Patents
Literature
605 results about "Torsional deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-frequency vibration motor for electric toothbrush
ActiveCN102111032AReduce in quantityReasonable structureMechanical energy handlingTooth cleaningVibration amplitudeReciprocating motion
The invention relates to the technical field of electric toothbrushes, in particular to a high-frequency vibration motor for an electric toothbrush. The high-frequency vibration motor for the electric toothbrush comprises a shell and a rear cover, wherein a stator, a rotating shaft and an adjusting pad are arranged in the shell; the output end of the rotating shaft is connected with the rear cover through a spring piece; the spring piece comprises a spring piece main body and an elastic arm; the motor generates power to drive the rotating shaft to rotate reciprocally so as to drive the springpiece connected with the rotating shaft to twist to generate torsional deformation; when the frequency of the motor generating reciprocating movement is close to or reaches the torsional resonant frequency of the spring piece, the torsional vibration amplitude of the spring piece reaches the maximum so that the swinging amplitude of the motor reaches the maximum; because of the influence of the reluctance force of the motor per se, the vibration amplitude of an overall system reaches a balanced state, and the spring piece and the motor generate movement under the balanced condition. The high-frequency vibration motor for the electric toothbrush is easy to manufacture and position, along with reasonable structure, less elements, simple machining process, low cost and long service life.
Owner:DONGGUAN LEBOND ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Optical deflector, optical scanner, image forming apparatus, and image projector
ActiveUS20100309536A1Improve driving efficiencyLarge rotationOptical elementsTorsional deformationEngineering
Owner:RICOH KK
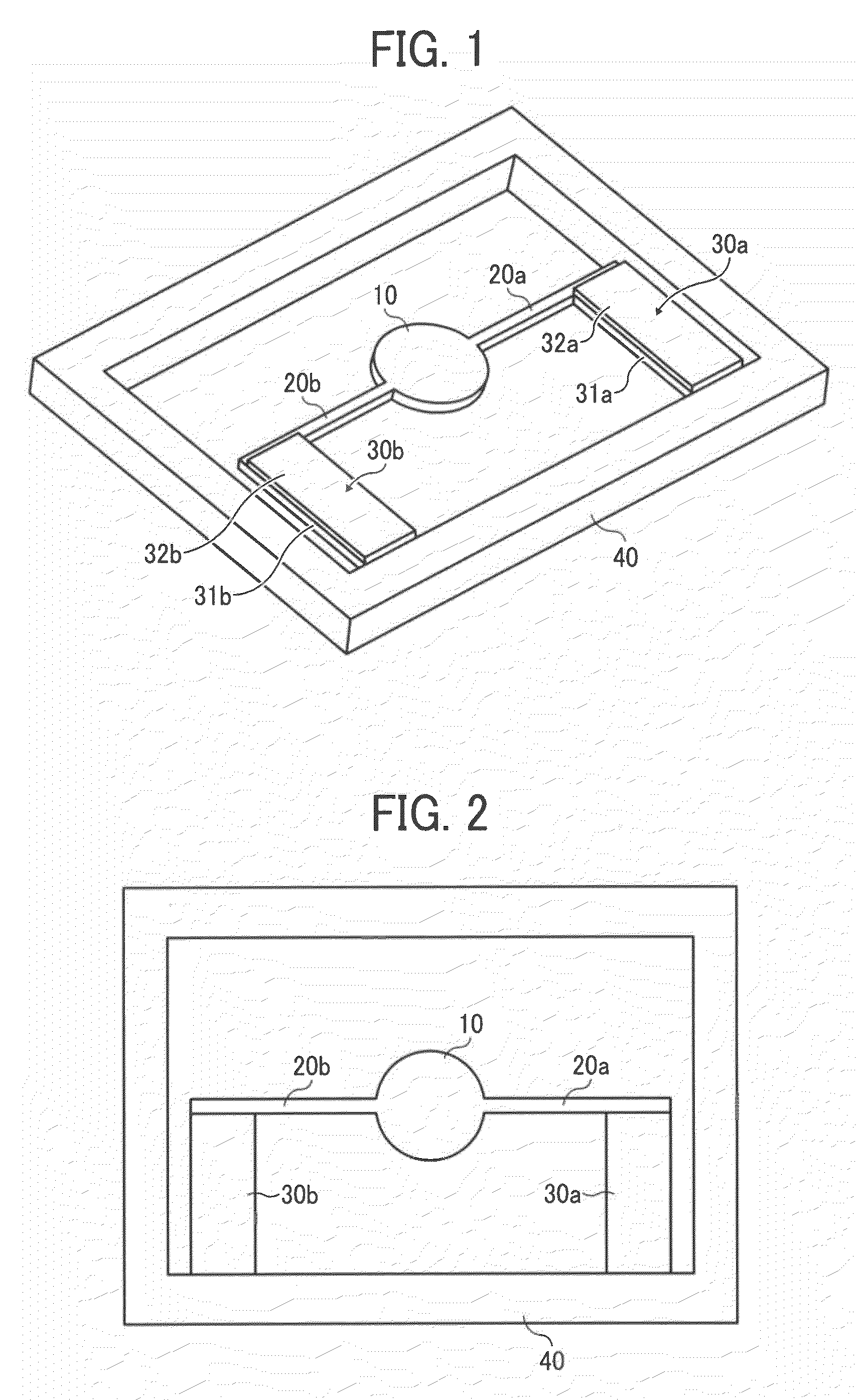
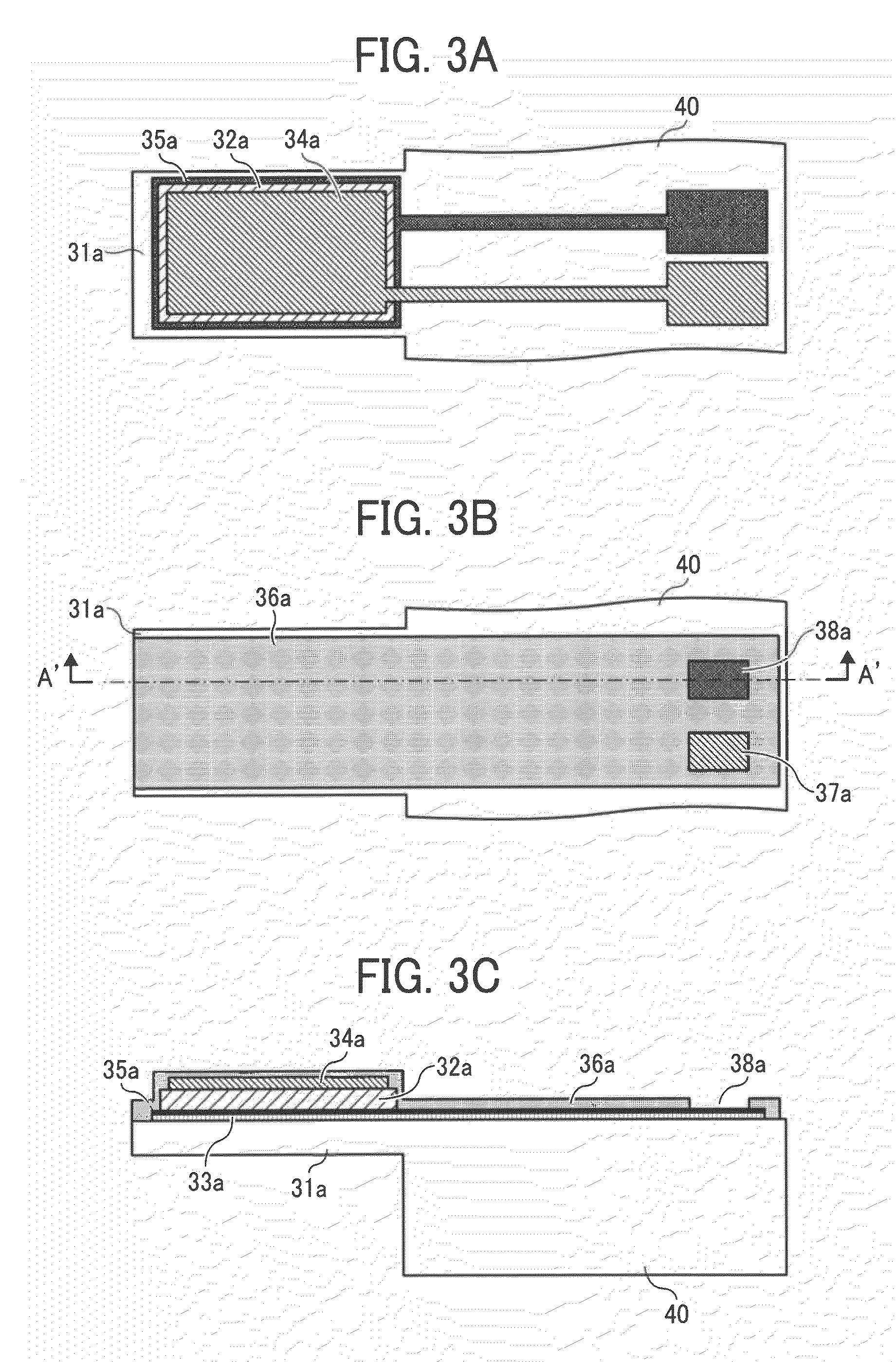
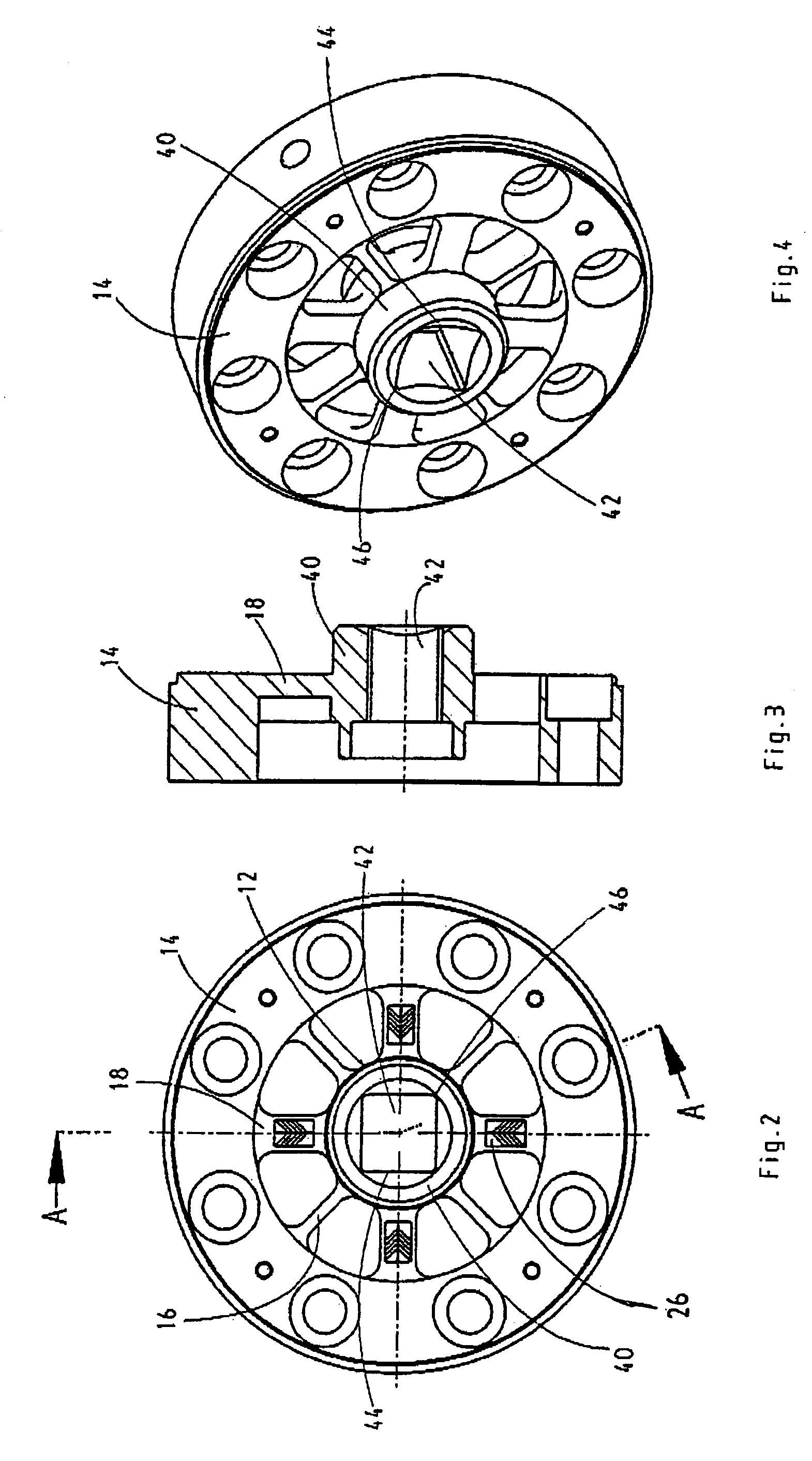
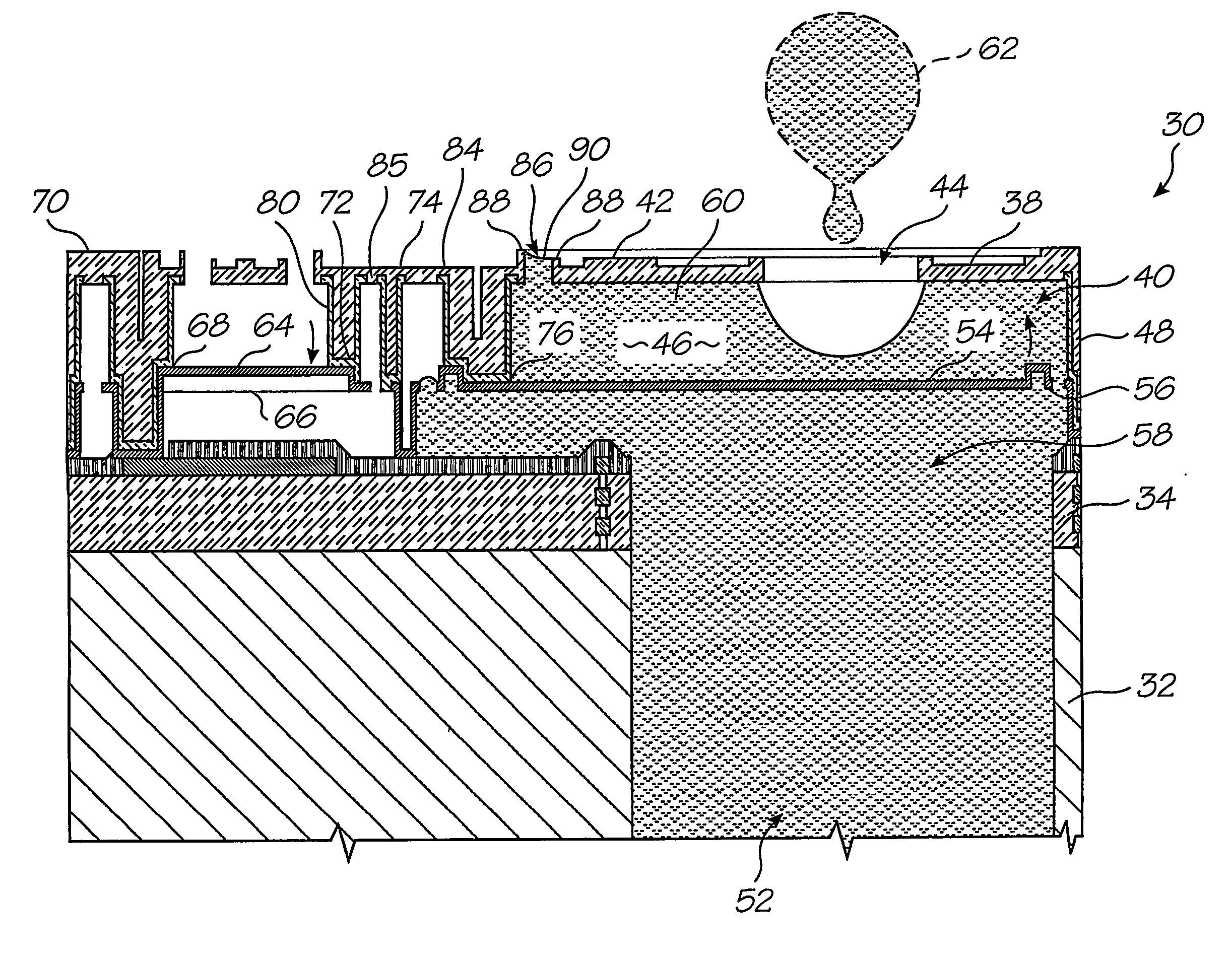
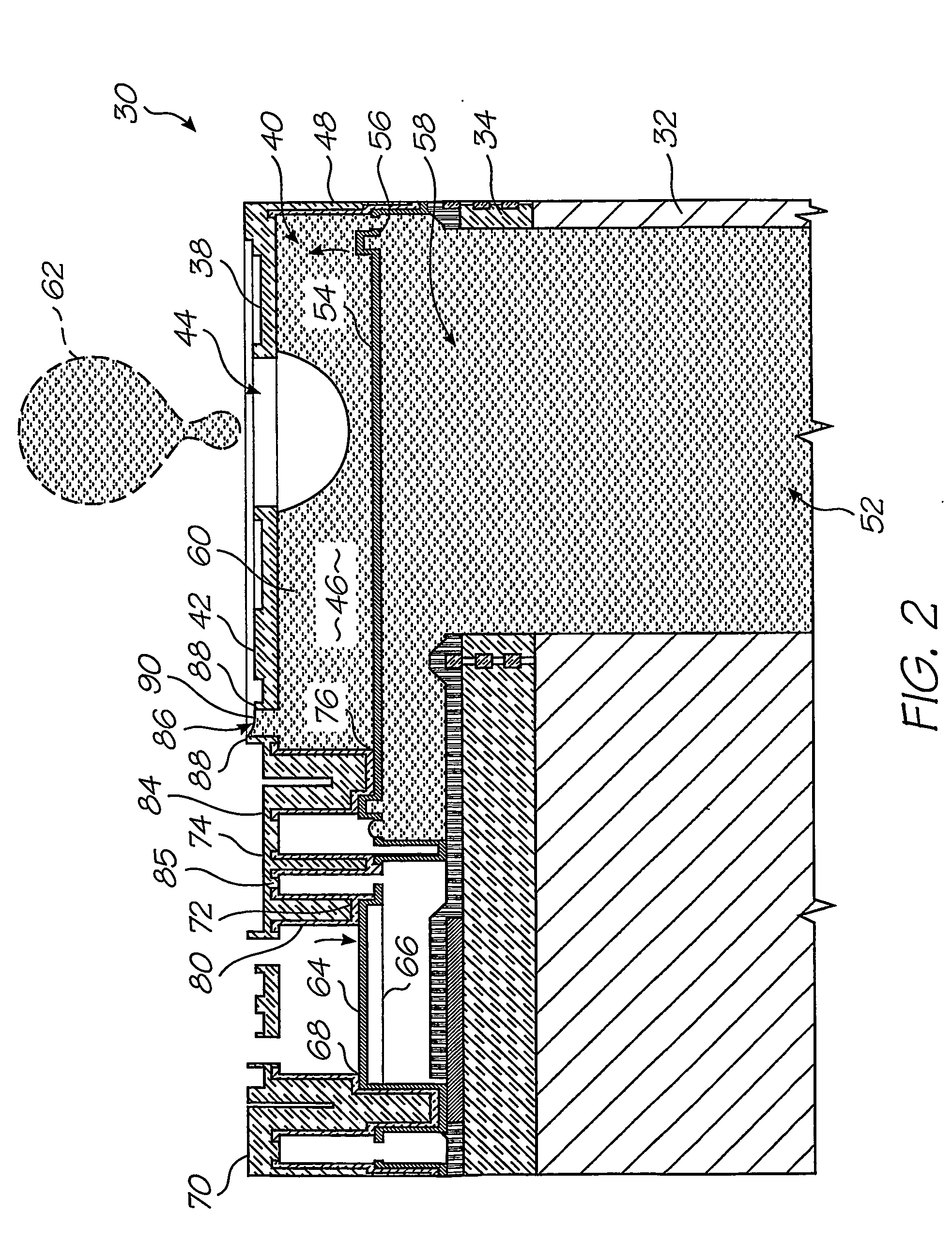
Motion transmitting structure for a nozzle arrangement of a printhead chip for an inkjet printhead
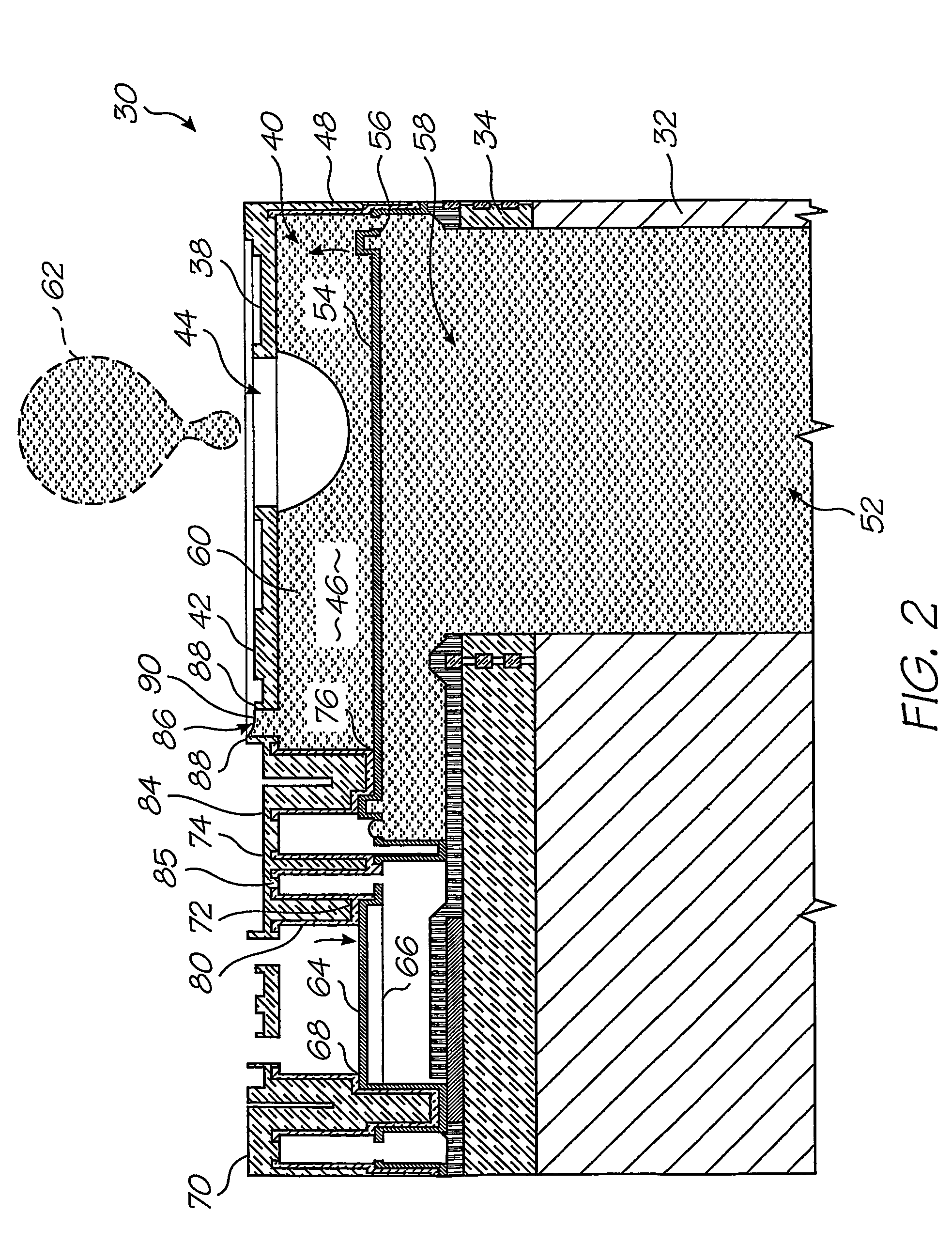
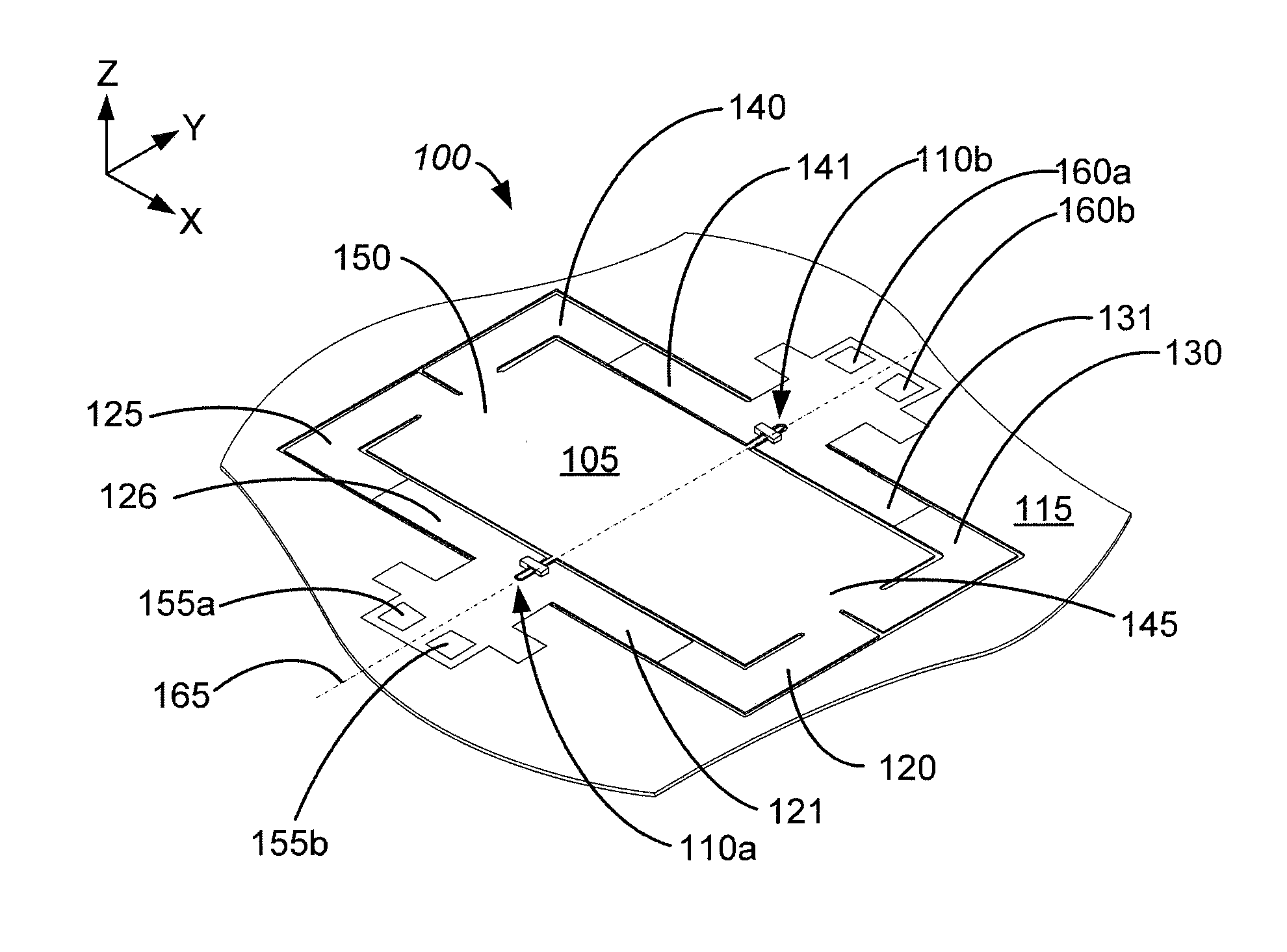
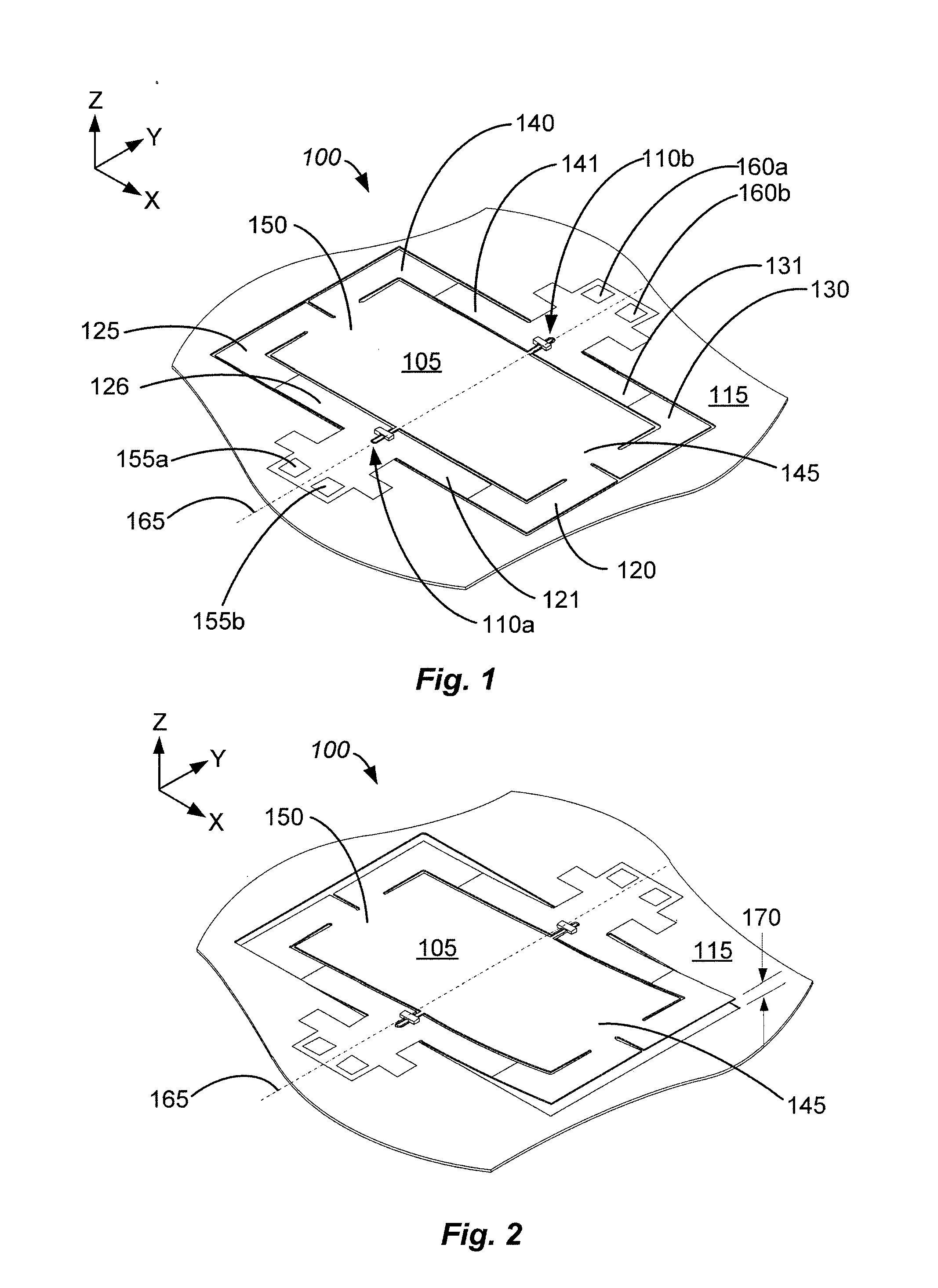
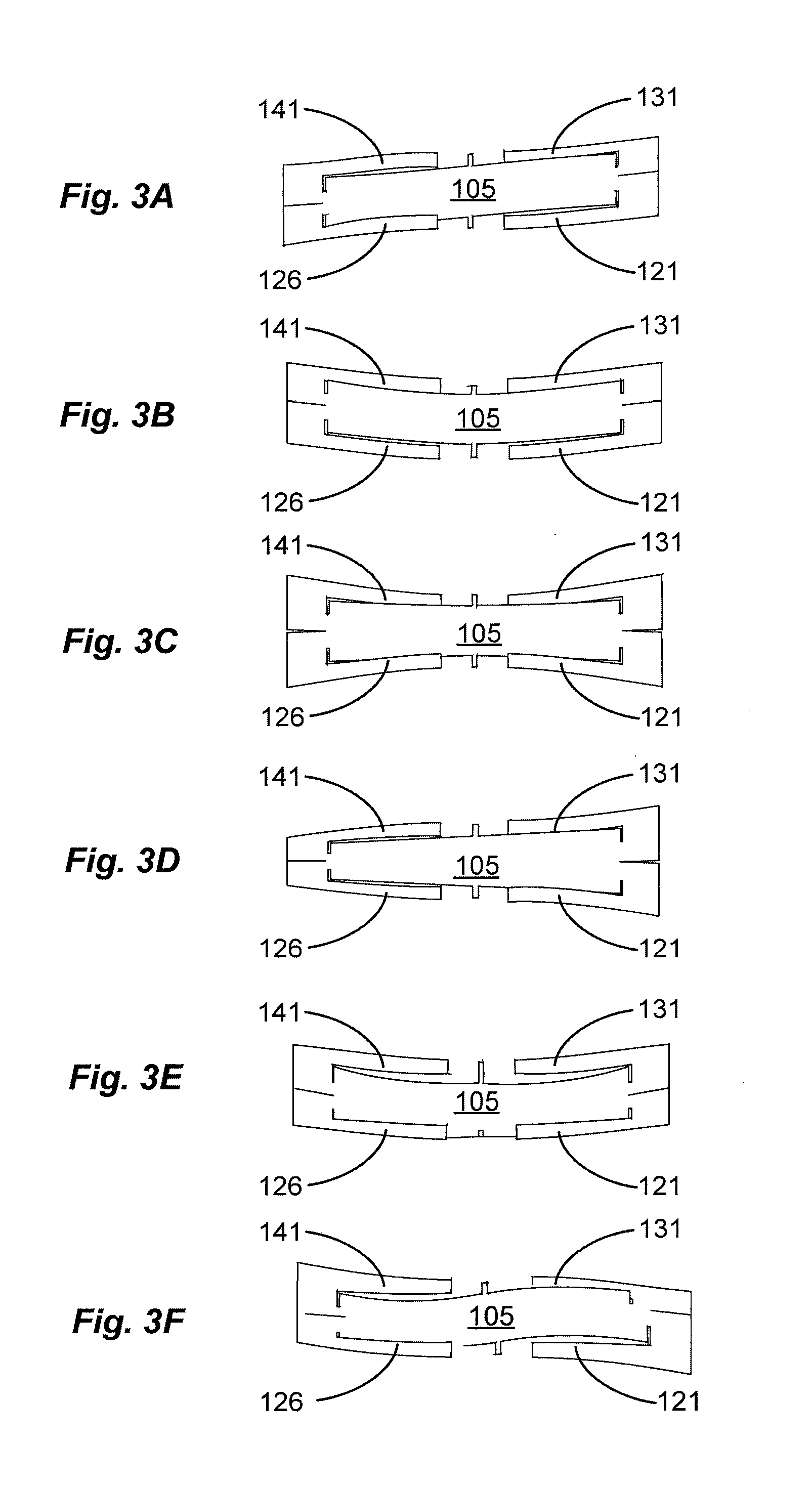
A printhead chip for an inkjet printhead includes a plurality of nozzle arrangements (100) positioned on a substrate (32). Each nozzle arrangement includes a chamber structure defining a nozzle chamber (106) that receives ink. An ink ejecting member (140) positioned in the nozzle chamber is displaceable in the nozzle chamber to eject ink from the nozzle chamber. Each nozzle actuator (148) is positioned on the substrate, the actuator having a working portion (156) displaceable with respect to the substrate when the actuator receives a driving signal. A sealing structure (130) is positioned on the substrate between the actuator and the ink-ejecting member inhibiting ink flow between the ink ejecting member and the actuator. A motion transmitting structure (122) pivotally bridges the sealing structure and interconnects the working portion (156) of the actuator and the ink-ejecting member (140) to transmit displacement of the working portion relative to the substrate to the ink ejecting member. Slotted openings (174) form a pair of opposed flexural connectors (178) between the outer structure (170) and the motion transmitting structures (122) allowing torsional deformation accommodating pivotal movement during operation of the nozzle arrangement.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
Spinning method
ActiveCN104858285AMeet SpinningFlexible settingsShaping toolsTorsional deformationMechanical engineering
The invention provides a spinning method. The outside spinning technology is combined with synchronous rotation and the spinning technology of a short core mold to achieve integral spinning forming of super-long thin-wall cylindrical parts, and the therefore the technical problem that the common outside spinning technological method cannot be used for spinning the super-long thin-wall cylindrical parts is solved. According to the spinning method, the function of synchronous rotation of the two ends of workpieces is increased, the problem of torsional deformation of the super-long thin-wall cylindrical parts is solved, and therefore the precision of products is improved; the short core mold is adopted, so that the problems that core molds of the super-long thin-wall cylindrical parts lower heads and vibrate, the manufacturing cost is high, and demolding is difficult are solved, and integral spinning forming of the super-long thin-wall cylindrical parts is achieved.
Owner:海鹰空天材料研究院(苏州)有限责任公司
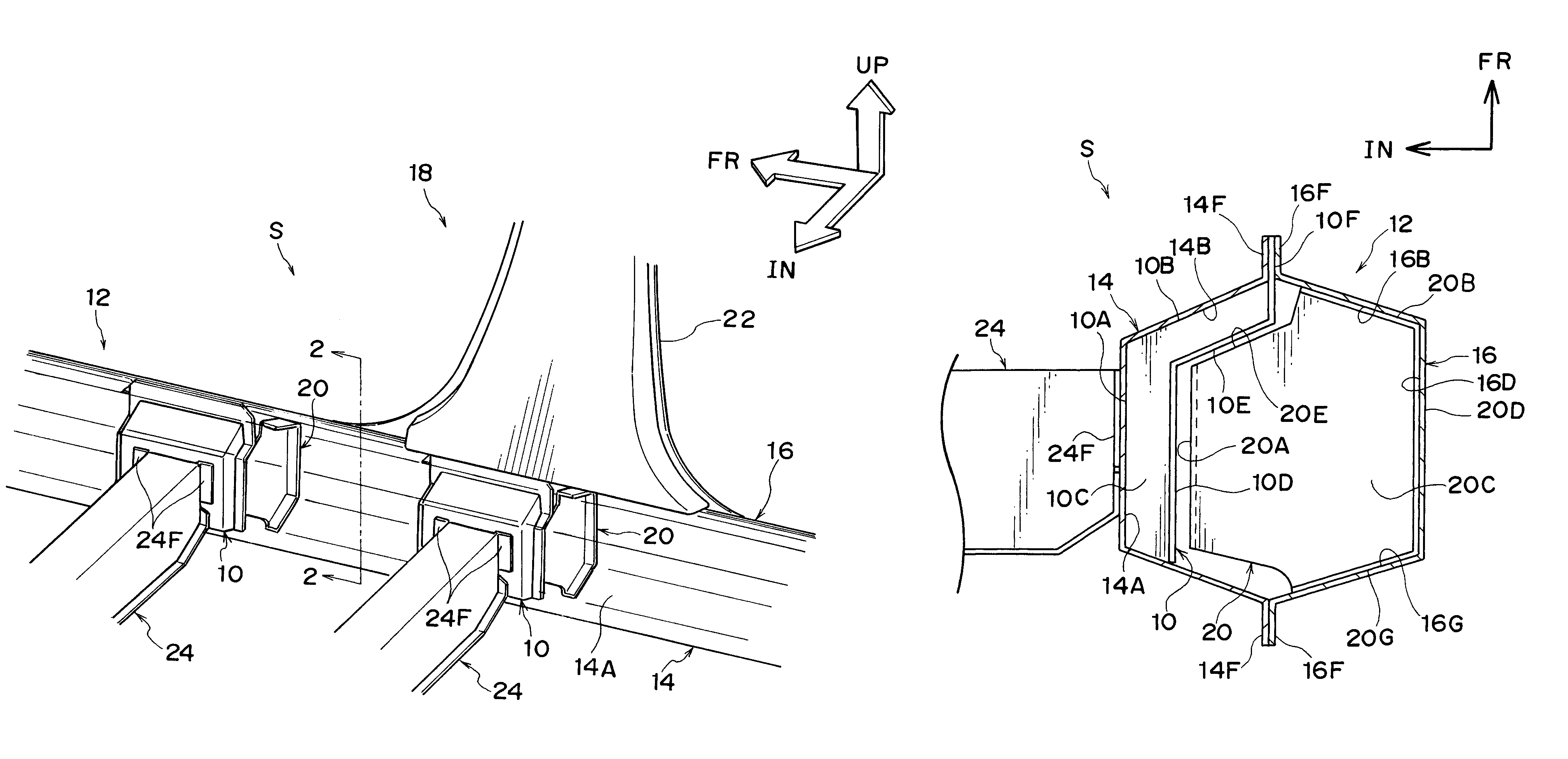
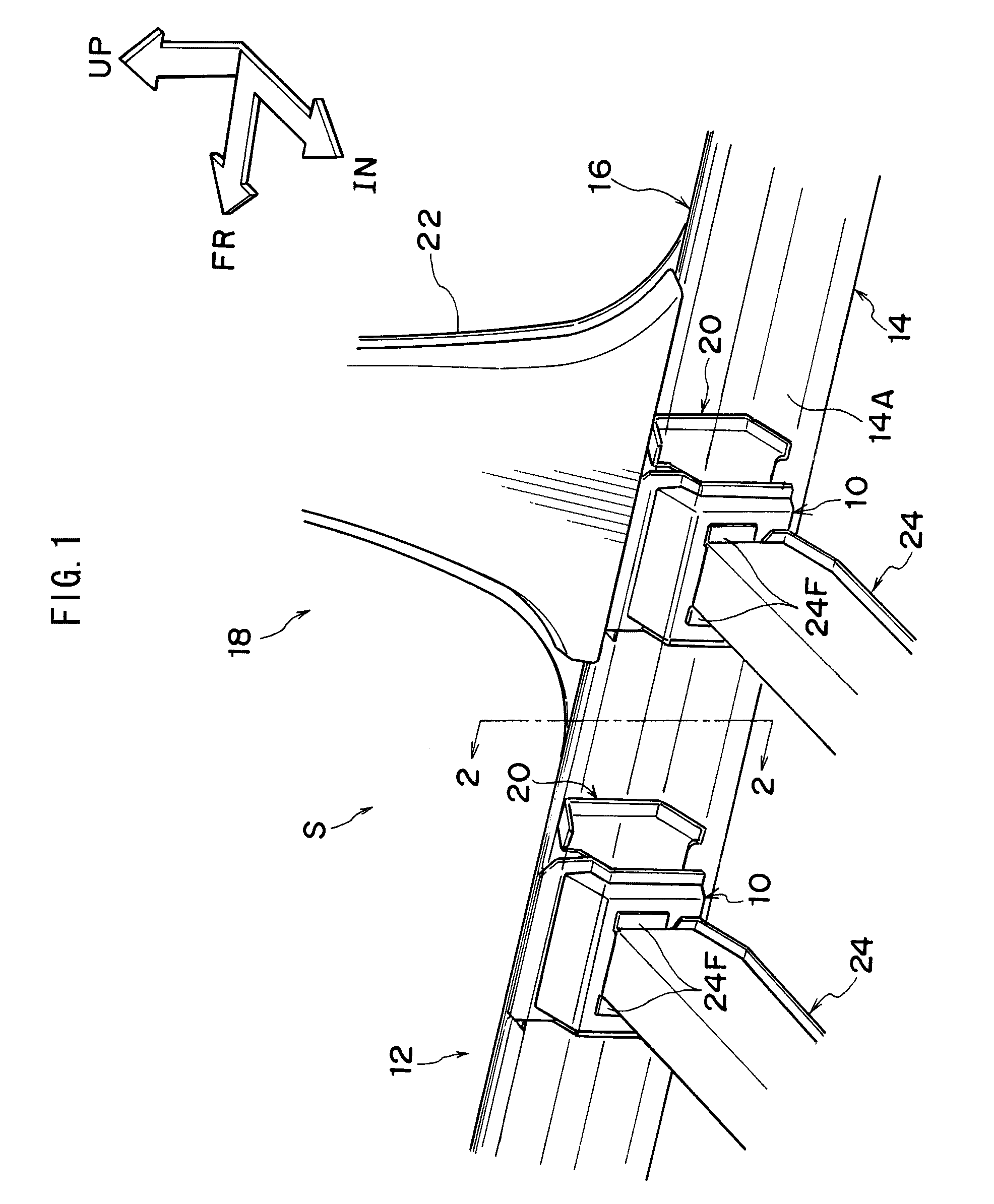
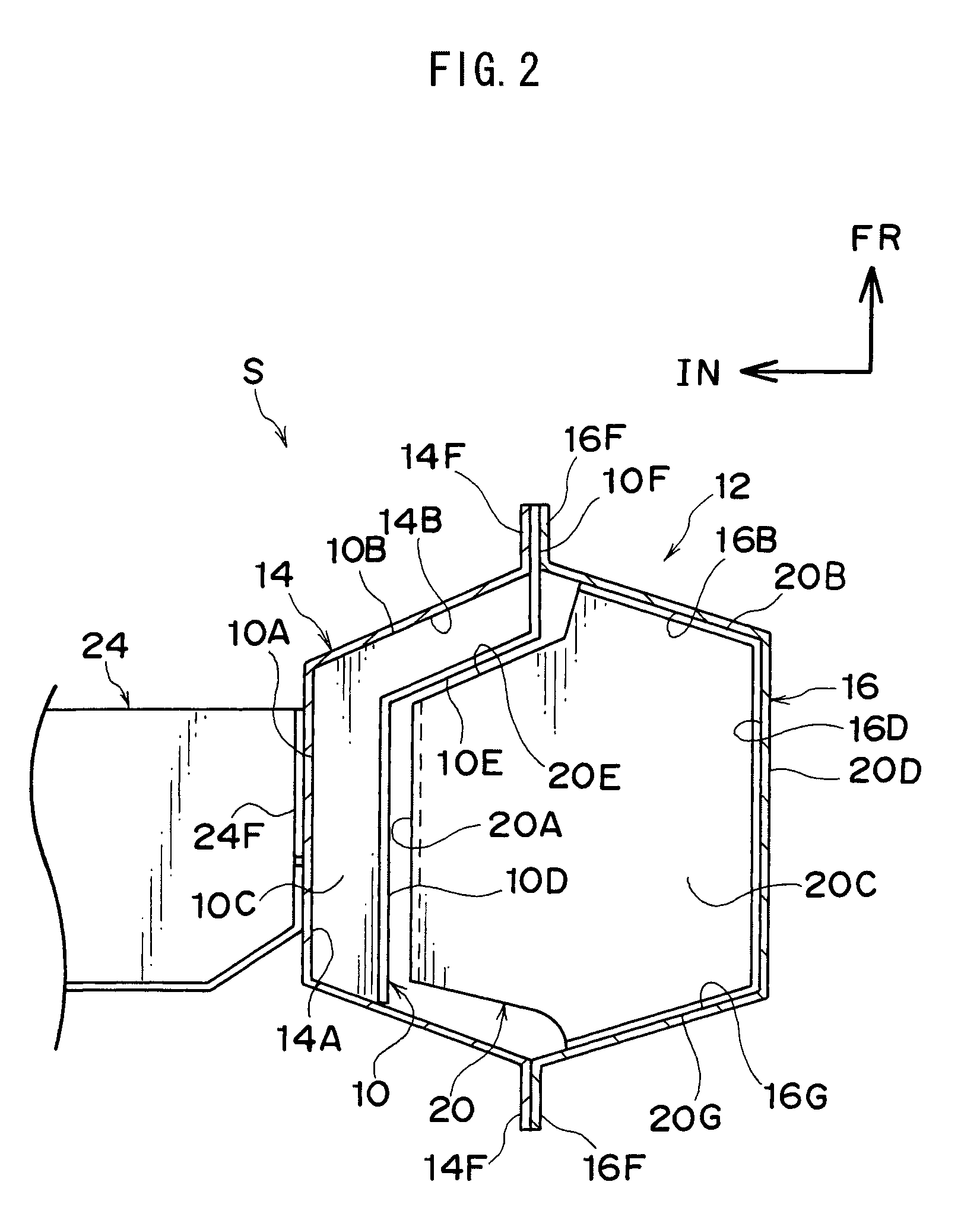
Vehicle body lower structure
ActiveUS7963588B2Suppression of deformationGood effectVehicle seatsUnderstructuresInterior spaceEngineering
An object is to suppress vehicle body deformation in a side collision without sacrificing a vehicle interior space.Provided is a first reinforcing member 10 disposed in a locker 12 at a vehicle lateral direction inner side, and a second reinforcing member 20 disposed in locker 12 at a vehicle lateral direction outer side, which opposes first reinforcing member 10 in a vehicle lateral direction, and which is provided with a side surface 20A and an end surface 20E (engaging portions) that engage with first reinforcing member 10 when locker 12 deforms. When locker 12 begins to deform due to a side collision to a vehicle 18, end surface 20E of second reinforcing member 20 contacts and engages flange 10E of first reinforcing member 10, and a torsional deformation can be suppressed, and side surface 20A contacts flange 10D, and a crushing deformation of locker 12 in a vehicle lateral direction can be suppressed. Since first reinforcing member 10 and second reinforcing member 20 are provided in locker 12, vehicle interior space is not sacrificed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
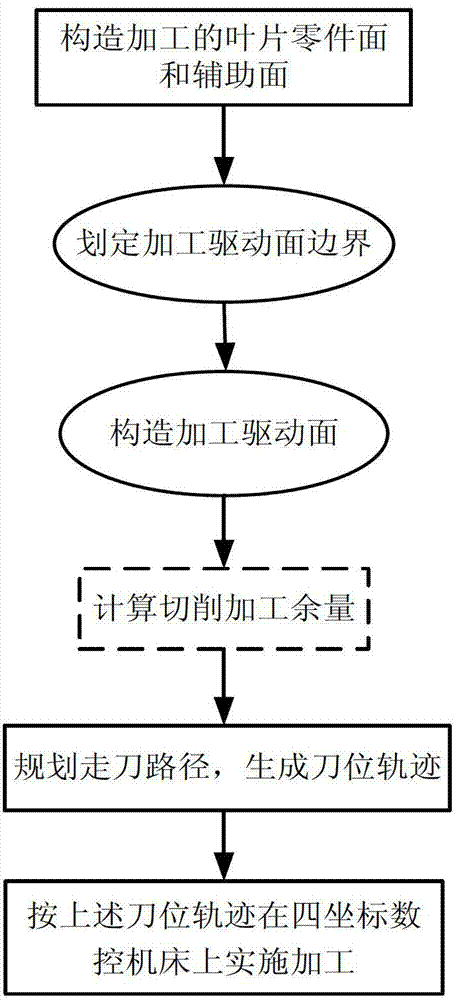
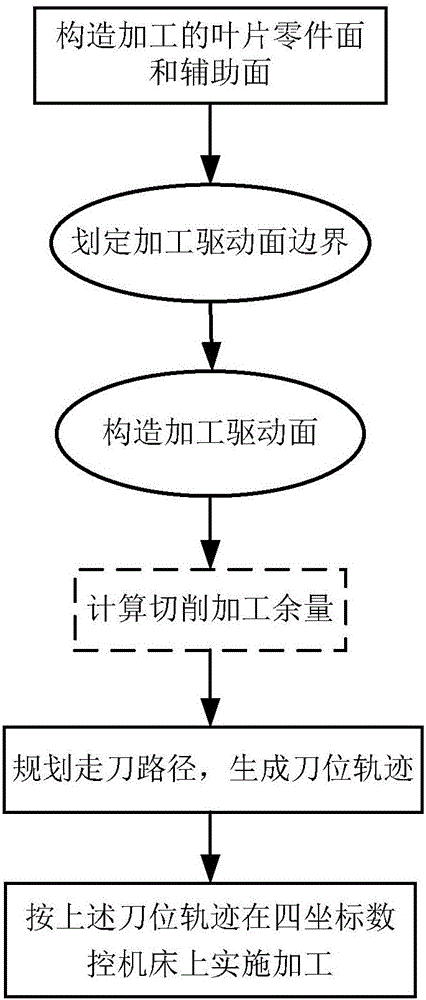
Precise milling processing method with variable inter-row allowance for thin walled blade of difficult-to-process material
ActiveCN102873384AThe direct effect is obviousImprove section positionMilling equipment detailsSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical controlTorsional deformation
The invention provides a precise milling processing method with a variable inter-row allowance for thin walled blades of difficult-to-process materials; four driving curved surfaces are obtained by cutting a blade root boundary surface and a blade tip boundary surface into a blade back curved surface and a blade basin curved surface; parameter lines with equal u on the driving curved surfaces are used as processing paths; a cutting row allowance for each processing path is set respectively; and finally processing on the four driving curved surfaces are completed circularly. The invention facilitates the improvement of the blade cross section position accuracy, facilitates the improvement of the blade surface profile tolerance, and facilitates the reduction of the blade torsional deformation; when compared with traditional vertical cutting with a constant allowance and spiral milling methods, the invention can solve the technical problems of large torsional deformation, poor profile precision, difficultly-controlled cross section position accuracy error, and the like, and can realize the high-efficient precise numerical control processing of thin walled blades of difficult-to-process materials.
Owner:西安三航动力科技有限公司
Movable cover for rigidifying and/ or protecting the front face of an article of footwear, such as a snowboard boot
InactiveUS7207126B2Ensuring lateral rigidityEnsuring torsional rigiditySolesUpperTorsional deformationEngineering
Owner:SALOMON SA
Improved torsion force indicator
InactiveCN1442680AEfficient outputReduce physical burdenWork measurementTorque measurementAudio power amplifierSheet steel
An improved torsional force detector for the pedal of electric bicycle has a torsional force sensing axle in the the 5-way tube of frame at the position of drive disk gear. Its both ends are connected with the pedals. A crank joint block, elastic steel plate and torsional force detector group are positioned on the inner surface of said drive disk gear. A deformation amplifier is contained by saidtorsional force detector group for outputting the torsional deformation signal.
Owner:李书贤
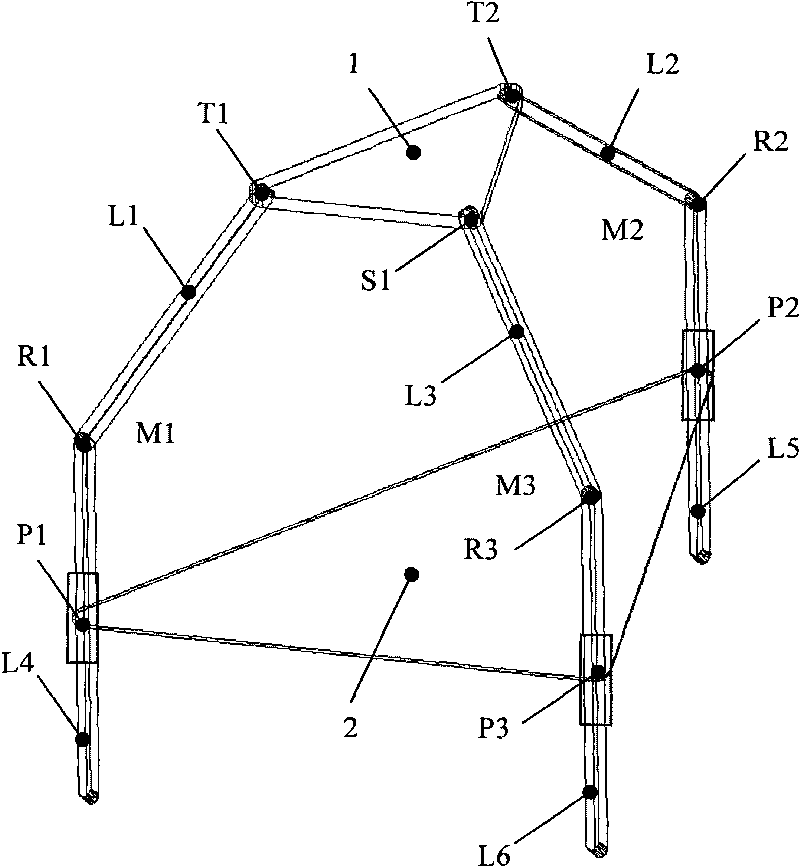
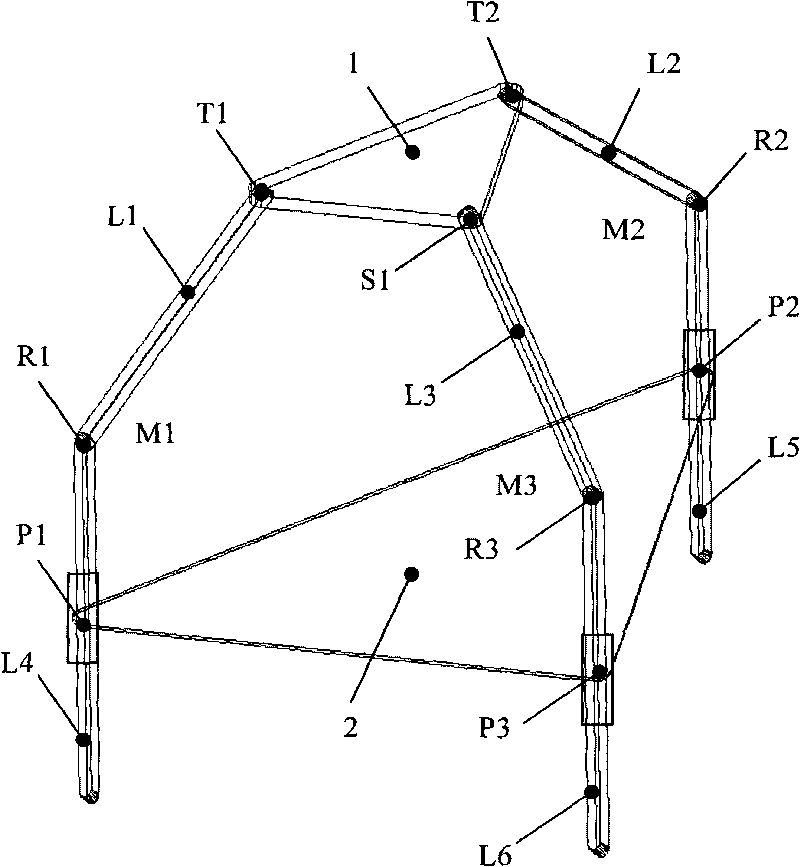
Fully decoupled three-degree-of-freedom parallel robot mechanism
InactiveCN101722511ARealize fully decoupled motion outputFew jointsProgramme-controlled manipulatorThree degrees of freedomEngineering
The invention discloses a fully decoupled three-degree-of-freedom parallel robot mechanism, which consists of a motion platform, a fixed platform and three fork chains connecting the two platforms, wherein two of the three fork chains have the same structure and each of the two fork chains consists of a hooke hinge, a rotary hinge, a moveable hinge and a connecting rod between the two fork chains from top to down; and the other fork chain consists of a spherical hinge, a rotary hinge, a moveable hinge and a connecting rod between the fork chains from top to down. The working platform of the mechanism of the invention can realize a one-translation two-rotation fully decoupled motion output; and the mechanism can effectively solve the problems of easy flexure and torsional deformation of the parallel mechanism caused by excessive freedom degrees of a motion pair and increase the whole load / weight ratio of the mechanism because the mechanism has few joints and only 13 freedom degrees of motion pair in total. In addition, a five-degree-of-freedom hybrid robot can be designed by connecting a two-degree-of-freedom rotary head with the motion platform in series and can be applied to complex curved surface machining and on other occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Actuator
InactiveUS20070025659A1Significant declineCompact structureMechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesEngineeringTorsional deformation
The actuator has a movable mass portion and a pair of drive mechanisms for driving the movable mass portion. Each of the pair of drive mechanisms includes a drive mass portion, a support portion for supporting the drive mass portion, a first elastic connecting portion interconnecting the drive mass portion and the support portion so as to allow the drive mass portion to be pivoted about a pivotal axis with respect to the support portion, and a second elastic connecting portion interconnecting the drive mass portion and the movable mass portion so as to allow the movable mass portion to be pivoted about a pivotal axis with respect to the drive mass portion. The first elastic connecting portion includes a pair of bending bars opposed to each other with interposing the pivotal axis of the drive mass portion therebetween. The first elastic connecting portion includes a pair of piezoelectric elements jointed respectively onto the pair of bending bars so as to bend the pair of bending bars in opposite directions to cause pivotal movement to the drive mass portion. The pivotal movement of the drive mass portion causes torsional deformation to the second elastic connecting portion so as to pivot the movable mass portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Push-bending forming process for hollow blade
InactiveCN103551472AOvercome stabilityImprove product qualityShaping toolsEngine componentsTorsional deformationLubricant
The invention discloses a push-bending forming process for a hollow blade. The process comprises producing a mould cavity curved surface according to a finished product hollow blade appearance curved surface; machining a mould according to the mould cavity curved surface and forming a mould cavity passage with two open sides in the mould; designing a chuck according to the blade tenon shape; fixing the chuck and the mould on a hot press; coating high-temperature lubricants on the inner surface of the mould cavity and the surface of a blade blank; mounting the blade blank on the chuck. The hot press acts, the mould is closed, the chuck drives the blade to move towards the mould to push the blade into the mould cavity from one end of the mould cavity passage, and the blade is forced to be bent under the action of the mould cavity inner surface and is subjected to torsional deformation; the mould is opened after the torsional deformation is kept for certain time, and the formed blade is dismounted. According to the process, slab hollow blade blanks can be formed into complex torsional forms and are provided with required torsion angles, the forming process is stable and convenient and fast, the speed is controllable, deformation distribution of all parts are uniform, and the production efficiency is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Pipeline inner wall bionic groove surface machining device and machining method thereof
ActiveCN107139251AGuarantee the quality of workCompact designMetal working apparatusTorsional deformationMachining process
The invention provides a pipeline inner wall bionic groove surface machining device and a machining method thereof. The device comprises a drive mechanism used for providing drive force, a traveling mechanism used for supporting the inner wall face of a pipeline, a machining mechanism used for machining a bionic groove in the inner wall of the machined pipeline, and a controller. The drive mechanism is installed on the traveling mechanism through bolts. The machining mechanism is fixedly connected with the traveling mechanism through bolts. The drive mechanism and the machining mechanism are electrically connected with corresponding control ends of the controller. The method comprises the steps that according to the diameter of the pipeline needing to be machined, a front and back traveling unit is adjusted in a rotating manner, after the machining mechanism is moved to the position, to be machined, on the inner wall of the pipeline, the traveling unit stops moving and presses the inner wall of the pipeline, the cutter position of the machining mechanism is adjusted, and the groove in the inner wall of the pipeline begins to be machined. The device has the beneficial effects that tangential counter force borne by three tools in the cutting machining process can be offset, thus, bending deformation and torsional deformation are avoided, and meanwhile the device is high in precision, simple in structure and easy to operate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for calculating rigidity of aircraft airfoil surface structure
InactiveCN105109705AMeet the design requirementsAccurate calculationGround installationsElement analysisTorsional deformation
The invention discloses a method for calculating the rigidity of an aircraft airfoil surface structure. The method includes the steps that an airfoil-surface-structure finite element analysis model is built, wherein the airfoil-surface-structure finite element analysis model should be corrected through a static test and can really simulate the rigidity of the structure; sections of the root are restrained in the finite element analysis model, and then finite element analysis is carried out; the torsional rigidity of the structure is reversely derived through torsional deformation of the sections, and then the rigidity center positions of the sections are determined through a torsional rigidity calculation formula; and when the bending rigidity of the structure is calculated, small-deformation assumption is adopted, the finite element analysis is fitted to obtain displacement at the rigidity centers of the sections, a structure bending rigidity calculation formula is obtained accordingly, and the rigidity, the rigidity center positions and the bending rigidity of the aircraft airfoil surface structure are rapidly and accurately calculated through the structure bending rigidity calculation formula. In this way, the rigidity, the rigidity center positions and the bending rigidity of the aircraft airfoil surface structure are rapidly and accurately calculated; and in addition, experiments in aircrafts in multiple types verify that the algorithm is correct in principle, easy and convenient to implement and capable of meeting the aircraft designing requirement.
Owner:JIANGXI HONGDU AVIATION IND GRP
Traction kite with deformable leading edge
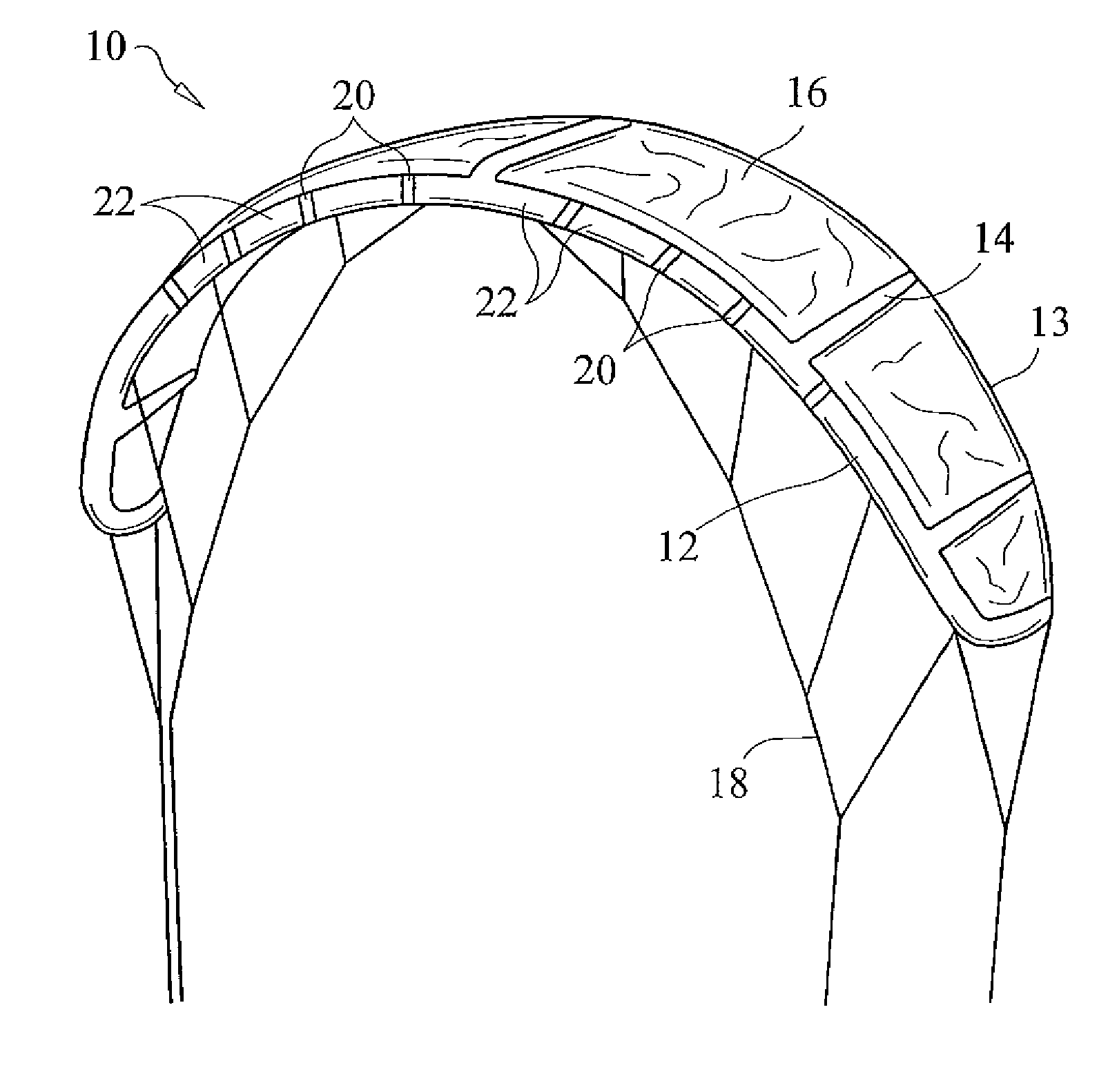
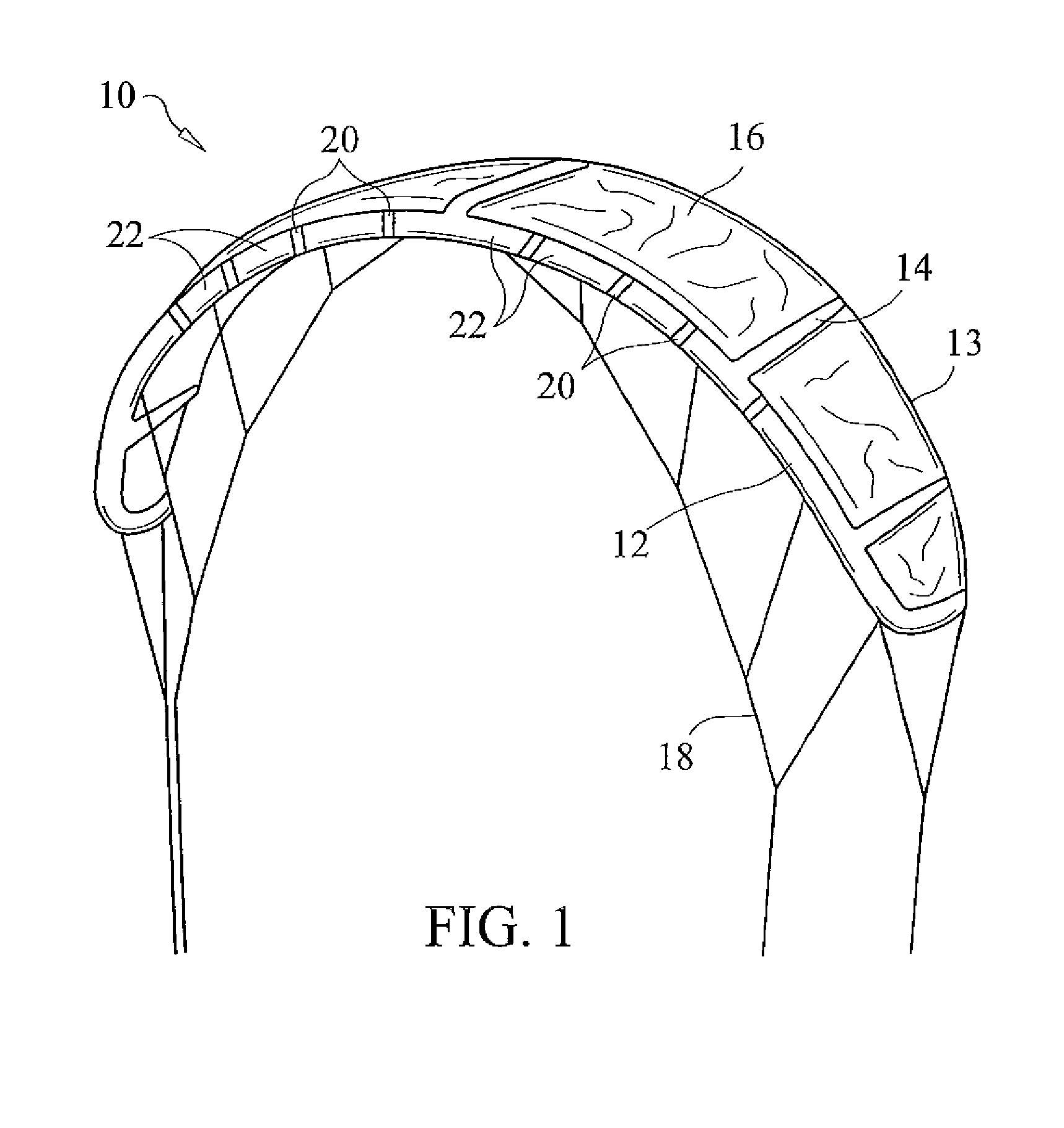
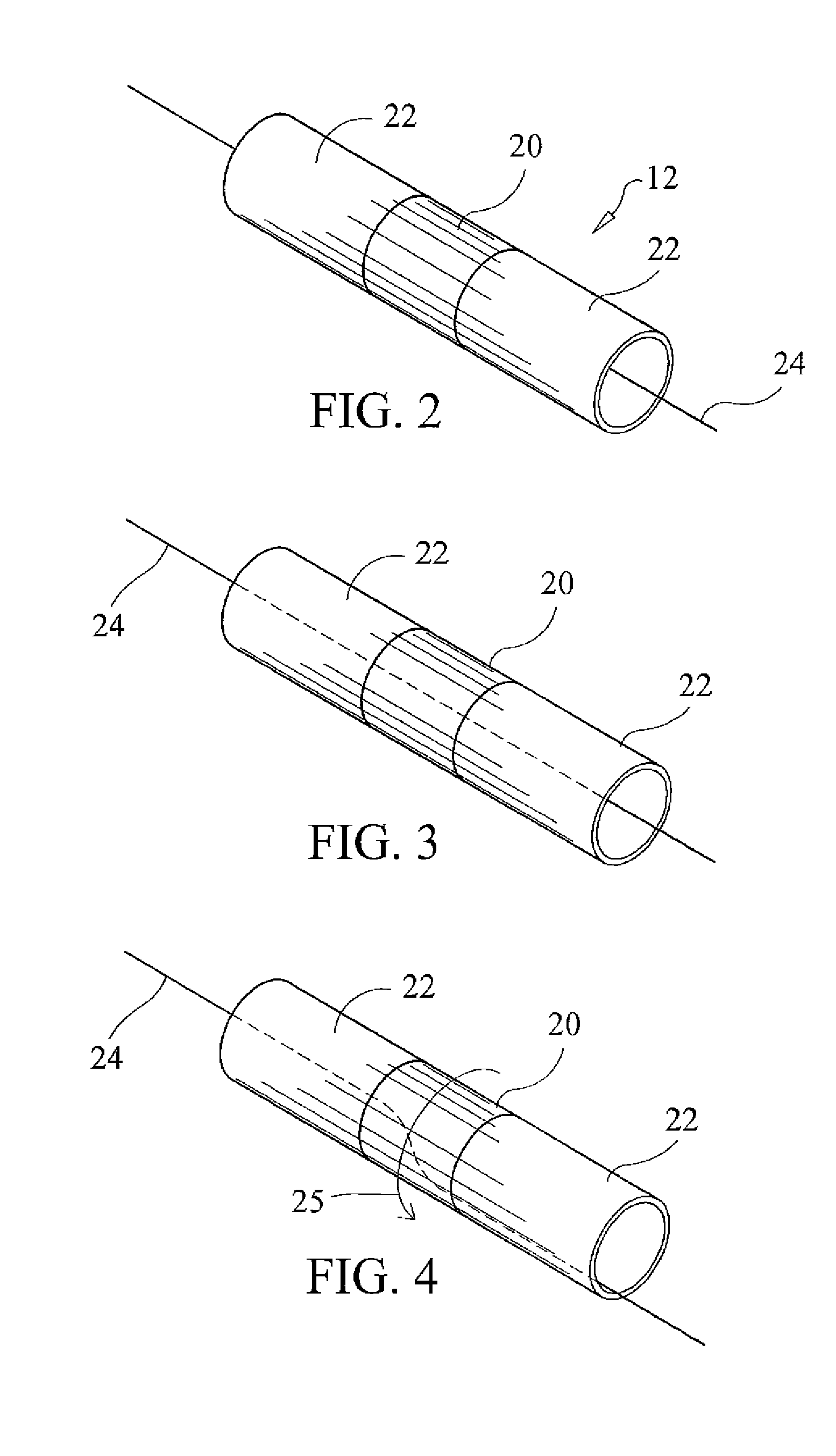
InactiveUS20090277997A1Convenient amountIncrease elasticityMarine propulsionKitesLeading edgeTorsional deformation
A leading edge inflatable traction kite wherein the leading edge structure includes a plurality of spaced segments that are fabricated from a material with a higher elasticity, thus allowing for a greater amount of twisting and bending. The inflatable leading edge includes a series of elastically deformable segments disposed throughout the length thereof to facilitate selective torsional deformation of the leading edge and resulting overall angle of attack of the kite. These elastically deformable segments are preferably integrally formed as part of the leading edge support and are comprised of a material with a high elasticity, namely a higher elasticicity than the remaining leading edge segments. Providing elastically deformable segments of high elasticitity dispersed along the leading edge combined with regions of lower elasticity maximizes responsiveness and control by allowing leading edge deformation in response to user applied force, while the providing sufficient support to maintain kite stability.
Owner:RIDE BEST
Method for eliminating vibration noise in shaft torsional deformation test
InactiveCN102494626AEliminate noise interferenceSimple structureUsing optical meansAnti jammingGrating
The invention relates to a method for eliminating vibration noise in shaft torsional deformation test. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging reflecting gratings on a tested shaft at equal intervals along an axial direction; arranging a group of laser fiber sensors at a position over against each reflecting grating to constitute a test channel; arranging another completely the same group of laser fiber sensors at a position which is orthogonal to the first group of laser fiber sensors to constitute another test channel; synchronously acquiring two paths of original signals through double channels for performing empirical mode decomposition (EMD) to obtain each order of intrinsic mode function (IMF) comprising different types of information; performing correlation analysis on each order of IMF for the two paths of signals; extracting an IMF reflecting a specific load function; and performing weighted averaging on the IMF to obtain tested information, i.e., shaft torsional deformation. The method has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, high anti-jamming capacity and adaptability to severe environments. Measuring accuracy is increased greatly.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七0四研究所
Three-dimensional shock absorbing support
ActiveCN101775842AImprove vertical bearing capacityStrong automatic reset abilityShock proofingTorsional deformationEngineering structures
The invention relates to a shock absorbing support for a building. The three-dimensional shock absorbing support comprises a laminated rubber support and a basin type support, wherein a lower connecting board is arranged under the laminated rubber support; the basin type support is matched with the lower connecting board; an inner flange used for limiting the movement condition of the lower connecting board is arranged on the basin type support; and the lower connecting board is buckled in a basin type chamber of the basin type support. The shock absorbing support can release the horizontal deformation and the torsional deformation of a supported engineering structure, reduce the risks of damages caused by the deficiency of horizontal deformation capability and torsional deformation capability of a structural component and improve the shock resistant performance of the engineering structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI RB RUBBER ISOLATOR TECH +1
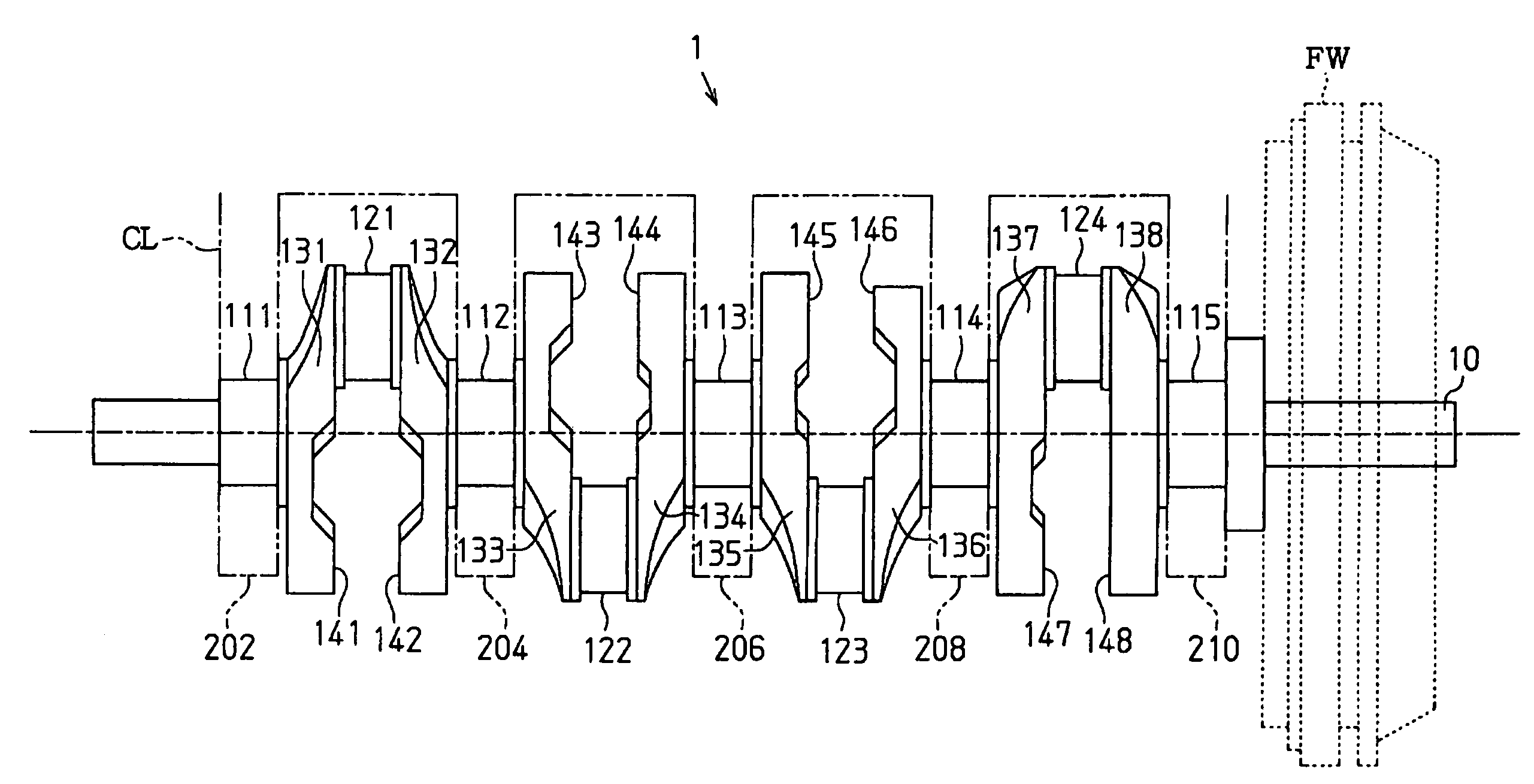
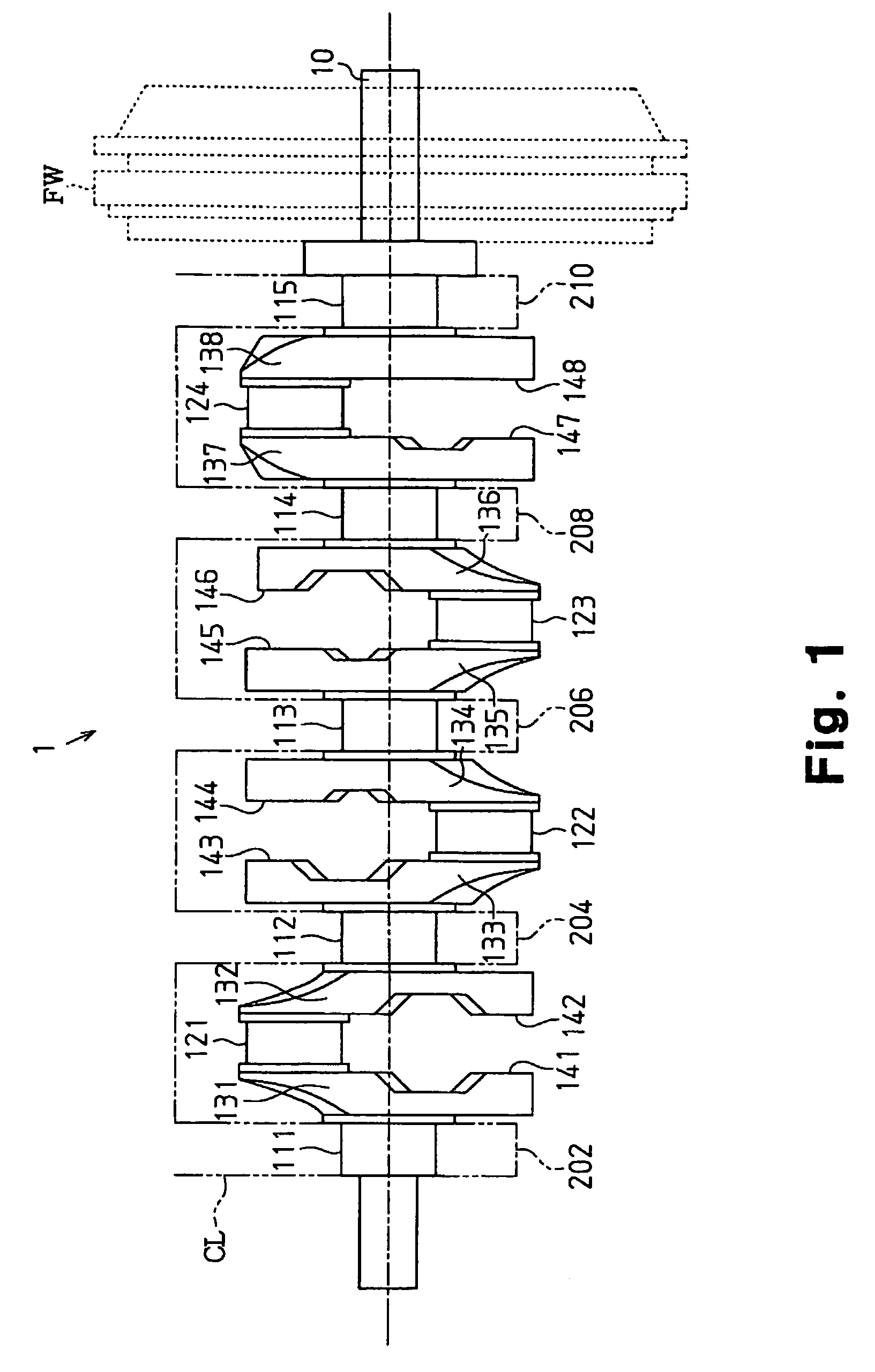
Crankshaft of in-line four-cylinder engine
InactiveUS7367303B2Reliably maintains rigidity against torsional deformationCurb weight gainCrankshaftsMachines/enginesTorsional deformationFlywheel
In a crankshaft of an in-line four-cylinder engine, an arm that is closest to a flywheel has a greater average thickness in a direction of the rotation axis of the crankshaft than those of other arms. Two of the arms that are coupled to both sides of the third journal from the flywheel each have a center of gravity closer to its own counterweight compared to the centers of gravity of the arms that face the two arms with corresponding crankpins in between. Accordingly, the rigidity against torsional deformation and the thickness of oil films on the journals are reliably maintained while suppressing increase in the weight of the entire crankshaft.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Test device for testing creep of metal materials under low stress
The invention discloses a test device for testing creep of metal materials under a low stress. According to a traditional uni-axial creep test device, due to the fact that the strain resolution ratio is low, so that the creep test demand of the metal materials under the low stress cannot be met. The test device for testing the creep of the metal materials under the low stress is based on a pure torsional deformation principle, a sample to be tested is processed into a spiral-shaped sample, a certain temperature and a small loading are imposed, a non-contact type optical measuring system is used to test the elongation of a screw pitch of the sample with the increase of time, and therefore the creep property of the metal materials under the low stress is researched. The test device comprises a main rack, the non-contact optical measuring system, a sample fixture, an open-window type high-temperature furnace, a spiral sample, a fixed support component, a computer and a connecting wire. Low-stress creep data tested by the test device for testing the creep of the metal materials under the low stress can provide a reference for safety evaluation and life forecast of pipelines of a nuclear power plant and a heat-engine plant.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Parameterized model reconstruction method based on point cloud
ActiveCN110442917AAdaptableImprove accuracySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsPoint cloudMeasurement point
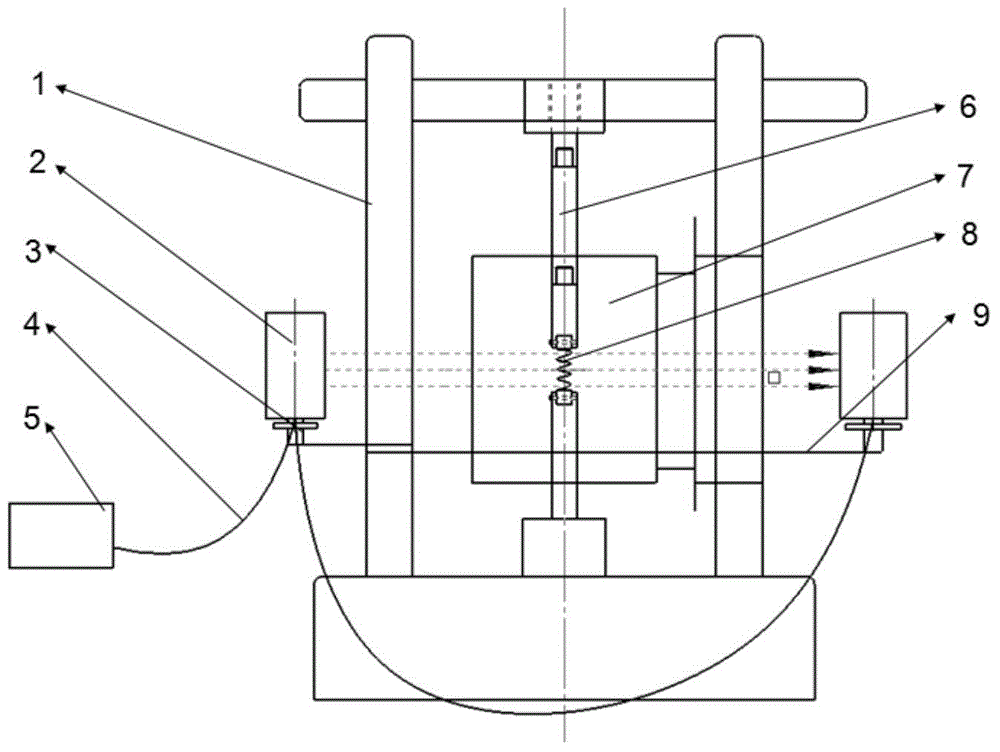
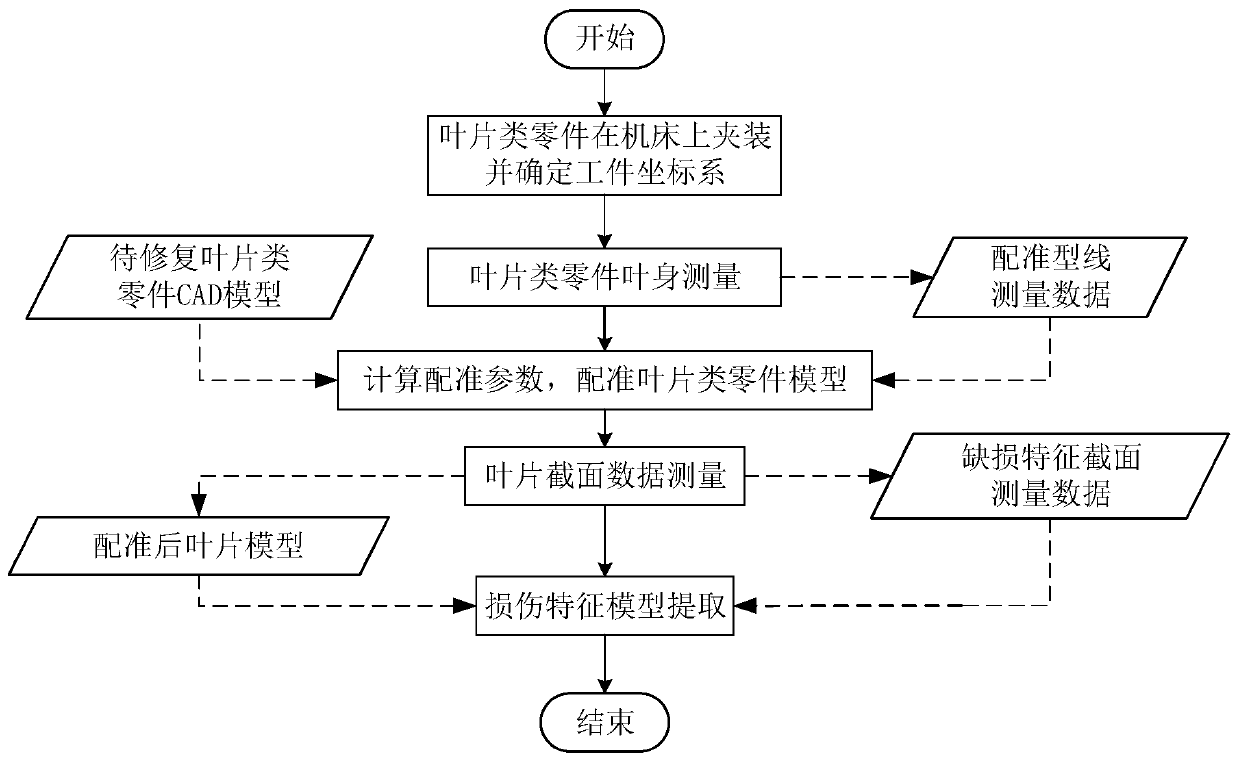
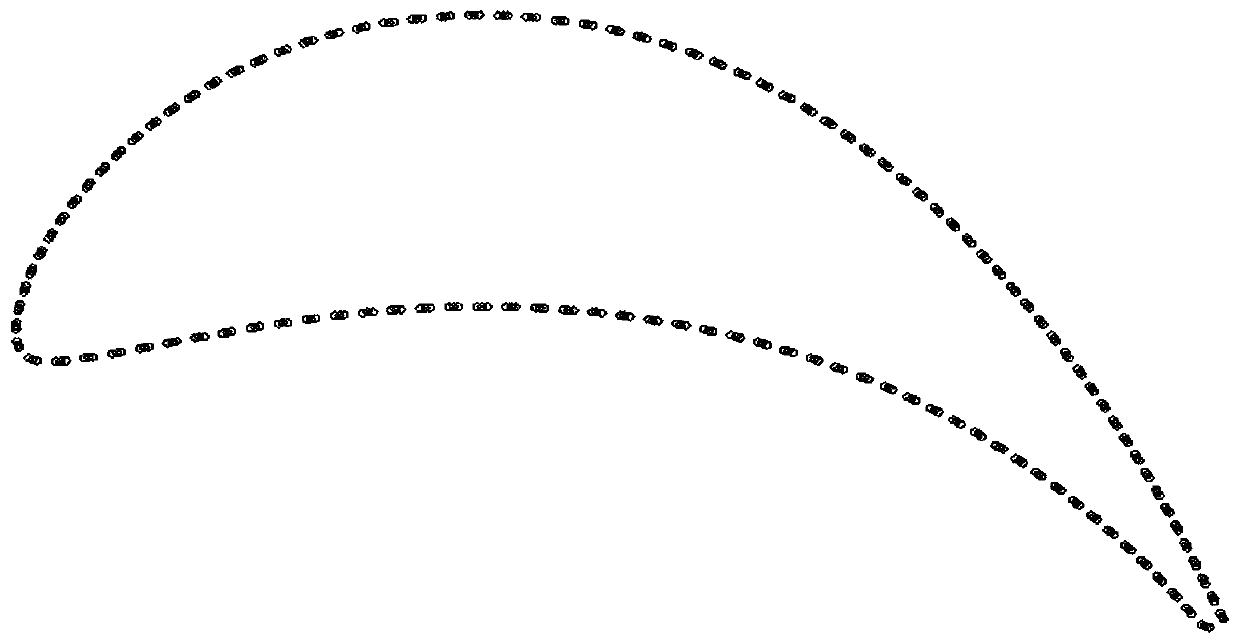
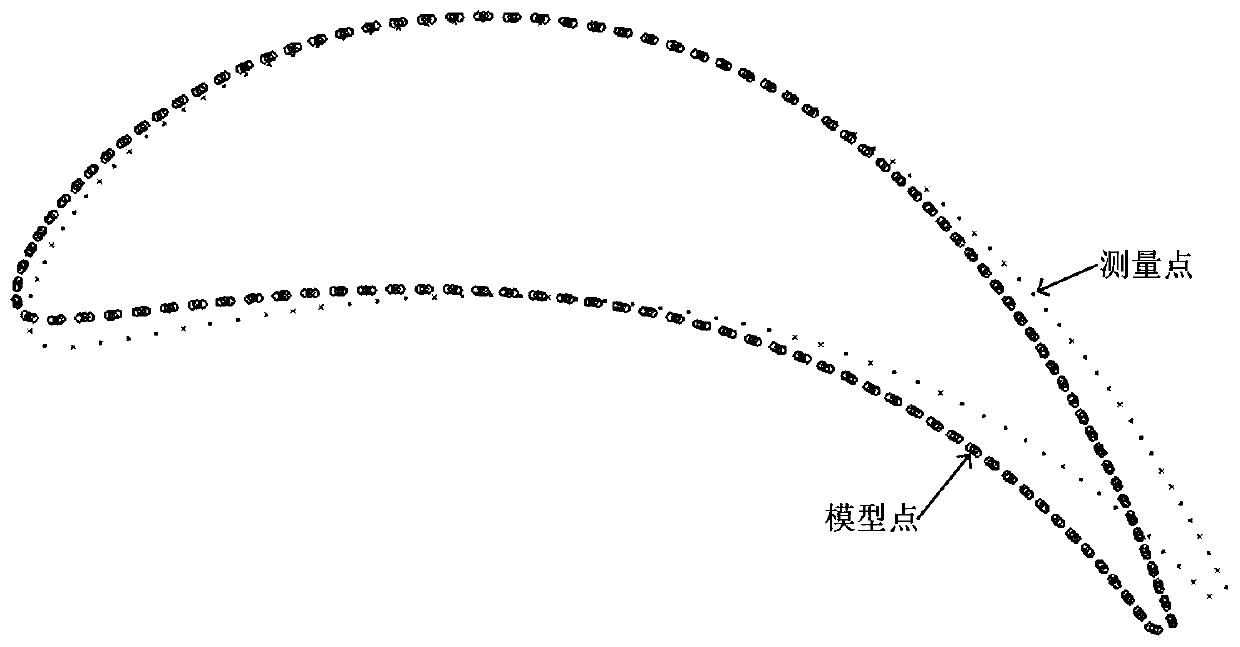
The invention discloses a parameterized blade part defect model reconstruction method based on point cloud. The method comprises the following steps: S1, measuring a blade body of a to-be-repaired blade part; s2, blade part molded line feature matching: performing registration calculation on the measurement point cloud data and the blade theoretical model point cloud data to obtain torsional deformation of a blade damage area, and performing registration transformation with a blade theoretical model to enable spatial positions of an actual to-be-repaired blade model and the theoretical model under a workpiece coordinate system to be consistent; and S3, extracting a blade part damage part model: acquiring section measurement data of an undamaged area of the blade, performing curve fitting on the measurement data, performing linear interpolation on a fitted curve towards the damage area direction of the model, and extracting a damage area model of the blade. According to the blade defectmodel reconstruction method provided by the invention, distortion and deformation of the blade model can be reproduced into the reconstructed blade model, and defect and wear parts are predicted andsubjected to high-precision modeling.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Conical surface mechanical sealing device
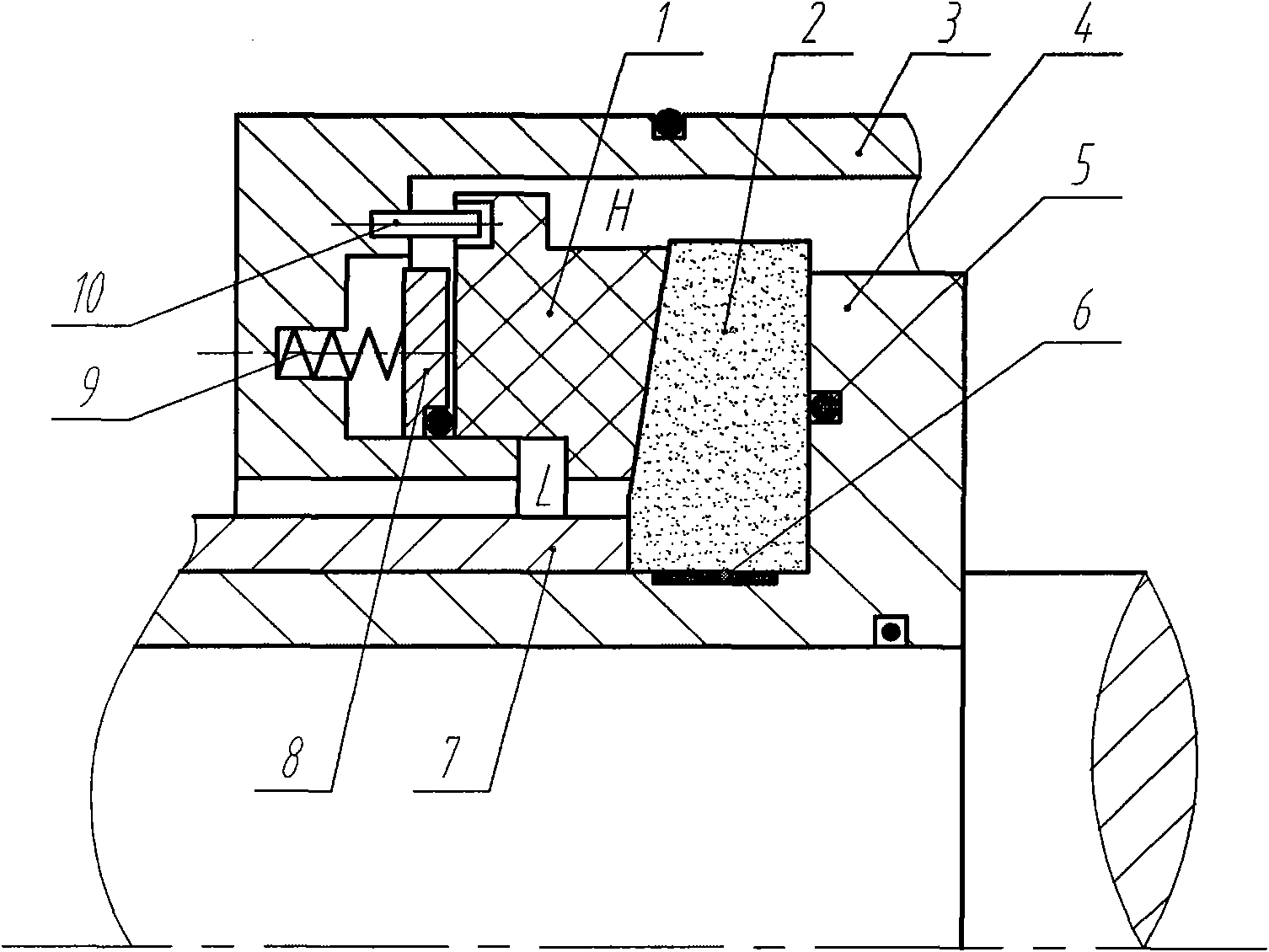
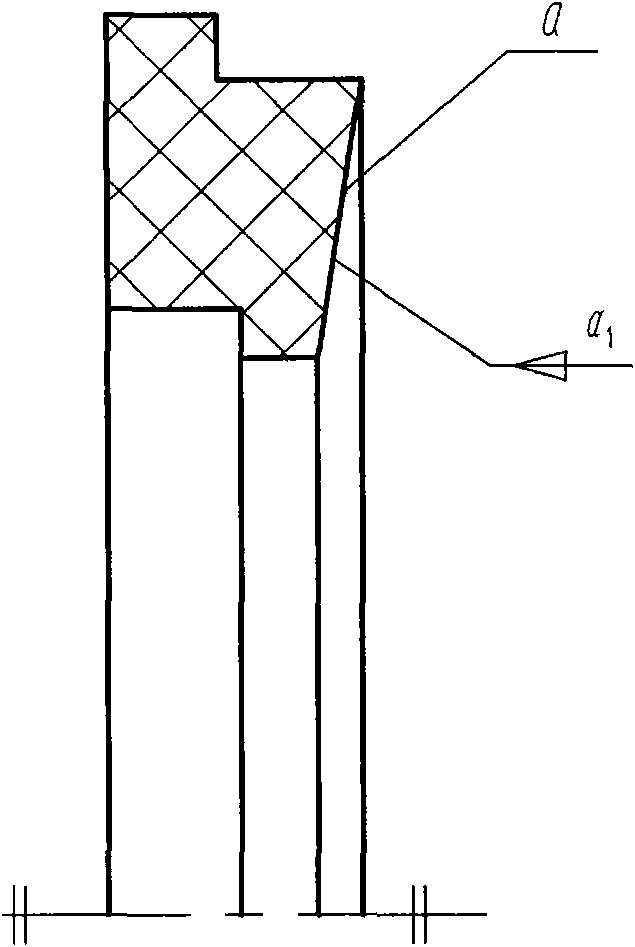
InactiveCN102128269AImprove bending deformationGood resistance to torsional deformation in axial sectionEngine sealsMicro gapTorsional deformation
The invention relates to a conical surface mechanical sealing device, which is characterized in that: a mechanical sealing static ring 1 is provided with a conical surface a; a rotary ring 2 is provided with a conical surface b; the conical surface a and the conical surface b are paired to form a sealing surface; and the sealing surface is that the conical surface a and the conical surface b are directly contacted, or are separated by a micro gap. Compared with the conventional mechanical sealing device, the conical surface mechanical sealing device has the advantages of higher automatic centering property and higher capability of resisting the torsional deformation of a shaft section and the bending deformation of a main shaft of a unit due to two sealing rings. The conical surface mechanical sealing device is suitable for the shaft end sealing of various rotary machines.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Cable protection and guide device
ActiveCN101994872AThe protection guide is effectivePrevent disengagementPipe supportsHauling chainsTorsional deformationMechanical engineering
The invention provides a cable protection and guide device that steadily protects and guides a cable by rigidly anchoring and preventing a connecting arm from being disengaged upwardly. The device smoothly flexes and reduces torsional deformation. The hinged connecting arm extends across the flexional outer peripheral side of a pair of spaced apart right and left link plates and has a hook portion at one end of an arm body and a hinge portion at another end. An engaging circular arc portion of the hook portion engages with an engaging shaft of the link plate. Engaging projecting portions extend from the edge of the engaging circular arc portion and interengage with engaging step portions arranged on the engaging shaft.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
Shot peen forming method realizing torsional deformation of high-rib integral panel
ActiveCN105598851ATwist bigReduce the stress areaBlast gunsAbrasive machine appurtenancesTorsional deformationEngineering
The invention provides a shot peen forming method realizing torsional deformation of a high-rib integral panel. The method comprises steps as follows: step 1, the high-rib integral panel is clamped and fixed; step 2, force pointing to the inner side of skin (1) is applied to two ends of the high-rib integral panel, and force pointing to the outer side of the skin (1) is applied to the middle of the high-rib integral panel; step 3, a shot peening area (3) is determined on the high-rib integral panel, a first nozzle (4) performs shot peen on the outer side of the skin (1) in the shot peening area (3) along a preset shot peen track, and second nozzles (5) perform shot peen on each high rib (2). According to the shot peen forming method, the application of shot peen forming to the integral panel with high rids, thin walls and a torsional shape is broadened, so that the development of the shot peen forming technology is promoted, more space and choices are provided for design and manufacture of the integral panel of an aircraft in the future, and further increase of the integral design level of the aircraft becomes possible.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
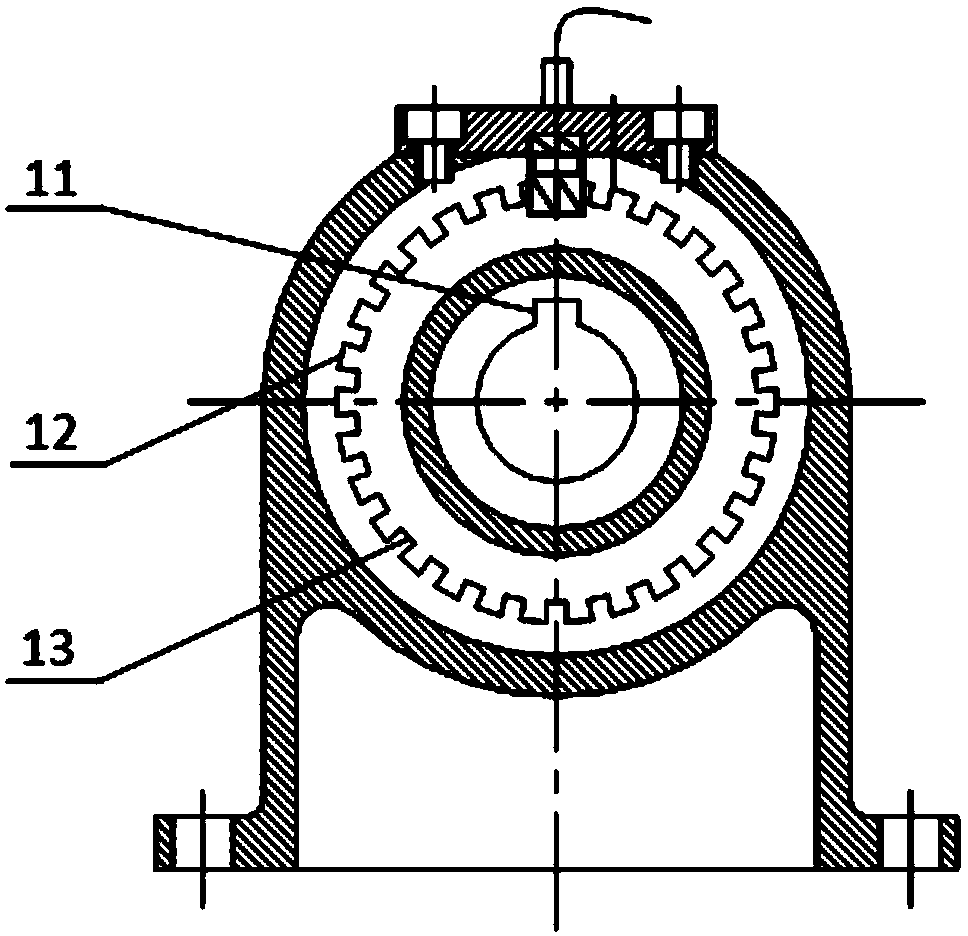
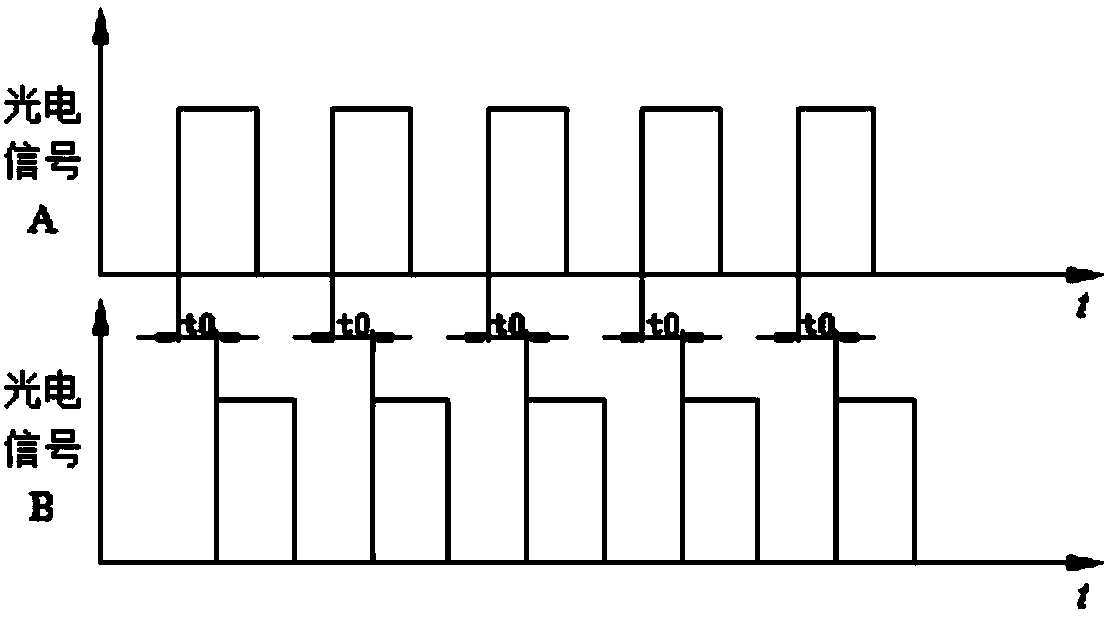
Torque measurement sensor based on phase difference of photoelectric encoder signals and measuring method
InactiveCN104198098AMeasuring high dynamicsHigh precisionWork measurementTorque measurementThumb oppositionBall bearing
The invention discloses a torque measurement sensor based on the phase difference of photoelectric encoder signals. The torque measurement sensor comprises a shell; an elastic drive sleeve is mounted in the shell by use of a ball bearing; an elastic link is arranged in the middle part of the elastic drive sleeve; a photoelectric encoder sleeves each of the two ends of the elastic link, and the central angles of the two photoelectric encoders are equal; a mounting base is fixed on the top of the shell; a photoelectric sensor A and a photoelectric second B are fixed in the mounting base, and arranged in opposition to the two photoelectric encoders. The two photoelectric encoders are arranged at the two ends of the elastic link of the elastic drive sleeve and the two photoelectric sensors are used for obtaining square wave output signals when the encoders rotate, and then the measurement of the torsional deformation and torque of the elastic drive sleeve can be realized according to the phase difference of the square wave signals output by the two encoders. The torque measurement sensor based on the phase difference of the photoelectric encoder signals is used for solving the problem that the measurement accuracy of an existing torque sensor is prone to be effected by a magnetic field and an electric field; the torque measurement sensor is simple in measurement principle, high in anti-jamming capability, and capable of realizing high-dynamic and high-accuracy torque measurement of a drive mechanism.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Thin-walled vane nine-point control variable-allowance milling method based on Newton interpolation
ActiveCN106001720AReduce bending deformationReduce torsional deformationWorkpiecesMilling equipment detailsPosition toleranceTorsional deformation
The invention provides a thin-walled vane nine-point control variable-allowance milling method based on Newton interpolation. Modeling is carried out by utilizing a three-dimensional modeling software, and an auxiliary surface and a boundary surface are formed, so that a driving surface is determined by utilizing a section line lofting process. Cutter machining paths are generated according to the driving surface, and the machining allowance of each cutter position point on each machining path is determined by adopting a Newton interpolation method. Finally, vanes are cyclically processed according to symmetrical milling rules. Compared with a traditional longitudinal fixed-allowance cutting and spiral milling method, the thin-walled vane nine-point control variable-allowance milling method has the advantages that technical problems, such as large torsional deformation, low contour precision, poor section position tolerance and difficult error control, in the machining process can be solved; and by adopting a Newton interpolation process allowance fine adjustment method, surface quality can be more comprehensively controlled, and problems, such as large bending deformation, poor section position tolerance and low surface contour precision, in the machining process can be effectively solved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Connecting rod length real-time active adjusting method and active anti-side-rolling torsion bar system
InactiveCN112158224AFix fixitySolve the adjustmentBogie-underframe connectionsBall screwStructural engineering
The invention relates to a method for actively adjusting the length of a connecting rod in real time. The length of the connecting rod can be actively adjusted in real time according to a control instruction by additionally arranging an active adjusting device on the connecting rod. Therefore, the defects that a traditional connecting rod is fixed in length and cannot be adjusted are overcome. Theactive anti-side-rolling torsion bar system comprises a connecting rod, a torsion bar and a supporting base, a ball screw mechanism is arranged on the connecting rod, and the length of the connectingrod can be rapidly adjusted in real time according to a control instruction, so that the torsion bar generates torsional deformation, and then anti-side-rolling torque is actively provided for a vehicle body; active adjustment of the side rolling angle of the train body is achieved, the speed and safety of the train passing through a curve can be improved, and therefore the running speed of the train is increased.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
Polyvinyl chloride mixture for wires and cables and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102775701ALow costSimple preparation processPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsClimate change adaptationEpoxyPlasticizer
The invention discloses a polyvinyl chloride mixture for wires and cables and a preparation method thereof. The mixture comprises 30-60 parts of polyvinyl chloride resin, 4-15 parts of nitrile-butadiene rubber, 17-60 parts of plasticizer, 0.5-3 parts of epoxy soybean oil, 5-20 parts of filler, 2-3 parts of stabilizer, 0.2-0.6 part of lubricant and 0.1-1 part of toner. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding polyvinyl chloride resin, plasticizer, stabilizer, filler, epoxy soybean oil, lubricant and toner together into a high-speed mixer, evenly mixing to a certain temperature, adding nitrile-butadiene rubber into the high-speed mixer to carry out secondary mixing, evenly mixing, mixing in a cold mixer while sending the mixture into a preheated granulator, and extruding and granulating to obtain the required polyvinyl chloride mixture for wires and cables. The polyvinyl chloride mixture disclosed by the invention still has the characteristics of torsion resistance, high elastic resilience, friction resistance, torsional deformation resistance and strong torsional fracture performance at -40 DEG C, and also has the advantages of low cost and simple preparation technique.
Owner:深圳市金环宇电线电缆有限公司
Acoustic sensor
ActiveUS20140053650A1Improve performanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioVibration measurement in solidsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Torsional deformation
A method of designing and manufacturing an acoustic sensor having a high degree of directivity is disclosed. The sensor includes a rotatable plate that is attached to a substrate with mounts. In one aspect the mounts are freely rotatable and the torque on the plate is measured using detectors disposed on springs that provide a resistance to rotation of the plate. In another aspect the plate is mounted to the substrate with mounts that torsionally deform during rotation of the plate. These detectors measure the torque on the plate according to the torsional deformation of the mounts. Methods of improving the signal to noise ratio of acoustic sensors having multiple detectors are also disclosed.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
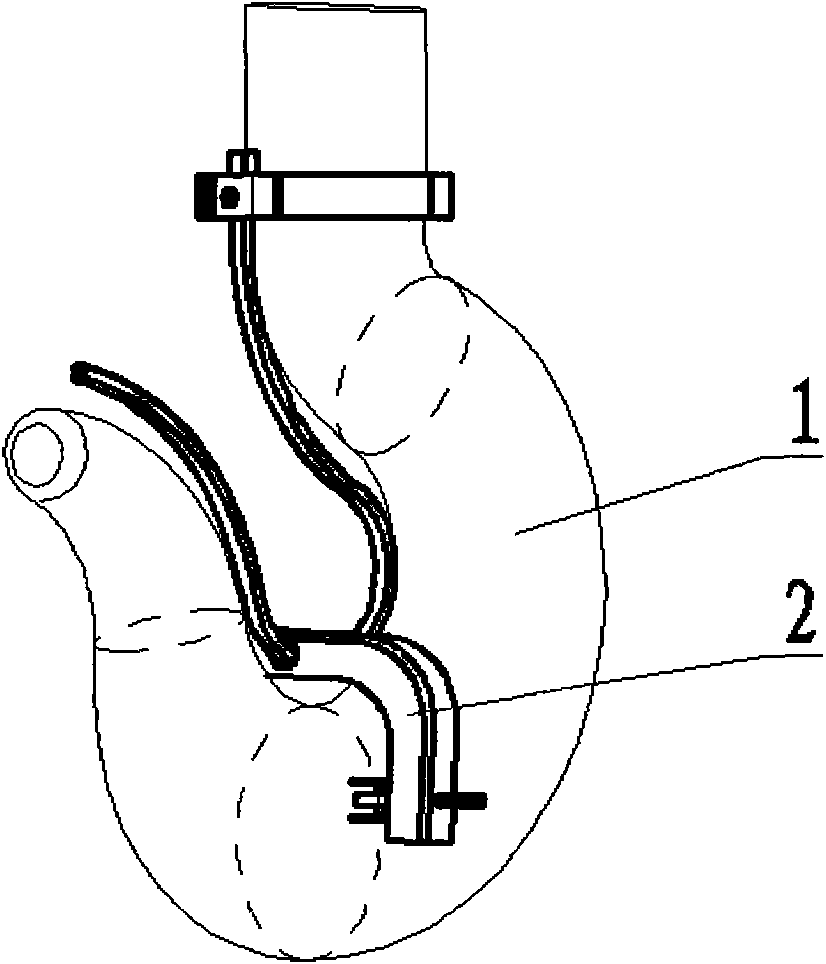
Detection device and detection method of torsional deformation of hoisting hook
InactiveCN101634543AFast online detectionEasy to operateAngles/taper measurementsMechanical solid deformation measurementsTorsional deformationObjective measurement
The invention provides a detection device of the torsional deformation of a hoisting hook. The device comprises a clamp, a reference hook frame and a slide measurement frame, wherein the reference hook frame is designed into a shape of a theoretical central line of a hook to be measured; and the slide measurement frame measures an actual central line in a slide mode along the reference hook frame. The invention also provides a detection method of the torsional deformation of the hoisting hook, which comprises the following steps: clamping and fixing the reference hook frame on a handle part of the hook to be measured through the clamp and a positioning pointer welded on the reference hook frame; operating the slide measurement frame and recording a lateral outline central line of the hook to be measured; fitting out the actual central line; and comparing the theoretical central line with the actual central line to calculate out a torsional deformation angle. The invention has quick and convenient measurement process, no need of extra shut down, quantitative and objective measurement result and simple manufacture and is suitable for inspection and detection of various hoisting hooks.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Torque sensor for calibrating screwing tools
ActiveUS7093477B2Low specific weightReducing moment of inertiaMeasurement of torque/twisting force while tighteningWork measurementTorsional deformationControl theory
The invention relates to a torque sensor for calibrating screwing tools such as dynamometric keys or impact screw drivers. A torque sensor for calibrating screwing tools has an inner body defining an axis with respect to which a torque is to be measured. The inner body has a seat for engaugement of a screwing tool to be calibrated. An outer annular body is held stationary. This outer annular body is coaxial with the inner body and is connected therewith through radial webs of a first type and through radial webs of a second type. The first type webs have relatively large widths circumferentially but have relatively small axial dimensions. The second type webs are relatively narrow circumferentially but have relatively large axial dimensions. The torque sensor further comprises torsion measuring elements attached to said first type webs for measuring torsional deformation due to torques exerted on said inner body.
Owner:EDUARD WILLE GMBH & CO KG
Motion transmitting structure for a nozzle arrangement of a printhead chip for an inkjet printhead
A printhead chip for an inkjet printhead includes a plurality of nozzle arrangements (100) positioned on a substrate (32). Each nozzle arrangement includes a chamber structure defining a nozzle chamber (106) that receives ink. An ink ejecting member (140) positioned in the nozzle chamber is displaceable in the nozzle chamber to eject ink from the nozzle chamber. Each nozzle actuator (148) is positioned on the substrate, the actuator having a working portion (156) displaceable with respect to the substrate when the actuator receives a driving signal. A sealing structure (130) is positioned on the substrate between the actuator and the ink-ejecting member inhibiting ink flow between the ink ejecting member and the actuator. A motion transmitting structure (122) pivotally bridges the sealing structure and interconnects the working portion (156) of the actuator and the ink-ejecting member (140) to transmit displacement of the working portion relative to the substrate to the ink ejecting member. Slotted openings (174) form a pair of opposed flexural connectors (178) between the outer structure (170) and the motion transmitting structures (122) allowing torsional deformation accommodating pivotal movement during operation of the nozzle arrangement.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com