Method for thinning crystalline grain of large low alloy cast
A low-alloy and casting technology, applied in the field of iron and steel metallurgy, can solve the problems of difficulty in realizing large-scale castings, burning and deformation of castings, and difficulty in actual operation, and achieves the effect of low cost, avoiding burning and deformation of castings, and improving competitiveness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] figure 1 It is a three-dimensional modeling drawing of a large casting made of 35CrNiMo. The entire casting is about 5000mm long, 1900mm wide, with a maximum wall thickness of about 600mm and a gross weight of about 50 tons. Castings not only have strict requirements on the conventional mechanical properties of materials, but also require that the overall grain size of castings should not be thicker than ASTM 7.5 grade.
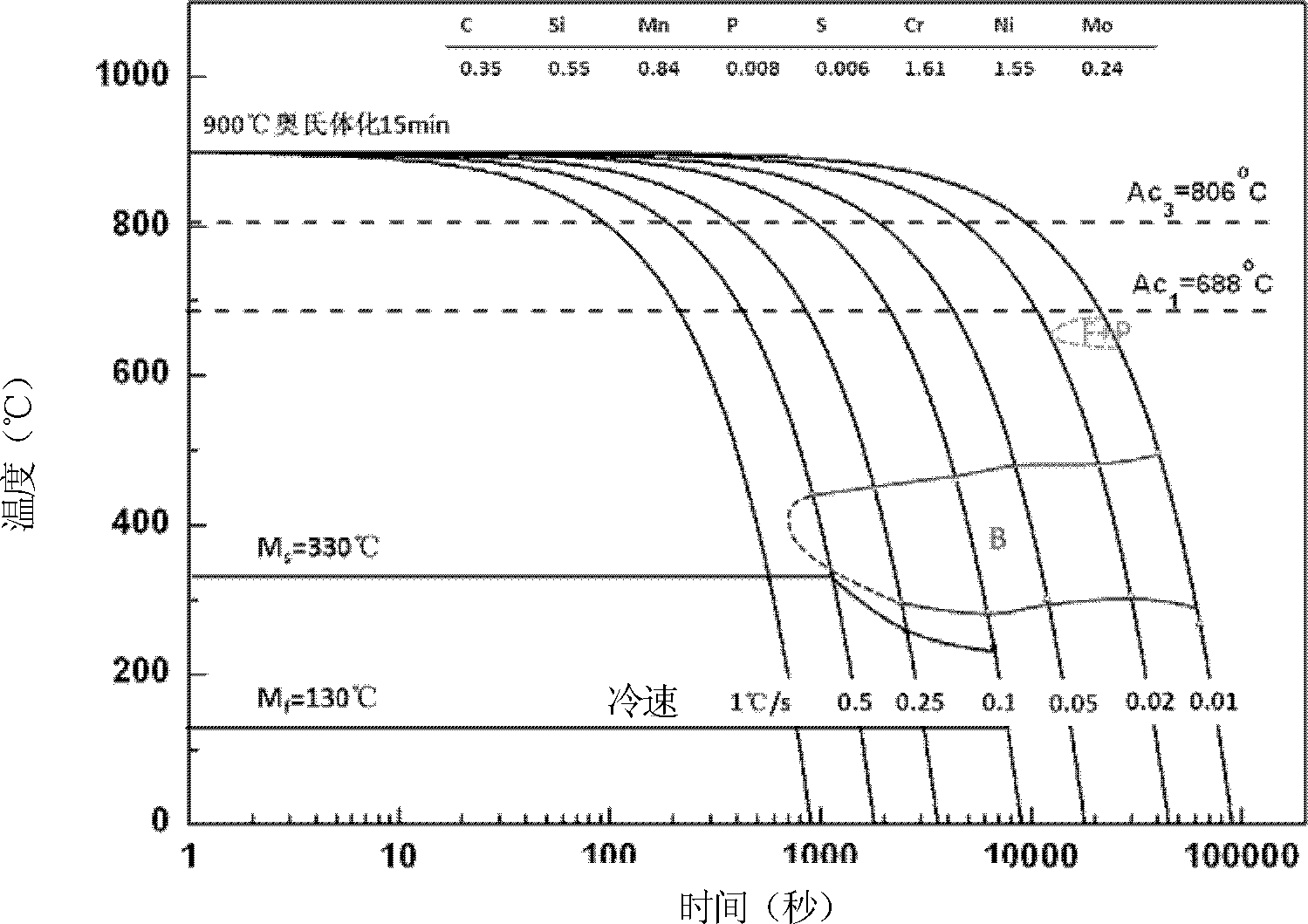
[0036] figure 2 From the CCT diagram of the 35CrNiMo material used for this casting, it can be seen that the A3 point temperature of this steel type is 806 °C. After austenitization, if the cooling rate is between 0.02°C / s and 0.5°C / s, bainite transformation occurs; when the cooling rate is greater than 0.5°C / s, martensitic transformation occurs; the cooling rate is less than Pearlite phase transformation occurs at 0.02°C / s.
[0037] On the basis of accurately measuring the thermophysical parameters of the relevant materials and the surface heat tr...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0043] A large casting made of 55NiCrMoV has a length of about 4000mm, a width of about 1500mm, a maximum wall thickness of about 400mm, and a gross weight of about 30 tons. Castings not only have strict requirements on the conventional mechanical properties of materials, but also require that the overall grain size of castings should not be thicker than ASTM 7.5 grade.
[0044] A 3 Above 30-80°C (this embodiment is A 3 For the austenitizing treatment above 40°C), the cooling method is furnace cooling. At this time, the grain size of the material is about 35.16 μm, and the grain size is 6.2. Then carry out tempering treatment, the tempering temperature of this embodiment is 630 ℃, and the holding time is calculated by increasing 1.5-2 hours for every increase of 25mm in effective wall thickness;
[0045] The second austenitizing temperature is at A 3 Above 30-50°C (this embodiment is A 3 Above 30°C), oil cooling is used to contro...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0048] A large casting made of 42CrMo has a length of about 4500mm, a width of about 1700mm, a maximum wall thickness of about 450mm, and a gross weight of about 40 tons. Castings not only have strict requirements on the conventional mechanical properties of materials, but also require that the overall grain size of castings should not be thicker than ASTM 7.5 grade.
[0049] A 3 Above 30-80°C (this embodiment is A 3 For the austenitizing treatment above 60°C), the cooling method is air cooling. At this time, the grain size of the material is about 30.84 μm, and the grain size is 6.8 grade. Then carry out tempering treatment, the tempering temperature of this embodiment is 680 ℃, and the holding time is calculated by increasing 1.5-2 hours for every increase of 25mm in effective wall thickness;
[0050] The second austenitizing temperature is at A 3 Above 30-50°C (this embodiment is A 3 Above 50°C), the oil-cooled sample is used ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com