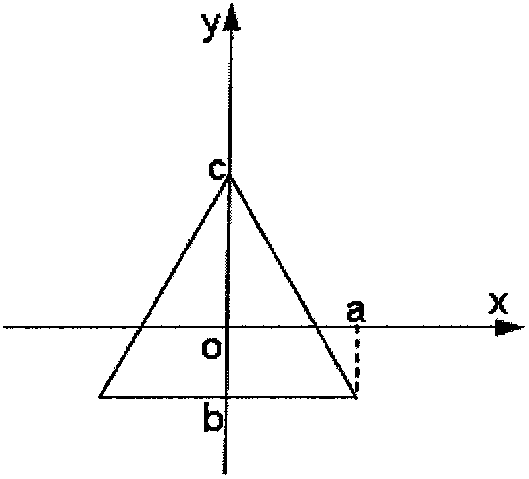Patents
Literature
95 results about "Mass element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic Masses. The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope.
Computer-implemented automated building design and modeling and project cost estimation and scheduling system
InactiveUS6859768B1Reduction in building delivery timeProductionGeometric CADBuying/selling/leasing transactionsObject compositionBuilding design
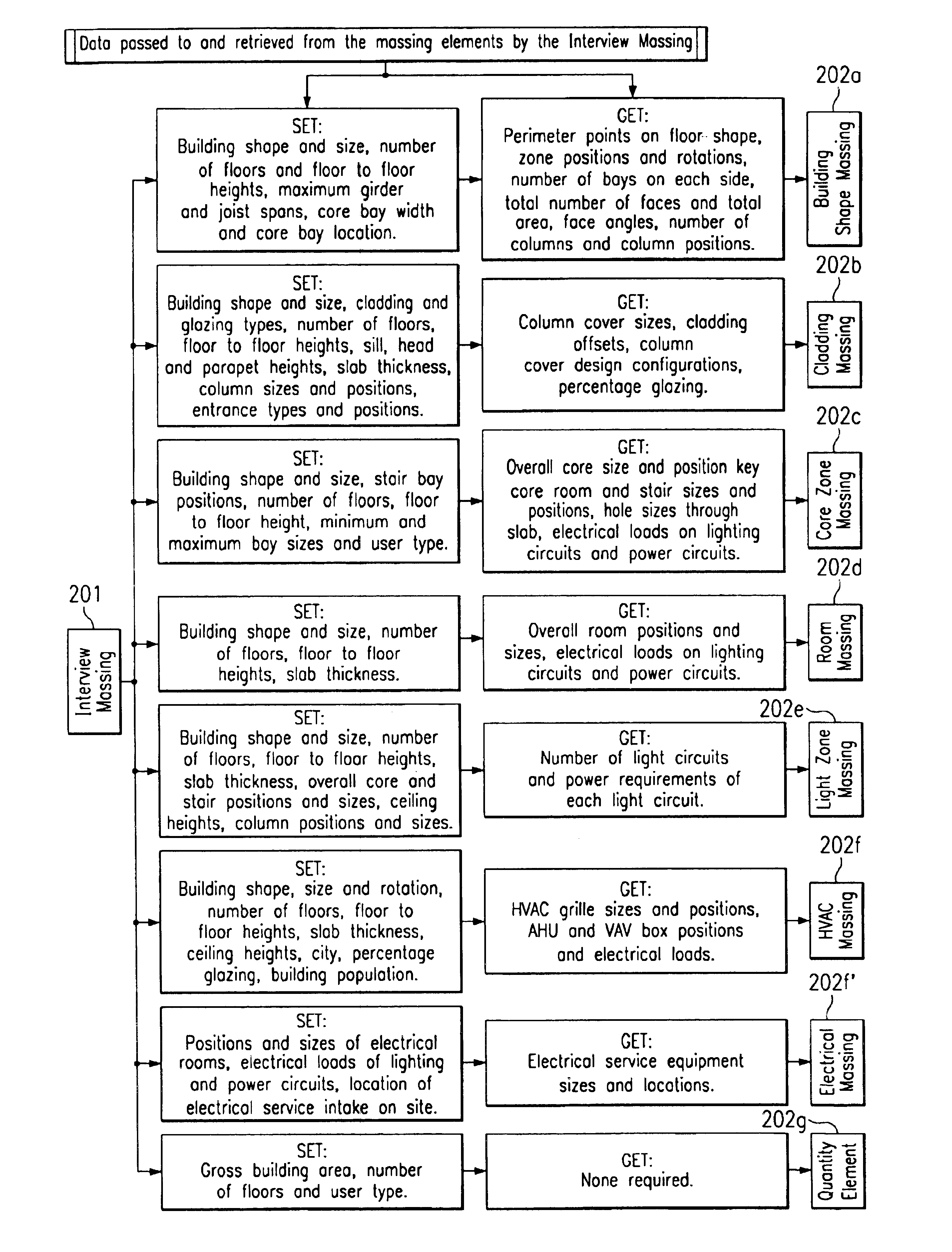
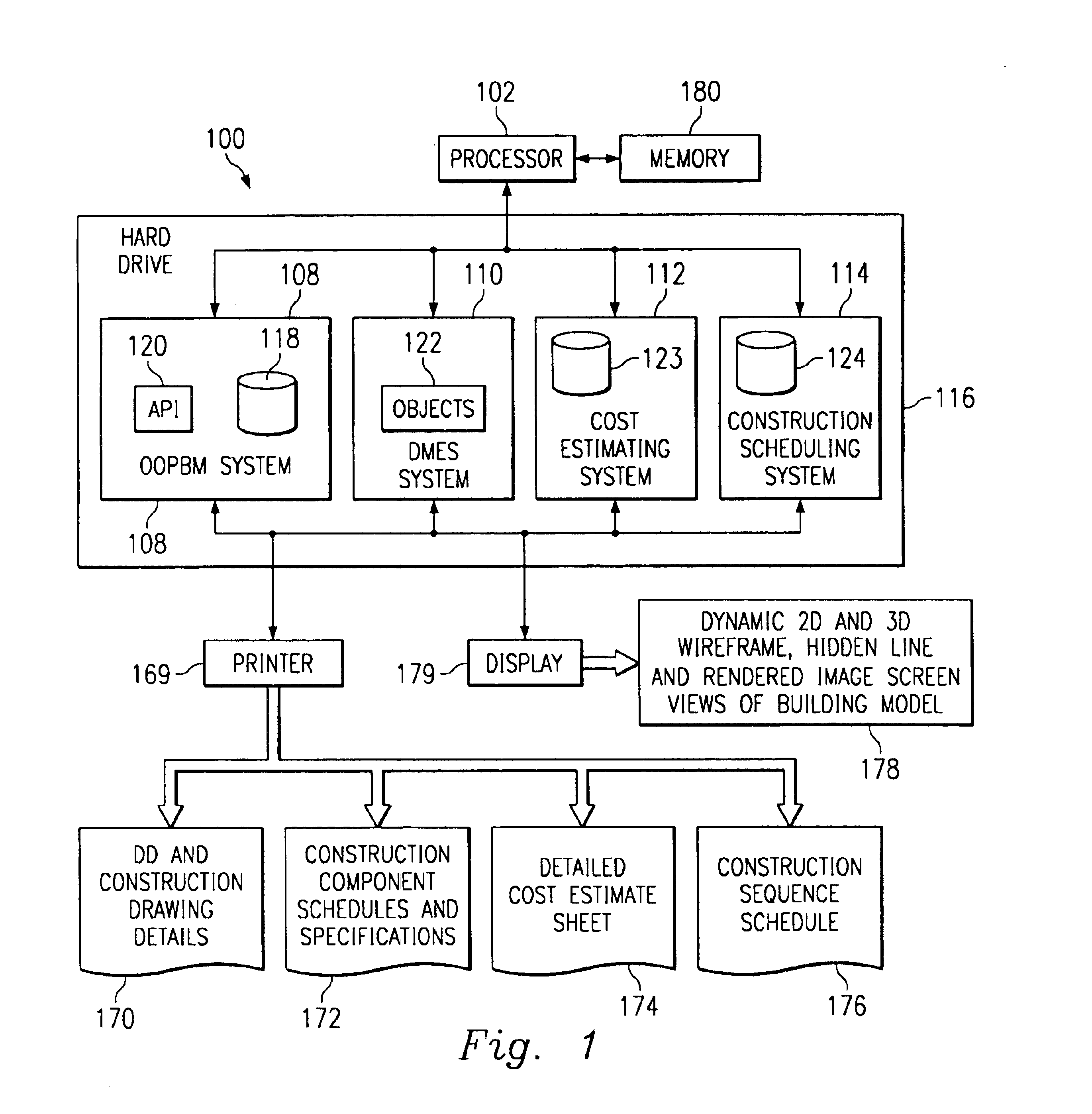
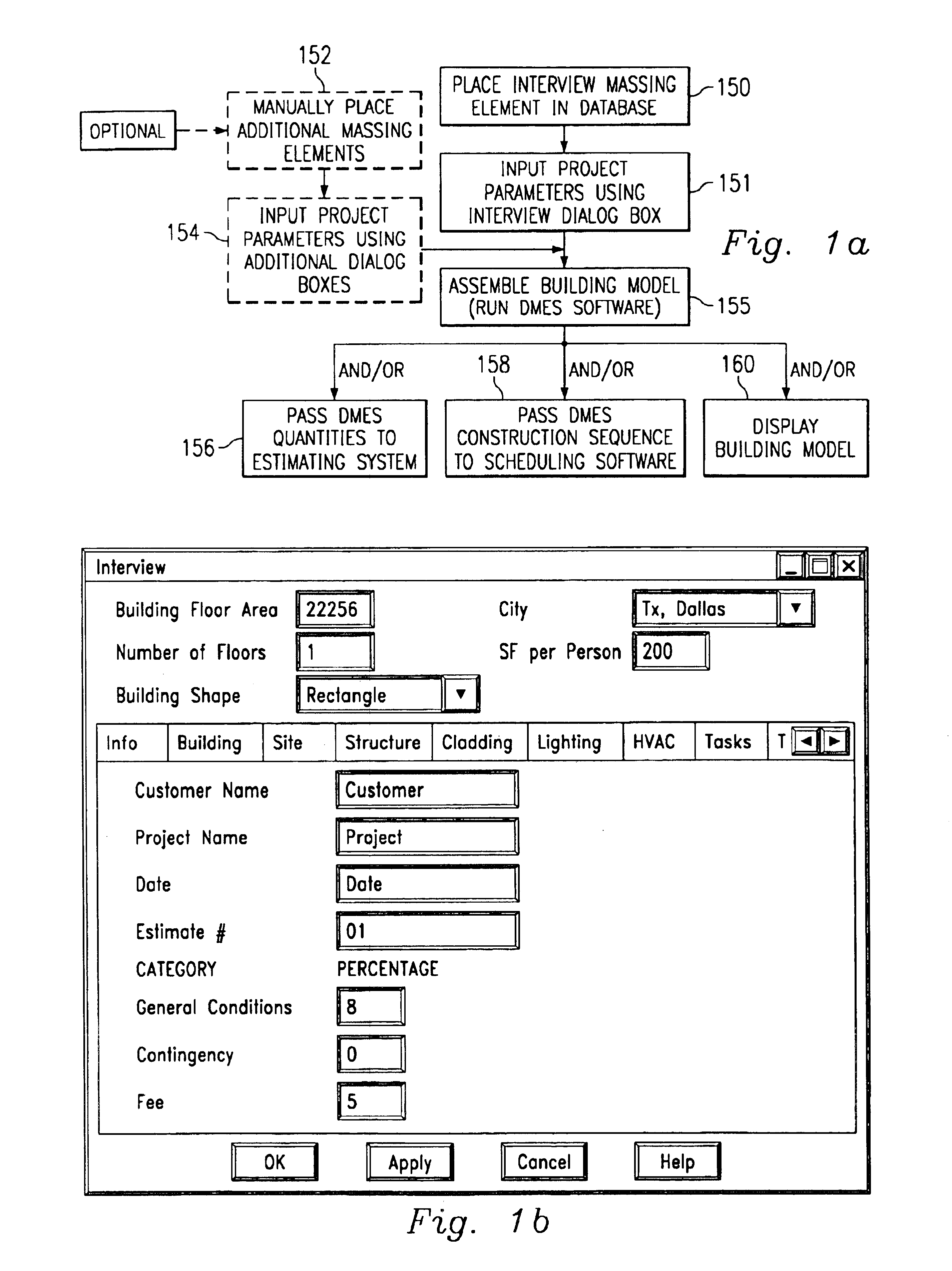
A computer-implemented automated building design and modeling and construction project cost estimating and scheduling system (“DMES system”) is described. The DMES system provides a central source for all of the design and construction information for a construction project in a coordinated two-dimensional and three-dimensional spatial database that is freely accessible by all of the members of an interdisciplinary construction project team as a means to produce automatically coordinated design development and construction document information. The DMES system acquires and stores all of the appropriate design, engineering, and construction expertise and information available for any building type for use in automatically assembling and coordinating the design, cost-estimating, and scheduling for a construction project. In one embodiment, the DMES system consists of a plurality of objects, comprising elements and massing elements arranged in an assembly hierarchy. Each of the objects includes programming code that defines an interface and discrete internal functions that define its behavior. When instantiated in the database, the objects automatically create further instances of other objects in the hierarchy, which in turn do the same, thus assembling a complete building model automatically from the initial manually-placed instance. The building model enables automatic generation of drawings and cost and scheduling information. By running automatic iterations of the building model, multiple designs may be evaluated to determine the optimum design.
Owner:BECK TECH
Frequency compensated oscillator design for process tolerances
InactiveUS20050073078A1Improve immunityImprove production yieldPortable framesImpedence networksEngineeringMass element
A continuous or distributed resonator geometry is defined such that the fabrication process used to form a spring mechanism also forms an effective mass of the resonator structure. Proportional design of the spring mechanism and / or mass element geometries in relation to the fabrication process allows for compensation of process-tolerance-induced fabrication variances. As a result, a resonator having increased frequency accuracy is achieved.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Torsional vibration damper
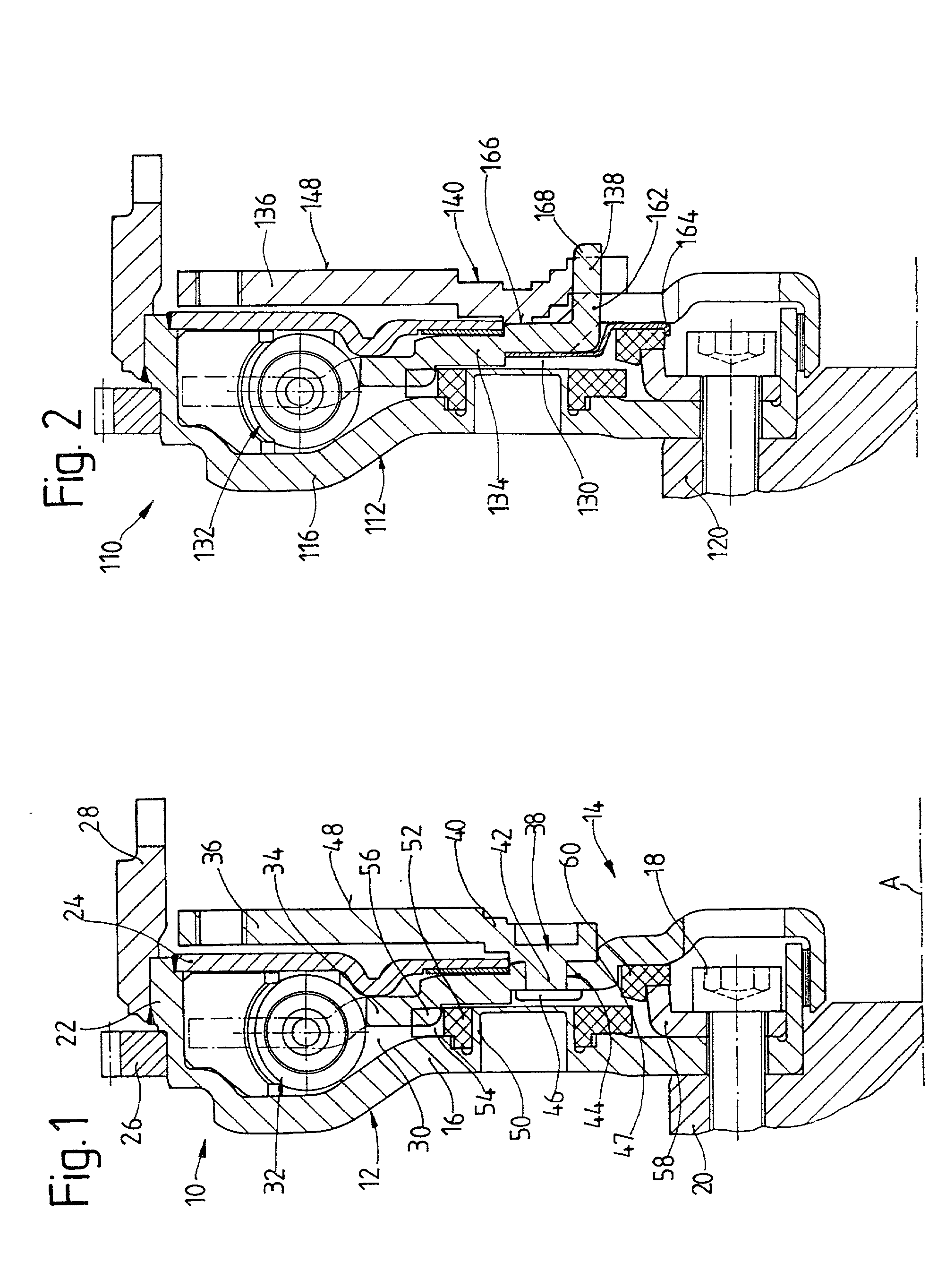
A torsional vibration damper on the bridging clutch of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement has a first connecting device, which can be brought into working connection with the clutch housing and with a drive-side transmission element. The drive-side transmission element is connected via first energy-storage devices to an intermediate transmission element. The torsional vibration damper also has a second connecting device for establishing a working connection via second energy-storage devices between the intermediate transmission element and a takeoff-side transmission element, which is connected to a takeoff-side component of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement. The intermediate transmission element accepts a mass element, located operatively between the two connecting devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Weighted bioacoustic sensor and method of using same
InactiveUS20070113654A1Low acoustic impedanceEfficient amplificationAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSamplingElectrical conductorTransducer
A sensor for sensing bioacoustic energy includes a housing comprising an interfacing portion configured to establish coupling with a body part during use. The sensor includes a transducer element coupled to the interfacing portion of the housing and configured to sense sounds produced by matter of biological origin. One or more conductors are coupled to the transducer element. A mass element is compliantly coupled to a surface of the transducer element. Intervening material is disposed between the transducer element surface and the mass element, and allows for differential motion between the transducer element surface and the mass element during excitation of the transducer element.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Mass damper
ActiveUS20140008163A1Reduce tensionSmall sizeRotating vibration suppressionNon-rotating vibration suppressionEngineeringTuned mass damper
A tuned mass damper comprising a frame, at least one bendable spring element being connected from its ends to the frame, and at least one mass element being connected to the spring element at a distance from the ends of the spring element, at least one movable spring support element for adjusting the tuning frequency of the damper, and means for moving the spring support element.
Owner:WARTSILA FINLAND OY
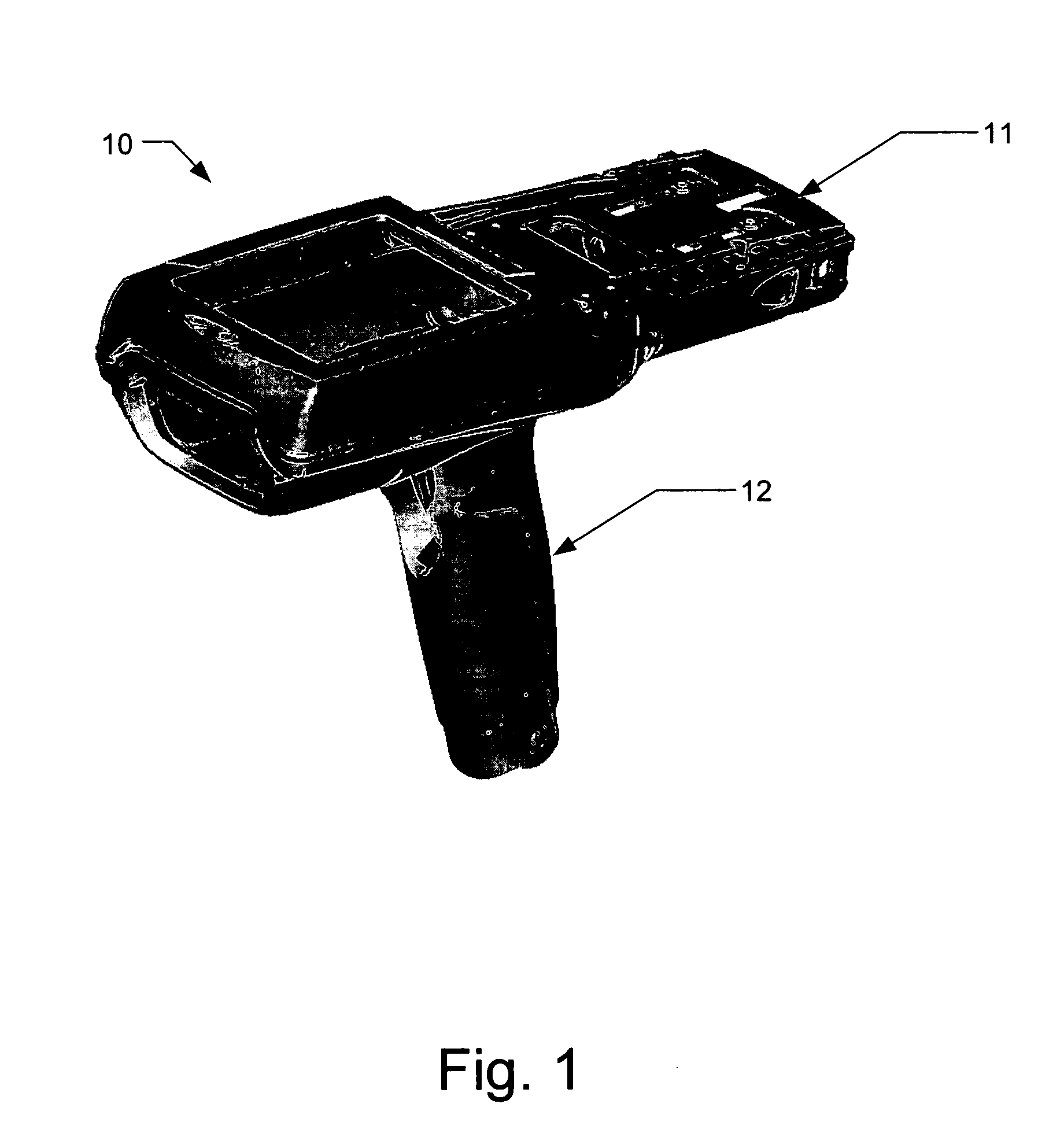
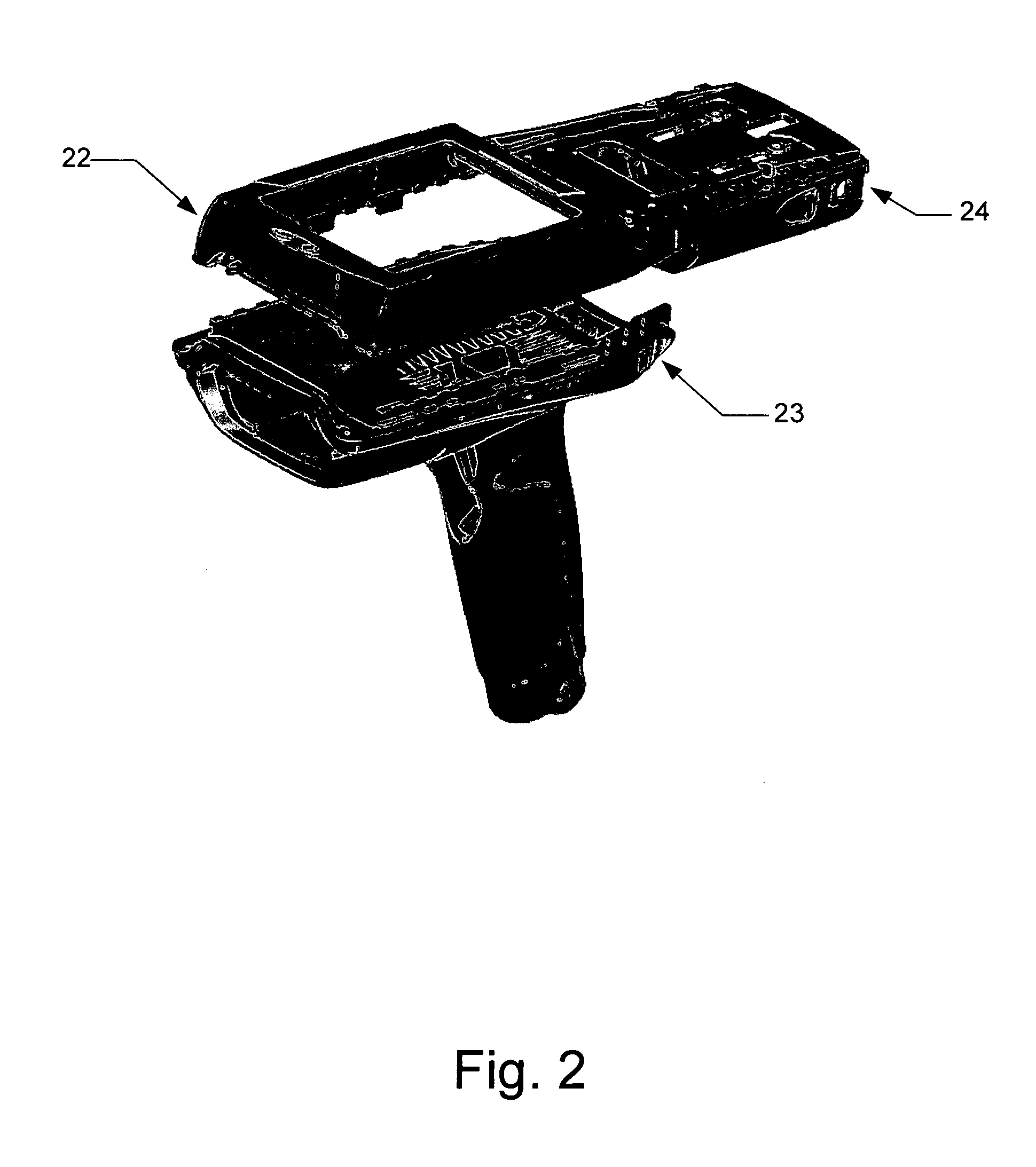
Mobile terminal with ergonomic housing
ActiveUS7195169B2Increase profitIncreased durabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationDisplay deviceHand held
The subject invention relates to systems and methods for employing a housing as part of a hand held scanner as to increase utility and add ruggedness. The housing comprises an upper top housing and lower bottom housing, with the top housing comprising a set of accessory rails adapted to accept accessories associated with the hand held scanner, and the lower housing including an adjustable mass element for balancing a weight of the scanner. Also, top housing can be adapted to accept various key pad configurations via a transitional mounting frame, and the bottom housing can hold a stylus. A bar code scanner system employing such housing can incorporate displays located on various sides of the housing and / or key pads to facilitate a reading from the scanner at slanted angles.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH LLC
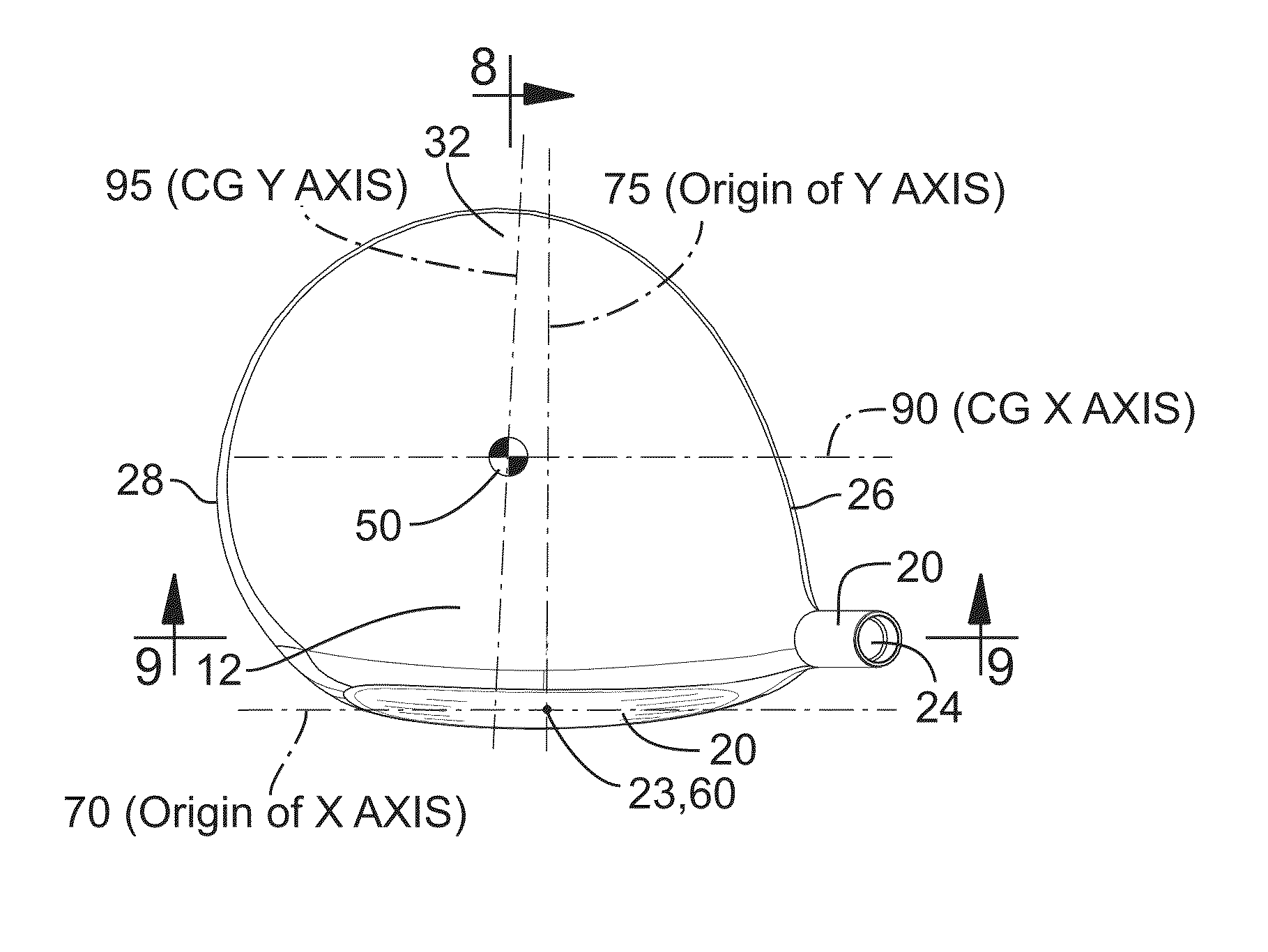
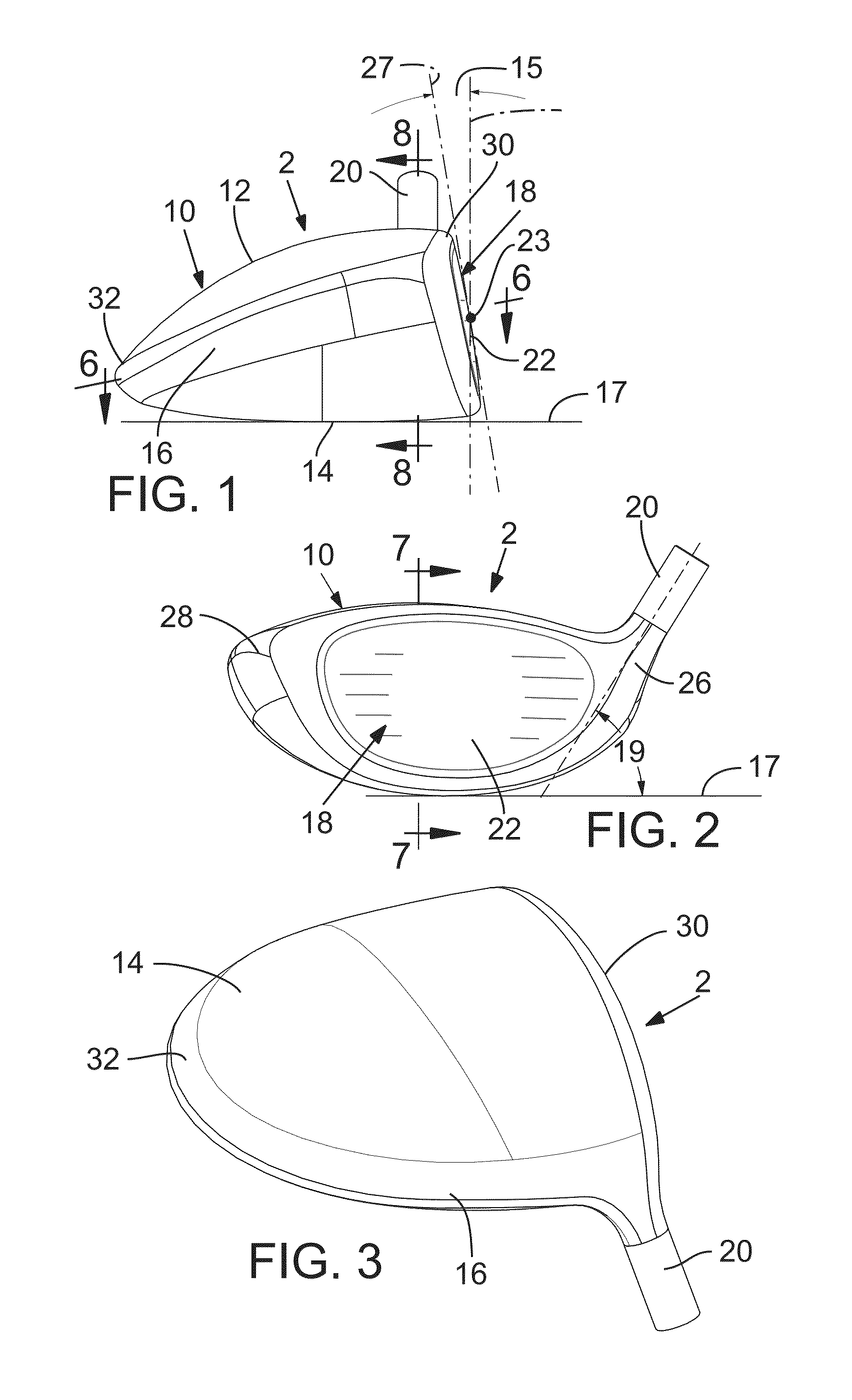
Golf club head
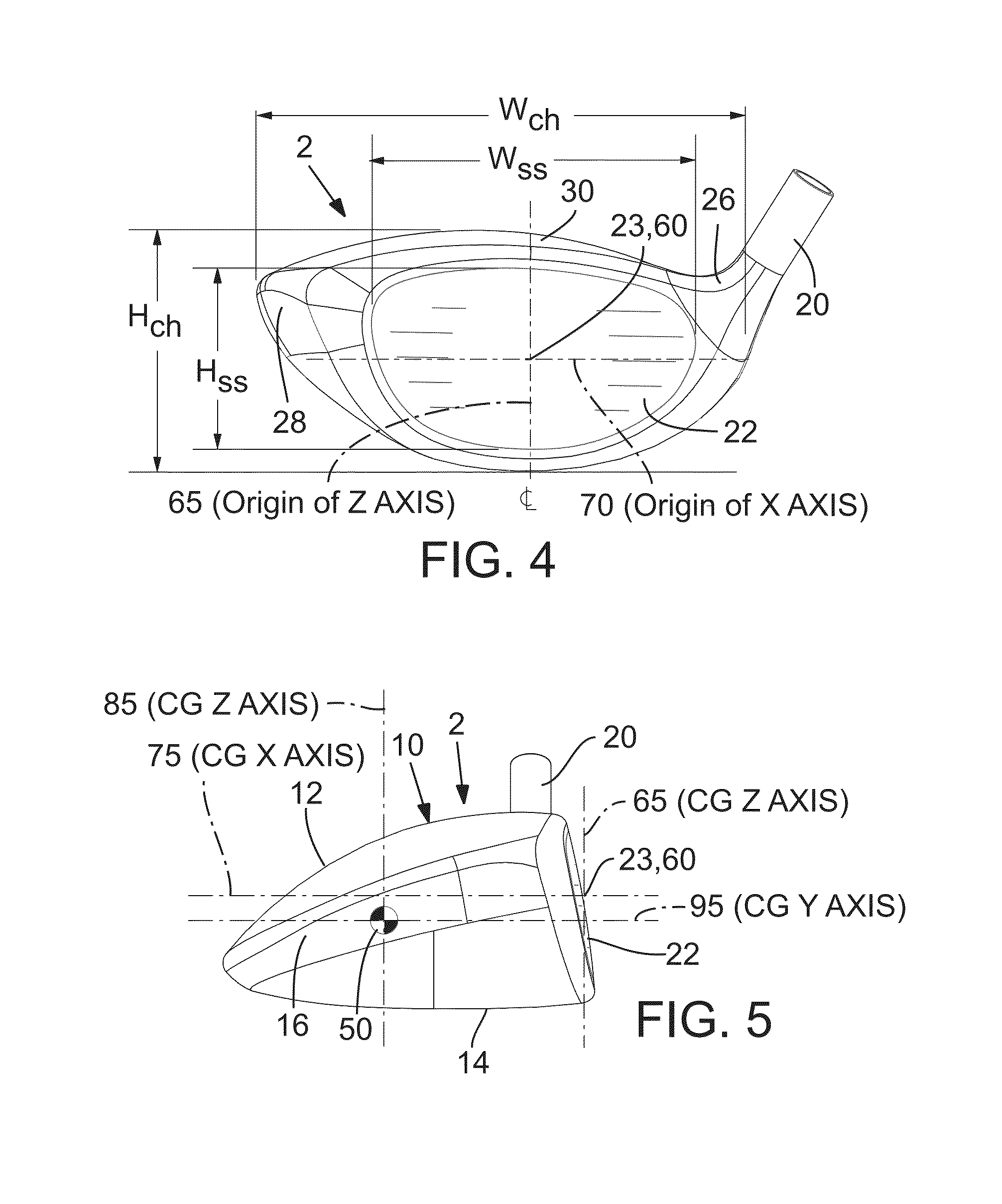
ActiveUS8647216B2Increased forgivenessSmall volumeGolf clubsRacket sportsEngineeringMoment of inertia
Disclosed herein are various embodiments of a golf club head having improved mass distribution characteristics. The golf club head includes a body and a face positioned at a forward portion of the body. The golf club head also includes one or more mass elements positioned at predetermined locations about the head. The mass elements assist in achieving desired relationship between the moment of inertia about a center of gravity x-axis and the moment of inertia about a center of gravity z-axis.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Torsional vibration damper
ActiveUS7073646B2Increase volumeIncrease the number ofYielding couplingRotary clutchesEngineeringTorsional vibration
A torsional vibration damper on the bridging clutch of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement has a first connecting device, which can be brought into working connection with the clutch housing and with a drive-side transmission element. The drive-side transmission element is connected via first energy-storage devices to an intermediate transmission element. The torsional vibration damper also has a second connecting device for establishing a working connection via second energy-storage devices between the intermediate transmission element and a takeoff-side transmission element, which is connected to a takeoff-side component of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement. The intermediate transmission element accepts a mass element, located operatively between the two connecting devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Golf club head having removable weight
The invention provides a golf club head having adjustable weight, allowing the golfer to fine tune the club for his or her swing. The club head includes a body having a ball-striking face, a sole, a crown, and a side extending rearwardly from the face. The body defines an interior cavity and a recess on a selected wall of the body spaced apart from the striking face. A threaded opening is disposed in the recess. The club head further includes a weight assembly having fastener and a mass element configured to be press-fit into the recess the such that a first end is adjacent the bottom of the recess. The mass element also has an aperture configured to receive the fastener flush. The fastener removably attaches the weighting assembly to the selected wall of the club head. Pressure from the fastener attachment provides a press-fit of the mass element in the tapered recess of the selected wall.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Rotary electric machine
ActiveUS20150333596A1Emission reductionEffective and efficient mannerAssociation with control/drive circuitsAssociation with grounding devicesElectricityElectric machine
A rotary electric machine, in particular an electric motor, has a winding, an electronic control device, and an electrically conductive shielding plate arranged between the control device and the winding. A connection device which includes at least one coupling element for electrically connecting the control device to one or more lines and a mass element provided for connecting to an electric mass potential. In order to improve the machine with respect to electromagnetic interference, the shielding plate is electrically conductively connected to the mass element by way of a sheet metal tongue via a first electric pressure-contact.
Owner:BROSE FAHRZEUGTEILE GMBH & CO KG HALLSTADT (DE)
Inertial sensor and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110146404A1Large widthIncrease distancePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesElectricityEngineering
Disclosed herein is an inertial sensor, which includes a diaphragm having a piezoelectric element or a piezoresistive element formed on one surface thereof, a mass element integrated with the center of the other surface of the diaphragm in which the distal end of the mass element has a larger width than the width of the proximal end in contact with the diaphragm, and a supporter formed along the edge of the other surface of the diaphragm, so that the use of the mass element having the above shape results in decreased spring constant and increased distance from the center of the diaphragm to the center of the mass element, thereby simultaneously realizing a reduction in the size of the inertial sensor and an increase in performance thereof. A method of manufacturing the inertial sensor is also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Energy harvester apparatus having improved efficiency
ActiveUS8350394B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesEnergy harvesterTransducer
An improved vibrational energy harvester includes a housing and at least one energy transducer. In an embodiment, a second mass element is arranged to receive collisionally transferred kinetic energy from a first mass element when the housing is in an effective state of mechanical agitation, resulting in relative motion between the housing and at least one of the second and further mass elements. The energy transducer is arranged to be activated by the resulting relative motion between the housing and at least one of the second and further mass elements. In a further embodiment, kinetic energy is collisionally transferred in a velocity-multiplying arrangement from the first to a second or further mass element that has a range of linear ballistic motion. The energy transducer is arranged to be activated, at least in part, by the ballistic motion of the second or further mass element. The energy transducer, or a portion of it, may be attached to the housing, or it may be attached to another of the mass elements.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK +1
Triaxial acceleration sensor
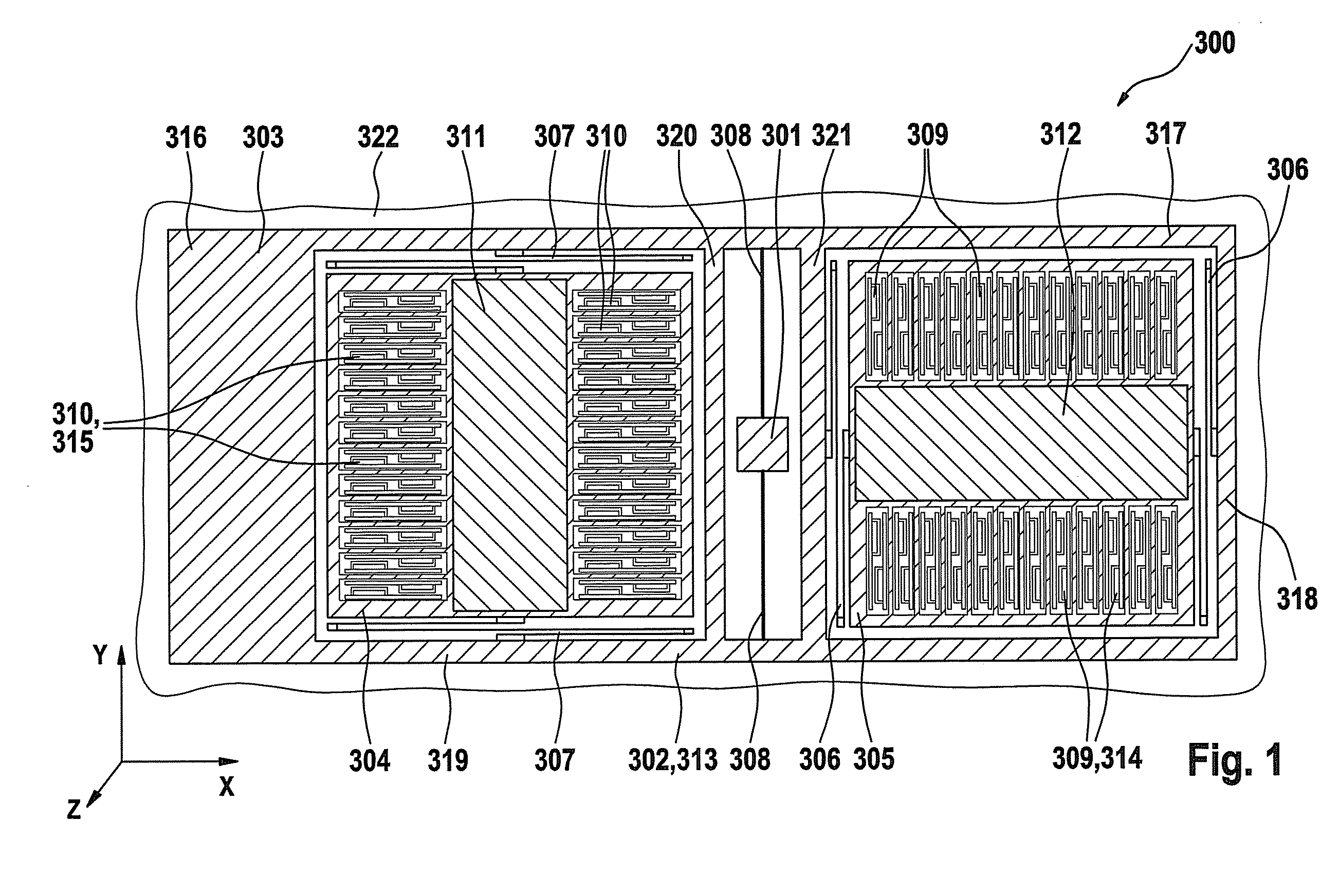
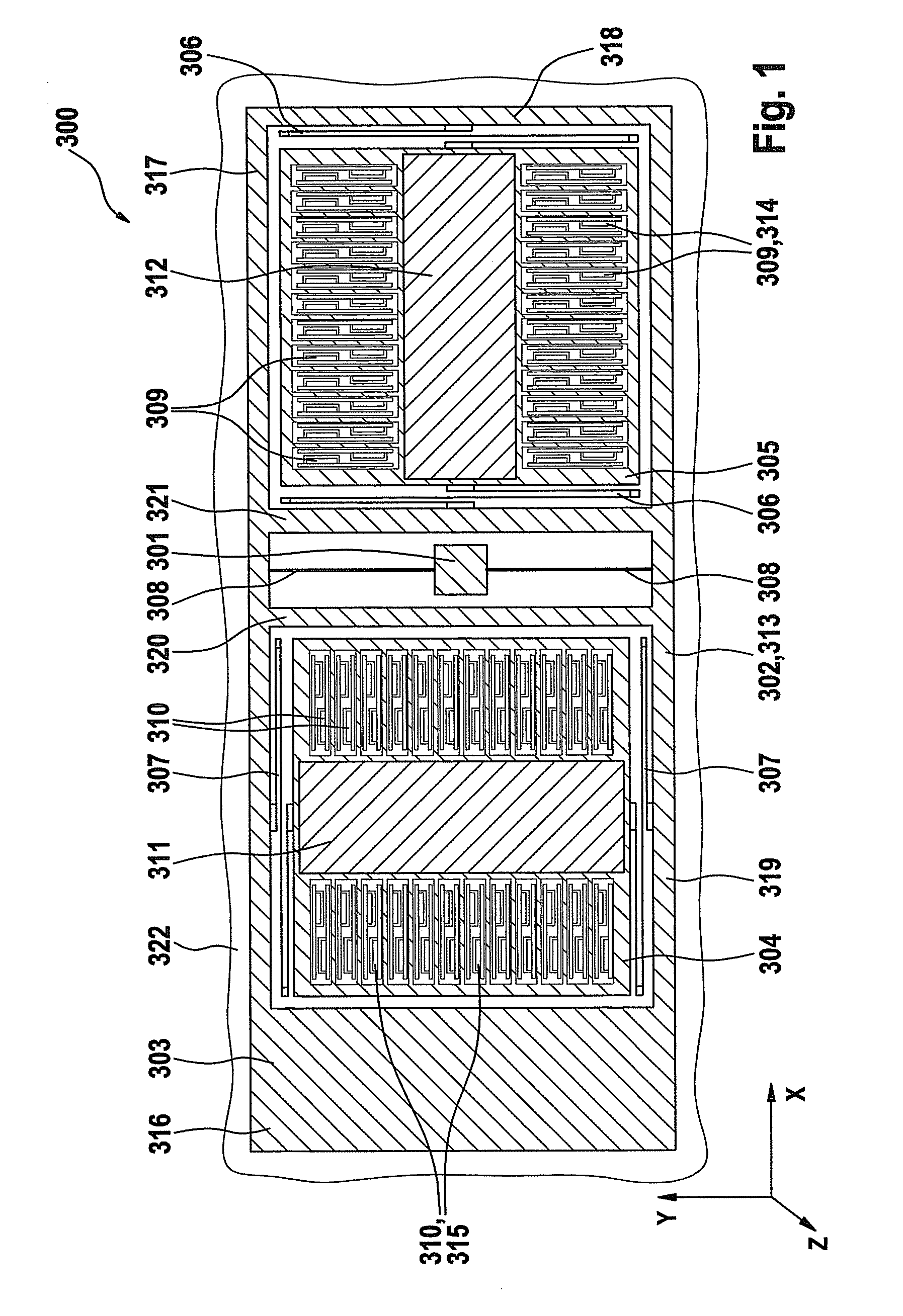
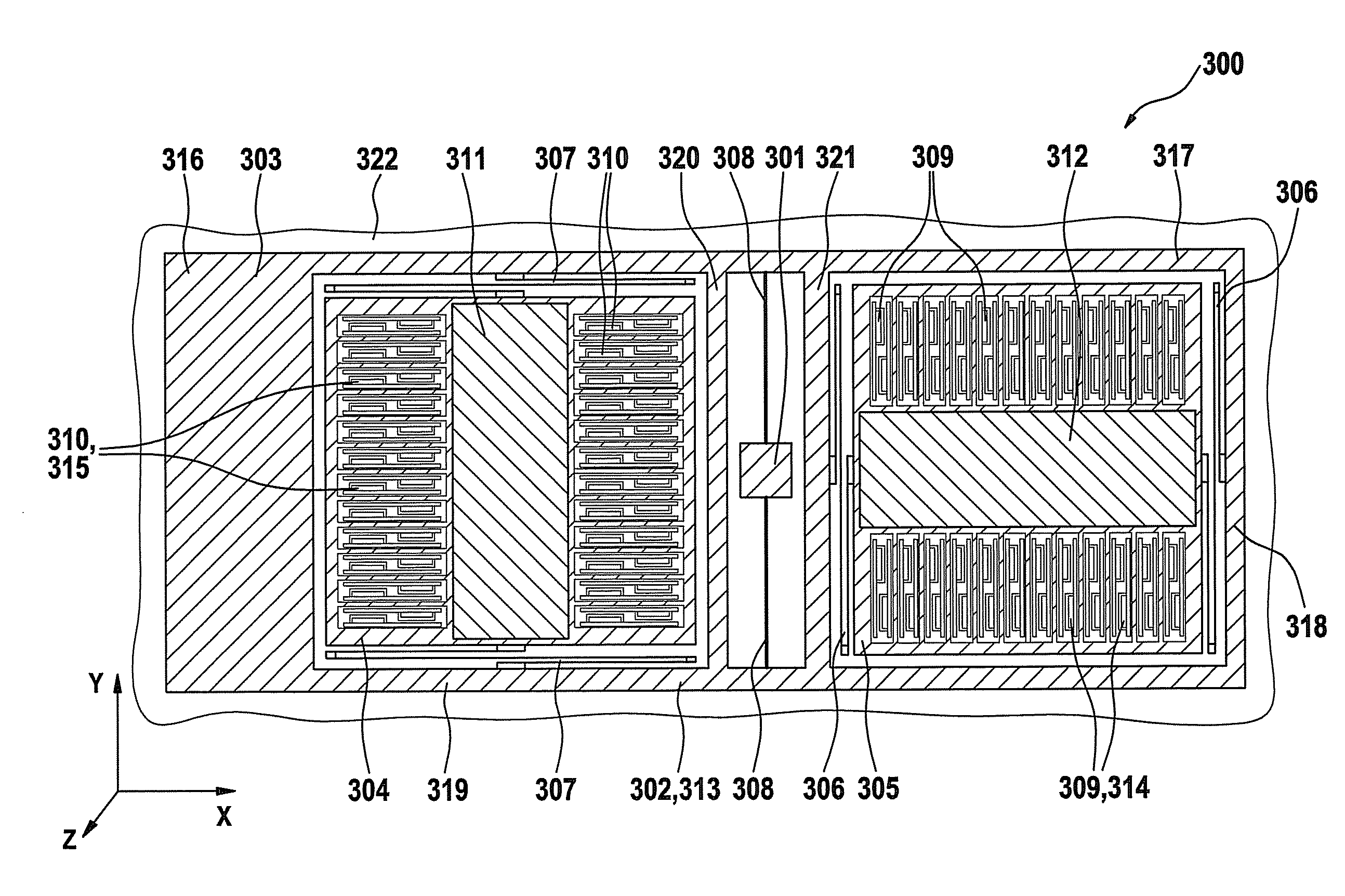
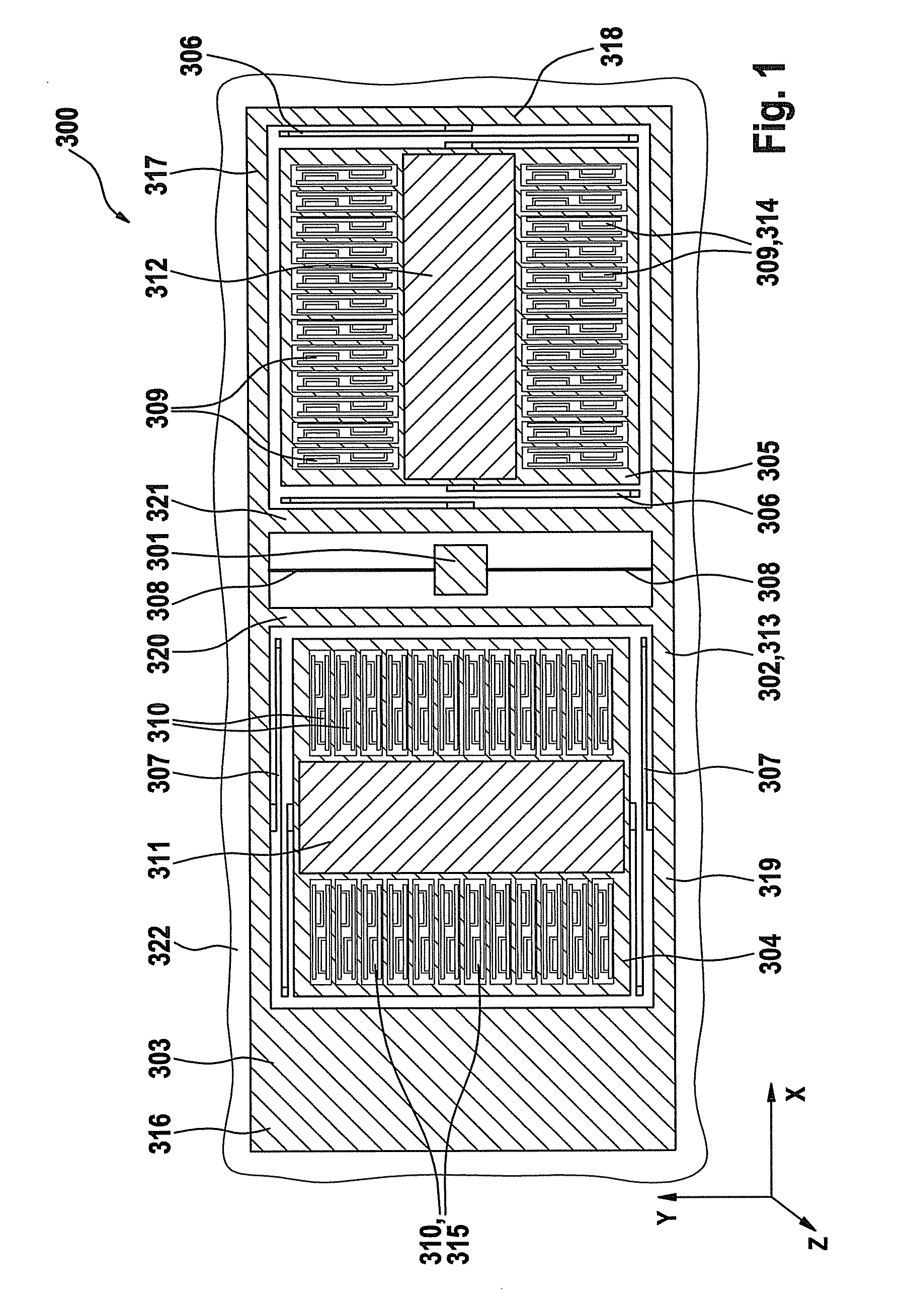
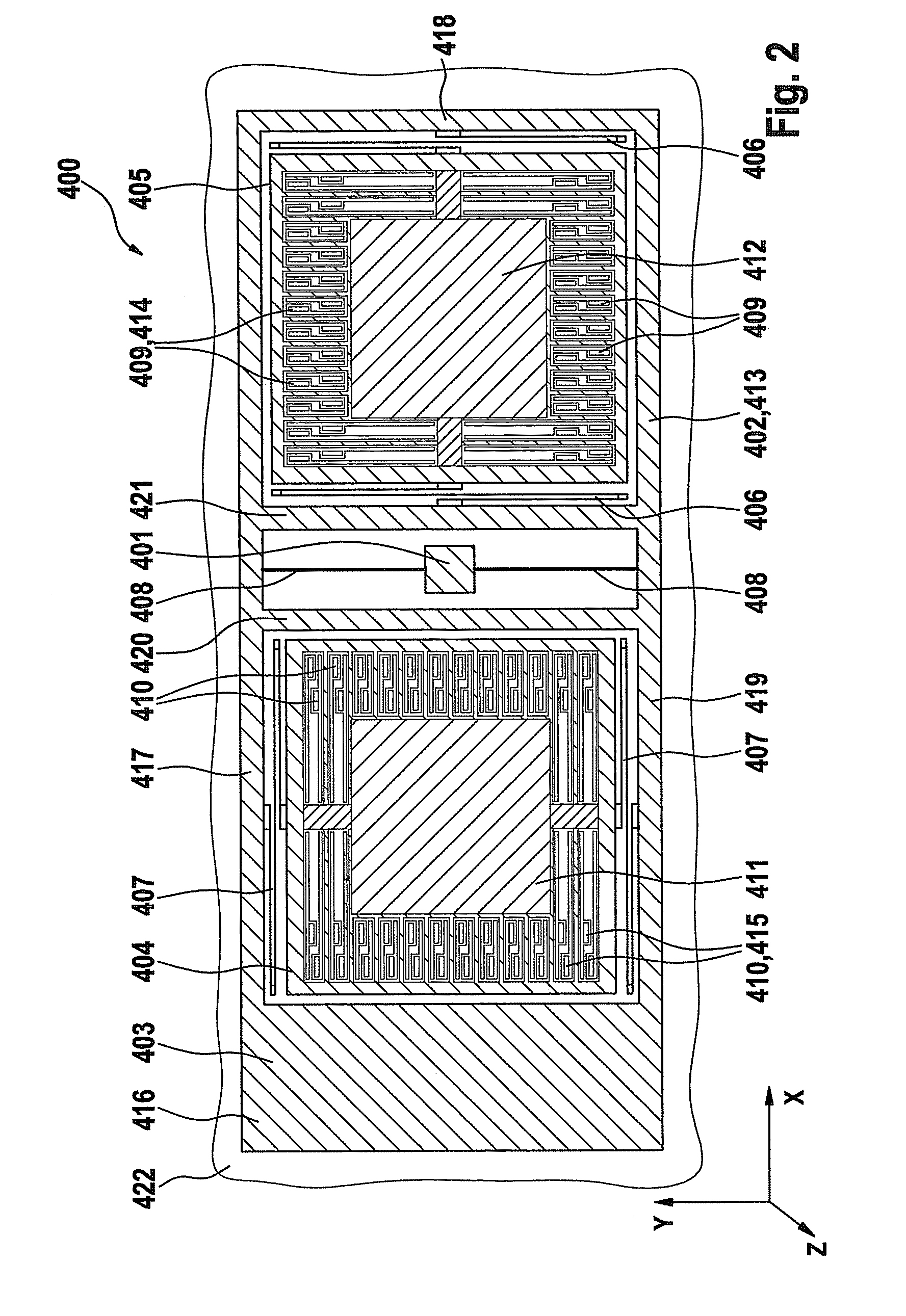
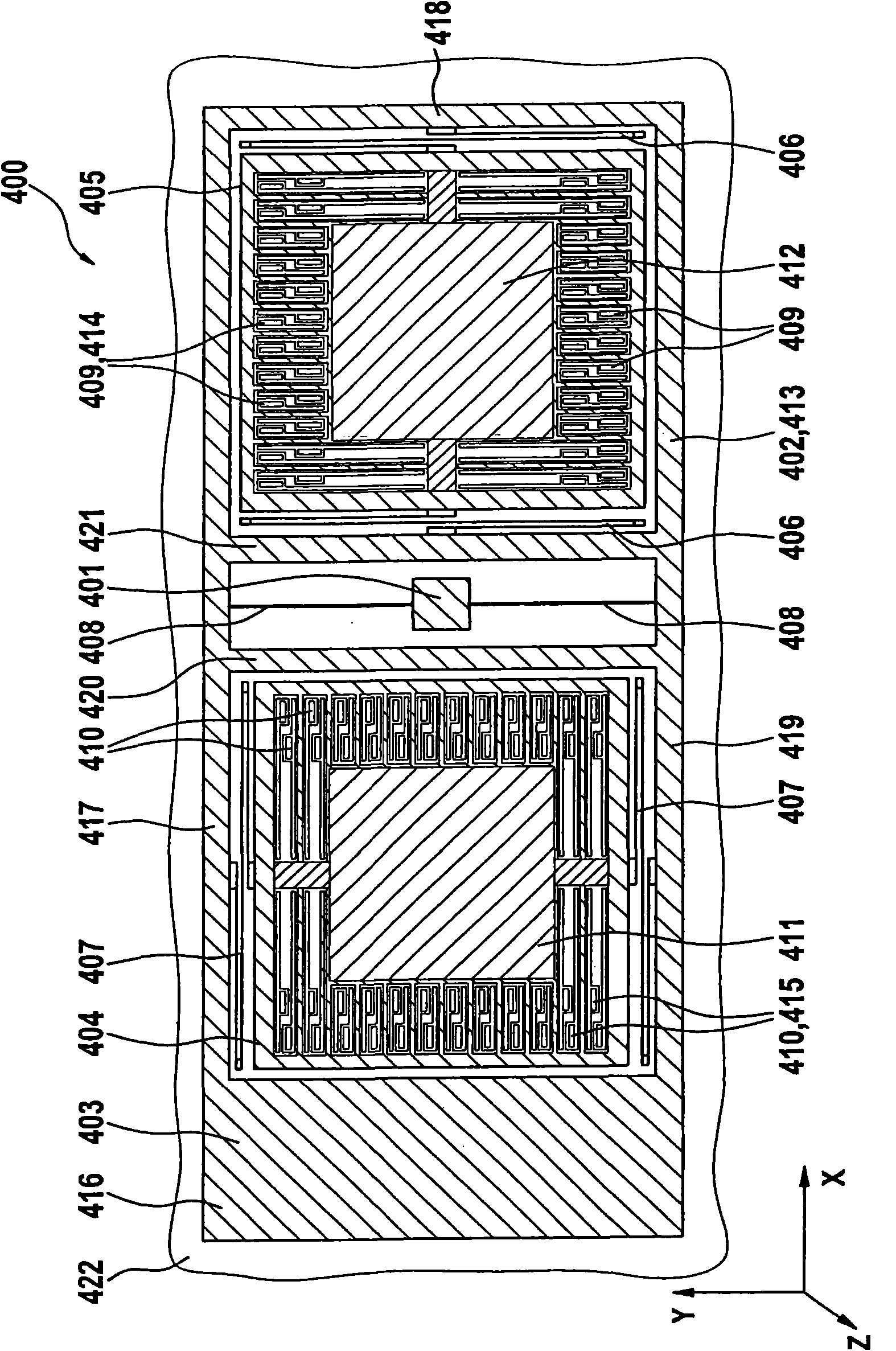
ActiveUS20100024554A1Easy to detectCompact designAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDevices characerised by mechanical meansClassical mechanicsMass element
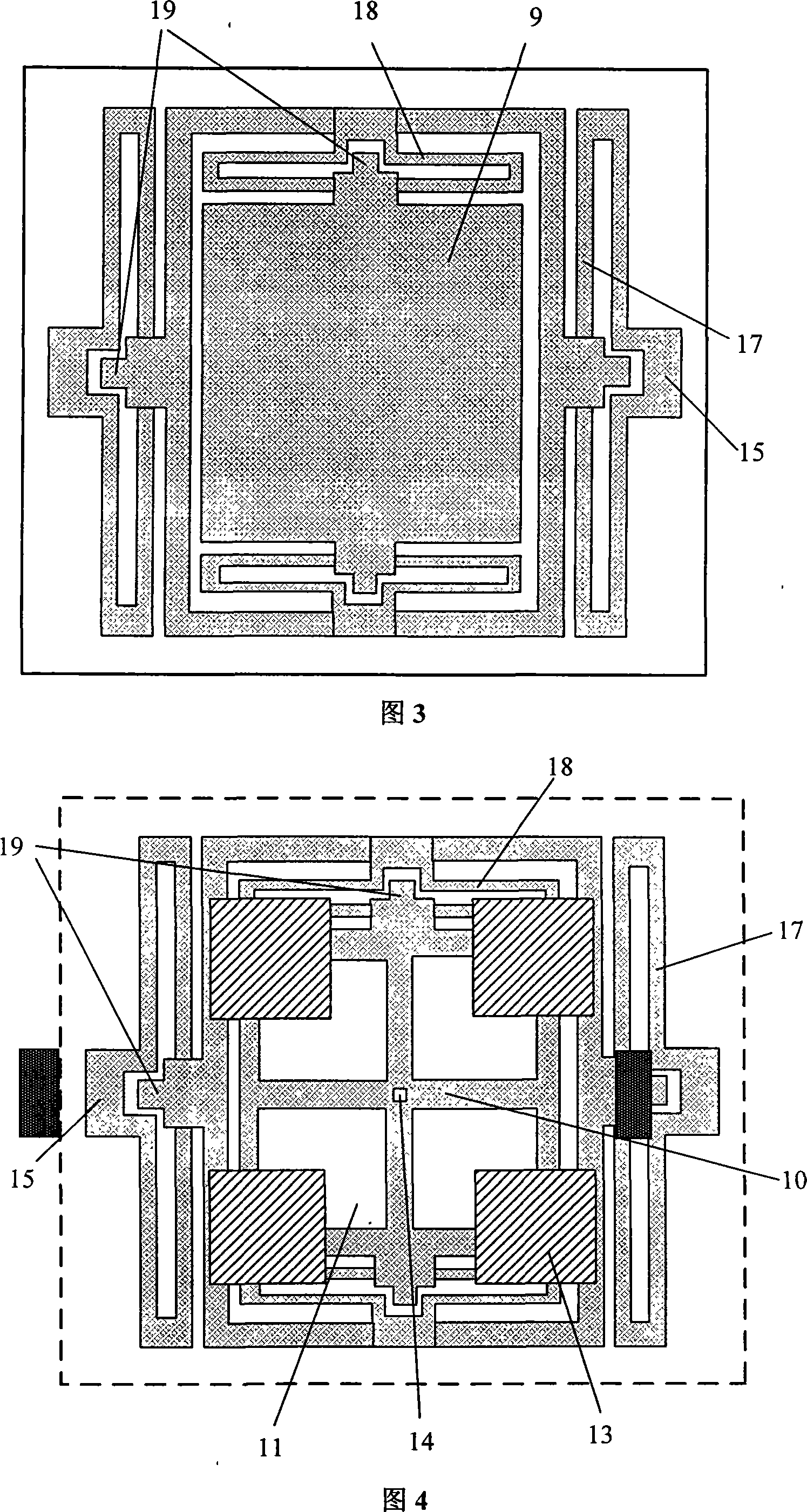
An acceleration sensor includes a substrate and a first mass element, which is connected to the substrate in such a way that the first mass element is rotatable about an axis, the first mass element being connected to a second mass element in such a way that the second mass element is movable along a first direction parallel to the axis, and the first mass element being connected to a third mass element in such a way that the third mass element is movable along a second direction perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Triaxial acceleration sensor
ActiveUS8333113B2Easy to detectCompact designAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDevices characerised by mechanical meansClassical mechanicsMass element
An acceleration sensor includes a substrate and a first mass element, which is connected to the substrate in such a way that the first mass element is rotatable about an axis, the first mass element being connected to a second mass element in such a way that the second mass element is movable along a first direction parallel to the axis, and the first mass element being connected to a third mass element in such a way that the third mass element is movable along a second direction perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Tire containing a component for reducing vibration-generated noise in a tire and method for reducing tire noise
This invention pertains to a tire having a plurality of vibration absorbers wherein, (i) the vibration absorbers have at least one spring element and at least one absorber mass element, each element having a first and second surface such that the first surface of the spring element is attached to the tire carcass or attached to or embedded into the tire inner liner, and (ii) the first surface of the absorber mass element is attached to the second surface of the spring element, or the absorber mass element is embedded into the spring element.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Broadband passive distributed tuned vibration and acoustic absorber for modally dense structures
A passive distributed vibration absorber that utilizes multiple discrete mass elements and a viscoelastic layer and that effectively attenuates vibration in modally dense structures excited by a broadband input noise excitation and is tunable to multiple natural frequencies in such modally dense vibrating structures including low frequencies
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Torsional vibration damper
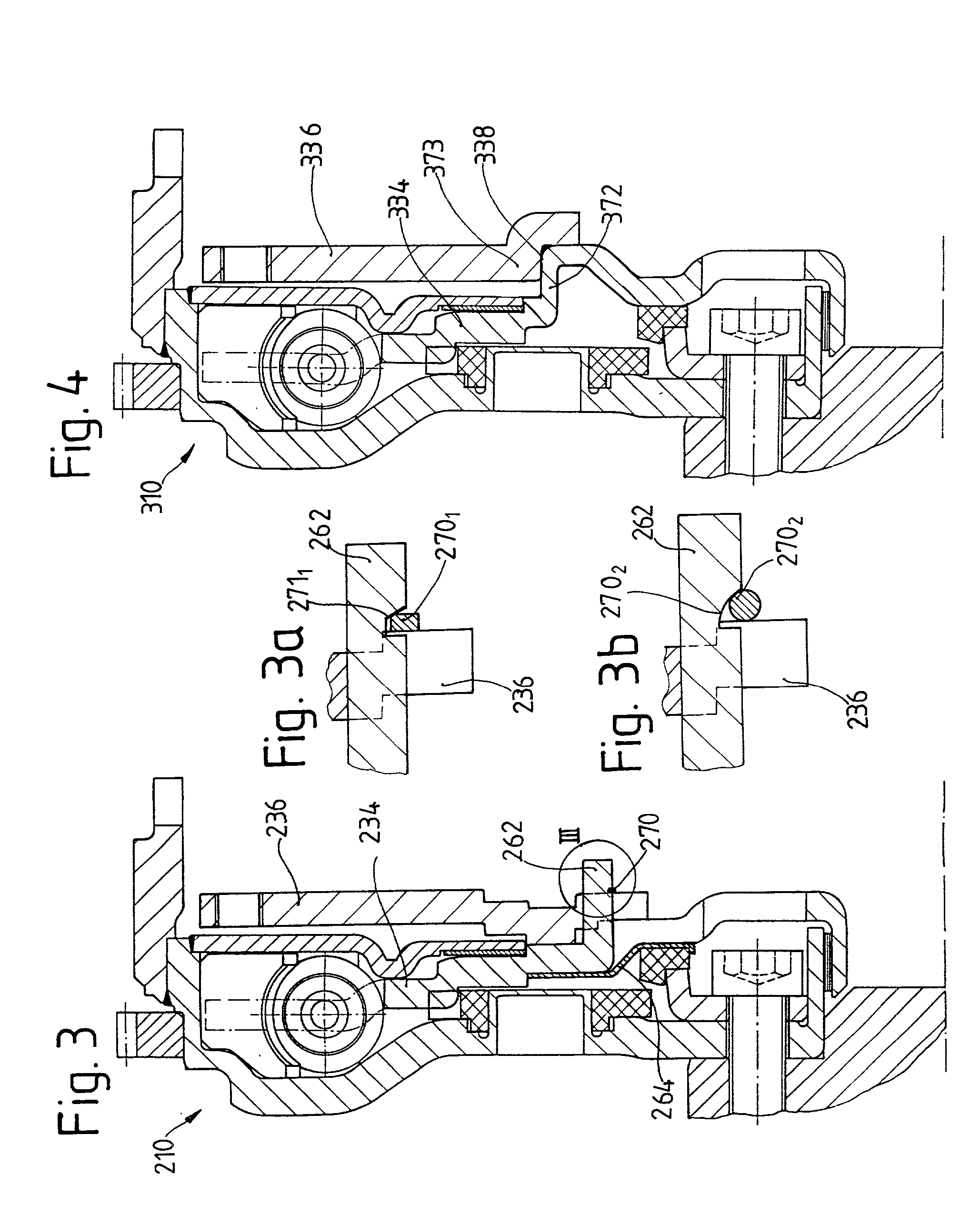
InactiveUS20010025762A1Great resistance to temperature and ruptureHigh elongation of the sheet metal materialRotating vibration suppressionClutchesMobile vehicleDrivetrain
A torsional vibration damper, particularly for a drivetrain in a motor vehicle, having a substantially disk-shaped flywheel mass element having a friction surface for cooperating with friction facings of a friction clutch and a damper element arrangement communicating with the flywheel mass element, wherein the flywheel mass element is produced from a sheet metal material.
Owner:MANNESMANN SACHS AG
Dual spindle differential capacitance type micromechanical accelerameter
InactiveCN101216498AAvoid breakingRealize overload protectionTelevision system detailsImpedence networksAccelerometerMass element
The invention relates to a biaxial differential capacitive micro-accelerometer, which belongs to the field of inertial sensors in a micro-electro-mechanical system. The micro-accelerometer comprises a sensitive mass element composed of a silicon sheet, four square movable electrodes arranged on the silicon sheet and insulating layers for isolating the movable electrodes, a substrate horizontally opposite to the silicon sheet, four square fixed electrodes arranged on the substrate and corresponding to the four square movable electrode, two lateral folding beams arranged on both ends of the silicon sheet for fixing the silicon sheet, two longitudinal folding beams for fixing the lateral folding beams, and pillars for fixing the two longitudinal folding beams on the substrate, so that the planes of the four movable electrodes are suspended and parallel to the substrate. The invention has the advantages of simple structure and high sensitivity, and can achieve high-accuracy two-dimensional acceleration measurement.
Owner:ZIGUANG COMM TECH
Torsional vibration damper for a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement
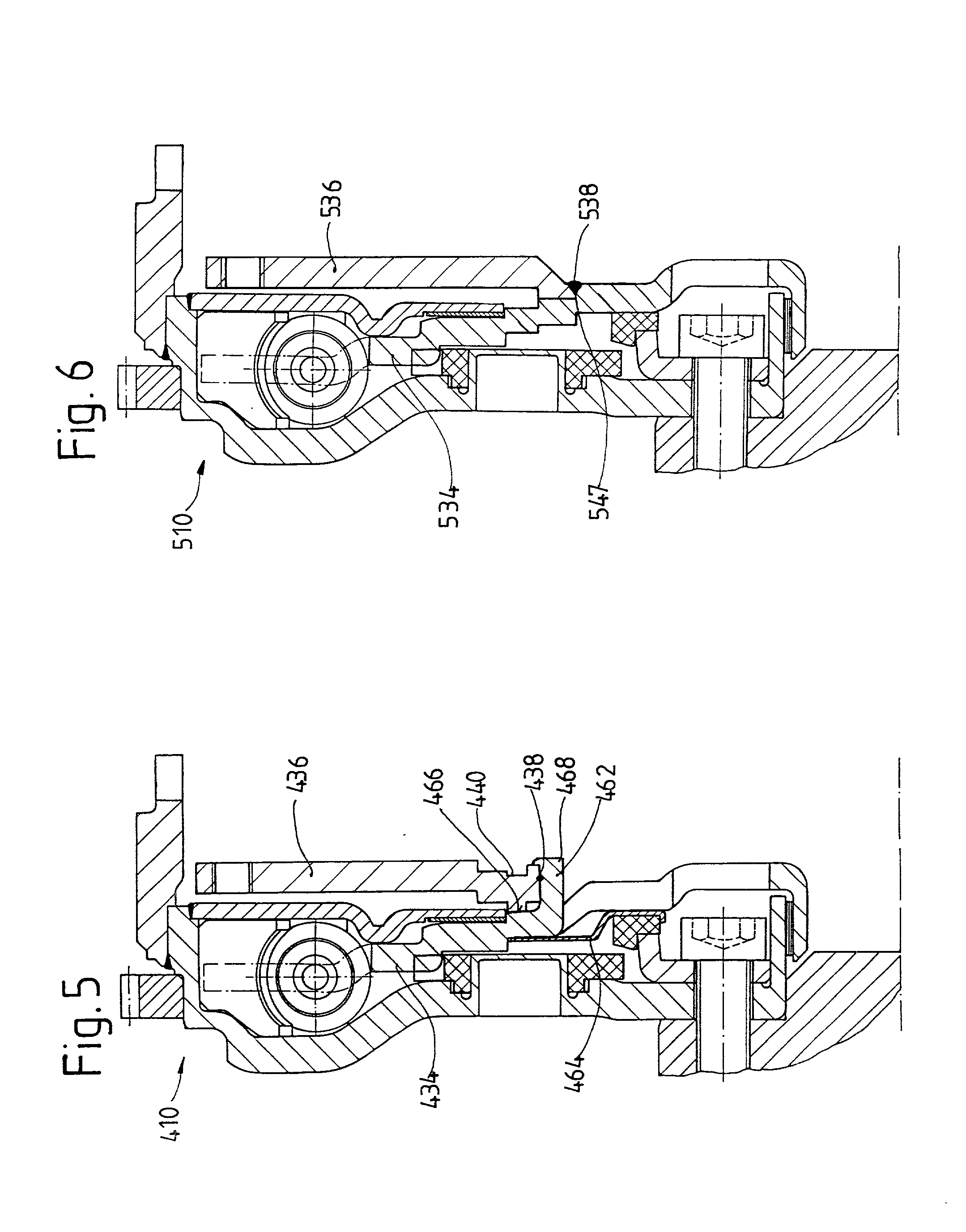
InactiveUS20070108006A1Easy to installWear minimizationYielding couplingRotary clutchesEngineeringTorsional vibration
The torsional vibration damper acting between a drive and a housing of a hydrodynamic clutch arrangement includes a flywheel mass element, a drive-side damping element having a first side connected nonrotatably to the flywheel mass element, a takeoff-side damping element, the second side of the drive-side damping element being connected by elastic elements to the takeoff-side damping element for rotation in common, the elastic elements also allowing a small rotation of the drive-side damping element relative to the takeoff-side damping element, and an axially flexible drive plate. The takeoff-side damping element can be connected to the housing of the hydrodynamic clutch arrangement nonrotatably but with a certain freedom of axial movement by means of the drive plate.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Systems and methods for acousto-haptic speakers
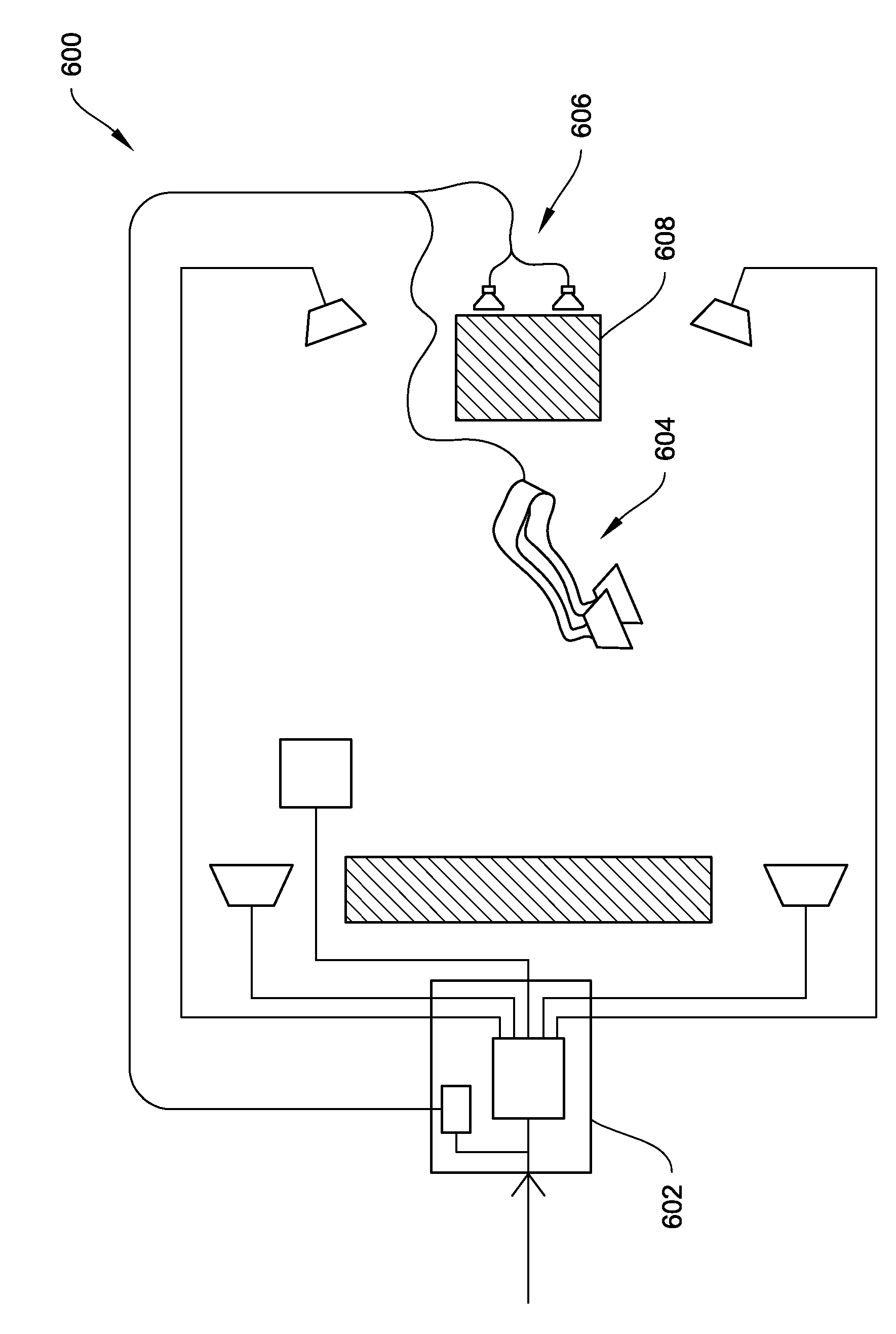
The systems and methods described herein relate to, among other things, a transducer capable of producing acoustic and tactile stimulation. The transducer includes a rigid mass element disposed on the diaphragm of a speaker. The mass element may optionally be removable and may have a mass selected such that the resonant frequency of the transducer falls within the range of frequencies present in an input electrical audio signal. The systems and methods advantageously benefits from both the fidelity and audio performance of a full-range speaker while simultaneously producing high-fidelity, adjustable and palpable haptic vibrations.
Owner:IMMERZ
Circuit Module
InactiveUS20090206703A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsPiezoelectric voltageComputer module
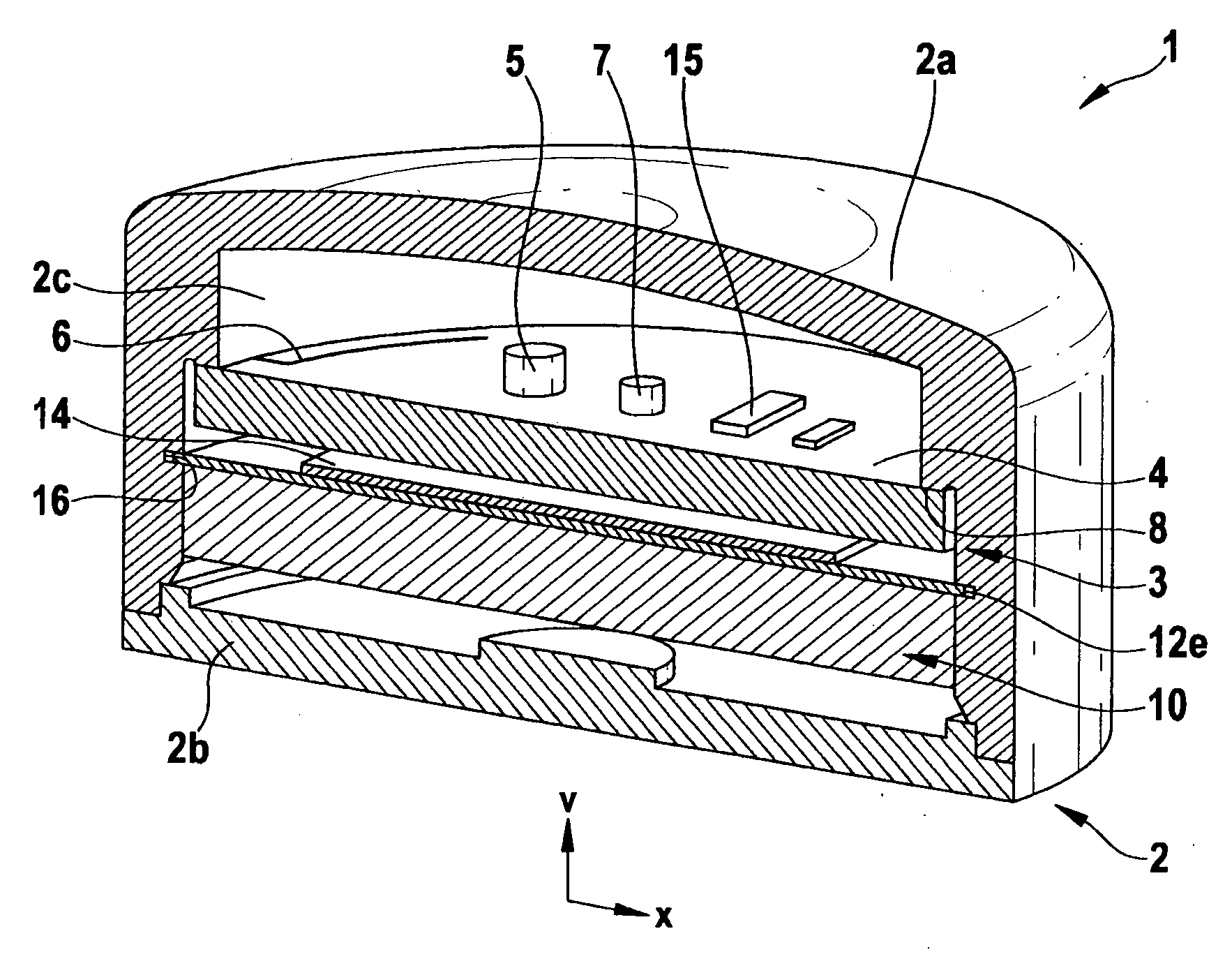
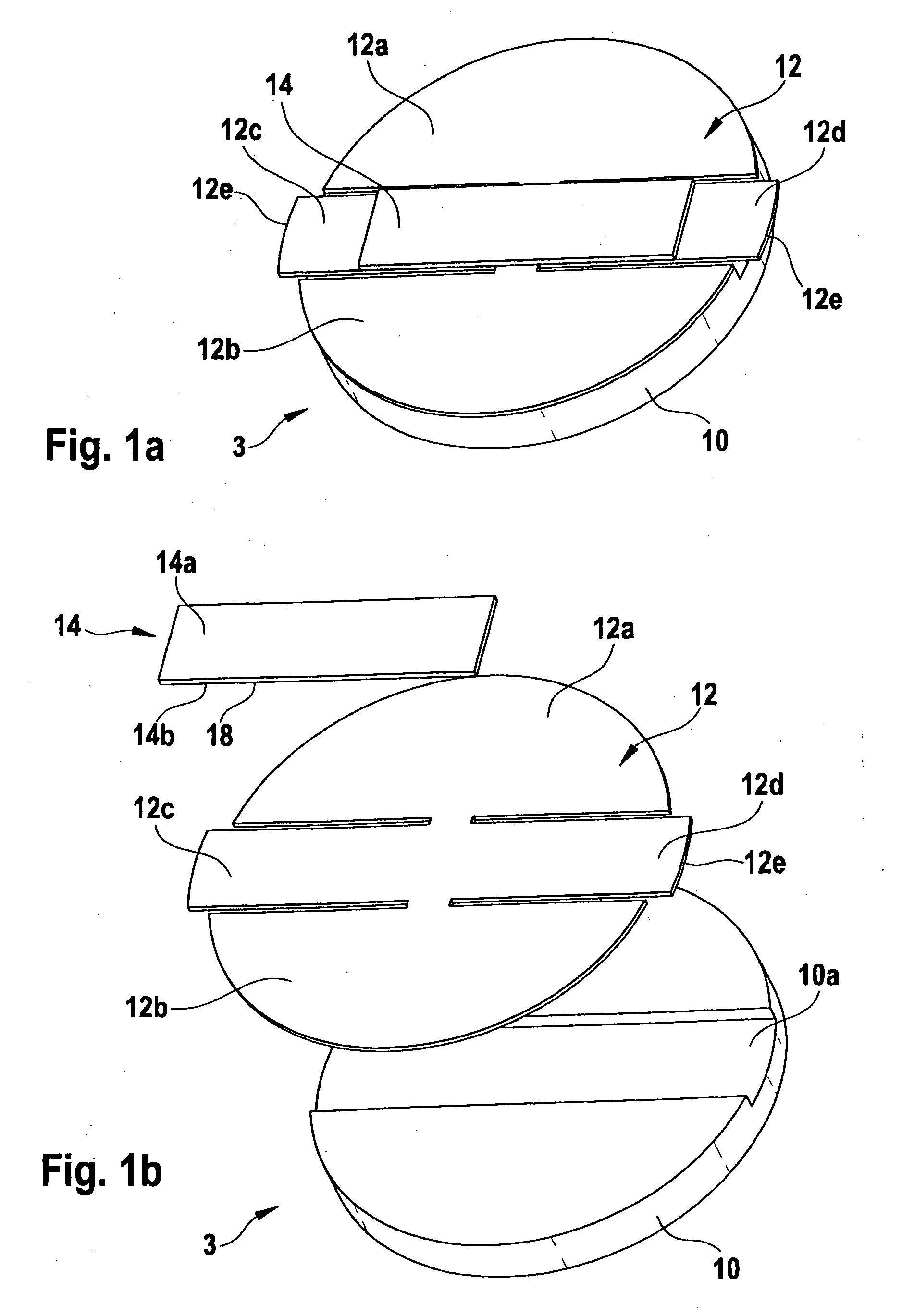
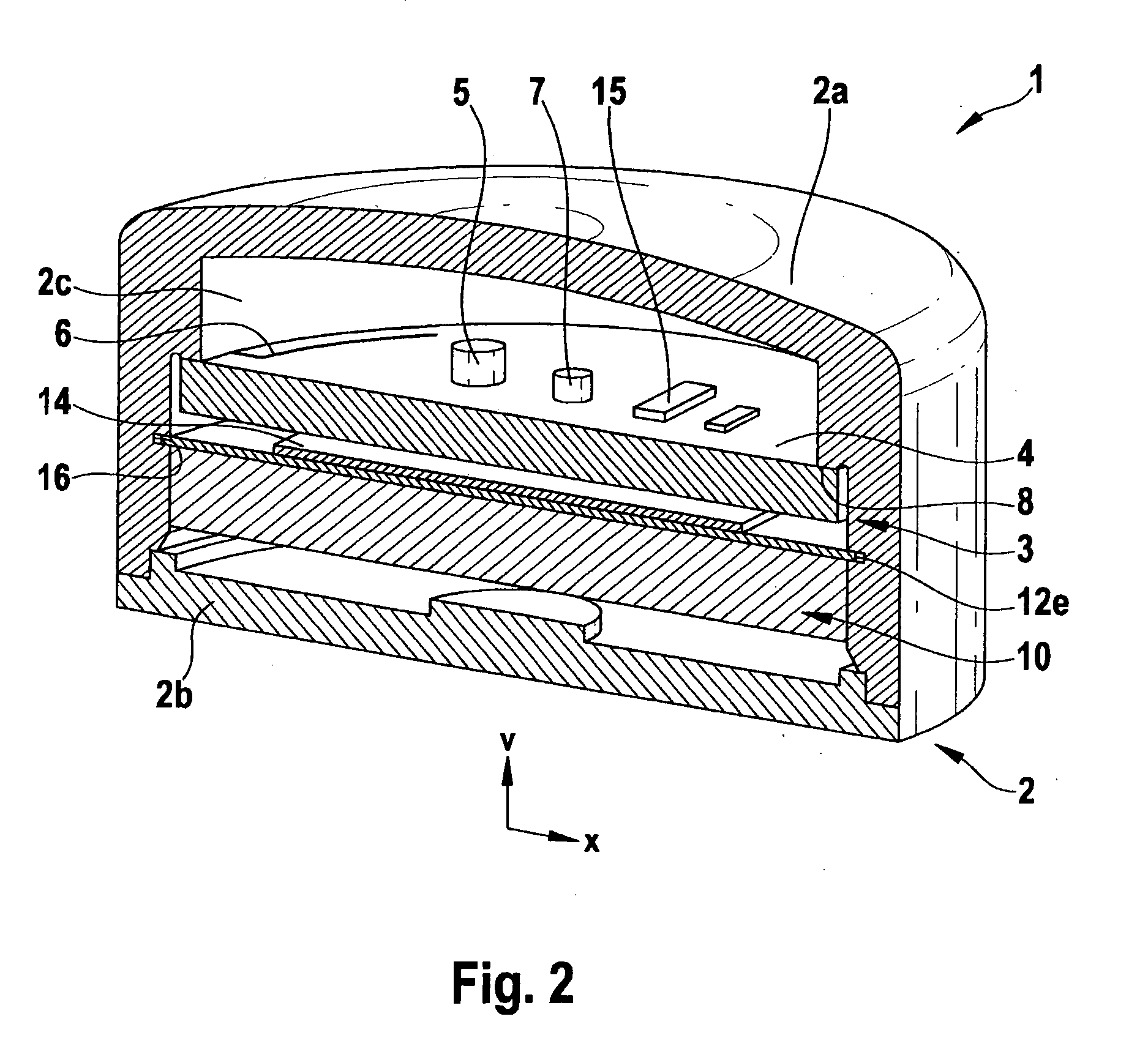
A circuit module, in particular for use in a vehicle tire, having at least: a housing (2), a piezoelectric generator (3), which has a mass element (10) that is movable within the housing (2) and a spring device (12, 14), which has at least one piezoelectric element (14), the mass element (10) and the spring device (12, 14) forming an oscillatory system, and the piezoelectric element (14) being elastically deformable in response to the oscillation of the oscillatory system (10, 12, 14); and a current-supply circuit (5) for receiving a piezoelectric voltage output by the piezoelectric element (14) in response to the mechanical deformation thereof and for supplying power to the circuit module (1).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Flywheel
InactiveUS20110023636A1Improve securityIncrease speedLaminationLamination apparatusFlywheelMass element
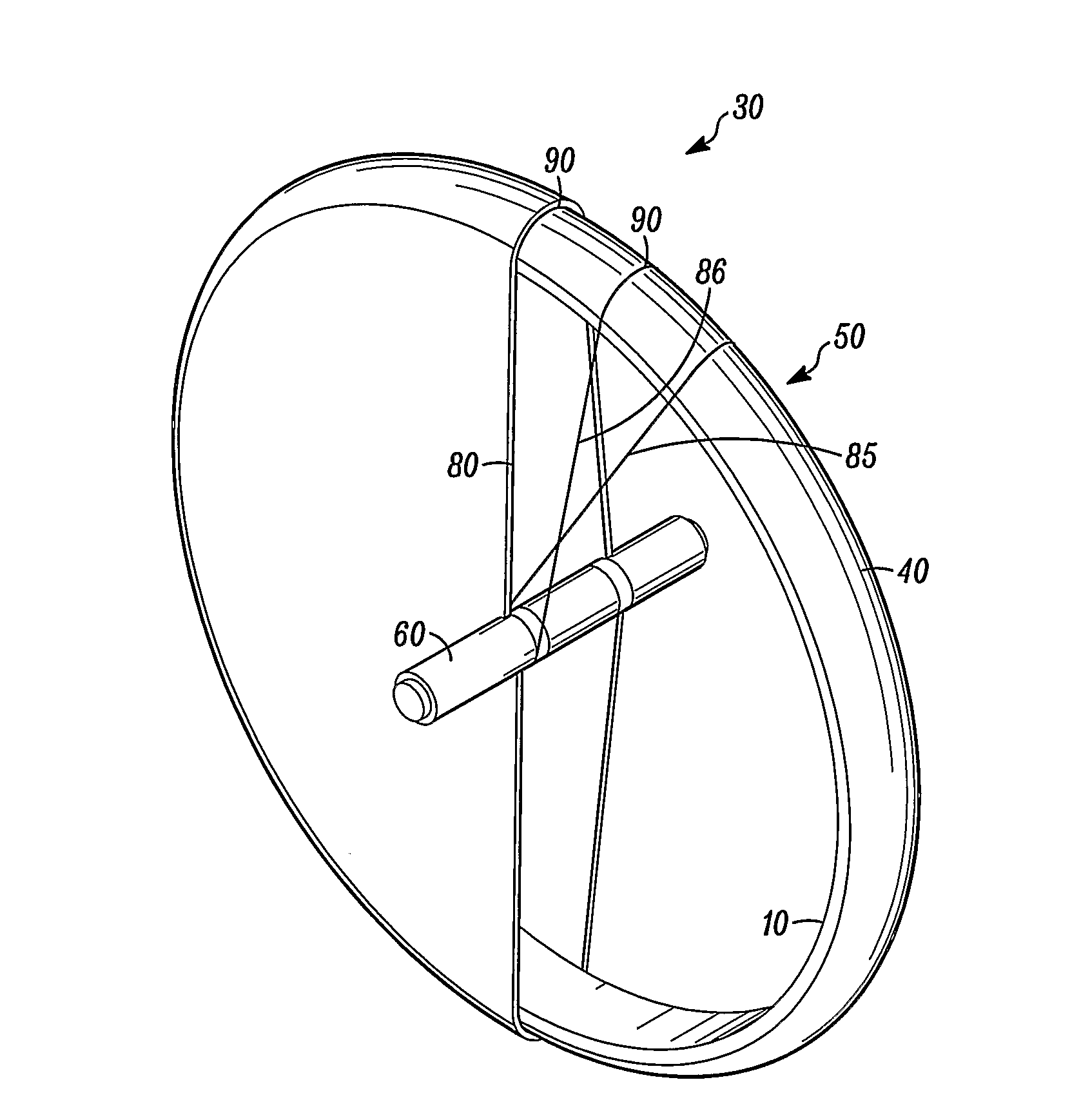
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for constructing a flywheel for energy storage, the flywheel having a drive transfer element (60) and a rim comprising a mass element (10), the drive transfer element being coupled to the rim by a winding (80) around each.
Owner:RICARDO UK LTD
Floating platform shock simulation system and apparatus
InactiveUS7051588B1Shock testingForce measurement by elastic gauge deformationEngineeringFloating platform
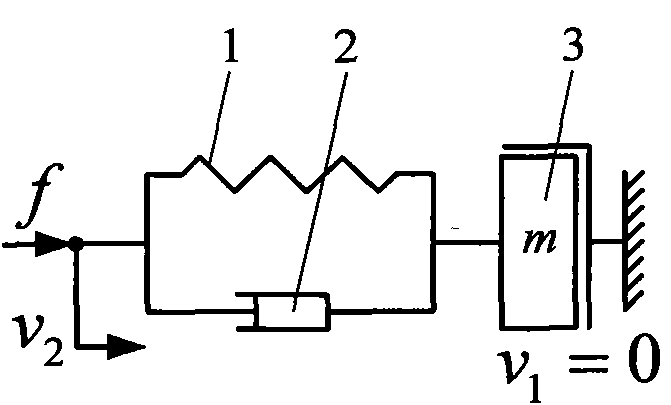
A shock simulation system including a support plane, a first mass element and a first spring element attached between the support plane and the first mass element. Also included, is a second mass element that is attached to the first mass element with a second spring element as well as a cocking apparatus, positioned between the support plane and the second mass element, that is capable of accumulating and storing energy in the spring elements. The system also includes a trigger for releasing the energy stored in the springs and for causing a mechanical shock event that is substantially transferred to the second mass.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
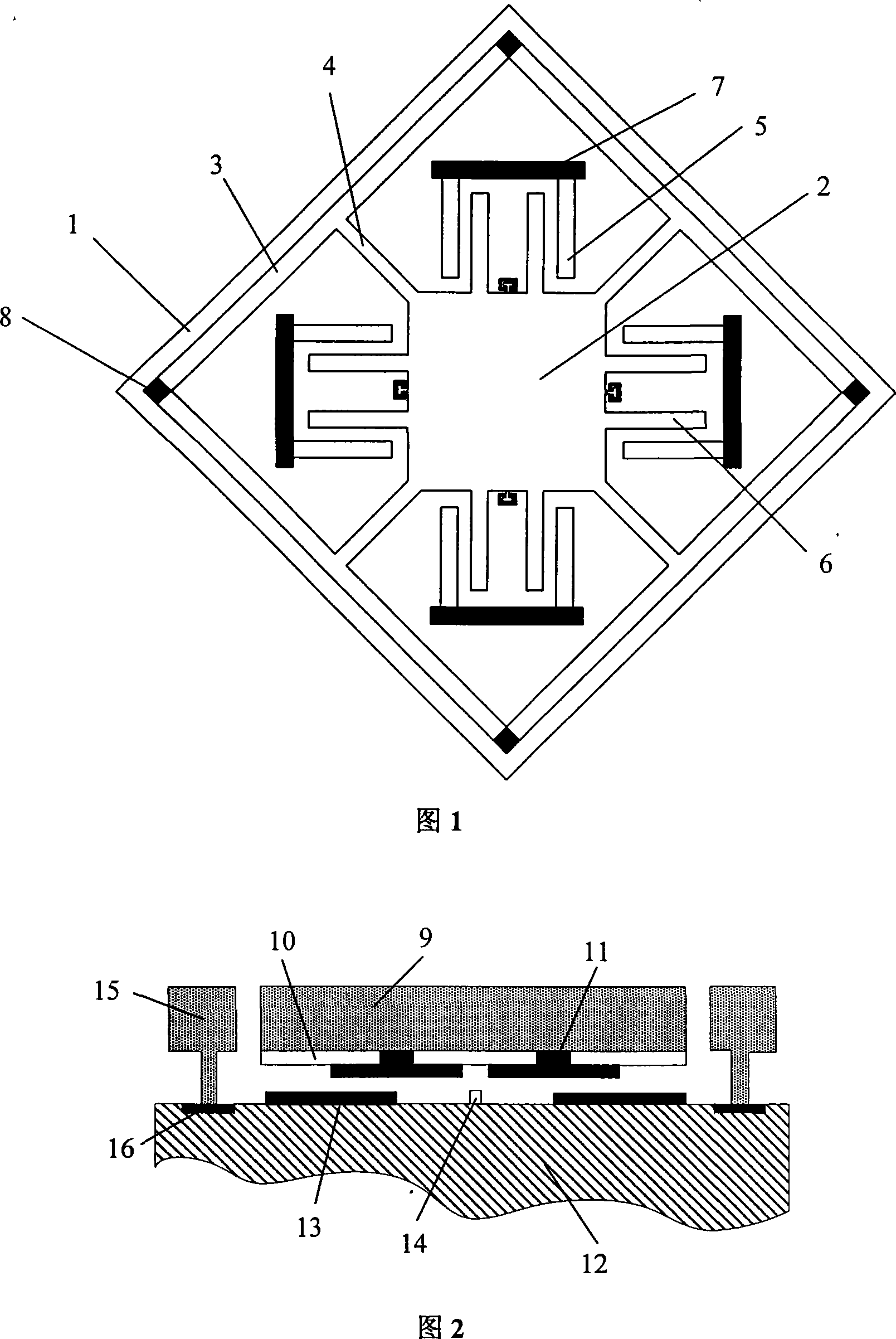
Piezoelectric ring gyroscope
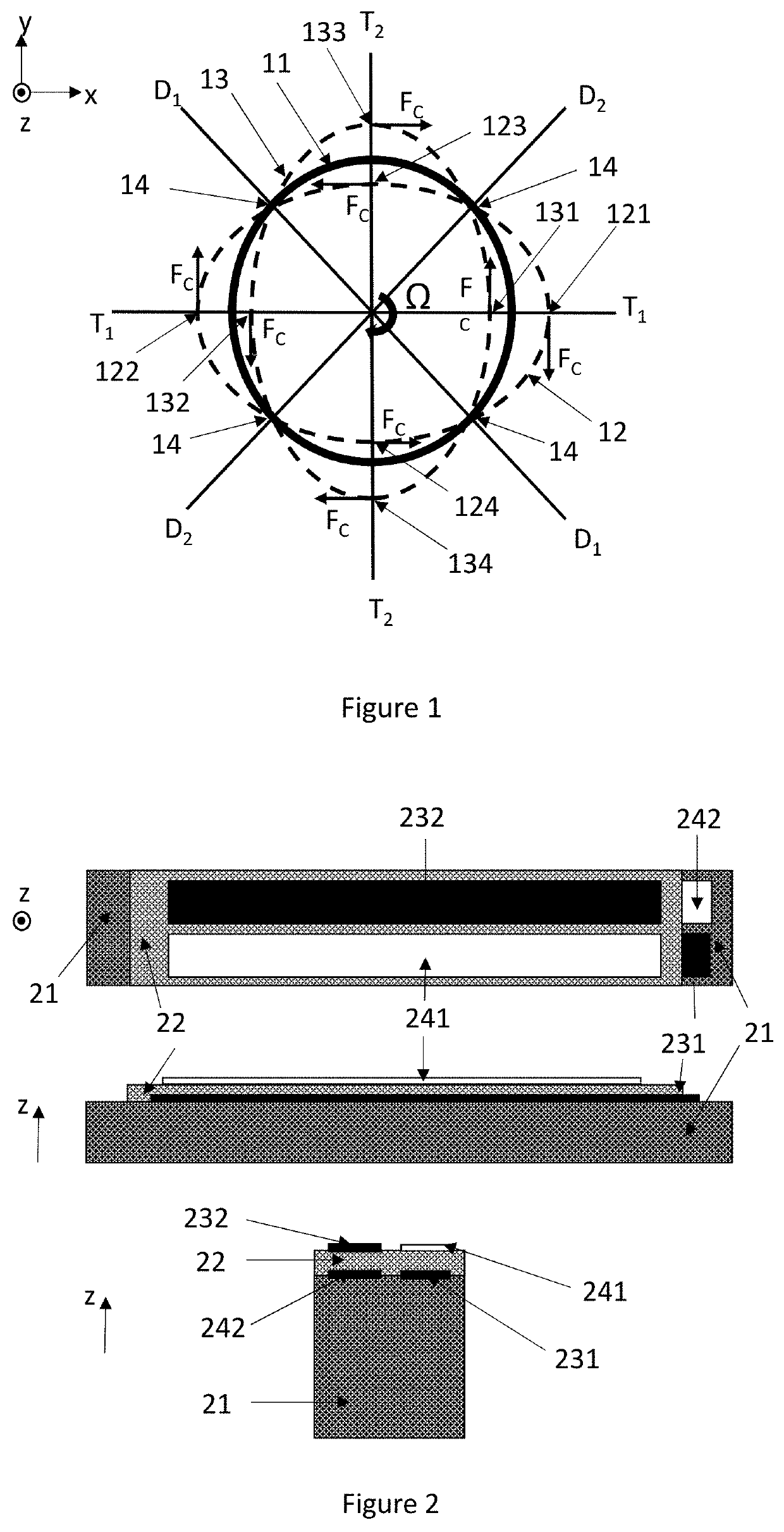
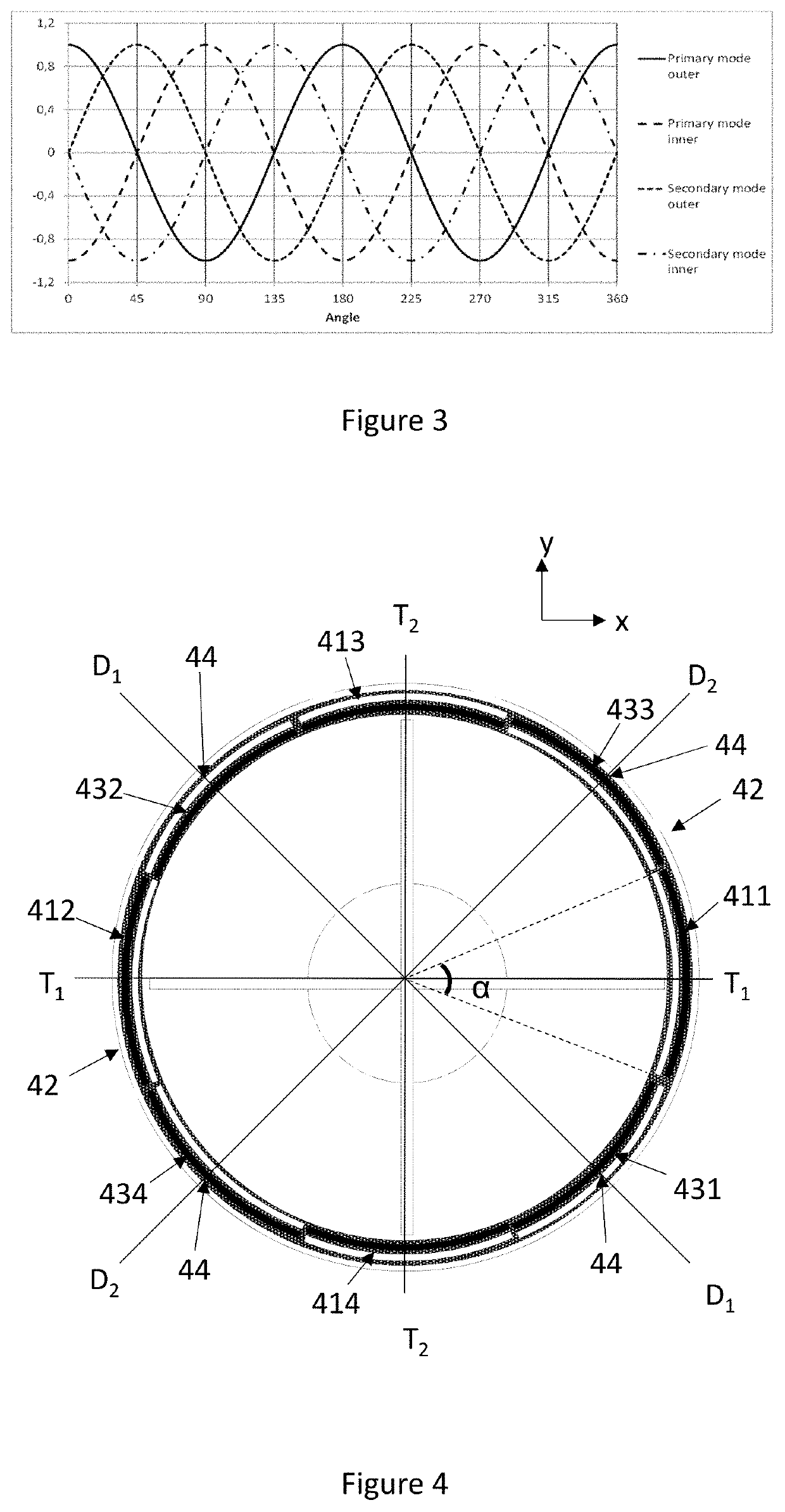
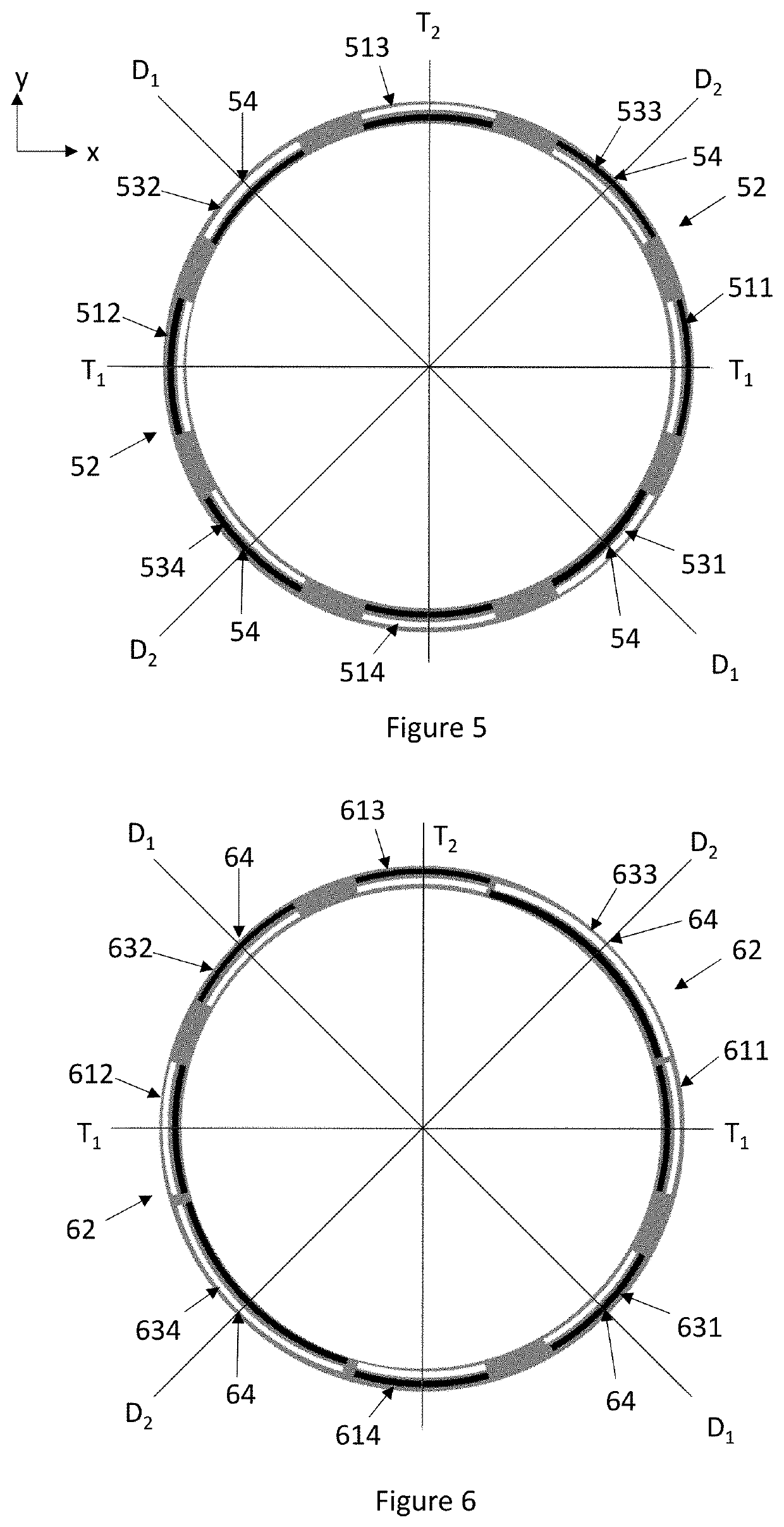
ActiveUS20190346266A1Reduce disadvantagesImpedence networksSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElectricityResonance oscillation
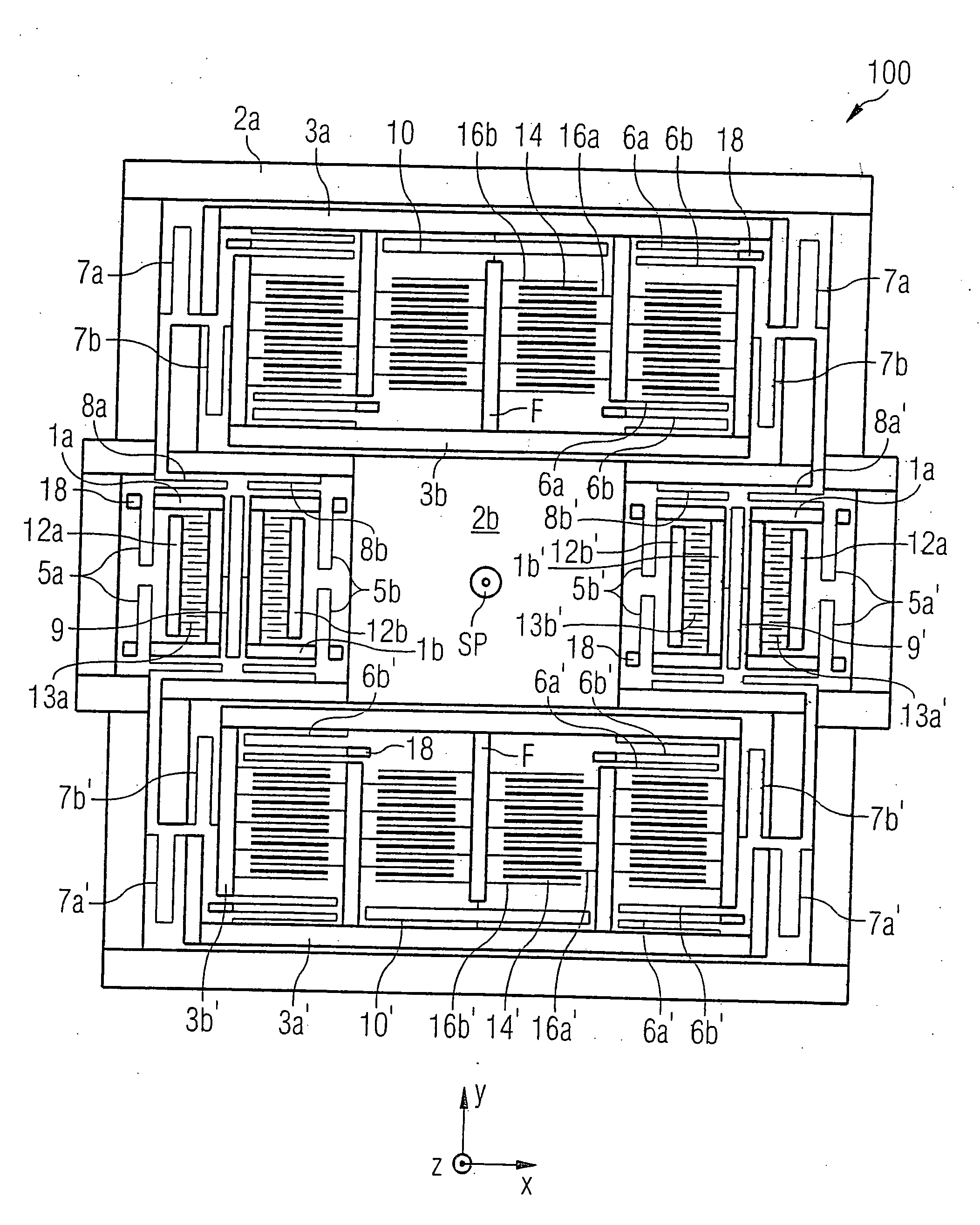
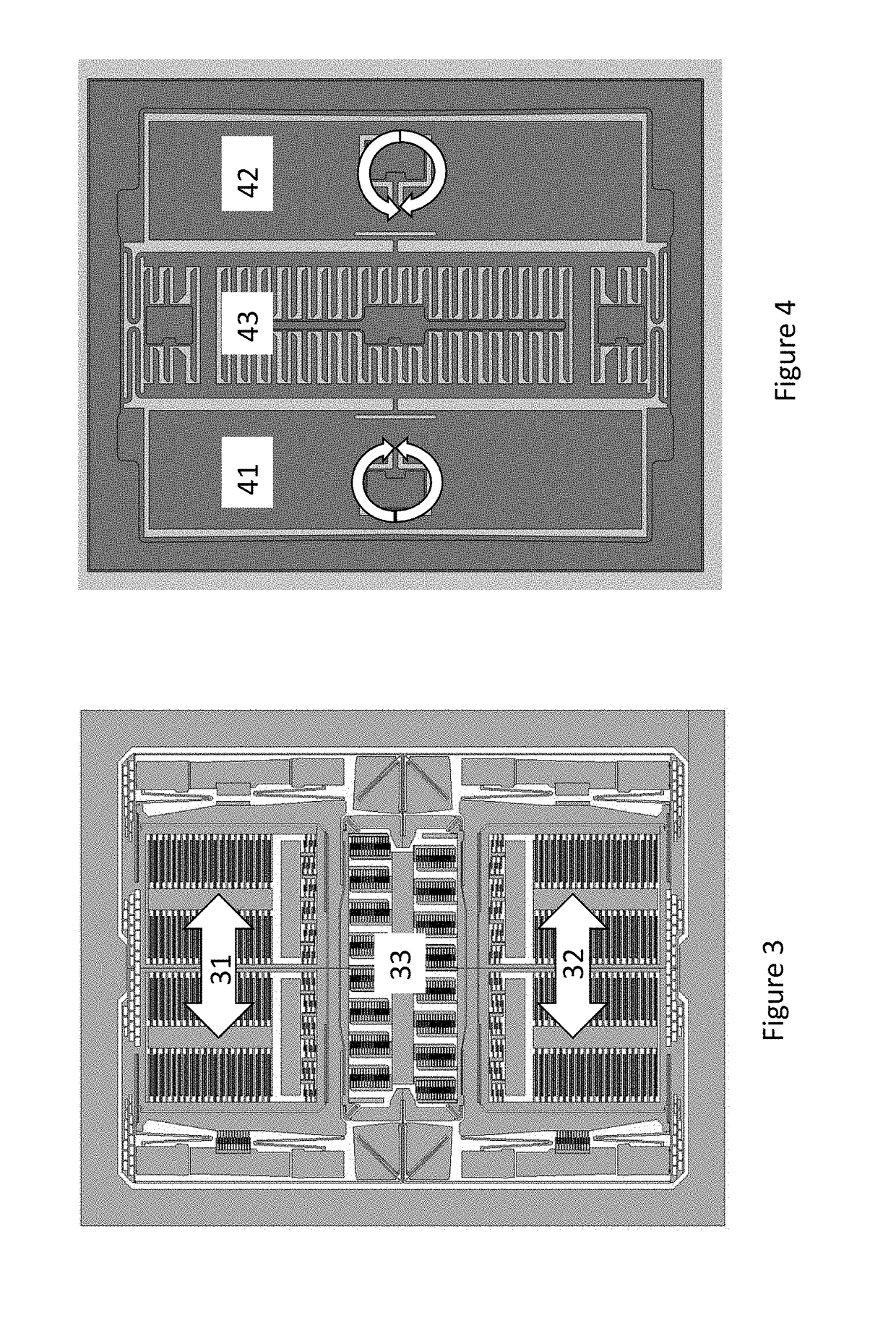
A ring gyroscope which comprises a substantially circular and flexible ring which defines a ring plane, one or more primary piezoelectric split transducers configured to drive the ring into resonance oscillation, four or more mass elements which form a symmetrical mass distribution in relation to both a first and a second transversal symmetry axis and to a first and a second diagonal symmetry axis. The ring gyroscope also comprises a suspension structure configured to support the weight of the ring and the mass elements, wherein the suspension structure comprises N outer suspenders, where N is an integer greater than or equal to two, and each outer suspender extends along a ring tangent from a suspension attachment point on the outer edge of the ring to an anchor point.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
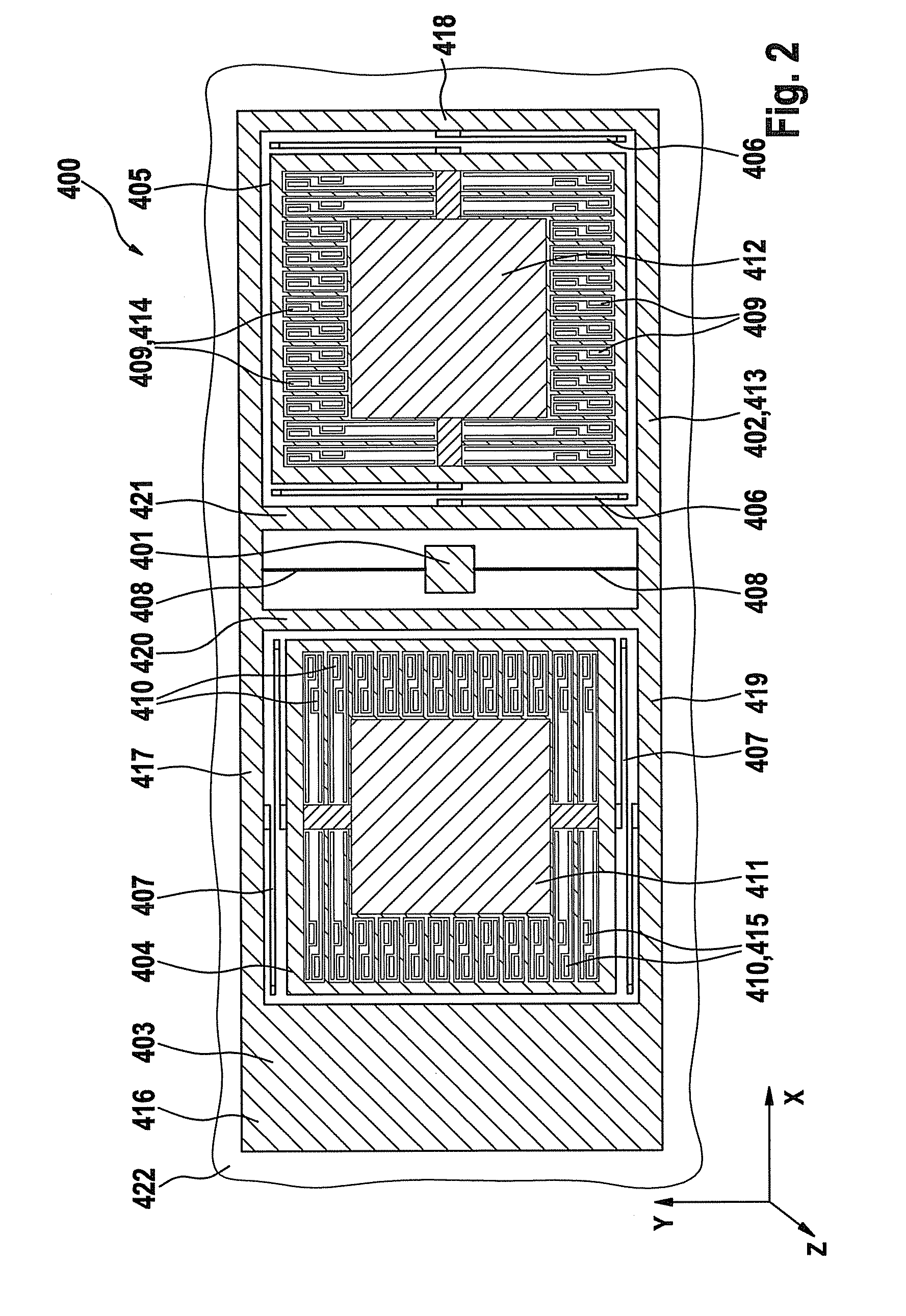
Triaxial acceleration sensor
InactiveCN101639487AEasy to detectTelevision system detailsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesMass elementAcceleration Unit
The present invention relates to an acceleration sensor, especially to a triaxial acceleration sensor, which includes a substrate and a first mass element, which is connected to the substrate in sucha way that the first mass element is rotatable about an axis, the first mass element being connected to a second mass element in such a way that the second mass element is movable along a first direction parallel to the axis, and the first mass element being connected to a third mass element in such a way that the third mass element is movable along a second direction perpendicular to the axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Two-free endpoint dynamic vibration absorber
ActiveCN101994776AEasy to installOptimize layoutNon-rotating vibration suppressionInertial massSnubber
The invention discloses a two-free endpoint dynamic vibration absorber, relating to the technical field of dynamic vibration absorber. The two-free endpoint dynamic vibration absorber comprises a spring (1), a damper (2) and an inertial mass energy accumulator (8); wherein the spring (1) is connected with the damper (2) in parallel and then is connected with the inertial mass energy accumulator (8) in series; the spring (1) is a helical compression one, and the damper (2) is a drum-type hydraulic one. The invention can be applied to the occasion that an endpoint can not be taken as a reference point and grounded and has wider application range compared with the traditional dynamic vibration absorber; the vibration absorber is provided with two free endpoints and can be placed horizontally, vertically and obliquely, vibration of master vibrator at any direction can be absorbed, thus being convenient to mount the vibration absorber; the inertial mass energy accumulator has the function of amplifying mass property, the weight thereof is far lighter than a mass element, thus greatly reducing the weight of large-scale dynamic vibration absorber.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Universal gravitation interference calculation method based on tetrahedral mass element division for pure gravity rail
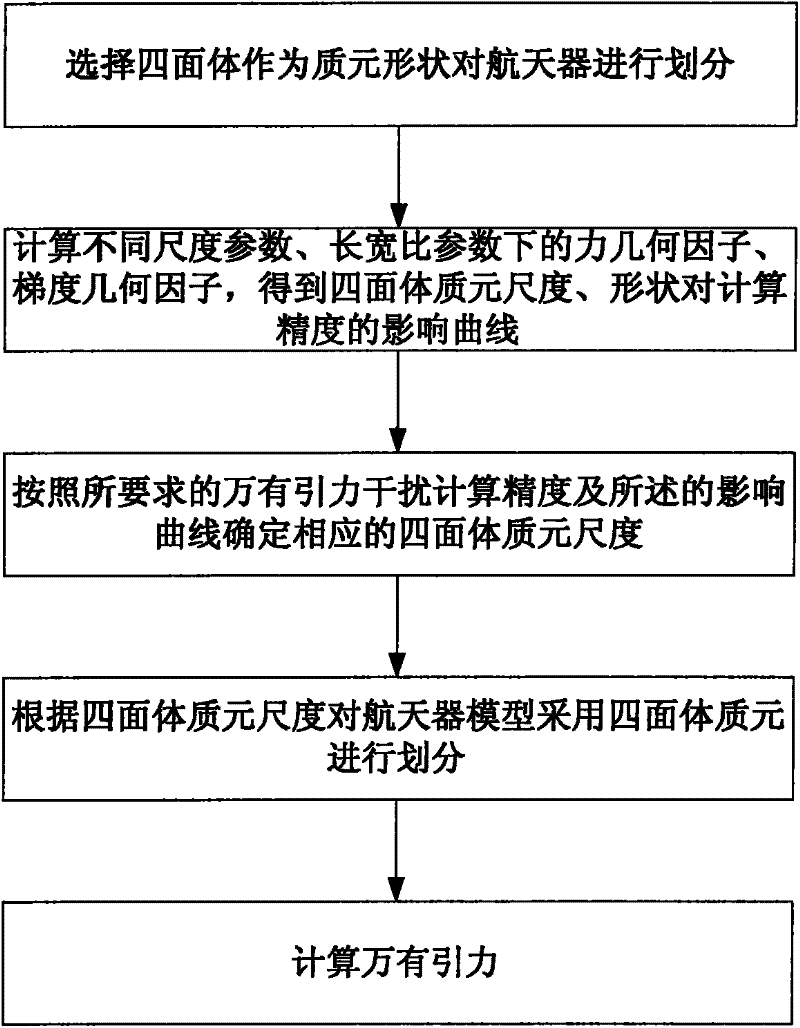
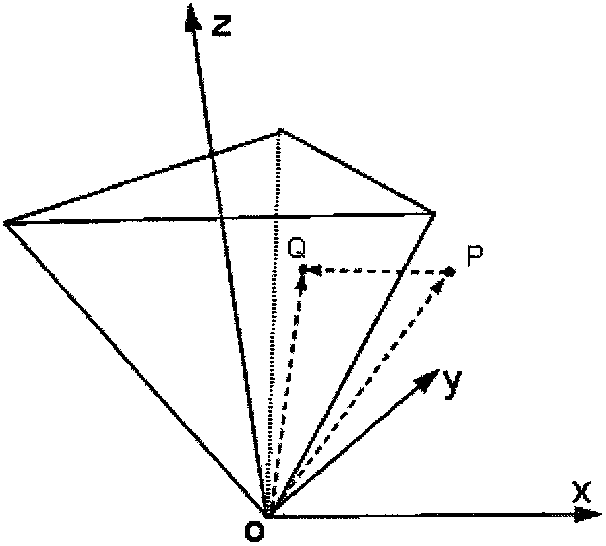
The invention discloses a universal gravitation interference calculation method based on tetrahedral mass element division for a pure gravity rail, belonging to the technical field of astrodynamics and scientific computing. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting a tetrahedron as the shape of a mass element to divide a spacecraft and defining the following parameters: a scale parameter SR, a length / width ratio parameter AR, a force geometry factor FGP and a gradient geometry factor GGP; then calculating the FGP and the GGP under different values of the SR and the AR toobtain a curve for representing the influence of the scale and the shape of the tetrahedral mass element on the calculation accuracy; then determining the scale of the tetrahedral mass element according to the required calculation accuracy and the influence curve and dividing a model of the spacecraft through the tetrahedral mass element according to the scale of the mass element; and finally, calculating the universal gravitation. Through the method, the universal gravitation of the spacecraft to the quality verification according to the required accuracy can be calculated. Under a given accuracy, the corresponding requirement on the scale of the tetrahedral mass element can be obtained and the mass element is divided according to the requirement so that the calculation of the universal gravitation is finished and the required accuracy is met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Micromechanical rotational rate sensor
InactiveUS20060107738A1Improve interferenceHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMass elementCoriolis force
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention creates a micromechanical rotational rate sensor having a first Coriolis mass element and a second Coriolis mass element which may be situated over a surface of a substrate. An exemplary embodiment of a micromechanical rotational rate sensor may have an activating device by which the first Coriolis mass element and the second Coriolis mass element are able to have vibrations activated along a first axis. An exemplary embodiment of a micromechanical rotational rate sensor may have a detection device by which deflections of the first Coriolis mass elements and of the second Coriolis element are able to be detected along a second axis, which is perpendicular to the first axis, on the basis of a correspondingly acting Coriolis force. The first axis and second axis may run parallel to the surface of the substrate. The detecting device may have a first detection mass device and a second detection mass device. The centers of gravity of the first Coriolis mass element, the second Coriolis mass element, the first detection mass device and the second detection mass device may coincide at a common mass center of gravity when they are at rest.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
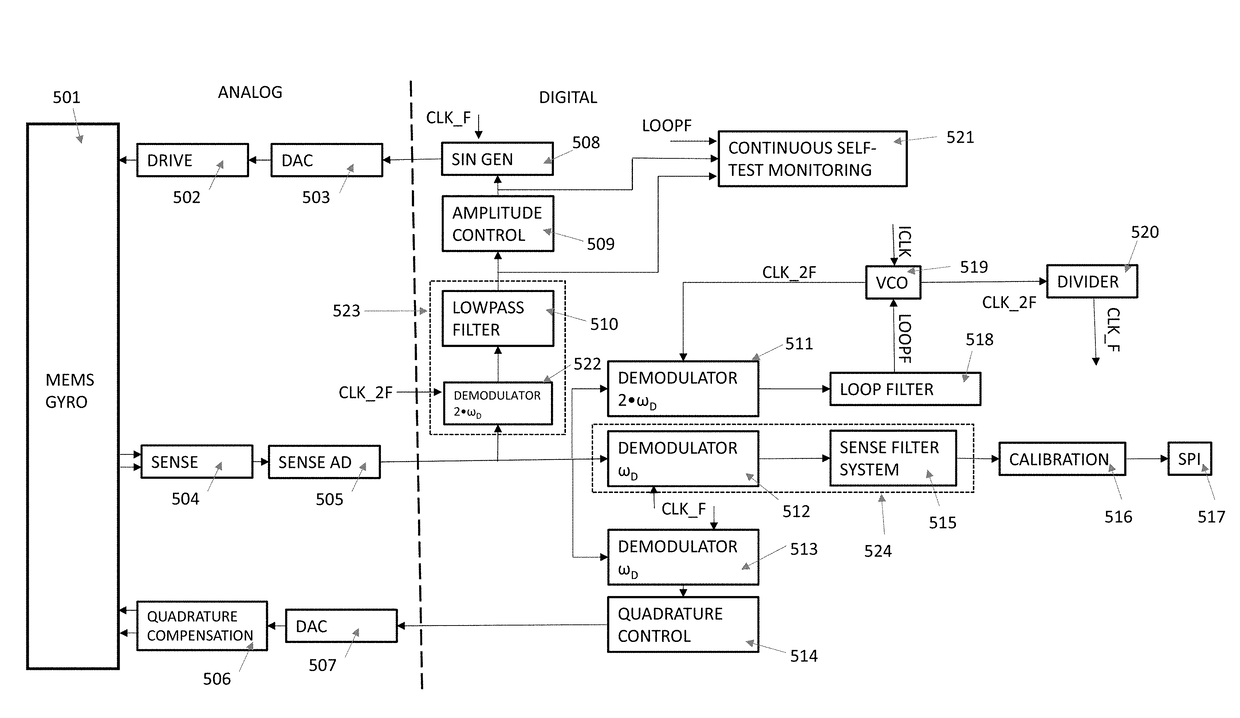
Continuous monitoring of drive amplitude in vibrating microelectromechanical gyroscopes
ActiveUS20170343351A1Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesVibration amplitudeGyroscope
The disclosure relates to a microelectromechanical gyroscope comprising at least one mass element, a drive actuator and sense electrodes. The at least one mass element is configured to be driven by the drive actuator into oscillating movement with a drive oscillation frequency ωD, and the sense electrodes are configured to produce a sense signal from the oscillating movement of the at least one mass element. The gyroscope control circuit comprises an amplitude detection unit which detects a sense signal amplitude at the frequency 2ωD. This amplitude yields a measure of drive oscillation amplitude. Amplitude detection at the frequency ωD yields a measure of angular rotation rate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
MEMS vacuum sensor based on the friction principle
InactiveUS20100024562A1Reduced dampingVacuum gauge using gaseous frictional resistance variationAtmospheric airEngineering
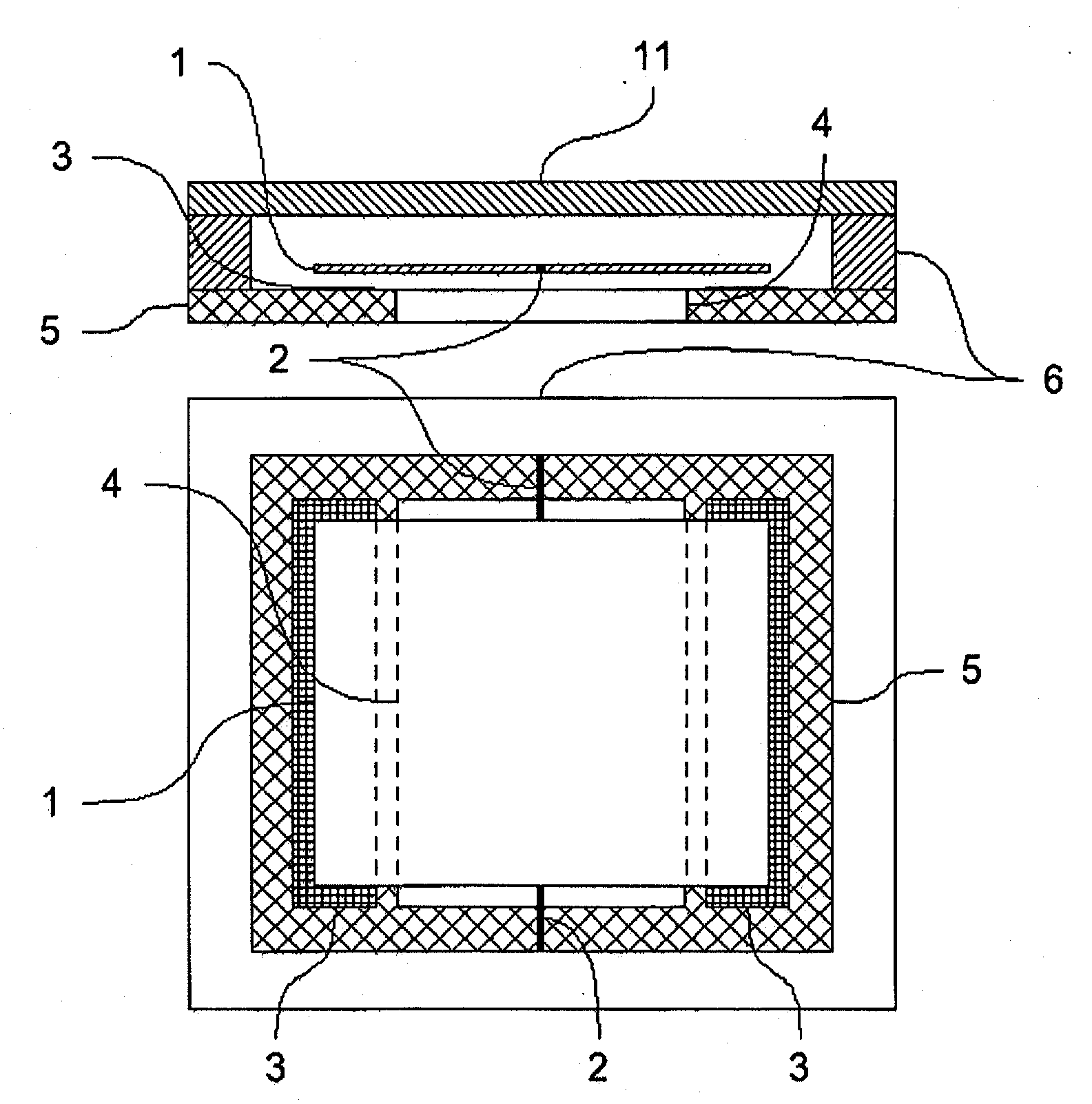
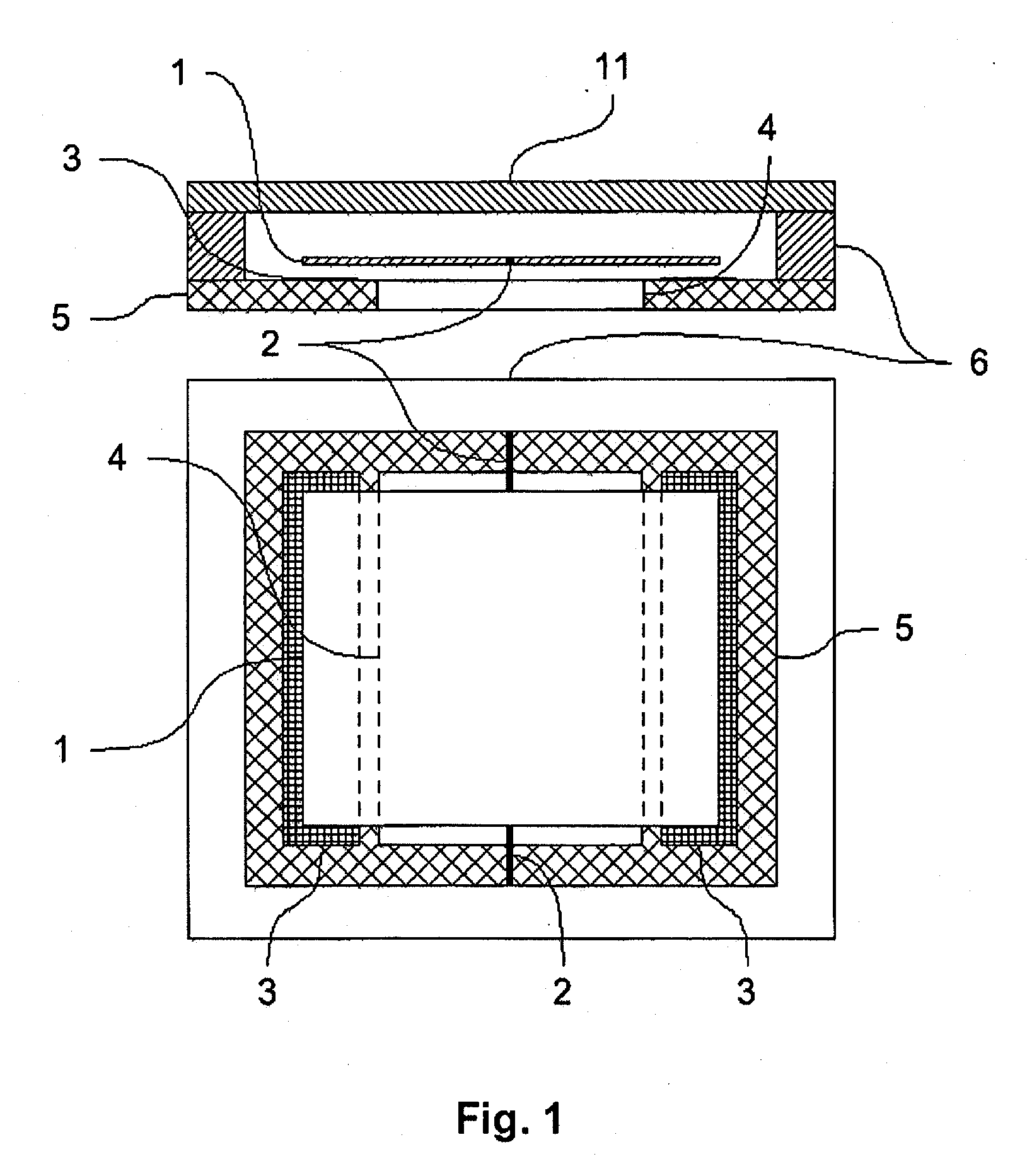
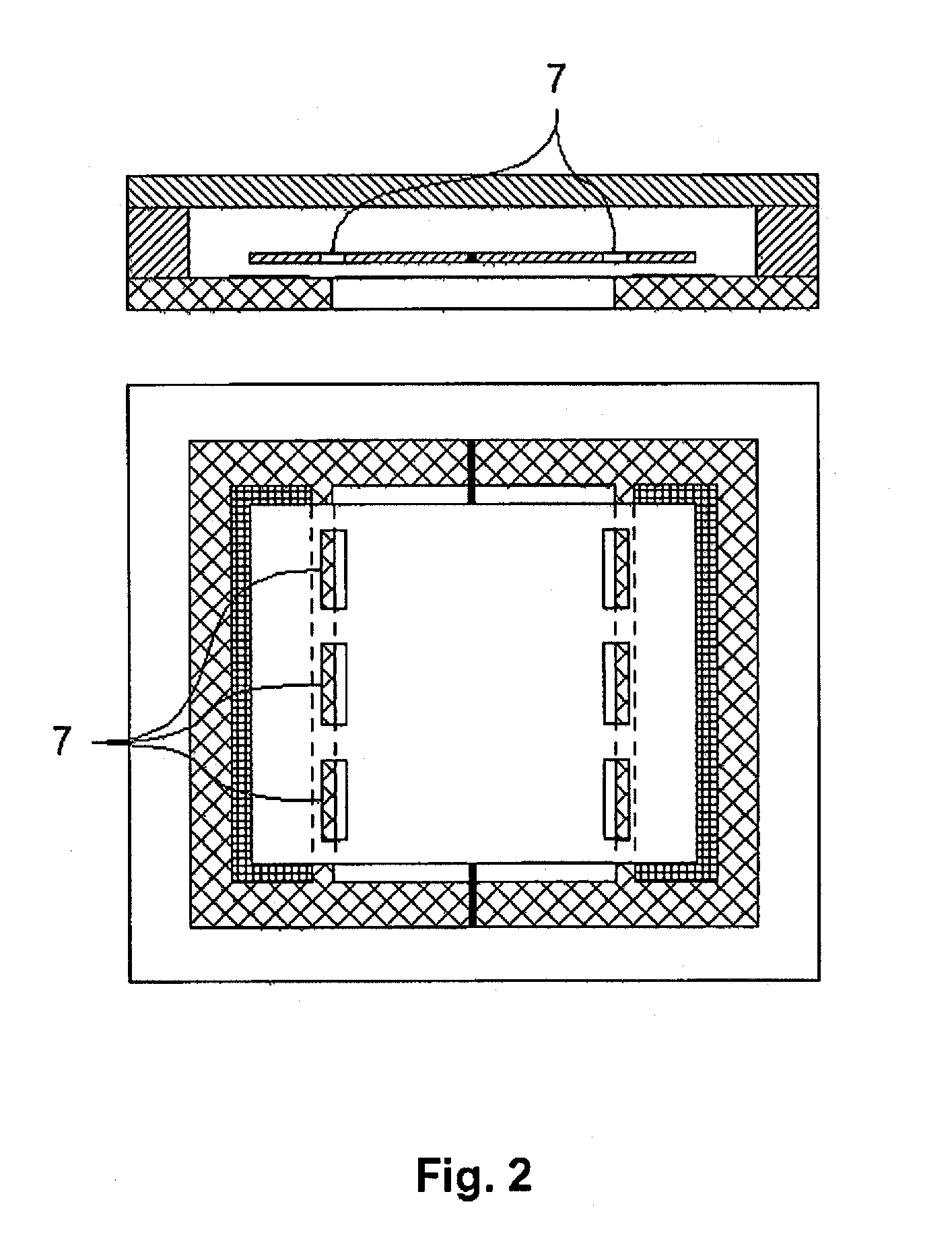
The invention relates to a sensor element for pressure measurement, having a substrate (5) and at least one mass element (1), which is arranged spaced apart from the substrate (5) and is connected in an oscillating manner to the substrate (5) and / or a support body (6) fixed relative to the substrate (5), so that a gap is formed between the mass element (1) and the substrate (5), the width of which can be varied through oscillations of the mass element (1). At least one recess and / or at least one bushing (4) is located in the surface of the substrate (5) delimiting the gap, which recess is used for reducing the damping of the oscillation of the mass element through the gas or plasma surrounding the mass element (1). The sensor element is used in particular in pressure sensors for measuring pressures in the vacuum range. Through the use of the sensor element according to the invention as a pressure sensor, maximum pressures up to the range of atmospheric air pressure can be recorded. The lowest pressures to be determined are in the range of 10−6 mbar.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com