Patents
Literature
142 results about "Fuel cell bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
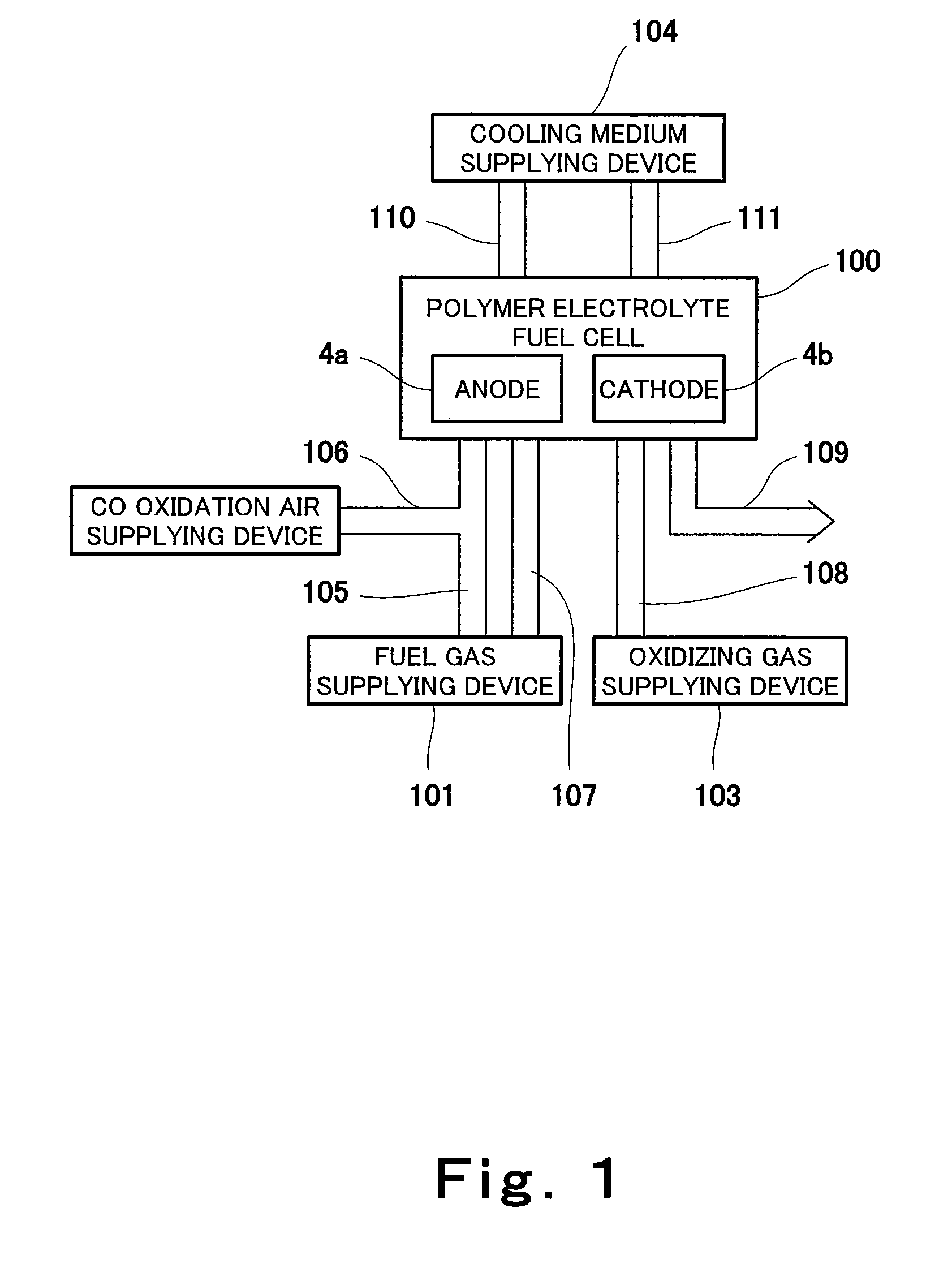
A fuel cell bus is a bus that uses a hydrogen fuel cell as its power source for electrically driven wheels, sometimes augmented in a hybrid fashion with batteries or a supercapacitor. Several companies have conducted hydrogen fuel cell research and practical fuel cell bus trials.
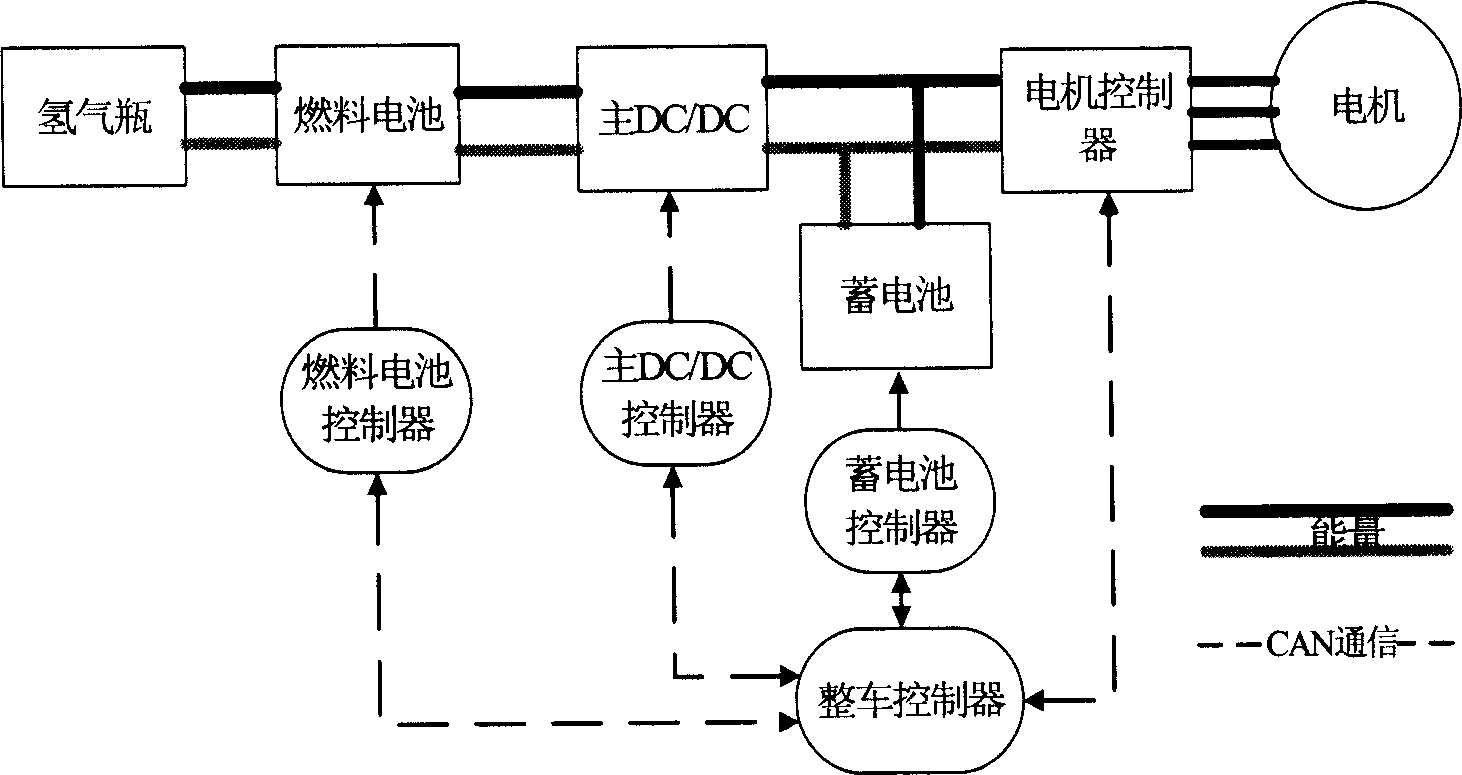
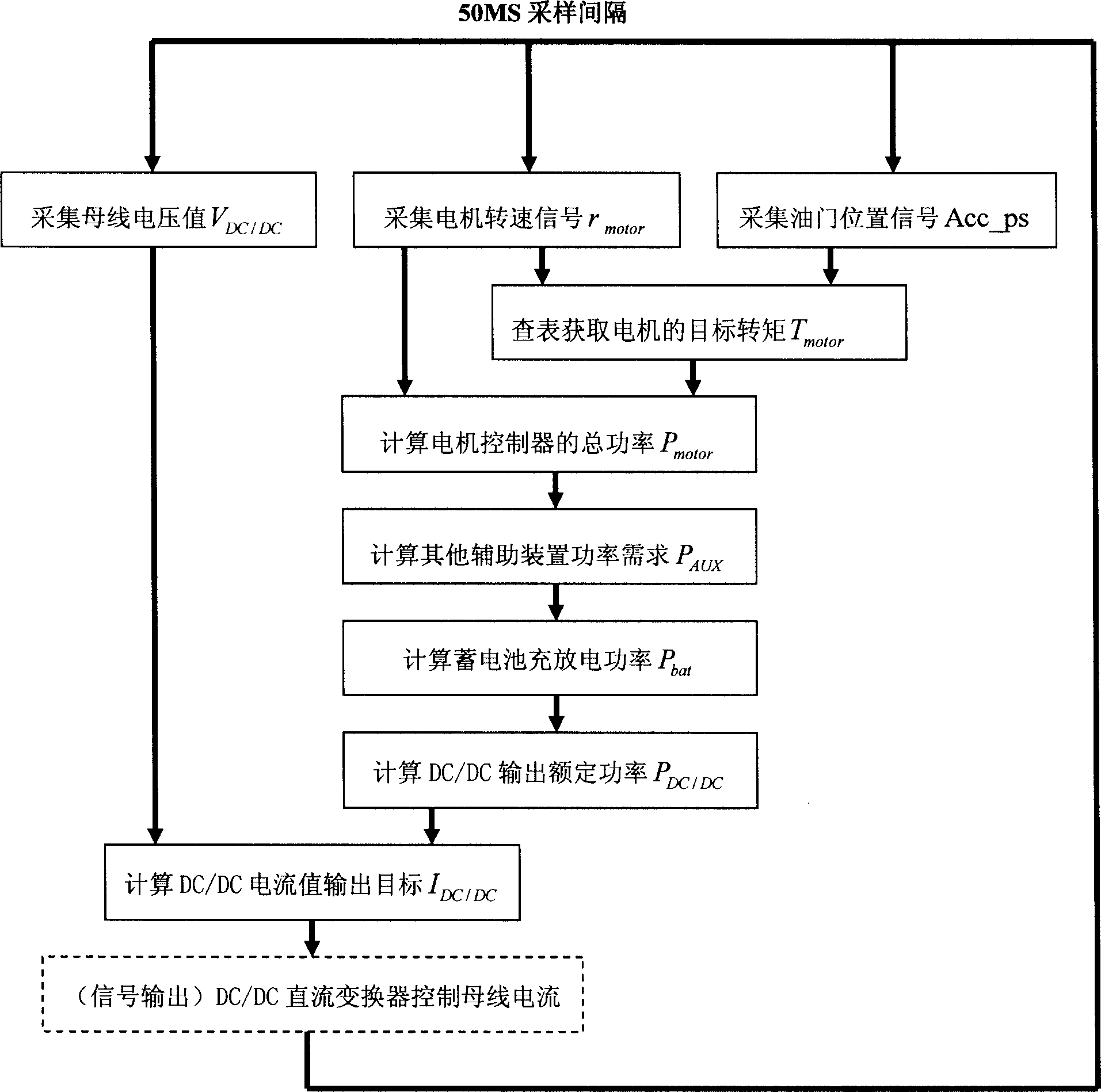
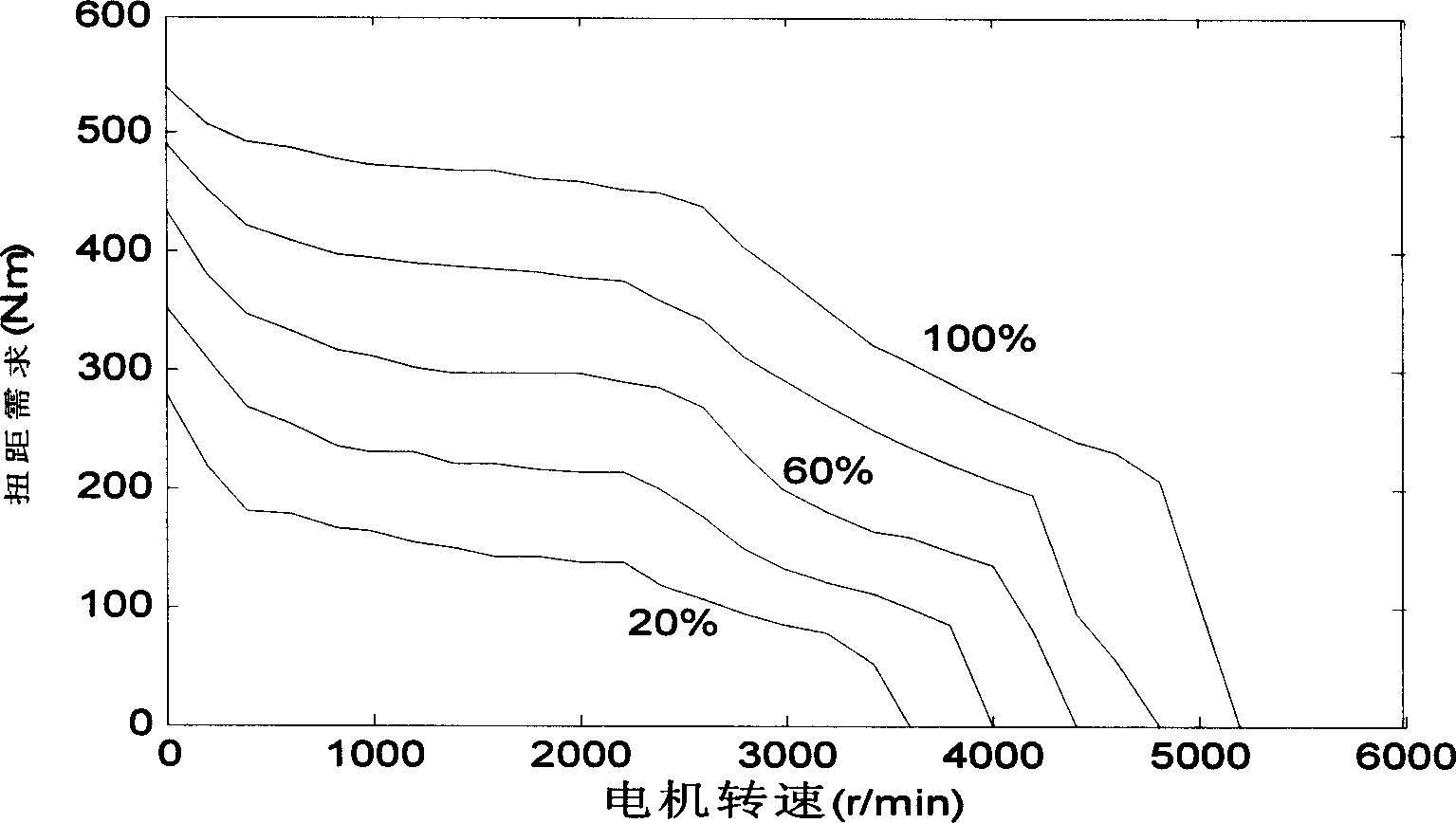
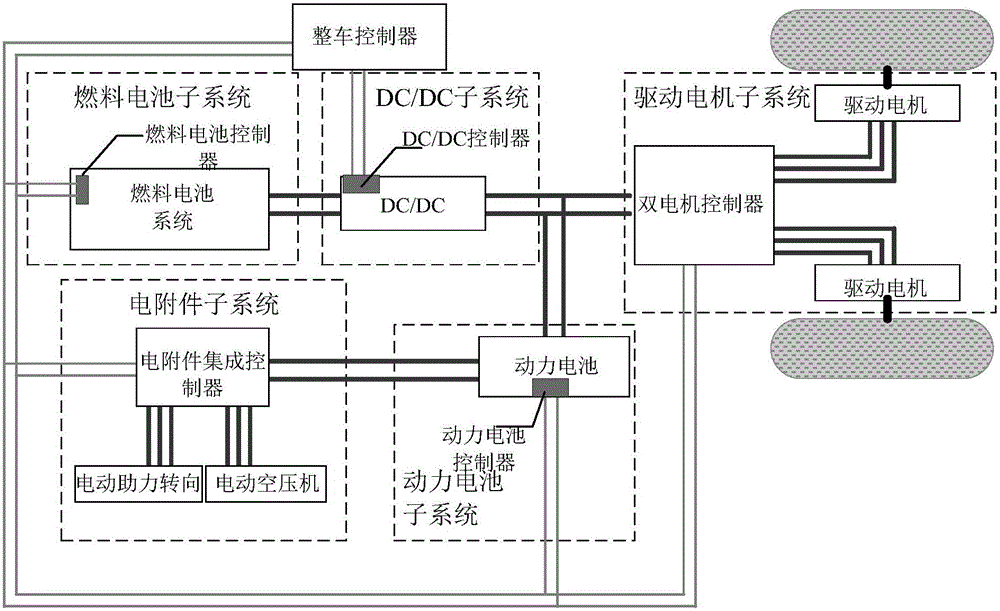
Fuel cell car energy control method based on CAN bus network communication
InactiveCN1807144AImprove efficiencySpeed controllerBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy controlFiltration
The invention relates the fuel battery coach controlling method on base of the CAN bus internet communication used for hybrid power system, using the direct converting means to carry out energy management control. The CAN bus sends the main voltage signal VDC / DC, motor rotation rate signal rmotor and throttle pedal signal Acc_ps to full control device; in full control device looking up goal torque Tmotor and calculate demand total power Pmotor, auxiliary device power PAUX and accumulator charge-discharge power Pbat; calculate DC / DC output current IDC / DC; IDC / DC passes first order filtration, after meeting the DC / DC converter dynamic regulator course, then the full control device sends it to DC / DC control device by CAN bus, and realize the DC / DC current control. The invention can realize the accurately control of load power, and provide the flat form for any kind of energy controlling method; the charge and discharge state provided by secondary energy can be controlled; the integral efficiency of power system is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
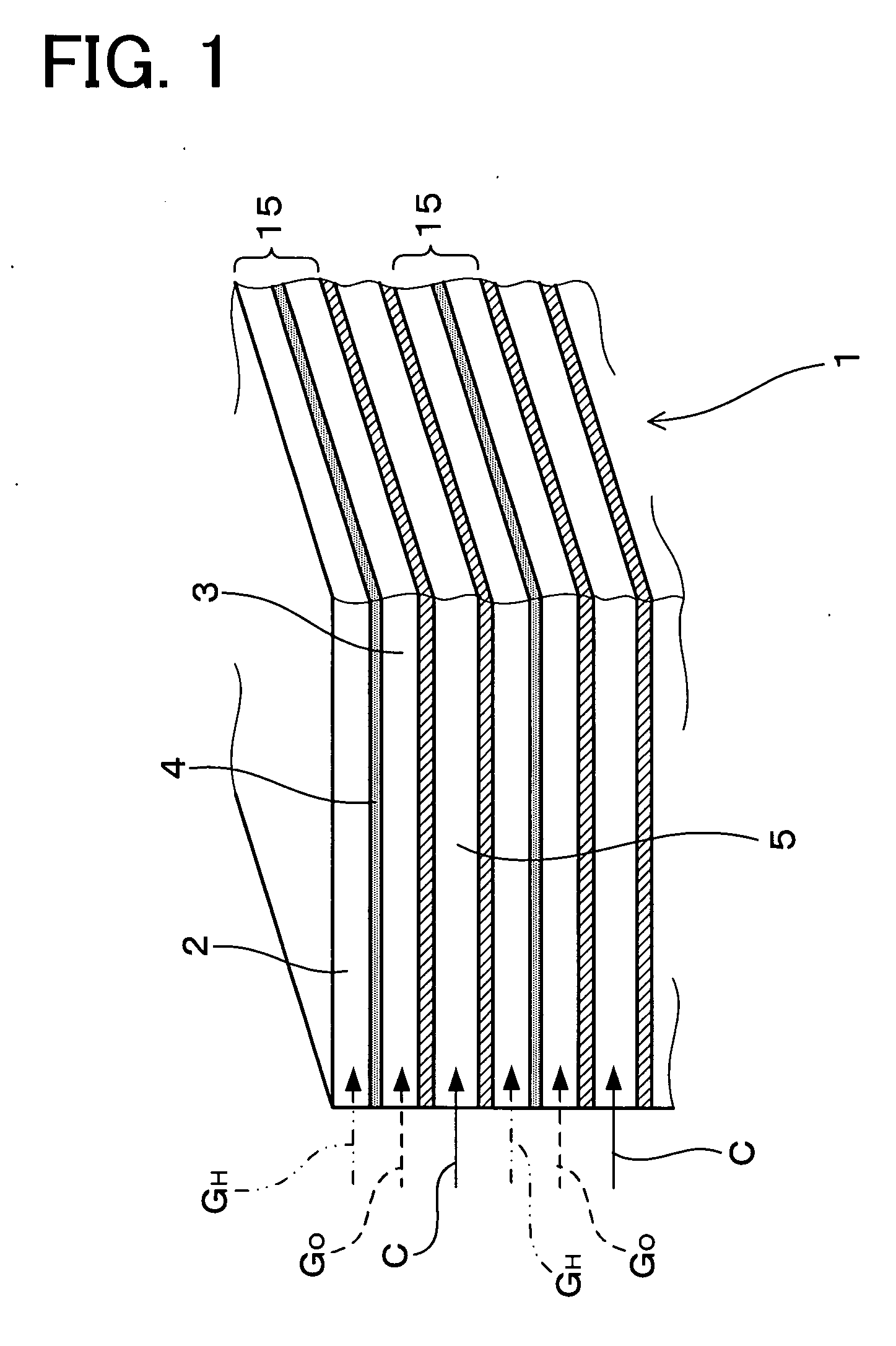
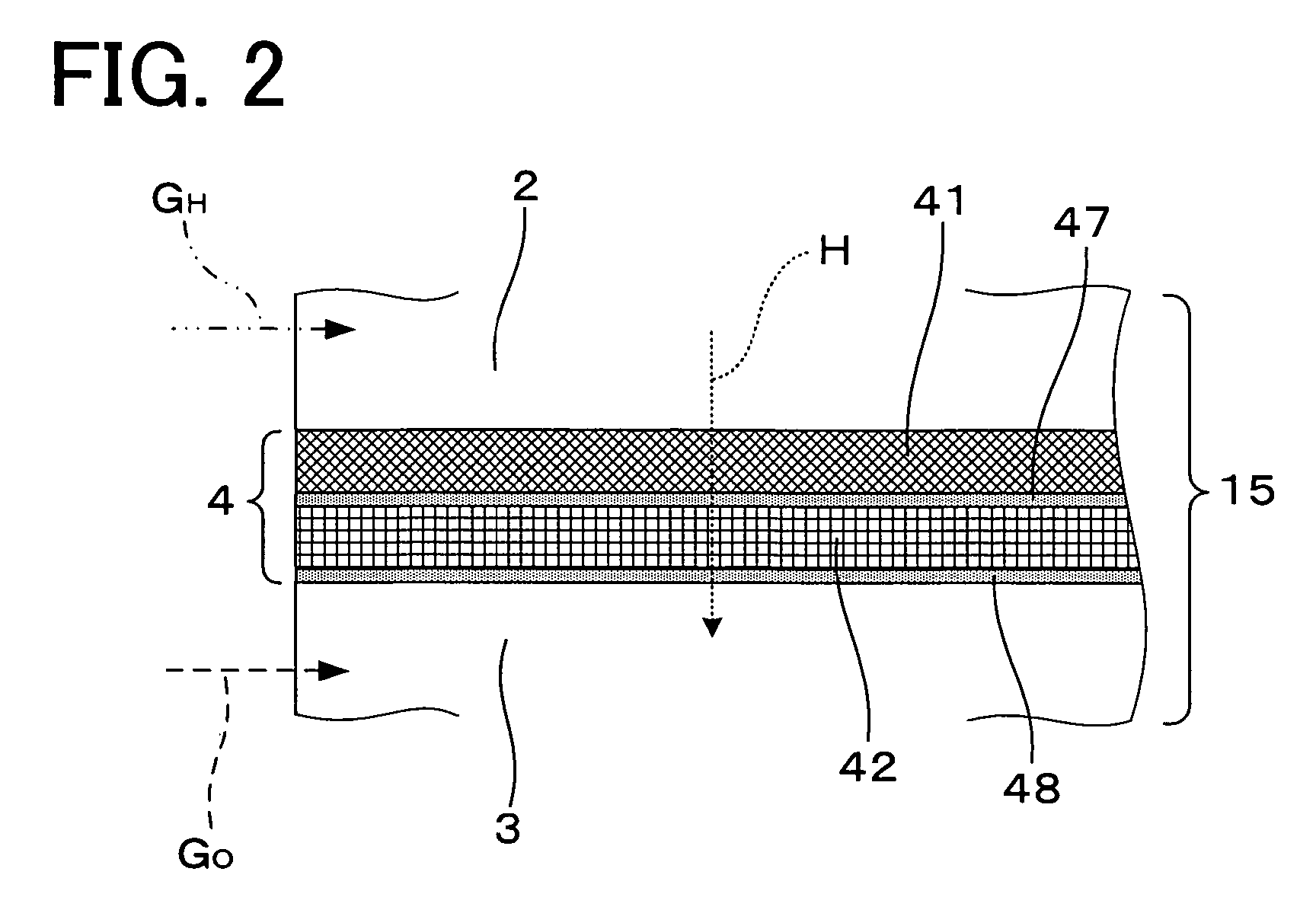
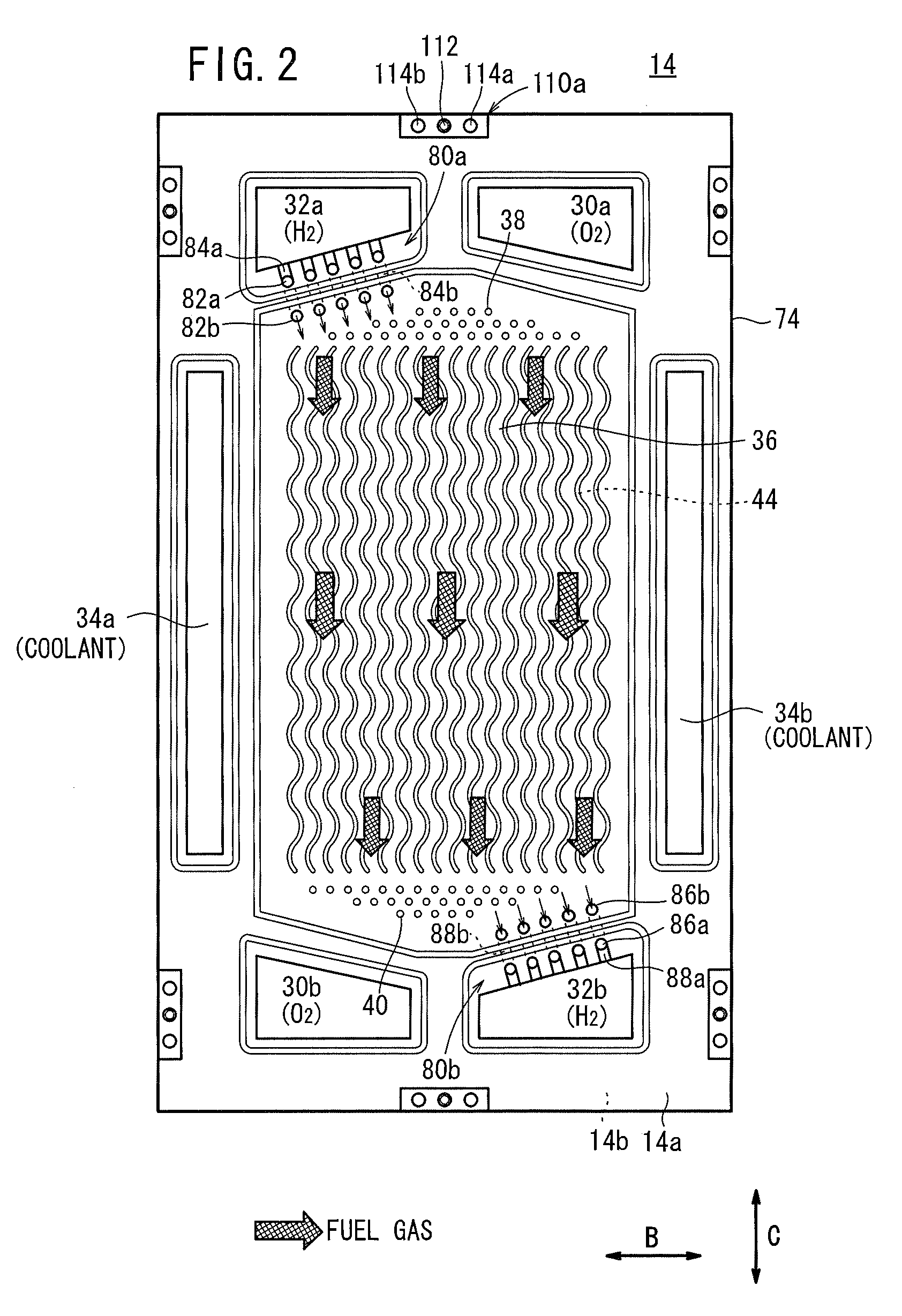
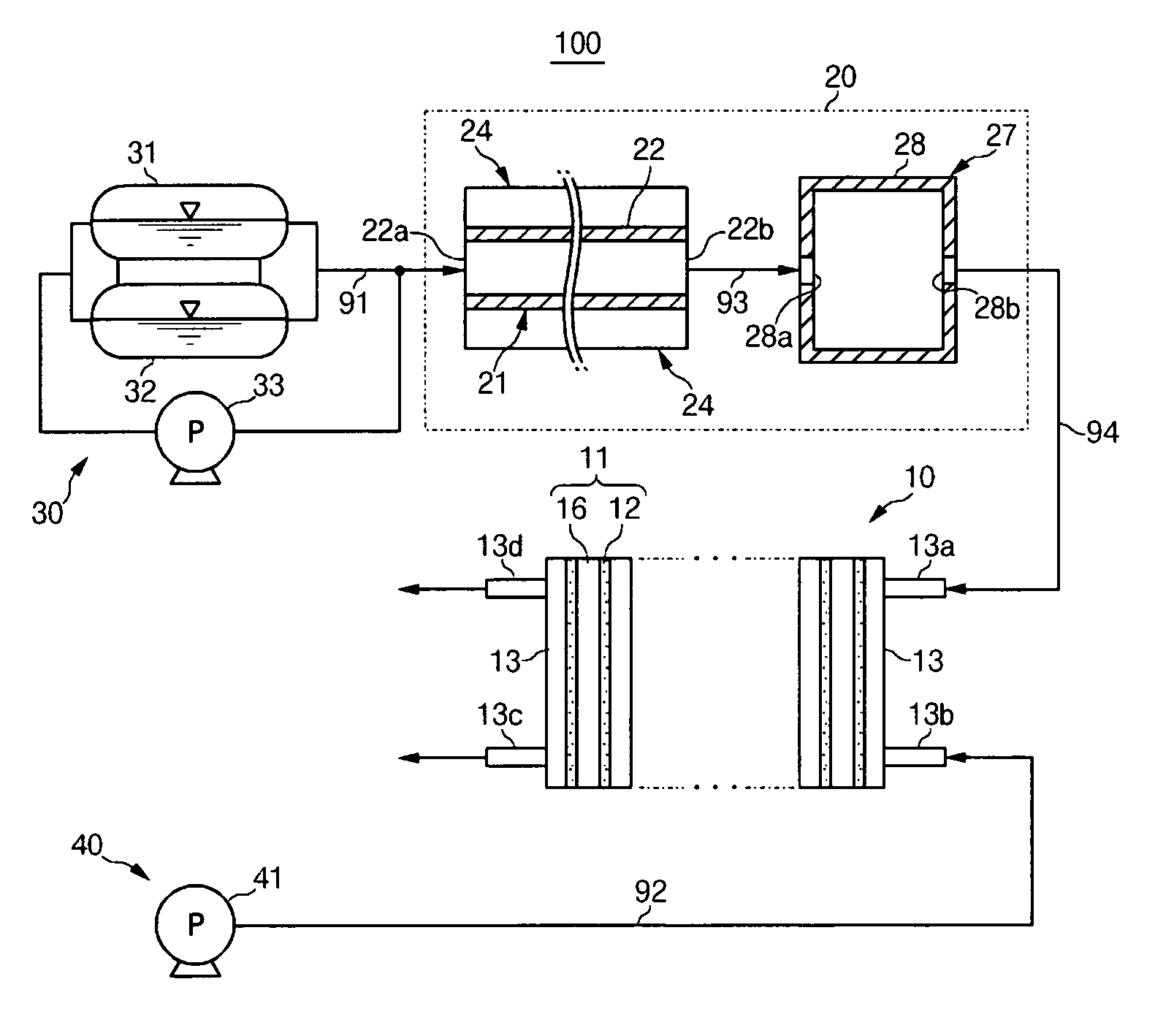
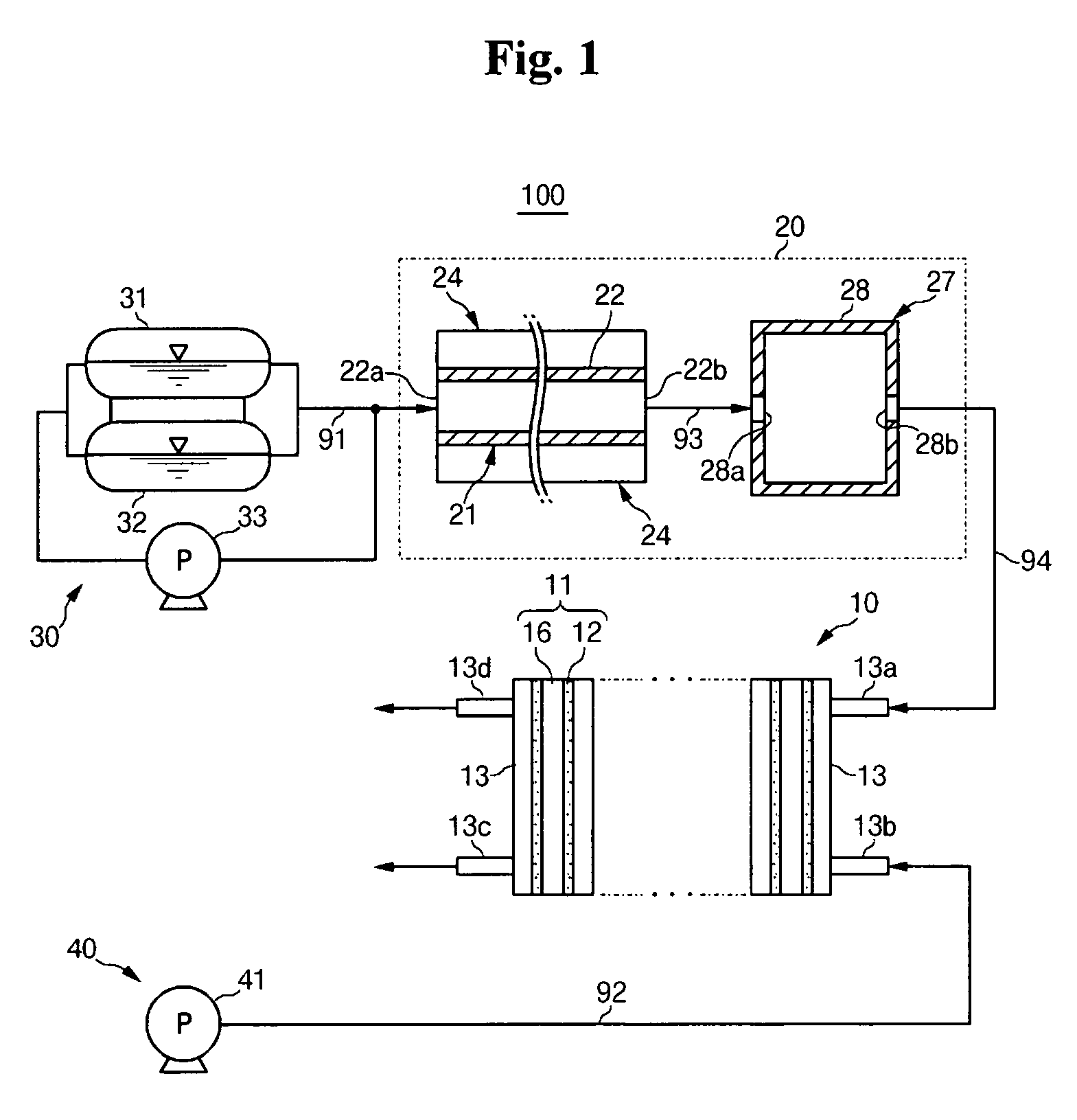
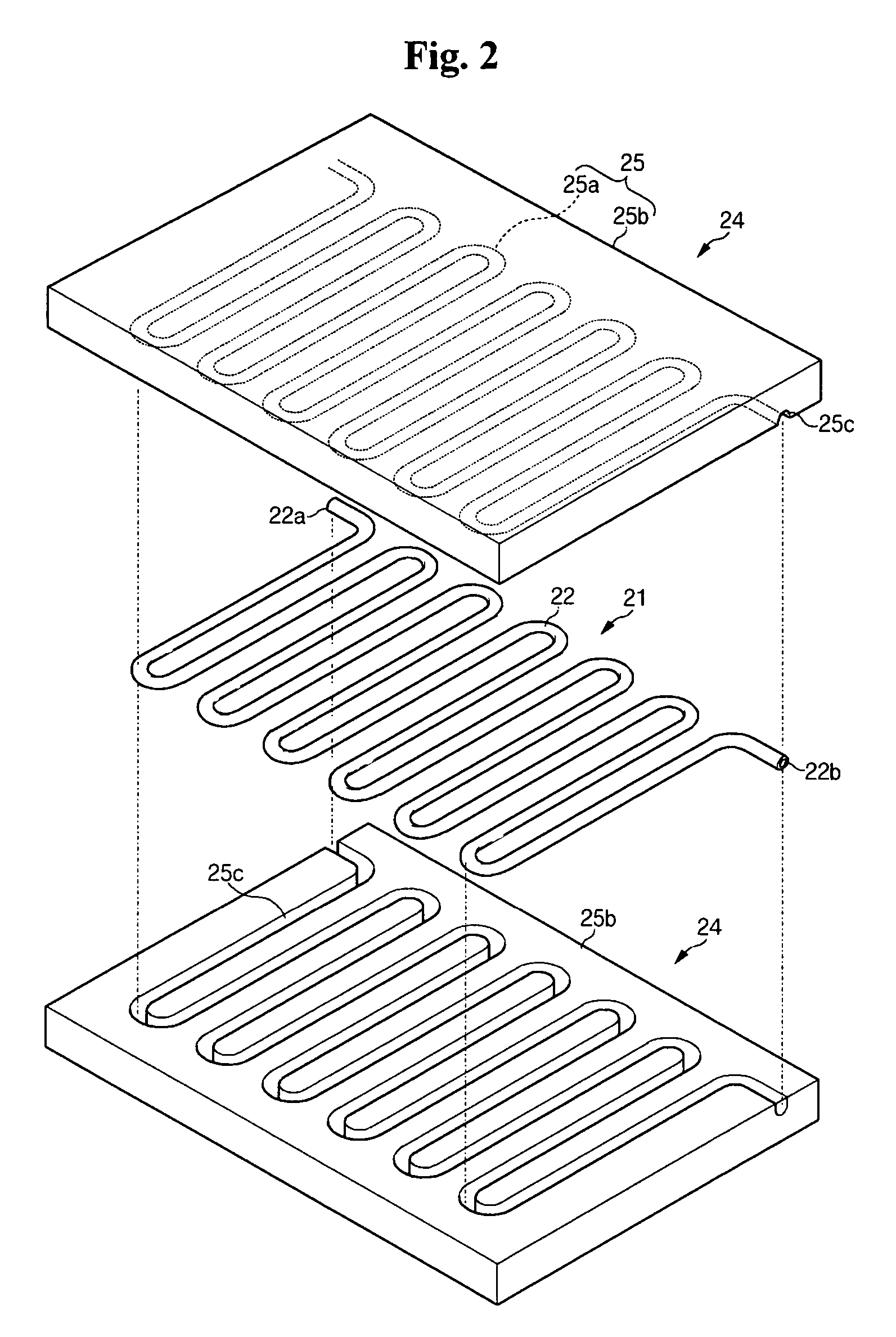
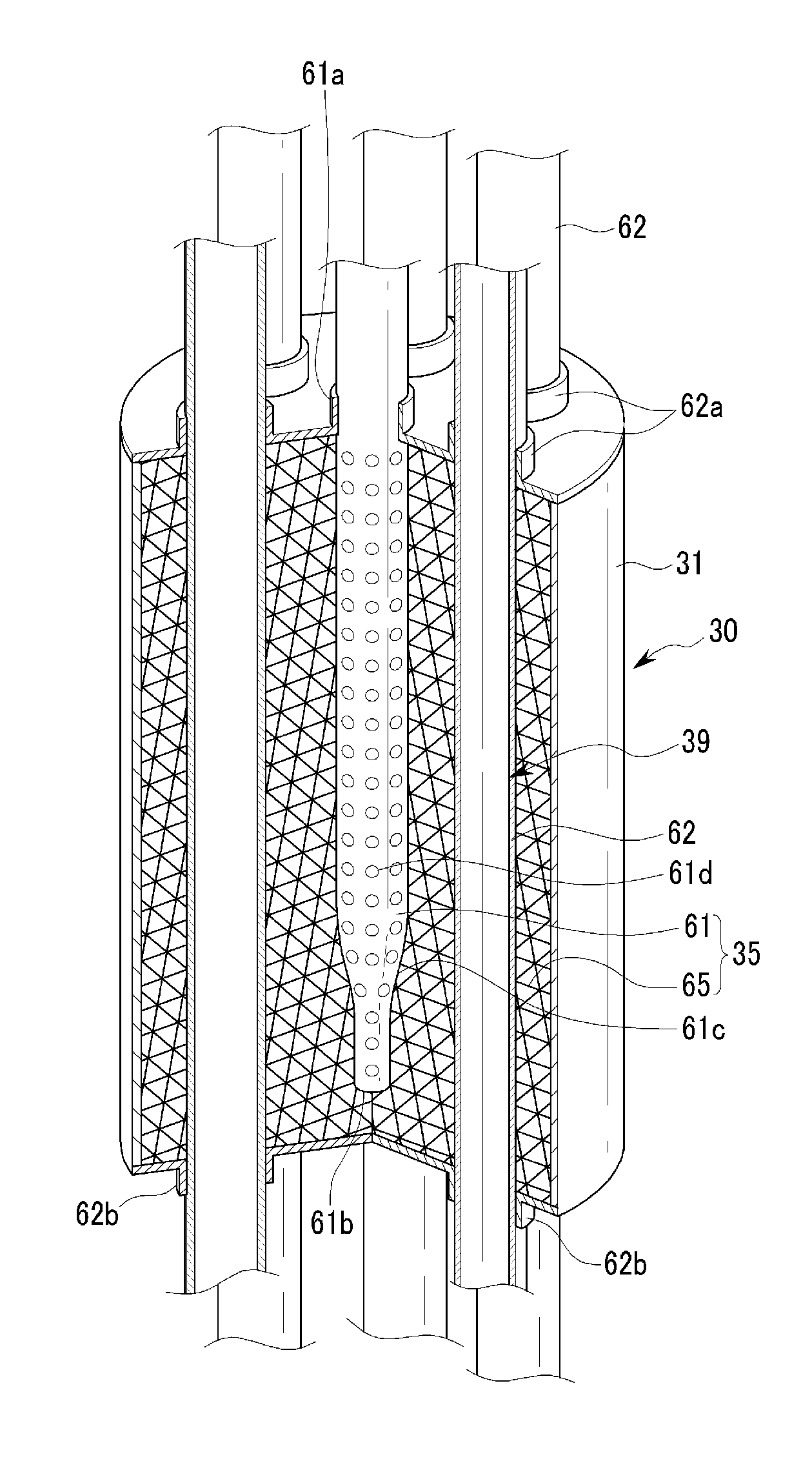
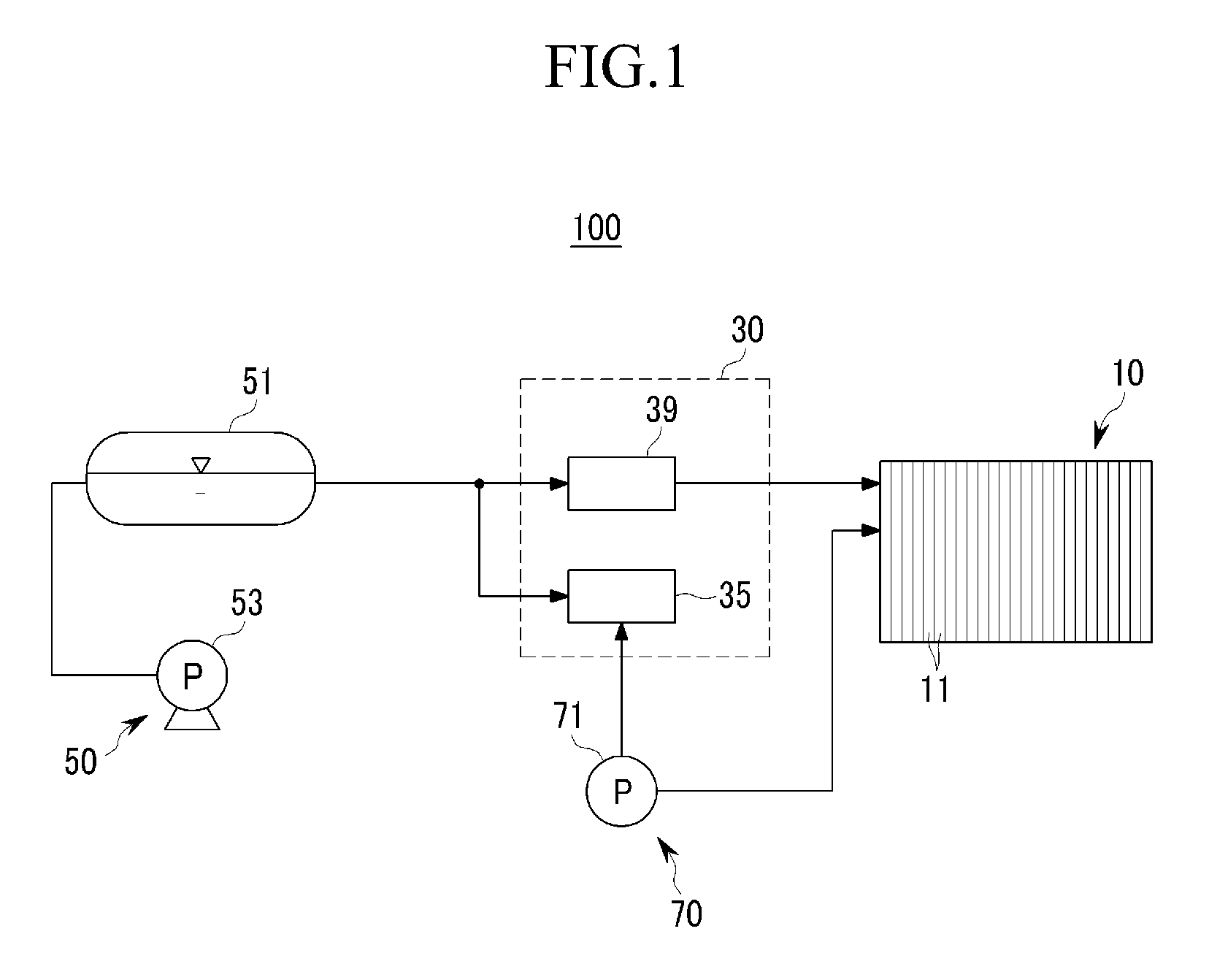
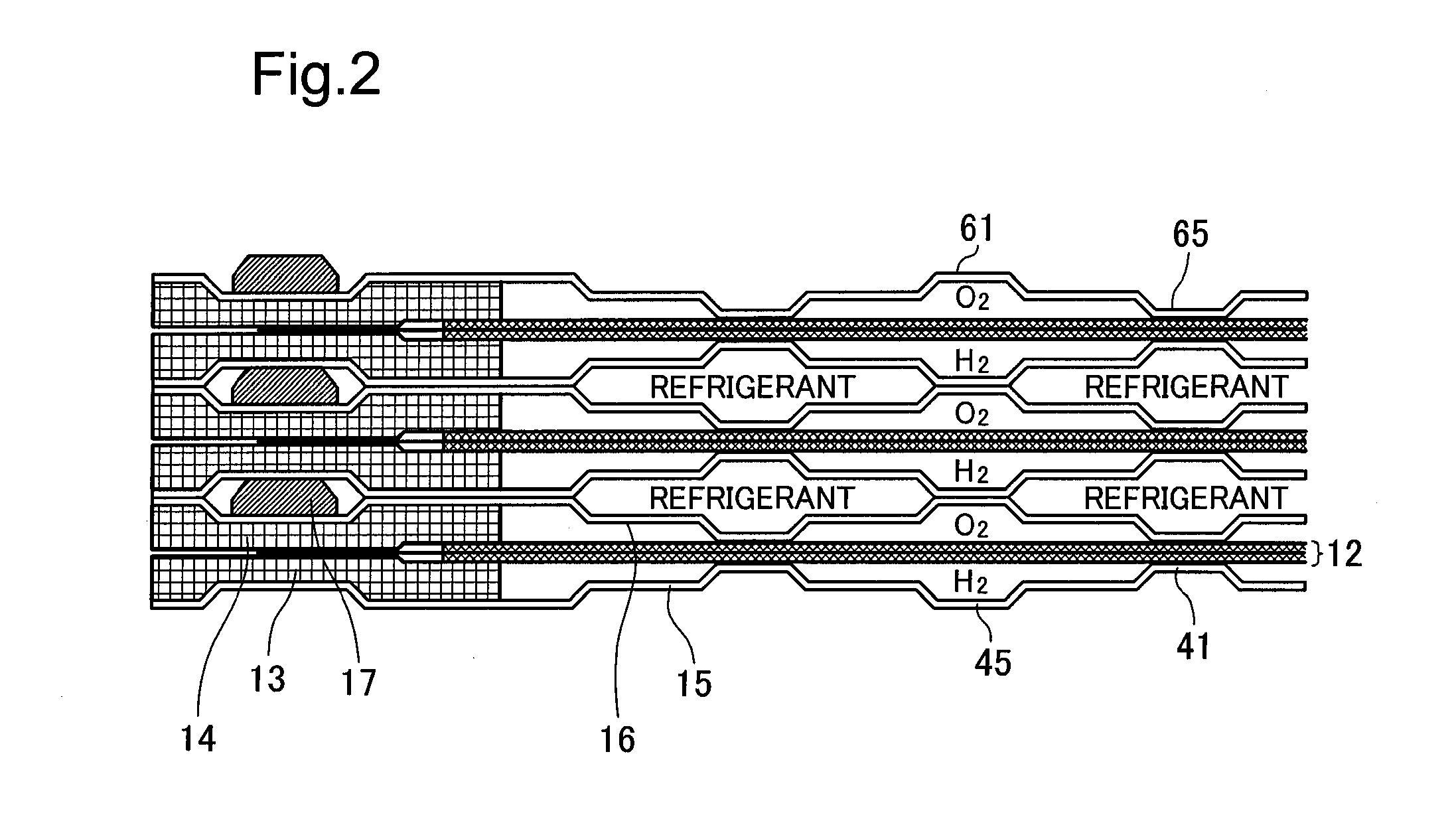
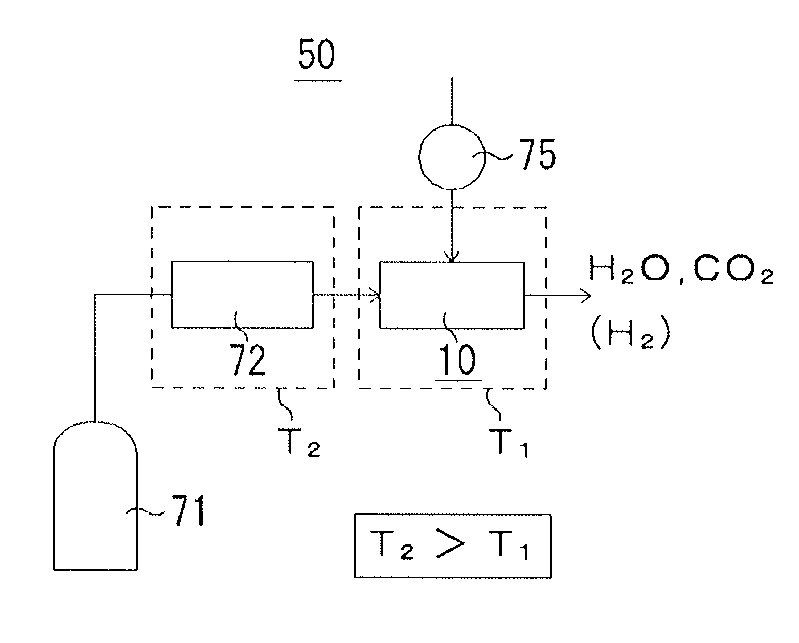
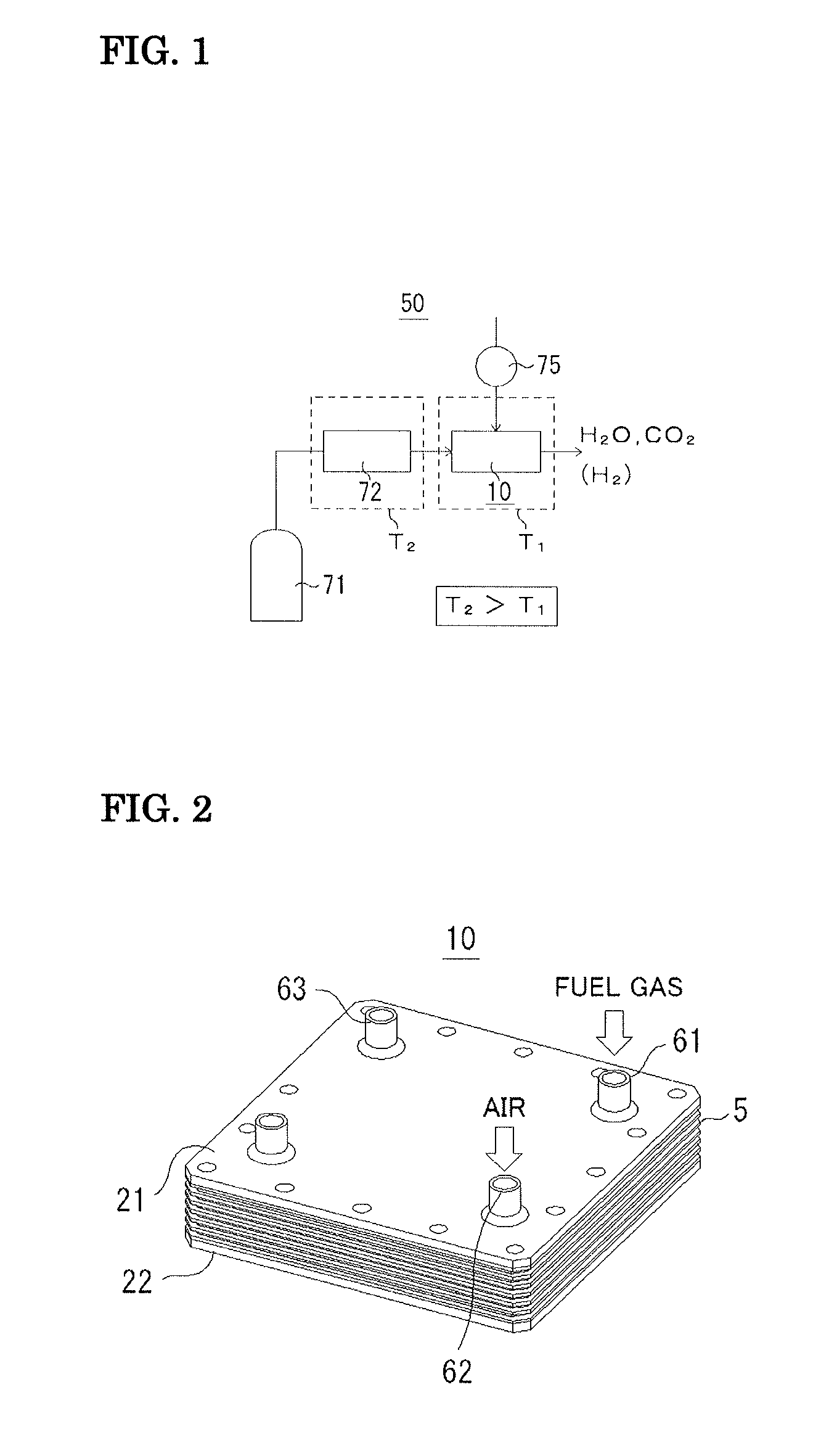
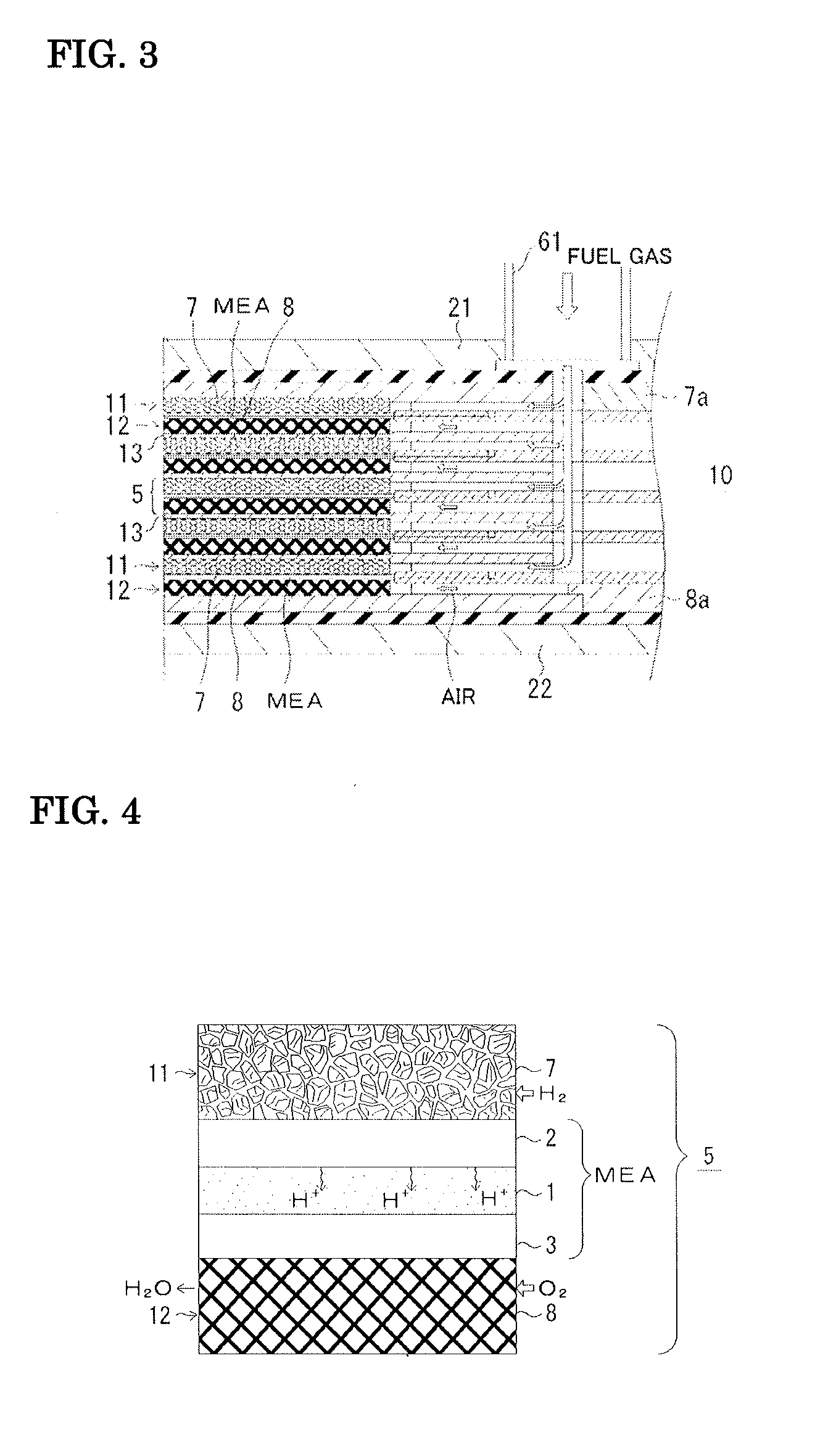
Fuel cell
InactiveUS20060257704A1Prevent deviation of temperature distributionPrevent heat transferFuel cell heat exchangeElectrolytesElectrical conductorHeat conducting
A fuel cell is made by laminating an anode channel 2 supplied with hydrogen or a hydrogen-containing gas gH, a cathode channel 3 supplied with oxygen or an oxygen-containing gas GO, and an electrolyte 4 arranged between the cathode channel and the anode channel. The electrolyte 4 is made by laminating a hydrogen separating metal layer for making hydrogen supplied to the anode channel 2 or hydrogen in a hydrogen-containing gas GH supplied to the anode channel 2 permeate; and a proton conductor layer made of ceramics, for establishing the hydrogen having permeated the hydrogen separating metal layer in a proton state and making it reach the cathode channel 3. In addition, the fuel cell has a coolant channel 5 for cooling the fuel cell 1. In the coolant channel 5, a low heat conducting section 55 having a heat conductivity smaller than that at a downstream side of a coolant C is formed at an inlet side of the coolant C.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
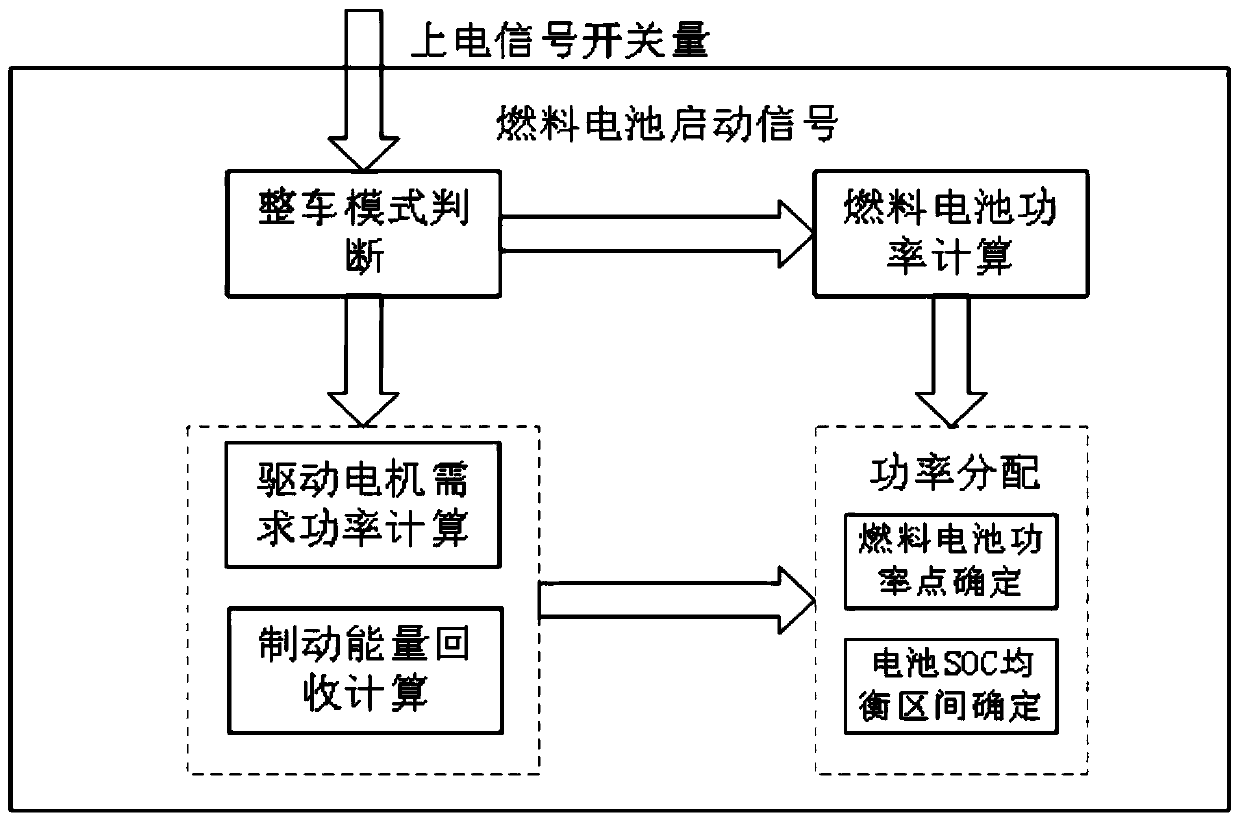
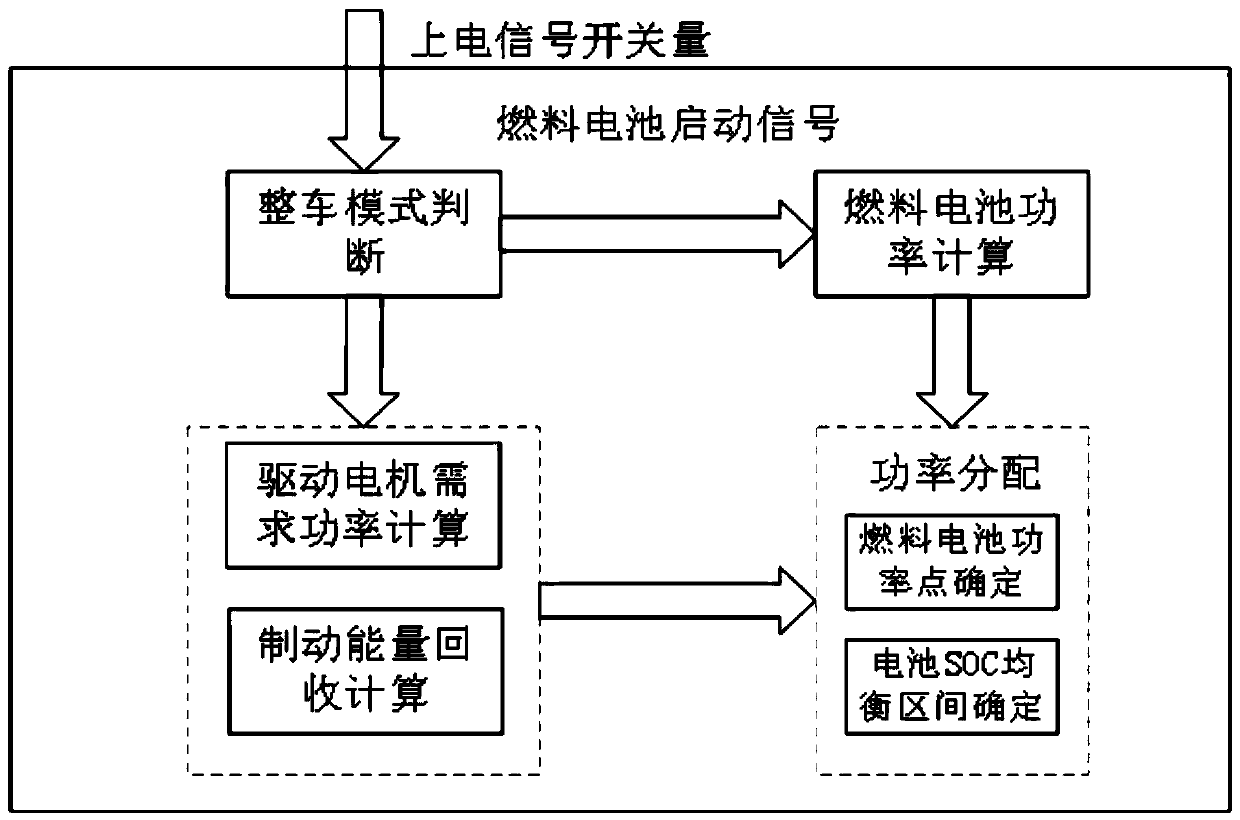
Hydrogen-electricity hybrid fuel cell bus energy management control method and system
ActiveCN110040038AExtended service lifeMeet the needs of the driving forceVehicular energy storageBattery/fuel cell control arrangementElectricityHydrogen
The invention discloses a hydrogen-electricity hybrid fuel cell bus energy management control method. The hydrogen-electricity hybrid fuel cell bus energy management control method comprises the following steps that vehicle pedal opening data and a SOC value of a power cell are collected; required power of a vehicle drive motor is calculated according to the collected data; a fuel cell power pointis determined according to the required power of the vehicle drive motor, a fuel cell polarization curve and the SOC value of the power cell; start and stop control over the fuel cell is determined according to the SOC value of the power cell; output power of the fuel cell is controlled according to the determined fuel cell power point; and on the basis of ensuring the vehicle drive required power, energy margin of the SOC of the power cell is maintained to the greatest extent, meanwhile, the fuel cell is enabled to work in an area with the optimal efficiency, and it is ensured in a balance interval of the SOC of the power cell, the service life of the fuel cell is prolonged on the basis of meeting the vehicle power performance.
Owner:ZHONGTONG BUS HLDG
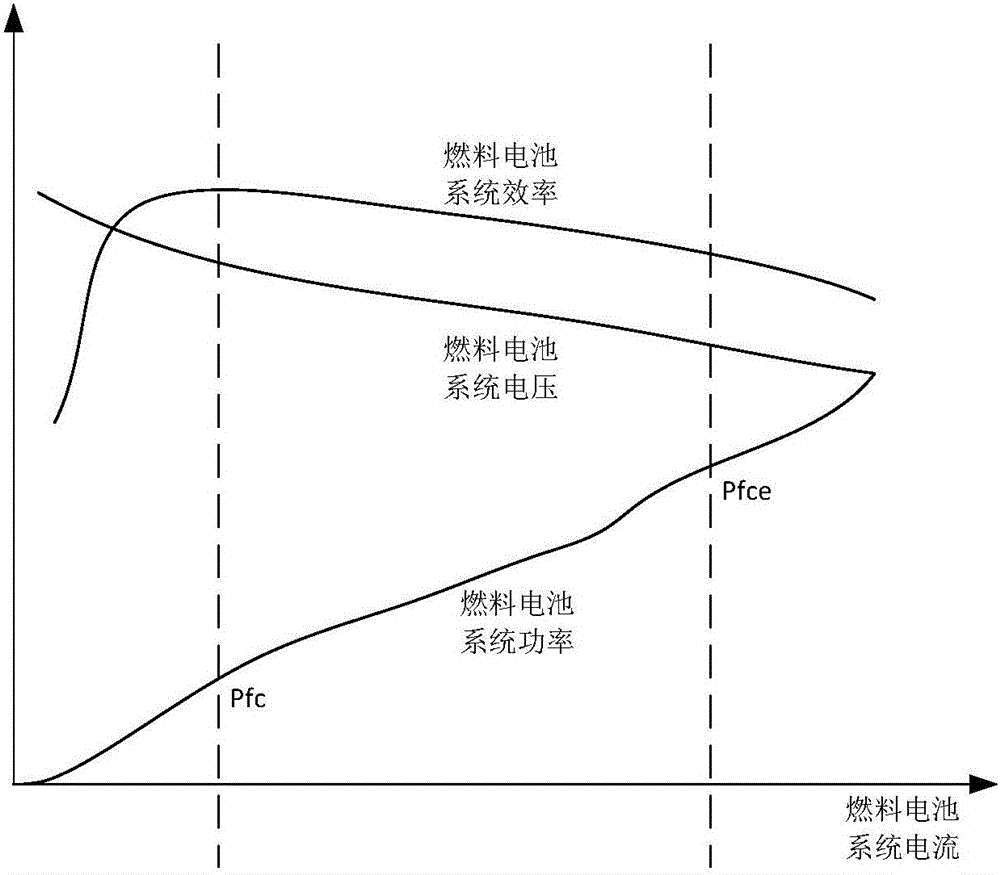
Power control method for fuel cell bus and power system of fuel cell bus
InactiveCN105835712AIncreased durabilityEasy to use for a long timeVehicular energy storageBattery/fuel cell control arrangementElectrical batteryEngineering
The invention relates to a power control method for a fuel cell bus and a power system of the fuel cell bus. The power control method comprises the steps that required power P of the bus is acquired in real time; when the required power P of the bus meets the condition that P is smaller than Pfc, a fuel cell operates at Pfc, and a (Pfc-P) part charges a power cell; when the required power P of the bus meets the condition that P is larger than or equal to Pfc and is smaller than Pfce, the fuel cell operates at Pfce, and a (Pfce-P) part charges the power cell; when the required power P of the bus meets the condition that P is larger than or equal to Pfce, the fuel cell operates at Pfce, and a (P-Pfce) part is provided by the power cell, wherein Pfc and Pfce are two set threshold values of certain output power of the fuel cell. With adoption of the control mode, the output power of the fuel cell is prevented from frequent fluctuation and continuous loading and unloading, the durability of the fuel cell can be improved, investment cost is saved, and reliable operation of the power system is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUTONG BUS CO LTD
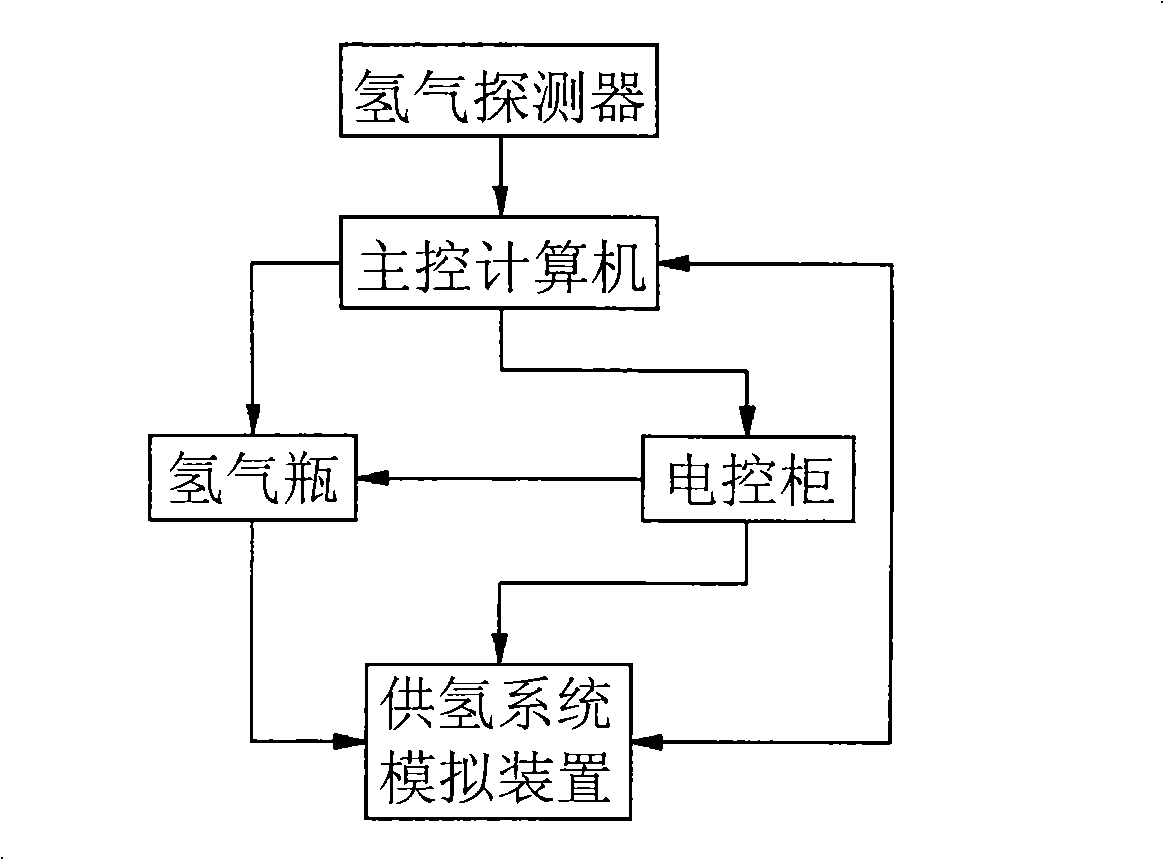
Test device and method for detecting security of fuel battery passenger car hydrogen feed system
ActiveCN101324485AImprove securityDerived performanceStructural/machines measurementHydrogen concentrationHigh pressure hydrogen
The invention relates to a test table for testing the security of a hydrogen supply system of a fuel cell bus and the test method thereof, and belongs to the security technology field of the fuel cell bus. The test table comprises a hydrogen supply system simulation device, a main control computer, an electrical control cabinet, a high pressure hydrogen bottle and a hydrogen detector, wherein the hydrogen supply system simulation device is connected with the output mouth of the high pressure hydrogen bottle, and bilaterally connected with the main control computer; the main control computer is connected with the electrical control cabinet, the high pressure hydrogen bottle and the hydrogen detector; the electrical control cabinet is respectively connected with the high pressure hydrogen bottle and the hydrogen supply system simulation device; the test table further comprises a bench for fixing and supporting the hydrogen supply system simulation device. The method comprises the following steps: a valve to be tested is connected with an identical valve in a pipeline of the hydrogen supply system simulation device in parallel; the working state of the valve to be tested is simulated; according to data such as gas pressure, flow, hydrogen concentration, etc. in an acquisition pipeline, whether the performance of the valve to be tested is qualified can be judged. The test table is used for dynamically testing the security of the key components of hydrogen supply system of the fuel cell bus.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江) +1
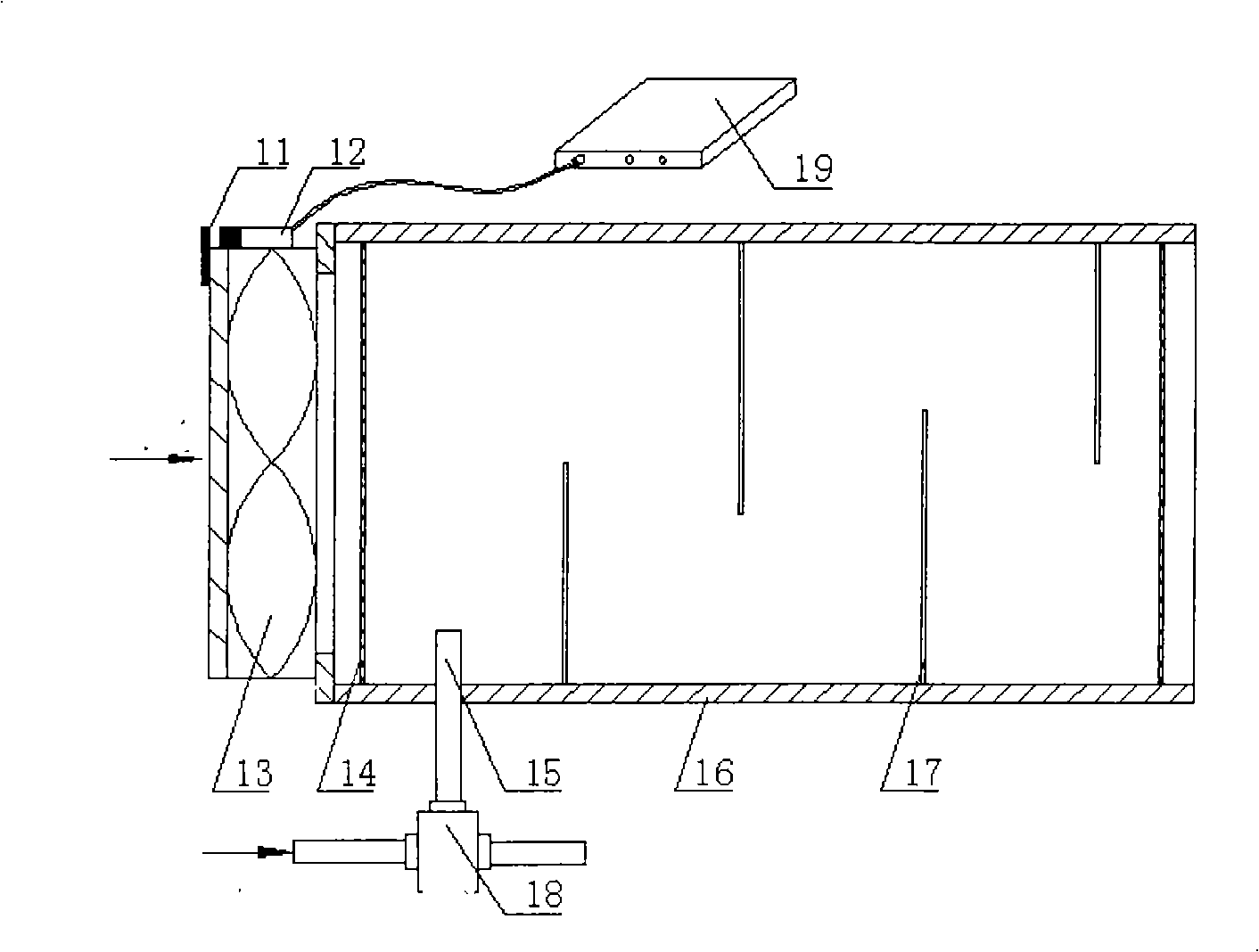
Dilution device for fuel battery passenger car discharging hydrogen concentration
ActiveCN101323247AReduce hydrogen concentrationGuaranteed cleanlinessElectric propulsionPropulsion unit gas exhaustHydrogen concentrationElectric machinery
The invention relates a concentration diluting device used for hydrogen discharged by a fuel cell passenger car, pertaining to the field of application technology of the fuel cell passenger car; the device comprises a photoelectric receiver, a photoelectric proximity switch, an electric fan, two static-free meshes, a hydrogen piping, a main body of the diluting device, a plurality of baffle plates, an electromagnetic valve and a fault detector of the electric fan. The main body of the diluting device is a body case with an opening on both ends; the two static-free meshes are connected with the inner walls on the both ends of the main body of the diluting device; the photoelectric receiver is arranged on the central shaft of the motor of the electric fan; the photoelectric proximity switch is arranged on the body case of the electric fan and connected with the fault detector of the electric fan; the hydrogen piping is communicated with the hydrogen inlet of the air inlet end of the main body of the diluting device and connected with a discharged hydrogen pipe by the electromagnetic valve. Under various working conditions of the passenger car, the device is capable of reducing the concentration of Purge to the safety level and has the advantages of small volume, compact structure, safety and reliability.
Owner:清华大学苏州汽车研究院(吴江) +1
Fuel cell
InactiveUS20100190089A1Prevent fuel leakageIncrease volumeCell component detailsSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesPorous substrate
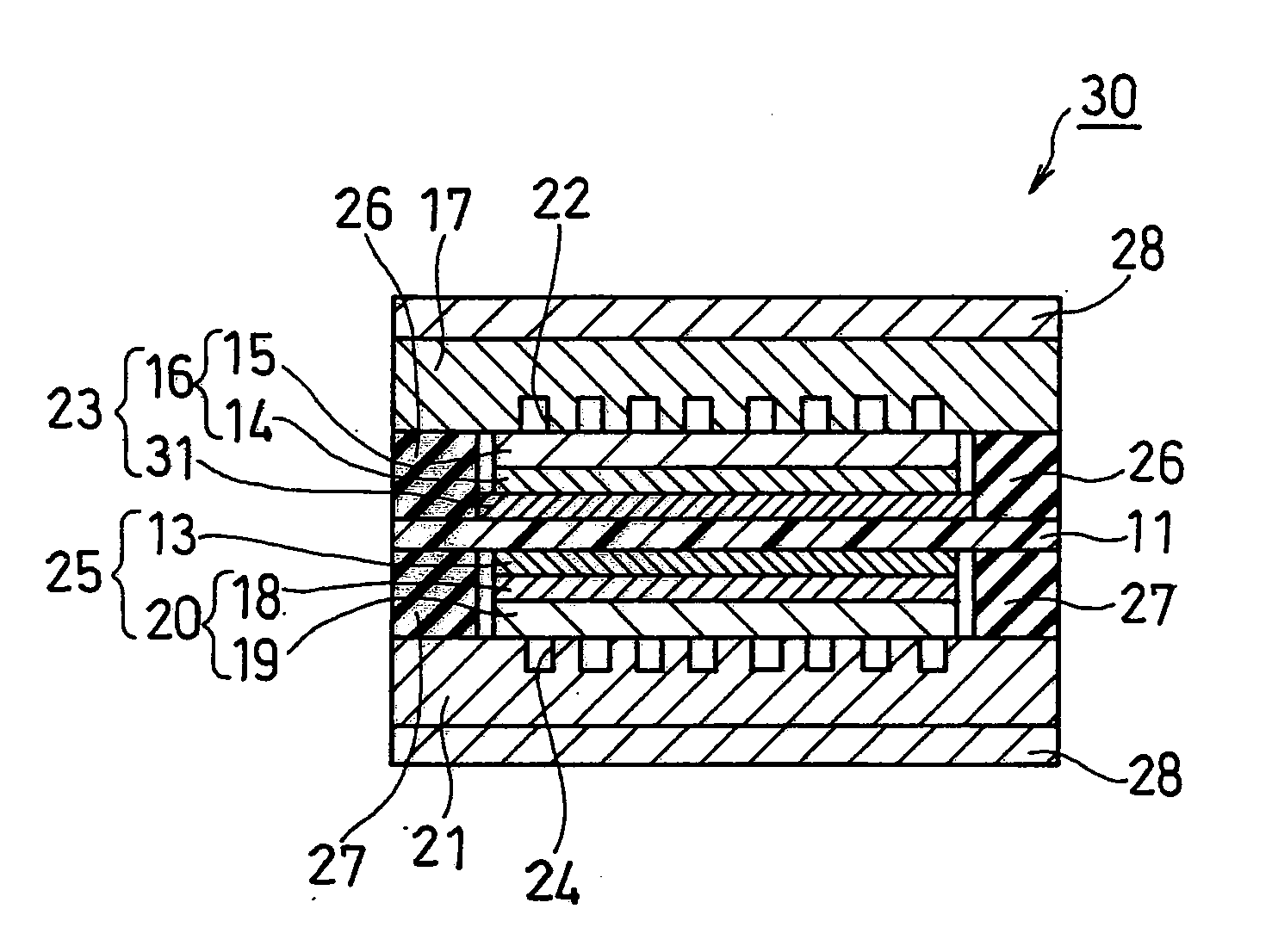
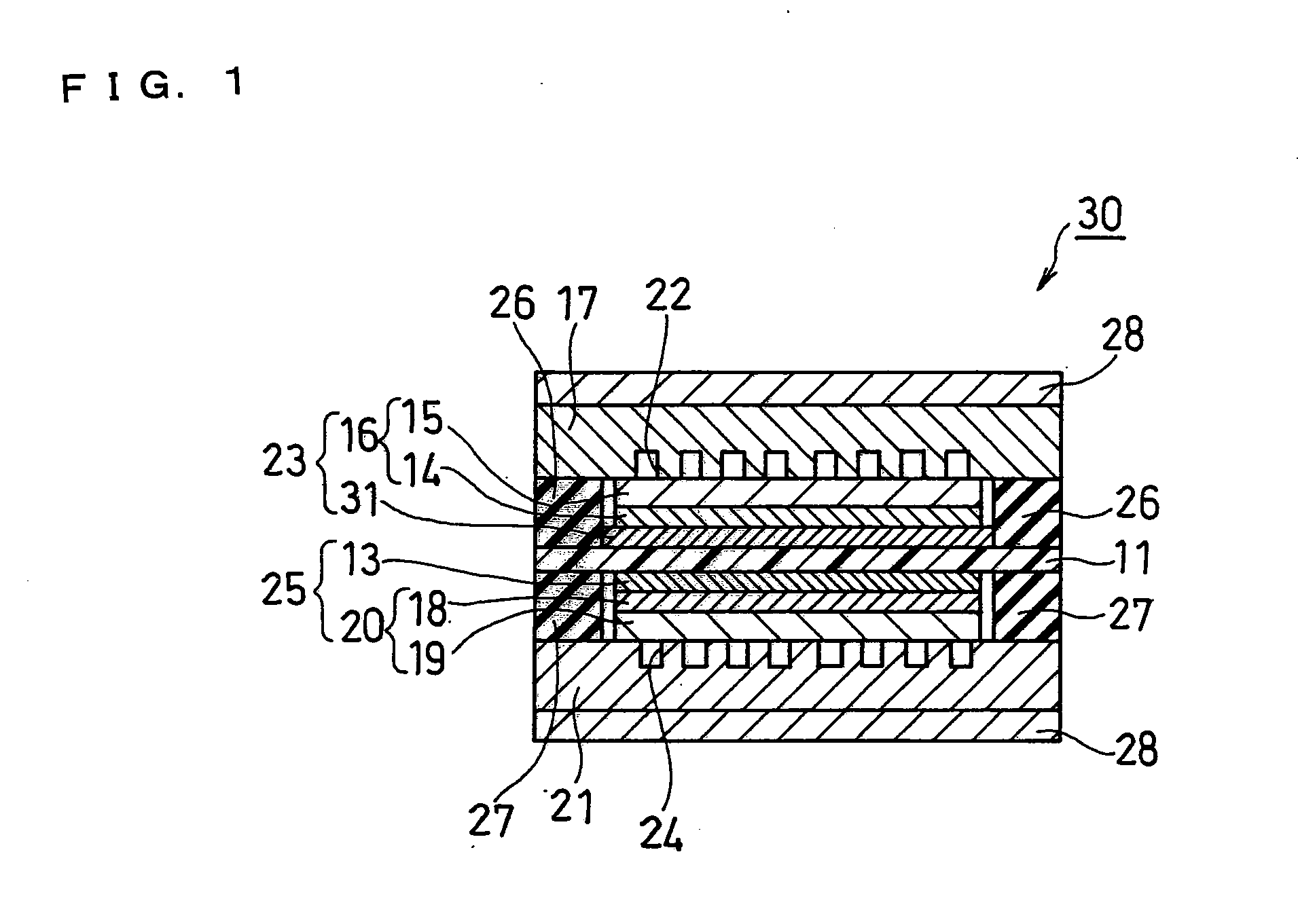
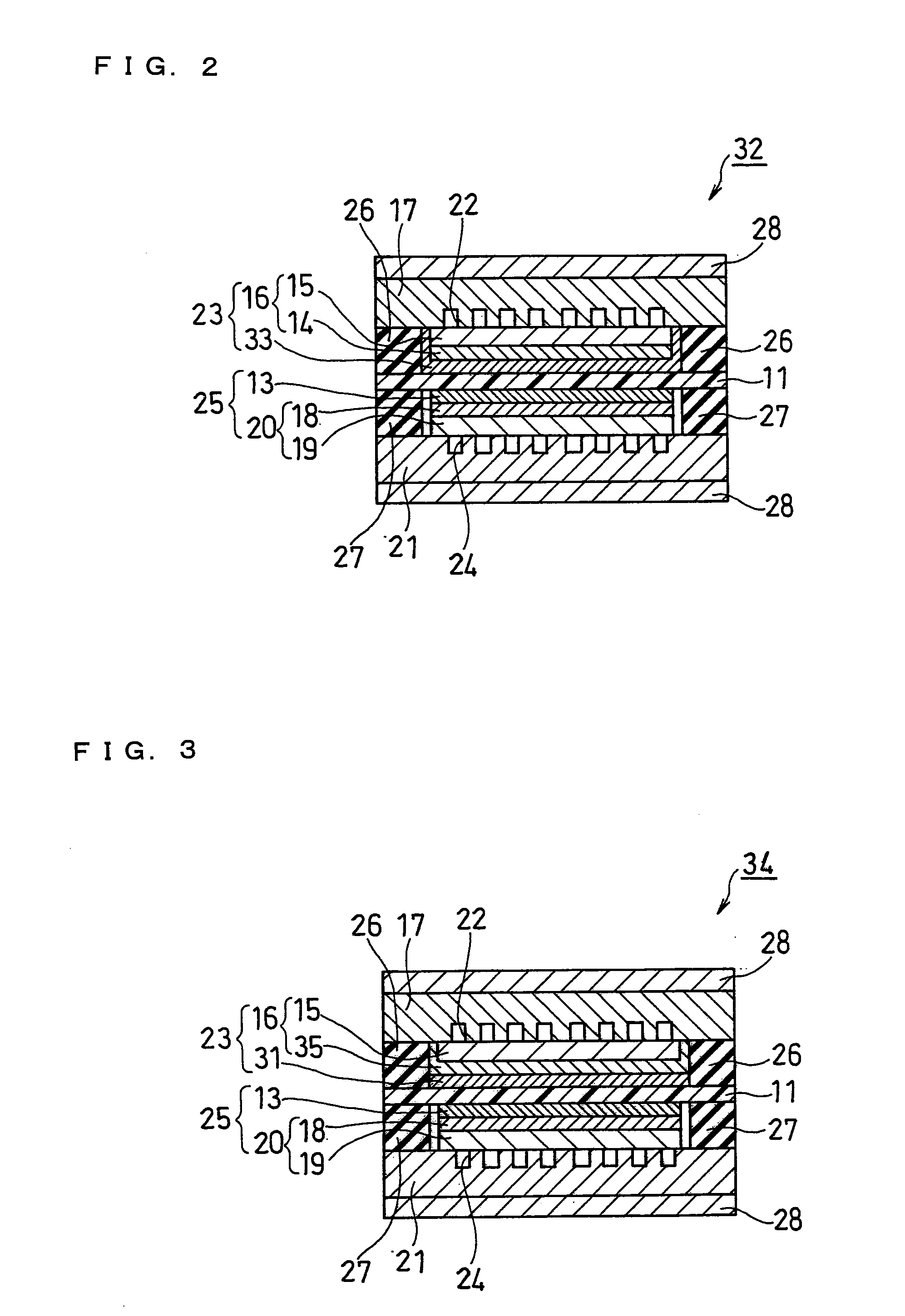
The present invention intends to provide a fuel cell being capable of preventing the methanol crossover in a simple and easy manner and being excellent in fuel utilization rate and the like. A fuel cell 30 of the present invention includes a polymer electrolyte membrane 11, an anode 23 and a cathode 25 sandwiching the polymer electrolyte membrane 11, an anode-side separator 17 having a fuel flow channel, a cathode-side separator 21 having an oxidant flow channel, and gaskets 26 and 27 interposed between the anode-side and cathode-side separators 17 and 21 and the periphery of the polymer electrolyte membrane 11. In the fuel cell 30, the orthographic projection area of the anode catalyst layer 31 included in the anode 23 seen from the direction normal to an MEA is set to be larger than the orthographic projection area of the anode porous substrate 15 included in the anode 23 seen from the direction normal to the MEA.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fuel cell
ActiveCN108878945AEasy to assembleQuality improvementWater management in fuel cellsFuel cell controlHydrogenControl system
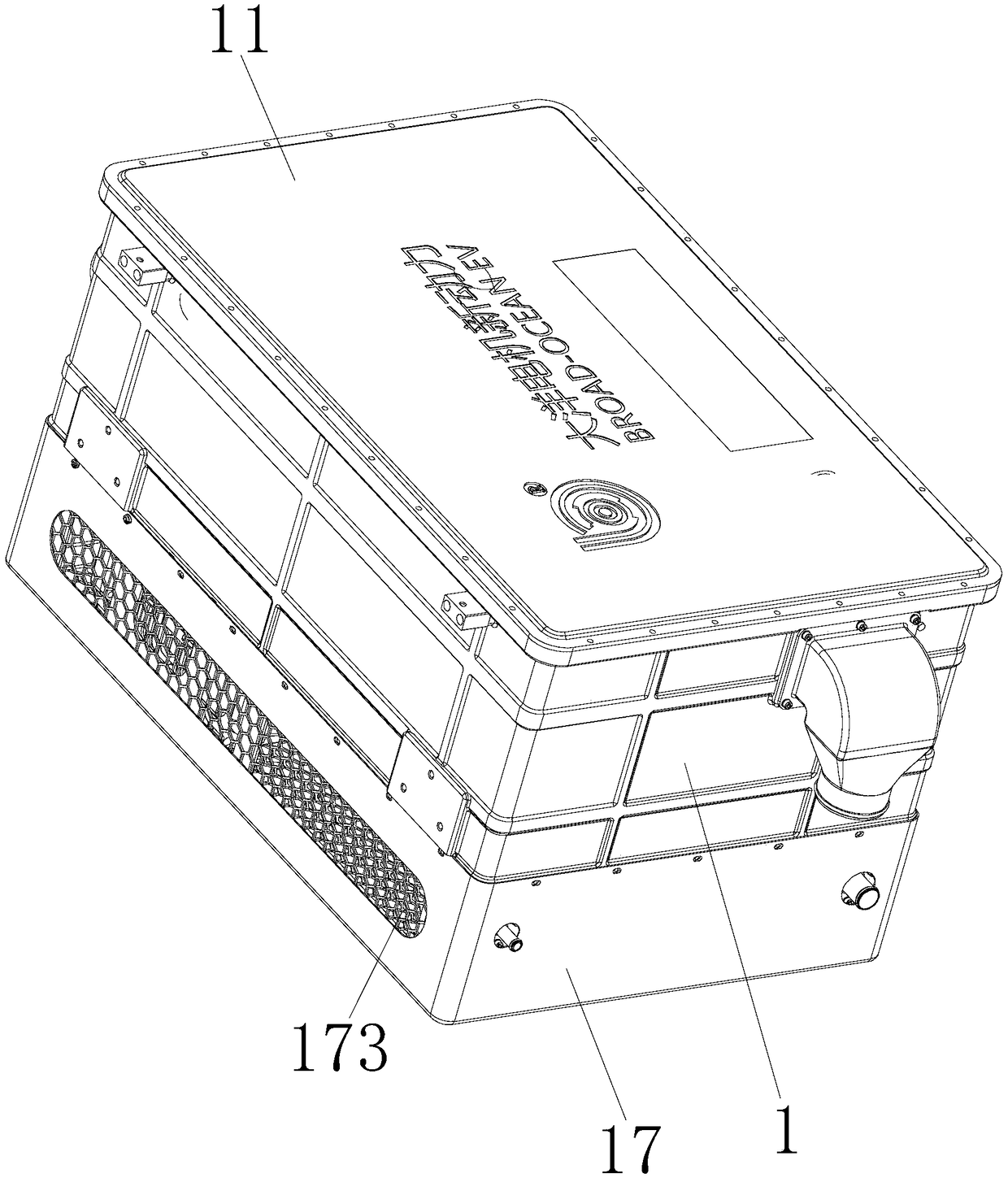
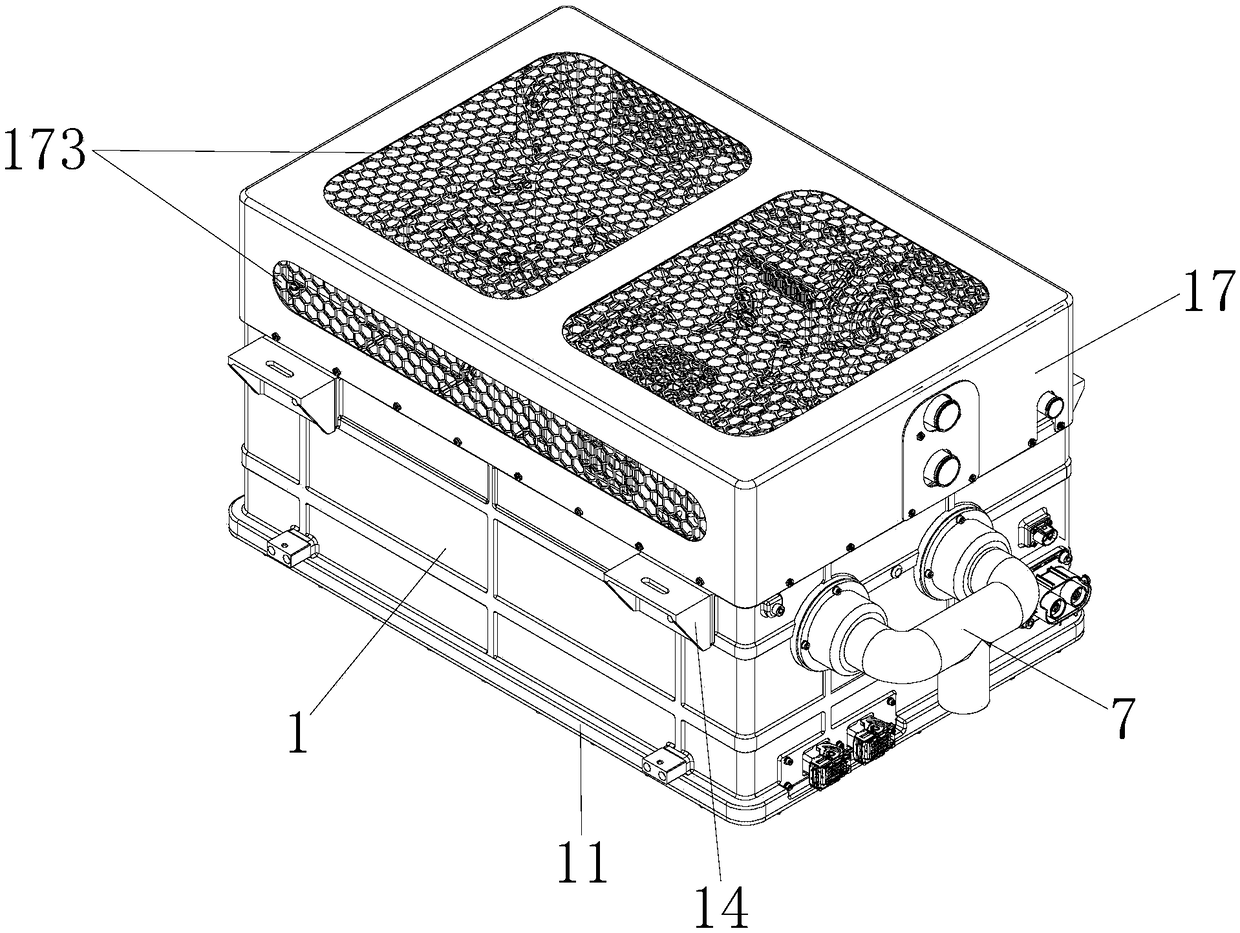
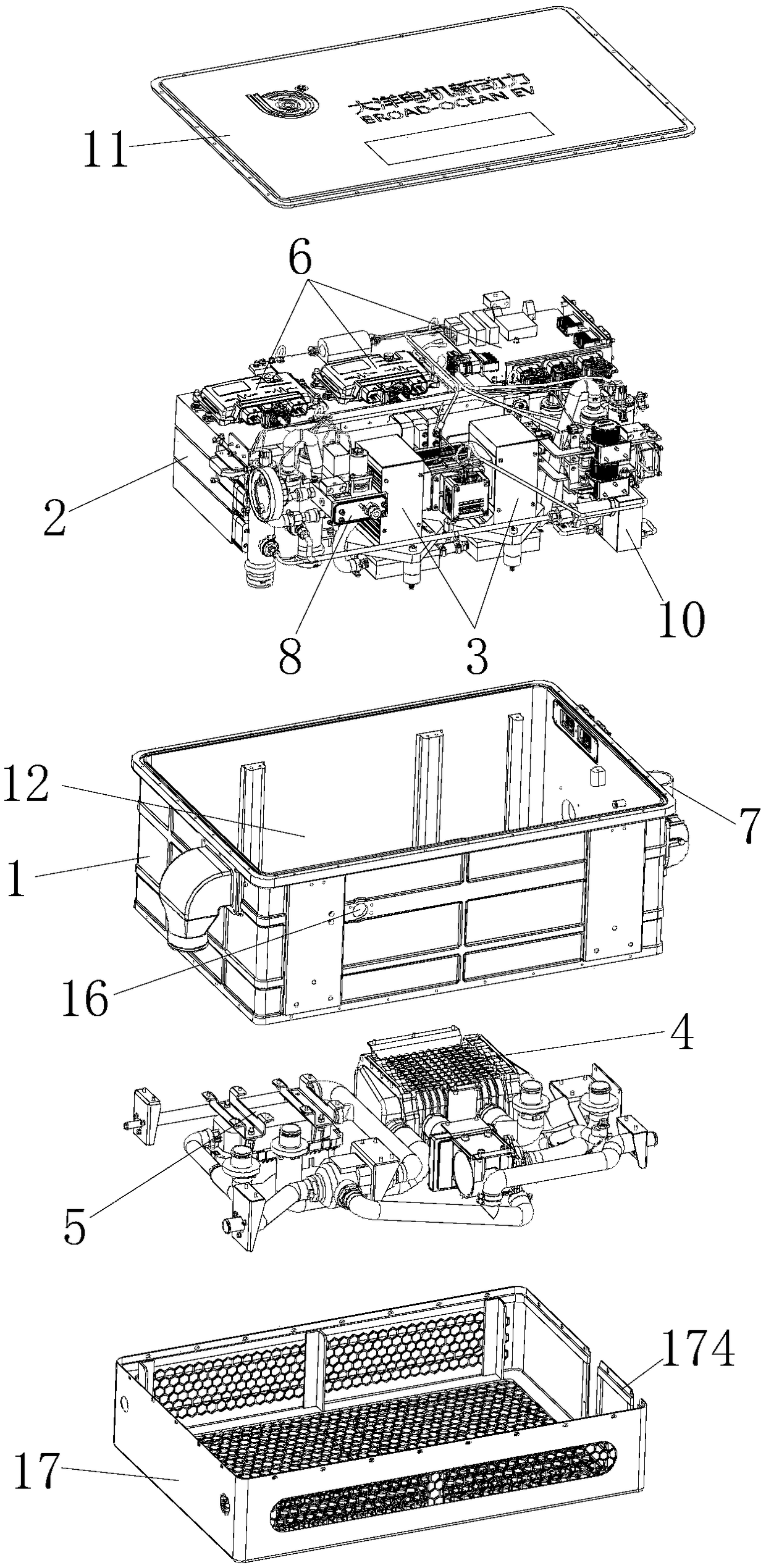
The invention discloses a fuel cell. The fuel cell comprises a box body, a box cover, a galvanic pile module, a hydrogen gas circulation pump, an air path system, a cooling system, a fuel cell controlsystem, a ventilation part and a hydrogen feeding integrated manifold, wherein the galvanic pile module occupies a position at one side of a first cavity of the box body; the fuel cell control systemis arranged above the galvanic pile module; a hydrogen gas inlet valve, an air inlet valve, a cooling liquid inlet valve, the hydrogen gas circulating, a hydrogen gas outlet valve, an air outlet valve and a cooling liquid outlet valve are distributed at the position of the other side of the first cavity of the box body; an opening is formed in one side face of the box body and an exhausting opening is formed in a side face of the box body at one opposite side of the opening; the ventilation part is mounted at the opening; the air path system and the cooling system are mounted on a first bottom plate at the outer side of the box body; the fuel cell disclosed by the invention is reasonable in layout, compact in structure and simple in finished product assembling; the cost is relatively lowand the quality is effectively controlled.
Owner:BROAD OCEAN MOTOR EV +1
Fuel cell
ActiveUS20100297525A1AssembleEfficient executionSolid electrolyte fuel cellsCollectors/separatorsCouplingEngineering
A cell unit of a fuel cell includes a first separator, a first membrane electrode assembly, a second separator, a second membrane electrode assembly, and a third separator. Resin connecting sections are provided in the outer circumferential ends of the first separator, the second separator, and the third separator. A coupling pin is molded integrally with the resin connecting section of the first separator. A first hole and a second hole are formed on both sides of the coupling pin for selectively inserting a rebuilt pin into either of the first and second holes. A hole for inserting the coupling pin is formed at the center, and the first hole and the second hole are formed on both sides of the hole, in each of the resin connecting sections of the second and third separators.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
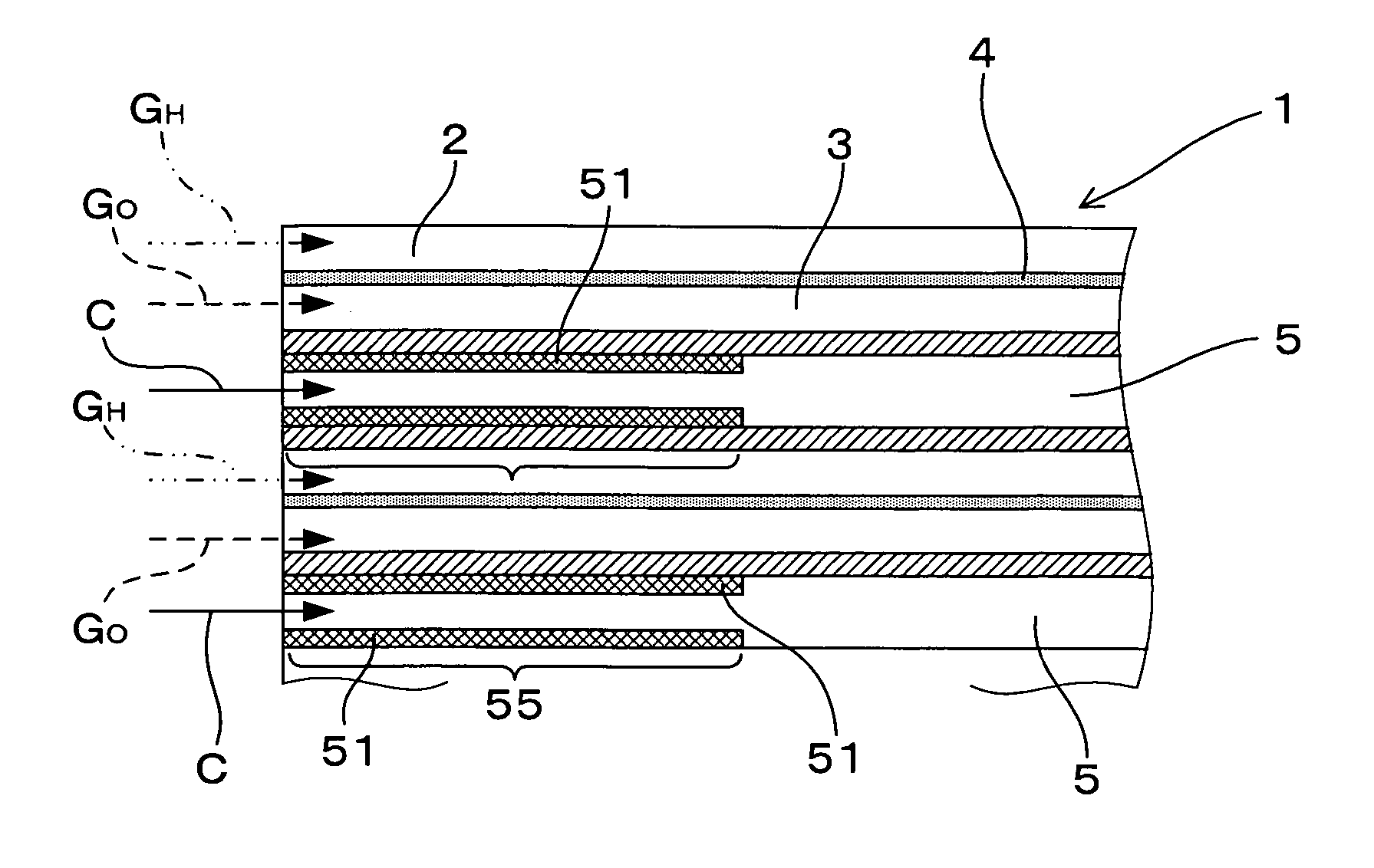
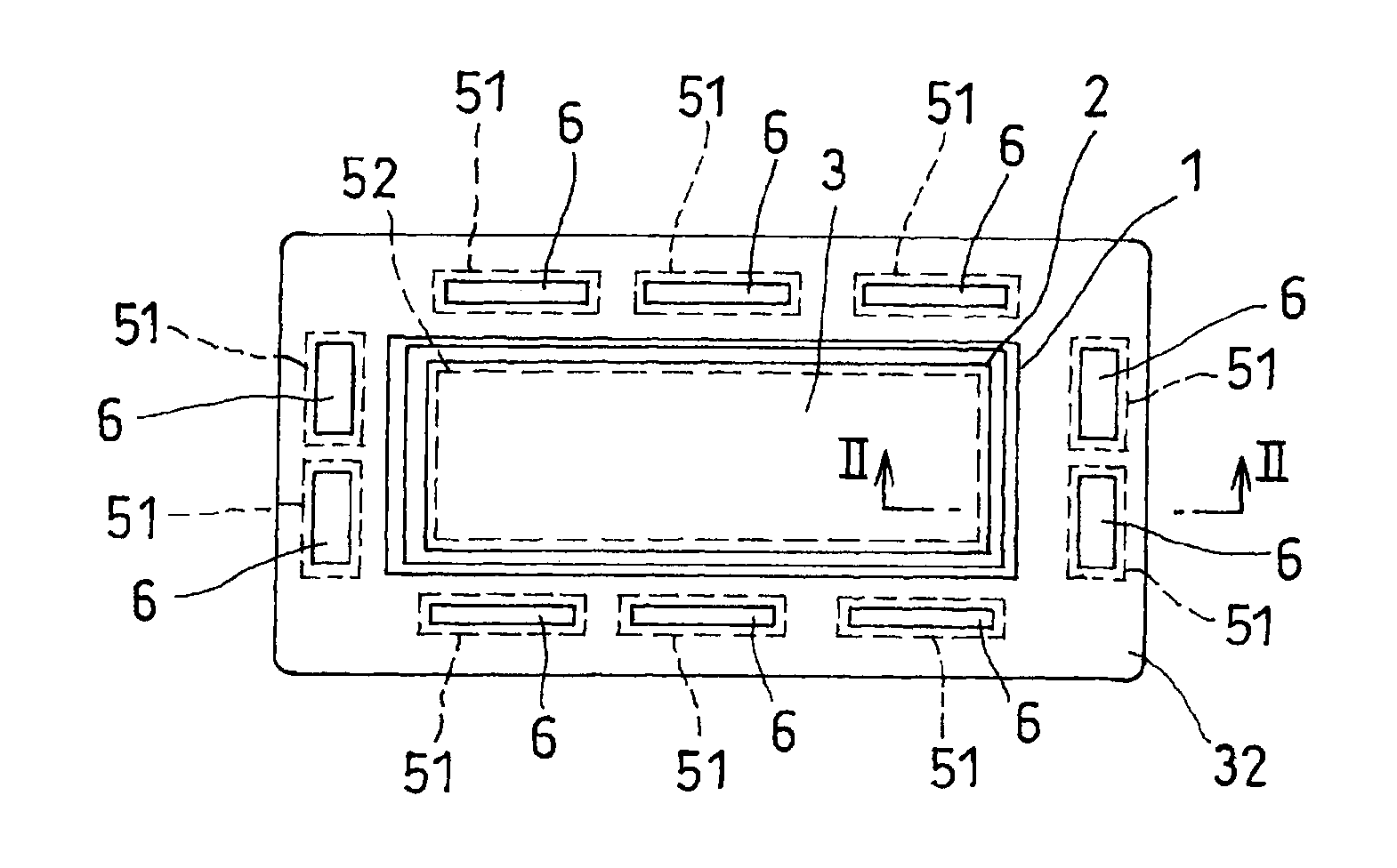
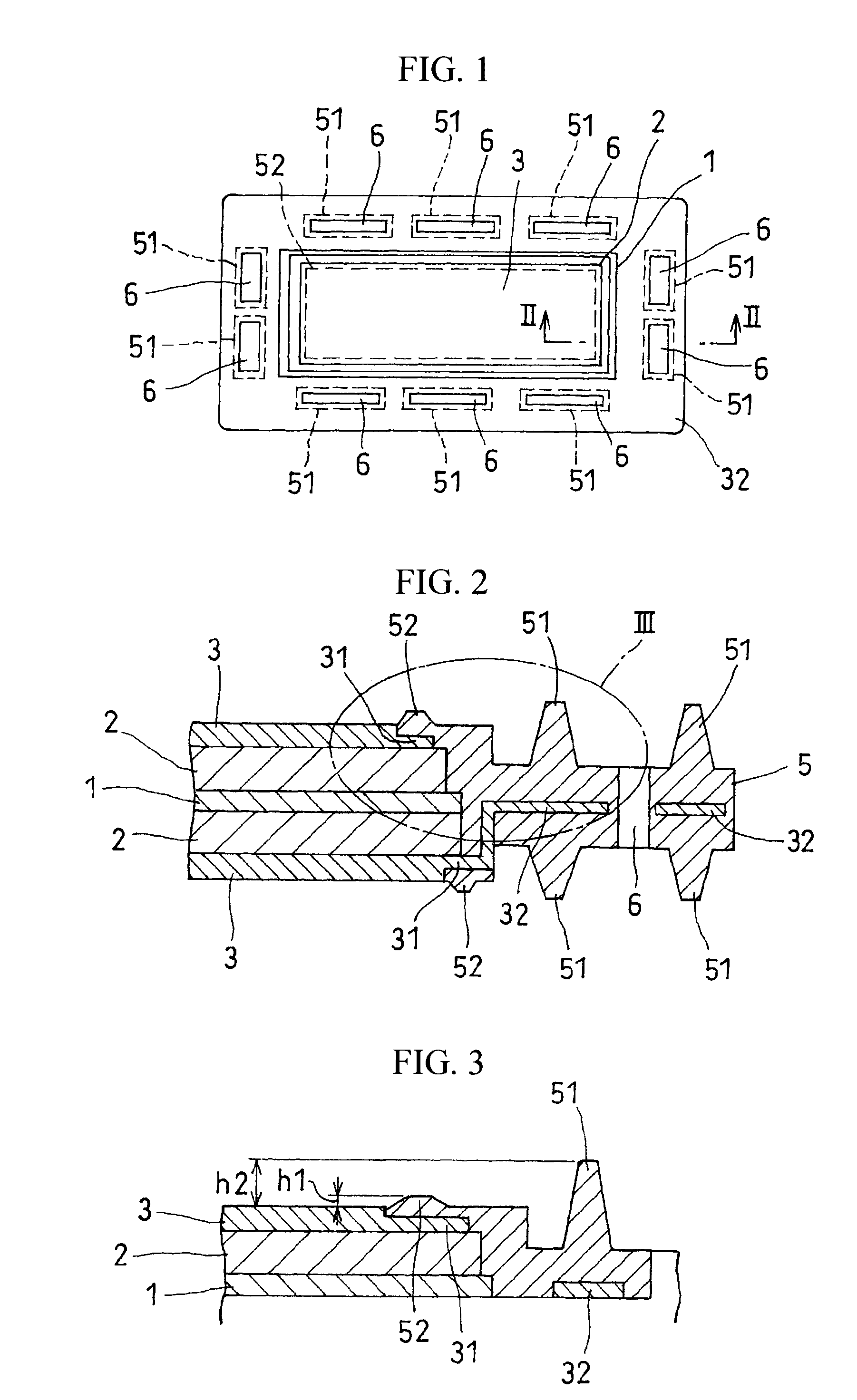
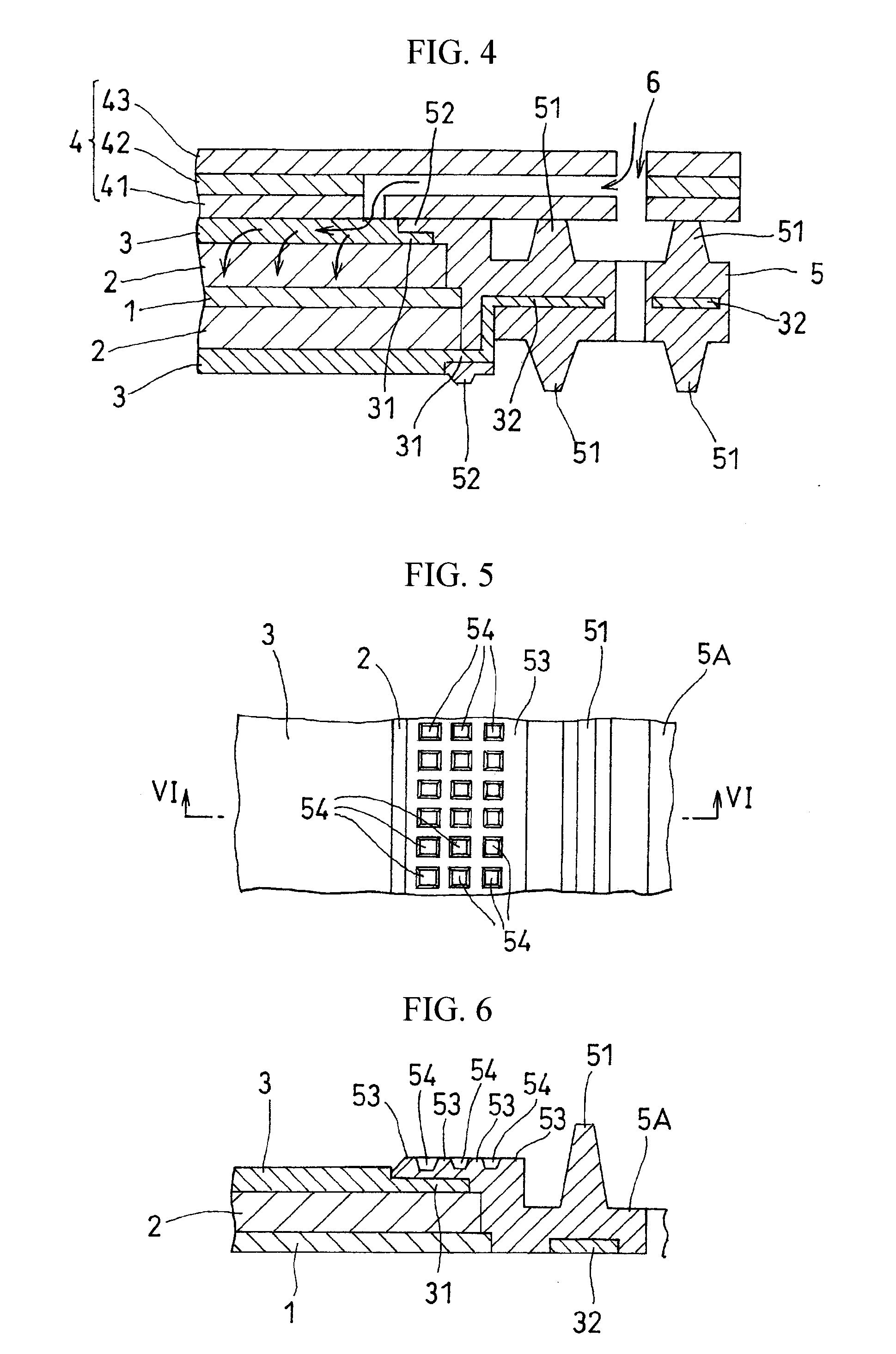
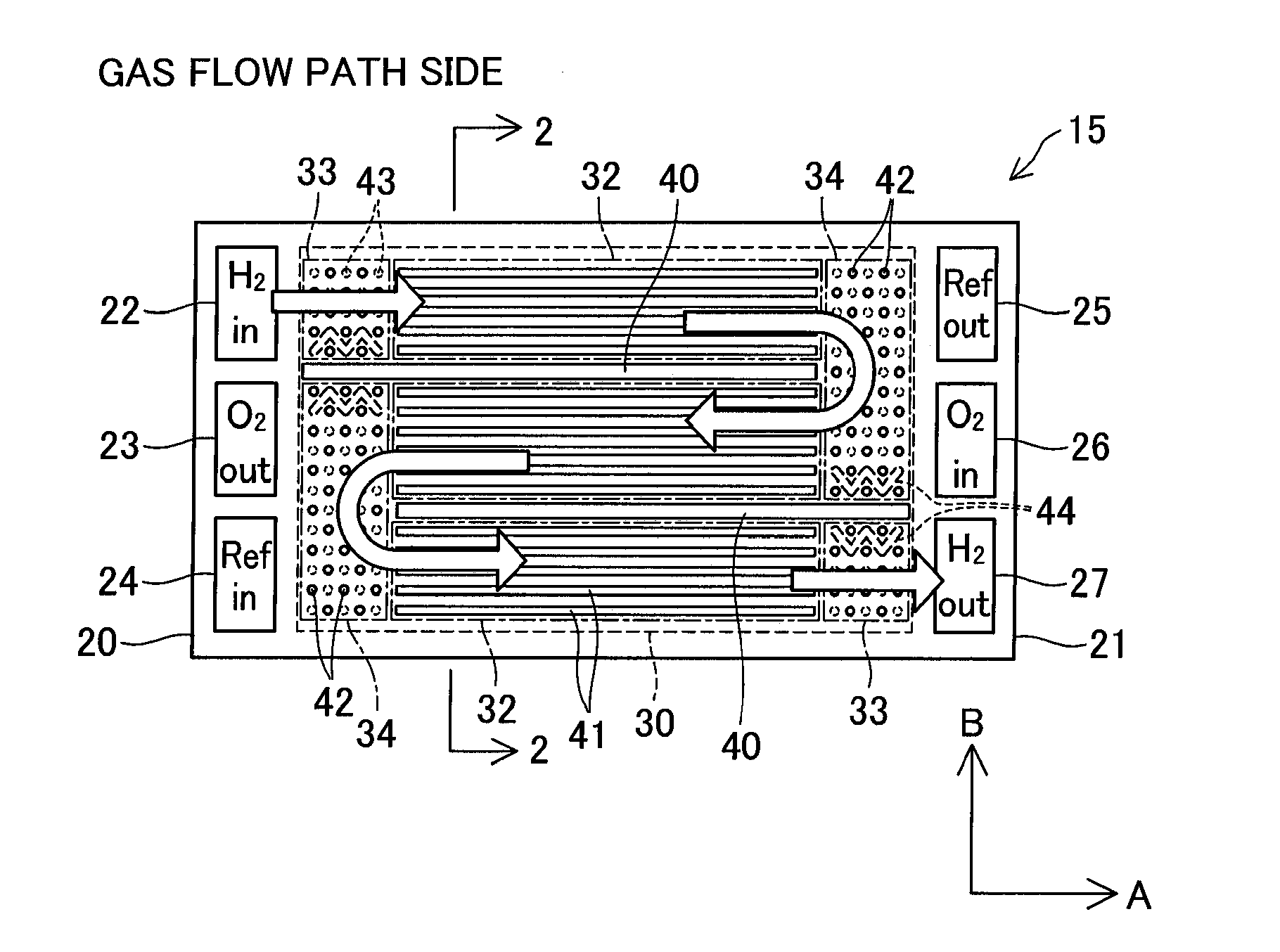
Fuel cell
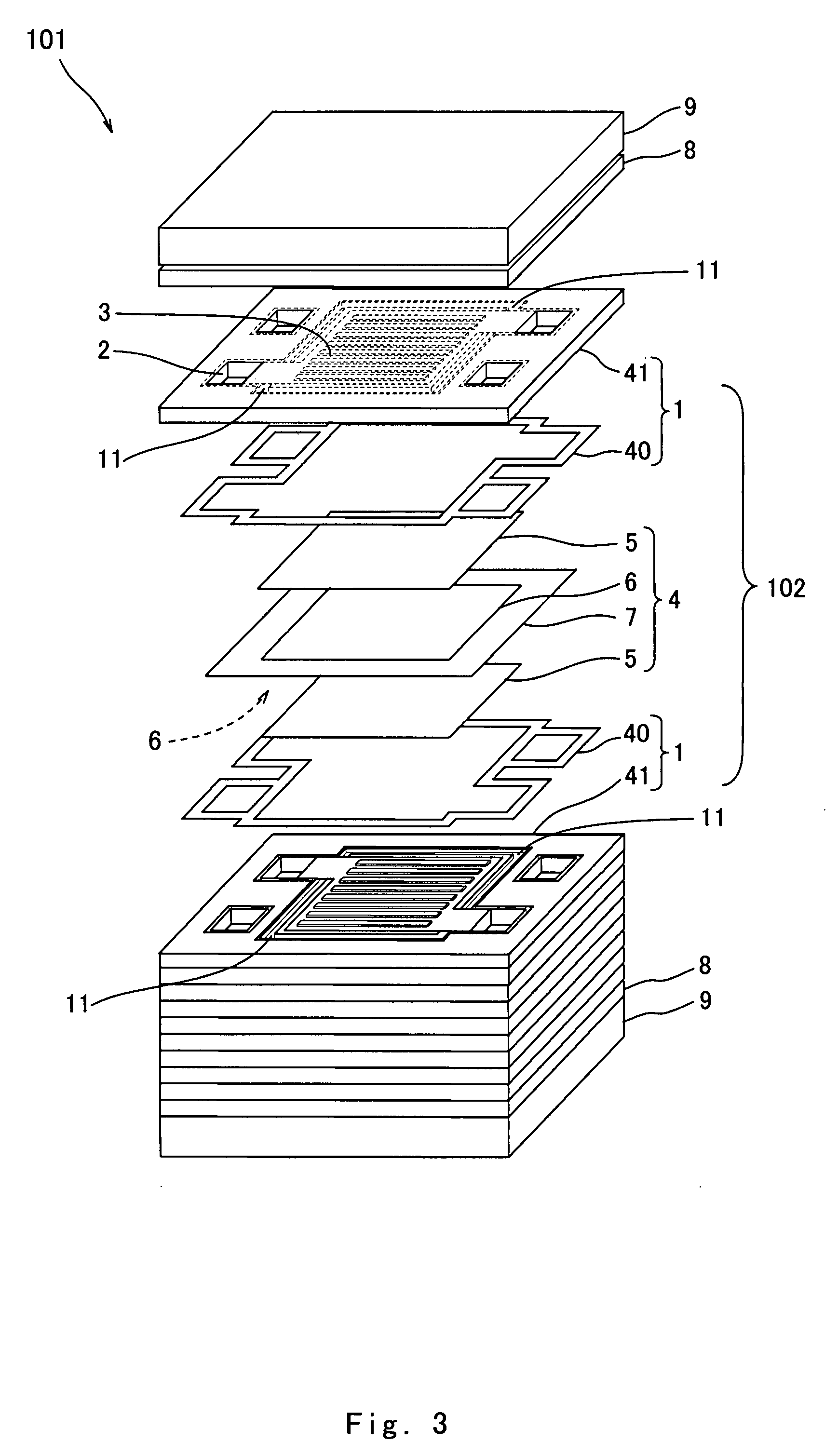
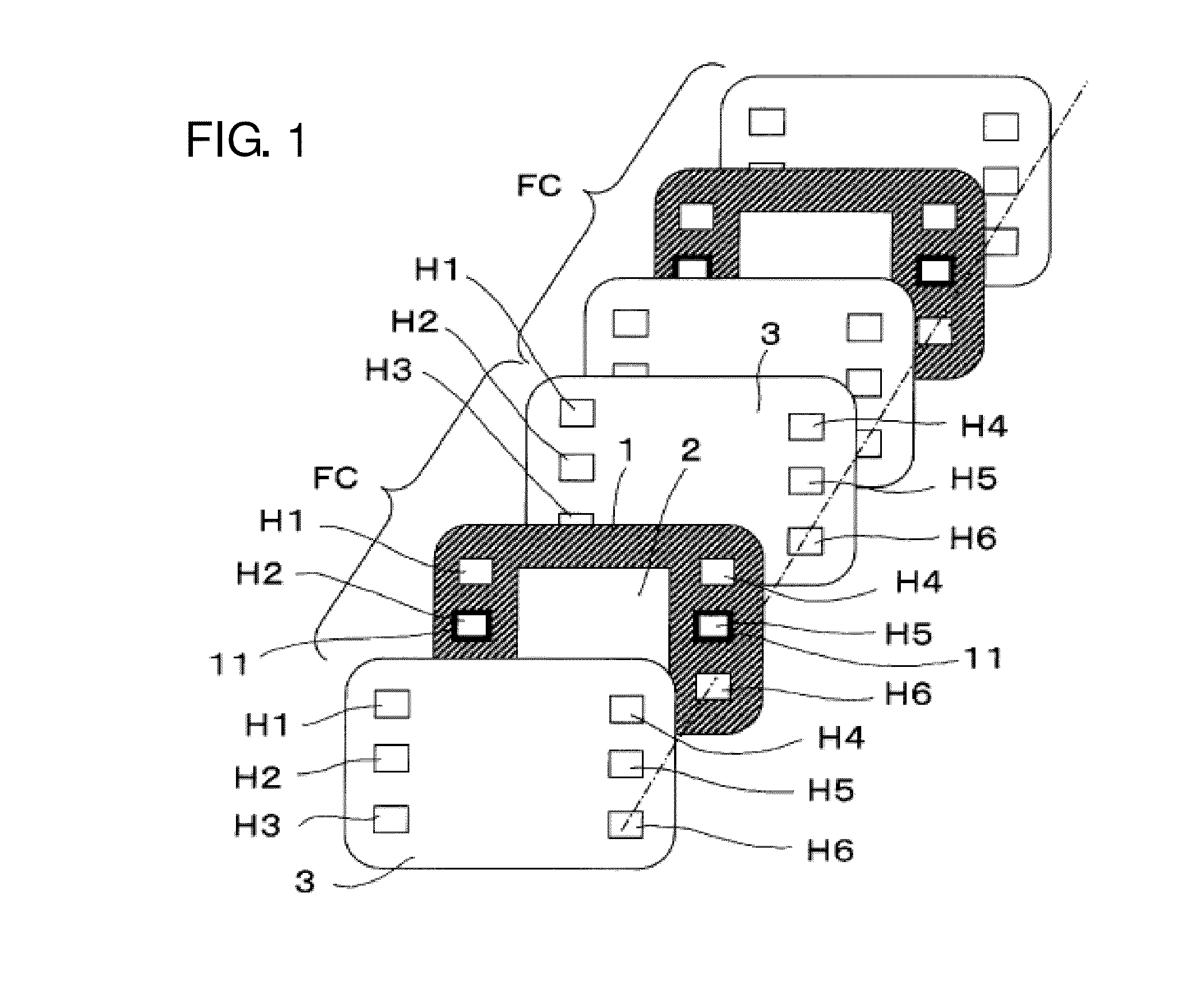
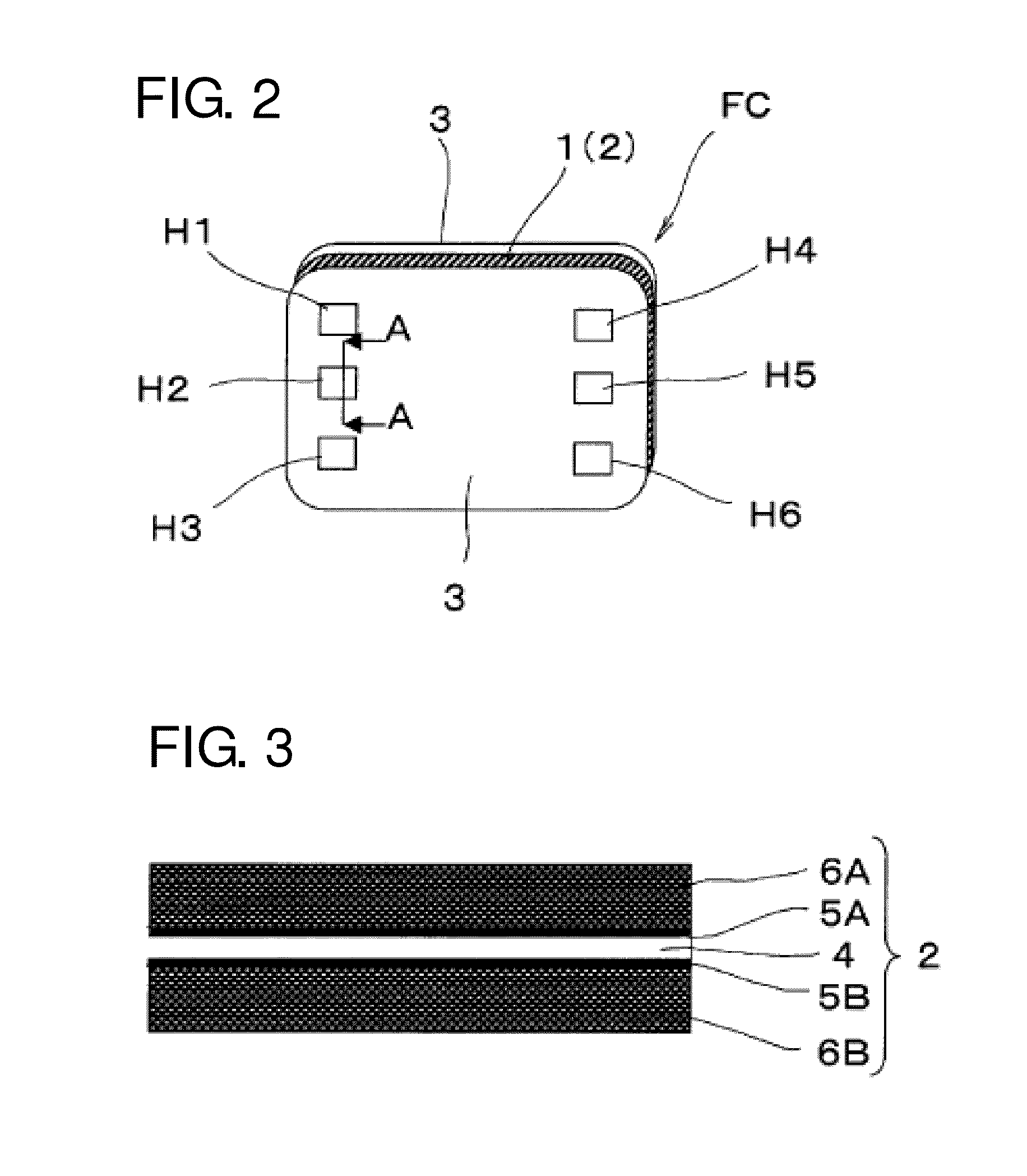
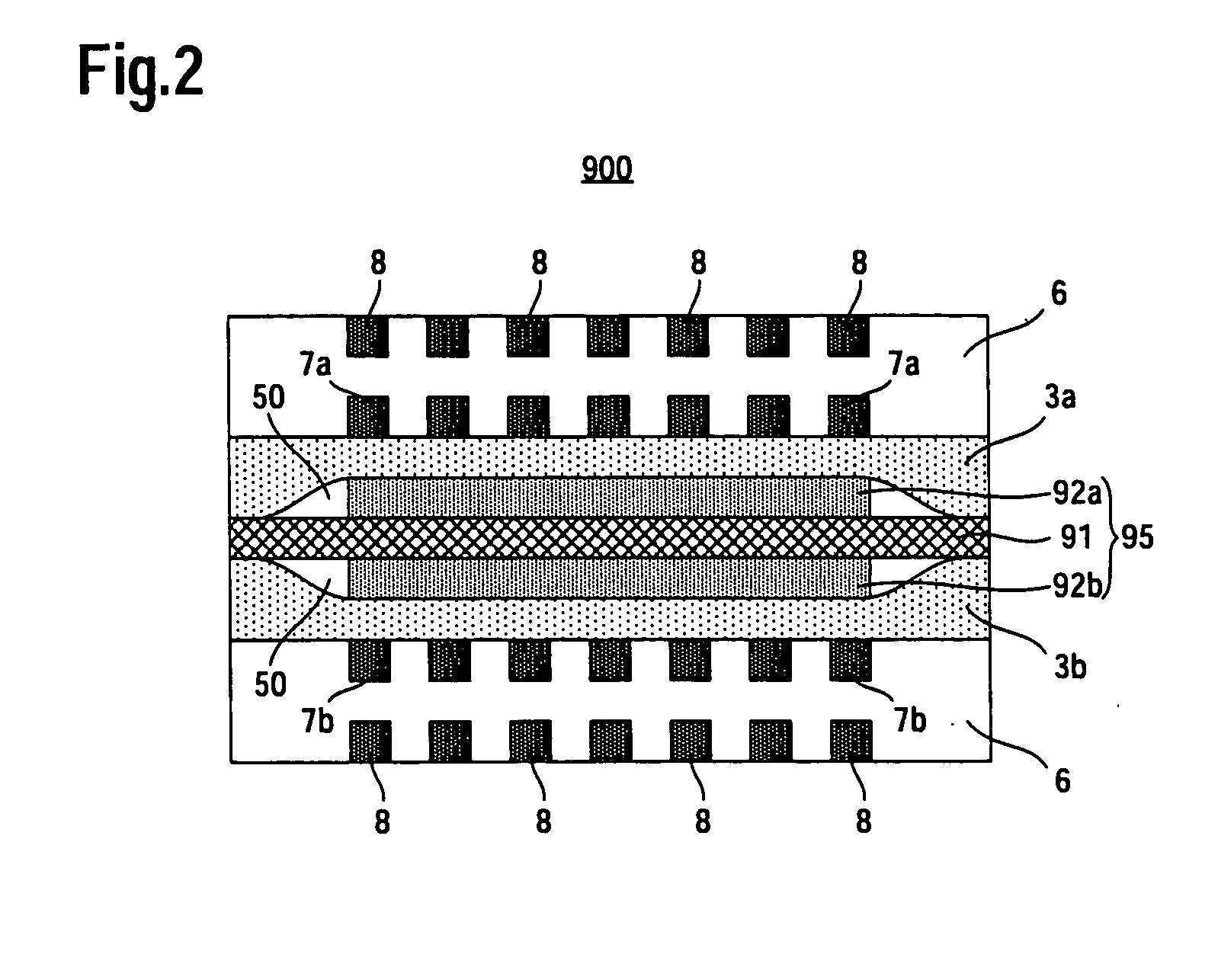
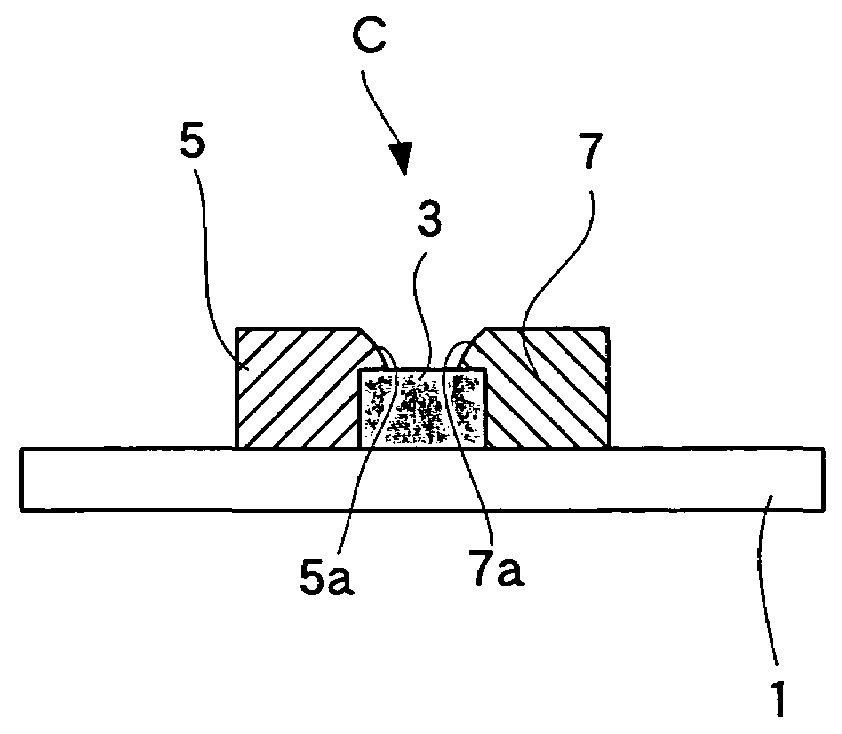
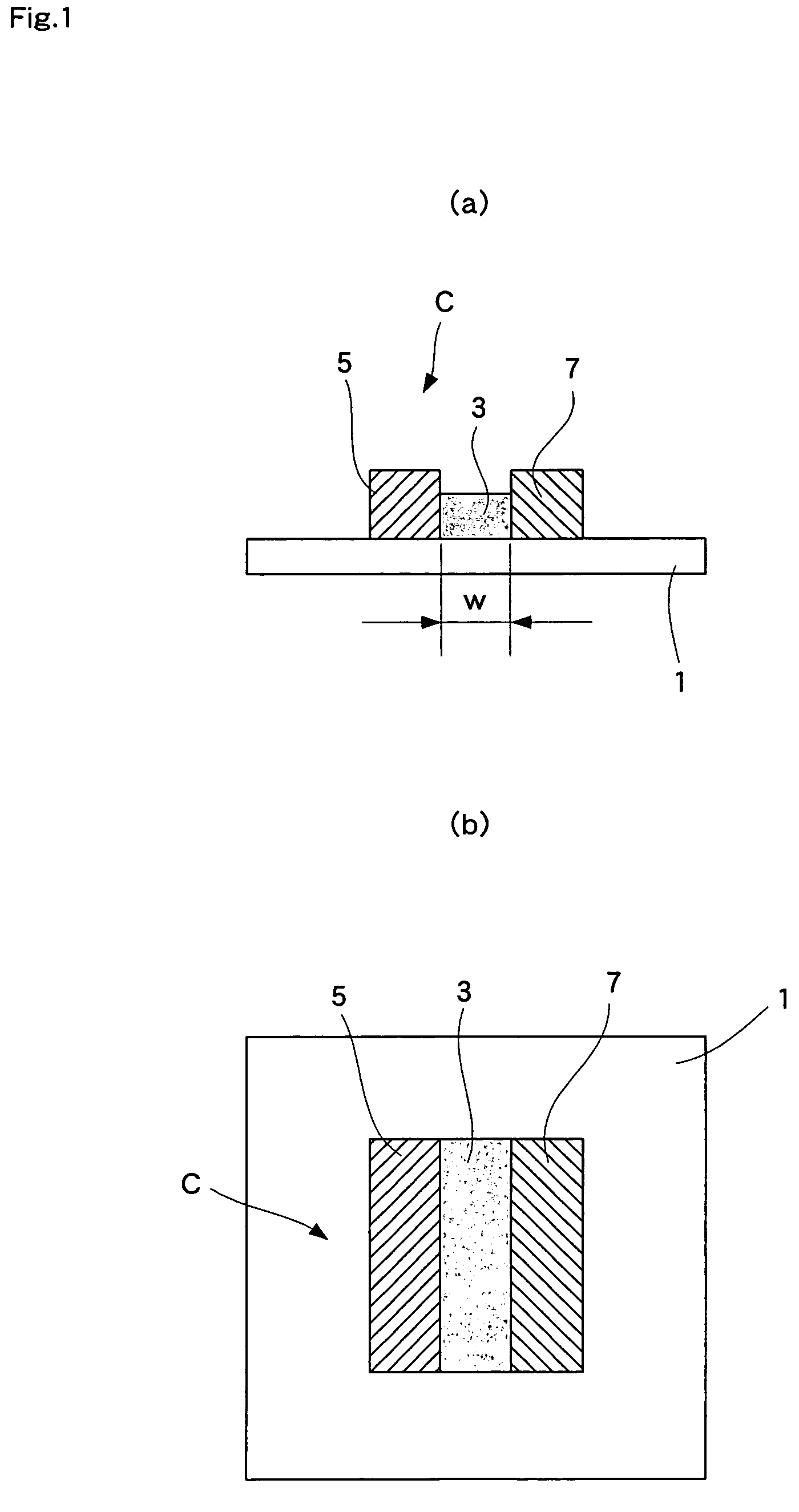
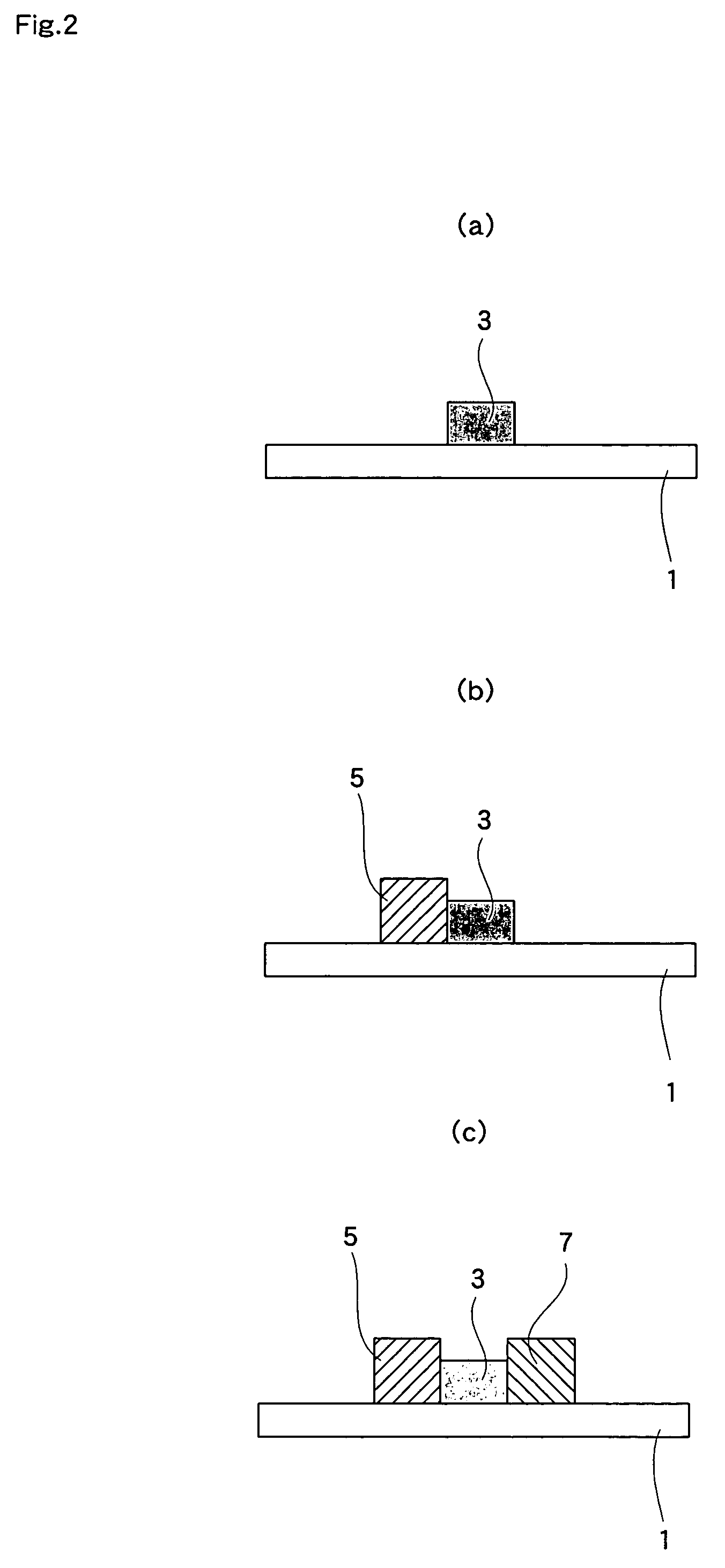
InactiveUS20110236786A1Improve power generation effectTightness of contactFuel cell auxillariesCell component detailsEngineeringFuel cell bus
There is provided a fuel cell having a seal structure that has high gas sealability and, further, is capable of supplying gas to a membrane electrode assembly without being path-cut even if there are conventional processing errors (variations) in the gasket. With respect to a gasket 5 provided at the periphery of the membrane electrode assembly, a first seal protrusion 51 is formed around a manifold 6. A notch 31 is formed at an end portion of a gas flow path layer 3. An end portion of the gasket 5 blocks the notch 31 and has at least one second seal protrusion 52 protruding from the surface of the gas flow path layer 3 and having a height of the same level as or less than the first seal protrusion 51. A separator 4 is in contact with the gas flow path layer 3 in a posture where the first seal protrusion 51 and the second seal protrusion 52 are compressed. At least one linear seal structure is formed by the second seal protrusion 52 and the separator 4.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
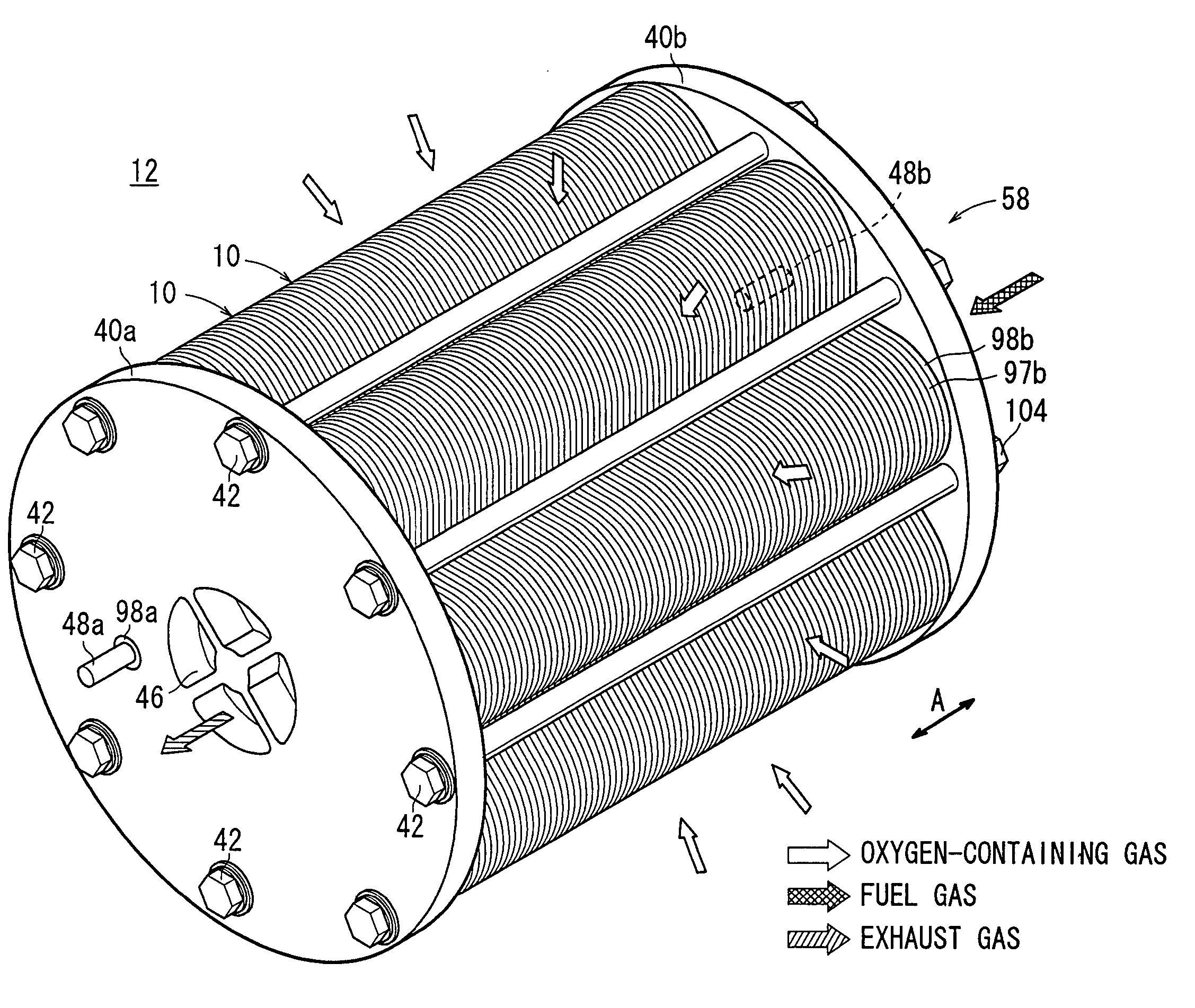
Reformer for fuel cell system and fuel cell system having the same
InactiveUS8486162B2Simple structureFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlElectricityElectrochemical response
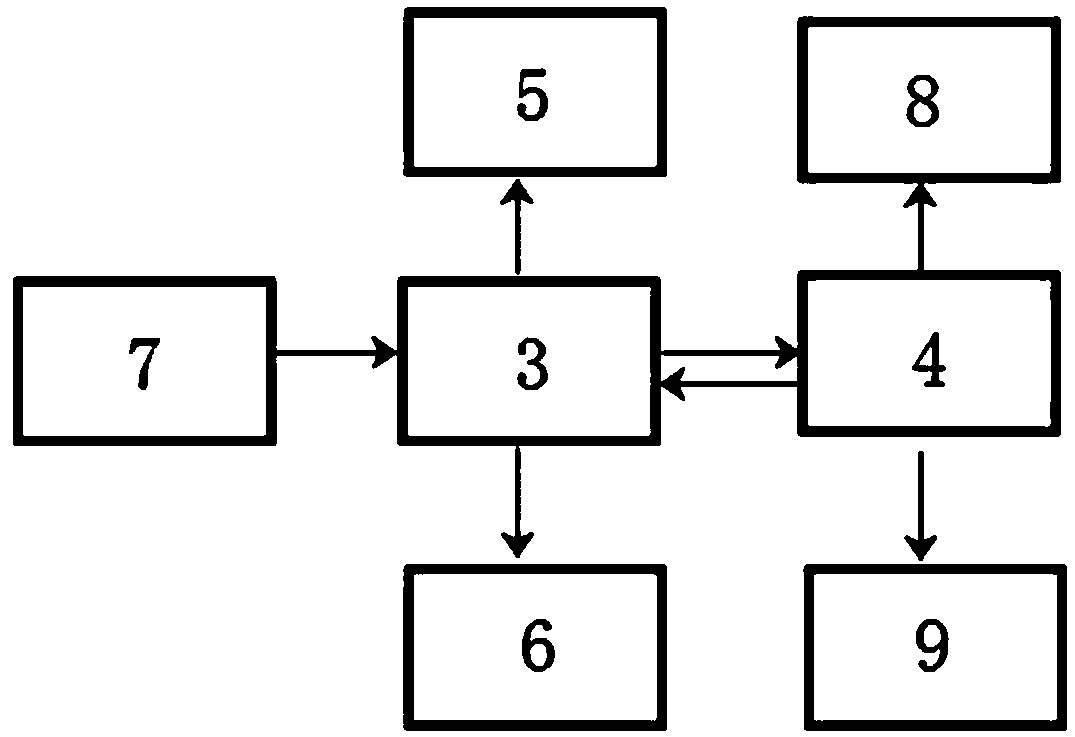
A reformer of a fuel cell system and a fuel cell system including a reformer are disclosed. The reformer includes a reformation unit comprising a pipe through which fuel passes. The pipe is formed from a material adapted to induce a catalytic reformation reaction in the pipe. The reformer includes a heat source unit for heating and evaporating the fuel by heating the pipe. The fuel cell system includes such a reformer, a stack for generating electricity through an electrochemical reaction between oxygen and hydrogen, a fuel supply unit, and an air supply unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Fuel cell system and reformer
InactiveUS7985506B2Prevent backfireUniform supplyHydrogenFuel cell auxillariesElectrochemical responseChemical reaction
A fuel cell system and a reformer for a fuel cell system prevents backfire and improves efficiency of heat transfer. The fuel cell system includes a reformer generating hydrogen gas from fuel including hydrogen by a catalytic chemical reaction using heat energy, and at least one electricity generating unit generating electrical energy by an electrochemical reaction between the hydrogen gas and oxygen. The reformer includes a case, a heat source, and a reforming reaction part. The case forms an external shape. The heat source is disposed in the case to generate heat energy by an oxidation reaction between fuel and a catalyst, and includes a mesh, an oxidation catalyst layer formed on a surface of the mesh, and at least one fuel injection nozzle supplying the fuel to the oxidation catalyst layer. The reforming reaction part is disposed in the case to generate hydrogen gas from fuel using the heat energy generated from the heat source.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Separator for fuel cell and fuel cell
ActiveUS20100239957A1Improve rigidityAvoid deformationFuel cell auxillariesFuel cell detailsConvex structureEngineering
A separator has a concavo-convex structure formed in mutually reversed shapes on two opposite sides thereof to define flow paths of different fluids on the respective two sides. The concavo-convex structure includes multiple first projections formed and protruded on one side of the two opposite sides and arranged at intervals having a preset regularity. The concavo-convex structure also includes multiple second projections formed and protruded on the other side of the two opposite sides in a specific area corresponding to an area for formation of the multiple first projections on the one side and arranged at intervals having a preset regularity. The concavo-convex structure further includes reinforcing elements protruded on the one side. Each of the reinforcing elements is formed as a convex in a specific shape of connecting multiple positions where the first projections are expected to be formed according to the preset regularity, while avoiding positions corresponding to the second projections formed on the other side. This arrangement effectively prevents a potential trouble caused by deformation of the separator due to a pressure difference between the flow pressures of the respective fluids flowing on the respective sides of the separator.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
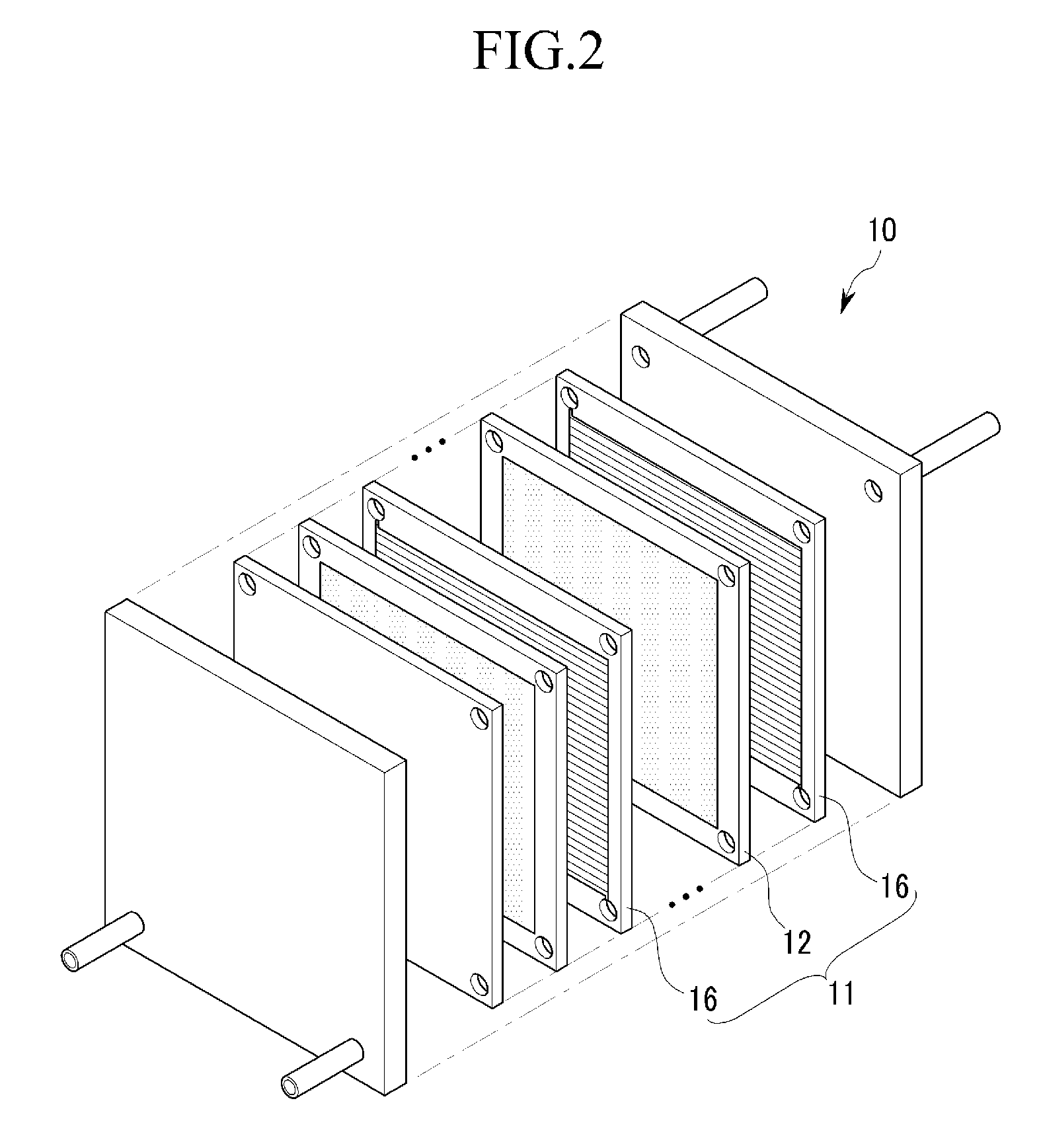
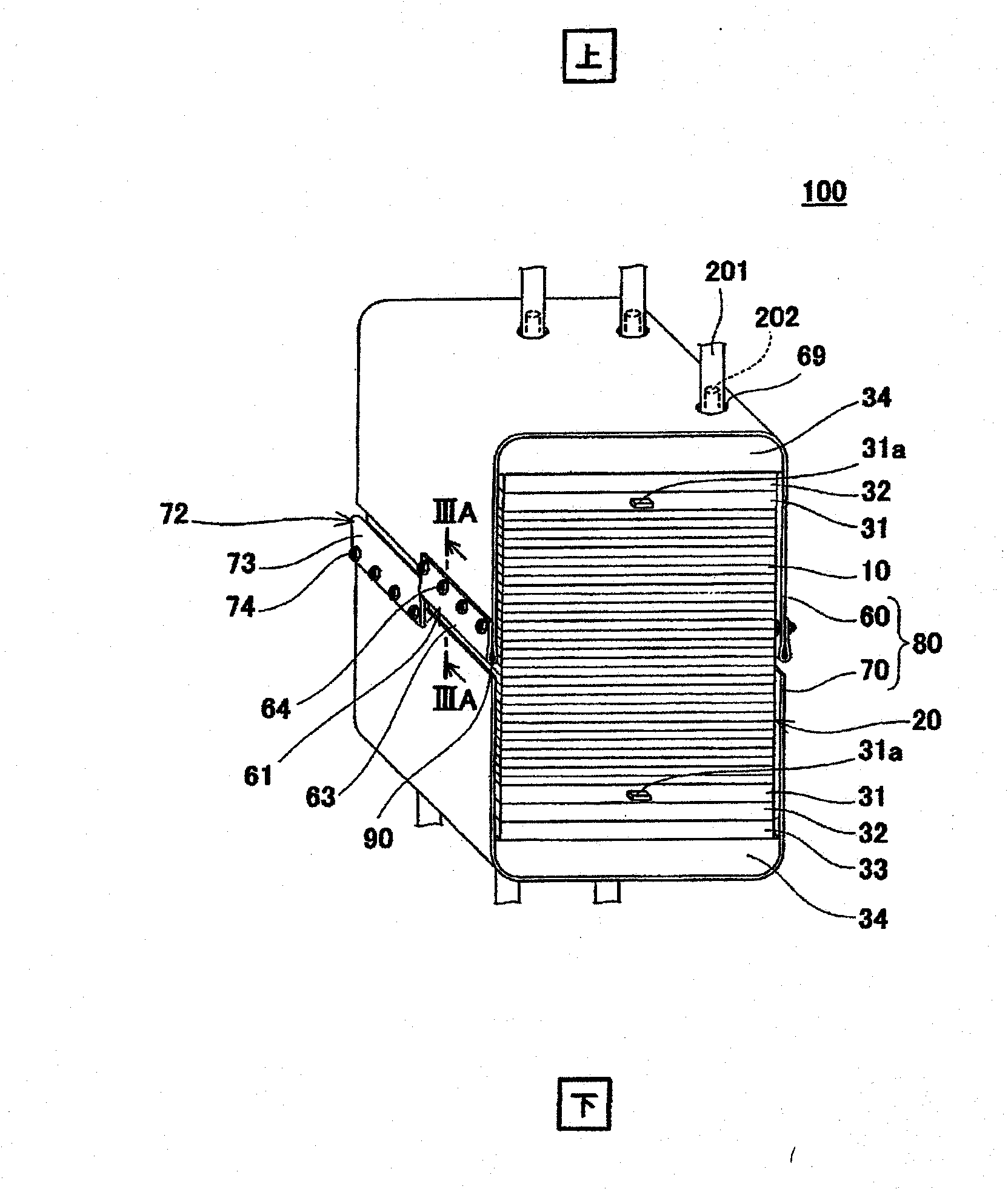
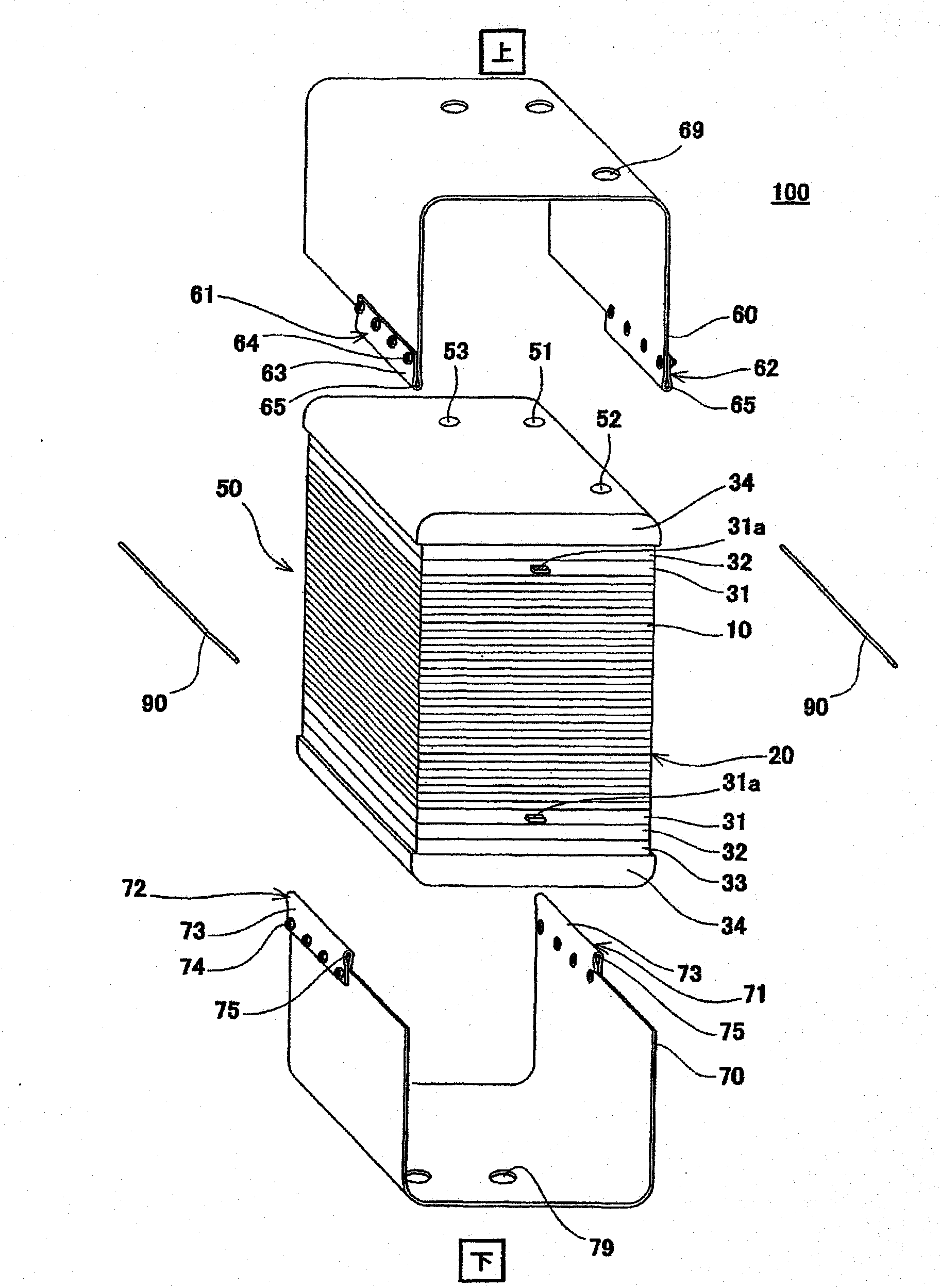
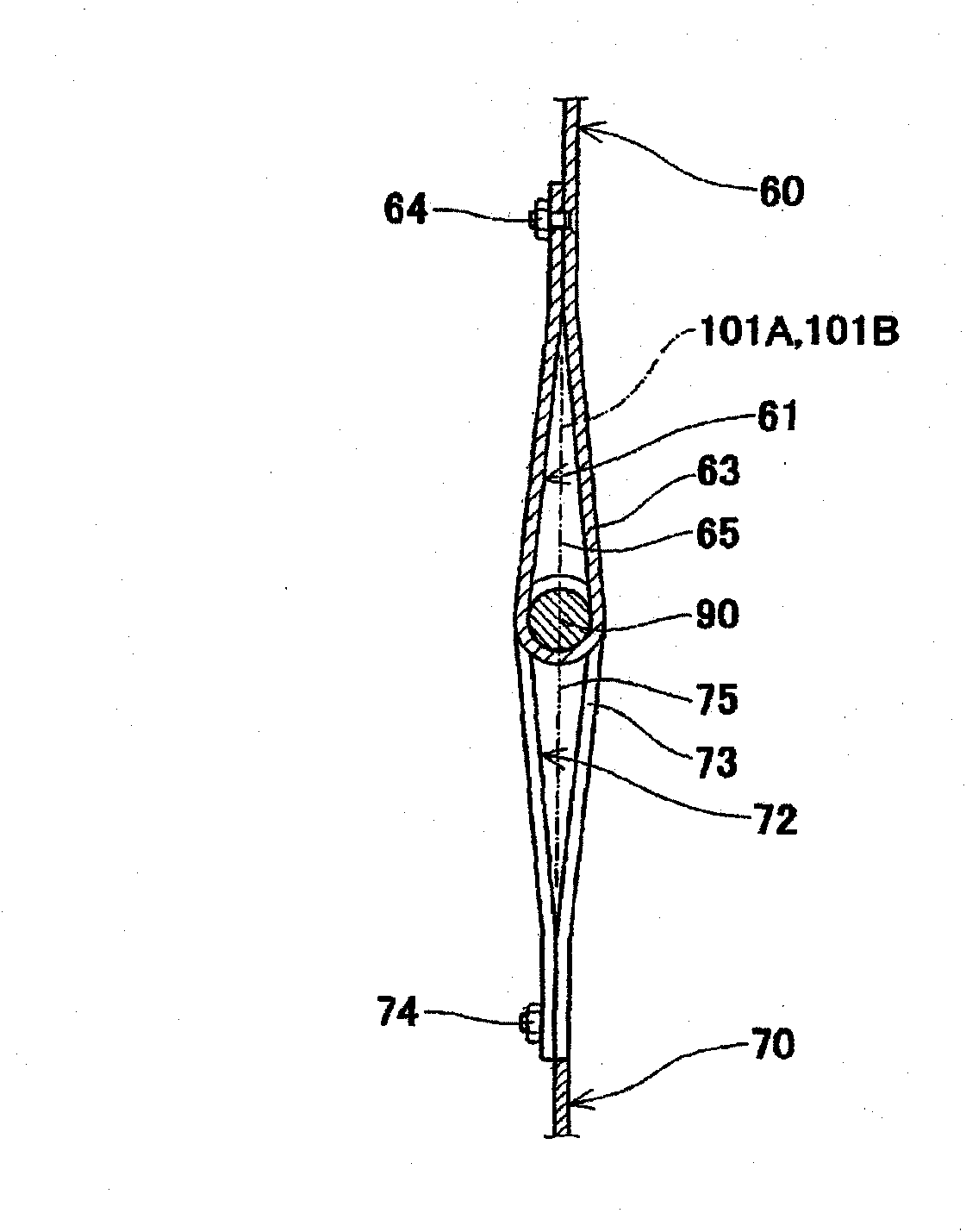
Cell stack of fuel cells and method for fastening cell stack of fuel cells
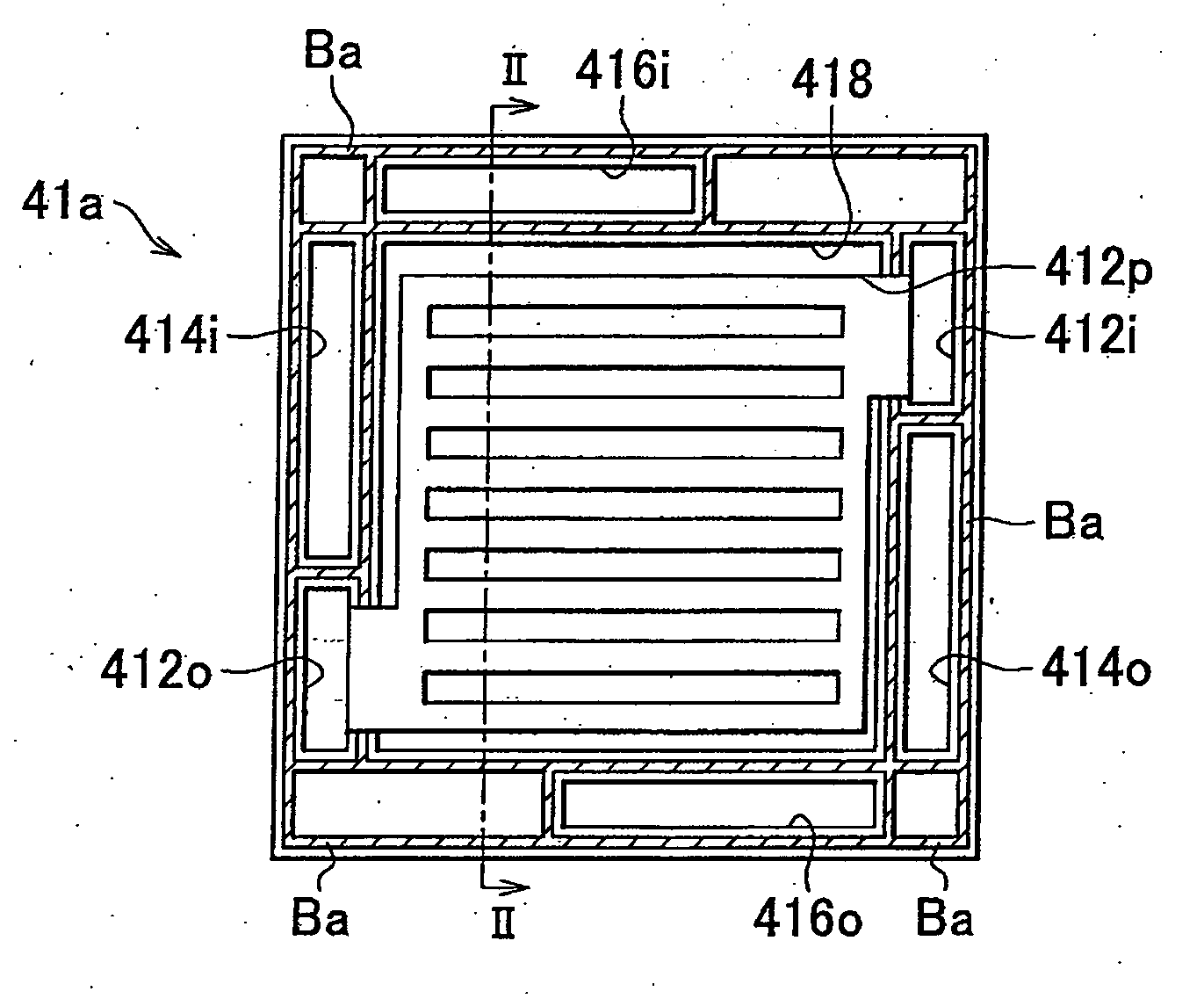
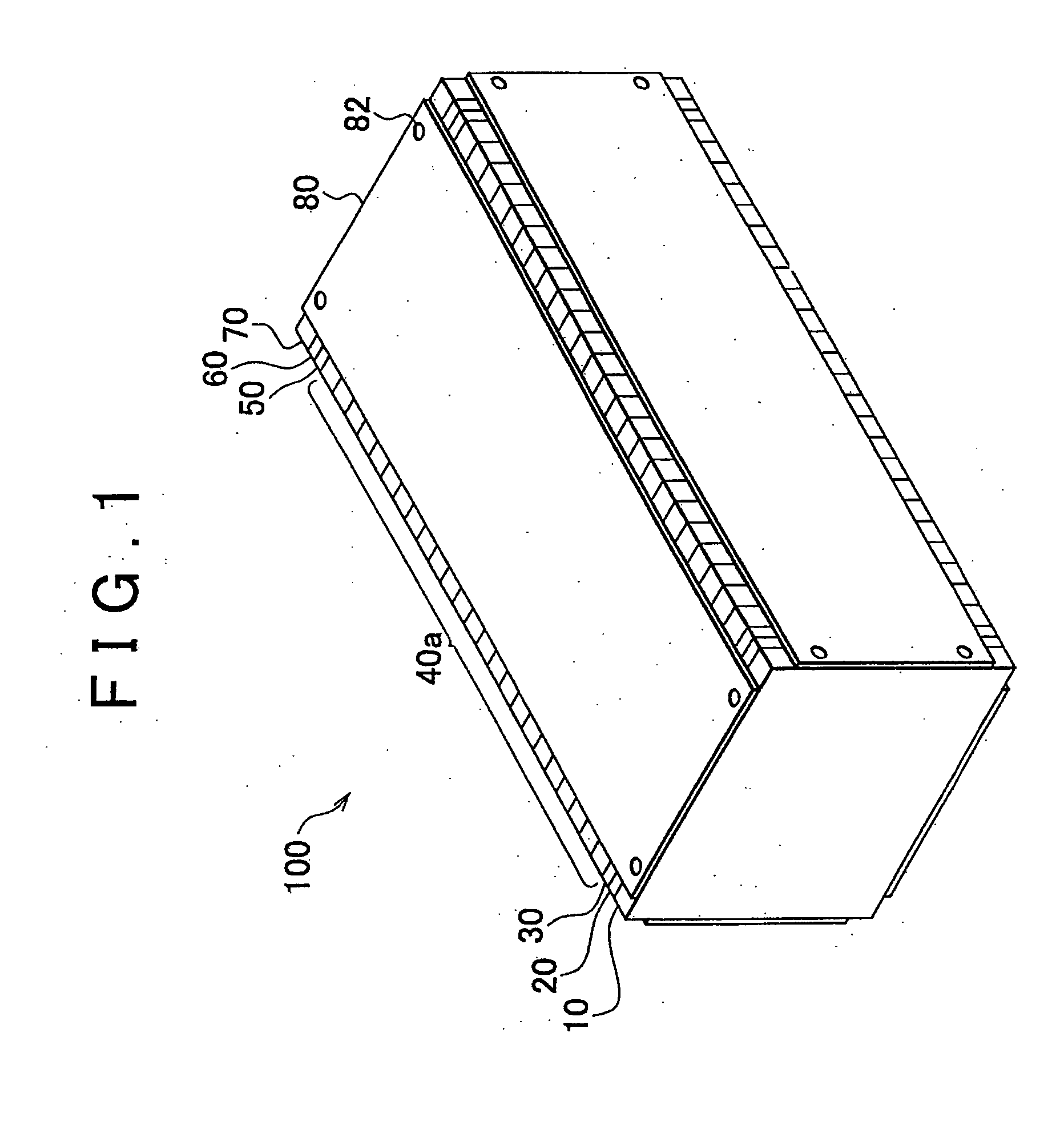
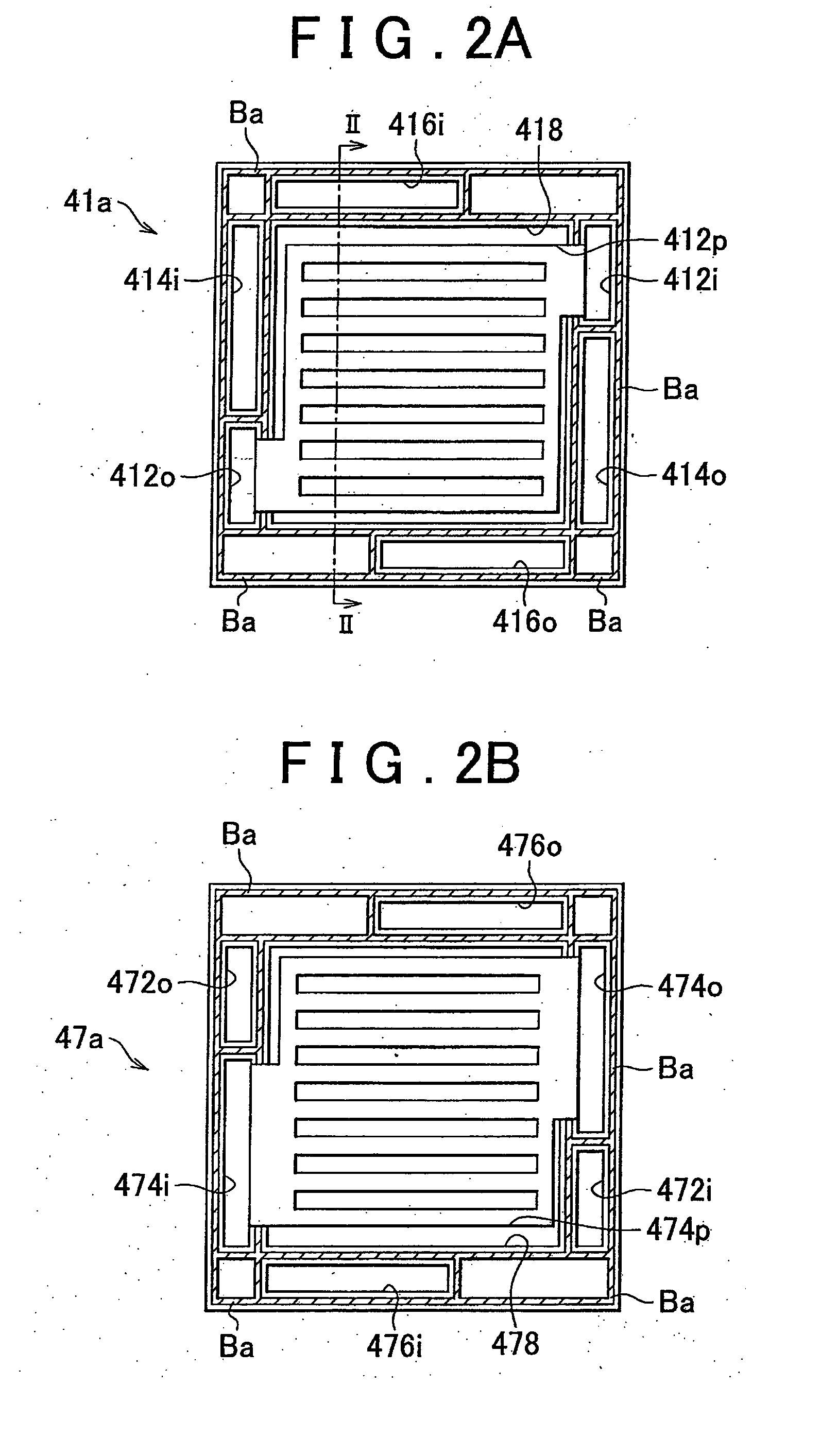
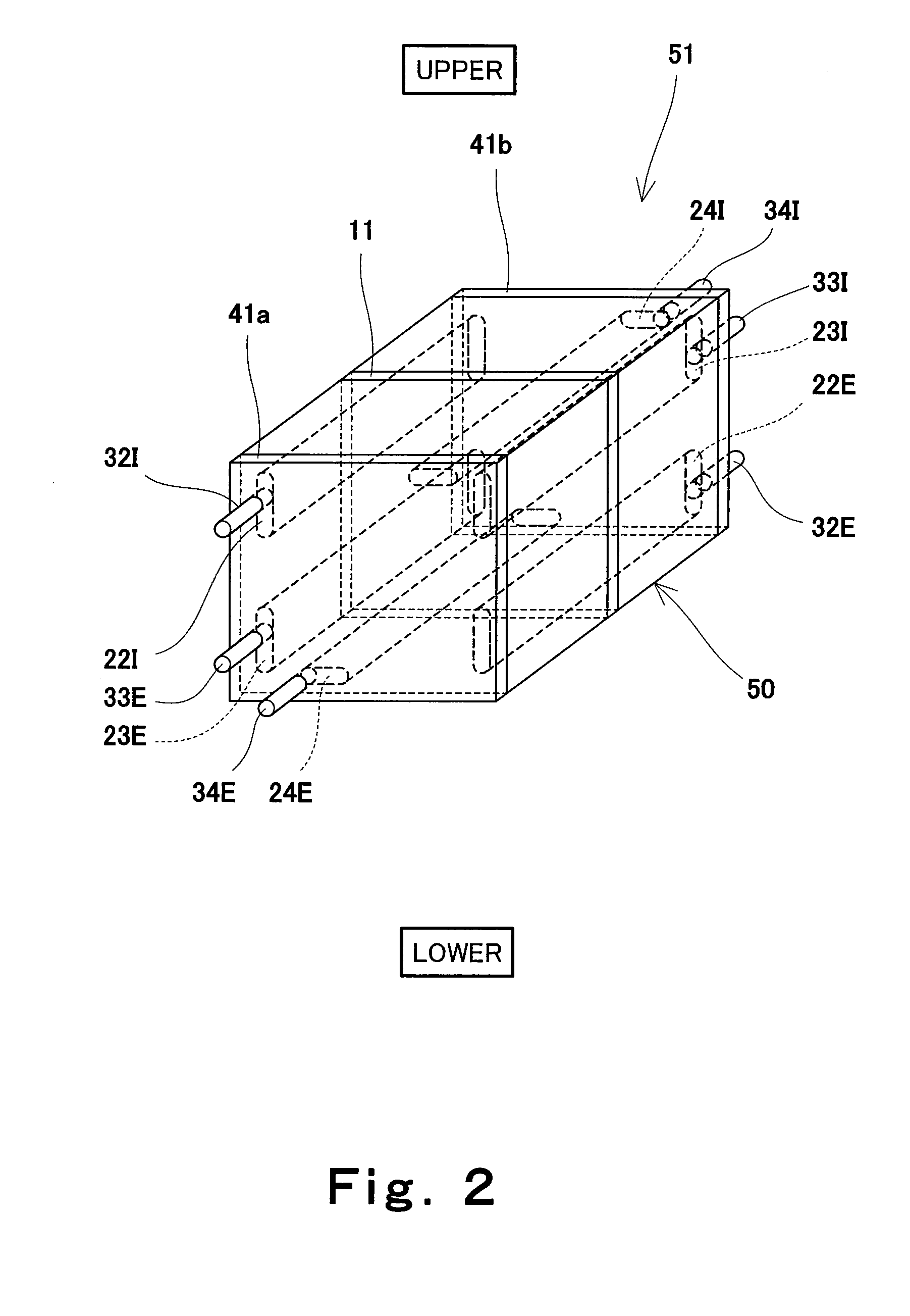
ActiveCN102171881ASmall surface areaFuel cells groupingSolid electrolyte fuel cellsEngineeringFuel cell bus
A cell stack of fuel cells is provided with: a cell stack body (50) having a stack of cells (20), an elastic member (33) arranged at the end of a cell (10) of the stack of cells (20) in the stacking direction, and a pair of end plates (34, 34) which sandwich the stack of cells (20) and the elastic member (33); and with a fastening band (80) which has a first band engaging section (68) and a second band engaging section (78) on both end sections and which extends around the cell stack body (50) so as to cover the pair of side surfaces facing the pair of entire end surfaces of the cell stack body (50). The cell stack body (50) is fastened by means of the fastening band (80) by direct or indirect engagement of the first band engaging section (68) and the second band engaging section (78).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fuel cell
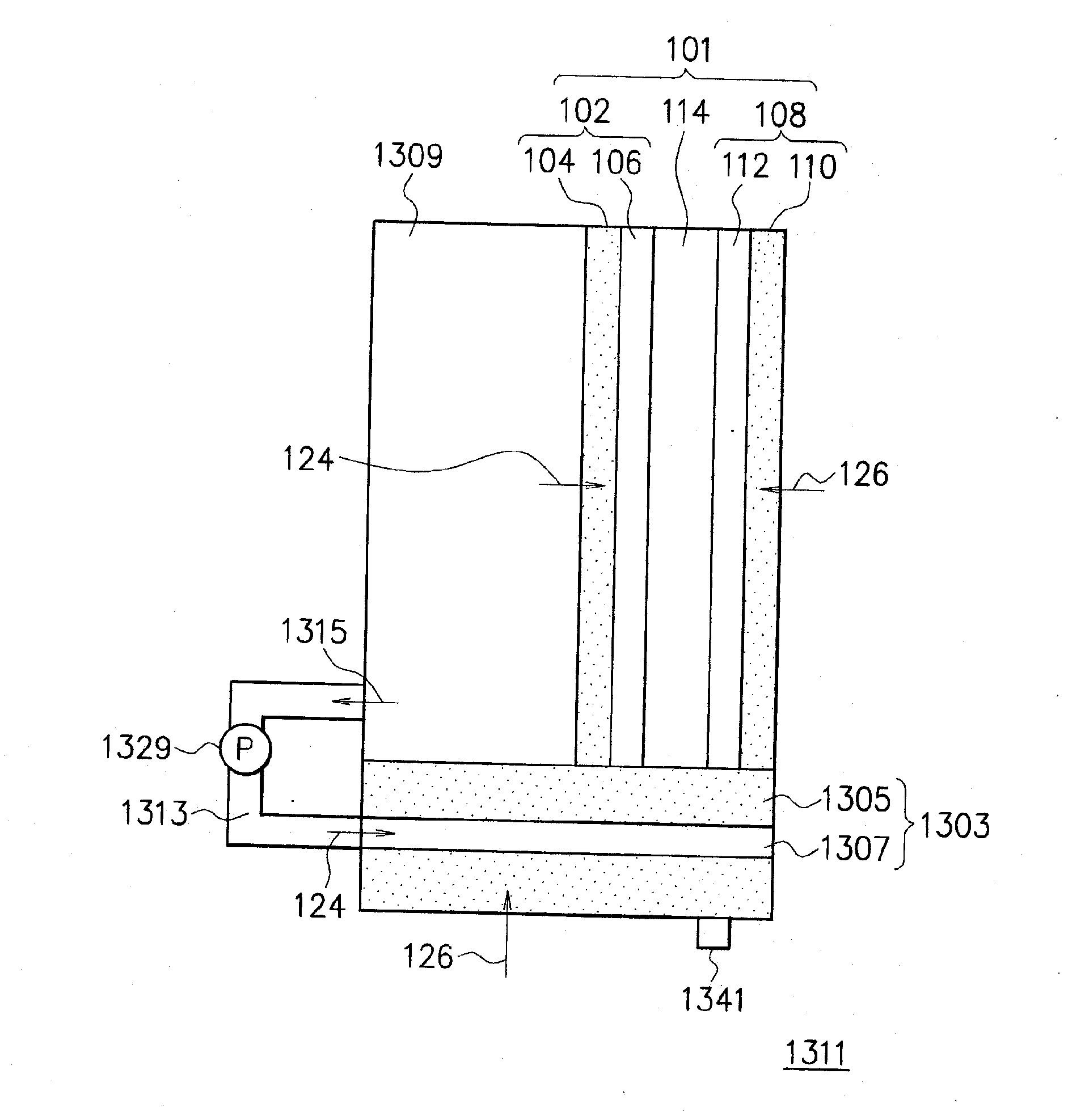
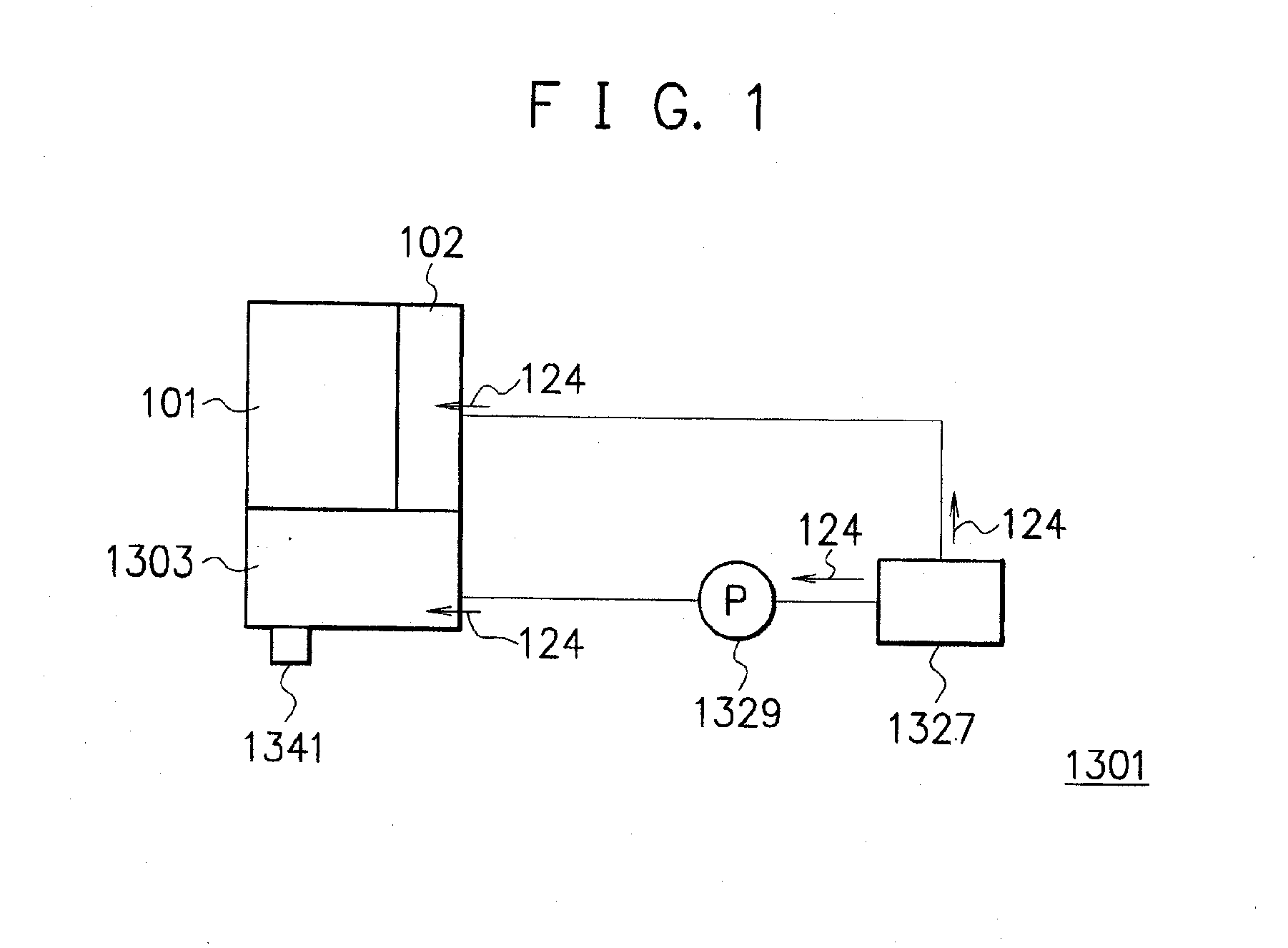
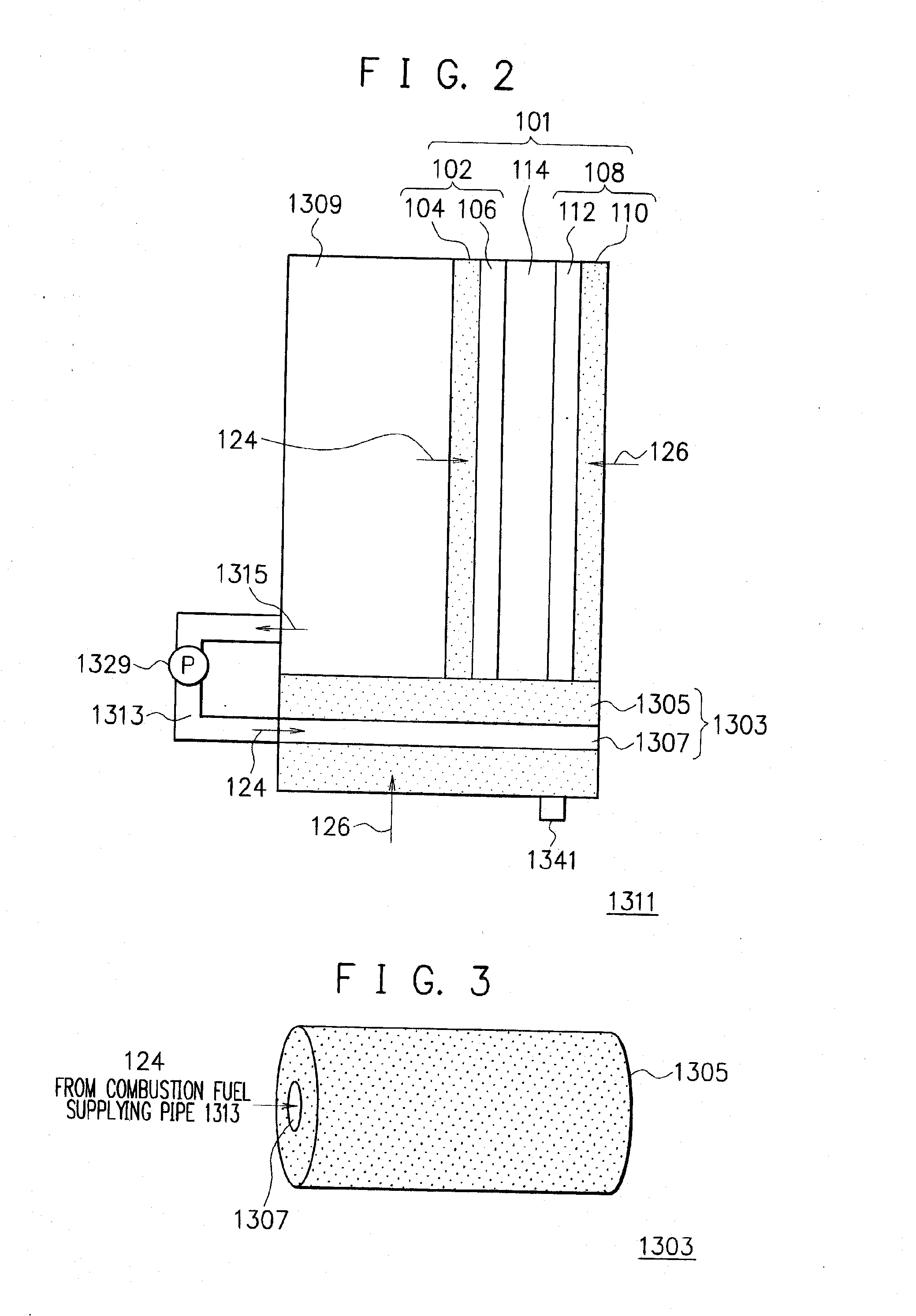
InactiveUS20070166587A1Increase fuel temperatureImprove usabilityReactant parameters controlFuel cells groupingCombustionFuel tank
Even when a temperature is lowered, a temperature of a fuel cell is raised, thereby improving the availability. In a fuel cell 1311, a combustion unit 1303 is provided in contact with a unit cell structure 101. In addition, a fuel tank 1309 is provided in contact with a fuel electrode 102 constituting the unit cell structure 101 and supplies a fuel 124 to the fuel electrode 102 directly. A part of the fuel 124 is supplied to the combustion unit 1303 from an combustion fuel discharging exit 1315 provided in the fuel tank 1309 via a combustion fuel supply pipe 1313.
Owner:NEC CORP
Fuel cell
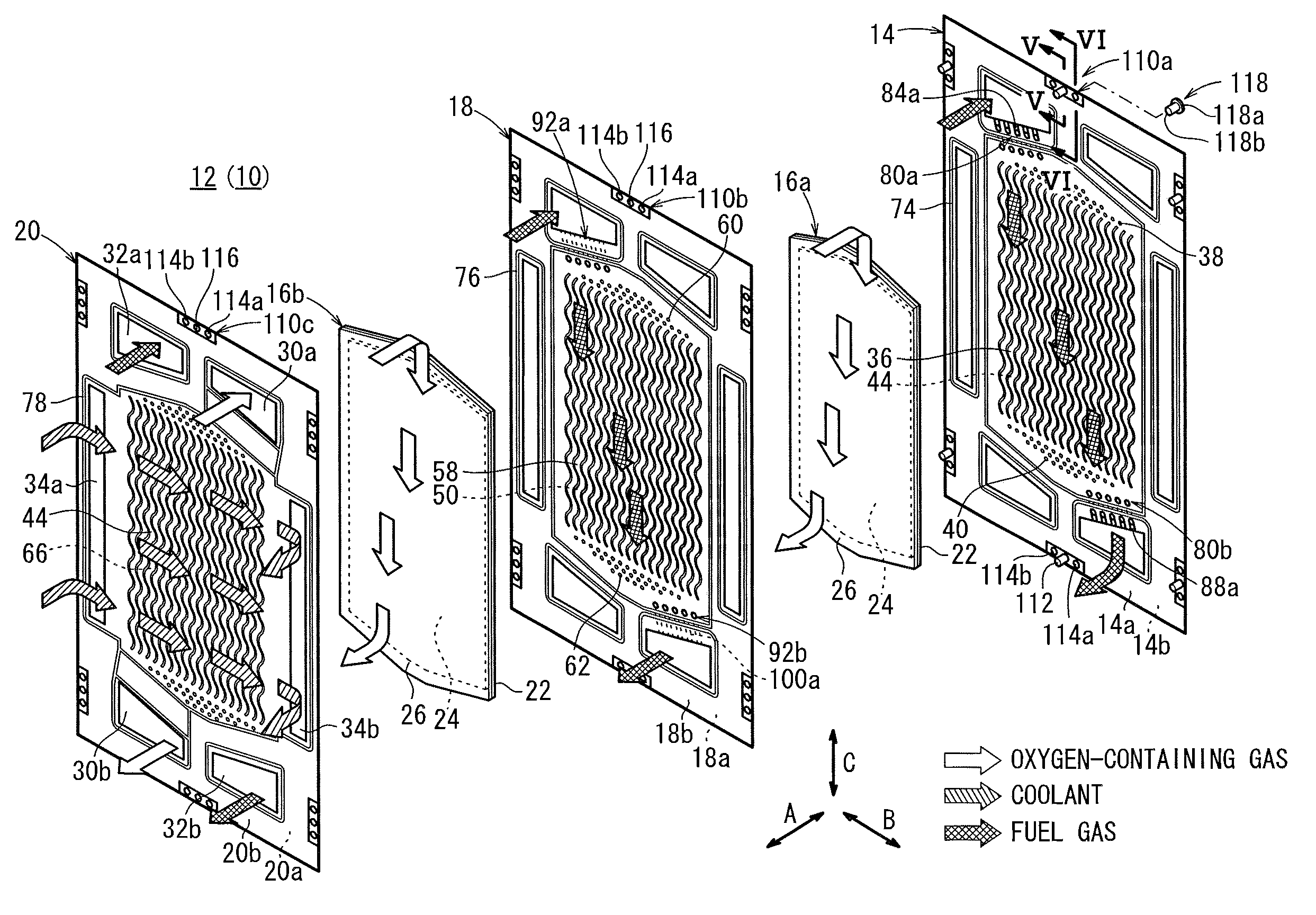
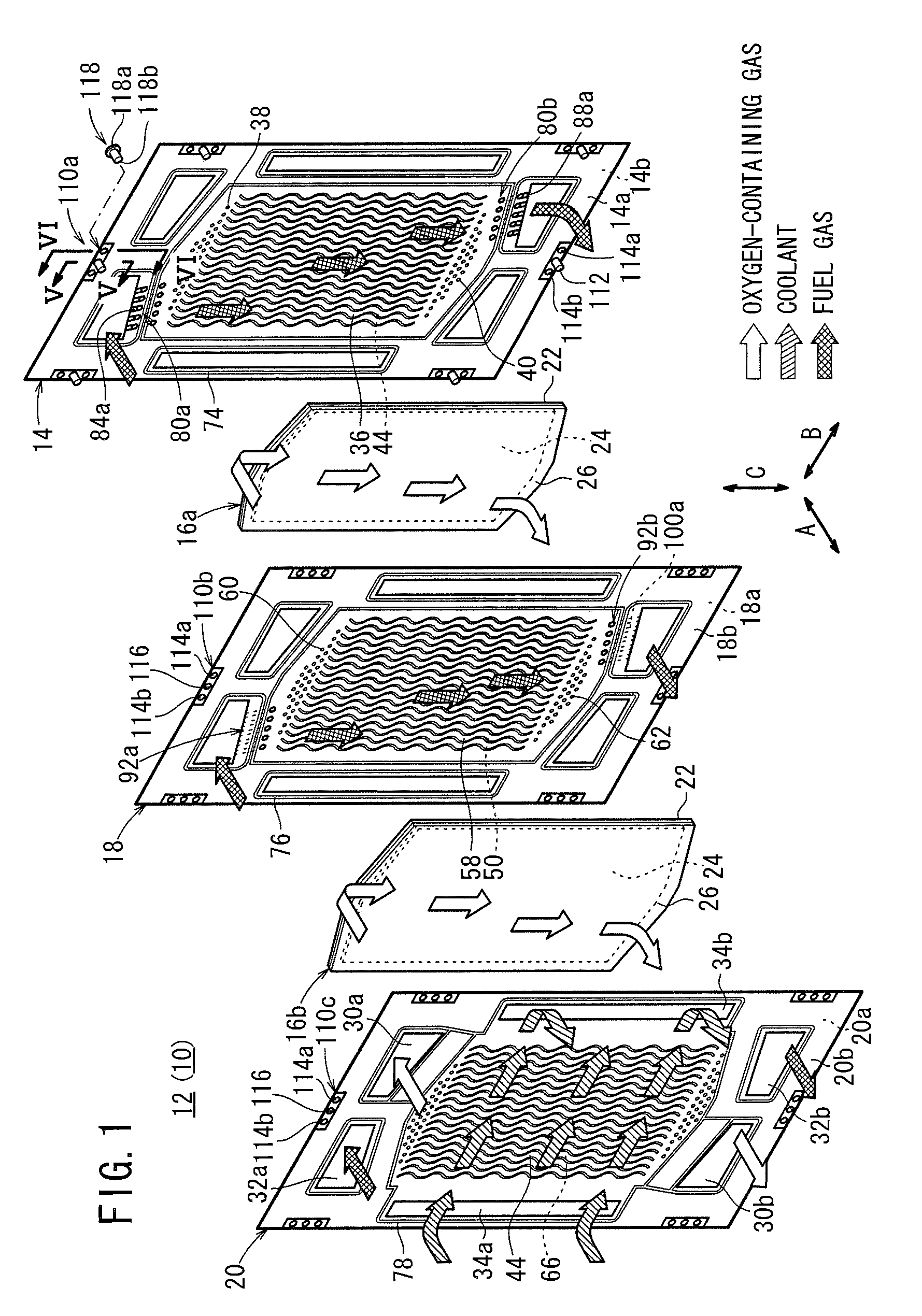
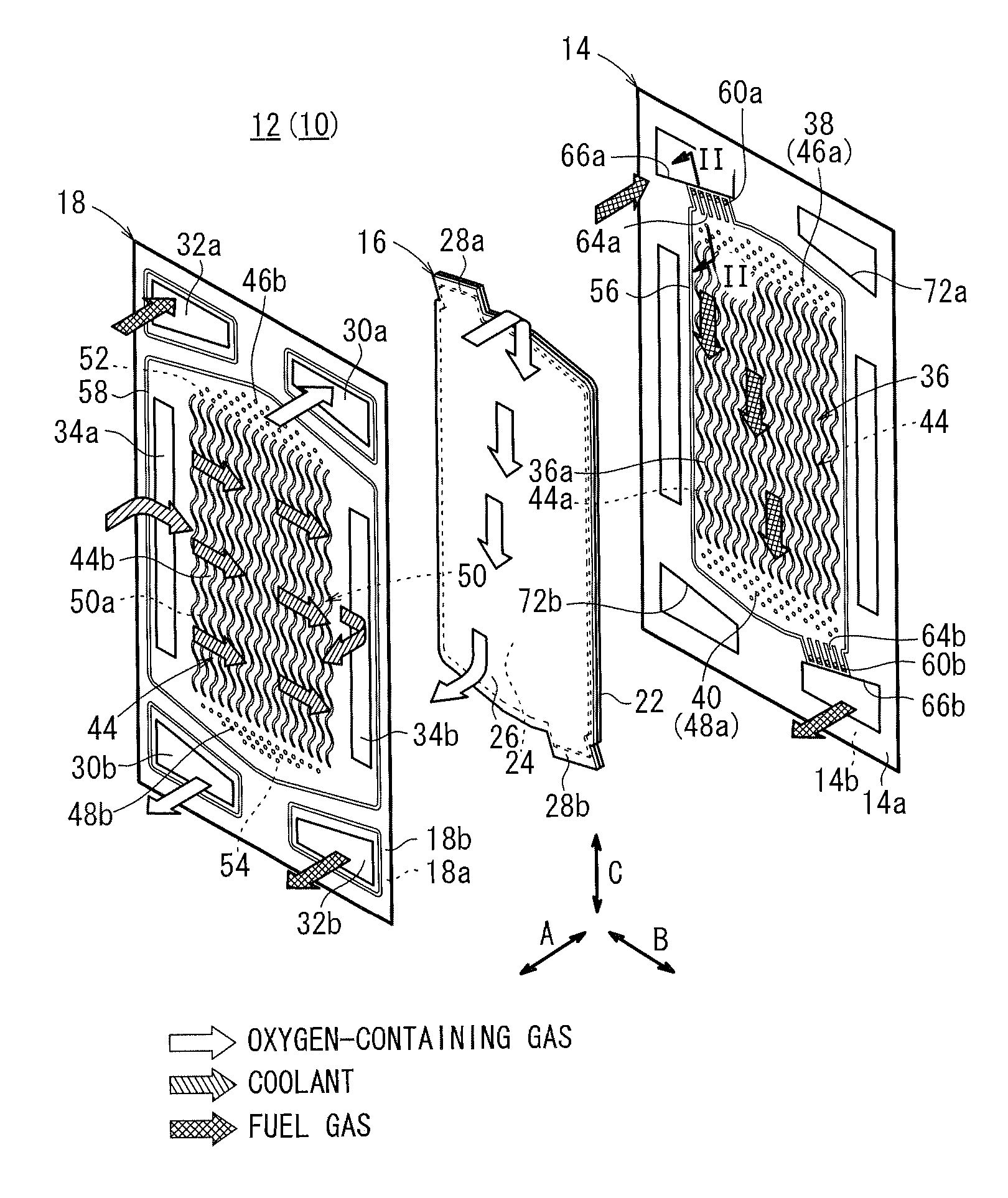
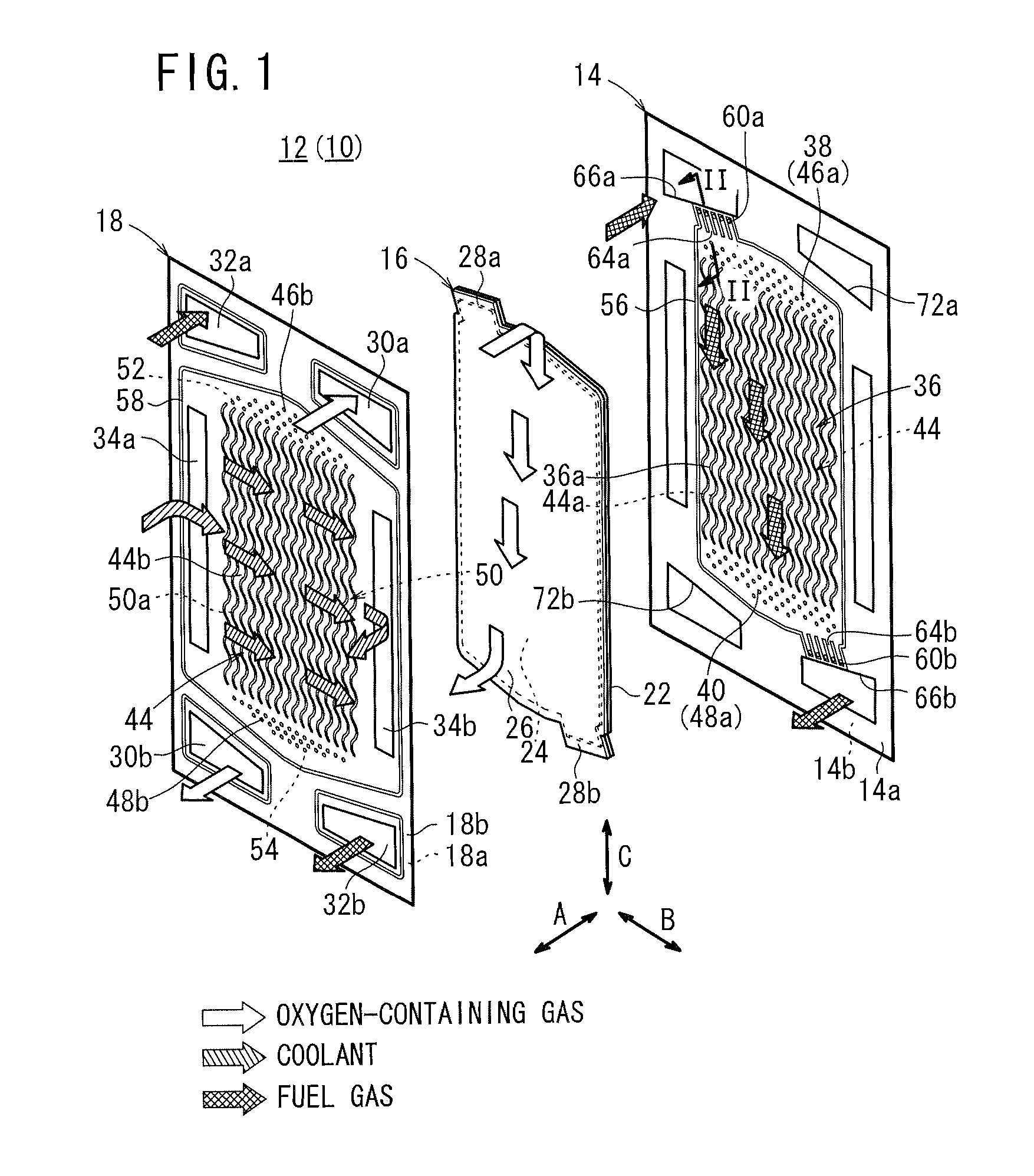
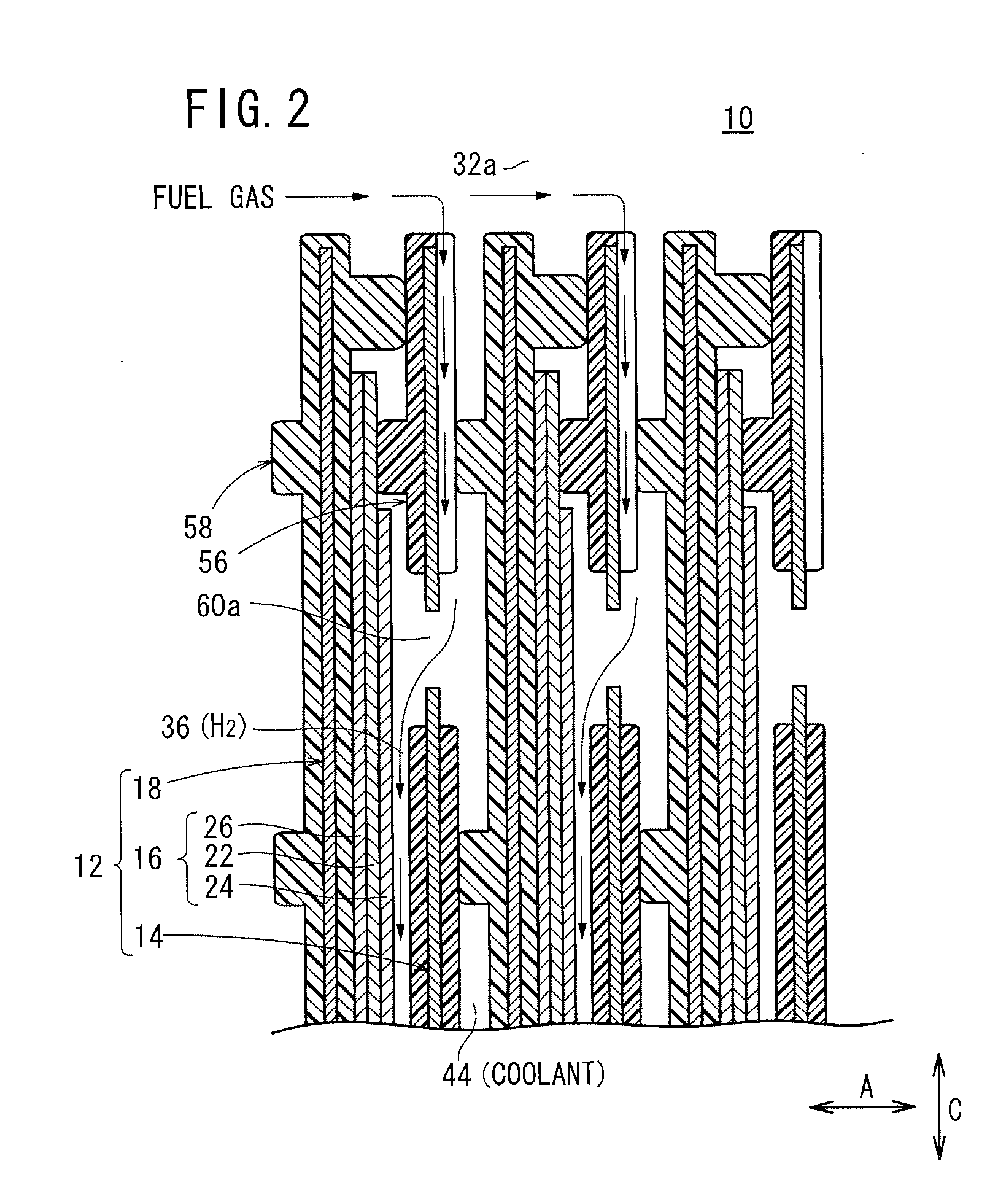
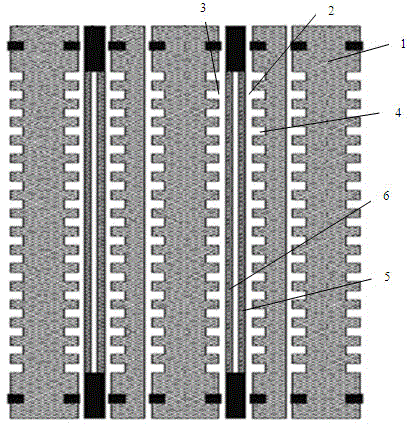
ActiveUS20110053031A1Simple structureIncrease the lengthFuel cells groupingCell component detailsEngineeringFuel gas
A fuel cell includes a plurality of power generation cells each having a first separator. The separator has a fuel gas flow field. A fuel gas supply passage extends through one corner of the power generation cell in the stacking direction, a fuel gas flowing through the fuel gas supply passage into a fuel gas flow field. An inlet buffer is provided upstream of the fuel gas flow field. The fuel gas supply passage and the inlet buffer are connected by a plurality of inlet connection grooves. The inlet connection grooves are inclined from a direction perpendicular to a wall surface of the fuel gas supply passage toward the center of the fuel gas flow field.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
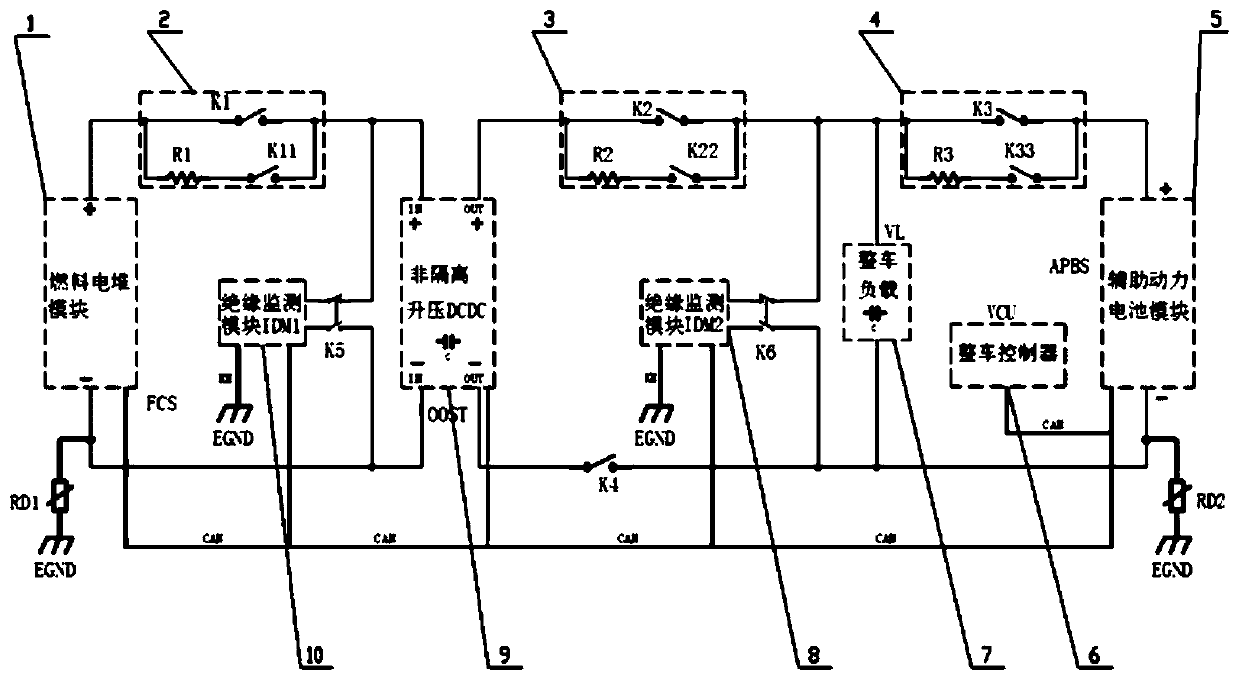
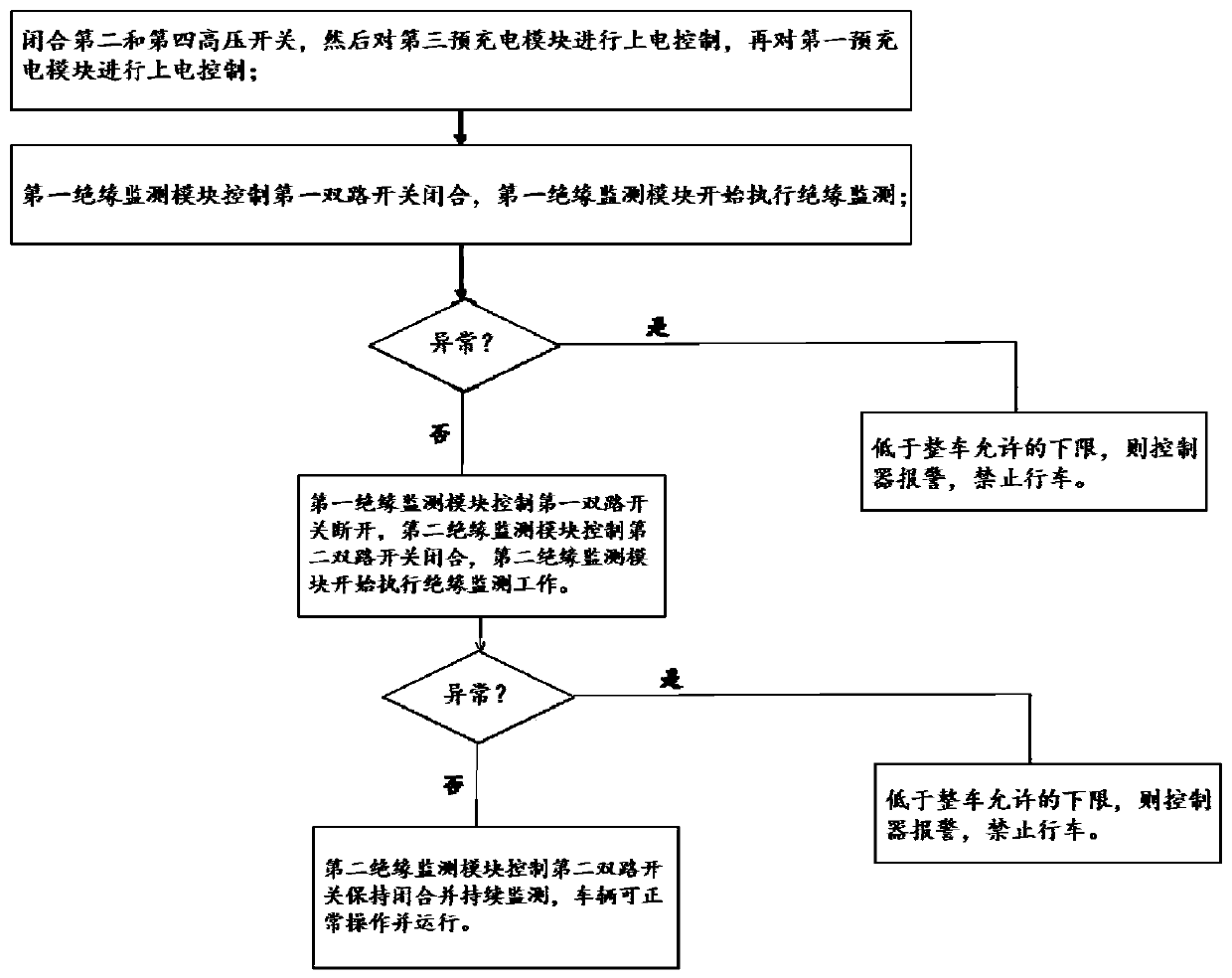
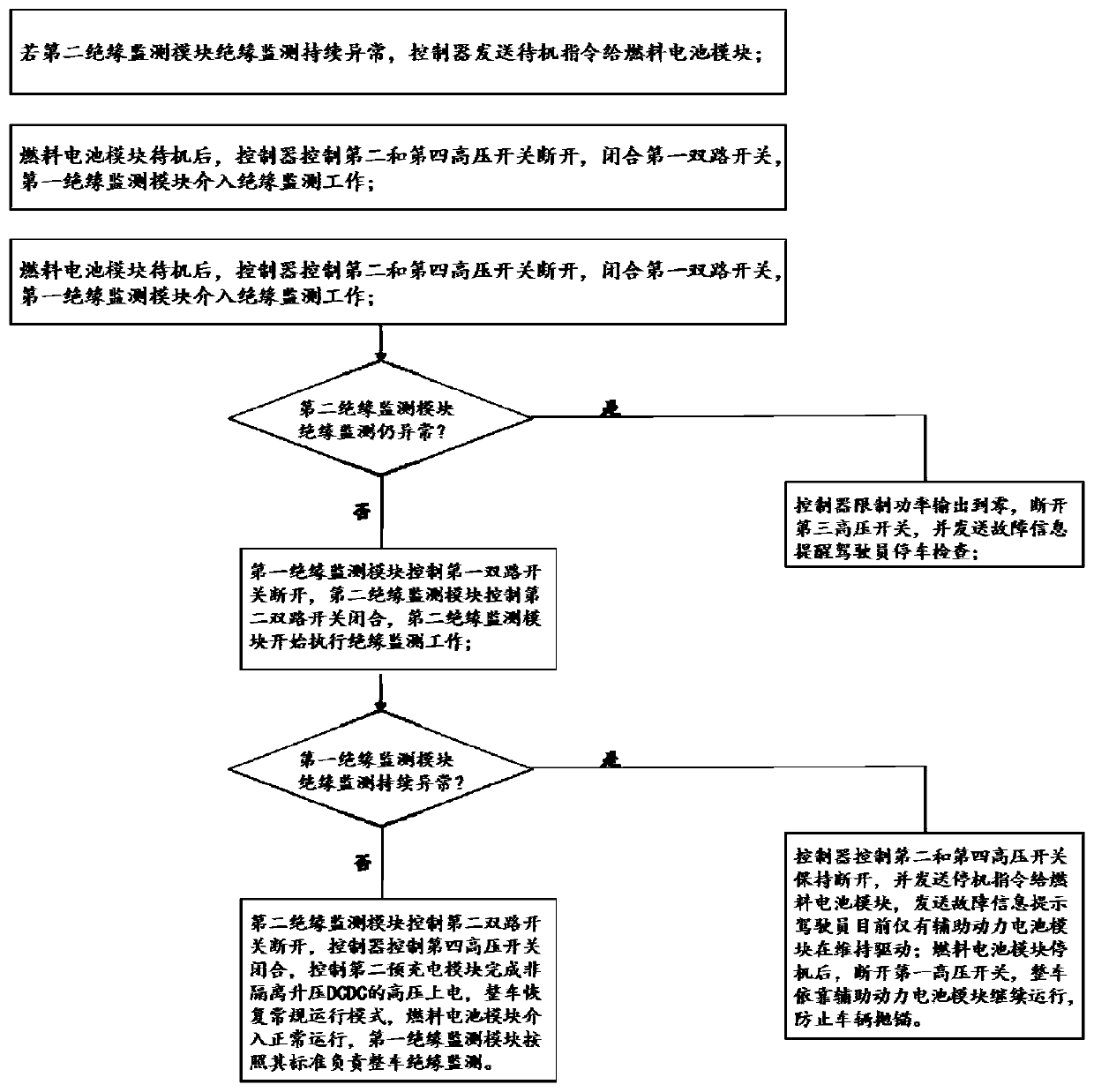
Insulation monitoring control system and method for fuel cell passenger vehicle, and vehicle
ActiveCN110053519ASolve the problem of abnormal operationRunning does not affectElectric devicesElectric energy managementPower batteryElectricity
The invention provides an insulation monitoring control system and method for a fuel cell passenger vehicle, and the vehicle. The insulation monitoring control system comprises a fuel cell module, anauxiliary power battery module, a non-isolated boost DCDC, insulation monitoring modules, a vehicle load and a controller; the auxiliary power battery module is directly used for supplying power to the vehicle load; the non-isolated boost DCDC is used for converting low-voltage platform power emitted by the fuel cell module to high-voltage platform power to be supplied to the vehicle load; the insulation monitoring modules comprise the first insulation monitoring module and the second insulation monitoring module, wherein the first insulation monitoring module is used for insulation monitoringof an input front end circuit of the non-isolated boost DCDC, and the second insulation monitoring module is used for insulation monitoring of an output rear end circuit of the non-isolated boost DCDC; and the controller is used for data communication with all the modules. The problem that the insulation monitoring standards of the fuel cell vehicle adopting the non-isolated boost DCDC are inconsistent, and consequently vehicle operation abnormity is caused is solved.
Owner:ZHONGTONG BUS HLDG
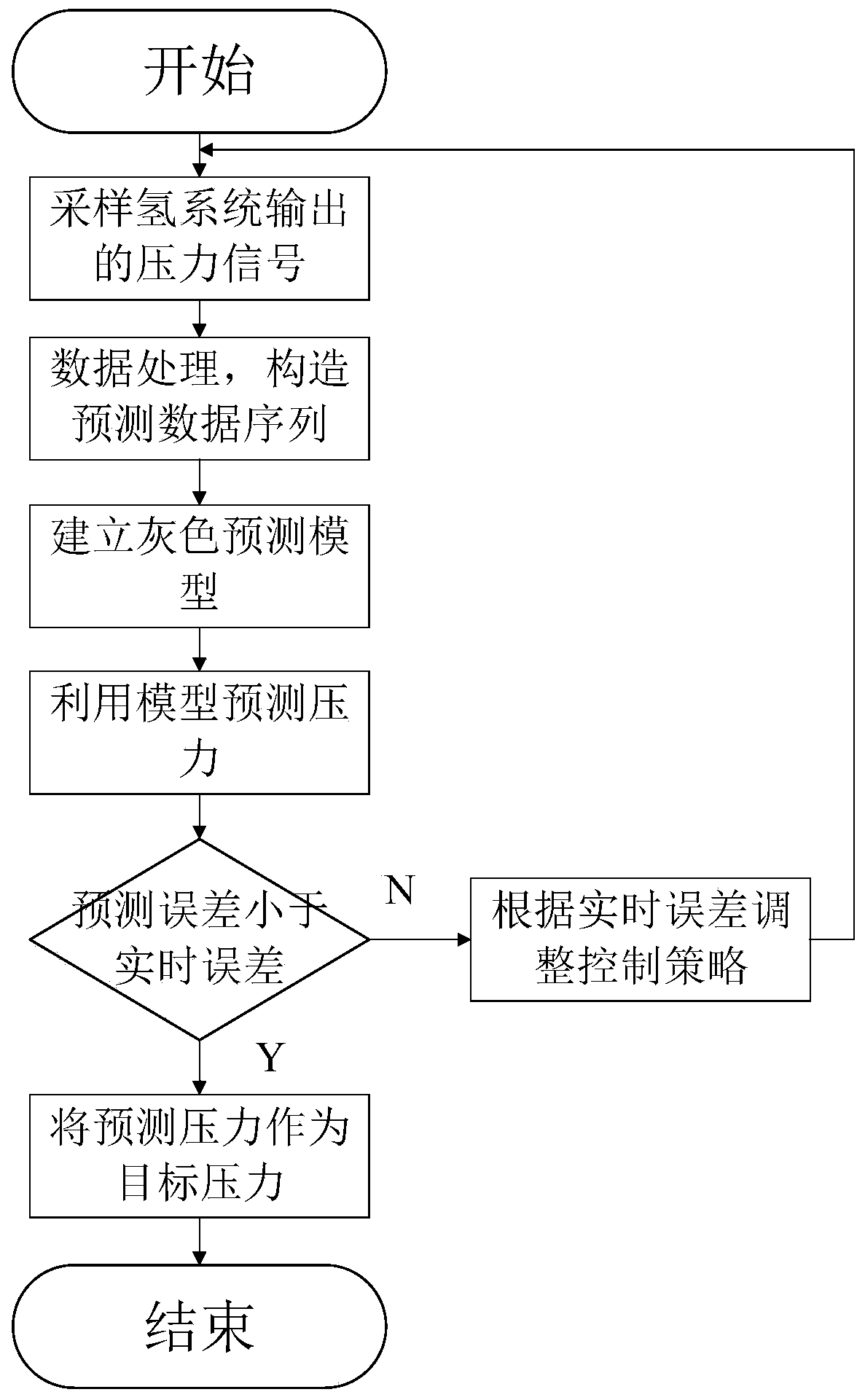
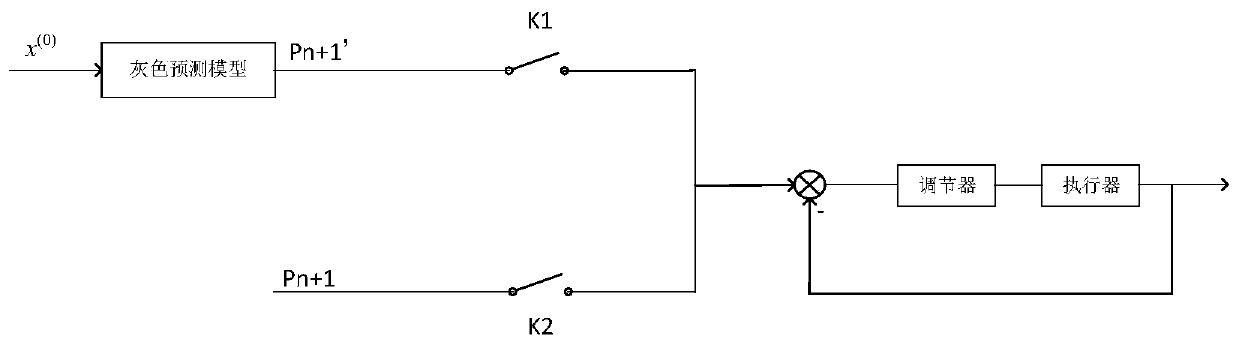
Control method and device of vehicle-mounted hydrogen system and vehicle-mounted hydrogen system
ActiveCN111244507AControl gas pressureMeet needsOperating modesBattery/fuel cell control arrangementThermodynamicsIn vehicle
The invention relates to a control method and device of a vehicle-mounted hydrogen system and the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system, and belongs to the field of fuel cell buses. The method comprises: establishing a pressure prediction model of an output gas of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system, and determining a pressure prediction value used for controlling the pressure of the output gas of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system according to the pressure prediction model; calculating a difference value between the pressure prediction value and a set target pressure value to obtain a prediction error; obtaining an actual pressure value of output gas of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system, and calculating a difference value between the actual pressure value and the target pressure value to obtain an actual error; and comparing the prediction error with the actual error, and when the prediction error is smaller than the actual error, outputting a pressure prediction value of the next momentby using the pressure prediction model as a target pressure of the next moment to control the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system to output gas. The change trend of the output pressure of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system is judged in advance, and the pressure of the output gas of the vehicle-mounted hydrogen system is adjusted in advance, so that the supplied hydrogen can meet the requirements ofa fuel cell system.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUTONG BUS CO LTD
Fuel cell and method for operating the fuel cell
ActiveUS20150263355A1Improve performanceEfficient power generationFuel cell auxillariesConductive materialCost effectivenessPower flow
Provided are a fuel cell that employs a fuel-electrode collector excellent in terms of thermal conductivity and the like, so that it is excellent in terms of power generation efficiency and cost effectiveness; and a method for operating the fuel cell. Included are a membrane electrode assembly (MEA), a fuel-electrode collector that is a porous metal body disposed in contact with a fuel electrode and performing current collection,and a heating device operated by electric power, wherein a solid electrolyte is a proton-permeable electrolyte, a fuel-gas channel is provided to cause a fuel gas to pass through the fuel-electrode collector, and the porous metal body constituting the fuel-electrode collector is formed of aluminum or aluminum alloy.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Fuel cell
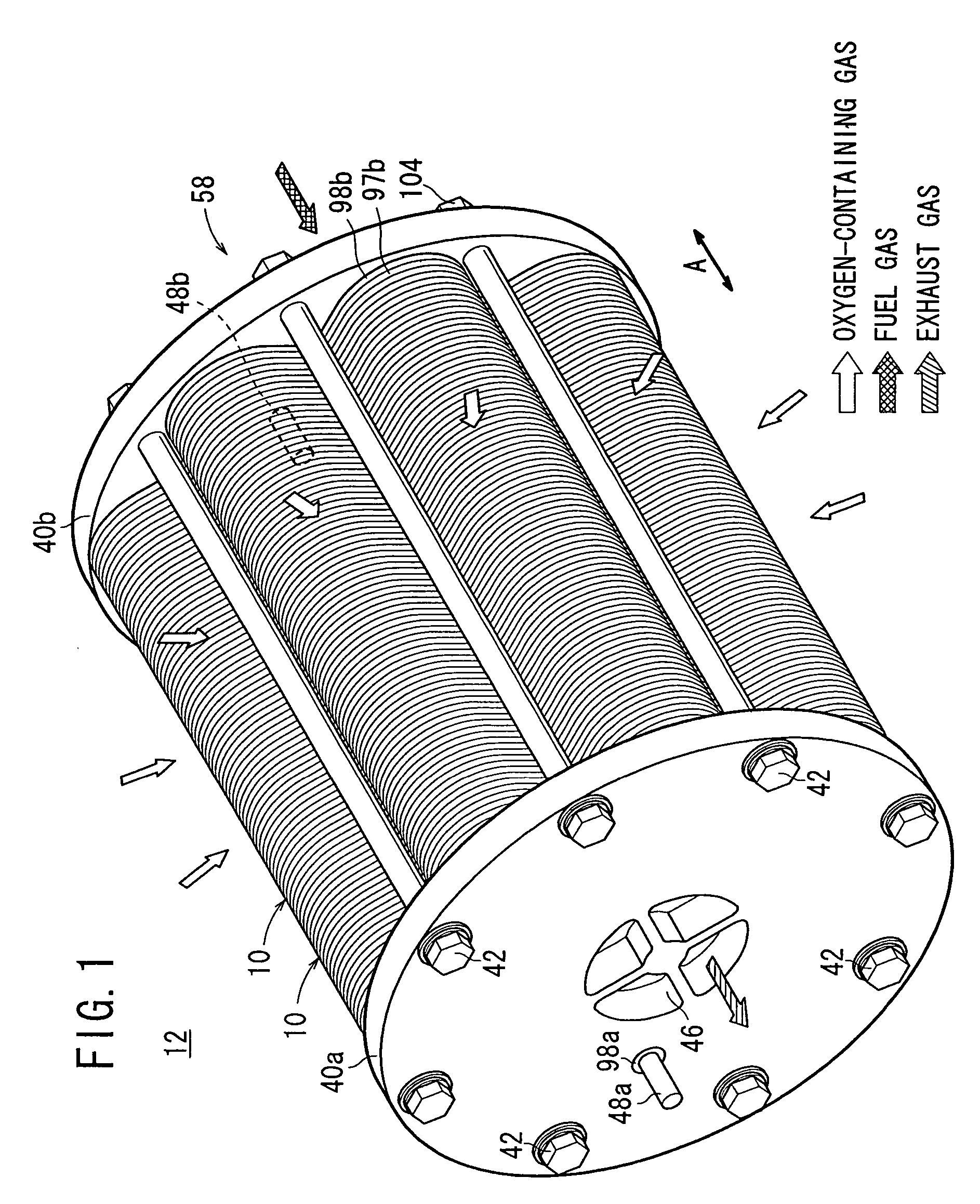
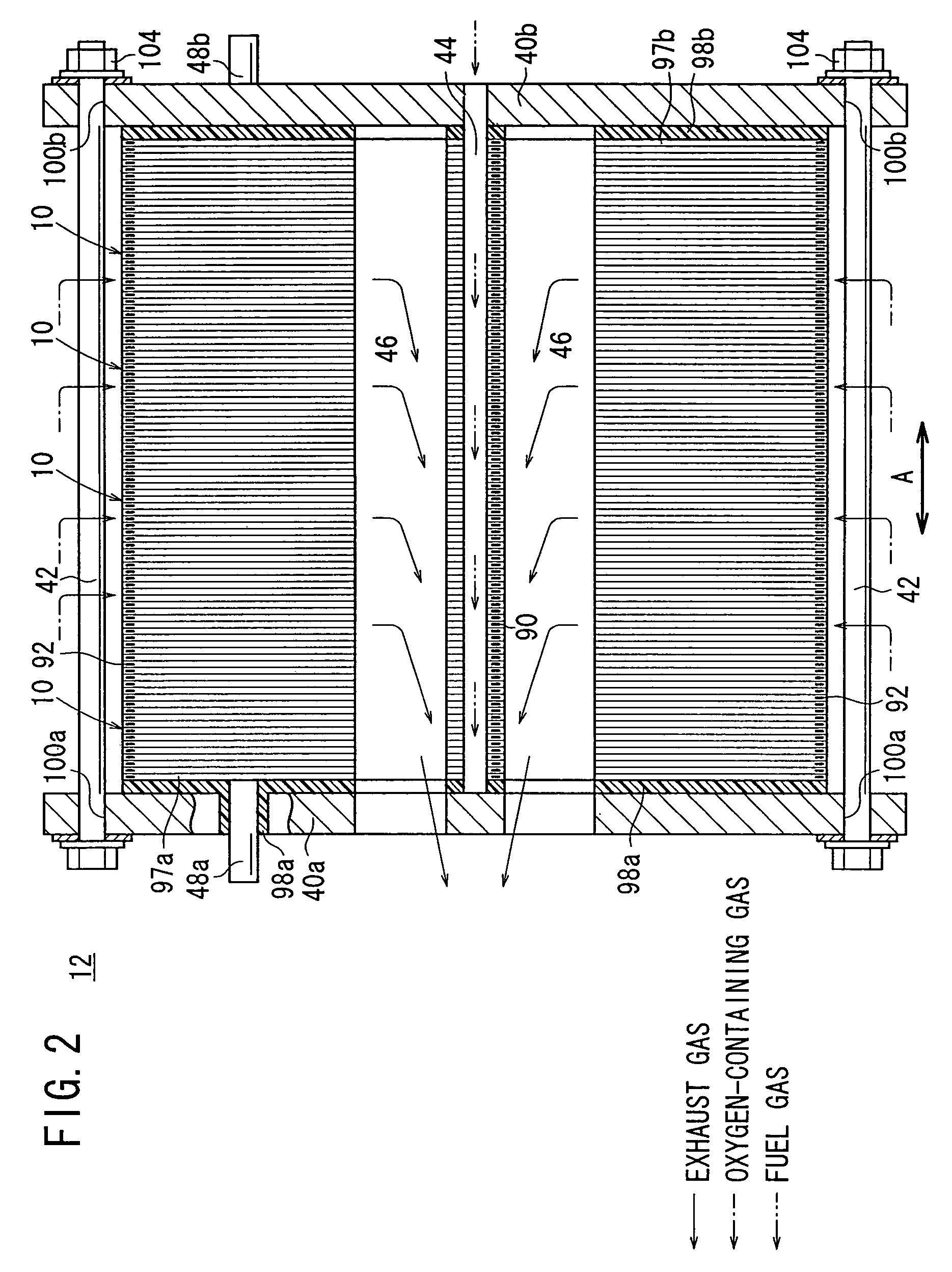
InactiveUS7049019B2Simple and compact structureReliable supplyFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingEngineeringOxygen
Each of separators for sandwiching a plurality of electrolyte electrode assemblies includes a pair of plates. A fuel gas channel and an oxygen-containing gas channel are formed between the plates. First and second circumferential ridges are formed integrally on curved outer sections of the plates to protrude away from each other. Further, outer projections and inner projections are formed integrally on opposite sides of the first and second circumferential ridges to protrude toward each other.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel cell
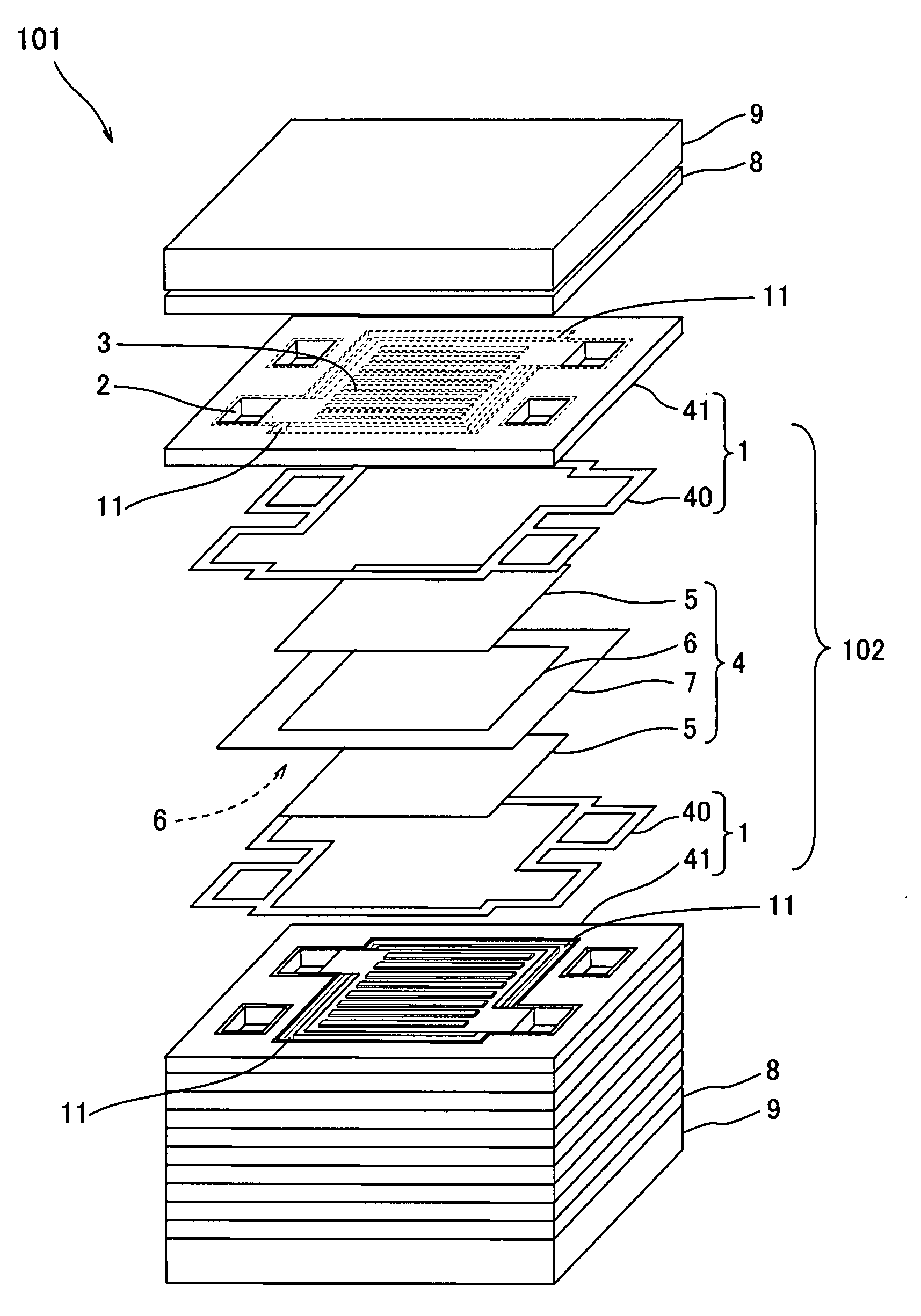
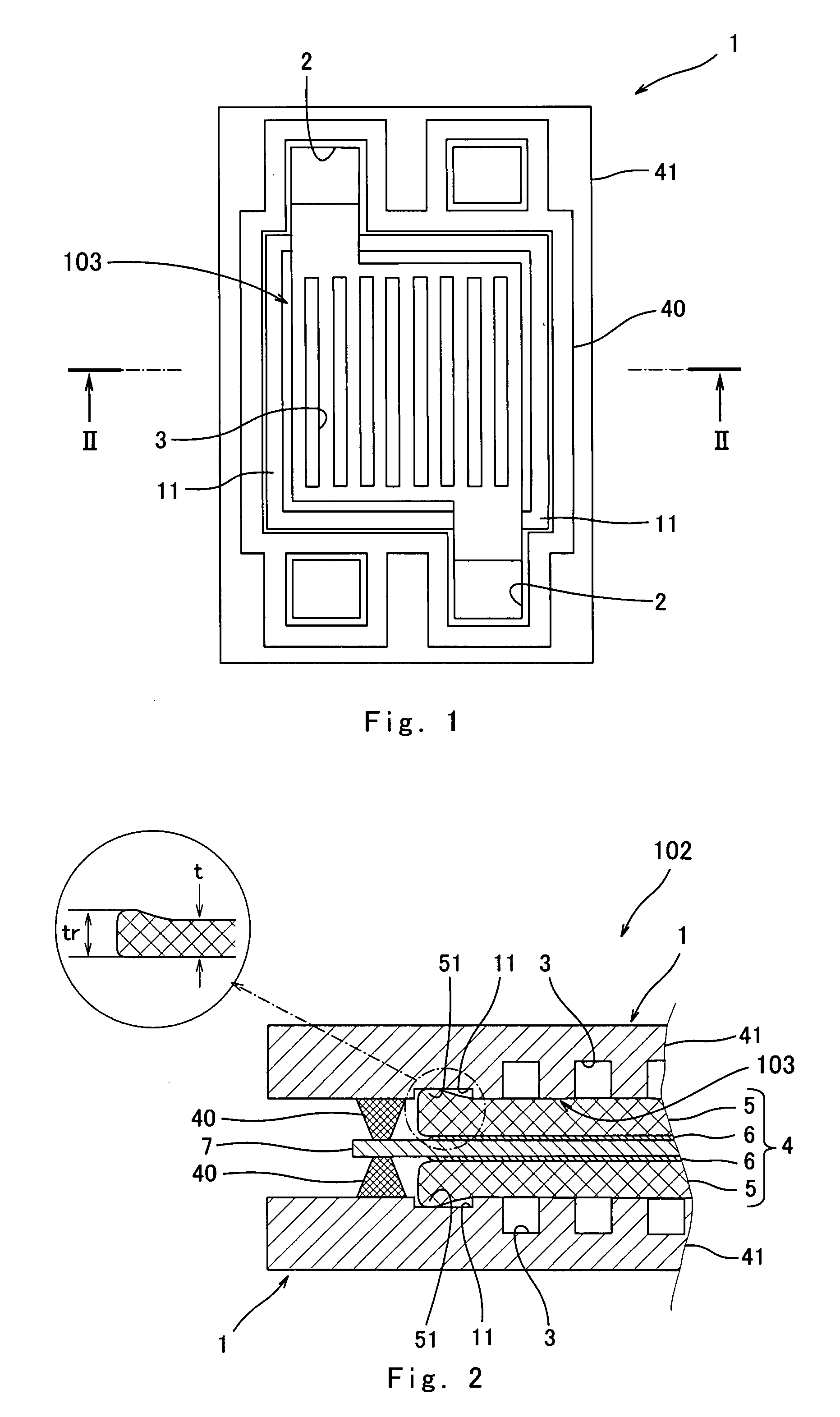
ActiveUS20090053573A1Active material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesPolymer
The invention provides a fuel cell comprising one or more cells (102) stacked therein, each of the cells (102) including:an MEA (4) having a polymer electrolyte membrane (7) and a pair of gas diffusion layers (5) sandwiching the polymer electrolyte membrane (7) except a peripheral region of the polymer electrolyte membrane (7); anda pair of self-sealing separators (1) disposed so as to sandwich the MEA (4), each of the self-sealing separators (1) being formed in a plate-like shape as a whole and composed of a separating part (41) having electrical conductivity and a sealing part (40) having more elasticity than the separating part (41), at least the separating part (41) being in contact with an associated one of the gas diffusion layers (5), the sealing part (40) being in contact with the peripheral region of the polymer electrolyte membrane (7) so as to enclose the associated one of the gas diffusion layers (5),wherein each self-sealing separator (1) has a lower area (11) for accommodating a raised portion (51) formed on the periphery of the outer surface of the associated gas diffusion layer (5) and the sealing part (40) is disposed within the lower area (11).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Fuel cell
InactiveUS20090291344A1Less likely can be bentAvoid crackingFuel cells groupingCell component detailsAdhesiveEngineering
On an anode side separator, an adhesive is applied linearly along the upper and lower edges of the four edges thereof, around a receiving part and around a through-hole and so on. On a cathode side separator, the adhesive is applied at the same locations as on the anode side separator. The adhesive functions as support members for supporting the fastening load on the edges of the separators.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fuel cell
InactiveCN1309820AAvoid technical difficultiesLow costFinal product manufactureCell electrodesCeramic compositeEngineering
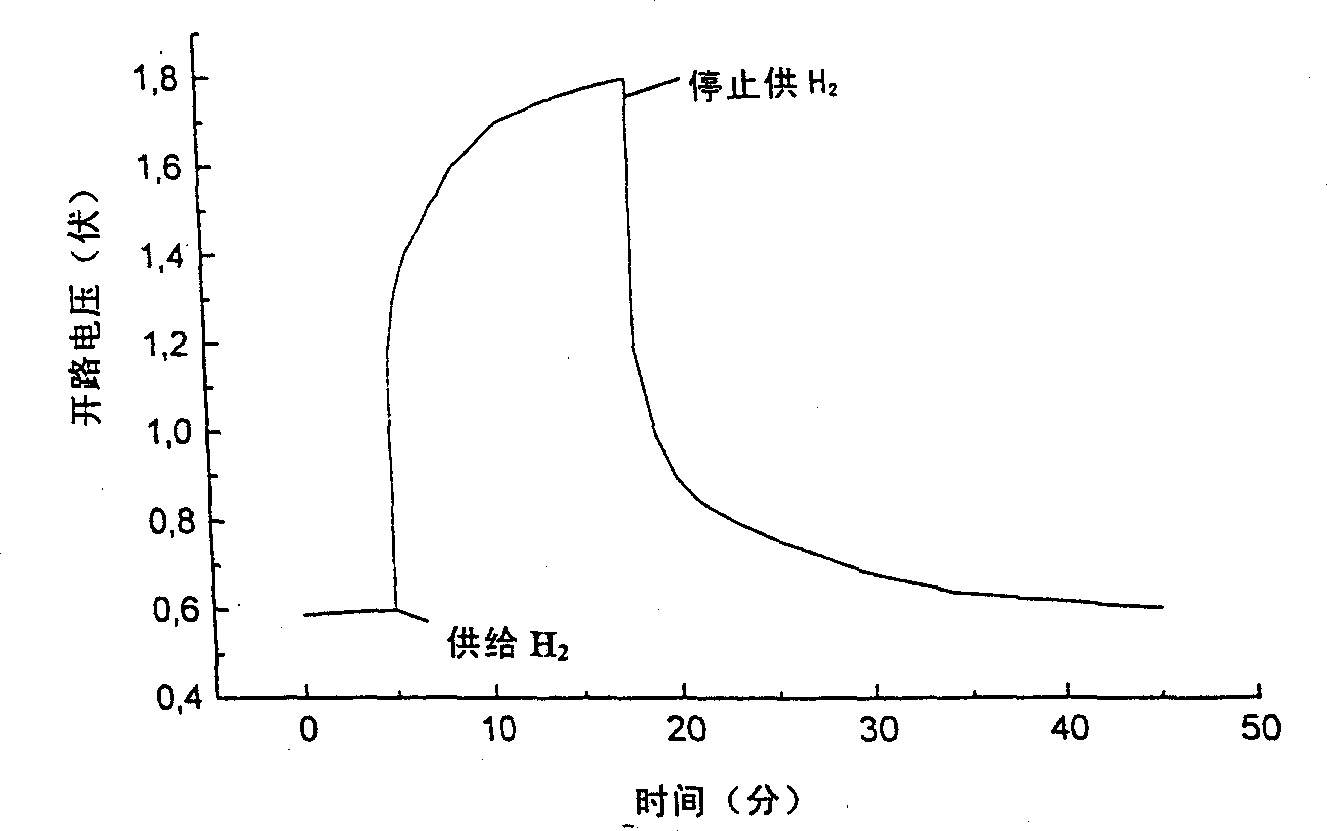
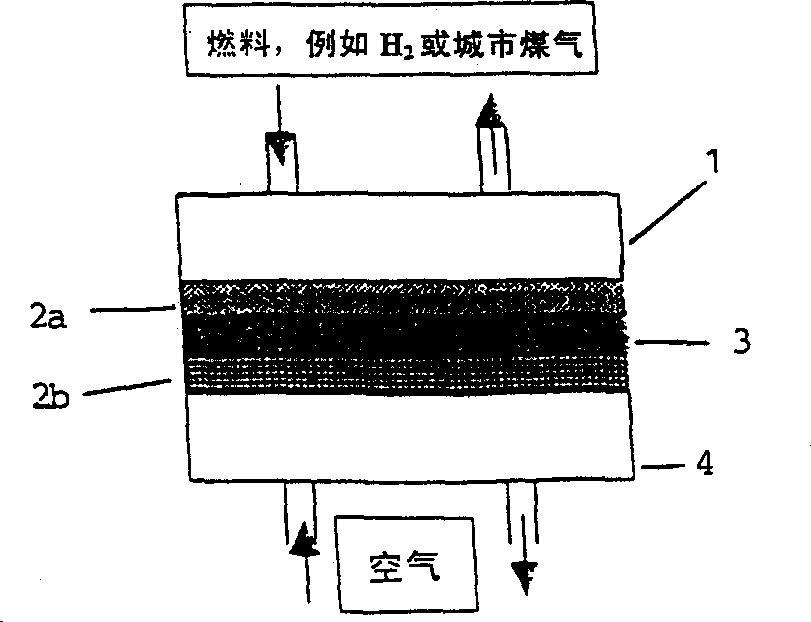
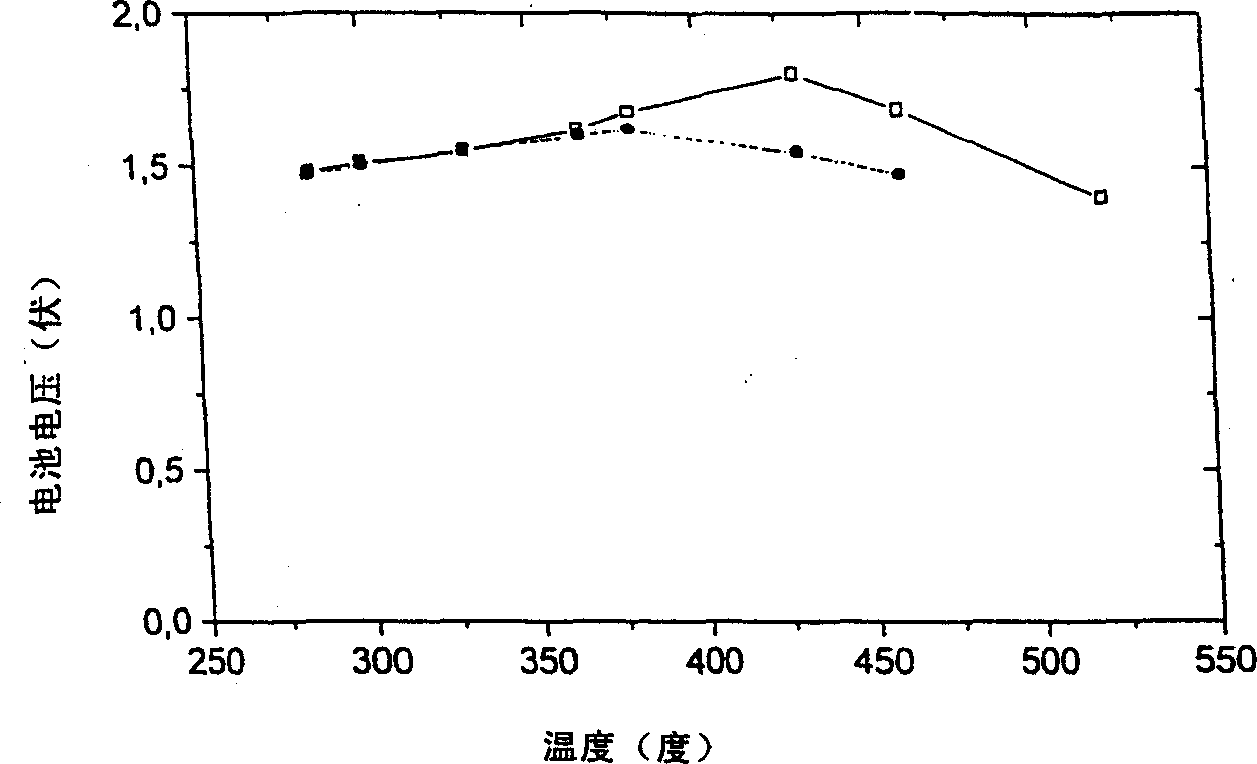
A fuel cell for production of electrical energy, such as a fuel cell, comprising a fuel chamber (1), an anode (2a), a cathode (2b), an electrolyte (3) disposed between said anode and said cathode, an oxidant chamber (4), wherein said chambers (1 and 4) enclose said anode, cathode and electrolyte, wherein a fuel flowing from the fuel chamber is oxidized at the anode, thereby producing electrical energy, wherein said electrolyte (3) is a ceramic composite electrolyte comprising at least one salt and at least one oxide in mixture.
Owner:朱斌
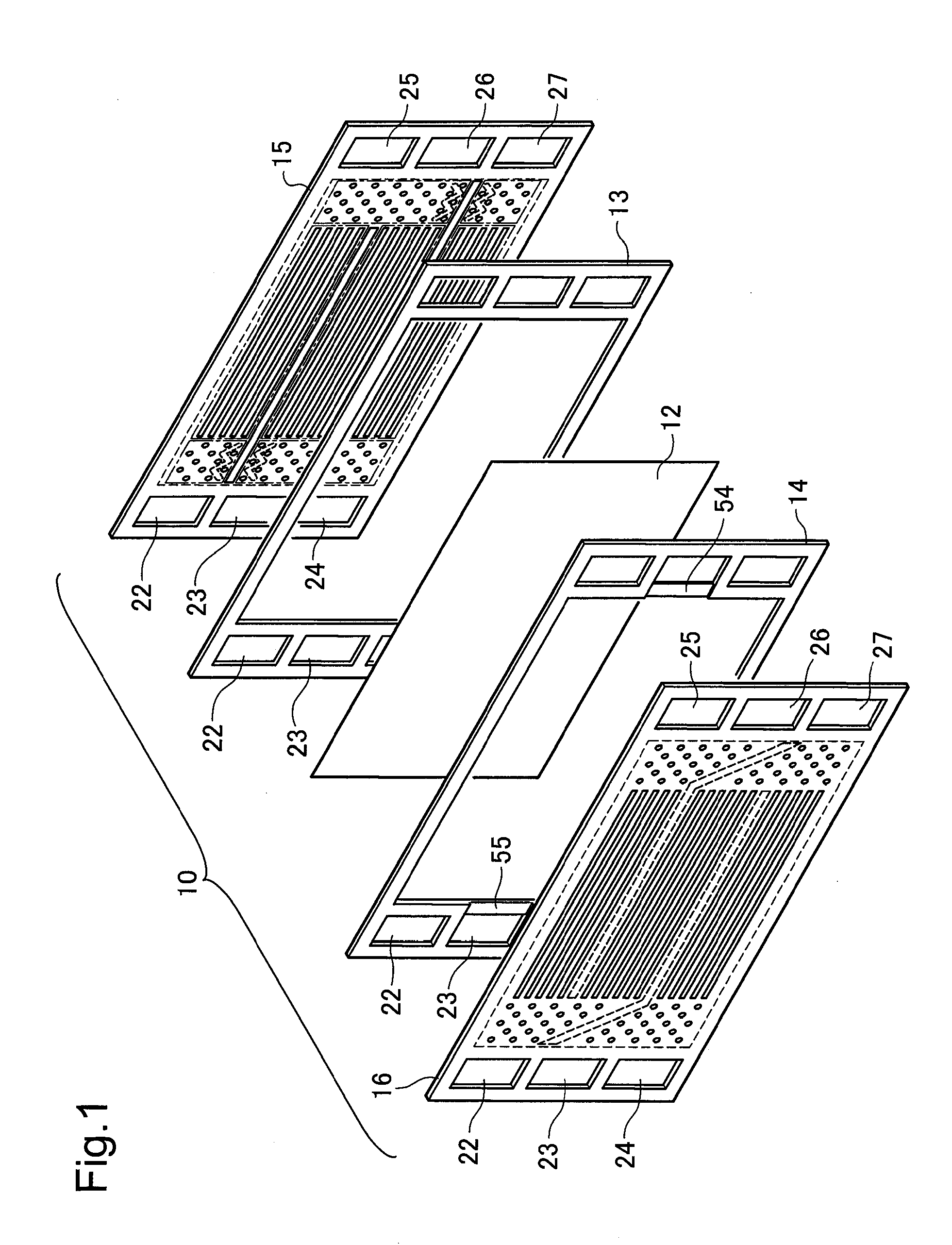
Fuel cell
ActiveUS20130115541A1Easy and reliable positioningFuel cells groupingCell component detailsMiniaturizationEngineering
A fuel cell is provided with a membrane electrode assembly provided with a frame, both of which are sandwiched between two separators. The fuel cell is configured such that reactive gas is circulated between the frame and the separators. The frame and both separators each have manifold holes, the rims of the manifold holes of frame extend into the manifold holes in the separators, and protrusions cover the inner peripheral surfaces of the manifold holes in at least one of the separators. This structure makes possible the easy and accurate position and integration of the separators and the frame, and fuel cell miniaturization can be achieved because space to position the protrusions is not needed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel cell
PendingCN105470542AReduce pressure lossSimple structureReactant parameters controlPore diameterHydrogen supply
Owner:SHANGHAI PRECISION METROLOGY & TEST RES INST
Power-on control protection system of fuel cell bus
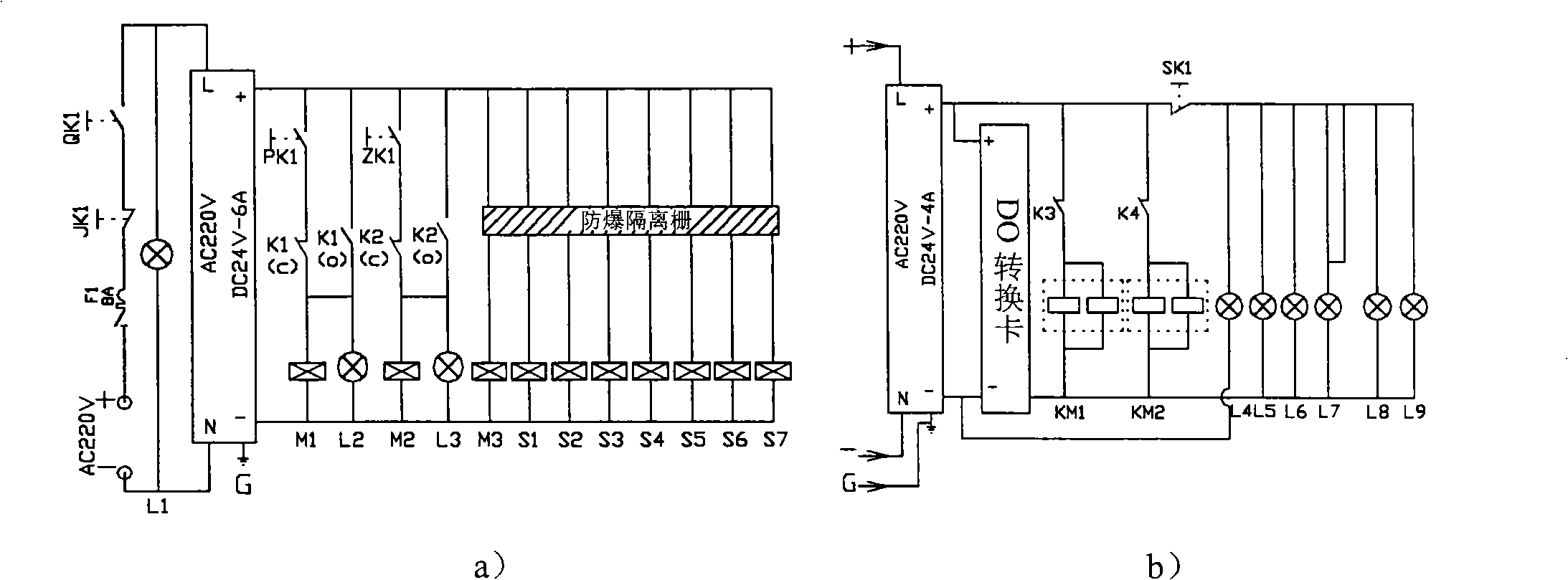
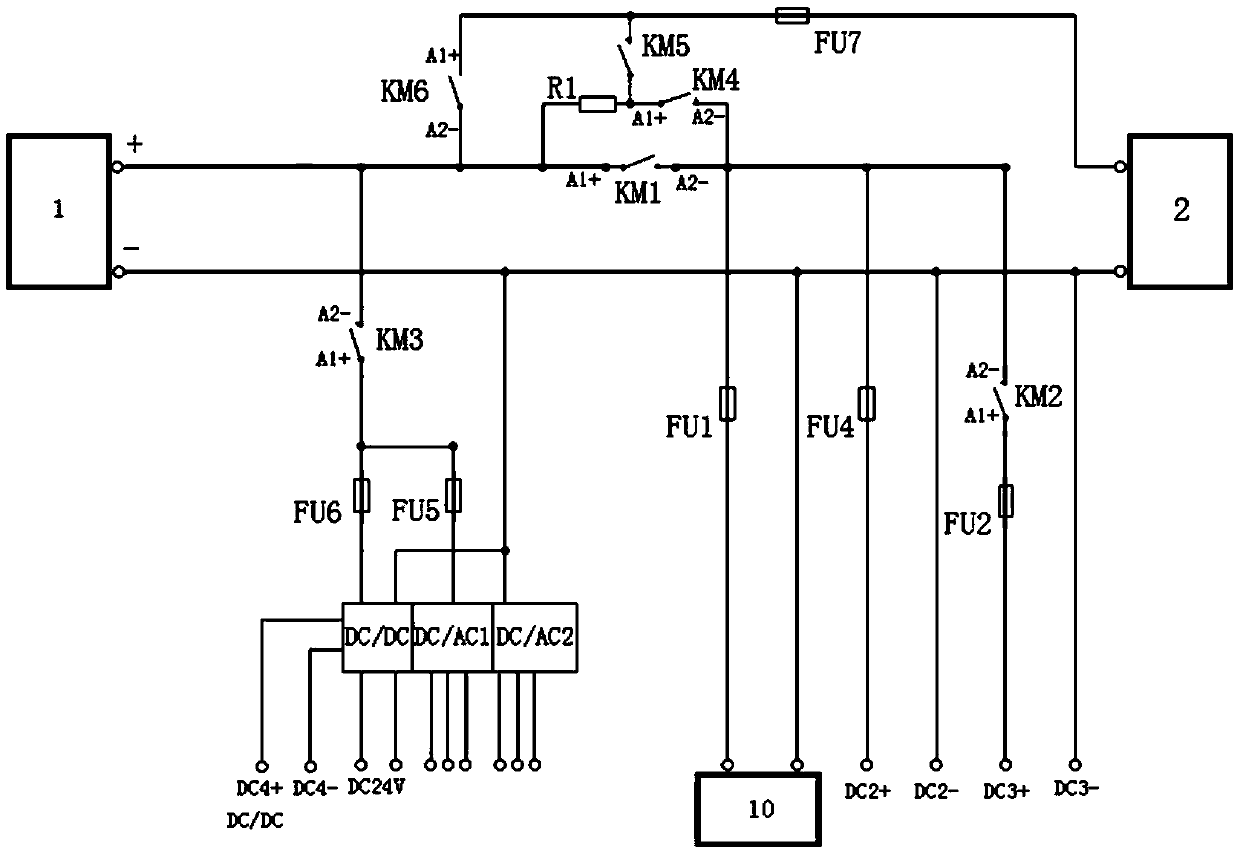
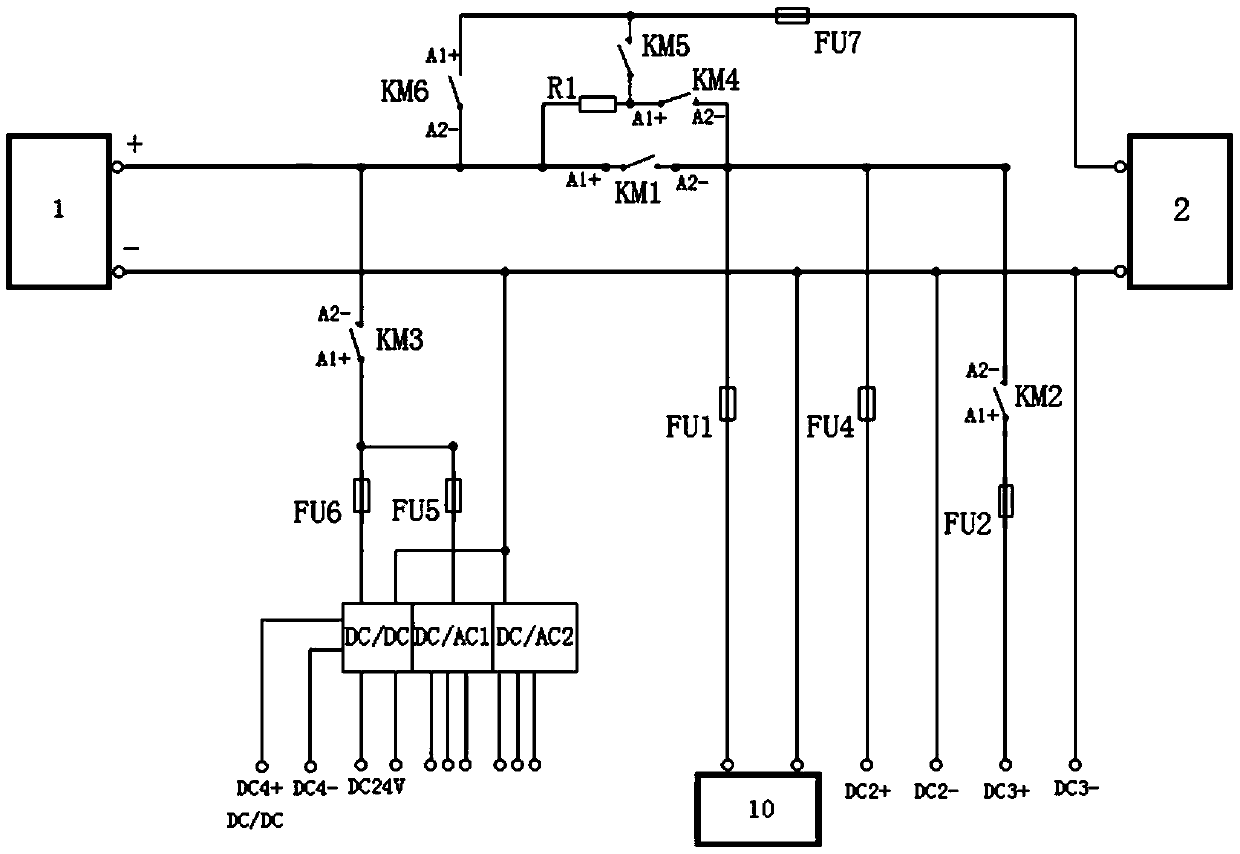
PendingCN111114325AWithout compromising securityImprove experienceElectric devicesAlarmsElectric controlControl theory
The invention relates to a power-on control protection system of a fuel cell bus. The system comprises a VCU, an FCU, pre-charging loops, a high-voltage contactor, a hydrogen concentration sensor, a display screen and an alarm, wherein the pre-charging loops are connected with the analog quantity output end of the VCU; two pre-charging loops are provided; each group comprises two branches which are connected in parallel; the first branch in the first group comprises a fuel cell relay; the second branch in the first group comprises a pre-charging resistor and a fuel cell pre-charging relay connected with the pre-charging resistor in series; the first branch in the second group is a main positive relay; the second branch in the second group comprises a pre-charging resistor and an electric control pre-charging relay connected with the pre-charging resistor in series; and the pre-charging resistor is shared by the two pre-charging loops. Compared with the prior art, it is ensured throughpower-on protection that the fuel cell bus cannot be powered on by high voltage when hydrogen leaks, so that the driving safety is improved, meanwhile, a pure electric system can work normally, and the error-tolerant rate and the customer experience are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI SUNLONG BUS
Fuel Cell
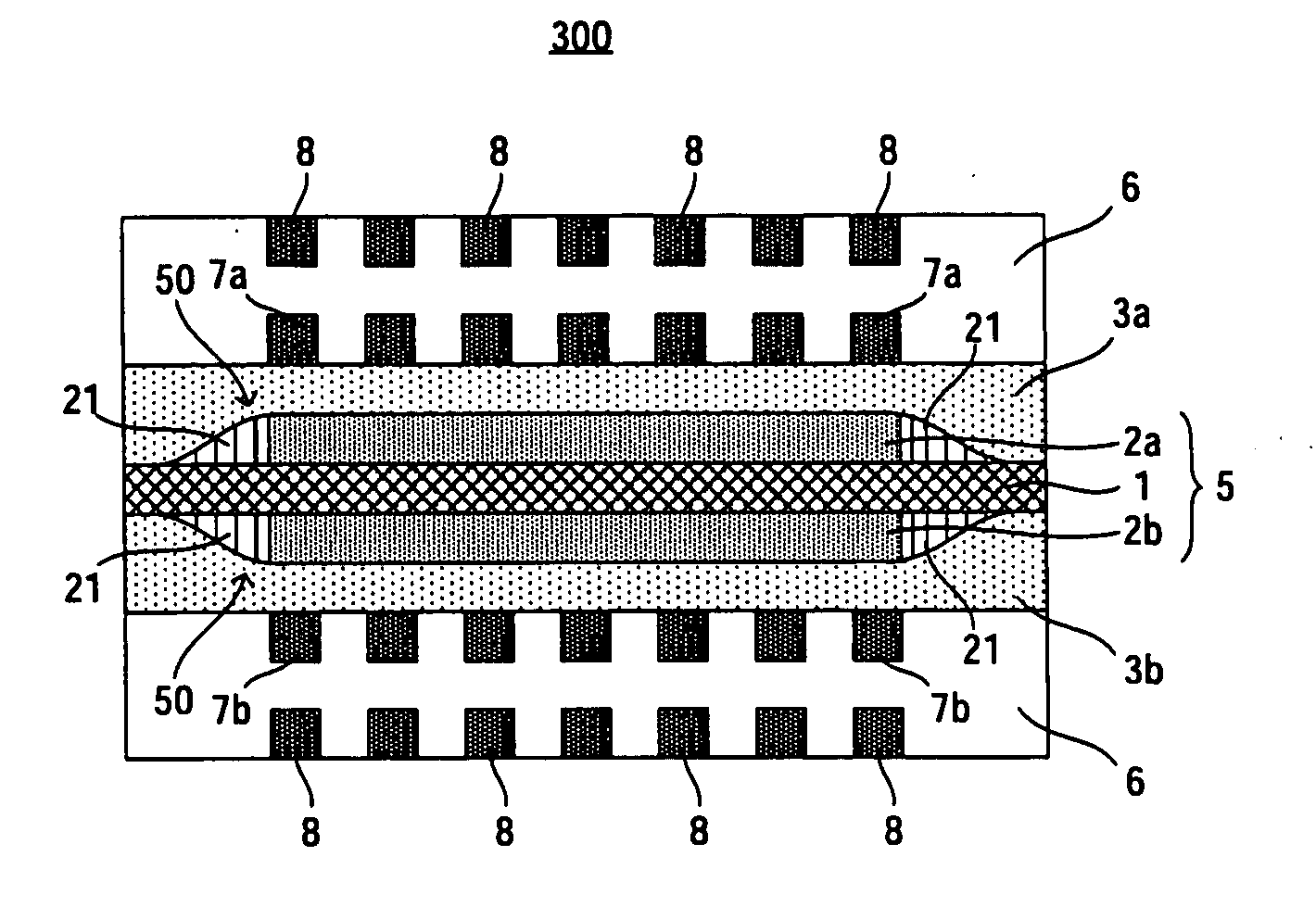
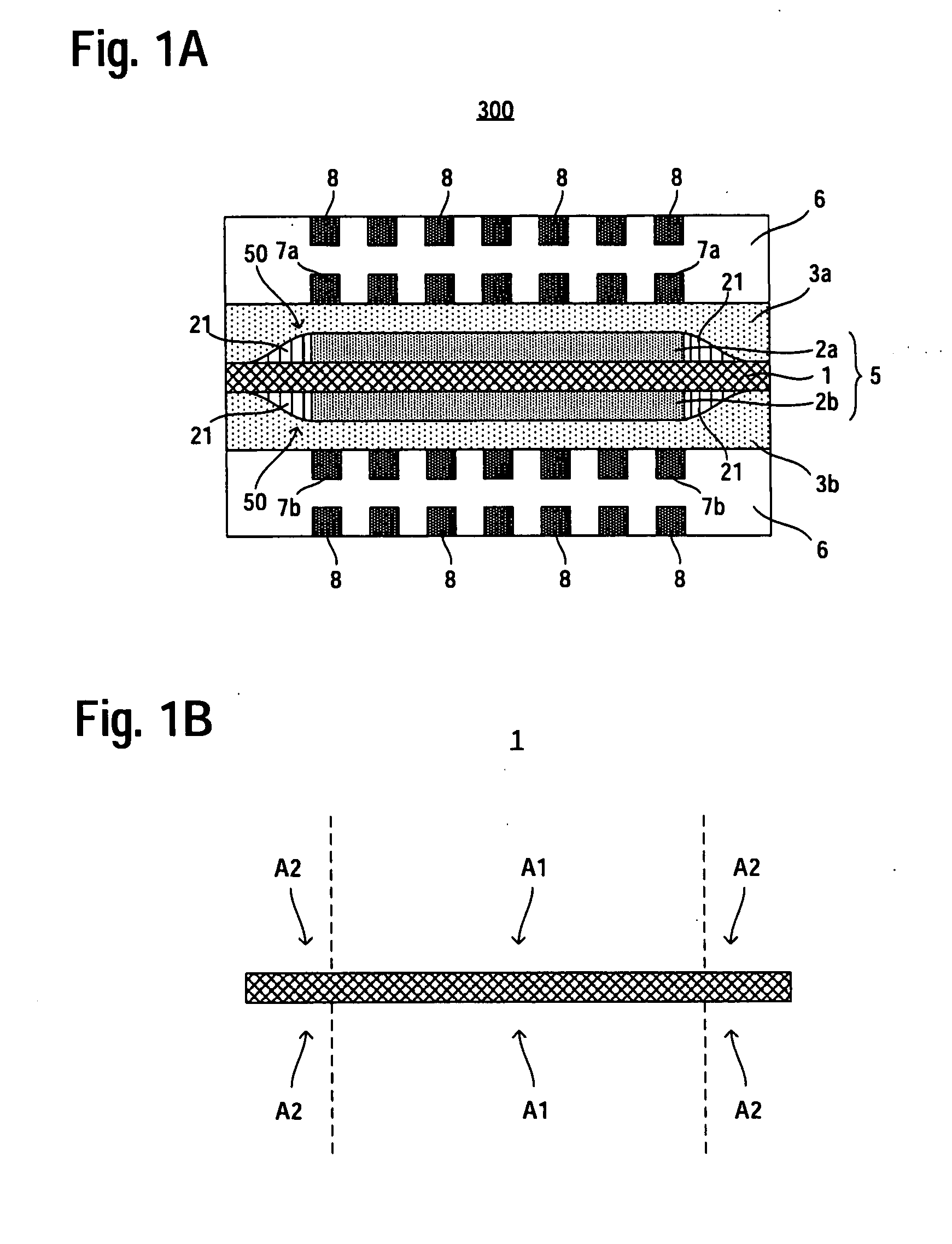
InactiveUS20090023028A1Increased durabilityReduce the amount requiredCell electrodesFuel cell auxillariesHydrogen peroxide breakdownEngineering
A fuel cell (100) capable of improving durability is provided. The fuel cell includes an electrolyte membrane (1), catalyst layers (2a, 2b) stacked on both sides of the electrolyte membrane (1), respectively, and diffusion layers (3a, 3b) stacked outside of the respective catalyst layers (2a, 2b). A stacked surface of each of the catalyst layers (2a, 2b) is smaller than a stacked surface of the electrolyte membrane (1), and a stacked surface of each of the diffusion layers (3a, 3b) is larger than the stacked surface of each of the catalyst layers (2a, 2b) and smaller than the stacked surface of the electrolyte membrane (1). If a surface of the electrolyte membrane (1) which surface is to contact with one of the catalyst layers (2a, 2b) is A1 and a surface of the electrolyte membrane (1) which surface is out of contact with one of the catalyst layers (2a, 2b) and on which a space is formed between the electrolyte membrane (1) and one of the diffusion layer is A2, the surface A2 contains a single metal element having a hydrogen-peroxide decomposing performance and / or a compound containing the single metal element.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Solid oxide fuel cell
InactiveUS7517601B2Good value for moneyGreat electrical powerFuel cells groupingCell electrodesEngineeringFuel cell bus
A fuel cell including at least one single cell C having an electrolyte 3, a fuel electrode 5, and an air electrode 7, wherein the single cell C is supported on a substrate 1 and the electrolyte 3 is disposed on a first surface of the substrate 1, with the fuel electrode 5 and the air electrode 7 disposed on the first surface of the substrate 1 so as to sandwich the electrolyte 3.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell and fuel cell system including the same
InactiveUS20090202882A1Avoid deterioration of cell performanceFuel cells groupingCell electrodesPolymer electrolytesEngineering
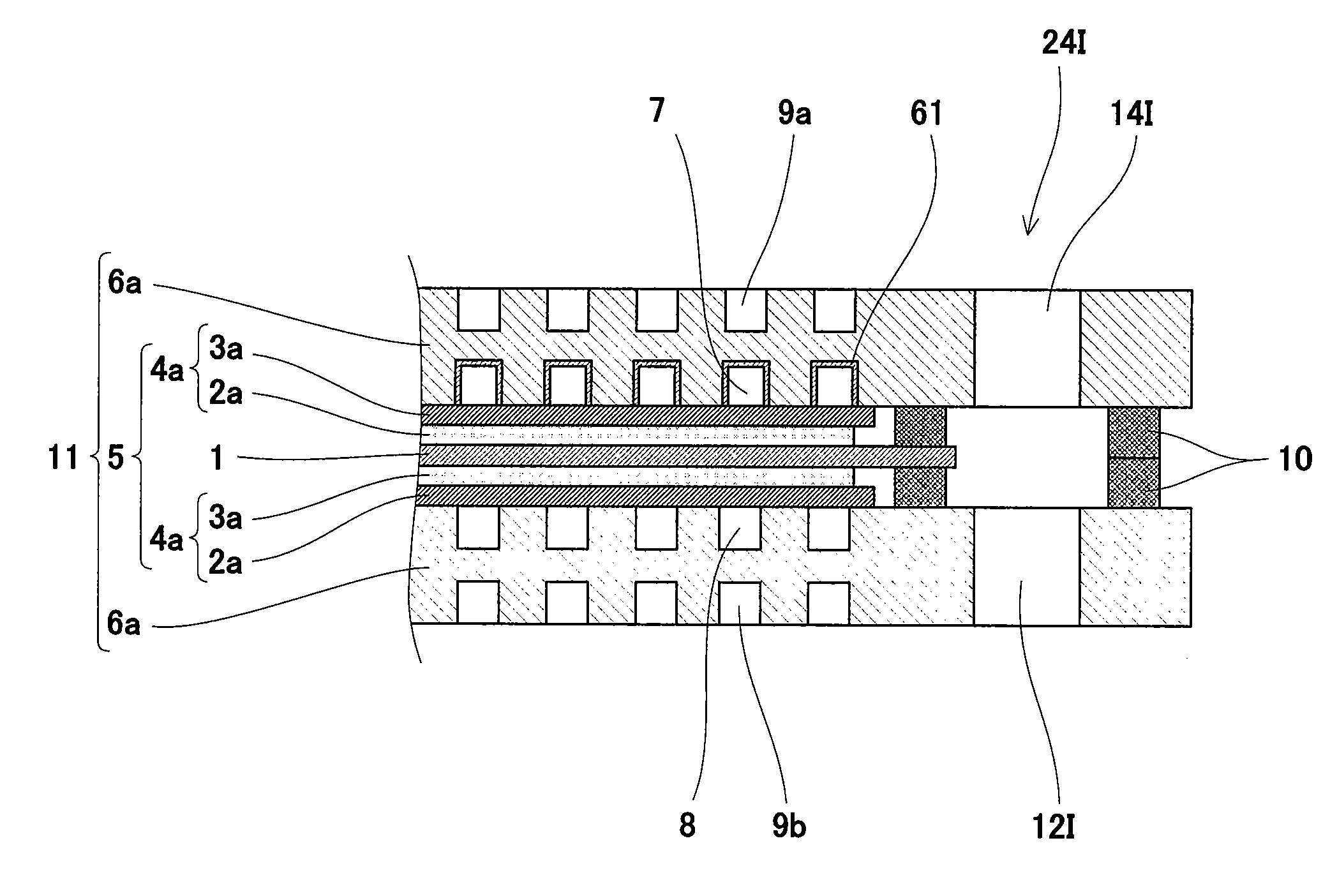
A polymer electrolyte fuel cell includes a cell stack (51) formed by stacking cells (11), each of which includes: an MEA (5) having a polymer electrolyte membrane (1), and an anode (4a) and a cathode (4b) sandwiching the polymer electrolyte membrane (1); and an anode separator (6a) and a cathode separator (6b) disposed to sandwich the MEA (5), an anode gas internal supplying channel is formed to supply a fuel gas and air to the anode (4a), and a CO removing catalyst layer (61) containing a CO removing catalyst is formed in the anode gas internal supplying channel.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Real-time global optimization intelligent control system and method for fuel cell bus
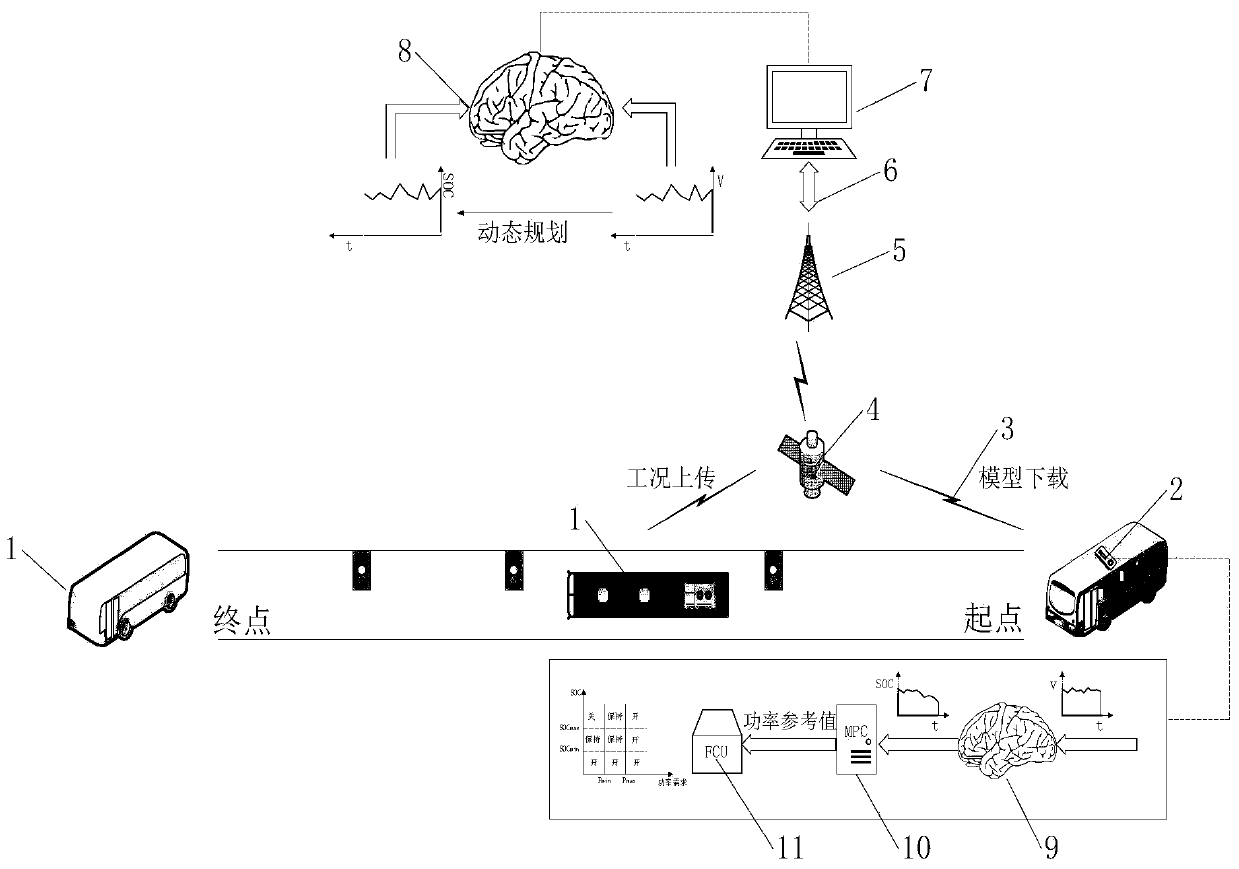
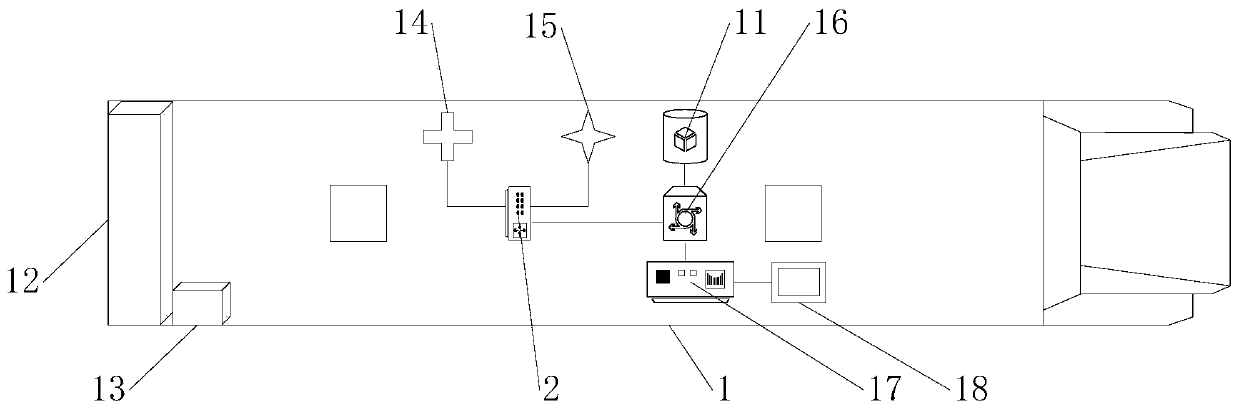
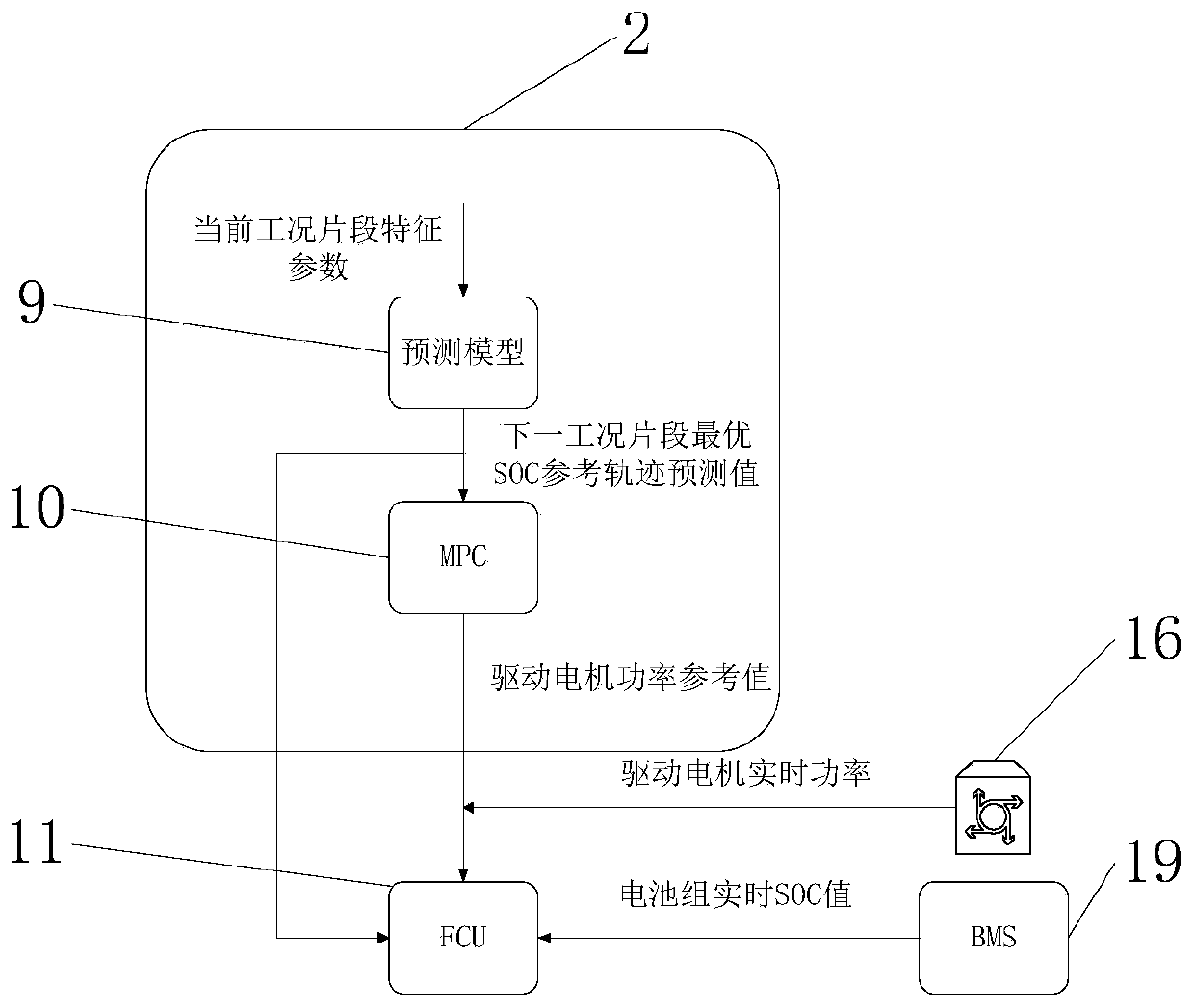
ActiveCN110852482AAvoid repetitionSave storage spaceKernel methodsForecastingCommunication unitElectric machinery
The invention discloses a real-time global optimization intelligent control system and method for a fuel cell bus, and the method comprises the steps that a vehicle driving communication unit downloads prediction model parameters to a fuel cell vehicle controller when the fuel cell bus is at a driving starting point; a battery management system and a driving motor real-time power calculation module respectively obtain the real-time SOC and the real-time power of the battery pack; an optimal SOC prediction model module obtains an optimal SOC reference trajectory prediction value of a next working condition segment, the MPC prediction control module obtains a power reference value, and all the parameters are input into the fuel cell control unit to judge the working state of the fuel cell. In the driving process, the bus continuously uploads fragmented working condition information through the bus driving communication unit, and after each travel is completed, the cloud analysis workstation performs incremental learning training through the working condition information uploaded in real time to update the optimal SOC prediction model. According to the invention, the fuel cell bus canbe accurately and flexibly controlled in real time, and the fuel consumption is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com