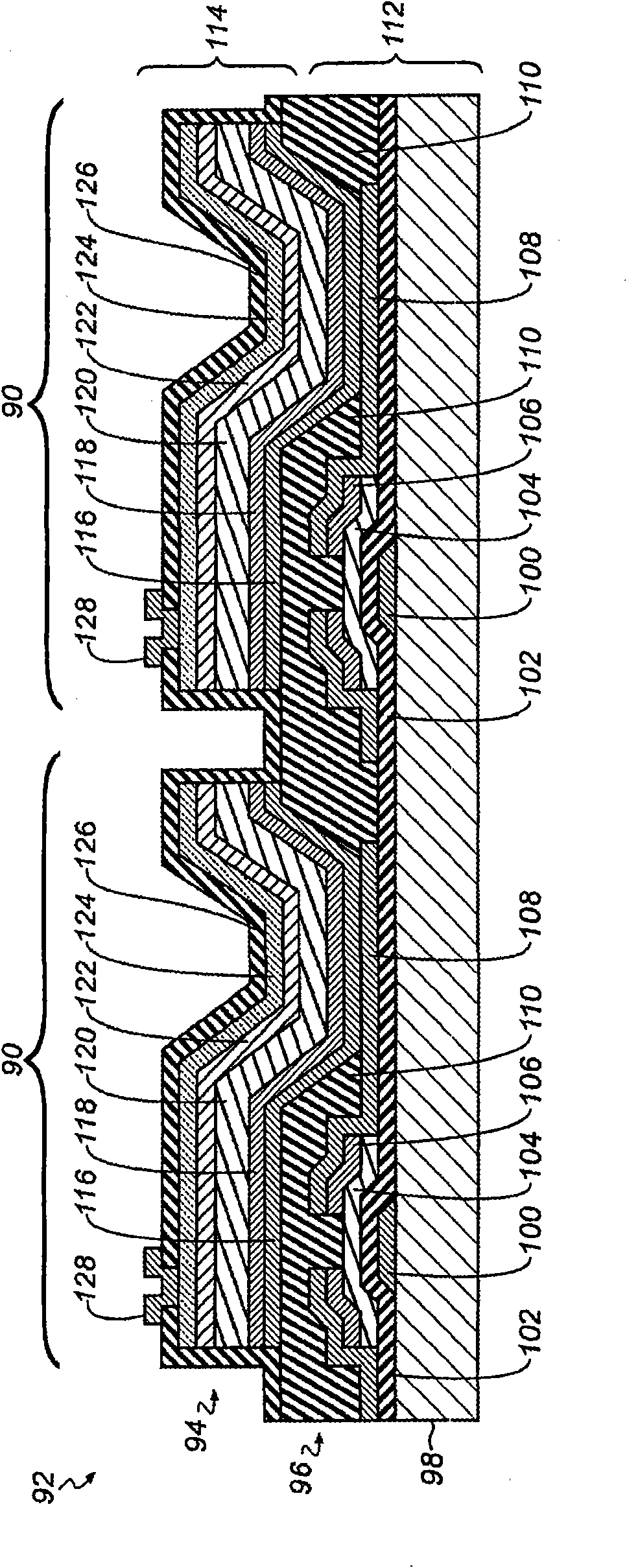
Intraoral tomosynthesis systems, methods and computer readable media for dental imaging
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
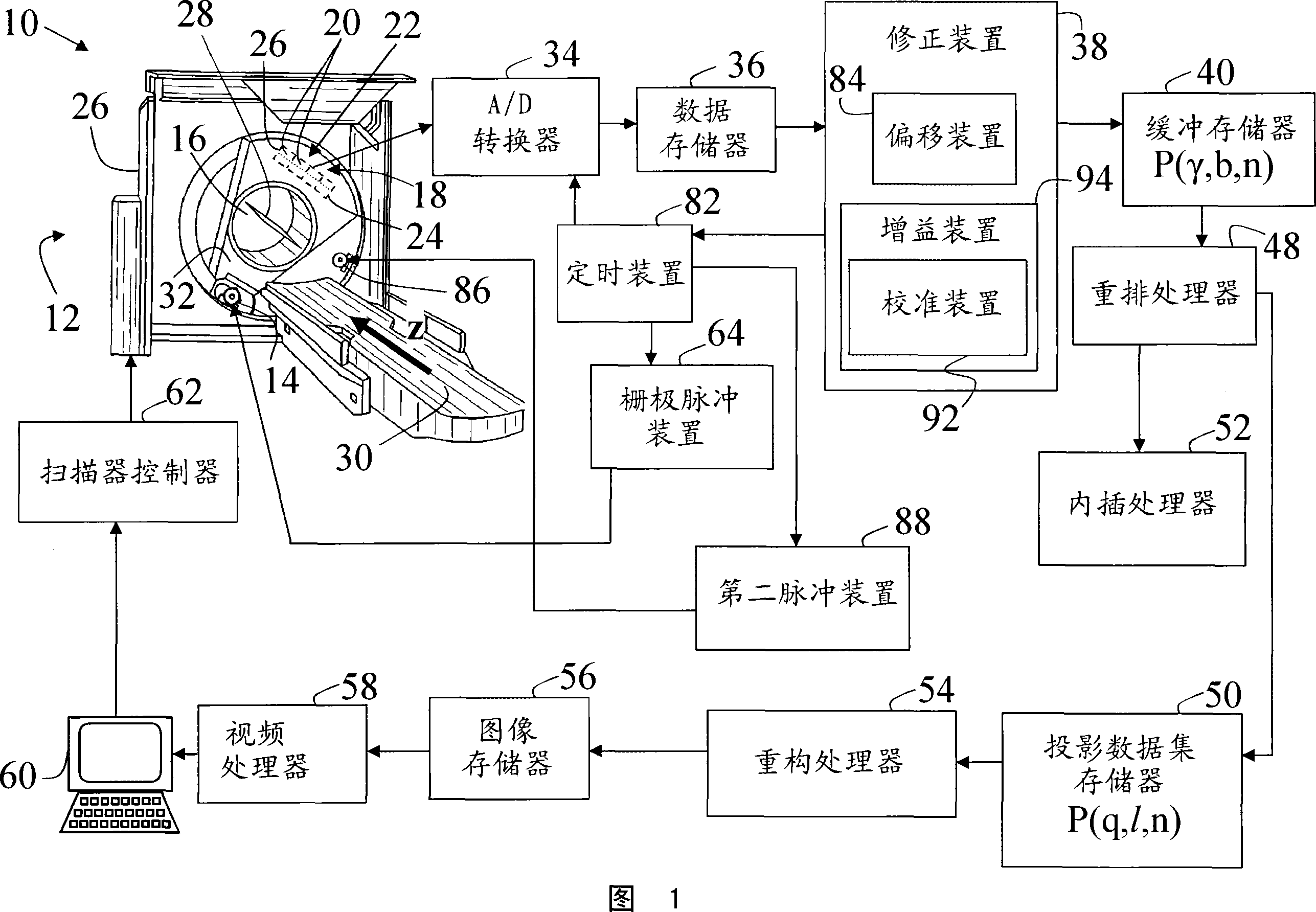
Pulsed X-ray for continuous detector correction
InactiveCN101080653AReduce scan timeAvoid artifactsTomographyRadiation diagnosticsX-rayUltimate tensile strength
A radiographic imaging apparatus (10) including a first radiation source (14) emitting a radiation beam to an examination region (16). The detector (18) converts the detected radiation passing through the examination area (16) into an electrical detector signal representative of the detected radiation. The detector (18) has at least one characteristic that changes in time, such as offset B(t) or gain A(t). The gate pulsing device (64) switches the first radiation source (14) on and off at a rate of 1000 to 5000 pulses per second, so that the offset B(t) is remeasured at least between 1000 and 5000 times per second, and Corrections are made many times during the detector signal generation process. The gain A(t) is measured using a second pulsing device (88) by pulsing a second pulsed source (86, 100, 138) of constant intensity (XRef). The gain A(t) is remeasured and corrected multiple times per second during detector signal generation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
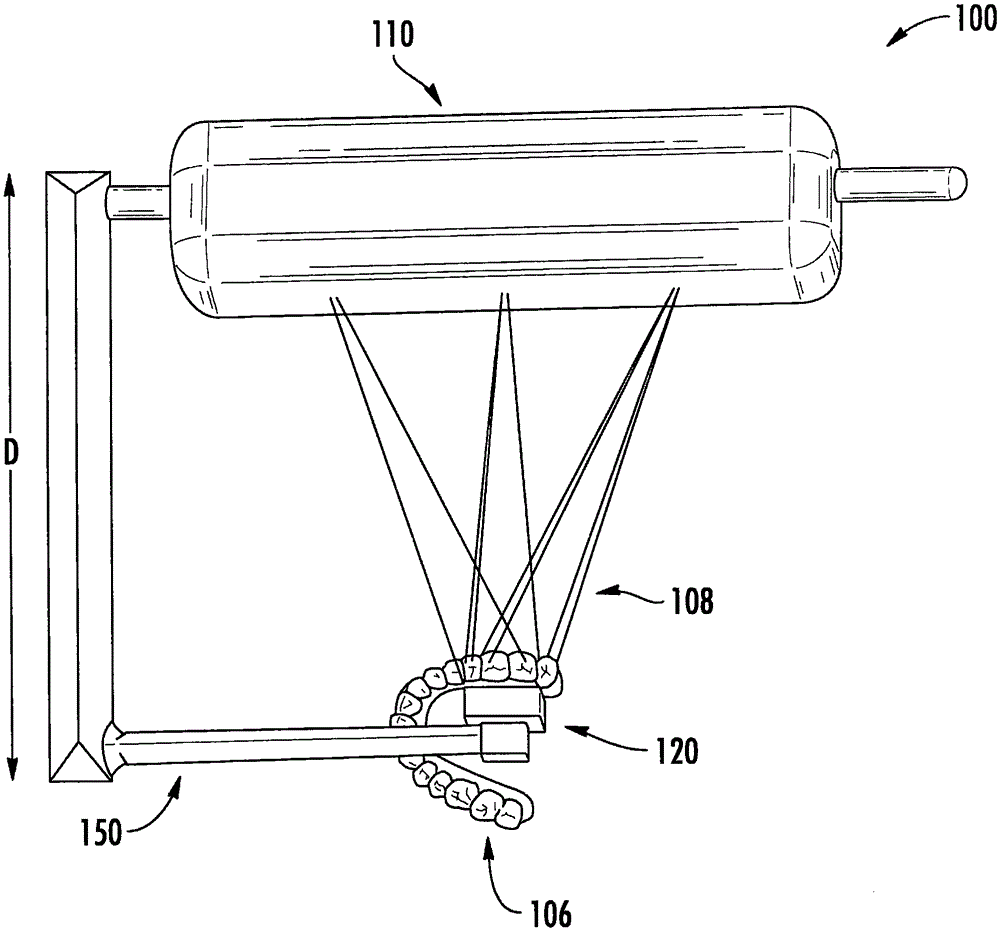
Mammographic paddle
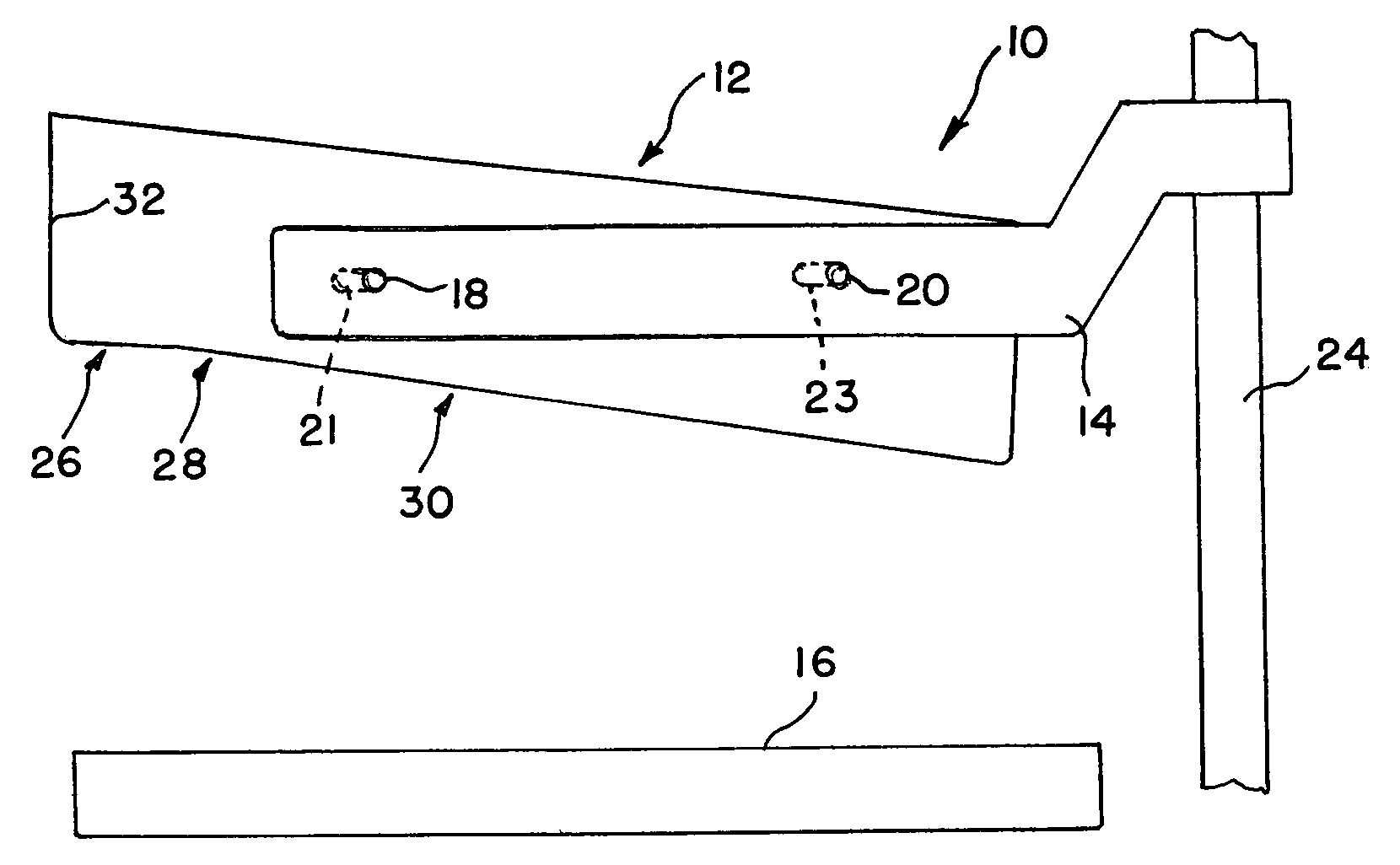
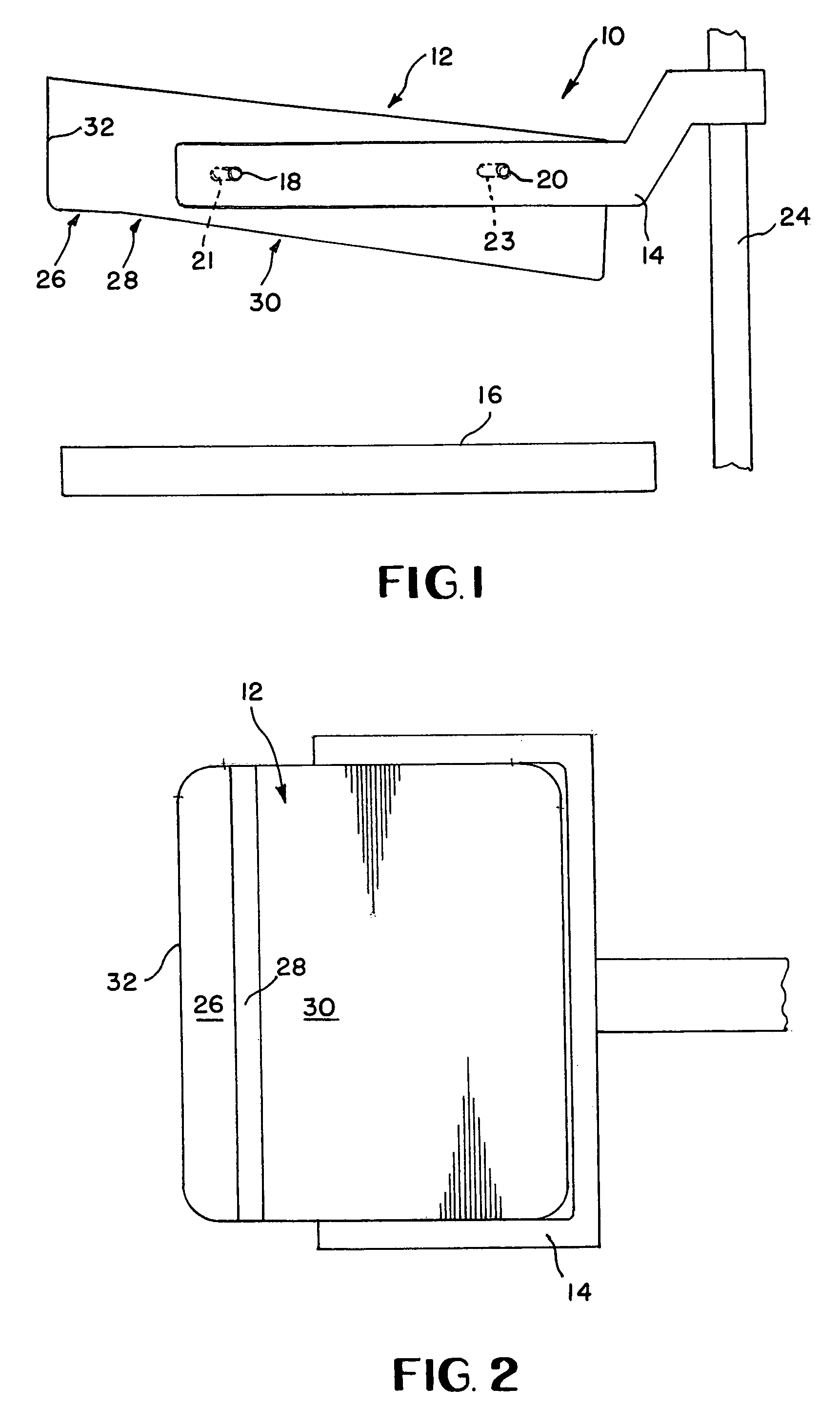
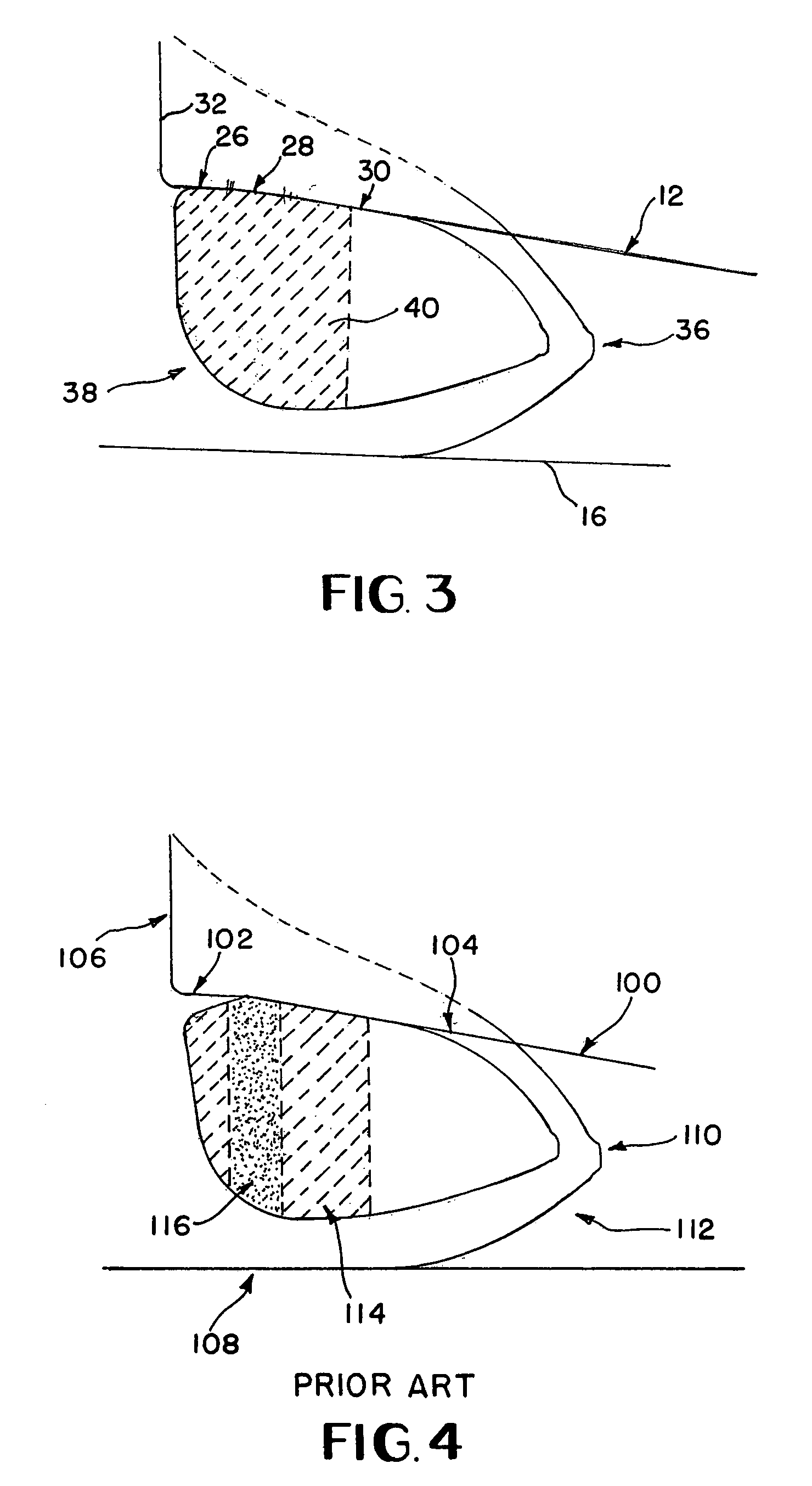
InactiveUS6974255B1Efficient compressionPrevent slippingPatient positioning for diagnosticsMammographyEngineeringConventional mammography
A breast compression device for use with a conventional mammography system is disclosed. The device comprises a paddle support frame which is slidably connected to a conventional mammography system's compression paddle carriage. A mounting arm may be provided for attaching the paddle support frame to the mammography system. The device further comprises a compression surface having a chest wall end and a nipple end. The paddle support frame is located between the x-ray tube and the detector of the mammography system. The compression surface of the device is comprised of three angled segments which conform to the normal contours of the breast.
Owner:AMERICAN MAMMOGRAPHICS
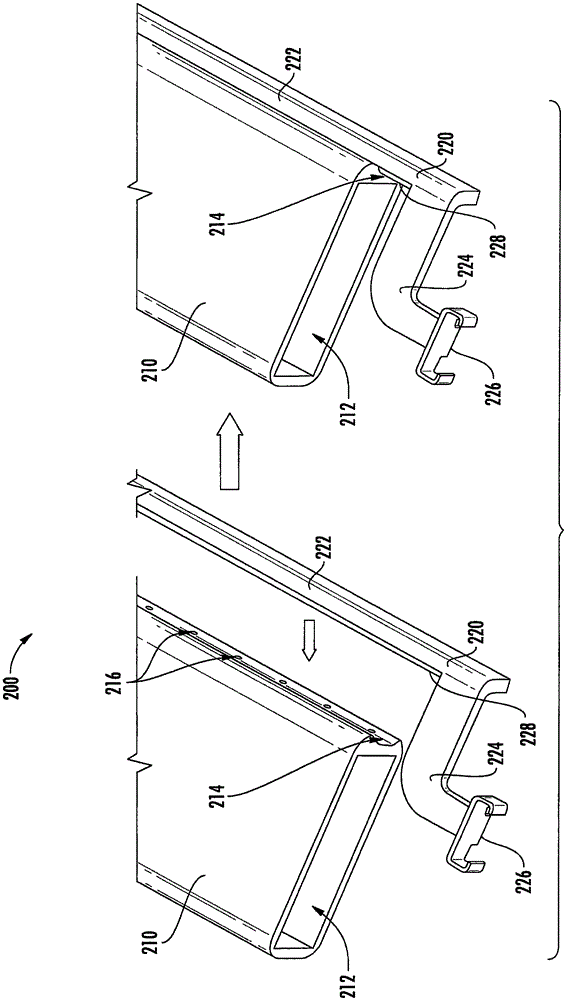
Compression paddle membrane and tensioning apparatus for compressing tissue for medical imaging purposes
Apparatus for compressing tissue to be scanned for medical imaging is provided. The apparatus may comprise a compression membrane and a tensioning apparatus coupled to the membrane to apply a tensile force to the membrane to place the membrane in a taut condition during an imaging process. In one exemplary application that combines ultrasound scanning with X-ray mammography, the compressing apparatus enables accurate, reproducible ultrasound images reducing distortion and attenuation, which may otherwise be introduced as a consequence of such a combination of imaging processes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
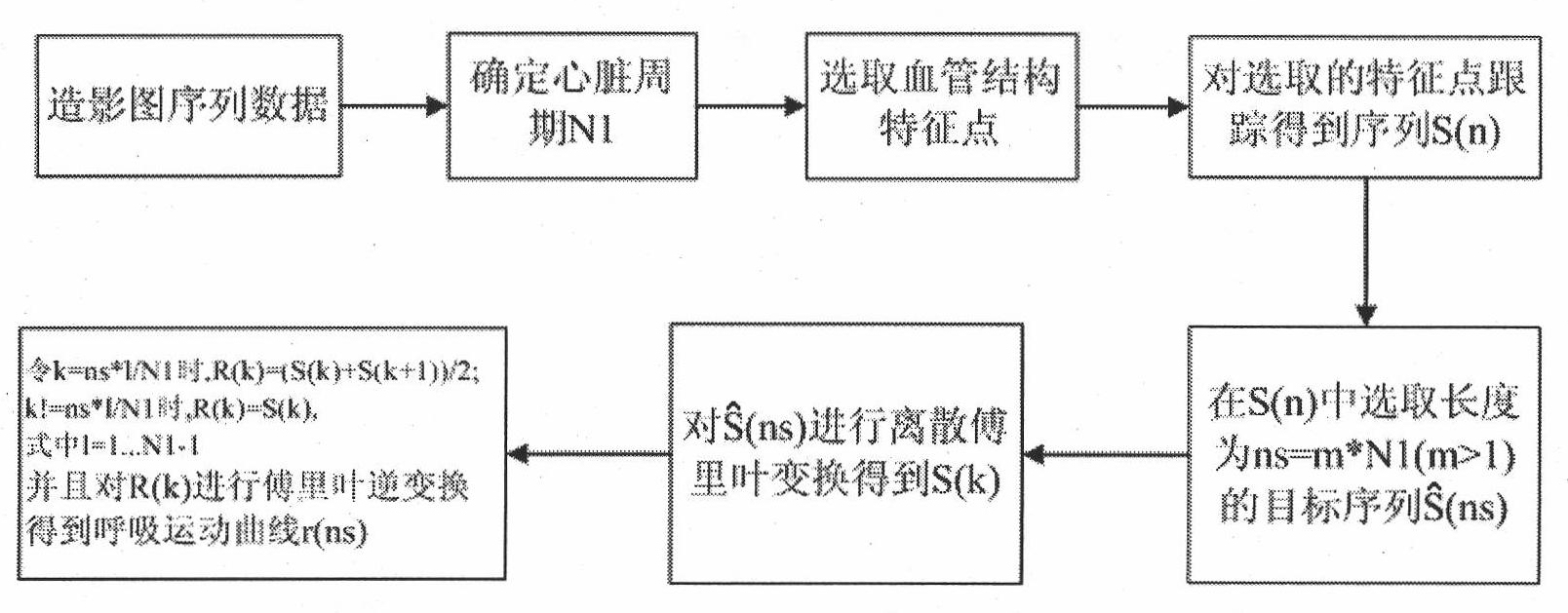
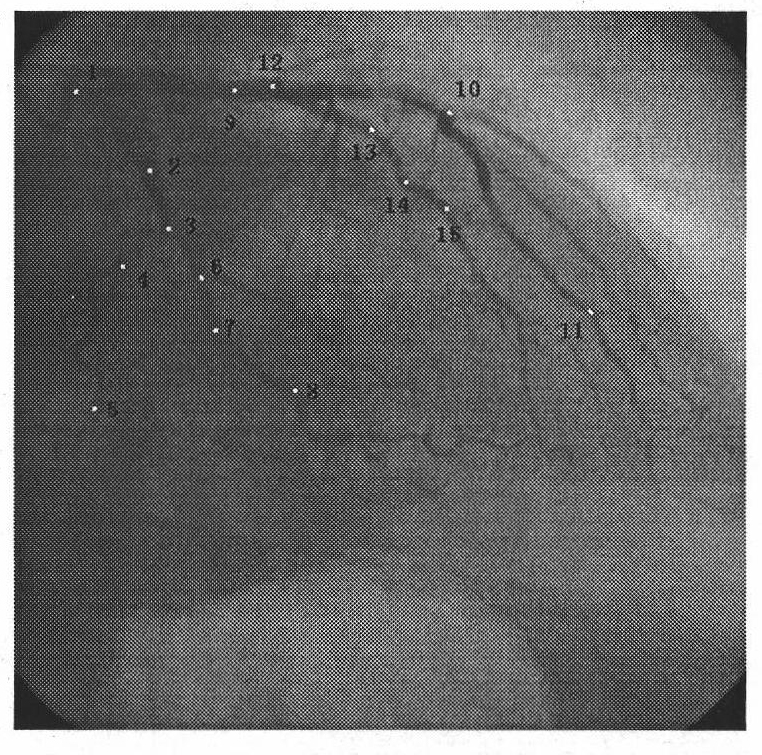
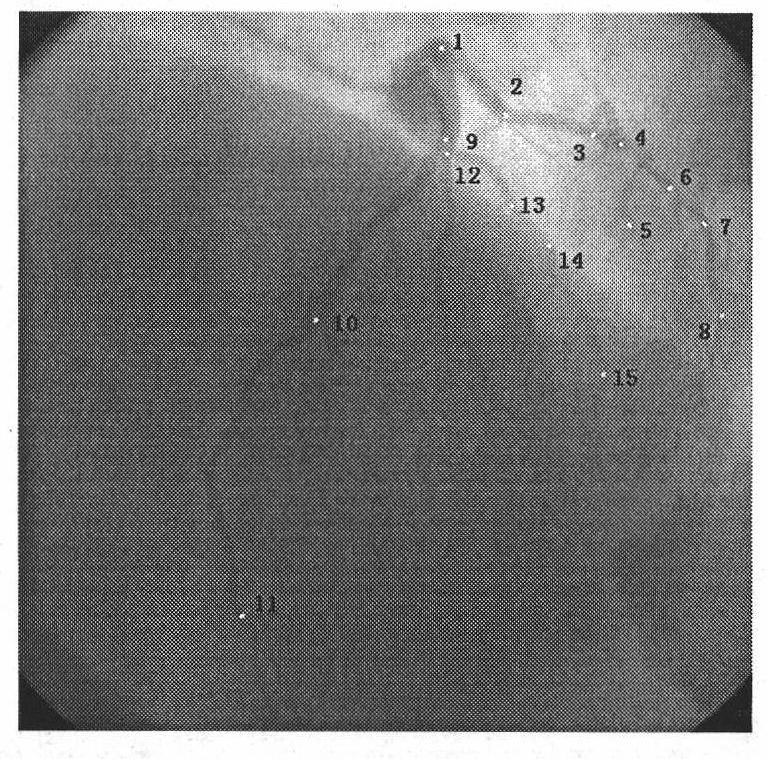
Method for extracting respiratory movement parameter from one-arm X-ray radiography picture
ActiveCN101773395AWide applicabilityImprove securityImage analysisRadiation diagnosticsDigital signal processingHuman body
The invention relates to a method for extracting a respiratory movement parameter from a one-arm X-ray radiography picture, which belongs to the crossed field of digital signal processing and medical imaging, and aims at separating the respiratory movement from the complex movement of an actual human body heart. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a group of architectural feature points (including the head and tail points of a vessel section) on a coronal artery vessel and tracking the motion curve of the architectural feature point along with the time in a sequence; and separating to obtain a bi-dimensional respiratory movement curve by the Fourier expansion and frequency-domain filtering method. In addition, in the invention, in order to describe the respiratory movement more intuitively and effectively, the bi-dimensional respiratory movement obtained from two different radiography visual angles is rebuilt according to the three-dimensional reconstruction theory of the mid point of a radiography system, therefore the three-dimensional respiratory movement is obtained. The invention has the advantages of better extracting result of the respiratory movement and wider applicability and flexibility, and meets clinical requirements.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus and method for interstitial laser therapy of small breast cancers and adjunctive therapy
Apparatus and method for performing interstitial laser therapy and adjunctive therapy on a patient are revealed. The apparatus employs a combination of a mammography unit, an interstitial laser treatment device attached to the mammography unit and a treatment platform positioned relative to the mammography unit to enable the interstitial laser therapy to be performed. The use of the treatment platform with the mammography unit enables the interstitial laser therapy to be performed and, if necessary, adjunctive therapy to be performed in the same treatment room without transferring the patient to a new platform.
Owner:NOVIAN HEALTH INC
Ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus, breast imaging system, and breast imaging method
InactiveUS20080249415A1Precise positioningShorten the timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPatient positioning for diagnosticsX ray radiographyVirtual image
A compression paddle of a mammographic diagnosis apparatus is provided with an opening portion which allows an ultrasonic probe to be fitted therein and slide. This apparatus performs ultrasonic scanning on a breast compressed / fixed to the compression paddle, and reconstructs a compressed breast image by using the obtained ultrasonic image as a virtual image, thereby acquiring an ultrasonic image and volume data of the compressed / fixed breast.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
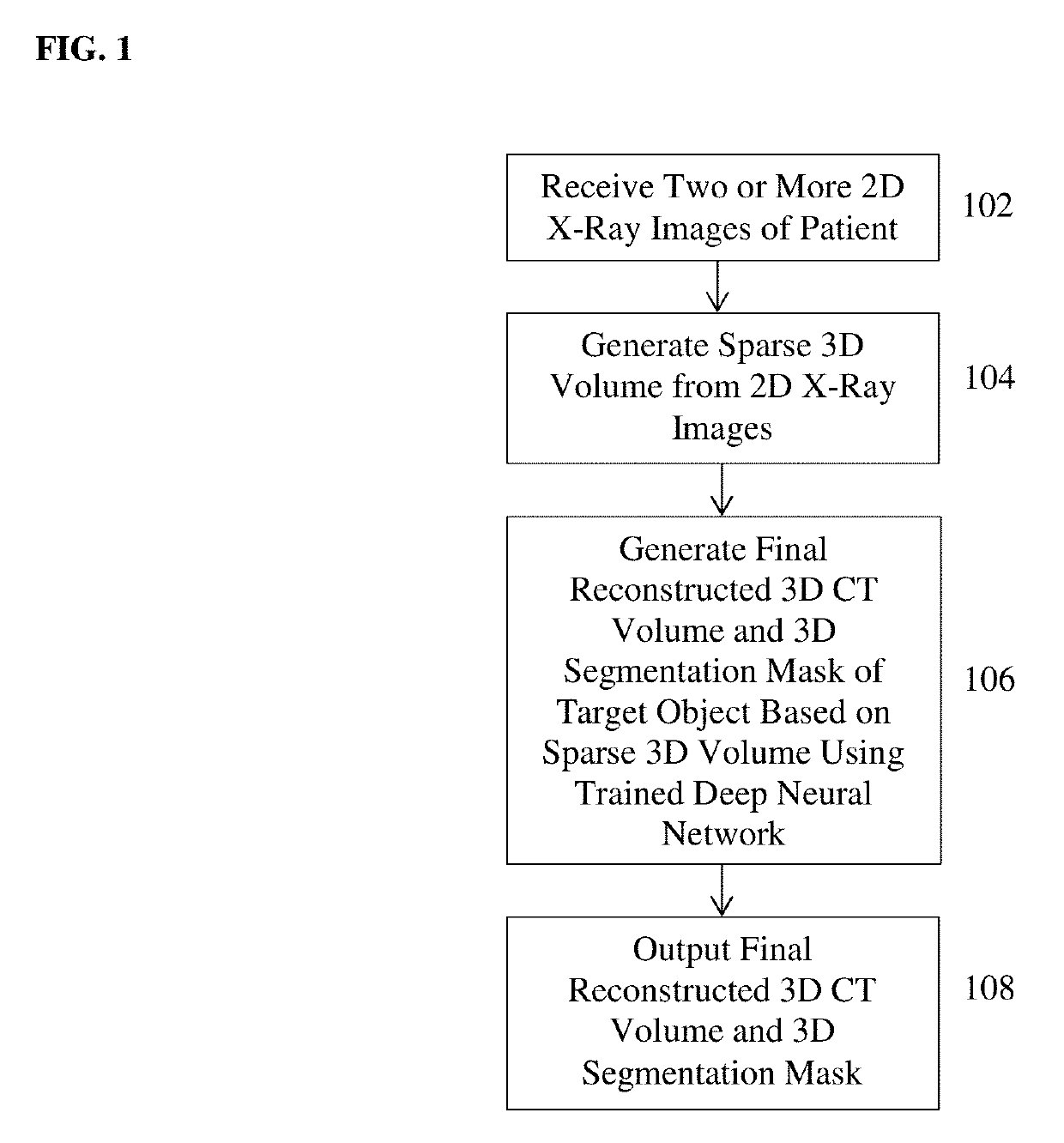
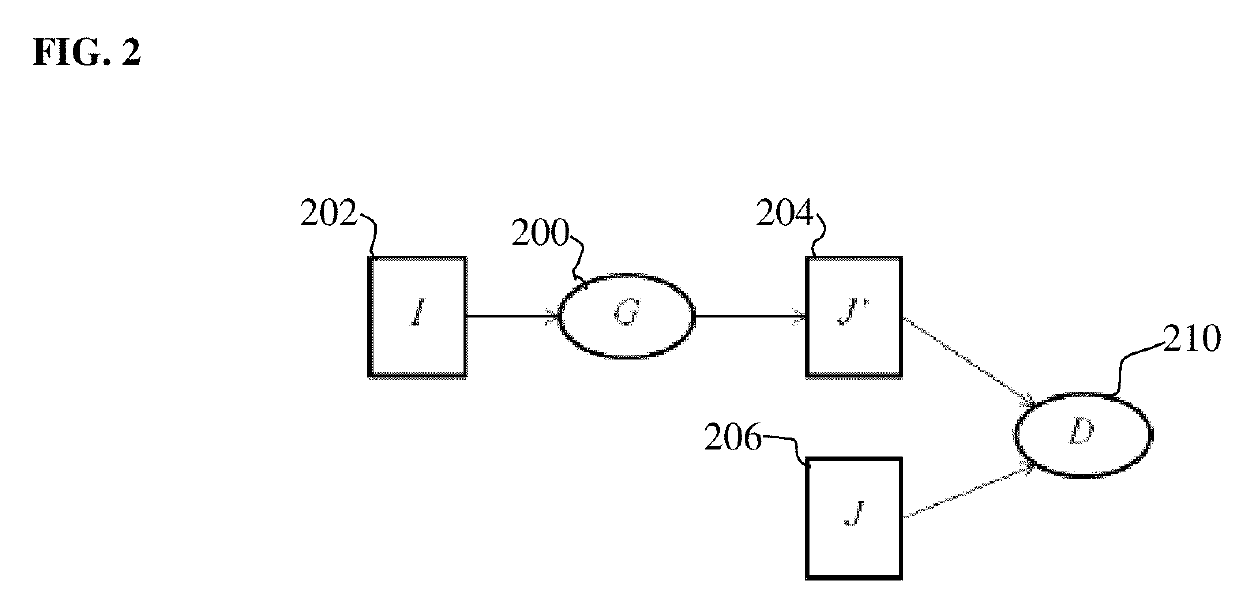
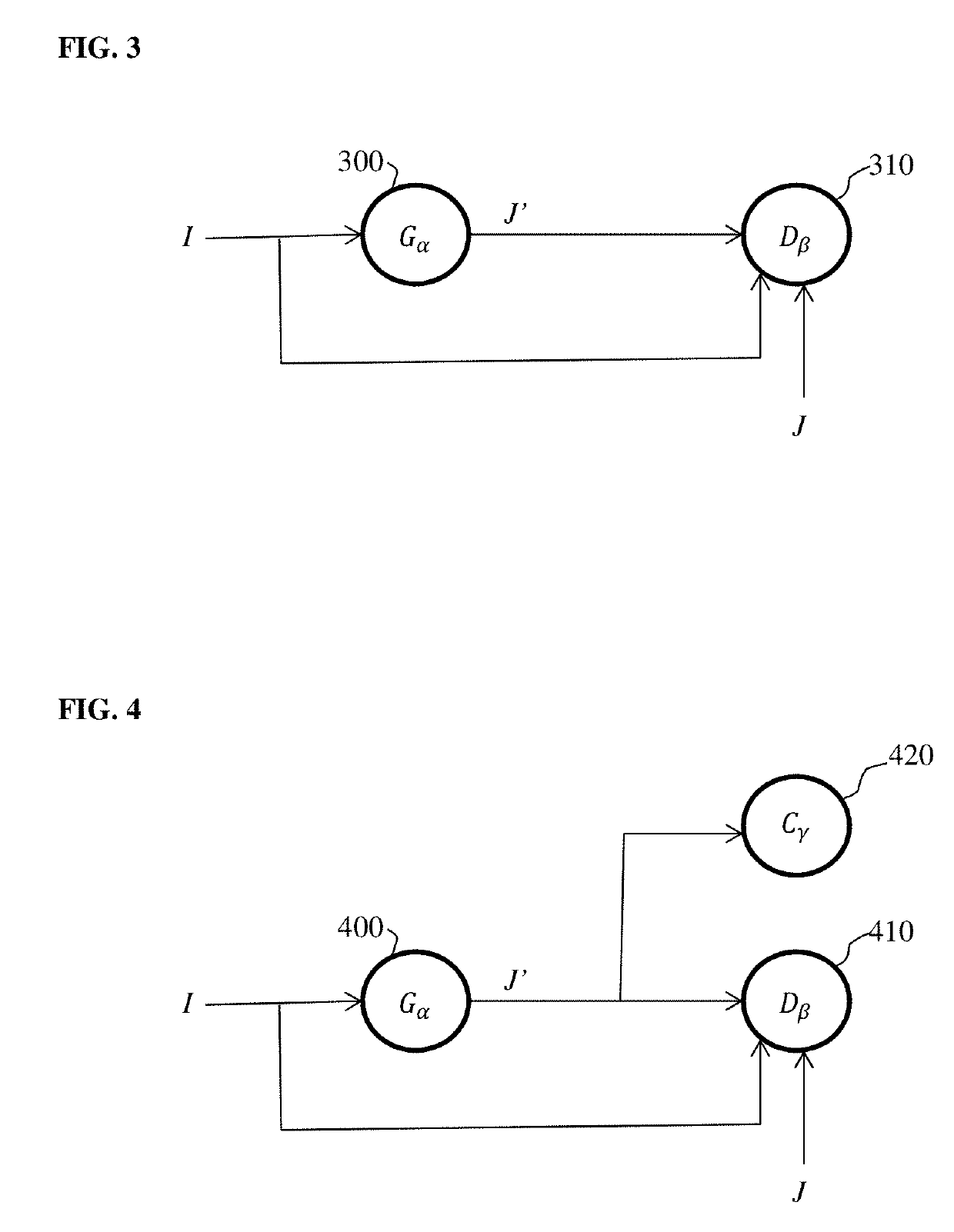
Method and System for 3D Reconstruction of X-ray CT Volume and Segmentation Mask from a Few X-ray Radiographs
A method and apparatus for automated reconstruction of a 3D computed tomography (CT) volume from a small number of X-ray images is disclosed. A sparse 3D volume is generated from a small number of x-ray images using a tomographic reconstruction algorithm. A final reconstructed 3D CT volume is generated from the sparse 3D volume using a trained deep neural network. A 3D segmentation mask can also be generated from the sparse 3D volume using the trained deep neural network.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
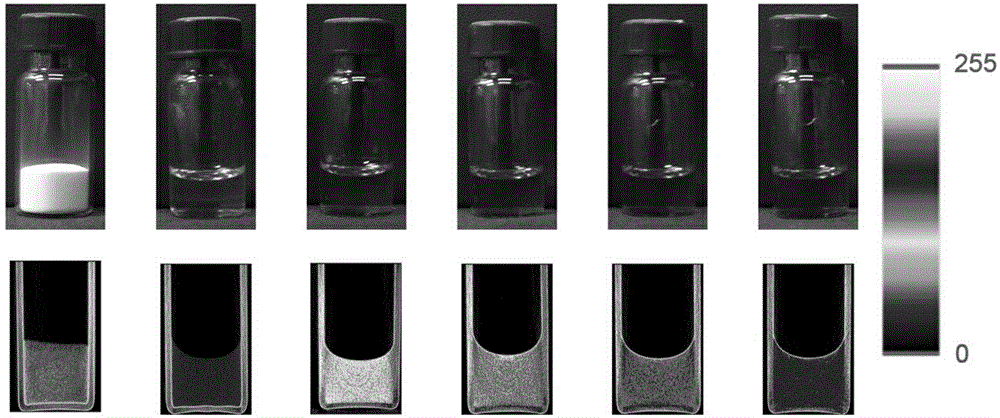
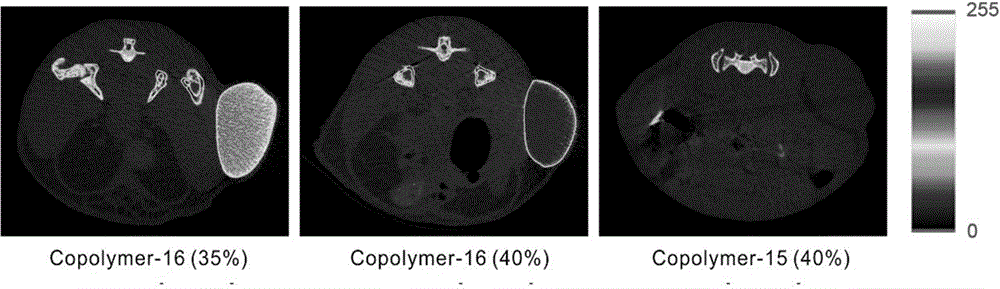
X-ray developing thermotropic hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104645356APossesses thermally induced gelation propertiesGood injectabilityAerosol deliverySurgeryTissue repairEmbolization Agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical polymer materials and in particular relates to X ray developing thermotropic hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The X ray developing thermotropic hydrogel comprises an iodine-containing amphiphilic block copolymer and a solvent, wherein the iodine-containing amphiphilic block copolymer is obtained by bonding an iodine-containing micromolecule and an amphiphilic block copolymer by virtue of a covalent bond, and thermotropic gelatinization phase transformation can be carried out on a water system of the X ray developing thermotropic hydrogel along with temperature increase. The thermotropic hydrogel can be implanted under the skin and implanted into an abdominal cavity, an articular cavity and other specific parts of a human body in a mode of injection, and in situ formed hydrogel has good X ray developing performance, clear positioning and long-term tracing observation can be carried out on the hydrogel by adopting an X ray radiography technique. The thermotropic hydrogel also can serve as a medicine controlled release carrier, a tissue repairing support, a blood vascular embolization agent, a tissue marker and the like and can be used for realizing integration of diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
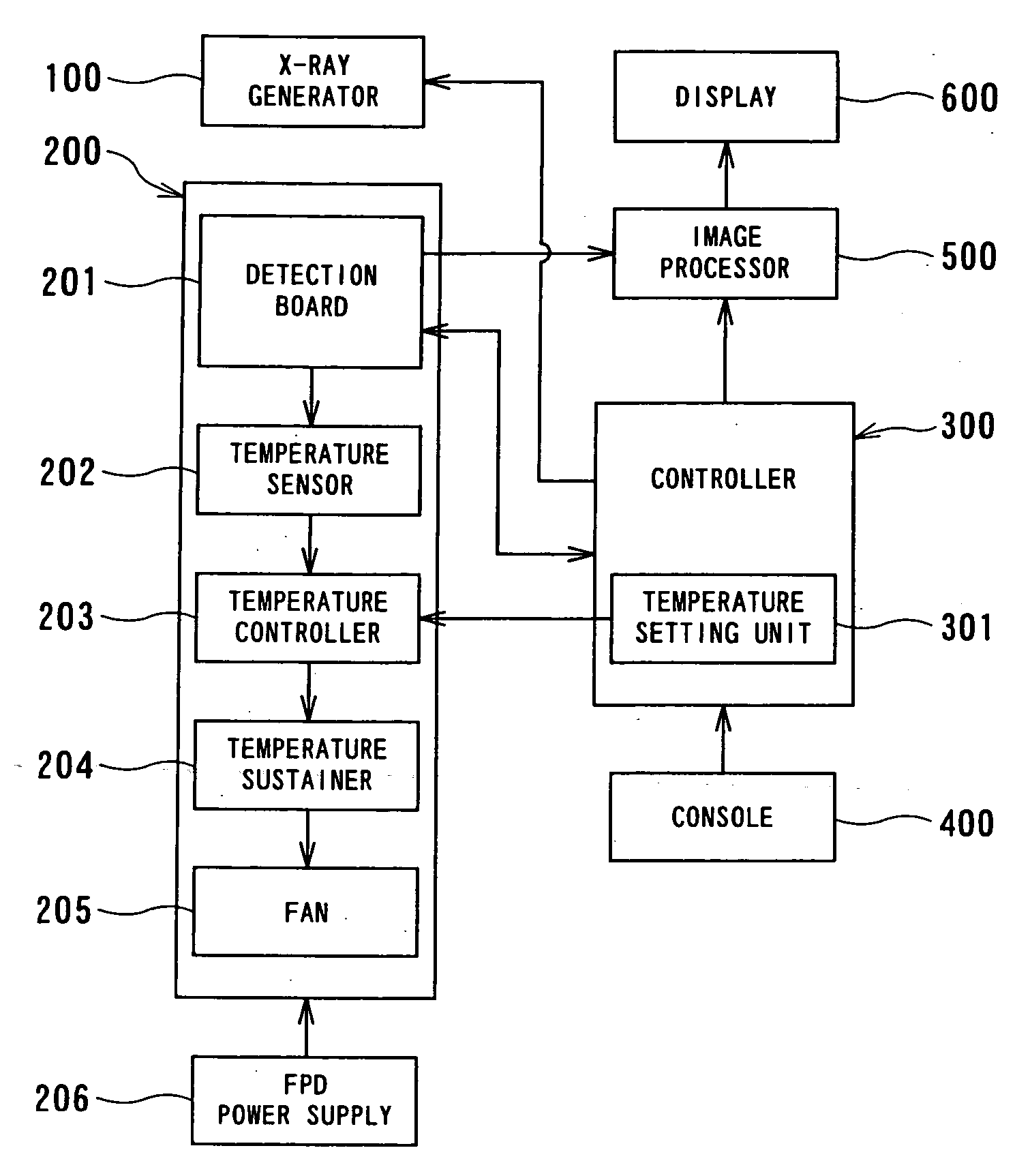
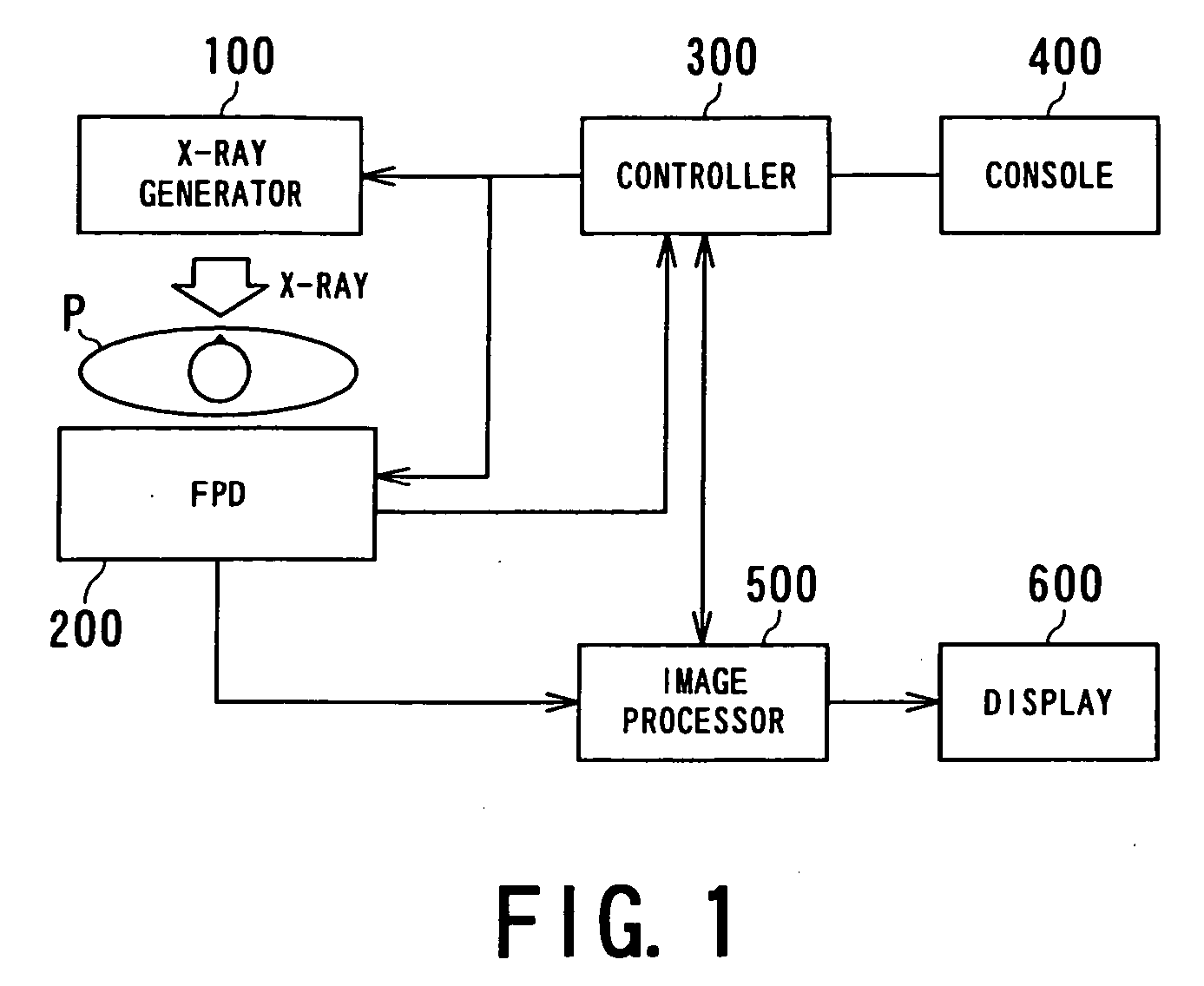
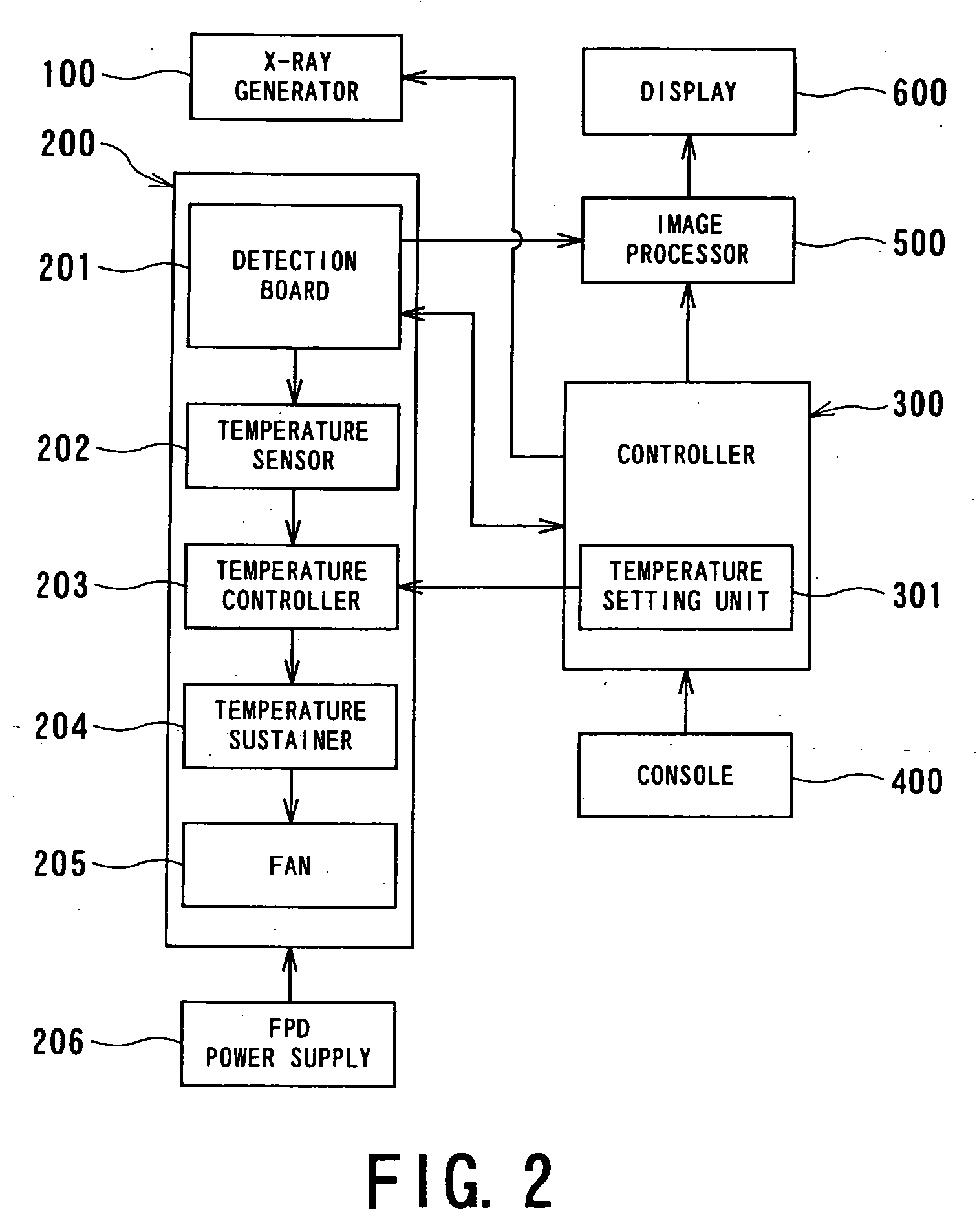
Control of temperature of flat panel type of radiation detector
InactiveUS20060076500A1Stable detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementFlat panel detectorTemperature control
A radiation detector is realized as, for example, a flat panel detector (FPD) for two-dimensionally detecting X-rays. The detector comprises a detection board and a control unit. The detection board on which a plurality of detection elements for detecting a radiation are two-dimensionally disposed in a matrix and circuits for collecting signals from the detection elements. The control unit for controlling the detection board so that the detection board is placed in a predetermined temperature state. The predetermined temperature state is defined, for example, as predetermined ranges of temperatures used during the operation and the non-operation states of the detector, respectively. This radiation detector can be mounted in a radiography system such as an X-ray radiography system.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
X-ray radiography system for differential phase contrast imaging of an object under investigation using phase-stepping
InactiveUS9453803B2Simple phase contrastHigh resolutionImaging devicesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingX ray imageElectron
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com