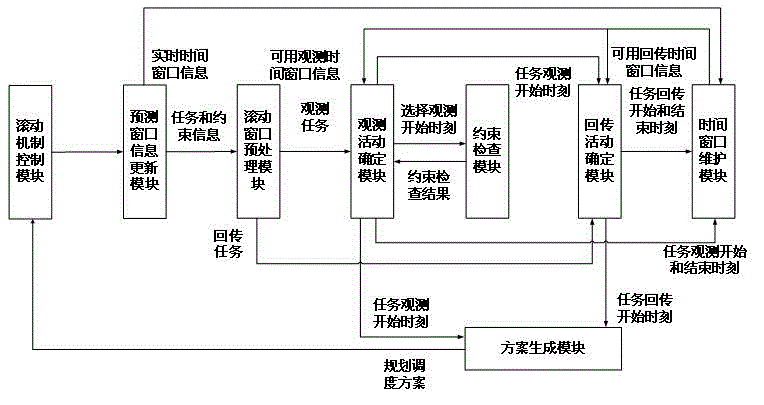
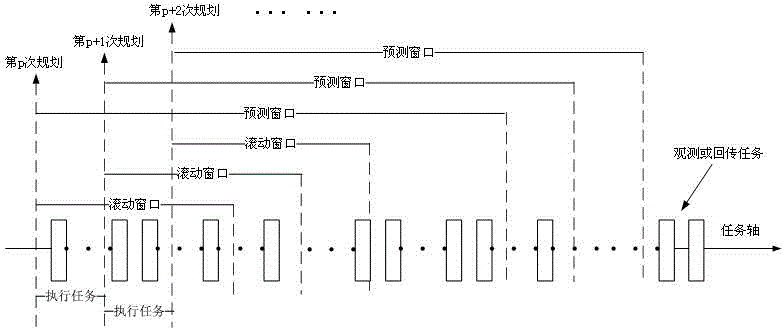
Imaging satellite autonomous mission planning algorithm based on receding horizon control
A technology for autonomous missions and imaging satellites, applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., to achieve the effect of good planning results, optimality and real-time integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] 1. Problem description:
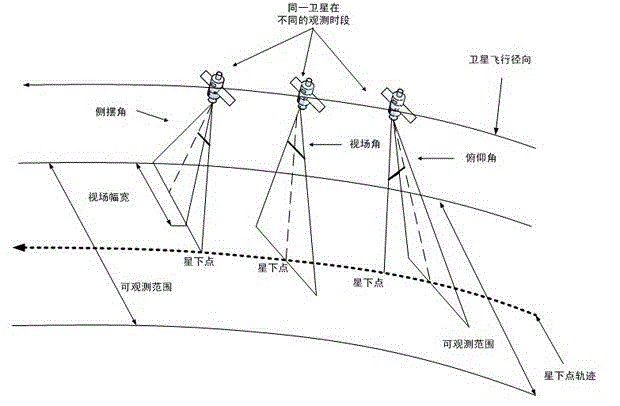
[0051] When imaging satellites observe the earth, they not only have to follow various strict constraints, but also can only observe the targets within their observation area. The observation area of the imaging satellite is jointly determined by the sub-satellite point, the roll angle, the pitch angle and the field of view angle, such as image 3 shown. During the planning period, imaging satellites may have multiple opportunities to observe an observation target, but each orbit has at most one opportunity to observe the target, and each observation task has certain observation benefits. Therefore, the problem of autonomous mission planning for imaging satellites can be described as, imaging satellites can generate mission planning schemes autonomously on the satellite according to their own state, external environment and other constraints in real time without ground intervention. Plan time and resource consumption to obtain the maximum p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com