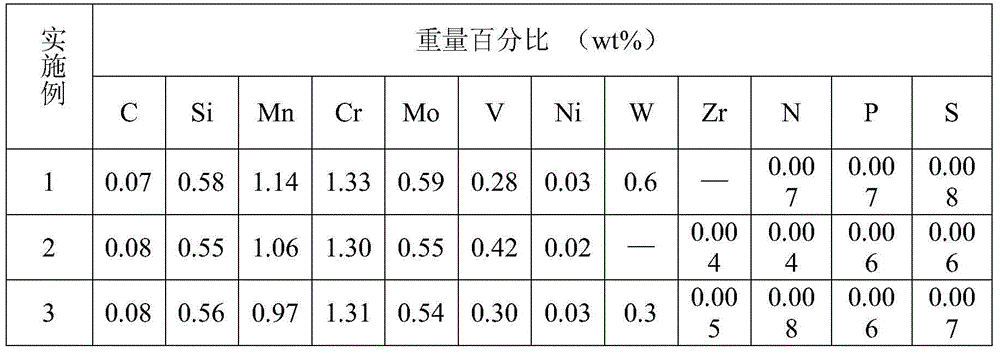
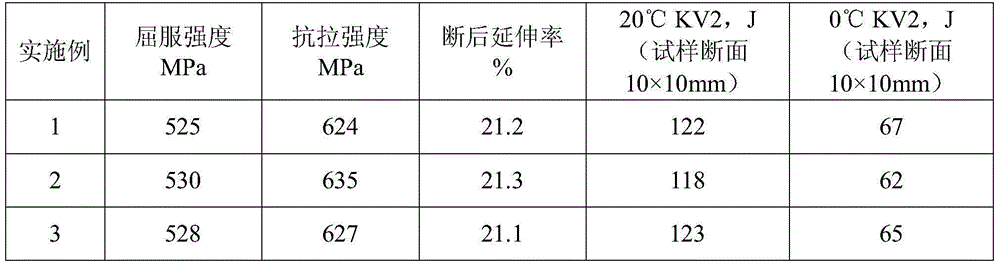
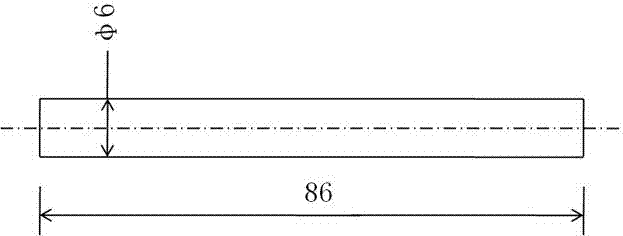
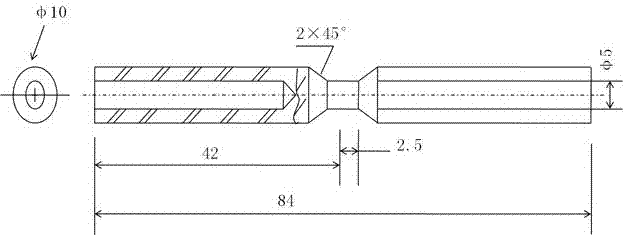
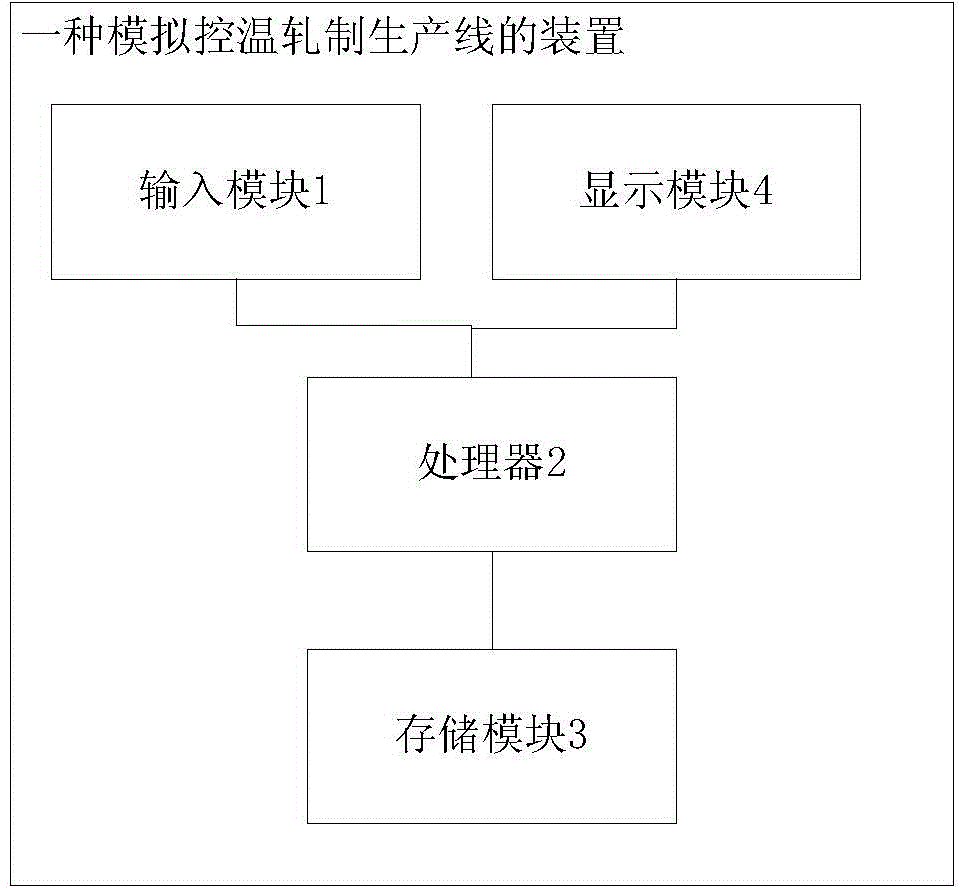
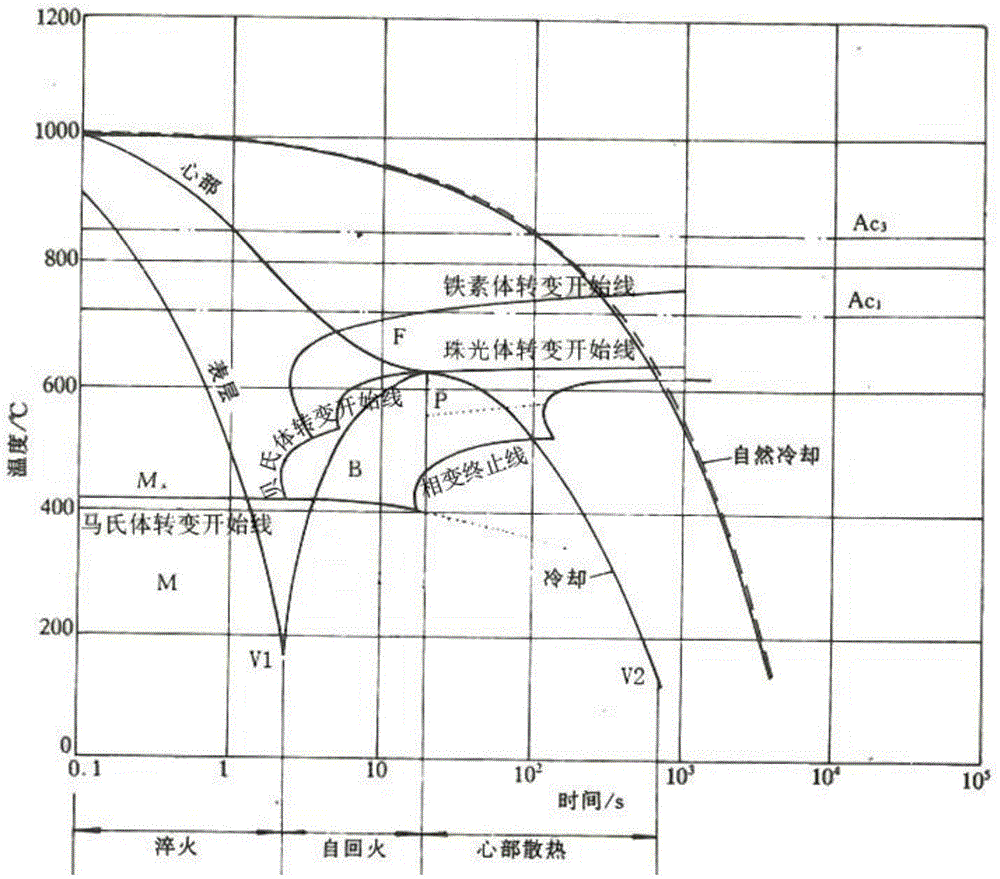
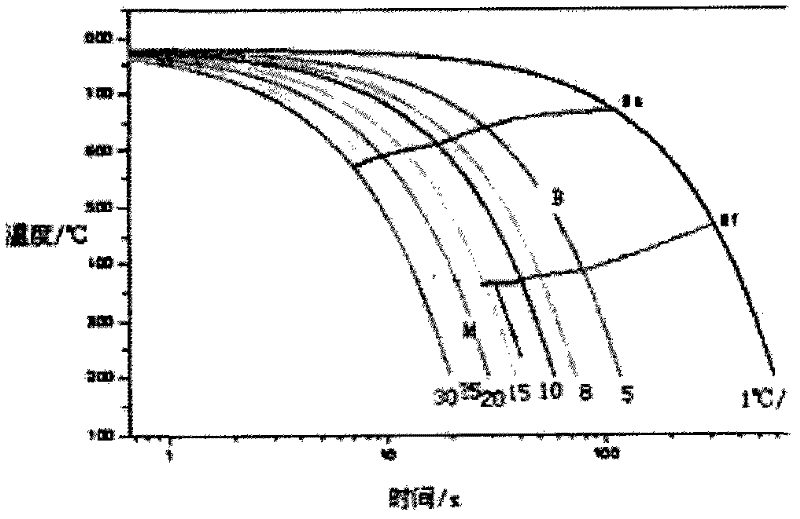
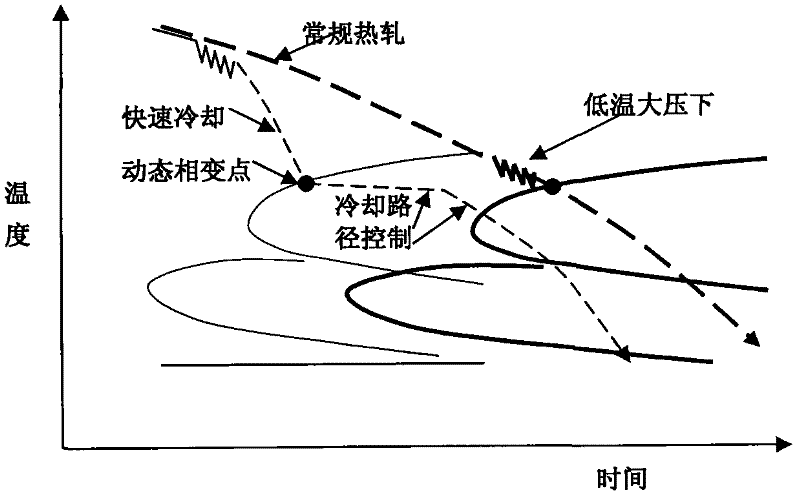
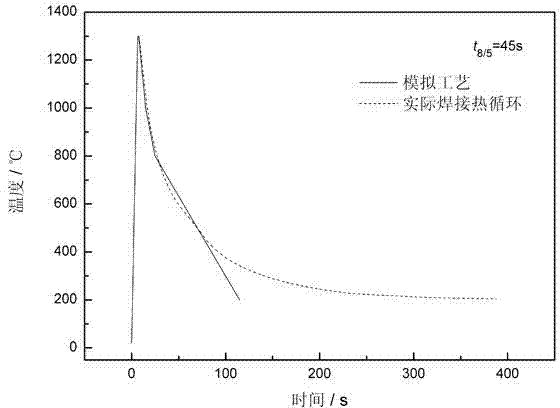
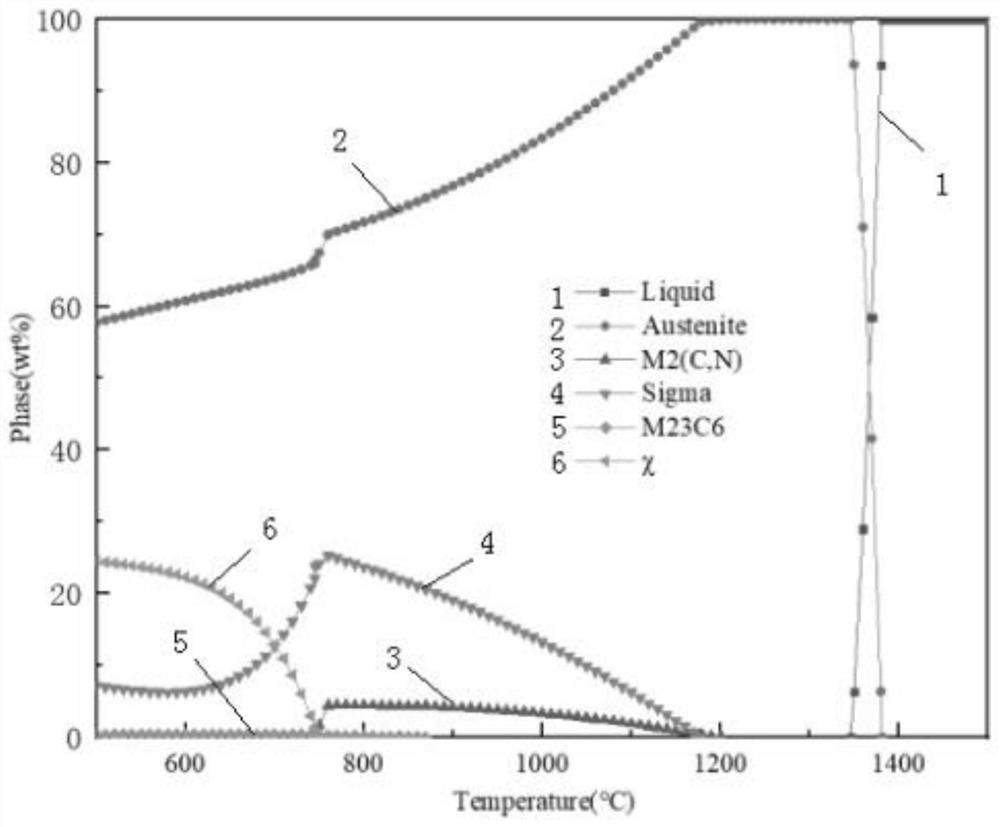
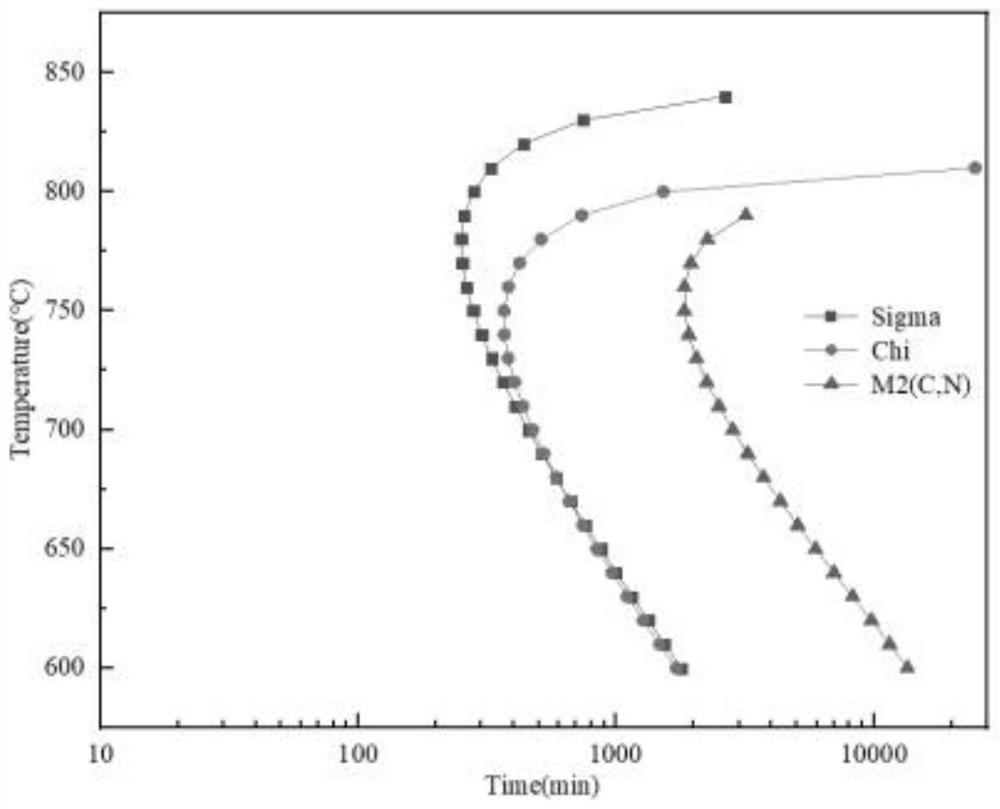
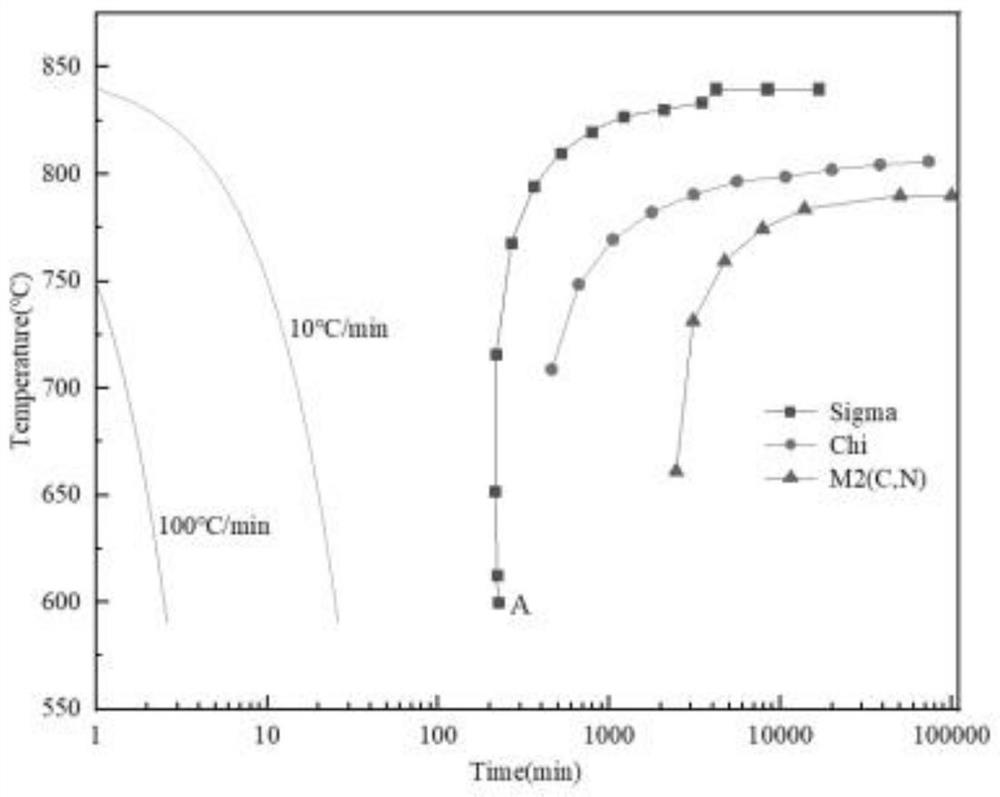
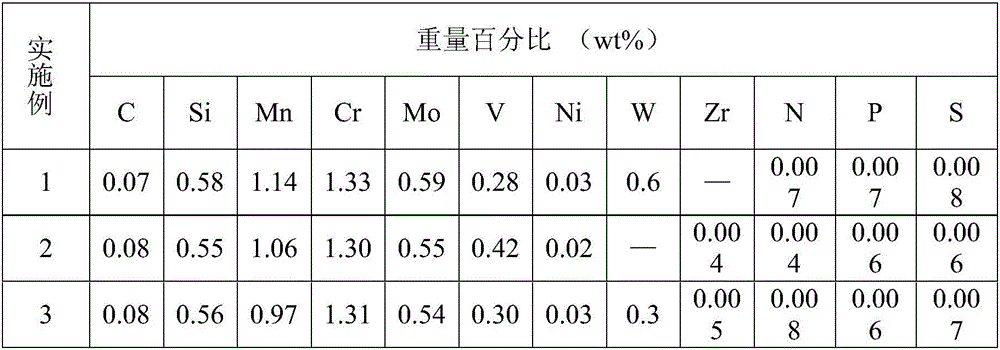
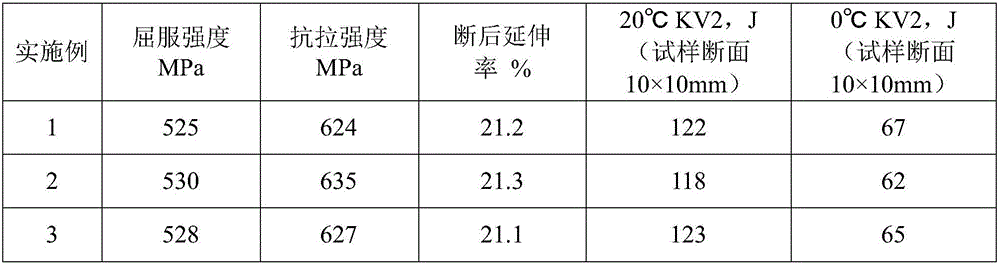
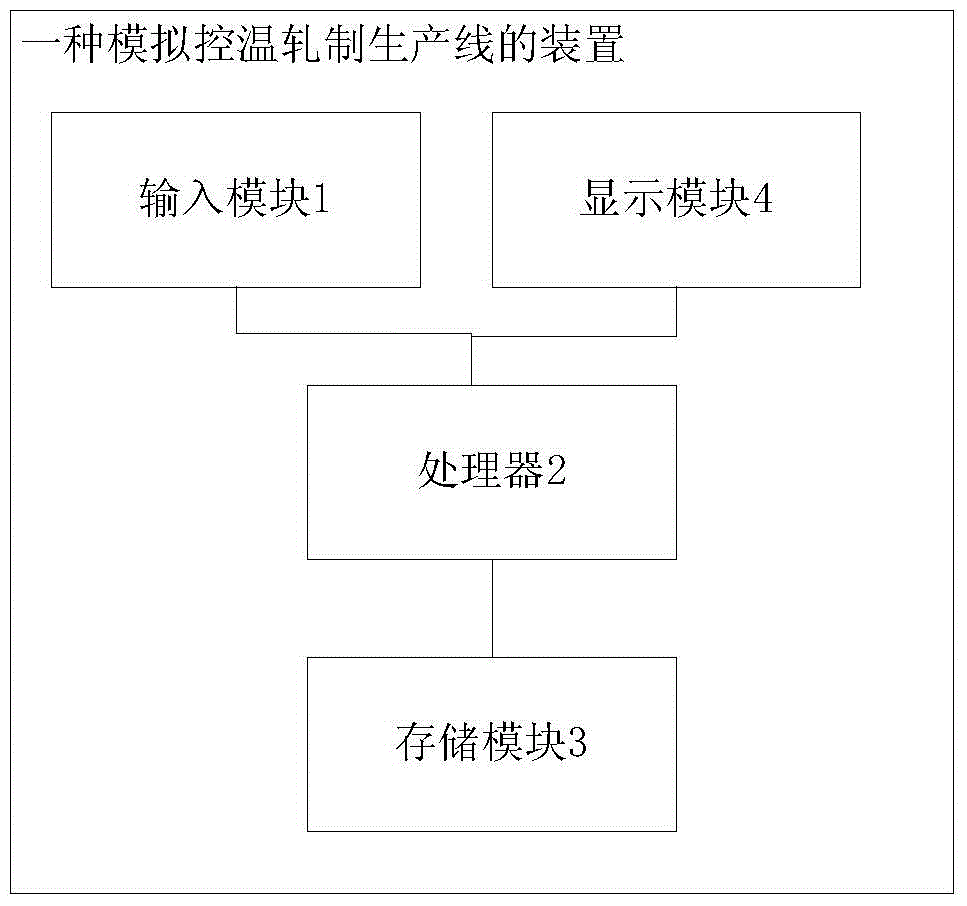
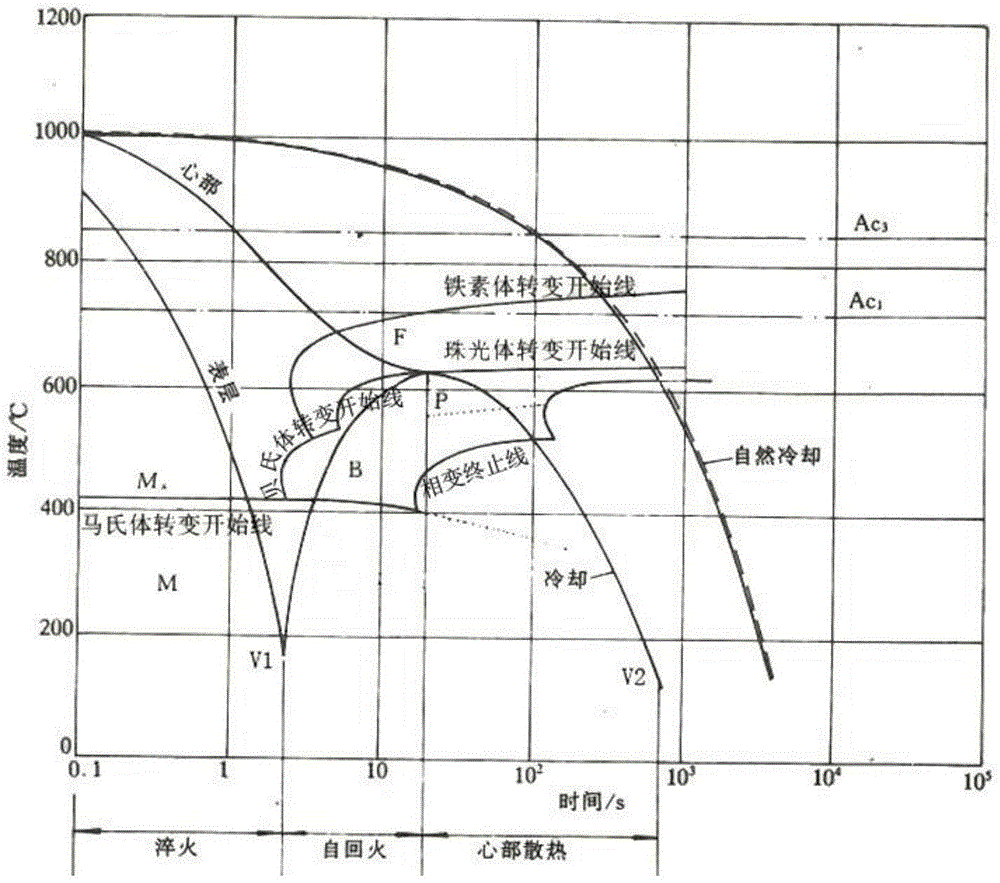
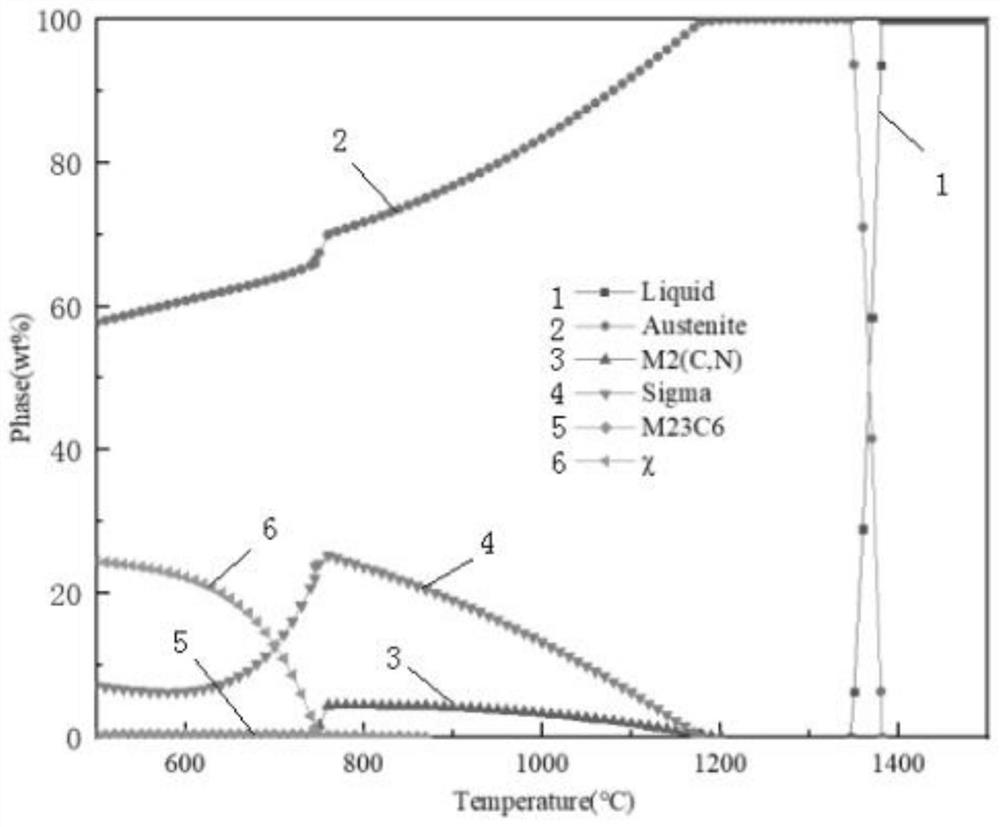
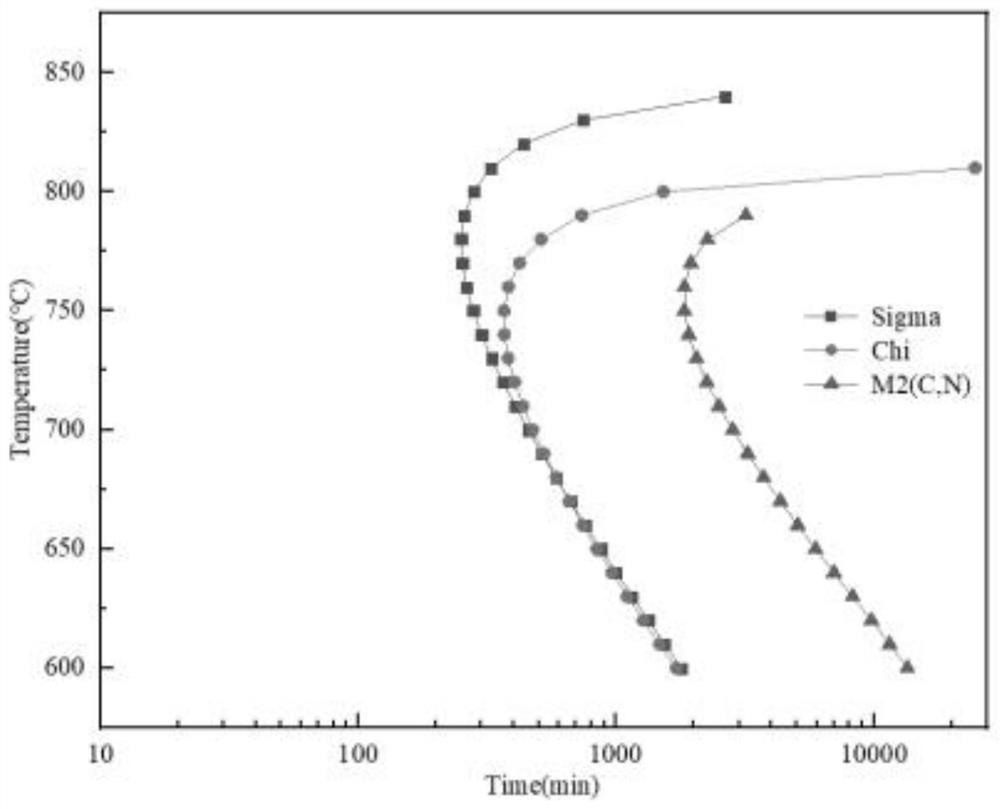
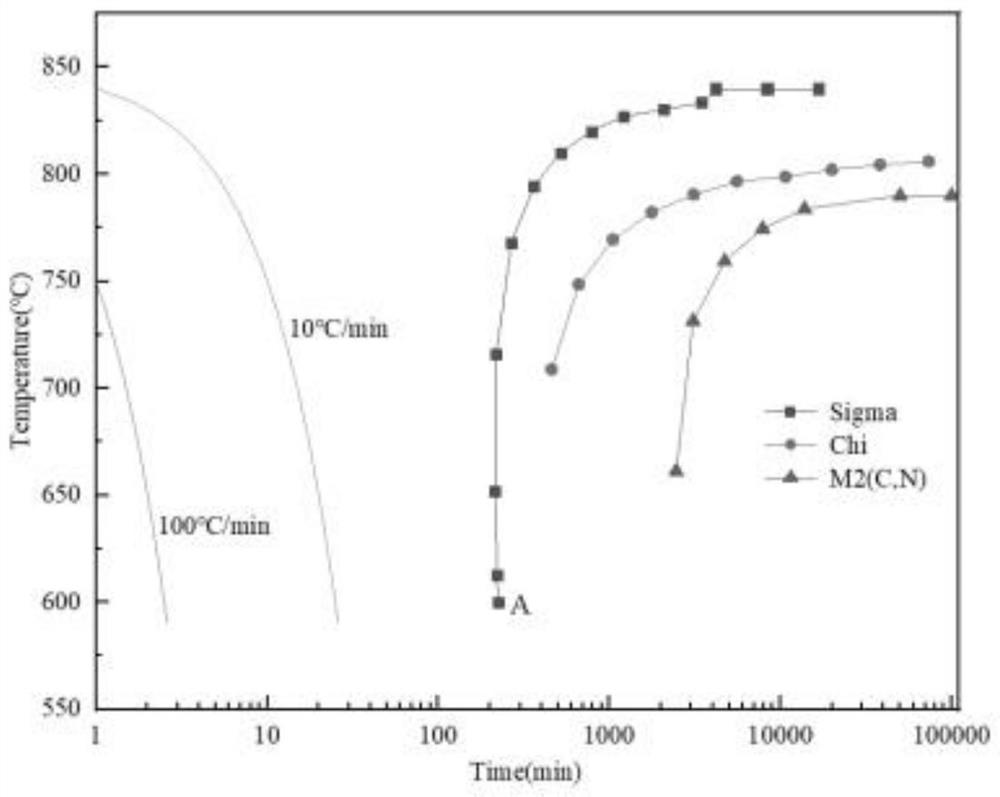
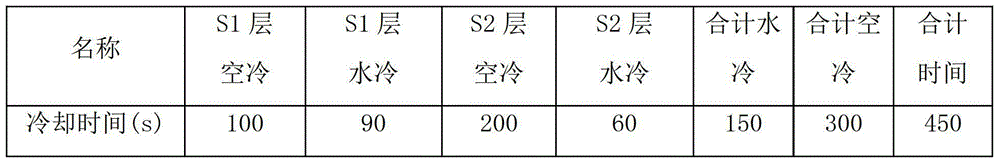
Patents
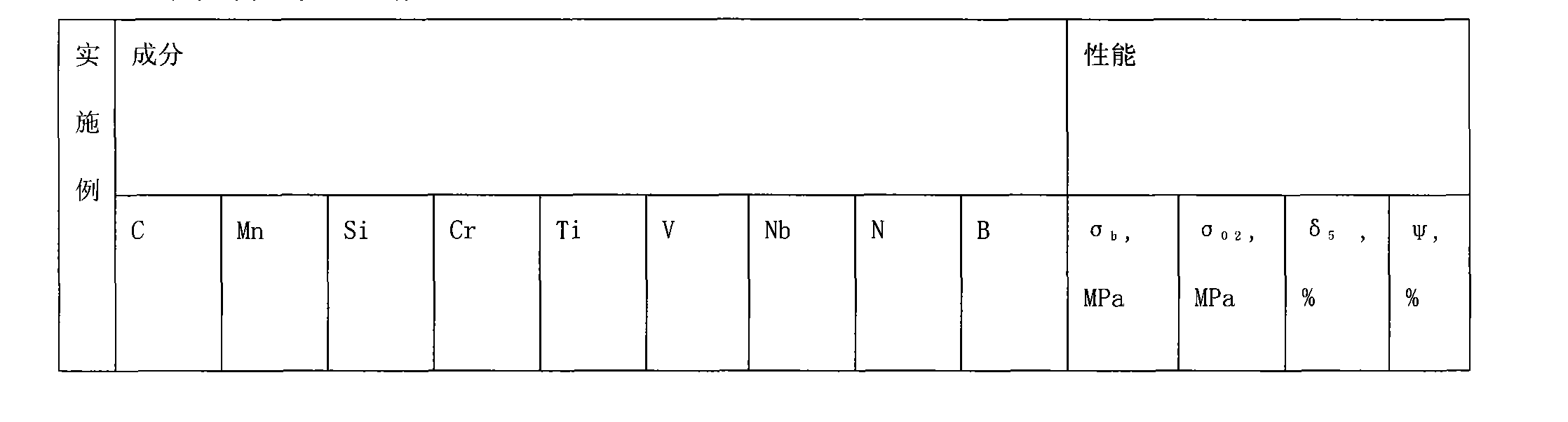
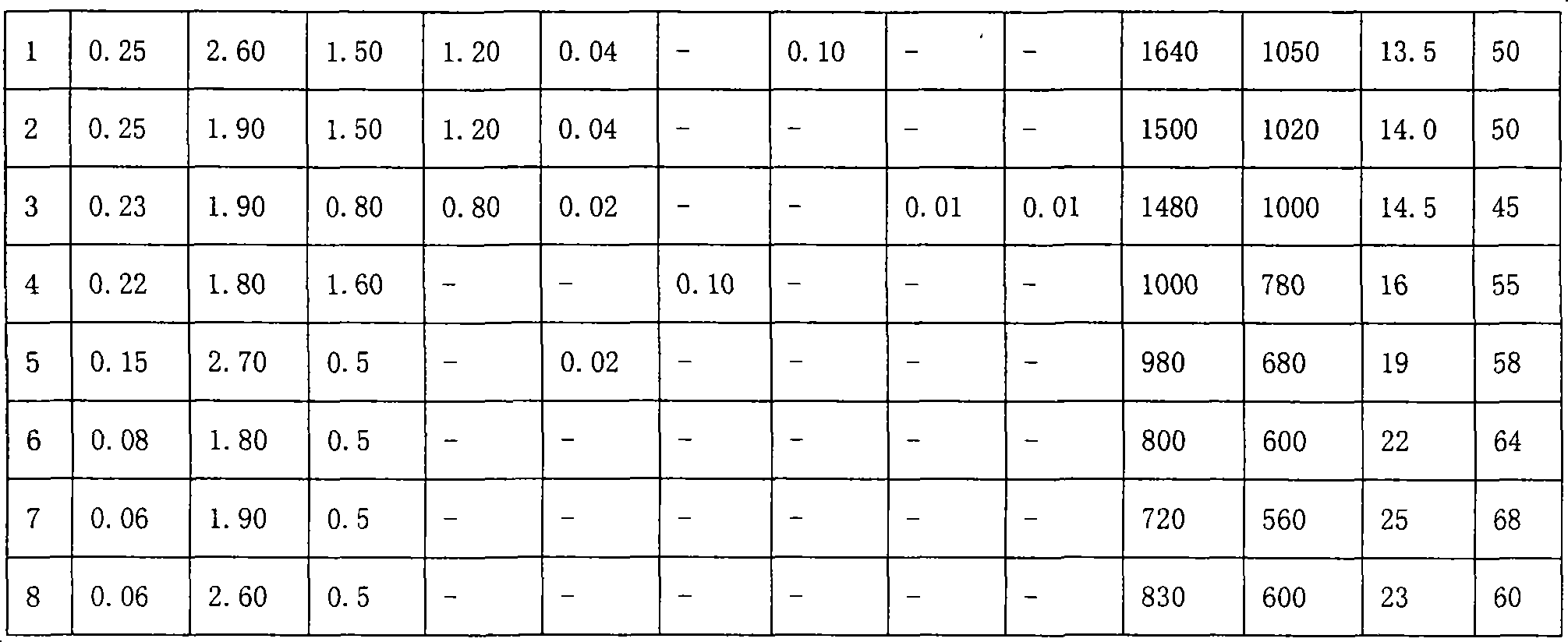
Literature
35 results about "Continuous cooling transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
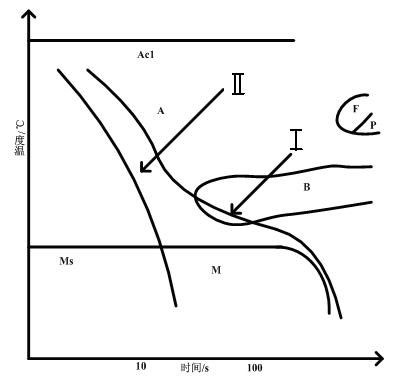
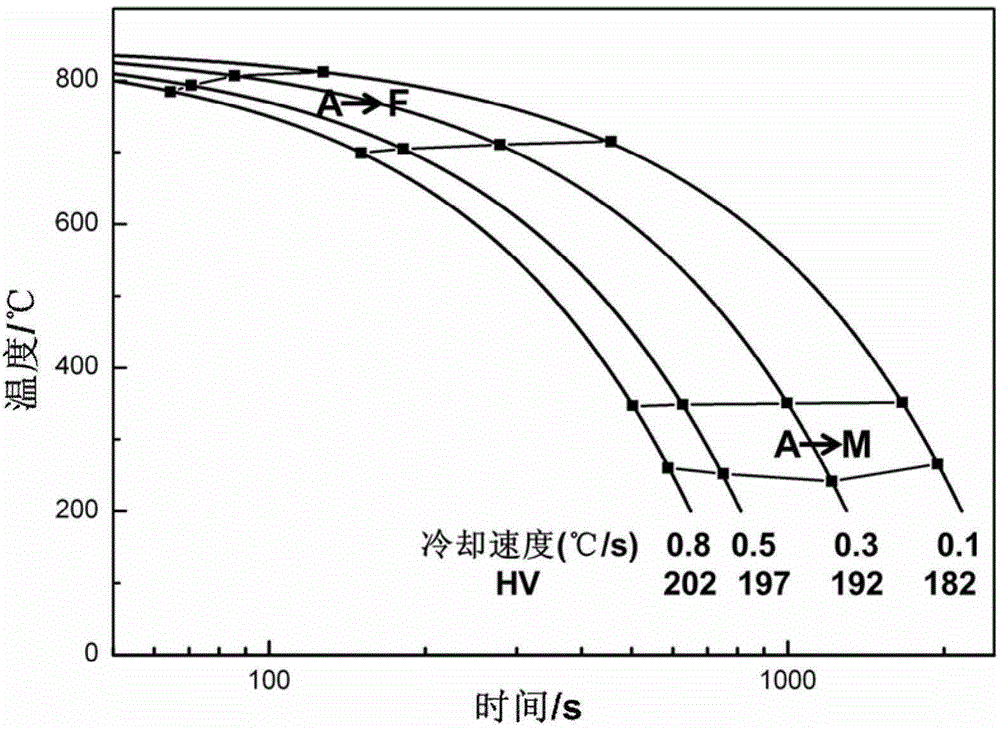
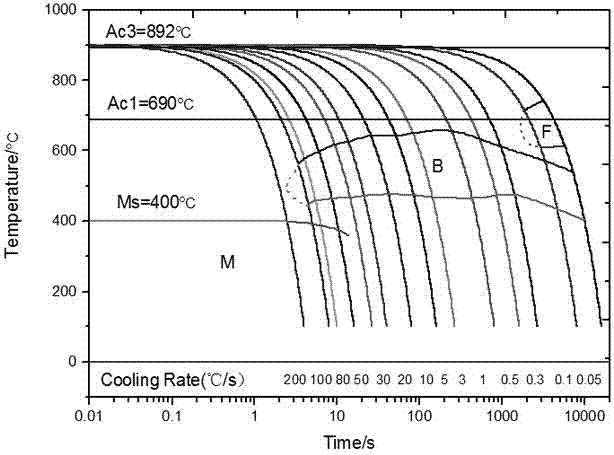
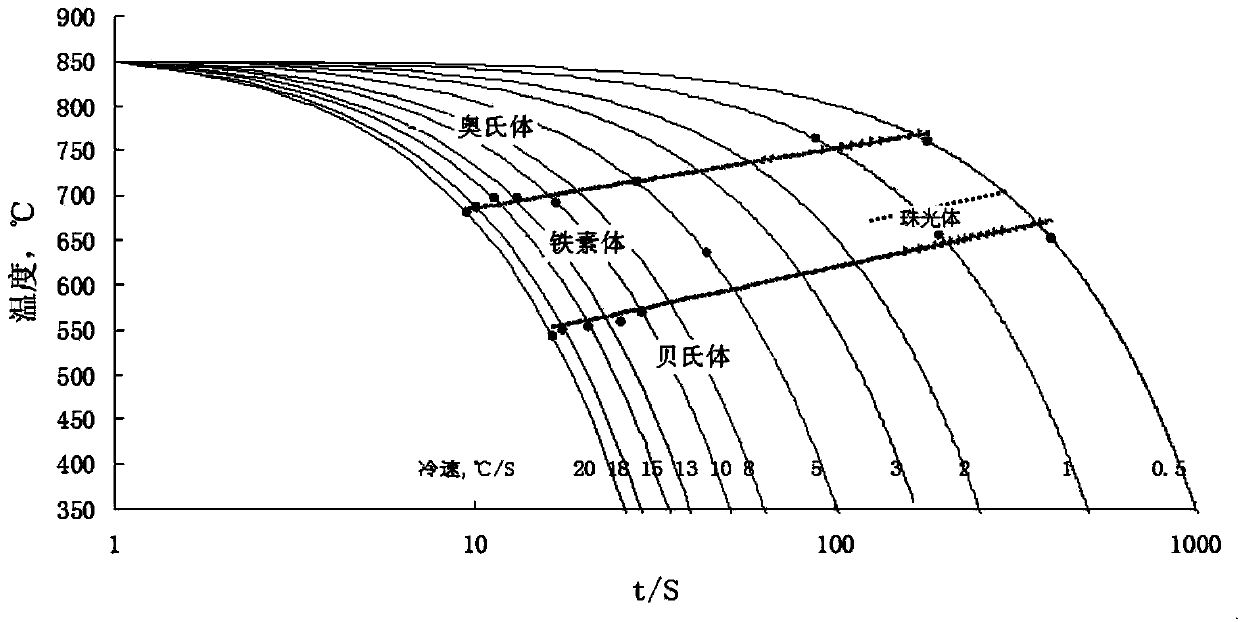
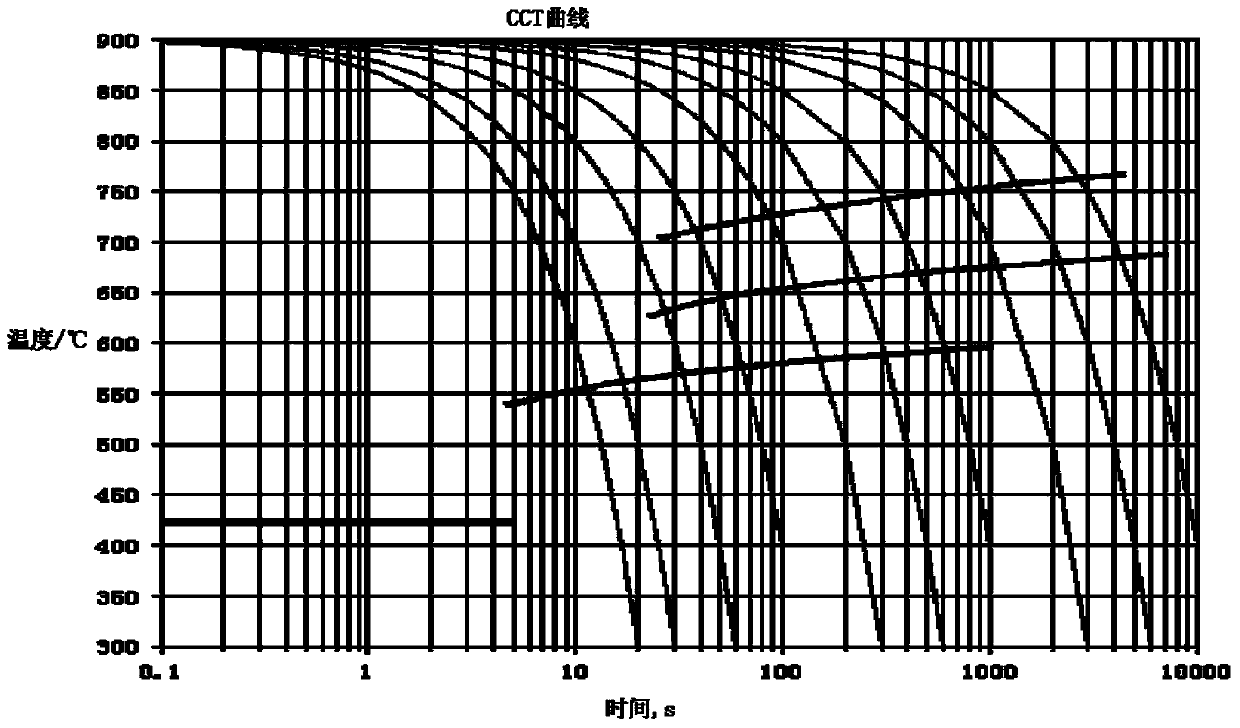
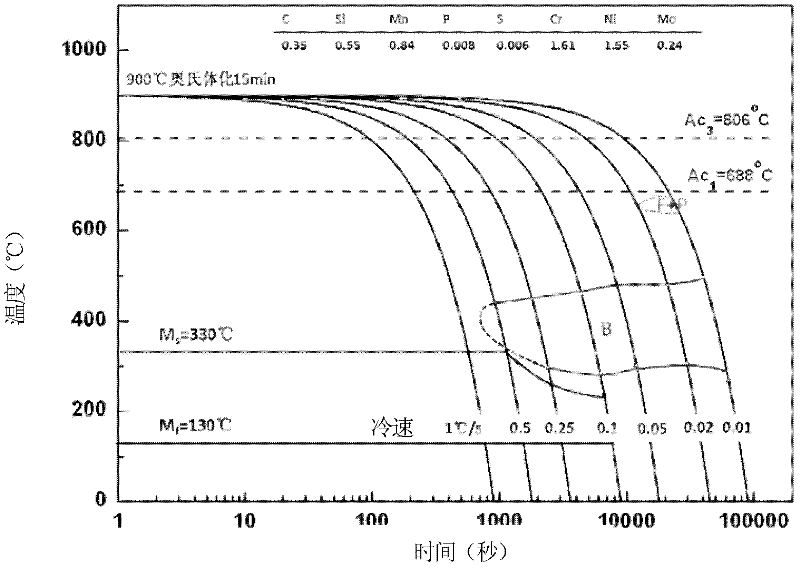
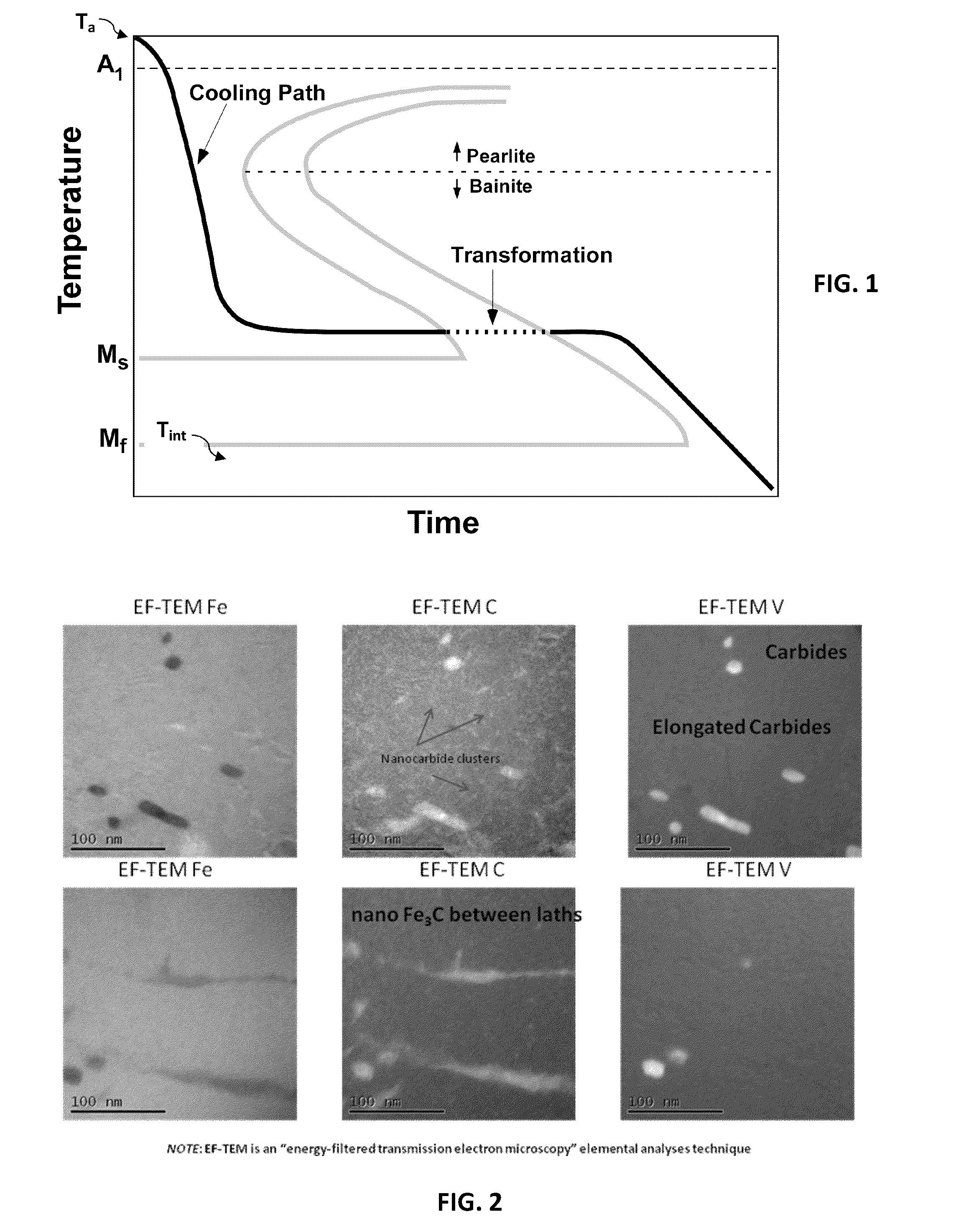
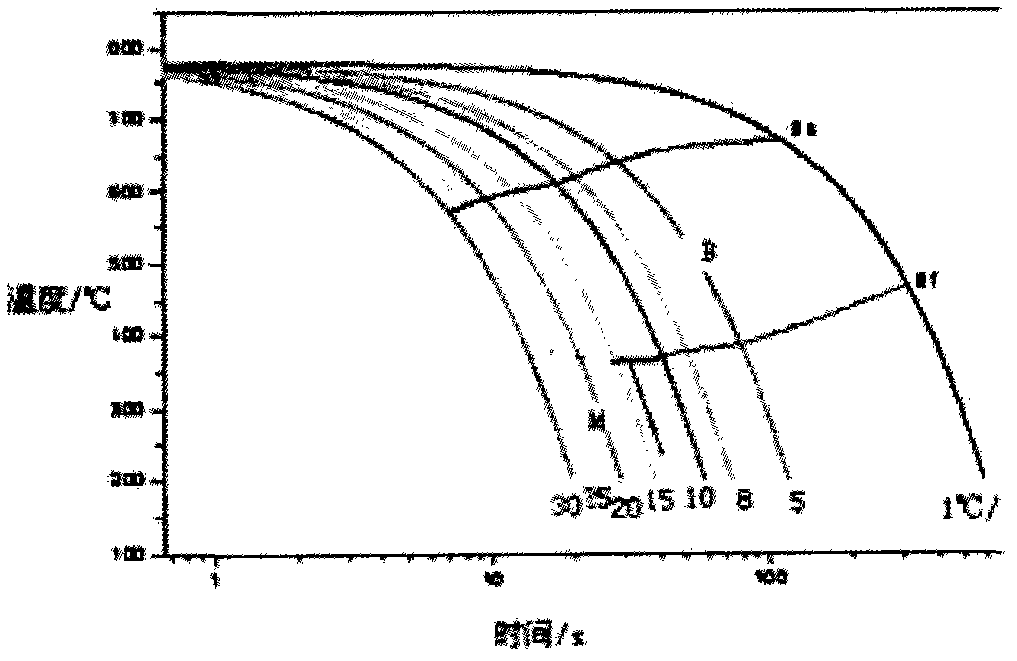
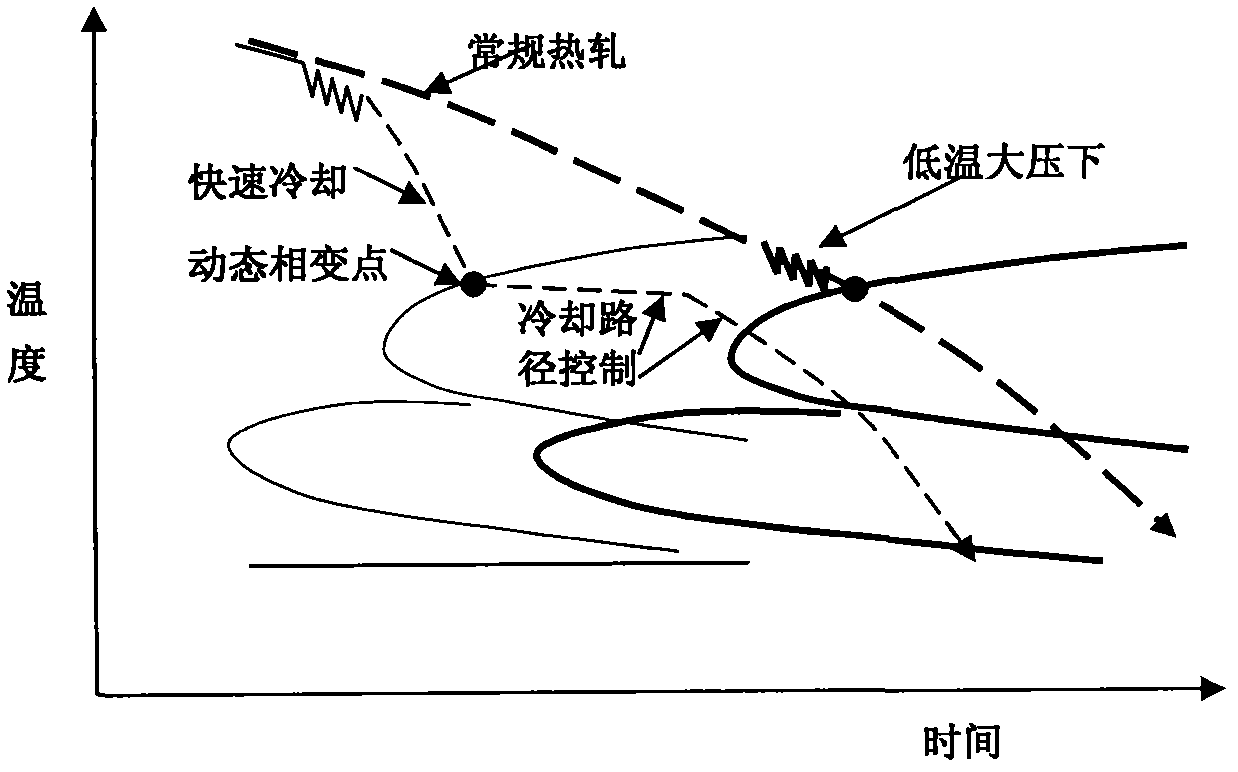
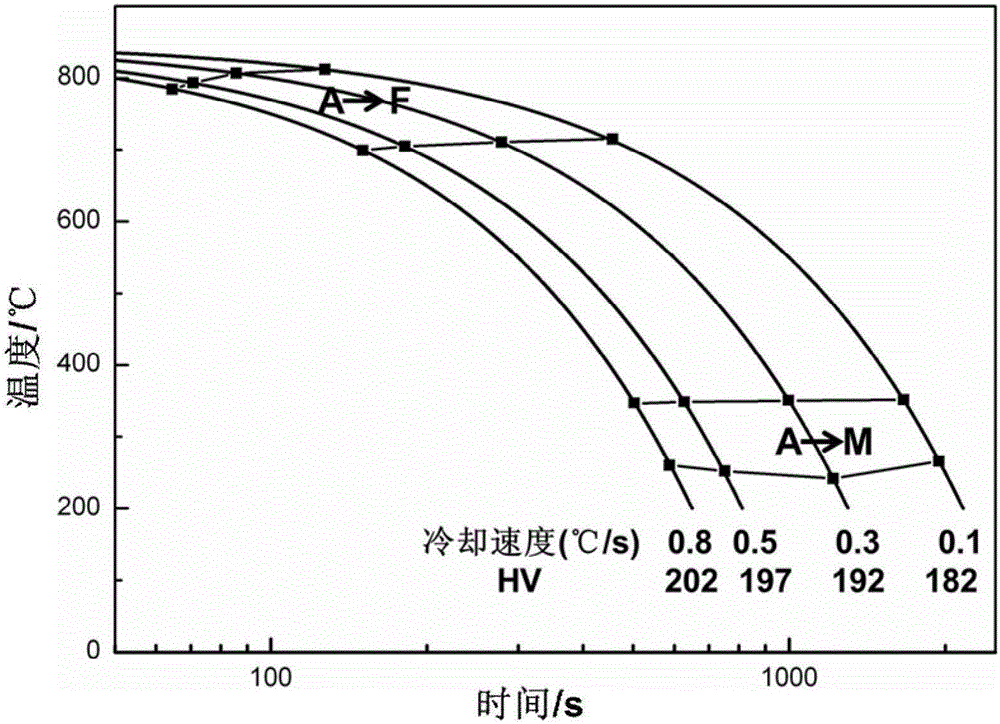
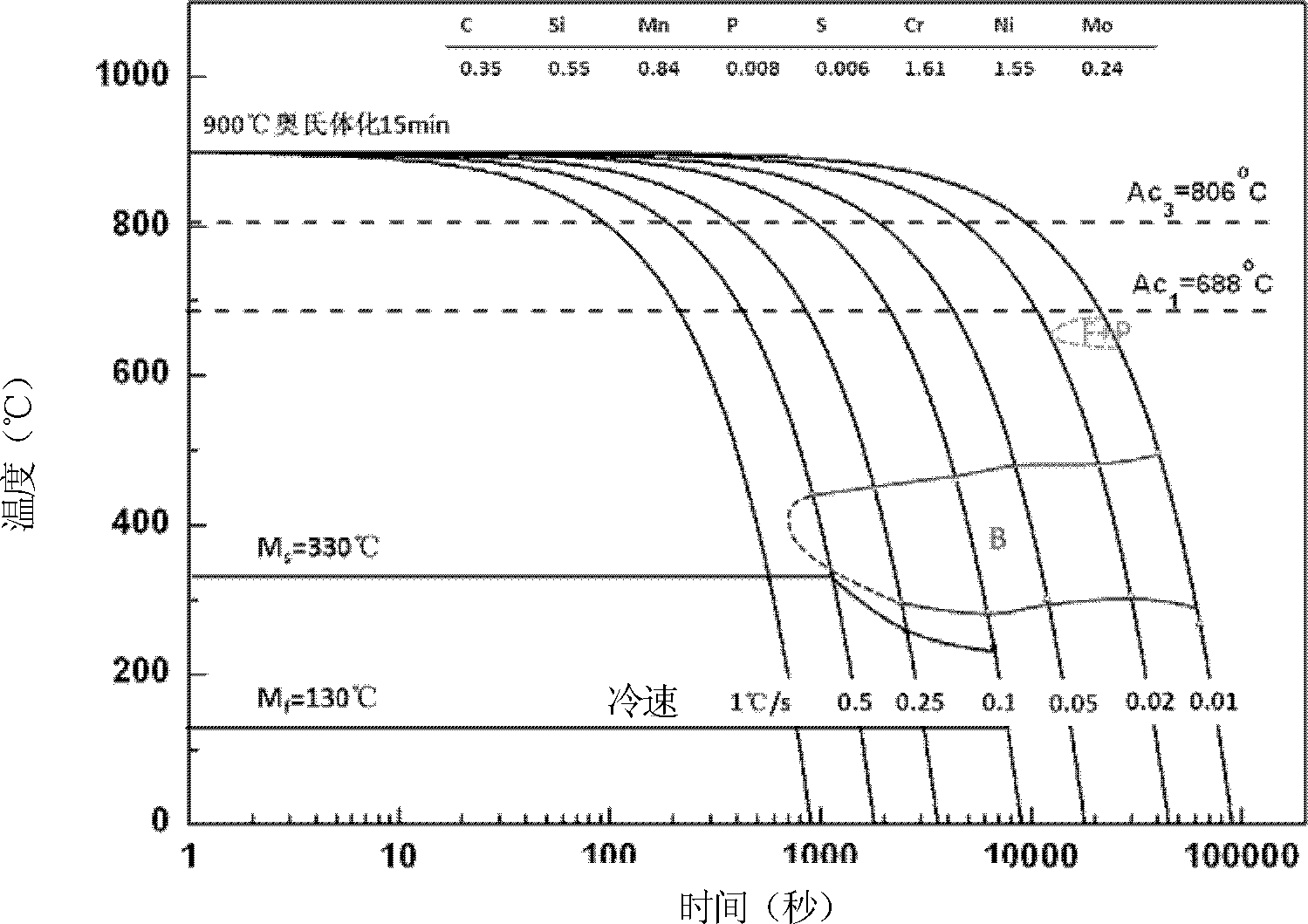
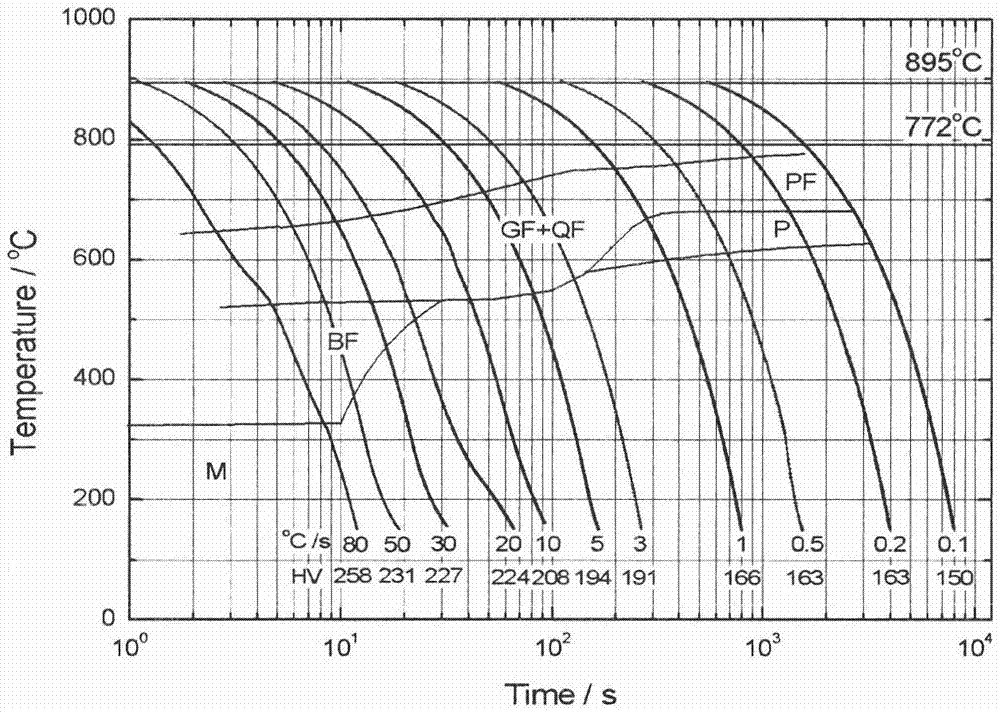
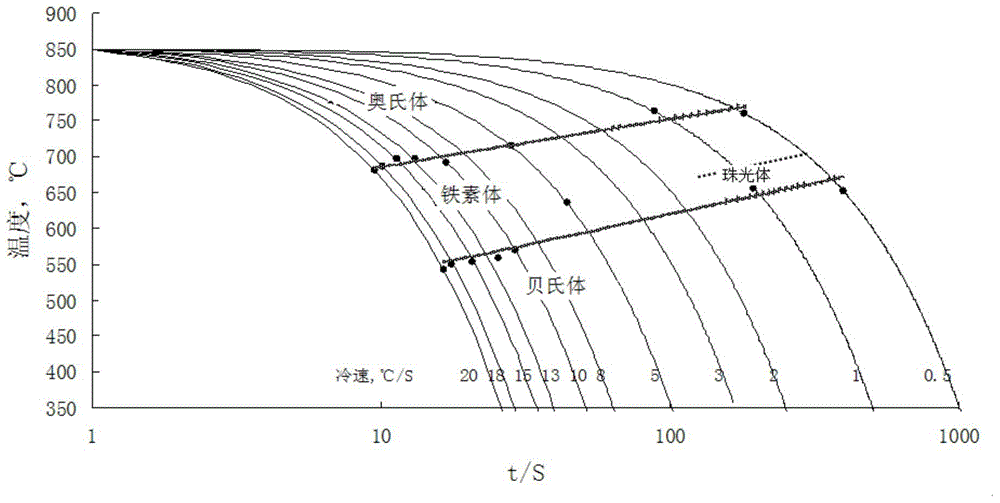
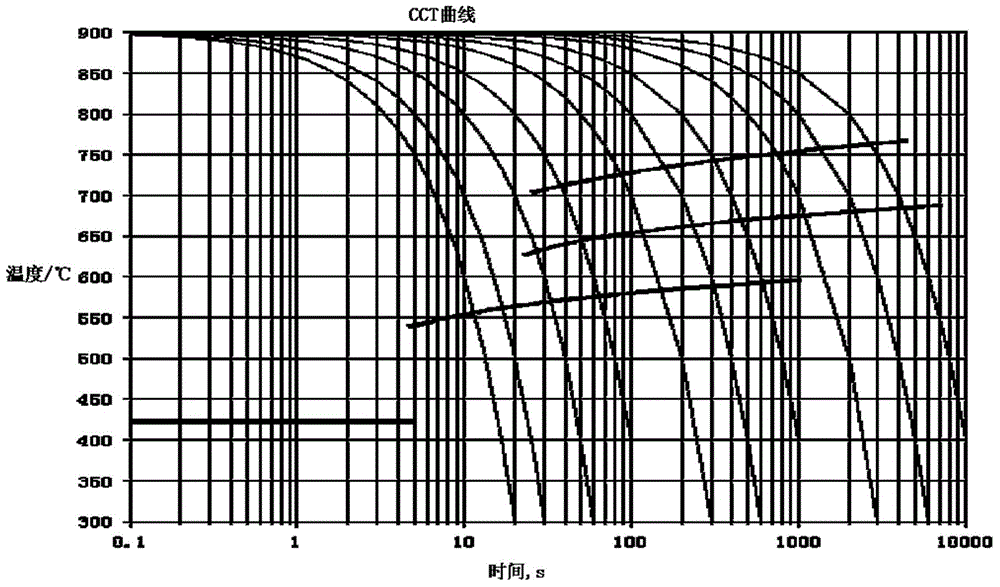
A continuous cooling transformation (CCT) phase diagram is often used when heat treating steel. These diagrams are used to represent which types of phase changes will occur in a material as it is cooled at different rates. These diagrams are often more useful than time-temperature-transformation diagrams because it is more convenient to cool materials at a certain rate (temperature-variable cooling), than to cool quickly and hold at a certain temperature (isothermal cooling).
Method for formulating water-air alternate time-controlled quenching process
The invention provides a method for formulating a water-air alternate time-controlled quenching process. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, predicating a structure composition of a part with required performance according to the performance detection part of an alloy steel piece and specific performance requirements; step 2, according to the super-cooled austenite isothermal cooling transformation curve or the super-cooled austenite continuous cooling transformation curve of a material, acquiring the longest cooling time or the minimum cooling speed which the structure needs to reach a certain temperature; step 3, dividing an alloy steel piece into a cooling speed control area and a slow cooling area along a section from the surface to the centre; step 4, determining the water-air alternation times of the cooling speed control area, and a water-cooling time and an air-cooling time each time; and step 5, determining the water-air alternation times of the slow cooling area, and a water-cooling time and an air-cooling time each time. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the alloy steel piece can obtain required performance or structure on the premise of avoiding cracking; and the method is suitable for a quenching treatment for the alloy steel pieces with various ingredients.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
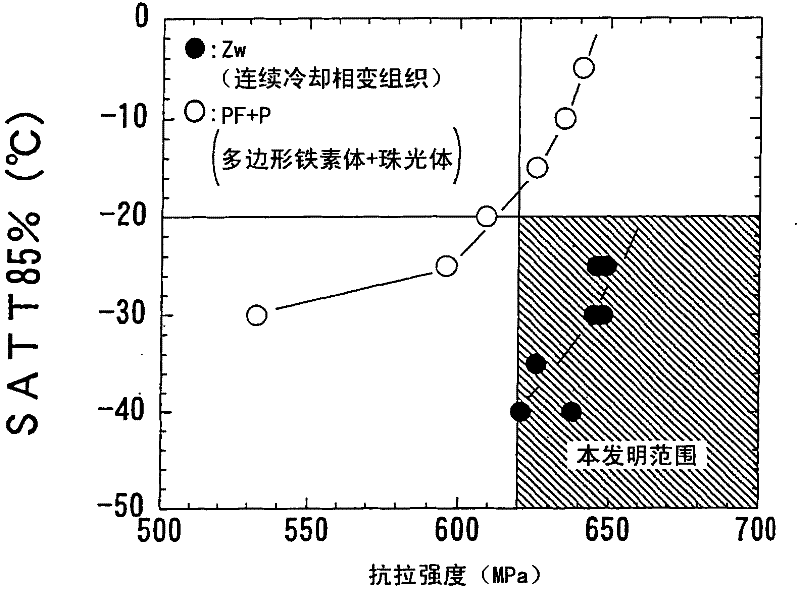
High strength hot rolled steel products for line-pipes excellent in low temperature toughness and production method of the same
InactiveCN101622369ACheap and stable manufacturingImprove energy absorptionMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelX-ray
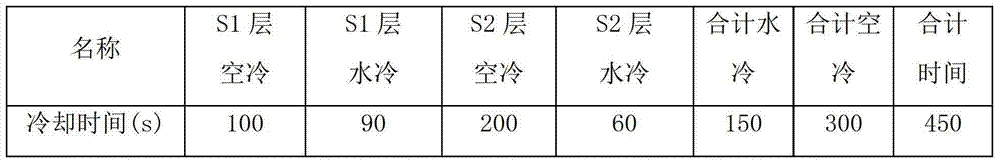
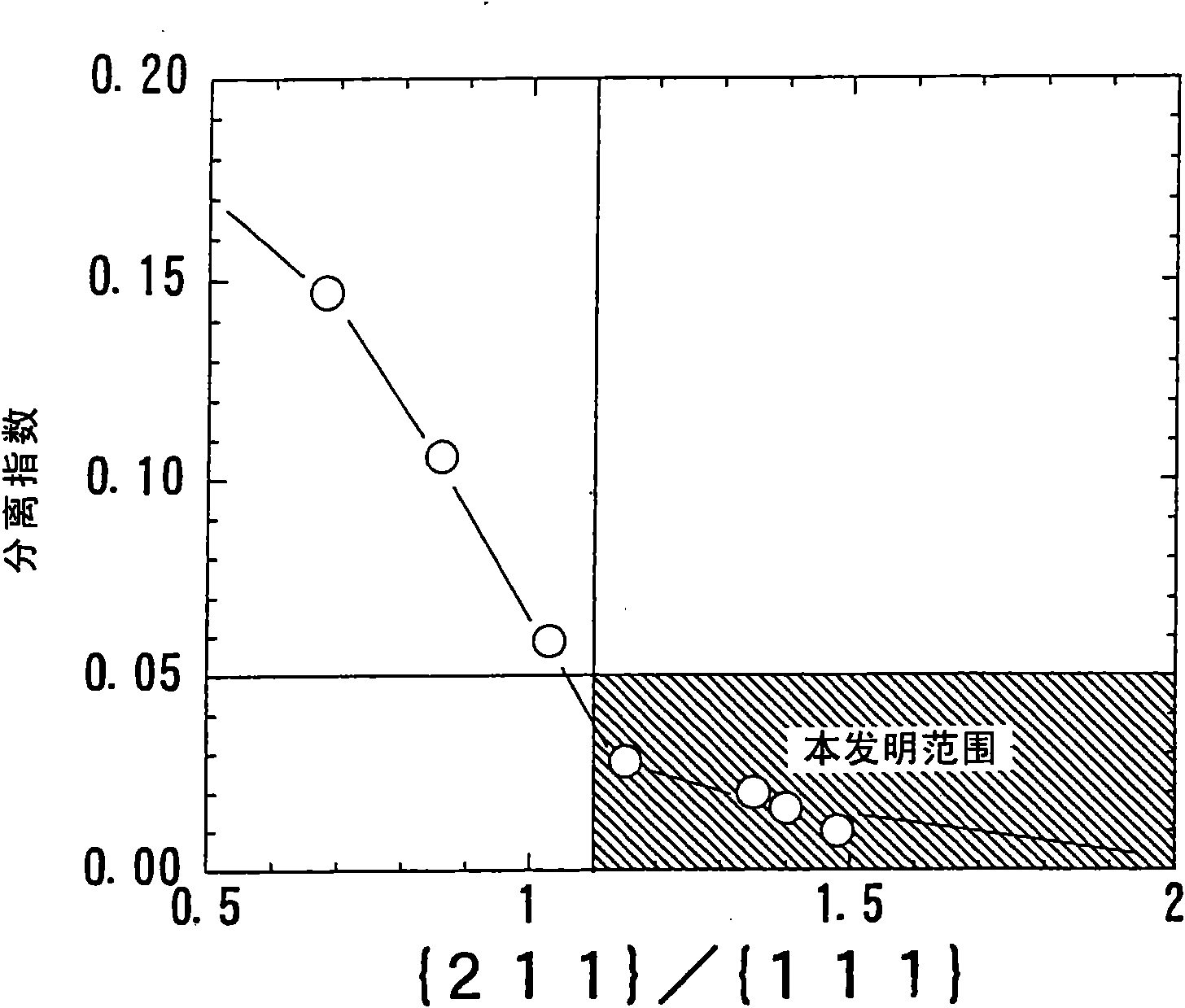
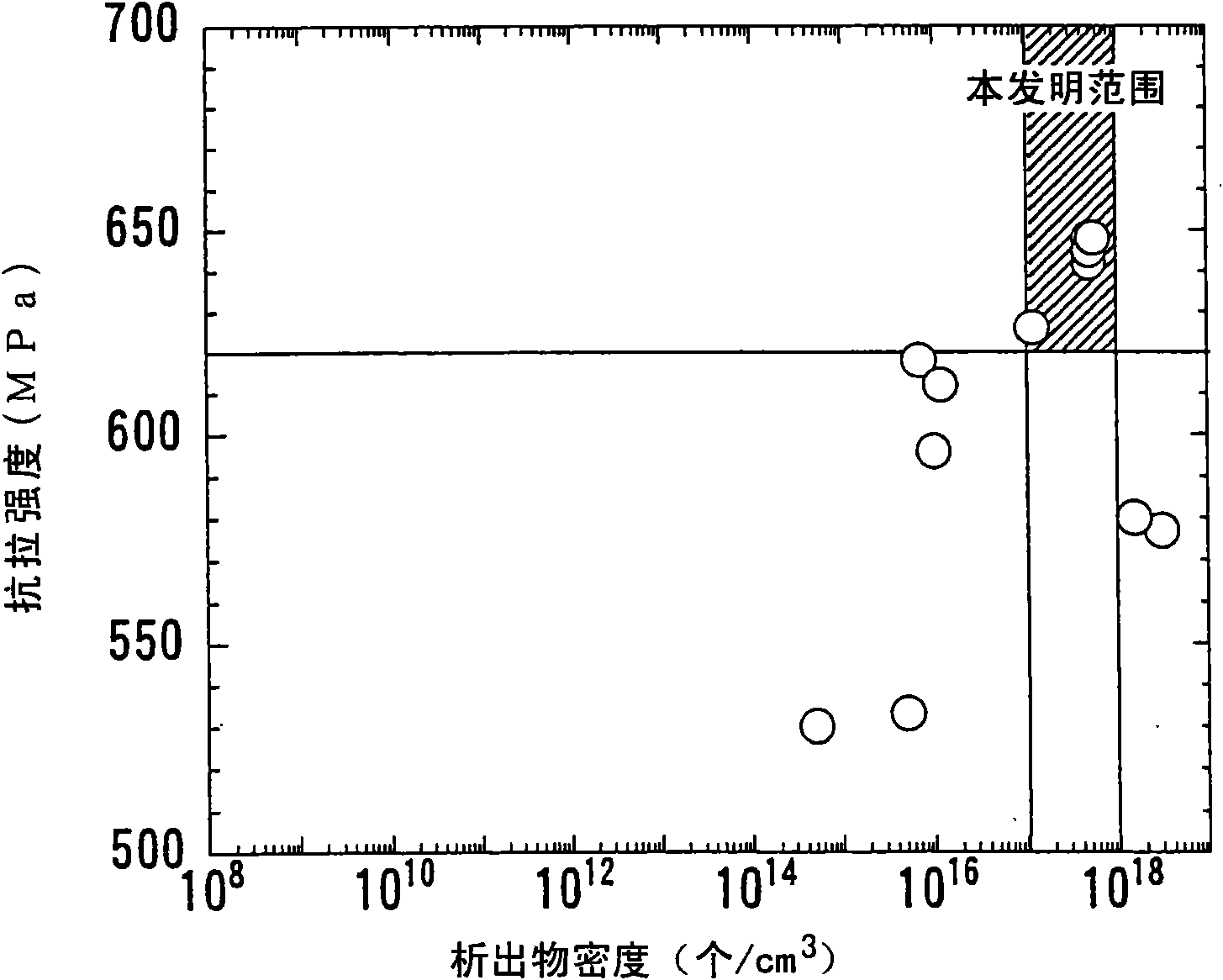
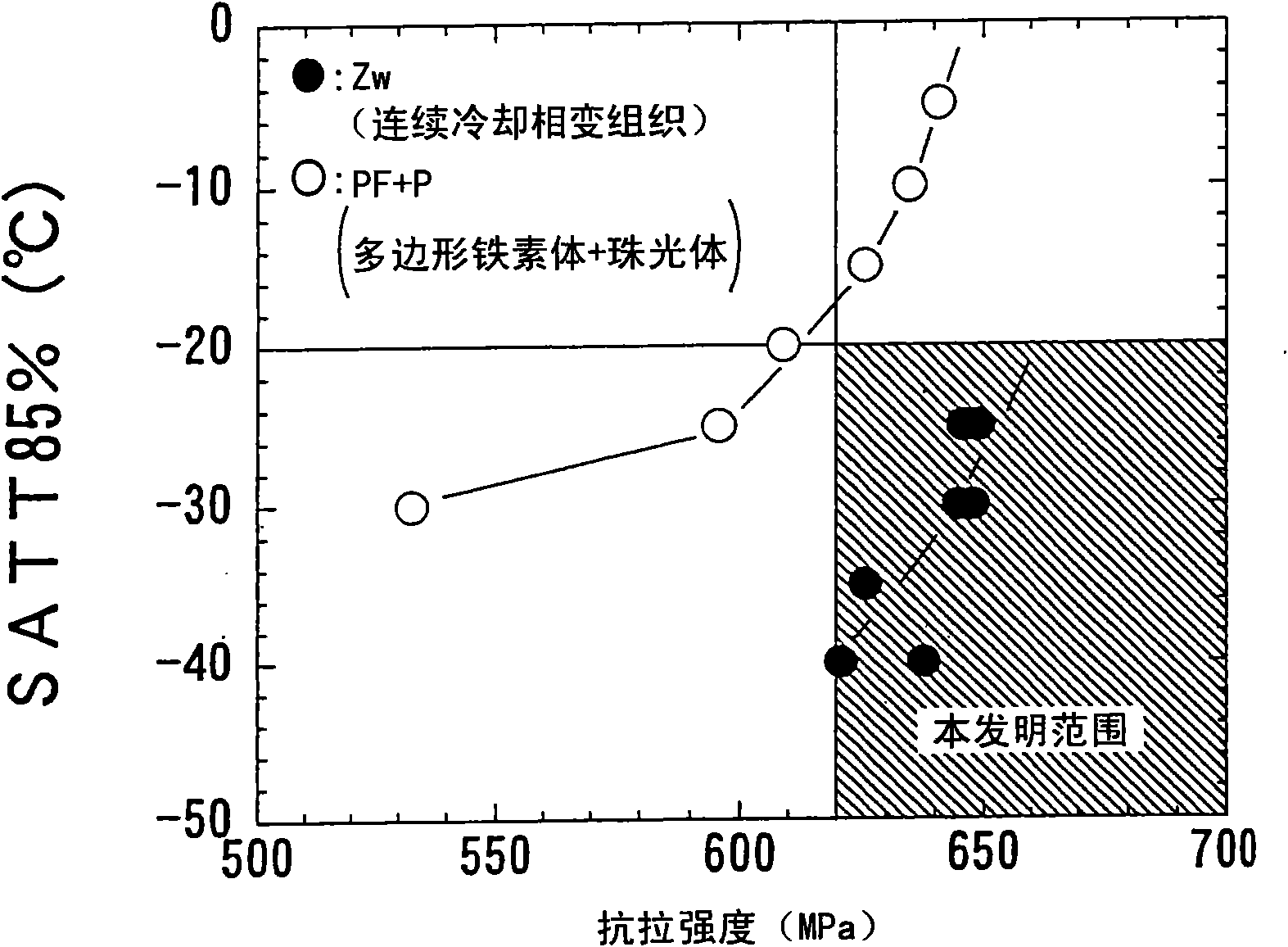
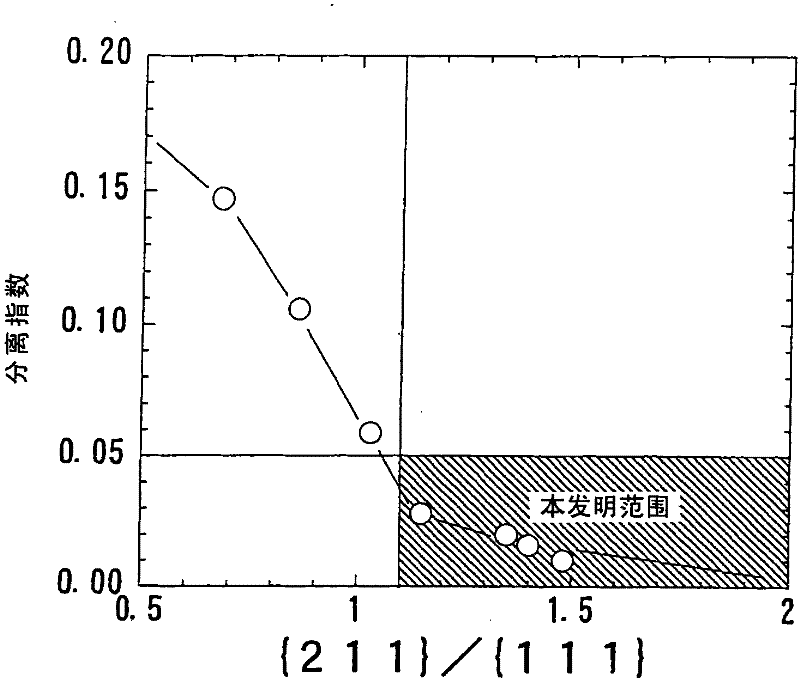
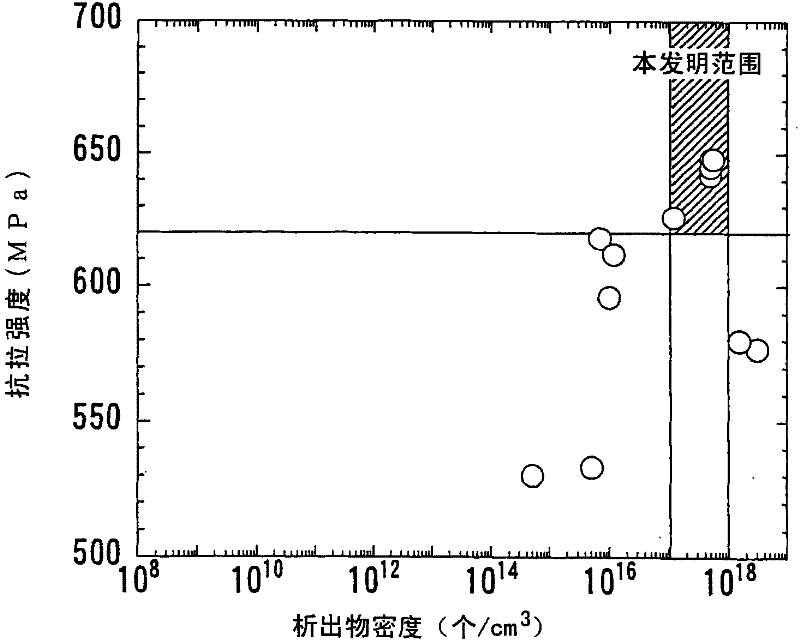
The invention provides a high-strength hot-rolled steel plate for line pipes which is excellent in low-temperature toughness and a process for the production of the same. A steel plate which contains by mass C: 0.01 to 0.1%, Si: 0.05 to 0.5%, Mn: 1 to 2%, P: 0.03% or below, S: 0.005% or below, O: 0.003% or below, Al: 0.005 to 0.05%, N: 0.0015 to 0.006%, Nb: 0.005 to 0.08%, and Ti: 0.005 to 0.02% with the proviso that relationships: N-14 / 48xTi>0% et Nb-93 / 14x(N-14 / 48xTi)>0.005% are satisfied and with the balance consisting of Fe and unavoidable impurities, characterized in that the microstructure is a continuous cooling transformation structure, that the reflected X-ray intensity ratio between {211} plane and {111} plane which are parallel to the plate face, {211} / {111} ratio, in the texture in the thicknesswise central part of the plate is 1.1 or above, and that the density of carbonitride precipitate of Nb and / or Ti in the grains is 10<17> to 10<18 >pieces / cm<3>.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method for controlling generation of cold crack in welding process based on electromagnetic induction heating
InactiveCN101786213AEvenly heatedImprove toughnessWelding/cutting auxillary devicesIncreasing energy efficiencyHeat-affected zoneEngineering
The invention provides a method for controlling generation of a cold crack in the welding process based on electromagnetic induction heating, relating to a method for controlling generation of the cold crack in the welding process. The invention aims to solve the problems that a welding seam and crystal grains in a heat influence region become coarse and the metal toughness is lowered due to using a pre-welding pre-heating method for preventing generation of the cold crack and the problems of difficult control of flame power, easy surface overburning, welding seam surface state change and welding production procedure increase in a post-welding heat treatment method in the traditional welding process. The method comprises the following steps of searching a welding continuous cooling transformation curve corresponding to special welding materials; determining a workpiece to be welded; welding a temperature field on the surface; determining induction heating process parameters; welding frock; and implementing welding until welding finish. The invention is used for welding.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Production method of heat-resistant steel welding wire
ActiveCN104668820AShorten the development processHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagAcid washing
The invention discloses a production method of heat-resistant steel welding wires. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of 1) performing steel ingot smelting according to designated chemical components to obtain a steel ingot; 2) testing the continuous cooling transformation curve of the welding wire steel by adopting a Gleeble thermal simulation test and deducing process parameters for rolling and cooling control; 3) rolling the steel ingot into coil rods with diameter of 5.5-8.0mm by referring to a process; 4) performing rough drawing to the coil rods after acid washing; 5) performing primary annealing treatment, the process of which is heating to 830-850 DEG C, preserving heat for 2 hours and then slowly cooling; 6) performing fine drawing after acid washing to obtain welding wires with diameter of 0.8-4.0mm. The drawing performance of the coil rods produced by adopting the production method disclosed by the invention is good, one time of annealing is only required in the process of drawing the coil rods into the welding wire finished products, the production efficiency is improved, the produced welding wires can be used for chrome-molybdenum heat-resistant steel welding, the electric arc is stable during welding, the spatter is less, the slag is easy to remove, and welded joints have excellent impact toughness, temper embrittlement resistance, high-temperature strength and creep resistance.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Method of measuring large deformation resistant pipeline steel SH-CCTA curve
InactiveCN107356625AMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionPreparing sample for investigationHeat-affected zoneThermal impact
The invention discloses a method of measuring a large deformation resistant pipeline steel SH-CCTA curve, which is a simulated HAZ continuous cooling transformation curve. According to the method, welding conditions are simulated to heat a sample; a CCT dilatometer is used to measure the critical points (Ac1 and Ac3), expanding curves under different cooling speeds are measured; a tangent method is used to determine the temperature of a phase transformation point under different cooling speeds; a metallographic method under the assistance of a hardness method is used to analyze and determine a room temperature tissue; and finally a complete SH-CCT curve is drawn. On one aspect, the method can be used to evaluate the welding property of steel or predict the tissue and performance of welding heat affected zone; and on the other aspect, a technical reference is provided for designing a proper welding technology, in particular, welding line energy.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Measuring method of aluminum alloy CCT (Continuous Cooling Transformation) diagram
ActiveCN101788509ALower requirementEasy to measureInvestigating phase/state changeTemperature curveTime changes
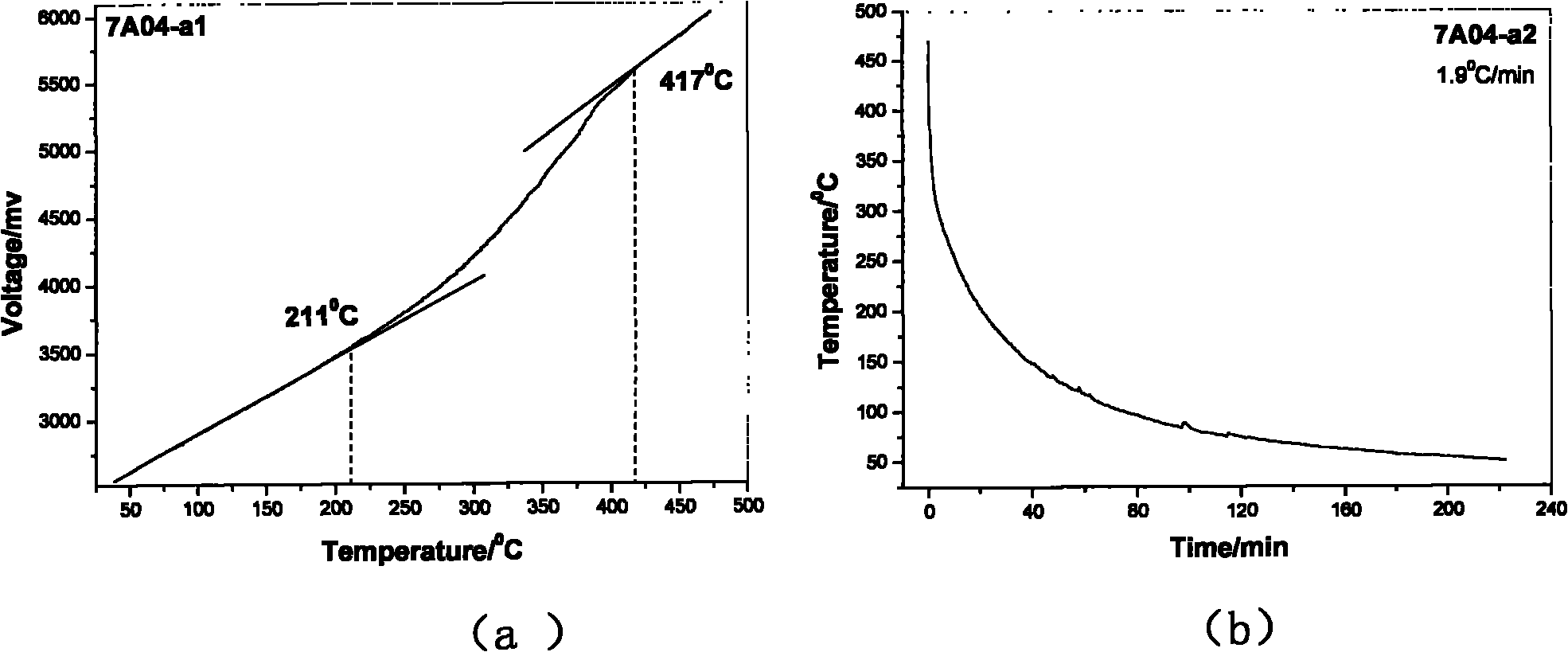
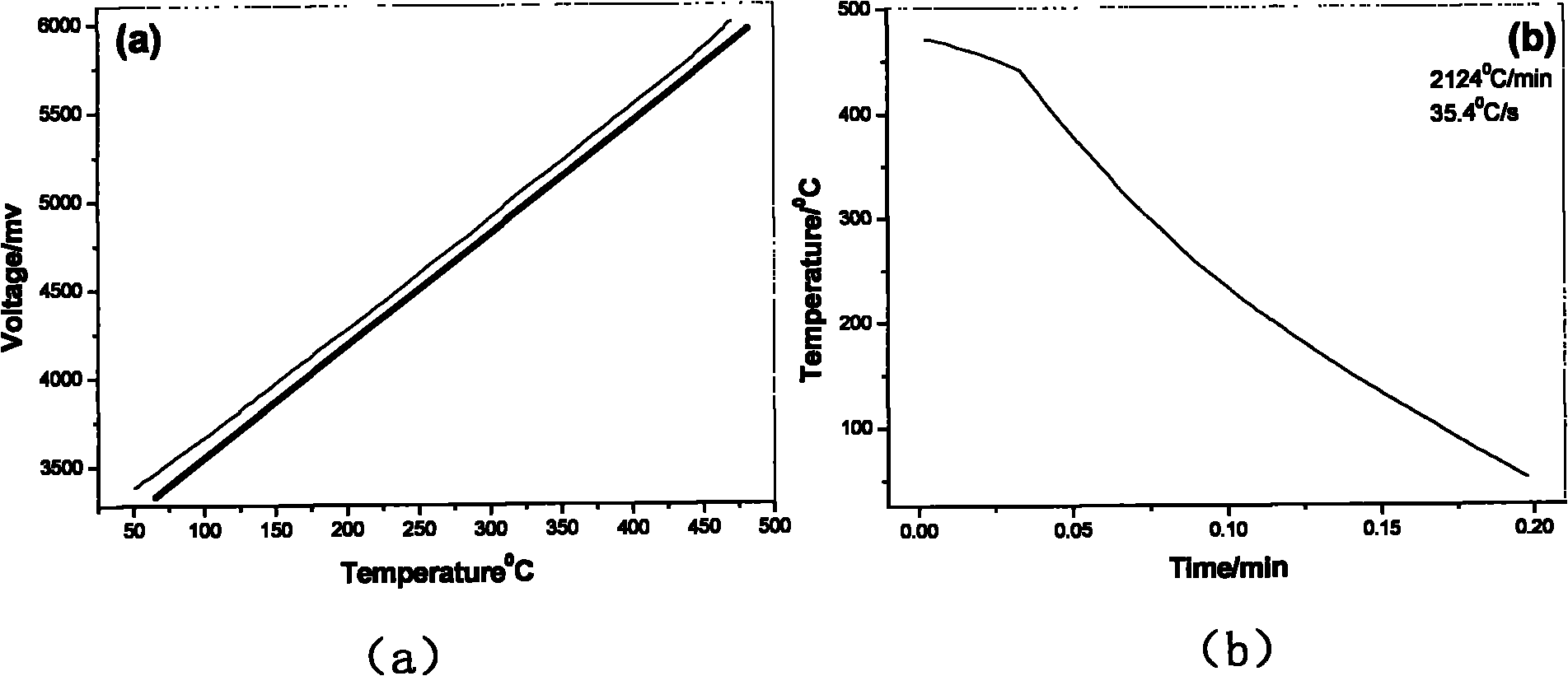
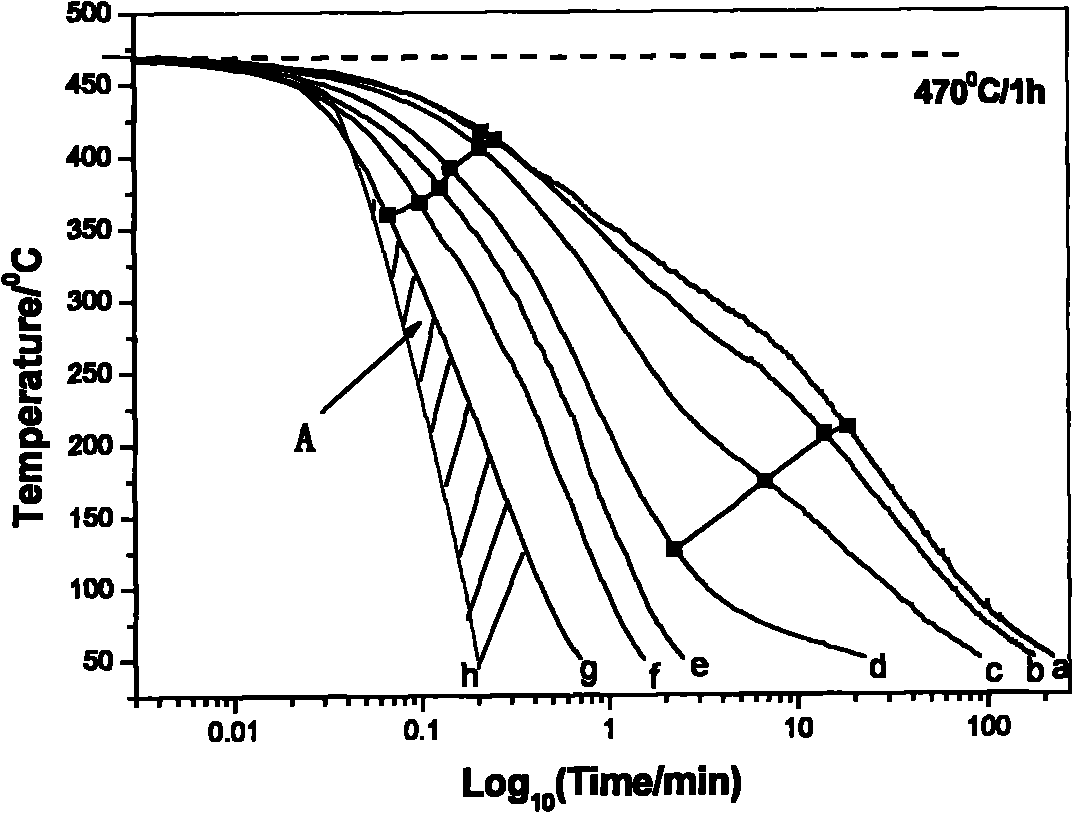
The invention discloses a measuring method of an aluminum alloy CCT (Continuous Cooling Transformation) diagram, which comprises the following steps: 1. measuring data of aluminum alloy voltage and temperature along with the change of time under various cooling regimes; 2. drawing a voltage-temperature curve and a temperature-time curve in the cooling process of a sample according to the data obtained by the first step; 3. determining phase transformation points: determining the temperatures of phase transformation starting points and phase transformation ending points of the aluminum alloy sample according to the change position of the slope of the voltage-temperature curve; and 4. drawing the CCT diagram: drawing the temperature-time curve of the sample obtained at different cooling speeds to a logarithmic coordinate system, labeling the phase transformation starting points and the phase transformation ending points on corresponding temperature-time curves according to the phase transformation starting points and the phase transformation ending points determined according to the voltage-temperature curve, and connecting the phase transformation starting points and the phase transformation ending points by lines to obtain the CCT diagram of the sample alloy. The method has the advantages of strong operability, simple process, simple operation, high speed, dense acquired points, measuring material saving and higher measuring precision, fills up the blank of a measuring technology of the CCT diagram of the aluminum alloy and is suitable for scientific research units to measure the phase transformation points of the aluminum alloy and the CCT diagram.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Bake-hardening hot-rolled steel sheet with excellent workability and process for producing the same
InactiveCN101107374AStable sinter hardeningHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesNiobiumManganese
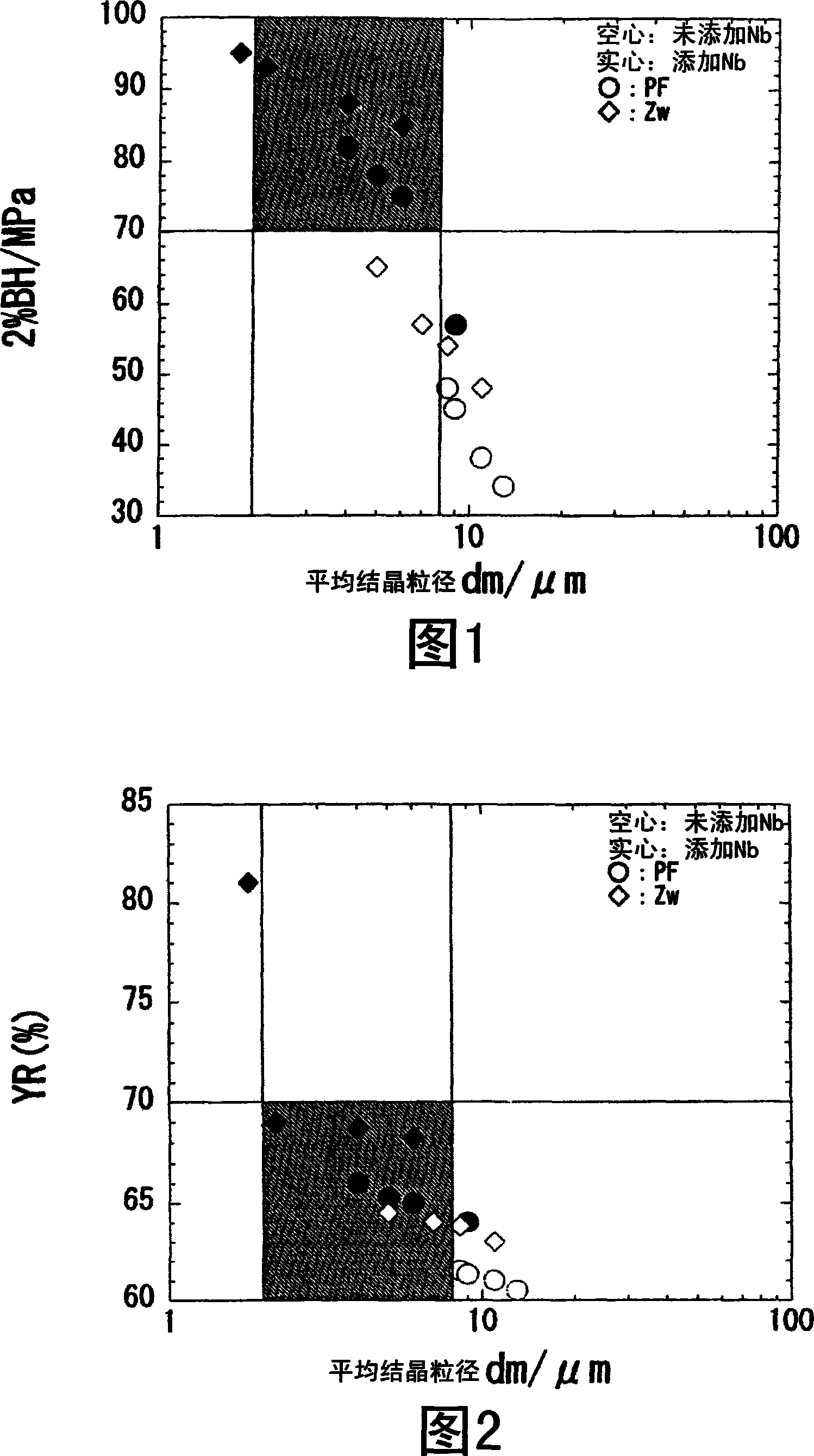
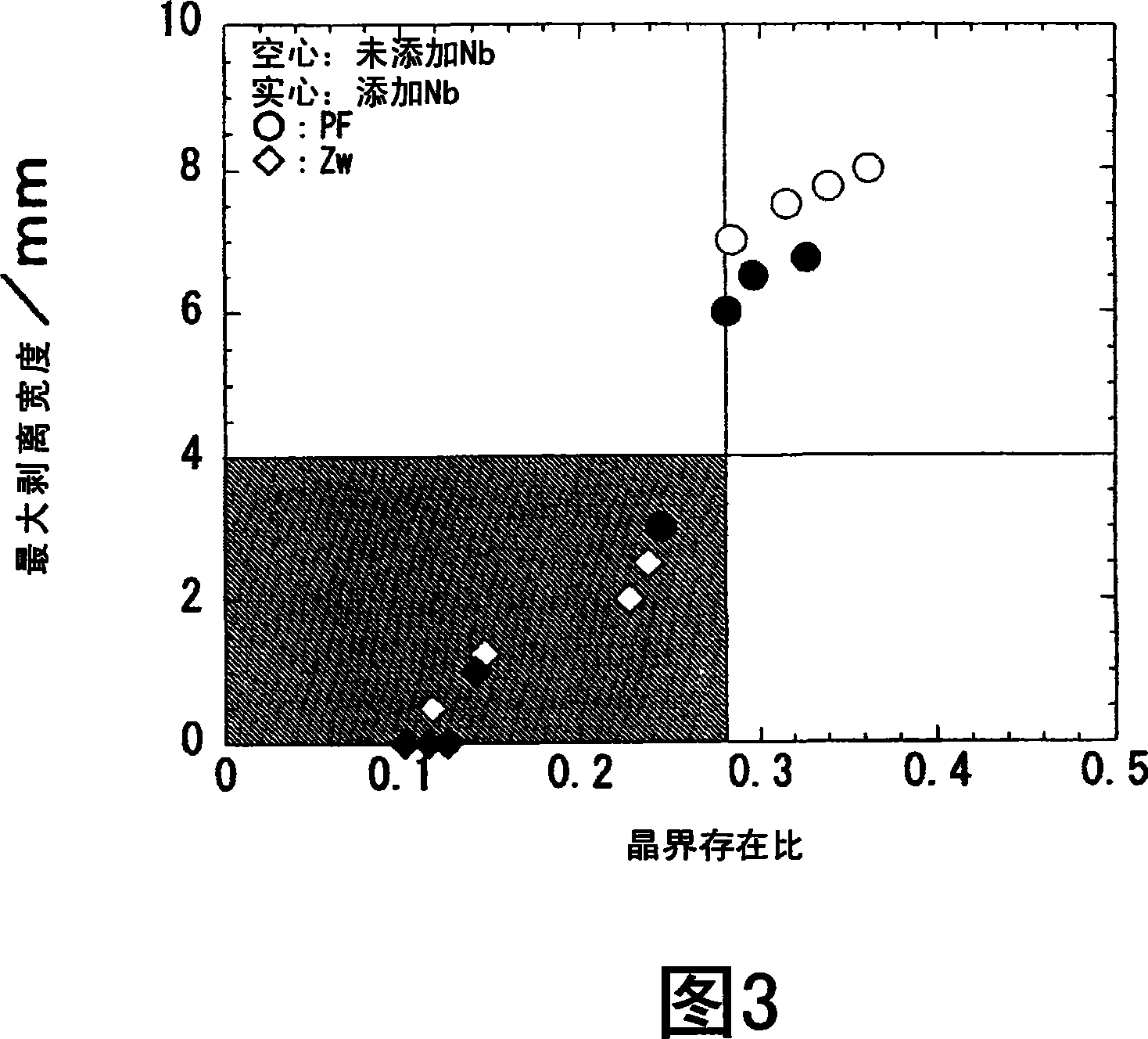
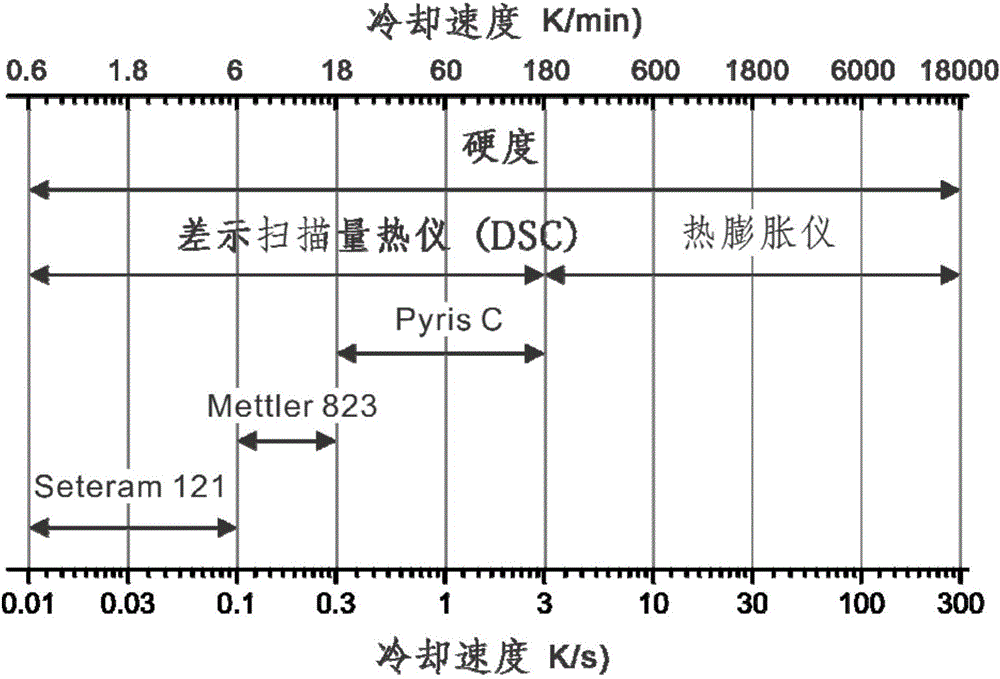
A bake-hardening hot-rolled steel sheet which contains 0.01-0.2 mass% carbon, 0.01-2 mass% silicon, 0.1-2 mass% manganese, up to 0.1 mass% phosphorus, up to 0.03 mass% sulfur, 0.001-0.1 mass% aluminum, up to 0.01 mass% nitrogen, and 0.005-0.05 mass% niobium, the remainder comprising iron and unavoidable impurities. The microstructure of the sheet is a polygonal ferrite having an average particle diameter of 2-8 [mu]m and / or a continuous cooling transformation texture. The proportion of a solid solution of carbon and / or a solid solution of nitrogen present at the grain boundaries in the sheet is 0.28 or lower. Also provided is a process for producing the hot-rolled steel sheet which comprises heating a steel billet comprising those ingredients to at least a temperature satisfying the equation SRT ( DEG C) = 6670 / {2.26-log(%Nb)(%C-273 (A) rough-rolling the steel billet heated, finish-rolling the sheet under such conditions that the final temperature is in the range of from the Ar3 transformation point to (Ar3 transformation point + 100 DEG C), cooling it at a cooling rate of 80 DEG C / sec or higher for cooling from cooling initiation to 500 DEG C or lower, and winding it up.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method for measuring aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve
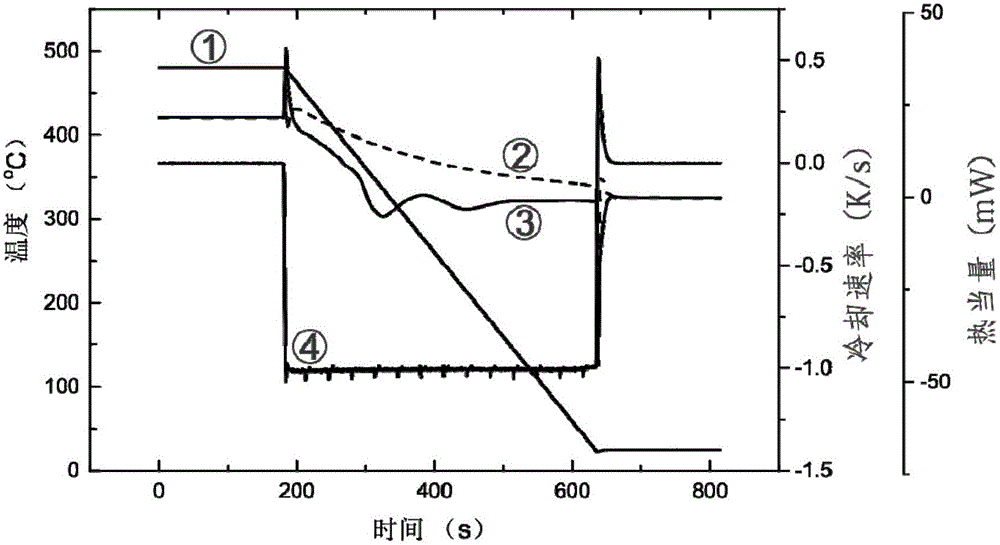
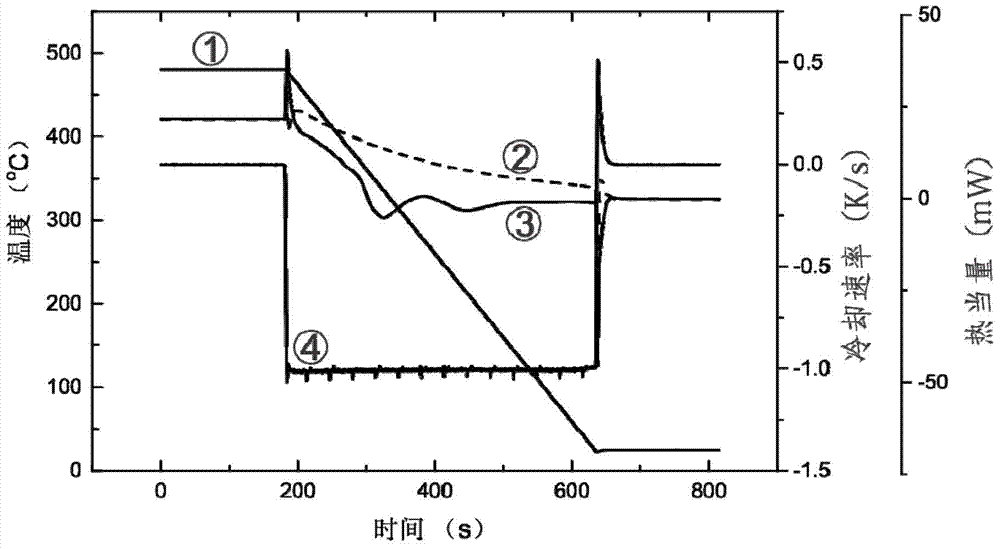
The invention relates to a method for measuring an aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal material preparation. According to the method provided by the invention, by recording the change of thermal equivalents in different temperature intervals, precipitation temperature intervals of quenching reaction in a quenching process are distinguished based on the change of the thermal equivalents. The method provided by the invention measures exothermic reaction of aluminum alloy in the quenching process by applying a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and combines with microstructure analysis and mechanical property testing, so as to obtain the aluminum alloy continuous cooling transformation curve. Compared with other methods, the method provided by the invention can distinguish initial and final temperatures of different quenching-induced precipitated phases based on accurate cooling curves in certain cooling intervals. The continuous cooling transformation curve obtained by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high precision, great guiding significance and the like.
Owner:深圳卓聚新材料有限责任公司
Method for linkage production of high-toughness pipeline steel by adopting jetting and laminar cooling
ActiveCN103740925AStable mechanical propertiesEasy to shapeFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlChemical compositionLine tubing
The invention discloses a method for linkage production of high-toughness pipeline steel by adopting jetting and laminar cooling, belonging to the technical field of production of medium-thickness plates. The super-cooled austenite continuous cooling transformation (CCT) curve of a steel plate is measured according to the chemical constituents of the steel plate. The steel plate comprises the following chemical ingredients in percentage by weight: 0.045-0.075 percent of C, 0.1-0.3 percent of Si, 1.55-1.85 percent of Mn, 0.045-0.085 percent of Nb, 0.1-0.2 percent of Mo, 0.1-0.3 percent of Ni, 0.01-0.02 percent of Ti and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The method has the advantages that the problems of low toughness of pipeline steel plates of over grade X80 produced by jet cooling and low strength of pipeline steel plates of over grade X80 produced by laminar cooling are solved, and the high-toughness pipeline steel is produced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Control method and control device of rod and wire production line temperature control rolling process
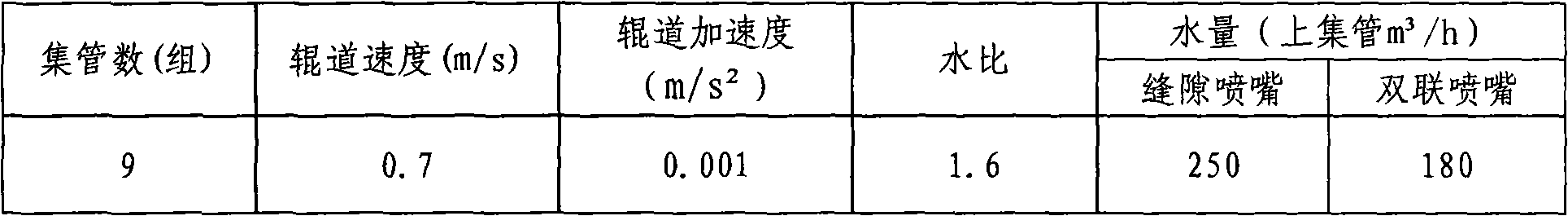
The invention is suitable for the field of low temperature rolling, and provides a control method of a rod and wire production line temperature control rolling process. The method comprises the steps of determining a critical phase change temperature and a critical cooling speed of a rolled piece generation phase change tissue according to the a steel type and a corresponding continuous cooling transition curve characteristic; calculating the water cooling time according to a length value of a water tank and a rolling speed of a rolled piece, and calculating a corresponding maximum water flow rate at the critical phase change temperature and the critical cooling speed according to the water cooling time and the cooling water temperature; acquiring an initial value of the water flow rate within the maximum water flow rate range; calculating a uniform temperature of the rolled piece according to a heat transfer relation of each node of the rolled piece; judging an absolute difference value of the uniform temperature and a target temperature to exceed a first preset threshold value, adjusting the water flow rate, re-calculating the uniform temperature, and calculating the water flow rate which cannot satisfy the first preset threshold value. By adopting the control method, the automatic derivation of process parameters in the temperature control rolling process can be realized, and the low efficiency and inaccuracy for a traditional method for referring to the existing engineering or experience in the prior art can be overcome.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Production method for rapidly cooling medium plate after rolling
ActiveCN102343372ALow carbon equivalentLow weld crack susceptibilityWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelPhase change
The invention discloses production method for rapidly cooling a medium plate after rolling, belonging to the technical field of production of medium plates. The method comprises the following process steps of: adjusting an ultrafast cooling (UFC) frame to 300mm+h till the cross point between extension lines of upper and lower nozzles of equipment is positioned on the central line of a steel plate; during ultrafast cooling, setting cooling rules and parameters according to the steel kind, specification as well as required final cooling temperature and cooling speed of the steel plate; startingmiddle spraying, side spraying and air blowing to remove residual water from the surface of steel plate to increase the cooling uniformity, starting UFC equipment, and spraying water onto the steel plate with a gap nozzle and a ganged nozzle for cooling; and controlling the cooling speed and cooling termination point according to the CCT (Continuous Cooling Transformation) curve of steel, whereinthe cooling speeds of steel plates of different thicknesses are 5-80 DEG C / s, and the final cooling temperature is controlled at 450-800 DEG C. The method has the advantages: by controlling the cooling process of the steel plate after rolling, control over phase change and organization is realized, and the aim of enhancing the roughness of the steel plate is fulfilled.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Solid section temperature change measurement system
InactiveCN103413059ASimple calculationNo loss of calculation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsCooling curveEngineering
The invention discloses a solid section temperature change measurement system. The solid section temperature change measurement system is characterized by comprising a module for intercepting solid surface temperature and time relations, a data fitting module, a fitting data differential module, a parameter input and calculation module and a CCT (continuous cooling transformation) and TTT (time temperature transformation) curve superposition module. Influences of internal heat sources, quality, physical properties and ingredients of solids on heat transfer are embodied on temperature time curves of the solid surfaces classified according to shape, and different temperature moments form a cooling curve from the measured section center parts of the solids to the random surface positions by measuring surface temperature time curves of to-be-measured objects, obtaining temperature change speeds of the object surfaces and calculating moments with the same temperature as the surfaces from the center parts of the measured solids to the random surface positions. The complex calculation process is simplified while calculation accuracy is not reduced, and the goal of practicality is achieved simultaneously.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
Preparation of manganese series water quenching bainite steel
The invention relates to a preparation method of manganese series water quenching bainitic steel, which belongs to the technical field of alloy steel preparation. First, the steel is smelted by a conventional steel smelting process, teemed or continuously cast and produced; the weight percentage of all components in the steel is as follows: C: 0.05 percent to 0.42 percent, Mn: 1.80 percent to 3.00 percent, Si: 0.20 percent to 1.80 percent, Cr: 0 percent to 1.60 percent, and the rest is Fe; after forge rolling, the steel is directly cooled by water or oil; and then, the steel is heated to 200 DEG C to 650 DEG C, and tempered after the temperature is preserved for 1h to 3h. In the preparation method, the alloying of an appropriate amount of Mn, Si, Cr and other elements changes the continuous cooling conversion curve of the steel grade, improves the hardenability characteristic of the steel and obtains components with good obdurability. The product produced by the preparation method has excellent performance, simple process and low cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for thinning crystalline grain of large low alloy cast
The invention relates to a method for thinning a crystalline grain of a large low alloy cast based on computer simulation, material continuous cooling transformation curve measurement and material phase change mode control, and belongs to the field of steel and iron metallurgy. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, measuring a continuous cooling curve of a related cast material and determining the critical cooling rate of the material with martensite, bainite and pearlite phase change; secondly, building a corresponding cast model, and determining the cooling rate of the parts of the cast under different cooling mediums by a way of computer simulation; and lastly, heating the cast to be A3<+> (30-80 DEG C) for austenitizing at first, slowly cooling to be room temperature, enabling the cast to be subjected to diffusion or semi-diffusion phase change, after that, heating the cast to be A3<+> (30-50 DEG C) for austenitizing, selecting a proper cooling way according to simulation calculation, enabling the cast to be subjected to bainite phase change, and thinning the crystalline grain of the cast to be below the ASTM (American Society for Testing Material) standard crystalline grain size 7.5 through the semi-diffusion bainite phase change.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
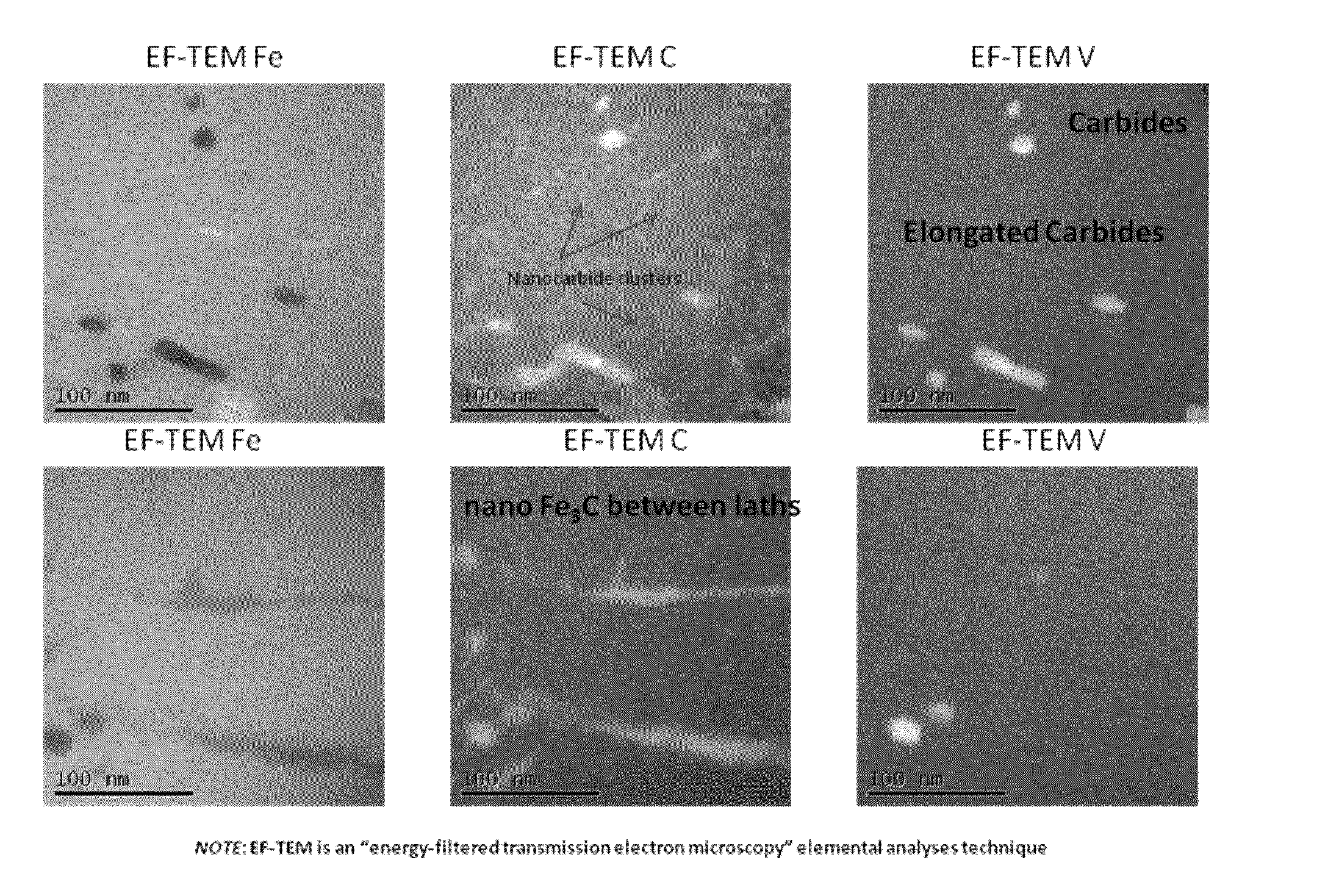
Method of magnetically processing an iron-carbon alloy
InactiveUS20130014863A1Improve mechanical propertiesImproves strength and ductilityFerritic matrixCarbide
A magnetic field assisted processing method entails heating an iron-carbon alloy at an austenitizing temperature for a time duration sufficient for the alloy to achieve an austenitic microstructure; cooling the iron-carbon alloy to an intermediate temperature defined by a continuous cooling transformation (CCT) diagram for the iron-carbon alloy at a rate sufficient to avoid phase transformation of the austenitic microstructure, the intermediate temperature being below a bainitic knee of the CCT diagram and above a martensite start temperature; and applying a high field strength magnetic field of at least about 0.2 Tesla to the iron-carbon alloy after reaching the intermediate temperature. The field is applied for a time duration sufficient to transform the austenitic microstructure into a fine dispersion of one or more iron carbide phases in a ferrite matrix in order to produce a magnetically-processed alloy having improved ductility and strength.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
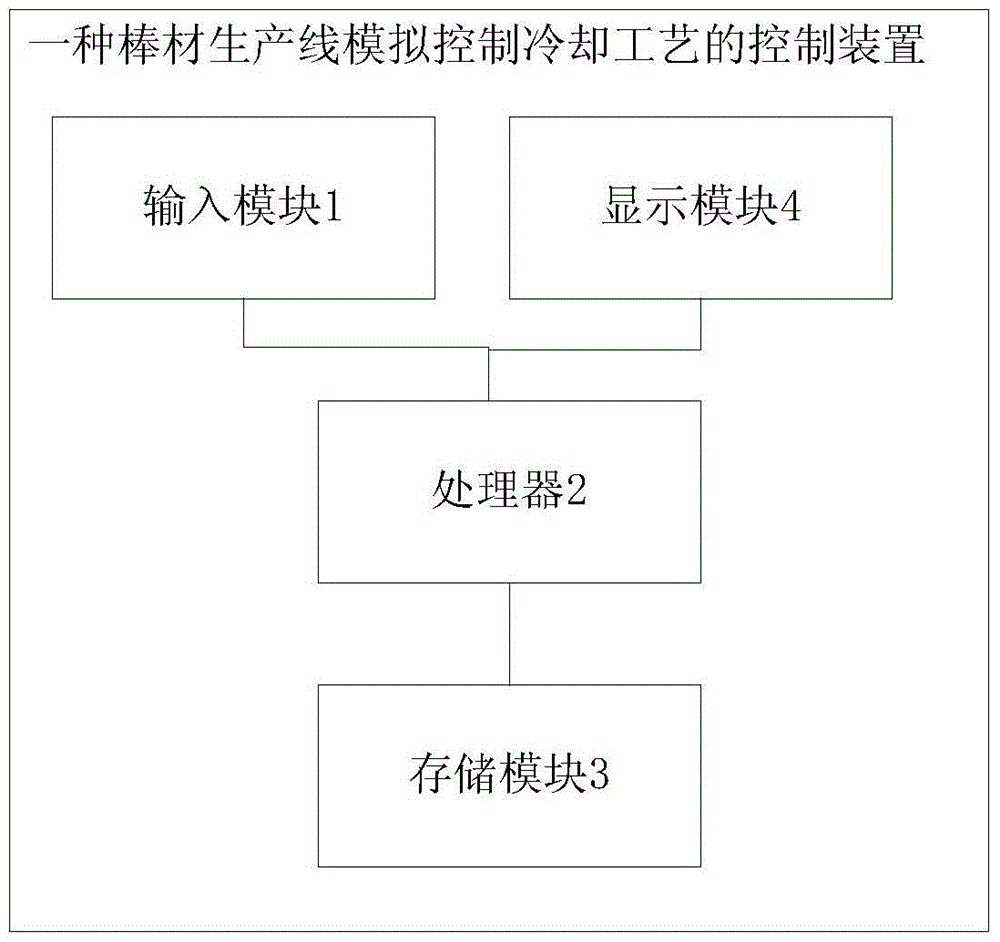
Control method and device for controlling cooling process in bar production line
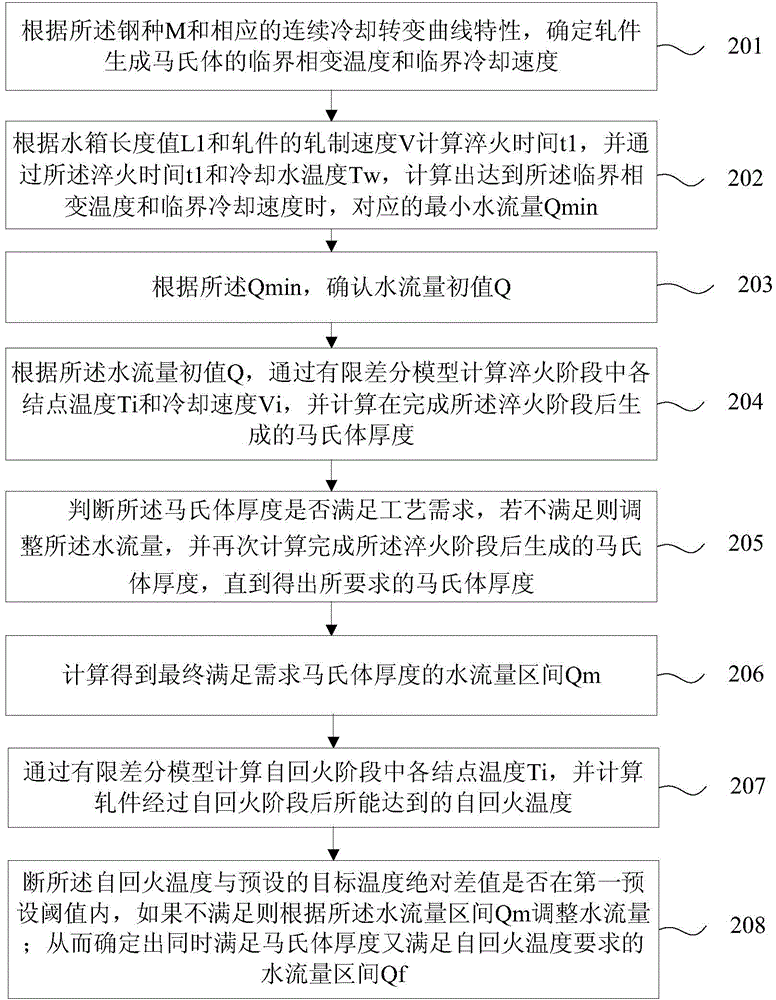
ActiveCN104673992ARealize automatic derivationHeat treatment process controlFinite difference modelMartensite
The invention is suitable for the field of bar online thermal treatment and discloses a control method for controlling cooling process in a bar production line. The method comprises the following steps: determining a critical phase-transition temperature and a critical cooling speed of a martensite generated on the surface of the rolled piece according to the steel type M and the corresponding continuous cooling transformation curve; calculating the corresponding minimum water flow Qmin when reaching the critical phase-transition temperature and the critical cooling speed; determining a water flow initial value Q according to the Qmin; according to the water flow initial value Q, calculating the thickness of the martensite generated after finishing the quenching stage through the finite-discrete scheme to obtain the required martensite thickness; and calculating to obtain the finial water flow zone Qm which satisfies the martensite thickness. By adopting the method, the technological parameters of the controlling cooling process can be automatically deduced; compared with the mode of copying or referring to the operated production line in the prior art, the method is more effective and accurate.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Test method for welding CCT (continuous cooling transformation) diagram of resistance type thermal simulation test machine
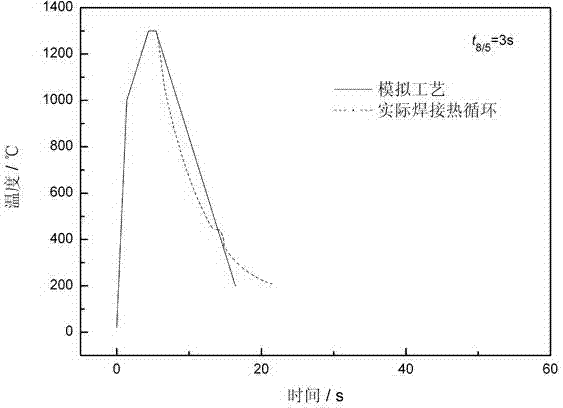
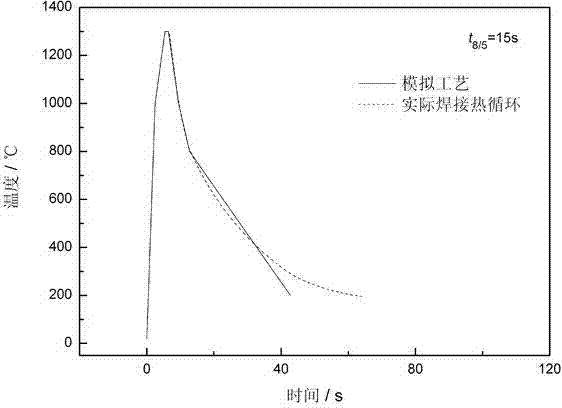
InactiveCN104123878AAccurate phase transition pointMaterial heat developmentEducational modelsCyclic processThree stage
Disclosed is a test method for a welding CCT diagram of a resistance type thermal simulation test machine. The test method includes the steps of heating a thermal simulation sample from the room temperature to the peak temperature Tp; staying for one second; subjecting the sample to linear cooling in three stages, wherein the first cooling stage is the cooling from the peak temperature Tp to 1000 DEG C, the second cooling stage is the cooling from 1000 DEG C to 800 DEG C, and the third cooling stage is the cooling from 800 DEG C to the room temperature; accurately identifying the start and end points of the phase transition on a thermal expansion curve according to a tangent method. The test method for the welding CCT diagram of the resistance type thermal simulation test machine takes the problems of heating rate, multi-stage linear cooling and temperature overshoot into overall consideration, so that the tested welding CCT diagram is close to the actual welding thermal cycle, and the measured phase transition points are accurate. The test method is applicable to the test of the welding of CCT on all resistance type thermal simulation test machines.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司
A thermodynamic calculation method for optimizing the high temperature brazing process of high nitrogen steel
ActiveCN111859642BReduce stretchLow elongationSoldering apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationCooling curveSS - Stainless steel
A thermodynamic calculation method for optimizing the high temperature brazing process of high nitrogen steel. The invention belongs to the field of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel brazing. The invention aims to study the influence of high-nitrogen and ultra-high-nitrogen stainless steel on the relative material properties of the precipitation in the brazing process, so as to optimize the high-nitrogen steel brazing process. The method of the present invention uses the thermodynamic calculation software Jmat Pro to calculate the equilibrium phase diagram of the high-nitrogen steel precipitation phase based on the CALPHAD calculation method, thereby obtaining the precipitation temperature range of the high-nitrogen steel precipitation phase, and then according to the nucleation kinetic equation Johnson- Mehl-Arvami calculates the isothermal cooling transition curve and continuous cooling transition curve of high nitrogen steel, and finally obtains the sensitive precipitation temperature range and incubation period of high nitrogen steel precipitates from the isothermal cooling transition curve, and avoids brazing in the above temperature range. The invention provides a stable calculation method for determining the optimum brazing parameters of the high-nitrogen steel high-temperature brazing process.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Production method for rapidly cooling medium plate after rolling
ActiveCN102343372BLow carbon equivalentLow weld crack susceptibilityWork treatment devicesMetal rolling arrangementsSpray nozzlePhase change
The invention discloses production method for rapidly cooling a medium plate after rolling, belonging to the technical field of production of medium plates. The method comprises the following process steps of: adjusting an ultrafast cooling (UFC) frame to 300mm+h till the cross point between extension lines of upper and lower nozzles of equipment is positioned on the central line of a steel plate; during ultrafast cooling, setting cooling rules and parameters according to the steel kind, specification as well as required final cooling temperature and cooling speed of the steel plate; starting middle spraying, side spraying and air blowing to remove residual water from the surface of steel plate to increase the cooling uniformity, starting UFC equipment, and spraying water onto the steel plate with a gap nozzle and a ganged nozzle for cooling; and controlling the cooling speed and cooling termination point according to the CCT (Continuous Cooling Transformation) curve of steel, wherein the cooling speeds of steel plates of different thicknesses are 5-80 DEG C / s, and the final cooling temperature is controlled at 450-800 DEG C. The method has the advantages: by controlling the cooling process of the steel plate after rolling, control over phase change and organization is realized, and the aim of enhancing the roughness of the steel plate is fulfilled.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
A kind of production method of heat-resistant steel welding wire
ActiveCN104668820BShorten the development processHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagAcid washing
The invention discloses a production method of heat-resistant steel welding wires. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of 1) performing steel ingot smelting according to designated chemical components to obtain a steel ingot; 2) testing the continuous cooling transformation curve of the welding wire steel by adopting a Gleeble thermal simulation test and deducing process parameters for rolling and cooling control; 3) rolling the steel ingot into coil rods with diameter of 5.5-8.0mm by referring to a process; 4) performing rough drawing to the coil rods after acid washing; 5) performing primary annealing treatment, the process of which is heating to 830-850 DEG C, preserving heat for 2 hours and then slowly cooling; 6) performing fine drawing after acid washing to obtain welding wires with diameter of 0.8-4.0mm. The drawing performance of the coil rods produced by adopting the production method disclosed by the invention is good, one time of annealing is only required in the process of drawing the coil rods into the welding wire finished products, the production efficiency is improved, the produced welding wires can be used for chrome-molybdenum heat-resistant steel welding, the electric arc is stable during welding, the spatter is less, the slag is easy to remove, and welded joints have excellent impact toughness, temper embrittlement resistance, high-temperature strength and creep resistance.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
A control method and device for a temperature-controlled rolling process of a rod and wire production line
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
Method for thinning crystalline grain of large low alloy cast
The invention relates to a method for thinning a crystalline grain of a large low alloy cast based on computer simulation, material continuous cooling transformation curve measurement and material phase change mode control, and belongs to the field of steel and iron metallurgy. The method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, measuring a continuous cooling curve of a related cast material and determining the critical cooling rate of the material with martensite, bainite and pearlite phase change; secondly, building a corresponding cast model, and determining the cooling rate of the parts of the cast under different cooling mediums by a way of computer simulation; and lastly, heating the cast to be A3<+> (30-80 DEG C) for austenitizing at first, slowly cooling to be room temperature, enabling the cast to be subjected to diffusion or semi-diffusion phase change, after that, heating the cast to be A3<+> (30-50 DEG C) for austenitizing, selecting a proper cooling way according to simulation calculation, enabling the cast to be subjected to bainite phase change, and thinning the crystalline grain of the cast to be below the ASTM (American Society for Testing Material) standard crystalline grain size 7.5 through the semi-diffusion bainite phase change.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for removing defects in medium carbon steel castings
ActiveCN105149727BReduce the chance of crackingAvoid crackingArc welding apparatusCasting defectContinuous cooling transformation
Owner:KOCEL STEEL
Obtaining method of large deformation pipe line steel double phase structure
InactiveCN103215420BMeet large deformation performance requirementsHeat treatment process controlDouble phaseYield ratio
The invention relates to an obtaining method of a large deformation pipe line steel double phase structure. The obtaining method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out compound design on a small part of pipe line steel according to design requirements; 2, determining a continuous cooling transformation curve (CCT curve) of the small part of the designed steel, wherein the CCT curve reflects a structure transformation law of the steel at different cooling rates; 3, selecting a cooling rate range meeting a requirement of bainite and ferrite double phase structure formation on the CCT curve; 4, determining various phase change points corresponding to the cooling rate range; and 5, determining the most important process parameters during steel manufacturing according to the determined phase change points, wherein the two most important process parameters comprise a cooling temperature and a cooling rate. According to the present invention, according to the existing process, the obtained cooling temperature and the obtained cooling rate are adopted to carry out batch production of steel plates, wherein a uniform elongation rate of the obtained double phase structure large deformation pipe line steel can be more than 12%, a working hardening index can be more than 0.15, and a yield ratio can be less than 0.77 so as to meet requirements on the large deformation pipe line steel in the standard.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
A method for measuring the continuous cooling transformation curve of aluminum alloy
The invention relates to a method for measuring the continuous cooling transition curve of an aluminum alloy, belonging to the technical field of nonferrous metal material preparation. The present invention distinguishes the precipitation temperature interval of the quenching reaction in the quenching process according to the change of the heat equivalent by recording the change of the heat equivalent in different temperature intervals; the present invention measures the aluminum alloy by applying the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) The exothermic reaction during the quenching process is combined with the microstructure analysis and mechanical property testing to obtain the continuous cooling transformation curve of the aluminum alloy. Compared with other methods, the method of the present invention is capable of obtaining precise cooling curves in a certain cooling interval and distinguishing the starting and ending temperatures of different quenching-induced precipitation phases. The continuous cooling transition curve obtained by the invention has the advantages of high precision, great guiding significance and the like.
Owner:深圳卓聚新材料有限责任公司
A control method and device for controlling the cooling process of a bar production line
ActiveCN104673992BRealize automatic derivationHeat treatment process controlFinite difference modelMartensite
The invention is suitable for the field of bar online thermal treatment and discloses a control method for controlling cooling process in a bar production line. The method comprises the following steps: determining a critical phase-transition temperature and a critical cooling speed of a martensite generated on the surface of the rolled piece according to the steel type M and the corresponding continuous cooling transformation curve; calculating the corresponding minimum water flow Qmin when reaching the critical phase-transition temperature and the critical cooling speed; determining a water flow initial value Q according to the Qmin; according to the water flow initial value Q, calculating the thickness of the martensite generated after finishing the quenching stage through the finite-discrete scheme to obtain the required martensite thickness; and calculating to obtain the finial water flow zone Qm which satisfies the martensite thickness. By adopting the method, the technological parameters of the controlling cooling process can be automatically deduced; compared with the mode of copying or referring to the operated production line in the prior art, the method is more effective and accurate.
Owner:WISDRI ENG & RES INC LTD
High strength hot rolled steel products for line-pipes excellent in low temperature toughness and production method of the same
InactiveCN101622369BCheap and stable manufacturingImprove energy absorptionMetal rolling arrangementsLine tubingPipe
The invention provides a high-strength hot-rolled steel plate for line pipes which is excellent in low-temperature toughness and a process for the production of the same. A steel plate which contains by mass C: 0.01 to 0.1%, Si: 0.05 to 0.5%, Mn: 1 to 2%, P: 0.03% or below, S: 0.005% or below, O: 0.003% or below, Al: 0.005 to 0.05%, N: 0.0015 to 0.006%, Nb: 0.005 to 0.08%, and Ti: 0.005 to 0.02% with the proviso that relationships: N-14 / 48xTi>0% et Nb-93 / 14x(N-14 / 48xTi)>0.005% are satisfied and with the balance consisting of Fe and unavoidable impurities, characterized in that the microstructure is a continuous cooling transformation structure, that the reflected X-ray intensity ratio between {211} plane and {111} plane which are parallel to the plate face, {211} / {111} ratio, in the texture in the thicknesswise central part of the plate is 1.1 or above, and that the density of carbonitride precipitate of Nb and / or Ti in the grains is 10<17> to 10<18 >pieces / cm<3>.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Method for linkage production of high-toughness pipeline steel by adopting jetting and laminar cooling
ActiveCN103740925BStable mechanical propertiesEasy to shapeFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlSuper coolingSheet steel
The invention discloses a method for linkage production of high-toughness pipeline steel by adopting jetting and laminar cooling, belonging to the technical field of production of medium-thickness plates. The super-cooled austenite continuous cooling transformation (CCT) curve of a steel plate is measured according to the chemical constituents of the steel plate. The steel plate comprises the following chemical ingredients in percentage by weight: 0.045-0.075 percent of C, 0.1-0.3 percent of Si, 1.55-1.85 percent of Mn, 0.045-0.085 percent of Nb, 0.1-0.2 percent of Mo, 0.1-0.3 percent of Ni, 0.01-0.02 percent of Ti and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The method has the advantages that the problems of low toughness of pipeline steel plates of over grade X80 produced by jet cooling and low strength of pipeline steel plates of over grade X80 produced by laminar cooling are solved, and the high-toughness pipeline steel is produced.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Thermodynamic calculation method for optimizing high-temperature brazing process of high-nitrogen steel
ActiveCN111859642AReduce stretchLow elongationSoldering apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationMetallurgySS - Stainless steel
The invention discloses a thermodynamic calculation method for optimizing a high-temperature brazing process of high-nitrogen steel, and belongs to the field of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel brazing. The invention aims to research the influence of precipitated phase of high-nitrogen and ultrahigh-nitrogen stainless steel on the performance of a material in the brazing process so as to optimize the high-nitrogen steel brazing process. According to the method provided by the invention, thermodynamic calculation software Jmat Pro is used, calculation is carried out based on a CALPHAD calculation method to obtain an equilibrium phase diagram of a high-nitrogen steel precipitated phase, and a precipitation temperature range of a high-nitrogen steel precipitated phase is obtained; then, an isothermal cooling transformation curve and a continuous cooling transformation curve of the high-nitrogen steel are calculated according to a nucleation kinetics equation Johnson-Mehl-Arvami; and finally, a sensitive precipitation temperature interval and an inoculation period of the precipitated phase of the high-nitrogen steel are obtained according to the isothermal cooling transformation curve, and brazing is prevented from being carried out in the temperature interval. The invention provides a stable calculation method for determining the optimal brazing parameters of the high-temperature brazing process of the high-nitrogen steel.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for formulating water-air alternate time-controlled quenching process
The invention provides a method for formulating a water-air alternate time-controlled quenching process. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, predicating a structure composition of a part with required performance according to the performance detection part of an alloy steel piece and specific performance requirements; step 2, according to the super-cooled austenite isothermal cooling transformation curve or the super-cooled austenite continuous cooling transformation curve of a material, acquiring the longest cooling time or the minimum cooling speed which the structure needs to reach a certain temperature; step 3, dividing an alloy steel piece into a cooling speed control area and a slow cooling area along a section from the surface to the centre; step 4, determining the water-air alternation times of the cooling speed control area, and a water-cooling time and an air-cooling time each time; and step 5, determining the water-air alternation times of the slow cooling area, and a water-cooling time and an air-cooling time each time. With the adoption of the method provided by the invention, the alloy steel piece can obtain required performance or structure on the premise of avoiding cracking; and the method is suitable for a quenching treatment for the alloy steel pieces with various ingredients.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com